Content
- 1 Algorithm for starting a business
- 2 Variants and features of growing greens
- 3 Soil selection
- 4 Selection of greenhouses and equipment
- 5 Harvesting and transportation
- 6 Profit calculation
- 7 Benefits and what greens can you grow in a greenhouse?
- 8 Types of greenhouses?
- 9 Preparatory work
- 10 Photo
- 11 Build a greenhouse for growing greenery all year round with your own hands
- 12 Useful video
- 13 Conclusion
- 14 Selection of greens to grow for sale
- 15 How much does growing greenery in a greenhouse pay off?
- 16 Conclusions on growing greenery in a greenhouse as a business idea
Growing greenery in a greenhouse as a business is an economical, profitable and profitable endeavor. The initial investment in it is low, but the profit from the sale of the product is rather big, especially in the cold season. To organize your own plant for growing greenery, you should draw up a business plan, calculate costs, decide on a sales market and cultivated varieties.
Growing greenery in a greenhouse is a profitable business
Algorithm for starting a business
Before you start growing greens on an industrial scale, you should decide on the options for selling products. Key sales options:
- self-sale of the crop at retail - takes a lot of time, and the financial return is small, but does not require official registration with government agencies;
Greens for sale
- delivery of greenery to resellers - eliminates problems with a wholesale organization, and the disadvantages of this option are the low cost at which the products will be purchased;
Greens in the package
- independent sale of grown greens to shops, catering outlets, supermarkets - the main advantage of such cooperation is that all considerable profits will remain for the entrepreneur, but to implement this option, you should visit the Tax Inspectorate and register as an agricultural producer (OKVED - A.01.12.2. ).
Selling greens in supermarkets
The second stage is the official registration of entrepreneurship. This procedure takes up to a month, after which you can legally grow greenery. In the Tax Office, you should register as an individual entrepreneur and choose a simplified tax assessment system - Unified Agricultural Tax (deductions are calculated depending on the profit received and amount to 6% of it).
Then they install greenhouses, equipment, fertilizers, plant seeds and start growing greenery.
Growing greens - income all year round
Variants and features of growing greens
If a beginner entrepreneur has a piece of land, then growing greenery all year round will not be a problem. But, the most profitable enterprise will be if the site is located in the south of the country, otherwise the costs of lighting, heating and other means necessary for growing greenery will exceed what can be gained by selling the crop.
There are several ways to grow your own greens:
- sowing seeds is the classic, most inexpensive option;
You can grow greens from seeds
- extended cultivation - if the greens grow in the beds, they are dug out of the ground before the onset of cold weather and transferred to the room;
Greens in the seedling box
- from seedlings - the minus of the method is that you have to grow it yourself or buy it, which will be more expensive than purchasing seeds;
Seedling parsley
- forcing is the most convenient method as the seed is ready to grow.
Forcing green onions
Choosing a variety of grown greens
Before you start growing greens, you should study the needs of the market and decide on varieties.
Dill:
- unpretentious;
- seeds germinate in a couple of weeks;
- the harvest can be realized in 45-50 days;
- the optimum temperature for crop growth is only 17 degrees;
- not susceptible to pests and diseases;
- cons of dill - requires additional lighting in cold weather and has a short shelf life.
Growing dill in a greenhouse
Kinza:
- for growing crops, it is preferable to use black soil and the soil must be regularly moistened;
- easily tolerates a cold snap;
- it is necessary to feed the plants after each cut;
- the crop is harvested within a month after sowing;
- the optimal temperature for growth is 20 degrees;
- for good plant growth, they are planted in volumetric containers and provided with constant illumination.
How to grow cilantro in a greenhouse
Parsley:
- in cloudy weather and in winter, it needs illumination with phytolamps, which are turned on daily for 4 hours;
- the harvest grows in a month;
- if the culture was planted with seeds, then the crop will be more than a year old;
- needs abundant and regular watering, fertilizing with fertilizers;
- grows well at 20 degrees Celsius.
Growing parsley in a greenhouse
Celery:
- more demanding to grow than dill or onions;
- resistant to coolness;
- of the minuses - seeds germinate for a very long time.
