Content
- 1 The best varieties of tomatoes for greenhouses made of polycarbonate
- 2 Instructions for growing tomatoes in a polycarbonate greenhouse
- 2.1 Stage one. Greenhouse preparation
- 2.2 Stage two. Soil preparation
- 2.3 Stage three. Seed preparation
- 2.4 Stage four. Growing seedlings
- 2.5 Stage five. Sapling picking
- 2.6 Stage six. Transplanting shoots to the greenhouse
- 2.7 Stage seven. Greenhouse tomato care
- 2.8 Video - Tomatoes: growing in a polycarbonate greenhouse
- 3 General rules for growing
- 4 Main steps
- 5 How to choose and prepare tomato seeds correctly?
- 6 How to prepare a greenhouse?
- 7 Soil preparation
- 8 How to grow seedlings?
- 9 Seedling picking
- 10 Transplanting shoots to the greenhouse
- 11 Follow-up care
- 12 Potential pests and diseases
- 13 Soil preparation
- 14 Photo
- 15 General landing rules
- 16 Greenhouse landing
- 17 Which greenhouse to choose?
- 18 Finally
- 19 Useful video
Many gardeners know about the method of growing tomatoes in a greenhouse, as it allows you to get fresh fruits almost all year round. However, along with many advantages, this process has a number of subtleties and nuances that depend on the type of greenhouse and climate characteristics. Below we will look at the basic rules and conditions that allow you to grow a good harvest of tomatoes in a polycarbonate greenhouse.
How to grow tomatoes in a polycarbonate greenhouse
The best varieties of tomatoes for polycarbonate greenhouses
The best option for polycarbonate greenhouses is the so-called indeterminate varieties, that is, those that are prone to unlimited growth.
The best varieties
The fact is that tomatoes with limited growth must be planted in the ground in the first half of May (otherwise they simply will not have time to give a full harvest), and at this time there is a high probability of a strong drop in temperature and frost. Another feature of indeterminate varieties is that they begin to bear fruit early, so the tomatoes have time to ripen before the end of summer. In addition, hybrids (Alexia F1, Ivanhoe F1, De Barao, etc.) are well suited for growing in polycarbonate greenhouses, since they are more resistant to diseases.
Indeterminate Tomatoes
Determinant and indeterminate tomatoes
|
De Barao red |
Tall bushes with oval-shaped fruits, not very large (weight 60-70 g), red. | The variety is not susceptible to late blight disease, the fruits reach ripeness about 120 days after germination. From one bush, you can get about 4 kg of fruits that tolerate transportation and storage well. |
|
Alexia F1 |
Fruits are round, slightly flattened, bright red in color with dense pulp, weight - 180-210 g. | It is characterized by resistance to most diseases characteristic of the culture, suitable for year-round cultivation. |
|
Ivanhoe F1 |
Forms tall, powerful bushes with shiny bright red fruits (average weight - 200 g), which have a sweetish taste. | A high-yielding variety of medium ripeness that is resistant to diseases and sunburn. Fruits of universal application, with good transportability and keeping quality. |
|
Pink Lady F1 |
Plants are tall, vigorous with large (230-280 g) pink fruits. The pulp has a satisfactory density and good taste. | The variety is distinguished by its high productivity, disease resistance, and is especially recommended for growing indoors. |
|
Demiros F1 |
Powerful bushes with large rounded pink fruits weighing 200-220 g. | New hybrid variety with early ripening (102-105 days). The fruits retain their commercial qualities for a long time and tolerate transportation well. |
You can also opt for the tomatoes Kashtanka, Eskimo, Almaz Yakutia, Stone Flower - these are early-maturing varieties that, with proper care, can give an excellent harvest.
Tomato Stone Flower
Instructions for growing tomatoes in a polycarbonate greenhouse
The main difficulties of the process are that in polycarbonate greenhouses there is often high humidity, temperature drops occur, and overheating of plants during the day is possible. This leads to too rapid growth of tomatoes, which can cause them to get sick and be attacked by pests, therefore, when growing a crop, it is very important to strictly follow the step-by-step instructions.
Tomatoes in a greenhouse - photo
Stage one. Greenhouse preparation
Preparation for growing tomatoes should begin a few weeks before planting plants (around the beginning of March), although in the case of polycarbonate greenhouses, large-scale events will have to be carried out. It is enough to check the ventilation and wipe the walls with a wet cloth.
Greenhouse preparation
Greenhouse preparation. Spring cleaning
The structure should be located in an open, illuminated place, as even the slightest shading can lead to a decrease in yield. It is important that there are hatches for ventilation on the end sides and on the roof of the structure - tomatoes will need a lot of fresh air, especially during the flowering period.
Polycarbonate greenhouse
Stage two. Soil preparation
High-quality soil containing the necessary substances and trace elements is one of the main conditions for the normal growth and fruiting of tomatoes.
The soil in the greenhouse requires preparation
Soil preparation is carried out in such a way that everything is ready about a week before the transplanting of shoots, and is performed as follows.
| Step 1 | Remove the top layer of soil about 10 cm thick, as it often contains bacteria, fungal spores and insect eggs. |
| Step 2 | Dilute a tablespoon of copper sulfate in 10 liters of water and spill the soil well for disinfection. |
| Step 3 | Add the necessary components to the soil, depending on its composition and type: · For loam or clay soils - peat, compost and sawdust (bucket per square meter); · For peat plots - sawdust, compost, sod land per bucket per square meter, coarse sand - 0.5 buckets; · Black soil - a bucket of compost and sand per square meter. |
| Step 4 | Apply mineral fertilizers - for one square meter, take a teaspoon of saltpeter and 3 tablespoons of superphosphate. |
| Step 5 | Dig up the earth well and form beds. Recommended dimensions: width - 90 cm, height - no more than 40 cm, and the intervals between the beds - no less than 60 cm. |
Soil for tomato seedlings
Stage three. Seed preparation
The seed should be selected of high quality, without damage or signs of disease. It is necessary to prepare and plant seeds in late February and early March, since the soil in polycarbonate greenhouses warms up quickly enough, so that the transplant can be started earlier than in the case of film structures.
|
Step 1 |
Place the seeds, wrapped in a cloth, in a solution of potassium permanganate (1 g per glass of water) for 20 minutes, then rinse well. |
|
Step 2 |
Prepare a nutrient solution from a teaspoon of nitrophosphate and a liter of water, put seeds in it, put in a warm place and stand for 12 hours. |
|
Step 3 |
After that, the seed, without washing, put in a container with plain water and place on the middle shelf of the refrigerator for 48 hours. During this time, it is important to monitor the constant moisture content of the seeds. |
Immediately after preparation, you need to move on to the next stage - planting seeds to obtain seedlings.
Stage four. Growing seedlings
