Content
- 1 Types of aquarium plants
- 2 Description of popular plants
- 3 How to plant aquarium plants correctly?
- 4 Diseases and care
- 5 Blixa dwarf or Japanese (Blyxa japonica)
- 6 Nymphea or tiger water lily (Nympheae lotus)
- 7 Nymphoides Flipper Taiwan
- 8 Banana aquatic, Banana plant (Nymphoides aquatica)
- 9 Hemianthus dwarf "Cuba" (Hemianthus callitrichoides "Cuba")
- 10 Micrantemum few-flowered (Micranthemum Micranthemoides or Hemianthus micranthemoides)
- 11 Pogostemon Helferi
- 12 Vallisneria
- 13 Vallisneria spiral (Vallisneria spiralis)
- 14 Aponogeton
- 15 Aponogeton wavy, viviparous (Aponogeton stachysporus, undulatus)
- 16 Cryptocoryne
- 17 Bacopa
- 18 Limnophila (Ambulia) (Limnophila)
- 19 Sagittaria or Arrowhead (Sagittaria)
- 20 Sagittaria broadleaf or arrowhead broadleaf
- 21 Sagittarius dwarf or arrowhead dwarf
- 22 Rotala rotundifolia or Rotala indica
- 23 Cyperus helferi
- 24 Eichornia azure or Eichornia aquatic (Eichhornia azurea, eichhornia aquatica)
- 25 Anubias
- 26 Echinodorus
I will write in simple language so that it is clear to those who have just bought an aquarium and want to see growing plants in it, and not quietly fading sprouts of a seemingly healthy bush bought, so I will not get into the endless terminology and description of the substances required for plants.
Very often I see the post: "- Tell me, what kind of seaweed I bought in the store?" Here you must immediately remember that algae is something that the aquarist tirelessly tries to get rid of, all algae belong to lower plants, for example, blue-green algae, brown algae, green algae, etc.
This is all that grows on the glass of the aquarium, stones and grottoes, green threads throughout the aquarium and the most unpleasant thing - fouling on plants, the plant loses its appearance, withers and may die.
Consider the standard case of a beginner, fish, grottoes, stones and finally, plants are bought (well, or already everything is bought plants), a few bushes are brought home, planted in an aquarium, after a few days of observation the question arises, why does not it grow ?? Unfortunately, after several attempts, many give up trying to settle live plants and do not try to understand the essence of the problem deeper, and it is not so difficult to create a garden of various plants in an aquarium (I do not mean Takashi Amano's aquarium - this is a whole art requiring deeper knowledge)
So, what you need to immediately understand is that aquatic plants, as well as plants that live outside the water, for example in a pot on a windowsill, need food and light, and not just water and stones or clean sand. In addition, the temperature of the water, soil, chemical composition - the amount of dissolved mineral and organic substances, the pH value (pH) and many others are important. Most plants prefer soft or medium hard water with neutral pH (7). Here, in order:
LIGHT: Without light in the aquarium, nothing will work! If you buy an aquarium with a lid, there are already built-in lamps, but, alas, this light is often not enough for growing plants. For plants, the light power for standard aquariums should be approximately 0.5-1.0 W / L for fluorescent lamps (I take fluorescent lamps as an example, since the most common), here you need to understand 0.5 W / L - for not very demanding light of plants, 1 w / l - for more whimsical and light-loving plants. It must be remembered that passing through the water column, there is a great loss of light, therefore, the higher the aquarium, the more difficult it is to illuminate it. To ensure the normal life of plants, you need the entire visible light spectrum, in an aquarium this is difficult to achieve. The most important role is played by two relatively narrow spectral ranges - blue-green and red, from which you need to build on when choosing lighting. Now there is a huge selection of various lamps. For freshwater aquariums, special lamps are expensive, but they were specially created with a spectrum for plants - there is even a full solar spectrum. You can also illuminate with ordinary inexpensive fluorescent lamps, you can combine ordinary lamps with special lamps, for example, one Grolux lamp, for the red spectrum of plants (if this spectrum is not enough red, the plants will not be saturated with red, but most likely will be either green or pale orange) and one usual one, with marking 865 (marking “865” indicates a color rendering index of 80 Ra, and a color temperature of 6500 K - indicate the color temperature of the lamp, the lower it is, the yellower the light, let's say 3000K will turn yellow, like incandescent lamps, 10000K will be used in marine aquariums with a blue tint).
If you install reflectors, you can noticeably increase the lighting in the aquarium. In general, you can write more than one page about light, but I promised briefly, the main thing is to understand that it is important for plants and you should pay attention to what kind of light you have.
FOOD: Do not underestimate the role of nutrition for aquarium plants, their lack leads to stunted growth, death and yellowing of leaves, curvature of the plant, etc.
Plants are able to actively extract the substances they need from the external environment. Aquatic plants are more dependent on the environment than terrestrial plants, which receive the bulk of their nutrition from the soil, since, unlike them, they absorb nutrients from their entire surface. Plants need macronutrients (nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus, chlorine, silicon, potassium, sodium, calcium, magnesium) and microelements (boron, zinc, copper, manganese, iron, molybdenum, cobalt, etc.). Some of them accumulate in the aquarium as a result of the vital activity of fish and other inhabitants, some come with fresh water when changing. But this does not exhaust the entire list of required connections. In such a situation, fertilizers of which in stores are also an impressive amount will help to solve the problem of deficit. Perhaps, you can make fertilizer yourself, but you already need to study this topic in more detail and it will not be very small. It should be noted that the use of fertilizers is advisable if you have a sufficient number of plants in the aquarium, and not 3 bushes. Excessive nutrients can lead to algae growth in the aquarium.
PRIMING: The soil is not only a decorative element, but also serves for the rooting of plants and a habitat for bacteria, which in turn maintain the biological balance in the aquarium, like plants that process fish waste products. The soil should not be too fine, but not too coarse, about 2-5 mm. Since most plants love soft water, it is advisable that the soil does not contain rocks such as marble, coral chips, limestone - these stones enrich the water with dissolved calcium and magnesium salts and make it hard, and the constantly growing GH and KH values will not be appreciated by plants. The shops now have a large selection of primers of all colors and shapes, but the painted primer will discolor over time and the paint will come off. I like the natural color of the soil, I don't really like colored (blue, red ...) soils - it's not natural, and the design looks better closer to a natural aquarium. There is also a nutritious soil, just for the herbalist, if there is an opportunity and it is planned to plant most of the aquarium with plants, it will be a good idea to use it.
I would also like to say about the use of CO2 in an aquarium - carbon dioxide, this is the most important food for plants.The breath of fish is sometimes not enough to saturate many plants with CO2, so you have to let it in additionally, they do this mainly by installing a balloon system with CO2 and dissolving it in water through various diffusers, this is a rather expensive method, but a stable supply of CO2 for several months. More budgetary is obtaining CO2 by fermentation (yeast + water + sugar) or by a chemical reaction (soda + citric acid), knead it in a bottle and bring it to the aquarium with a tube, where, using the so-called bell (an inverted glass in which carbon dioxide is collected ) gradually dissolves in water CO2. This method has drawbacks - it is a short fermentation reaction of 1.5-2 weeks, the reaction is unstable, at first there is a violent evolution of gas, but every day it will be less. You need to be careful when using CO2, because if during the day the plants absorb it and release oxygen, then at night everything is exactly the opposite, and this can lead to the fact that the fish may not have enough oxygen until the morning, so you should take care of additional aeration of the aquarium at night ... CO2 also lowers the pH in the aquarium, which is good if you have a high one, but you should not overdo it with the supply, constant fluctuations in the pH value have a bad effect on the inhabitants, therefore, a stable and in the right amount supply of CO2 is good. Carbon dioxide dissolves easily in water, but it also erodes quickly, you should not create unnecessary currents on the water surface. And again, it is worth thinking about saturating the water with carbon dioxide if you have enough light, fertilizers for plants (when CO2 is supplied, nutrients are consumed much faster) and of course there should be a lot of plants themselves, and not a Vallisneria bush with a twig kabombs, otherwise you can only make it worse.
