Content
- 1 Specific features and varieties
- 2 Growing conditions in open areas
- 3 Growing rules in containers
- 4 Planting and transplanting
- 5 Bloom
- 6 Growing problems
- 7 Reproduction
- 8 Purchase features
- 9 Lavender: description
- 10 Varieties of lavender
- 11 Features of lavender care
- 12 Lavender breeding methods
- 13 Reproduction by dividing the bush
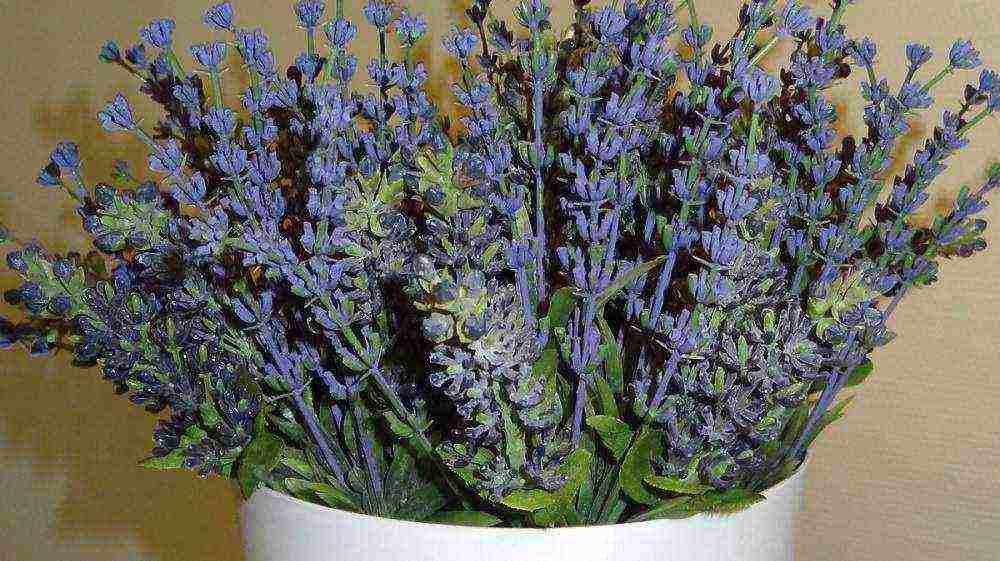
- 14 Lavender: home cultivation
- 15 Watering the plant
- 16 Description and characteristics of lavender
- 17 Advantages and disadvantages
- 18 Planting and leaving
- 19 Problems of growing in a pot at home
- 20 Protection against diseases and pests
- 21 Types and varieties of lavender grown at home with photos
- 22 Necessary conditions for growing
- 23 Planting lavender
- 24 Plant care
- 25 Potential Difficulties When Growing Lavender in a Pot
Lavender (Lavandula) is a genus of ornamental herbaceous plants, the home of which is the Mediterranean, southern Europe. Lavender is grown in gardens as single bushes, decorated with plant borders, alpine slides, planted along hedges, paths, on open terraces. Lavender bushes look great among border roses, perennial grasses with bright green foliage up to 50 cm high.
Specific features and varieties

In France, in the province of Provence, you can find huge plantations of lavender, which is grown on an industrial scale.
The natural habitat of the lavender plant is the mountainous regions of the Mediterranean, Spain, Italy and France. Fragrant shrubs and shrubs are common in the Alps, Greece, Algeria, Corsica and Sardinia. The plant is actively cultivated in the Caucasus and Kuban, in Moldova, Central Asia.
Lavender is a small (30 cm to 1 m) evergreen perennial shrub or subshrub, belongs to the family Lamiaceae or Labiatae. The plant, such as basil, mint, sage, lemon balm, rosemary and other representatives of this family, is aromatic, widely used in the culinary and perfumery industry, folk medicine, aromatherapy.
The shrub has no central stem. On numerous branched shoots, densely covered with silvery-green foliage, inflorescences are formed, similar to spikelets, with flowers of white, pink, lilac, blue or purple color.
There are more than 20 types of lavender, from which many varieties have been derived. They differ in the size and shape of the bushes, the color of the flowers. The most widespread in home floriculture are two types of lavender.
- Narrow-leaved (aka English). The bushes reach 80 cm in height and about 1 m in diameter. Flowers are often purple in color, but can be white, pink, or blue. Flowering begins at the end of spring. And the buena vista variety blooms twice - in spring and autumn. This is the most frost-resistant species, which you can not dig out during the winter, it is enough to insulate the bushes.
- Broadleaf (aka French). A hybrid of narrow-leaved and spikelet lavender is called lavender. Bushes with very beautiful inflorescences formed by flowers of burgundy, lilac, purple color. Lavandin varieties have a rich aroma, are used in the production of lavender oil, cooking.

