Content
- 1 Hybrids or variety: making the right choice
- 2 Pollination and ripening dates
- 3 The use of cucumbers and conditions for them
- 4 Popular varieties of cucumbers for the greenhouse
- 5 Growing cucumbers in a greenhouse
- 6 What is important to know about the peculiarities of growing and choosing the right variety?
- 7 Differences in ripening time
- 8 Growth features
- 9 The best varietal cucumbers
- 10 A simple test: what are your expectations?
- 11 Which is better: conventional or hybrids?
- 12 What are the greenhouse cucumbers?
- 13 What are the manufacturers talking about?
- 14 A real "Russian" cucumber: in pimples and without bitterness!
- 15 Popular varieties in Russia
- 16 Exotic, or how to surprise your neighbors
- 17 Same variety and different harvest?
- 18 Criterias of choice
- 19 Video "The best varieties of cucumbers for 2017"
- 20 Exotic varieties
- 21 Video "Growing cucumbers in a greenhouse is very easy"
The choice of varieties depends on what cucumbers you plan to cultivate and what expectations you have for the future harvest. There are many such varieties on the seed market now. Some are ideal for outdoor cultivation, others at home, and others in greenhouses, including those made from polycarbonate. Today we will find out what are the best varieties of cucumbers for polycarbonate greenhouses.
The variety of varieties is so great that among them you can choose exactly those that suit you in terms of their taste, size, type, growth rate and other parameters.

The best varieties of cucumbers for polycarbonate greenhouses
Hybrids or variety: making the right choice
Novice summer residents, most likely, at first will confuse these two concepts - hybrid and variety. However, there are fundamental differences between them.
The most important difference between a variety and a hybrid is the possibility of inheritance by a plant grown from seeds of one type or another, hereditary genetic traits. Crops grown from the seeds of the varieties will produce seeds from which you can get exactly the same plant as the mother one next year. This plant will inherit all the characteristics and qualities of the parent species. And the seeds obtained from hybrid cucumbers will either give completely different plants, unlike their parents, or even refuse to grow at all. The qualities, properties, features of the hybrid will not be preserved in the offspring.

The properties of hybrid cucumbers are not preserved in the offspring
On a note! It is easy to distinguish a hybrid from a variety at the stage of buying seeds - all hybrids have the F1 marking in the name.
Table. The main differences between hybrids and varieties in comparison.
| The price of such seeds is lower. | Hybrids tend to be more expensive. |
| You will be able to collect seeds yourself in the fall and plant them for seedlings the next year without spending additional funds. | Seeds collected from hybrids in the fall will not produce good offspring. A rare exception is the first generation. You will have to buy them again in the store. |
| Varietal plants are resistant to diseases declared on the packaging for several generations. | In general, hybrids are resistant to plant diseases only in the first generation. |

Outwardly, the fruits of hybrids do not differ from the fruits of ordinary varieties.
Why are hybrids so good and why are they recommended to buy (especially for beginners)? Why are they more expensive than varietal seeds? It's simple - they have a number of advantages.
So, hybrid cucumbers:
- not afraid of temperature changes;
- they are not afraid of most plant diseases, have excellent immunity (whoever this hybrid is not afraid of is usually indicated on the package with the seeds);
- tolerate adverse weather conditions well and perfectly adapt to different climates;
- as a rule, high-yielding (this indicator is about 40% higher in hybrids);
- give larger and tastier fruits;
- bear fruit earlier, and the fruits ripen faster and are well stored.
That is why many people prefer to buy hybrids instead of conventional varieties.
Advice! When buying seeds, stop at Russian, accustomed to specific natural conditions, cucumbers. Of course, Dutch seeds have long been popular in the same way as German seeds, but you must agree that the climate in those countries is milder than in Russia, and you will have to provide more comfortable conditions for the plants obtained from such hybrids.

Give preference to domestically produced seeds adapted to the natural conditions of the country
By the way, what does the F1 marking that accompanies the name of the hybrid mean? It's simple: F is the initial letter of the Italian word for "children", and 1 indicates that generation is the first. Translating, we get the phrase "children of the first generation." Hybrids are obtained by crossing two different varieties with specific characteristics.

F1 is the designation for first generation hybrids
By the way, hybrids and varieties of cucumbers also differ in care. It even matters how you pinch the bushes. For example, as soon as varietal cucumbers grow 4-5 leaves, their top is pinched. Then the lateral shoots will go into active growth, on which the female (necessary for the formation of fruits) flowers are mainly formed. In this case, there will be more of the latter, which will have a positive effect on the volume of the harvest. And in hybrids, on the contrary, the lateral shoots are pinched.

Cucumber Connie F1
Growing eggplants in a polycarbonate greenhouse
In this article, you'll find everything you need to know about growing eggplant in a polycarbonate greenhouse! We also recommend reading the article on why tomatoes crack when ripe.
Pollination and ripening dates
Those who first decided to grow cucumbers on their own should definitely know that the seeds of this culture are not only divided by hybrids, varieties, species, but also differ in terms of fruiting times and the way in which they are pollinated.
There are three types of pollination:
- self-pollinated;
- parthenocarpic;
- pollinated by insects.
How are they different? The latter type is capable of pollinating, as the name implies, only through the transfer of pollen from flower to flower with the help of insects. Man can also pollinate such varieties manually. The second, parthenocarpic, have flowers of a mostly female species, and in order for them to have greens, they do not need pollination at all.
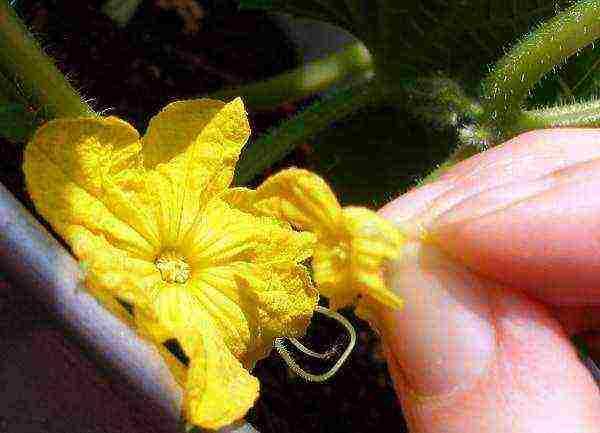

Insectable varieties can be manually pollinated
On a note! In fruits obtained from parthenocarpic cucumbers, seeds are often completely or partially absent.
But self-pollinated cucumbers have bisexual flowers, which have pistils and stamens. Such plants are capable of pollinating on their own.
Advice! It will be extremely difficult to drive pollinators in the required quantity into the greenhouse, therefore, parthenocarpic cucumbers or self-pollinated species are traditionally grown in it. Pollinated by insects are usually grown outdoors.
Cucumbers can also be divided according to the time it takes for them to grow, develop before the start of fruiting, into:
- super early;
- early;
- medium early;
- mid-season;
- late ripening.
The first two types are the species from which the harvest can be obtained as quickly as possible. Some begin to bear fruit just 40 days after sprouting. Mid-early ones give the first cucumbers about 47 days, and from mid-season ones, you will wait for them no earlier than 51-52 days. Late ones bear fruit in 55-56 days.

