Content
- 1 Plant, growing conditions, distribution areas
- 2 Flax fiber production and processing
- 3 How linen fiber fabric is made
- 4 Types of fabrics
- 5 Properties of linen fiber fabrics
- 6 A fly in the ointment
- 7 What is linen fabric made of
- 8 Flax fiber properties
- 9 Varieties of linen fabrics and their properties
- 10 Weave classification
- 11 How to care for linen products
 The first mention of linen and its use can be dated back to several millennia. Some historians estimate its age as 5000 years. Its earliest application is Ancient Egypt. It was an expensive material, so only wealthy families, the pharaoh's family and courtiers could afford clothes and textiles. Also, the mummies of the pharaohs were wrapped in linen.
The first mention of linen and its use can be dated back to several millennia. Some historians estimate its age as 5000 years. Its earliest application is Ancient Egypt. It was an expensive material, so only wealthy families, the pharaoh's family and courtiers could afford clothes and textiles. Also, the mummies of the pharaohs were wrapped in linen.
Among the Slavic peoples, linen fabric became famous somewhere in the 9th century. Thanks to the properties of the fibers of the plant, textiles and clothing were simultaneously thin and durable, allowing the product to be used for a long time. Unlike other countries, linen was not a luxury. Clothes could be seen among representatives of various social classes. The difference was in the thickness of the fibers, the finish, and the presence of fabric dye.
Since the moment when Empress Catherine II allowed the export of linen threads outside the state, most of the weaving factories in Europe worked precisely on fibers grown in the Russian Empire.
Plant, growing conditions, distribution areas
Cultural flax, which is used for a variety of industrial purposes, comes in a variety of forms. Most of the crop is grown for seed, fiber, or oil. It is fiber flax that is used for the production of fabrics. The stems from which the fibers are obtained can be different, the quality of the resulting threads depends on them.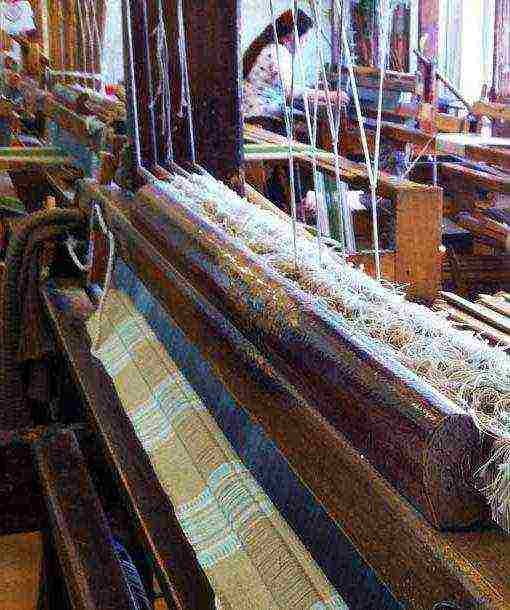
Flax is capricious to grow. It is best to grow the plant in regions with a temperate climate and non-black soil. The culture is very demanding on the composition of the soil, mineral fertilizers in it and the weather - precipitation during the ripening period can destroy the entire crop. At the same time, seedlings appear in early spring, at a temperature of + 4-5 degrees, and can withstand frosts down to -4 degrees. From the moment the first shoots appear until the harvest of flax, it takes from 68 to 84 days. In Russia, the culture is grown in various areas, on areas that are estimated at thousands of hectares. But very little land is given for the cultivation of the variety, which provides the best raw material for the production of fine fabrics. Therefore, the products are quite expensive.
Flax fiber production and processing
To obtain the highest quality and finest fibers, there is a certain harvest time, since the thinner the raw material obtained, the better the linen. The stems of the plant should be light yellow, the seed pods should be green. The flax is collected together with the roots and soaked so that the necessary fibers are detached from the rest of the tissues without hindrance. Then it is dried and sent to production.
Further processing does not differ much from that which was used in antiquity. Flax is crumpled, pulled and combed. Only in modern factories such operations are performed by machines.
How linen fiber fabric is made
The production of linen fabrics is quite expensive for several reasons. First of all, it is the complexity of processing the plant. In addition, fiber flax comes in different varieties, and the quality of the fabric and the complexity of production directly depend on this. Linen fabric can be thin or thick, coarse or smooth, depending on the length of the plant fibers obtained.
After the harvest is harvested, the raw materials go to the flax processing plants. Long and short fibers are obtained after processing on a scutching machine, which, although considered waste, is used for the production of a product such as coarse linen.
