Content [show]
The content of the article:
- The importance of grain crops in modern Russia
- Overview of the main grain crops in Russia
- The importance of industrial crops
- Overview of the main industrial crops in Russia
When deciding which crop to grow, any farmer is guided by two main criteria - the actual ability to grow a particular type of plant in their fields and their profitability. The first criterion is determined by a combination of various factors, from climatic conditions to the technical equipment of the enterprise. The second criterion is determined mainly by market conditions. Based on these two criteria, the most preferable for growing in Russia are cereals, as well as some industrial crops.
The importance of grain crops in modern Russia
 The world crop production is based on a group of grain crops, which account for the lion's share of the industry's production. In this sense, Russia is by no means an exception. In our country, about half of the sown area is allotted annually for wheat, rye, barley and other cereals, which in itself testifies to the importance of plants of this group.
The world crop production is based on a group of grain crops, which account for the lion's share of the industry's production. In this sense, Russia is by no means an exception. In our country, about half of the sown area is allotted annually for wheat, rye, barley and other cereals, which in itself testifies to the importance of plants of this group.
Such popularity of cereals among Russian farmers is explained not only by suitable climatic conditions, which allow them to successfully grow them in a significant part of the country, but also by the great economic value of these plants. According to experts, every Russian eats about 120 kg of bread and pasta annually. Also, our fellow citizens eat a lot of cereals. In terms of weight, these products account for a quarter to a third of all products consumed by the average Russian.Thus, it is grain crops that form the basis of the diet of our compatriots, which is why the domestic demand for grain products in Russia is consistently high.
 Also, cereals are of great importance for the livestock industry, which is closely related to crop production. Many livestock feeds are also high in grains. For example, about 70% of the grown barley and almost all of the oats are used to feed farm animals. Livestock farms would not have been able to achieve their current productivity levels without large-scale grain supplies.
Also, cereals are of great importance for the livestock industry, which is closely related to crop production. Many livestock feeds are also high in grains. For example, about 70% of the grown barley and almost all of the oats are used to feed farm animals. Livestock farms would not have been able to achieve their current productivity levels without large-scale grain supplies.
All of the above means that the allocation of large areas of arable land for growing grain crops is an objective necessity. This product is in dire need of both the food industry and animal husbandry. Having sowed a field with wheat, rye or barley, a Russian farmer can be completely sure that he can easily sell the grown crop.
Overview of the main grain crops in Russia
Russian agrarians specialize in growing the following grain crops:
 wheat;
wheat;- rye;
- barley;
- oats;
- corn;
- millet;
- buckwheat;
- rice, etc.
Without a doubt, wheat is the most important agricultural plant in Russia. About 45-50 million tons of wheat grain is annually grown in the country's fields, the importance of which is absolutely impossible to overestimate. Firstly, flour is made from it, which is used to bake bread and bakery products - almost a sacred product for the Russian people. Also flour is used for making pasta and confectionery. Even in the production of vodka and beer, this cereal is often used. Finally, feed wheat varieties are included in livestock feed mixes. According to many farmers, wheat is the most profitable crop in crop production in Russia, as it has fairly high profitability rates, is relatively unassuming to weather conditions and is easy to grow.
 The second largest crop is barley. Its great popularity is ensured by its excellent resistance to various weather conditions. Barley is so hardy and unpretentious that it is grown in almost all regions of the country up to the permafrost zones. About 30% of the barley grain grown by Russian farmers is used in the food industry. In particular, large volumes of these products are consumed by enterprises producing beer, pearl barley and barley groats. The remaining 70% of barley is used as feed for farm animals.
The second largest crop is barley. Its great popularity is ensured by its excellent resistance to various weather conditions. Barley is so hardy and unpretentious that it is grown in almost all regions of the country up to the permafrost zones. About 30% of the barley grain grown by Russian farmers is used in the food industry. In particular, large volumes of these products are consumed by enterprises producing beer, pearl barley and barley groats. The remaining 70% of barley is used as feed for farm animals.
Speaking about what kind of grain crops are in crop production, one should not forget about rye. Historically, rye ("black") bread was called bread in Russia. Today it is significantly inferior in popularity to the "white" wheat, so rye is gradually losing its value, and the sown area under it is steadily decreasing. In addition, rye grain is cheaper and therefore less profitable. However, the demand for rye remains significant both in the food industry and in the production of alcohol and animal husbandry.
Oats are an important crop for those regions of Russia where wheat is not doing very well. Mostly it is grown for forage, but some of the harvest goes to the production of cereals.
Corn, millet, buckwheat, rice and other grain crops are also grown in Russia, but in much smaller volumes. Corn and millet are used as both feed and food crops. Buckwheat and rice are used almost exclusively in the production of cereals.
The importance of industrial crops
 It is customary to call industrial crops those types of agricultural plants that are grown for the sake of obtaining technical raw materials from them. A classic example of such a culture is flax, from which fibers (raw materials for the textile industry) and non-edible vegetable oil are obtained.However, many industrial crops can also be grown for food. For example, potatoes are both a staple vegetable and a source of starch. Thus, the division of crop production into food and industrial crops is rather arbitrary.
It is customary to call industrial crops those types of agricultural plants that are grown for the sake of obtaining technical raw materials from them. A classic example of such a culture is flax, from which fibers (raw materials for the textile industry) and non-edible vegetable oil are obtained.However, many industrial crops can also be grown for food. For example, potatoes are both a staple vegetable and a source of starch. Thus, the division of crop production into food and industrial crops is rather arbitrary.
It is important to note that the technical raw materials obtained as a result of plant processing are not necessarily used in the future for the production of non-food products. Much more often, it is food products that are obtained from industrial crops, which are used to impart certain taste or other qualities to finished food. For example, sugar obtained from sugar cane and sugar beet is a popular sweetener, and vegetable oil, which is obtained from dozens of different plants, is used for frying food, dressing salads and other culinary purposes.
As a rule, the cultivation of industrial crops is a more complex production task than the cultivation of cereals. Plants of this group are more demanding on weather conditions and soil characteristics, which is why the list of industrial plants cultivated in Russia is quite small. Also, the cleaning process is fraught with certain technical difficulties, since special cleaning machines are required. Finally, the plants harvested from the fields must be properly processed. While grinding grain into flour is an extremely simple technical task, processing beets into sugar or flax into fibers will require much more effort and expensive technology.
Considering the difficulties one has to face when growing industrial crops, it is obvious that the only reason for their cultivation is high profitability. It is the prospect of making a good profit that pushes agricultural enterprises to grow such demanding and fastidious plants.
Overview of the main industrial crops in Russia
This group covers a fairly wide range of plants that can be combined into several subgroups:
- spinning;
- oilseeds;
- sugar bearers;
- dyeing;
- rubber plants.
 To date, Russian crop production has focused mainly on sugar, oilseeds and spinning non-food crops. At the same time, the subgroup of oilseeds is most represented. The first violin here is, of course, the sunflower. It accounts for two thirds of the area allocated for all industrial crops in Russia. Sunflower is grown for the sake of vegetable oil, which totally dominates domestic cooking. On a much smaller scale, other oilseeds are grown in our country - soybeans, rapeseed, mustard, flax-flax - which together give only about 10% of vegetable oil in Russia.
To date, Russian crop production has focused mainly on sugar, oilseeds and spinning non-food crops. At the same time, the subgroup of oilseeds is most represented. The first violin here is, of course, the sunflower. It accounts for two thirds of the area allocated for all industrial crops in Russia. Sunflower is grown for the sake of vegetable oil, which totally dominates domestic cooking. On a much smaller scale, other oilseeds are grown in our country - soybeans, rapeseed, mustard, flax-flax - which together give only about 10% of vegetable oil in Russia.