Many hybrid varieties with large double flowers have been bred from narrow-leaved lavender.
Growing conditions in open areas
Growing lavender requires regular maintenance, including:
- weed removal;
- loosening the soil;
- systematic watering;
- fertilization;
- pruning;
- preparation for winter.
Lighting and watering
It is best to grow lavender in open, well-ventilated, sunny places. In the shade, lavender blooms will be short, sparse. Watering is carried out only in severe drought - excessive moisture is harmful to plants, it can lead to decay of the root system.
If the place is chosen correctly, the shrub can grow on the site for at least 25 years. Indoor lavender, grown on balconies in containers, loses its decorative appearance 4–5 years after planting, since its growth and development is limited by the volume of the planting capacity.
Temperature
Lavender bushes tolerate summer heat normally. And low temperatures can destroy them, so plants need to be insulated in autumn. If thermophilic lavender cannot be grown due to the harsh climate, it is planted in flowerpots, and with the onset of cold weather they are placed in a cool place with a temperature of at least 10 ° C.
Fertilization
To grow lush bushes, in the spring, during the period of active growth, they need to be fed with fertilizers with a high nitrogen content. At the beginning of flowering, lavender is fed with complex mineral fertilizers with a high potassium content. Organic fertilizers are applied at the end of summer.
If the soil is mulched with compost, the plant may not be additionally fed throughout the season.

Potash fertilization will ensure abundant and long-lasting lavender bloom.
Additional care
In addition to the listed recommendations, the following will help to ensure the normal development of an ornamental shrub:
- mulching the soil on the site with decorative substrates or decayed foliage;
- ensuring normal access of oxygen to the root system - regular hilling of bushes, loosening the soil, removing weeds;
- timely pruning of shoots;
- preparation for winter.
Pruning
Pruning is necessary to grow a lush lavender bush. Shoots are not cut off much, shortened by a few centimeters. It is advisable to cut off the shoots only to the lignified part, otherwise the plant may die.
Pruning is carried out after wintering. Simultaneously with shaping the crown, it is necessary to remove broken, frozen, old branches (they need to be cut off by no more than a third of the length).
Preparing for winter
In snowy winters, the plant tolerates frost normally. But if little snow falls in winter, lavender can freeze and die. Additional insulation of the bushes with branches of coniferous trees will help to avoid this. Plants cannot be insulated with ordinary foliage - they will rot.
Growing rules in containers
The content of lavender grown in an apartment (in containers on the balconies) is slightly different from the care of garden plants.
- Lavender planted in a container should be fed with any complex mineral fertilizer every 2 weeks.
- As soon as the need arises, transplant into a large container using the transshipment method (while preserving the earthen ball).
- For planting or transplanting, use a soil substrate consisting of sand or gravel (1 part), humus (1 part), turf (2 parts).
- Water only after the soil is completely dry.
- Plant the plant in light-colored pots. Dark containers exposed to full sun become very hot. As a result, the root system overheats, and the plant, even such a heat-loving one, dies.

Lavender grown in pots and containers needs more feeding than bushes growing in open ground.
Planting and transplanting
For good and quick adaptation, it is better to plant varieties adapted to the climatic conditions of the region in which they will grow. Planting is carried out in early spring, when frosts have passed. Less often, the plant is planted in the fall - from the end of September until the onset of the first frost.
When planting, you need to follow several rules:
- form a bed with a height of about 40 cm;
- immediately before planting, place the bush in water for 1 hour;
- on the eve of planting, cut off the upper part of the bush, small, damaged shoots;
- plant at a distance of 80 to 120 cm, depending on the size of an adult shrub of the planting variety;
- make a hole about 30 cm deep so that the roots can freely fit in it.
The culture does not tolerate a transplant, therefore it is better to immediately allocate a permanent place for the plant in the garden or on the site. If you need to move the bushes to another place, they are transplanted very carefully, with a large clod of earth, so as not to damage the root system.
Lavender bushes thrive in alkaline loamy and sandy loam soil. The soil should be good for air and moisture. During planting, coarse compost is introduced into the soil. And acidic soil can be neutralized by adding wood ash or limestone.
The ornamental shrub has a very powerful root system: the length of the roots can reach 2 m. Therefore, in areas with a high level of groundwater, the plant may die as a result of root decay. In humid climates, lavender should be planted in high beds, and it is advisable to spread very coarse sand or fine gravel around the base of the bushes with a layer of 5 cm.
Heavy clay soils, poorly permeable to air and moisture, lavender will withstand only in a dry hot climate.

