Content [show]
Current version of the page so far
not checked
experienced participants and may differ significantly from
versions
Retrieved March 10, 2018; verification requires
1 edit
.
Current version of the page so far
not checked
experienced participants and may differ significantly from
versions
Retrieved March 10, 2018; verification requires
1 edit
.
List of countries producing wheat - an informational list of states that are the world's largest wheat producers, ranked by years and quantity (metric tons).
Production
Data source: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nation, FAO.
| 1 | PRC PRC | 117,4 | 121,0 | 121,9 | 126,2 | 130,2 | 131,7 |
| 2 | India India | 86,9 | 94,9 | 93,5 | 95,9 | 86,5 | 93,5 |
| 3 | Russia, Russia | 56,2 | 37,7 | 52,1 | 59,7 | 61,8 | 73,3 |
| 4 | USA USA | 54,4 | 61,7 | 58,1 | 55,1 | 55,8 | 62,9 |
| 5 | Canada Canada | 25,3 | 27,2 | 37,5 | 29,4 | 27,6 | 30,5 |
| 6 | France France | 36,0 | 37,9 | 37,8 | 38,7 | 42,8 | 29,5 |
| 7 | Ukraine Ukraine | 22,3 | 15,7 | 22,8 | 24,1 | 26,5 | 26,1 |
| 8 | Pakistan Pakistan | 25,2 | 23,5 | 24,2 | 26,0 | 25,1 | 26,0 |
| 9 | Germany Germany | 22,8 | 22,4 | 25,0 | 27,7 | 26,5 | 24,5 |
| 10 | Australia Australia | 27,4 | 29,9 | 22,9 | 25,3 | 23,7 | 22,3 |
| 11 | Turkey Turkey | 21,8 | 20,1 | 22,1 | 19,0 | 22,6 | 20,6 |
| 12 | Argentina Argentina | 16,4 | 11,0 | 8,0 | 13,9 | 11,6 | 18,6 |
| 13 | Kazakhstan Kazakhstan | 22,7 | 13,3 | 13,9 | 13,0 | 13,7 | 15,0 |
| 14 | United Kingdom United Kingdom | 15,3 | 13,3 | 11,9 | 16,6 | 16,4 | 14,4 |
| 15 | Iran Iran | 13,5 | 13,8 | 14,0 | 13,5 | 11,5 | 11,1 |
| 16 | Poland Poland | 9,3 | 8,6 | 9,5 | 11,6 | 11,0 | 10,8 |
| 17 | Egypt egypt | 8,4 | 8,8 | 9,5 | 9,3 | 9,6 | 9,0 |
| 18 | Romania Romania | 7,1 | 5,3 | 7,3 | 7,6 | 8,0 | 8,4 |
| 19 | Italy Italy | 7,6 | 7,4 | 7,0 | 7,1 | 7,4 | 8,0 |
| 20 | Uzbekistan Uzbekistan | 6,5 | 6,5 | 6,8 | 7,0 | 7,0 | 6,9 |
| 21 | Brazil brazil | 5,7 | 4,4 | 5,7 | 6,3 | 5,5 | 6,8 |
| 22 | Spain Spain | 6,9 | 4,7 | 7,6 | 6,5 | 6,4 | 6,4 |
| 23 | Bulgaria Bulgaria | 4,5 | 4,3 | 5,1 | 5,3 | 5,0 | 5,7 |
| 24 | Czech Republic Czech Republic | 4,9 | 3,5 | 4,7 | 5,4 | 5,3 | 5,5 |
| 25 | Hungary Hungary | 4,1 | 3,8 | 5,1 | 5,3 | 5,3 | 4,8 |
| 26 | Afghanistan Afghanistan | 3,4 | 5,1 | 5,2 | 5,4 | 4,7 | 4,6 |
| 27 | Ethiopia Ethiopia | 2,9 | 2,9 | 4,0 | 4,2 | 4,7 | 4,5 |
| 28 | Denmark Denmark | 4,8 | 4,5 | 4,1 | 4,9 | 5,0 | 4,2 |
| 29 | Mexico mexico | 3,6 | 3,3 | 3,4 | 3,7 | 3,7 | 3,9 |
| 30 | Lithuania Lithuania | 1,9 | 3,0 | 2,9 | 3,2 | 4,4 | 3,8 |
Data source: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nation, FAO.
| 1 | PRC PRC | 99 636,13 | 93 873,23 | 90 290,26 | 86 488,26 | 91 952,24 | 97 445,20 | 108 466,27 | 109 298,30 | 112 463,30 | 115 115,36 | 115 180,30 |
| 2 | India India | 76 368,90 | 69 680,90 | 72 766,30 | 65 760,80 | 72 156,20 | 68 636,90 | 69 354,50 | 75 806,70 | 78 570,20 | 80 680,00 | 80 710,00 |
| 3 | USA USA | 60 757,49 | 53 001,00 | 43 705,00 | 63 813,91 | 58 737,80 | 57 280,26 | 49 489,60 | 55 822,70 | 68 026,40 | 60 365,70 | 60 102,60 |
| 4 | Russia, Russia | 34 455,49 | 46 982,12 | 50 609,10 | 34 104,29 | 45 412,71 | 47 697,52 | 44 926,88 | 49 367,97 | 63 765,14 | 61 739,80 | 41 507,60 |
| 5 | France France | 37 353,40 | 31 540,33 | 38 939,20 | 30 474,74 | 39 692,94 | 36 885,50 | 35 363,60 | 32 763,50 | 39 001,70 | 38 332,20 | 38 207,00 |
| 6 | Germany Germany | 21 621,55 | 22 837,84 | 20 817,74 | 19 259,81 | 25 427,21 | 23 692,70 | 22 427,90 | 20 828,08 | 25 988,60 | 25 192,40 | 24 106,70 |
| 7 | Pakistan Pakistan | 21 078,60 | 19 023,70 | 18 226,50 | 19 183,30 | 19 499,80 | 21 612,30 | 21 276,80 | 23 294,70 | 20 958,80 | 24 033,00 | 23 310,80 |
| 8 | Canada Canada | 26 535,50 | 20 630,20 | 15 961,30 | 23 048,60 | 24 795,50 | 25 748,10 | 25 265,40 | 20 054,00 | 28 611,10 | 26 847,60 | 23 166,80 |
| 9 | Australia Australia | 22 108,00 | 24 299,00 | 10 132,00 | 26 132,00 | 21 905,11 | 25 173,00 | 10 822,00 | 13 039,00 | 21 397,00 | 21 656,00 | 22 138,00 |
| 10 | Turkey Turkey | 21 008,60 | 19 007,00 | 19 508,00 | 19 008,20 | 21 000,00 | 21 500,00 | 20 010,00 | 17 234,00 | 17 782,00 | 20 600,00 | 19 660,00 |
| 11 | Ukraine Ukraine | 10 197,00 | 21 348,00 | 20 556,00 | 3 599,30 | 17 520,20 | 18 699,20 | 13 947,30 | 13 937,70 | 25 885,40 | 20 886,40 | 16 851,30 |
| 12 | Iran Iran | 8 087,76 | 9 458,62 | 12 450,00 | 13 439,57 | 14 568,48 | 14 307,97 | 14 663,75 | 15 000,00 | 10 000,00 | 13 484,50 | 15 028,80 |
| 13 | Argentina Argentina | 16 146,62 | 15 427,82 | 12 399,04 | 14 710,18 | 16 139,17 | 12 721,98 | 14 662,95 | 16 486,53 | 8 427,65 | 8 851,18 | 14 914,50 |
| 14 | United Kingdom United Kingdom | 16 704,00 | 11 580,00 | 15 973,00 | 14 288,00 | 15 473,00 | 14 863,00 | 14 747,00 | 13 221,00 | 17 227,00 | 14 076,00 | 14 878,00 |
| 15 | Kazakhstan Kazakhstan | 9 073,50 | 12 706,80 | 12 699,98 | 11 537,40 | 9 936,93 | 11 198,40 | 13 460,50 | 16 466,87 | 12 538,20 | 17 052,00 | 9 638,40 |
| 16 | Poland Poland | 8 502,87 | 9 283,04 | 9 304,00 | 7 858,16 | 9 892,48 | 8 771,43 | 7 059,67 | 8 317,27 | 9 274,92 | 9 789,59 | 9 487,80 |
| 17 | Egypt egypt | 6 564,05 | 6 254,58 | 6 624,87 | 6 844,69 | 7 177,86 | 8 140,96 | 8 274,23 | 7 379,00 | 7 977,05 | 8 523,00 | 7 177,40 |
| 18 | Italy Italy | 7 463,97 | 6 413,30 | 7 547,76 | 6 229,45 | 8 638,72 | 7 717,13 | 7 181,72 | 7 170,18 | 8 855,44 | 6 341,00 | 6 900,00 |
| 19 | Uzbekistan Uzbekistan | 3 532,00 | 3 689,80 | 4 967,40 | 5 436,80 | 5 377,51 | 6 057,20 | 6 099,30 | 6 197,40 | 6 146,50 | 6 637,70 | 6 730,40 |
| 20 | Brazil brazil | 1 661,53 | 3 364,95 | 3 105,66 | 6 153,50 | 5 818,85 | 4 658,79 | 2 484,85 | 4 114,06 | 5 886,01 | 5 055,53 | 6 036,79 |
| 21 | Romania Romania | 4 456,00 | 7 764,00 | 4 421,00 | 2 479,05 | 7 812,43 | 7 340,66 | 5 526,19 | 3 044,46 | 7 180,98 | 5 202,53 | 5 811,81 |
| 22 | Spain Spain | 7 293,62 | 5 007,70 | 6 822,16 | 6 290,10 | 7 096,72 | 4 026,69 | 5 521,58 | 6 349,50 | 6 714,30 | 4 723,90 | 5 610,70 |
| 23 | Denmark Denmark | 4 693,42 | 4 663,94 | 4 056,24 | 4 701,38 | 4 758,50 | 4 887,20 | 4 801,60 | 4 519,20 | 5 018,70 | 5 940,40 | 5 059,90 |
| 24 | Morocco morocco | 1 380,70 | 3 316,38 | 3 358,68 | 5 146,84 | 5 539,84 | 3 043,08 | 6 326,76 | 1 582,63 | 3 769,45 | 6 371,43 | 4 876,14 |
| 25 | Afghanistan Afghanistan | 1 469,00 | 1 597,00 | 2 686,00 | 3 480,00 | 2 390,00 | 4 266,00 | 3 363,00 | 4 484,00 | 2 623,00 | 5 064,00 | 4 532,00 |
| 26 | Czech Republic Czech Republic | 4 084,11 | 4 476,08 | 3 866,47 | 2 637,89 | 5 042,52 | 4 145,04 | 3 506,25 | 3 938,92 | 4 631,50 | 4 358,07 | 4 161,60 |
| 27 | Bulgaria Bulgaria | 2 781,24 | 4 077,50 | 4 122,77 | 2 003,94 | 3 961,18 | 3 478,07 | 3 301,88 | 2 390,61 | 4 632,21 | 3 976,85 | 3 994,90 |
| 28 | Hungary Hungary | 3 692,47 | 5 196,76 | 3 910,24 | 2 941,25 | 6 006,82 | 5 088,22 | 4 376,24 | 3 988,18 | 5 653,70 | 4 419,16 | 3 763,68 |
| 29 | Mexico mexico | 3 493,21 | 3 275,46 | 3 236,18 | 2 715,80 | 2 321,20 | 3 015,18 | 3 378,12 | 3 515,39 | 4 019,40 | 4 116,16 | 3 676,71 |
| 30 | Syria Syria | 3 105,49 | 4 744,62 | 4 775,44 | 4 912,99 | 4 537,46 | 4 668,75 | 4 932,00 | 4 041,10 | 4 041,10 | 3 701,78 | 3 600,00 |
| — | Other | 40 502,30 | 45 311,65 | 46 908,68 | 45 458,32 | 52 154,75 | 50 139,51 | 48 148,53 | 47 458,31 | 49 881,40 | 53 823,32 | 50 577,27 |
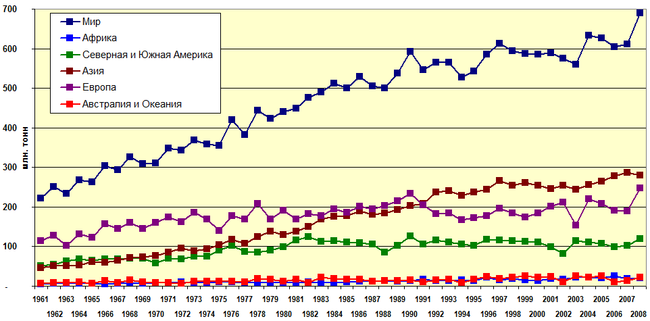
World wheat production statistics, 1961-2008 (according to FAO)
Ending stocks
Data source: United States Department of Agriculture, USDA.
Notes (edit)
 More than 85% of the world's grain never leaves the state borders
More than 85% of the world's grain never leaves the state borders
More than 1.7 billion tons of grain are grown every year all over the world. That is, there is about 250 kg per inhabitant of the earth. The most popular crops are corn and wheat.
Grain is grown in most countries of the world - where the climate permits, but more than 85% of the grain never leaves the borders of their homeland.
Only a little more than 14% of grain is exported. And of this number, 3/4 falls on only 5 countries.
250 kg of grain per person per year
In 2010/2011, the world has grown 1.75 billion tons of grain crops. These include wheat, corn, rye, oats, barley, buckwheat, sorghum, and triticale - a cross between wheat and rye.
It turns out that one inhabitant of the planet accounts for about 250 kg of grain per year.Of course, it should be borne in mind that grain is also fed to livestock, so that part of the grain ends up on our table in the form of meat, eggs and milk.
Since 2010, the world has grown less grain than consumed. For example, for 2011/12, the International Grains Council predicts that 1.808 million tons of grain will be grown in the world, and about 1,821 million tons are used for food and livestock feed.The difference can be compensated for by existing stocks - they are estimated at about 20% from world production.
Most countries grow grain exclusively for their own needs. Thus, more than 85% of the world's grain is used entirely in the country where it was grown.
Explore an interactive map of grain production. By clicking on the territory of any country, you will see how much grain it produces.
World grain production
Corn - the queen of the fields
The most farmed grain crop in the world is corn. In 2010/2011, it was grown in the amount of 820.6 million tons - 117 kg for each earthling.
The queen of the fields is used all over the world to feed livestock and only in Latin America is it more actively used for food.
The leader in corn cultivation is the United States, where slightly less than 40% of the world's corn is grown. Manufacturer # 2 - China with an indicator of 20%. In third place are the 27 EU countries with a share of about 7%. Brazil, Argentina and Mexico together grow another 12% of the world's corn.
Wheat rules
The world silver medal for the volume of cultivation belongs to wheat. In 2010/2011, it was grown in the amount of 648 million tons - 95 kg for each inhabitant of the earth.
Now the leaders in wheat cultivation are the EU countries, China, India, the USA and Russia. From time to time, Ukraine also breaks out into the leaders of wheat exporters, although last season it dropped to 6th place.
Although the main grain crop ranks second, in fact, it is wheat prices that are the benchmark for other export crops - in particular, barley.
Rice is counted separately
Despite the fact that rice is also a grain crop, international organizations account for it separately from wheat and forage crops.
In 2010, the world grew 448 million tons of rice. The main producing countries are China (137 million tons), India (89 million tons), Indonesia (37 million tons), Bangladesh (30.5 million tons) and Thailand (2 million tons)
Surprisingly, much less rice is grown in India and China than wheat.
For example, in 2010 China grew 2.3 times more wheat and India 40% more than rice.
Who sells grain to the world
Most countries grow crops for themselves, and only about 13-14% of the produced grain is exported. The annual export volume ranges from 240-250 million tons.
The 5 largest exporters - the United States, Argentina, Australia, Canada and the European Union - accounted for 75% of international grain trade in 2010/2011.
Let us remind you that Ukraine has left the list of the largest grain exporters due to export quotas. Russia also remained on the sidelines, as it completely banned grain exports from August 15, 2010.
Largest grain exporting countries of the current marketing year *
| USA | 82,7 |
| Argentina | 25,9 |
| Australia | 22,8 |
| Ukraine | 22,4 |
| Canada | 21,1 |
| EC-27 | 17,8 |
| Russia | 11,6 |
| Brazil | 9,8 |
| Kazakhstan | 7,1 |
| Turkey | 4,1 |
| India | 2,9 |
| South Africa | 2,3 |
| China | 1,2 |
| Other | 12,3 |
| General export | 242,9 |
* Forecast by the International Grains Council
World trade in rice is about 30 million tons per year. The largest exporter of rice in the world is Thailand, accounting for about 30% of world exports.
The top five exporters also include Vietnam, India, Pakistan and the United States. The United States grows about 8-9 million tons of rice annually, of which about 3-3.5 million tons are exported.
Read also how Russia and Ukraine are shaking the world grain prices, as well as why bread is so cheap in Ukraine.
Subscribe to our telegram and be aware of all the most interesting and relevant news!
Which countries grow grains the most (map)
There are about 250 kg of grain per inhabitant of the earth, although the world consumes more than it grows.

