Content
- 1 Propagation of grapes by cuttings.
- 2 Growing grapes in the middle lane: subtleties. Grape care in the middle lane
- 3 Growing from cuttings
- 4 Rooting of planting material
- 5 Growth stimulation
- 6 Furrowing
- 7 Placing cuttings in a kilchevator
- 8 Planting cuttings in a temporary location
- 9 Harvesting cuttings
- 10 Germination of grape cuttings
- 11 Transplanting shanks in a container
- 12 Dormant period
- 13 Blank
- 14 Storage
- 15 Checking the planting material before rooting
- 16 Germination in cups
- 17 Green cuttings
- 18 Kilchevanie
- 19 Growing grapes in central Russia
- 20 Soil preparation, planting and care
- 21 Formation of grapes and shelter for the winter
- 22 How to properly remove the shelter
- 23 Dry garter
- 24 Green fastening of grapes to the trellis
- 25 How to grow grapes at home
- 26 Growing features
- 27 Step-by-step technology for growing grape bushes from cuttings
- 28 Growing grapes in the middle zone of Russia
- 28.1 Growing grape seedlings in the conditions of central Russia
- 28.2 Storage of grape seedlings and preparation for planting
- 28.3 Choosing a place for grapes on the site
- 28.4 Preparation of soil and planting pit for grapes, fertilization
- 28.5 Planting and transplanting grapes in the conditions of central Russia
- 28.6 Grape care, feeding and treatment against diseases and pests
- 28.7 Video: grapes in Nizhny Novgorod
- 28.8 Watering grapes in the middle zone of Russia
- 28.9 Pruning grapes in the middle zone of Russia
- 28.10 Preparing grapes for winter in the conditions of central Russia
- 28.11 Reproduction of grapes in the conditions of central Russia
- 29 Methods of growing grapes in the conditions of central Russia
- 30 Features of the cultivation of various types of grapes in the conditions of central Russia
Propagation of grapes by cuttings.
Similar articles
After soaking, the sections of the shanks are updated. Shallow longitudinal cuts are made in the "heel" of the shank, and the lower kidney is removed. A layer of cotton wool is laid at the bottom of the container for germination and water (settled or melted) is poured. The water level should be at a distance where roots are expected to appear. We put the shanks in the container and wait until the tops and roots appear.
Everyone can grow a grape seedling from a cutting, if simple rules are followed.
Preparing cuttings
Cuttings are soaked in water with the addition of growth stimulants, for example, Epin, for one day.
It is very easy to grow large beautiful brushes and propagate the grapes with shanks in the middle lane. You just need to act consistently.
In the spring, when the snow melts, these shelters are removed and the grape bushes are sanitized. Extra weak shoots, frostbitten and broken vine are cut out.
Germination of cuttings
If the plants are grafted, then the grafting site during planting should be above ground level.After the grapes are planted, it must be tied to a prepared support, water abundantly and mulch the soil with humus or manure, so the moisture will remain in the soil longer.
A successful choice of a place for grapes is already half of the success. This plant grows well in places open to sunlight and well protected from the wind. In areas with harsh climates, grapes are successfully grown against a fence or wall of a house facing southwest or south. Places with stagnant cold air are not suitable for this plant.Prepare the soil for planting.
In late April and early May, cuttings already have 4 to 5 leaves, and their roots grow to the walls of a glass or bottle. They can be transplanted into large containers ranging from 2 to 3 liters and placed in a greenhouse for further growth. At the end of July, the grown plants are transplanted into containers up to 10 liters (buckets can be used for this), and placed in the open air.
In the first option
With the development of amateur gardening, grapes have stepped far to the north. It can be seen now not only in the gardens of central Russia, but in the Urals and even in Siberia. Grapes are grown as a cover crop. During wintering, the vine sometimes dies or deteriorates, which forces gardeners to take care of restoring plantings.
Often, green shoots appear before the roots. This absolutely does not interfere with the further development of the seedling root system. In the event that a second shoot began to develop from one bud, but there are still no roots, the first stronger sprout should be carefully broken off. This will save the strength and energy of the cuttings for root germination.The first and important stage in the process of growing seedlings is the preparation of shanks. The quality of the harvested planting materials determines the quality of future seedlings and the yield of the grown bush.
The stalk is removed from the growth stimulation solution, 2 cm long scratches are made with a knife above the lower end.
How to grow grapes from a cuttings:
Grapes are now grown in almost every region. Let us repeat everything about grapes in central Russia once again. Agrotechnology for growing grapes in this area boils down to a good choice of a place for grapes, proper planting and vine care. The place should be chosen as the sunniest in this area, in addition, cold northern winds should not penetrate there, for this they install a screen or plant grapes along the southern wall of the house or fence.
Growing grapes in the middle lane: subtleties. Grape care in the middle lane
Another technique for planting grapes is planting grapes on beds, the height of which is about 25 cm. The edges of the beds are reinforced with plastic bottles dug with their neck into the ground. This method of planting allows more heat to flow to the roots and thereby accelerate the ripening period of the crop.
Growing grapes. Step-by-step instruction
The soil for this southern plant should be well-drained, and the reaction should be close to neutral (pH 6.5-7.0). The location of the future vineyard has been selected, now let's start preparing the soil.
- Build supports for the seedlings.
- If by mid-September the stems of the seedlings mature into 2 - 3 buds, woody and acquire a light brown color, they can be planted in a permanent place, in a trench. If the shoots are not ripe, they are brought in buckets into a heated room and left until the end of December. At the end of December, they are cut into 3 - 4 ripe buds, in the spring they are transferred to a greenhouse, and in mid-September they are planted in a permanent place.
- Use clear plastic cups with a capacity of 0.5 liters and clear plastic bottles with a cut-off bottom. Several holes are made in the bottom of the glass.
- There are many ways to propagate grapes. This is growing from seeds, grafting, layering, and propagation using cuttings. The last method is the fastest and most common.It is based on the ability of the vine to recover from part of its shoot, the cuttings. Cuttings can be summer green and woody winter. For propagation of grapes, lignified stem cuttings, or, as they are called, shanks, are usually used.
- From the emergence of shoots to the germination of roots, an average of 2-3 weeks pass. The appearance of a white build-up on the heels indicates the imminent appearance of the long-awaited roots. When the roots reach 2 centimeters, the shanks are planted in containers with soil mixture for further cultivation.
- Grape cuttings are harvested in the fall during the pruning of mature bushes. For harvesting, a ripe healthy vine is selected, which has yielded a crop. The vines should be light green in color. The cut is made only with a sharp, clean instrument to prevent infection. The vine is cut into shafts, each of which has 3-4 eyes. Depending on the interrenal distance, the length of the shank varies between 40-70 cm.
- Furrowing activates the formation of roots at the site of the scratches.
- 1. Harvesting grape cuttings in the fall: the cut should be green on the cut, 2-3 buds, 12-15 cm long and 8 mm thick;
When planting young grapes, it should be borne in mind that the bush in this place will grow and bear fruit for many years, therefore, planting must be taken responsibly. Good drainage and nutritious soil must be laid in the planting hole. Broken brick is used as drainage. If the soil is heavy, sand should be added. Nutrient soil can consist of rotted manure or humus, to which 200-250 g of superphosphate must be added, this fertilizer is necessary for the future harvest.
Choosing a place for grapes
The task of pruning vines is to form a powerful fruiting bush. Annual shoots are cut off. The thinner the vine, the less buds are left on it. So, for example, on a shoot with a diameter of 10 mm during autumn pruning, a maximum of 10-11 buds can be left, and only 5 buds are left on a shoot with a diameter of 5 mm.
Successful cultivation of grapes in the middle lane begins with the preparation of the soil. These activities should be carried out 15-20 days before planting young seedlings. In order to reduce the acidity of the soil, lime is introduced at the rate of 150-200 grams per 1 sq. m. landing area.
Soil preparation
Plant seedlings.
Propagating grapes is not easy, but very interesting. Try it, it is quite possible that you will succeed!
Support for grapes
For germination, sand and a mixture of earth with leaf humus are needed. 2.5 cm of earth is poured into the bottom of the glass. A hollow cylinder with a diameter of 3 cm and a height of 10 cm is placed in the middle of the glass. Earth is added to the sides of the cylinder, moistened and compacted. Washed and calcined river sand is poured into the cylinder, and then the cylinder is removed.
Planting seedlings
This method of propagation of grapes preserves the properties of the mother vine. It is used both in its industrial cultivation and in amateur gardening. Here is how grapes are propagated using cuttings in Siberia:
The soil for grape seedlings is harvested in the fall. It includes sod land, river sand and humus. If it was not possible to prepare the soil in advance, you can purchase ready-made soil mixture for seedlings in the store.
For storage, the shanks are tied. A tag with the name of the variety is attached to them. The lower part of the cuttings is wrapped with a damp cloth or paper and placed in cellophane. As such, the cuttings will overwinter in a basement or refrigerator. The optimum temperature for storing shafts is 0-5 degrees above zero.
A two-liter bottle is used as a kilchevator: the upper part is cut off, several holes are made in the lower part of the bottle to drain water and filled with sawdust.
Pruning
2. Cutting grape cuttings: make an oblique cut of the cutting with a sharp knife, the cut must be clean, without mold, it must not be dry;
If done correctly, young grape bushes begin to bear fruit in the 3rd year. Further care consists in the competent formation of the bush and pruning. In hot summers, grapes require watering about 5 times per season. Watering should be sparse but abundant.
Shelter for the winter