The main sugar crop in the world is sugar cane, but there are no regions in our country where the climate is completely suitable for its cultivation. At the same time, a significant part of the Russian territory is suitable for growing sugar beets - the world's # 2 sugar beet. Sugar is not just a sweet addition to tea or coffee - it is a strategic raw material for the food industry. It is used in the production of not only confectionery and sugary soft drinks, but also most other ready-to-eat foods, from baked goods to fruit juices. Some sugar is used in the chemical industry.
 Spinning industrial crops in plant growing in Russia are represented by fiber flax, three quarters of the world harvest of which is grown in our country. For flax, the conditions of the Non-Black Earth Region are simply ideal, where it is quite cool and rainy in summer.The fiber obtained from flax is used for the production of linen fabrics, which are distinguished by high strength and attractive appearance. Linen yarns are considered to be more durable than cotton and woolen yarns. Only silk can compete with flax in this matter.
Spinning industrial crops in plant growing in Russia are represented by fiber flax, three quarters of the world harvest of which is grown in our country. For flax, the conditions of the Non-Black Earth Region are simply ideal, where it is quite cool and rainy in summer.The fiber obtained from flax is used for the production of linen fabrics, which are distinguished by high strength and attractive appearance. Linen yarns are considered to be more durable than cotton and woolen yarns. Only silk can compete with flax in this matter.
The content of the article:
- Types of crop production: main branches of production of plant products
- Types of crop products - the most demanded goods
- Cereals - the backbone of Russian crop production
- Industrial crops
The consumer market, food and light industries create demand for a variety of plant products. To satisfy the market demand, farmers grow various types of plant crops, from which, in the process of processing, they obtain specific products: from ready-made food (fresh fruits / vegetables) to industrial raw materials (technical oils, fibers for fabrics, etc.)
Types of crop production: main branches of production of plant products
In addition to the initially existing demand for various types of plant agricultural products, the variety of directions in the industry is also explained by the high level of its dependence on climatic conditions. When determining the list of crops that will be profitable to grow, the heads of agricultural enterprises are guided not only by the needs of the market, but also  weather conditions in the area where they have to work. Temperature regime, rainfall, solar radiation level, soil characteristics - all this is of fundamental importance when choosing a specialization of an agricultural producer.
weather conditions in the area where they have to work. Temperature regime, rainfall, solar radiation level, soil characteristics - all this is of fundamental importance when choosing a specialization of an agricultural producer.
According to the most common classification, there are seven types of crop production:
- growing grain crops;
- vegetable growing and melon growing;
- gardening and viticulture;
- floriculture;
- growing industrial crops;
- production of feed;
- forestry.
Types of crop products - the most demanded goods
Already the very terms denoting the branches of crop production make it clear what types of plant products they specialize in.
Thus, enterprises that grow grain crops supply wheat, rye, barley, oats, corn, millet, buckwheat, rice and other grains to the market.
Vegetable growing and melon growing provides the population with a variety of vegetables, of which the most important in Russia are:
- potato,

- onion,
- tomatoes,
- carrot,
- cucumbers,
- cabbage,
- Bell pepper,
- beetroot,
- eggplant,
- pumpkin and others.
Agrofirms engaged in horticulture and viticulture produce fruits and berries. In our country, they grow in large volumes:
- apples,
- pears,
- grape,
- plums,
- apricots,
- strawberries,
- raspberries,
- currants, etc.
Industrial crops are plants that are grown for the sake of raw materials for the food and light industries. This can include both some vegetables (for example, potatoes, from which starch is extracted) and grains, and plants that, in principle, are not eaten by either people or livestock (for example, cotton). In Russia, the main industrial crops are sunflower (sunflower oil is obtained from it), sugar beets (sugar), flax (fabrics and industrial oils are made from it), and potatoes.
Fodder farming is the foundation on which the entire livestock industry is built. Almost any cultivated plant can be used to some extent as feed for livestock. Very often, spoiled or substandard vegetables, fruits and grains are fed to animals. However, some plants are grown specifically for the production of feed from them:
 forage grasses (clover, alfalfa),
forage grasses (clover, alfalfa),- silage crops (fodder varieties of corn, cabbage),
- fodder root crops (some varieties of beets, carrots),
- cereals (feed oats, barley).
Forestry is of great importance for the economy, providing raw materials for many industries.In Russia, logging companies specialize primarily in pine, larch, spruce, oak and ash.
Floriculture stands apart. While other types of crop production have practical value (food, animal feed, raw materials for industry), flowers have an exclusively decorative function. In our country, this direction is relatively poorly developed. On an industrial scale, mainly roses, tulips and chrysanthemums are grown.
Cereals - the backbone of Russian crop production
For most countries of the world, including Russia, the most important area of crop production is the cultivation of grain crops. This industry produces the most important foodstuffs that form the basis of the diet of modern people and also play a key role in the production of feed for farm animals.
Russian agrarians specialize in growing the following grain crops:
- wheat;

- rye;
- barley;
- oats;
- corn;
- millet;
- buckwheat;
- rice, etc.
The most important are wheat, rice, rye and barley. The grain of these plants, almost without exception, is present in one form or another in any meal of a modern Russian. It is also the main product used in the production of animal feed and a strategic raw material for some industries.
The queen of modern plant growing - wheat - has been known since the times of Ancient Mesopotamia and Ancient Egypt. It is believed that this culture comes from the steppes of the "fertile crescent" (modern Middle East), but today it is cultivated in almost all countries of the world, which became possible thanks to the development of many different varieties adapted to any climatic conditions. Nevertheless, the main wheat producers are the countries of the temperate zone of the Northern Hemisphere: USA, Canada, Russia, Kazakhstan, Ukraine, China. In the Southern Hemisphere, most wheat is grown in Argentina and Australia.
Rice is the second most important grain crop (after wheat) in the world. At the same time, in some regions of the planet (Southeast Asia, tropical countries of Africa and Latin America), rice is the first grain crop in terms of area of crops and volumes of harvest, which forms the basis of the diet of people. It is not only used in its usual form (like porridge), but also flour is made from it, starch is extracted, alcohol is boiled, rice processing waste is used for cattle feed.
According to the most common version, rice was first grown in the central and southern regions of modern China about three thousand years ago. Despite the work of breeders, this culture still remains very demanding on weather and climatic conditions: it needs a hot and humid climate. In this regard, about 90% of world rice production falls on its historical homeland - Southeast Asia. The world's largest rice producers are China, India, Indonesia, Thailand, Japan and Brazil. Rice is also grown in relatively small quantities in Russia - in the southern regions, where the climate is most suitable for it.
 Corn is the main fodder resource in the United States and Western Europe, and in Asia, Africa and Latin America, it is used primarily as a food crop. It is also of great importance as a technical culture. In modern Russia, corn is grown in relatively small quantities.
Corn is the main fodder resource in the United States and Western Europe, and in Asia, Africa and Latin America, it is used primarily as a food crop. It is also of great importance as a technical culture. In modern Russia, corn is grown in relatively small quantities.
This plant comes from the territory of modern Mexico, from where it was brought to Europe several centuries ago. The world's major corn producers are countries with warm temperate or subtropical climates. Most of all it is grown in the USA, China, Brazil, Ukraine, Mexico, Argentina and India.
