Content
- 1 A winter greenhouse for cucumbers: what should it be?
- 2 Photo
- 3 Growing cucumbers in a greenhouse in winter: the best varieties for greenhouses
- 4 Choosing the right seeds
- 5 Soil and fertilizer requirements
- 6 How to grow cucumbers in a greenhouse in winter
- 7 Features of care after transplant
- 8 Useful video
- 9 Greenhouse requirements
- 10 Variety selection and seed preparation
- 11 Planting cucumbers
- 12 Care during the growing season and fruiting
- 13 Popular varieties of cucumbers

Fresh cucumbers in winter - a real delicacy and a powerful vitamin bomb.
Delicious fruits are rarely found in stores, so experienced gardeners decide to grow them on their own, in conditions of capital heated greenhouses.
There are many varieties bred specifically for winter fruiting, they can be cultivated in cold regions, getting stable yields. The technology of growing cucumbers in a greenhouse in winter is successfully used in many regions of the country. It has been tried and tested with good results. From this article you can learn how to grow cucumbers in a greenhouse all year round.
…
A winter greenhouse for cucumbers: what should it be?
So, where to start growing cucumbers in a greenhouse in winter. Primarily, for winter cultivation need a greenhouse on a solid concrete foundation. Constructions buried in the ground have proven themselves well. The soil layer serves as an additional insulation and protection, deepening allows you to make the structure less high, without limiting the plants in space.
The best greenhouses for cucumbers are built from polycarbonate, reinforced on a metal frame with an anti-corrosion coating. They are not cheap, but pay off in 2-3 years. Believe me, a high-quality greenhouse for growing cucumbers will bring excellent results all year round.
In addition, it almost does not require repair, durable cellular polycarbonate does not crack under a layer of snow, calmly tolerates temperature extremes. It is possible to use greenhouses with tempered industrial glass, but such a coating is more fragile.
The structure must also be equipped with vents for ventilation and curtains for shading from too hot the sun.
The system of automatic drip irrigation is very convenient, which guarantees optimal soil moisture. Cucumbers love high air humidity, so do not forget about the climate control system and foggers.
It is equally important to properly organize the lighting for cucumbers in the greenhouse in winter. This requires powerful electric lamps with adjustable height.
Heating is a very important issue. Cucumbers are a thermophilic culture that can hardly tolerate even a short-term drop in temperature.
Warm greenhouses you can use electric boilers or compact wood-burning stoves. Biofuel made from humus and straw, spread out along the ridges, as well as sheets of roofing material placed around the perimeter of the greenhouse for the winter cultivation of cucumbers, will help maintain the desired temperature.
The lower the outside temperature, the more perfect the heating system should be. In regions with a particularly cold climate, it is better to use a combined method, combining several heating methods at once.
Most often, cucumbers are planted in the ground. But in spacious industrial greenhouses, rack growing in 2 and even 3 tiers is also practiced. This approach makes harvesting easier and saves on scarce greenhouse space.
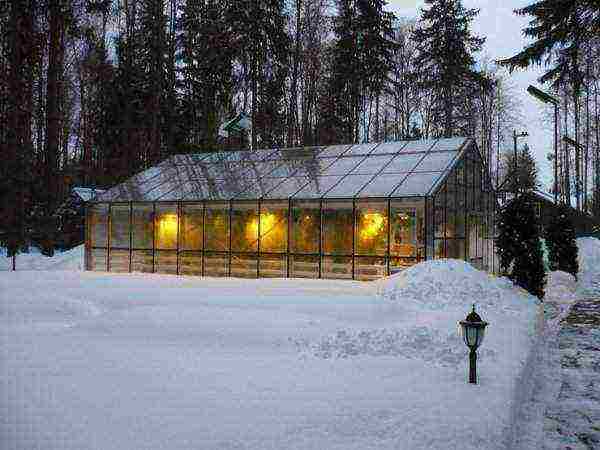
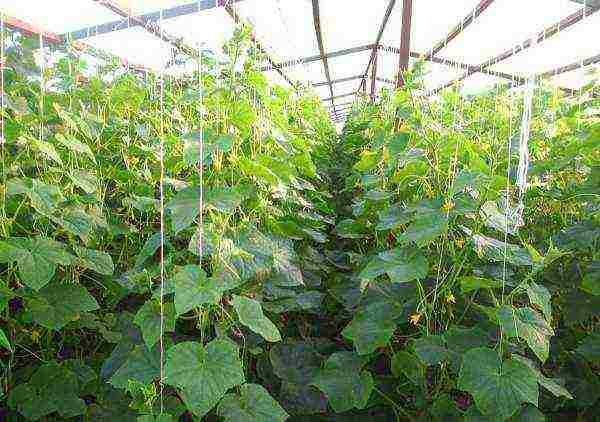
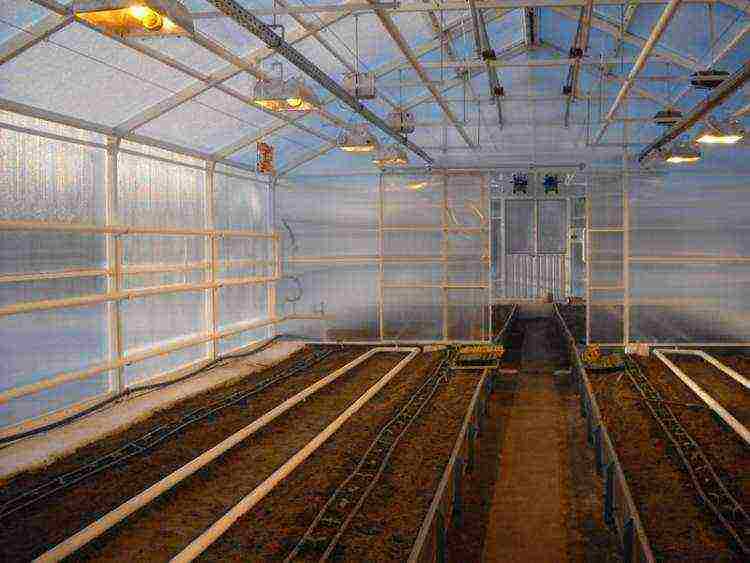
Photo
In the photo below: a greenhouse for growing cucumbers all year round, cucumbers in a polycarbonate greenhouse in winter.
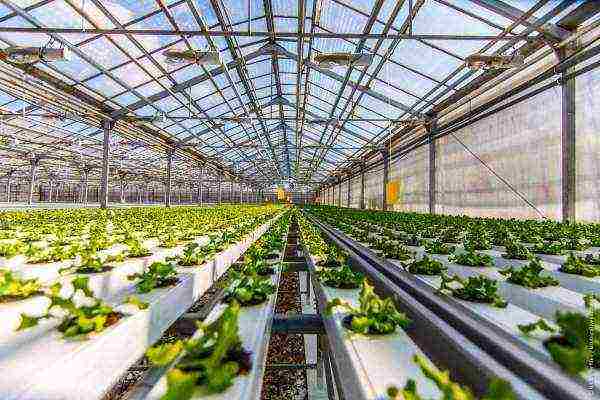