FISH and PLANTS: think carefully about what kind of aquarium you want to see at home, you should not try to settle many fish and many plants in one aquarium, fertilizers and CO2 can negatively affect fish, and most fish, in turn, are incompatible with plants, so you should think before you buy fish from the herbalist if it spoils it. Therefore, you need to decide what you want more on that and focus on it.
The above could be described in much more detail, but I did not have such a task, this is an article for those who have just started growing something in their aquarium, you need to understand that if you want to see what will be in your "reservoir" pleasing the eye will have to make at least some effort for this.
In conclusion, I want to say that if you strive for the correct ratio of all elements - light, fertilizer, CO2, you will eventually get a good result that will delight you with a beautiful underwater garden.
I found this article on the aquarists forum and, I hope, it will definitely come in handy for someone!
Best wishes for your creativity!

Beginner aquarists who decide to practice
growing plants , are often asked questions on the forums: how to apply fertilizers, how to supply CO2, how to plant, how to prune, what to do with black bloom on the leaves, etc. and so on ... They are usually advised to "achieve balance" ... And this is certainly true, but all this general words, there is no instruction such as: "How to achieve balance in the aquarium, step by step ..." Recently, I am also often asked about similar topics and the idea came to me to write such an instruction based on my own experience. Why not? After all, we all launch new banks and use the same launch schemes and parole.
In order to immediately avoid the wrath of the great gurus, who are always and everywhere, I will give a photo of my aquarium (at the bottom of the article) and how it looks at the time of this writing. Since the launch, all this has gone through all types of algae without chemistry and technical means such as CO2 cylinders, external filters, UV lamps ... Ordinary T4 6400k daylight lamps stand instead of the standard ones, as I wrote earlier ... No super-spectra and similar super-means for super loot no!
My instruction will most likely turn out to be multivariate, and the number of options will depend on the goals of the aquarist and the initial conditions.However, it seemed to me possible to average it, so to speak)) Therefore, I decided not to take the initial conditions into account at all! No, no, I'm not feverish and I'm not delirious)) But since we need to achieve a balance, it means there is still no balance ... which means that the initial conditions are as they are. Well, I think it will be clearer further ...
Perhaps I'll start with the simplest option: the aquarist grows plants for himself and the growth rate of plants is not important for him. If only it was clean and without algae. A gardener-aquarist does not grow plants for sale in bulk, does not cut them after three days and does not have technical devices such as CO2 installations and expensive parole, which, by the way, for example, I did not need at all. As I already wrote, I use my self)
So the first option and let's call it:
Growing plants in the simplest way.
We have an aquarium 1 or 6 months old with a flip-flop, a beard and black bloom on the leaves, the water is clean but periodically come out, green threads, sometimes blue-green (for example, in the ground or at the roots) ... The light in the aquarium is just very important. LIGHT AND NOT SUPER LAMPS! For example, I have ordinary fluorescent lamps, but: 100 watts per 140 liters ...
Let's start, as it was previously suggested, with a change of water. But first, let's take a couple of steps. To do this, we need clay balls and udo, which are described by me below.
Step one: We plant the aquarium tightly with plants such as valisneria, hornwort, hygrophila and, for example, rotal indica ... In short, we add cheap but very unpretentious plants that grow quickly and are designed to consume excess nitrates and phosphates. Plants are selected by me so that there are both lovers of nitrates (hornwort) and big lovers of phosphates, or rather quickly absorbing them - as a rule, plants actively give aerial roots and are ready to eat not only leaves ... By the way, contrary to popular belief, it perfectly eats both nitrates and phosphates Well, this is so, by the way I had to ... The main problem is the amount of fish and organic matter in the water. therefore
Step two: We cultivate in the ground, EXACTLY IN THE GROUND, the culture of nitrobacteria. I would recommend Nitrivek, I use it myself when starting up .. Why in the ground? Because since the water is full of organic matter, the filter (simple, with a sponge) needs to be washed often! Once a week and thoroughly.
We put clay balls in the soil to the plants, which you can make yourself, there would be clay. This is necessary in order to make less udo by water ... After feeding, we begin to change the water.
The first week - every other day by 30%. The second - in two days by 30%, the third week - once by 50%. Then change the water weekly by 25 - 30%. And it is important: we try to keep the temperature, if possible, not higher than 25 degrees! The fact is that at low temperatures, plants that have not yet started growing properly will have the advantage of supplying nutrients over algae. At higher temperatures, plants are less likely to grow unless they are already actively growing. Algae will start much faster!
At this stage, we are not pouring any udo at all! We only rely on fish. The number of fish can be calculated like this.
Optimally 7cm for 10-12 liters of water. Those, if you have a can of 120 liters, then it is advisable to have no more than 12 fish there, the size of which is about 7 cm ... This is of course roughly and rough, but the principle is clear, fish is the best producer of fertilizers, but also organics, and we need it in such a proportion that would have time to decompose and feed our grass. The task is for bacteria to quickly decompose organic matter and plants have time to assimilate it faster than algae.
Step three: We take a time out ... About 2-3 weeks ... We change the water and don't do anything .... The aquarium is a self-regulating system .. Clay does its job in the soil .. We do not interfere and wait for the biological balance to manifest itself, and this will happen in about 2-3 weeks. How to see it? Just.You will see that the filter has become clogged more slowly, the water is always transparent, and you wipe the glass less and less often from plaque ... and ... you cut the rotala once every 10 days and the valsnria begins to spread its processes along the bank ... All this is still not in perfect condition, but you can see that the life of the grass began to spread throughout the volume ..
Now we are one step away from what we want !!!
Step four: This step depends on the results of the previous steps. Namely:
If algae disappear in the aquarium, and the plants grow, then you should not give extra udo .. In general, you do not need to climb into the biosystem while it heals itself! Then, when cleanliness comes, you feed the plants on the leaf and improve their size, but for now just watch the miracle: everything grows by itself! This is really a miracle, nature regulates itself very effectively without our intervention and chemistry ... You can add more complex and beautiful plants)
If the cleanliness has already come, then with a planned change of water, we begin feeding with sammes. Very careful! Macro and micro + separately iron citrate. Slowly. We continue to keep the temperature not high. If the temperature is reduced to 23-24 gr. then you can increase the number of fish by 50 percent! Temperature and light are the most important factors, and in my opinion, temperature is more important.
That's all! It's simple. but there are small additions.
- if the aquarium is young, less than 6 months old, the tighter you plant it, the better.
- if the jar is older than 6 months, then the stocking density will affect the amount of CO2 in the water, the rate of UDO absorption and metabolism, and it can be changed arbitrarily by changing the amount of UDO and the amount of CO2, respectively.
- if the light in the aquarium is less than 0.6 watts per liter, then CO2 is not needed at all when planting 30% grass. If the light is brighter, then either give CO2 mash or tighten the landing.
- I will separately note the usefulness of settling cherry shrimps, Beeline snails, etc. into the aquarium. Organic matter will become several times less and black plaque, respectively, too. With thick grass, cherries will survive even with barbs and cichlids - it's proven, I'll publish the video soon.
In the next article, I will describe in more detail and accurately the schedule and amount of making parole by me personally. How much CO2 to give and more about the temperature ... and maybe something else))








The aquarium is a corner of wildlife in your home. The correct selection of fish and other inhabitants is important. In this review, we will tell you about which plants to choose for your aquarium and briefly describe the main aspects of care.