Lavender bushes grow large and tall when grown in regions with hot summers and mild winter frosts, and in more severe conditions, the plants are compact.
Bloom
The bushes bloom from April to the end of summer, and the peak of flowering occurs in the middle of the summer period. Collecting flowers annually helps maintain the vitality, longevity and decorativeness of lavender shrubs.
Lavender flowers can be dried. It is better to harvest raw materials when the inflorescences are fully open - 1-2 weeks after the beginning of flowering. You need to dry flowers in a well-ventilated, shaded room (optimally in the attic).
Growing problems
Lavender, like other garden and indoor plants, is attacked by various diseases and pests. The most susceptible to disease are thickened plantings of shrubs that are not properly ventilated.
Gray rot is the most dangerous fungal disease that affects a plant when it is grown in high humidity conditions (rainy summers, excessive watering). Treatment consists of pruning and burning the affected shoots. Some growers are trying to get rid of gray rot by spraying the shrub with Bordeaux mixture or fungicides. But in this way it is not always possible to get rid of gray rot.
Of the pests, the most common parasites of lavender are the penny tree and the rainbow beetle, cicadas. Beetles and cicadas are harvested by hand, after which the mulch layer must be replaced. Pennitsa and its larvae are washed off the bushes with a stream of water.
Reproduction
There are three ways to propagate lavender:
- layering;
- cuttings;
- seeds.
Layers
Reproduction by stem layering is considered the simplest and most affordable method. A strong and healthy bush shoot is bent down, laid horizontally, sprinkled with soil. A load is placed on top. After a few months, when the shoot takes root, it will be able to grow without the mother plant. It is necessary to separate the young shoot with a sharp knife, and the place of the cut must be treated with powdered coal.
Cuttings
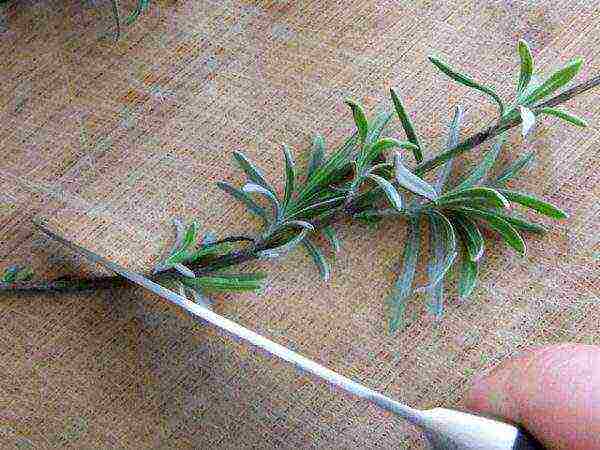

The root system in plants grown from cuttings develops much more slowly than in shrubs grown from seeds.
For reproduction, undamaged, healthy cuttings 8-10 cm long are taken. They are cleaned of the lower leaves, planted in clean sand, perlite, or in a mixture of sand (2 parts) with wood chips (1 part).Cuttings are planted in common containers (the distance between the cuttings should be 6 cm) or in separate pots.
Planted cuttings should be covered with foil or glass, regularly ventilated and sprayed for 5-6 weeks. The rooting process can be accelerated by providing bottom heating of the soil. At the same soil and air temperature, the root system develops more slowly.
Propagation by cuttings and layering is best done in early spring or September.
Seeds
The seed method of propagation of lavender is the most difficult and lengthy, it is used only in cases where it is not possible to propagate the plant by cuttings or layering. The main problem is that fresh seeds do not germinate well. Seed steeping and stratification procedures help to increase germination rates.
The seeds are soaked in warm water for 12 hours or in a solution of hydrogen peroxide (2 teaspoons per 200 ml of water) for 2-3 hours.
Stratification can be done in several ways.
- Place the seeds mixed with sand in the refrigerator for 1-2 months.
- In the fall, sow seeds in a pot, dig in on the site and cover, in March, move the container to the house.
- Keep the container with the sown seeds in the refrigerator until shoots appear.
Stratified seeds are sown in February or March. For planting, a mixture of humus (2 parts) and coarse river sand (1 part) is used. Before sowing the seeds, the soil is sieved, calcined in an oven at a temperature of 110–130 ° C, or watered with a bright pink solution of potassium permanganate. The treated soil is placed in a container with drainage holes and a drainage layer.
Seeds are scattered over the surface of the soil substrate, sprinkled with a layer of sand 3 mm thick, sprayed with warm water, covered with glass or polyethylene. Crops are placed in a bright place with an air temperature of 15 to 22 ° C. Crops are periodically ventilated by lifting a film or glass.