Growing cucumbers in a greenhouse in winter: the best varieties for greenhouses
In the greenhouse, it is convenient to grow cucumbers that do not give long lashes. Such plants are compact, delicate stems are not damaged during care and harvest. It is worth paying attention to varieties and hybrids with a shortened growing season that do not require pollination. There are a lot of suitable options, it is recommended to try several varieties and choose 2-3 of them that are most suitable.
- Valaam - a very productive early ripe hybrid, suitable for temperate and cold climates. The fruits are very tender, without bitterness, rich green color with small black tubercles.
- Suomi - a hybrid suitable for winter cultivation, easily tolerates a slight drop in temperature. Fruits are small, neat, almost never outgrowing. They have a pleasant, non-watery taste.
- Bouquet - one of the earliest varieties, the crop can be harvested a month after moving the seedlings into the ground. Typical is "bouquet" fruiting, producing several fruits from each leaf axilla.
- Sarovskiy - a fruitful hybrid, characterized by endurance and productivity. "Bouquet" variant, giving high yields of medium-sized, even and very tasty cucumbers.
- Okhotny Ryad - an early ripe hybrid with an extended fruiting period. The fruits are small, elongated, very delicate in taste.
Choosing the right seeds
 Experienced growers recommend choosing cucumber seeds harvested 2-3 years ago. They are distinguished by better germination, the sprouts are healthy and strong.
Experienced growers recommend choosing cucumber seeds harvested 2-3 years ago. They are distinguished by better germination, the sprouts are healthy and strong.
The material prepared for sowing needs iterate over manuallyby removing ugly and empty seeds. Then they are disinfected by placing them for 10-12 hours in a damp cloth soaked in aloe juice or an aqueous solution of nitrophoska, copper sulfate and boric acid.
After processing, the seeds are washed, wrapped in a clean, damp cloth and transferred to the lower compartment of the refrigerator. This hardening strengthens the plants and stimulates good fruiting. The seeds should spend 5-7 days in the refrigerator, the fabric should be constantly moistened.
Soil and fertilizer requirements
Cucumbers love light soil, neutral or slightly alkaline. Excessive acidification is unacceptable. The ideal soil consists of old garden soil, peat, rotted humus and river sand. Do not forget that the fertile soil layer changes every year, this is especially important for rack cultivation.
For feeding cucumbers, you can alternate complex mineral and organic fertilizers, but some gardeners rely on organic matter. Cucumbers respond well to an aqueous solution of mullein or chicken droppings. The first fertilizing is carried out after the appearance of the third leaf on the seedlings, the second fertilization begins during the flowering period. During fruiting, cucumbers are fed with organic matter at least 4 times.
How to grow cucumbers in a greenhouse in winter
Cucumber seedlings can be grown in an apartment or directly in a greenhouse. Seeds it is advisable to sow in peat pots, young plants do not tolerate digging well. To get harvests in January, sowing is carried out in early September.
The pots are filled with the prepared substrate, the seeds are placed in holes 2 cm deep. Some gardeners plant 2 seeds in each glass, meaning the subsequent pick.
The soil in the pots is moistened with a spray bottle, and the containers are covered with glass on top. Another way is to cover the pots with a damp cloth. You can sow cucumbers every 2 weeks, seedlings of different ages will help ensure an uninterrupted harvest.
The optimum temperature for germination is 25 degrees. After emergence, the temperature drops to 15 degrees during the day and 12 at night. Plants should be watered 2 times a week using room temperature water. After feeding with a mullein, it is recommended to wash the sprouts from a spray bottle.
The next stage: transplanting cucumber seedlings into a winter greenhouse. A month after sowing the seeds, the grown seedlings are transferred to the prepared soil of the greenhouse. The distance between plants is 20-30 cm, between rows - about 90 cm.
Features of care after transplant
Cucumbers - enough demanding culture... To achieve a good harvest, you will have to carefully monitor the level of moisture and soil fertility.
For good health and quick formation of ovaries, cucumbers need feeding once every 2 weeks, with alternating mineral and organic fertilizers. You also need to maintain high humidity - 80-85%. To ensure such indicators, the floor and heating pipes are regularly watered. 
In the greenhouse itself, open tanks are located. They not only humidify the air, but also defend and heat the water for irrigation.
Before flowering period the plants are watered twice a week, after the flowers appear, watering becomes more frequent and abundant.
It is important to monitor the condition of the leaves, they must be firm and juicy. Sluggish, drying sheets signal an acute lack of moisture in the soil.
Light intensity is very important for winter growing. Daylight hours should last at least 12 hours. Young plants are illuminated by low hanging lamps, with an increase in the growth of cucumbers, the lamps rise higher. It is believed that the condition of plants is positively influenced by the warm light spectrum.
Temperature should not fall below 20 degrees, the optimal mode is from 25 degrees during the day to 15 at night. Ventilation should be very careful, excluding the ingress of cold air currents on the plants. Cucumbers stop the formation of ovaries even with a short-term cold snap, and this greatly affects the yield of cucumbers in a greenhouse in winter.
Useful video
How cucumbers are grown in winter greenhouses can be found in the video below:
Fresh cucumbers from your greenhouse in the middle of winter - what could be tastier? With the development of modern technologies, growing vegetables in winter greenhouses has ceased to be a rarity. It's quite easy to get fresh cucumbers to your table or to sell. You just need to properly equip the greenhouse and follow the recommendations of experts on the choice of varieties and technology.

Growing cucumbers in a greenhouse in winter
Greenhouse requirements
Cucumbers are thermophilic and moisture-loving crops, so any drop in temperature or humidity will inevitably affect the yield and health of plants. A winter greenhouse for cucumbers must be insulated and equipped with a heating system.

Winter greenhouse for cucumbers
Best results can be achieved when the following conditions are met:
- correct design and placement of the greenhouse;
- complex heating of soil and air;
- adjustable humidity;
- additional artificial lighting;
- fertile loose soil.
These conditions can be created in a glass or polycarbonate greenhouse. Film greenhouses are poorly suited for winter use due to the low strength of the film: during heavy snowfalls, the film sags, snow lingers on it and can collapse the structure.

Polycarbonate greenhouse
Greenhouse construction
The main requirement for winter greenhouses is the protection of plants from the cold and maximum transmission of sunlight. The best performance is provided by double-glazed back-wall greenhouses with a sloping south wall. Glass or polycarbonate is used as a coating, the frame is made of a wooden bar or a shaped metal pipe. It is better to choose the height of the greenhouse so that the condition of the ratio of area and volume of 2: 1 is observed - for cucumbers it is optimal.

Wall greenhouse scheme
The slope of the roof and south wall in such a greenhouse depends on the angle of the sun above the horizon in your area. It is optimal if the midday rays pass through the glass at a right angle - the reflection coefficient in this case is minimal.

The angle of the sun above the horizon and the correct design of the greenhouse
The beds in the greenhouse are also made inclined or in the form of stepped terraces for better heating. This will allow the sun's rays to illuminate each plant unimpeded. It is recommended to paint the back blind wall white or sheathe it with foil - reflecting from it, the rays will illuminate the plants from behind.
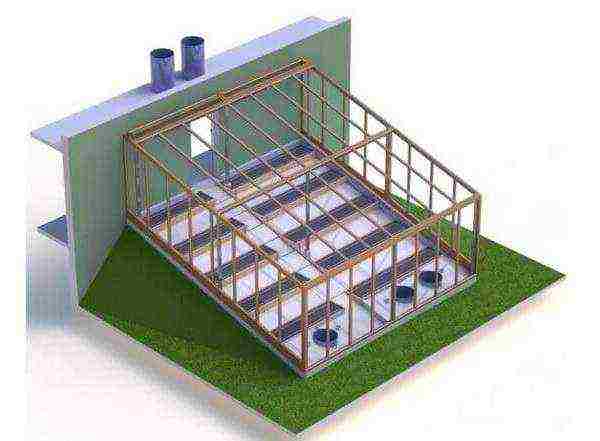
The arrangement of ridges in the form of terraces
It is better to enter the winter greenhouse through the vestibule - this will save the plants from cold air currents. A storage tank for water and heating equipment can be placed in the vestibule. The ventilation system, unlike summer greenhouses, cannot be done through the vents - drafts are contraindicated for cucumbers. It is performed supply and exhaust and is made of plastic pipes.