More than 1.7 billion tons of grain are grown every year all over the world. That is, there is about 250 kg per inhabitant of the earth. The most popular crops are corn and wheat.
Grain is grown in most countries of the world - where the climate allows, but more than 85% of the grain never leaves the borders of their homeland.
Only a little more than 14% of grain is exported. And of this number, 3/4 falls on only 5 countries.
250 kg of grain per person per year
In 2010/2011, the world has grown 1.75 billion tons of grain crops. These include wheat, corn, rye, oats, barley, buckwheat, sorghum, and triticale - a cross between wheat and rye.
It turns out that one inhabitant of the planet accounts for about 250 kg of grain per year. Of course, it should be borne in mind that grain is also fed to livestock, so that part of the grain ends up on our table in the form of meat, eggs and milk.
Since 2010, the world has grown less grain than consumed. For example, for 2011/12, the International Grains Council predicts that 1.808 million tons of grain will be grown in the world, and about 1,821 million tons are used for food and livestock feed.The difference can be compensated for by existing stocks - they are estimated at about 20% from world production.
Most countries grow grain exclusively for their own needs. Thus, more than 85% of the world's grain is used entirely in the country where it was grown.
Explore an interactive map of grain production. By clicking on the territory of any country, you will see how much grain it produces.
World grain production
Corn - the queen of the fields
The most farmed grain crop in the world is corn. In 2010/2011, it was grown in the amount of 820.6 million tons - 117 kg for each earthling.
The queen of the fields is used all over the world to feed livestock and only in Latin America is it more actively used for food.
The leader in corn cultivation is the United States, where slightly less than 40% of the world's corn is grown. Manufacturer # 2 - China with an indicator of 20%. In third place are the 27 EU countries with a share of about 7%. Brazil, Argentina and Mexico together grow another 12% of the world's corn.
Wheat rules
The world silver medal for the volume of cultivation belongs to wheat. In 2010/2011, it was grown in the amount of 648 million tons - 95 kg for each inhabitant of the earth.
Now the leaders in wheat cultivation are the EU countries, China, India, the USA and Russia. From time to time, Ukraine also breaks out into the leaders of wheat exporters, although last season it dropped to 6th place.
Although the main grain crop ranks second, in fact, it is wheat prices that are the benchmark for other export crops - in particular, barley.
Rice is counted separately
Despite the fact that rice is also a grain crop, international organizations account for it separately from wheat and forage crops.
In 2010, the world grew 448 million tons of rice. The main producing countries are China (137 million tons), India (89 million tons), Indonesia (37 million tons), Bangladesh (30.5 million tons) and Thailand (2 million tons)
Surprisingly, much less rice is grown in India and China than wheat.
For example, in 2010 China grew 2.3 times more wheat and India 40% more than rice.
Who sells grain to the world
Most countries grow cereals for themselves, and only about 13-14% of the produced grain is exported. The annual export volume ranges from 240-250 million tons.
The 5 largest exporters - the United States, Argentina, Australia, Canada and the European Union - accounted for 75% of international grain trade in 2010/2011.
Let us remind you that Ukraine has left the list of the largest grain exporters due to export quotas. Russia also remained on the sidelines, as it completely banned grain exports from August 15, 2010.
World grain market: main producers and consumers. reference
The main types of grain crops on the world market are wheat, barley, oats, corn, rice, buckwheat and peas. Currently, the world grain market is controlled by five main exporters: the USA, Canada, Australia, Argentina, and the EU. The total export offers of grain from the main "five" exporters account for over 84% of the total volume of world trade. The leading position in the grain market belongs to the United States, which accounts for 28% of trade, followed by Canada - 17%, Australia and the EU - 15% each and Argentina - 11%.
According to the Minister of Agriculture Alexei Gordeev, as of June 2008, Russia ranked third in the world in terms of wheat exports and was one of the five leading countries in grain production.
USA
The USA is the largest grain exporter. A third of the cultivated area in the United States is planted specifically for overseas sales. Among the grains in the United States, the leading place is occupied by corn and wheat, a significant part of which is exported.
The United States has long maintained its leadership as a corn producer. Corn is grown there almost everywhere: the sown area is 28.6? 35.0 million hectares. The yield ranges from 9 to 10 tons / ha. The USA produces 267.5? 331.2 million tons of corn, which is half of the total world corn harvest. 44.5? 61.9 million tons are exported, and most of it goes to domestic consumption, which is 230.7? 261.7 million tons. Up to 0.3-0.5 million tons are imported. Carry-over stocks - 33.1? 45.5 million tons.
The sown area for wheat is 18.9-22.5 million hectares. On average, 3 tons of harvest are obtained from each hectare. Thus, about 49.2? 68.0 million tons are produced. Moreover, on average, one half is exported (24.7? 34.4 million tons), the other - for domestic consumption, which is 28.6? 34.3 million tons. 3.0-3.3 million tons are imported. The carryover stocks range from 8.3 to 17.8 million tons.
Canada
Canada is an exporter of grain (this applies to all major crops, including wheat, rye, oats, barley, corn, buckwheat) and one of the main players in the global grain market. In this regard, grain imports are insignificant.
On average, the sown area for wheat is 8.6 - 11.0 million hectares. Productivity varies from year to year and ranges from 1.8 to 2.9 tons / ha. On average, the gross harvest of wheat varies from 16.2 to 28.6 million tons, with 9.4? 19.4 million tons are exported. Imports range from 0.2 to 0.4 million tons. Domestic consumption consumes 6.3-9.0 million tons. Wheat carry-over stocks in the country amount to 4.8-9.7 million tons.
Barley is also an important export crop. The sown area for barley is 3.2-4.6 million hectares. The yield varies from 2.2 to 3.4 tons / ha, which ensures the production of 7.5-13.2 million tons of barley. The country exported 0.4-3.0 million tons. The imports are negligible. The country's domestic consumption of this grain crop is 7.9-11.6 million tons. Carry-over stocks - 1.5? 3.4 million tons.
The production of corn in the country averages 8.8-11.6 million tons, which does not always cover the domestic consumption of this crop in the country, which varies from 10.3 to 13.8 million tons, so the missing amount of corn is imported.
Australia
Australia is one of the world's largest grain producers and exporters. Wheat is of the greatest importance among cereals. The sown area for wheat on average ranges from 11.1 - 13.4 million hectares. It accounts for over half of all cultivated areas. Wheat yield varies from year to year depending on climatic conditions and ranges from 0.9 to 2.1 tons / ha. This is mainly winter wheat, which is very sensitive to droughts.
On average, the gross harvest of wheat ranges from 10.1 (in dry years) to 26.1 million tons. Exports - from 7.5 to 18.0 million tons. Import - 0.1? 0.3 million tons. Domestic consumption - 5.3-6.5 million tons. The carryover stocks amount to 3.2? 9.6 million tons.
The sown area for barley is 3.5-4.6 million hectares. Productivity 1.0? 2.3 tons / ha. Production fluctuates within 3.9x10.4 million tons. Exports - 1.9? 6.4 million tons, depending on the global situation. Domestic consumption is 2.2-3.8 million tons. Carry-over stocks - 0.6? 2.7 million tons.
Other grain crops include corn (used mainly for fodder), sorghum (grown for grain and fodder), triticale (a hybrid of rye and wheat), and oilseeds - groundnuts, sunflowers, safflower, rapeseed, canola, soybeans.
Argentina
Argentina has traditionally been one of the world's leading producers and exporters of grain and flour, but is subject to fluctuations in the largest export market in neighboring Brazil.
The sown area for wheat ranges from 4.2 to 6.8 million hectares. Productivity - 2.1? 2.9 tons / ha. Production ranges from 9.5-16.3 million tons.Export - 4.3? 11.8 million tons. Domestic consumption - 4.9-5.5 million tons. The carryover stocks are 0.3-1.5 million tons.
Maize takes a significant part in agricultural production. The sown area for corn is 2.4-3.3 million hectares. Productivity 5.5-8.0 tons / ha. Production of 14.7? 22.5 million tons, of which exports are 9.0? 15.3 million tons. Domestic consumption - 4.1-7.5 million tons. Carry-over stocks - 0.2? 1.7 million tons. The imports are negligible.
European Union
The sown area for wheat is 24.3-26.8 million hectares. Productivity 4.5-5.7 tons / ha. Thus, the UES produces 110.6-150.5 million tons of wheat. Of these, from 113.2 to 127.5 million tons are spent for domestic consumption, 9.8-20.1 million tons are exported, carryover stocks amount to 10.4-27.5 million tons. Wheat imports range from 3.5 to 10.7 million tons.
The sown area for barley ranges from 13.7 to 14.7 million hectares. The yield of 4.0? 4.7 tons / ha allows to produce 55.8? 65.6 million tons of barley. Most of it goes to domestic consumption, which amounts to 54.1? 58.0 million tons. Exports range from 2.6 to 7.2 million tons. About 0.1-1.4 million tons of barley are imported. The carryover stocks amount to 5.7? 11.1 million tons.
The gross harvest of corn in the UES is 47.7? 66.5 million tons. Domestic consumption - 60.5? 63.5 million tons. Depending on the yield, imports vary from 2.5 to 14.0 million tons, exports are 0.5–0.7 million tons. Carry-over stocks - 5.0? 9.5 million tons.
Russia