Industrial crops
Among the main types of crop production in Russia, one should also talk separately about industrial crops.This group covers a fairly wide range of plants of very different species and families. Some of them can be cultivated both as conventional food / feed and as technical ones. Their main feature is that they are grown for the sake of technical raw materials that can be obtained from them after special processing. There are several types of such plants:
- spinning;
- oilseeds;
- sugar bearers;
- dyeing;
- rubber plants.
Sugar and oilseed industrial crops are most actively grown in Russia. Sugars are mainly represented by sugar beets. It accounts for 60% of the world's sugar production. The remaining 40% comes from sugar cane, which practically no one cultivates in Russia. In addition to us, beets are also grown in large volumes in the EU countries, Ukraine, Belarus, Turkey, Iran, China, Japan, the USA and Canada.
As for oilseeds, sunflower is in the first place. Russian farmers cultivate rapeseed, flax and soybeans to a much lesser extent. In the countries of Southeast Asia, the oil palm is of great importance, in Africa - the peanut. The largest producers of vegetable oils are:
- Indonesia (palm oil),
- Malaysia (palm oil),
- Argentina (sunflower oil),
- Ukraine (sunflower oil),
- USA (soybean oil),
- India (peanut and sunflower oil),
- China (cottonseed and rapeseed oil).
From spinning crops, fiber is obtained, which is used as a raw material for the textile industry. Globally, the most widespread are cotton, fiber flax, jute and hemp. Russian farmers grow mainly flax and cotton in much smaller quantities. In the production of cotton, the leading countries are Asia, America and Africa. About 75% of flax is produced by Russia and Belarus, the main jute producer is Bangladesh.
Approximately about 70 percent of the food consumed worldwide is plant-based. That is why crop production is one of the key industries that serves as the fundamental basis of agricultural production.
Thanks to the climatic conditions and the presence of a large amount of fertile land in Russia, it is possible to grow a huge number of agricultural crops on an industrial scale. Crop production in Russia is mainly concentrated in the territory located in the temperate continental climatic zone. If we talk about the regions, then these are the Ciscaucasia, the Urals, the Central Volga region and Western Siberia. Both industrial and food crops are grown on the territory of these regions.
The importance of crop production for the country's economy
Crop production is one of the main economic engines of agriculture. In our country, vast territories are occupied by arable fertile lands located in favorable climatic conditions, so Russia is able to grow huge yields of wheat. At the same time, the agricultural complex not only fully meets the needs of our country, Russia is also one of the leaders in grain export to other countries.
What crops are cultivated in Russia?
Many technological and cultivated plants are grown in our country, but spring and winter wheat varieties, which are grown in many regions of Russia, have the highest yield. Barley is also very successfully cultivated, which ranks second after wheat in terms of production, and its share is 25% of all products. The great popularity of barley is due to the fact that it tolerates frost well, so it can be grown in many regions of the country, and it also ripens very quickly. The main uses for barley are brewing and animal husbandry.
Also, the climatic conditions of our country make it possible to collect large harvests of rice, rye, buckwheat, corn, sunflower, potatoes and many other crops. Despite the fact that their production volumes are much less than that of wheat and barley, nevertheless, farmers collect good harvests of these crops. Recently, great efforts have been made to increase the volume of rice cultivation.
Potatoes and sugar beets are grown on a large amount of arable land, but their production is still far from industrial scale. Sugar beet also plays an important role in Russian crop production, since sugar is made from it, and the tops are used as feed for pigs. On an industrial scale, sunflower is cultivated in Russia, the seeds of which are used for the production of vegetable oil.
Melon and vegetable growing
Crop production is not only the cultivation of grain crops. Vegetable growing and melon growing are also actively developing in Russia. Basically, these areas of crop production are concentrated in the southern regions of the country, where the climate is milder and warmer, and the summer is not too dry. Crops such as cucumbers, tomatoes, onions, cabbage, carrots, watermelons, eggplants, squash melons and many others are grown in large volumes. Some crops are used exclusively for domestic needs, while some are exported to other countries.
The importance of crop production for agriculture
Crop production is one of the leading branches of agriculture, largely stimulating the economic development of the country. It is aimed at growing cultivated plants and supplying them to the domestic market in order to provide the country's food base. It is important to understand here that the level of development of this industry has a direct impact on the level of development of animal husbandry. This is due to the fact that farmers grow many types of fodder crops that are used to feed livestock. Therefore, colossal amounts of money are annually allocated from the state budget, which are spent on the development of crop production.
What factors influence the development of crop production?
The development of plant growing industries is vital for the economic development of the country, as well as ensuring its food security. Therefore, neither the state nor the agrarians spare financial resources and time to achieve the desired result.
But for development to be as effective as possible, the following factors must be taken into account:
- Rehabilitation of depleted and depleted areas of land. This is very important, since the yield of any crop depends on the availability of nutrients and macronutrients in the soil.
- Development of innovative technologies. An equally important aspect, since product quality and yield require constant improvement of plant cultivation methods, as well as the use of reliable technology. Mechanized work in crop production also plays an important role, which makes it possible to significantly increase the volume of production without significant financial and labor costs. This requires support from the state.
- Healthy competitive environment. The lack of competition in the market negatively affects the development of crop production, which, in turn, slows down the country's economic growth.
- Technological progress and scientific developments. The more innovations are introduced into this industry, the lower the cost of crop production will be. Moreover, the more profitable the industry is, the greater the financial contributions to the state treasury will be.
From all of the above, it follows that enterprises engaged in crop production will be concentrated in those regions of the country in which scientific and technological progress, favorable social and economic factors, fertile lands and suitable climatic conditions are well developed.The last two factors are key, since the yield of industrial and food crops depends on them.
Main industries
As mentioned at the beginning of this article, crop production provides about 70 percent of the world's food.
There are the following crop industries focused on the cultivation of certain crops:
- cereals (wheat, rye, barley and others);
- potatoes and tuber crops;
- industrial crops;
- vegetables and melons;
- grapes and fruit;
- forage crops.
Each branch of crop production has certain characteristics, so let's take a closer look at each of them.
Cultivation of cereals
This industry is the most important not only in Russia, but all over the world, since grain crops are not only consumed more than others for food, but also act as food for pets. Which is very, very much in demand in animal husbandry. In addition, grain is used in many industrial sectors. About half of the world's fields are planted with cereals.
The most common crops in this industry are wheat, rice and corn. Thanks to the efforts of breeders around the world who have developed new varieties of cereals, as well as the continuous development of new technologies and innovative cultivation methods, the cultivation of cereals today has become possible in almost every part of our planet.
Cultivation of potatoes and tuber crops
Russia occupies a leading place in the world in terms of potato production. Also in our country, sugar beets and cane are grown in large quantities, from which sugar is made. Despite the fact that beets are grown on an industrial scale, nevertheless, in terms of production volumes, Russia is significantly inferior to many countries.
Industrial crops
The technology of plant growing in the field of growing industrial crops in Russia is very well developed, therefore, in our country, fibrous crops are cultivated in large volumes, from which fabric, rubber, as well as crops that act as raw materials for the production of various oils are produced. The most common fiber crops grown in our country are cotton, flax and jute. Rubber is also of great value because it is used by industry for the production of many natural and synthetic materials that are used in various spheres of human life.
Vegetable growing and melon growing
Crop production, the types of which are considered in this article, is also aimed at growing vegetables and melons. But the scope is much smaller than that of those discussed above, since the optimal climate for their cultivation is inherent only in the southern regions of the country, nevertheless, much attention is paid to their production. The most common vegetable crops are carrots, cabbage, onions, zucchini, tomatoes, eggplants and some others. As for melon growing, in Russia watermelons and melons show good yields.