Greenhouse with a vestibule
Heating
Cucumbers do not tolerate too dry air, therefore, it is not recommended to install heating devices in the greenhouse that dry the air: convectors, oil heaters, as well as metal stoves. It is better to mount a water heating system: the soil is heated using pipes laid in the beds, and the air is heated using radiators or registers stretched along the perimeter of the greenhouse.

Greenhouse hot water heating system
A furnace or boiler is used to heat the coolant. The second option is preferable: the boiler burning time is longer, and the level of automation is higher. The boiler for heating the greenhouse can be gas, electric or solid fuel. The power of the boiler for a greenhouse with a height of 2-2.5 meters is chosen at the rate of 1 kW per 8-10 m2 of area. So, for a greenhouse with an area of 30-35 m2, a 4 kW boiler is enough.

Heating boiler in a greenhouse
You can also connect the greenhouse to your home heating system if it is located in the immediate vicinity of your home. In this case, the boiler must have a power reserve sufficient to heat the greenhouse. There are other ways to heat a polycarbonate greenhouse in winter.
Greenhouse lighting
The winter day is short and the sun's activity is low, so cucumbers require additional lighting in winter. This can be done using lamps of different types, while two parameters must be observed - the level of illumination and color temperature.
Plants need light that is as close to daylight as possible, that is, having a color temperature of 5000 ° K. Such light is possessed by fluorescent, mercury (MGL) and metal halide (DNaT and DNaZ) lamps. At the same time, in the growth phase, it is better to use lamps with a colder color - 6500 ° K, and in the flowering and fruiting phase - with a warmer one, i.e. about 4000 ° K. At the same time, the plants do not stretch, remain strong and form ovaries well.
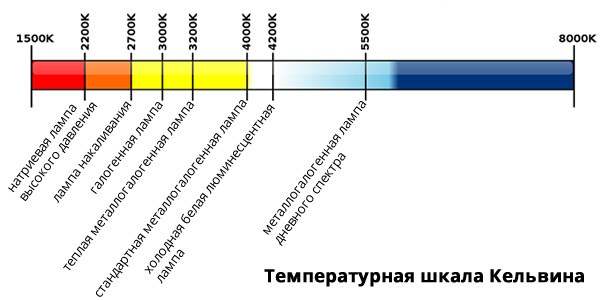
Color temperature of different types of lamps
In terms of light output, fluorescent lamps are much worse - much more of them will be required for the same area. At the same time, their price is lower, and they practically do not heat up. A comparison of the light output of different types of lamps is shown in the figure. The specified number of different lamps will provide a luminous flux of 50,000 lumens, which corresponds to the illumination of 4-5 m2 of a greenhouse for cucumbers.

Luminous flux of various types of lamps
The number of lamps required for full illumination of winter greenhouses of different sizes is shown in Table 1.
Table 1. Calculation of lighting for a winter greenhouse for cucumbers.
| 5 | 1 | 5 | 10 |
| 10 | 2 | 10 | 20 |
| 15 | 3 | 15 | 30 |
| 20 | 4 | 20 | 40 |
You can also use LED lights designed specifically for growing plants to illuminate your plants. These lamps are distinguished by a red-blue spectrum, which allows for faster growth and improved fruiting.

LED phyto-lamps in the greenhouse
Note! Prolonged exposure to the red-blue spectrum can be detrimental to vision. Working in a greenhouse is best done in natural light.
Soil preparation
The soil in the greenhouse for cucumbers should be loose, fertile and moderately moist. This can be achieved by preparing a soil mixture suitable for plants and a drainage device.
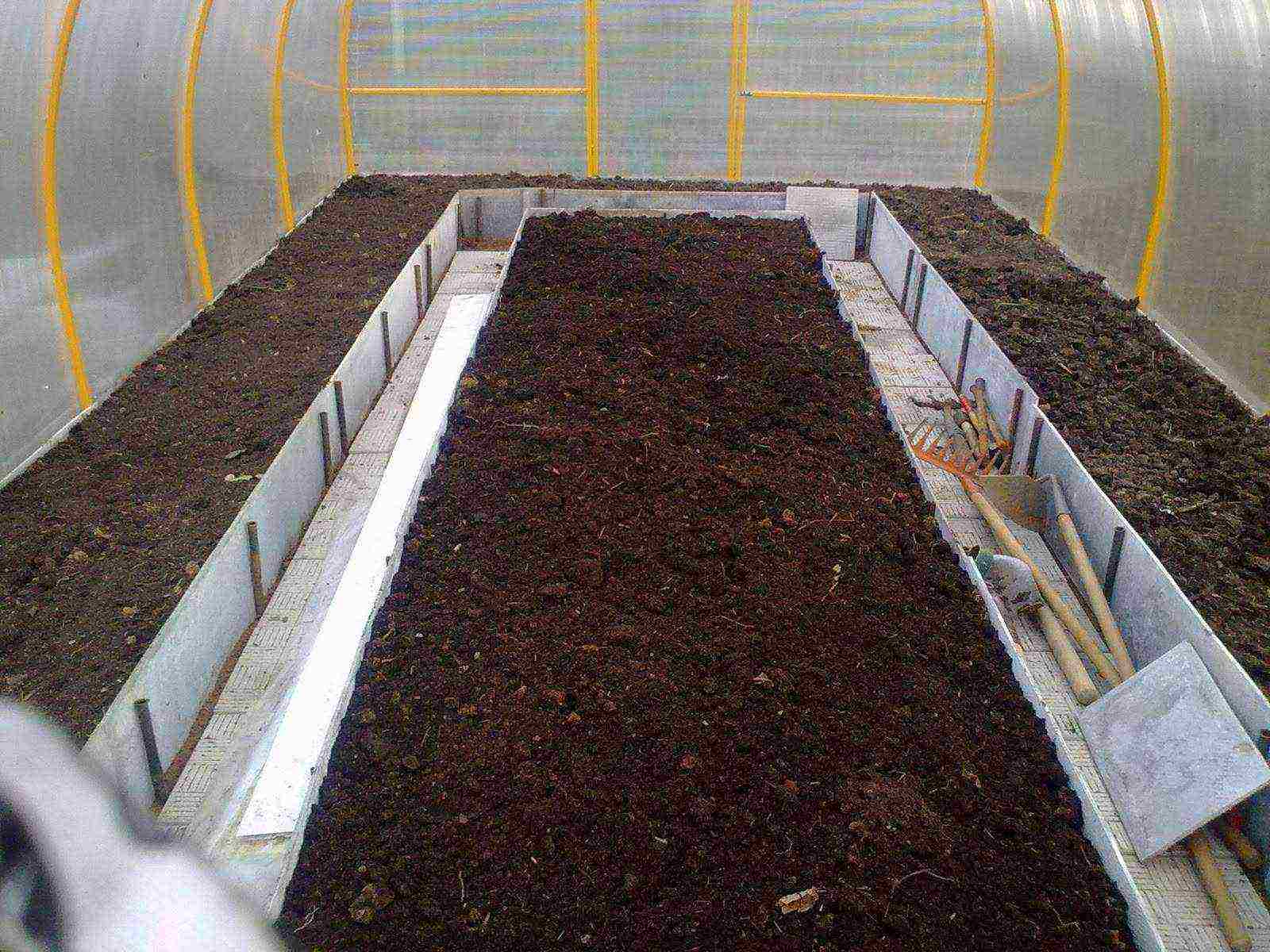

Greenhouse soil
The beds in winter greenhouses can be of two types:
- insulated or heated from below box;
- trench filled with biodegradable organic matter.
Both types of beds help protect plants from freezing of the roots. Insulation is performed using polystyrene or polyurethane insulation plates laid on the bottom of boxes and trenches. Heating can be water, in the form of heating pipes, or electric (heating cable).