Under normal storage conditions, the germination of lavender seeds does not decrease over the years.
Seedling care
The emerging seedlings need to be provided with suitable conditions and care:
- additional lighting (so that the seedlings do not stretch out);
- temperature from 15 to 20 ° C;
- daily airing (glass or polyethylene is removed for a while so that the seedlings get used to the surrounding conditions);
- gentle, gentle watering;
- picking after the appearance of two leaves (seedlings are planted at a distance of 5–6 cm from each other);
- pinching seedlings when their height reaches 4–5 cm.
At the end of May, lavender is planted in a garden. Before planting, the roots are pruned a little. When planting, the root collar of the plant is deepened into the ground by 4–6 cm. After planting, lavender is watered abundantly.
When lavender is grown in regions with a hot, dry climate, seeds are sown in October directly into the ground to a depth of 3-4 cm. The ground surface is slightly compacted after planting. If the autumn is without rain, the crops are watered a little. When the first snow falls, they throw a small snowdrift over the area.
Lavender grown from seeds will bloom only after a year or two, when the bushes grow and get stronger. After three years, the plant acquires maximum decorative effect, so growing lavender as an annual is not justified. An exception is the one-year hybrid variety "Normandy", derived from multi-cut lavender. The plant is characterized by rapid growth and blooms in the first year, but it is also suitable for the role of a container perennial. Sometimes, subject to the sowing rules, the strongest seedlings of other varieties also bloom in the first year.
Despite the complexity, seed propagation has two advantages:
- in plants, the adaptation period passes easier and faster;
- if you collect seeds from grown plants and plant them, the new generation of lavender will be more resistant to unfavorable climates (this way, in the future, you can increase the resistance of any variety to low temperatures).
Purchase features
When lavender is grown from seeds, planting material is acquired in autumn or early winter in order to complete stratification by spring.
Also, for planting, you can purchase a ready-made plant in specialized flower shops, greenhouses, winter gardens.Purchased lavender can be propagated immediately by cuttings in order to preserve the variety in case of unsuccessful wintering. And if the plant takes root and overwinters, in the future it can be propagated by layering.
But not all purchased plants take root. The reason for this may be the wrong choice of the variety, inappropriate growing conditions, or poor-quality planting material, the care of which did not meet the standards. Therefore, if possible, it is better to take healthy shrub cuttings from neighbors or relatives.
Lavender is not difficult to care for. In order for the plant to develop normally, it is enough to plant it in a sunny place, regularly water and huddle, remove weeds. Therefore, many flower growers are happy to arrange real lavender fields on their plots, delighting the owners with long flowering, and filling the garden with a delicate fragrance.
Lavender is familiar to many as an essential oil crop that has soothing properties and helps relieve headaches. An evergreen plant that requires an abundance of warmth and light, it grows naturally in the Canary Islands, India and the Mediterranean. This plant, which is successfully used in medicine, cosmetology, interior decoration, is especially popular in domestic open spaces.
The endurance of lavender, the ability to withstand heat and frost make it possible to grow such a crop on an industrial scale.
Lavender: description
Lavender at home is an effective insecticide: planted in orchards and vegetable gardens, it repels pests. In particular, the plant is not tolerated by moths and Colorado beetles.
In gardens and flower beds, lavender creates a chic backdrop, highlighting the individuality of the rest of the plants. Its harmony with roses is gorgeous, as well as the combination of aromas of these two beautiful plants.
Outwardly, lavender, the cultivation of which is not particularly difficult, is a bush with an approximate diameter of 0.5 to 2 meters, with narrow, silvery leaves; flowers (from blue to dark purple) are collected in spike-shaped inflorescences. Dried twigs have a delicate, somewhat bitter aroma. Used at home as an effective anti-moth remedy. They look harmoniously in "folk" interiors: chalets, provence, country.
In ancient Greece, lavender was used for washing and washing, which is the reason for its today's name: "lava" from Latin means "wash".
Varieties of lavender
In nature, there are about 25 species of this plant.
Lavender is English or narrow-leaved. Has a strong fresh smell. The bush is approximately 1 meter in height and in diameter. Leaves are gray-green, narrow, small. The flowering period is in the middle of summer. Inflorescences are large, placed on long stems. The variety is quite easy to care for, adapted to low temperatures.
Lavender is French or broadleaf. It is considered the ancestor of decorative varieties. Has a wide range of colors. Flowering begins in May. The aroma is very strong, not always pleasant.
Hybrid Dutch lavender. Popular in Southern and Central Europe. Narrow-leaved tall (up to 2 meters) variety, characterized by large inflorescences located on long stems. Blooms in July. It is widely used in industry.
Lavender toothed. The variety is thermophilic; in the conditions of the domestic climate, it is suitable only for indoor cultivation. It has silvery, soft leaves. The inflorescences are composed of large blue flowers.
Features of lavender care
Lavender at home takes time and some patience. The plant prefers sandy soil, direct sunlight, does not need frequent watering. In the shade, the plant will take root, but it will not please with abundant flowering. It is not recommended to plant lavender near bodies of water.Being a long-term plant, lavender needs pruning, the purpose of which is to form a beautiful lush crown of the plant. It is required to produce it in the fall (after wilting of the spikelets-inflorescences), shortening the bush to a height of 3-5 cm above the soil surface. Pruning should be done carefully, until woody shoots.
Lavender, which is not difficult to care for, needs constant loosening. This will provide good air circulation and get rid of nearby weeds. Also, the ground can be mulched, rotted foliage, needles or wood chips can be used as mulch. The soil should remain open near the base of the trunk, which will protect it from rotting.
The plant is transplanted in spring or autumn, during the dormant period, before the onset of cold weather. For the winter, it is recommended to cover lavender with spruce branches or needles. If the plant is still frozen, the dead parts should be cut off. The bush will recover quickly enough.
Lavender breeding methods
Lavender is cultivated in several ways: by seeds, layering, cuttings, dividing the bush. The seed growing method is little used due to its duration. Lavender seeds must be sown in a prepared container with sandy soil, moistened and left for 30-40 days; the recommended temperature for this is + 5оС. After this time period, it is recommended to transfer the box with seeds to a warm, bright place, where to wait for the first shoots to appear. Disembarkation is carried out in May.
Seed lavender will grow better if the seed is stratified. To do this, the seeds should be mixed with a certain amount of sand, placed in a container, which must be wrapped in polyethylene and placed in the refrigerator for a month and a half. This will ensure faster germination of the plant. At the end of this procedure, lavender seeds can be sown. That's the whole procedure.
Lavender at home, planted with seeds, will not bloom soon: at first, the seedlings will develop, grow the root system. The plant will be able to appear in all its beauty only in a year, or even two.
The method of propagation by layering is convenient and not laborious. It is required to prepare a groove near the bush, into which to bend several lower branches. The latter must be attached and covered with soil. By next spring, the layering is ready for independent existence, it only needs to be carefully trimmed on both sides, dug up and transplanted.
When grafting, it is recommended to use woody annual shoots. They need to be cut into pieces of 7-10 cm and immersed in a loose earthy mixture, covered with a film and constantly moisten the soil. Rooted branches must be carefully dug out, leaving an earthen lump on the roots, and transplanted to a permanent place of growth.
