Content
 From the school course, many remember well that the highest fertility rate is in the black soil, for which Russia was once famous. However, when trying to give a precise and detailed definition of the concept, difficulties may arise.
From the school course, many remember well that the highest fertility rate is in the black soil, for which Russia was once famous. However, when trying to give a precise and detailed definition of the concept, difficulties may arise.
At the same time, summer residents simply need to have an idea of what black soil is and what is its main difference from other types of soils and types of soil.
Chernozems are formed in certain soil and climatic conditions and are a living ecosystem. But today there are many companies specializing in the supply of soil to any region of Russia, which expands the possibilities of summer residents and owners of private houses to improve the soil on their land plot.
Characteristics and properties of chernozem
Chernozem is a special type of soil that forms on loess-like loams or loes under the influence of a temperate continental climate with periodic changes of positive and negative temperatures and moisture levels with the participation of living microorganisms and invertebrates. As can be seen from the definition, chernozem cannot be produced in artificial conditions or obtained by applying various types of fertilizers.

The main characteristic of the soil is the percentage of humus. Chernozem has a record high humus content (organic matter formed in the course of complex biochemical reactions and is the most accessible form for plant nutrition). In the chernozems of our ancestors, its level was 15% or more, but today it is considered to be a maximum of 14%. The fact is that during intensive farming, humus does not have time to recover and the soil is depleted.
Do not assume that black soil is just fertile soil. In fact, its concept is much broader. It cannot be compared with organic fertilizers such as manure or humus, since the concentration of nutrients in them is so high that excessive application of them can adversely affect plant growth. In black soil, all substances are balanced and are in an easily accessible form.
The next distinguishing feature of chernozem is its high calcium content, the need for which in cultivated plants is the highest at all stages of growth.
Chernozem is characterized by a neutral or close to neutral reaction of the soil solution, which makes it versatile for growing crops.
Chernozem has a granular-lumpy structure, which is resistant to leaching, crusting, weathering and compaction. Thanks to this structure, optimal water-air exchange with the atmosphere is ensured and favorable conditions for root growth are created. However, according to experts, chernozem is not loose enough and requires the addition of sand or peat.
Subtypes of chernozem
In different climatic zones (Central Chernozem, Volga, Northern Caucasus and Western Siberia), chernozem is formed with some peculiarities. In total, 5 subtypes are distinguished: podzolized (deciduous forests), leached (forest-steppe zone), typical (meadows and forest-steppe), ordinary (steppes) and southern (steppes of the southern regions). The southern chernozem has the highest humus content.
How to recognize black soil?
Chernozem differs significantly from humus and manure.Manure is a waste product of livestock and poultry farming and is a partially digested plant fiber with a high organic matter content. Manure that has rotted over several years under the influence of microorganisms and invertebrates (worms and insects) turns into humus, containing nutrients in a form more accessible to plants. Both manure and humus contain a very large amount of nitrogen and its compounds.
Peat is very close to chernozem in origin, which is also formed as a result of long-term decomposition of plant residues, but in other climatic conditions.
You can give some tips on how to distinguish black soil from other soils:
- has a rich black color;
- due to the high content of humus, leaves a greasy mark on the palm after compression;
- when wet, it resembles clay in consistency and does not dry out for a long time, retaining moisture (unlike peat);
- has a coarse-grained structure.
It is rather difficult to acquire real chernozem with a quality certificate in the Moscow region, since its extraction is limited and there is a high probability of buying just dark soil. At best, you will be lucky to get a mixture of black soil with low-lying peat, which, with the right proportion, can even be a plus.
The use of black soil at their summer cottage
The desire of summer residents to increase the fertility of the soil on their site to obtain high yields of high quality fruits explains their willingness to use all available means. To achieve a high effect and keep it for several years, you need to know how to use black soil in the garden without harming the already established ecosystem.

The main delusion of gardeners is that by completely replacing the soil with chernozem, it is possible to solve the problem of plant nutrition for all time without the subsequent introduction of fertilizers and the use of humus or compost. The nutrients in black soil are actively used by plants for the formation of crops and seeds, therefore, without their replenishment, the humus content drops sharply and the soil is depleted.