Growing celery in a greenhouse
Onion:
- unpretentious;
- gives up to 4-5 harvests per year;
- spicy onions ripen quickly, but the feathers have a small mass;
- sweet varieties of crops ripen longer, but their weight is greater;
- planting of plants takes place in February, in boxes, and in March they are transplanted into a greenhouse;
- after planting the first batch, you can immediately start growing the second.
Growing onions in a greenhouse
Watercress:
- unpretentious;
- harvesting is possible after 12 days;
- grows in shaded areas;
- after cutting, the plants must be fed.
Watercress
Leaf salad:
- more picky than watercress;
- need regular abundant watering;
- does not tolerate heat.
Growing lettuce
Growing salads is the most cost-effective activity, with plants having a maximum vegetation period of 25 days. In terms of demand among buyers, the undoubted leader is the onion-feather, and the second and third places are occupied by dill and parsley.
Soil selection
The following types of soil are suitable for growing greenery.
- Gravel. It is inexpensive, practical and has excellent air permeability, but is quite heavy and does not retain moisture at all.
- Earth... Available, but requires the introduction of sand, peat and other fertilizers before planting seeds.
- Hydroponics... This method is based on growing plants in a special system, which is a tray of water. It is designed in such a way that only the roots of the greenery touch the water, and food flows to the roots through the tubes. The hydroponic method completely eliminates the use of soil and stimulates the development of green leaves, not roots. The main disadvantage of this technique is the cost of the apparatus.
Hydroponic plant
- Expanded clay... Used in conjunction with hydroponics. This primer is lightweight, inexpensive, and retains liquid.
- Sawdust... The material is poured over with boiling water and placed in containers. The advantages of the soil - the plants do not rot and there is no unpleasant smell from them.
- Coconut fiber. Environmentally friendly, versatile and durable, but expensive.
Coconut fiber
- Hydrogel... The newest soil material in the form of granules that swell with water and retain moisture for a long time. It is breathable, does not harm plants, but is expensive.
Selection of greenhouses and equipment
Greenhouses are:
- covered with plastic wrap;
Film greenhouse
- made of wood and glass;
Country greenhouse made of wood and glass
- made of polycarbonate.
Polycarbonate greenhouses
The best option for growing greenery at any time of the year are polycarbonate greenhouses - they perfectly retain heat, let in sunlight, and heating them is not difficult. It should be noted that for the uninterrupted cultivation of crops, at least 3 greenhouses will be required:
- in 1 - seeds are sown;
- in 2 - seedlings rise;
- at 3 - harvesting.
Polycarbonate greenhouse for year-round use with heating, lighting and ventilation
Basic equipment
To grow greens, you need to purchase a certain set of equipment that provides comfort, convenience and the right level of temperature and lighting.
- Heaters or conducted heating is necessary to maintain the temperature level regardless of the weather conditions outside the greenhouse. In a moderately cold winter, a pair of heaters will be enough for one greenhouse to maintain a 20-degree temperature.
Infrared heating for greenhouses
Greenhouse solar heating
Oven in the greenhouse
How to make biological heating correctly
- Lighting devices, lamps - ideally, fluorescent light bulbs or phytolamps are installed, giving the level of illumination the plants need. Each greens crate requires 1 lamp. Reflectors are additionally installed.
Greenhouse lighting
- Hydroponics system. Growing greenery on an industrial scale without this system is fraught with difficulties and difficulties - from decay of the root system to the defeat of the culture with diseases.
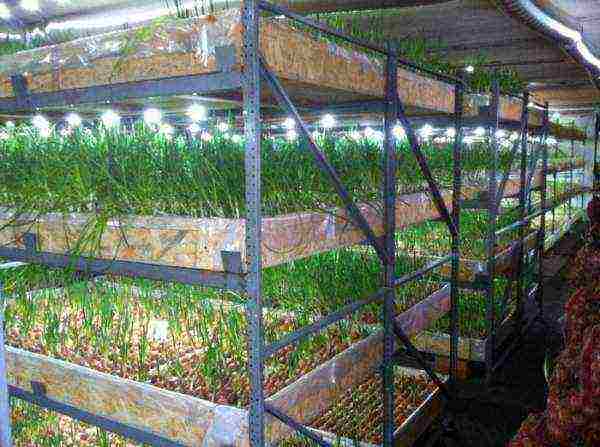
- Shelves - containers with herbs will be installed on them.