The resulting yarns are checked according to their technical characteristics with GOSTs and are distributed for further processing. Long fibers are used to make fabrics in the textile industry. From the fleece, the foundations for finishing materials and floor coverings are excellent. Waste fibers that do not meet any of the standards are used in construction in the form of tow.
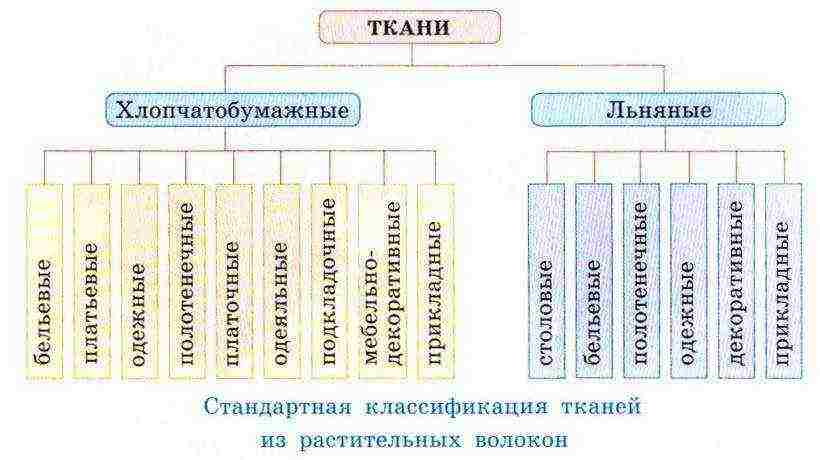
Types of fabrics
Linen fabric is subdivided into technical and household. However, the former are produced in greater quantities than the latter, since cheaper substitutes from chemical fibers or nonwovens have been found. They can be pure linseed or mixed in content. For this, cotton, viscose, lavsan are added to them.
Depending on the purpose, linen fabric is subdivided into toweling, dining room, canvas, dress and dressing, sideboard, canvas, bedding and linen. For sewing clothes, such as cambric, edging, matting, kolomenok, fine linen are used. Painting canvases are made from raznduk and canvas. Teak and Damascus are used for upholstery. Overalls, footwear, tourist accessories are made of canvas.
Properties of linen fiber fabrics
Despite the variety of fabrics and materials from which they are made, linen remains in demand. This is due to its characteristics and qualities. First of all, it is worth noting the high hygroscopicity of the fabric: it perfectly absorbs moisture. By using linen clothing, you can avoid heatstroke, or, more simply, overheating. The fabric perfectly cools in the heat and warms in the cold. In addition, it does not accumulate static electricity, which has a positive effect on overall well-being.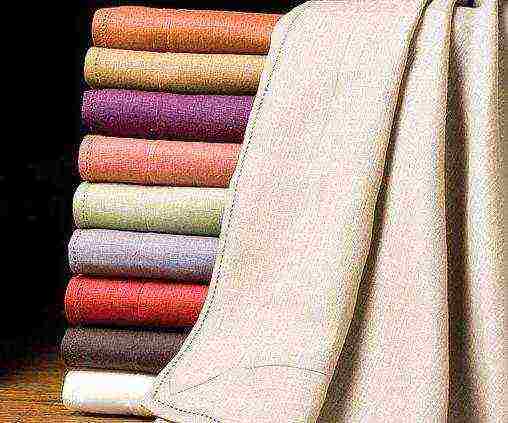
All the properties of linen fabric can be enumerated for a long time, which is its ability to inhibit pathogens. It acts as an antiseptic, therefore it is not only environmentally friendly, but also very hygienic. In addition, linen fabric does not cause allergies, which allows its use for children's textiles, medicine and in those places where an increased level of sterility is required.
All things that use the fibers of this plant have a long service life, are easy to care for and wear well. Linen clothes do not turn yellow, and over time they only bleach.
A fly in the ointment
The biggest disadvantage of linen is that it is very difficult to iron it after washing. However, the process can be simplified by ironing slightly damp items or using a steam iron. It is better to store clothes made of such material on a hanger in a wardrobe, and not in a closet on a shelf. Then things will last longer.
Spinning production
Weaving production
Finishing production
The process of growing flax and obtaining flax fiber is quite laborious. After ripening, the flax is “pulled” and spread on the field in the form of a ribbon so that fungi begin to develop on the flax under the influence of natural moisture (dew, rain), which destroy the pectin substances that connect the fiber with the wood of the stem. As a result, a "trust" is obtained from the flax straw, in which the separation of the fiber from the stem is facilitated. Then, the thus obtained flax raw material ("trust") is supplied for further processing at flax factories.