Reproduction by dividing the bush
The way lavender propagates by dividing the bush requires some preparation. In autumn, the plant must be cut off by 8-10 cm, and then sprinkled with earth. Sprinkle again in the spring: this will lead to the formation of numerous shoots. In the fall, the lavender bush will be completely ready for division.
New lavender bushes are planted depending on the size of the latter; the approximate distance is 0.5-1.5 meters between each other.
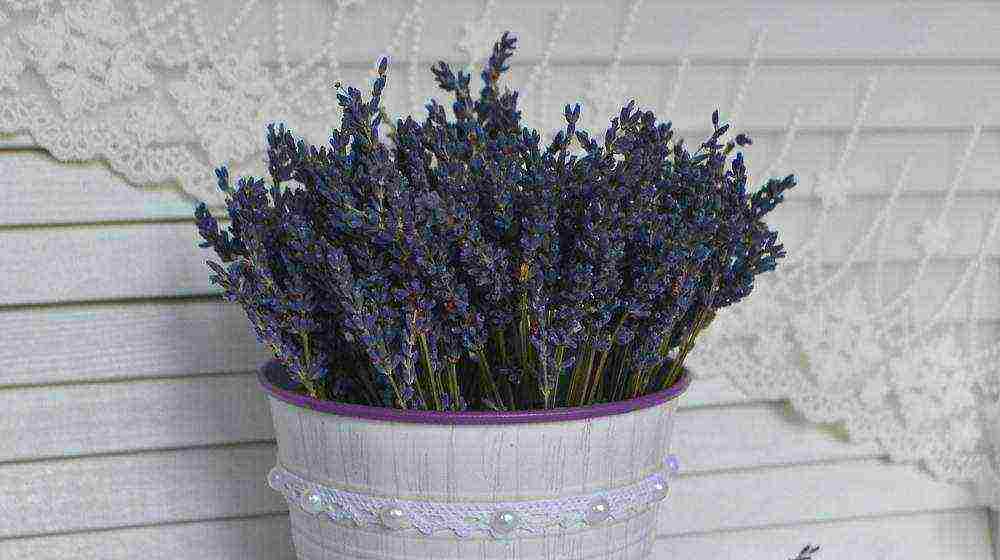
Lavender in a pot is beautiful, it is fragrant, it is unusual! Growing such a culture indoors is somewhat more difficult than in the open field. In this case, compliance with the temperature regime and careful care will be important components of its high-quality growth. Indoor specimen of lavender is an order of magnitude smaller than its street compatriot, which does not detract from its decorative effect.
Lavender: home cultivation
So, for growing lavender at home, you will need a deep and wide container due to the massiveness of the plant's root system.The bottom of the pot should be covered with a layer of drainage; the soil for planting is recommended to be soft and well fertilized. Moreover, lavender does not like organic and nitrogen fertilizers; good growth will be provided by potassium-containing dressings. Mineral preparations are recommended to be applied to the root area during flowering. The most optimal soil composition is as follows: 3 parts of leafy soil, part of sand and two parts of humus. Sandy soil with added lime will create ideal conditions for lavender to grow.
Potted lavender prefers cool, sunny locations. It will feel most comfortable on a terrace, a cool balcony, from the outside of the window.
Watering the plant
It is enough to water the plant once a week (in the morning or in the evening), in the cool season - twice a month, using additional humidification. To form a lush crown, it is recommended to water it mostly on the green part of the plant. Water stagnation should not be allowed, otherwise the lavender at home will simply die.
Seeing once a blooming lavender in a pot and breathing in its subtle delicate scent, you will definitely want to plant this mountain flower from the southern shores of the Black Sea in order to enjoy the fresh healing scent without leaving your home. What you need to know about growing a plant at home will be discussed below.
Description and characteristics of lavender
The thermophilic lavender comes from the mild warm climate of the Mediterranean and loves space and abundance of sunlight. It is a low-growing shrub up to 1 m high with narrow silvery-green leaves and lilac flowers.
 Flowering lavender in a pot
Flowering lavender in a pot
There are two varieties of colors: English and French.
The English species have narrow leaves, and the purple inflorescences are elongated. English lavender is unpretentious and winter-hardy, suitable for growing outdoors and even in central Russia does not require digging in the fall for wintering in pots.
French, unlike English, has wider leaves, lavender inflorescences and is shorter in size. In cultivation, this species is more capricious, when the air temperature drops to -15 ° C, the plant dies, therefore this species is grown mainly in pots.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantage of room lavender is its aromatic scent.exuded during flowering, has a calming effect and relieves headaches.
Lavender is an essential oil plant and has many beneficial properties.
An essential oil is made from flowers, which is used in medicine, aromatherapy, cosmetology and perfumery.
Lavender oil is used to treat burns, joint pain, and as a massage oil to help relax and relieve muscle tension. It has a strong antimicrobial effect.
Lavender basket
When growing a flower at home, you can use them by cutting and drying flowering shoots:
- for making sachets - aromatic pillows for adding a delicate aroma to linen and repelling moths;
- add to the formulations of herbal pillows that help with spasmodic headaches and fight insomnia;
- use as a freshener for shoes (put into shoes at night, they remove an unpleasant odor);
- as an addition to green and flower tea;
- in cooking, add to baked goods, salads, vegetable and fish dishes.
The plant has no drawbacks, except that the individual intolerance of the rich bitter aroma.
Planting and leaving
There are several ways to grow lavender at home:
Dawn on a lavender field
- By cuttings. Cuttings 10 cm long are cut from an annual shoot, leaves are removed from the lower end. The cuttings are placed in a light moist soil, covered with a film to maintain moisture and wait for the roots to appear. Cuttings take root easily.
- Seeds. Before planting, seeds must go through a stratification process, i.e. processing them with cold to increase germination. The seeds are placed in a moist substrate, covered with a plastic bag and placed on the lower shelf of the refrigerator for 1.5-2 months. After the stratification period has elapsed, the seed containers are placed in a bright and warm place until shoots appear. The grown seedlings are dived into cups, and then transplanted into pots as they grow. Seedlings will bloom in 1-2 years.
- By dividing the bush. You can separate the part of the shrub growing in the garden and place it in a pot to grow in the house.
Growing lavender in a pot culture requires certain rules to be followed:
- the brightest place is chosen, preferably southern windows, but in the summer, during the hottest midday hours, a little shading is required;
- the soil should be light, nutritious and consist of 3 parts of leafy earth, 2 parts of humus and 1 part of sand, it is imperative to add 1 tbsp. wood ash or lime;
- when planting a flower in a pot, there must be a good drainage layer, excluding stagnant water.
Lavender loves calcareous soils, so it is advisable to add crushed eggshells to flower pots.
Plant care consists of:
- in watering as the soil dries up, the flower does not like waterlogging;
- dressing: after planting and pruning, nitrogen fertilizers are applied for good growth of green mass, complex mineral fertilizers are applied before and during flowering;
- in spring before flowering and in summer after, lavender is pruned to shape the bush and stimulate flowering.
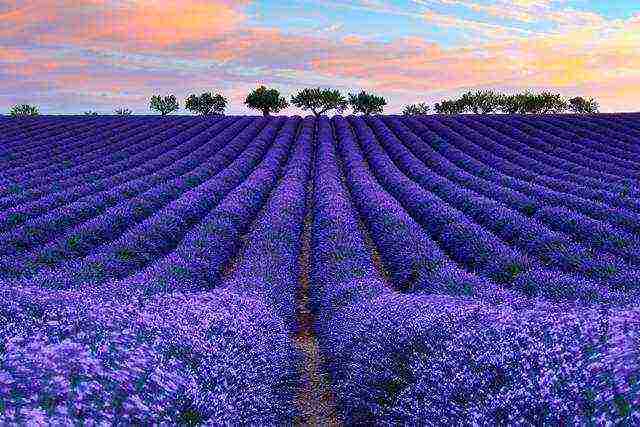 Fragrant lavender fields
Fragrant lavender fields
Problems of growing in a pot at home
There are no particular difficulties in growing a plant at home., but some of the nuances of planting and care are still worth considering.
- Since the plant loves space, and this applies not only to the surrounding space, but also to the volume of the pot. Lavender has a long root, if in the process of growth it rests against something, then it stops growing, which means it stops growing entirely. Given this feature of the plant, pots for growing need to be taken wide and deeper.
- When growing, the plant needs direct sunlight for at least 8 hours a day.
- In summer, lavender needs to be taken out into the garden or on the balcony, it needs fresh air.
- In winter, the plant needs the lightest windowsill, the temperature is not higher than 15 ° C and moderate watering.
- From spring to autumn, flowers must be fed regularly, otherwise the plant may stop developing normally, which will certainly affect flowering.
- It is necessary to replant lavender annually, changing not only the soil, but also the size of the pot to a larger one.
In no case should the soil in the pot be allowed to dry out. Drying out of the earthen coma of a plant even once leads to its death. No growth stimulants will help to restore the root system.
Protection against diseases and pests
Lavender is rarely affected by pests and diseases at home.... Infection of the plant with gray rot.
With waterlogged soil, the plant may become infected with gray rot. In this case, the affected stems are removed.
Having learned about the intricacies of growing lavender at home and making sure that there is nothing too complicated in this process, you can safely take on flower experiments. Having grown a beautiful and fragrant bush on your windowsill, you will not only fill your house with the smells of summer and the Crimean coast, but also provide yourself with useful flowers and leaves without leaving your home.
Lavender is an ornamental herb native to the Mediterranean and southern Europe. Flower lovers grow it on plots with single bushes, use it on alpine slides and as a border in flower beds.