Heating of the ground with a cable

Soil heating with heating pipes
Warm beds with biodegradable organic matter are filled with wooden chocks, branches, straw, dry foliage and grass, and on top - with fertile soil. At the same time, large chocks and branches are placed on the bottom - they additionally play the role of drainage.
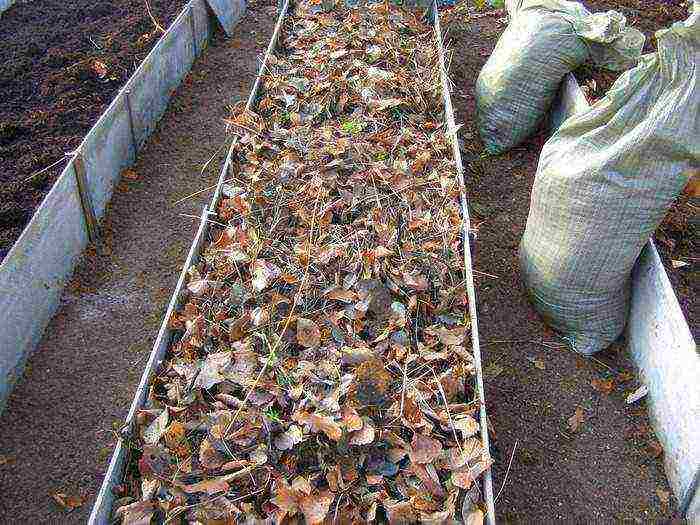

Cooking a "warm bed"
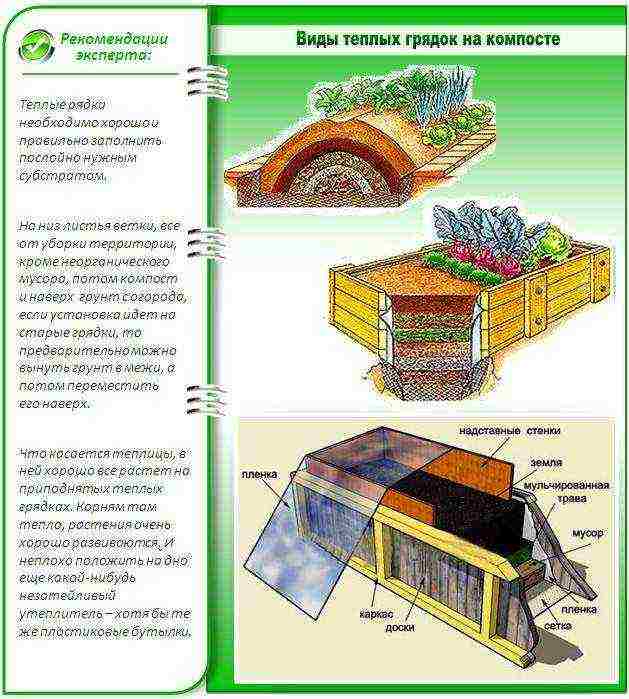
Types and arrangement of warm beds
After the beginning of organic decomposition, the components of a warm bed contain all the elements necessary for plants; it is enough to carry out regular feeding during the entire growing season. The soil for the heated beds must be properly prepared.
The composition of the soil for growing cucumbers:
- last year's hardwood sawdust - 1 bucket;
- humus - 2 buckets;
- peat - 2 buckets;
- wood ash - 1.5 cups;
- nitrophoska or nitroammophoska - 150 grams.
The specified amount is enough to fill a garden bed 30 cm high and approximately 1.5 m2. The components are mixed in a separate container or directly in the box, the bed is watered with a warm solution of potassium permanganate to disinfect it from bacterial infections. Then the soil is treated with a solution of "Fitosporin" against fungal rot.
After holding for two days, the bed is watered with an EM-preparation diluted in warm water ("Baikal", "Emochka", "Shining") and covered with a film or covering material for a week. During this time, the soil is structured, the active work of soil bacteria begins, and fertilizers pass into a form that is well absorbed by plants. The greenhouse is ready for planting seeds or seedlings.
Variety selection and seed preparation
Not all varieties of cucumbers are suitable for growing in winter greenhouses. In order not to be disappointed with the result and get a decent harvest, it is important to follow several rules when selecting a variety.
- In winter, there are no bees or other pollinating insects in the greenhouse, so self-pollinating (or parthenocarpic) varieties and hybrids should be chosen. When choosing bee-pollinated varieties, it is necessary to carry out manual pollination, as well as plant several roots of cucumbers with a male type of flowering - they will give the necessary pollen.

Cucumbers for winter cultivation must be self-pollinated.
- Natural illumination in the winter months is insufficient, and it is quite difficult to create artificial illumination in a spectrum close to the sun. For this reason, light-loving plants will not yield a decent harvest in winter. Shade-tolerant varieties should be chosen.
- It is quite difficult to maintain natural humidity in a winter greenhouse: due to heating, the air dries up, you have to humidify it with the help of frequent watering or spraying. At the same time, fluctuations in humidity occur and conditions are created for the rapid development of diseases. You should choose varieties that are resistant to bacterial and viral infections, fungal rot.
- Forming plants in a greenhouse is necessary - thickening of plantings leads to disease. To facilitate this task, you should pay attention to hybrids with limited branching - these do not give long lateral lashes, directing all forces to the growth of the main stem. It is convenient to form them vertically, with a garter to the supports.

Hybrid varieties of cucumbers for greenhouses
For a guaranteed result, it is better to plant two or three varieties; all the described requirements are met by the following hybrids:
- Cupid F1;
- Cheetah F1;
- Dynamite F1;
- Berendey F1;
- Garland F1;
- Courage F1;
- Ant F.
After purchasing the seeds, it is necessary to prepare them - this will allow you to achieve friendly shoots and uniform growth of seedlings, as well as simultaneous fruiting. The preparation consists of several stages.

Preparing cucumber seeds for sowing
Step 1. Seed calibration. A teaspoon of salt is diluted in a glass of cool water and the seeds are lowered there for 10-15 minutes. The floating ones are removed - they will not sprout or give weak plants. In a winter greenhouse, it is inappropriate to spend time and place on them.
If the seeds are expensive and it is a pity to throw them away, rinse and dry them, and then use them for summer planting.
The remaining heavy seeds are washed in running water. Seeds can also be calibrated by size, choosing the smoothest and largest.

Seed calibration
Step 2. Disinfection. Selected seeds for the prevention of bacterial infections are dipped for 20-30 minutes in a bright purple solution of potassium permanganate or three percent hydrogen peroxide.

Potassium permanganate treatment
Step 3. Treatment for fungal infections. From fungal rot, the seeds are soaked for 2-3 hours in a solution of "Fitosporin", which is prepared according to the manufacturer's recommendation indicated on the package. The seeds are washed and dried.

Seed treatment in Fitosporin solution
Step 4. Warming up. It is carried out to prevent viral diseases and increase female flowers on the plant. It is most convenient to warm up the seeds in a thermos - a constant temperature is maintained there. Water with a temperature of + 60 ° C is poured into a thermos, the seeds are lowered there and kept for 4-8 hours.