Types of aquarium plants
The following types of vegetation in the aquarium can be distinguished:
- mosses and ferns - there are no full-fledged roots and leaves, there is no flowering, no care is needed, they grow in different conditions, are unpretentious, they perfectly decorate the aquarium (azolla, bolbitis, cladofora);
- stem plants - are distinguished by the presence of a trunk (alternantera, tradescantia, rotala);
- rosette plants - do not have a stem, foliage grows from one point, forming a rosette (Cryptocoryne, Echinodorus, Vallisneria);
- ground plants - planted in the ground (hygrophila, kabomba, echinodorus);
- unpretentious plants - require a minimum of attention (nayas, hornwort, elodea);
- floating plants - float freely on the surface (duckweed, salvinia, marsh flower);
- ground cover plants - very undersized up to 10 cm, their shoots and roots beautifully envelop driftwood and stones, decorate the facade (riccia, sitnyag, hemiantus cuba);
- fast-growing plants - they grow rapidly, absorb organic and inorganic substances, enliven the landscape (ludwigia, lemongrass, ambulia);
- meristemic plants - they are obtained through microcloning, they are identical to each other, not susceptible to snails, algae and fungi.
Description of popular plants
There are many options for aquarium plants. Here is a small overview of the most common ones.
Schisandra
The plant smells like lemon, grows to a large size, has pointed leaves, is sensitive to chemicals in the water, requires a weekly replacement of a quarter of the water and the introduction of mineral fertilizing. Lemongrass grows in nutritious silted soil, has a strong root system, needs intense lighting and propagates by cuttings.
lemongrass
Hornwort
This dense perennial plant decorates the aquarium, acts as a shelter for fish, and filters water from harmful substances. Hornwort is characterized by long, hard stems, it has no roots, the alga grows a meter in a month, floats in the upper and middle layers of water, has small inflorescences and fruits.
hornwort
Elodea
Aquatic Elodea reproduces successfully, grows rapidly almost all year long, requires a lot of light and cool water, does well in all but tropical aquariums, can attach to soil or swim freely. The plant resembles a tropical liana, requires pruning and minimal maintenance, has a long stem with bright green translucent leaves.
elodea
Anubias
Anubias is a tropical aquatic evergreen with a thick creeping root, rarely blooms in an aquarium, loves nutritious soil and shade. The grass requires a lot of organic matter, grows slowly, has hard, rounded leaves, becomes overgrown with parasites in bright light, multiplies by dividing roots and seeds.
anubias
Cryptocoryne
The Cryptocoryne plant is often found in home aquariums, there are many species that are difficult to distinguish from each other, the flowers are quite beautiful and rarely appear. It is possible to breed in dimly lit aquariums without supplying carbon dioxide, food comes from the ground without additional feeding.
cryptocoryne
Echinodorus
Aquarium lovers prefer Echinodorus for its high adaptability in different conditions, there are excellent decorative properties, most species have roots, petiole leaves and are arranged in a spiral. The plant requires bright light, often grows overgrown with algae, needs carbon dioxide feeding.
echinodorus
Kabomba
You can grow a kabomba in different aquariums, it is very beautiful, it takes root pretty well almost everywhere, it is unpretentious and does not create problems, which is why aquarists love it so much. This plant has a high growth rate, prefers a moderately warm or tropical environment and has a pronounced effect on the metabolic processes of the habitat.
kabomba
Nymphea
Nymphaea has not thick, but strong roots, is in demand due to its beautiful flowering, large heart-shaped leaves, it can only be grown in spacious aquariums. In the soil where the plant is located, there should be enough nutrient organic substances, for example, peat, charcoal, clay acts as top dressing.
nymphea
Riccia
Water moss is generally unpretentious, but it grows better in intense light, it floats in water of any temperature, likes frequent water changes. Riccia has stems filled with air and collected in rosettes, does not require fertilizing with minerals.
Riccia
How to plant aquarium plants correctly?
Priming
Aquarium soil is neutral, with a nutritious substrate, granular, earthy. This product can be natural, such as crushed stone, sand, pebbles and stones. Also on sale you can see the soil obtained after processing natural raw materials with chemicals. And one more group is artificially produced materials.
Most of the plants are attached to the ground, only a few are buoyant. The top layer should be fine gravel or sand. The substrate is selected based on the wishes of the breeder. For an aquarium, gravel with fractions of 3-4 mm and river sand with fractions of 1.5-2 mm are optimal. Fine sand such as sea sand or quartz is not appropriate.
The soil should have normal porosity, an appropriate nutrient medium and as little limestone as possible. Dark color and absence of harmful impurities are welcomed.
Before placing the soil in the tank, it is washed and boiled for about 15 cans with stirring. Alternatively, you can use a warm solution with 25% hydrochloric acid for preparation, this allows you to fill the material with potassium useful for plants. After such treatment, a triple rinsing is required.
There are plants that can only be found in soft water. The soil is suitable for them, cleared of magnesium and potassium salts. This is done with sulfuric acid. When the aquarium vegetation requires an anaerobic environment, then planting is done in clay pots. A good primer is usually unpainted. Most plants are comfortable with a soil thickness of 5-7 cm.
The soil collects bryozoans, fungi and bacteria on its surface. It promotes the processing of fish waste products, filters water.
For planting plants, it is preferable to use natural soil, for example, small stones, quartz and quartz sand, lava, volcanic sand, pebbles. Application possible without treatment. This material lacks nutrients. Plants planted in such soil give flowering after six months. At this time, enough silt will appear.
It is undesirable to use glass, expanded clay, layered soil, garden soil for planting plants. Artificial multi-colored shop material made of plastic and glass is appropriate.
Fertilizer
Aquatic plants will not do well with regular garden flower food. Against the background of nitrogen deficiency, aquarium plants suffer - their leaves are destroyed and fall off. When there is not enough potassium, brown spots and holes appear on the foliage.
With iron deficiency, intense yellowing of the leaves is observed. Calcium and boron are also important for plants; without these elements, deformation of plants occurs, small leaves that turn white at the edges appear.
Fertilizers are applied to the water in strict accordance with the attached instructions. The most significant factors are the volume and types of vegetation, carbon dioxide nutrition, the nature of lighting, and the properties of water. Novice aquarium enthusiasts will not be mistaken if they start with ready-made fertilizers.
Modern nutrients are available in liquid form, as well as in the form of tablets or capsules. The liquid is poured into water, this fertilizer is useful for floating plants. Tablets and capsules are placed in the aquarium soil, they feed the roots well. There are also clay balls on sale, they contain trace elements, birch coal, sapropel, peat.
Before starting the aquarium, until the vegetation has adapted, usually no additional feeding is added, only potassium is used. It is also obvious that it is useless to add additives to an unbalanced aquatic environment. Therefore, you must first set all the parameters correctly. Care should be taken when adding different products together, it is worth checking the compatibility in advance, and in the worst case, a precipitate is formed that does not dissolve.
At the beginning, the dosage of the new top dressing should be small, it is reasonable to add a third of the usual dose. So you can observe the changes. In case of an overdose, algae begin to multiply actively, which is undesirable.
As a rule, macronutrients are added in the dark, and micronutrients in the morning. Nutrients have a delayed effect, after about a month, changes appear.
Examples of well-known manufacturers of aquarium food for the growth of beautiful and healthy plants:
- Tetra;
- Aqua Medic;
- Florastim;
- ADA;
- Sera;
- JBL;
- Aquarium Pharmaceuticals;
- Tropical;
- AquaPlants;
- Zooworld;
- Dennerle.
Lamps and light
Daylight hours in the aquarium should be close to the natural environment where the plants live. For example, for a tropical aquarium, this is 12 hours. With a lack of light, plants grow slowly, their leaves fall off. Due to the excess of light, aquatic vegetation can also suffer and blue-green and green algae will begin to grow.
Today, fluorescent, LED, metal-halogen, mercury-organic lamps are popular.When choosing lighting, you should build on the depth and volume of the tank, plant varieties.
