Content
- 1 When to grow?
- 2 Creation of optimal conditions
- 3 Seeds: how to choose a variety and prepare seeds for growing
- 4 How to grow?
- 5 How to care?
- 6 Diseases and their treatment
- 7 Benefits of greenhouse growing vegetables
- 8 Greenhouse preparation
- 9 Planting cucumbers in the greenhouse
- 10 Features of planting and caring for cucumbers in polycarbonate greenhouses: how to grow a rich harvest
- 11 Watering
- 12 Top dressing
- 13 Cucumber bush formation
- 14 Plant problems
- 15 Pest and disease control
- 16 Features of growing cucumbers in the regions
- 17 How to grow a great crop of greenhouse cucumbers?
- 18 How to grow cucumbers and tomatoes?
- 18.1 How to grow cucumbers and tomatoes in polycarbonate greenhouses?
- 18.1.1 Preparing greenhouses for sowing tomatoes and cucumbers in them
- 18.1.2 Features of preparing the land for planting seedlings of cucumbers and tomatoes
- 18.1.3 How to plant seedlings correctly?
- 18.1.4 How to properly care for tomatoes in polycarbonate greenhouses?
- 18.1.5 Feeding tomatoes
- 18.1.6 How to grow cucumbers in a greenhouse
- 18.1.7 Care for cucumbers in the greenhouse
- 18.1 How to grow cucumbers and tomatoes in polycarbonate greenhouses?
- 19 Secrets of growing cucumbers in polycarbonate greenhouses: the best varieties, care and formation
- 19.1 Advantages of growing cucumbers in polycarbonate greenhouses
- 19.2 Equipment for growing cucumbers
- 19.3 How to plant cucumber seedlings in a greenhouse (video)
- 19.4 The best cucumber varieties suitable for polycarbonate greenhouses
- 19.5 Preparation and preventive tillage
- 19.6 Scheme and timing of landing
- 19.7 Care rules
- 19.8 Problems with growing cucumbers in polycarbonate greenhouses
- 19.9 When and how to feed cucumbers in a greenhouse (video)
- 19.10 Condition 3. Loose, breathable soil
- 19.11 Condition 4. Correct watering
- 20 Is it difficult to form whips?
- 21 Landing features
- 22 Care for cucumbers in the greenhouse
- 23 Pest and disease control
- 24 Growing cucumbers in a greenhouse from polycorbanate
- 25 How to grow cucumbers in a polycarbonate greenhouse
- 26 Growing tomatoes and cucumbers in honeycomb polycarbonate greenhouses
- 27 Greenhouse preparation
- 28 Pepper and salad in greenhouses
- 29 Advantages and disadvantages of growing cucumbers in a greenhouse
- 30 Greenhouse preparation
- 31 How to grow cucumbers in a polycarbonate greenhouse: planting and care
- 32 Care and watering rules
- 33 What and when to feed
- 34 Cucumber bush formation
- 35 Problems and solutions
- 36 How to treat plants from diseases and pests
- 37 Features of planting and growing cucumbers in different regions
Growing cucumbers in a polycarbonate greenhouse will allow you to harvest as early as possible. It is the cucumber that is considered the most popular greenhouse plant.
Polycarbonate greenhouses are great for growing this vegetable. The material retains heat, is able to transmit the required amount of light and protect cucumber leaves and ovaries from burns. The main condition for a polycarbonate greenhouse is the presence of vents through which the structure will be ventilated, since cucumber seedlings need not only heat, but also fresh air.
These greenhouses are good for creating a favorable microclimate for early cultivation of cucumbers. Polycarbonate greenhouses are easy to prepare for spring planting. It will be necessary to check the tightness of the structure and wipe the plastic cover.
When to grow?
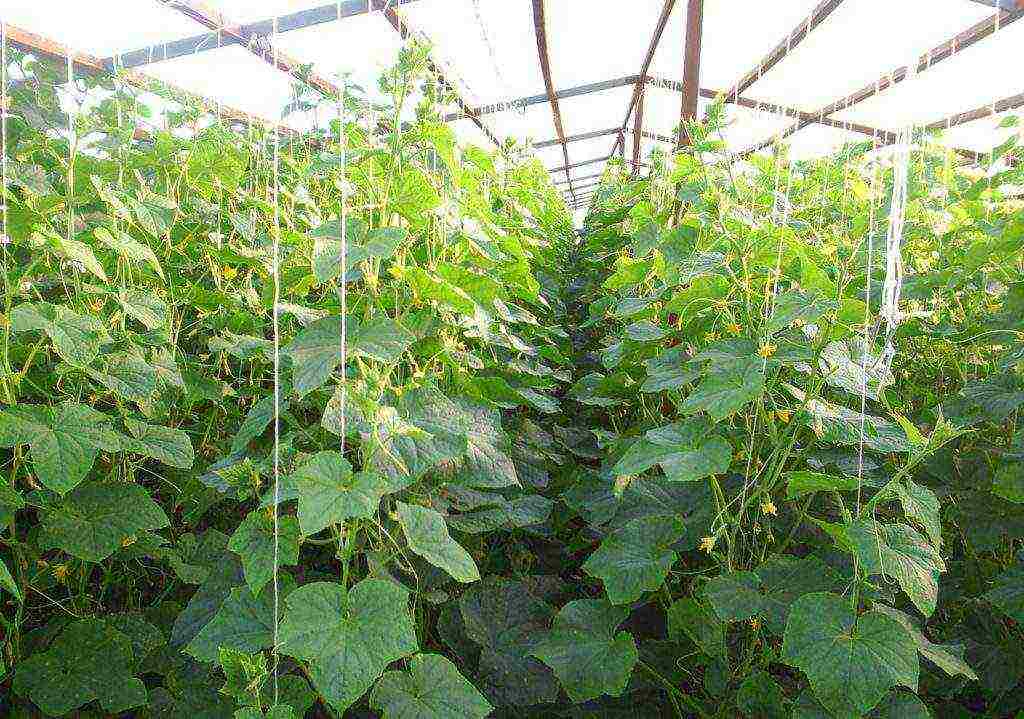

In polycarbonate greenhouses, you can plant seeds in the ground between 15-20 April. Seedlings can be planted from May 15th. In the southern regions, seme can be planted at the end of March, and seedlings - at the 20th of April.
Creation of optimal conditions
Humidity level
Three days after planting, within two weeks, watering must be carried out strictly in the root part for the development of a good root. With excessive watering, an excess of moisture can occur, which will destroy the entire root system, and it will rot.
If there is a need for an additional increase in the humidity of the greenhouse, polycarbonate can simply be poured from a hose or from buckets. Plastic will create a greenhouse effect. You can also put a bucket of water inside the structure. The optimum humidity level for air is 80%, and for soil - 60%.
Air temperature
An improperly organized temperature regime (above 30-40 C) or too high a greenhouse effect, in which moisture is formed above 90%, can harm cucumbers. The optimum air temperature is from 25 to 28 degrees.
Seeds: how to choose a variety and prepare seeds for growing
 You need to start preparing for planting with the purchase of seeds. Regardless of which variety you are going to purchase, seed preparation and processing should already be done beforehand. When seeds come across without much processing, you can prepare them yourself.
You need to start preparing for planting with the purchase of seeds. Regardless of which variety you are going to purchase, seed preparation and processing should already be done beforehand. When seeds come across without much processing, you can prepare them yourself.
An ideal place for germinating seeds can be gauze soaked in water, previously disinfected with a solution of potassium permanganate. It is suitable for disinfection. If it is difficult to get potassium permanganate, then you can replace it with a 2-3% solution of hydrogen peroxide.
First, the peroxide must be heated to a temperature of about 40 C, moisten gauze in it, and then place the seeds in it. Soak the seeds of cucumbers for 7-8 minutes. Before planting, rinse the soaked seeds well under water.
Boric acid can be another component for germination. To do this, you need a solution with an optimal temperature of 25-30 C, which consists of half a teaspoon of boric acid diluted in a glass of water. Soak in such a solution for at least two to three hours.
Ready and hardened seedlings can be considered when four viable leaves appear. Seedlings are planted in the greenhouse at the age of 30 days.
How to grow?
Step-by-step instructions for growing:
- Cucumber loves warmth, so it is recommended to plant it in "warm" beds.
- Manure is ideal for warming the soil. The bottom of the bed is insulated with a fresh layer of manure, which is covered from above with 25-centimeter soil.
- Then the soil is watered and sown with seeds.
- One square meter of a plot of land should contain 4-5 bushes.
- Arcs are installed along the length of all beds. A film is stretched over them to create a greenhouse effect. The heat will create the process of decomposition of the manure laid out on the bottom of the bed.
How to care?
Lash formation
If the vegetable is not formed in time, then it will grow chaotically. When processing a plant, you can transfer all the ovaries and remain without a crop.
It is due to the lack of timely formation of lashes that a huge number of climbing plants are obtained, on which there are almost no fruits.
There are three main stages in the formation of lashes:
- First step: "Blindness". At this stage, it is necessary to free the first three leaves of the plant from shoots and buds. This gives a certain stimulus to the plant for further development and obtaining a large number of ovaries, because after the appearance of the first shoots, the plant has no reason for further growth.
- Second step: This stage is characterized by the removal of lateral shoots at a distance of up to half a meter from the root. Then the second half a meter is freed from excess leaves, it is necessary to leave one sheet at a time. Further, over the course of a meter, it is enough to leave three sheets.
- Third step: The second row of the plant is processed, that is, all lateral shoots are pinched onto one leaf.
To clarify the number of shoots that must be left on the plant, it is worth focusing on its height. As the plant grows, the main stem will need to be thrown over the trellis and pinched again, leaving up to 60 cm.
From this moment, the weekly plant formation begins. During this period, it is necessary to inspect the plants so as not to miss yellowing of the leaves or their diseases. Such procedures are recommended to be carried out before lunch, so that the wounds dry out by the evening.
Top dressing
It is recommended to use 3 types of feeding:
- Take potassium sulfate, urea and superforsfate (1 tsp). Dilute with 10 liters of water.
- Combine humanate (1 tablespoon) with 10 liters of water.
- Fertilize with a mixture of liquid mullein (1 cup).
Pollination
Pollination in the greenhouse can be carried out in 2 methods:
- Use of insects. In the warm season, you need to open a window in the greenhouse so that the bees can fly in on their own.
- Manually. The process is carried out with a brush. Use the tip of the brush to remove the pollen from the male flower and carefully transfer it to the female flower.
Airing
The greenhouse needs to be ventilated regularly. To do this, you need to raise the panel or open a window for a couple of hours. On warm days, you can leave the greenhouse open all day. When ventilating, the optimum temperature in the greenhouse should be from +18 to +30 degrees.
Watering
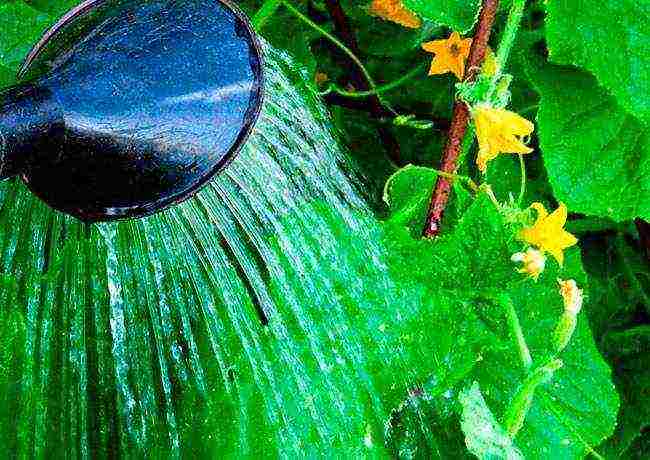

Watering rules:
- Do not pour water on the surface of the leaves. Polycarbonate retains moisture, and plants can become sore if not well ventilated. Ideally, the plants are watered under the root with settled warm water.
- You can not organize watering during the day under bright sunlight, and especially pour water on the leaves. This can lead to the formation of small water droplets that act as lenses. Because of them, light will be refracted, which can burn the plant.
- Plant bushes must be watered with warm water. The temperature should be appropriate for the environment to avoid early shedding of the ovaries. It is recommended to take running water in advance and leave it outside to reach a temperature of 15-20 degrees. This is best done in large drums or tanks.
Before the first ovary appears, watering should be done 2-3 times a week, and then every day until the first fruits.
Diseases and their treatment
Possible diseases that can harm plants:
Drying of the lower leaves