Excessive introduction of chernozem for vegetable and flower crops will be a gross mistake, since their thin root system is not able to maintain the required porosity, which will eventually lead to soil compaction. It is recommended to add black soil mixed with garden soil and peat. A good result is obtained by its introduction into greenhouses, hotbeds and flower beds for perennial ornamental plants. For these purposes, it is very convenient to use black soil in bags.
Areas where chernozem was introduced should be dug up only with a pitchfork to prevent soil compaction. Earthworms are a good biological indicator of soil conditions.
Before applying, it is advisable to check the acidity level of chernozem using indicator strips. With a weakly acidic reaction, you will need to add lime, dolomite flour or wood ash, and with a slightly alkaline reaction, acidic mineral fertilizers.
How much does black soil cost?
In organizations specializing in the sale of fertile soil, you can buy black soil with delivery to any settlement in the Moscow region.

At the same time, the average price of 1 m3 of chernozem with delivery is 1300 rubles. when ordering a car for 20 m3. When ordering a dump truck for 10 m3, the price increases to about 1650 rubles. To calculate how much a car of chernozem costs, let's take a volume of 10 m3 as the initial data. The result is a quite acceptable amount of 16,500 rubles. The larger the volume, the lower the price per m3.
However, for summer cottages, there may not be a need for such volumes. In such cases, you can purchase prepackaged black soil in bags of 40 or 50 liters. The cost of one bag ranges from 180 to 300 rubles. Bulk discounts apply for more than 50 bags from most suppliers.
When planning delivery and unloading operations, the weight of chernozem must be taken into account.Depending on the structure and composition, 1 m3 of chernozem weighs from 1 to 1.3 tons.
Chernozem is rightfully considered the most fertile type of soil. It is formed naturally in certain climatic conditions. This is a land saturated with humus (a rotting product of plant residues). It has a grainy-lumpy type of structure and a black color.
Due to its qualities, black soil is highly valued by farmers, farmers and gardeners. It is perfect for growing fruit crops, cereals, flowers. Trees and bushes grow well on it. In Russia, most of the chernozem soil species is found in Western Siberia, the North Caucasus, and the Volga region.
How is black soil formed?
Why of all types of soil the most fertile are chernozems? The secret of their superiority lies in the peculiarities of soil formation. There are three main factors influencing the maturation of "black gold":
- climatic;
- biological;
- geological.

Chernozems have the highest fertility rates
Russian chernozem is formed in steppe and forest-steppe climatic zones. In addition to the climate, vegetation plays an important role in the formation of this type of soil. In the process of its decay, humus is formed - humus - which is considered the main criterion of fertility.
Another important factor in the formation of chernozem is groundwater. From underground waters, plant roots absorb useful trace elements and minerals. Having received the necessary substances, the root system penetrates the soil, which contributes to the loosening of the earth. Loose soil facilitates the passage of air masses.
Different types of microorganisms live in the soil, which also play a positive role in the formation of "black gold": they contribute to the loosening of the earth and participate in the processing of vegetation residues. However, for planting flowers and other plants with a poorly developed root system, chernozem is a dense soil, so it must be diluted with peat.
to the menu ↑
Classification of chernozems
Depending on the conditions of formation, the type of chernozem soils can be divided into several subtypes:
- Podzolized.
- Leached.
- Typical.
- Ordinary.
- Southern.
Podzolized chernozems develop under the deciduous forests of the forest-steppe zone. Due to the humidity of the climate, such processes as leaching (dissolution and washing out of salts in the soil by water) and podzolization (removal of clay particles, aluminum and iron oxides, etc. from the upper parts of the soil, etc., which leads to a decrease in fertility) ). Podzolized soil is widely used in agriculture for the cultivation of cereals, vegetables and fruit crops.
Leached chernozems are formed under forb-cereal vegetation. In terms of its properties, this species is similar to that of podzolized chernozems, with the exception of some characteristics.