Racks in the greenhouse
- Thermometer - required for monitoring the air temperature in the greenhouse.
- Foil - experienced gardeners recommend using it to wrap pots with plants to avoid overheating the soil.
- Irrigation system (ordinary watering cans can be used).
Drip irrigation system
Fogging systems
- Containers - pallets for plants, for water sedimentation, boxes, bottles and others.
Harvesting and transportation
The disadvantage of greenhouse greenery is that it requires a careful attitude towards itself - the slightest wrong movement and the culture will be damaged, lose its presentation and will not be stored. For this reason, harvesting begins with a preliminary abundant watering of the plants 5.5-6 hours before they need to be pulled out of the ground.
After this time, each plant is carefully poured in with a spatula at the roots. If the harvest of feather onions is harvested, then the feathers are collected together with the heads - the plant is kept at the base of the growth of feathers and is slowly pulled out of the ground. After removing the greenery from the ground, it is necessary to rinse the roots from excess soil, pack and transport to customers.
Greens grown in winter - photo
It is recommended to store and transport greens in waterproof containers, while the bundles should be leaves up and tightly adjacent to each other. To keep the plants fresh longer, water and special additives are added to the containers. A simple and inexpensive mixture has proven itself well - you need to dissolve an aspirin tablet in a liter of water.
Profit calculation
The business of growing greenery in a greenhouse becomes as profitable as possible in winter - at this time the price of products reaches its maximum. With a price of 200 rubles per kilogram of greenery and a yield of 1.5 kilos per square meter, and the harvest ripens within a month, about a ton of products can be obtained from a greenhouse of 6 acres. Accordingly, the profit will be about 200,000 rubles.
Profitable business
Of the money received, about half will go to pay taxes, wages, transportation costs, purchase of materials, seeds and fertilizing. As a result, the net profit for the month will be about 100,000 - 120,000 rubles. And the total costs of organizing and starting a business will amount to a maximum of half a million rubles, this includes:
- purchase and installation of greenhouses;
- heating or installation of heaters;
- lighting installation;
- purchase of soil and fertilizers;
- purchase of seeds and containers for planting and care;
- business documentation and other costs.
At first, the profit should be spent on expanding production in order to be able to grow greenery on a larger scale. The demand for high-quality and fresh greens is only growing, so investing your money in this business is the right decision.
Video - Growing greens in a greenhouse in winter: secrets for beginners

When choosing a field of activity for a business, pay attention to the cultivation of greenery. Having built a good greenhouse, you can take several crops per year and it’s quite good to make money. For success, it is important to choose the most popular crops and organize the distribution channels correctly.
For household needs, you can limit yourself to a small greenhouse or a wall-mounted mini-greenhouse.
But for those who plan to establish contacts with stores and sell greens in solid volumes, need industrial greenhousesequipped according to all the rules. They allow you to plant seeds and harvest crops throughout the year.
…
Benefits and what greens can you grow in a greenhouse?
If desired, you can grow sorrel, cilantro and any other type of greenery.
This method of growing has a number of undoubted advantages:
- growing in a greenhouse allows you to grow greens in March or even in winter, in January-February;
- in the greenhouse you can create ideal conditions for a particular type of plant. This will allow you to get rapid growth green mass and excellent taste;
- you can use a mini-greenhouse and grow greens in your own apartment: on the balcony, veranda, etc.;
- can grow several harvests per year.
The same greenhouse can be used to grow other cruciferous and umbrella crops (radishes, carrots, and others).
Types of greenhouses?
Mini greenhouse
Compact greenhouse, used for growing greenery in the apartment... It is a glazed box, in which, in turn, smaller boxes are located, filled with earth. Greens grow in them. The simplest version of such a greenhouse is a regular old aquarium adapted for a new function.
Greenhouse
 A greenhouse is not even a greenhouse in the full sense of the word, but its simplified counterpart. Represents a structure of thick wire arcs on which the film is stretched.
A greenhouse is not even a greenhouse in the full sense of the word, but its simplified counterpart. Represents a structure of thick wire arcs on which the film is stretched.