Warming up seeds in a thermos
Step 5. Hardening. For winter greenhouses, it is important to grow plants that are resistant to temperature changes and short-term drops in temperature in case of severe frosts or interruptions in heating. The seeds are placed in a napkin, moistened and placed on a saucer. Quenching is carried out on the lower shelf of the refrigerator at a temperature from 0 ° C to + 2 ° C for 2 days.
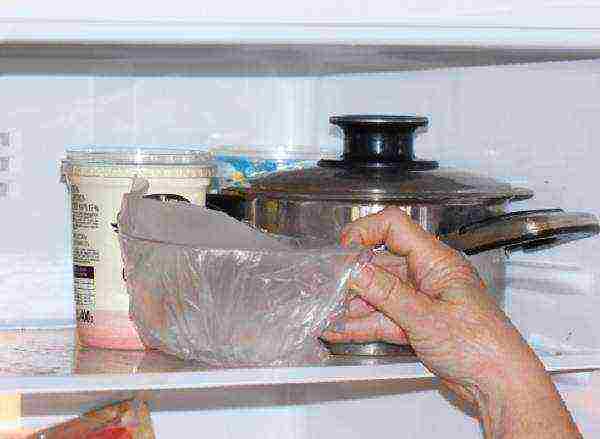

Seed hardening
Step 6. Stimulation. This technique allows you to accelerate germination and activates plant immunity. Stimulation is carried out in a solution of the drug "Epin" or "Zircon" according to the instructions on the sachet. A popular recipe gives good results: the aloe leaf is torn off, cut in half lengthwise, the seeds are placed on the cut, covered with the cut part and wrapped in a napkin. Leave overnight, and in the morning they are planted without rinsing.

Stimulation of seeds in "Epin"
Note! Most of the purchased seeds have already been processed! Follow the manufacturer's information on the packaging!
Planting cucumbers
You can plant cucumbers in winter directly in the ground or in seedlings. The second method has its advantages: you can plant plants with a stock, and then choose the strongest and healthiest. In addition, it is much easier to provide the necessary conditions for germination at home.

Scheme of planting a cucumber in a greenhouse
To make the plant easier to transfer the transplant, it is necessary to choose the right seedling cups. The root system of cucumbers in the first phase of the growing season does not develop in depth, but to the sides, so the glasses should be wide enough. The volume of the cups is not less than 0.5 liters.
For planting seedlings, you can use the soil prepared for the greenhouse or a purchased mixture. It is advisable to disinfect a mixture of your own production by heating to 80 degrees for an hour.
Step 1. Prepare seedling cups. The glasses are treated with a solution of potassium permanganate and filled with soil mixture to half, lightly crushed and watered. Withstand at least 2-3 hours so that moisture is evenly distributed throughout the volume.

Preparing seedling cups
Step 2. Landing. The treated seeds are placed flat on the soil. Often in the literature, there is a recommendation to plant 2 seeds in each glass, so that later you can choose a stronger sprout, and pluck the second one. However, for expensive hybrid seeds, this technique is rarely used: they usually germinate well, and it is a pity to throw away healthy shoots. 1-2 cm of dry soil mixture is poured onto the seeds on top. There is no need to water the planted plants - there is enough moisture from the lower soil layers for germination, and the upper dry layer will allow the seeds to breathe.

Planting seeds
Step 3. Germination. Cups with seeds are covered with foil or glass and placed in a warm place. The temperature before germination should not fall below 25 ° С, optimally 28-30 ° С. Light at this time is unimportant, the seeds germinate in the dark. The cups are inspected twice a day, at the same time removing the film for airing for 10-20 minutes. When shoots appear, the cups are immediately removed under the lamp.

Germination
Step 4. Phase of cotyledonous leaves. The most important stage during which the strength and productivity of the plant is laid. When a loop appears, the sprouts are placed under a lamp and for the first 2-3 days they are illuminated for 18-20 hours a day. This will prevent the plants from stretching. If the sprouts are still stretched out, they sprinkle the earth along the very cotyledons.
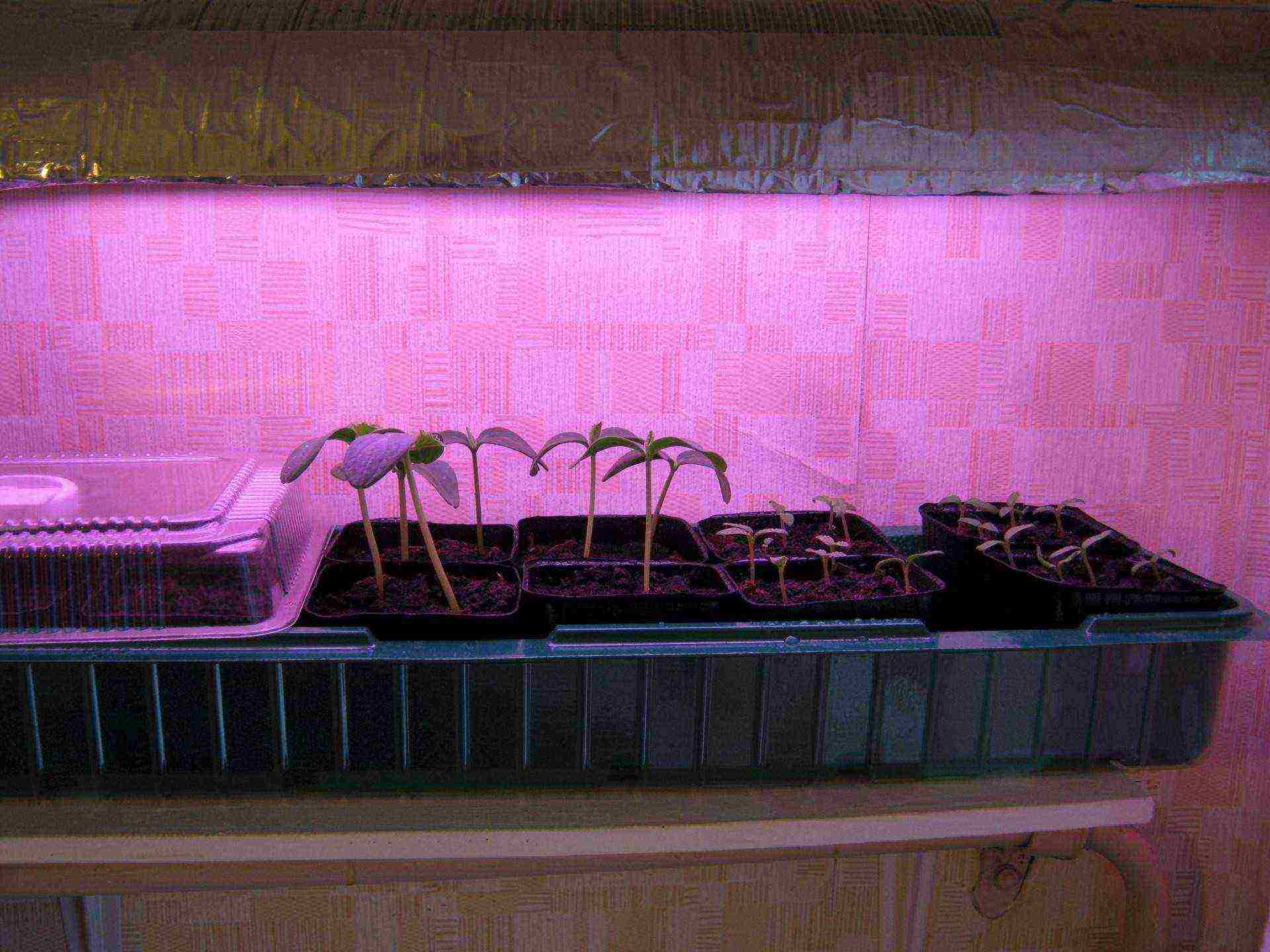

Seedlings under the lamp
Step 5. Phase of the first two or three leaves. Plants get stronger and grow rather quickly. The backlight is reduced to 14-16 hours a day. In the phase of the second or third leaf, fertilizing is carried out with a complex fertilizer with microelements ("Kemira", "Zdraven") .A few days after feeding, the plants can be planted in the greenhouse, choosing the strongest ones.