This problem appears when the plant lacks moisture. In this case, the upper branches bloom and stretch upward, tying fruits, and the lower ones begin to dry.
There are several recommendations for fixing this problem:
- Gradual cutting of the lower leaves. This procedure can be carried out for several days.
- Placing the plant gently on the soil. In this case, it is necessary to remove the stem from the net and roll the plant into a ring.
- Fastening the stem with wire in the form of a fork and sprinkling it with earth. The top with leaves and flowers must always remain at the top.
- After all the above procedures, the plant is daily watered, processed and fed. This should result in a new root build-up on the stem under the soil. After that, the plant will start growing again.
Lack of ovaries
Particularly popular are bunch varieties with hybrids, which give high yields and are distinguished by excellent fruit quality. One node of such plants, if properly cared for and processed, can produce up to seven ovaries.
At the first experience of growing this type of plant, you may encounter the problem of the absence of ovaries. There are several reasons for the absence, drying up and falling off of the ovaries:
- The absence or lack of male flowers in the plant.
- Insufficient number of pollinated flowers due to the lack of pollinating insects, which can happen due to bad and cloudy weather.
- Insufficient soil nutrition. Modern hybrids require a lot more vitamins for growth and development. It is necessary to carry out their regular supply. As a result of improper organization of plant care, it can give many ovaries, but only one cucumber will grow, everything else will dry out and disappear. To prevent such a problem, it is necessary to carry out weekly feeding with mullein with urea.
- For the formation of new ovaries, it is necessary to harvest cucumbers as often as possible. In the presence of already ripe cucumbers, the plant does not need to form new ovaries, it gives all the nutrients to the overgrowths. Fruiting is favorably influenced by carbon dioxide released by the mullein solution, which is recommended to be placed in a container in a greenhouse and stirred periodically. The same effect can be obtained from burning a newspaper right inside the greenhouse.
Slow fruit growth
For the active growth of fruits, you can make a "poultice". This should be done in sunny weather. The entire surface of the polycarbonate greenhouse is poured with water, and all the vents are closed. Plants and soil are also watered and left for an hour. After this procedure, you can start gradual ventilation. Harvesting regularly also promotes faster growth of new cucumbers.
It is recommended to remove fruit no more than 12 cm long and 5 cm thick. Harvesting is advised every day in the morning and in the evening, otherwise in a day you can find an overgrown cucumber in the garden. This is due to the lack of stimulation for the plant to make new ovaries and all the energy is spent on continuing the growth of existing fruits.
Bitter cucumbers
The taste of cucumbers, or rather their bitterness or sweetness, depends on the level of cucurbitan substance in the plant. Its amount directly depends on the growing conditions, variety and duration of fruit ripening. It is believed that fruit that ripens more than two weeks after pollination is more likely to taste bitter.
Invasion of aphids or greenhouse whiteflies
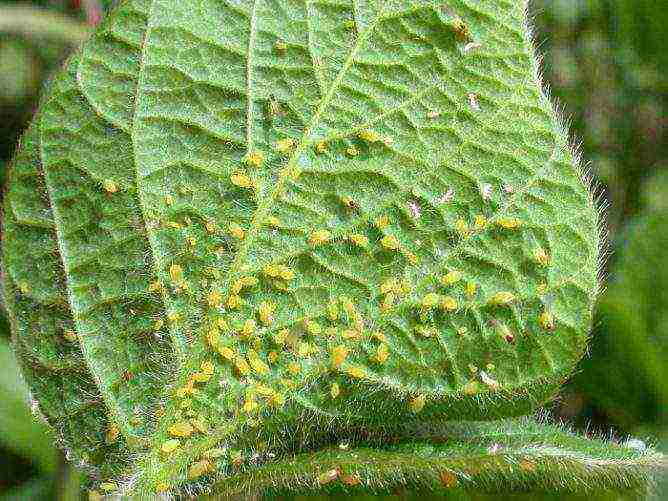

Aphids usually appear in places where a lot of weeds accumulate and the pedicels of the vegetable become its target. In such cases, it is advised to treat the plants with a solution of hot pepper (2 g per 2 liters of water).Whitefly infects leaves, its sap forms a fungus on the surface of the plant. You can get rid of it by covering all the vents with gauze.
Powdery downy mildew
This is the formation of green and oily spots on the leaves of cucumbers.
The polycarbonate greenhouse is the perfect place to grow fresh and crispy cucumbers. In these greenhouses, the plants require minimal maintenance and yield excellent yields.
When growing cucumbers in greenhouses, many gardeners ask themselves questions: which greenhouse to prefer - purchased, or do it yourself, which is better - film, glass or polycarbonate, how to rationally use all the advantages of a greenhouse when planting vegetables? With proper care in the middle lane, a good harvest can be grown at any time of the year.
Benefits of greenhouse growing vegetables
Cucumbers are undoubtedly one of the most common and favorite vegetables for gardeners. Along with the cultivation of this crop in the open field, greenhouses are increasingly used. And this is not surprising. Observance of correct agricultural technology gives a big plus to the greenhouse option for growing cucumbers in front of open ground.
Advantages of greenhouse cultivation:
- the yield from the same area is several times higher;
- the possibility of getting an early harvest;
- the extension of the growth of this vegetable in the middle lane until the beginning of October;
- the use of varieties of cucumbers, zoned for the southern regions.
Using the correct varieties of cucumbers and the technology of cultivating them in a greenhouse, special technical means to maintain optimal temperature and humidity, it is possible to grow this vegetable in the middle lane all year round.
If desired, growing cucumbers in a greenhouse, gardeners can harvest for personal consumption, and engage in a fairly lucrative home business.
The only drawbacks can be considered the financial costs for the manufacture or purchase of the greenhouse itself and the investment of great physical strength.
Cucumbers can be grown in a heated greenhouse all year round
Greenhouse preparation
Before planting seedlings of cucumbers or seeds, it is necessary to carry out work to prepare the greenhouse itself. They can be divided into autumn and spring periods.
Autumn after harvest
In the autumn, when the harvest of cucumbers is harvested, the frame is examined and repaired, the damaged areas of the coating are changed. The condition of the film or glazed coating is monitored throughout the winter season. Wooden parts are treated with a 3% solution of copper sulfate (70 g per 10 liters of water). The metal parts of the frame are painted. Glasses are sprayed with formalin (2 g per 1 liter of water), 1 liter per m2. If the operation is foreseen in the winter period, the electric lighting fixtures and technical means for heating are checked and adjusted.
Garbage, remnants of old plants are removed from the ground, and the top layer (4–6 cm) of the soil is changed, because it is here that pests and sources of diseases accumulate. Then the earth is disinfected with a solution of copper sulfate at the rate of 1 tbsp. l. 10 liters of water. Processing consumption - 10 liters per 20-25 m2 of greenhouse area. Also, for disinfection of the soil, you can use a mixture of potassium permanganate and lime: 6 g of potassium permanganate per 15 liters of water and 20 g of lime per 6 liters of water. If it is impossible to prepare the greenhouse in the fall, disinfection is carried out in the spring - 1 tablet of Intra-vira and 2 tablets of Oxychom are dissolved in 10 liters of water. This amount is sufficient for 15–20 m2.
Organic and mineral fertilizers are introduced: 20-25 kg of fresh manure, 30-40 g of phosphorus and potash fertilizers per square meter. m. In case of increased acidity of the soil, add 200-500 g of lime per 1 m2. Then the earth is dug to a depth of 30–35 cm.
In the spring before landing
In the spring, when the ground warms up enough, an additional layer of film is stretched over the greenhouse to avoid damage to the cucumber plantings by low night temperatures.
Form beds with a width of at least 1 m and a height of 25-30 cm, leaving a space for a passage between them 60-70 cm. all this ridge is watered abundantly and seeds are sown. Instead of manure, you can pour ready-made compost (sawdust, decomposed peat, rotted straw and grass, etc.) on the beds. Then the seeds are not sown, but ready-made seedlings are planted. If the formation of high ridges is not envisaged, and the plants will be grown directly in the soil, then in this case, add a simple - 80 g or double - 40 g of superphosphate per sq. m.
A prerequisite is the presence of a horizontal trellis made of hard wire, located at a height of 2 meters above the beds, to which cucumber lashes are tied. This prevents overheating of the bushes and the development of fungal diseases.
Tall beds retain heat well in the soil
Planting cucumbers in the greenhouse
Cucumbers are planted in a greenhouse by seedling or by sowing seeds directly on the beds. The timing of planting and the technology of soil preparation in the greenhouse depend on the chosen method. The planting time is significantly influenced by the greenhouse coating material: film, glass or polycarbonate coating. You also need to take into account the methods of heating the greenhouse - with biofuel or a convector. In the latter case, cucumbers can be grown throughout the year.
General rules
When planting cucumbers in a greenhouse, you must be guided by the following:
- when planting, the seeds must be pre-checked for quality and germinated;
- seedling method is preferable to planting seeds in the ground. An exception is a polycarbonate greenhouse;
- seedlings should be 25 days old and have 3-4 true leaves;
- for 1 sq. m. no more than four plants are planted;
- the planted seedlings are formed vertically, tying them to the trellis;
- the earthen lump of the seedling should be 1–2 cm higher than the level of the garden;
- for better pollination, cucumbers of different varieties are planted nearby.
Seed planting
For sowing, large, full-weight seeds are selected and their quality is checked - they are immersed for 20-30 minutes in a 5% salt solution. Pop-ups are empty, they are deleted. Before sowing, the seeds are soaked or germinated. Before soaking, the seeds are suspended in a cloth bag, preferably over the battery for a day. Soak for about 10-12 hours just before disembarking. Seeds are germinated by wrapping them in a damp cloth and placing them in a warm place for 20–25 hours, and low-quality sowing material is additionally rejected.
Seeds are planted in prepared holes for 3–3 seeds. The seeding depth depends on the composition of the soil: on loose soil - about 3 cm, on heavy less - 1–2 cm.
Seedlings of cucumbers from seeds planted in the garden
Seedling planting method
Using the seedling method of growing, you can accelerate the entry of cucumbers into fruiting by one and a half to two weeks than when planting with seeds.
Planting seeds for seedlings is best in soft paper cups or peat pots. In this case, when planting in the ground, there will be no damage to the roots of plants. Land for seedlings can be purchased ready-made in the store or made homemade - from a mixture of 1 part of garden soil and 0.5 parts of sawdust and humus. Before planting seeds, soil in pots should be shed with a weak solution of potassium permanganate. The seeds are planted to a depth of 1–2 cm and covered with glass or polyethylene to create a microclimate. The temperature in the room during seed germination must be maintained within 22-28 ° C, and after 5-7 days, when seedlings appear, it should be reduced to 18-20 degrees. In order to prevent stretching, it is necessary to install additional illumination of the seedlings.
When planting seedlings in a greenhouse, the soil temperature should be at least 16-18, and the air temperature - 20-22 degrees. If overgrown plants are planted, they are placed obliquely in the planting holes. Important: in the first days after planting, the seedlings are abundantly watered and shaded from the sun.
Seedlings in peat pots have three leaves and are ready for planting in a greenhouse
Landing dates
According to the ripening time, cucumbers are divided into early, mid-season and late varieties. Therefore, you can give the following general recommendations on the timing of sowing seeds for seedlings.
- Early varieties - from March 15 to April 20. They have the highest maturation rate.
- Mid-season varieties - from early to mid-May.
- Late varieties - from the end of August. Hybrid varieties of cucumbers are planted. Their ripening period is 60 days, so the harvest can be harvested until November.
When growing cucumbers in a seedless way, the planting time is determined as the soil matures and the air temperature is stable. The earth should warm up to 16 degrees, and the air - up to 20 ° C.
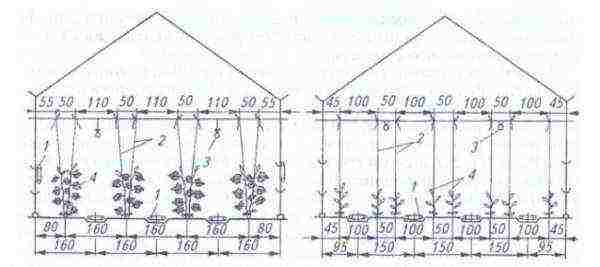
Planting schemes
In addition to soil and care, the correct choice of planting scheme affects the successful cultivation and obtaining sustainable yields. The condition and development of cucumbers depends on this. In greenhouses, one- and two-line and staggered planting patterns should be used.
The most productive and large-leaved varieties of cucumbers are planted in one line (row). The beds are long and narrow. The disadvantage of this method is that there is no saving in the area of growing plants due to the wide aisles between the rows.
With a two-line scheme, cucumbers are arranged in two rows, one bush is opposite the other. This scheme is suitable for plants with medium-sized leaves.
In order to improve illumination, plants can be planted in a checkerboard pattern, while the parameters of the beds are similar to the two-line scheme. The bush planted in the second row "supports" the one planted in the first one by half the distance between the plants in the row. This scheme involves the cultivation of cucumbers with large large leaves and long fruits.
Table: intervals for planting cucumbers
When growing cucumbers, various planting schemes are used.
When planting cucumbers with seeds in the soil, it is recommended to thicken the planting with the possibility of not germinating some of the seeds. Then the seedlings can be thinned out by transplanting "extra" bushes to another place.
Features of planting and caring for cucumbers in polycarbonate greenhouses: how to grow a rich harvest
Using greenhouses made of cellular polycarbonate, you can start growing cucumbers already in March. Heat loss in them is less than in film greenhouses and it is easier to create additional heating. The advantage is that in polycarbonate greenhouses, seeds can be sown directly on the beds with biofuel - this reduces the cost of preparing seedlings. And the plants themselves will be spared from temperature adaptation - in the process of growing they get used to low temperatures. Using seeds of early varieties, planting seeds in the ground begins in early March. After 21 days, the sprouted shoots are dived and planted in a permanent place of growth.
Video: highlights of planting cucumbers in a greenhouse
Watering
Cucumbers are a very moisture-loving crop. It is necessary to properly organize the process of watering plants in a greenhouse. When watering, it is important not to overdo it - excessive watering leads to diseases (decay) of plants.
After planting the plants before flowering, the cucumbers are watered moderately - by 1 sq. m pour 4-5 liters of water. Such a watering rate will prevent the growth of leaf mass of plants and promote active formation of ovaries.
During the period of ovary formation, during all active fruiting and after harvesting, cucumbers require the greatest watering. Therefore, from the beginning of flowering until the end of the growing season, the irrigation rate is increased to 9–12 liters per 1 m2.
Watering frequency depends on the condition of the ambient temperature. In hot weather, water it daily, in moderate heat or on cloudy days, 1-2 waterings per week are enough. During abundant fruiting, watered every other day.
Watering should be guided by the following rules:
- it is necessary to control the condition of the soil under the bushes: it should be moderately moist, but not waterlogged;
- when the leaves wither, the plants need to be watered urgently;
- at the beginning of fruiting, soil drying can be applied in order to accelerate the development of ovaries;
- no changes in soil moisture level should be allowed;
- it should be watered with water not lower than 18–20 ° С;
- the most favorable time for watering is in the evening, after sunset;
- after watering, be sure to loosen the ground.
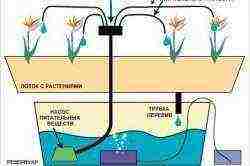
Advantages of drip irrigation in greenhouses
Various implements are used for irrigation: watering cans, buckets, hoses, etc. There are also automatic irrigation systems:
- sprinkling;
- aerosol auto-irrigation;
- drip irrigation system.
The drip irrigation system is the most convenient and rational for irrigating cucumbers in a greenhouse. Let's consider the advantages of this method:
- water flows directly under the root of each plant;
- automation of the process, which allows gardeners to visit their garden and summer cottages less often;
- there is no danger of soil erosion;
- accurate dosage of supply, and therefore water saving;
- simultaneously with watering, you can feed the plants;
- ease of maintenance;
- reduction in physical costs;
- ultimately, increased yields.
The main disadvantage of drip irrigation is the high price of standard irrigation equipment offered by manufacturers. But gardeners have come up with many homemade drip irrigation devices. And anyone who knows how to hold a tool in their hands will be able to build such a system in their greenhouse.
Drip irrigation allows water to be delivered to each plant directly under the root
Top dressing
During the entire growing season, cucumbers must be fed. In different cultivation cycles, different types and rates of organic and mineral fertilizers are used. During the season, the plants are fed at least four times.
Table: feeding cucumbers during the season
The fertilizer rates indicated in the table are applied at the rate of 0.5 liters per plant.
Wood ash is a very valuable food for cucumbers. It is diluted in a ratio of 100 g per 10 l of water and used at any time of plant cultivation with a break of 10 days.
Video: how to properly feed cucumbers
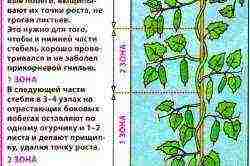
Cucumber bush formation
The formation of cucumbers is the most important agricultural technique in their cultivation. This helps to improve the quality of fruits, increase yields, and it is much easier to take care of the plants - there will be no continuous thickets in the greenhouse. In addition, plants are less susceptible to disease and invasion of harmful insects. The formation of bushes consists of the following activities:
- choosing the direction of growth of the bush;
- garters for trellises;
- trimming the plant.
To form bushes of cucumbers in a greenhouse should be in one stem, since the fruits are tied precisely on the central stem. For this, the following work is carried out:
- 3-5 days after planting the seedlings, the plant is tied with a cord to a wire stretched horizontally;
- when the bush reaches 6 leaves, the top is pinched off;
- from the bottom remove all leaves and shoots up to 5 leaves. This protects the plant from diseases and ventilates the soil well;
- pinching is carried out: one ovary is left in each bosom and pinched after the third leaf;
- on the next shoot, 2 ovaries are left, and cut off after 4 leaves;
- when the main shoot reaches the wire, it is also pinched.
The scheme of the formation of a cucumber bush in one stem
Important: to increase yields, it is necessary to systematically remove male flowers on the plant.
With the correct implementation of these actions, the cucumber bush will bear fruit for a long time.
Video: how to form a cucumber bush correctly
Plant problems
Growing cucumbers, many gardeners are faced with various troubles: flowers fall, leaves and ovaries turn yellow, plant growth stops.This can be caused by many factors.
- Poor quality seeds. You should always check the seeds in a 5% salt solution - floating seeds are not suitable for sowing, they must be thrown away. You can also test the seeds for germination by wrapping them in a damp cloth - if more than 60% do not germinate, the seed is discarded.
- Lack of nutrition. In this case, the leaves turn yellow and dry, and the ovaries fall off or do not grow. The plant stops growing. It is necessary to apply a complete mineral fertilizer to stimulate growth.
- Waterlogging of the soil. The growth of plants slows down, they look rickety, undersized, oxygen does not get to the roots well. You should give air to the root system, that is, "dry up" the soil: loosen and mulch - add dry earth, peat.
- Low night air temperatures. Symptoms are the same as with excessive soil moisture. It is necessary to control and maintain the optimum (22–26 ° C) air temperature in the greenhouse.
- Plants are not pollinated. In the absence of pollinating insects, cross-pollination is carried out manually. One male flower pollinates no more than 5 female flowers.
- Plant disease or pest damage. The leaves dry and curl up, a brown or yellow spot appears on their surface, the fruits take on an ugly shape. It is necessary to carry out regular measures to protect plants from pests and diseases.
Leaves turn yellow with lack of nutrition
Pest and disease control
Although in greenhouses, compared to growing in open areas, cucumbers are more protected from diseases and pests, preventive measures should be taken. And in the event of diseases or damage to plants by pests, take the necessary measures to save the plants.
Table: Disease and Pest Control
The table shows the main diseases and pests of cucumbers when grown in a greenhouse. It should be borne in mind that adherence to the basic rules for the cultivation of this crop, from preparing a greenhouse, planting seeds for seedlings and ending with harvesting, will save the plants from the threat of infection with diseases or damage by pests.
Photo gallery: diseases and pests of cucumbers
Features of growing cucumbers in the regions
Using greenhouses, especially glazed and polycarbonate greenhouses, cucumbers can be grown in all corners of Russia. The difference will be in the time span of the periods of plant growth. If in the south they are harvesting, then in the middle lane cucumbers are just appearing, and in the northern regions and Eastern Siberia flowering just ends. It goes without saying that when cultivating cucumbers, it is necessary to choose zoned varieties: those that are planted in the Kuban will not grow in Yakutia. Pollinated varieties will not give a crop where there are no pollinator insects - it is necessary to plant hybrids and parthenocarpic varieties of cucumbers.
More and more gardeners are coming to the decision to grow cucumbers in greenhouses. Currently, there are modern types of greenhouse coverings, a lot of auxiliary equipment that helps in the cultivation of vegetable crops. By applying advanced cucumber farming techniques in greenhouses, gardeners can always count on a good harvest.
My name is Sergey. I am 56 years old, I am a “young” pensioner. Higher education, graduated from the Faculty of Philology of the Pedagogical Institute. I live in Vladimir. Married. Rate the article:
(3 votes, average: 5 out of 5)
How to grow a great crop of greenhouse cucumbers?
Many summer residents today prefer to grow vegetables on their plots in homemade greenhouses, which allow them to harvest a larger crop. Most often these are small greenhouses or miniature greenhouses, which are made of wooden or aluminum construction and covered with plastic wrap.But the harvest in the greenhouse is small - it is best to grow seedlings in it, which will then be transplanted into large and equipped greenhouses.

