Useful properties and chemical composition
Fern contains carbohydrates and related compounds, organic acids, triterpenoids, phenol carboxylic acids (and their derivatives), flavonoids (the largest class of plant polyphenols) and lipids. The maidenhair leaves themselves contain steroids and lipids.
Note: The information below is a study of traditional medicine. For serious matters, it is better to consult a doctor.
Consider personal intolerances.
Adiantum has medicinal properties and is actively used in traditional medicine in Western Europe. Water extracts of this plant kill bacteria well, infusions and syrups are used as an expectorant for respiratory problems, have an emollient effect.
Maidenhair can be used to bring down the temperature. The herbal collection is used in folk medicine to treat respiratory tract infections, and the plant also facilitates the course of diseases of the liver, bladder and spleen. In India, a paste made from crushed leaves is used to heal wounds and abrasions. A mixture of juice and honey is good for gastralgia.
The main application of maidenhair is to help in quitting smoking, strong coffee and drinking alcoholic beverages.
Fern is also used in pharmacology to improve the taste of syrups.
Signs and superstitions associated with the maidenhair
Since ferns have existed on earth long before humans appeared, the plant is of interest. Numerous folk signs and superstitions that have come down to our time tell about what changes can occur in life when meeting him in nature or when breeding at home.
Another important feature of the fern is that it is a magnet for financial flows. Those wishing to improve their financial situation are advised to have a maidenhair in the apartment. In addition to money, the miracle plant also attracts good luck. That is why gamblers love it so much. There is a legend that if you find a fern flower on the night of Ivan Kupala, any wish will come true.
Problems, diseases and pests of the maidenhair
Maidenhair is a long-lived houseplant. Despite the fact that this fern is a rather effeminate creature. Even with care errors, parasite attacks and illness, it can be restored to a healthy appearance. It should be noted that insect pests infrequently attack the maidenhair.
Table: what to do if the leaves turn yellow, turn black, dry or curl
| Problem | Cause | Elimination |
| Leaves turn yellow from the base. On adults - brown spots, leaves die off. | Too warm air, overheating Insufficient watering Drafts. | Most likely, there is a heating battery nearby, move the plant away from it. Protect with a screen. Observe the watering regime and avoid drafts. |
| Yellow leaves with brown tips, no new growth. | Air is too dry. | Humidify the air in all suitable ways. |
