Content
- 1 The best potato varieties for the middle Urals
- 1.1 The governor
- 1.2 Balabay
- 1.3 Equator
- 1.4 Sante
- 1.5 Spiridon
- 1.6 Nevsky
- 1.7 Luck
- 1.8 Alyona
- 1.9 Bashkir
- 1.10 Spring white
- 1.11 Vineta
- 1.12 Zhukovsky early
- 1.13 Lyubava
- 1.14 Fast-growing
- 1.15 Bullfinch
- 1.16 Bezhitsky
- 1.17 Crown
- 1.18 Lukyanovsky
- 1.19 Oredezhsky
- 1.20 Svitanok Kiev
- 1.21 Story
- 1.22 the effect
- 1.23 Aspia
- 1.24 Lugovskoy
- 1.25 Belousovsky
- 1.26 Lorch
- 1.27 Nikulinsky
- 2 Types of varieties
- 3 Potato varieties for the Urals: photo and description
- 4 New varieties of potatoes for the Urals
- 5 Requirements for the choice of variety
- 6 Potatoes: variety selection (video)
- 7 Ways to increase yields
- 8 How to plant potatoes (video)
- 9 Reviews and comments
When choosing a potato variety, one should focus on the geographical location and climatic conditions of the area where the crop will be planted. You should also consider what kind of harvest you want to get - early or late. Consider the most popular potato varieties for the middle Urals - the Chelyabinsk region and others.
The best potato varieties for the middle Urals
The Middle Urals are characterized by a temperate climate and high humidity. There are no severe frosts in the area, but summer is also without heat. Average t in winter is -10, -15 degrees, and in summer up to +10, +20. The heat starts in late spring and lasts until early autumn... In the Urals, it is better to plant the following varieties.
The governor
Early, with reddish skin of tubers and lemon pulp. It comfortably transfers transportation, it is famous for its high yield (2 kg per bush). Contains up to 14% starch. The ripening period is 2 months, at the beginning of summer you can try the first young potatoes.
The average mass of a tuber is 100-150 gr. From a hundred leaves up to 250 kg of root crops... It tolerates diseases well.
 The governor
The governor
Balabay
Mid-season, harvests in the third month of summer. The skin is red, the pulp is lemon. Resistant to heat and excess moisture. Contains up to 14% starch.
Intended for table use... The ripening period is 90-100 days. Sowing takes place in mid-May. Potato mass 120-140 gr.
Equator
Mid-season, you can try new potatoes in mid-July. The fruits reach 100-120 grams, the skin is pink-red, the pulp is light beige. Potatoes boil well due to their high starch content up to 20%. Ripening period equals 90-100 days.
Sante
Medium early, matures in 80-90 days. The yield per one hundred square meters is 300 kg, up to 20 fruits per bush. Weight reaches 120-150 grams. The skin is yellow. Contains a small amount of starch 10-12%, therefore potatoes do not boil over boiling... The variety contains amino acids and trace elements, a large amount of vitamin B.
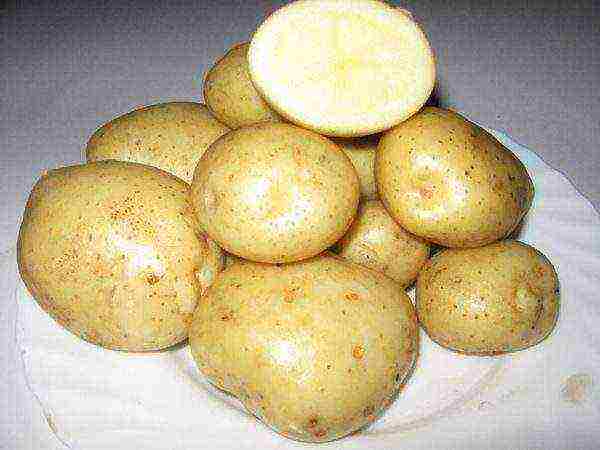 Santa
Santa
Spiridon
Mid-season, has a raspberry-red skin. Weight reaches 110-150 grams. Starch in the variety is about 12-15%. Not prone to disease.
 Spiridon
Spiridon
Nevsky
Early, young potatoes can be tasted 40-50 days after germination. The entire growing season is 65 days. The variety is considered one of the most productive. The skin color is lemon, the flesh is white.
The advantage of the Nevsky variety - does not darken when cleaning... One bush gives up to 15 tubers. The mass of one is on average 90-120 gr. It tolerates late blight well, although it poorly tolerates viral diseases.
 Nevsky
Nevsky
Luck
Early maturing, appears one of the first on sale. The skin is dark lemon-colored, smooth to the touch with reddish eyes. Contains up to 12-14% starch. The pulp is light, yellowish when cooked. The average weight is 120-150 grams. Harvest depends on the climate and soil.