For aquariums high up to 50-70 cm, it is advisable to use mercury-organic lamps. Of the power is 80 and 125 watts. The light from the lamp reaches the bottom.
For an aquarium with a depth of 1 metric, metal-halogen lamps are needed, they are not cheap and give good light output, color rendering and intensity.
It should be borne in mind that individual plants do not like bright light. And some of them can change their appearance under the influence of light. Most species thrive at 0.5-0.8 watts per liter. When buying an aquarium with built-in lighting, you need to match the plants to the existing environment.
Aquariums with dense vegetation require at least 0.8 watts of light per liter. The best choice for a home herbalist (a water reservoir inhabited by plants) is a special phyto-lamp.
Water parameters
The total hardness (GH) of the water should be 6-8 degrees. Plants do not need a too soft environment, and the maximum show is 15 degrees.
The temporary hardness (KH) of the water is also important. The indicator of RN and KN are interrelated. If the KN is equal to 2-4 units, then the PH should be equal to 6.6-7.5 units. This environment is good for vegetation growth.
You will also have to monitor the pH level, the best range is 6.6-7.5. In such conditions, plants grow well and absorb CO2 as much as possible.
There must be an optimal concentration of nutrients in the water, therefore, all fertilizers should be applied in a timely manner. The average temperature is 24-25 degrees. If it drops below 24 degrees, then the plants may grow sluggishly, less algae appears. When the temperature exceeds 25 degrees, algae grow intensively. In the first week of a herbal tank's life, it is recommended to start at 22 degrees and gradually increase the degree.
Diseases and care
Why don't plants grow in the aquarium?
If you notice a slowdown in the growth of aquatic plants, then you will need to check the hardness of the water, populate fish that are careful about the landscape. Some plant species take a long time to get used to a new place. Try cleaning the soil and partially replacing the water. And most importantly, reconsider the temperature.
Why does plaque appear?
The cause of black plaque is infection with harmful algae. To get rid of this problem, it is necessary to regularly change the water, remove all unwanted impurities from the soil. Blackbeard is treated with a remedy called JBL Algol. It may also be necessary to update the entire aquarium, replace some of its inhabitants and the feeding regime.
Why do plants rot and turn black?
Blackening and rot on the roots is a consequence of soil problems. It is possible that organic deposits lie deep in the ground. Excessive soil density can also be a problem; loosening is required. And soil acidification is also undesirable.
Rotting and depletion of stems occurs with poor lighting. It is worth revising the light supply schedule.
Sometimes Cryptocoryne and some other plant species get rotted. This disease is provoked by oversaturation with nitrates, sudden cooling or a change in the properties of water. For treatment, you do not need to touch the plant, it is enough to set the correct parameters of the environment and change the water frequently.
How to disinfect aquarium plants?
Plants are disinfected according to the instructions given by the manufacturer. They are kept in a disinfecting liquid for some time. Only experienced aquarists can do everything right. Here are the suitable drugs:
- bicillin;
- whiteness solution;
- buprofezin;
- methylene blue;
- imidacloprid;
- alum solution;
- trichlorfan;
- peroxide solution;
- ammonia solution;
- sodium permanganate solution.
How to care for plants?
Aquarium plants must be pruned on time and skillfully propagated, fed well, created for them the correct temperature and other water parameters, and set optimal lighting.
It is also important to control siltation, change water strictly on schedule.
It is wise to buy a book on aquarism, consult with experts, or watch training videos on a regular basis. Some fish can damage leaves and stems, this should be considered.
Blixa dwarf or Japanese (Blyxa japonica)
A beautiful aquarium plant. The shape of the bush, its height, the color of the leaves largely depend on the growing conditions. Embossed groves, formed due to the compact planting of plants at different levels of capacity, look decorative.
 Blixa Karlikova
Blixa Karlikova
Optimal living conditions. Fatty, nutrient-rich soil, bright lighting for 10-12 hours a day, soft, sour water, temperature 22 ° C-28 ° C. It is advisable to regularly change water to fresh water of similar parameters, apply root dressings (clay, etc.) Under conditions of light deficiency and mineral starvation, as well as in too hard and alkaline water, the growth of the blix is inhibited (however, it grows rather slowly under ideal conditions), internodes are elongated, the lower part of the stem is exposed, and the color of the leaves becomes faded.
Vegetative propagation - by cuttings.
Nymphea or tiger water lily (Nympheae lotus)
 Tiger water lily
Tiger water lily
A plant with green to reddish-brown leaves and a variable amount of purple spots.
Before the floating leaves form, it grows many underwater... If you do not want admit the appearance surface leaves, then pinch the roots and cut off the emerging leaves. The flowers are beautiful and fragrant.
The nutritious substrate stimulates growth.
Temperature 22 ° C-30 ° C, pH 5.0-8.0.
Nymphoides Flipper Taiwan
Height 20-70 cm. Underwater rosette pale green leaves, produces floating water lily leaves. In this species of nymphoids, floating leaves are no different from underwater ones. Above the water level, the plant does not grow, since its leaves are very thin and delicate, the same as their underwater counterparts, and when threatened with drying out they quickly decompose.
Look after not difficult. It does not react to the hardness and active reaction of water, it feels good in slightly silted soil. Lighting loves bright, even with its lack, it responds with increased stem growth, stretching strongly, but all the vital functions of the plant at the same time remain normal, which suggests that it is also quite democratic about the amount of light. Although, if you need a more compact version of the specimen, then add light to it. Shoots that are too long and old leaves should be removed if you want successive leaves to be on a shorter petiole.
Breeds vegetatively, by creating a maternal bud on the cutting of an adult leaf, which takes root and leaves, a new plant is formed along the edges of the plate of old leaves. After that, the daughter plant is detached, since the petiole is rotting. The baby can be safely transplanted into the ground, it easily takes root and begins to create a rosette.
If you don't have time to wait for the mother's bud to form on the leaf, try simply cutting off an adult leaf and planting it. The roots will cut through rather quickly, and the new plant will begin an independent life.
Banana aquatic, Banana plant (Nymphoides aquatica)
The plant got its name from the formations on the roots, which are somewhat reminiscent of bunches of bananas. The leaves are round with a bright green or reddish color. They are located on long stems and tend to float freely on the surface of the aquarium water. The water banana reaches a height of 25-35 cm.
Hardness 5-10 °, pH 6.0-7.2, T 20-25 ° C. He loves bright light, so the lighting should be very bright, it is desirable to get direct sunlight into the aquarium, with this lighting the plant will grow relatively quickly (on average, the plant gives 1-2 leaves per month). Plain washed gravel can be used as soil.
Breeds by dividing the rhizome, on which the daughter processes are formed.You can also plant the cut leaf in the ground, in this case, over time, it takes root.
Hemianthus dwarf "Cuba" (Hemianthus callitrichoides "Cuba")
 Hemianthus dwarf Cuba
Hemianthus dwarf Cuba
One of the smallest in the world of aquarium plants with millimeter-sized leaves. If fixed on small stones a few centimeters apart, the plant will quickly spread and cover the bottom like a carpet.
Hemianthus - very unpretentious and a very attractive foreground plant in small aquariums. Found in Cuba.
Temperature 18 ° C-28 ° C, pH 5.0-7.5
Micrantemum few-flowered (Micranthemum Micranthemoides or Hemianthus micranthemoides)
 Micrantemum low-flowered is a delicate plant with an elongated, erect and slightly branching stem. Light green leaves without petioles are arranged in whorls of 3-4 leaves. The leaf plate is up to 1 cm long, up to 0.3 cm wide, lanceolate or oblong, wedge-shaped base, obtuse apex. The root system is creeping, underdeveloped, well suited as a ground cover aquarium plant for creating compositions. In height, low-flowered micrantemum grows up to 20-30 cm.