Cucumber growth phases
Advice! In order for fresh cucumbers to appear on your table as long as possible, it is best to cultivate several different varieties in a greenhouse that differ in the ripening time of the greens.
The use of cucumbers and conditions for them
In order to choose the right variety of cucumbers for cultivation in greenhouses or greenhouses, you will have to decide what you need the fruits of this culture for. You can make salads, blanks from them, and you can also sell them.
By type of use, cucumbers are divided into:
- salad;
- salting;
- universal.

Salad cucumbers
Advice! Usually, the seed producer indicates the purpose of each variety on the packaging. But if it happened that you lost the packaging and forgot which variety it was, then the purpose of the fruit will help determine the color of the thorns on them. If they are white, then they are salad cucumbers, since pickles have darker thorns.
Salad cucumbers are not recommended to be salted, as they lose all their taste - their skin is too thick, through which salt cannot penetrate in sufficient quantities. And pickles do not crumble into salads, as they will be too tough. But on the other hand, their thin skin perfectly passes the brine inside the fruit, and pickles from such varieties in winter will delight you very much.

Pickled cucumbers cannot be crumbled into a salad
There are cucumbers and versatile. They are best suited for those new to the gardening business. The fruits of these varieties are used for the preparation of salads, as well as for all types of culinary processing, including pickling and pickling. Zelentsy do not lose their taste in any of the cases.
By the way, varieties are also divided according to growing conditions. There are types for open and closed ground. Of course, some can be cultivated in any conditions, but it is still better to take note of what is written on the packaging with seeds: "street" cucumbers cope better with winds, cold weather, dry air, but greenhouse cucumbers are usually better protected from the effects of pests and diseases , since they have undergone the appropriate processing. It is better not to change their places - there is a great risk that heat-loving greenhouse plants on the street will simply wither and die.
Cucumbers can also vary in size - this is what often depends on how they will be used.
Table. Types of cucumber fruits by size.
|
Pikuli |
The tiniest cucumbers, ranging in length from 3 to 5 cm, are a common type of short-fruited. |
|
Gherkins |
Slightly larger fruit than pickles. The length of one cucumber varies from 4 to 9 cm. Also belongs to the general type of short-fruited. |
|
Medium-fruited |
Any cucumbers, the dimensions of zelents in which range from 10 to 15 cm. The diameter is about 55 mm. |
|
Long-fruited |
These are the largest cucumbers, the fruits of which can be 15 cm, and even giant 1.5 m. |

And this, although not the largest, but certainly the most unusual of the cucumbers
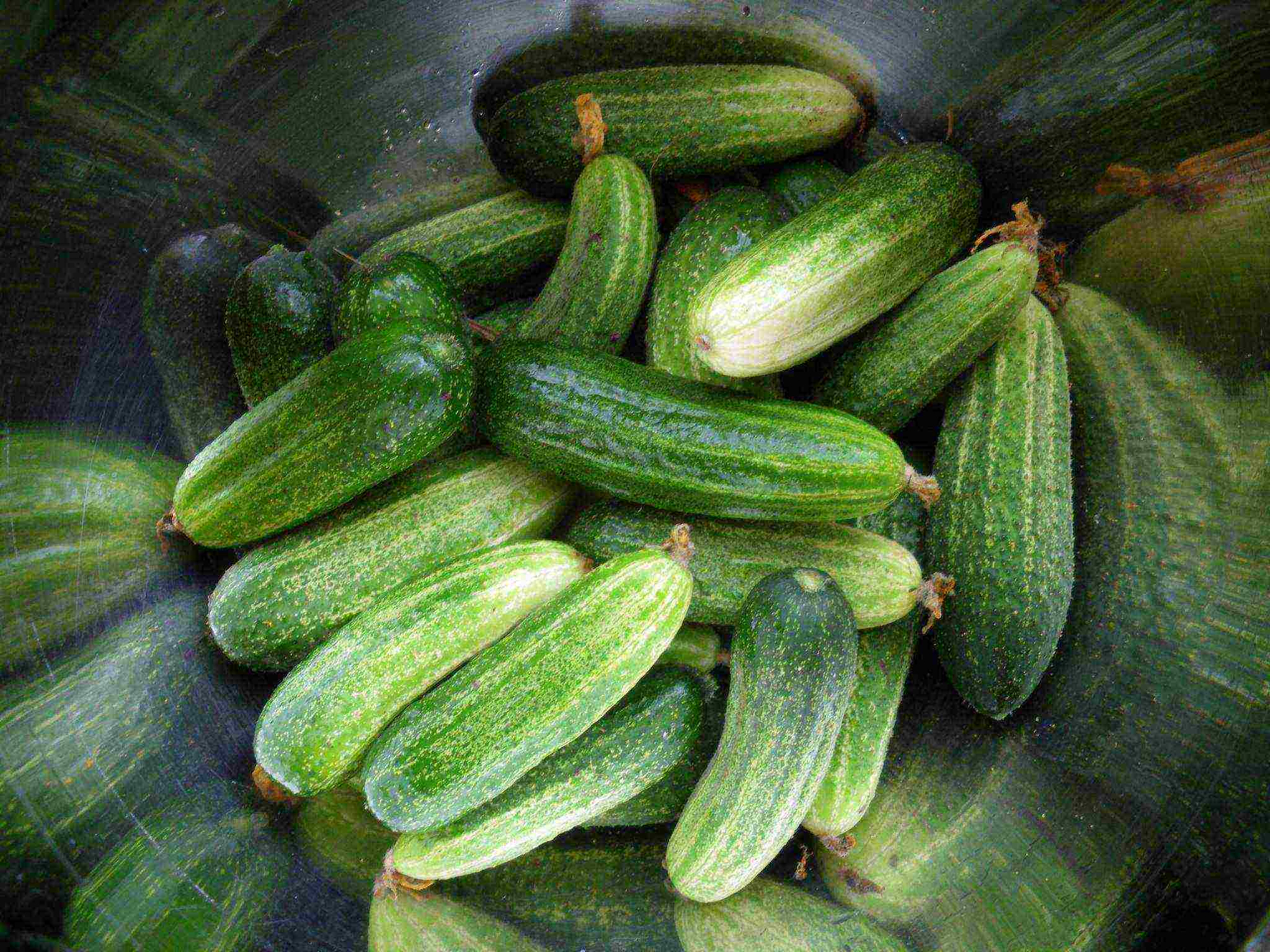
On a note! Short-fruited cucumbers can be obtained by collecting growing greens of the required size from absolutely any bush. But specially bred varieties of gherkins are still tastier.