Lavender is a shrub without a central stem from the Lamiaceae family. On the shoots, spike-shaped inflorescences of white, blue, purple or pink are formed. The name of this plant comes from two Latin roots "lava".They say that the flower got this name in connection with its use in antiquity as an additive during bathing. Lavender exudes a pleasant, light aroma, therefore it is often used as perfumery fragrances.
Some growers are sure that lavender is a capricious plant and requires increased attention. But knowing some of the secrets allows you to grow it on your own site, without much effort. If lavender is grown in a pot, home care also has some peculiarities and nuances. One of the main conditions is choosing the right variety for growing in the room.
Types and varieties of lavender grown at home with photos
There are about 20 types of lavender in nature, including many varieties. All of them differ in the shape and height of the bush, the color of the flowers. Some species are intended for planting exclusively in open ground.
In order to grow lavender in a pot, you must choose the following types:
- Narrow-leaved lavender (English). Among the varieties of this species, there are plants with a height of no more than 30 centimeters. Inflorescences are located on long stems covered with gray-green, narrow leaves.
- Lavender broadleaf (French). The ancestor of decorative varieties. Flowers have a wide range of colors. The disadvantage of this species is a somewhat unpleasant aroma.
- Lavender toothed. A heat-loving species intended exclusively for growing at home. The leaves of this species are silvery, soft. The inflorescences are covered with large, bright blue flowers.