Micrantemum low-flowered is a delicate plant with an elongated, erect and slightly branching stem. Light green leaves without petioles are arranged in whorls of 3-4 leaves. The leaf plate is up to 1 cm long, up to 0.3 cm wide, lanceolate or oblong, wedge-shaped base, obtuse apex. The root system is creeping, underdeveloped, well suited as a ground cover aquarium plant for creating compositions. In height, low-flowered micrantemum grows up to 20-30 cm.
Micrantemum small-flowered unpretentious... Planted in a group in the foreground or middle ground of the aquarium. The delicate leaves and stems of the plant can be attacked by some fish (cichlids, barbs, etc.), as well as snails. In good conditions, the low-flowered micrantemum grows rapidly (it grows by 10 cm in a month) and is an excellent shelter for fish during spawning.
Hardness 2-15 °, pH 6-8, temperature 15-28 ° C. Filtration and weekly changes of up to 20% of the volume of water in the aquarium are required. Prefers bright lighting. Fluorescent lamps with a power of 0.6-0.7 W / l can be used as light sources. In bright light, the micrantemum begins to actively release oxygen. The plant is very sensitive to algae growth. For micrantemum of few-flowered, it is desirable to fertilize in the form of adding clay to the soil.
Multiply low-flowered micrantemum by dividing the stem and separating the shoots from the base of the root. If you pinch the growth point of the main stem, the plant begins to eject additional lateral shoots from the leaf axils. They are planted in an aquarium where they quickly take root and begin to grow.
Pogostemon Helferi
 The plant is 5-6 cm high with corrugated along the edges of the leaves emanating from the stem-rosette. The leaves look like rays of a multi-pointed star. Pogostemon Helfer is handsome and unlike anything else.
The plant is 5-6 cm high with corrugated along the edges of the leaves emanating from the stem-rosette. The leaves look like rays of a multi-pointed star. Pogostemon Helfer is handsome and unlike anything else.
He is good both in moderately warm and in a tropical aquarium, but in natural conditions the temperature of the surrounding water does not exceed 20 ° C. Pogostemon is also indifferent to the level of water hardness and acidity, but the most intensive growth was observed in this plant at pH 7 and dKH 4 °. Pogostemon withstands partial shade, but the growth rate is significantly reduced, the distance between the nodes on the trunk increases, and there have been cases of complete cessation of growth under insufficient lighting. So you can't do without powerful lamps here.
Priming b. nutritious, moreover, the natural amount of nutrients is not enough, additional application of special fertilizers under the roots is necessary. It is not so important, but it is still desirable to introduce top dressing into the water. A signal about the lack of obtained microelements is the pale green or yellow color of the leaves. The supply of carbon dioxide to the water should also be organized whenever possible. Without this, the pogostemon will not die, but it will have a pale and not the same juicy appearance as we would like. It is also necessary to avoid abrupt changes in the physical and chemical parameters of water. Precisely - sharp. Please note that a wide range of such indicators is, in general, admissible, but their changes should take place without sharp jumps. It is impossible, for example, to change a large volume of water at a time, from this the pogostemon may simply die.
Reproduction. In a tall plant, you can cut off the top with a couple of whorls and plant it in the ground, where it will take root very soon and become an independent plant. And on the remaining stump, numerous side shoots will appear, which can also be separated and planted. If there is no elongated pogostemon in the aquarium, you just have to wait, sooner or later, side shoots will appear on their own.
Vallisneria
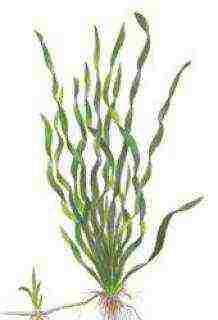 B. twist-leaved
B. twist-leaved
Temperature: 24-28 ° C
Water: KN up to 15 °, pH 6-7.5
Lighting: 0.5 W / L
Description. Stem shortened... Leaves linear forms, petiolate... Venation parallel... There are cross veins.
They are planted as a group in nutritious soil in the background and middle ground, as well as in the corner of the aquarium. Propagated by layers formed on a creeping shoot.
Under no circumstances should individual leaves be shortened. At the same time, they turn yellow, and the cut leaves are doomed, despite all the vitality of the plant. Vallisneria rots for the same reasons and even if there are some minerals in the aquarium.
Vallisneria spiral (Vallisneria spiralis)
Description. Leaves from light to juicy green, less often reddish, up to 80 cm long, 0.4-0.8 cm wide, often even, sometimes spirally twisted, with very fine teeth at the apex.
Water: 20-28 ° C. It grows about 2 leaves per month.
Aponogeton

Description. The rhizome has tuberous form, translucent patterned leaves and with a narrowed apex reach 25 cm in length and 4 cm in width. In favorable conditions, the bush reaches 70 cm in height.
Aponogeton wavy, viviparous (Aponogeton stachysporus, undulatus)
Temperature: 22-28 ° C
Lighting: 0.4-0.5 W / L of fluorescent lamps and 1.2-1.5 W of incandescent lamps.
Description. Unpretentious... Leaves are light green with beautiful checkerboard pattern... Place wavy aponogeton must be in the background of the aquarium. In small containers, even under the most favorable conditions, the plant is small, but retains its originality and attractiveness. Usually grows evenly throughout the year, but looks best in late summer and fall. In natural conditions, it blooms at the end of summer, rarely blooms in an aquarium.
 A. leathery A. ulvate A. viviparous
A. leathery A. ulvate A. viviparous
Needs to bright lighting... For artificial lighting, you can use fluorescent lamps such as LB and incandescent lamps. The plant does not tolerate long-term shading. Natural light is very useful for him.
In water less than 22 ° C, growth slows down and the plant can shed its leaves. At the same time, the tuber is preserved in the soil, which, when favorable conditions are restored, quickly gives new leaves. The plant prefers soft water with a neutral or slightly acidic reaction. Optimum conditions: hardness less than 4 °, pH less than 7, but it can grow in harder water with a slightly alkaline reaction. At a stiffness of more than 8 °, aponogeton grows relatively slowly and does not reach large sizes.
The soil should be nutritious and contain a moderate amount of silt. IN heavily silted soil tender root system of the plant decays... It is better to use coarse sand and small pebbles as a substrate. In a substrate consisting of larger particles, the roots develop worse. The soil must be laid with a layer of at least 3 cm, for adult plants - about 5 cm.
 A. mesh
A. mesh A. distachius
A. distachius
In an aquarium, aponogeton reproduces very easily vegetatively. A parent plant can form 7 daughter plants in one growing season. Mother plant forms arrowsstretching towards the surface. At the top of every arrow a small nodule appearsfrom which the leaves of the new plant emerge. Over time, the nodule grows and takes the form small tuber... Such a young plant, which does not yet have a root system, can be separated and planted in the ground. Its roots grow very quickly.If a young plant is not separated from the arrow soon after its formation, its tuber increases in diameter to 4-5 mm, after which the arrow, on which the daughter plant was formed, rots. The young plant remains free to float near the surface of the water, throwing out smaller and smaller leaves. At the same time, old leaves die.... In the end, the young plant drowns under the weight of its own tuber. Having descended to the ground, it quickly forms a root system and rosette of large leaves... Due to the peculiarities of its reproduction wavy aponogeton got the name "viviparous".
Cryptocoryne
K. Wavy K. Neville, photo with roots
K. Neville, photo with roots
Description. The genus Cryptocoryne includes aquatic and marsh plants that tend to reproduce vegetatively through underground shoots... All Cryptocorynes usually creeping (less often upright), more or less thick rhizomese, on which leaves are formed in the form of a rosette... They (with the exception of the winter leaves of C. retrospiralis) have a petiole and leaf blade, and an inconspicuous vagina at the base. Unlike the genus Lagenandra, which young leaves wrapped at both edges (involute budding), in Cryptocoryne species they rolled up on one side (convolute bud formation).