It is convenient to grow tomatoes in individual containers
Seedlings in pots
To grow tomato seedlings, you will need low (5-7 cm) containers and soil mixture. You can use a special commercial mixture, but experienced gardeners are advised to take the land directly from the greenhouse, so that after transplanting, it will be easier for young plants to adapt. For correct sowing of the seed, the following sequence of actions should be performed.
| Step 1 | Pour the soil into a container, moisten and tamp a little. |
Earth boxes |
| Step 2 | Make grooves in the soil no more than 1.5 cm deep at a distance of 7 cm from each other. |
In the photo there is a box with soil and grooves
Sown seeds |
| Step 3 | Place the containers in a warm, well-lit place. The optimum temperature is 20-25 ⁰С. |
Seedlings of tomatoes |
In the first 20 days, shoots grow very slowly, after which growth increases and reaches a peak by the fortieth day. During this period, seedlings need properly organized care, otherwise they will stretch out and become weak.
- During the first month after the emergence of seedlings, they need to be watered three times under the root: the first - immediately after they appear above the soil surface, then - with an interval of two weeks. The water temperature is not lower than 20⁰С.
- The appropriate temperature regime is very important: in the daytime - 18-20⁰С, and at night - 15-16⁰С.
- In order for the shoots to grow evenly and simultaneously, they need to be turned daily so that the previously shaded side is under the rays of the sun.
Growing tomato seedlings at home
Seedlings on the windowsill
Stage five. Sapling picking
It is recommended to pick the seedlings twice so that the shoots do not stretch out, but at the same time gain strength. The first procedure is performed after 2-3 leaves appear on the sprouts, and the second - after 25 days.
Tomato seedlings before and after picking
Step 1
Fill containers no more than 8x8 cm in size with soil (you need to take the same mixture that was used for growing seedlings) and spill it with a warm solution of potassium permanganate (dissolve 0.5 g in 10 liters of water).
Step 2
Carefully remove the seedlings from the container using a small spatula. At each of them, pinch the long tip of the main root.
How to pick tomato seedlings
Step 3
Shoots should be planted to a depth of no more than 6 cm, paying special attention to the location of the root system: if it bends, the hole needs to be deepened a little.
Dive tomatoes one at a time into individual pots
Tomato seedlings: dive
Step 4
Water the transplanted plants with warm, settled water.
Step 5
The second pick is carried out 25 days later in pots 4-7 cm larger in the same way as described above.
Caring for plants at this stage is as follows.
- The first three days after the procedure, the daytime temperature should not fall below 20-22⁰С, the nighttime temperature - 16-18⁰С. After that, it can be reduced by 2-3 degrees.
- Watering is carried out about once a week so that the shoots do not stretch out and rot.
How to water tomatoes
- Top dressing is carried out according to the following scheme. The first - with a solution of nitrophoska (a tablespoon per bucket of water) two weeks after the first pick, pour about half a glass into each container. The second - 14 days after the second transplant: a tablespoon of superphosphate and potassium sulfate is taken into a bucket of water, a glass of solution is poured into each container.
Top dressing of seedlings
- In May, in the room where the seedlings are located, you need to constantly open the window to harden the shoots.
Note: some gardeners dive plants only once, and there are those who do without a dive at all, planting shoots immediately in a greenhouse. It is better to make the choice based on your own experience, climate characteristics and a particular variety.
Lighting for tomato seedlings
It is recommended to transplant plants into greenhouse conditions at the age of 50 days, and the shoots should be 25-30 cm in height, have 8-12 strong leaves and 1-2 inflorescences.
Stage six.Transplanting shoots to the greenhouse
Seedlings before planting in the ground
Transplanting tomato seedlings into a polycarbonate greenhouse can be carried out in the second half of May or early June, but it is recommended to first measure the temperature of the soil at a depth of twenty centimeters - it should be at least 13⁰С. The optimal arrangement of the bushes is chosen depending on the variety - they can be planted in a checkerboard pattern, in one or two rows. Plants that have one stem are recommended to be planted with an interval of 25 cm, and tall (more than 1.5 m) bushes - with an interval of 60 cm.
Seedlings with a clod of earth
The soil around the stem is compacted
On the beds, you need to dig holes about 25 cm deep, pour into each of them a liter of a weak solution of potassium permanganate (1 g per bucket of water). From plants, pinch off 3-4 lower leaves, place them in the holes and cover them with earth, without deepening them too much into the ground. After 10-12 days, after the bushes take root well, the earth can be filled up no higher than the level of the lower leaves.
Planted seedlings
Stage seven. Greenhouse tomato care
- The optimum temperature inside the greenhouse is 20-22⁰С, and during flowering it is two degrees higher.
- It is recommended to water the bushes for the first time only two weeks after transplanting to the greenhouse, after which watering is carried out about once a week with settled water under the root, not too abundantly.
Watering
- The soil should be loosened regularly, and the room should be well ventilated, since tomatoes do not tolerate moisture stagnation, and I can simply rot.
- You can tie up and form the bushes two weeks after transplanting them into the greenhouse. The formation of plants is carried out in the morning, and it is recommended to leave 7-8 brushes with flowers on the bushes, and remove the side shoots. In the future, this procedure should be carried out regularly, otherwise the yield of foliage will be greater than the yield of fruits.
Formation of tomato bushes
Garter
- It is necessary to feed tomatoes growing in a polycarbonate greenhouse 3-4 times (the first - about 20 days after transplanting) with nitrophosphate, organic fertilizers and superphosphate in turn.
- Despite the fact that tomatoes are considered a self-pollinating crop, artificial pollination significantly increases the yield of plants. To do this, on sunny days, you need to gently shake the flowers or transfer pollen with a brush, then water the plants, and after two hours ventilate the greenhouse.
Subject to all the rules and proper care of the plants, growing tomatoes in a polycarbonate greenhouse quickly pays for all the efforts spent, and gives a rich harvest of fruits with excellent taste.
Greenhouse tomato care
Video - Tomatoes: growing in a polycarbonate greenhouse
Growing tomatoes in a polycarbonate greenhouse is a very popular activity not only for large agricultural companies, but also for individuals living in the CIS countries. Today we will talk in detail about how to plant tomatoes in polycarbonate greenhouses, what is needed for this, and why it is needed at all.
General rules for growing