A favorable temperature for growing cucumbers will be 20-25 degrees, which is why cucumbers are almost always grown in greenhouses or greenhouses.
The best option for a summer residence is the ability to build a small but efficient polycarbonate greenhouse. Manufacturers today offer great prefabs that anyone can assemble in a matter of hours. The sizes and shapes of polycarbonate greenhouses can be very different, their equipment consists of irrigation systems, sources of additional lighting, heating systems. But in each case, the purchase and installation of such equipment will depend on the size and purpose of the greenhouse itself.
Today we will consider how you can grow an excellent harvest of cucumbers with the help of such a structure, what conditions must be observed for polycarbonate greenhouses. We will give some useful tips that will definitely help novice summer residents in growing delicious vegetables and fruits in greenhouses and greenhouses.
Before you build a greenhouse, you need to decide on the varieties of cucumbers; Claudia, Aquarius, Nezhinsky, Evita, Talisman, Alliance, Farmer are best suited for this.
Greenhouse and soil preparation

The lashes of plants are tied up so that they do not come into contact with the ground, and also do not get entangled with each other.
You can assemble a greenhouse from ordinary boards or aluminum profiles, which are covered from above with polycarbonate sheets. At the same time, it is necessary to provide that the building has a sufficient number of vents for ventilation, an irrigation system, artificial lighting and heating. This will maintain the necessary conditions for successful cultivation.
Attention must be paid to the preparation of the soil, which must be treated with a solution of bleach. This will make it possible to kill all pests and pathogens.
Forming cucumbers in the greenhouse
Using a greenhouse, you can get a bountiful harvest, but for this it is necessary to deal with the correct formation of plants. Experts advise installing vertical trellises that will reach two meters in height, do not forget about pinching.
It is necessary to shape the cucumbers when they reach the sixth to eighth leaf phase. All shoots are pinched, including flowers (in the first axils). This will form a beautiful, regular shrub that will bear fruit well.
Temperature conditions
The temperature for growing should not fluctuate much or be too low. The greenhouse allows you to maintain normal growing conditions, this should not be neglected. It is impossible to lower the temperature level to 13-15 degrees, since cucumbers will not be able to absorb water in such conditions, which will lead to their diseases. The room temperature is considered optimal; it can be raised to 25 degrees.
Watering, humidity level
Watering and the correct level of humidity are very important if a greenhouse is used for growing cucumbers, since failure to comply with these conditions can lead to diseases, reduced yield, and plant death.
For vegetables, moisture should be kept at 75-90 percent (air) and 50-60 percent for soil. To maintain this level, sprinkling with a water flow rate per square meter is recommended in the summer. m up to 4-5 liters. Watering cucumbers should be from 11.00 to 12.00 noon and from 13.00 to 15.00.
Fertilizers for cucumbers

Pruning the plant helps to reduce its vegetative mass, which requires more nutrition.
When using a polycarbonate greenhouse for growing cucumbers, you need to take care of plant nutrition. After sprouting in the first weeks, cucumbers do not really need fertilization, but adding nitrogenous replenishment is necessary to ensure their correct growth.When flowering begins, top dressing is replaced by phosphorus, and with fruiting - by nitrogen-potassium.
The top dressing itself is recommended to be done in the evening, after which the cucumbers are watered with a small amount of water, a little fertile soil should be poured under the plants themselves.
When using a greenhouse for growing, you can use the same fertilizers as for open ground, for example, bird droppings, mullein, slurry. Regularly, under each bush, it is necessary to make solutions that consist of superphosphates, potassium salt, nitrate.
Diseases, pests and control of them
When using a greenhouse for growing vegetables, you must carefully monitor that cucumbers are not affected by various diseases or insects. This can happen due to non-compliance with the rules of care or infection from improperly prepared soil, diseased seedlings.
There are many ways to solve such problems, we offer the main ones:

If a melon aphid is found, it is necessary to immediately begin to eliminate it.
- The greenhouse can be used to grow several crops at once, in which case there is a high probability that the cucumbers will be affected by the greenhouse whitefly. This insect sucks out the juice, leaves secretions on the surface of the leaves, which become an excellent medium for the development of sooty fungi. There are several ways to deal with this pest, but it is best to remove all weeds in time and set up glue traps. If you notice insects in the room, then you need to inspect all the plants, rinse their leaves, remove the affected ones.
- The melon aphid may appear in the second half of summer, but it will attack with lightning speed. In just a couple of days, the insect is able to destroy stems, leaves, ovaries and young shoots, so you need to start fighting it at a time when it is just noticed and did not have time to spread throughout the greenhouse. First, it is necessary to thoroughly weed out all the weeds, and then process the plantings with infusion of water with tobacco dust, red pepper. The composition is as follows: for a bucket of very hot water, you need to take 200 g of tobacco dust and 30 g of pepper. It is necessary to spray once a week, for each square meter, two liters of liquid are used;
- One of the most common problems when growing cucumbers in polycarbonate greenhouses is powdery mildew. The first sign of damage is the appearance on the leaves of a white, powdery bloom. Gradually, the lesion affects the stems, the plant dies. In order to cure cucumbers, a mullein solution is used: a liter of liquid mullein and a tablespoon of urea are taken in a bucket of lukewarm water. After infusing the liquid, it is necessary to spray the cucumbers so that the solution gets on all their parts.
In addition, when using a greenhouse for growing, it is necessary to provide for the appearance of diseases such as root and gray rot, brown spot. Pathogens can penetrate the soil, the diseases themselves are provoked by cold air, excessive watering, lack of ventilation in a polycarbonate greenhouse. It is recommended to regularly inspect cucumbers, leaves and stems for damage, start treatment at the first sign so as not to lose the crop.
Helpful Hints: Harvesting Bountiful Harvests
When constructing polycarbonate greenhouses, many ask questions related to the peculiarities of growing. We offer the help of experienced gardeners who will be happy to share some of their secrets.
- How to choose the right seeds for growing? It is recommended to purchase seeds that have been harvested and properly processed, only from good yields. If you harvest them yourself, then you must carefully sort them out, do not take seeds from a poor harvest, where the plants have been damaged by various diseases. Only in this case will the greenhouse give you a delicious, plentiful harvest of cucumbers.
- Why do plants start to rot in a greenhouse? The reasons for this negative phenomenon can be improper humidity conditions, watering with cold water at night, a decrease in temperature below the permissible value. All this provokes the development of a wide variety of diseases in cucumbers, the root system and stems of which quickly begin to rot.
- Why are many ovaries formed, and the number of cucumbers is minimal? The problem may be a lack of feeding, you can start giving the plants a mullein at this time. If there is a sharp decline in the yield, it is recommended to water the cucumbers with humus or urea diluted in a bucket of water.
- What is the landing pattern? For cucumbers that will be grown in polycarbonate greenhouses, the planting scheme depends on the selected variety, the size of the structure, and the growing methods used. The following scheme is considered optimal: when using trellises, the distance between them should be about a meter; for ordinary rows, the parameters 40 * 40, 50 * 50, 80 * 100 are recommended.
As we can see, using a polycarbonate greenhouse for growing vegetables is very simple: you just need to follow the simplest care conditions in order to get a bountiful and tasty harvest of cucumbers.
How to grow cucumbers and tomatoes?
How to grow cucumbers and tomatoes in polycarbonate greenhouses?
Today, a huge number of gardeners and amateur gardeners pay attention to polycarbonate greenhouses. They have the most modern design, combined with the best production and fabrication of frames, are perfect for creating a favorable climate for growing garden crops in suburban, home gardens and farms.
The layout in the greenhouse and the size of the beds for tomatoes.
Preparing greenhouses for sowing tomatoes and cucumbers in them
Adult seedlings are planted in the greenhouse approximately in early May. But at this time it is still cool outside, especially at night. Therefore, it is recommended to plant seedlings in a polycarbonate greenhouse. Greenhouses and greenhouses intended for tomatoes must have holes on both sides. This is due to the fact that tomatoes, especially during flowering, need careful ventilation. To avoid plant diseases in greenhouse conditions, it is not recommended to grow tomatoes for several years in a row in the same place.
Formation of cucumbers in the greenhouse.
Usually agronomists and amateur gardeners resort to alternating planting of tomatoes with cucumbers. So, for example, if you planted tomatoes in a polycarbonate greenhouse last year, then this year it is better to plant cucumbers in it. But recently, cucumbers and tomatoes have begun to suffer from the same fungal disease called anthracnose (or it is also called root rot by the people).
Therefore, if the tomatoes are planted in the greenhouse after the cucumbers, it is necessary to remove all the soil of the greenhouse soil, or at least remove the layer of soil on top (about 15 cm), in which most of the parasites accumulate. After that, the soil will need to be well watered with a hot solution, which includes 1 tbsp. copper sulfate and 10 liters of boiled water.
Tomatoes require more ventilation, low humidity and temperature compared to cucumbers. Greenhouses and greenhouses should be fully illuminated by sunlight from morning to evening. It should be remembered that even a small tree or shrub causes a decrease in activity during the period of growth, ripening of fruits and negatively affects the yield.
Features of preparing the land for planting seedlings of cucumbers and tomatoes
For 1 square meter of land, consisting of loam or clay soil, one bucket of peat, sawdust and humus is added. In addition, add potassium sulfate, urea and superphosphate granules. The amount of added ingredients depends on the quality of the soil.Therefore, before using them, you should carefully study the label and the instructions for use of soil additives.
How to plant seedlings correctly?
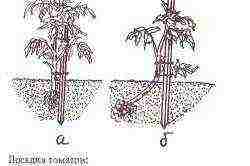
Planting tomatoes.
Non-overgrown seedlings (25-35 cm) are planted vertically, filling only the pots for mixing the soil. Even if for some reason the seedlings are too elongated (for example, if they have been in the darkened part of the room for too long), then it is not recommended to bury the stem deeply when planting. In this case, it is recommended to lay the stem slightly horizontally from below. This is necessary in order for it to gain a foothold in the ground and then continue to grow as needed. This event is made possible due to the fact that both the main trunk and lateral shoots of tomatoes very quickly give rise to roots that strengthen the plant in the ground.
That is why one can observe such a phenomenon in which a fallen branch almost immediately grows to the ground. If this does not happen, then this will stop the growth of plants and will contribute to the fact that the flowers of the first brushes will fall off. That is why, in the event that the seedlings outgrow, gardeners are encouraged to transplant the bushes first in the same land into some container intended for one-time use (and it is even better to use peat pots in this case), and to plant seedlings in the ground, having previously removed the bottom this dish.
After a few days, when the roots will have to fix in the main soil, you can take out this dish.
By the way, old buckets, pots and basins can be used as it.
So that nothing leaks through the remote bottom, you will need to put a bag on the container from below, and then install the entire structure in a larger container (for example, a bucket and a saucepan can be put in a basin). After the plant is in its place, it should be well watered. All plants must be planted at a fairly wide distance from each other - at least 50 cm. Otherwise, it will be difficult and problematic to cope with plant care and harvesting. And the plants themselves will not be comfortable enough to grow in cramped conditions.
How to properly care for tomatoes in polycarbonate greenhouses?
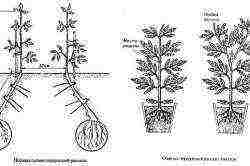
Planting and pruning overgrown tomato seedlings.
Once you have planted tomato seedlings according to all the rules, you need to water them well for 2 weeks. This is necessary so that all plants are approximately equal in height, do not stretch or become excessively depleted. If there is no proper watering, then this can lead to a delay in flowering, ripening, or even death of the plant.
Usually tomatoes have a fairly dense main stem, from which brushes with inflorescences extend at equal distances. Their number can sometimes even reach 8 pieces. However, this does not mean at all that the harvest will be impressive. In most cases, in order to achieve a solid harvest, only 2-3 brushes are needed.
By cutting off the extra branches, you can count on the fact that the tomatoes will be large and ripe. If, in the process of growth, all the lateral shoots are left, then an ovary will form on each of them, but in this case it will be difficult for the plant to completely supply the fruits with useful substances. There is a risk that the set small, but numerous tomatoes will remain small.
In most cases, it is advised to leave only the lower stepsons, all the rest can be removed either manually (if the branches are thin), or using tools such as scissors or pruning shears. If pinching occurs already during the flowering period, then preference is given to those stepsons who have already started a peduncle. The rest can be deleted. Experts advise to carry out this event early in the morning, when the stepsons are not strong enough, and the plant in this case will not experience any negative effects on itself.
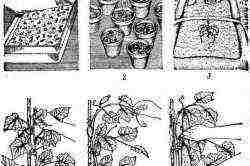
Agrotechnical techniques for growing cucumber: 1 - sowing seeds on a damp paper towel, 2 - transplanting sprouts into pots, 3 - planting plants in a permanent place, 4 - pinching the top, 5 - pinching side shoots, 6 - picking fruits (cut: with a sharp knife ).
Particular attention should be paid to the seed labels. Here, in addition to such factors as pinching, the ripening period and the peculiarities of care, it is necessary to pay attention to the method of pollination of plants. They, in turn, can be self-pollinated and bee-pollinated. The difference is that the first group is the simplest option, since in this case you will not need to worry about how exactly the process of fertilization of a flower and, accordingly, the birth of tomato fruits occurs.
The second option assumes that someone's help is needed for the ovary. In other words, pollen from one plant must somehow get to the inflorescence of another plant. In this case, your helpers will be bees, bumblebees, wasps and other insects that feed on nectar flowers. But there is practically no guarantee that the pollen got to the exact plant that needs it.
In order not to worry about the future harvest, you need to help the plants yourself. Your help is in shaking the inflorescences. This can also be facilitated by light watering of the plants, but after it you should not forget that excess moisture remaining on the walls of the greenhouse can adversely affect the tomatoes. Therefore, immediately after watering, leave the door open, and if there are windows, then leave them.
Airing should be slight, especially in those cases when the stage of active flowering of a given fruit crop begins. Ventilation has the best effect when the sides are open in the same way as on the top panel. This will ensure that the tomatoes are in the greenhouse without condensation. Waterlogged soils lead to a decrease in the amount of sweetness in tomato fruits. Such tomatoes are characterized by increased wateriness, they have too many seeds.
Drip irrigation system.
Of course, such fruits will be very sour and unsuitable for making salads or for canning. Therefore, it is necessary to ensure such irrigation, in which the crop will not only be distinguished by increased quantity, but also by improved quality. Before flowering, tomatoes need systematic watering no more than once every 5 days. In this case, the amount of water is determined depending on the quality of the soil. But on average, it is advised to pour about 5 liters of water for each square meter.
It should also be remembered that a warm temperature is constantly maintained in the greenhouse, which leads to the need to use exceptionally warm water for irrigation. Its temperature should not fall below 20 degrees, therefore, in order for this to become possible, collect water in any large vessel in the garden or in the garden in advance so that it can warm up from the sun's rays.
Feeding tomatoes
Planting scheme for tomatoes.
During the growing season, 3-4 root feeding should be done. For the first time, they are carried out no earlier than 2.5 weeks after the seedlings are planted in a permanent place. The amount of feeding should be calculated separately in each case.
Usually, all instructions for preparing and mixing ingredients are indicated on the packaging with the composition. you can seek advice from a specialist who provides services for the sale of plant fertilizers.
After the first feeding, at least 10 days should pass, only then it will be possible to fertilize the soil again and strengthen the root system of the plant.
The third part of the dressing is poured onto the plants 12 days after the previous one. If you need to repeat this procedure, then the break between all subsequent activities should be at least what was done between 2 and 3 procedures.
How to grow cucumbers in a greenhouse
Planting scheme for bee-pollinated cucumbers in greenhouses with heating.
Seedlings of cucumbers, like tomatoes, must be grown at home, only then they can be transplanted into a greenhouse, which was prepared using some additional source of heating. Planting cucumbers in unheated greenhouses in the middle zone of our country should not be carried out earlier than May 10-15. During early sowing, the planted bushes can be damaged by frost, which occurs even in early June.
Thus, as soon as the soil in the greenhouse is warmed up to the required temperature, seedlings can be planted. It is necessary to use special utensils that will allow you to transplant it without harm to the plant. At best, this is a peat pot that supplies the plant with useful trace elements. It is worth noting separately the fact that you do not need to remove the plant from the pots. Therefore, when planting seedlings in a greenhouse, you will only need to dig holes of the required size and, placing pots in them, sprinkle them with earth on top. When irrigated, peat will disperse into the ground, enriching it with the necessary useful elements.
Planting cucumber seeds in the greenhouse is allowed. However, this increases the time to fruiting. Therefore, this method is rarely used. An exception is planting seeds in warm regions of the country. Planting technique - described for planting seedlings.
Care for cucumbers in the greenhouse
Forming a cucumber in a greenhouse.
Here it is important to pay special attention to the process of forming a bush, watering and fertilizing. At first, the cucumbers need to be watered only a little, so as not to blur the roots. And only after the length of the cucumber bushes reaches about 30 cm, they can be hilled and then watered as you like. Bushes of varieties grown in greenhouses are formed according to the same pattern. Pinch the top of the main stem when the stem grows to 20-30 cm, so that the lateral stems grow, which produce much more fruit.
After the upper stem is removed, you will observe (with proper watering and care) the active growth of side shoots, and after a while they will bloom. It is better to remove the trunk so that its tip is broken off or even bent.
In the future, the strict system of forming a bush can be neglected, because the bush is already growing and will be strong enough. The main thing is to cut off leaves and shoots only so that the shoots do not go out onto the paths and neighboring beds. Depending on the age of the plants, it will be possible to gradually remove those shoots that no longer bear fruit, but still feed on the main stem, preventing the plant from giving all its strength to the formation of new fruits.
When growing bee-pollinated varieties and hybrids, it is necessary to provide access to plants inside the greenhouses of bees and other insects. On hot summer days, bees are reluctant to fly in the greenhouse. They can be attracted by organizing feedings with sugar syrup. Both cucumbers and tomatoes should be planted in early and mid-May.
Secrets of growing cucumbers in polycarbonate greenhouses: the best varieties, care and formation
Category: cucumbers

Cucumbers are the most popular crop for growing in polycarbonate greenhouses Cucumbers are the most popular and demanded crop for growing in polycarbonate greenhouses. The conditions created in these structures are ideal for them. High light transmission, low thermal conductivity and inertness to the effects of chemical and physical factors have turned this material into a real panacea for obtaining record yields. The microclimate created inside the polycarbonate garden structures contributes to the active growth and fruiting of cucumbers. However, even here there are secrets of cultivation.
Cucumbers: basic information
|
|
Photo: |
|
Advantages of growing cucumbers in polycarbonate greenhouses
Polycarbonate is a polymeric cellular material that has almost completely replaced glass and film today. Even a non-year-round cultivation of cucumbers from it in greenhouses can not only satisfy the need of a gardener's family for green plants, but also allows you to get a good income from the sale of surplus crops.
The advantages of a polycarbonate greenhouse are obvious:
- Good light transmission, coupled with the delay of too bright rays that can harm plants.
- Excellent heat-insulating qualities, acquired due to the numerous vacuum mini-chambers (cells) in the cavity of the polycarbonate sheets.
- Lightness and flexibility, which make it possible to erect massive structures on soils unsuitable for high loads, even without a foundation and a reinforced frame.
- Durability and strength, thanks to which a polycarbonate greenhouse can withstand temperature extremes throughout the year, snow and wind loads.
In addition to the above, it should be added that when growing cucumbers under this material, ideal conditions are created for them for the growth of lashes and fruiting.

Polycarbonate greenhouse withstands temperature extremes throughout the year
Equipment for growing cucumbers
For the successful growth of cucumbers in the greenhouse, it is necessary to take full care of them. Without a set of special equipment for greenhouses and garden tools, this will be problematic.
In order for the harvest of Zelentov to really surprise and delight, it is advisable for summer residents to purchase the following tools:
- shovels, hoes and other devices for digging and loosening the soil;
- buckets and watering cans for watering or a full-fledged drip irrigation system;
- heating devices (for year-round cultivation of cucumbers) or temporary heating (for early spring or autumn cultivation of zelents);
- automatic or semi-automatic installation on the vents for regular ventilation of the greenhouse;
- phyto-lighting for growing cucumbers in the winter or autumn-spring period;
- water tanks made of dark polymer material;
- shelves, racks and boxes for storing inventory inside the greenhouse.
The larger the polycarbonate greenhouse, the more devices you need to purchase, or you should rely not on the amount of equipment, but on its power (performance). In small greenhouses, it is quite possible to do without an irrigation system, heating and automatic vents.
How to plant cucumber seedlings in a greenhouse (video)
The best cucumber varieties suitable for polycarbonate greenhouses
Before mastering a polycarbonate greenhouse, it is important to correctly approach the choice of varieties of cucumbers. Ideal for greenhouses are:
- self-pollinated (parthenocarpic) varieties that do not require bees and other insects in the greenhouse for normal fruiting;
- varieties resistant to viral, bacterial and fungal diseases;
- varieties and hybrids that tolerate overheating and cooling well.
These can rightfully include the following cucumbers:
| Variety / hybrid name | Ripening terms | Yield | Appointment |
| Tempo (F1 hybrid) | Early ripe | High due to the harmonious return of the harvest | For fresh consumption and harvesting |
| Blanka (F1 hybrid) | Early ripe | Above average, long-term yield | Universal purpose |
| Aristocrat (F1 hybrid) | Mid-early | High | For fresh consumption |
| Halley (variety) | Mid-season | High | For salads, preparations and fresh consumption |
| SM 5341 (F1 hybrid) | Mid-season | Very high, stable | For processing and fresh consumption |
| Herman (F1 hybrid) | Early ripe | Above average or high | For canning and salads |
| Courage (F1 hybrid) | Early ripe | High due to the formation of a large number of large greens | For salting and fresh consumption |
| Moscow greenhouse (hybrid F1) | Early maturing | High | For preparations, salads and fresh consumption |
| Zozulya (hybrid F1) | Mid-season | Very high | For pickles, marinades and salads |
| Relay (F1 hybrid) | Mid-season | High | Universal |
Joint planting of several varieties and hybrids allows growing greenhouses of greenhouses of various sizes and purposes.
Preparation and preventive tillage
Greenhouse varieties and hybrid forms of cucumbers are subject to various diseases. To prevent infection and normal development of plants, it is necessary to prepare the soil in the greenhouse in advance. To do this, it is enough to take the following steps:
- In the fall, treat the soil in the greenhouse with bleach or fungicides - Phytocide, Phytosporin or Trichodermin.
- Fill the soil with organic matter - fresh manure, fallen semi-rotten leaves or hay (straw), embedded in the soil to a depth of no more than 30 cm.
- Before planting, loosen the topsoil to a depth of at least 20 cm and spill it with hot water.
The cucumber beds prepared in this way in the greenhouse will provide the plants with nutrients, as well as generate heat, creating a microclimate suitable for the culture.