 Luck
Luck
Alyona
Early, ripens within 60-70 days. Contains a high level of starch 15-17%. Has a pinkish peel, white flesh. Weight 80-160 gr. Poorly tolerates nematodes and late blight. Good tolerates heat and drought.
 Alyona
Alyona
Bashkir
Early maturing, bears fruit in 1.5 months. The entire ripening period takes 60-80 days. Skin color - scarlet with pink. The advantage of the variety is that it is difficult for the Colorado potato beetle to cling to the leaves of the plant.
The mass of one is 90-150 gr. On the bush up to 10 fruits can form... Productivity per hectare is 150-250 kg.
Spring white
Ultra early, appeared in 1994 by a 3-species hybrid mutation. The skin is muted lemon, the fruit is white inside. Root weight 80-140 gr. Poorly tolerates viral diseases and late blight.
Up to 15 tubers can be obtained from one bush. Contains 12-16% starch. Store well in winter and withstands transportation.
 Spring white
Spring white
Vineta
Vineta is a universal variety in terms of early maturity. The skin is yellow, white inside. Mass of potatoes 70-90 gr. Contains 12-15% starch. Up to 12 root crops can form on one bush. The full ripening period is 70 days.
The first harvest after germination can be obtained on day 50. Suitable for long-term storage, resistant to disease.
 Vineta
Vineta
Zhukovsky early
Early, with smooth pink skin, white inside. Contains up to 15% starch. It tolerates diseases well: scab, nematode, cancer. Poorly tolerated fungal and infectious diseases... Up to 1.5 kg are obtained from one bush. Ripens within 60 days.
 Zhukovsky early
Zhukovsky early
Lyubava
Early, stored for 7 months. The ripening period is 60-80 days. Weight 150 gr. Productivity up to 500 kg. The skin is light scarlet, white inside.
 Lyubava
Lyubava
Fast-growing
Early ripe. Ripening period 60-70 days. The skin is yellow, white inside. Weight 60-120 gr. Contains 12-17% starch. Productivity from 1 are 350 kg.
Bullfinch
Early ripe, with light scarlet skin, cream inside. The weight is 60-90 grams. Contains 16-18% starch. Ripening period 50-60 days. Average yield from 1 are 300 kg. Variety well resistant to potato crayfish, parasha, viruses, late blight.
 Bullfinch
Bullfinch
Bezhitsky
Medium early, oval-round in shape. The peel is pink-red, the flesh is creamy, does not darken when peeling. The average weight of the root crop is 70-110 grams. Can get scab infestation. The full ripening period is 70-90 days.
Crown
Medium early with dark lemon skin, white inside. Potato mass 70-130 gr. Contains 13-15% starch. Does not get sick with nematode, cancer. There are risks of contracting late blight. Productivity up to 270 kg of potatoes.
 Crown
Crown
Lukyanovsky
Medium early, pale lemon shade, white inside. Ripening period is 70-80 days. Weight reaches 90-150g. Good drought tolerance, easy to transport, no damage.
Oredezhsky
Medium early, yellow, white inside. Root weight 80-140 gr. Contains a starch level of 13-15%. From one hundred square meters, you can collect up to 300 kg of potatoes. Wonderful preserved in winter time... Resistant to late blight.
 Oredezhsky
Oredezhsky
Svitanok Kiev
Medium early, has established itself in the Urals. The tubers weigh 90-120 grams. Potatoes are smooth, reddish skin, white inside. Contains high percentage of starch 19%.
From 1 hundred square meters, you can collect up to 300 kg of potatoes. The crop is harvested closer to August.
 Svitanok Kiev
Svitanok Kiev
Story
Medium early. The average weight of tubers is 70-130 gr. The skin is red with pink eyes, white inside. Up to 25 fruits can be obtained from one bush. The variety prefers loamy and sandy loam soils. Doesn't like excess moisture... Contains 14-17 starch.
 Story
Story
the effect
Medium early. Muted lemon shade, white inside. Contains 12-15% starch. Average weight 80-120 gr.
Potato variety The effect easily tolerates many diseases, but still needs preventive protection with chemical solutions when planting. Stores well in winter and is well transported.
Aspia
Mid-season, with a ripening period of 80-100 days. Root crops are light yellow, white inside. Average weight 70-120 grams. Starch content 12-14%. Needs protection against late blight when landing.
 Aspia
Aspia
Lugovskoy
Mid-season, with a ripening period of 70-95 days. The skin is pink, the flesh is white. Average weight 100-130g. Contains 12-19% starch. Tubers are rich in proteins, vitamins, amino acids. Good disease resistant.
 Lugovskoy
Lugovskoy
Belousovsky
Medium late, ripening period 100-110 days. Has a light yellow tint, white inside. Potato weight 80-100 gr.Contains 18-19% starch. Resistant to drought and heat. Well tolerates viral diseases, moderately resistant to scab.