Spiny gherkins
As for the height of the bush, in greenhouses, by and large, you don't have to worry about it too much. In a greenhouse, low bushes should be grown, and in a greenhouse structure, you can afford not only medium-sized varieties, but also very tall bushes.
Popular varieties of cucumbers for the greenhouse
What varieties of cucumbers for polycarbonate greenhouses are the most popular and have already proven themselves on the good side? Of course, experienced summer residents know about this, but if you are a beginner, then we will try to share this valuable information with you.
The best varietal cucumbers
Table. The best hybrid cucumber varieties for polycarbonate greenhouses.
|
Goosebump F1 |
Parthenocarpic, super-early, medium-sized | Very high-yielding variety, lateral shoots do not actively branch. Produces fruits of medium size (up to 12 cm), covered with black thorns. Great for pickling, but also used raw. Absolutely not afraid of powdery mildew. |
|
Suomi F1 |
Super early, cold-resistant, parthenocarpic | A species with excellent immunity, not afraid of bad weather conditions, root rot. Fruits up to 6 cm long appear as early as 38 days after the first shoots. A distinctive feature is that the greens cannot outgrow their sizes declared by the seed manufacturer, and therefore there will be no overgrown cucumbers. Free from bitterness. Perfectly salted and delicious fresh. |
|
Emelya F1 |
Parthenocarpik, early maturing, vigorous | A hybrid that produces fruits that are great for all kinds of pickles and salads. Zelentsy are oval or cylindrical, up to 15 cm. White thorns. Suitable for greenhouse cultivation only. |
|
Valaam F1 |
Super early, fast growing, parthenocarpic | Not afraid of low temperatures, ideal for growing in greenhouses in regions with cold climates. Produces fruits in the form of a cylinder up to 6 cm with large tubercles. Such cucumbers do not taste bitter and do not outgrow, but bear fruit for a very long time. Suitable for salads, pickling. |
|
Alekseich F1 |
Medium-sized, self-pollinated, early maturing | An excellent universal hybrid of cucumbers, producing medium-sized fruits up to 8 cm long with high quality taste. Not afraid of powdery mildew. |
|
Sarovskiy F1 |
Parthenocarpic, super early | Not afraid of harsh climatic conditions, bears fruit for a long time. Cucumbers are beautiful, have the shape of an elongated oval, up to 13 cm long, with white thorns. The skin is thin. The pulp tastes great. Can be preserved and used for salads. |
|
Real Colonel F1 |
Partenocarpik, vigorous, early maturing, high-yielding | Zelentsy resemble a spindle in shape, up to 15 cm long, weighing up to 120 g, almost not ribbed, with large tubercles. Delicate in taste, not bitter, but, on the contrary, a little sweet. |
|
Benefit F1 |
Self-pollinated early maturing | Produces tasty fruits about 12 cm long, not bitter. They are universal, therefore they are used in any culinary recipe. The hybrid is not afraid of rot, powdery mildew. |
|
Finger Boy F1 |
Super early, parthenocarpic | Produces non-prickly fruits up to 11 cm and weighing up to 65 g. This variety is perfect for those who love gherkins. Not afraid of most common plant diseases. |
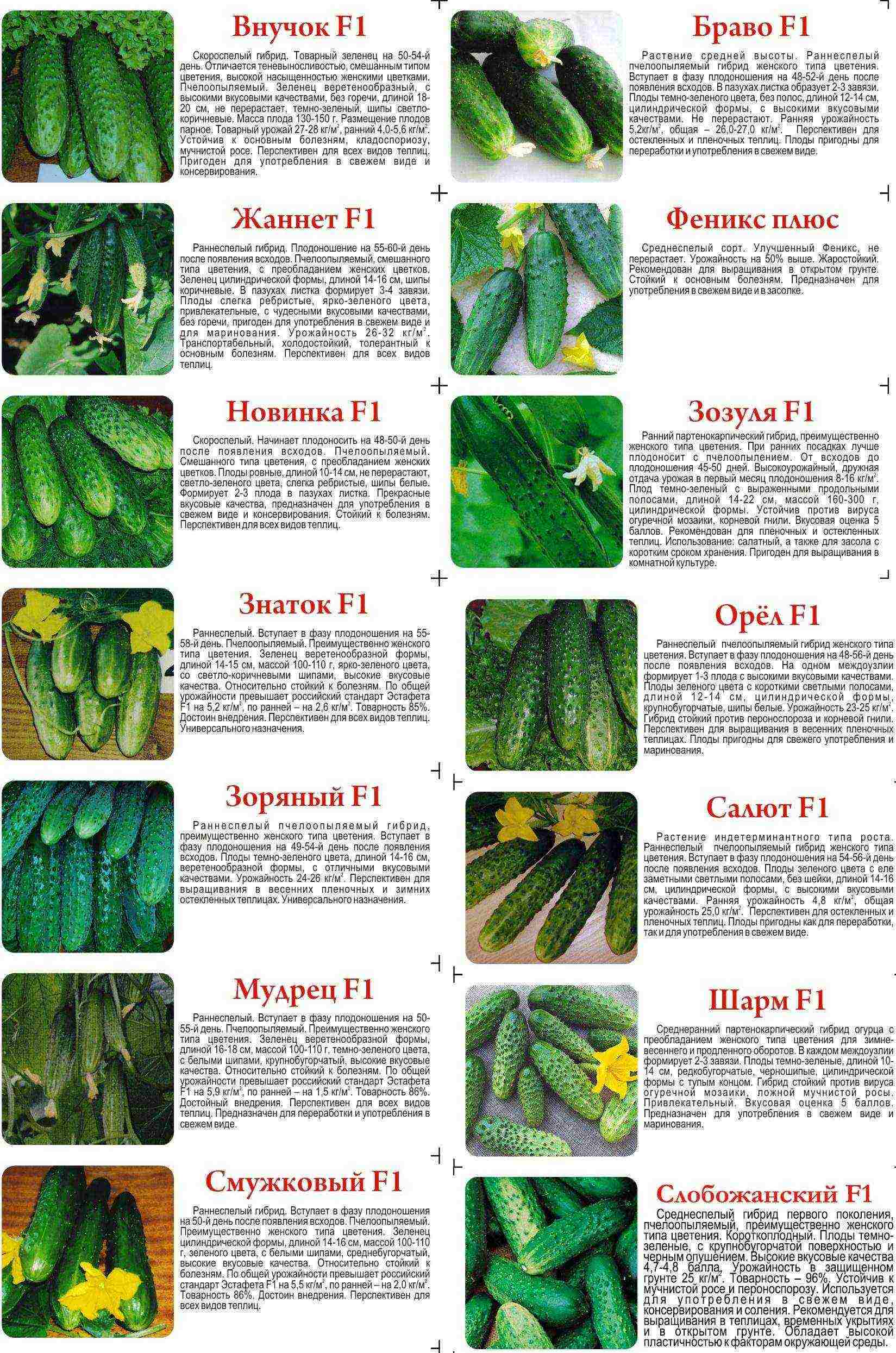
Recommended varieties of cucumbers
Growing cucumbers in a greenhouse
So, you have chosen a type, maybe even several, and are ready to start growing cucumbers in a new polycarbonate greenhouse.
Step 1. To begin with, you must grow seedlings from seeds. When is it to be done? You will have to calculate everything yourself, depending on the climatic conditions of the region of residence. Cucumbers love warmth, they can be moved to the greenhouse no earlier than the soil temperature in it will be +15 degrees. For example, if this figure reaches the desired level at the end of May, then plant the seeds at the beginning of this month 3 weeks before moving to the greenhouse.