Before delving into the topic of growing tomatoes in greenhouse conditions in detail, you should take a look at the general rules, which are indicated in the following paragraphs:
- The foundation of the greenhouse must be strong enough to withstand the heavy wind and the weight of the snow.
- Seedlings are grown in separate greenhouses or at home.
- The design of the greenhouse must necessarily allow the vertical garter of tomatoes.
- You should have plenty of free time, as it will take regular chipping of excess buds as well as unnecessary foliage on your tomato bushes.
- Take care of the sources of organic fertilizers in advance, which will require a fairly large amount.
- If you plan to have more than 10 long tomato beds in your greenhouse, it is more convenient to place drip irrigation in it.
- There must be enough free space in the greenhouse for maneuvering with buckets of water (a lot of water will be required)
Main steps
The process of growing tomatoes in greenhouse conditions consists of the following main stages:
- Greenhouse preparation;
- Selecting the right seeds;
- Greenhouse soil preparation;
- Growing seedlings;
- Planting seedlings;
- Post-seedling care and harvesting.
How to choose and prepare tomato seeds correctly?

There are special varieties of tomato that are focused on growing in greenhouse conditions.
Such varieties have a combination of the following qualities:
- High productivity.
- High or low ripening rate.
- Gastronomic quality.
- Resistance to diseases and adverse environmental factors.
- Dimensions of the fruits themselves.
- Suitability of the variety for long-term storage, without loss of taste and aesthetic qualities.
Depending on which of the above qualities appeals to you, choose the appropriate tomato variety.
So, if high yields are important to you, seeds of the following varieties are suitable for growing:
- De Barao;
- Banana Legs;
- "Auria";
- "Honey Drop";
- "Pink Raisins".
If a fast ripening rate is important to you, pay attention to the seeds of the following varieties:
- Typhoon, Druzhok, Ilyich, Poisk, Verlioka, Semko-98. These varieties are early maturing;
- Hurricane, Samara. These varieties are early maturing;
- "Junior", "Amber", "Joy of Summer", "Bear in the North". These varieties are super early maturing.
If the most pronounced taste is important to you, pay attention to the seeds of the following varieties:
- Cherry. The variety has a high taste both fresh and excellent for drying and preservation.
- "Caspar-F1". The variety fits perfectly into diet salads, and is great for pickling or pickling.
- "Friend", "Sultan", "Rosemary". The varieties have a juicy and tender flesh, a thin skin and a slightly sweet taste, which makes them an excellent option for fresh consumption.
- "Malachite Box". One of the most delicious varieties of green tomatoes.
- "Bull's Heart", "Truffle". One of the most delicious varieties of red tomatoes.
- "Yellow Long", "Honey King". One of the most delicious varieties of yellow tomatoes.
- Marisol Violet, Black Cherry. One of the most delicious varieties of black tomatoes.
- "Dimensionless", "Pink Flamingo". One of the most delicious varieties of pink tomatoes.
If you are looking for disease-resistant and weather-resistant tomatoes, take a look at the following varieties:
- "Verlioka", "Olya", "Ural" and varieties "De Barao", "Admiralteisky". Varieties that tolerate a lack of sunlight well.
- Barberry F1, Lyubanya, Orange Giant, Banana Legs, Pink Raisins, Orange Icicle, Carrot, Zinulya, Siberian Giant. High temperature and drought tolerant varieties.
- "Roma", "Erema", "Eupator", "Intuition", "Blagovest". And varieties: "Budenovka", "Chio-chio-san". The varieties are the most resistant to fungal invasions.
If you are looking for varieties with the largest fruits possible, the following seeds are suitable for growing:
- Siberian Giant;
- The Pink Giant;
- De Barao.
If you want the smallest fruits possible, the following seeds are good for you:
- "Cherry";
- "Grape";
- "Balcony Miracle";
- "Sweet Tooth".
The most mature tomatoes for growing include the following varieties:
- F1 Salahaddin;
- F1 Ivanovets;
- Volgogradets;
- "F1 Krasnobay".
Having decided on the variety, you should prepare the seeds for further planting, for which follow the following points:
- Remove any overly small and damaged seeds, leaving only large and intact seeds.
- A month and a half before planting the seeds, wrap them in a dry cloth, and warm them up by putting them on a battery or a warm place, the temperature of which reaches 40-50 degrees, for a period of 3-4 days.
- Before planting, disinfect the seeds by placing them in a 1% solution of potassium permanganate for 20 minutes.
- Before planting, soak the seeds for a day in one of the solutions of Virtan-Micro, Epin, Immunocytophyte.
How to prepare a greenhouse?

If you want to grow tomatoes in a greenhouse environment, you will need to properly prepare your greenhouse.
The preparation of the greenhouse should take place according to the following scheme:
- Inspect the greenhouse for damage, especially if the polycarbonate cover has survived the winter.
- Prepare the places for the beds in advance.
- Stretch the wire along the entire length of the greenhouse, at a height of about 2 meters. The wire should run at the same level as the center of each bed.
- Disinfect the greenhouse with hydrated lime. Take 3 kg of slaked lime, mix it with 10 liters of water, and add 500 grams of copper sulfate there. Process the frame of the greenhouse and its inner walls with the resulting liquid.
- Tomatoes require frequent ventilation, which means you should check or install vents in the greenhouse, preferably on the ceiling.
- Check the operation of the irrigation system (if any), as well as the heating systems (if you plan to grow tomatoes in winter).
Soil preparation