In the spring, fruiting shoots of the current year will develop from them. In order for the cultivation of grapes in the middle lane to be successful, it is better to prune it in two steps. The first pruning is carried out in the fall after fruiting, it consists in the removal of immature vines and too thin and damaged shoots. The second stage of grape pruning is carried out in early spring, after the winter covering material has been removed. Here, damaged and frozen shoots are also removed and a decision on the load is made, in accordance with this, pruning is carried out.
The soil at the site of the future vineyard must be dug deep. Poor soil is flavored with rotted manure or compost. To do this, add one bucket of organic matter per 1 sq. m and be sure to add one of the complex mineral fertilizers, for example, superphosphate.
In the hot summer, watering is necessary.
Grape is a thermophilic plant, it feels good in the southern regions. Growing grapes in the middle lane is now quite possible. People have tried to grow grapes in more northern regions since the time of Peter. Michurin was the first to obtain varieties that are resistant to cold climates. He bred the first two early and winter-hardy varieties Amursky and Baitur. These varieties are still popular with gardeners. In the Moscow region, they winter even without shelter.
Agrotechnology of grapes: growing grapes in the middle lane
The sand is moistened, a hole 4 cm deep is made in it and a cutting is planted in it for rooting. Sand is poured into the glass from above, and the handle is covered with a plastic bottle, from which the bottom is cut off beforehand. The neck of the bottle must be open. Cuttings are watered every day or every other day. The amount of water for irrigation is 30 ml.
Cuttings are harvested in advance. They are usually taken during the autumn pruning of grapes. For cuttings, the middle part of fruit shoots fruiting in the summer is used or a shoot cut off into a replacement knot. The diameter of the shoots should be from 7 to 10 mm, and the length of its internodes should be 7-10 cm. The shoots are cut, the leaves, stepsons, unripe tops, antennae are removed from them and cut into cuttings so that each has 3 or 4 buds, or peephole.
The seedling container should be about 1 liter in volume. Cutted plastic bottles, juice bags, dense plastic bags are perfect for this. Drainage holes must be made at the bottom of the containers, and a drainage layer is placed in the container itself (pebbles, washed crushed stone, etc.).
At the end of February, cuttings are taken out of storage, examined and prepared for germination.
Then the sawdust is poured with a solution of potassium permanganate and the solution is allowed to drain. Cuttings should stand in wet sawdust near the battery for 3 weeks. When the first leaves appear, the cuttings are checked for rooting.
3. Storage of grape cuttings in the refrigerator: the prepared cuttings are placed in a tight bag and stored in a damp, cool place, the room temperature should be maintained at + 5 ° C until the end of winter.
To avoid freezing, even frost-resistant grape varieties in areas with cold winters must be covered.
Growing from cuttings
In late autumn, before the first frost, the vine is removed from the trellis, pruned, the remnants of the leaves are removed, carefully tied and laid on the ground. The base of the bush must be highlighted. If there is a graft, then hilling must be done in such a way that it is completely hidden by the ground.
On the site of the future vineyard, you need to build a support for the vine. In the landing row, after 2.5 meters, it is necessary to drive in wooden poles 3 meters long.They are driven into the ground to a depth of 60 cm. A metal wire is stretched between the posts. The first is located at a height of 40 cm, then the distance between the wires is 30 cm. In the future, the vine will be fixed on them.
The grapes need pruning.
For the successful cultivation of grapes, you must:
Rooting of planting material
Cuttings can be germinated previously in a plastic bag, placing them there so that their lower ends are in contact with the foam rubber soaked in water placed in the bag. At room temperature, after 10 days, callus and small roots appear, and then the cuttings are transplanted into glasses.
Above the upper kidney, at a distance of 1 - 2 cm, a cut is made at an angle, with an inclination from the eye. The lower part of the cutting is cut in a straight line, at a distance of 0.5 cm from the lower eye. In the lower part of the cutting, 3 vertical grooves are made with a knife or a needle, up to the bast, about 3 cm long. The cuttings are tied into bundles according to varieties and marked. During the day they are soaked in clean water, then pickled in 5% copper sulfate and dried. Then they are placed in plastic bags or wrapped in film.
Growth stimulation
Transplanting shafts in a container must be carried out very carefully so as not to damage fragile roots. The container is 1/3 filled with the mixture. A stalk is placed in the center and covered with earth. After planting the seedling, the soil is well spilled with settled warm water.
Furrowing
The first step is to conduct a visual inspection of the shanks. They should be free of stains, rot, mold. After updating the cuts, you need to check the condition of the vine inside (it should be "alive" and have a light green color in the section).
In the spring, planting of grapes by cuttings is first carried out in buckets, in which holes are made for drainage. The soil is made up of sand, humus, leafy earth. In June, the grown plants are planted in a permanent place. In autumn, a young vine should grow up to 1.5 m in length, have several branches and a developed root system.
Placing cuttings in a kilchevator
In early spring, the cuttings are dipped in a pink solution of potassium permanganate for 6 hours. The stalk is trimmed to the desired size.
Propagation of grapes by cuttings (shanks) is a proven method of obtaining a healthy vine without changing varietal characteristics.
Planting cuttings in a temporary location
Further, before the onset of stable frosts, the vine is covered. The easiest way is to cover with spruce branches. Varieties specially bred for the middle lane, covered in this way, winter well.
Some subtleties of growing grapes in the middle lane still exist. First you need to choose a suitable early maturing variety. If in the southern regions grapes can be planted from October to March, then for areas with a colder climate (middle lane) the most suitable time for planting is early spring, before the leaves bloom (early May).
Shelter for the winter.
Harvesting cuttings
Select the desired variety.
Second option
Cuttings prepared for propagation are stored at temperatures from 0 to 2 ° C in a cellar, basement or refrigerator. During storage, the cuttings need to be inspected and turned over 1 - 2 times.
Germination of grape cuttings
Further care of the seedlings consists of regular watering (without stagnant water), loosening the soil, if necessary, and top dressing. Also, the seedlings need to be hardened, taking them outside for 10-15 minutes first, gradually increasing the time the seedlings stay in the fresh air.
Before laying the stems for germination, they must be rinsed in running cold water and soaked. For soaking, settled or melted water is used. The melt water will saturate the shanks with all the necessary microelements, which, by the will of Mother Nature, is endowed with snow. Alternatively, the cuttings can be placed in a container and simply covered with snow. Place the capacity closer to the battery.The shanks should be 1/3 covered with water.
The dream of many summer residents is to have on their site a vineyard with beautiful, sweet, juicy clusters of grapes. Recently, the cost of grape seedlings has increased significantly, as well as the risk of acquiring a low-quality seedling and not the variety that we would like. For confidence in the variety and quality of planting material, growing seedlings with their own hands for summer residents has become a matter of honor.
The upper cut is coated with garden varnish (raw linseed oil (40 g), pure alcohol (75 g), spruce resin (600 g)), the lower cut is renewed by 2 mm, then the cuttings are soaked in melt water for 3 days.
The first year, the seedlings need to be well looked after. How to root grape cuttings and when to cut off grape cuttings depends on the growing area and variety. Success can be achieved by using local varieties.
Another method widely practiced by gardeners is the use of non-woven covering material, such as sugril. It is wrapped around grape bushes tied and laid on the ground, and covered with roofing material on top.
If planting is carried out along a fence or wall, then the distance from it to the seedling should be at least 40 cm, and in a row between plants, the gap must be maintained at 1.2 m.In case of planting in an open place, the distance in a row is 1.5 m, between grape rows - 2 m.
Transplanting shanks in a container
The cultivation of grapes in the middle lane has recently become more and more interesting for summer residents and gardeners. This is quite possible, you just need to choose a suitable early ripening variety. Basically, caring for grapes in the middle lane is reduced to proper pruning, the introduction of organic and mineral fertilizers, and removing from the trellises and preparing the vine for winter is a matter of technology.
Decide on the landing site.
: The cutting is placed obliquely in a plastic bottle, making 2 - 3 holes in its bottom and pouring 6 - 7 spoons of soil mixture onto the bottom. Wet sawdust is poured on the sides of the cutting, the cutting is covered with a plastic cup and the bottle is placed in the light, with an eye from the window. Watering is carried out from the pallet. When the stalk grows to the top of the glass, it is removed. To accelerate the formation of roots, pallets with glasses or bottles are placed above the heating radiators so that the lower part of the cuttings is at a temperature of 20 - 25 ° C, and the upper part at 12 - 18 ° C. Accelerated root formation improves plant nutrition.
In late January - early February, grape cuttings are taken out and prepared for germination. To do this, they are soaked in warm water for two days, changing it. Then, for a day, they are placed in a solution of a root formation stimulator. After that, the cuttings are put on germination. This is done in two ways.
Planting ready-made seedlings to a permanent place of growth is carried out after the threat of frost has passed.
The shanks are soaked for 2 days. After the first day has elapsed, any root growth biostimulator that is sold in the store can be added to the water.
Grape cuttings should be purchased only in nurseries that guarantee the varietal compliance of the material, as well as the absence of diseases. It is extremely dangerous to buy seedlings in regions infected with phylloxera! Any planting material should be disinfected both in the place of preparation and before planting!
Dormant period
Grapes go through a one-year cycle in a year. It consists of two periods - dormancy and vegetation. The first lasts from leaf fall to spring climatic warming. During the rest period, all processes are very weak. Even at a favorable temperature, the buds do not germinate. This period lasts until mid-January and is called physiological rest.