Russia accounts for 10% of all arable land in the world. Most of the area is used for wheat: 7.4 × 10.6 million hectares for winter crops and 13.8-15.5 million hectares for spring crops. The total gross harvest of wheat on average ranges from 34.1 to 50.6 million tons with a yield of 2.1–3.0 tons per hectare and 1.3-1.6 tons per hectare of winter and spring wheat, respectively. Domestic consumption accounts for 36.4? 44.2 million tons. 8.0? 15.0 million tons are exported. Import - 0.3? 1.3 million tons. The carryover stocks amount to 2.3? 7.1 million tons.
The sown areas for winter and spring barley are significant, 0.5 - 0.7 million hectares and 8.6 - 9.7 million hectares, respectively. With the yield of winter barley 2.6 - 3.9 tons / ha, and spring barley 1.6? 1.9 tons / ha, the total gross yield of barley is 14.1-19.5 million tons. Domestic consumption accounts for 15.5-16.5 million tons. 1.3? 1.7 million tons of barley are exported. Imports amount to 0.2 million tons. Carry-over stocks - 1.0? 2.1 million tons.
Ukraine
Agricultural production in Ukraine forms 16-22% of the country's national income. In the structure of agriculture, two main areas are distinguished - plant growing and animal husbandry. In the structure of grain production, more than half is accounted for by winter wheat. The sown area for winter and spring wheat is 5.5-6.6 million hectares. The yield of 2.3? 2.8 tons / ha allows you to get 13.9? 18.7 million tons. Domestic consumption consumes 11.7-12.9 million tons of wheat. Exported from 1.2 to 6.5 million tons. Imports amount to 0.1? 0.3 million tons. Carry-over stocks - 1.4? 4.1 million tons.
The second place for the gross harvest is taken by barley. The sown area is 4.1-5.2 million tons. Productivity ranges from 1.5 to 2.2 tons / ha. Gross duty? 6.0 × 11.4 million tons. Domestic consumption consumes 4.9-6.5 million tons of barley. 1.0? 5.1 million tons are exported. Imports are up to 0.1 million tons. Carry-over stocks - 0.7? 1.2 million tons.
In third place in terms of gross harvest is corn, in fourth? rye. Oats, millet, buckwheat, rice, legumes are significantly inferior to them in terms of gross harvest.
Kazakhstan
Grain farming is the main branch of agriculture in Kazakhstan. In recent years, the total sowing of grain crops has occupied over 80% of the sown area of agricultural crops.
Kazakhstan produces 13.5-20.1 million tons of grain, which gives the country the right to be in third place in the CIS after Russia and Ukraine. The average grain yield is 1.0? 1.3 tons / ha. The growth in grain production contributes to an increase in its sales and an increase in the profitability of the industry. On average, 2.8-7.0 million tons of grain are shipped for export.
Spring wheat occupies over 3/4 of the grain crops. The total sown area for wheat is 11.8 x 13.3 million hectares. The yield of 0.9? 1.3 tons / ha allows you to get 11.2? 16.6 million tons of wheat.Of these, 7.4? 7.5 million tons are spent on domestic consumption, and 3.0? 8.2 million tons are exported. The carryover stocks amount to 1.0-3.0 million tons.
Crops of barley, oats, corn are found everywhere, and millet occupies large areas in the north-west of Kazakhstan. The sown area for barley is 1.6? 1.8 million tons. The yield of 0.9? 1.4 tons / ha allows providing a gross harvest of 1.5? 2.8 million tons. 1.35-1.6 million tons of barley is needed for domestic consumption. Exports are 0.1-0.8 million tons, imports are insignificant. Carry-over stocks - 0.2? 0.6 million tons.
The sown area for corn is 0.1 million hectares, with a yield of 3.0? 3.2 tons / ha, the country receives about 0.3 million tons of corn for domestic consumption.
Main consumers of grain
Egypt (the largest importer of soft wheat - 7.3? 8.2 million; the share of corn in the import structure is on average 4.1? 5.3 million tons).
Tunisia (import of wheat is 1.1? 1.4 million tons, barley - 0.5? 0.9 million tons);
Saudi Arabia (the largest importer of barley in the world - about 7.3 million tons), etc.
Countries in the Asia-Pacific region:
China (up to 6.7 million tons of wheat are imported);
Japan (the annual volume of cereal imports is about 25 million tons, including maize 66%, wheat 21%, barley 6%, rice (unpeeled) 3%, rye 1%, oats 0.5% ) and etc.
On May 4, 2009, the International Grain Council (IGC) raised the forecast for the gross grain harvest in the world in the 2009/2010 season. The grain harvest is expected to be the second highest ever, after a record 1,784 million tonnes harvested this season, at 1,727 million tonnes. The forecast for world trade this season has also been raised to 230 million tonnes.
Experts say that the main reason for the upward adjustment in the assessment of world grain trade is the increase in imports of Black Sea grain by such countries as Egypt, Iran, Pakistan. According to IGC, the volume of world wheat trade in the 2008/2009 marketing year (MY) will amount to 122 million tons, while corn trade will amount to 79 million tons, which is 22 million tons less than the record figure in 2007/08 MY. Due to high demand from feed producers and a decrease in production in a number of countries, should we expect a 23% increase in trade in barley this season? up to 19 million tons.
The activity of the world grain trade in the 2009/2010 season, according to the IGC forecast, will decrease due to a decrease in demand for imported grain from the EU and some African countries, Iran and Turkey.
The user undertakes to speak out respectfully towards other participants in the discussion, readers and persons appearing in the materials.
Comments are published only in those languages in which the main content of the material is presented, under which the user posts the comment.
On the websites of the MIA "Russia Today" media group, comments can be edited, including preliminary. This means that the moderator checks that comments are in compliance with these rules after the comment has been posted by the author and made available to other users, as well as before the comment has become available to other users.
A user's comment will be removed if he:
does not correspond to the topic of the page; promotes hatred, discrimination on racial, ethnic, gender, religious, social grounds, infringes on the rights of minorities; violates the rights of minors, harms them in any form; contains ideas of an extremist and terrorist nature, calls for a violent change in the constitutional order of the Russian Federation; contains insults, threats against other users, specific individuals or organizations, defames honor and dignity or undermines their business reputation; contains insults or messages expressing disrespect to the MIA Rossiya Segodnya or agency employees; violates privacy,distributes personal data of third parties without their consent, discloses the secrecy of correspondence; contains links to scenes of violence, cruelty to animals; contains information on methods of suicide, incites suicide; pursues commercial purposes, contains inappropriate advertisements, illegal political advertisements, or links to other online resources containing such information; has obscene content, contains obscene language and its derivatives, as well as hints at the use of lexical items that fall under this definition; contains spam, advertises the spread of spam, mass mailing services and resources for making money on the Internet; advertises the use of narcotic / psychotropic drugs, contains information about their manufacture and use; contains links to viruses and malicious software; is part of a campaign in which a large number of comments with identical or similar content are received ("flash mob"); the author abuses the writing of a large number of meaningless messages, or the meaning of the text is difficult or impossible to grasp ("flood"); the author violates netiquette by displaying forms of aggressive, mocking and offensive behavior ("trolling"); the author shows disrespect for the Russian language, the text is written in Russian using the Latin alphabet, in whole or predominantly typed in capital letters or not broken into sentences.
Please write correctly - comments that disregard the rules and regulations of the Russian language may be blocked regardless of the content.
The administration has the right, without warning, to block the user from accessing the page in the event of a systematic violation or one-time gross violation by the participant of the commenting rules.
The user can initiate the restoration of his access by writing a letter to the email address
The letter must indicate:
Topic - restoring access User login Explanations of the reasons for the actions that were in violation of the above rules and resulted in the blocking.
If the moderators find it possible to restore access, this will be done.
In case of repeated violation of the rules and repeated blocking, access to the user cannot be restored; blocking in this case is complete.
World wheat production
Wheat is the main cereal in world trade with an average production of 650-685 million tons, a consumption of 654-660 million tons and an annual reserve of 160-190 million tons.
China is the largest wheat producer in the world. Ending stocks in this country are about 130 million tons; the second place is occupied by India with an indicator of 90 million tons; in third place are the United States and the Russian Federation with ending stocks of 60 million tons per country.
Average wheat yields on different world continents are very different. The temperate climate of Northern and Central Europe promotes high wheat yields, while areas with more severe climates, such as arid or cold regions, are less favorable for wheat cultivation. The range of indicators is quite wide: from Ireland with an average of 9.86 t / ha and to Venezuela (Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela) with an average of 0.31 t / ha. The current world record was set in New Zealand in March 2010 at 15.64 t / ha.
The Committee for World Food Security considers that the main problem today is the lack of growth in crop yields in many countries of the world, while the world's population is constantly growing, and every day the issue of food supply of the population becomes more and more urgent.
Growing wheat: planting and care features