| Leaves turn pale, lose color. There are traces of burns on the sheet plate. | The light is too bright. Direct sun. | Move the maidenhair deeper into the room, further from the window, shade it. |
| Pale leaves, slow growth in spring and summer. | Nutrient deficiency. | During active growth, feed the plant regularly, but little by little. |
| Leaves die off en masse. | Dry air, overdried earthen lump. | Remove dry leaves, if necessary, cut them to the ground. Follow the rules of caring for the plant (spray and water regularly). |
| The leaves are withering, but the soil is moist. | Decay of the root system. | Dry the soil, adjust the watering regime. If it does not help, remove the plant from the pot, remove rotten roots, transplant into a new sterilized substrate. |
| Leaves curl but don't dry out. | Maidenhair is too cold, waterlogged soil. | Move the plant to a warmer place. Let the earthy one dry out. |
| Maidenhair leaves darkened, brown streaks appeared. | Salt has accumulated in the soil. | Check the acidity of the soil, it should be slightly acidic. If the pH is below 5.5–6.5, replace the soil. |
| The maidenhair leaves turn bronze at the edges, from the edge, and then entirely. | This is a viral disease, carried by thrips, small flying insects. | Not amenable to treatment. Destroy the plant to prevent the virus from spreading. Get rid of thrips, spray the plants with insecticide. |
| Leaves turn pale, curl, die off, tiny insects are visible. | Defeat by aphids. | Treat the plant with a special aphid remedy, follow the instructions for the preparation. |
| The leaves are discolored and dry, sometimes red-brown spots and white spider webs appear. | Spider mite infestation. | Spray maidenhair with a systemic insecticide (fitoverm). |
| Hard brown plaques on the leaves. If you do not take action, the leaves turn yellow and become covered with a sticky coating. | The defeat of the scabbard. | Remove insects with a damp cloth, treat the plant with an insecticide solution (fitoverm). Repeat the treatment regularly until the pest is completely eliminated. |
Types of maidenhair
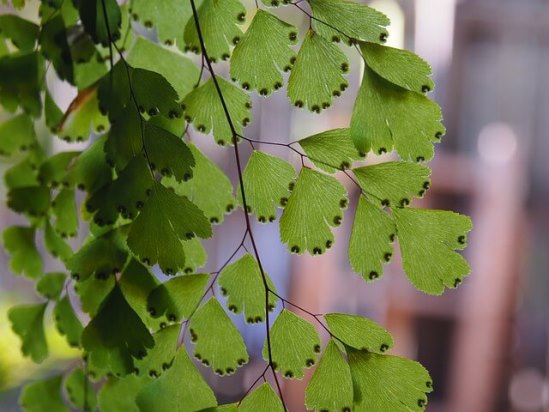
Adiantum capillus-veneris
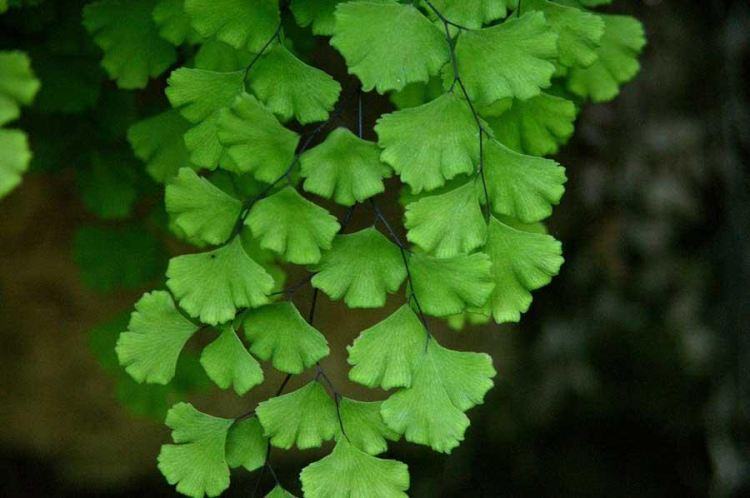
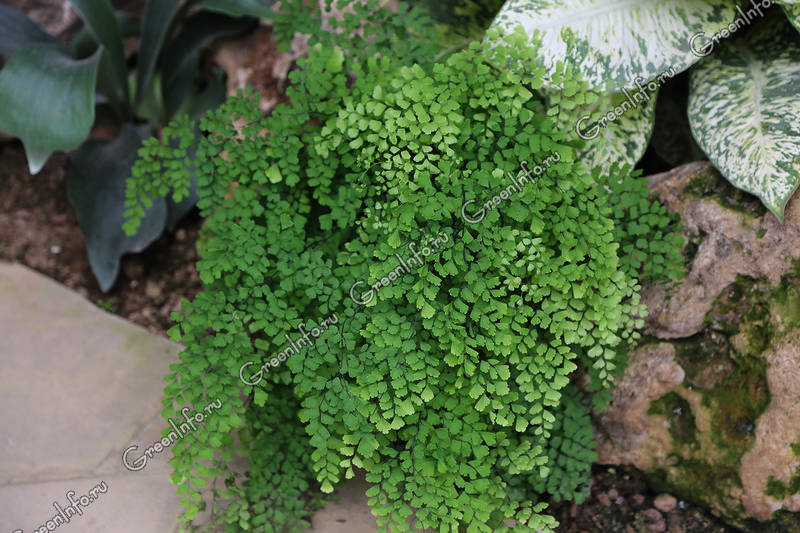
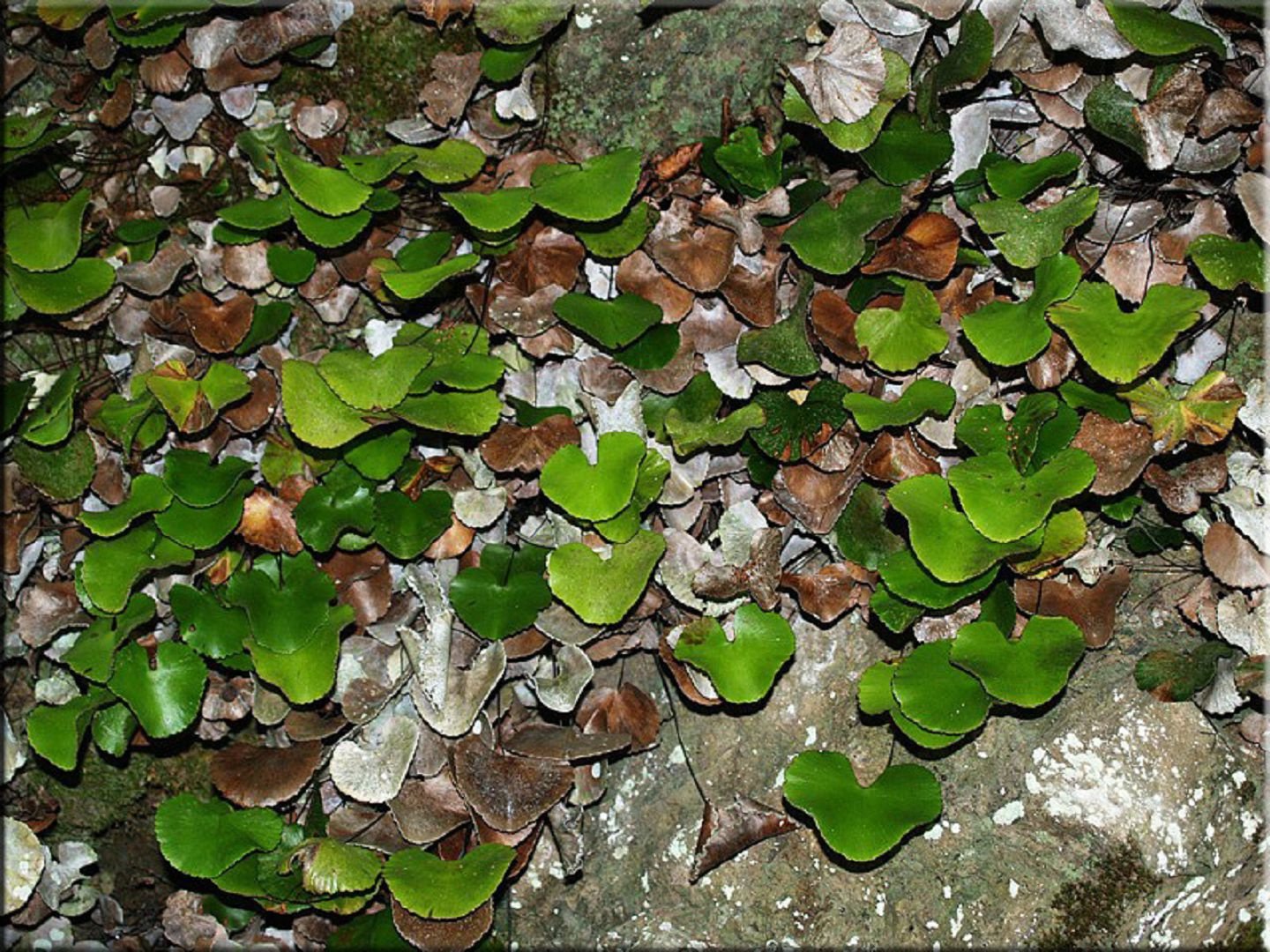
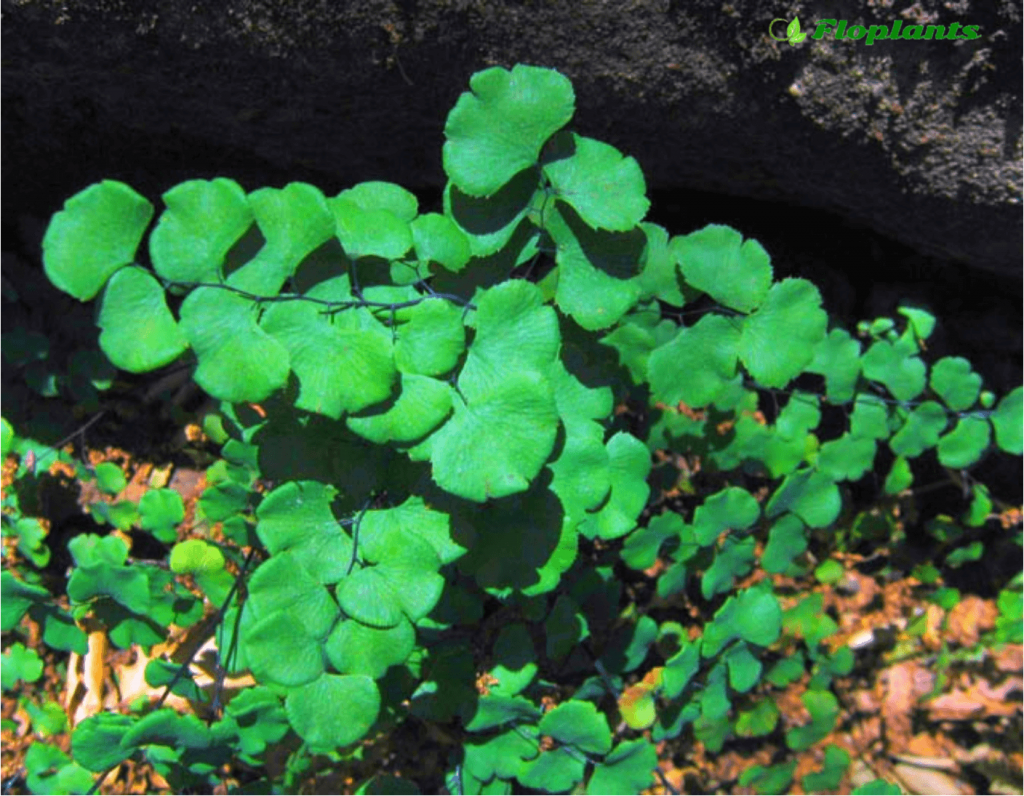
It grows in the wild in the mountains of the Caucasus and Crimea, in Central Asia, preferring moist limestone stones near water sources. It has thin black rhizomes. The plant is so named because of the light, delicate fan-shaped light green leaves on petioles up to 25 cm long. It is grown mainly as a houseplant.