Lorch
Medium late, with a ripening period of 100-120 days. The skin is yellow, cream inside. The potato weighs 90-120 grams. You can collect up to 1 kg of root crops from a plant.
Variety moderately resistant to root rot, late blight, scab. With a lack of calcium and fluoride, they can be drawn out.
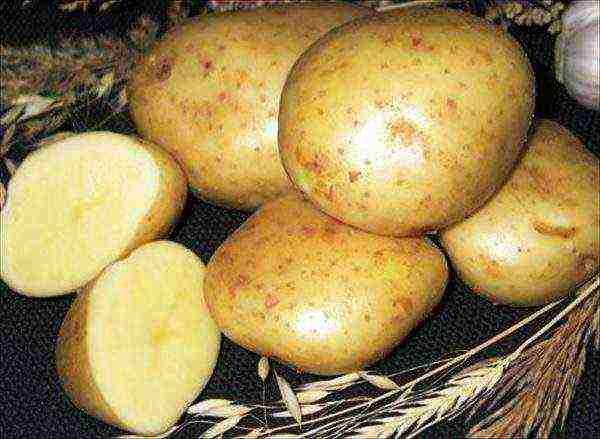 Lorch
Lorch
Nikulinsky
Medium late. The skin is yellow, cream inside. Contains 15-20% starch. The average weight of a root crop is 70-120 gr. When slicing the fruits do not darken... Poorly tolerates late blight, needs protection when landing.
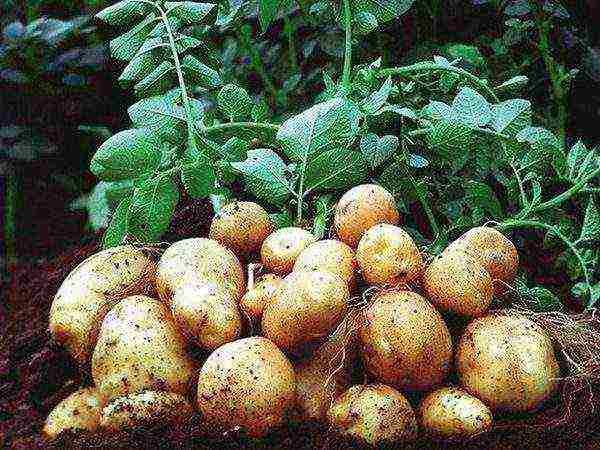 Nikulinsky
Nikulinsky
Types of varieties
Varieties can be classified into 4 types:
- Seed... It is a seed for the future potato crop. Recommended for cultivation in a summer cottage. They are characterized by a starch content of 12-17%.
- Early... Ripening period is 50-65 days. They are ready for use before anyone else and are divided into subspecies depending on the timing of ripening: early maturing, early maturing, mid-maturing.
Early potatoes are good to eat during the summer, as they generally do not tolerate winter well and are unable to store moisture. They are characterized by fast growth and a short growing season.
- Mid-season... The ripening period is 85-95 days. It is a more unpretentious variety and is better stored than the early one. Harvest in early August. It is considered a rather unpretentious variety with excellent taste.
Universal varieties - can be canteen, technical and fodder and perform any task. They have a thick skin and are usually suitable for long-term storage, suitable for frequent transportation.
Also, potatoes can be distinguished depending on the purpose:
- stern... The root crop is large in size and contains a large amount of protein;
- food... Sowed in government fields for sales and use in government institutions;
- technical... Used for the preparation of alcoholic products;
- universal... Has a wide range of uses.
| Seed | Early | Mid-season | Universal |
| Riviera
Karlena Vega Inara |
The governor
Nevsky Alyona Zhukovsky Lyubava the effect Bullfinch |
Balabay
Equator Spiridon Luck Bashkir Early Bezhitsky Crown Lukyanovsky Oderezhsky Svitanok Kiev Story Aspia Lugovskoy |
Luck
Vineta Belousovsky Nikulinsky Lorch |
 The variety of varieties allows you to easily choose the variety you need for growing based on its characteristics
The variety of varieties allows you to easily choose the variety you need for growing based on its characteristics
The future harvest depends on the choice of potato variety, so you should carefully consider the planting seeds. This is especially true of the middle Urals, where the climate is not as stable as in the south. I wish you a rich harvest!
A sign of a successful potato cultivation is a rich, high-quality harvest. This is not at all difficult to achieve if the summer resident takes into account the peculiarities of the soil, the regional microclimate, and ensures timely processing of the beds (hilling, weeding, fertilizing). There is another important factor - the selection of the appropriate potato variety. For the Urals, this is of paramount importance, since this region is located in three climatic zones at once. The so-called agricultural zone of the Urals includes 4 regions - Chelyabinsk, Kurgan, Perm, Sverdlovsk. Weather conditions here have their own characteristics.