Then the plant begins the next phase. It is called forced rest. In this state, the grapes are capable of rapid awakening when the temperature rises to +10 degrees.This time is used for winter grafting, as well as for accelerated growing of seedlings from cuttings of a matured annual vine. They are selected from high-yield mother bushes with pronounced varietal characteristics.
Blank
Cutting grapes is the selection of parts of a mature vine of any size, even with one eye. The most rational choice is the vine with two or three buds.

The most viable cuttings are those that are harvested in the fall after the end of the growing season. For this, shoots with a diameter of 8-10 mm are selected. Thin cuttings take root less well. In some varieties, the vine itself is not thick. Then the workpieces will be thinner.
The grapes are cut as follows:
- The vine is cleared of stepchildren and antennae.
- The lower cut is made obliquely and 3 cm below the node from which the bunch or tendril departed. After each use, the knife is dipped into a solution of potassium permanganate.
- The top cut is made straight and 4 cm above the knot.
The grafting of grapes is completed, and the prepared material is collected in bunches, aligned along the bottom end and tied in two places. Then a label is attached with the name of the variety.
Storage
Bunches of cuttings are soaked in water for a day, then dipped in ferrous sulfate (3% solution). These measures will protect them from drying out and mold. The cuttings can now be stored.
There are several ways to do this:
- The cuttings are placed in plastic bags and stored in a ventilated basement at temperatures from 0 to +6 degrees.
- Beams are placed horizontally in a pit 50 cm deep and sprinkled with wet sand until it completely covers them. A wooden control lid is placed on top. Then they cover everything with sand to the top.
- If there are not very many cuttings, then it is convenient to use one and a half liter plastic bottles with cut bottoms for storing them. Prepared material is placed in one, two longitudinal cuts are made on the other and put on the first. This method does not require binding, and ventilation is carried out by opening the plugs 2-3 times during the entire storage period.
Checking the planting material before rooting
When to germinate grape cuttings? This can be done in winter (February) and spring.
The stored material is carefully removed, cleaned of sand, washed with potassium permanganate, then its appearance is checked. The condition of the wood is determined by the updated cut, which has a bright green color. And when it is compressed, insignificant moisture appears. In a longitudinal section, the kidneys should also be uniformly green. Cuttings with any deviations (black or brown bark, various spots or dots, and other damage) should be discarded.

Some moisture may be lost during storage. It must be restored by soaking the cuttings in soft (rain, melt) water for a period of days to three. Before rooting, all cuttings must be labeled with the name of the variety. The bottom slice is updated to the full diaphragm node itself - a storehouse of nutrients. Part of the bark can be scratched to form additional roots. This is done from the lower end of the cutting with a sharp knife.
The upper cut is not renewed, it is immersed for a second in molten paraffin or wax to avoid the formation of fungus and putrefactive bacteria. It is better to remove the lower kidney - this way you can once again check the condition of the planting material.
After everything is prepared and you know when to germinate grape cuttings, you can start rooting them. This is done in winter in small containers, and in the spring in a school.
Germination in cups
The most acceptable and common method. Growing grapes from cuttings in cups will be more effective if their lower part is kept in a heteroauxin solution for 24 hours. At the same time, the kidneys are not wetted. The dishes with seedlings are covered with a plastic bag and placed in a warm place (for example, near a battery).
A day later, when the preparation of grape cuttings for germination is completed, they are planted in cups with soil. The earthen mixture consists of the following components:
- Humus - 1 part.
- Peat - 1 part.
- Sod land - 2 parts.
- Coarse sand - 1 part.
Containers for planting cuttings can be made from 1.5 liter plastic bottles. A glass with a height of 20 cm is cut from the bottom, a hole is made in the bottom. The top of the bottle is not discarded. It will come in handy later to close the glass and provide a microclimate for the handle.
The earth in glasses needs to be watered, a hole should be made in the center almost to the bottom with a diameter of 2 cm. Then you need to make a pillow of sand and fill the hole completely with it after installing the cutting.

In order for the cultivation of grapes from cuttings to take place according to all the rules, that is, first the formation of roots, then the awakening of the buds, certain conditions must be observed. The temperature for the bottom of the glass should be up to +30 degrees, and for the kidneys - no higher than +15. This is quite difficult to achieve, but it is possible. For example, if you grow grapes from cuttings at home, then such conditions can be created on the window. The glasses are placed on a metal tray, which is fixed to the battery. The inner window frame is opened and the seedlings are isolated from the room with a polyethylene screen. The temperature can be additionally adjusted with a vent. When growing grapes from cuttings at home, watering can be provided from below by supplying warm water to the pan. Through the drainage holes in the cups, it will flow into the soil.
After the roots begin to be seen through the transparent walls, the cooling of the kidney zone is stopped. When shoots begin to develop from the buds, the corks on the tops of the bottles are opened, and with active growth, the shelter is completely removed.
Green cuttings
In spring, stepchildren and pruned shoots can be used. Green cuttings with two buds are immediately placed in water. Then they are planted in glasses or boxes, create partial shade until they start to grow. In the summer months, the cuttings will develop, and in the fall they are removed to the cellar. In the spring, the seedlings are placed in buckets of fertile soil, and in September - in a permanent place in the vineyard. Cutting grapes in spring is a rather risky business, since during the winter you can lose most of the already grown plants.
Kilchevanie
If you want to learn how to cut grapes quickly, you need to apply one agronomic technique. It allows you to create a circular callus in them, from which roots will appear in a short time. In order for the grape cuttings to be successful, the soil is removed from the greenhouse. Then they dig a trench 20 cm deeper than the length of the seedlings, put a lattice on the bottom and tightly put the bundles upside down to each other, filling them with river sand. The lower ends (they turned out closer to the surface) should be at the same level. Then they are covered with a layer of sawdust or moss of 2 cm and a layer of humus of 12 cm, watered and covered with frames, with the help of which the temperature will be regulated (+ 22 ... + 24 ° C). The soil periodically needs to be moistened and loosened. In the southern regions, ice is placed on the bottom of the trench or spilled with cold water. Kilchevoy ends in two or three weeks.
Growing grapes in central Russia
It is believed that the cultivation of this plant is possible only in the southern regions. But today a technology for growing grapes has been developed for central Russia as well.

First you need to choose a landing site. It should be sunny and calm. During the growing season, the plants should be arranged in ribbons in a north-south direction.
Soil preparation, planting and care
After the cultivation of early grape seedlings is successful, they will need to be correctly placed on the site. They do this at the end of May, when the last frosts have passed. Garden soil mixed with humus is poured into a planting hole measuring 50 X 50 cm. The plant is placed on this dais.

Abundant watering should be carried out at the root. Weeding and loosening are required. Grapes respond well to fertilizing with mineral and organic fertilizers. Liquid mullein should be applied in the spring for a quick build-up of green mass. And at the end of summer, phosphorus is needed so that the vine ripens well and has time to finish the growing season. Potassium is also needed throughout the growth.
In order for a large number of productive vines to form, it is necessary to break out the lateral shoots - stepchildren - in time.
Formation of grapes and shelter for the winter
In the fall, after the foliage has fallen, they are engaged in light pruning and the creation of sleeves (vines). In the first year, in the conditions of central Russia, they are left 2-3 on one plant.
For the winter, grapes need to be hilled high and covered. You can do it like this:
- Gather the vine into a bunch and tie with twine.
- Wrap it in spandball and roofing felt.
- Drag with rope.
- Lay the resulting structure on boards, stones or bricks.
Moisture will not get into such a shelter during thaws, and the vine will not get wet. Frost is not terrible for a dry plant.
How to properly remove the shelter

The structure is disassembled in reverse order at the beginning of May. But you do not need to tie the vine to the trellis as long as there is a possibility of recurrent frosts. While it is lying on the ground, you can always cover it with the same spandball or non-woven covering material. In addition, it is always warmer at the surface of the earth, and in the event of a cold snap, the vine will not freeze.
In early June, it can be safely placed on a trellis, but then another problem arises. By this time, the shoots have already reached a decent size, so you need to be very careful not to break them off.
The garter of grapes and shoots (dry or green) increases the yield and its quality. It allows for ventilation of the bushes and more lighting, and also frees up the approaches to the plants for mechanical work.
Dry garter