Adiantum pedatum
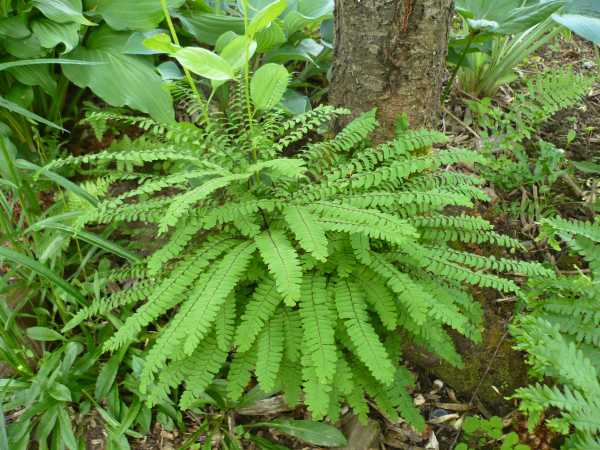
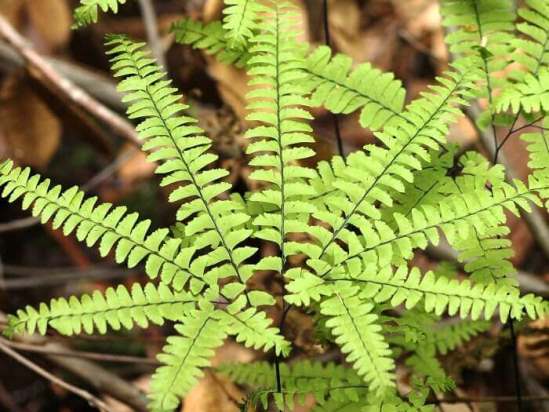
One of the most spectacular ferns, a graceful, openwork plant in the deciduous forests of East Asia and North America. This type of maidenhair reaches 60 cm in height, its leaves are flat, shiny, one-sided, light green, pinnately dissected, incised along the edges, located horizontally on thin shiny petioles.
The species is extremely winter-hardy - it can survive frosts down to -35 ºC. The best varieties of the species are:
- Compactum is a fern reaching a height of 35 cm;
- Imbricatum is a dwarf variety, a plant up to 15 cm tall;
- Aleutikum - the height of this maidenhair is only 10-12 cm with a bush width of 15-20 cm. Most often it is grown in a pot, since it tolerates the sun better than other ferns;
- Yaponikum - the height of this variety is about 45 cm, the diameter of the bush is about 30 cm. It differs in copper-pink shoots at a young age, which gradually turn green.
Tenerum adiantum (Adiantum tenerum)
Or maidenhair pink, lives in nature in the Lesser and Greater Antilles and in the tropical regions of America. This is a plant with a creeping short rhizome and with triple-feathery, wedge-shaped at the base and broadly lobed leaves about 70 cm long and up to 50 cm wide on the upper edge, located on petioles up to 30 cm long. Varieties:
- Farleyens - maidenhair with beautifully curled leaves;
- Scutum Roseum - young leaves of this variety up to 30 cm high have a changeable color from pale pink to green.
Small-haired maidenhair (Adiantum hispidulum)
Or small pubescent maidenhair, grows in the African mountains along the snow line, as well as in India, Australia, New Zealand and Madagascar. The rhizome in plants of this species is creeping, the leaves are hand-dissected, 15 to 25 cm long, on petioles up to 35 cm long, covered with small bristles. Leaflets of the second order up to 2 cm long and up to 0.5 cm wide, also pubescent on both sides with small bristles, have a rhomboid shape. A wonderful houseplant.
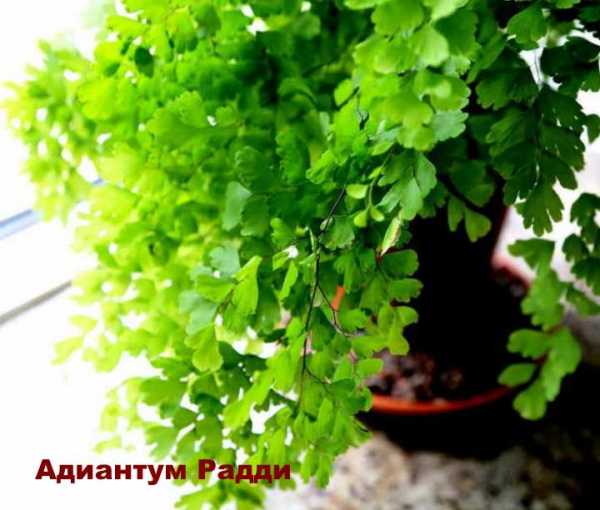
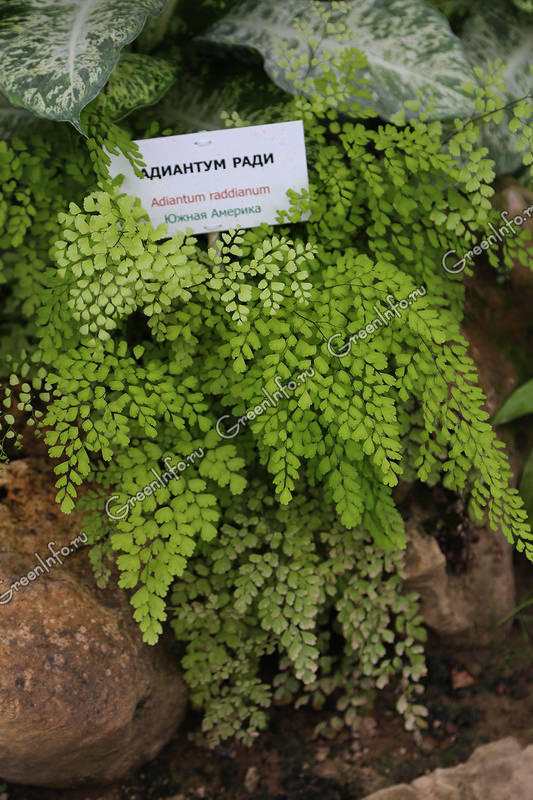
Adiantum raddianum
Or wedge-shaped (Adiantum cuneatum) - an epiphyte native to the subtropical forests of Brazil. Leaves up to 45 cm in length and up to 25 cm in width are gracefully curved and dissected into many bright green leaves on shiny black petioles. The most common varieties in culture:
- Grasillium and Micropinnulum - these maidenhair leaves are finely dissected and require high humidity, so it is best to grow these varieties in a florarium;
- Fritz Luth and Festum are much more resistant varieties that can be grown as indoor plants.
