Flowers blooming in October
These plants are not afraid of the first night frosts. Bright colors in the garden will drive away the autumn depression.
Ageratum
This representative of the Astrov family has another common name - "long-flowered". And this is no accident. Fluffy flowers of ageratum, similar to pompons, bloom until late autumn and add blue, purple, white and pink colors to the garden.
Perennial aster
The unpretentious Oktyabrinka are not afraid of frost and feel great even during the first snowfall. With proper care, perennial asters of late varieties continue to decorate the flower bed even in the first half of November.
Marigold
Marigolds were introduced to Europe in the 16th century. In Russia, these were the first overseas flowers. Flower baskets of cream, yellow, orange and brown color exude a strong spicy smell, and in dried and infused form they are a curative remedy for colds, asthma, bronchitis, stomatitis. Marigolds bloom from June to mid-autumn.
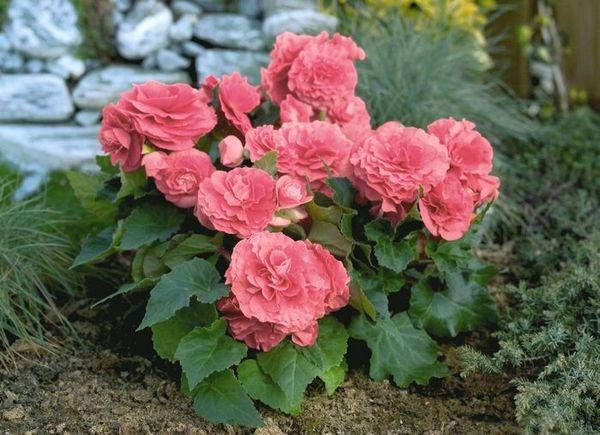
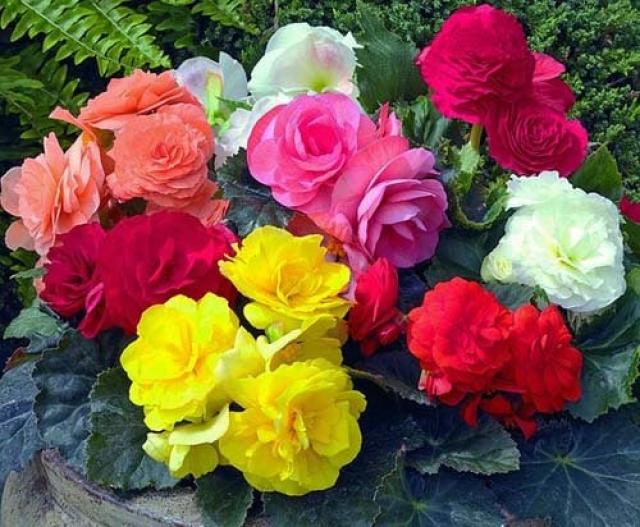
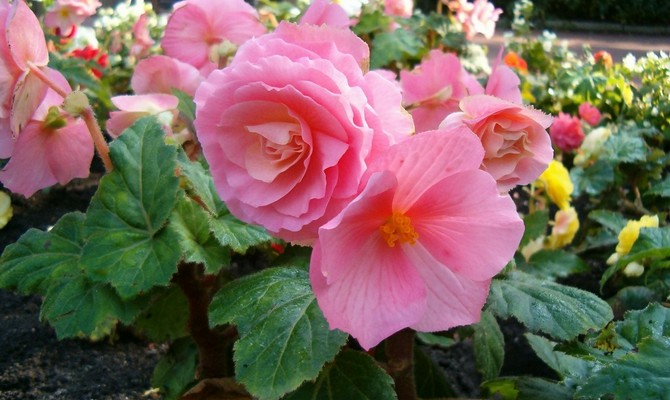
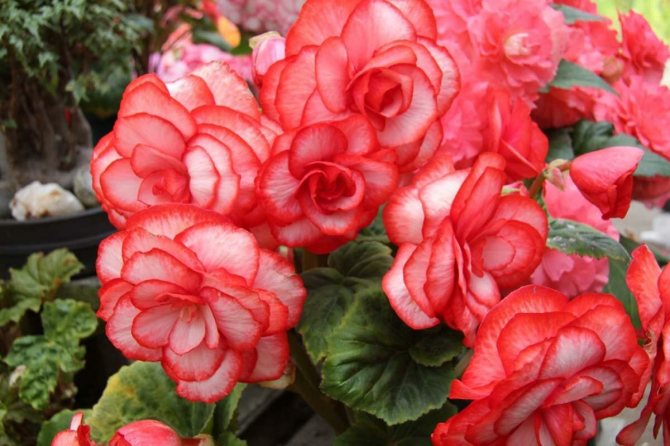
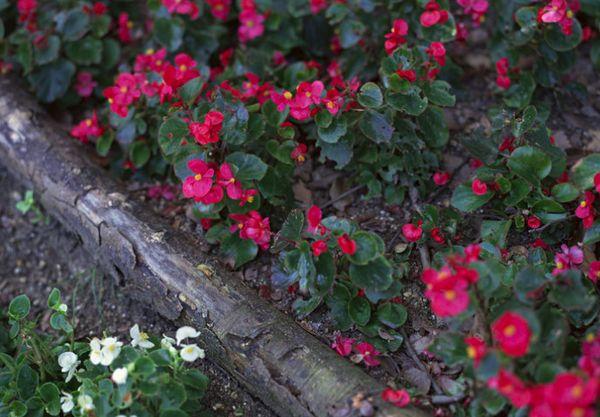
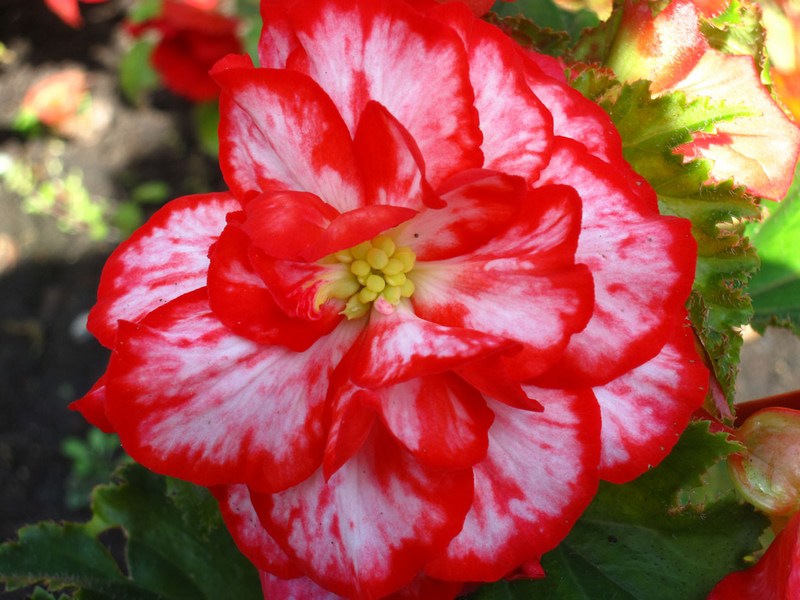
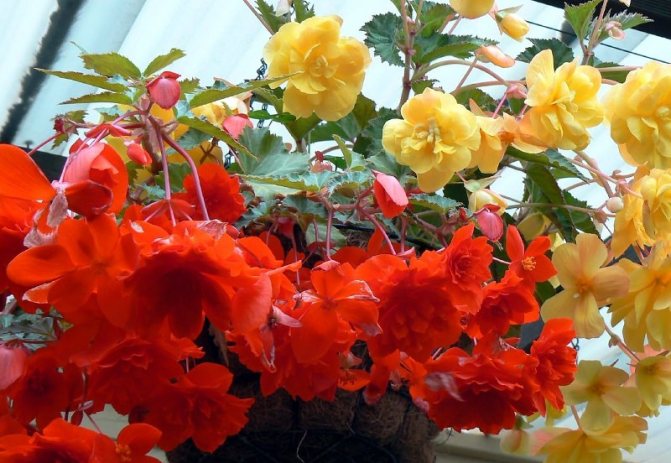
Tuberous begonia
This beauty with lush flowers in calm areas is able to bloom until mid-October. And if you grow begonia in a hanging planter, then with the onset of cold weather it can be transferred to the veranda or winter garden. And then she will delight you with her attractive appearance until November.