It is done during sap flow, but before the buds swell. When they start to bloom, it is very easy to break them off. Last year's shoots are tied up in an upright position to form a stem. If it is high, then you need to fix it in two or three places. A long vine, intended for harvesting, is tied up horizontally, achieving maximum illumination.
For this method, a special rope is used, consisting of steel wire and paper winding. With a garter, you need to leave a margin for thickening the shoots.
If the bush is small, then the entire fruit vine is attached to the lower trellis in one row. With large plant sizes, part of the shoots is tied to a second wire.
Green fastening of grapes to the trellis
You will have to tie it up several times per season. The first one - with a length of shoots of 50 cm. Then, as it grows and reaches the second tier of the wire. Green shoots are tied up vertically, no more than 2-3 pcs. together. This is done with twine, sponge, textile waste or strips of plastic film.
Fastening is carried out in the form of a figure eight, excluding chafing and burns of shoots. Where possible, it is best to distribute them at a 45-degree slope. Thus, the illumination of the plant increases, photosynthesis is enhanced. Accordingly, the sugar content and the amount of tannins and aromatic substances in the fruits increase.
If in the upper tier the wire is stretched in two rows, then there is no need to tie it up. Shoots simply wind up between them, where, with the help of antennae, they are fixed on their own.
Grapes are a very thermophilic plant and we are used to growing them on huge plantations, mainly in southern countries. But over the past few decades, through the efforts of breeders, many hybrid varieties have been bred that can bear fruit in central Russia, and even closer to the north in closed greenhouses. At an average ripening temperature of + 18 ° C, you can get a harvest of juicy, fragrant berries in just 100-110 days.We will talk about the cultivation and cultivation of such grapes further.
How to grow grapes at home
Grapes are exactly the kind of culture that does not propagate by seeds, since in this case it does not retain its original genetic characteristics. It is not always possible to buy a ready-made seedling of a favorite variety. That is why the most accessible and widespread method of propagation of vines - cuttings.
Its availability lies in the fact that at home it is very easy to preserve, plant and root grape cuttings, prepare them for planting in open ground or a greenhouse. It is best to do this at home, since the rooting process should begin no later than late February - early March.
The most important thing is to choose a grape variety that is good at rooting.
Now, very many hybrid varieties have this ability, since cuttings are one of the main areas of work for breeders. Most often, gardeners like to plant table varieties on a garden plot with excellent taste, sugar content, large berries (preferably seedless), with early or mid-ripening periods. The varieties meet almost all these requirements: Delight, Kesha, Pleven, various varieties of Kishmish, Laura, Kodryanka, Anyuta, Aleshenkin, Veles and many others.
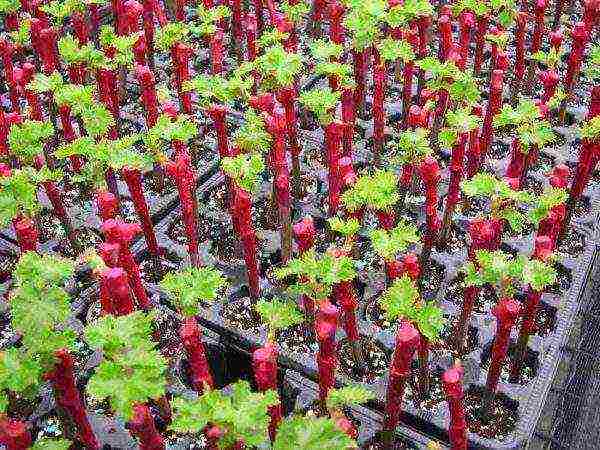 Before planting grapes in the ground, it is necessary to germinate the cuttings and wait for the first leaves to appear.
Before planting grapes in the ground, it is necessary to germinate the cuttings and wait for the first leaves to appear.
Growing features
Growing grapes in a greenhouse or in the open field directly depends on the natural climatic conditions of the region. It is clear that in the southern regions in the open field, grapes will have time to ripen not only early varieties, but also later ones. But in the Middle zone, the Moscow region and further to the north in open soils, only the harvest of the earliest varieties will ripen.
In regions where summers are short and winters are cold, it is best to grow vines in greenhouses in order to enjoy the taste of berries with different ripening periods for a longer time. But indoors, you will have to more carefully monitor the health of the bushes., microclimate, soil condition, since cases of fungal and other infections spread much faster. In an enclosed space, it is easier to prevent the occurrence of typical diseases than to eradicate them.
Step-by-step technology for growing grape bushes from cuttings
The whole process of obtaining rooted seedlings takes several months, but it is not very difficult in terms of labor intensity. Even novice gardeners who decide to take up viticulture are able to achieve the best results - this culture is so unpretentious, although it requires some attention. The main thing is to properly care for and carry out certain activities on time.
 Chopped grape cuttings
Chopped grape cuttings
Cutting and storing shanks
The very first stage is the preparation of planting material. During the pruning of grapes in the fall, when all the branches bearing fruit this year are removed, cuttings are being prepared. It is the fruit branches that serve as the best material for future seedlings. What is necessary take account:
- pruning is carried out after leaf fall, before the onset of the first frost;
- the vine should be as straight as possible, healthy, light brown or sandy;
- the longer the stalk, the better the reproduction will be.
The branch should be without visible damage, with a light bark, on the cut - green, with droplets of liquid (juice) protruding on it, the lower cut is made straight, and the upper cut oblique. Cutting length - at least 40-45 cm, cut diameter - 10-12 mm + 3-4 living buds with an interval of 10 cm between them.Sections should be made with a very sharp secateurs or a knife so that their tissues do not wrinkle, at a distance of at least 2 from the buds -3 cm.
Cut cuttings must be prepared for storage:
- soak in cold water for 1-2 days, changing the water 2 times a day;
- process with a solution of vitriol or potassium permanganate (it is best to soak for half an hour);
- spread out on paper napkins (towels) and dry well from excess moisture;
- collect cuttings in a bunch, wrap tightly in plastic wrap, tie, fix a tag with the name of the variety (if there are grapes of several varieties, you need to store them in different bags, since different varieties have a bad effect on each other during storage); instead of a film, you can use plastic bottles - lower the vine through the neck and close the lid.
Store the cuttings at t 0 + 5 ° C (a refrigerator, a glazed balcony, a basement will do).
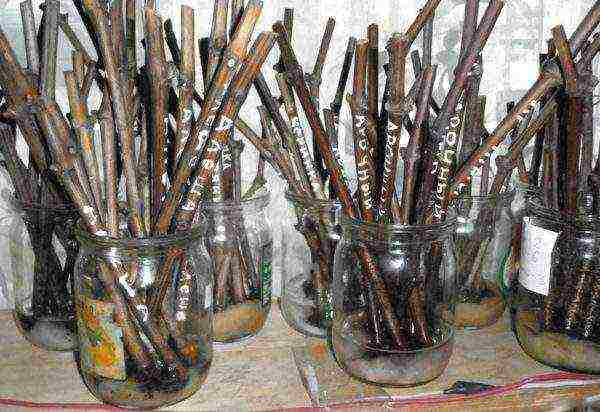 Cuttings can be stored both in the refrigerator and in the basement
Cuttings can be stored both in the refrigerator and in the basement
Preparation for rooting
In late February - early March, they begin to root the planting material. First you need to check how the material was preserved. To do this, the sections are updated, each at a distance of 0.5-2 cm from the upper and lower buds, respectively, in an oblique and direct way - they should be green and moist. Then the cuttings are immersed in water for 1-2 days (depending on the degree of dryness of the branches), to stimulate growth, it is necessary to add honey, aloe juice or humate (1 tablespoon / 10l of water).
At the lower heel, where the roots will grow, several grooves 2-3 mm deep and 2 cm long should be made with a needle - this will help to get a more developed, lush root system. The upper cut can be treated with paraffin.
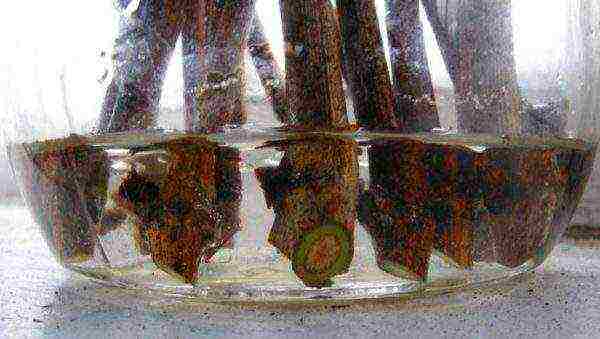 Checking cuttings for safety
Checking cuttings for safety
Germinating the cuttings in water
Put a layer of cotton wool about 2 cm on the bottom in an ordinary glass liter jar, pour the same amount of water (melted water is best), lower the cuttings. The heel - the bottom edge - should be in the water at a depth of 4-5 cm. To avoid decay of the liquid, you can put 2-3 tablets of activated carbon, add water periodically. On top of the jar, you can put on a plastic bag to create a greenhouse effect, put it on the windowsill.
Grapes, like any plant, need an abundance of light and warmth to grow vigorously. Twigs will appear first, and then roots. In order for the root system to develop, the shoots should be broken off; for a bush, one, the very last shoot will be enough.
Planting in pots in a greenhouse or greenhouse
The soil for the seedlings must be prepared in the fall by mixing equal amounts of turf soil, peat, sand, rotted manure or compost; ready-made mixture from the store is also suitable. As a container, you can use plastic bottles, larger disposable cups, etc., make drainage holes. A little drainage is poured at the bottom of the container, then the prepared soil, the cutting is carefully lowered onto it, poured with soil, slightly (!) Moistened.
The heel of the seedling should be at a depth of 1/3 of the container, and young shoots above the ground. Approximately until the end of May - beginning of June, young seedlings will have time to root well, develop full-fledged leaves and branches, and prepare for planting in the ground.
 Planted shanks in pots
Planted shanks in pots
Rooting in sawdust or soil
In the southern regions, where in March the soil warms up to a temperature of 10-12 degrees at a depth of 10 cm, cuttings after processing and soaking can be planted directly into the ground - a school. Planting is done in prepared, well-fertilized soil to a depth of 40 cm. The cuttings are laid in pits (or a furrow), covered with earth up to half, tamped well, watered abundantly, pits are filled up to the top. 2 buds should remain on the surface of the earth. Focusing on the climate of the region, you can cover the surface or temporarily cover it with a film.
Another fairly common way to germinate cuttings is in sawdust.
The sawdust should only be of deciduous trees, without any admixture of harmful plywood or chipboard sawdust. They must be steamed before use - pour boiling water, then cool and in a deep dish (bucket) first pour a small layer on the bottom. Then, in an inclined state, lay out the sawdust in layers, placing the cuttings vertically between them.After planting, cover the dishes with foil, put them in a warm place and moisten the environment from time to time until sprouts and roots appear.
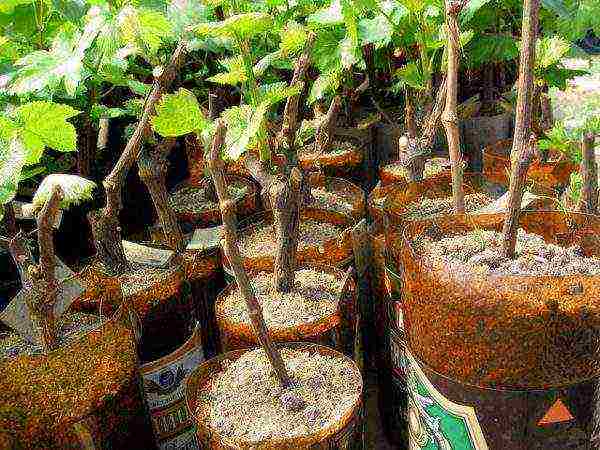 Rooting grapes in sawdust
Rooting grapes in sawdust
Correct planting of seedlings in open ground
The technology for planting in open ground is simple. The finished rooted seedling is first prepared for planting in open ground. To do this, within 5-7 days, seedlings in pots are taken out into the street, avoiding direct sunlight. After hardening, cuttings are lowered into the prepared holes together with an earthen lump, the holes are poured with earth mixed with humus, watered with warm water. The main thing is not to deepen the plant and water it moderately. In order not to damage the roots during planting, it is better to carefully cut plastic cups or other containers, then remove the seedling with an earthen clod.
 Rooted grapes ready to plant
Rooted grapes ready to plant
Be sure to immediately fix the support next to the grape seedling planted in the ground!
Germinating a grape stalk, rooting it and growing a seedling of your favorite crunchy sweet berry is not a lot of work. This can be done both in a polycarbonate greenhouse or greenhouse, and in the open field. Proper care for your pet - and he will thank you with active growth and a rich harvest, literally, in two or three years.
Grapes in garden plots in the middle zone of our country can be found more and more often. The achievements of breeders and the enthusiasm of summer residents are doing their job, and the southern vitamin berry "just from the garden" is now a frequent guest on the tables of those regions where it was impossible to think about it before. A vineyard in the country requires the application of strength, but its establishment and maintenance are not insurmountable difficulties.
Growing grapes in the middle zone of Russia
For the successful cultivation of grapes in the middle lane, one must understand the peculiarities of the life of this southern plant.
- Grapes need sunlight. With its lack, good berries cannot be obtained.
- Grapes love warmth. For normal growth and formation of the crop in summer, temperatures are needed not lower than 20 ° C. Grape leaves freeze at –1 ° С, and even perennial wood perishes when frosts are stronger than –25 ° С.
- Grapes are a drought-resistant crop, but with justified watering, the yield increases several times.
If earlier newcomers to viticulture were offered to start with planting Lydia or Isabella, now this advice, even in the middle lane, can hardly be called correct. Rather, on the contrary, the taste of Isabella, who goes only for wine, can be discouraged from such an interesting activity. And growing many varieties with very tasty berries, especially early ones, is a little more difficult. Any novice grower with basic gardening skills can handle this.