Wheat requires a certain pre-sowing soil preparation, the organization of spring fertilizers, the correct enrichment of the land, and most importantly - the study of the rules for combating diseases and pests. In order for the crop of farmers to be impressive, you should not neglect the listed rules.
Wheat is the most common cereal crop. And it is not for nothing that it is cultivated all over the world. Last 2015, world wheat production was 723.8 million tons, making this crop second only to 1.016 million tons of corn. Wheat is grown in vast areas, giving it a place of honor among other crops, both in the commercial sphere and in food. The indicator of the world volume of wheat in trade is much higher than that of other cereals, because wheat is an integral part of the food supply of countries. It is considered one of the main sources of vegetable protein in the human food chain. The protein content in wheat is much higher than in other crops such as rice, corn and others. So, when cultivating this crop, it is not always possible to obtain maximum yields, since wheat is quite demanding on soils and climatic conditions. This article will outline the main aspects of wheat cultivation.
Place of wheat in crop rotation

Wheat is rather capricious about the crops cultivated in front of it. This is due to the weak root system of the wheat crop, as well as to the phytosanitary state of the soil. The whole crop will not be achieved if the soil is poorly prepared. Wheat will pay back with high yields if perennial and one-year grasses, green manures, corn, buckwheat, rapeseed, and legumes become its predecessors. These plants help the soil, saturate with nitrogen, fight weeds, contribute to the accumulation of easily digestible nutrients in the soil, and also reduce the spread of putrefactive diseases, if crops are properly harvested.
Wheat will feel good enough after cultivating oats on a plow, since this crop is not exposed to root rot, but, on the contrary, contributes to the accumulation of nutrients in the soil, since it leaves behind a sufficient amount of organic matter in comparison with other agricultural crops. Observing the crop rotation and guided by the agro-technological rules of wheat cultivation, you can achieve optimal yield results. The standard terms for sowing wheat in a crop rotation are two-year breaks; re-sowing can be done only after two years, when the soil is cleared of pathogens to which the crop is susceptible. It is not recommended to sow wheat after barley, as the similarity of predispositions to diseases can cause outbreaks of diseases such as root rot.
Presowing soil preparation
Soil preparation for sowing should be aimed at ensuring aeration of the root system, retaining moisture, exterminating weeds, and maximizing plant residues from the previous crop. Presowing preparation should provide an optimally leveled surface of the soil and seedbed for further seeding. Presowing processing directly depends on the weather conditions, the equipment you have, the state of the arable land and the previous crop. Moldless tillage, before sowing wheat, is used after unpaired crops, 10-12 centimeters deep, using combined row-crop units.
The classic cultivation of arable land is harrowing and cultivation, aggregates with rollers or harrows. Before sowing, the field must have a compacted soil structure, a pre-sowing layer; large clods are not allowed in the sowing layer. The predominance of soil particles in the soil should not exceed 3 millimeters.To ensure the harmony of wheat seedlings, it is necessary to establish optimal contact between the seed and the soil. It is important to organize autumn tillage on plowing, after harvesting the previous crop, this procedure will increase the soil's resistance to moisture accumulation and reduce the number of weeds and harmful insects. If perennial grasses were cultivated on plowing, disc plowing of the soil is carried out, with an interval of ten days, plow plowing is also carried out, sometimes the grown crop is trimmed with a flat cutter to a depth of 12 centimeters.