Verbena Bonar, Argentinean, Buenos Aires, or high
The Bonar verbena does not look very similar to other members of the Verbena family. Its almost leafless stems (up to 1.5 m high) with small purple-violet flowers, collected in umbrella-shaped inflorescences, fit perfectly into the autumn flower garden. Most often, this verbena is grown as an annual: in May, the seedlings are planted in open ground, and from August to October the plant adorns the flower bed with delicate flowers and safely tolerates short-term autumn frosts.
Gatsania, or gazania
This undersized flower (up to 30 cm high) is often called the African chamomile, but its flowers are more like a gerbera. They are single baskets with a diameter of 5 to 9 cm, consisting of orange, red, yellow reed flowers with dark spots at the base, which form a ring pattern around the yellow middle. There can be up to 35 such inflorescences on one plant. In good lighting, gatsaniya blooms until frost.
Autumn Gelenium
If there are enough warm and sunny days in the fall, helenium will continue to decorate the flower garden in early October. Its yellow, orange, purple, brown or bicolor inflorescences-baskets (3-5 cm in diameter) look best in the vicinity of perennial asters.
Hydrangea paniculata
The spreading bushes of panicle hydrangea look attractive from mid-summer to late autumn. In October, plants of varieties that have the property of changing the color of inflorescences are especially effective. So, in the first half of October, paniculate hydrangeas of Grandiflora, Little Lime, Pink Diamond still flaunt in the gardens.
Goldenrod, or solidago
The bright yellow pyramidal inflorescences of goldenrod enliven the autumn garden until the coldest days. Tall specimens can reach a height of 2 m, and dwarf plants grow no higher than 40 cm. All goldenrods are absolutely unpretentious and, thanks to their honey aroma, attract bees to the garden.
Canna
This stately flower (up to 3 m high) blooms from June to late autumn. Leaves are large, elliptical or oval-oblong, pointed, (25-80 cm long and 10-30 cm wide), green, striped or purple-bronze. The flowers are red, orange, yellow, pink or white. They are located on tall stems and do not wither until frost.Canna is completely unpretentious, almost does not get sick and does not attract harmful insects, even if it is not treated with anything, but in the middle lane it is not able to hibernate without good shelter.
Lantana Montevideo, or Selloviana
The egg-shaped leaves of this climbing lantana are covered with delicate pubescence, and they are jagged along the edge. Flowers - very small, tubular, lilac-pink with a yellow core, collected in compact spherical inflorescences. Bloom is observed from June to October. And when grown in a sunny, wind-protected area, Montevideo lantana can "hold out" on a flower bed, balcony or open terrace until November. And her bright flowers won't even fade.
Nasturtium, or capuchin
In the middle lane, nasturtium is grown as an annual, because in winter, in an unstable climate, this tropical flower freezes out. Most of the nasturtium species cultivated in our latitudes bloom from June to October. Flowers are simple, double and semi-double. Coloring - bright red, salmon, yellow, orange, apricot, cream.
How to care outdoors in a flower bed
Florists should remember that outdoor begonia, which is planted and cared for in the open field, loves increased attention.
It is important to carefully consider the watering regime, pest control, feeding
If you regulate such conditions for the growth and development of the plant, then the begonia in the flower bed will be a magnificent flowering bush with bright leaves. Additionally, you need to plant the flower in a place suitable for its variety, where the sun and moisture will play a major role.
Note! Timely pruning of branches will be additional factors for care. To extend the flowering time, you need to immediately remove the withered buds
The procedure must be carried out carefully and only with a sharp pruner so as not to damage live stems or inflorescences.
Fertilizing and feeding garden begonia
Growing and caring for begonia in the garden requires the utmost attention. This is especially true for fertilizing the soil. This moment is very important for the plant, since begonias take a lot of energy to bloom and maintain the color of the leaves.
During the active growing season, especially in spring, you need to apply mineral fertilizers at least once a month. When the flowering period begins, the soil must be fertilized especially carefully and often - once every 2 weeks.
Plant care before planting
Begonia prefers active outdoor care. Therefore, in addition to mineral fertilizers, it is worth using organic fertilizers. It is advisable to avoid homemade product as it can harm the plant.