Blooming lavender
The most popular varieties of lavender are:
- Dwarf blue;
- Hydcote;
- Sweet;
- Sharon Roberts;
- Lavender Lady;
- Snowman (white lavender);
- Manstead;
- Nana Alba.
Necessary conditions for growing
Lavender on the windowsill is a very real phenomenon. The main condition is the selection of dishes, soil and compliance with the requirements of maintenance in the apartment.
Pot for lavender
When choosing a pot, an important condition is sufficient space to accommodate the root system. For planting, you can use a pot or oblong container. Lavender loves space, so to start growing, the diameter of the pot must be at least 30 centimeters. A smaller diameter will negatively affect flowering: the less nutrition at the roots, the smaller and more inconspicuous the flowers. A container for lavender is selected with a volume of at least 2-3 liters. Several bushes, planted in an oblong container, look spectacular.

Lavender needs to be planted in a large pot
The grow tank should have enough drainage holes to drain off excess water when watering. The material of the pot does not matter. But experienced flower growers advise using an unglazed ceramic pot, since in a plastic one the roots can suffer from waterlogging. A drainage layer at the bottom of the pot with a height of at least 5-6 centimeters will help protect the plant from waterlogging.
The container for planting lavender must be light. Dark dishes get very hot in the sun, and the earthy ball will dry out too quickly. Overheating of the roots of even such a heat-loving plant will adversely affect its well-being, and may even lead to death.
Location and lighting requirement
Lavender is extremely demanding on lighting and will not grow if it is lacking. She needs a southern window sill in the apartment. In summer, it is advisable to put the plant on the balcony, and it is better to take it out into the street.
Potted lavender in winter, even on the southern windowsill, will suffer from a lack of sunlight, so it must be additionally highlighted. For the organization of supplementary lighting, you can use special phyto- or fluorescent lamps. Daylight hours for a plant should be at least 10 hours.

Lavender needs additional lighting
Selection of soil for lavender in a pot
The ideal soil composition for lavender consists of sand or gravel, humus, turf or leafy soil in a 1: 1: 2 ratio. If the substrate cannot be prepared on your own, ready-made flower soil from the store is quite suitable. You need to add a small amount of fine gravel to it for looseness and breathability.
Simple garden soil cannot be used for planting lavender, as it becomes denser during watering, and the roots of the plant begin to "suffocate".
Planting lavender
At home, lavender can be grown in three ways:
- sowing seeds;
- rooting cuttings;
- reproduction by layering.
Seed sowing rules
The most affordable way to grow lavender is by sowing seeds. Before sowing, you should carefully study the question of how to grow lavender in a pot at home.

Lavender can be grown by seed
Before sowing, seeds must undergo a cold stratification procedure for 30-40 days. The seeds are shifted with peat or sphagnum moss, slightly moistened and kept at a temperature of plus 5-6 degrees in a refrigerator or cellar.
For sowing, the seedling containers are filled with a mixture of peat, sand and a little crushed shell is added. The soil must be homogeneous, without lumps, so it must be thoroughly kneaded and sifted through a sieve with large cells. If lumps remain in the soil, the seeds may not be able to cope with the pressure and will not sprout.
Seeds are planted to a depth of 2-3 centimeters. The crops are covered with foil and placed in a cool place (balcony or lower shelf of the refrigerator). After 2 weeks, the container with crops is moved to a bright place with a temperature of + 15 ... + 18 degrees.
Seedlings, depending on the quality of the seeds, appear in 30-40 days. Seedlings at the age of 2-3 weeks dive for growing in a more spacious box, and then they are seated in separate pots.
Rooting cuttings
The method of growing lavender from seeds has one drawback: flowering begins after one to two years. You can get a blooming specimen the next year by cuttings.