To prevent infection and normal development of plants, it is necessary to fill the soil in the greenhouse with organic matter in advance
Landing scheme and timing
There are two ways to plant cucumbers in polycarbonate greenhouses:
- seedlings;
- seeds.
In the first case, the planting material is sown in advance, about 4 weeks before placement in a permanent place. It is better to do this in the last decade of March or early April. At the age of three weeks, grown cucumbers are planted in a greenhouse, trying to place no more than 5 plants per square meter.
When planting by seed, the planting dates are shifted to mid or late April, depending on the temperature of the soil in the greenhouse. The seeds are placed in small holes to a depth of no more than 2 cm, watered and covered with plastic foil or caps to create a greenhouse effect. The planting scheme for the seed method does not differ from the seedling one. However, it is recommended to sow several seeds in one hole. As they grow, the strongest specimens are left in them.
The planting scheme for the seed method does not differ from the seedling
Care rules
Classic cultivation of cucumbers in polycarbonate greenhouses implies the usual set of agrotechnical measures:
- Regular watering with water heated to a temperature of 20-23 degrees. It is for this that dark containers are installed inside the greenhouse, inside which the liquid is heated under the influence of sunlight.
- Loosening and / or mulching the soil with rotted sawdust, decayed leaves and hay or humus. In addition to retaining moisture in the soil, mulch will to a certain extent replenish the need for nutrients in cucumbers.
- Daily airing of the greenhouse, which helps to strengthen the plants and prevents the development and spread of diseases of cucumbers, especially fungi, throughout the greenhouse.
- Top dressing with mineral and / or organic fertilizers. At the beginning of the growing season, you can use nitrogen fertilizing, and with the beginning of flowering, enrich the diet of cucumbers with potassium and phosphorus, as well as trace elements.

Growing cucumbers in polycarbonate greenhouses implies the usual set of agrotechnical measures
The formation of lashes is no less important for cucumbers. This culture grows very quickly, so you need to form whips once a week. Branching varieties are pinched over the 6th leaf to form a large number of fruiting shoots, while some hybrid parthenocarpic forms are recommended to be grown in one stem. It is better to cut off male flowers almost completely. The tendrils, damaged leaves and fruits, as well as thickening or weakened shoots are subject to removal.
It is important to tie the lashes to the supports (trellises) in a timely manner. For multi-stem cultivation, the central whip is placed vertically, and the side ones are at an angle of 60 degrees to it. Single-stem cucumbers are always tied vertically.
We also invite you to read the article, which tells about the causes and elimination of problems in the formation and growth of cucumber ovaries.