Pest control
You need to start caring for begonias already in the greenhouse: carefully monitor the appearance of insect pests. Colonies of scale insects, aphids, whiteflies, nematodes, thrips can develop on the leaves.
In addition to parasitic insects, the plant is affected by common diseases that are relevant for horticultural crops:
- gray mold that spoils the root system. Difficult to get rid of. Long-term and constant treatment is required;
- powdery mildew, which worsens the condition of the aerial part. The main criterion for treatment is to establish the correct microclimate around the flower;
- bacterial spotting spreads to all parts of the plant. It is associated with the formation of bacteria, therefore, first of all, you need to get rid of the pathogen;
- ring spot spreading on leaves and stem. Often occurs due to the fact that the soil with bacteria gets on the leaves and stem at the time of watering. It is necessary to adjust the principle of the procedure.
To grow a healthy bush, you need to fight with special agents against fungus and insects. Mixtures and powders, in particular fungicides, must be used to treat the plant in the proportions indicated on the package.
Powdery mildew on a leaf
Many diseases can be avoided by following the care guidelines.If watering and feeding are periodic, then the plant will be strong. But these procedures should be performed correctly.
Watering in the garden
The main condition is timely, moderate watering. The plant loves moisture, but it is strictly forbidden to fill the soil with water. There are several nuances to consider when drawing up an irrigation schedule:
- watering should be done at the moment when the ground under the bush begins to dry out, but it is not recommended to wait for a dry crust to appear;
- it is enough to pour about 1-2 liters under one copy. The water should be at room temperature;
- it is impossible for moisture to get on the leaves, so it must be poured in the area of the stem. Pouring over the stem is also not recommended, since the crown can deteriorate, dry out, and burn.
Note! Additionally, you need to constantly push the soil under the bush, since a dry crust can cause rotting of the root system
Begonia in the country does not like it when the position of the upper roots is violated, so you need to carry out the weeding procedure especially carefully in the area near the stem
Preparing begonias for winter
Begonia must be dug out of the soil at the end of November. Usually, the procedure should be performed after the first frost. After flowering and dying off of the stems, the tubers begin to accumulate nutrients. Blooming in the new season depends on their quantity and quality.
Preparing begonia tubers for winter
Wintering begonias involves the complete extraction of tubers from the ground for the period of frost. The root system extracted from the soil must be placed in a box with peat or sand, put the container in a cellar or basement. The dormant state should last for about 2-3 months, that is, throughout the winter.
Further, each bulb is prepared for planting in a certain way: much depends on the species, plant variety, climatic conditions of the region. Usually, tubers can be planted back into the ground as early as May-June.
Preparation for wintering
Under natural conditions, begonia belongs to perennial evergreen crops that bloom continuously in winter. Unfortunately, in the conditions of central Russia, this is impossible, therefore begonia should be removed from the street for the winter in order to prepare it for further planting in the spring.
Inflorescences and leaves begin to dry out and fall off. At this point (usually in mid-September), it is necessary to carefully dig out the tubers from the ground, rinse them in warm water, and then dry them naturally. When the tubers are completely rid of the soil and dried, it is necessary to place them in a paper box or wooden box, cover them with river sand and send them to storage in a cellar or underground, where the air temperature is kept at 3-7 degrees.
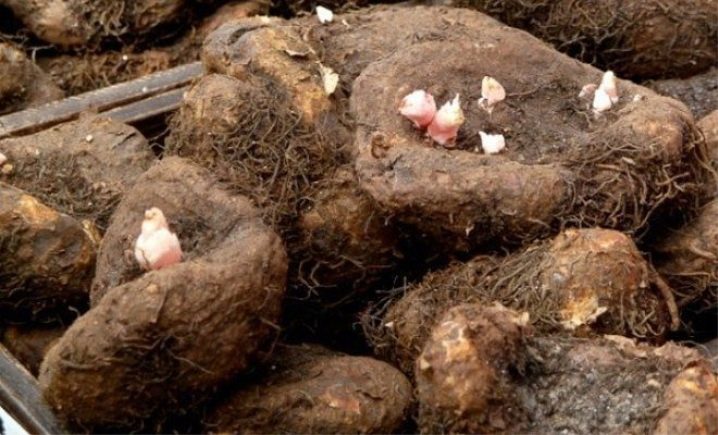

Outdoor care in a flower bed
Begonia in the garden requires attention and adherence to certain rules of care.