There is no heating, it is replaced by the sun and rotting manure and compost, which is introduced into the soil (fresh manure is best applied in narrow paths on which there are no plants);
Classic version
Represents greenhouse with a wooden frame, covered with foil or polycarbonate. You can also use old windows or other materials at hand for the greenhouse.
Greenhouse for greenery is usually smallerthan for other crops, because one potbelly stove, infrared burner or electric heater is enough for heating. The foundation can be made columnar.
Winter
This is a more substantial structure than a classic greenhouse for greenery. It is distinguished by increased requirements for strength (because it must withstand a lot of snow in winter), insulation and lighting. Lighting should be regular, from 12 to 18 hours a day (depending on the culture). Use fluorescent lamps.
Used for insulation double layer of covering material (usually film) and additional foil thermal film, with which the northern and western walls of the greenhouse are covered, the western slope of the roof. The roof should be gable with a high ridge or in the shape of an arch so that the snow slides down.
Greenhouse thermos
 This greenhouse dug into the ground to some depth (from a few centimeters to 2.5 meters). This is done in order to achieve better thermal insulation and save on wall materials (walls may be low or absent altogether).
This greenhouse dug into the ground to some depth (from a few centimeters to 2.5 meters). This is done in order to achieve better thermal insulation and save on wall materials (walls may be low or absent altogether).
Preparatory work
Before building a greenhouse, you should decide on its type.
If we are talking about a mini-greenhouse, then a special place is not required for it: it will stand on the veranda or balcony, and will be mobile.
For other types of greenhouses, you need to choose and clear a place... It's best if it will rectangular sectionoriented along the north-south axis. Its size can be smaller than the size of a greenhouse for cucumbers or tomatoes. The width should not exceed five meters, the length may be ten meters. If you are going to grow greens only for myself, size is enough 2.5X5 meters.
Then decide on the materials and sketch out the final design.
After that, you can proceed to foundation construction... With such dimensions, a columnar foundation is sufficient. With a shovel or a drill, holes are dug into which wooden pillars are buried.
To prevent them from rotting, they need to be treated with an antiseptic and / or painted. You can also charcoal the part that will be buried at the stake. Alternatively, concreting the pillars or using a casing made of plastic or the same concrete.
You need to prepare and
materials for the frame. The wood is cleaned of nails or screws and treated with an antiseptic, iron can be painted, etc. Foil, polycarbonate or glass is marked and cut into pieces in accordance with the dimensions provided in the drawing.
The film is cut with a knife, scissors or blade, polycarbonate - with a saw, grinder or tin scissors, and glass - with a glass cutter.
For large greenhouses, you can also use a strip foundation or concrete, wood or cinder block.
Photo
You can visually highlight the main elements in the construction of a greenhouse for greenery with your own hands, in the photo below:
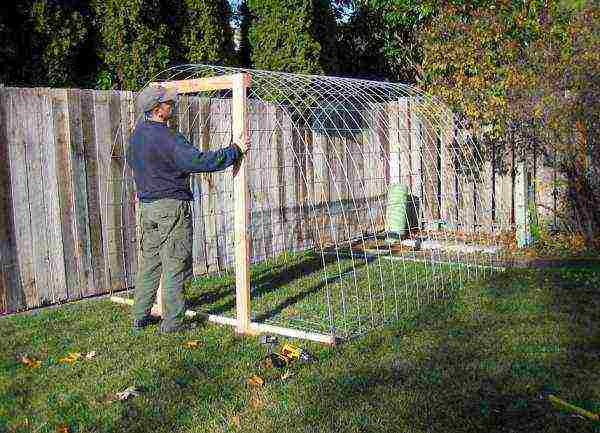
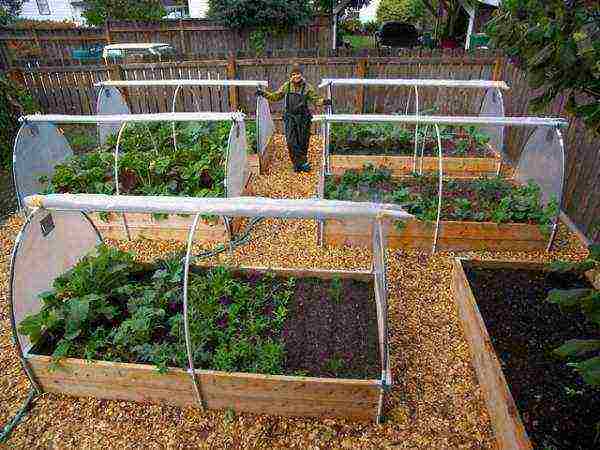




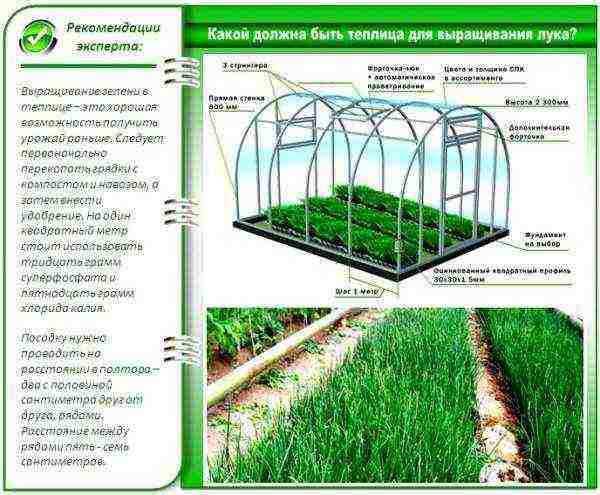
Build a greenhouse for growing greenery all year round with your own hands