Isabella will grow up almost without leaving, but she will bring a little pleasure
Growing grape seedlings in the conditions of central Russia
The most common way of propagating grapes is from cuttings; it is quite feasible in the conditions of central Russia. Cuttings are cut from strong annual shoots during autumn pruning. Shoots should have a thickness of at least 5 mm, any length for autumn cutting: it is convenient to take 30–40 cm each. Each should have 4–5 well-developed buds. Until February, cuttings are stored in a cellar or refrigerator in loosely tied plastic bags at a temperature of about 0 ° C.
In February, cuttings are taken out and cut into pieces with 2-3 buds. The upper cut is made straight, 2-3 cm above the kidney, the lower slanting 1-2 cm under the kidney. Chopped cuttings are soaked in water for a couple of days. After that, several longitudinal scratches are made in the lower part of the cuttings to facilitate root formation.
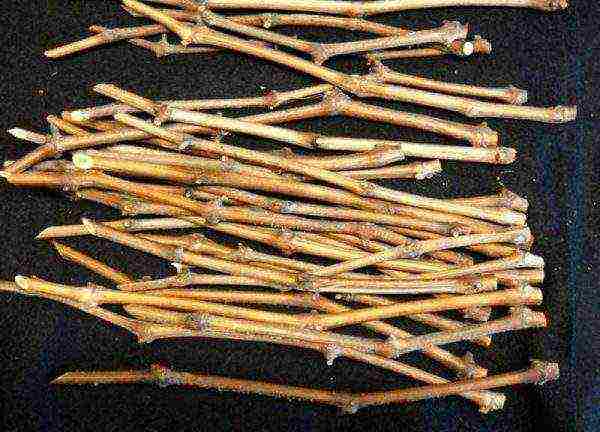

Before planting, cuttings are cut so that they have three buds, and the lower cut is made oblique
Cuttings can be planted in any liter container with a substrate, but most conveniently - in plastic bottles with a cut off top and holes in the bottom to drain excess water.Any light soil (sand with soil, sand with peat, pine sawdust, etc.) is suitable as a substrate. The stalk is planted so that one bud remains on the surface. Pour it over with a pink solution of potassium permanganate and cover with a plastic bag for the first time.
Containers with cuttings are placed in a warm place (25-28 ° C). When the first leaves appear, the stalk is gradually accustomed to being without a bag. Good light is definitely needed at this time. After another 3-4 weeks, you should try to pull the stalk out of the substrate. If it holds on tightly, then the roots are already there.

When several leaves have appeared on the cuttings, they may already have roots, but this should be checked
Cuttings are systematically watered with settled water, fed twice with complex fertilizer. For the rest, the main thing in care is compliance with temperature and light conditions. A rooted cutting will become ready for planting in a permanent place as a young seedling by summer.
In the retail network and in the markets, more mature seedlings are more often sold, which have already lived in the open field for a year and have grown both aboveground shoots and a good root system. Such seedlings are usually sold without a clod of earth, and when buying, you need to carefully monitor that the roots are alive and healthy.
Storage of grape seedlings and preparation for planting
The best time for planting two-year-old grape seedlings in central Russia is the end of April. If they were bought with an open root system, and you can't plant them right away, they must be properly saved. At least, wrap them in a large wet sacking: so, in a wet rag, they will quite last a week and a half. In the same state, the seedlings must be taken to the country. If you have to wait several days for planting, you can simply bury them in damp ground.
Before planting, it is necessary to remove all the upper roots, if any, and leave the roots only on the heel itself, cutting off and broken. The seedlings must be soaked for one or two days in water, or better in a weak urea solution: 1 tablespoon per bucket of water, placing both the roots and the vine in the solution. Immediately before planting, the roots are dipped in a mash made of clay, mullein and water.
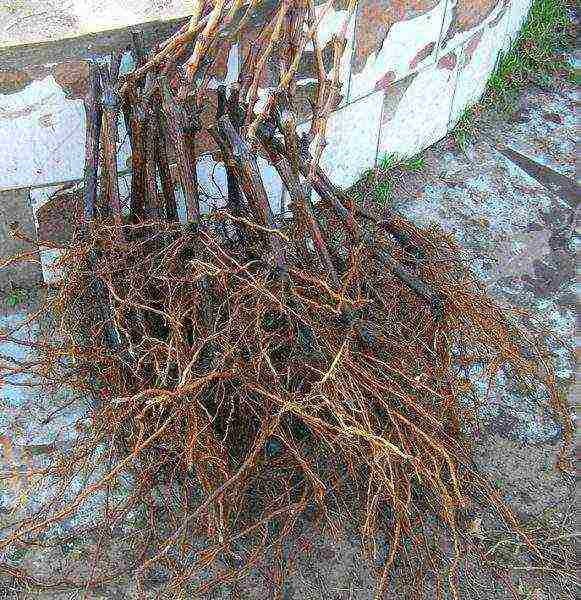