Seat selection
The place for the bushes is chosen sunny, but one where direct sunlight does not fall. Sometimes the plant drops buds if the place is open to the scorching sun. In this case, the bush will have to be moved along with the earthen lump to a shady place.
On the ground around the bushes, you can lay a layer of mulch from expanded clay, tree bark and chips. This frees the grower from the need to weed and loosen the flower beds, and helps maintain the required level of humidity.
Soil fertilization
Fertilizers for begonia are applied every two weeks. Phosphorus-potassium dressing is done from the moment of flowering. It is needed to stimulate the ovary, improve budding. The flowering density will be higher and the plant will look healthier. Products for flowering plants from Etisso (Germany) have proven themselves well.
Nitrogen fertilizers are intended for deciduous varieties as they help build green mass. It should be remembered that nitrogen slows down the formation of buds.
Watering
Originally from the tropics, begonia loves high humidity, so you need to water it regularly, every three days during the period of active growth.The water is taken soft, settled. Garden peat can be added to the water - about 1 kg per 10 liters of water. It is better to water the bushes in the morning. In summer, in the heat, you can water the flower beds every other day and make sure that no water lingers in the ground.
To prevent powdery mildew, which appears from an excess of moisture, it is recommended to spray the plants with a liquid agent for flower crops. If white spots are found on the leaves, it means that the disease has already hit the bush. A diseased plant will have to be removed so as not to infect neighboring specimens. With an excess of moisture, the bush sheds buds. This is a signal that watering should be reduced.
Important! Healthy bushes are not sprayed - leaves and buds will begin to rot

White color of flowers
Pests
Most begonia suffer from aphids, scale insects, thrips, whiteflies, nematodes and spider mites. To get rid of them, the bushes are sprayed with a solution of laundry soap, followed by rinsing with clean water. For spraying, special garden chemicals are also used.
For treatment and prevention, sticks or tablets from insect pests help. The advantage of these sticks is that they have a double effect: they not only protect the plant, but also fertilize. It can be a nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium fertilizer containing trace elements such as zinc, boron, iron. With each watering, the soil receives another portion of protection and fertilization.
Why begonia doesn't bloom
If ovaries do not form, you need to revise the main parameters of the external environment:
- lighting;
- air temperature;
- watering mode;
- humidity.
If the soil is poor in nutrients, you should select high-quality fertilizers for flowering plants and apply them, focusing on the manufacturer's instructions. The soil must be selected loose, with a high content of peat and sand. Sometimes only plant transplanting or complete soil replacement helps.
Preparing for winter
Around the middle of autumn, begonias are removed together with the tuber, the stems are cut, leaving only short ones, 2-3 cm tall. Tubers need to be cleaned of soil, rinsed and dried well. They can then be removed to a cool place and checked from time to time for mold growth.
Varieties
Today there are quite a few types of garden begonias. In landscape design, several varieties are considered the most popular. Let's consider them in more detail.
Tuberous
These flowers are distinguished by a rather long and abundant flowering, which lasts from the very first days of summer until the last decade of November. The height of the bush is 25-35 cm, the plant is distinguished by fleshy tubers and strong stems. Inflorescences can be double or smooth, variable color (red, scarlet, white, pink, yellow). The size of one flower is 6-20 cm.
Ampere
These varieties are intended for growing in hanging pots and tall flowerpots. The shoots of the bush are rather long (up to 80 cm), the stems are falling. These types of begonias are great for decorating all kinds of vertical designs. They tolerate any temperature well and retain their decorative effect even with the onset of light frosts.