In the description of potato varieties for the Urals, one can often find such a characteristic item as frost resistance. This should be considered when choosing varieties, since a heat-loving plant is not suitable for this agrotechnical region. Due to the short duration of the warm period, many summer residents recommend opting for early potato varieties.For the Urals, there is a wide range of this vegetable, so every novice gardener will be able to choose exactly the one that will meet all his requirements.
Potato varieties for the Urals: photo and description
- Riviera... The peculiarity lies in the fact that under certain conditions it is possible to harvest twice a season, but this is possible only if the household is located in a temperate climatic zone. It is for this region, according to experts in gardening, that the Riviera is ideal. The tubers have a light yellow tint, a slightly rough surface, and a thick rind. There are very few eyes on the fruit and they are not deep. In shape, the fruits look like an irregular oval, rather large. Best for eating (both in taste and in the range of nutrients). Riviera potatoes can be stored very well and for a long time.
- Zhukovsky early... This is the fruit of the work of Russian breeders. Designed for the weather conditions of the Ural region. You can recognize this vegetable by its external features - the peel is pale pink, with reddish eyes, it is covered with the white flesh of roundly oval fruits. According to many summer residents, this is the best potato variety for the Urals. Reviews say that experienced summer residents harvest up to 350 kg of crops from one hundred square meters. Absolutely all types of soils are suitable for its cultivation. He is not picky about frequent watering and special care.
- Ariel. An early ripe table potato variety for the Urals, Gollan selection. Perfectly adapted to the conditions of the climatic zones of the region. The tubers are round or round-oval in shape. The rind is light white and the flesh is creamy. The first fruits can be obtained as early as 45-50 days. Ariel is considered one of the most productive potato varieties in the Urals. This category also includes Rocco, Colombo, Tiras, Lugovskoy, Bella Rossa.
- Timo... It is famous for its early maturity and taste. This is the development of Finnish breeders. According to its characteristics, it is suitable for any climatic zone of the Urals. It has frost-resistant qualities and excellent resistance to many common diseases (powdery mildew, late blight, alternaria). The tubers are characterized by a rounded-oval shape, white thin skin and excellent taste. The pulp is light creamy. It is recommended to increase the yield of this wonderful, one might say the best potato variety for the Urals with the help of organic fertilizers (compost or well-dried manure), in combination with superphosphate.
In addition to the above, you should also pay attention to a number of unpretentious, productive best potato varieties (see photo) for the Urals:
The best potato varieties for the South Urals:
The best potato varieties for the Middle Urals:
Universal, the best potato varieties for the Urals (including Siberia):
New varieties of potatoes for the Urals
Breeders do not get tired of constantly improving the quality characteristics of potatoes for the Ural regions. As a result of fruitful work, new varieties appear. They are quickly becoming popular (modern information technology contributes to this in the best possible way).
First of all, people are looking for a plant with high yields, since it is this quality that allows you to collect a rich harvest from a small area. What is the most productive potato variety in the Urals?
Of the new varieties, preference should be given:
- Burnovsky... Medium early table light beige potatoes. Those who have already grown it on their backyards appreciated the tender, crumbly pulp of the vegetable. The variety turned out to be quite fruitful (about 200 c / ha). It has many qualities, including disease resistance and unpretentious care.
- Bullfinch... One of the most frost-resistant types of potatoes. Designed for cultivation in the Northern Urals. It belongs to the early ones.Has a pink skin, light white flesh, oval shape. The weight of one fruit does not exceed 1/10 of a kilogram. It is very well stored in freezing temperatures (up to 100 above zero).
- Rosara Elite... You can safely refer to the group of elite potato varieties for the Urals. Main characteristics: frost resistance, disease resistance, excellent taste, yield. The ripening period is measured in two months from the moment of planting in the soil.
You should also pay attention to such new varieties as Red Lady, Felox, Baron.
Many summer residents say that growing this wonderful vegetable is not at all difficult. This is indeed the case. But, nevertheless, it should be remembered that in order to collect a bountiful harvest, it is necessary to purchase the appropriate variety.
 It is quite difficult to find potato varieties for the Urals. Many other vegetable crops, which are successfully grown in the territories of neighboring regions, show a very low level of survival here. This feature is due to sharp climatic changes and the presence of fairly cold and gusty winds.
It is quite difficult to find potato varieties for the Urals. Many other vegetable crops, which are successfully grown in the territories of neighboring regions, show a very low level of survival here. This feature is due to sharp climatic changes and the presence of fairly cold and gusty winds.
Requirements for the choice of variety
Potato varieties for cultivation in the Urals have been very carefully selected for a long time. The most adapted species include early and mid-season, as well as universal varieties of potatoes. Such potatoes are distinguished by a high level of unpretentiousness and are perfectly adapted to growing in rather difficult climatic and weather conditions.
It should be remembered that both new and traditional Belarusian potato varieties are not included in the list of varieties recommended by the Ministry of Agriculture for planting and growing in the Northern and Southern Urals. Good varieties are classified as zoned.