It is necessary to tie the lashes of cucumbers to the supports
Problems with growing cucumbers in polycarbonate greenhouses
In general, there are not so many problems with greenhouse cucumbers as when growing this crop in the open field. However, there are many diseases and pests that prefer to live in greenhouses. Most often, cucumbers in polycarbonate shelters suffer from rot, anthracnose and various wilting.
To avoid problems, it is enough, at the first signs of disease damage to plants, to treat the entire greenhouse, including the soil surface and walls, with microbiological fungicidal preparations - Gamair, Alirin, Trichocin or Glyocladin.
When and how to feed cucumbers in a greenhouse (video)
Polycarbonate greenhouses are much more ergonomic and efficient than glass or film greenhouses. With the proper approach, the yield of cucumbers from one square meter in it is 3-4 times higher than in the open field.
Condition 3. Loose, breathable soil
For growing cucumbers, soil is well suited, with a close to neutral pH, without excess nitrogen. Cucumber roots love oxygen, and this can only be provided by loose, well-permeable soil. Therefore, actively feed the "soil engineers" with organic matter - bugs and worms.
Growing cucumbers in a greenhouse is rarely complete without mulching. Use mowed grass (only without seeds) or sawdust for this purpose. What for? Firstly, in order to retain moisture in the ground as much as possible, and secondly, so that the fruits themselves do not touch the ground, because they rot from it.
Make sure that the surface roots are not exposed - sprinkle them from time to time. It is also important to observe that a dry crust does not form on the ground, for which it is advisable to mulch the beds with a thin layer of hay or dry humus. Just do it all on well-warmed soil.
Condition 4. Correct watering
According to the results of an official chemical analysis, a cucumber contains 96-97% water, and therefore regular and competent watering is the alphabet in the cultivation of greenhouse cucumbers. See how actively this is done in industrial greenhouses:
Three days after planting, 10-12 days, water the cucumbers only in the root part, little by little, so that a good root develops. If you flood the plant, the root system will begin to rot.
Further, before the first ovary, watering is enough once every few days, and after that - every day, until you begin to collect the first fruits.
It is also important to properly water the cucumbers in the greenhouse:
- Never pour water directly on the leaves - indoors there is no such good ventilation as in the vegetable garden, and here the plants will just start to hurt. The ideal option is under the root, with settled water.
- Watering cucumbers during the day, under the sun's rays and directly on the leaves, is also impossible: this is how small water lenses are formed from drops that refract light, and the plants eventually get burned.
- You only need to water the cucumber bushes with warm water, otherwise they will also start dropping the ovaries.Just take cold tap water in the morning and put it in large barrels outside - let it reach ambient temperature.
But if you need to additionally increase the humidity of the greenhouse, then just water the structure or put a bucket of water next to the plants.
You need to tie cucumbers like this: tie the twine around the plant with a free loop, and leave it that way for now. Do not pull tight, as as it grows, the thickness of the stem will increase. Then, once every few days, twist the main stem around the twine, but only in one direction.
By the way, there are several options:
Or put trellis nets in greenhouses:
Also make sure that no grooves are left near the root collar of the plant. If irrigation water gets into them, this will lead to cracking of the root collar, and subsequently to root rot.
Is it difficult to form whips?
You have probably already noticed more than once in novice gardeners the impenetrable jungle in the greenhouse - this is simply not a formed cucumber in time. But the comparison here is especially apt - the cucumber is in fact the simplest tropical liana, from where curious travelers brought it to our lands. But the deaf thicket in the greenhouse is destructive for the harvest - after all, now there is little light and air here, it is too humid and the risk of developing various diseases is high. Therefore, learn how to form this vine correctly and in time.
After all, it is not without reason that one of the most common failures in such a matter as growing cucumbers in a greenhouse is the resulting large number of lashes and very little fruit. Basically, such a "harvest" is received by beginners. And all because cucumbers, during their development, did not go through an important stage of formation. And now we will tell you in detail how and what you will need to do.
There are three stages:
- Step 1. "Blinding". Remove all shoots and buds from the axils of the first three true leaves. So we give the plant an incentive to develop further and make a lot of ovaries, otherwise it is "content" with the first success and slows down in the dew.
- Step 2. Now we remove the side shoots on the stem to the 0.5 m mark, from 0.5 to 1 m we leave on the side shoots one sheet at a time, from 1 m to 2 m in three.
- Step 3. Next, we pinch all the side shoots of the second row onto one sheet.
Focus on the height of the plant: the higher the cucumber, the more shoots and cucumbers you need to leave on it. Then we throw the main stem over the trellis and pinch it again, leaving only 40-60 cm. This is where the main formation of the cucumber ends.
But there is also a weekly formation in which plants need to be examined for yellowed or diseased leaves. Do such an examination only in the first half of the day so that new wounds can dry out by evening.
Pay special attention in terms of formation to hybrids of branched-type protected ground cucumber:
|
The presence of a polycarbonate greenhouse on the site provides its owners with an excellent opportunity to grow vegetables with a high level of yield. At the same time, thanks to ideal greenhouse conditions, the ripening time of the fruits is significantly accelerated. Most often, tomatoes, bell peppers, eggplants, and, of course, cucumbers are grown in polycarbonate greenhouses. With proper care, greenhouse cucumbers can bear fruit for almost a whole year, so it is very profitable to grow them. Landing featuresFor planting in the open field, cucumber seedlings are usually grown in separate boxes or pots, and only then are they transplanted into the ground. When growing this crop in a greenhouse, this is not necessary. However, using seedling samples, you can get the harvest at the earliest possible date. In this case, the seeds should be planted in small pots, such as peat cups. This must be done at least 25 days before planting the seedlings in the greenhouse soil. For planting seedlings, you can use a purchased soil mixture, or prepare it yourself.Usually peat and humus with the addition of sawdust are used for this purpose. In order for the seedlings to ripen faster, nitrophoska should be added to the soil. 5 days before transplanting the seedlings to a permanent place, the soil is prepared - it is loosened, fertilized and watered. Also, beds are formed, about 35 cm high and 60 cm wide. It should be remembered that between the beds it is necessary to leave a passage, the minimum width of which is 80 cm. The finished beds are covered with foil. This maneuver will keep the ground warm and moist before landing. Direct planting of cucumber seedlings begins with the fact that water is poured into each hole. Then a pot with a plant is inserted there and covered with earth no more than a third of the length of the stem. The distance between the plants should be approximately 20 cm. Care for cucumbers in the greenhouseGreenhouse cucumbers, like other vegetables, need regular watering first of all. For this purpose, you cannot use cold water, the water temperature must be at least 23 ° C. Water the plant about once every 5 days. During the flowering period, the number of waterings should be doubled. Cucumbers also need to be weeded from time to time, while removing all weeds. Loosening the soil also contributes to better growth of cucumbers, so it is recommended to do it regularly. Do not forget about the timely airing of the greenhouse. In warm weather, open the window or raise the panel for the whole day. The harvest of greenhouse cucumbers largely depends on the quality and quantity of dressings. Fertilizer is advised to be applied no more than five times per season. A good feeding will be all sorts of organic mixtures - mullein, chicken droppings, fermented nettles. It is also necessary to use special mineral fertilizers: nitrogen - for sandy soils and potash - for floodplains. After about two weeks, all the plants in the garden need to be tied up. For this, it is convenient to use wire and twine. During tying, the formation of cucumbers into one stem is also carried out. Pest and disease controlDespite the fact that the most comfortable conditions are created for cucumbers in the greenhouse, in some cases they suffer from all sorts of pests. Most often we are talking about aphids and melons. It appears mainly in August and affects inflorescences and young shoots. It is recommended to fight aphids with a tincture of bitter red pepper. At the same time, you also need to carefully remove all weeds from the garden, since aphids also live on them. Cucumbers in the greenhouse are also often annoyed by a pest called the greenhouse whitefly. This insect secretes a special sap, which subsequently infects the plant with a fungus. To prevent the appearance of whiteflies in the greenhouse, you can tighten the windows with gauze or buy special mosquito nets. In addition, cucumbers are susceptible to certain diseases. Most often they suffer from powdery mildew. The symptom of this disease is a whitish coating that usually appears on the leaves. As a result, the leaves turn yellow and then dry. In the fight against powdery mildew, you can use both purchased preparations and homemade products. In particular, a good result is obtained by spraying the leaves with ground sulfur. |
Growing cucumbers in a greenhouse from polycorbanate
How to grow cucumbers in a polycarbonate greenhouse
3.45 / 5 (69.09%) 22 votes
The presence of a greenhouse on your site is a great way to increase yields several times and bring the quality of vegetables grown to a qualitatively new level. Today we'll talk about how to grow cucumbers in a polycarbonate greenhouse.
A comfortable microclimate in a polycarbonate greenhouse is one of the ways to create optimal conditions for growth and development for your crops. Polycarbonate greenhouses are durable and reliable; gardening is a pleasure in them.
Preliminary preparation for disembarkation
Cucumber seedlings are most often grown in pots or plastic containers for at least 25 days before planting them directly in the greenhouse. However, if you plan to grow cucumbers in a greenhouse made of cellular polycarbonate, there is no need to pre-plant. For additional provision of the most comfortable climate for seedlings, you can additionally cover the greenhouse with a film or some other protective coating.
Care for cucumbers in the greenhouse
The main operations for the care of cucumbers in the greenhouse are
- Loosening the soil
- Airing
- Watering (best automatic drip)
- Top dressing
Cucumbers need abundant moisture for good growth. In winter, plants should be watered in the morning and, if possible, on sunny days (about twice a week). Water for irrigation should be warm, as cold water can provoke diseases in plants. To avoid burns, water should not be poured directly onto the leaves - it is better to use a drip irrigation system.
It is important to pay sufficient attention to the soil on which your cucumbers grow. It must be well loosened and breathable, otherwise the root system will stop developing and the plants will die. Loosening must be done very carefully so as not to damage the roots.
Airing is done by opening the vents (forced or automatic). If the weather is warm, the vents can be left open for the whole day.
Fertilizing cucumbers in a polycarbonate greenhouse
In order for the crop to be rich, the soil must be rich in organic matter. That is why it is necessary to fertilize with manure - cucumbers are not afraid of large doses of organic matter. The soil should be fertilized with manure, rotted debris, peat or sawdust. Fertilizers should be applied locally. In addition, fertilizing cucumbers in the greenhouse should be carried out with mineral fertilizers.
For the whole summer, cucumbers in the greenhouse are fed no more than five times. The first feeding is carried out at the beginning of flowering. When the fruiting period is underway, feeding is carried out four more times.
If the soil on your site is sandy, it is also necessary to additionally apply nitrogen fertilizers, and if the floodplain, potash fertilizers are well suited. At the beginning of spring, it will not be superfluous to feed your cucumbers with ammonium nitrate, which should be introduced into special furrows.
So that during low temperatures the vital activity of the roots is not disturbed, the plant is supported by foliar dressing. For these purposes, ammonium nitrate is used.
Threats to cucumbers in the greenhouse: pests and diseases
In addition to the proper care that you can provide to your cucumbers, you also need to protect them from various pests and diseases.
Pests
- Greenhouse whitefly... The juice secreted by this insect on the foliage of cucumber seedlings contributes to the development of various fungi. Subsequently, the leaves dry out and rot. To cope with the whitefly will help you eradicate weeds and tighten the vents and doors with gauze.
- Melon aphid... It affects mainly flowers and young shoots. Its appearance should be expected around the second half of the summer. In order to fight aphids, it is first of all necessary to remove all weeds from the greenhouse and spray the entire planting with an infusion of bitter red pepper.
Diseases
Downy mildew... It affects the plant at any stage of its development and appears as green oily spots on the leaves of plants. This disease is extremely dangerous because, despite preventive measures, the infection persists on the ground for several years. Watering plants with cold water leads to the spread of downy mildew. In order to fight it, it is necessary to temporarily stop feeding and spraying the plants, and then treat them with a solution of copper sulfate. Powdery mildew attacks cucumbers in polycarbonate greenhouses. It appears as a white bloom. With the development of the disease, the leaves dry up and the plant dies.The causative agents of the disease are spread from weeds and flowers. Do not use cold temperature water for irrigation and constantly plant plants in the same soil.
How to prevent yellowing of cucumbers
You can often notice that cucumbers in polycarbonate greenhouses turn yellow. This may be an indication that your plants are stuffy and hot, or they lack phosphorus or nitrogen. It is also necessary to pick the fruits on time on time, preventing them from overripe and thereby further burden the seedlings. To avoid this, it is necessary to carefully and timely feed the soil, water it, and also prevent plants.
Growing cucumbers in a polycarbonate greenhouse is always fresh, tasty and healthy cucumbers right from the garden, with which you can pamper your loved ones from early spring to late autumn, being confident in their quality and naturalness. A polycarbonate greenhouse is an ideal place for planting any plant crops, including cucumbers, because it helps to create an ideal microclimate for harmonious growth and development.
Growing tomatoes and cucumbers in honeycomb polycarbonate greenhouses
Having decided to buy a greenhouse made of cellular polycarbonate, you get the most modern design, during the production the best projects for the manufacture of frames are combined, to create a microclimate favorable for growing garden crops in summer cottages, personal plots and on farms.
Greenhouse preparation
The grown seedlings are planted in the greenhouse on May 1-10. It is still cool during this period, especially at night, so we recommend a greenhouse with a honeycomb polycarbonate cover. A greenhouse intended for tomatoes should have vents on both sides, since tomatoes, especially during flowering, need careful ventilation. In order to avoid diseases, it is not recommended to plant tomatoes in the same greenhouse for several years in a row.... Usually they are alternated with cucumbers, that is, one season - cucumbers, the second - tomatoes. But recently, cucumbers and tomatoes have begun to suffer from the same fungal disease - anthracnose (root rot). Therefore, if tomatoes are still planted after cucumbers, then it is necessary to remove all soil from the greenhouse or at least remove its top layer by 10 - 12 cm, where the entire infection is located. After that, the soil must be sprinkled with a hot (100 ° C) solution of copper sulfate (1 tablespoon per 10 liters of water) or two OXICHOM tablets.
Tomatoes require more ventilation, lower humidity and temperature compared to cucumbers. The greenhouse should be completely illuminated by the sun from morning to evening, even slight shading by trees or shrubs leads to a decrease in yield... Ridges are made along the greenhouse, their number depends on its width. The ridges are made 8 - 10 days before planting the seedlings, 35 - 40 cm high, the width of the beds depends on the greenhouse (usually 60 - 90 cm), a passage of at least 60 - 70 cm is made between the ridges.
Soil preparation
On a bed of loamy or clayey soil, add one bucket of peat, sawdust and humus per 1 m2. If the beds are made of peat, then add one bucket of humus, sod land, sawdust or small shavings and half a bucket of coarse sand. In addition, add 3 tablespoons of double granular superphosphate, 1 tablespoon of potassium sulfate and potassium magnesium sulfate, 1 teaspoon of urea or sodium nitrate, 1 - 2 cups of wood ash and dig up everything. And before planting, the seedlings are watered with a solution of potassium permanganate at a temperature of 50-60 C (1 g of potassium permanganate per 10 liters of water) at the rate of 1.0 - 1.5 liters per hole.
We plant seedlings correctly
Non-overgrown seedlings (25-35 cm) are planted vertically, filling only the pot with soil mixture. Even if the seedlings are stretched out for some reason, then when planting it is not recommended to deepen the stem... The stem, covered with soil mixture, immediately gives additional roots.This stops the growth of the plant and promotes the dropping of flowers from the first brush. Therefore, if the seedlings are outgrown, then I advise you to plant them as follows. Make a wide hole 12 cm deep, in it the second hole is deeper to the height of the pot, put a pot of seedlings in it and cover the second hole with earth. The first hole remains open for now. After 12 days, as soon as the seedlings take root well, cover the hole with earth.
Hybrids and varieties of tall plants are planted in the middle of the beds in one row or staggered 50-60 cm apart.
Tomato care
After planting, the plants are not watered for 12-15 days., while the plants are not stretched. In 10 - 12 days after planting, the tomato plants are tied to a trellis 1.8 - 2 m high. Tomatoes are formed into one stem, leaving 7 - 8 flower clusters. You can leave only one lower stepson with one flower brush, and all the other stepsons are removed from the axils of leaves and roots when they reach a length of 8 cm. This is best done in the morning, when the stepsons break off easily. In order to avoid infection with viral diseases, the stepsons do not cut off, but break off to the side so that the plant sap does not get on the fingers, since you can transfer the disease from a sick plant to a healthy one with your hands. The columns from the stepsons are left 2 - 3 cm high.
Pollinate flowers during the day in warm sunny weather by gently shaking the flower brushes. In order for the pollen to germinate on the stigma of the pistil, it is necessary to water the soil immediately after shaking or spray it with a fine spray on the flowers. 2 hours after watering, the air humidity is reduced, that is, the window and door are opened. Airing is mandatory, especially in the flowering phase of tomatoes... In addition to the side vents, the upper vents should also be open so that there is no condensation (water drops) on the film. Waterlogged soil reduces the content of dry matter and sugar in tomato fruits, they become acidic and watery, and their fleshiness decreases. Therefore, it is necessary to ensure such watering, which will allow you to get a high yield and not reduce the quality of the fruit.
Before flowering, plants are watered after 5 - 6 days at the rate of 4 - 5 liters per 1 m2 during flowering and fruit formation - 10 - 15 liters per 1 m2. The water temperature should be 20 - 22 ° C.
Top dressing
During the growing season, it is necessary to make 3 - 4 root dressings... The first is carried out 20 days after planting the seedlings in a permanent place (for 10 liters of water, take 1 tablespoon of nitrophoska, 0.5 liters of liquid mullein) at the rate of 1 liter per plant. The second feeding is done 10 days after the first (for 10 liters of water, 1 tablespoon of complete fertilizer and 1 teaspoon of potassium sulfate) at the rate of 5 liters per 1 m2. The third is carried out 12 days after the second (for 10 liters of water, 1 tablespoon of superphosphate and 2 tablespoons of wood ash), watered at the rate of 6 - 8 liters per 1 m2.
During full fruiting, tomatoes are fed with the following composition: 1 teaspoon of dry powder or a tablespoon of liquid sodium humate with the addition of 2 tablespoons of superphosphate is taken for 10 liters of water. Water at the rate of 5 liters per 1 m2. This dressing helps to speed up the fruit filling.
A Few Care Tips
Gardeners have a lot of questions about caring for tomatoes: flowers fall, leaves curl, and so on. Of course, if for some reason the tomato growth is disturbed and suspended, then this primarily affects the formation of the plant and the inflorescence, that is, few fruits are formed on the flower brush, and this sharply reduces the yield.
If the plant is "fattening"
For example, if the top leaves of a tomato are constantly twisted, there is a rapid growth, and the plant itself is powerful, the stems are thick, the leaves are dark green, large, juicy, that is, as the gardeners say, fattening is going on, then such a plant will not give a crop, since everything goes into the vegetative mass, into the greenery. In such plants, as a rule, a very weak flower raceme with a few flowers is formed.This happens from abundant watering when applying large doses of nitrogen and organic fertilizers and a lack of illumination.
How to straighten such plants? First of all, it is necessary not to water them for 7 - 10 days, increase the temperature for several days in the daytime to 25 - 26 ° С, and at night to 22 - 24 ° С (doors and vents are not opened in the greenhouse). It is also necessary to correctly pollinate the flowers of these plants, that is, from 11 to 13 o'clock, manual shaking of the flower brushes is carried out in warm dry weather. To delay growth, root top dressing is done with superphosphate (for 10 liters of water, you need to take 3 tablespoons of superphosphate) at the rate of 1 liter for each plant. And in a short time, the plants are corrected.
If flowers and fruits fall
It happens that the leaves of plants are directed upward at an acute angle and do not curl either at night or during the day. Flowers and even small fruits often fall on such plants. The reason for this is dry soil, high temperature in the greenhouse, poor ventilation, low light. In this case, it is urgent to water the plant, reduce the temperature in the greenhouse, ventilate, etc. And vice versa, in well-developed plants, the upper leaves curl slightly during the day, and straighten at night, the flowers do not fall off, they are bright yellow, large, in a flower there are many of them. This means that the plant receives everything it needs for growth: light, nutrition, etc. From such plants, and get a good harvest.
If fruits do not grow on the second and next brushes
It often happens that beautiful large fruits are poured on the first brush, and on the second and third brushes the filling is slow. In order to speed up the pouring of fruits on the second and third flower clusters and improve the flowering of subsequent ones, it is necessary to remove the first crop from the first cluster as early as possible, without waiting for the reddening of the fruits. The removed brown fruits ripen quickly on a sunny windowsill (literally in two days). In addition, immediately after harvesting, it is necessary to water the soil at the rate of 10 - 12 liters of water per 1 m2. Stepsons and leaves are not cut, the temperature in the greenhouse must be reduced to 16 - 17 ° C (open the vents and doors), especially at night. Under these conditions, the crop is quickly formed on subsequent clusters and ripens at an earlier date.
If the plants are thin, weakened
Sometimes, in a good new greenhouse, gardeners have slender plants with long internodes, a loose flower cluster, and few fruits. What's the matter?
- Lack of illumination. Perhaps there are trees or berry bushes growing around the greenhouse, and the illumination inside the greenhouse is low. As a result, the yield is 3-4 times lower than in a greenhouse well-lit by the sun. Therefore, remember that tomatoes are the most light-loving crop. The fruits are sweet from the sun.
Green salad in spring, autumn and winter, cucumbers, tomatoes and bell peppers in summer and autumn - these vegetables "fill" the bulk of our greenhouses. Despite the opposite opinion of many amateur gardeners, cucumbers and tomatoes "get along" well next to each other - taking into account the fact that cucumbers are thermophilic, and tomatoes love light. Cucumbers and pumpkins (melons) prefer high air humidity, so they are planted in sheltered and semi-shaded corners of the greenhouse. Tomatoes and eggplants, on the other hand, need dry air to get pollen onto the stigmas of the pistils and set the fruit. Therefore, they need to be planted close to ventilation and doors. Even fewer problems with bell peppers. First of all, it needs a lot of light, like eggplants and green peas.
Pepper and salad in greenhouses
Sweet and hot peppers
Sowing: from early March to early April. Germination: 8-14 days at a temperature of 18-25 ° C. Landing scheme: 40 x 50 cm. Harvesting: from late June to October. Productivity: 2.5-4 kg / m2 from 4-5 plants.
Green pepper - not fully ripe. Each fruit eventually turns red, and in the intermediate stages of ripening, depending on the variety, it becomes purple, black, yellow or orange.
Native to the South American Andes, this nightshade plant has very different fruit shapes. For stuffed peppers, large, deeply grooved, tender-tasting vegetables are preferable. However, there are varieties of peppers in the shape of a sweet cherry, with round and sharp fruits for pickling, in the shape of a pin of red, yellow or black, with a taste ranging from mild to spicy (pepperoni). Meaty varieties of “tomato-like” pepper are very aromatic and delicate in taste.
Varieties: thick-walled vegetable peppers for stuffing and salads with a delicate taste. Tomato pepper: mildly spicy for pickling. Hot pepperoni.
Care: heat-loving peppers are well suited for sunny places between widely planted tomatoes, peppers can also be planted in separate beds. The soil should be loose, nutrient-rich and moist. In extreme situations, such as dryness or stagnant moisture, as well as temperatures below 15 ° C, pepper reacts by dropping flowers and fruits. First, the main portion (100 g / m2) of organic fertilizer is applied, then 5-6 weeks after transplanting, the plants are fed another 50 g / m2, or watered weekly with liquid fertilizer. Paprika, like tomatoes, but the strings stretched in greenhouses tend upward. Pegs are also suitable as a support.
Advice: the harvest can be increased in a simple but effective way: pick the first fruits on time, new ones will soon appear in their place. Hot pepperoni will be less hot when the seeds are removed from the center.
Salad
Sowing: for a pack of crops in a greenhouse from late August to March. in other cases, it can be sown all year round
Germination: 5-12 days at a temperature of 5-18 ° C.
Landing scheme: 15 x 25 cm. Harvesting: from October to May. Productivity: 10-15 heads / m2.
The plant is thought to be native to India, but wild lettuce forms are also found in Europe. By the way, they are often used to strengthen the immunity of grown plants against viral diseases. It is unlikely that in any garden you will not find a garden bed with green salad both in the open field and in a greenhouse. However, lettuce forms really large, dense and at the same time tender heads only in spring. As a leafy vegetable, it is particularly light dependent. Tolerance to cooler temperatures is determined by the variety.
Varieties: although there are hundreds of varieties of lettuce on the market today, most are for outdoor cultivation. For hobbyist gardeners with greenhouses, the number of disease-resistant varieties is quite small.
Care: lettuce requires humus-rich, loose garden soil, seasoned with compost, moderately fertilized (50 g / m2 organic or 20-30 g mineral full fertilizers before replanting seedlings to the beds). Plants are planted on the beds at intervals of 25 x 25 cm. It is very profitable to sow lettuce at the end of August in order to harvest for Christmas, it is less profitable, but you can sow lettuce at a later date.
In spring and autumn, you can grow as much lettuce as you want.
In the winter months, the lack of light is unlikely to contribute to normal plant growth, lettuce stretches. Advice: temperature determines success. Germination decreases sharply if the temperature is above 18 ° C. For sowing, the ideal temperature will be 15 ° C. Already 2-3 days after the emergence of seedlings, the temperature must be lowered to 12-15 ° C during the day and 10-12 ° C at night and on cloudy days. At this temperature, plants will grow stocky and sturdy. If you heat the greenhouse too much in winter, you will end up with loose heads of cabbage and weak plants.
Harmful insects and diseases: with all their hearts they love snail and aphid salad. Only the red-brown leafy lettuce mysteriously protects its jagged leaves from these molluscs. You can buy varieties that are resistant against fake powdery mildew and viral diseases.
Gray rot affects lettuce when conditions are not favorable.
Advice: in order to avoid mistakes when watering, it is customary to plant seedlings "high", that is, just drop a lump of earth into loose soil. With good watering, the plants will anchor well in the ground. At the same time, the root collar will not be at risk of injury, and ventilation will also improve.
Curly Lettuce: These hybrids from oak leaf lettuce produce very lush foliage but a very loose head. Because they grow well, they are often sown outdoors. From January to March, they are propagated by seeds and harvested in greenhouses, and they develop like a head lettuce.
Chicken salad: This particularly fast growing lettuce only produces leaves. It is popular as a lettuce that can be quickly grown in beds that are vacant for short periods. From this type of salad, a crop is obtained, like from spinach, after 4-8 weeks. The lettuce is simply sown, then spread in rows at 20 cm intervals in greenhouses where the temperature does not drop below freezing.
The burst lettuce (pictured on the left) yields for many months.
Greenhouse-friendly salads
Ice salad: it needs a little more space (30 x 25 cm), it grows 2-3 weeks longer, crispier and more delicate in taste. It is no different from green salads. Lettuce: Has a variety of delicious leaves, but they do not curl up into the head. More and more varieties of this group appear. Burst lettuce: A type of lettuce that has its lower leaves plucked as needed. New leaves are constantly growing from the middle of the head, so the harvesting period lasts several months. This culture does not need a lot of heat, it is enough for it to be free from frost.
Summer in most of the territory of our country is short and changeable. Heat often gives way to cold even in mid-July. And cucumbers do not like to freeze, they start to get sick, and reduce productivity. During prolonged cold snaps, life in plants freezes and can die out completely. Therefore, for a long time, gardeners have tried to grow these vegetables under cover. Nowadays, it has become much easier to grow stable yields of cucumbers, planting and maintenance does not require large expenses. It is enough to build a greenhouse made of polycarbonate or other materials on the site.
Advantages and disadvantages of growing cucumbers in a greenhouse
Long ago in Russia, overseas vegetables were grown for the tsar's table: cucumbers, melons, watermelons. For this, already in the 17th century, they used warm or steam beds, hotbeds. Peter I welcomed the emergence of new technologies in horticulture in Russia. Under him, the first glazed greenhouses appeared, in which southern fruits were grown. Glass greenhouses are expensive and not available to everyone. But the appearance in the second half of the twentieth century of cheap polymer materials contributed to the development of new methods of growing thermophilic crops under temporary shelters or in small unheated greenhouses.
Currently, almost every summer cottage has small greenhouses. They differ only in materials for the frame and coating. Frames are metal or wooden. And the coating is film or polycarbonate. Such greenhouses make it possible to cultivate cucumbers and other vegetables in all regions of our country. Growing cucumbers indoors has advantages and disadvantages.
pros
- A guaranteed harvest in any weather, especially in the central and northern regions. Frost protection.
- Earlier harvest.
- Prolonged fruiting period.
- The ability to get several crops in one season in the southern regions.
- Minimum material costs, which are paid off by abundant fruiting.