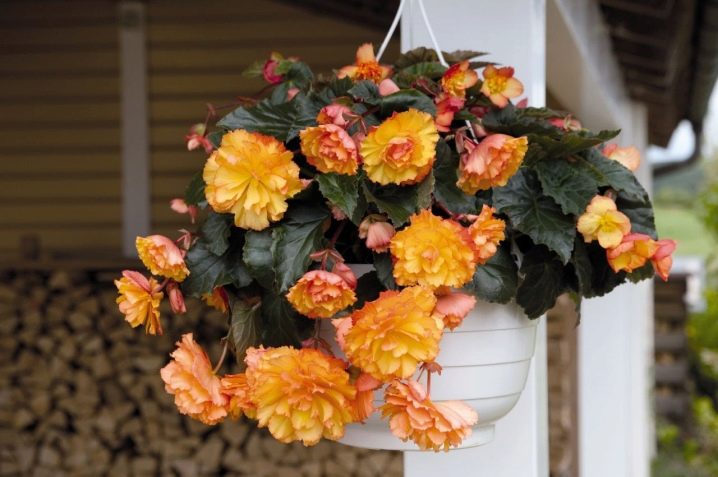

Eternally blooming
These are miniature plants 15-20 cm high. They are widely used for garden landscaping due to their unpretentiousness, abundant flowering and rich color (from milky white tones to bright purple and red shades). Leaves are oval, with a glossy surface. Their color ranges from deep green to brown.


Plants that can be planted in the country in the shade: description and photo
To create a flower bed in the shade, you can choose one plant variety, but compositions from several types look the most advantageous.
When wondering what kind of flowers to plant, you should pay attention to the cultures listed below
Periwinkle
This perennial plant is a kind of "green carpet" of dense creeping stems covered with dark green leaves. Such a culture blooms profusely in spring, and the shade of the petals can be white, blue, blue, lilac or purple.
The advantage of small periwinkle is that it can grow in any light: in the sun, in partial shade or in shaded areas. In addition, all its varieties are cold-resistant and calmly winter under a cover of snow.
Read about growing the Periwinkle plant from seed outdoors.
Kupena
This plant also has a second name - "Solomon seal". This culture has a strong, branched rhizome and is abundantly covered with large leaves that have a dark green or variegated color with light veins.
The flowering period of the kupena falls in May and lasts 21-28 days. At this time, bell-shaped flowers appear on the bushes, painted in a white, cream, pink, greenish or purple hue. After their wilting, the fruits ripen in the form of red or dark blue berries.
Such a culture will perfectly take root in the shade and will look good next to ferns, doronicum, irises, tulips or primroses.
Find out more about the care and planting of Kupena outdoors.
Lungwort
This low shrub from 30 to 40 cm, covered with small leaves and forming a large number of ground cover flowers, is an excellent honey plant. If you taste the flower stalk, it will be sweet.
You can recognize the lungwort by the white spots on the leaves and flowers, the petals of which can change their color from pink to blue. This crop belongs to the early flowering, and the first buds appear in April.
The plant is perennial, and it is recommended to divide and replant it every 3 years.
We offer for reading a complete description of the garden plant Medunitsa.
Primrose
This culture forms buds in early spring and pleases the eye with beautiful flowers from April to May. Primrose bushes are not tall, from 10 to 20 cm in length, and flowers are terry, decorated with "rims" of various shades along the edge of the petals.
Such a perennial will feel great in the shade, sheltered from the sun's rays by tall plants. There are many varieties of this culture and you can combine several varieties with different colors of petals in a flower bed.
Find out more about transplanting and growing the Primrose plant.
Rogersia
These are large plants, capable of reaching from 1 to 1.8 m in height. Such plantings will look good along the fence in a shaded area.
Rogers can be recognized by the finger-like leaves on long stalks and petalless flowers gathered in fluffy panicles. This perennial multiplies by dividing the bush, such manipulations are allowed in spring or autumn.
Caring for Rogersia involves abundant watering in dry summers and cutting the bush at the root in the fall, after flowering ends.
Read on to learn how to grow Rogersia outdoors from seeds.
Smilacin
If there are corners on the personal plot where the sun practically does not penetrate, smilacina will be the best option for decorating a flower bed in this place.
These are perennial plants with a height of 60 to 90 cm, with arched stems and racemose inflorescences consisting of small stellate flowers. They adorn the bushes from May to June and exude a delicate, pleasant aroma, and at the end of the flowering period they are replaced by red berries.
When choosing a place for smilacin, it is important to pay attention to the fact that the sun's rays practically do not penetrate this area, and, if necessary, create shading
Tiarella
Such a perennial crop with a height of 30 to 50 cm blooms at different times, depending on the species. For some, this period occurs in May and June, and some varieties bloom from early summer to September.