Growing fruit crops and grapes
This branch is directed to the cultivation of various grape varieties and a variety of horticultural crops, from which wine and juices are subsequently made. Viticulture and horticulture is best developed in the southern and central regions of Russia.
Fodder crops
This industry, like the cultivation of grain crops, acts as the basis of crop production, since the level of its development directly affects the level of development of animal husbandry. Residues from some forage crops are excellent feed for pigs. In addition, some crops are specially cultivated for feeding livestock. Therefore, much attention is paid to increasing the production of forage crops, increasing the level of their quality and yield, as well as reducing costs.
Secondary areas of crop production
Above, the main branches of crop production were considered, which have a significant impact on the economic development of our country. But there are still secondary directions that are also developing, but not on such a scale. Such industries include floriculture and seed growing.
Floriculture is aimed at breeding and growing new varieties of indoor and garden plants. This direction in Russia is poorly developed due to insufficient funding, so most of the products of this group are purchased abroad.
Seed production is a fundamental industry that underlies all crop production. It is aimed at growing seeds of agricultural crops, which, in turn, are planting material. Not only the yield depends on the quality of the seeds, but also the quality of the products.
Conclusion
Russian plant growing is primarily aimed at growing cultivated plants that are used to form a food base. But also crops are cultivated that are involved in the processing of crop products. These include many types of crops that are raw materials for light industry.
Today, crop production in our country is experiencing many problems associated with low infrastructure development, lack of innovative and modern cultivation methods, as well as poor technical equipment. For its development, the state is making great efforts, allocating money from the budget and carrying out various reforms. Despite the problems, our country is one of the main suppliers of plant products to the world market.
It should be noted that in recent years, the level of development of crop production has entered a completely new stage. After the introduction of economic sanctions against Russia by Western countries, the state significantly increased subsidies to farms, thanks to which new technologies began to be introduced that made it possible to reduce the cost of production and increase the profitability of agricultural business. In the future, the country's government is also going to improve the development of crop production in the country, thanks to which the economy can significantly improve.
Agricultural crops: cereals, vegetables, industrial crops:

Agricultural crops are called crops cultivated by farmers and large agro-industrial enterprises in order to obtain food, feed for livestock, technological raw materials. There are several main types of such plants. Of course, the cultivation of crops must be carried out in strict compliance with certain technologies.
Main types
Most agricultural enterprises are broad-based and grow a wide variety of crops. It can be cereals, vegetables, fruit trees, root crops, etc. But most often in Russia such agricultural crops are cultivated as:
- wheat, barley, rye and oats;
- potato;
- sunflower;
- forage grasses;
- sugar beet.
These are the main types of agricultural crops in our country. Of course, domestic farmers sometimes grow vegetables as well. Such crops are most often cultivated in greenhouses.
Grain growing technology
When cultivating oats, wheat, barley and rye, agricultural enterprises perform the following activities:
- basic and pre-sowing soil preparation;
- fertilization;
- seed preparation;
- sowing;
- planting care;
- harvesting.
Sowing dates
Grain crops can be cultivated using the winter or spring method. In the first case, sowing takes place in the autumn, in the second - in the spring. The most important task in the cultivation of grain crops is to determine the timing of planting seeds in the soil.
They should be chosen so that winter cereals reach the tillering phase before the onset of cold weather and form at least 3-4 shoots. Therefore, the optimal time for sowing grain crops in the non-chernozem zone of Russia is the first decade of September. Sometimes planting is carried out at the end of August.
When cultivating spring crops, the sowing time is determined by the condition of the soil. Most often, cereals are planted in mid to late April.
Plowing the land
Soil cultivation before sowing cereals is carried out so that as much post-harvest residues as possible remain on the surface. This is necessary in order to avoid erosion and retain as much moisture as possible in the ground.
For plowing, in most cases, various kinds of mineral fertilizers are applied. Further, early spring harrowing is carried out for spring crops, and pre-sowing cultivation for winter crops.
Sowing seeds
After the soil is prepared, the actual planting of cereals is carried out. In this case, only healthy, undamaged seeds that meet the stipulated standards are used. Before sowing, they are pickled to avoid infection with fungal, bacterial and other diseases.
Winter crops are grown from the seeds of last year's harvest. For their storage at agricultural enterprises, special funds are created. Freshly harvested seeds are rarely used when planting. The fact is that they have a reduced germination rate.
At the final stage of planting, the seeds are rolled to improve their contact with the soil.
Grain care
Subsequently, to obtain a good harvest, the following activities are carried out:
- Protection of cereals from pests and diseases. As necessary, they are treated with fungicides and insecticides.
- Weed removal. In this case, crops are treated with herbicides.
- Top dressing. Cereals are fertilized during the season, usually using nitrogenous compounds.
Harvest
This operation can be performed in two ways: directly or separately. Two-phase harvesting is performed for unevenly ripened, lodged or heavily weeded crops. In all other cases, the usual direct combining is carried out.
Potato cultivation technology
Cereals are the main type of plants cultivated by domestic agricultural enterprises. However, potatoes are also quite widespread. The cultivation technology of this crop includes the following stages:
- soil preparation;
- landing;
- plant care;
- harvesting.
Land preparation and planting
Plots for potatoes are usually chosen with loose soil that allows moisture and air to pass through well. Only in such areas can you get good harvests of this crop. The best precursors for potatoes are winter cereals, corn, perennial and annual grasses.
Prepare the soil for potatoes, usually in the fall. At the same time, plowing (autumn) is carried out with the introduction of fertilizers. In April, the soil surface is leveled and early spring harrowing is carried out.
Only healthy, undamaged tubers of large and medium size are used for sowing. 10-12 days before disembarkation, they are unloaded from the storage and sorted out. Further, the tubers are germinated or simply wilted. Sometimes, before planting, potatoes are treated with ash, mineral fertilizers and fungicides.
Tubers are planted only in well-warmed soil. At the same time, 55-60 thousand bushes are placed on 1 hectare. Early varieties are usually planted denser, later ones less often. The landing itself can be ridge, semi-ridge or smooth. The first two methods are more often used on wet or heavy soils. The combs are cut a few days before planting.
Potato care
The first shoots of this culture appear in about two to three weeks. With a smooth planting, harrowing is carried out in agricultural enterprises. It can be performed before germination or after germination.In the future, caring for potatoes is reduced to hilling and weeding.
The first operation is performed twice a season: with a bushes height of 15-18 cm and before flowering. Weeding is carried out as needed.
Plantings of this variety, among other things, should be periodically treated against phytophthora (fungicides) and the Colorado potato beetle ("Decis", "Volaton").
Cleaning
The ripening time of tubers depends primarily on the variety of potatoes. To facilitate mechanized harvesting in agricultural enterprises, the tops are usually mown. This operation is performed in 3-5 days. Cleaning itself can be done in three ways:
- direct combining - on light crops;
- by separate technology - on heavy soils;
- in a combined way.
Seed tubers before storage are kept in the light for 10-12 days until light greening. Table potatoes are air-dried for several hours. Of course, like any other staple crop, potatoes must be stored properly. Tubers are laid for the winter in dark cool rooms in bulk or in boxes.
Sunflower cultivation technology
It is customary to grow this crop after winter and spring cereals.
Presowing preparation of land for sunflower includes operations such as plowing, harrowing and leveling the soil with special drags. Cultivation is carried out to the depth of planting seeds (6-10 cm).