Calculate the time of planting seeds based on the climatic characteristics of your region
Attention! Seeds that are planted too early can cause your seedlings to outgrow.
Step 2. Prepare the seedling soil. It should be fertile and contain peat, humus, or compost. Mix, for example, turf, peat, humus and sawdust in a 1: 1: 1: 1 ratio. It is better to steam the soil so that it is disinfected.

Preparing the soil for seedlings
Step 3. Prepare containers for cucumbers - plants do not like transplants, so plant them immediately in separate pots. Take the latter at least 10 cm in diameter. Wash and disinfect the containers well, drain at the bottom so that there is no waterlogging.
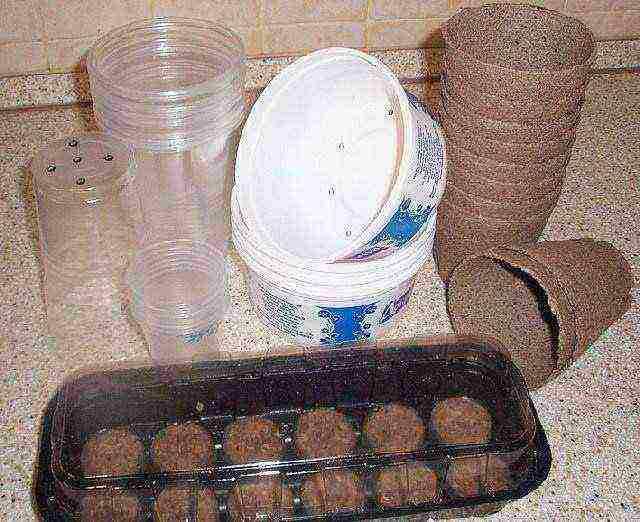

Preparing seedling containers
Step 4. Prepare your seeds. Wrap them in a damp cloth for 2-3 days. As soon as the first shoots appear, the seeds can be planted.
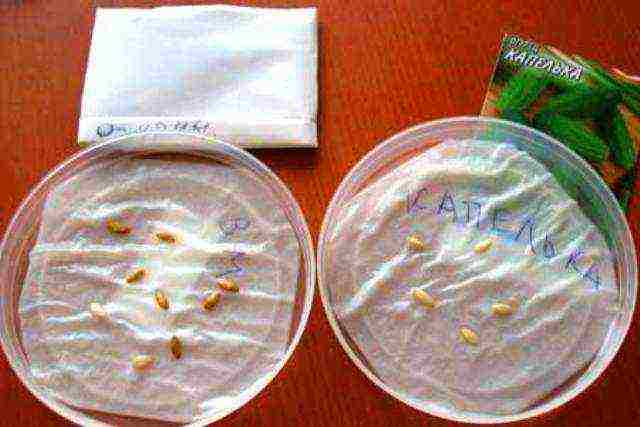

Germinating seeds
Step 5. Fill containers with ready-made soil, place a seed in each, sprinkle with a thin layer (about 1 cm) of earth, lightly compact. Watering is necessary 2 times every 7 days.
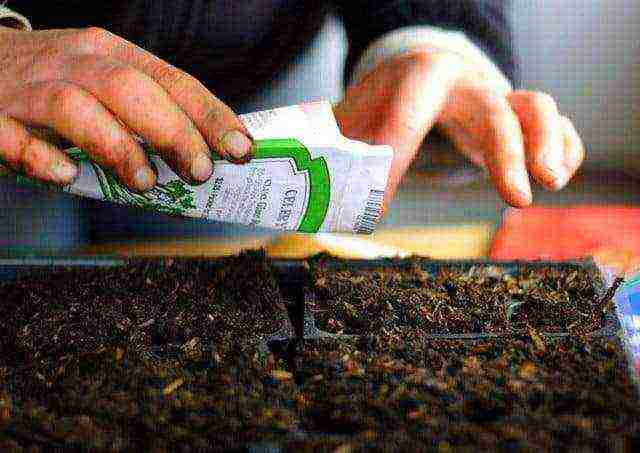

Planting cucumber seeds
Step 6. Spill over with water and cover with foil to create a mini greenhouse. Place where it is warm and light.
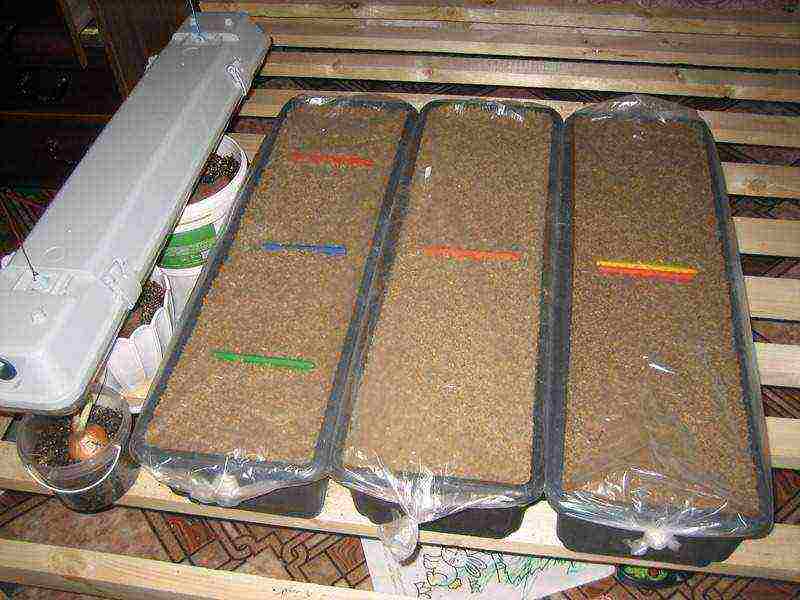

The containers are covered with foil
Attention! The air temperature in the first days should be at least 25 degrees. As soon as the cucumbers rise, lower it to 22 degrees during the day and 17 at night.
Step 7. The grown seedlings, when they get stronger, can be rearranged into the greenhouse if the structure is heated.

The grown seedlings can be transferred to a heated greenhouse
Step 8. It's time for the seedlings to move to the greenhouse, which means it's time to start preparing. The soil in your greenhouse should be prepared in the fall, so just loosen it slightly, spill it and make holes in a checkerboard pattern at a distance of 60 cm from each other. The holes should have a depth equal to the height of the pot in which the seedlings are located.