Adiantum caudatum
It is grown as an ampelous plant, since it forms leaves up to 60 cm long. The petioles of the leaves are brown, on the tops of the leaves there are offspring. Plants of this species react very painfully to the drying out of the earthen coma.
Beautiful maidenhair (Adiantum formosum)
Or beautiful maidenhair - a large plant up to a meter high with a very fragile rhizome and multi-pinnate leaf plates on purple-black petioles. Segments of leaves are dark green, triangular-obovate.
Adorable adiantum (Adiantum venustum)
The fern growing in Nepal and Kashmir forms narrow, up to 20 cm long, light green leaves on black-purple petioles with slightly pointed segments. After frost, the shade of the leaves becomes brownish.
Wedge-shaped maidenhair (Adiantum cuneatum)
It is very similar to the beautiful maidenhair, it differs only in the shape of the sori, which resembles a horseshoe. In nature, this species grows in the south of Brazil.
Transparent adiantum (Adiantum diaphanum)
Herbaceous plant 25-40 cm high with feathery leaves, double-pinnate at the base. Fries up to 3 cm wide and up to 20 cm long on thin twenty centimeter petioles with bare broad-oval leaves of a dull green color.
Adiantum Fragrans
Very often, maidenhair fragrant is grown in culture - it lives in the South American Andes and South Asia and forms dense bushes. It is a gentle, rapidly developing plant up to 50 cm high with pale green oval leaves up to 3 cm long and up to 1.5 cm wide on petioles 10-15 cm long.
Features of the maidenhair
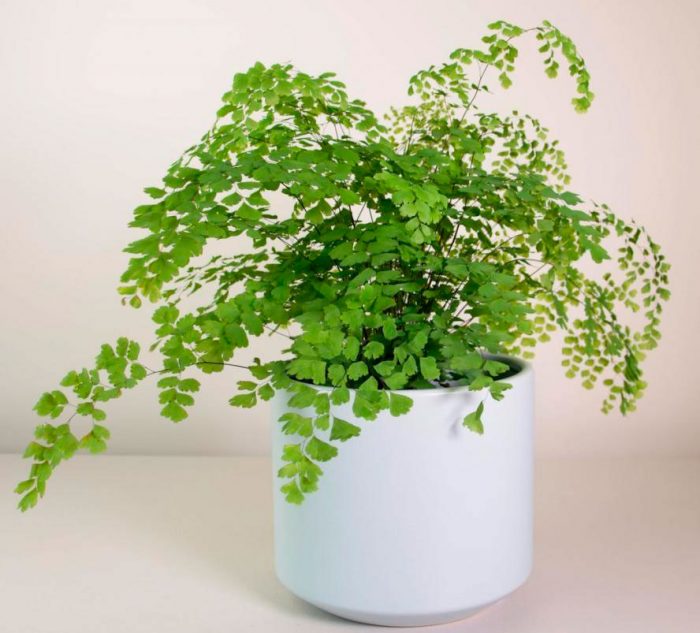

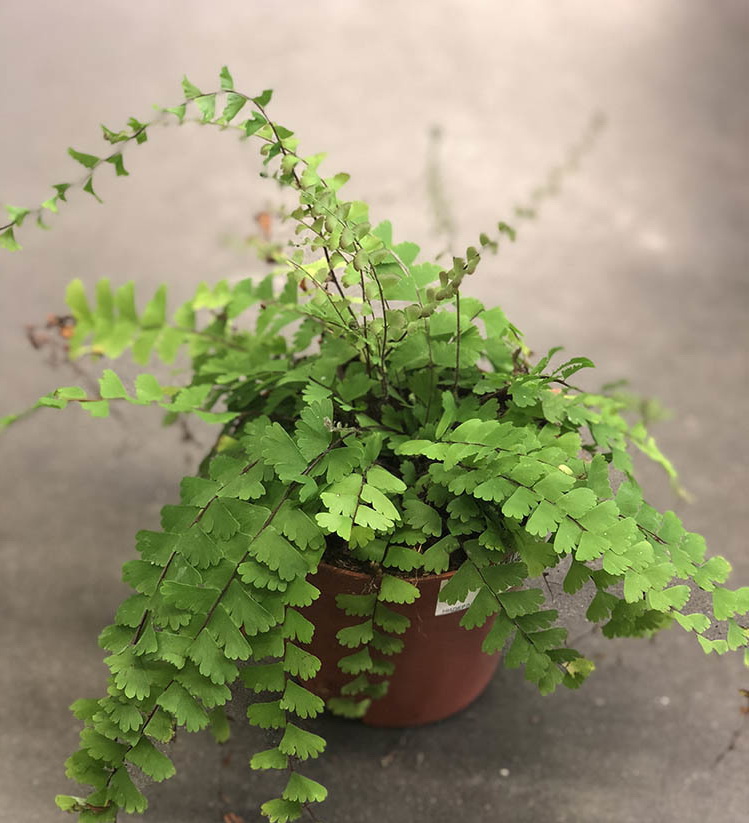
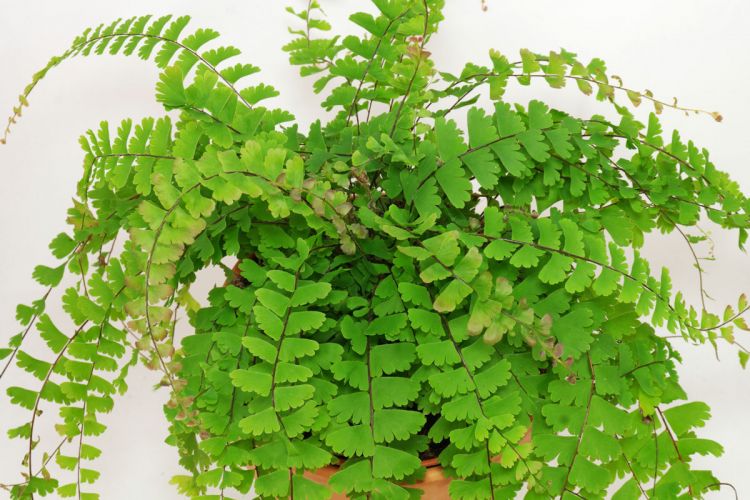
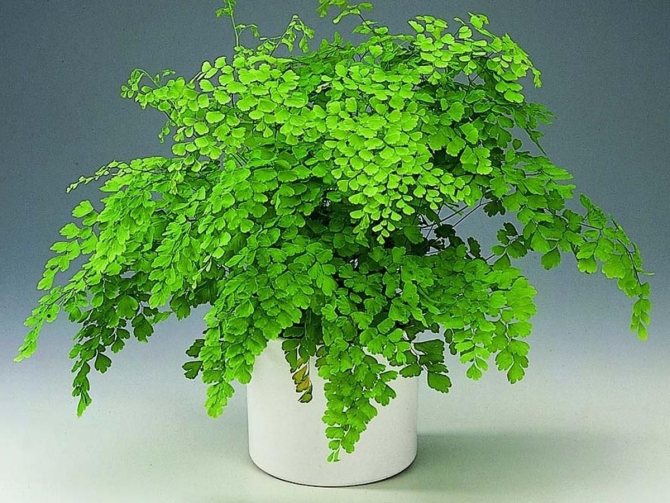
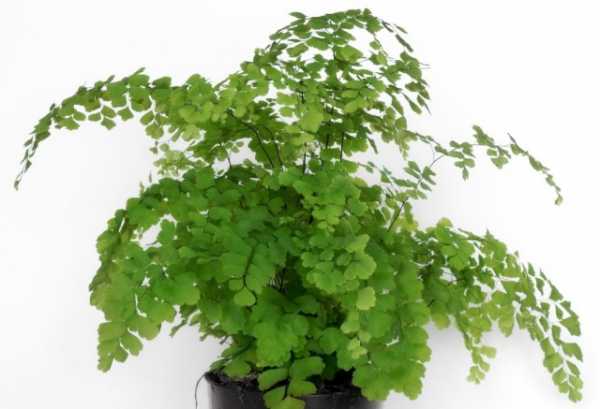
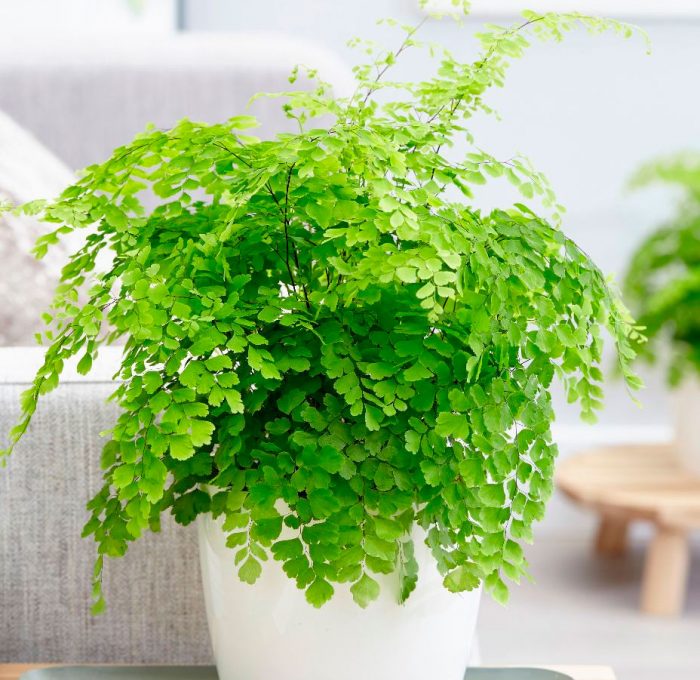
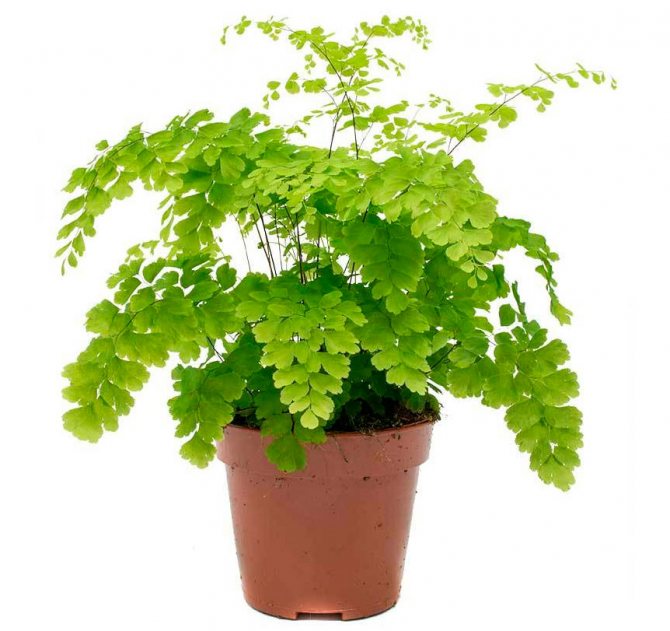
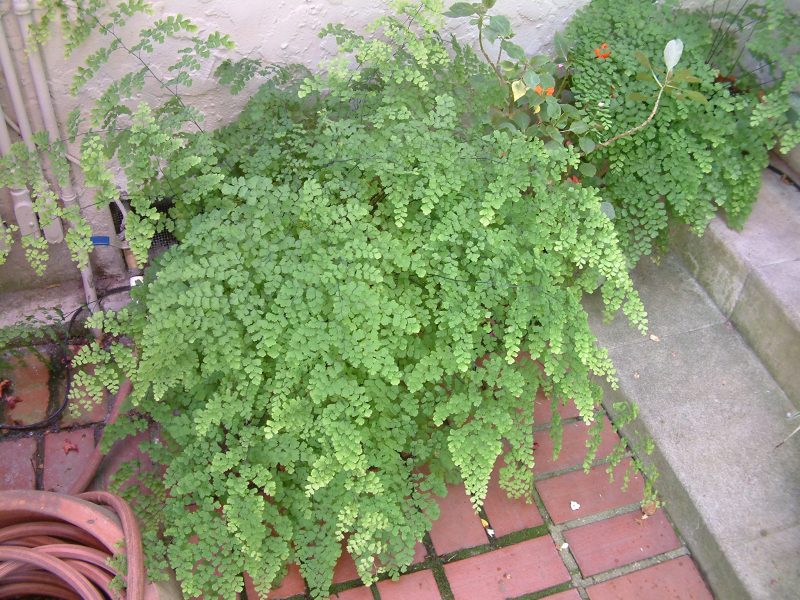
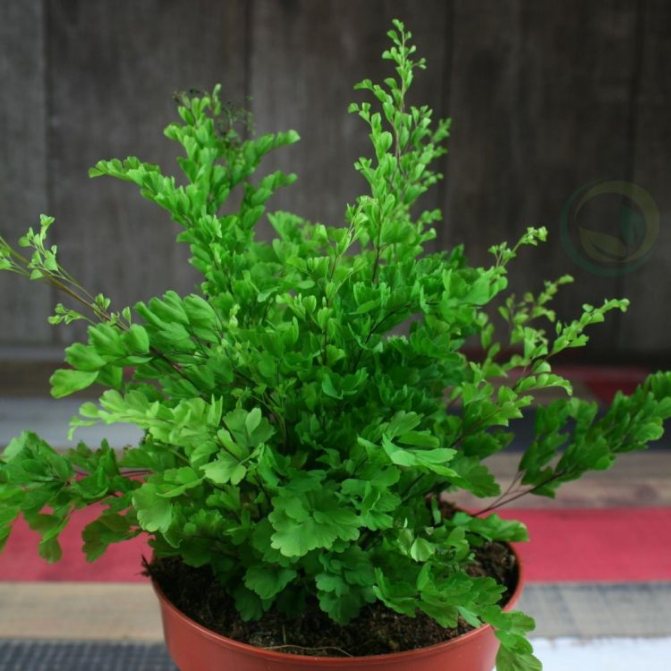