- As mentioned in the previous paragraph, start off construction is needed from the foundation, which can be columnar or tape and consist of different materials, depending on the possibilities.
- Then you need to go to assembly of the frame... With a columnar foundation, the pillars themselves are part of the frame, to which other elements are attached. If the foundation is strip, vertical supports are installed in specially provided holes and poured with concrete.
- Since the greenhouse is winter, you can make small base up to half a meter high, and if the foundation is columnar, then the base can be replaced with formwork from boards nailed on both sides of the pillars to make a double wall.
The space between these layers can be filled with, for example, mineral wool. Such protection will not only serve as thermal insulation, but also protect the foil greenhouse in winter from snow and ice breakthrough.
-
 When the concrete has hardened, you can proceed to the next stage of assembly.
When the concrete has hardened, you can proceed to the next stage of assembly.
The elements can be fastened with nails, but since increased strength is needed for a year-round greenhouse, then it is better to fasten them with bolts and nuts through the pre-drilled holes. Be sure to provide a gable or arched roof, from which snow will slide, and two doors at the ends.
A small greenhouse does not need windows, but if the width reaches 5 meters, and the length is 15-20 meters, one or more windows must be provided.
- In the roof should be provided place for pipe (plank square with a hole in the center of the size of the pipe). If there are several ovens, prepare several such places.
- When the frame is ready, you need to think about heating and lighting... For lighting, you need electricity (an extension cord is enough), and hooks on the ceiling for the lamps. For heating, you can use potbelly stoves or any other stoves.
- Covering material needs two layers. The film is nailed to the frame from above and from the inside through a shingle (long yards), polycarbonate is screwed with large washers.Then the north and west sides can be additionally sheathed from the inside with foil film, which will reflect the sun's rays into the greenhouse and provide better thermal insulation.
- The last thing to install is vertical chimney.
The greenhouse is then ready for use.
Those who have chosen a film as a covering material should know that there is a special frost-resistant film that is ideal for year-round greenhouses.
Useful video
You can see the built greenhouse for greenery in the video below:
Conclusion
Greens all year round are tasty, healthy and profitable, because the surplus can be sold to neighbors or sold on the market. To grow greenery, you will need a greenhouse, which can be of various sizes, from the size of a home aquarium to quite solid ones, reaching 30 meters in length. Fortunately, you can build such a greenhouse yourself without any problems.
Growing greens in a greenhouse - quite attractive and money-making business.
The start-up costs are low when compared to how much you can make selling finished goods, especially during the winter season.
To begin with, in order to implement a conceived business project, you will need to write a clear business plan, calculate all possible risks, and also set up sales markets for your products.
Selection of greens to grow for sale
Before you plant your greenhouse with vegetation, you need to track the needs of buyers.
The most sought-after product is feather onions, followed by parsley and dill.