Seedling holes in a greenhouse bed
Step 9. Spill each well with organic fertilizer, carefully remove the seedlings from the pots and place in them. Sprinkle lightly with earth. Now, subject to careful and proper care, the cucumbers will quickly grow and will soon delight you with the first greens.
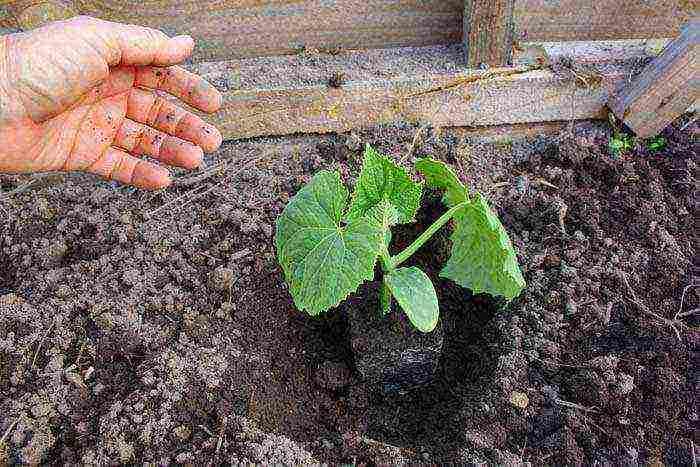

Planting seedlings in a greenhouse
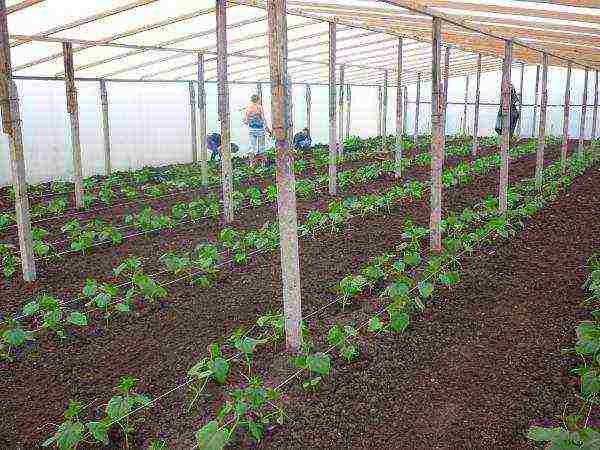

Growing cucumbers in a greenhouse
Fertilizer dosage table for feeding cucumbers
It is very easy to grow cucumbers in a greenhouse, especially in one made of polycarbonate (a minimum of cracks, there are practically no drafts). And if you choose the right variety or hybrid that is right for you, then the harvest will definitely not disappoint you.
Video - Cucumber varieties for greenhouses
Video - Choosing varieties of cucumbers
Let's try to make an overview: which varieties are better for planting in polycarbonate greenhouses, and which ones in open ground? Which varieties are early ripening, and which ones ripen for a long time, but they please with the harvest in September. How to achieve a large harvest, what varieties to plant and how to avoid the most common mistakes in care - first things first.

What is important to know about the peculiarities of growing and choosing the right variety?
Cucumbers are varietal and hybrid. Varietal - grown from the seeds of a certain variety, they inherit the traits and properties of their "parents". Hybrids are produced by crossing several species. You can see the F1 icon on the hybrid seed package. The breeding is carried out with the aim of developing varieties that are more resistant to diseases, parasites, cold weather and other unfavorable conditions, as well as to increase yields and a faster ripening rate. These are the advantages of hybrids, the disadvantages include the fact that you will not get seeds from them, from which you can independently grow the same fruits.
By the type of pollination, they are divided:
- Insect-pollinated - As the name suggests, flowers are pollinated by insects (bees);
- Parthenocarpic plants are plants that can set fruit without pollination. The flowers are usually feminine. It is easy to distinguish from self-pollinated ones - there will be no seeds in their fruits. It would seem - a great option, the plants do not need pollination to set fruits. But there is a significant drawback: parthenocarpic ones do not tolerate temperature changes;
- Self-pollinated - the flowers of such plants combine both male and female characteristics, that is, they are hermaphrodites, which helps them to self-pollinate.
For planting in open ground, most often, insect-pollinated varieties are chosen, and for greenhouses - self-pollinated and parthenocarpic ones.

Differences in ripening time
- Early ripening (ripening period from the moment of planting about 40 days);
- Early ripening (ripening period is about 45 days);
- Mid-ripening (ripen on average in 50 days);
- Late ripening (ripen for 55 days or more).
It would seem that the difference in timing is small, but with a skillful approach to the selection of various varieties, you can constantly have fresh cucumbers on the table from early summer to late autumn.
- By appointment: salad, pickling and universal. Salad cucumbers have a denser skin than pickled cucumbers. Pickles are usually small in size;
- In size, they are short-fruited, medium-fruited and long-fruited. Small cucumbers mature well in the open field even in the short Siberian summer, long-fruited and medium-fruited are usually grown in polycarbonate greenhouses.

Growth features
It doesn't matter what kind of cucumber you choose to plant in the greenhouse if the plant cannot grow there due to improper conditions and insufficient care.
For growing cucumber crops in a greenhouse, it is important:
- Provide the correct temperature and avoid sudden fluctuations. The optimum temperature is 25˚s;
- It is better to water the cucumbers in the evening, keeping the soil moisture at 60%. Water for irrigation should be warm. Watering with cold water provokes the appearance of powdery mildew;
- Prepare and enrich the soil by saturating it with nitrogenous fertilizers during the period of plant growth, phosphorus-containing mixtures during flowering, and nitrogen-potassium fertilizers during the months of fruiting;
- Remove infected or diseased leaves, shoots and stems in a timely manner. One of the most common diseases of cucumbers is powdery mildew; plants are also susceptible to fungal diseases and the appearance of mold. The reason lies in insufficient ventilation of the greenhouse, over-moisture in the soil, and cold air. In addition, late-ripening varieties of cucumbers are especially susceptible to powdery mildew disease;
- Provide greenhouse ventilation. For this purpose, the walls of the polycarbonate greenhouse are equipped with vents, into which, in addition to fresh air, insects can enter and pollinate plants. Drafts should be avoided;
- Loosen and mulch the soil to avoid waterlogging and provide air access to the roots, to prevent rotting and better nutrition;
- Regularly process a polycarbonate greenhouse - clean the walls and ceiling, remove the old tops every autumn, regularly remove the topsoil, apply fungicides if diseased plants were noticed;
- Tie up and form bushes in a timely manner. Plants are best planted at a sufficient distance from each other, about 40-50 cm, ensuring also the optimal distance between the rows.

| Goosebump F1 | Early maturing, parthenocarpic. Resistant to powdery mildew and other diseases. The fruits are medium. High productivity. Poorly tolerates temperature changes | Suitable for both salting and fresh consumption |
| Benefit F1 | Early ripening, self-pollinated, fruits are medium and small, cylindrical in shape | Suitable for pickling and preserving |
| Annushka F1 | Mid-season, insect pollinated. Medium-sized, high yield. | Suitable for pickling and preserving |
| Claudia F1 | Mid-season hybrid, fruits - gherkins | Mini cucumbers are suitable for pickling, canning and use as a snack |
| Evita F1 | Early ripe, high-yielding hybrid, fruits - gherkins, very crispy, without bitterness | Ideal for canning |
| Regina F1 | Mid-early hybrid, belongs to the parthenocarpic. Disease resistant | Fresh consumption |
| Zozulya F1 | An early ripening hybrid with large fruits, one of the most popular in Russia. It is appreciated for its high yield and large fruits. Bears fruit for a long time | Fresh consumption |
| Nord-158 F1 | The hybrid is mid-ripening or even late-ripening. Resistant to most diseases | Canning |
The best varietal cucumbers
| Solar | Mid-season variety, medium-sized. High productivity. Weak point - prone to powdery mildew | Canning |
| Courage | Early maturing, insect pollinated. The fruits are not large, they are stored for a long time. Disease resistant, tolerates adverse conditions | Canning and eating in salads |
| Martha | Self-pollinated variety. Beautiful fruits, resistant to rot and various diseases. High yield | Canning |
| Erofey | Mid-season variety, the plant grows very strongly, due to which it bears fruit for a long time | Salting and fresh consumption |
| Competitor | Mid-season, insect-pollinated variety, very tasty crunchy small cucumbers | Ideal for pickling |
| Salting | An early variety, insect pollinated, tolerates common diseases and temperature extremes | As the name suggests - ideal for salting |
| Altai | An early variety, insect pollinated, tolerates common diseases and temperature extremes | Is universal |
| Reliable | An ultra-early ripening variety of zelents, early ripening excludes powdery mildew disease. Extremely unpretentious in care | Suitable for canning and fresh consumption |
Based on the foregoing, the best varieties for greenhouses have the following properties:
- Resistant to complex external factors: waterlogging, lack of ventilation, temperature changes, lack of light, etc.;
- Resistant to most diseases: gray mold, powdery mildew;
- Self-pollinating or parthenocarpic;
- Precocious - to minimize powdery mildew damage.
And finally, advice for a high yield - the more often you pick cucumbers, the more they will bear fruit!