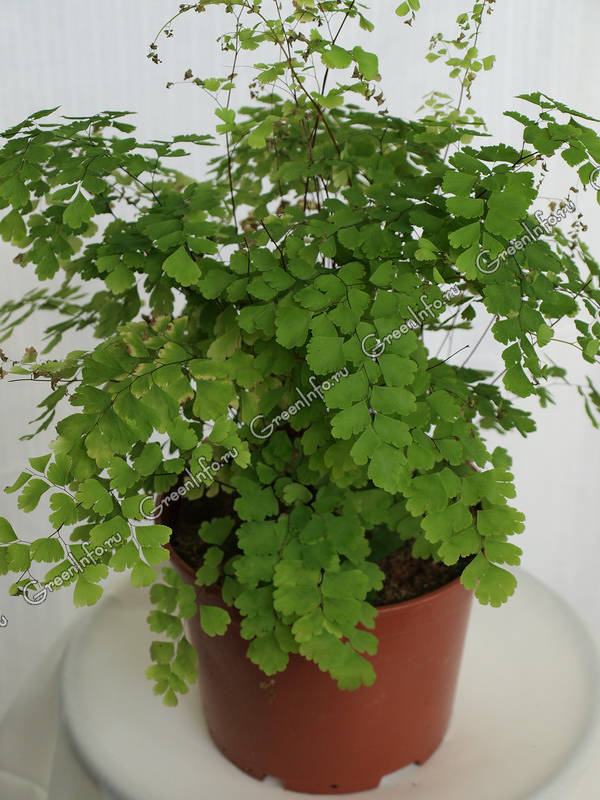
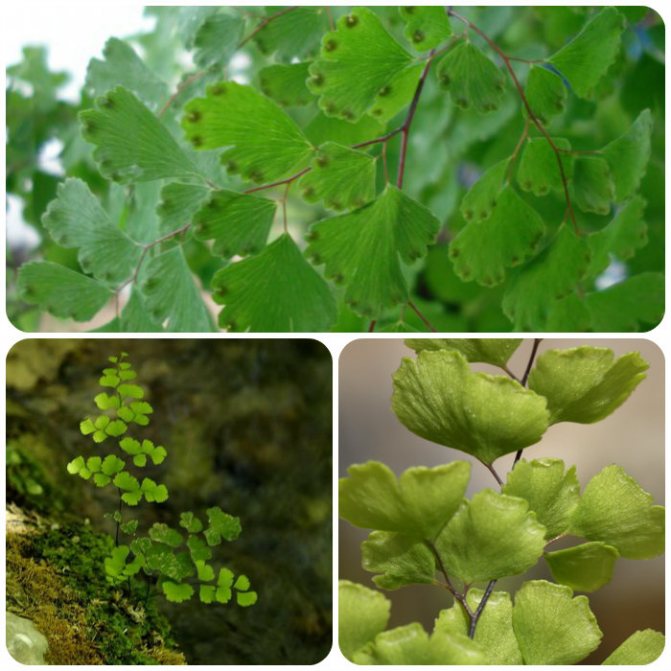
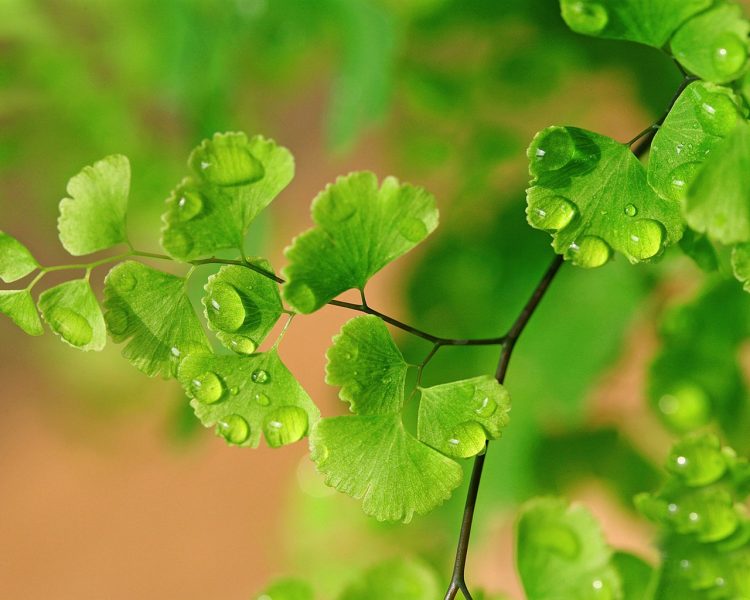
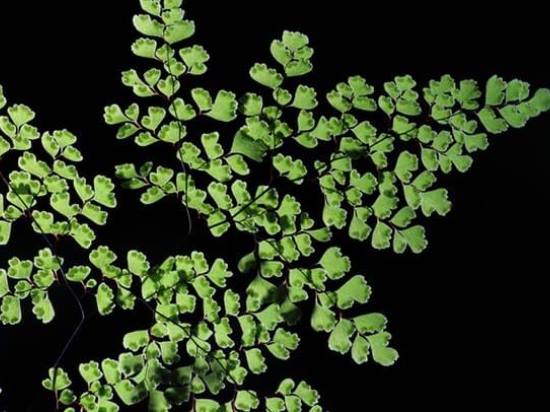
The maidenhair fern is a perennial herb, its rhizome is thin and creeping, it is covered with matte scales of brown or black color. The leaf plates can be alternately or oppositely located, they have dark glossy petioles, which reach about 25 centimeters in length. Petioles at the base are covered with scales. Smooth and wide, strongly dissected foliage is colored green or gray. Its segments are fan-shaped; they are obovate, wedge-shaped and trapezoidal. On the seamy surface of the segments along the veins, there are sori with sporangia of an oblong, round or linear shape. Most often, the maidenhair is grown in the garden, and at home, the maidenhair, called "Venus hair", is most often cultivated, as well as the transparent maidenhair, Ruddy, gentle, etc.