After the agrotechnical procedures, two weeks later, plowing is carried out with a plow, with cultivated dumps and skimmers to a depth of about twenty centimeters, sealing the layer at the bottom of the furrow so that the weed cannot germinate. Processing with two peeling, disk, and then ploughshare is carried out after the cultivation of leguminous plants, stubble plants, as well as in fields contaminated with weeds. As perennial weeds grow, plow plowing or early plowing by 22 centimeters with harrowing, or several cultivations in the fall, is carried out on plowing to combat weed and volunteer seedlings.
The bedded plow is preferable for early spring sowing of wheat, this also applies to heavy soils. After the cultivation of crops such as sunflower and corn, the soil is cultivated by cross-disking and plowing with plows with skimmers to a depth of 20 centimeters. Without preliminary peeling, the soil is plowed after the cultivation of such crops as beets and potatoes, and on the slopes, processing is carried out aimed at eliminating soil erosion, which reduces the washout of the fertile layer by floods and rains.
The sowing of wheat can vary, depending on various factors, climatic and biological characteristics. The optimal time for sowing winter wheat will be the second decade of September. And for the spring, the first decade of spring. On scanty soils and after unpaired crops, sowing is carried out at the optimum time in early September, and after fallow crops and on rich soils, sowing should take place at a time close to winter, so that wheat is less attacked by cereal flies, and also so that the culture does not overgrow.