Manure is usually used as a fertilizer for plowing. Sometimes mineral fertilizing can also be used (depending on the composition of the soil).
For sowing, seeds of varieties and hybrids entered in the register are used with a germination rate of at least 95%. Planting is carried out in well-heated soil at the rate of 30-50 thousand plants per hectare. Sowing is carried out in a dotted manner. At the final stage, the plots are rolled in.
Sunflower care in our country is carried out using exclusively mechanized methods. The first is such an operation as harrowing before and after sprouting, with simultaneous weeding and the use of herbicides. Further, sunflower care includes procedures such as:
- Fight against voidness. For this, hives are placed on the allotment at the rate of 1.5-2 per hectare.
- Pest and disease control using chemicals.
Harvesting is done after the back of the baskets turns yellow. The reed flowers should fall off. Sunflower is harvested, like most other agricultural crops, with special combines.
Technology for growing forage grasses
Crops of this group can be cultivated as pasture or for hay or silage. There are many types of forage grasses. But most often in our country alfalfa, clover, vetch and legumes are grown. The technology of their cultivation, like any other agricultural crops, includes soil preparation, sowing, care and harvesting.
A feature of growing herbs is very deep, 25-30 cm, plowing (due to long roots), the possibility of sowing perennial crops under the cover of annuals and fertilizing with mineral fertilizers during the growth period. Plants are harvested in the budding or flowering phase.
Growing sugar beet
About 21 thousand hectares of arable land are used for this crop in Russia. The optimum depth of plowing the land for beets is 25-30 cm. Such cultivation of the land is carried out in the fall - usually in September. At the same time, manure is applied in the amount of 40-80 t / ha. For sowing, pickled seeds are used.
Planting is carried out to a depth of 25-35 mm, depending on the type of soil, using special seeders. Caring for beets is mainly about weeding or applying herbicides, as well as protecting plants from pests and diseases using chemicals. Harvesting of this crop usually begins on September 20-25.
In this case, in-line, transshipment or combined technologies can be used. The last two methods are usually used with increased contamination of areas.
Growing vegetables in greenhouses
A feature of the cultivation of crops of this variety in greenhouses is the periodic use of top dressing and land replacement. After all, the soil in greenhouses is very quickly depleted.
Also, in such farms, maximum attention should be paid to the fight against pests and diseases. Infections spread very quickly in greenhouses.
Seeds of agricultural crops of this variety are necessarily pickled before planting.
Most often, cucumbers, tomatoes, eggplants, peppers and melons are grown indoors. The greenhouses themselves can be film, glass or polycarbonate.
Among other things, when growing vegetable crops, special attention is paid to their selection for compatibility.
This takes into account such factors as the feeding and irrigation regime, climatic conditions, the need for pollination, the frequency of ventilation, etc.
Varieties and hybrids
Farms and large agricultural enterprises mainly grow only varieties of agricultural crops entered in the state register. The only exception is experimental stations where breeding work is carried out. When developing new varieties, the following methods can be applied:
- selection with the consolidation of certain valuable features;
- hybridization in breeding nurseries.
The resulting varieties and hybrids are tested and, if the value for agriculture is established, are entered into the state register.
The cultivation of crops, therefore, must be carried out on well-prepared soils, using suitable fertilizers and seeds of the best varieties. In the absence of violations of technology, even in the case of adverse weather conditions, you can get good harvests and at the same time avoid such negative consequences as erosion and soil depletion.
Top 10 agricultural crops in Russia
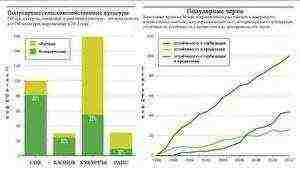
What kind of agricultural crop occupies record areas in Russia?
What is grown in our country? What is the leading crop in terms of acreage? The area, of course, changes from year to year, but the proportions remain approximately the same.
10. Soy
This leguminous plant is one of the most ancient cultivated plants. Soybeans have been known as a food product since the 3rd millennium BC. Soy is often called the "miracle plant".
It was awarded this prestigious title both for its high yield and, most importantly, for its high protein content - up to 40% and even up to 50% for certain varieties. Soy is the main source of protein for vegetarians.
Thousands of hectares are occupied by soybeans in Russia.
9. Sugar beet
In the 18th century, sweet lovers received a new source of sugar - sugar beets. By the efforts of breeders, by the end of the 20th century, it was possible to raise the sugar content of root crops to 20%.
Sugar beet does not require heat, like sugar cane, and grows well in middle latitudes. So in Russia, 21 thousand hectares are used for it.
But sometimes the harvest is such that a lot of beet sugar is exported.
8. Potatoes
Potatoes were brought to Europe from America in the middle of the 16th century, and even then they were first used as an ornamental plant. The overseas product had a hard time taking root in European cuisines. In Russia, the situation was even worse: neither the efforts of Peter I, nor the decrees of Catherine II instilled in Russians a taste for the "damn apple."
Only after a series of "potato riots" in the middle of the 19th century did the population come to terms, and potatoes began to be planted everywhere. And then they got a taste. Now it is impossible to imagine a family menu without potatoes. And they plant it on an area of one thousand hectares.
But this is without household plots and other plots, and no one will undertake to calculate how many "hundred parts" the staple food occupies there.
7. Corn
The corn admirer Nikita Khrushchev made sure that in the public consciousness the "Queen of the Fields" went into the category of anecdotal characters (together with Khrushchev). But in vain. Child of the New World (like potatoes) - corn is a very valuable and high-yielding product. It is no coincidence that the Maya had a separate corn god Quetzalcoatl.
It makes more than one popcorn. Corn flour, flakes, the famous hominy, and a lot of other things from different countries and peoples make corn the second most salable product in the world. Unripe corn, stalks and leaves also go into business, that is, for livestock feed. More fodder corn is planted in Russia (21.1 thousand hectares).
This is understandable: corn, despite the efforts of Khrushchev, prefers a warmer climate for ripening. But they also borrow enough for grain: with an indicator of 12.5 thousand hectares, grain corn would enter the Top 10 on its own.
Well, the total corn of thousands of hectares put it in seventh position in the ranking.
6. Oats
Once upon a time, futurists predicted that in the future, transportation will be seriously limited: it simply will not be possible to grow enough oats to feed the required number of horses. The invention of the automobile solved this problem, oats have ceased to be a source of food for transport, but have not completely lost their position among agricultural crops.
Oats are still an important forage crop for a variety of livestock. And people with pleasure and with health benefits use not only oatmeal, but also oatmeal and oat flour. By the way, other plants for making popular cereals - buckwheat and millet - were not included in the rating: they are not fed to livestock, and human needs are small.
But oats in Russia occupy thousands of hectares.
5. Rye
The rye varieties developed to date prefer colder climates. Therefore, the countries with the largest yields are Germany, Poland and, of course, Russia. It is impossible to imagine Russia without rye bread or kvass.
And the alcohol from rye is excellent. Both bread and kvass are not just favorite foods, they also have medicinal properties. thousands of hectares for rye crops provide it with a worthy place in the ranking.
4. Barley
Thousands of hectares of land are allocated for barley in Russia. Why are the crops of barley more than rye and oats combined? Because barley is an excellent fodder for livestock, 70% of the area is occupied by fodder barley. Well, don't forget about beer. You cannot cook "liquid bread" without barley.
3. Forage grasses
Grain - grain, but even without hay or grass meal, numerous heads of large and small livestock cannot be grown. Perennial and annual grasses, all these clover, alfalfa, timothy, fescue and others and others occupy as many as thousands of hectares of agricultural land. And without grass - no milk, no meat.