To grow tomatoes, you need to prepare the soil. Soil preparation can be carried out in different ways, a complete list of which would require writing a separate book.
For this reason, we will describe the most optimal way to prepare tomato soil in a greenhouse, which consists of the following points:
- In the greenhouse, remove 40 centimeters of old soil over the entire tomato growing area.
- At the very bottom, you should put a 3-5 centimeter layer of old branches, as thick as a raspberry shoot.
- The second layer is made of sawdust, the layer of which should reach 5 cm. If possible, a thin layer of weeds can be put on top of the sawdust, but not the tops of garden plants.
- If tomatoes are planned to be grown in winter, the third layer should consist of manure, 10 cm thick. If tomatoes are planned to be grown only in autumn or spring, the manure is replaced by a layer of peat of the same thickness.
- After the manipulations done, we fill it all up with the previously acquired soil.
The soil itself for the greenhouse is prepared based on the following ingredients:
- garden land;
- vegetable humus a year ago;
- compost regardless of type and age;
- sod land;
- sand;
- peat.
Sod and garden land in the total mass should occupy 60% of the soil for a tomato. Compost, sand, peat and humus should account for 10% for each component.
The soil prepared in this way should be laid in the greenhouse in late summer or early autumn, after which it should be infused at least until spring. Immediately after laying the soil, treat it with a phytosporin solution, abundantly watering its surface with this solution from a watering can. This is necessary to control the destruction of possible fungal spores.
We recommend buying ready-made soil for growing greenhouse tomatoes from garden stores, as this will save you a lot of time and effort.
How to grow seedlings?
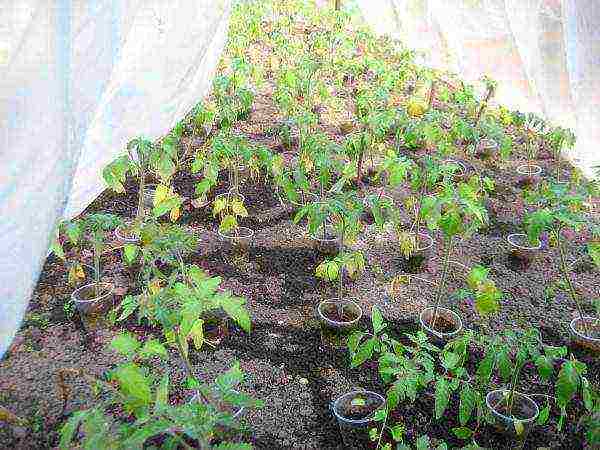

If you want healthy tomatoes, you need to learn how to properly grow and care for your seedlings.
To do this, you should initially prepare a container for future seedlings, which should be one of the following types:
- Wooden boxes with a side height of 7 cm, the bottom of which must be shipped with foil.
- Plastic containers 28 cm wide and 32 cm long.
- For the subsequent picking of seedlings, you will need liter plastic bottles, from which you should cut off the neck, or get plastic cups, the depth of which should be at least 15 cm.
Having decided on the container, we proceed to the direct planting of future seedlings, relying on the following points:
- Take the prepared container and pour a 5 cm layer of soil into it.
- Tamp the sprinkled soil evenly.
- Take a ruler and make some kind of grooves, the depth of which should be half a centimeter.The grooves should be marked along the entire length of the container area, with a distance of 3 cm from each other.
- Prepared tomato seeds are placed in each of the grooves, at a distance of 3 cm from each other.
- After planting the seeds, the grooves are carefully covered with a 1 cm layer of soil, lightly tamped, and moistened with a sprayer.
- The container is closed with a plastic bag, and placed in a warm place until the first shoots appear. The temperature of the place where the seeds will germinate should not fall below 25 degrees. Otherwise, the seeds will germinate much longer. Monitor the moisture level under the film, and spray the soil in a timely manner, without letting it dry out.
After the first shoots appear, move on to the next growing steps, such as:
- Remove the film and place the container on a windowsill, the temperature on which should not drop below 20 degrees during the day, and 14 degrees at night.
- Organize the seedlings with additional lighting, for which fluorescent lamps or special phytolamps for seedlings with a pink glow are ideal. It is advisable to keep the backlight on for at least 16 hours a day.
- Spray the seedlings in a timely manner to keep the soil moist. It should be sprayed, not watered.
- Feed the seedlings every 10 days using chicken manure or cow dung. Chicken manure is bred at the rate of 100 grams per 10 liters of water, and cow dung at the rate of 300 grams per 10 liters of water. For one container of the size indicated above, no more than 500 ml of this kind of fertilizer should be spent.
- If you feel the need, in the intervals between feeding, you can water the seedlings with fresh water, the temperature of which should not be lower than 20 degrees.
After completing all the above points, grow the seedlings until they are picked.
Seedling picking
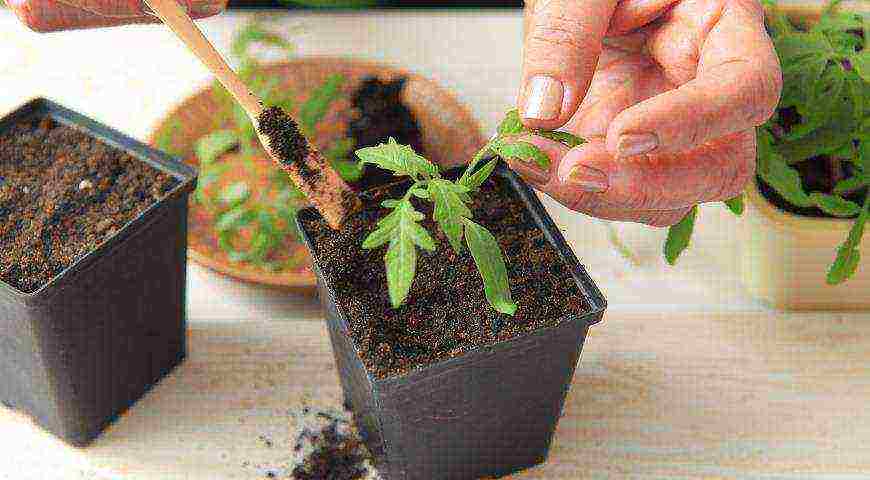