Most commonly, pet stores sell Cryptocoryne affinis, C. beckettii, C. cordata, C. crispatula, C. parva, C. pontederiifolia, C. undulata, C. wendtii, and C. x willisii. In general, keeping these species in an aquarium does not cause any complications. Sometimes C. albida, C. aponogetifolia and C. moehlmannii, C. hudoroi and C. usteriana are also bred. All of the listed Cryptocorynes develop well on sand and pebble soil, in which, for example, a little clay or fertilizer is added for the nutritional value of the soil. Medium intensity lighting is recommended for an optimal crop. Although most species develop in low light, however, in bright places they grow much better.
 K. Wendt
K. Wendt
Cryptocorynes are very vulnerable plants. When growing them underwater, you should mainly try to transplant them less often... They often respond to the intervention with the so-called cryptocoryne disease, when suddenly the leaves begin to decompose quickly. Rotting can also affect well-developing plant specimens. In this case, we are not talking about the disease, but about the ph reaction, the changed environmental conditions, lead plants to physiological disorders. At the same time, already insignificant displacements of one of the water parameters, for example, during its replacement, or replacing a defective fluorescent lamp, can serve as a catalyst for the onset of cryptocoryne disease, as a result of which the luxurious bush will die within just a few days. In this case, a lot of patience is needed, bye rhizome, remaining in the ground, will not give new shoots... Not all cryptorinas react to changing environmental conditions in such an extreme way. Thus, it can be observed that C. undulata suddenly perishes, while C. wendtii develops beautifully in the same aquarium. The best preventive measure against decay is to create an environment with constantly maintained parameters, for example, to undertake partial water changes regularly, just as fertilizers were applied only in small quantities and distributed over a long period of time.
K. aponogenolytic K. pontederia
K. pontederia
Almost all Cryptocoryne species can be grown above water at high atmospheric humidity and in moist soil. An empty aquarium covered with glass is suitable for this purpose. Artificial lighting is sufficient. A simple cultivation method is to fill the aquarium with enough water so that the pots of Cryptocorynes are submerged 1-… cm in water. A spray immersed in a small separate vessel with water achieves high air circulation and at the same time high humidity. Additionally, you can let the water flow slowly through the filter to ensure even circulation of water and the supply of nutrients.
Bacopa
Temperature: 22-28 ° С, in colder water growth slows down and old leaves begin to rot
The size: reaches a height of 20-40 cm
Description. Leaves are bright and rich green shades, mostly oval in shape.Erect shoots, dotted with medium-sized flowers. Unpretentious, multiplies rapidly and therefore widespread among aquarists. In an artificial reservoir it grows throughout the year.
 B. Madagascar B. Monier
B. Madagascar B. Monier
For all aquatic bacopes the most important criterion for growing it in an aquarium. is an intense lighting... If it is weak, then with an increase in the height of the plant, the lower leaves will begin to fall off. If the depth of the aquarium is more than 30 cm, it is better to place it in a separate bowl on the side shelf, raised closer to the lights, or create a side illumination. Natural, and especially diffused sunlight is very useful for the plant. For artificial lighting, it is best to use fluorescent lamps of the LB type, it is also possible to use incandescent lamps. The power of the lamps is selected individually. Artificial and natural light can be combined in any way. The duration of daylight hours is desirable at least 12 hours.
The aquarium soil can be moderately silted. Bacopa gets most of its nutrition directly from water. The root system of the plant is poorly developed. As a substrate, sand or very small pebbles should be used, laid in a layer 2-4 cm thick. Additional mineral fertilizing is not needed, the plant usually has enough nutrients supplied with fresh water and fish food.
B. Karolinskaya
Bacopa easy propagated by cuttings of the stem... Apical shoots can be planted directly into the ground without waiting for roots to appear. In this case, the lower whorl of the leaves is deepened. After a short time, roots appear at the base of the leaves.
Since bacopa is weakly branched, the multilevel ones look the most picturesque. group bakop, consisting of at least 15-20 plants. They are usually located in the middle zone or along the perimeter of the reservoir. An excellent background for bacopa are thickets of anubias, dark-colored cryptocorynes, film and relief backgrounds of rich gray, brown and black tones.
Plant care, in fact, comes down to only periodic thinning of thickets and pruning overgrowths. Plucking off the top of the main stem not only helps to maintain the decorative value of the “bacopic grove”, but also encourages the plants to form new shoots. Shoot development can be enhanced. Bacopa develops slowly even in bright light, with a lack of light, the leaves turn yellow, become smaller and the plant dies off. In good conditions, Bacopa grows out of the water.
Limnophila (Ambulia) (Limnophila)
 Limnophila or Ambulia
Limnophila or Ambulia
Water temperature: 18-30 ° C
The size: up to 50 cm high
Hardness of water: 2-16°
Acidity of water: 6.0-8.5 pH
Description. Plant rooting in the ground. The leaves are whorled or opposite. The diameter of the whorls can reach 12 cm. The leaf plate is pinnately dissected, up to 3 cm long, light green in color. The stem is elongated, erect. Flowers bloom above the water. Upon reaching the surface of the water, the plant forms very beautiful dense rosettes of leaves of a darker color and begins to creep along the surface of the water.
L. Indian
In an aquarium, limnophila is planted in one row along the back wall or placed in bunches in the far corners. The plant “feels” the volume well, so it is necessary that the container is at least 80 liters and a height of 50 cm. In favorable conditions, the long stems of the plant create dense thickets. If you look from above at the aquarium where limnophila grows, you can see an unusually beautiful carpet. Also limnophila is excellent a refuge for fry, very actively oxygenates and purifies the water in the aquarium. Is growing fast, about 15 cm per month... But Ambulia aromatic develops rather slowly.
At the lower temperature limit, the growth rate of the plant slows down. For quite a long time, limnophila can withstand a decrease in temperature and up to 14-15 ° C. Needed filtration and weekly substitutionand up to 25% of the volume of water. Necessary bright lighting... Fluorescent lamps of the LB type with a power of 0.5 W per 1 liter and incandescent lamps as additional illumination can be used as artificial light sources. Plant also can survive and at low light, but at the same time, the stems of limnophils begin to stretch and appearance her much worsens... To check if the plant has enough light, you need to pay attention to its tops... If there is enough light, the leaves of the crown of the limnophila are lifted up and close the growth point of the stemfolding in this direction. The duration of daylight hours is 10-12 hours. Long stems are divided into parts 10-15 cm long with 4-5 leaves and planted in the ground, deepening the lower whorl of leaves. After 4-5 days, the cuttings develop their own root system. In cuttings taken from the middle of the stem, a lateral shoot is formed, from which a new plant develops, but only after a fairly long time.
 Ambulia or Limnophila aromatic
Ambulia or Limnophila aromatic
Delicate and weak root system, therefore it is necessary to use sand... In a substrate consisting of large particles and when cleaning the bottom, the base of the stems are injured and start rot, as a result of which the plant floats to the surface water. Floating shoots grow very slowly, become smaller and lose their attractiveness. The level of siltation of the soil does not play a significant role, since the plant extracts nutrients from the water. Additional feeding into the new soil can be omitted; for limnophila, the gradually increasing natural silting is quite enough.
Propagate limnophila cuttings... Long stems are divided into parts 10-15 cm long with 4-5 leaves and planted in the ground, deepening the lower whorl of leaves. After 4-5 days, the cuttings develop their own root system. In cuttings taken from the middle of the stem, a lateral shoot is formed, from which a new plant develops, but only after a fairly long time.
Limnophila can be propagated dividing the rhizomecreeping along the bottom. The rhizome is divided into parts, each of which has a vertical shoot with a developed root system. With this method of reproduction, the plant in a new place continues to grow almost without interruption, if favorable conditions are created for it.
The sprouts must be planted at a sufficient distance from each other to avoid shading. If you cut off the top of the stem, the plant can be shaped like a bush, since several shoots form at the cut site at once.