The best early varieties
Early potatoes are usually subdivided into ultra-early, which tubers can be used for food 45-60 days after germination, and early ripe, with ripening in 60-70 days. In such varieties, ripening begins in July.
| Name | Tuber description | Description of the pulp | Ripening period | Sustainability | Yield |
| "Governor" | Red rind | White, starch up to 14% | Early maturing | High | Up to 2 kg per bush |
| "Vineta" | The peel is slightly reticulate, yellow | Light yellow, starch up to 15.2% | Early | Drought resistant | L60 kg / 10 sq. m |
| "Lyubava" | The peel is red | White, starch up to 16.9% | Early ripe | To the causative agent of potato cancer | Up to 400 c / ha |
| "Bullfinch" | The peel is red | White pulp, starch up to 16% | Early ripe | To the causative agent of potato cancer | Up to 271 c / ha |
| "Spring white" | White tubers | White pulp, starch up to 16% | Ultra early | Cancer, highly resistant to macrosporiosis | Up to 41 kg / 10 sq. m |
The best mid-season varieties
Medium early potato varieties fully ripen in 70-80 days. As a rule, Ural potatoes of this ripening period are better stored and have a brighter taste and pronounced potato aroma during heat treatment. The best mid-season varieties manage to form a decent harvest even before the onset of a stable cold snap in the Ural region.

Also read: Technology and secrets of growing Chinese cabbage from seeds
Potatoes: variety selection (video)
When planting seed in this region, a shovel is not always used, but most often a hoe is preferred, and the optimal planting depth is 5–8 cm. The spacing between the rows should be one meter. Furrows should be directed from north to south, which is very important for proper illumination of plants.
During planting, it is necessary to treat the tubers with wood ash, which will help protect the seed from pests. Processed and germinated tubers are placed in the furrows at the rate of four pieces per meter.
Seed material spread along the furrows must be covered with humus soil or well-rotted manure, and then with garden soil.By means of a hoe, the surface of the site is leveled.
The ridges formed during planting will grow as a result of further hilling and will serve as additional protection for plants from adverse weather factors. Further care for potato plantings consists in the timely implementation of the main activities.
| Care activities | Dates of the | Features of the |
| Watering | when the sprouts rise 7-10 cm above the soil level, that is, about two weeks after mass shoots | in hot and dry weather, it is necessary to use at least 12 liters of water for each bush |
| at the budding phase, which marks the beginning of the stage of tuber formation | ||
| at the stage of gaining weight by tubers, which occurs in the Urals at the end of June - beginning of July | ||
| Weeding and loosening | loosening at all stages of the growing season allows you to increase the flow of oxygen to the tubers, and weeding is carried out as weeds grow | surface loosening of the soil, carried out to a depth of no more than 3 cm, is carried out before the appearance of the first shoots and is supplemented by weeding |
| Hilling | the first hilling is advisable after the appearance of the first three leaves, the second is carried out 2-3 weeks after the first, before the plant blooms, and the last one - before the tops close | the first method consists in raking the soil from all sides to the plant and forming them into one "bouquet". The second method involves pushing the stems apart from each other, adding soil to the middle and raking it from the outside to the stems |
| Top dressing | during the germination phase with pale green leaves and poor development | first feeding: 10 l of water + 1 tbsp. l. urea + 0.5 l mullein or 1 tbsp. l. bird droppings |
| during budding | second feeding: 10 liters of water + 1 tbsp. l. potassium sulfate + 2-3 tbsp. l. ash | |
| at the time of flowering potatoes | third feeding: 10 l of water + 2 tbsp. l. superphosphate + 200 g mullein or chicken droppings | |
| Disease prevention | Spraying during the growing season: first - preventive, subsequent - with an interval of 7-14 days | Means "Pennkoceb", with the calculation of 400 l / ha or "Ditan M-45", with the calculation of 300-500 l / ha |
About ten days before harvesting, the tops should be mowed at a height of 10-15 cm, which will reduce damage to the tubers during the digging process and accelerate the maturation of the potatoes.