The picking of plants must be carried out so that in the future they can be easily transplanted into the garden without the risk of injuring the root system. Moreover, without a pick, the root system of the seedlings can get confused with each other, and then their transplant can be fatal for them.
The picking of seedlings after cultivation should be carried out in accordance with the following points:
- The pick is carried out about a month after the first shoots appear.
- A pick is carried out only when the seedlings have 6 leaves.
- Before picking, the seedlings are watered abundantly.
- In cups or plastic bottles, soil should be poured to the brim, and tamped.
- After tamping the soil, take a stick and press a hole in the soil with it, 2-3 cm deep.
- Drop a pinch of superphosphate at the bottom of the hole.
- Take a fork, and gently pry the seedling bush under its root system, and then remove it from the container. The first two leaves of the sprout must be plucked.
- Shake off excess soil from the root system of the sprout, and plant it in a glass or bottle.
- Fill in the hole, tamp lightly and pour 30 milliliters of sodium humate solution on the sprout.
- Hold the transplanted shoots over additional lighting for about a week;
- Water the seedlings as the soil dries.
Transplanting shoots to the greenhouse
The final stage in growing seedlings is transplanting them into a greenhouse.
The transplant is carried out on the basis of the following points:
- Seedlings are transplanted into the greenhouse for about 45-50 days of growth.
- Bushes are placed at a distance of 50 cm from each other.
- A meter-long peg is driven in near each bush, tying the bush to it, and to the previously stretched wire, which was discussed at the very beginning of the article.
- The holes in which the bushes will be planted should have a depth of 2-3 cm exceeding the length of the root system of the seedlings.
- Humus is added to the bottom of the hole, the layer of which should not exceed 1 cm.
- Before transplanting, the formation of a bush consists in removing almost all of its leaves, with the exception of a few of the topmost ones.
- After the bush is in the hole, fill it up, tamp it lightly and water it abundantly.
- Mulch the soil with sawdust or manure. The thickness of the mulch should be about 10 cm.
- If you wish, you can water the planted seedlings with mineral fertilizers, but in general, this is not necessary.
Follow-up care
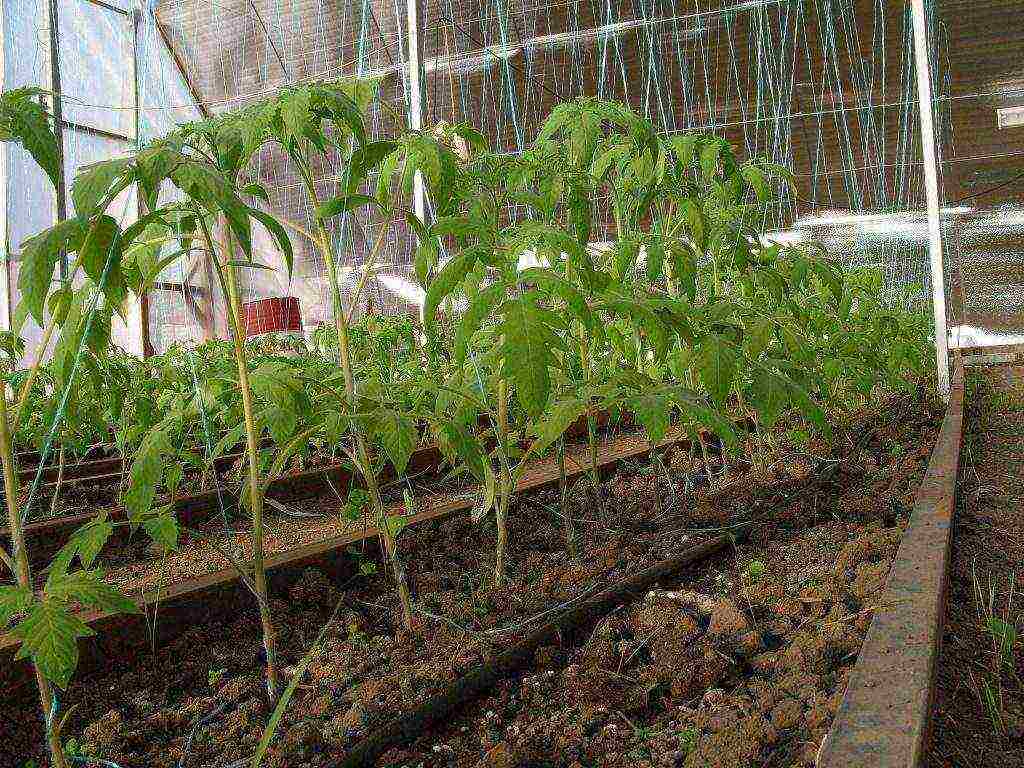

Subsequent care of grown tomatoes is carried out as follows:
- Water the seedlings on the 12th day after planting (except for the first watering immediately after planting in the ground, so that the earth settles).
- Before flowering, one bush consumes about 4 liters of water, and during flowering, about 12 liters.
- Watering is carried out every 5-6 days.
- Spraying is optional.
- The temperature in the greenhouse should not exceed 25 degrees, and not fall below 16. During the flowering period, the temperature can be raised to 27 degrees.
- Plant feeding is carried out from the moment the first ovary appears. Feeding is carried out with superphosphate, potassium sulfate, wood ash, or liquid mullein;
- Light mode should be at least 12 hours.
- Cut off the leaves touching the ground on the bushes, and also get rid of the stepchildren.
Potential pests and diseases
After growing your tomatoes may be susceptible to the following diseases:
- Top rot. Treat with a solution of copper oxychloride, at the rate of 30 grams per 10 liters of water.
- Gray rot. Treat the plant with "Barrier" and "Barrier". Substances are sold in different concentrations, which means they need to be diluted based on the instructions on the package.
- White spot. Treat the plant with 1% Bordeaux mixture or 0.5% copper oxychloride.
- Streak. Treat the plant with 1% manganese solution.
As for parasites, they can be completely avoided with proper maintenance and care of the greenhouse. We will discuss more detailed information on treatment, signs and possible diseases in another article.
 Tomatoes are a demanding culture and it takes a lot of effort to provide them with decent conditions. Every gardener knows that the key to a large and healthy harvest is proper tomato care in your polycarbonate greenhouse. Following the recommendations will help everyone to achieve their cherished goal. We also recommend that you watch the video at the end of this article "How to prevent tomato diseases in the greenhouse"
Tomatoes are a demanding culture and it takes a lot of effort to provide them with decent conditions. Every gardener knows that the key to a large and healthy harvest is proper tomato care in your polycarbonate greenhouse. Following the recommendations will help everyone to achieve their cherished goal. We also recommend that you watch the video at the end of this article "How to prevent tomato diseases in the greenhouse"
Caring for tomatoes is primarily about creating conditions suitable for growth, flowering and fruiting. The greenhouse climate is suitable not only for tomatoes, but also for viruses, pathogenic bacteria and parasites.

Tall tomatoes in a greenhouse
Some tips for proper tomato care
To grow tomatoes in a polycarbonate greenhouse, every step is important. From germinating seeds to harvesting. In order to choose the right care, use the advice of experienced gardeners.
Healthy seeds
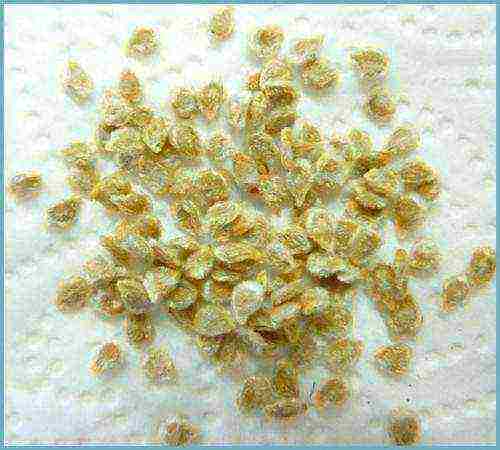

First of all, your future harvest depends on the quality of the seeds.
Use healthy seeds for growing. If you do not know the history of the seeds obtained, process them. Subsequently, this will simplify the care of the seedlings and prevent a lot of diseases. Processing can be carried out in several stages:
- warming up the seeds;
- chemical treatment;
- soaking in water;
- hardening of seeds.
To obtain disinfected and high-quality seeds, they must be warmed up at a temperature of 50-60 ° C for at least 3 hours.
Important! Do not raise the temperature, fried seeds will never sprout.
Next, the seed must be treated with manganese (1 g per 250 ml of water). Soak in clean water and harden in a refrigerator for 1-2 days at a temperature of 2 ° C.
Seedling
Do not feed seedlings before transplanting to a polycarbonate greenhouse. Caring for young tomatoes consists in maintaining the temperature and airing. Watering is carried out 4-5 times during the entire growth period.