2. Sunflower
Sunflower area - thousand hectares. The most common vegetable oil in Russia is sunflower oil.
Before the arrival of this guest from the distant American shores, they treated linseed, hemp or imported wood, that is, olive. The British were the first to think of making oil from sunflower seeds.
But the industrial production of sunflower oil was the first to be mastered by Russia. From here the technology has spread all over the world. As well as the spread of this crop.
1. Wheat
The real "Queen of the fields" is the wheat. Winter alone, that is, sown before winter, in autumn - 252.8 thousand hectares. And if you add 137.2 thousand hectares of spring, that is, spring planting, you get thousands of hectares. And how could it be otherwise, because "bread is the head of everything."
And also - pasta, all sorts of cookies, gingerbread cakes, the best ethyl alcohol ... And the necessary feed grain. Wheat is one of the oldest cultivated plants. Wheat was domesticated 10,000 years ago, studies show, in the Levant, near the eastern Mediterranean coast.
From here it spread throughout the world.
Crop production is a branch of agriculture that cultivates crops. Crop production in Russia:

Approximately about 70 percent of the food consumed worldwide is plant-based. That is why crop production is one of the key industries that serves as the fundamental basis of agricultural production.
Thanks to the climatic conditions and the presence of a large amount of fertile land in Russia, it is possible to grow a huge number of agricultural crops on an industrial scale.
Crop production in Russia is mainly concentrated in the territory located in the temperate continental climatic zone. If we talk about the regions, these are the Ciscaucasia, the Urals, the Central Volga region and Western Siberia.
Both industrial and food crops are grown on the territory of these regions.
The importance of crop production for the country's economy
Crop production is one of the main economic engines of agriculture.
In our country, vast territories are occupied by arable fertile lands located in favorable climatic conditions, so Russia is able to grow huge yields of wheat.
At the same time, the agricultural complex not only fully meets the needs of our country, Russia is also one of the leaders in grain export to other countries.
What crops are cultivated in Russia?
Many technological and cultivated plants are grown in our country, but spring and winter wheat varieties, which are grown in many regions of Russia, have the highest yield.
Barley is also very successfully cultivated, which ranks second after wheat in terms of production, and its share is 25% of all production.
The great popularity of barley is due to the fact that it tolerates frost well, so it can be grown in many regions of the country, and it also ripens very quickly. The main uses for barley are brewing and animal husbandry.
Also, the climatic conditions of our country make it possible to collect large harvests of rice, rye, buckwheat, corn, sunflower, potatoes and many other crops. Despite the fact that their production volumes are much less than that of wheat and barley, nevertheless, farmers collect good harvests of these crops. Recently, great efforts have been made to increase the volume of rice cultivation.
Potatoes and sugar beets are grown on a large amount of arable land, but their production is still far from industrial scale.
Sugar beet also plays an important role in Russian crop production, since sugar is made from it, and the tops are used as feed for pigs.
On an industrial scale, sunflower is cultivated in Russia, the seeds of which are used for the production of vegetable oil.
Melon and vegetable growing
Crop production is not only the cultivation of grain crops. Vegetable growing and melon growing are also actively developing in Russia.
Basically, these areas of crop production are concentrated in the southern regions of the country, where the climate is milder and warmer, and the summer is not too dry.
Crops such as cucumbers, tomatoes, onions, cabbage, carrots, watermelons, eggplants, squash melons and many others are grown in large volumes. Some crops are used exclusively for domestic needs, while some are exported to other countries.
The importance of crop production for agriculture
Crop production is one of the leading branches of agriculture, largely stimulating the economic development of the country. It is aimed at growing cultivated plants and supplying them to the domestic market in order to provide the country's food base.
It is important to understand here that the level of development of this industry has a direct impact on the level of development of animal husbandry. This is due to the fact that farmers grow many types of fodder crops that are used to feed livestock.
Therefore, colossal amounts of money are annually allocated from the state budget, which are spent on the development of crop production.
What factors influence the development of crop production?
The development of plant growing industries is vital for the economic development of the country, as well as ensuring its food security. Therefore, neither the state nor the agrarians spare financial resources and time to achieve the desired result.
But for development to be as effective as possible, the following factors must be taken into account:
- Rehabilitation of depleted and depleted areas of land. This is very important, since the yield of any crop depends on the availability of nutrients and macronutrients in the soil.
- Development of innovative technologies. An equally important aspect, since product quality and yield require constant improvement of plant cultivation methods, as well as the use of reliable technology. Mechanized work in crop production also plays an important role, which makes it possible to significantly increase the volume of production without significant financial and labor costs. This requires support from the state.
- Healthy competitive environment. The lack of competition in the market negatively affects the development of crop production, which, in turn, slows down the country's economic growth.
- Technological progress and scientific developments. The more innovations are introduced into this industry, the lower the cost of crop production will be. Moreover, the more profitable the industry is, the greater the financial contributions to the state treasury will be.
From all of the above, it follows that enterprises engaged in crop production will be concentrated in those regions of the country in which scientific and technological progress, favorable social and economic factors, fertile lands and suitable climatic conditions are well developed. The last two factors are key, since the yield of industrial and food crops depends on them.
Main industries
As mentioned at the beginning of this article, crop production provides about 70 percent of the world's food.
There are the following crop industries focused on the cultivation of certain crops:
- cereals (wheat, rye, barley and others);
- potatoes and tuber crops;
- industrial crops;
- vegetables and melons;
- grapes and fruit;
- forage crops.
Each branch of crop production has certain characteristics, so let's take a closer look at each of them.
Cultivation of cereals
This industry is the most important not only in Russia, but all over the world, since grain crops are not only consumed more than others for food, but also act as food for pets.
Which is very, very much in demand in animal husbandry. In addition, grain is used in many industrial sectors. About half of the world's fields are planted with cereals.
The most common crops in this industry are wheat, rice and corn. Thanks to the efforts of breeders around the world who have developed new varieties of cereals, as well as the continuous development of new technologies and innovative cultivation methods, the cultivation of cereals today has become possible in almost every part of our planet.
Cultivation of potatoes and tuber crops
Russia occupies a leading place in the world in terms of potato production. Also in our country, sugar beets and cane are grown in large quantities, from which sugar is made.Despite the fact that beets are grown on an industrial scale, nevertheless, in terms of production volumes, Russia is significantly inferior to many countries.
Industrial crops
The technology of plant growing in the field of growing industrial crops in Russia is very well developed, therefore, in our country, fibrous crops are cultivated in large volumes, from which fabric, rubber, as well as crops that act as raw materials for the production of various oils are produced.
The most common fiber crops grown in our country are cotton, flax and jute.
Rubber is also of great value because it is used by industry for the production of many natural and synthetic materials that are used in various spheres of human life.
Vegetable growing and melon growing
Crop production, the species of which are considered in this article, is also aimed at growing vegetables and melons.
But the scope is much smaller than that of those discussed above, since the optimal climate for their cultivation is inherent only in the southern regions of the country, nevertheless, much attention is paid to their production.
The most common vegetable crops are carrots, cabbage, onions, zucchini, tomatoes, eggplants and some others. As for melon growing, in Russia watermelons and melons show good yields.
Growing fruit crops and grapes
This branch is directed to the cultivation of various grape varieties and a variety of horticultural crops, from which wine and juices are subsequently made. Viticulture and horticulture is best developed in the southern and central regions of Russia.
Fodder crops
This industry, like the cultivation of grain crops, acts as the basis of crop production, since the level of its development directly affects the level of development of animal husbandry.