Winter wheat should germinate for wintering and gain two or three shoots, usually the growing season of a plant is about two months before the beginning of winter. The approximate seeding rate will vary around 500 viable per square meter of plowed land. The rate, with a favorable outcome during the harvest period, can reach 650 productive plants per square meter. To provide late sowing with the optimal number of fruiting stems, the seeding rate is increased by 15 percent. Wheat seeds are covered to a depth of about three centimeters, with the obligatory compaction of the sown area, with rollers. The planting depth of wheat depends on the sowing time, if the sowing is late, then the planting depth should accordingly be less. Wheat is sown in a row method with a row spacing of 15 centimeters.
Fertilization
Like all crops, wheat responds well to fertilization. Wheat grows well on soils enriched with nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus. The approximate consumption of a wheat crop of 30 centners is about 90 kilograms of nitrogen, 60 kilograms of potassium, 25 kilograms of phosphorus. At the same time, the dynamics of nutrient consumption depends on the vegetation phase of the plant. During the initial period of growth, wheat consumes nitrogen, but in small quantities. The situation changes when the plant begins to gain ears and form additional stems, then wheat sharply increases its nitrogen consumption.

But during the period of grain formation, the need for this trace element is minimized. Since nitrogen absorption is in large quantities, it will provoke a decrease in the indicators of grain ripeness.Phosphorus fertilization is important during tillering and stemming. Phosphorus fertilization plays an important role in the formation and development of the plant root system, as well as ears. Potassium, in turn, has a direct effect on wheat; if the wheat lacks potassium, then you will not get a good harvest, since heading directly depends on the percentage of potassium in the soil. Potassium increases the resistance of wheat to certain diseases, affects grain size, accelerates the delivery of carbohydrates from the stems to the grain, as a result of which the grain is poured and enlarged.
For sowing spring wheat, it is necessary to prepare saturated, fertilized lands, because if the root system of the plant reaches optimal development, then in the future it will be able to use moisture more efficiently and better withstand drought. On the soils of the central strip and on podzolic lands, the introduction of organic and mineral fertilizers in a complex has a beneficial effect. Combined application with organic manure and peat compost will double your wheat yield. Fertilization should be determined by its timing, which will depend on the growing season of the plant. During sowing, a smaller part of the mineral fertilizer is applied. And before sowing, the main part of organic and mineral fertilizers is applied. Top dressing is carried out during the growing season of wheat, by irrigation.

The main fertilizers for wheat are peat, manure, green manure, and mineral fertilizers are phosphorus and potassium. Wheat gives good yields with complex fertilization of the soil, before sowing. The main fertilizer is often applied together with the seeds in the rows when sowing. This method of fertilization will fully provide wheat seeds with complex nutrition for the entire period of crop growth, thereby increasing the chances of getting a good harvest. Increasingly, agricultural technicians are using new bacterial-type fertilizers, the most common of which are azotobacterin and phosphorobacterin. This class of fertilizers can increase the yield of about 1.5 centners per hectare.
Ways to increase grain yield
Global demand and consumption of crops for food, feed and fuel are growing rapidly. This requirement for plant materials has been expanding over the years. Recently, however, the rise in meat consumption in emerging economies, coupled with the accelerating use of grain for biofuel production in developed countries, has led to new spikes in pressure on global grain supplies.

In order to meet the growing demand for grain around the world, today there are two options:
- The area for wheat production should be increased.
- Cereal productivity can be increased on existing farmland.
The two options are not mutually exclusive and both will be used to generate an additional 200 million tonnes per year of corn and wheat, as estimated by the global market in 2017. Both options will make their own changes to the environment in the course of agricultural production of zarnov.
Of the two options, increasing productivity on existing agricultural land is preferred as it avoids greenhouse gas emissions and large-scale destruction of existing ecosystems associated with bringing new land into production. In some countries, breeders, agronomists, and farmers have a documented history of increasing yields. ... In Russia, over the past two years, the increase in wheat yields is due to the development and widespread use of new agricultural technologies, such as hybrid maize, synthetic fertilizers and improved agricultural equipment.

The introduction of biotechnology and the development of a new breeding technique using DNA markers based on an additional increase in yields are giving their positive results. Outside Russia, similar farming methods have been adopted in some agricultural countries, but today, in many large grain-producing countries, yields is still lagging behind the world average. Continuing to develop new agricultural technologies for the cultivation of cereals and their implementation at the global level, will fully meet the global demand for feed, fuel and food. Undoubtedly, with this approach, the criteria for increasing yields can be met without the participation of large land plots for new production.
Increasing the productivity of existing agricultural land will in turn have environmental impacts, both negative and less burdensome, and in some cases may be positive, depending on how the land was previously used. cereals, can increase nitrous oxide emissions, reduce water quality, and increase the size of hypoxic zones.