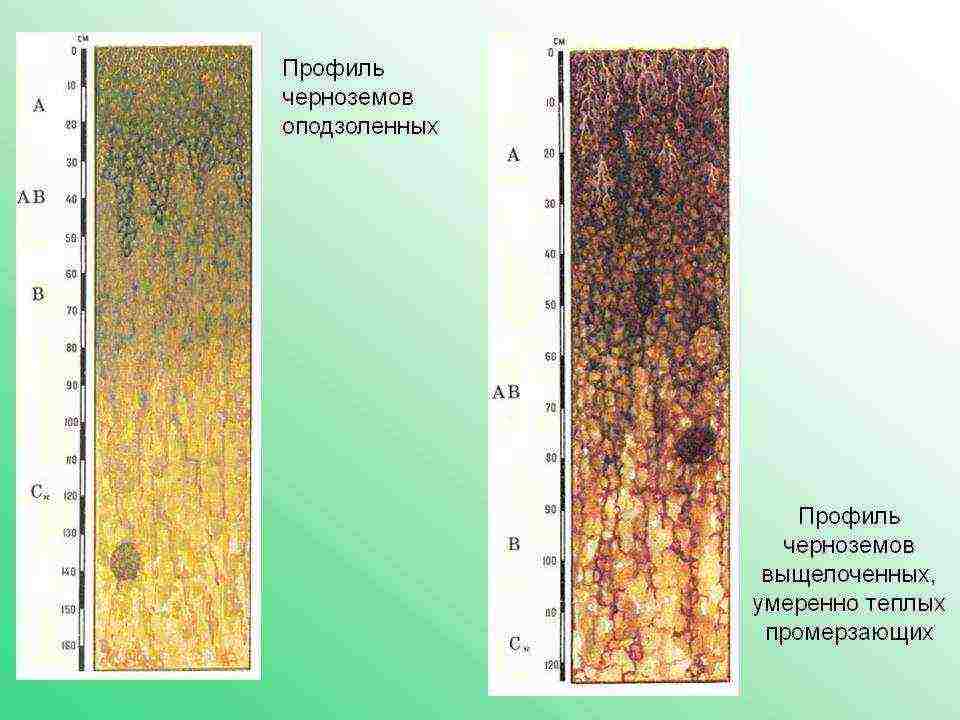
Profile of podzolized and leached chernozems
Typical chernozems have the best qualities inherent in this type of soil. They are formed under the herb-grass vegetation in the southern subzone of the forest-steppe zone. The humus content in the soil of this subtype is high and sometimes reaches 15%.
Ordinary chernozems are widespread in some parts of the steppe zone. They formed under the herb-fescue-feather grass vegetation. They have a smaller layer of humus compared to typical chernozems.
The southern subtype of chernozems was formed under fescue-feather grass vegetation in the southern part of the steppe zone. The humus content reaches 4-7%. A carbonate layer in the form of a white-eye is observed under the humus layer.
According to the thickness and humus content, 4 groups of chernozems are distinguished, the presence of which is characteristic of certain territories.
The South European group of chernozem soils is distributed in the territory of Moldova, southern Ukraine and the Ciscaucasia.They are characterized by a large thickness of the humus layer with a low humus content, abundant carbonate content in the form of cobwebs, veins, etc.
The East European group includes chernozem soils of the European territory of Russia. The colder and drier climate caused the formation of a less powerful humus horizon with a higher humus content.
The group of Western and Central Siberian chernozems is located on the territory of Western and Central Siberia, as well as Kazakhstan. This group is characterized by deep drips of humus along cracks that form in the ground due to freezing of the soil, as well as a high concentration of humus with a sharp decrease with depth.

Profiles of regional features of chernozems
The East Siberian group occupies the territory of the Trans-Baikal steppes. Due to low temperatures, the biological circulation here is at an insignificant level. This caused the formation of a small humus layer. The humus content in it is also low.
to the menu ↑
Purchase of black soil
Chernozem is the most fertile soil in the world. This is influenced by the composition of the earth and the amount of organic matter in it. However, when acquiring such a soil, one must bear in mind that in an unnatural environment for oneself, over time, it loses those qualities for which it is so valued. But if you decide to increase the level and quality of fertility, to improve the characteristics of the soil on your site - black earth soil is perfect for this purpose.