The seedlings of the second year have very powerful roots, but before planting, it is better to remove some of those on the trunk.
If we are talking about planting a self-grown seedling in a container (pot, bottle, etc.), the conversation is somewhat different. They will have to be planted only at the beginning of summer, and before that time it is necessary to have time to harden them, taking them out to the balcony on not too cold days. It is necessary to bring the pots with seedlings to the dacha on the day of planting, and just water it well before planting.
Choosing a place for grapes on the site
Grapes can be planted both on level ground and on not very steep southern and southwestern slopes. Dangerous placement in the lowlands and on the northern slopes: damage to fruit buds by late spring frosts is possible. Grapes grow on any soil, except for heavily swampy areas and areas with a close occurrence of groundwater. For planting grapes in central Russia, you need to choose the sunniest areas, well protected from winds, especially northern ones.
All common fruit trees are good precursors for grapes. It cannot be planted only in the place where grapes have already grown before; after uprooting the grape bushes, vegetables, flowers or herbs should be grown in this place for several years. Most often, grapes are planted after vegetables, but it is better to sow siderates - oats, vetch, mustard in the last year before planting grapes.
Almost everything can be planted next to grapes, and its most beloved neighbors are peas, onions, beets, strawberries, cucumbers, sorrel. Not very fond of grapes with tomatoes and corn. Competing for water and nutrients with horseradish.
Surprisingly, grapes do not tolerate being close to marigolds growing even at a distance of 5–6 meters.
Preparation of soil and planting pit for grapes, fertilization
Long before planting grapes, the soil must be carefully prepared. Since in the conditions of central Russia grapes are planted almost exclusively in the spring, this should be done in the fall. Pre-planting soil preparation at the summer cottage consists in digging onto a shovel bayonet with the simultaneous application of fertilizers. In advance, before planting, they enrich the soil around the future bush with rotted manure, phosphorus and potash fertilizers. Of course, they are also brought into the landing pit.
When digging, it is not necessary to throw out pieces of bricks and small stones from the ground: grapes love stony soils.
In the conditions of central Russia, it is better to dig a hole near any buildings that block the grapes from the cold northern winds. A large pit is being dug: its dimensions are not less than 80 × 80 × 80 cm. There are different approaches to filling the pit. In the conditions of the middle lane, it is necessary to force the grapes to take root as deep as possible, and for this you can apply a little trick: make a small barrier to the nutrient layer with fertilizers. To do this, a well-mixed mixture of humus, sod land, sand and mineral fertilizers must be laid on the bottom of a deep hole with a layer of 20–25 cm. You can take a complex fertilizer - for example, nitrophoska, 400 grams, and the rest of the mixture components in approximately equal volumes. The second layer, ten centimeters, must be made of drainage: rubble, broken brick, slate fragments, etc. Through this barrier, the grapes will let their active roots in search of nutrients.
The entire space above the drainage will be covered with soil mixed with humus during planting (approximately 3: 1). On very acidic soils, you can add a couple of handfuls of slaked lime to this mixture. It is impossible to fertilize this soil too much - young roots will be damaged. But it is not necessary to fill up the soil before planting a grape seedling. It will be necessary to bury the seedling in the conditions of central Russia deeply, placing it almost on the drainage layer. And beforehand, a couple of buckets of water can be poured into a pit filled with fertilizers and drainage.
If several bushes are planted at once, you need to know about the distances between them. For low-growing varieties, the minimum distance between bushes in a row should be 1.3-1.5 m, for medium-growing varieties - 1.5-2 m, vigorous ones - from 2 to 3 m.
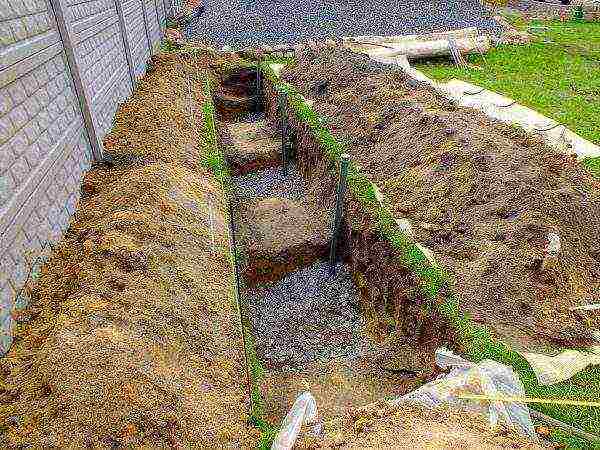

When planting several seedlings, the pits almost close into a trench, but each has its own seat being prepared
Planting and transplanting grapes in central Russia
You should immediately agree on which seedling you are holding. If this is a two-year-old with powerful bare roots and still without leaves, then it is still early spring. It should be planted in the middle lane in April. If this is the seedling that was a cuttings back in February, you grew it at home yourself, and it is in a container, covered in leaves, then it will need to be planted only at the beginning of June. Autumn planting of grapes in the middle lane is possible, but undesirable.
Before planting grapes in a prepared hole, you need to try them on. It will have to be in the hole so deep that only 1-2 buds are visible from the ground. Therefore, it is necessary to pre-pour so much of a mixture of soil with humus so that the seedling, placed with the heel on the bottom, looks out. In advance, you need to drive in a stake for a garter of an intensively growing vine, as well as a piece of a solid inch pipe, through which the first 1-2 years will need to water the seedling to the very roots. If there is enough rainfall in the region, and the soil is light, permeable, the pipe is not needed. Then a small mound is poured and a grape seedling is planted. If this is a strong seedling with an open root system, it is planted like ordinary bushes: set on a mound, spread the roots, fill the hole and water it well. If this is a very young seedling grown at home from a cuttings, you should try to plant it with a lump of earth, carefully removing it from your home container.Such a seedling can be planted higher so that several leaves can be seen from the ground.