Seedling tomato
Only transfer mature seedlings to the greenhouse. You can plant tomatoes that have reached 20-30 cm, in the presence of 9-10 full sheets.
Greenhouse conditions
Adhere to the temperature regime: during the day 25-28 ° С, and at night not lower than 15 ° С. Soil temperature is also important. It should not fall below 17-18 ° C. Humidity of air and soil in the greenhouse is not higher than 65%. Timely airing is also important. In good weather, the opening of the greenhouse is allowed: this will get rid of dampness and prevent a lot of diseases.

Violation of the microclimate of the greenhouse causes disease and death of plants
Perform root watering of tomatoes. So there will be no high humidity in the greenhouse. It is best to use a drip irrigation system.
Bush formation
A timely garter will make it easier to care for tomatoes in the greenhouse. Tied tomatoes are better ventilated and less prone to diseases such as white or gray rot.

Grasshopping tomato bush
Carry out the formation of a tomato bush, do not let them grow. With correct pinching, the yield of the crop increases. Remove all unnecessary stepsons, preventing them from developing. This will prevent them from pulling important nutrients from the plant.
Diseases of tomatoes and how to deal with them
It is impossible to grow tomatoes without making a single mistake in the care. In a polycarbonate greenhouse, tomatoes get sick no less often than in any other. There are many bacteria that infect tomatoes, they cause a variety of diseases. Some of them are incurable, while others can still be fought.
Stem necrosis
A disease caused by a virus. It appears on a developed plant during the formation of the first fruit clusters. Tomato stems are affected. Erosion of tissue is observed on the infected bush. The plant slowly dies: it does not receive nutrients in the proper volume, leaf lethargy is observed, the fruits do not have time to ripen. It is difficult to fight such a disease. Most often, infected tomatoes are pulled up and destroyed by burning. After them, the earth is treated with a solution of Fitolavin-300 (0.2%).
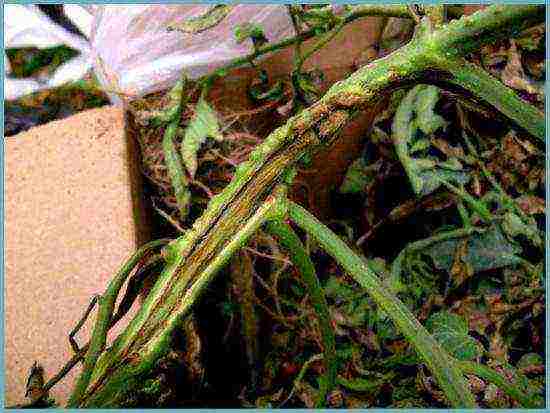

Tomato stem necrosis
Late blight
The most common disease of all nightshades. Fungal disease. It develops with high humidity and poor ventilation of the greenhouse. It can also be caused by sudden changes in air temperature. It is manifested by blackening of the leaves, and then the fruit. Disease can be prevented by spraying tomatoes with milk whey, it does not allow the development of the fungus.
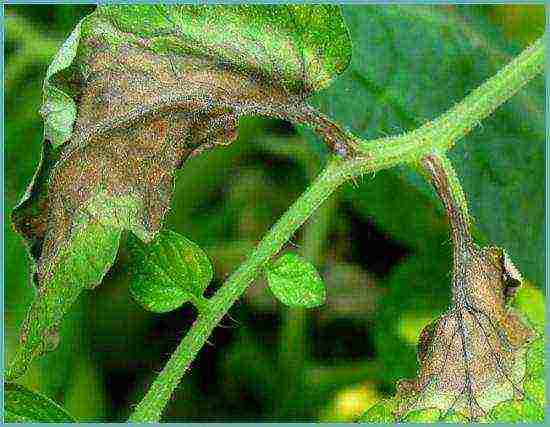

Fungal disease late blight
Attention! To prevent an increase in humidity in a polycarbonate greenhouse, use drip irrigation of plants.
Top rot
This disease affects only tomato fruits. It occurs when the greenhouse is waterlogged or lacks moisture, it can also develop with an excess of nitrogen. It appears as round brown spots. As the disease progresses, the spots darken and increase in size, the fruits rot, and fluid can be seen in the affected areas.

Top rot on tomato fruits
To combat top rot, it is necessary to regularly and carefully inspect ripening tomatoes for signs of disease. If a fetus has been seen affected by this disease, it must be urgently removed. Disease can be prevented by adding calcium to the soil (crushed eggshell or ash) at the stage of planting seedlings in a polycarbonate greenhouse.
Septoriasis
Also known as tomato leaf blight. Caused by a fungus. It is manifested by the presence of small light spots on the sheet. Leaves are affected first, then stems. With the development of the disease, the leaves dry up and fall off. To fight septoria will help drugs containing copper - Cineb, copper oxychloride. The leaves, when the first symptoms are detected, are removed, and the plant is immediately processed.
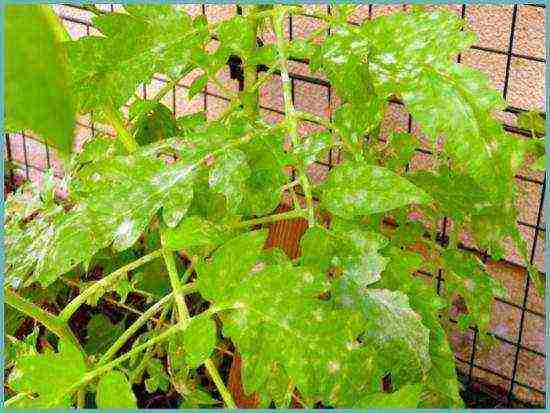