The first task that needs to be solved, having acquired a new "Orange" or "Uralochka", and dreaming of collecting a rich harvest in it, is what varieties of cucumbers for a polycarbonate greenhouse are better to grow? How to avoid diseases, crooked and bitter fruits, various problems? And why in the same area the neighbors get the completely opposite result? In total, about 60 greenhouse species are known, and the most popular of them are hybrids. There are also special for cold regions with low light, special for sale, tender for salads and many, many other types. Read this article carefully to help you figure it all out!
A simple test: what are your expectations?
Plan the cultivation of this vegetable based on what kind of crop you want to get, how soon to harvest it and how beautiful it should be. In choosing a variety, industrial greenhouse farms, for example, are guided by how well the fruits are then stored during transportation, how much they keep their presentation. All this is rarely interesting for an ordinary summer resident, and therefore it is not worth focusing on the "most bought" ones.
When choosing seeds for planting in your personal greenhouse, proceed from what is important for you in the first place: taste, yield, salad and pickling qualities, disease resistance, ease of growing? The fact is that there are seeds specifically for greenhouse farms, which are only interested in yield and presentation, there are seeds for home cultivation, which are most suitable for salting conservation, and the market offers simply breeding novelties that can give the most unexpected result. It's simple: when buying hybrids for industrial cultivation, don't expect either taste or quality.
Which is better: conventional or hybrids?
To make you understand the notation a little, we will reveal this mysterious F1. This is how hybrids are denoted, "F" in Italian is the first letter of the word "children", and "1" is the first generation. Hybrids are always more expensive because such plants are obtained by crossing two species already.
What is good, the seeds of modern hybrids from well-known companies do not need to be disinfected or hardened - usually all this has already been done. And there is even a difference in how to form hybrids and varieties.

So, if you planted cucumbers, then when 4-5 leaves appear in plants, pinch the top. Thanks to this method, side shoots will begin to grow much more actively, which will have a good effect on the future harvest. What's the secret? There are more female flowers on the lateral processes, and it is from them that the fruits are formed. But if you are planting hybrids, then we do not touch the central stem, and we pinch only the lateral stepsons. We leave two leaves on the first, four on the second, up to 6 on the third, and up to 8 on the fourth.
But know that there is no point in collecting seeds from hybrids for subsequent planting - you will have several plants that are unlike each other at once, which will either give a poor harvest, or even leave without it.