The primary processing of flax takes place at the flax mill. On crumpled-scutching aggregates, in the process of crumpling and scutching, the fibers take the form of long strands, the length of which is approximately equal to the length of the stem. At the same time, part of the fibers breaks off or breaks off and ends up in the scutching waste.
The destroyed wood of the stem (fire) also falls into the scuttling waste.Meanwhile, all the elementary fibers contained in the stem are approximately the same in their morphological, physical and chemical properties. Fiber separation and various processing are the result of the adopted technology.
According to modern technology, a long scutched fiber of various quality is obtained from a flax stalk and processed scattering waste - a short fiber.
Long flax fiber is divided into numbers 8-14 according to GOST 10330-76 ("Scutched flax"), short - into numbers 2-6 according to GOST 9394-76 ("Short flax fiber"). Scattering waste that does not comply with GOST for short flax fiber is used in construction and is usually called "tow".
For further processing, flax fiber is usually sent to flax mills, where long scuttled fiber is subjected to carding, after which it is divided into combed and combed. After that, all types of fibers are processed using various technologies, wet and dry spinning methods and used for the manufacture of various fabrics.
From combed long flax fiber, fine high-quality yarn is obtained, which is used for the manufacture of various fabrics for clothes, bed linen, etc. Feathers are used for the manufacture of nonwovens (base for linoleum). Coarser yarn is obtained from short flax fiber by dry spinning - for twines, ropes, burlap, etc.
The production is carried out thanks to specially designed spinning machines and technology for the production and preparation of fibers for the spinning process.
The flax collected from the fields can be soaked, and thanks to rework, the time required for soaking has been significantly reduced to eight days. From time to time, the soaking stems are immersed in constantly fresh water, and this made it possible to increase the speed of soaking. After that, the stems are dried and buried in round comas for ease of movement. Comas are delivered to the fluttering workshop. With the help of a drum, special equipment for scutching, the round ball is loaded into the area where the fibers, which are so necessary for the production of linen fabric and threads, are extracted from the stems. Each of the flax stalks is straightened and separated from the original coma. Further, the rotating rollers allow the separated stems to move to the scutching stage. Gradually, the stalks gather in bunches and fall under the rotating blades. It is the blades that make it possible to separate the unnecessary part of the stem from the fibers necessary for production.
Flax production technology provides for the further production process in the spinning shop on special machines. First, the fibers go through a carding stage. For this, a special machine is provided. After the fibers have been converted to a suitable state, they go to the spinning machine. There it turns out a thread. This is what the fabrics will be made of. Linen thread is often used in various fabrics. Due to the fact that linen thread is used in different ways, the resulting fabrics can consist only of linen threads, and can consist of threads obtained from various plants. And even chemically synthesized. Depending on the needs of the market, or concluded contracts for the supply of fabrics, fabrics can be obtained according to the required characteristics, using threads of various origins, not just linen.

FABRIC STRUCTURE
The basis of all any fabric is made up of threads, which are made from various kinds of fibers. The fibers used in the production of tissues differ in composition, structure and properties. The main features of the classification of textile fibers are: the region of origin of the fibers and the chemical composition. All the basic properties of not only the fibers themselves, but the fabric woven from these fibers depend on these features. Fabric fibers are divided into two main groups:
1. Natural - fibers of natural origin. 2.Chemical - fibers of artificial or synthetic origin.
NATURAL FIBERS
The group of natural fibers includes fibers of plant, animal or mineral origin. There are four types of natural fibers:
-
Flax is a fiber of plant origin.
-
Cotton is a fiber of plant origin.
-
Silk is a fiber of animal (protein) origin.
-
Wool is a fiber of animal (protein) origin.
|
|
Cotton (cotton fiber)
Cotton is a natural fiber of plant origin, which is made from the fibers of the seeds of cotton plants. Cotton fiber is a thin-walled tube with a channel inside, which is slightly twisted around its axis. The cross-section of the fiber has a very varied shape and depends on its maturity.
Ripening, cotton bolls open, and seeds appear on the surface, covered with these very fibers, which are called raw cotton. 