Septoria tomato bushes
Root rot
The disease develops with mechanical damage to the root system of the plant. Most often this happens when planting seedlings in a polycarbonate greenhouse or when loosening the soil. The infected tomato stops receiving nutrients from the root and dies.To avoid this kind of injury, it is necessary to carefully and accurately transplant the plant, apply top dressing on time and huddle the crop to form additional roots.
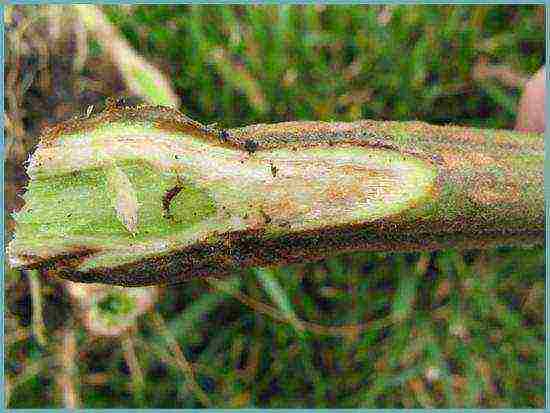

Root rot
Fruit cracking
It is a disease caused not by a virus or infection, but by the physiology of tomatoes. The reason is the abundant watering of the plant after a long drought. The culture does not have time to properly distribute all the moisture received and directs all of it to the ovary. There is a rupture of the skin and cells of the fetus.
Prevention and control measures for the disease:
- timely moderate watering;
- spraying with lime solution.
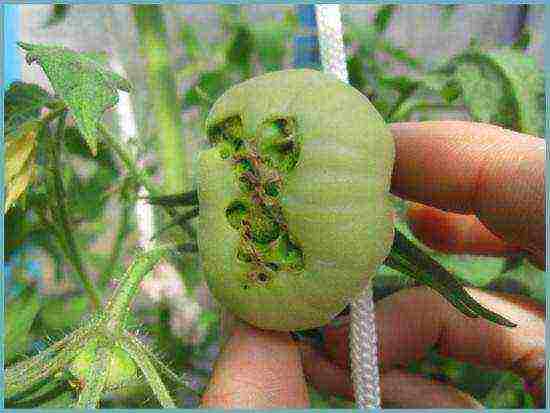

Cracking tomato fruit
Advice. For growing in a greenhouse, it is better to choose hybrid varieties of tomatoes, they are less susceptible to viral diseases. Such crops are bred with increased immunity in order to simplify their care.
How to get an early harvest
You can get an early harvest of tomatoes only in a greenhouse. For this, seeds are germinated earlier than usual, not in February - March, but in January. Typically, the growing season for tomatoes is 120-150 days, depending on the plant variety. But proper care will help speed up the ripening process by 2-3 weeks. Fertility of the soil, compliance with the temperature regime, watering with clean water at room temperature, prevention of diseases - all this accelerates the growth rate of the plant.

Growing tomato seedlings in a greenhouse
The main factor is choosing the right tomato variety. There are many species, the fruiting of which begins already on the 80th day:
- Mandarin is an indeterminate variety of tomatoes, fruits appear on the 90th day;
- Early ripening greenhouse hybrid F1 - determinant variety, fruiting on the 80th day;
- Present F1 - medium-sized tomato variety, bears fruit on the 90th day;
- Meal is a tall variety bred only for greenhouses, fruiting on the 85th day.
Pick the right tomato variety and care for it properly. They will surely thank you with a healthy and abundant harvest.
How to prevent tomato diseases in a greenhouse: video
How to grow tomatoes in a greenhouse: photo



Soil preparation
Greenhouse soil preparation under the tomatoes in the spring is a very important event, because with improperly prepared soil, the plants will not give a good harvest and will constantly hurt. It will be best if you remove the top layer of soil (about 10 cm), and pour copper sulfate on the renewed soil for tomatoes in the greenhouse (1 tablespoon per bucket of water). After that, be sure to ventilate the room.
Then you should dig up last year's beds with humus and close the greenhouse before planting tomatoes. Such processing before planting tomatoes is simply vital.
Important! Fresh manure cannot be used as fertilizer!
Reference. In no case should you plant tomatoes in the same greenhouse for more than 2 years in a row! Most infections remain in the ground anyway, and new plants will become infected.
Important! Crops after which it is impossible to plant a tomato are all nightshade: tomatoes, eggplants, peppers, physalis, and for example, after cucumbers and potatoes, on the contrary, it is necessary.
Reference. Plants such as tomatoes require loamy, neutral or slightly acidic soil that is well ventilated.
Due to poor frost resistance, tomatoes need to be transplanted on the heights... The beds, the height of which should be about 40 cm, must be formed about 1.5 weeks before planting seedlings on them.
Reference. Maximum acceptable age
seedlings
for transplanting - about one and a half months, at the end of this period the seedlings have an optimally mature root system.
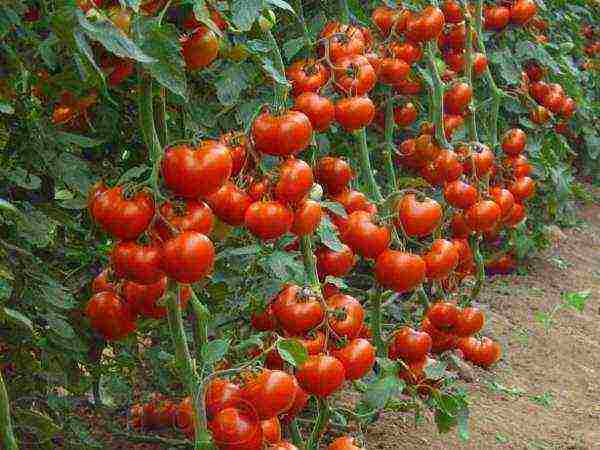
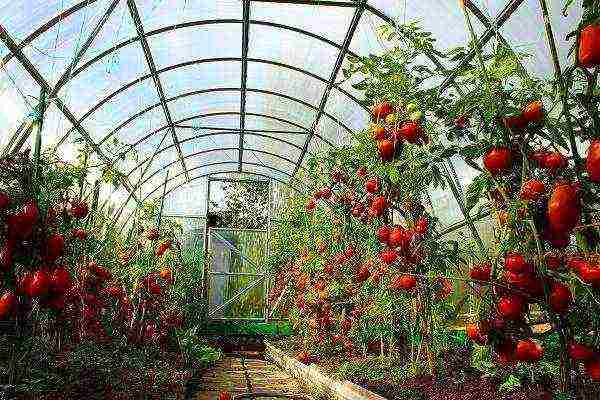
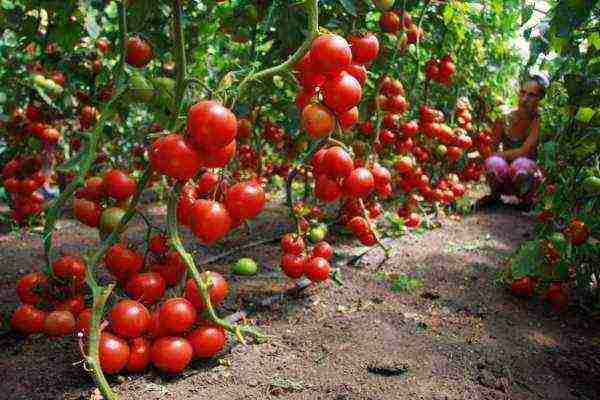
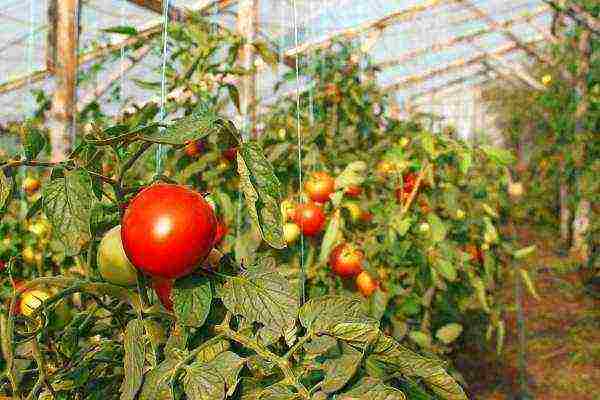
Photo
Below in the photo: planting a tomato in a greenhouse.