A seedling grown from a cuttings in the spring must be planted with a clod of earth, trying not to damage it
If it was necessary to transplant a grape bush, it is rather difficult to do this, and if the bush is more than 5 years old, it is almost unrealistic. Younger bushes can be transplanted in the middle lane, but only in early spring. The older the bush, the larger clod of earth you should try to leave on the roots. The transplanted bush must be well pruned, and a few days before digging it up, water abundantly, despite the fact that there is still enough moisture in the soil in the spring. The bush should be dug in so as to damage the minimum of the roots, that is, dig a circular trench far from the center of the bush. The roots sticking out of the remaining coma are cut off. The lump is wrapped on all sides with a strong rag, a strong sheet of any material available in the household is placed under the bottom and the lump is taken out. In a new place, the bush is very well watered and mulched.
Grape care, feeding and treatment against diseases and pests
Having planted grapes on a site in central Russia, one must realize that now there will be a lot of work. True, most of the troubles are quite accessible to an experienced gardener, but new knowledge will also be required. Not everyone can visit the site all year round, but there is work in the vineyard in winter. Basically, these are insulation measures: throwing snow on the bushes sheltered for the winter. And the main work begins with the arrival of spring, in the middle lane - around the end of March.
At this time, it is necessary to open the bushes wrapped for the winter. If possible, apply basic fertilizers by burying them in shallow holes. In mid-April, the vines can already be lifted and tied to the trellis. When the thermometer goes through 0, you can spray the grapes with nitrafen or Bordeaux liquid. At the end of April, tie up the vines, distributing them along the stretched wires. In May, in the middle lane, the grapes begin to wake up, but the processes on it go very quickly: soon the buds open, leaves appear, and flowering begins. As soon as the intensive growth of young shoots has begun, the extra ones must be immediately broken out, without waiting for them to grow large and shade the growing berries. At the end of May, you can give the bushes a liquid top dressing.
In the summer, as they grow back, they tie up new shoots, remove extra stepsons and bunches. It is imperative to feed the bushes during the growth of berries, which is most conveniently done by spraying the leaves with solutions of complex fertilizers. August dressings should no longer contain nitrogen. In mid-August, the harvest of early varieties ripens.
September is the main harvest month. If the harvest is very large, foliar dressing with phosphorus-potassium fertilizers is required. If there are signs of disease, and the berries have not yet been harvested, the bushes are sprayed with sulfur preparations or potassium permanganate. After the autumn frosts and falling leaves, the main pruning must be done. After pruning, the vines are removed, tied in bunches and covered for the winter. In dry weather, water-charging irrigation is carried out. Shallowly dig the soil around the bushes, introducing rotted manure.
Fertilizers have to be given to grapes systematically, starting from planting. Grapes consume a lot of potassium, so potash fertilizers, preferably wood ash, can be used in maximum doses. In autumn, manure and compost are buried under the grapes, to which you can add superphosphate and ash. In the spring, any fertilizers are used, including nitrogen fertilizers. And two to three weeks before the beginning of flowering, several liter cans of ash should be poured under the bush, sealed to a depth of 10-15 cm and watered well.
In summer, foliar feeding is much more convenient, that is, spraying the bush with weak fertilizer solutions. They are held in the evening. The first such feeding is needed a week before flowering. For her, solutions of complex fertilizers (for example, nitrophosphate) are used.The next top dressing is after flowering, as well as with the beginning of ripening of berries. Fertilizing solutions must be prepared strictly according to the instructions on the package.
Sometimes top dressing is combined with spraying with Bordeaux liquid to fight diseases. In the case of a clear absence of diseases, it is better to use wood ash for preventive purposes. During the day, it is infused in water (a liter of ash per bucket). After that, filter it so as not to spoil the sprayer. If the grapes are clearly ill, it is necessary to study the special literature: here you cannot do without powerful medicines, but it is better not to bring diseases to disease. As a rule, they appear only in a poorly maintained vineyard, where they do not pay due attention to fertilizing, watering, and the bushes are not properly cut.
Video: grapes in Nizhny Novgorod
Watering grapes in the middle zone of Russia
Fortunately, in most regions of central Russia, there is usually no shortage of rain, so in other years watering is almost not required: the vineyard does not need extra water. Watering of young bushes is absolutely obligatory: in the year of planting they are watered several times with 4–5 buckets per bush, mulching after irrigation with humus or peat. For fruiting grapes in case of dry weather, even in the middle lane, watering is required immediately after flowering. But before flowering or during it, watering is unacceptable: the bulk of the flowers can crumble from excess water. A lot of water is required during the growth of berries, but watering should be stopped a month before harvesting. But in general, the roots of grapes penetrate deeply, and if there was nothing unusual with the weather, in central Russia they will find their own water.
In almost any autumn, even in the middle lane, water-charging irrigation will not interfere. Without it, the soil freezes deeply, the icy earth spoils the roots. Podzimny watering is carried out after the leaves fall.
Pruning grapes in the middle zone of Russia
Pruning grapes is an art: it is more difficult to learn it than the art of pruning an apple or pear, and for this you need to study the relevant literature. It is impossible to approach a grape bush with a pruner without knowledge. Unless to cut out clearly broken and dead shoots. Pruning can increase the yield several times or, conversely, reduce it to a minimum, and the outcome depends on how skillfully it was performed with hands. Pruning is not needed only in the first year after planting. The first few years can be pruned in early spring, and after entering fruiting - only in the fall.
Without going into the details of the methods of forming bushes, it is possible to recommend, without experience, only thinning pruning: cut out clearly unnecessary shoots thickening the bush. Their number also depends on the grape variety: some varieties are more successful when forming a bush in the likeness of a tree, while others give a dozen or more independent sleeves to grow from the base. Pruning is performed with a sharp pruner, the wounds are not covered with anything. Slices are tried to be done at an angle of about 45o, 1–2 cm above the kidney.
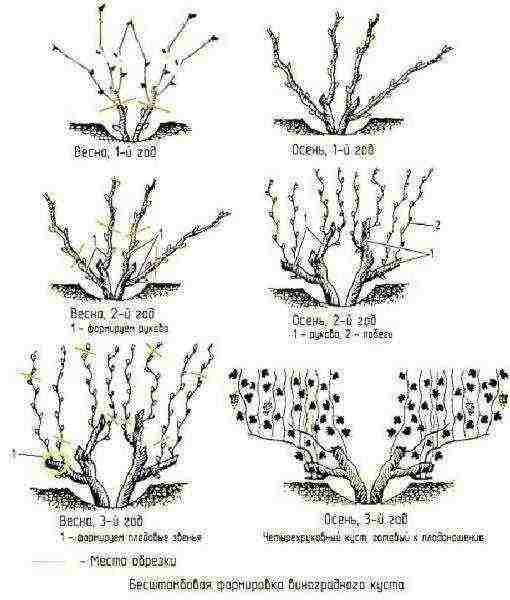
One of the simplest bush formation schemes
In order to facilitate the work of pruning, it is necessary to constantly break out excess green shoots in the summer, while they are very small. The bush reacts to their breaking almost painlessly, in contrast to cutting a ripe vine. Green shoots are removed by hand, breaking them off from the place of growth. Cutting should not be carried out only during flowering.
Correct pruning in the first 3-4 years should be aimed at obtaining the most illuminated bush, which makes it easy to take care of itself and gives a bountiful harvest of berries, each of which will have enough space and sunlight.
Preparing grapes for winter in the conditions of central Russia
In the middle zone of our country, almost all grape varieties have to be sheltered for the winter from frost. Without shelter, only semi-wild varieties can exist, which are usually grown for the sake of a hedge and in some cases for the preparation of simple wines.
Shelter for the winter is done at the end of October. Before the shelter, a thorough pruning of the grapes is carried out, removing also unripe shoots. After the very first light frosts, they break, or even fall off themselves. They should be cut out to healthy, mature areas. After that, the vines are removed from the trellises and lightly tied into bunches so that it is easy to lay them on the ground. It will be a good idea to whitewash the vines at this time, especially the lower parts.
Most of the new varieties bred for the middle lane can withstand frosts down to about -25 ° C, so there is no point in wrapping up the bunches of vines too much. Nevertheless, many gardeners in the middle lane dig deep trenches for laying bushes and cover them with a large layer of earth in the trenches. In most cases, this is clearly unnecessary. At the same time, one must envy a good owner if he dug a trench next to the grapes, upholstered it with boards from the inside, puts the vines in the resulting box, covers it with boards, and fills the boards with spruce branches. This is ideal, but it takes time and effort.
If there is less enthusiasm, the bunches of vines should simply be packed more compactly, and covered with slate sheets, plywood, spruce branches, a thick layer of dry foliage, etc. The main keeper of heat for grapes is snow, and the shelter must be designed so that it can cope with frost before a powerful snow cover is established. Wrapping up with old blankets, sweatshirts and other rags is bad: mice will start and gnaw the bark, the grapes will disappear. Mice are not that afraid of spruce needles, but they do not really like to inject. Better yet, put a special treat for them - poison. It is not necessary to wrap the vines in plastic wrap, as many summer residents do, in the middle zone: unlike Siberia, here frosts alternate with thaws, and the drying out of the bark during a thaw is no better than freezing.
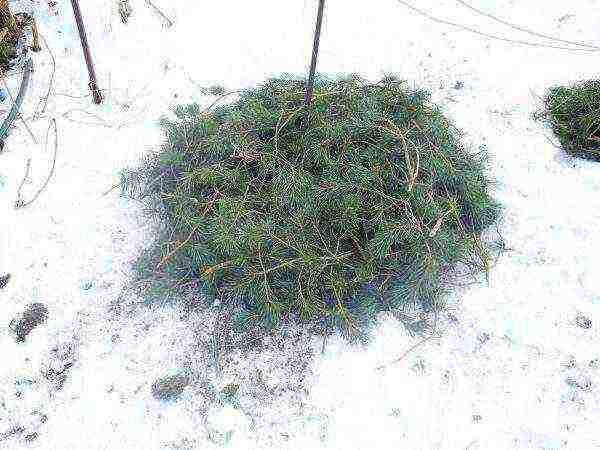

Lapnik and snow - the most reliable shelter in the middle lane
Reproduction of grapes in the conditions of central Russia
A summer resident in the conditions of central Russia can only recommend one method for propagating grapes - with the help of cuttings, as described at the beginning of this article. The guarantee that a good seedling will grow, subject to strict adherence to the rules, is close to 100%. And the difficulties in growing seedlings from cuttings are not great. All other breeding methods are either more difficult or do not lead to guaranteed success. These are ways such as:
- seed reproduction;
- reproduction by layering;
- grafting of grapes on grapes.
There is too much trouble with seeds, seedlings from cuttings are not produced as quickly and not as powerful as from cuttings, and grafts on grapes are worse than on fruit trees.
Methods of growing grapes in the conditions of central Russia
Grapes are essentially a liana, and to ensure a normal existence, they need strong supports. True, in the dacha conditions, he himself is lazy to climb the supports, although most of the young shoots still cling to the tendrils of structures that come close to them. It is these structures on the site that need to be created for grapes.
Growing on a trellis
Trellis cultivation is the main method of forming a grape plant. It can be any structure consisting of vertical posts and horizontal supports. Recently, there are a variety of large mesh nets on sale: both metal and durable plastic. They can also serve as such supports. But traditionally, tapestries are arranged by driving strong posts or metal pipes into the ground. Different grape varieties have a bush of different sizes. There are also very powerful ones, for example, one of the new varieties in the middle lane Furshetny, for it the pillars can be three meters high, but usually they try not to create bushes higher than 2.5 meters for convenience. Therefore, the pillars must be of the appropriate size.