Raw cotton is the main raw material of the textile industry. It is harvested and sent to ginneries. There, the primary processing of raw cotton is carried out: it is cleaned of impurities (from particles of stems, bolls and other debris), fibers are separated from seeds (this process is called ginning), cotton fibers are pressed into bales and packed. Thus, we get a finished product called cotton. In bales, cotton goes for further processing at cotton spinning factories, where cotton yarn and fabrics are made.The cotton group is represented by the following types of fabrics: satin, cambric, gauze, chintz, denim, flannel, rosin, teak, coarse calico, marquise, percale, nansuk, organdy, pique, poplin, veil, etc. - all of these fabrics are made on the basis of cotton. Sometimes viscose is added to fabrics, and then a pleasant shine or pattern appears on their matte surface.



Linen fabrics are a natural material made from the bast of flax - the structural layer of the supporting and protective parts of the plant. Twines, ropes, and canvas are made from the bast fibers of other plants.
Linen flaps were found during excavations of archaeological layers, the age of which is estimated at several millennia. In ancient times in Russia, linen was called silk.
What is linen fabric made of
For textile purposes, certain varieties of flax are grown - fiber, curly. In the first stages, the harvested plant undergoes:
- soak,
- drying,
- creasing,
- fluttering.
 This is how flax grows
This is how flax grows
After the primary processing of the plant material, the resulting raw flax is sent to the spinning mill in compressed bales.
For the manufacture of textiles, long fibers, short tows, and strips are used. Towers and strips are used to make technical products.
Long flax fiber has a polygonal cross-section with a space in the middle. The outer surface is smooth.
Flax fibers contain 80% cellulose, small amounts of other polysaccharides: pectosans, pectin substances. In addition, linseed raw materials contain representatives of simple lipids, lignins, and some proteins.
Flax fiber properties
- Good mechanical properties are manifested in high strength, abrasion resistance. When wet, the strength additionally increases by 10-20%, depending on the type of raw material. The elasticity and elongation properties of linen fibers are low.
- Physical properties are characterized by high hygroscopicity (up to 12%), the ability to swell (the volume can increase by 45%), heat resistance (withstand temperatures up to 170 ° C), lightfastness (higher than that of cotton).
- Chemical resistance is recognized as high. Although this opinion is conditional. Flax withstands the action of acids. After acid treatments, the material becomes softer. Alkaline solutions cannot withstand. When heated in a solution containing alkali ions, the web loses strength.
Linen yarns are made from fibers using traditional spinning technologies. The process includes three main stages:
- preparation of the mass of fibers;
- prespinning;
- spinning.
As a result, threads are formed from which textile materials are made.
Varieties of linen fabrics and their properties
Linen fabrics are in increasing demand due to their combination of advantages.
- Flax is a material native to the Slavs. It evokes pleasant associations, looks great, does not irritate the skin, and does not cause allergic reactions.
- Linen has micropores through which air circulates well. The fabric breathes better than most other textile materials.
- Linen fabrics provide thermal comfort. In hot weather, a person in linen clothes does not overheat.
- Linen is a very durable material that is difficult to abrade.
- High wrinkling of fabric is now perceived positively by consumers, as it demonstrates the naturalness of the fabric, its high cost.
- Some rigidity of the material can also be assessed as a positive characteristic that allows designers to model products with a pronounced shape.
 Flax is native to the Slavs, it looks beautiful
Flax is native to the Slavs, it looks beautiful
There is information in the media about the bactericidal qualities of linen materials. This raises reasonable doubts. The likelihood of maintaining a sufficient concentration and activity of substances with antimicrobial action during the entire production cycle of transforming a plant into a final product is too small.There are many stages, the conditions are tough.
A close study of the issue made it possible to understand the following:
- In botanical reference books there is information about the content of mucus-forming substances in flax, which can swell in hot water, envelop the wound. We are talking about the presence of such substances in plants of a certain species, and not in tissues.
- Linen fabrics have a high sorption (absorbing) capacity.
- Absorbing secretions on damaged skin certainly has a beneficial effect. Microbes do not remain in the wound, but are absorbed by tissue that can be replaced.
- A method for producing linen wool with a high absorbing capacity has been introduced at domestic enterprises. The technology for the production of dressings from flax has been successfully tested and is being prepared for mass introduction.
- The development of methods for applying coatings with bactericidal properties to flax fibers and threads.
From this, an inappropriate conclusion was made about the bactericidal qualities of linen fabrics.
This material has many true advantages, proven by many years of practice.
Weave classification
- Of all types of simple weaves, linen is used for linen threads.
- In the assortment of linen fabrics there are products with a small-patterned type of weave (modification of the matting).