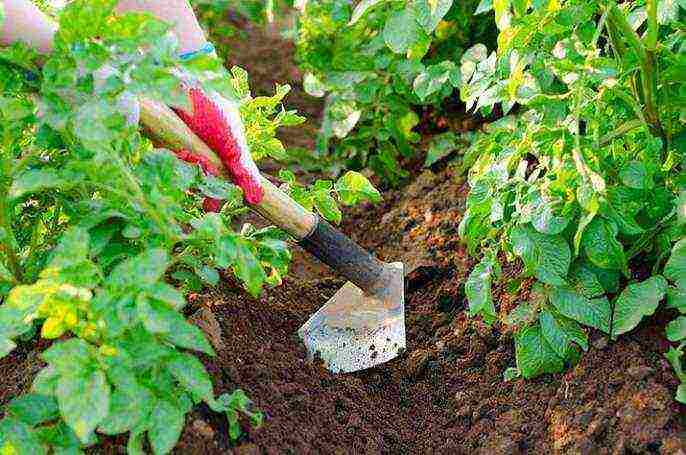

Ways to increase yields
Currently, the potato growers of the Urals practice several time-tested methods that can increase the yield of vegetable crops:
- harvesting potatoes, which were planted with larger and better germinated planting material, is possible three weeks earlier, and the harvest itself will consist of heavier tubers;
- destruction of flower stalks on plants at the beginning of budding, which allows to reduce the outflow of nutrients and increase the yield of potato tubers by 20-25%;
- very good results are obtained from the use of such modern means as biological fertilizer "Urgas" based on the concentrate of bacteria "Baikal-EM 1", as well as supercompost "Piksa" and Finnish complex chlorine-free fertilizers saturated with microelements, "Kemira-universal" and "Kemira";
- you can achieve high efficiency and a significant increase in yield and quality of potatoes by placing organic components in all areas of the potato field.
In addition, it is very important to use seed for planting, which has passed not only the stages of warming up, landscaping and germination, but also treated with biofungicides and biostimulants of growth.
How to plant potatoes (video)
Not enough time has been allocated for the growing season and the formation of the potato crop in the climatic and weather conditions of the Urals. Therefore, in order for the harvest of this popular vegetable crop to be good and to provide the whole family with high-quality, environmentally friendly products, one should not only choose the right variety, but also comply with all agrotechnical requirements, and also not neglect modern and highly effective means for feeding and protecting plants.
Attention, only TODAY!
Reviews and comments
Did you find a mistake in the text? Please select it and press Ctrl + Enter. Thank you!
Rating:
(
estimates, average:
out of 5)
Seed material
The yield of potatoes depends on the quality of the planting material, the condition of the soil and compliance with the technology of growing potatoes. Viral diseases cause great harm to potatoes, vegetatively propagated crops. High-quality potato seeds provide a yield of at least 300-700 tzha.
Crop rotation, Competently composed, is the main conduct of agricultural production. The alternation of crops in crop rotation improves the structure of the soil, cleans the soil from pests, diseases, weeds. Legumes such as peas, alfalfa, lupine and others, due to the presence of root nodule bacteria, enrich the soil with nitrogen. Cruciferous rapeseed and mustard, especially when used as green manure, when they enter the soil in the form of green fertilizer, heal the soil from potato diseases. Alfalfa roots, going deeper into the soil, improve water and air permeability, conditions for potato growth and heals the soil from fusarium.
The main difference between household plots is the lack of crop rotations, potatoes are usually planted permanently in the same place for several decades in a row, therefore, diseases and weeds specific to potatoes accumulate in the soil. Soil health improvement from disease is partly due to the application of large amounts of organic fertilizers, which activate the activity of soil microbes and, ultimately, increase the suppressiveness of the soil. With weeds, the situation on personal plots is more complicated - they are heavily infested with bindweed, sow thistle and other weeds.
On small household plots, with an area of 10-30 acres, where it is difficult to organize a 4-field crop rotation, you can proceed as follows: divide a potato field into two areas of the same area. In the first half of the plot, choose one of the following options:
- Sow a mixture of alfalfa and oats (under the cover of oats, alfalfa will develop better). After mowing the oats, alfalfa can be grown in this area for another 2 years.
- Every spring, sow the area with annual crops (vetch-oat mixture, rye, mustard, rapeseed, etc.) to regularly mow the green mass, preventing weeds from blooming.
In the second half of the site (by planting potatoes annually), it is necessary to promote the restoration of soil fertility - after harvesting the potatoes, scatter organic fertilizers (50-60 tha) as evenly as possible, and sow the field with fast-growing crops - mustard, winter crops, cultivate and plant potatoes in the spring.
After three to four years, the two halves of the plot must be reversed. Thus, the first half of the plot will rest from potatoes for three to four years and be free from specific diseases and weeds. The soil under the potatoes will also improve the structure, and be free from diseases through the use of green manure and organic fertilizers.
Boundary strips are breeding grounds for weeds in personal plots. Therefore, flowering and the formation of seeds in weeds should also not be allowed on them; it is necessary to regularly mow them.
Tillage
We recommend cultivating the soil to a depth of 15 cm in spring. To remove the plow sole, once in the fall, carry out a moldboard-free deepening (preferably with a chisel plow or an ordinary plow with removed dumps) to a depth of 25-30 cm.
It is necessary that the remnants of the roots of previous crops form a capillary system, along which moisture and mineral elements rise from the depths, and the top layer of the soil with organic fertilizers and plant residues, as quickly as possible turns into a mulching layer. With this technology, the soil gradually becomes more and more loose and, what is especially important, it is able to accumulate more moisture from precipitation, from the air, as a result, plants suffer less from drought.