Tapestries can be constructed from any suitable material at hand
Several horizontal rows of wire are pulled between the posts. The lower tier is at a distance of 50 cm from the ground, the subsequent ones - every 30–50 cm. In the spring, overwintered vines are tied horizontally to the lower wire. Powerful green shoots growing in summer are tied up vertically, at the same time breaking out unnecessary ones. Leave 20-30 shoots per adult bush, depending on the variety, sometimes even up to 50. They monitor in time both the number of shoots and the mass of the future harvest, removing extra brushes.
Growing in a greenhouse
With the advent of frost-resistant grape varieties, greenhouse cultivation is slowly becoming a thing of the past, but it is still often used, including in the conditions of central Russia. Of course, grapes are not tomatoes, and the construction of greenhouses for such a large plant requires considerable investment, but when you want an early harvest, they go for this: most varieties ripen in a greenhouse two to three weeks earlier.
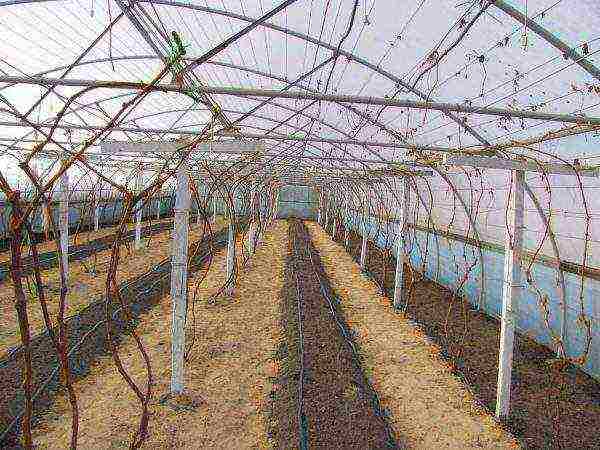

The device of greenhouses requires money and in the middle lane is more suitable for industrial cultivation of grapes
Bushes are planted in a greenhouse more often than in open ground: after 1-1.5 meters. The greenhouse protects the grapes from hail, unnecessary rain, light frost. We are talking, of course, about the unheated version. In the greenhouse, grapes are watered at least three times per season, combining watering with top dressing. They stop watering a month before the litter of the harvest, but they also carry out winter watering.
In the summer, you have to ventilate the greenhouse, monitor the humidity of the air. Shelter for the winter is also required in the greenhouse.
Benefits of greenhouse grape cultivation:
- guaranteed harvest;
- prolongation of the warm period, allowing the vine to grow and the berries to ripen;
- the convenience of caring for grapes in bad weather.
Flaws:
- high cost of the crop;
- the risk of diseases of the bush due to poor ventilation;
- lack of natural lighting of berries.
Greenhouse grapes, of course, are also useful, but if you remember how we are waiting for a summer cucumber from the garden, although greenhouse grapes are sold all winter in stores ... That's about the same with any fruit and vegetables.
Growing in barrels
In the middle lane, you can grow grapes even in barrels, placing them on a glazed loggia. Growing in barrels in garden plots is hardly worth it, although this is done in the northern regions. In the middle lane, the climate is quite favorable for growing grapes and "no frills". And in barrels ... The barrel should be 250 liters. Drainage is placed at the bottom, then fertile soil. The vine is grown for no more than 10 buds, that is, the harvest is small. When grown in summer cottages, barrels for the winter, along with vines, are dropped in the open ground, and in early spring they are brought into a greenhouse, where they are kept until the berries are tied. At the beginning of summer, grapes are taken out to the garden and placed in the sunniest place. In barrels, grapes can grow up to 8-10 years.
Growing in containers
If there is no room for placing a huge barrel, you can try to use smaller plastic containers: 50 liters. Or you can just take a regular plastic bag measuring 50 x 50 x 50 cm. getting the harvest. Of course, the berries can only be tasted. The maximum is to collect another small crop, but after that the plant will simply begin to lack soil, and it will have to be transplanted into the ground (open ground or greenhouse) by cutting the container.
Smolensk method of growing grapes
In the last decade, such a concept as "Smolensk Ridge" was born. The technology developed in the Smolensk region allows us to grow excellent yields of high-quality grapes, which are in no way inferior in sugar content to most southern berries. The essence of the technology is planting on high ridges. It allows the layers of soil directly adjacent to the roots to quickly warm up in the spring, and in the fall, when the bushes need to leave for the winter, to cool down.
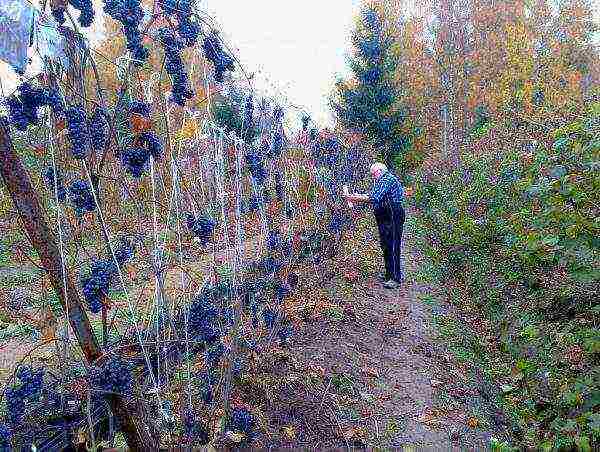

Smolensk inventor Yuri Chuguev at his garden
As a result of planting on high ridges, the berries ripen a month earlier than when planting in the usual way. With this technology, it is easier to care for the bushes. The slopes of the ridges are made gentle, and the snow evenly and reliably covers them in winter. From accidental freezing in especially harsh winters, the ridges are covered with corrugated cardboard.
All basic operations with grapes are performed a little differently in comparison with conventional technology. So, the timing of harvesting cuttings and the technology of their rooting have been shifted. For the second winter, very young seedlings are transplanted into containers and withstand winter at a low positive temperature. Already completely independent plants are planted in ridges from containers, which in a year already give the first berries.
The Smolensk technology is very interesting, and there will undoubtedly be those who wish to use it. A detailed description is easy to find on the Internet.
Growing on a long vine
The term "growing grapes on a long vine" only means the way the grapes are planted. Then an ordinary bush develops, which is looked after by forming on a trellis. Inexperienced summer residents do not always succeed in planting ordinary cuttings in the middle lane, and in this case, you can try another planting method. It actually needs a long vine: a young shoot up to two meters long. This shoot is cut off in the fall, soaked for a day, and then buried in the planting pit, twisting it in a spiral and releasing only 1-2 buds from the pit. They are covered with earth, watered and left for the winter, covered with spruce branches or spunbond.
Often more powerful roots are formed on a long vine, but an irrigation pipe buried in a hole is definitely required: water is needed for the lower parts of the vine, from where the roots will form.
Features of the cultivation of various types of grapes in the conditions of central Russia
In addition to the usual edible grapes, many gardeners plant decorative varieties of this vine on their plots just to decorate the garden. And cultural grapes are not always grown in the form of a familiar liana.
Maiden grapes
Maiden grapes are a decorative liana, used mainly to decorate the site, since they very quickly twine around all the supports provided to it with beautiful shoots and leaves. In spring and summer, its leaves are dark green, in autumn they are red. Curly shoots cling to any possible obstacles, they can grow up to 20 m in height. The dark blue small berries are completely inedible.
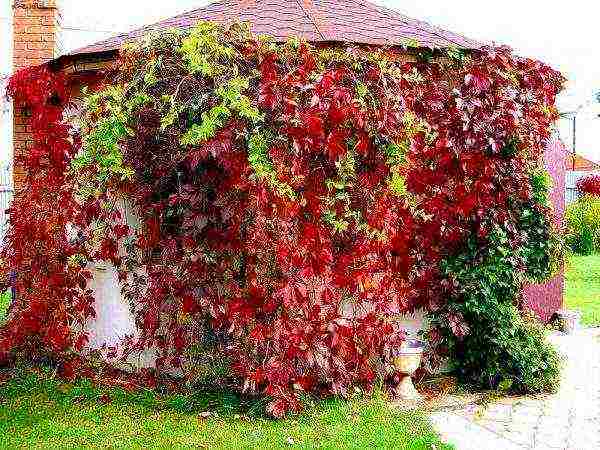

Maiden grapes are used to decorate the site
Maiden grapes can grow anywhere, and in the middle lane, there are no obstacles to its cultivation. On the contrary, it often becomes very annoying on the site, so you must first decide where to plant it. He can damage many structures that come his way.
It can be grown from seedlings, but it reproduces well by self-sowing, in fact, being almost a weed. Requires care only in the first years: several watering and loosening around young bushes. Then - only pruning interfering shoots. It is completely frost-resistant and does not require any shelter for the winter. Resistant to most diseases and pests.
Standard grapes
In the standard form, that is, in the form of a tree, in central Russia, only the most winter-hardy varieties can be formed that do not take shelter for the winter. The formation of the trunk in trees occurs naturally, and in the case of grapes it must be carried out by correct pruning. The height of the trunk can be from half a meter to two meters.

The grape tree is easy to maintain but difficult to cover for the winter
Formation of standard grapes takes several years and is carried out strictly according to the rules that can be found in special literature. The standard crop allows you to increase the total number of berries per plant by a third. Care is also made easier, and some operations become completely unnecessary. But the harvest on standard grapes is somewhat late in comparison with the usual form of the bush. In addition, stronger supports are needed. The main limitation still lies in the fact that standard grapes cannot be covered for the winter, and therefore this form is more preferable for the southern regions.
The cultivation of grapes in central Russia is becoming commonplace. The climate of most regions is quite suitable for the ripening of many grape varieties, and caring for them is only slightly more difficult than in the wine-growing regions of the country. Desire, diligence and some new knowledge will allow you to grow southern berries in any summer cottage.