Residues from some forage crops are excellent feed for pigs. In addition, some crops are specially cultivated for feeding livestock.
Therefore, much attention is paid to increasing the production of forage crops, increasing the level of their quality and yield, as well as reducing costs.
Secondary areas of crop production
Above, the main branches of crop production were considered, which have a significant impact on the economic development of our country. But there are still secondary directions that are also developing, but not on such a scale. Such industries include floriculture and seed growing.
Floriculture is aimed at breeding and growing new varieties of indoor and garden plants. This direction in Russia is poorly developed due to insufficient funding, so most of the products of this group are purchased abroad.
Seed production is a fundamental industry that underlies all crop production. It is aimed at growing seeds of agricultural crops, which, in turn, are planting material. Not only the yield depends on the quality of the seeds, but also the quality of the products.
Conclusion
Russian plant growing is primarily aimed at growing cultivated plants that are used to form a food base. But also crops are cultivated that are involved in the processing of crop products. These include many types of crops that are raw materials for light industry.
Today, crop production in our country is experiencing many problems associated with low infrastructure development, lack of innovative and modern cultivation methods, as well as poor technical equipment.
For its development, the state is making great efforts, allocating money from the budget and carrying out various reforms. Despite the problems, our country is one of the main suppliers of plant products to the world market.
It should be noted that in recent years, the level of development of crop production has entered a completely new stage.
After the introduction of economic sanctions against Russia by Western countries, the state significantly increased subsidies to farms, thanks to which new technologies began to be introduced that made it possible to reduce the cost of production and increase the profitability of agricultural business. In the future, the government of the country is also going to improve the development of crop production in the country, thanks to which the economy can significantly grow.
What is technical culture? Industrial crops
Many people perceive almost everything that is grown on the earth as food, but this is a misconception. Most of the world's agricultural land is dedicated specifically to the cultivation of industrial crops. Every year more and more goods are produced from them.
And it's not just clothes. Soap, tires, medicines, cigarettes, building materials and biofuels - this is not a complete list of the possibilities of such plants.
In the commodity circulation of many countries, industrial crops are of the same great importance as oil, iron ore or gas.
Types of industrial crops
Industrial culture is a raw material for industry. For convenience, these crops were classified according to the principle of obtaining finished raw materials from them.
- Starchy crops. They are grown, as the name implies, for the sake of obtaining starch from them. It is usually found in tubers. Examples are potatoes, yams, or sweet potatoes.
- Sugar-containing crops. Plants that are grown to extract sucrose from them. The most famous representatives of such crops in our country are sugar beets and sugar cane. But there are also more rare plants, such as sugar maple, carob or chicory.
- Oilseeds. This is a large group of industrial crops. Its typical representatives: sunflower, soybeans, peanuts, oil trees, castor oil plants, rapeseed, sesame and others.
- Essential oil. Plants containing essential oils. The group is huge too. Crops such as rose or lavender are world renowned raw materials for the global perfumery and cosmetics industry.
- Fibrous, or spinning. This group also includes bast crops. These are flax, cotton, hemp, kenaf, sisal, ramie.
- Rubber plants. The most famous are hevea and guayula.
- Toning. This group includes all plants from which tea, coffee, coca-cola, cocoa, tobacco are produced.
- Cork or cork-bearing. This includes cork oak and Amur velvet.
- Other groups: dyeing (sophora, saffron, indigo), tanning (badan, oak, spruce), gutta-percha (euonymus, payena), medicinal crops.
Cultivation of industrial crops
Industrial crops occupy a large cultivated area in all countries. Before growing one or another of them, they take into account not only climatic conditions, but also the proximity of processing plants, the market need for raw materials that are produced from a particular crop.
In Russia, industrial crops are not cultivated very actively, since the natural conditions make their cultivation labor-intensive, and large investments are required. In Ukraine, the geographical position of which is favorable for industrial crops, sugar beets, sunflowers and flax are actively cultivated.
All grain and industrial crops require the use of special harvesting machines and special tools. Usually this is also taken into account when preparing areas for certain crops.
Due to the growing interest of people in healthy, environmentally friendly lifestyles, the cultivation of many industrial crops brings additional profits to producers.
An example is the lavender plantation in French Provence. People from all over the world come to admire the flowering of this amazingly beautiful and fragrant plant.
Celebrations and festivals are arranged for them, which bring a hefty additional income.
First of all, such an industrial crop as sunflower is actively cultivated in Russia. Our country ranks second in the world for the production of sunflower seeds (Argentina is in the lead). This culture came to Russia under Peter I along with potatoes. At first, the sunflower was grown for decorative purposes, but then they were able to appreciate the enormous benefits of this plant.
Once upon a time, the British had a monopoly on sugar production, as all the sugarcane crops belonged to them. Already in the eighteenth century, other countries began to look for how to meet the needs of their market for sugar.
As a result, in 1747, the German chemist Andreas Marggraf found sugar in sugar beets. Now sugar beet is included in the main crops (industrial) in many countries, and in Russia it occupies one percent of all cultivated land.
Russia has long been famous for the production of flax. In Belarus and Russia, two-thirds of the world's flax fiber is cultivated. Russia's cool and rainy summers are ideal conditions for growing flax.
Although it is a fibrous crop, flaxseed oil has a high nutritional value and is used to make high quality paints.
Linen fabrics are very durable, beautiful, they are used not only in light, but also in the aviation and automotive industries.
Industrial crops in the world
More than 20 million tons of cotton are produced in the world every year. It is the main technical culture in the world. One-fifth of the world's total is harvested by the United States and China, ten percent are cultivated by Pakistan and India, and a lot of cotton is grown in Turkey, Uzbekistan, Egypt and Syria. From a ton of cotton, 400 kg of fiber is made, from which three thousand meters of fabric are obtained.
India, China, Bangladesh and other Asian countries are famous for growing jute, sesal, supplying the whole world with burlap, ropes and rough fabrics. In Southeast Asia, hevea grows, from which rubber products are made.
Essential oil and dyeing plants are grown in many countries. For example, almost all of the world's saffron harvest belongs to Iran. It is not only a colorant, but also one of the most expensive condiments in the world. In order to get a kilogram of saffron, you need to collect 200 thousand crocuses.
It happens that industrial crops become a symbol of the country. For example, a rose in Bulgaria. In this country, in the Kazanlak Valley, there is a world-famous rose museum. The rose oil produced by the country has brought worldwide fame to Bulgaria.
Industrial crops such as tobacco and hops are also popular in the world. Cuban and Turkish tobacco is prized by smokers all over the world, and Germany is famous for its hop cultivation.
Genetically modified crops and their capabilities
Soybeans are currently the main technical crop in the world. American scientists believe that this will be the main source of protein for humanity. The United States produces three quarters of all soybeans in the world.
Every tenth ton of all grain crops is soybeans. It is not only eaten, but also used for technical needs. Soybean oil can be used to make plastics, paints, biofuels.
Scientists are currently working on the widespread use of such a technical culture as lupine. Its possibilities are even wider than that of soybeans. This industrial culture is surprisingly multifunctional: fibers give excellent quality tissue, oil with antioxidant properties is obtained from the plant, and coffee is made from the roots. The world leader in the production of promising crops is Australia.
Gasoline from industrial crops
The earth's oil reserves are running out, and scientists around the world are working to create the optimal biofuel. The best technical culture for this purpose is being sought.
Soybeans, rapeseed and cotton are the leaders in this field, but there are also lesser-known plants.Among them are the South American jatropha, Syrian cottonwood, copaiba, which grows in the tropics of the Amazon. In China, they found the plant of the Klabra syndrome. Its juice ignites like oil.