Greenhouse landing
Note! If you plant cucumbers directly on greenhouse beds, they need to provide the same conditions.

Planting a cucumber directly into the ground
Video - Winter planting of cucumbers
Care during the growing season and fruiting
Cucumbers are planted in prepared and warmed soil. To do this, prepare holes, water them and wait for moisture to be absorbed. Carefully remove the plant from the cup, set it together with an earthen lump in the hole, deepening it to the cotyledon leaves, and sprinkle it with earth.

Planting cucumbers in warm beds in a greenhouse
After planting cucumbers in the greenhouse, it is necessary to provide them with conditions for the best growth and development. Cucumbers do not like strong changes in day and night temperatures: rot of various origins appears, growth is inhibited, ovaries fall off, and the fruits become bitter. The optimal conditions for cucumbers in the greenhouse are shown in table 2.
Table 2. Microclimate in a winter greenhouse for cucumbers.
| Day temperature, ° С | 23-25 | Below 8, above 37 |
| Temperature at night, ° С | 17-18 | Below 8, above 37 |
| Soil temperature, ° С | 20-22 | Below 15, above 35 |
| Humidity, % | 75-80 | Below 40 |
| Illumination, lx | 10000-15000 | Continuously below 2500 |
Watering cucumbers
The soil for cucumbers should ideally be moderately moist. This can be achieved using drip irrigation or regular watering at the root. Cucumbers are watered only with settled warm water with a temperature of 25-27 ° C until the ten-centimeter soil layer is moistened. To reduce the amount of watering, the beds are mulched with rotten sawdust, peat or straw.

Watering cucumbers from a watering can
To soften the water, you can add a minimum amount of organic fertilizers to it - 5-10 ml of mullein or bird droppings infusion per bucket of water. With such watering, root fertilization with organic fertilizers is not needed, the plants will receive nitrogen fertilizers with watering. Soft water is better absorbed by the roots.
The best varieties of cucumbers for polycarbonate greenhouses
The choice of varieties depends on what kind of cucumbers you plan to cultivate and what expectations you have for the future harvest. Now there are many such varieties on the seed market, but in order to choose the most suitable option, we recommend reading this article.
Fertilization and disease prevention
It is necessary to fertilize the plants regularly - cucumbers build up a large vegetative mass and quickly consume useful elements from the soil. Lack of nitrogen affects the growth of bushes and the process of photosynthesis, lack of phosphorus and potassium affects the shape and size of the fruit.
For feeding, use an infusion of mullein 1: 5 or chicken droppings 1:15. To enrich the infusion with potassium, calcium and trace elements, wood ash is added to the solution - a glass on a bucket. Stir the components in water and leave for two or three days.
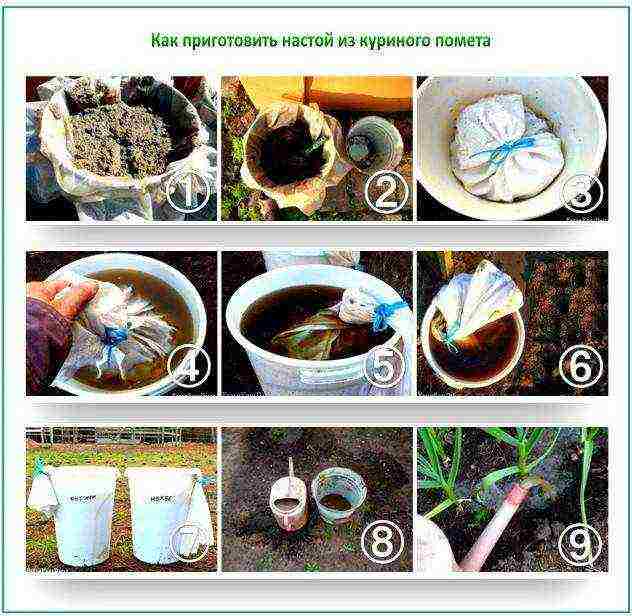

Preparing chicken droppings solution
You can also use complex fertilizers for melons and gourds for feeding cucumbers.They are bred according to the instructions and watered at the root or sprayed on the leaves.
Note! When infusion of fertilizing from organic matter, carbon dioxide is released. It is useful for plants, so a bucket of infusion can be left in the greenhouse near the ridges.
Video - Feeding cucumbers
For the prevention of diseases, the plants are sprayed with "Fitosporin" three times during the growing season with an interval of 15 days. It helps to avoid the appearance of fungal diseases. You can also use watering the soil with warm solutions of potassium permanganate and boric acid.

Spraying with Fitosporin - prevention
Forming and collecting fruits
To prevent plants from shading each other, they must be properly formed. In greenhouses, cucumbers are grown vertically to provide ventilation, reduce the likelihood of disease and facilitate access to plants. In addition, with a vertical garter, more plants can be placed on one meter of area.
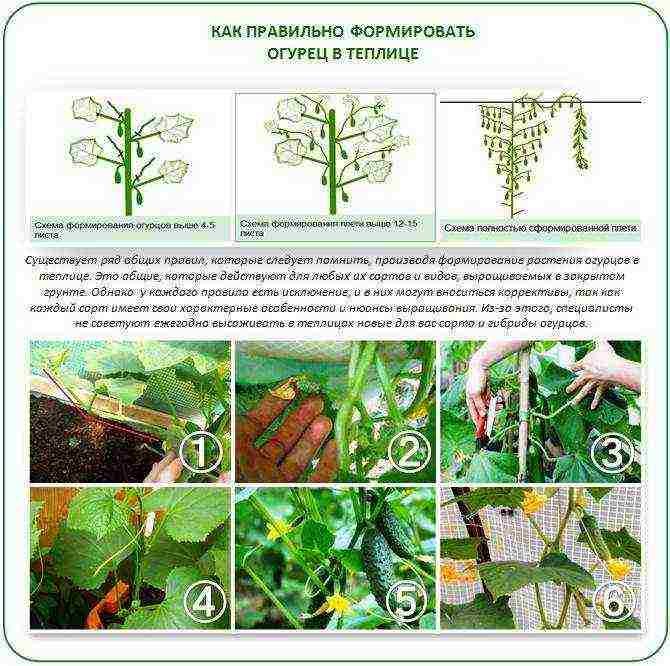
Cucumber molding rules
After planting the plants and the appearance of the first peduncles, the main stem is tied with twine to the supports or structures of the greenhouse. The first peduncles are immediately cut off - they mainly consist of barren flowers, but at the same time they inhibit the growth of cucumbers. After the appearance of the first lateral shoots, they begin to pinch according to schemes depending on the variety.
Cucumbers with a bouquet-bearing type of fruiting tie many fruits in each internode. The main crop for such varieties and hybrids is obtained from the main stem. They pinch the side shoots, allowing the plant to give the crop as much as possible.

Forming cucumbers of a bouquet type of flowering
Cucumbers with a small number of ovaries in each internode are formed differently. On the fifth and sixth side shoots, one leaf and an ovary are left, on the next - two leaves and two ovaries. This will maximize the yield of the crop.