It is not recommended to carry out moldboard plowing, in which the upper living layer of soil with organic residues, saturated with processing microbiota - a community of microbes, protozoa, fungi - turns over, gets to a great depth and dies, and weed seeds remain at a depth and return to the surface during the next plowing.
To obtain 100 tzha of potato tubers, 60 kg of nitrogen are needed. 20 kg of phosphorus and 80 kg of potassium by d.v. Depending on the availability of nutrients in the soil and in the fertilizers used, the amount of fertilizers needed to be applied to the soil is calculated. In the absence of soil analyzes to obtain a potato crop of 20 tenge, mineral fertilizers can be applied at the rate of 100 sq. K: Mg = 40: 3) Annual application of 50-60 tha of organic fertilizers, additional application of mineral fertilizers (to obtain a yield of 300 tzha).
Potatoes are very sensitive to foliar feeding - the yield increases, the resistance to diseases increases, and the quality of tubers improves - the content of starch, proteins, vitamins increases. potato yield (by 30-50%), impairing the quality of tubers.
Seed preparation for planting
An effective way to increase yields and reduce diseases is sprouting potatoes before planting. Germination of potatoes accelerates the growth and development of potatoes and allows you to get a harvest in a period shorter by 7-10 days, which reduces the risk of infection of potato plants with diseases, including viral, fungal-late blight, macrosporiosis and others. Germination is recommended for 4-5 weeks in diffused light, and the first week at a higher temperature of 12-15 degrees C. And in the next 2-3 weeks at a temperature of -8 degrees C. With this germination mode in tubers, all eyes form short strong shoots, in case of violation of the regime, apical dominance can occur, when only one apical ocellus grows, which is undesirable. It is believed that for each grown stem, on average, two tubers are formed, therefore it is so important to ensure the germination of all eyes. Desirable sprout length 0.2-0.5 cm (longer ones can break off when planting)
During germination, tubers latently infected with diseases (fusarium, phomosis, phyto-tuberculosis, bacterial rot) appear, which increases the efficiency of culling diseased tubers before entering the field.
Landing
When determining the timing of planting potatoes, they are guided by soil maturation and its temperature. Planting potatoes should be carried out at a temperature of 7-8 degrees C of the soil at a tuber depth of 8 cm. It is not recommended to plant potatoes in cold, unheated soil - sprouts can be affected by rhizoctonia, seedlings are delayed. Planting too early in wet conditions also increases the risk of Fusarium disease and seedling thinning. Usually, the most favorable conditions for planting in the republic come in the second decade of May. It is also not recommended to be late with planting potatoes - when planting in early June, the yield of potatoes is significantly reduced. The planting depth affects the germination time of tubers, according to new technologies, potatoes are planted in small ridges, where the soil quickly warms up and the potatoes germinate in 12-18 days. With a deep planting, the tubers may delay germination, and will sprout only when the soil warms up at the depth of the tuber planting. Also, with deep planting, tender underground sprouts of potatoes can be more damaged by diseases.At the same time, if the planting is too shallow, the tubers may freeze during spring frosts or appear on the surface of the ground after heavy rain - depending on the mechanical characteristics of the soil. According to the new recommendations, the planting depth should be equal to the diameter of the tuber. - about 5-6 cm. On light soils, the depth can be increased to 7-8 cm. Planting density of 55-60 thousand plants per hectare (planting pattern 75 * 24 cm or 70 * 26 cm) provides in our conditions the maximum yield at the lowest cost of seed material when planting tubers can be powdered with wood ash.
Planting care
10-14 days after planting, the field must be buried. It is important not to miss the moment when most of the weeds will begin to germinate and be in the phase of the white thread, at which time up to 80% of the weeds can be destroyed during the plucking. If you are only a few days late with this technique, then it will be much more difficult to destroy the rooted weeds. After another 1-2 weeks, potato shoots will begin to appear. At this moment, as soon as the first shoots hatch, we recommend that you carry out a good hilling with the formation of a trapezoidal ridge, the tuber remains under a layer of loose soil at a depth of 12-15 cm, but above the bottom of the furrow by 2-3 cm. During hilling, we destroy the weeds again. Then, during the growth of the potatoes until the tops are closed, you can additionally huddle the potatoes, especially if such a need arises after the rains that have compacted the soil and eroded the ridges. Potato tubers during their growth cannot move apart the dense soil and if the soil is too dense, then the growing tubers can come out and turn green in the sun. Therefore, it is very important, with the help of crop rotation, the introduction of organic matter and proper tillage, to create such conditions so that the soil under the potatoes is always loose and structural.
We recommend weeding by hand from weeds after the rain - it is at this moment that the roots of the weeds are not able to stay in the soil, with your hands you need to grab the base of the plant deeper, carefully pulling them out, you can remove the underground roots of the bindweed up to 3 meters long (usually the roots of the bindweed break off when length 5-10 cm). In this way, the weeding effect can be significantly increased.