The cultivation of industrial crops has long gone beyond traditional agriculture and is turning into a modern high-tech industry with great prospects. Whoever understands this today will gain a lot tomorrow.
The results of 2015 in the agro-industrial complex industry State statistics of Ukraine usually calculate by April 1, April Fools' Day. Anyway, in 2016 - these events coincided.
Both that, and another cause excitement interest of Ukrainians. Regarding the indicators of the profitability of the agro-industrial complex, they are indeed atypical for the last year.
The average profitability of the crop production industry was 50% in 2015 against 29.2% in 2014.
Sunflower is a constant favorite
Sunflower is traditionally the most profitable crop in crop production, the average profitability over the past 10 years is 40%. At the end of 2015, sunflower, according to UkrGosstat, reached a record high of 80.3%. In 2014, farmers earned a more modest income from sunflower - 36.5%.
Today it is already clear that farmers will be forced to reseed a part of winter crops with spring crops, compensating for the undersowing of winter crops in 10% and replacing the dead in 13-15% of the area. And here the main "reserve player" in the fields continues to be sunflower, which traditionally occupies about 15-16% of all Ukrainian agricultural lands.
The high marginality of oilseeds attracts farmers so that many would gladly replace all dead winter crops with sunflowers, but it is limited by the high demands of the crop on soil and climate, as well as the requirements of crop rotation.
Although climatic changes have already "pushed" sunflower further to the north of the country, therefore, there is a possibility that the sown area under sunflower may exceed the maximum level taken already in 2012, -5.2 million hectares.
Vegetables at the peak of popularity
Open field vegetables "pulled out" in terms of profitability in second place in 2015. In Ukraine, the profitability of the production of open field vegetables is 47.6% according to the results of 2015, which is almost three times more than the level of 2014 - 16.7%, according to the data of the State Statistics Service of Ukraine.
This was due to the ultra-high prices for vegetables, which were established at the beginning of autumn.
The high profitability of vegetable production spurred the interest of producers in this segment and gives reason to predict an increase in the production of borsch set vegetables in 2016.
According to the results of the past season, the most profitable crops were white cabbage, tomatoes, onions, and carrots. The cost of growing vegetables in 2015 was 126.5 UAH / c, which is 37.5% higher than in 2014.
New players enter the vegetable growing industry every year, many agricultural holdings begin to grow vegetables and berries along with field crops in order to diversify the risks of agricultural production.
The acreage under vegetables due to the high profitability of 2015 will show growth to the maximum level - not less than 450 thousand hectares in 2016.
And here Ukraine still has many discoveries in the context of vegetable crops.
The promotion of a healthy lifestyle calls for expanding the range of vegetables and bringing it closer to European traditions - increasing the share of green crops, especially salads and other niche vegetables.
Today there is a danger of overproduction of vegetables in 2016. With the loss of the Russian market, there is practically nowhere to export vegetables in significant volumes, and the domestic market will not consume large volumes due to the growing poverty of the population.
Rape is going out of fashion
Rape is losing popularity among agricultural producers, despite an increase in profitability from 29% in 2014 to 44% in 2015.
In Ukraine, mainly winter rape is grown, which is becoming an increasingly risky crop due to the high probability of freezing and frequent autumn droughts, when it is sometimes simply impossible to sow a crop for the winter.
The costs of growing rapeseed are high, and with increasing risks, the area under crops is in a clear downward trend. In 2015, the minimum area for the 2016 rapeseed crop was sown in Ukraine - about 650 thousand hectares. Today, the death of this winter oilseed in some regions is 20-60% of crops.
Cereals are a great four
On the 4th place in terms of profitability in crop production - cereals and legumes. This group is primarily maize, but also wheat, barley, rye and other crops. Grain profitability rose from 25.8% in 2014 to 43.2% in 2015.
Corn is one of the main contenders for replanting winter crops and the leader in terms of sown area in Ukraine, along with sunflower. The advantages of corn are its unpretentiousness to soil and climatic conditions; it can be grown in almost all regions of Ukraine. Therefore, maize has a high chance of replacing winter crops in the fields.
Farmers are constrained by the high resource intensity of crops and the fall in world prices for this grain, which has been going on for two years. Taking into account the mood of farmers, corn may occupy about 4.5 million hectares.
Perhaps this indicator will be higher if the upward price trends in favor of corn, which we observed in February-March 2016, continue in the world market.
Today farmers are very interested in sowing barley. If the area under crops has decreased over the past 5 years, then in 2016 the area under spring barley will be increased by 22% to 2.15 million hectares.
There is a demand for Ukrainian barley in the world market, which has become one of the factors in favor of increasing the area under this crop.
Farmers with limited funding find it profitable to sow barley. Such crops will be more efficient even with low yields, since they require minimal costs.
In particular, in the Kherson region it is planned to increase the crops of spring barley by 30 thousand hectares. In the Vinnitsa region, it is planned to sow about 75 thousand hectares with spring barley. In total, 904.7 thousand hectares were sown with spring barley as of April 1, that is, almost half of the planned crops.
Speaking of wheat, it should be noted that the majority of Ukrainian production belongs to winter crops, not spring crops. For the 2016 harvest, farmers were unable to sow winter crops in full. Due to the autumn drought, the sown area under winter crops decreased to the lowest values for a ten-year period - to 7.06 million hectares.
A large decline in areas under strategically important winter wheat, which sown for the next harvest amounted to 5.6 million hectares. Despite the fact that up to 60% of winter crops were at risk at the beginning of winter, today it is already clear that replanting will make up no more than 15% of the area.
According to the forecasts of the Association "Ukrainian Club of Agricultural Business" (UCAB), the harvest of winter grains (wheat, rye and barley) in Ukraine, while maintaining favorable weather conditions, will amount to 22.7 million tons.
Burnt soy
The soybean boom continues in Ukraine, although the enthusiasm of agricultural producers has diminished. According to the State Statistics Service, soybeans ranked 5th in terms of profitability in 2015 - at 38.4%, but this indicator did not increase significantly, compared to 2014 - 34.5%.
Soy is a relatively new crop for Ukraine. The technologies for growing oilseeds are not as delicately perfected as, for example, for winter wheat, which has been grown in Ukraine for centuries.
The growth of soybean acreage at the boom level indicates that a large number of new players join the cultivation of a fashionable crop every year and the first experience of growing soybeans is not always successful. Ukraine has not yet achieved high levels of soybean yield.
The drought is partly to blame for this, and farmers already understand that soybean production will not be effective in all regions. However, a decrease in the area under crops is not expected, at least 2-2.2 million hectares will be sown by farmers in Ukraine.
Sugar bewilderment
In conclusion, about a crop that was not included in the TOP-5, but showed a decent profitability of 26.9% at the end of 2015 - sugar beet. Crop areas are decreasing every year.
After the sugar scandal that erupted in the spring of 2016 due to the interventions of the Agrarian Fund and the theft of sugar on an especially large scale from the warehouses of this department, farmers are at a loss whether it is worth sowing sugar beets.
After all, after these events, when the price of sugar in Ukraine fell below the cost price, in 2016 producers do not count on good earnings on beets. However, it is impossible to drastically change sowing plans, and farmers only hope for a favorable price environment, because a sugar deficit is predicted worldwide in 2017.
Oksana Korol, an expert on agriculture, IC "Infoindustria"
See the full version of the article in the magazine "Agroindustry", which is available at the link:
Infoindustry