A polycarbonate greenhouse allows you to get the first harvest of cucumbers 2-3 weeks earlier than from the garden
Negative aspects of greenhouse cultivation of cucumbers
- The need to invest in the construction of a greenhouse.
- The rapid spread of fungal diseases in an enclosed space, the need for preventive measures to prevent diseases.
- In case of disease outbreaks, the obligatory use of expensive and unsafe for health preparations for disinfecting greenhouses.
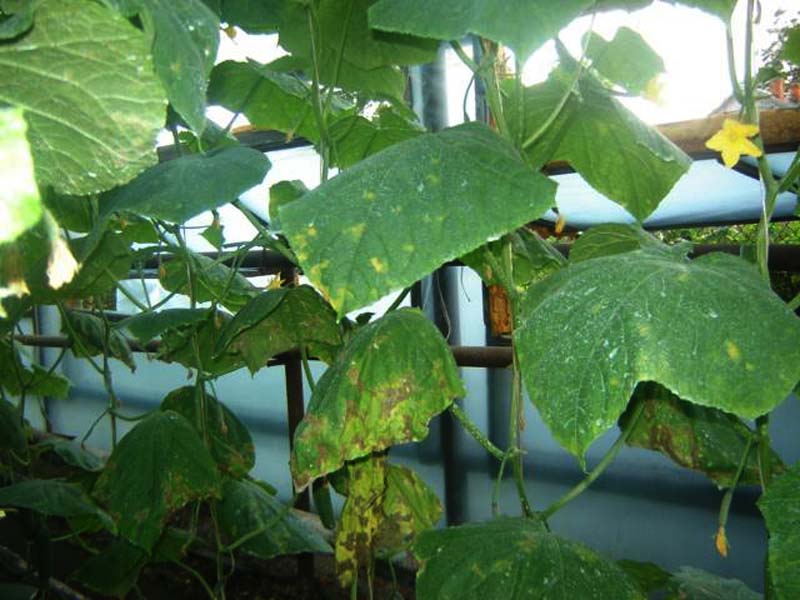

Cucumber diseases spread much faster in a greenhouse than outdoors.
In order for a greenhouse to justify the funds invested in its construction, it must meet certain requirements:
- Ventilate to reduce excessively high temperature and humidity, but no drafts.
- Have sufficient height to grow cucumber lashes vertically.
- In the greenhouse, it is required to provide for the possibility of regular watering of the plants. It is best to equip a drip irrigation system.
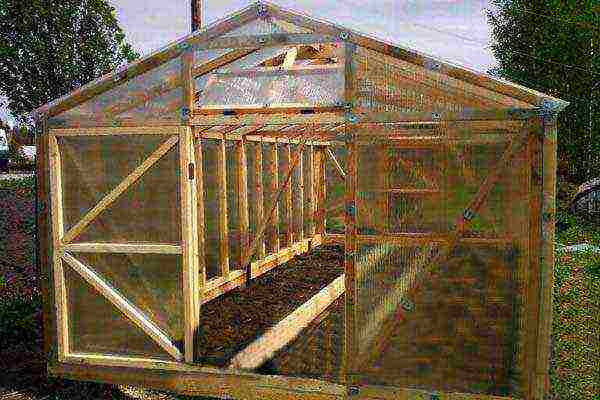

A vent for ventilation of a cucumber greenhouse is equipped at the very ridge of the roof so that the plants do not fall under the draft
Greenhouse preparation
Before planting cucumber seedlings or sowing seeds in a greenhouse, it must be prepared. To do this, carry out a certain list of works that contribute to the health and proper development of plants in it. Greenhouse preparation begins with preventive maintenance and gardening.
Preventive maintenance in spring
First of all, they check the integrity of the frame and cover of the greenhouse. If the snow has not melted yet, clean the roof surface from snow. The soil around the building is 1.5–2 m free of snowdrifts and covered with a black film for faster warming up.
Examine the surface of the coating. The film is changed annually. For polycarbonate, the places to be replaced are determined. These can be various deformations, darkened parts. Remove damaged fragments and replace with new ones.
In a wooden greenhouse, the condition of the frame is checked, rotten parts are replaced, and the loosened ones are strengthened. The metal base of the greenhouse is inspected, revealing rusted or bent places, leveled, cleaned, replaced if necessary.
The inner surface of the greenhouse is disinfected by washing with a dark pink solution of potassium permanganate. The soil in the beds is also disinfected by pouring a boiling solution of a slightly pink solution of potassium permanganate. With a strong infection with diseases and pests last season, you can use special sulfur bombs to disinfect the greenhouse, but such treatments are harmful for metal structures.
Video: preparing the greenhouse for planting cucumbers in spring
Arrangement of beds
If the greenhouse is new, the method of growing cucumbers in it and the type of beds are determined. They can be very different:
- Low, level with the soil.
- High (warm), with sides 40-60 cm high.
- Racks for containers with soil.
You can grow cucumbers in different ways:
- On vertical supports: cords, ropes.
- On a vertical grid.
- In pots, bags or other containers.
To make a warm flat bed in the greenhouse, they dig a trench 20–25 cm deep, fill it with organic debris, cleanings, chopped branches, weeds, foliage, etc. Lightly sprinkle with earth and watered with hot water to cause heating. Then they completely fall asleep with the removed earth and cover with a dark film. If the bed is in a box, the organic matter should occupy 2/3 of the depth, and the layer of fertile soil should be at least 15–20 cm. In two weeks, you can plant it.
Photo gallery: arrangement of beds in a greenhouse and methods of growing cucumbers
The soil in the beds, especially if only cucumbers are constantly grown in the greenhouse, must be renewed. To do this, it is not necessary to take out the old soil and replace it with a new one. It is enough to add 1-2 buckets of humus for each running meter of the bed, water the bed with the addition of any EM preparations (Baikal-EM1, etc.) and cover it with a dark film for warming up. This should be done no later than two weeks before planting seedlings in the ground.
How to grow cucumbers in a polycarbonate greenhouse: planting and care
When determining the timing of planting cucumbers in the greenhouse, many factors have to be taken into account.The determining factor is the climate in the region where the site is located. But the material of the greenhouse covering is also important. If it is covered with polycarbonate or two layers of film, cucumbers can be sown directly into greenhouse beds without growing seedlings indoors.
In the middle lane, it is possible to do this on April 15-25, pre-warming the soil to 14-16оС. You can warm the soil by watering the garden bed with hot water before sowing.
At the same time, you can plant cucumber seedlings grown indoors, which were sown at the end of March. The timing of sowing and planting of plants is determined in each case individually, based on specific day and night temperatures and the possibility of additional heating of the greenhouse in case of sudden cold snaps.
For normal development and health of plants, the temperature in the greenhouse should be from 16 ° C and above during the day, and not below 14 ° C at night.
In single-layer film greenhouses, cucumber seedlings are planted or cucumber seeds are sown 1-2 weeks later, in early May. Additional shelters are arranged over the greenhouse beds to protect against recurrent frosts and prolonged cold snaps.

Installation of additional shelter above the greenhouse beds, makes it possible to plant cucumbers earlier in the greenhouse
Placing plants in the beds
The health and productivity of plants in a greenhouse directly depends on the degree of plant thickening. The denser the plants are planted, the greater the likelihood of diseases of fungal diseases and root rot.
On a greenhouse bed, which is usually 60–70 cm wide, cucumbers are arranged in one row at a distance of at least 40–50 cm from each other. Decrease in distance leads to loss of crops, disease and plant death.
Video: how to plant cucumbers
Care and watering rules
Cucumbers, whether they grow outdoors or in a greenhouse, love water. Their root system is superficial, and the topsoil dries quickly. Cucumbers need frequent watering, at least once every two days, and in hot weather, twice a day. But not all vegetable growers have the opportunity to live permanently near their site. There are many different ways to solve the problem of watering cucumbers in a greenhouse.
It must be remembered that cucumbers need to be watered with great care. Sprinkling in greenhouses is contraindicated for them. When watering at the root, there is a high likelihood of damage to fragile roots. Therefore, the stream of water is directed, stepping back from the plant by 10-15 cm. Water for watering cucumbers must be warm, not lower than 22-25 ° C.
Irrigation in grooves
Along the row with cucumbers, stepping back 10-15 cm from the plants, draw a groove 5-7 cm deep and direct water from a hose along these furrows. Some vegetable growers use instead of furrows in greenhouses with flat beds, row spacing, flooding them with water. This technique is useful in extreme heat, since water evaporates from a large surface and cools the air.
Drip irrigation in greenhouses
Vegetable growers have come up with many methods of drip irrigation of plants. This method allows you to maintain the required soil moisture for a long time. Such systems first appeared in the 60s of the last century in hot Israel, where water is scarce and very expensive. The method allowed to save up to 50% of water. Savvy growers quickly picked up this idea and came up with their own original methods based on it.
Watering with a perforated hose. In the greenhouse, a barrel is installed on a hill, which is filled with water. A hose with holes is fixed in it, which fits into the irrigation furrows. Water is gradually poured out of the barrel by gravity through the hose. The pressure is regulated by the installation height of the water tank.
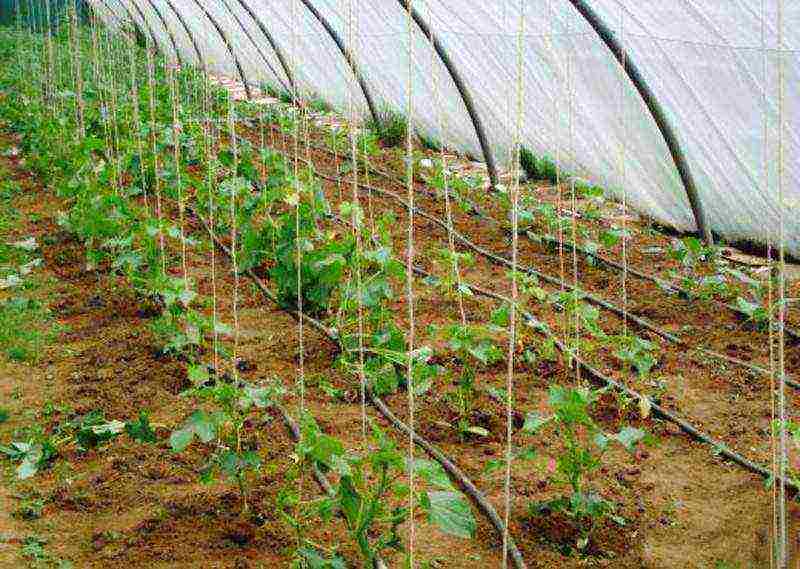

Using industrial drip irrigation systems with adjustable drippers. Such a system allows you to regulate the amount of liquid supplied to the roots and most fully satisfy the plants' need for water.
Using plastic bottles. For those who come to the dacha once a week, it is convenient to use for watering in this way: they take 1.5-liter plastic water bottles in an amount corresponding to the number of plants. In the walls of each bottle, 2–3 cm from the bottom, a thick needle is pierced with rows of holes at a distance of 2 cm from each other to the very neck. Bottles are dug in at a distance of 10-15 cm from the plants, the caps are unscrewed and filled with warm water. Water seeping through the punctures in the walls of the bottles goes directly to the roots of the plants.
When watering cucumbers with bottles, moisture goes directly to the roots
Irrigation by means of industrial drip irrigation units with adjustable drippers. Such a system allows you to regulate the amount of liquid supplied to the roots and most fully satisfy the plants' need for water.