Another method of increasing yields on existing agricultural land is based on transgenic extermination of harmful insects and rodents, as well as on plowing. Plowing can reduce erosion, maintain soil moisture, and increase soil organic matter deposition, and transgenic insect control can reduce a wide range of insecticide uses.
Factors that reduce yields
While breeders, agronomists, and farmers work to increase yields, there are a number of factors that can reduce yields. Over the next two decades, the effects of climate change in central Russia are predicted to increase night air temperature values, the number and severity of adverse weather events, and an increase in the frequency of insect pests and diseases. As a result, these factors can affect the yield of grain crops.
Rapid adaptation of crops to changing climatic conditions can help mitigate these effects. Rapid crop adaptation is achieved through breeding programs that continually develop by introducing locally adapted hybrids and varieties.

Nitrogen is another factor that can limit yields. Nitrogen, or rather its absence in the soil, can be a compelling reason for a negative impact on the crop. Climatic factors can affect the harvest and completely destroy it. Finally, a sharp downturn in the global economy could constrain demand for meat and fuel, which would indirectly understate economic incentives to boost wheat yields.
Wheat diseases and pests
Like all cultivated crops, wheat is susceptible to many diseases, and there are plenty of pests and insects that will happily feast on fresh grains. Wheat diseases are common but depend mainly on the cultivation area and climatic boundaries. Wheat plants are susceptible to disease at any stage of the growing season. Diseases, in addition to reducing yields, also have a detrimental effect on the quality of the grains. Some of the most common diseases are head smut, hard smut, ergot, rust, root rot.
If wheat becomes infected with a head smut, the disease will reach its climax on all parts of the ear, acquiring a black color, and then turning into a dusty gray mass. The method of dealing with head smut is the processing of seed raw materials.

Hard smut, an unpleasant disease that can spoil the harvest. It is caused by a fungus and mainly affects the spikelets.In the ear, hitting the grains, spores of the fungus are formed, with an unpleasant putrid odor. To combat this scourge, it is also necessary to process the planting material.
Root rot, another of the diseases that can cause irreparable damage to the wheat crop. The causative agent of this disease is a fungus of various types. The disease proceeds rather quickly, exposing the root system of the plant to rot and completely destroying it. Helminthosporioses, or wheat root rot, develops at the root collar, causing it to rot and die.
Stem rust, or brown rust, is a fungal disease that mainly affects the stems of the plant and the leaf surface of wheat. It looks like brown spots or yellow bloom, voids form on the stem or leaves, if an ear is affected, the grain in it will stop developing. Methods for combating this disease include a set of measures, namely, compliance with crop rotation, pre-sowing treatment of the soil with pesticides, sowing wheat in the allotted time, as well as timely fertilization of the soil with potash and phosphorus fertilizers.

Ergot is considered no less dangerous. It is mainly the ears that suffer from it, they form eggplant-colored sclerotia, which eventually destroy the ear, along with the grains. Wheat disease control methods include mainly chemical treatment of seedbed and soil before sowing. However, at the moment, agricultural technicians of the country are paying more and more attention to solving the issue of the potential of the agroecosystems themselves and its regulation, because the introduction of pesticides and herbicides into the soil leaves its mark on the ecosystem. Therefore, environmentally friendly methods of combating diseases will be compliance with crop rotation and optimal sowing times, as well as the use of green manure and the introduction of environmentally friendly means to combat pathogens, among other things, maintaining the necessary moisture content in wheat, minimizes the damage to the plant by cereal flies and wheat thrips.
Wheat is widely cultivated in many countries of the world, as a cash crop, because it gives a good yield per unit area, grows well in temperate climates and even with a moderately short growing season, gives a versatile, high-quality flour, which is widely used in baking bread and bakery products. ... Therefore, the popularity of wheat flour products creates a strong demand for grain, even in countries with significant food surpluses.
xn - 80ajgpcpbhkds4a4g.xn - p1ai
Russia came out on top in wheat export
Russian farmers have replaced their American counterparts as the main exporter of grain crops. Russia got the lion's share of the wheat purchased by Egypt this year. Cairo traditionally buys huge quantities of wheat to provide the Egyptians with cheap bread.
The countries of the Black Sea basin, including Ukraine and Romania, writes Bloomberg, often take the lead in grain exports at the beginning of the year. Usually France joins them later. However, no strong competition from France is expected this year. Due to severe floods, the French grain of the new harvest will be of poor quality and therefore it is not in great demand in the international markets. French farmers haven’t had such a bad wheat situation in five years. The projected wheat harvest, according to BayWa AG, this year will decline by 17% to 34 million tons.
The low prices of Russian wheat also contributed to Russia's leadership to a certain extent. A weak ruble, good weather conditions and additional investment in agriculture have led to its recovery and displacement from the first place by American farmers, who have held it for more than half a century.
According to the US Department of Agriculture (USDA), Russia is exporting a record 25.5 million tons of wheat in the new season, which began in July. According to this indicator, it ranks first for the second year in a row.
World wheat production will also be at a record, for the fourth consecutive year. Not surprisingly, prices on the Chicago Stock Exchange, the most respected for grain, fell to their lowest level since 2007 in July. As of the end of last week, a ton of wheat in the Black Sea ports cost $ 165. This is almost 11% cheaper than French wheat with a minimum 11% protein content, ready for loading in Rouen.
Meanwhile, Egypt in July agreed to buy 480 thousand tons of wheat. Half of the grain will be supplied by Russia, and the other half - by Ukraine and Romania. Last year, recalls Bloomberg, French wheat accounted for 17% of the Egyptian market.
Last year, Russia, then, however, for the first time in three years, was also in the lead in wheat sales. Such a pace will allow it to increase its share in the world wheat market to almost 16%. The increase compared to last year, when it was 14.4%, is tangible.
The share of France this year is likely to decline from last year's 12.1 to 11%. The share of America will also grow - up to 14.9%, but they will not be enough for the first place.
“The position of Russia on the wheat market is changing,” explains Sergey Feofilov, director of UkrAgroConsult, “because Russian farmers received a huge margin from the sale of their crops last year. They invested this money in more efficient technologies for growing wheat. Added to all this are almost ideal weather conditions. "
According to BMI Research's forecast, Russia, Ukraine and Kazakhstan will be the main suppliers of wheat to the Middle East and North Africa in the next five years.
World markets disappointed with the volume of Russian wheat exports
Given the record wheat harvest in Russia this year, reduced demand in world markets and restrictions on grain imports from Egypt, cereal producers are in no hurry to enter the market.
- "Expert Online"
- growth in consumption in the domestic market (including an increase in the demand for feed in the livestock industry);
- development of the logistics infrastructure, which made it possible to significantly increase the volume of exports;
- increasing the yield of wheat. Analysis of average annual indicators over a long period allows to largely exclude the influence of natural and climatic factors and determine the contribution of the use of advanced technologies to changes in wheat yield in Russia. The average annual yield of this main type of grain in Russia, according to calculations based on Rosstat data, in 1991-2000. amounted to 16.4 c / ha, in 2001-2010. - increased to 20.5 c / ha, in 2011-2015. - reached 22.5 c / ha.
Wheat is a popular cereal crop that is grown in many countries of the world with favorable climatic conditions for this. Russia is no exception. Cereal grains are used for grinding into flour, after which it is used to prepare various products (baked goods, pasta, etc.). There are more than 300,000 varieties of wheat, and every year their number only increases. Breeders are developing new forms that are highly resistant to various diseases and have significant yields. What is the average yield, where is grain production in Russia widespread and what varieties are common, you should understand in more detail.
Main growing regions
Grain production in Russia is possible in almost all regions. The main advantage of any type of cereal is its picky to weather conditions. The main cultivation areas are the Stavropol and Krasnodar Territories. In these territories, grain harvest reaches almost a quarter of the total state harvest and has a higher yield.
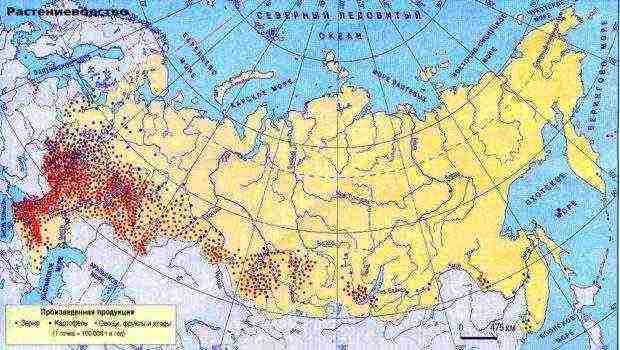
Good yields are also observed in other areas:
- Volgograd.
- Saratov.
- Omsk.
- Kursk.
- Voronezh.
- Altai Territory.
Each of the regions provides 3-5% of the total amount collected throughout the country. A significant wheat harvest in Russia can be traced in the Belgorod and Penza regions.Here, wheat production in Russia is at a high level, while some northern regions are completely unsuitable for growing such crops.
Modern crops
Russia is a northern country with a cool climate for growing grain crops. But even with these difficulties, you can find ways to optimize production.
Grain plays an important role in the economy of the Russian Federation. The state is distinguished by higher yields than most tropical countries, therefore it exports the product in large volumes.
Since the 2000s, wheat production per hectare has increased sharply. The authorities decided to sow almost half of all sown area allocated for grain. In 2006, more than 60% of all cereal fields were already filled with this crop.
In post-war times, NS Khrushchev decided to make corn the second bread in the country. In the 1950s and 1960s, corn was planted en masse, but throughout the Khrushchev government, wheat held the leading position.
Almost 70 years have passed and the current Russian government says that Khrushchev's strategy was successful. The yield of corn is much higher - it is less nutritious and healthy product. It can be actively used as feed for domestic animals, which could contribute to the development of agriculture and animal husbandry.