What are the greenhouse cucumbers?
The varieties are divided into greenhouse and open field varieties. Many of them are suitable for both those and those conditions, but some types have a strict purpose. So, for open beds, hybrids are usually bred that are well adapted to the wind and low air humidity. And for greenhouses, seeds are well processed to protect against diseases and pests, which are especially fond of a humid and hot microclimate.
In addition, those that must grow in direct sunlight in the seven winds are completely unadapted to the difficulties of closed wet ground and quickly begin to hurt.
For salad, pickling or sale?
According to economically useful characteristics, varieties are divided into pickling, salad and universal. Salad is not salted, because they lose their properties, and fresh pickling is a little rough.
The sweetest and most tender, ideal for salad, are Armenian long vegetables of an unusual yellow-green color. The Dutch also have a wonderful taste, with a thin skin and no coarse seeds. Lemon cucumbers, yellow, round, sweet and seedless, are also gaining popularity. But the Persian ones are like cybri, delicate in taste and generally without crunch.
Early, super early or late?
So, early and super early are those that are intended for a quick harvest.
According to the ripening period, there are the following:
- The early ones, which begin to bear fruit as early as 40-45 days.
- Medium early - 46-50 days.
- Mid-season - 51-56 days.
- Late ripening - bear fruit after 56 days.
And usually varieties with different ripening rates are planted in the greenhouse - in order to harvest as long as possible.
What will we pollinate with?
According to the method of pollination, the varieties, like hybrids, are bee-pollinated and parthenocarpic, i.e. self-pollinated. For the first, pollinating insects (bees, bumblebees) are needed, or you will have to wield a brush yourself, and in the second, both the pistil and the stamen are in the same flower:
Parthenocarp is the ability of a plant to set its fruits without pollination. The term "self-pollinating" is not entirely correct for them: such cucumbers are not pollinated at all, they develop ovaries on their own. This is a valuable property for greenhouse vegetables, especially winter ones. Even by the fruit, you can easily recognize these varieties - they do not contain the seeds at all, which you usually see when cutting. Although some parthenocarpic species have few seeds, in some part of the fruit, which makes it pot-bellied or pear-shaped.
Of the parthenocarpic species, which all flowers produce with an ovary, the Dutch "Hector" is considered the best. The fruits do not turn yellow, do not outgrow, grow small and the bush itself does not require a garter.
For the greenhouse, of course, self-pollinated varieties are more suitable, because there is less trouble with them. But many adherents of "everything natural and natural" are sometimes ready to walk day and night with brushes, just to grow a "natural" variety. And, I must say, with a competent approach, the harvest will turn out to be much larger and better than any scientist agronomist could have planned for his androgynous brainchild.
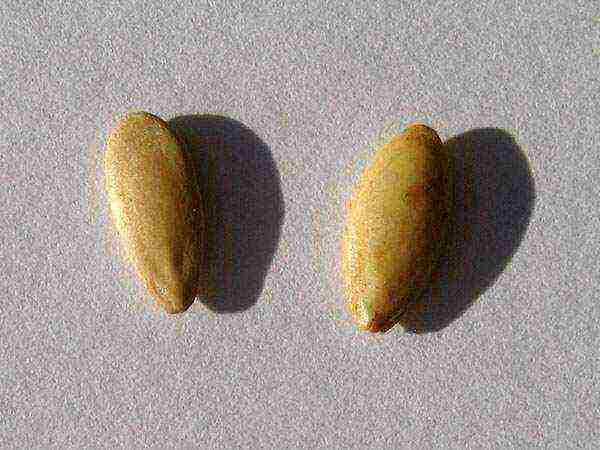
Experienced gardeners can even distinguish between male and female seeds. So, the seed of the boy-cucumber is flat on one side, and there is a slight break in only one plane, while the woman has a break in the edges on both sides, and the seed itself looks a little pot-bellied.
It is possible to plant different varieties for greenhouses, but they must all be either parthenocarpic or bee-pollinated. Note: some authors of books on gardening even recommend mixing these two species, some are categorically against, because if parthenocarpic ones receive stronger pollen from pollinated ones, then the fruits will be crumpled (blown away from the uneven filling with seeds).
Shade tolerance for winter cultivation
Distinguish between fruits and shade tolerance. So, if you purchase hybrids for the spring-summer period, such cucumbers are photophilous and will bear fruit well only in good sunlight. But, if some outbuildings or trees give shade, there will be little fruit.
But winter ones tolerate shade well and feel quite comfortable in a greenhouse even in January, but there is no point in sowing them in the middle of summer: firstly, the fruits will be late, and secondly, such varieties are in no way protected from typical summer diseases.
Cold resistance and hardening
There are differences in cold resistance between cucumbers. And this is already one of the most important indicators for different regions, because there is a difference, do you grow vegetables at the equator or in Siberia? Even with good thermal insulation in the greenhouse, plants can catch colds - in the morning, for example, when cold dew and condensation accumulate on the plastic wrap. Therefore, at the end of summer, only cold-resistant species should be planted, which are more protected from viral diseases (with hypothermia, a physiological weakening occurs in plants).
Productivity and number of ovaries
Recently, varieties with the so-called bunch fruiting have begun to be produced more and more often, when several ovaries develop in the leaf axil at once. These are short-fruited species with particularly intense fruiting, which is important to properly care for. What is their advantage? In a huge number of small cucumbers, which are great for pickling.
Plants also differ in such a feature as branching - the intensity of the growth of lateral shoots. There are three groups of them: with good branching, with moderate and weak. When good, lateral shoots appear from almost every node from the main stem, they are long and need to be pinched. With moderate branching, there are many side shoots, but they are short. And cucumbers with weak branching form very few lateral shoots, all of them with short internodes, "bouquet". But remember that the intensity of branching depends not only on genetics, but also on external conditions. So, at low temperatures and shading, side shoots grow weaker, and in sunny weather and with generous watering, they are already bolder.
If you decide which vegetables are best to plant in your own greenhouse so as to get the maximum yield in a short time, literally in 3-4 weeks, then take weakly branching hybrids. Only they need to be planted densely, 5-6 plants per square meter, instead of the standard 2-3. If the crop is needed within one month, then plants with moderate branching are suitable for you. But for salting, when the sugars in the fruits are the most, hybrids with rich branching are suitable for you.
Another difference is the duration of fruiting. If you grow for sale and it is important for you to get a good harvest in a short period, then buy seeds of early ripening sprinter hybrids, which will give most of the fruits in the first month. But in order to regularly collect small cucumbers for pickling and not rush anywhere, use hybrids with the so-called extended fruiting period.
What are the manufacturers talking about?
When buying seeds, pay special attention to the information from the manufacturer, which is usually indicated on the package.
When choosing seed bags for the greenhouse, pay attention to the image of the fruit itself. Namely - on the thorns. Thorns can be dense or almost absent, thorns can be small or large enough. And even different in color - white, black and brown.
- Cucumbers with white thorns are salad-type fruits, they are not used for pickling. And it is they who can most often be seen on the shelves, and at any time of the year.
- Brown or black thorns are pickled vegetables, sometimes universal. They are good both fresh and salted and preserved.But, unlike white thorns, they overripe faster, also quickly turn yellow and become tasteless.
By the way, it is not recommended to soak the seeds processed at the plant, so as not to wash off the color protection from them. But many summer residents still break the rule by using simple wet gauze that does not wash anything. After two days, a tail just appears on the seeds, and the color remains the same.
A real "Russian" cucumber: in pimples and without bitterness!
Interestingly, in Russia they really love cucumbers with thorns, considering them "real". But in Europe, fruits with a smooth skin are preferred, while "pimples" are called cucumbers "in a Russian shirt."
Where does the bitterness come from in the fruit? This is the merit of a special substance - the alkaloid cucurbitacin, which is most actively produced in dry hot weather, especially if you did not water the plants much. Sometimes the soil is also to blame, or rather its composition. In simple terms, bitterness accumulates under the green skin if the active vegetation process slows down and the fruits stop growing within a few days.
Most cucurbitacin accumulates in dark green fruits. Although sometimes bitter cucumbers are grown on purpose - according to some sources, such cucumbers kill cancer cells in the body. If you need just such a crop, take not the newest species and just water less. Indeed, thanks to breeders, modern varieties have practically lost the ability to accumulate cucurbitacin, and therefore are not bitter.
Popular varieties in Russia
There are a lot of them, but we will note those that are most popular today:
- If you grow vegetables for sale, then "Courage" is 100% suitable for you, thanks to its marketable appearance and good harvest.
- Also one of the most popular in Russia - "Emelya". Yielding, strong, good in preservation and salting.
- One of the most beloved among modern summer residents is "Courage". The harvest is good, it almost does not get sick.
- The fruits of "Connie" are not prickly, without bitterness, have a good presentation and give an excellent harvest.
- Summer residents also speak well of the Claudia variety, which is ideal for growing in a small greenhouse.
- The famous "Athlete" is famous for its rich harvest and wonderful taste, but only bees (or you by hand) can pollinate it.
- Amur has a delicate sweet taste, grows well in a greenhouse, and Malyshka has a wonderful aroma.
Exotic, or how to surprise your neighbors
But if you dream of experimenting, you can grow white cucumbers in your own greenhouse. These are unusual hybrids that are gradually gaining in popularity. One of them is the Bride F1 variety, whose fruits are tender, fragrant, and behave well in conservation.