MAIDENHAIR. Everything about care - LIGHTING, IRRIGATION, FERTILIZER, HUMIDITY, SOIL, PESTS and DISEASES.
3. Propagation of maidenhair
This fern grows from rhizomes that spread horizontally below the soil surface.
Most often, the plant is propagated in the spring by dividing a large bush during transplantation. Only large mature plants that have sufficient growth points in the root system can be divided.

- Before dividing, the fern is not watered for several days, drying the soil.
- The rhizomes are divided into several parts with a sharp sterile instrument.
- The wound surface resulting from the division with charcoal powder or ash is treated and seated in separate pots.
- Each division should have its own leaves - 2 - 3 fronds and well-developed roots.
- To help plants adapt to new conditions faster, the delenki are covered with a transparent plastic bag or plastic cap to maintain a high level of humidity and occasionally sprayed with warm water from a spray bottle.

You can try to propagate the maidenhair using spores, but this method will require much more time and labor, but it will allow you to observe the development of the fern from the very beginning.
Spores can be sown over the soil surface in the spring.
- For sowing spores, a plastic transparent container with a lid is selected and a small drainage layer is placed on its bottom.
- The container is filled with a fresh loose peat-based substrate with leaf humus and river sand.
- The soil in the container is thoroughly moistened with warm water using a spray bottle.
- Since the fern spores are too small, they are pre-mixed with a small amount of sand or used for sowing with the tip of a toothpick, slightly moistened with water.
- Spores should not be covered with a layer of earth.
- Crops are covered with a transparent lid to create a greenhouse effect and maintain high humidity.
- The container is placed in a well-lit, but out of direct sunlight, place with a temperature of about 22 ° C.
Fresh spores have good germination, and it can also be increased by using bottom heating.
Every day, the crops are ventilated by removing the shelter and removing condensate that has emerged from it. Airing time is gradually increased.

The first shoots may appear within a week. Germination does not occur at the same time - some bushes can stay in the ground for 2 - 3 months.
If most of the spores have sprouted in the container, then the shelter can be completely removed and from time to time humidify the air around the plants with warm, settled water.

When each bush can boast 2 vayami, you can make a pick, carefully transferring the plants of 2 - 3 bushes into small cups.
When diving, they try to disturb the tender bark system of young plants to a minimum.
The first feeding is done 2 - 3 weeks after the dive. The nutrient solution is used at a very low concentration.
Sometimes plants kept in good conditions self-seeding.

Problems: what to do if ...
"What if all the leaves are dry and yellow?" - no problem! It is necessary to cut off the entire leaf mass and spray it twice a day with warm melt water until the plant gains the proper mass.
“… If the leaves are wrinkled and brown at the edges?” - abundant watering is required. Additionally, high humidity is required. It will increase the chance of survival of the maidenhair. Leaves dry from tobacco and regular smoke.
“… Have the leaves fallen?” - it is either a deciduous variety or the air is very dry. Increase the humidity before cutting off the yellow leaves. Spray the plant with warm water daily.
“… Have the leaves turned pale?” - move the maidenhair to a shady place. Perhaps the sun burned him.
"... the leaves are thin and lifeless?" - top dressing is required if this happened in the summer.
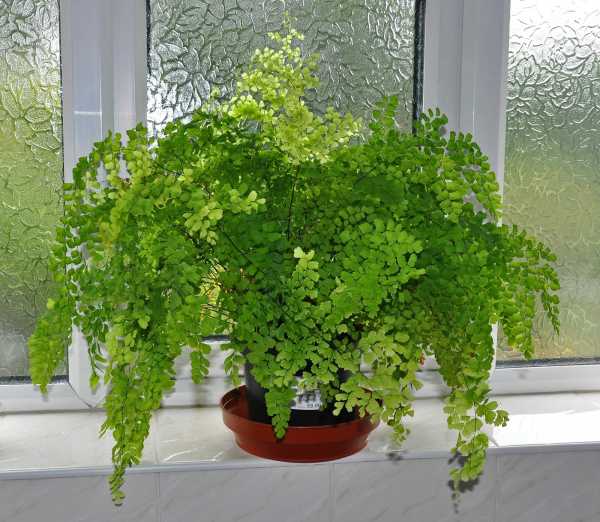
Maidenhair care
Lighting. Maidenhair are shade-loving plants that do not like too bright sunlight. Sunlight causes browning and death of leaves (wai). Grows well near north-facing windows.
Temperature. For good growth in summer, the optimum temperature is 21 ° C, with low air humidity, the plant cannot tolerate temperatures above 22 ° C. In winter, the optimum temperature is in the range of 15-20 ° C, lowering the temperature below 10 ° C can lead to the death of wai, and sometimes to the death of the plant. Tolerates a fairly wide range of temperatures, most cultivated varieties can grow outdoors in summer.
Peculiarities. Plants do not tolerate drafts, cold air and dust. Also, the maidenhair is badly affected by the products of gas combustion and tobacco smoke.
Watering.In the summer, the maidenhair is watered regularly, the earthen lump should not dry out, this can lead to the withering away of wai, and waterlogging should also not be allowed. It is optimal to water by lowering the plant into a vessel with water, as soon as the top layer shines with moisture, remove the pot, drain the excess water and put it in a permanent place. In winter, watered moderately, depending on the requirements of the plant and the dryness of the air. For irrigation, use soft water at room temperature.
Moisturizing. Maidenhair loves frequent spraying; in summer, at high temperatures (above 22 ° C), dry air can lead to the death of wai, if this happens, cut them off, spray the plant regularly, and new frond will soon appear. Place the pot in a larger bowl filled with damp peat, or on a tray with damp pebbles. In winter, you should spray the maidenhair with soft warm water every day; if the room is cool, then spraying should be reduced to avoid mold.
Fertilizer. In the summer, once every three weeks when watering, feed the maidenhair with half the recommended dose of liquid fertilizer for indoor flowers.
Pruning. Only damaged or very old leaves should be trimmed. If the maidenhair bush accidentally dries up, cut off the dried leaves, and what remains, regularly water and spray twice a day - young leaves will soon appear. Among other things, daily spraying keeps the plant clean. Do not use any formulation to make the leaves shine.
Transfer. The maidenhair is transplanted in the spring (if the pot is too small for the plant), after the plant starts to grow. The earthen mixture is made up of equal parts of turf, leaf, peat land and sand (1: 1: 1: 1). Small shards and pieces of charcoal are added to this mixture. When transplanting, dead roots are removed, and live ones are not cut off and, if possible, do not damage, since they grow very slowly. Don't push the soil too hard - ferns love loose soil at the roots. After transplanting, the plant is watered and sprayed. Choose a wide pot for planting.
Reproduction. The maidenhair is propagated by dividing the bush and spores.