- Beautiful products are obtained from canvases made with a combined translucent weave. These can be whole products or separate fragments.
- Cloths for sewing light dresses, blouses, curtains can be made using the technique of a complex leno weave, which is called openwork.
- Fabrics for tablecloths, napkins, curtains, dresses, suits are often obtained by performing large-pattern weaving on special jacquard machines.
The above types of weaving are performed in the production of uniform linen or blended fabrics.
How to care for linen products
- Uniform products of natural color tolerate high temperatures well. They can be washed at a temperature of 90 ° C, if necessary, even boiled.
- For washing dyed fabrics, a maximum temperature of 60 ° C is recommended.
- Use whitening products carefully. Under the influence of some aggressive oxidants, flax pigments can change.
- Dry linen products should be straightened out, preventing additional creasing.
- You can iron products at high temperatures using the steaming function.
- It is better to store products in linen or paper bags. Ventilate the cabinet to prevent the absorption of odors.
With proper care, linen products do not lose their original qualities for a long time.
A film from the series "It's Interesting" about how flax is produced:
 Flax is a natural and environmentally friendly fiber that is obtained from the stem of the herb of the same name. Elementary flax fiber has a layered structure, which is the result of the gradual deposition of cellulose on the fiber walls, with a narrow channel in the middle and transverse shears along the length of the fiber. This occurs in the process of fiber formation and growth, as well as during the mechanical effects of the primary processing of flax. In cross-section, the flax fiber has a five- and hexagonal shape with rounded corners.
Flax is a natural and environmentally friendly fiber that is obtained from the stem of the herb of the same name. Elementary flax fiber has a layered structure, which is the result of the gradual deposition of cellulose on the fiber walls, with a narrow channel in the middle and transverse shears along the length of the fiber. This occurs in the process of fiber formation and growth, as well as during the mechanical effects of the primary processing of flax. In cross-section, the flax fiber has a five- and hexagonal shape with rounded corners. 
 To obtain flax fiber, flax stems are soaked in order to separate the bast bundles from each other and from adjacent stem tissues by destroying the pectin (adhesive) substances by microorganisms. The necessary microorganisms develop when the stem is wet. After that, flax is subjected to physical influences (crumpled, bent, etc.) to soften the woody part of the stem. As a result of this processing, raw flax (or crumpled flax) is obtained. Further processing consists in scutching and carding, after which technical flax fiber (or scutched flax) is obtained. Linen fabrics are hygienic, moisture and air permeable, washable, soft, have specific plasticity, expressiveness, are highly durable and do not irritate the skin. Linen fabrics also have disadvantages - due to their low elongation and low elasticity, the fibers of the fabric wrinkle and iron poorly, and also shrink strongly. Considering these disadvantages, it is necessary to carry out the flax shrinkage procedure before cutting. It is necessary to wet the flax, let it dry, then moisten it again and iron it thoroughly, after which you can start working with the fabric. In the manufacture of fabric, linen is not dyed, therefore, most often, linen products have a natural color (from gray to beige). Linen fabrics, without the addition of other fibers, always have a pleasant shine. With the addition of cotton, they become lighter and softer, the surface becomes matte. With lavsan, they shrink less, are easily washed, but they are even more difficult to iron than natural linen.
To obtain flax fiber, flax stems are soaked in order to separate the bast bundles from each other and from adjacent stem tissues by destroying the pectin (adhesive) substances by microorganisms. The necessary microorganisms develop when the stem is wet. After that, flax is subjected to physical influences (crumpled, bent, etc.) to soften the woody part of the stem. As a result of this processing, raw flax (or crumpled flax) is obtained. Further processing consists in scutching and carding, after which technical flax fiber (or scutched flax) is obtained. Linen fabrics are hygienic, moisture and air permeable, washable, soft, have specific plasticity, expressiveness, are highly durable and do not irritate the skin. Linen fabrics also have disadvantages - due to their low elongation and low elasticity, the fibers of the fabric wrinkle and iron poorly, and also shrink strongly. Considering these disadvantages, it is necessary to carry out the flax shrinkage procedure before cutting. It is necessary to wet the flax, let it dry, then moisten it again and iron it thoroughly, after which you can start working with the fabric. In the manufacture of fabric, linen is not dyed, therefore, most often, linen products have a natural color (from gray to beige). Linen fabrics, without the addition of other fibers, always have a pleasant shine. With the addition of cotton, they become lighter and softer, the surface becomes matte. With lavsan, they shrink less, are easily washed, but they are even more difficult to iron than natural linen.