Forming parthenocarpic cucumber hybrids
Video - Forming and garter cucumbers
After the start of fruiting, picking cucumbers is carried out regularly, ideally daily. Even one large fruit left on the plant inhibits the setting of new cucumbers and the growth of the bush. Harvesting is carried out in the morning or evening. It is more convenient to do this after watering - this way the cucumbers prick less.
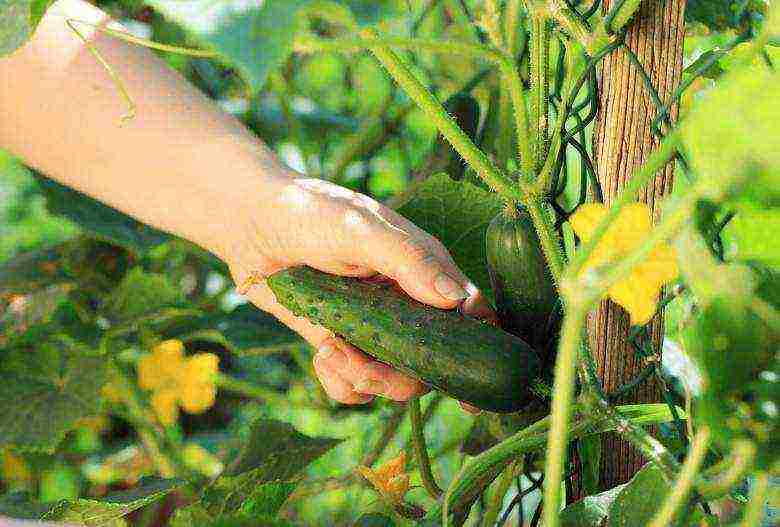

Picking cucumbers
Winter greenhouse cucumbers will delight you throughout the cold months. To prolong the period of active fruiting, they can be planted in several stages, constantly updating the planting. With proper agricultural technology and selection of varieties, fresh vegetables will always be on your table.

Climatic conditions in central Russia do not allow growing cucumbers from seeds in open beds without additional film shelters. This popular vegetable crop is very demanding for heat and light. With frosts down to -1 degrees, young shoots can easily die, and when shaded, adult plants will bear fruit poorly. Therefore, growing cucumbers in a greenhouse is the most popular and widespread option among Russian vegetable growers.
Popular varieties of cucumbers
Cucumbers in a greenhouse in winter and summer are capable of producing high yields if the conditions are suitable for the plants. This means that if you have a heated greenhouse, even in the winter months you will be able to please your loved ones with fresh vegetables grown without chemicals.
Before you start planting, you need to select varieties of cucumbers for greenhouses, because not every variety is suitable for growing in such conditions. For example, bee-pollinated varieties will have to be manually pollinated every day (insects are reluctant to fly into the greenhouse, and in winter they are not at all), otherwise the ovaries will fall off. Most popular:
- Self-pollinated high-yielding cucumber hybrids: Hercules F1 (salad), Emelya F1 (pickling), Dynamite F1 (universal), Zozulya F1, Anyuta F1, Picnic F1, Lilliput F1, Hummingbird F1, Machaon F1, Calendar F1, April F1, Courage F1, Lukhovitsky F1, etc.
- Yields and at the same time rather unpretentious varieties: Moscow hothouse, Zarya, Manul, Pomegranate, Surprise 66.
- The varieties Marfinsky, Relay, Domashny, NK-mini, Iva, Regata, Rykovsky, Rossiysky are distinguished by special shade tolerance and adaptability to low humidity.

Before you start planting, you need to select varieties of cucumbers for greenhouses.
Detailed technology for growing cucumbers in a greenhouse
For germination of cucumber seeds, a temperature of + 22 + 25 degrees is recommended. Therefore, if the greenhouse is unheated, of the film type, the seeds are sown at home in the first half of April in order to transplant ready-made seedlings into the greenhouse by mid-May. In heated greenhouses, you can sow cucumber seeds at any time of the year.
Soil preparation
Cucumbers love fertile soils saturated with organic fertilizers. In order for the cultivation of greenhouse cucumbers to bring good results, prepare the soil mixture in advance: humus and peat in 2 parts, 1 part of sawdust (preferably old), wood ash 3 tbsp. and nitrophoska 1 tbsp. You can buy ready-made soil with fertilizers. Level the soil surface and sprinkle mineral fertilizers on top. Then cover the surface with plastic wrap and let it sit for a couple of weeks to absorb the fertilizer. This will help protect seedlings from diseases of cucumbers, increase the yield and improve the palatability of the fruit.
Video about growing cucumbers in a greenhouse
Calibration and disinfection of seeds
It is best to grow cucumbers in a greenhouse from seeds that are 2-3 years old, as they will provide the highest yield. Calibrate the seeds manually by removing diseased and empty seeds. Then you should disinfect the seeds from diseases and pests by putting them for 12 hours in a cloth moistened with aloe juice or a solution of trace elements (add boric acid and copper sulfate at the tip of a knife to a liter of hot water, as well as a teaspoon of nitrophoska). Then rinse the seeds in running water and place them between layers of damp gauze to place in the refrigerator for hardening. Hardening is carried out at a temperature of about 0 degrees for a week, do not forget to moisten the gauze from time to time.
Growing seedlings
It is recommended to grow seedlings in small pots or plastic cups. Each seed is placed one at a time in a pot to a depth of 2 cm, covered with a layer of soil and covered with a damp cloth on top so that the top layer of soil does not dry out. You can sow seeds for seedlings for 10-15 days - planting cucumbers in a greenhouse using a conveyor method will provide you with a continuous harvest throughout the year.
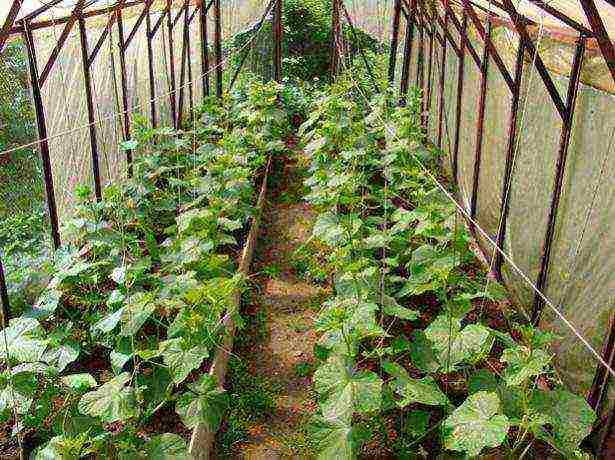

It is recommended to grow seedlings in small pots or plastic cups.
Until the first shoots appear, the temperature in the greenhouse should be maintained at +25 degrees, and with the appearance of sprouts for 5 days, the daytime temperature should be reduced to +15, and the night temperature to +12 degrees. Watering the seedlings should be every 2 days, periodically feeding the mullein solution (at the rate of 1: 6). After feeding, wash the seedlings with clean warm water.
Transplanting seedlings and caring for cucumbers
A month later, transplanting seedlings begins. In shelving greenhouses, seedlings are planted on shelves covered with soil, while in other types of greenhouses they simply form even ridges. Plants can be planted in beds directly in pots, buried in the ground by ¾ of the height of the pot. The distance between plants should be at least 20 cm, and between rows - at least 90 cm.
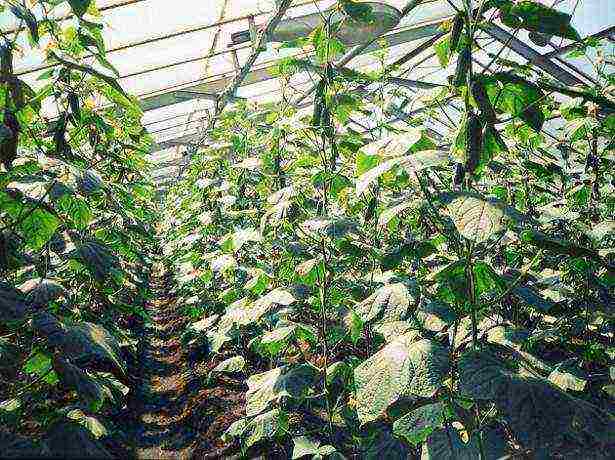