Salads show excellent profitability, their growing season is up to 25 days.
The best options for growing greens are: onion, dill, parsley, cilantro, celery, lettuce, watercress, basil.
Each type of greenery needs a special approach.
It will not be problematic to understand this, since today there is a lot of specialized literature on the care of these plant species.
How to grow cucumbers in a greenhouse: 4 steps to care
1) How to choose a soil for growing greenery?
Consider 6 main soil options for growing greens:
-
Gravel
pros: practical, low cost, good air permeability.
Minuses: has more weight, does not hold moisture. -
Earth
pros: high availability.
Minuses: needs to be carried in various fertilizers and nutrients. -
Hydroponics system
pros: stimulates the leaves, not the rhizomes.
Minuses: very high cost. -
Sawdust
Pros: no unpleasant odor, plants do not rot.
Minuses: require care (must be filled with hot water and placed in a container). -
Coconut flakes
Pros: environmentally friendly, durable, versatile primer.
Minuses: high price. -
Hydrogel
Pros: retains moisture for a long time, allows water to pass through, does not harm plants.
Minuses: high price.
How much do different types of soil cost:
| Gravel | from 50 rubles per kg |
| Earth | from 700 rubles per cubic meter |
| Hydroponics system | From 1500 rub. for 1 installation |
| Sawdust | from 300 rubles per cubic meter |
| Coconut fiber | from 100 rubles per kg |
| Hydrogel | from 1500 per kg |
2) How to choose a greenhouse for growing greenery?
Choosing the right greenhouse is the key to success. To choose the right greenhouse, you first need to decide on the area on which the greens will be grown.
The design of the greenhouse is quite simple: it consists of a frame and a material that is installed on it. An important feature of this material is that it must transmit sunlight.
Usually, glass, plastic wrap or polycarbonate is used for the covering material.
Polyethylene film at the price the most affordable option, but in quality it is inferior, since the shelf life is 1-2 seasons.
Glass It is also one of the most popular materials, its advantage is that it transmits up to 85% of the sun's rays, is easy to clean, and has good moisture resistance.
The disadvantages are its fragility and gentle handling, as well as its high weight.
Polycarbonate has proven itself well. Durable polymer plastic, consisting of two layers, between which there are cavities with air. It diffuses sunlight well, has high thermal insulation, is lighter and stronger than glass.
After you have chosen the covering material, you should decide on the frame.
The main materials used to build greenhouses are polypropylene pipes, metal profiles, galvanized pipes, and aluminum frames.
Best fit aluminum frames, since this material is lightweight, withstands heavy loads and does not lend itself to corrosion, but it scares off at its cost.
If the greenhouse is to be used as a temporary structure, then it may be suitable for the frame polypropylene pipes, they are good because they do not allow moisture to pass through, are not afraid of mold and mildew, and are easy to install. However, the downside is that in a strong wind, such greenhouses can take off, after which they quickly lose their usefulness.
Having dealt with the materials for the greenhouse, we turn to the issue of ventilation of the room. Good quality greenhouses should be equipped with windows or doors that can be opened for ventilation if needed.
You can make a greenhouse for growing greenery yourself or buy a ready-made one.
When buying, it is best to give preference to large producers, as they rely on quality and often give guarantees for their greenhouses.
Here are examples of the main types of greenhouses available for sale:
- Wooden greenhouse
- Polycarbonate greenhouse
- Greenhouse made of polyethylene film
Additional equipment for the greenhouse
In order to grow greens efficiently and quickly, it is necessary to purchase a number of equipment that can be used to provide temperature comfort for green sprouts and maintain the required humidity level.
Despite the weather conditions outside, the air temperature in the greenhouse must always be kept to a certain level, especially when cold weather sets in. Several heaters will need to be installed.