Lavender can be grafted successfully
For rooting, annual shoots are cut, divided into segments of 10 centimeters. The lower cut must be made at an angle of 45 degrees and treated with a rooting stimulator (Heteroauxin, Kornevin, Radifarm, Zircon). Then the cuttings are placed in a moistened mixture of sand and peat and covered with transparent caps to create greenhouse conditions. After rooting, the cuttings are planted in separate pots.
Propagation of lavender by layering
Layers are the extreme shoots of the lavender bush, deliberately rooted in the soil. In March-April, the shoot is bent to the ground and fixed with a metal or wooden slingshot. The place of contact with the ground is sprinkled and moistened. Roots begin to form on the layering. The rooted cut is separated from the mother bush after about 2 months.
Dividing the bush
The procedure for dividing the bush is carried out in late September - early October. Digging a lavender bush from the soil is not worth it. A small part of the bush is separated with a shovel, cutting the roots. In this state, the plant should overwinter. In the spring, the separated part of the bush is dug out of the soil and transplanted into a pot. Such an instance begins to bloom after 30-40 days.

Lavender can be propagated by dividing the mother bush
Plant care
Proper care of lavender in an apartment is a guarantee of its correct development and abundant flowering. Any violation of the conditions of detention immediately affects the appearance of the plant. Lavender requires regular watering, without overdrying the soil and without waterlogging. Water for irrigation is used warm, settled. The soil in the pot should be moist without stagnant water. Excess moisture from the pallet after watering must be drained.
A feature of lavender watering is foliage hydration. Watering is carried out in such a way that the water falls on the leaves, and then flows into the soil. On particularly hot summer days, additional spraying of the foliage is necessary to maintain the humidity level.
In spring and summer, lavender is watered 2-3 times a week, preventing the earthen coma from drying out. In the fall, watering is reduced to 1 time in 2 weeks. In winter, when the plant is dormant, it should be watered once every 30 days with a minimum amount of water.
Lavender needs regular feeding. They are introduced in liquid form, combined with watering, every 2-3 weeks. Nitrogen-containing complexes are used before bud formation begins. After the beginning of the formation of buds and until the end of the growing season, phosphorus-potassium mixtures are used. During this period, nitrogen is excluded from top dressing, since its excess will lead to an increase in leaf mass to the detriment of flowering.
Lavender requires regular feeding
Lavender needs pruning to form the correct spherical shape. Shoots knocking out of the main crown are pruned with garden shears, giving the bush a rounded shape. Formative pruning is carried out twice during the growing season:
- in spring - before flowering;
- in late summer or early autumn at the end of flowering.
In summer, during flowering, sanitary pruning is carried out. Its purpose is to remove damaged, drying out shoots and wilted flowers. The procedure gives the lavender bush a neat look and stimulates the formation of new flowers.
In the spring, it is recommended to transplant lavender into a large container. The procedure is carried out annually, as the root system grows rapidly and becomes cramped in a small pot. The purpose of replanting is also to replace the soil with a more nutritious one.
When replanting, old soil is not removed from the roots. The lavender is carefully removed from the old pot along with the earthen lump and placed in another pot, 3-4 centimeters in diameter larger than the previous one. The resulting empty space along the edge of the roots is covered with fresh soil.
As the bush ages, from about the fifth or sixth year of life, the bush is divided into several parts. This technique allows you to get new, full-fledged specimens of the plant, and also serves to rejuvenate lavender. After division, lavender begins to actively form new shoots and blooms more profusely.
Potential Difficulties When Growing Lavender in a Pot

The successful cultivation of lavender is about following certain rules.
If you follow all the recommendations for growing lavender at home, there are practically no difficulties. But some of the nuances of leaving still exist:
- Lavender forms a long central root that should always have enough room. If the root starts to rest against the bottom of the pot, the lavender stops growing. Given this feature, deep pots need to be selected for growing.
- The plant needs fresh air. In a stuffy, unventilated room, the plant will begin to "suffocate" and slow down its growth. The room where lavender is grown should be regularly ventilated. In summer, the plant should be taken out onto the balcony or outside.
- Even a single complete drying out of the earthen coma should not be allowed. If the plant withers from lack of moisture, no growth stimulants or resuscitation procedures will help revive the plant.
- Diseases and pests generally do not affect the plant, but waterlogging can lead to the appearance of a gray rot disease. In this case, the stems begin to droop. If the lavender is affected by gray mold, you need to remove it from the pot and transplant it into new, partially replaced soil. After transplanting, the plant is watered with Fitosporin-M. Diseased stems should be cut. With a strong defeat of lavender with gray rot, the plant cannot be saved.
If you follow all the recommendations for caring for lavender when growing it at home on a windowsill, it will bloom profusely and give a healing, soothing aroma.
You can get acquainted with the peculiarities of planting lavender by watching the proposed video material. Happy viewing!