General landing rules
So, how to plant tomatoes in a polycarbonate greenhouse correctly? The main thing is to follow a few simple rules.
- choice of the day;
A cloudy day is considered a good day for planting.If the day is sunny, then it is better to plant in the late afternoon to reduce stress from the hot sun. The soil when planting plants should be well warmed up.
- landing depth;
The root should be completely in the ground, but the growth point should not be closed - it is about 15 cm deep, it will be good to put humus or other fertilizer in the grooves.
Remove yellow and cotyledon leaves at ground level before planting. Necessary compact the soil around the plant and sprinkle with soil. To prevent diseases such as late blight, each plant can be sprayed with copper oxychloride (40 g of copper per bucket of water).
- watering.
After the transplant, you need water abundantly tomatoes, under each bush. Further, it is better not to water the plants for a week, since otherwise all development will go to the growth of the stem. In the future, it is worth watering the tomatoes rarely, but abundantly, preferably in the morning hours.
It is very important to choose a specific the order of planting seedlings tomatoes, depending on the varieties. And also decide which tomatoes to plant, when to plant and at what distance.
Tomatoes in a polycarbonate greenhouse: planting scheme
- two-row, which means that the width of the bed should be about 1.5 meters, and the length - as much as you like, taking into account the fact that the distance between the plants should be about 30-60 cm.
- checkerboard - planting bushes in 2 rows, with an interval of about 50 cm, at a distance of 30-40 cm from each other with the formation of 2-3 stems. This scheme is suitable for undersized early maturing varieties.
- staggered order, but for tall species, every 60 cm with a distance of 75 cm between the rows.
In the photo below: tomatoes in a greenhouse planting scheme
Important! You need to plant prepared seedlings in a greenhouse. The preparation takes place by hardening - taking the seedlings out into the street for about 2 hours during the warm time of the day.
Reference. 2-3 days before planting, the seedlings, if they are in separate containers, need to be watered, it will be more convenient to remove them during transplanting. And the seedlings that grow in a common container, on the contrary, stop watering in 2-3 days, and watered abundantly before transplanting.
How to plant tomatoes in a greenhouse: distance
Planting tomato seedlings has its own specific algorithm. In order not to be mistaken in distance between plants, study the packaging from the seeds, planting in the ground will be most accurately described there. In any case, you should not plant more than 30 cm apart and no further than 80 cm.When the distance is too small, the tomatoes will wither from lack of nutrients, and with a large distance there will be a small crop and the fruits will grow and ripen more slowly ...
Greenhouse landing
For a better harvest, you should take into account not only the placement of the tomatoes, but also the correct date for planting the tomatoes. First of all, you need to wait for the most constant warm weather.
- plants can be planted in a heated greenhouse from April 29;
- to an unheated greenhouse, but with a double film layer - from May 5;
- to an unheated and not insulated greenhouse - from May 20;
- in open ground, but with a film coating - from May 25.
The air temperature, on average, when planting in a greenhouse should be about 25 ° C.
Reference. To improve the quality of the yield, the plants should be fed every 20 days with mineral fertilizers, and after transplanting, 10 days later, the first feeding should be carried out (half a liter of liquid mullein, 1 tablespoon of nitrophoska per 10 liters of water), and about a liter of fertilizer should be used for each bush ...
Which greenhouse to choose?
An important factor in improving productivity is the material from which your greenhouse is made.
Now the more popular coating materials are polyethylene film and polycarbonate.
Polycarbonate - the material is not cheap, but durable and does not wear out immediately, unlike film. Although it perfectly protects plants from ultraviolet radiation, it is more suitable for winter heated greenhouses due to its thermal insulation properties, but for summer greenhouses, polycarbonate is not particularly needed and will not pay off.
And the temperature in such structures will be simply unbearable for plants on hot days, and even ventilation holes will not help. You will also have to insulate the soil in the greenhouse for the winter, otherwise it will freeze.
Have film coating there are significant advantages over polycarbonate.
- it is easier to cover the greenhouse with a film, and in case of a breakthrough, it is easy to replace;
- in winter, since the film is removed, you should not think about covering the soil, snowdrifts will do an excellent job with insulation;
- film is a cheap material, albeit quickly deteriorating.
Principled difference between these two materials- number of harvests, in a polycarbonate greenhouse, you can plant tomatoes earlier and several times, and therefore you can harvest more often.
Finally
Growing tomatoes is not an easy task even for experienced gardeners; planting tomatoes in a greenhouse requires a competent approach. However, if you adhere to the basic rules and tips, you can get good results even for a beginner.
Useful video
We hope that we have answered your question on how to properly plant tomatoes in a greenhouse. And in the video below: planting tomatoes in a polycarbonate greenhouse