Drippers installed on the irrigation pipes allow you to regulate the amount of water entering the plant roots
What and when to feed
Growing cucumbers at their summer cottage allows you to get environmentally friendly vegetables without the use of chemical fertilizers. For plant nutrition, you can use improvised means: bird droppings, manure, infusion of fermented grass, oven ash, etc. You should not be especially zealous with dressing, since cucumbers can increase the green mass to the detriment of the harvest.
Top dressing for cucumbers in the greenhouse - table
With obvious signs of fattening cucumbers, and these are too large and fleshy leaves, rapid growth, the plants should be watered with infusion of ash. To do this, pour 1 glass of ash with 1 liter of boiling water and leave for 2-3 days, add another 9 liters of water and water the plants. 1 liter of infusion is poured under 1 bush.
Cucumber bush formation
In greenhouses, parthenocarpic cucumber hybrids grow best, which do not require pollination. To obtain a generous harvest and long-term fruiting, cucumber bushes must be properly shaped. Since female flowers with ovaries in hybrids are located on the central shoot, the plants form into one stem. Up to the fourth sheet, all stepsons and ovaries are removed from the lash. This method is called "blinding". Then, up to the eighth leaf, the stepsons pinch, leaving only one ovary with a leaf. In the next four leaves, two ovaries and two leaves are left on the stepchildren, etc. When the lash grows to the top of the greenhouse, the top is thrown over the crossbar and allowed to grow freely downward until there is a distance of 1 m to the soil.Then the top is pinched.
The formation of cucumber bushes is a creative business. Nothing terrible will happen if the stepsons and ovaries are removed not up to 4, but up to 5 leaves, etc. The main thing is not to thicken the plants so that they have enough food and light. Some vegetable growers do not remove their stepchildren and do not pinch the lashes, growing cucumbers on mesh trellises, and each new shoot is attached to the cells, distributing it evenly. And they also get high yields.
Video: how to properly form a cucumber bush in a greenhouse
Problems and solutions
Cucumbers in a greenhouse can get sick, be attacked by insects, for some unknown reason, their leaves may turn yellow and the ovaries may fall off. Each of these problems needs to be addressed.
If the leaves and ovaries of a cucumber turn yellow
The leaves and ovaries of cucumbers can turn yellow for various reasons. But the most likely ones are:
- Plants do not have enough light, especially the lower parts of the plants that are in the shade. The yellowed leaves must be carefully cut off, making room for light.
- Too much watering and the roots suffocate without oxygen.
- Insufficient watering of plants.
- Lack or excess of fertilizer.
- The temperature in the greenhouse is below 14 ° C for a long time.
- Cold water is used for irrigation.
Video: prevention of yellowing of leaves on cucumbers
Diseases of cucumbers in the greenhouse
More than 2–3 plants should not grow on one square meter of a garden bed in a greenhouse.Otherwise, fungal diseases can develop on cucumbers, which spread very quickly in dense thickets, and it is difficult to fight them. Cucumbers get sick from drafts, so the airing of the greenhouse must be done very carefully. The most common diseases in greenhouses are:
- bacteriosis;
- anthracnose;
- root rot.
Diseases should be prevented by carrying out preventive spraying of plants with Fitosporin, which is harmless to humans, but copes well with causative agents of fungal diseases, once every 14 days.
At the first signs of the disease, it is necessary to remove and burn the damaged leaves, and spray the bushes, frame and greenhouse covering from the inside with a pink solution of potassium permanganate. Ventilate the greenhouse well, remove thickening leaves and shoots.
Photo gallery: what are the diseases of cucumbers in the greenhouse
Pests
The most dangerous insects:
- Spider mite, a small insect that settles on the back of a leaf. Sucks juices out of it. It can affect cucumbers in a greenhouse only with poorly organized watering. Loves heat and dry air. At high humidity, which cucumbers love, it rarely settles. But if, nevertheless, infection has occurred, treatment with drugs that are not toxic to humans with a short decay time will help: Fitoverm, Akarin (Agrovertin), Bitoxibacillin, etc. Treatments must be carried out at intervals of 10-14 days.
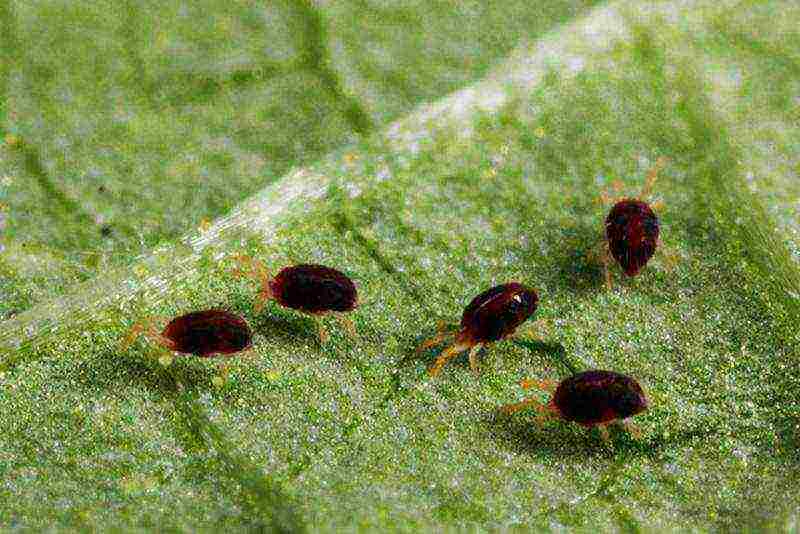

Spider mite weakens the plant and carries viral diseases
- The cucumber gnat is brought into the greenhouse with manure, but more often with sowing onions, in the scales of which it hibernates. The damage is significant. With a strong population, it can ruin the crop. The larvae settle at the base of the stem and roots, gnawing spiral tunnels in them. The fight against it comes down to preventive measures: disinfecting the soil in the beds by watering with a boiling pink solution of potassium permanganate. If the infection does happen, watering the beds with a solution of ammonia (1 ml per 5 liters of water) will help.
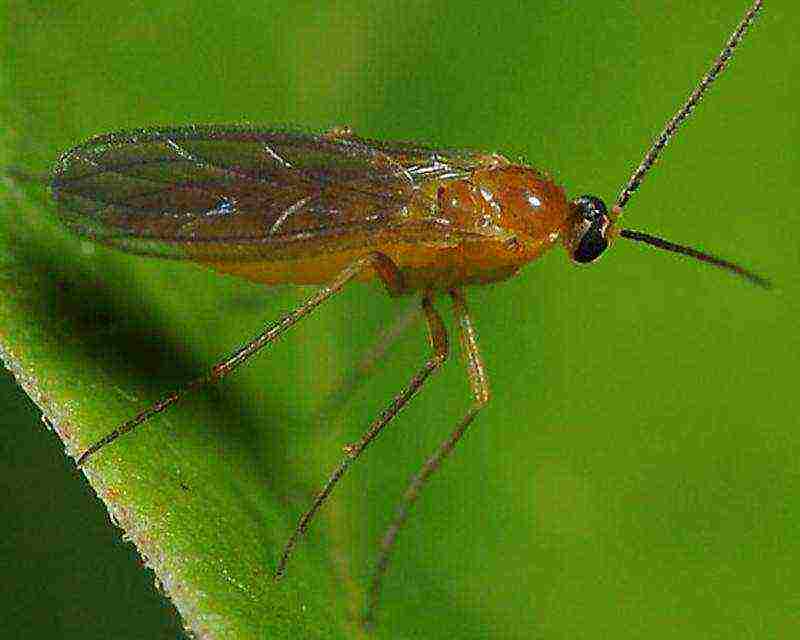

Cucumber gnat larvae settle at the base of the stem and roots of cucumbers, causing their death
- Aphids not only suck the juices from the colonized plant, but also spread viral diseases. Infection most often occurs with the help of ants, which feed on the sweet liquid secreted by aphids. Spraying the leaves with a solution of Bitoxibacillin and Fitoverm preparations helps well. You can spray the foliage with a solution of ammonia (1 ml per 5 liters of water).
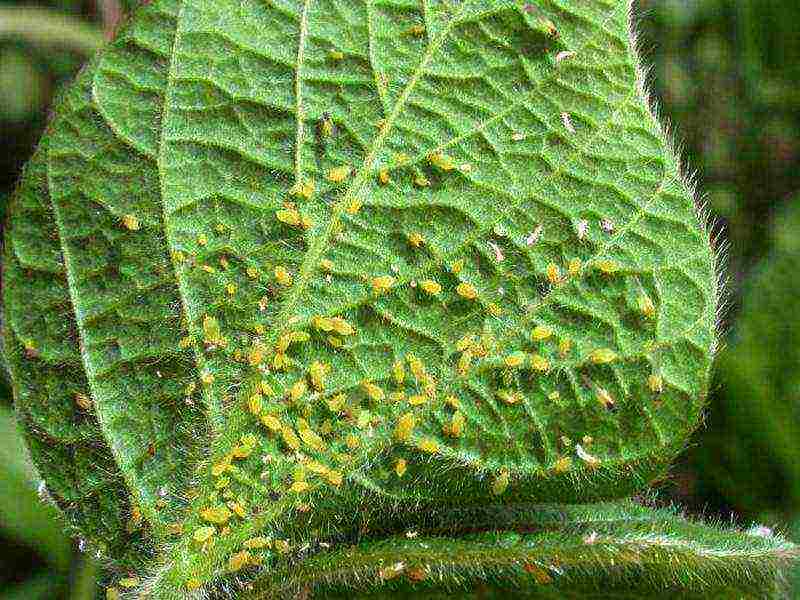

Settling on young leaves and shoots, aphids suck out juices and weaken the plant
How to treat plants from diseases and pests
There are many different drugs for diseases and pests. But it will be most correct to keep the plants so that they are strong, healthy and resistant to infections and insects. Preventive treatments will be useful for plants:
- To ten liters of water add 1 liter of whey and 50 drops of iodine. With this solution, you can water the plants at the root and spray the leaves. An important condition: the temperature of the solution must be at least 30–35 degrees. Protects against any root rot and fungal diseases.
- In one liter of water, dissolve two tablets of Ekoberin and Healthy Garden. To this solution add 2-4 drops of herbal preparations Epin-extra, Zircon and Cytovite. Cucumbers are sprayed with this solution once every two weeks. The immunity of plants is increased. If Fitoverm is added to this solution, the plants will be protected from the attack of harmful insects.
Features of planting and growing cucumbers in different regions
Each region of our country has its own rules for growing cucumbers in greenhouses, dictated by the climatic features of the area. The timing of planting and sowing of plants, the duration of fruiting, the frequency of watering, etc. are different. The differences are also due to the number of sunny days, the average air temperature, and the duration of the summer season.If in the Kuban cucumbers can be sown in a greenhouse already in March, in the Urals this is done only at the beginning of June.
In the Moscow region, summer begins late, not earlier than mid-June, and ends in mid-August, when night temperatures become critical for cucumbers. Warm beds and additional shelters above them at the beginning of the season help to extend the period of fruiting. Growing seedlings indoors contributes to an early harvest.
Many vegetable growers in the Moscow region plant cucumbers in several stages:
- At the end of March, the earliest varieties are sown indoors for seedlings. After 25-30 days, the plants are planted in a greenhouse under additional shelter.
- In mid-May, cucumbers are sown in the greenhouse with seeds, choosing medium-ripening hybrids.
- In early June, the last batch of seeds is sown, late ripening.
These techniques help to extend the fruiting of cucumbers in the greenhouse for the entire season.
Thanks to inexpensive small greenhouses, even in cold regions, summer residents grow tasty and healthy vegetables. Cucumbers are eaten in summer, harvested for the winter. The cost of building a greenhouse pays off in a few years. Therefore, more and more various greenhouses appear in summer cottages, delighting their owners with generous harvests.
All her life she worked as the head of the library. I am fond of gardening, horticulture, I love the computer and the Internet, I have experience in creating sites manually in HTML, occasionally I blog. Rate the article:
(1 vote, average: 1 out of 5)