Tiarella is distinguished by beautiful green leaves, which acquire a bronze or red hue in autumn, and small flowers are collected in racemose panicles. The plant takes root well under tall trees with a dense crown, does not tolerate direct sunlight and is intolerant of a lack of moisture.
Read about the varieties of Tiarella and how to care for this plant.
This is not a complete list of plants that can grow in the shade. Here are some of the most common, low-maintenance species.
1 Fragrant lilies of the valley and lupins
The most common perennials for shade are lilies of the valley. These plants are short (maximum 30 cm in length), have broad-lanceolate oblong leaves that resemble hare ears. The flowers are like a brush in which 6 to 20 whites jugs. Lilies of the valley are bestowed with their buds from May to June, and they also emit a refined and strong aroma.
To grow shade-loving perennials in your area, you need to plant them correctly. Most often, this process is performed in the fall (end of September). It is better to place them under bushes or trees, and also choose places protected from the winds. The soil is required wet, slightly acidic or neutral. Before planting, it is necessary to fertilize the soil with humus or peat compost (10 kg per 1 m²). Placing lilies of the valley in open ground is carried out using sprouts with part of the rhizomes in even rows in grooves, and the distance between flowers is 10-12 cm. The furrow should be about 1.5 cm deep. If the soil is dry, it must be watered after planting the lilies of the valley. As soon as frost sets in, you need to cover the area with mulch. This will protect from freezing in the event of a snowless winter. It must be remembered that without a transplant, flowers can last for 5 years.
Plants take great care of themselves - they displace other representatives of the flora from the site. The only thing that needs to be done is to water the crop in hot weather. In addition, loosening the soil and getting rid of weeds is imperative. In case of diseases, it is required to treat the plants with fungicides.
Another shade-loving garden flowers are lupins. The buds are blue, pink, dark red, white, yellow. The plant propagates by seed or cuttings. It is completely undemanding to the soil, but when planting it is necessary to enrich it with peat.
Caring for flowers in the first year of life consists in removing weeds and loosening the soil. It is imperative to add soil if the root neck of the plant suddenly becomes exposed. It will not hurt for a flower bed with lupins to fertilize with mineral fertilizers. After 5-6 years, the bushes need to be removed and new ones planted, since old flowers will not be presented with lush buds. If lupins grow in windy areas, then they must be tied up. Watering the culture is carried out in moderation, otherwise it can get sick.
Growing begonias outdoors
When, where and how to plant in soil
When the spring frosts pass, the begonia can be transplanted into the ground. The distance between the shoots should be about twenty centimeters, and the tuber itself should be covered with a layer of soil of two centimeters.

It is better to plant begonia in a country house in a conspicuous place, since the plants are perennial and have a long flowering period - from July to early autumn. In addition, so that they do not lose their decorative effect (flowers do not need frequent transplanting), they can be transplanted once every 7 years, while the soil is not depleted, and the concentration of pests or plant diseases is not observed.
If the soil is limited, tuberous begonias can be planted in pots or containers, which is very convenient for planting from year to year. For planting flowers in the soil, a loose, permeable earth with a slightly acidic reaction of the environment is best suited. If the site is cultivated, then there is no need for liming it.

Flower care
Watering is done regularly, watering the ground around the flowers.Abundant watering should be alternated with fertilizing with organic and mineral fertilizers. At temperatures above 22 degrees and good lighting, the tubers will sprout quickly, and in a month we will see new shoots. Flowering occurs in about three months.
Every autumn we dig up the ground at the planting site and weed well, removing the roots of the weeds. If for many years we have been growing begonia in the same place, then after weeding it must be fertilized with compost (a bucket per square meter of land).
Sometimes, due to improper care, begonia can be covered with rot or powdery mildew. Then we will be helped by treating flowers with pesticides or loosening the land with a decrease in irrigation.
Peculiarities
Terry begonia is especially common in the subtropical zone. Its homeland is considered to be Africa and India, from where in the 17th century it was actively imported to Europe in order to decorate flower beds of noble persons with it. Since then, various varieties of this flower have been bred, which can perfectly take root in the climatic conditions of the temperate zone of Russia. The main feature of this plant is its appearance. Begonia buds are very reminiscent of rose flowers - the same multi-layered and delicate.