To illuminate the greenery in the greenhouse, you will need lighting fixtures and lamps. It is best to install regular or phytolamps. One light bulb per rack with vegetation.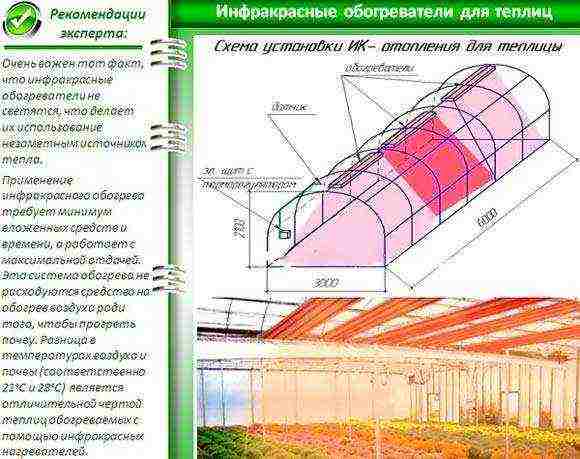
Are you looking to turn green cultivation into a profitable business? Then it is imperative to install a hydroponic system in the greenhouse, this will protect against decay of plant roots and various diseases.
A thermometer should be installed in the greenhouse itself so that the temperature can always be monitored.
To properly manage the space, you should install racks.
Do not forget about the irrigation system. You will also need several pallets for settling water, bottles, tools, and more.
How much will the equipment for greenhouses cost:
3) How to transport the grown greens?
Transporting greenhouse greens is a very neat process, since greens are very whimsical and can be easily damaged.
Damaged vegetation will lose its presentation and become unsuitable for sale.
That is why, before harvesting, it is watered abundantly for 4-5 hours. After the expiration of time, the greens must be carefully dug out, rinsed with roots and packaged.
It is best to transport products in sealed packages, laying them with the leaves up and pressing tightly. To maintain freshness, a special solution is added to the containers.
You can make such a solution yourself: 1 tablet of acetylsalicylic acid is placed on 1 liter of water.
Greenhouse business plan: in detail
4) Choosing a marketing strategy for greens
To begin with, it is worth choosing the direction in which the sale of your products will be realized.
Three main marketing strategies:
-
The first way is retail.
You can open a point in the market where you can sell your products, but this option takes a lot of time and effort, and the profit is quite low.
-
The second way is to sell greenery to dealers.
It is worth noting that you will not have to deal with the distribution of products, but the disadvantage is that resellers will buy the vegetation at the lowest price.
-
The third way is the independent sale of products to shops, supermarkets, as well as to catering points.
This method is the most cost-effective, since all profits fall directly into the hands of the entrepreneur, however, in order to achieve this option, the entrepreneur must visit the tax office to register his business.
After choosing a business strategy, it is necessary to officially register with the tax office.
The most suitable option is to register as an individual entrepreneur and use the Unified Agricultural Taxation (a system for simplified tax assessment for farmers). Under this system, you will give only 6% of your income to the treasury.
How much does growing greenery in a greenhouse pay off?
If you grow greens in a greenhouse for the purpose of mass deliveries to store shelves, you will need an amount of 275,000 rubles or more.
This is when you take into account the costs of buying a greenhouse and equipment, seedlings, seeds, soil, fertilizers and related costs.
| Business registration | from 20,000 |
| Equipment | from 150,000 |
| Greenhouse | from 50,000 |
| Priming | from 10 000 |
| Seedlings and seeds | from 10 000 |
| Other expenses (elimination of breakdowns,) | from 25,000 |
| Freight transportation | from 10 000 |
Considering that a greenhouse of 300-400 sq. m will yield a yield of 1.7 kg per sq. m and ripen within a month, then we will receive 600 kg of greens during this period.
At a cost of 150 rubles per kg, the monthly income will be 90,000 rubles.
Approximately 30-35% of this amount will go to cover costs, and the net profit will be 60,000 rubles. And if you take into account that the prices for greens grow in winter, the income will almost double.
Conclusions on growing greenery in a greenhouse as a business idea
Considering all of the above, we can conclude that growing greenery in a greenhouse Is a fairly profitable business with a payback period of up to six months.
First of all, the initial income should be invested in expanding your business in order to take up the production of products on a larger scale.
According to the latest market research, there is a clear jump in demand for fresh and quality greens, so investing in this business is the right decision.
How is fresh greens grown in greenhouses all year round?
Look clearly and get inspiration for organizing your business:
And do not forget that in winter the payback period becomes even shorter, since the level of prices for greens exceeds its summer market value by 1.5-2.5 times.

Helpful article? Don't miss new ones!
Enter your email and receive new articles by mail