So how do you choose this item? And what should you be guided by in your choice? We advise you to pay attention to several factors.
to the menu ↑
Territory of soil formation
The composition and characteristics of chernozem depend on this factor. Therefore, before buying, you need to ask where it was brought from. The difference in the composition of the soil directly depends on the territory of its formation. Therefore, taking into account this detail will help you make a better choice.
to the menu ↑
Soil composition
Chernozem soil must be saturated with all the necessary trace elements. Of course, it is best to detect their presence using agrochemical analysis in the laboratory. But something can be learned without the help of special devices. There are some tips to help you choose the right type of soil.

Sale of black soil
Chernozem is highly saturated with potassium. Loamy and sandy soils poor in potassium, where sand is located at a depth of 20-30 cm under the black earth. Therefore, if you notice the presence of sand in the soil, then this soil will be of low quality.
You can shake the ground a little. It should be dry from above, but at a depth of about 20 cm. It will be moist and crumbly. This is a good sign. You can also wet a lump of soil and make a circle out of it. If it crumbles, this indicates a low humus content.
to the menu ↑
How to identify black soil (video)
to the menu ↑
How much does black soil weigh?
Before buying, you should find out how many kilograms weighs 1 cube of chernozem soil. The question is quite difficult, since the weight depends on its condition and humidity. On average, the weight of 1 cubic meter of chernozem ranges from 1000 to 1200 kg.
to the menu ↑
Price
Of course, a very important question is how much Russian black soil costs. When buying soil, you should pay attention to what factors affect its value. This can include the place of formation of soil, as well as the location of the customer.
In addition, the price will depend on the supplier. For example, the price of such soil per cubic meter in Moscow and the Moscow region can be in the range of 1110-1500 rubles per cubic meter. The price per cubic meter depends on the set of soil qualities. If you want to buy black soil in bags, its cost will be from 350 rubles per bag. Bagged black soil is very convenient for transportation and storage.
For more information, you'd better contact qualified professionals.In Russia, many companies are engaged in the delivery of this type of soil. Therefore, it will not be difficult for you to find a supplier on the most favorable terms for you.
Current version of the page so far
not checked
experienced participants and may differ significantly from
versions
Retrieved January 15, 2018; checks require
2 edits
.
Current version of the page so far
not checked
experienced participants and may differ significantly from
versions
Retrieved January 15, 2018; checks require
2 edits
.

Chernozem (from Russian black earth) is a humus-rich, dark-colored soil type formed on loess-like loams or clays in a subboreal and temperate continental climate with periodically flushed or non-flushed water regime under perennial herbaceous vegetation.
Conditions of soil formation
The climatic zone is temperate, the sector is moderately continental, characterized by an alternation of humidification and desiccation, as well as the predominance of positive temperatures. Average annual temperature - + 3 ... + 7 ° C; the annual amount of precipitation is 300-600 mm.
The relief is undulating-flat (periodically cut by depressions, gullies, ravines, river terraces).
The vegetation is perennial herbaceous meadow-steppe and steppe subzones, which annually leave a significant amount of plant residues in the soil. Under appropriate hydrothermal conditions, they decompose with the formation of humic compounds (humification), accumulated in the upper layers of the soil. Together with humus, plant nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, iron, etc., are fixed in the soil in the form of complex organo-mineral compounds.
Parent rocks are loesses and loesslike loams.
Soil profile structure
- A - humus-accumulative horizon
- B - transitional horizon
- C - mother breed
- D - bedrock
Properties
Chernozems have good water-air properties, are characterized by a lumpy or granular structure, content in the soil absorbing complex from 70 to 90% of calcium, neutral or almost neutral reaction, increased natural fertility, intense humification and high, about 15%, content in the upper layers of humus ...
Views
Divided into 2 gradations:
By the thickness of the humus layer (A + AB)
- a) heavy duty (more than 120 cm thick)
- b) powerful (120-80 cm)
- c) medium-sized (80-40 cm)
- d) low-power (less than 40 cm)
By humus content% in Ap
- a) obese (> 9%) (black color)
- b) medium humus (9-6%) (black)
- c) low-humus (6-4%) (dark gray)
- d) slightly humus (
The soil is the most superficial, loose, often thin layer of the earth's crust, covered with vegetation and fertile, that is, capable of producing a crop of plants.