The plant is distinguished by a neat compact bush, as well as large buds, whose petals have a double edge. The flowers themselves can have a different shade depending on the variety. Traditional classic varieties tend to have red, white or yellow buds, while newer ones offer gardeners to decorate their plot with pink or orange begonias. At the same time, the color of the petals can be uneven, which, in combination with the terry edge, makes the appearance of the bush even more interesting. The leaves of the plant themselves are large in size and carved edges, which is an additional decorative highlight of the plant. Thus, the buds on their background look more delicate and fragile. In some begonia varieties, the leaves are reddish or streaked.
In begonia, as it grows, two unisexual flowers form - a male and a female. It is the male buds that have a double edge and perform the main decorative function, while the female ones are necessary for the further reproduction of the plant - they have a seed capsule on them. Most varieties are planted in open ground at the end of spring, when the soil has already warmed up enough. The plant blooms all summer, and some varieties of begonias, for example, ever-flowering, can delight the owner with their flowering until the onset of winter, and in regions with a warm climate - all winter. Begonia can be grown not only outdoors, but also at home.
How to plant begonias in the ground?
A crucial stage is planting.
Each tuber must be planted in a separate container, preferably in a peat pot. This will make planting easier and the root system protected.
A few tips:
- The soil should be chosen peaty, enriched with organic matter. Begonias love acidic soil, grow poorly in alkali and do not bloom. A rational solution is to purchase ready-made land for garden begonias for the growth of seedlings.
- When planting, it is necessary to ensure that the root tuber is planted with sprouts up (if present). It is necessary to fill it with a layer of no more than 25 mm, otherwise the sprouts will not hatch to the surface.
- The temperature regime for high-quality growth is not lower than plus 18 C, optimally - plus 21-22 C.
The plant culture grows actively - neat leafy rosettes will hatch after a week. It is easy to care for them - regularly water and feed with a liquid composition 1 time in 7 days.
Plant diseases and insect pests
When grown, bushes are often attacked by harmful insects. Flowers are most often infected when growing in a greenhouse.
The main pests:
- Greenhouse aphid.
- Shield.
- False shield.
- Whitefly.
- Thrips.
- Nematodes.
The problem should be dealt with by systemic agents, the dose of which is indicated in the instructions. Diseases develop due to improper care, frequent watering, improperly selected land.
It usually affects:
- Powdery mildew.
- Gray rot.
- Bacterial spotting.
- Ring spot.
Therapy is aimed at eliminating the fungi that provoke the disease. The bushes must be treated with fungicides.
What can be combined with garden begonia?
Garden begonias look perfect in plantings with lawn herbaceous plants, ornamental deciduous crops, and border summer plants:
- Surfinia.
- Iberis.
- Lobelia.
- Lobularia.
Plant well next to low-growing bushes, which will give begonias some shade and beautify the site.
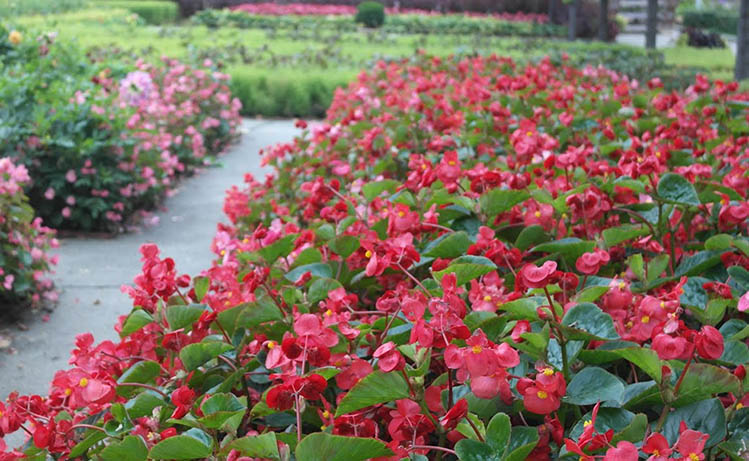

Ever-flowering begonia