By dividing the bush, the overgrown bush is propagated, usually in the spring, when transplanting
The bush is carefully separated by hands, paying attention to the number of growth points. If there is only one growth point or they are few in number, then it is impossible to divide the plant, this can lead to death. Young plants after division do not immediately start growing.
Young plants, after division, do not immediately start growing.
You can try to propagate the plant from the spores that form on the underside of the leaves. They are sown in early spring, best of all in a nursery, heated from below, where a temperature of 21 ° C is maintained.
Cut off a leaf from the plant and scrape the spores onto paper. Fill the nursery with a layer of drainage and decontaminated soil for sowing seeds. Water the soil well and scatter spores as evenly as possible. Cover the nursery with glass and place in a dark, warm place. Remove the glass briefly every day to ventilate, but do not let the ground dry out. The nursery should be kept in the dark until the plants appear (this will happen in 4-12 weeks). Then transfer it to a lighted place and remove the glass. When the plants grow, thin them out, leaving the strongest at a distance of 2.5 cm from each other. Young specimens that develop well after thinning can be transplanted into pots with peat soil - 2-3 plants together.
How to propagate maidenhair
It's a simple and fun process. The maidenhair can be divided by the rhizome at the beginning of the summer season. Delenki are placed in separate pots and await growth. This usually takes a long time. Be sure to treat the cut points with activated carbon, otherwise the cuttings will die from rot.
Spores form on the underside of the leaves of the maidenhair - you can propagate them.To peck, you need a nutritious soil based on peat and a temperature of exactly 21 degrees Celsius. Make a mini-greenhouse and bottom heating of the soil - if possible, it will not be superfluous.
How to propagate by dividing rhizomes
For dividing rhizomes, adults, large plants are suitable:
- You will need two growing containers. Provide them with drainage and a layer of nutrient soil;
- Remove the adult maidenhair from the pots and remove the soil;
- Divide the rhizome with your hands, so that root shoots and stems remain on each plot;
- Plant the cuttings in different pots.
Reproduction by spores
Spores for reproduction are located on the inside of the leaf. The process consists of several important steps:
- Cut off the spore leaf and gently scrape the planting material onto paper or foil ;;
- Warm the tray with the nutrient mixture slightly (up to 21 degrees Celsius), creating a mini-greenhouse;
- Sow seeds over the surface of the soil and cover the container with glass, plastic and a transparent lid.
Further care of the seedlings consists in daily ventilation. It is like prevention against rot. But, the soil should not dry out. Maintain high humidity and temperature for 8-12 days. By the end of the incubation period, the maidenhair should have scales and small sprouts.
How to remove the transparent cover - young ferns are taken out to a lighted place (avoid sunlight). Adiantums dive, removing frail plants, leaving the most grown and strong ones. There should be a distance of 2.5 cm between the seedlings.
After about 2-4 weeks, transplant the young into new, more spacious pots, 2-3 pieces each. The planters should be small - already the root system.
Home care
Adiantums react very painfully to a change in habitat. Therefore, having purchased a flower, try to immediately find a place of permanent residence for it. And place it there.
If the maidenhair is to become a part of the collection among other shade lovers, then for the period of quarantine after the purchase it is better to rearrange all the other plants, and not a beginner, as is usually done. After 2 weeks, residents can be returned to their places.
Lighting and humidity
Caring for this fern is not as difficult as it is sometimes described.
Two main points are known and unshakable: adequate watering and light shading.
It is important not to overdry the soil, but it is equally important not to overmoisten. It happens that the maidenhair dries the leaves, the owner, in order to remedy the situation, increases watering
As a result, the plant dies
It happens that the maidenhair dries the leaves, the owner, in order to remedy the situation, increases watering. As a result, the plant dies.
This does not happen immediately, but if the soil in the pot has turned into a swamp, then sooner or later it will happen - the roots will rot
The soil should be wet, not wet all the time, this is important
As for lighting, you should definitely not expose the plant to direct sunlight. If you still grow it on the windowsill, then only on the north side.
Very often, among the recommendations for care, you can find the desire to spray it daily. I would like to immediately make a reservation about this: if you have a lot of free time, then you can spray even several times a day. It will not harm the plant. But it won't do any good either.
The fact is that maidenhair, unlike other ferns, repel water and are not wetted by it. It is even defined in the name - "a" - negation, not, "dianio" - to wet, get wet (Greek).
But since adiantums do not like dry air very much, one should go the other way. It is necessary to ensure that the air around the plant is constantly moist. To do this, you can place several containers of water around the pot. Or place the pot on wet expanded clay.
The pot should be with a tray, the roots through the hole should not come into contact with water - we are interested in moist air, not rotten roots.In these two cases, you need to ensure that there is always water in the containers.
The most optimal way to maintain air humidity is to group plants. Place the plant in a flower arrangement of a variety of ornamental foliage plants that have similar environmental requirements (temperature and light). Most of them need spraying.
Here it will be very appropriate, unlike spraying a free-standing maidenhair. Water droplets evaporating from the leaves of surrounding plants will create air humidification.
Watering and feeding
In the summer, watering should be regular. In summer, it is recommended to completely immerse them in water (in a pot). The earth should be well saturated with water and shine. After the procedure, it is necessary to let the excess moisture go away. The main thing is not to overdo it. Only when all the excess water is drained can the maidenhair be put back.
In winter, maidenhair is watered depending on the temperature in the room and the humidity of the air. If the ground is clearly too dry and requires watering, you need to water the fern with not too much warm (but not hot!) Water.
During the summer months, you need to feed the maidenhair with special houseplant liquid mixes, which can be found at any gardening store like OBI. In winter, feeding is not worth it.
Temperature
The temperature of the content of maidenhair is the same as for most ferns - moderate.
Here the rule works well: the higher the temperature in the room, the more humid the conditions should be.
That is why in houses where central heating "rages" in winter, you need to take special care of this.
Most of the maidenhair perishes after the start of the heating season.
Some species are able to withstand low temperatures down to minus 25 degrees and are able to spend the winter outdoors even without shelter.
Other winter-hardy ferns suitable for cultivation in the garden or on the backyard include: Ostrich, Kochedyzhnik, Osmunda, Bubble, Orlyak, Mnogoryadnik, Shitovnik
Pruning
Dried parts of the plant should be regularly trimmed over the substrate. Ferns do not need a special crown-forming pruning.
Transfer
As with many other plants, the most favorable period for maidenhair is spring. It is in the spring that the fern should be transplanted. Take a large, wide pot so that the maidenhair has room. Rotten rotten roots should be cut off, and good ones should be left. After planting the maidenhair in the ground, do not crush it! The roots of this plant love loose soil. After transplanting, you need to spray and water the fern.




















