The soil arose as a result of changes in rocks under the influence of various organisms in different climates and landforms. Soils are as varied as the natural conditions of the land. Soils were formed with the emergence, development and activity of living organisms. It took many millions of years for microorganisms to develop from the first tiny living things, and then higher plants and animals. The process of soil formation intensified with the emergence and development of higher green plants, which annually shed a huge mass of dying parts - leaves, shoots, roots. many animals also take part - rodents, earthworms, various insects. Having formed under the influence of living beings, the soil itself has become the most important source of life. The main property of the soil is fertility, that is, the ability to produce crops. This distinguishes soil from rock, barren stone. Fertile soil contains sufficient supply of food and moisture for plant development. Air circulates freely in it, which is necessary for the life of soil bacteria and respiration of the root system of plants.The most fertile soils are chernozems, which are formed under optimal conditions for humus accumulation. It is in these soils that the reserves of humus in the meter-deep soil layer are especially large. The natural productivity of soils is closely related to humus reserves, which can be expressed by the value of the annual increase in biomass per unit area. Under the influence of long-term tillage, the reserves of nutrients are gradually lost, and their structure is destroyed. In an effort to raise the productivity of agriculture, a person invests some work in cultivating the soil, applies fertilizers to it, uses special agrotechnical methods, with the help of which he seeks to change many important properties of soils in the direction he needs. Thanks to this, many cultivated soils have become more fertile than their virgin counterparts. Natural resources for expanding arable land in Russia are almost exhausted, so it is necessary to increase effective soil fertility. To preserve soil fertility, a grass-field system has been created, where sowing of perennial grasses is introduced into crop rotation, which create a lumpy structure. soil and enrich it with organic substances. For example, perennial grasses - timothy, fescue - dismember the soil into lumps with their roots and help improve its structure. Perennial legumes - clover, alfalfa - contribute to the accumulation of nitrogen and calcium in the soil (such plants are called siderates). Herbs improve the soil and restore its fertility. Crops sown after perennial grasses produce high yields. In addition, perennial grasses are used to feed livestock. The founder of soil science V.V. Dokuchaev discovered geographical patterns in the distribution of soils on the globe. On the plains, the soils are located, depending on the climate and vegetation, in wide stripes - zones. The boundaries of these bands coincide with vegetation zones. In mountainous regions, such a change in soil types depends on the height of the mountains and is subject to vertical zoning. The formation of soil varieties is influenced by many conditions: the parent rock (rock) on which the soil is formed, the terrain, the degree of moisture, the nature of vegetation, the microclimate, and much more. Classification of soils in Russia1. Arctic soils are formed on the low plateaus and low shores of the Arctic islands, in areas without ice. They are very young, poorly developed, and fragmented. Large areas are devoid of even primitive soils. The upper horizons contain a lot of mobile iron. Soil 2. To the south of the arctic soils are replaced by tundra soils. The most common here is the tundra-gley type of soil formation, which manifests itself on clay and loamy rocks under closed vegetation. Typical tundra soils are characterized by a bright manifestation of the gley process and slow decomposition of plant litter with the formation of coarse humus. The arct-tundra humus gley soils that form to the north are usually minimally waterlogged and gleyed. Tundra soils are thin, have a low humus content and high acidity. 3. Podzolic soils are the most widespread type of soil in Russia. They are formed under coniferous and mixed forests in conditions of excess moisture, which provides a leaching regime for soils during a significant part of the growing season. There is an intensive removal of chemical elements from the upper horizons of the soil. Easily soluble compounds are carried outside the soil profile. The podzolic soils and podzols that arise under these conditions are most characteristic of the middle taiga. They are characterized by a small amount of humus and an acidic reaction of the soil solution. With temporary excess surface moisture, the process of podzol formation is complicated by the gley process.Under such conditions, gley-podzolic soils are formed, which are most characteristic of the northern taiga with its more severe climate. In the southern taiga and mixed forests, the litter of grasses growing under the forest canopy plays an increasingly important role; sod-podzolic soils are widespread. When they are formed, a soddy process (humus accumulation) is superimposed on the podzolic process. The reserves of humus and the thickness of the humus horizon increase. In the taiga, podzolic-boggy soils are widespread, associated with a change in the leaching regime to stagnant and vice versa, which causes a constant combination of podzolic and bog processes. Under conditions of constant excessive moisture, bog soils are formed: peat and peat-gley (peat-bog) soils, which are widespread in forest zones. 