All actions with limnophil must be carried out very carefulsince the leaves of the plant very gentle and are afraid of rough treatment.
Views: Limnophila sessiliflora, ambulia sessiliflora (Limnophila sessiliflora). Limnophila heterophylla Bentham. Limnophila aquatic, Ambulia giant (Limnophila aquatica). Indian Limnophila (Limnophila indica). Ambulia aromatic, Limnophila aromatica.
Sagittaria or Arrowhead (Sagittaria)
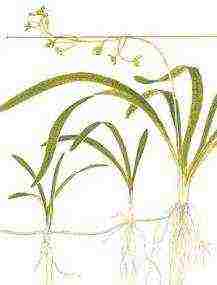 S. subulate, fig. Sagittaria
S. subulate, fig. Sagittaria
Sagittaria, arrowhead - both names came from the Latin sagitta, which in translation means arrow.
Leaves sagittarii are short, curved, much wider at the ends, pointed, juicy and fleshy, there is a clearly expressed vein... This plant is bright green in color. Has a highly developed root system, white roots with a short tuberous or nodular rhizome.
The best soil for sagittaria - sand mixture fractions 3-4 mm with silt, but in bright natural light it can grow only in sand. It is not demanding of water temperature, it is suitable for any warm-water aquarium. The arrowhead does not like the neighborhood with other plants, as it grows magnificently and independently able to decorate decorative aquarium. Among other plants, it grows poorly, remaining a small bush.
It is better to propagate vegetatively. Adult specimens are thrown to the sides mustache, on which rosettes of daughter plants are formed. Once a few leaves have emerged and the roots are sufficiently developed, the young plant can be detached and transplanted to a permanent location.
Sagittaria broadleaf or arrowhead broadleaf
Unlike ordinary sagittarii, it has wider leaves up to 3-4 cm and up to 25 cm long. It has proven itself well in aquariums with goldfish and cichlids. Just like ordinary sagittaria, it grows well in coarse-grained soil in bright, diffused light.
Sagittarius dwarf or arrowhead dwarf
 C. subulate
C. subulate
Dwarf sagittaria is a low-growing plant that forms dense thickets. The height of the bushes does not exceed 10 cm. The plant is suitable for growing in a small aquarium. In large aquariums, it is better to place dwarf sagittaria in the foreground. The plant is unpretentious, recommended for beginners aquarists. Grows evenly throughout the year.
To temperature conditions, dwarf sagittarius is unpretentious, grows satisfactorily in the temperature range from 18 ° C to 28 ° C, can withstand a temperature drop to 12 ° C. The hardness and active reaction of water does not play a significant role. The use of filters in the aquarium is necessary, as suspended particles in the water settle on the leaves and they turn yellow and die off.
Lighting should be moderately bright. With a lack of light, the leaves of the sagittarius stretch upward, their color becomes faded, dense thickets are not formed. In strong light, the plant forms dense thickets. You can also select the brightness of the lighting depending on the need for other plants. Both natural and artificial light are suitable for lighting.
As a soil for a dwarf arrowhead, it is better to use sufficiently fine sand, which should be moderately filled with organic matter. If large and medium pebbles are used in the aquarium, then at the landing site sagittarii need make zones of sand... The thickness of the sand layer must be at least 3 cm.
Dwarf sagittaria easily propagates vegetatively, a young plant is taken from the formed thickets, having previously cut the mustache and transplanted to a new place.
Hygrophila
There is a large number of varieties this plant, differing in color, leaf shape and size.
Gigrofila - unpretentious a plant capable of growing in a wide temperature range from 18 ° C to 30 ° C. If necessary, it can grow and develop in low light and no soil. To receive large plants, you need a nutritious soil and bright, long-term lighting. Beautiful, large bushes are very decorative and serve as a decoration for the aquarium. At the same time, the plant is universal, it can also be used as a natural substrate for fish spawning. It is even suitable for applications where eggs or fry require low light. Even in such conditions, the hygrophila is able to survive.
 Gygrophila pinnately cut
Gygrophila pinnately cut G. varifolia
G. varifolia G. polyspermous marble
G. polyspermous marble Hygrophila heterogeneous G. "lemongrass" G. willow leaf
Hygrophila heterogeneous G. "lemongrass" G. willow leaf
Gigrofila easy reproduces vegetatively - by cuttings. The stem calves into pieces containing 5-6 leaf whorls. Each piece, planted in the ground, with the deepening of the lower pair of whorls, gives rise to a new plant. The root system of the cuttings is formed very quickly.
Rotala rotundifolia or Rotala indica
 The plant is kept in both aquariums and polydariums. Plant not whimsical. OIndividual branches planted in the ground have no appearance. However, if the branches are collected in a bunch, then the plant is immediately transformed. In an aquarium, the plant looks like this: retracted leaves are arranged in pairs on a fragile thin stem; in paludarium conditions, the leaves are rounded when leaving the water. Below, the leaves turn red with sufficient lighting. The plant is long-stemmed, therefore, it is planted in the background, forming a beautiful background.
The plant is kept in both aquariums and polydariums. Plant not whimsical. OIndividual branches planted in the ground have no appearance. However, if the branches are collected in a bunch, then the plant is immediately transformed. In an aquarium, the plant looks like this: retracted leaves are arranged in pairs on a fragile thin stem; in paludarium conditions, the leaves are rounded when leaving the water. Below, the leaves turn red with sufficient lighting. The plant is long-stemmed, therefore, it is planted in the background, forming a beautiful background.
Water parameters. The plant prefers soft water, or medium hardness, in hard water the plant quickly degrades the leaf becomes smaller and the plant dies. The active reaction is weakly acidic. The temperature of the content is not lower than 24 degrees.
Lighting. Moderately strong. The fact is that for each aquarium it is necessary to select its own lighting for this plant. The specificity of the plant is such that the upper leaf shades the lower one, which becomes smaller over time, exposing the lower part of the stem. When the overhead lighting is increased, a bloom of algae forms on the leaves, which are detrimental to the plant. Based on this, it is advisable to illuminate the plant with side light. By combining lamps and lighting power.
Any soil. The plant has an underdeveloped root system, so it receives most of the microelements from water.
The plant propagates vegetatively by separating lateral shoots or by dividing the stem.
Cyperus helferi

The size: up to 40 cm
Temperature: 18-26 ° C
Acidity of water (pH): 5,0-7,5
Carbonate water hardness (dKH): 2-18°
Lighting: bright, 0.7 W / L
Special Requirements: CO2 fertilization is desirable
It has a creeping, very branched rhizome, which is 5 cm long and about 8 mm thick. The leaves are collected in a bush-shaped rosette. The sheet plate is ribbon-shaped, pointed at the end. The leaf, as it were, consists of two lobules in the center of which there is a rather deep groove. The edge of the leaves is covered with tiny denticles, which make the leaves appear rough. The color of the leaves is green.
In the presence of nutrient soil, the plant acquires an attractive appearance. Long leaves of Cyperus easily reach the surface of the water and flock along it in the form of stripes. The growth rate is slow. Leaves never rise above the surface of the water. When properly maintained, it develops into a beautiful and rich looking plant. The main problem with cyperus is its tendency to overgrow the leaves with algae. In case of their appearance, experimentally select the intensity of the illumination.
Reproduction. Dividing the rhizome and daughter plants. The rhizome is cut into pieces so that each leaves at least one leaf. The processes of cyperus develop directly next to the mother plant, and once formed, they immediately begin to release leaves. Adult plants can form umbrella-like shoots on the branches, which, upon contact with water, form roots and can grow on their own. Young plants can be separated and transplanted when they reach a height of 4-6 cm.
Cyperus Helfer is also successfully cultivated in a paludarium on clay soil in humid air.