In shelving greenhouses, seedlings are planted on shelves covered with soil
During the day in the greenhouse, the temperature should be maintained at + 25 + 30 degrees, with mandatory ventilation on sunny days, and at night - within +15 degrees. When the third true leaf appears, the first fertilizing is done with fertilizers, the second feeding is carried out at the beginning of flowering. During fruiting, you can feed the cucumbers 4 times with a mullein solution, or a solution of chicken droppings.Before flowering, it is recommended to water the cucumbers every 5 days, after flowering - every other day, but if you notice that the leaves have begun to wither, this is a signal for urgent watering. As the plants grow, they will need to be carefully tied to two wires stretched across the top of the greenhouse.
Features of growing cucumbers in greenhouses in winter
Before growing cucumbers in a greenhouse, it is worth considering the most likely difficulties that you will have to face. The first problem is the lack of moisture in the air due to stove or water heating of greenhouses. Since cucumbers are very moisture-loving, you will have to constantly take care of maintaining a comfortable air humidity. Arrange baking sheets, barrels of water, moisten floors, pipes, spray plants with a spray bottle, etc.
Video about growing cucumbers in a greenhouse in winter
If you are interested in growing cucumbers in winter, in December-January, then start sowing seeds at the end of September, and planting seedlings at the end of October. But keep in mind that due to the lack of sunlight in January-February, growing cucumbers in a greenhouse in winter is almost impossible without additional artificial lighting. With an increase in lighting, the quality of the fruit improves and the content of ascorbic acid and sugars in the fruit increases. It is advisable to hang the lamps first at a height of 50 cm above the plants, and as they grow, raise the lamps higher, up to 1.5 m.
Be sure to monitor the temperature regime in the greenhouse: there should be no sudden daily temperature changes and temperature drops below +10 degrees, otherwise the leaves will actively grow, but the fruits will stop pouring, and the root system will not be able to absorb water.
Now you know how to grow cucumbers in winter, which means that by the New Year's table you will have your own harvest of delicious homemade cucumbers!
Rate the article:
(2 votes, average: 1.5 out of 5)
Table of contents:
- Technology of growing cucumbers in winter greenhouses
- Disinfection and calibration of seeds
- Seedlings for growing cucumbers
- Tools needed to grow cucumbers in winter
Recently, it has become fashionable to grow cucumbers in winter.
It is very unusual, but to please yourself in winter, when there is snow and frost outside, fresh cucumbers from your own garden are nice. To harvest cucumbers in winter, you need to create the right microclimate in winter greenhouses. Growing cucumbers in winter is a process very similar to growing in summer, but there are some nuances.

It is better to place the greenhouse in length from west to east.
Technology of growing cucumbers in winter greenhouses
In order to properly grow cucumbers, you need to adhere to the following scheme:

A favorable temperature for growing cucumbers will be 20-25 degrees.
- Heating. For growing in a winter greenhouse, a heating system must be installed. Without heating in a winter greenhouse, you can plant cucumbers only in spring, closer to May. And then, the seeds need to be planted in the apartment, and already the seedlings should be planted in the greenhouse.
- Preparing the soil for planting. In winter, cucumbers like the soil to be saturated with organic and mineral fertilizers. If the gardener wants to get a good harvest, then he needs to prepare a solution of mineral fertilizer: humus, sawdust, wood ash. Fertilizers need to be tamped well and covered with plastic wrap. Leave the soil in this state for a couple of weeks so that the fertilizers take root well and begin to give results.
- Selection of a variety of cucumbers. Now the choice of cucumber varieties is quite wide. You can sort them according to several principles. Among them: high-yielding self-pollinated hybrids Emelya F1, Hercules F1, Zozulya F1, Picnic F1, Liliput F1, Anyuta F1, etc.
There are varieties that are not hybrids, but they are also quite good, have high yields and are unpretentious.These are: Zarya, Pomegranate, Surprise 66, Moscow hothouse, Manul, etc. There are varieties of cucumbers that can grow in the shade and with low humidity: Relay, Willow, Russian, Marfinsky, etc. Growing different varieties in different conditions gives different results ...
Back to the table of contents
Disinfection and calibration of seeds
The best way to plant cucumbers is with seeds. But before planting, the seeds must be sorted out, all damaged and empty seeds must be removed. Then you need to prepare a solution for disinfection.
For this, boric acid, nitrophoska and copper sulfate per liter of hot boiled water are suitable. After disinfection, the seeds are placed in the refrigerator, where the air temperature is zero. In the refrigerator, the seeds should be hardened for a week. They should lie in gauze soaked in water. Water must be periodically poured into cheesecloth.
Back to the table of contents
Seedlings for growing cucumbers 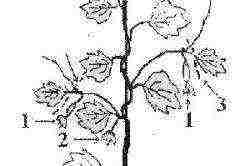
Cucumber pinching scheme
Seedlings are usually grown in cups or paper pots. The planting process looks like this: a seed fits into each glass to a depth of 2 cm, then it is covered with a damp piece of cloth so as not to dry the soil in a glass.
After planting the seeds, in winter greenhouses, the air temperature should not be lower than +25, after the seedlings rise, the temperature is reduced to +15 during the day and to +12 at night. Seedlings should be fed with manure and watered twice a day.
Transplanting seedlings into a greenhouse and the process of caring for plants. Seedlings can be planted in the greenhouse directly in pots or cups. The main thing is that the air temperature is +25 degrees. Cucumbers are planted at a distance of 20 cm from each other, and between the rows - 90 cm. During the day, the greenhouse must be ventilated. The winter greenhouse should have a thermometer. When the third leaf appears on the plants, it needs to be fed.
The second time in winter greenhouses, feeding is carried out when the plant is blooming, and when it bears fruit, you need to feed it with chicken droppings or mullein 4 times. Before the seedlings have bloomed, they need to be watered every 5 days, and after flowering - every other day. If the leaves begin to wither, then you need to water immediately. Seedlings should be tied to a wire so that they do not fall, but grow neatly.
Back to the table of contents
Tools needed to grow cucumbers in winter
- warm greenhouse with heating;
- seed pots and cups;
- solution for disinfecting seeds;
- organic fertilizers: manure, droppings, straw, sawdust, humus, food waste, grass, cleaning from vegetables and fruits;
- agricultural implements: hoe, rake for loosening and straightening the earth;
- plastic film for covering seedlings;
- wire;
- watering system or watering can;
- chemical preparations for the control of plant pests and diseases;
- thermometer;
- greenhouse ventilation system;
- greenhouse lighting system.
Secrets of a good harvest of cucumbers in winter
- In winter, heating is indispensable, and electric heating takes up a lot of moisture. Therefore, the air in a winter greenhouse must be more humidified than in summer. You can put containers with water, spray air more often, wash the floor, walls, etc.
- In winter, natural light is weak, the sun does not warm and illumines the room poorly. Therefore, electric lamps are a must for plant growth, especially during the winter months. Without them, cultivation will become impossible. Lamps should be hung in greenhouses above the plants at first low, and as the seedlings grow, raise them up.
- Sudden changes in temperature must not be allowed. The air temperature should not fall below 10 degrees with a plus sign. A thermometer must be installed in the room. If the temperature drops, the plant will stop bearing fruit.
Thus, we can conclude that it is possible to grow cucumbers in winter, but it is not so easy. The process will require additional financial costs for the greenhouse, due to the fact that heating and lighting systems must constantly work in the room. But in the end, in winter there will be fresh cucumbers - the result of hard work.