Many beginners in this business are also interested in the "Chinese" fruits. Note that in the greenhouse they do not always grow even, the presentation is almost completely absent, but the taste will definitely please. The best variety is Peking, which produces tender juicy fruits with small seeds. This variety bears fruit until the very frost, even in an unheated structure.
In any case, when choosing, give preference to varieties that are designed specifically for your region. These are more designed for specific weather conditions, are resistant to local diseases and bear fruit on time.
Same variety and different harvest?
The most important first step is choosing good seeds. In fact, this is another task, because it is important to acquire that planting material that:
- Suitable for growing in a greenhouse.
- Designed for your region.
- Will give a crop of the desired quality and presentation.
- It is not a fake, impregnated with chemicals hazardous to health.
- Possesses high germination and disease resistance.
And finally, the last thing. You may have already noticed that the same variety can be found in a variety of packages.We definitely advise you not to purchase ordinary pre-packaged transparent bags with inserts, because the simpler the packaging itself, the easier it is to stamp fake substandard material somewhere in the basement. But serious manufacturing firms, which value their reputation, produce seeds of a different quality, and the packages with them are recognizable, have different degrees of protection against counterfeiting and are more expensive. In addition: poor quality seeds sold may also be contaminated.
Got good seeds and exactly the ones you wanted? Then let's go!
Rate the article:
(6 votes, average: 4.5 out of 5)
Growing cucumbers is not difficult, but troublesome. Especially those who plant a vegetable in a greenhouse will have to tinker with. You can get a rich harvest, taking into account all factors of the development of the culture and following the recommendations for its cultivation. It is also important to make the right choice of cucumber varieties for a polycarbonate greenhouse. Today there are a great many of them. Therefore, every gardener will find what he likes.
Criterias of choice
Most often, hybrids are grown in protected ground conditions. It is easy to distinguish a hybrid from a variety. The hybrid seed is labeled "F1" on the package. This code stands for "first generation hybrid". It is impossible to get seeds from such plants or prepare them yourself. They have to be bought annually. What varieties of cucumbers are there for growing in a greenhouse? And how do you choose the best ones for yourself?
To choose seeds for growing a vegetable correctly, you need to pay attention to a number of factors: seasonality, pollination, cold resistance and yield of the variety. And most importantly, the variety must be ideal for the area of its cultivation. It is better that it was bred there. Only by focusing on these criteria can you find a hybrid that is suitable for certain growing conditions and satisfies the wishes of everyone.
Seasonality
All greenhouse varieties of cucumbers are divided into winter-spring, spring-summer and summer-autumn. The first group of plants gives an excellent yield and is independent of the quality and quantity of light. True, such varieties do not bear fruit for long. Also, vegetables of this group are susceptible to diseases that are common in the warm season. Therefore, it is not recommended to plant such varieties in summer. After all, the crop from plants can not be harvested at all.
Vegetables of the spring-summer type are unpretentious to growing conditions, and the yield is good. The culture of the group practically does not get sick and tolerates low temperatures well. In the bulk, such cucumbers love light and are practically unstable to shade.
Summer-autumn vegetables are the most popular among gardeners. They bear fruit for a long time, bringing a good harvest to the owners. And also do not require a lot of light.
Pollination
Cucumbers that are pollinated by insects can only be grown in professional greenhouses. For greenhouses built by amateurs, it is better to use self-pollinating hybrids. The best of them are Zozulya F1, Bogatyrskaya Force F1, Courage F1, Tournament F1, Sultan F1. Most of the vegetables intended for indoor growing belong to this group.
Young sprouts of such self-pollinating varieties grow on their own, without requiring careful care and specific additional actions of the gardener. There are varieties that partially self-pollinate. They can also be grown in greenhouses, but only with specific care.
Sometimes gardeners still grow cucumbers indoors, which are pollinated by insects. Summer residents believe that the fruits obtained through pollination of the plant by bees are more juicy and tasty. But in order to grow cucumbers of such varieties, it is necessary to lure insects into the greenhouse. To do this, it is worth spraying the bushes with a sweet solution.
It will also be effective to install a bucket of flowers at the entrance.They can also be sprinkled with a sweet solution. Insects are also lured by pieces of sugar or jam spread around the greenhouse. But you shouldn't do that, because the delicacies will "overshadow" the cucumber flowers, and the bees will lose interest in them. What varieties pollinated by bees are applicable in a polycarbonate greenhouse? The best of them are the mid-season Springs F1 and Libella F1.
Having planted early varieties of cucumbers in a heated greenhouse at the end of winter, the first harvest can already be harvested in late spring. But for this you need to use winter hybrids, for example, Blagovest. These vegetables are not limited in growth and are resistant to many diseases, in particular, powdery mildew. In shape, the fruit resembles a cylinder, covered with medium "pimples". The mass of one cucumber is more than 80 g. The variety is pollinated independently.
Cold resistance and hardening
Cucumber hybrids and varieties differ in terms of cold resistance. This indicator is very important for certain growing conditions. Growing cucumbers in the northern regions of the country or in the southern regions is a significant difference. Even if the greenhouse is well insulated and heated, the plants can become overcooled.
For example, in the morning, cold dew is formed under the cellophane, flowing down onto the plants. Therefore, at the end of summer, it is necessary to grow varieties that are resistant to cold weather and have natural protection against diseases. After all, hypothermia significantly affects the state of culture.
Yield
Today, varieties of cucumbers appear that bear fruit in a bunch, namely, at the base of the leaf, several ovaries appear at once. This is how varieties with short vegetables bear fruit. But they need to be carefully and carefully looked after. The advantage of such hybrids is in the harvest of small gherkins, ideal for pickling and preservation.
There are different types of vegetables and the level of branching: high, moderate and low. Good branching implies the emergence of lateral stems from each node. The shoots are long, so you need to pinch them. Medium branching - the appearance of a large number of short lateral stems. The low level of branching provides few lateral processes with short internodes.
It should be noted that the level of branching is determined not so much by the genetic characteristics of plants as by the conditions of their growth and development. Thus, low temperature and lack of light interferes with the growth of side shoots, and warm weather and sufficient watering promote it.
If your goal is to get a large harvest in a small amount of time, it is better to get cucumbers with little branching. It should be planted often, in the amount of 5-6 pieces per square meter. Need a month's harvest? Grow medium-branch cucumbers. Pickling cucumbers that do not contain a large amount of saccharides are vegetables with good branching of the bush.
The types of cucumbers differ in the length of the harvest period. Large yields in a small amount of time will give sprinter hybrids. Hybrids with an "extended" fruiting period will allow you to regularly collect gherkins.
Video "The best varieties of cucumbers for 2017"
The video tells about the best varieties of cucumbers for planting in a greenhouse and open ground for 2017, and also explains in detail the criteria for their selection.
Exotic varieties
Today there is a wide variety of varieties of almost all vegetables, including cucumbers. These are not only early types of culture, but also exotic ones, which have become extremely popular today. Therefore, if the soul wants experiments and admiration of neighbors, there is a chance to achieve all this.
For example, in a greenhouse, you can harvest white cucumbers. Such fruits give hybrids, in particular, the F1 Bride. The fruits of this variety are juicy and aromatic, they are also ideal for conservation.
There are also so-called "Chinese" vegetables, the fruits of which are uneven, but extremely tasty. The Beijing variety is famous for its juicy cucumbers with small seeds.The culture of this species bears fruit even in cool greenhouse conditions without heating.
The best varieties with a touch of exotic for growing in greenhouses are ABC, Silver Melon and F1 Baloven. The first hybrid is popular due to its bunchy fruiting and, as a result, high yields. The fruits ripen quickly and are resistant to most diseases. The taste of the hybrid cucumbers is wonderful. Fruits can be salted using the barrel method.
All exotic lovers will appreciate the taste of Armenian cucumber. The fruit of the silver melon (the second name of the variety) looks like a vegetable marrow. The leaves of the culture are similar to pumpkin leaves. The culture got its name because of the light aroma of melon in the fruit.
The best varieties of exotic cucumbers include F1 Pet. He forms ovaries in a bunch, and his cucumbers are not bitter.
Many gardeners who love everything unusual grow Golden Dragon Egg cucumbers. It has high yields and yellow fruits. They taste like fruit.
So, there are many varieties of cucumber to grow in a greenhouse. You can choose any. It is worth remembering, however, that the best hybrids are the ones for your region. They adapt well to the climate, are resistant to local diseases and give a rich, and most importantly, timely harvest.
Video "Growing cucumbers in a greenhouse is very easy"
In this video, we will talk about the technology of growing cucumbers in a polycarbonate greenhouse, as well as how to get the maximum yield with a minimum of effort?