In 2016, the scale of wheat planted areas in Russia was 27704 thousand hectares, and this is almost 59% of all fields allocated for grain crops.
How many centners per hectare are harvested of wheat: it is almost unrealistic to answer unequivocally. It depends on soil, climatic conditions and other factors.
Varieties of culture
Wheat varieties are grown on the territory of Russia:
- spring;
- winter;
- soft varieties;
- hard varieties;
- dwarf, etc.
Hard varieties are not grown very actively. Such varieties do not show high yields. The grown durum wheat is more often used to make good pasta. The ear of such a culture is distinguished by its dense structure and long awns. Large volumes of durum wheat from warmer countries are annually imported to Russia, as it is in demand among consumers and is of high quality.
Soft varieties are much more common - the grain is used for baking bread. Flour is great for making confectionery. There are no bones here at all. The seed has a rounded shape.
Dwarf varieties are rarely grown, but most confectioners claim that this flour is best for baking cakes, pastries, cookies, etc.

The technological map of the cultivation of spring crops suggests that it is better to plant it in the spring and harvest it in the fall.
Where to grow spring wheat in the Russian Federation: this is the most picky variety that takes root in almost all regions of Russia.
The main thing is to follow some spring wheat cultivation procedures in order to get a good harvest, the table of requirements of which is known to everyone involved in crop cultivation.
Winter wheat is sown in late autumn or winter. The advantage lies in the fact that in the spring it receives useful substances along with melt water. Thanks to early sprouting, the crop is less weedy. This is demonstrated by the record grain harvest.
Grain collection in the USSR by years
The volume of wheat cultivated in the USSR was categorically insufficient, so imports flourished. Exports also accounted for 8% in the 60s, and later - only 0.5%. Imports, on the other hand, grew literally every day and, as a result, exceeded 20%. The yield by republic is presented in the table below.
| Year | Production, tons |
| 1961 | 62 494 000 |
| 1965 | 56 105 008 |
| 1970 | 93 750 000 |
| 1975 | 62 250 000 |
| 1980 | 92 500 000 |
| 1985 | 73 200 000 |
| 1990 | 101 888 496 |
| 1991 | 71 991 008 |
There is an opinion that in the USSR they grew grains of 3-5 classes, and bought high-quality wheat of 1-2 classes. There is no confirmation of this, but since the 70s, the USSR began to purchase wheat several times less than to export - this trend continues to this day.
Production in Russia by years
Based on statistical compilations of the Federal State Statistics Service, it is easy to analyze the dynamics of wheat production from 1 ha / ton in Russia over the years:
- 1992 — 46,2;
- 2000 — 34,5;
- 2005 — 47,5;
- 2008 — 67,8;
- 2009 — 61,7;
- 2010 — 41,5;
- 2011 — 56,2;
- 2015 — 56,7;
- 2017 — 57,2.
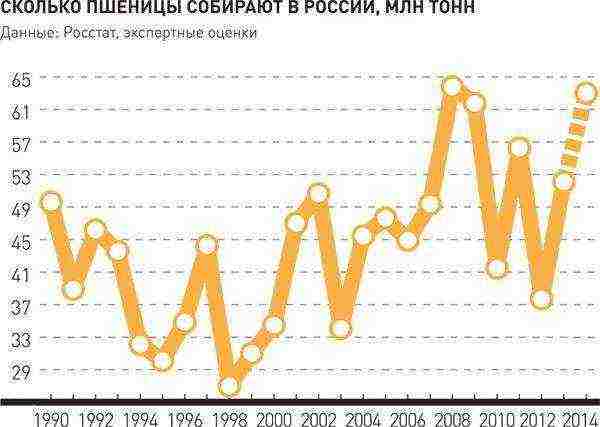
The base growth rate is 112.8%. Today wheat production has increased by 12.8%. The main reason why such changes have taken place is that the structure of demand in the domestic and foreign markets has changed, and the selling prices are also strikingly different.
Productivity by region
Wheat production as of 2017 allows us to consider the development trend by region. The main producing region is the Rostov region - 9,031.3 thousand tons. The share in the total fees is 11.9%. The Krasnodar Territory is also not inferior - collections here amount to 8,957,000 tons. The third place went to the Stavropol Territory - 7 713 thousand tons. The Volgograd region collects 3 353.4 000 tons with 4.4% of the total collection for the year. Altai Territory - 2,977.8. Saratov region at the level of 2 795.1 thousand tons. Omsk takes an honorable seventh place in grain production and produces 2,568.4 thousand tons. Voronezh and Kursk regions in the range of 2299.7-2493.4 thousand tons. The Republic of Tatarstan ranks 10th in the rating of regions with collections of 2,142.6 thousand tons.
The top 20 in terms of gross receipts includes the following regions:
- Orenburg region - 2073.8.
- Orlovskaya - 1883.5.
- Tambov - 1877.0.
- Lipetsk - 1791.3.
- Krasnodar Territory - 1745.0.
- Novosibirsk region - 1631.6.
- Bashkortostan - 1576.1.
- Kurgan region - 1565.9.
- Penza region - 1392.6.
- Belgorodskaya - 1381.6.
All other regions not included in the top 20 produced 14,547.2 thousand tons of wheat.
Russia is a large grain trader that supplies many countries of the world with the most essential varieties for baking bakery products. Even despite the large harvest, the Russian Federation imports durum wheat for the manufacture of high-quality pasta.
In some areas, climatic conditions do not correspond to normal indicators for the growth and development of wheat and other grain crops, therefore, genetically modified products are often used in such areas. This does not mean that only Russia produces such crops. Most of the world leaders in grain production also use this practice. Now you know where wheat grows, which varieties are most common, and what they are used for.