Protection against diseases and pests
We recommend protecting against the main pest of potatoes - the Colorado potato beetle - in a new way. To do this, you need to process the tubers before planting with Prestige at the rate of 0.8 liters. To process 35 kg of potatoes, add 30 ml of Prestige to 200 ml of water and process the tubers with the resulting solution before planting (respectively, add 0.8 liters of Prestige to 1 ton of potatoes in 5-6 liters of water). It is better to place the tubers on a film, which will facilitate their uniform wetting with the solution and prevent loss of solution. Please note that the beetle will completely eat self-seeding - plants grown from untreated tubers that have wintered since last year, and plants grown from treated tubers will not be damaged by the pest until late July - early August. With this treatment, plant leaves will be protected from planting (May) until a new crop of tubers appears (early August). On such plantings, all adult beetles emerging from the soil will die, as well as those arriving from neighboring areas, there will be no egg-laying. And, therefore, the larvae. The check showed the absence of Prestige insecticide in the tubers of the new crop of potatoes, as in the initial stages of tuber formation. So in later. Prestige also protects potatoes from wireworms. In addition, due to the presence of a fungicide in its composition, Prestige protects potatoes from rhizoctonia disease.
From the dangerous potato disease caused by the fungus Phytophthora, it is necessary to carry out protective treatments with fungicides. Phytoftora develops intensively in the presence of moisture and low temperatures of -14-16 C. Fungal spores can only move in water.Therefore, moisture is needed for the spread and subsequent reproduction of the fungus. The intensity of late blight development in a particular field depends on many factors, including the main ones - the resistance of the variety and favorable weather conditions for the development of the fungus, the presence of sources of infection in the seed material, the density of planting, the location of the site are also important points. The permeability of potato plants, etc. If the weather is cool and humid, late blight can cover the entire field in 1-2 weeks. The most dangerous is early blight by late blight, when the damage to the leaves leads to large losses in the yield. In some years, such an early development of the disease was observed in the conditions of the republic on unstable varieties already at the end of June. Later, in the month of August - with the onset of cool nights, accompanied by the fall of night dew, potato leaves are usually affected by late blight every year.
To protect against late blight - when predicting the onset of cool rainy days lasting more than 5 days - it is necessary to process potato planting: in the period before potato flowering and in the period after flowering.
Alternaria (macrosporiosis) or early dry spot of potatoes is a fungal disease. Especially rapidly developing against the background of high temperatures with periodic rains. Single gray necrotic dots appear on the underside of the leaves, then the leaves turn yellow and brown spots with concentric patterns appear on them. Contact fungicides are effective for protection against Alternaria.
Fusarium wilting is caused by a fungus of the genus Fusarium, which primarily affects weak plants. Degenerate potato seeds are more affected by fusarium. Therefore, it is necessary to regularly purchase seeds of higher reproductions. Symptoms of the disease on plants - the apical leaves fold in a boat, and on the cross-section of the lower part of the stem, corked vessels clogged with a fungus are visible. Dry rot from the stolon end sometimes appears on the tubers. Latently infected tubers obtained in the offspring from infected plants may not sprout, leading to thinning of seedlings, and the emerged plants may be weakened to varying degrees.
Cleaning and storage
An obligatory technique before harvesting potatoes is mowing the tops. Mowing must be carried out on food plantings - 7 days before the start of harvesting, on seed crops - 10-14 days.
When harvesting potatoes without preliminary mowing of the tops, the tubers are much more infected with late blight and fusarium due to the penetration of fungal spores through damage to the fragile peel. With preliminary mowing of the tops, the peel of the tubers has time to get stronger before harvesting and practically does not peel off, and the tubers are much less injured.
Potatoes are best harvested in the absence of rain. When harvesting, potatoes (healthy) can be immediately stored in the cellar. Only wet (caught in the rain) potatoes are best dried under a canopy, then sorted out and stored. Small volumes of potatoes can be stored in naturally ventilated cellars at 2-4 C, where humidity should be 90-95%.
In the fall, after placing the potatoes in the cellar, the cellar lid only needs to be covered so that the potatoes are ventilated and the cellar cools down. After lowering the outside air temperature to 5-10 C of frost, the hole in the cellar must be insulated, leaving a small hole for ventilation. This hole must be checked and adjusted during the winter period.
A mistake often made by potato growers in personal subsidiary plots is the complete lack of ventilation in the cellars (the hole is closed tightly). This leads to the fact that the warm air formed during the respiration of the potato, reaching the cold stream, does not succeed, forming droplets that flow down onto the potato.In some years, over a long winter period, such dripping can lead to massive crop rot. Potatoes can be stored with natural ventilation at the height of the embankment up to 1-1.5 m, with an increase in the height of the embankment it is necessary to use active ventilation.