Eichornia azure or Eichornia aquatic (Eichhornia azurea, eichhornia aquatica)
 Stem. Above-water oval-rounded, with a ribbed surface, the leaves have a long petiole and internodes. The bright green leaves are 8 cm long and 7 cm wide. The underwater form of eichornia azure has a regular arrangement of leaves on short internodes. The leaf blade of the plant has a narrowly linear shape, reaching a length of 15 cm and a width of 1 cm. The appearance of the bluntly pointed apex of the leaf blade of Eichornia resembles a palm tree.
Stem. Above-water oval-rounded, with a ribbed surface, the leaves have a long petiole and internodes. The bright green leaves are 8 cm long and 7 cm wide. The underwater form of eichornia azure has a regular arrangement of leaves on short internodes. The leaf blade of the plant has a narrowly linear shape, reaching a length of 15 cm and a width of 1 cm. The appearance of the bluntly pointed apex of the leaf blade of Eichornia resembles a palm tree.
Peduncle the plant has an inflorescence, consisting of 6-12 large flowers of blue color with a lilac tint, and towards the center of the flower the color changes to a darker one. The flower petals have a fringe, each top petal is decorated with a round yellow speck.
Eichornia azure grows up to 60 cm. Eichornia azure is planted in a group, preferably in the middle or background of the aquarium. Especially beautiful is the planting of the eichornia with a ladder so that the leaves have a parallel arrangement. For cultivation in aquarium conditions, only the underwater form of the plant is used. Eichorniy is needed quite often undercut so that it does not grow on top of the water. If this is not done, the plant quickly loses its decorative effect.
Temperature water in the range of 18-28 ° C, pH 4-7, hardness from 2 to 16 °. Filtration water is required, availability is required currents... A change of about 25% of the water is recommended to be carried out weekly. For eichornia azure, it is necessary to have strong lighting, organized by fluorescent lamps with a power of 0.7 W / l. Daylight hours should be more than 12 hours.
Priming. A mixture of clay and sand. Eichornia azure responds very well to the application of liquid and soil fertilizers.
An additional supply of carbon dioxide is useful for the plant.
Reproduction. Eichornia azure occurs by dividing the stem or by separating the lateral shoots of the plant.
 Anubias dwarf
Anubias dwarf
Anubias
Temperature: 22-28 ° C (a decrease in T leads to a growth arrest)
Description. Perennial slow growing herbs with thick creeping rhizome.
Anubias - shade-tolerant and have tough oval leaves with a sharp tip. Well suited for landscaping aquariums with cichlids and herbivorous fish, as its tough leaves are few to everyone's taste.
When planting, only the roots are buried, horizontal the rhizome is put over the ground, in no case without burying.
This plant does not require bright lighting (0.3 W per liter is sufficient). Direct sunlight to him contraindicated, it is better to block the aquarium from them.
A. graceful A. Barter narrow-leaved
One of the prerequisites for good growth of anubias is pure waterwhen turbidity settles on its leaves, it begins to be capricious and stops growing. Therefore, in an aquarium with such a plant, it is very desirable filter availability... If the water in the aquarium is changed weekly, then additional mineral fertilizing is not required for anubias, for its nutrition there will be enough substances dissolved in tap water. It is not necessary to siphon the soil near the roots of the plant, the plant receives its main nutrition through the roots (the accumulated silt is enough for this).
Anubias reproduces by shootsthat are formed on its rhizome. When 5 leaves are formed on such a shoot, it can be separated from the mother bush and planted as an independent plant.
A. B. coffee leaf A. Barter Glabra
You can not plant in the ground, but strap its roots with a fishing line to snag, coconut or stone... Over time, anubias, like grapes, braids the object to which it is attached, after which the line can be cut off and the plant itself will choose the option how to grow further - the main thing is not to disturb it.
Is growing anubias very slowly, on average, the plant produces 1-2 leaves per month. Attempts to accelerate the growth process, for example by adding CO2, have come to nothing.
Plant it is desirable in the aquarium groupth. Anubias is also well suited for aquariums with fish that are constantly dig in the ground, pulling out plants together with roots - at Anubias roots are very strong and they are unlikely to be able to do this with him. Anubias is also very Good grows in humid conditions paludarium.
Echinodorus
There are about 50 underwater species of the genus Echinodorus. This diversity is due to their ability to easily form hybrids, both in natural and in aquarium conditions.
The size: there are small ones up to 5 cm, medium ones and there are giants up to 1-2 m.
Description. Leaves are collected in dense or loosesocket, on form ribbon-like, petiolate or petiolate, oval, cordate, elliptical, lanceolate or ovate. The edges of the leaf blade are even or wavy, longitudinal veins usually up to 5 or 7, 9 (less often up to 3), or 11 or more. Petioles in cross-section are rounded, grooved, triangular or triangular-flattened. Coloration leaf plate - from pale to dark green, almost black, different shades of red (golden brown, wine, raspberry, cherry, etc.). Some plants have leaves with purple, dark red and white spots.
Echinodorus can be divided into two groups: simple and complex in cultivation... Simple ones form stable underwater forms and in an adult state have a height of at least 15-20 cm. These are: E. aschersonianus, E. intermedins, E. horemanii, E. horizontalis, E. maior, E. osiris, E. portoalegrensis, E. umguayensis, E. "aspersus", E. "barthii", E. "janii", E. "Osiris doppelt Rot", E. "Rose" and many others.
For those who are simple in content, the following rules must be observed:
Adult powerful specimens do not tolerate new conditions well and often die from lack of nutrition or, for the same reason, change the growth point. Or, once in a favorable environment, they tend to quickly transition to a surface form, which we do not need. Therefore use for planting necessary young plants grown from seeds, as well as seedlings obtained by vegetative propagation from dormant buds on peduncles or rhizomes. It is necessary to cut the rhizome so that both on the separated and on the remaining part there are several leaves and roots. It does not matter if it is an emergent plant or an underwater one. Such plants quickly adapt to the conditions of the new aquarium, begin to grow actively, and the leaves of above-water forms are replaced by underwater ones in the coming months.
Are able to fit To wide range of conditions external environment (hardness, illumination, chemical composition of water). But it is desirable that the water is not very hard (no more than 20 °). The temperature should not fall below 15 ° C. BUT best if water will have hardness up to 10-and etc.temperature above 20 ° C... They live in both sunny and shaded areas. But a prerequisite good development and growth of echinodorus is a neutral or slightly alkaline reaction of water (pH 6.8-7.6) and bright enough lighting. Not less than 200 W per square meter, which makes it possible to create illumination of the order of 16,000 lux on the water surface. The duration of daylight hours during the cultivation of Echinodorus underwater should not exceed 10-12 hours. This is enough for their growth. In addition, not an overabundance of lighting excludes the possibility of the transition of plants to the above-water form. If possible, it is necessary to exclude the impact on the aquarium with echinodorus natural light, even scattered light.
These plants do not tolerate the acidic reaction of the soil. Thoroughly washed gravel or crushed stone with a grain diameter of 3-7 mm is best suited. Such soil is well ventilated, easily cleaned by the "suction" method and does not sour anymore. Cleaning should be done at least after 7-10 days, over the entire bottom area. In this case, 1 / 5-1 / 3 of the water is replaced with settled fresh, because it is with her that the required amount of trace elements enters the aquarium. The need for additional application of mineral fertilizers, as a rule, does not arise.
- Aquarium plants
Photos of Echinodorus:
 E. osiris E. Ocelot E. speckled E. ruby E. pointed E. narrow-leaved
E. osiris E. Ocelot E. speckled E. ruby E. pointed E. narrow-leaved E. Goremana E. small-colored E. Red flame
E. Goremana E. small-colored E. Red flame E. "Jungelstar"
E. "Jungelstar" E. Asherson heart-shaped
E. Asherson heart-shaped E. subaltus
E. subaltus E. shovel-leaved
E. shovel-leaved E. large, Barta E. cordate
E. large, Barta E. cordate