4. In the areas where permafrost is spread, peculiar taiga-permafrost soils develop under forests. The peculiarities of soil formation here are associated with low temperatures, which is due to the slowdown in the processes of chemical weathering and decomposition of organic matter. Therefore, poorly decomposed organic matter, coarse humus, accumulates in the upper soil horizon. Permafrost serves as an aquiclude, therefore, when it is shallow, there is no through washing of the soil layer. During periods of snow melting and precipitation, the soil is washed out, but the removed compounds accumulate in the suprapermafrost layer, and in rainless periods they, together with soil moisture, are pulled to the surface, therefore there is no leaching horizon (podzolic). it is known that water expands when freezing). For these reasons, the taiga-permafrost soils are characterized by an undifferentiated soil profile. Melting of permafrost causes more or less prolonged waterlogging of the soil profile or its lower part, which is associated with the presence of gleying signs in taiga-permafrost soils. 5. Under the deciduous and coniferous-deciduous forests of the southern Far East, in the southern part of the Kaliningrad region, in the Caucasus, brown forest soils appear; they are formed under the conditions of a leaching water regime, warm and humid summers. Clay is a characteristic feature of the formation of brown forest soils. On rocks with a heavy texture, these soils are highly waterlogged, therefore, surface gleying phenomena are often observed in them. 6. In the mountains of the south of the Far East, Southern Siberia and the Urals, under the southern taiga forests with deciduous trees and grass cover, brown taiga soils are widespread, transitional between sod-podzolic and brown forest soils. 7. In the forest-steppe zone, where the moisture balance is close to neutral, gray forest soils are widespread, the formation of which is associated with broad-leaved, and in the Asian part - with small-leaved forests. From soddy-podzolic soils, gray forest soils are distinguished by a large amount of humus and its more uniform distribution along the profile. showing signs of podzolization. They are transitional between sod-podzolic soils and chernozems. 8. Chernozems dominate under the steppe vegetation in the forest-steppe zone and in the steppes. They stretch in a continuous strip from the western borders of the country to the foothills of Altai (to the east they are found only in separate massifs). In the formation of chernozems, the sod process plays a leading role. The water regime of chernozem soils is non-washable, and the rich steppe vegetation annually supplies the soil with a large amount of organic matter; therefore, chernozems are distinguished by a high humus content. The profile of chernozems is characterized by a well-developed dark humus layer of lumpy-granular structure and the presence of a carbonate horizon. 9. Chestnut soils are widespread in dry steppes and semi-deserts.They occupy small areas in Russia and are distributed in the southeast of the East European Plain, in the Middle and Eastern Ciscaucasia, on the Kulunda Plain and in some intermontane basins of South Siberia. Chestnut soils are formed under conditions of moisture deficit and rarefied cereal and wormwood-cereal herbage. Therefore, chestnut soils contain much less humus than chernozems and are less thick. Chestnut soils are divided into three subtypes: dark chestnut, chestnut and light chestnut. Among chestnut soils, solonetzes are widespread, less often - salt marshes. Soils of mountains. In terms of their genetic properties, mountain soils correspond to soil types of plains. However, all mountain soils have some common features that distinguish them from the corresponding types of plains: they are all shallow, rocky, rich in primary, weakly weathered minerals. Only the soils of subalpine and alpine meadows have no analogues on the plains. The higher the height of the mountains, the better it is. However, the latitudinal position of the mountains also affects the diversity of soils. The further north the mountains are located, the more uniform the soil cover within them, since the set of soil belts begins with the zonal type of soil that is developed on the plains at the foot of the mountains. Therefore, no matter how high the mountains of the North-East are, you will not find anything other than mountain taiga-permafrost and mountain-tundra soils within them. The further south the mountains are located and the higher they are, the more complete and varied the set of soils on their slopes. The most diverse are the mountainous soils of the Caucasus - the highest and southernmost mountain system in Russia.


