Content
- 1 Variety selection
- 2 Site preparation
- 3 Growing seedlings
- 4 Landing in the ground
- 5 Outdoor Pepper Care
- 6 Land preparation
- 7 Video "Growing and caring for pepper"
- 8 Top dressing of seedlings
- 9 Top dressing after planting
- 10 Stimulation of fruiting
- 11 Watering features
- 12 Video "Growing pepper in a greenhouse"
- 13 Seed handling technique
- 14 Growing pepper seedlings
- 15 Growing pepper on a windowsill
- 16 Bell pepper, cultivation and care in the open field
- 17 Bell pepper growing in a barrel
- 18 Features of agricultural technology
- 19 The principles of growing on the site
- 20 Potential diseases and pests and their control
- 21 Growing greenhouse peppers
- 22 Collection and storage
- 23 Conditions for growing sweet peppers
- 24 Agrotechnics growing pepper: planting seeds for seedlings
- 25 How to grow a good crop of peppers outdoors
- 26 Planting sweet pepper seedlings in open ground
- 27 Proper care of sweet peppers in the open field: watering and feeding
- 28 Pests and diseases of pepper: photos and control measures
- 29 The best varieties of sweet peppers for open ground: photo and description
- 30 Using sweet peppers
.
How to properly cultivate peppers in the open field and create care? Bell peppers are a southern culture and require warmth and humidity. In the middle lane, peppers are grown in open soil through seedlings and greenhouses. To grow the desired crop crop, you need special care.

Pepper grows well in the open field of the middle lane
Soil preparation
Growing pepper in the open field requires proper preparation of the land.
Outdoor sweet peppers grow better in places with a mild climate and in an area where there is more sun and less wind. To protect from the wind, they make a shield from plants or erect a wattle fence.
To grow peppers in an open area, it is important to understand after which crops it is more effective to grow peppers.
Planting peppers is best done in the place where cabbage, pumpkin, cucumbers, legumes, table roots grew. In places with a previous harvest of tomato, eggplant, potatoes, it is not recommended to plant peppers for three years, since diseases of these vegetables spread through the ground.
The soil allocated for the pepper should be fertile and retain moisture. They begin to prepare the ground in the fall. Harvesting in the fall, you need to carefully collect the remains of the previous crop and dig up the ground. They also fertilize the soil, enriching the following substances (per 1 square meter):
- superphosphate in a volume of 30-50 g;
- wood ash - 50-80 g;
- humus - from 5 to 10 kg.
In places where it was fertilized with fresh manure, sweet peppers cannot be planted, since there is no need for organic fresh feeding. Excessive nitrogen in the soil causes the active growth of the vegetative parts of the pepper, and the ovary is so poorly preserved, which affects the yield.
In the fall, the place where they plan to place the pepper is dug deeply. In the spring, the soil is loosened and fed with fertilizers with phosphorus, potassium and nitrogen. The earth is slightly dug up and leveled before planting seedlings.

Pumpkin is a great precursor for pepper
How to properly plant seedlings?
Only when the frost is over is it recommended to plant peppers. This is in the second half of May. Planting is carried out according to the scheme 60-70 x 20-30 cm.
Before planting, it is important to water the seedlings well so that the pepper does not wilt.Withered pepper does not take root well, its growth is delayed, which leads to the dropping of the first buds. So the early harvest is lost.
If the weather is hot, it is best to plant in the evening. In gloomy weather, morning disembarkation is recommended.
Prepare the holes for planting and water. It is recommended to pour up to two liters of water (at least a liter) into each hole, which should be heated in the sun. The seedlings are planted deeper than they were planted in pots, like seedlings. On the stalk covered with earth, adventitious roots are formed that can feed the plant.

Pepper seedlings are planted in the holes, while ensuring sufficient watering
How to water bell peppers properly?
Sweet pepper seedlings require special care.
In order for the seedling to take root faster, it is necessary to water the root every 2-3 days. For one seedling, 1-2 liters of water are consumed. If the weather is hot, water it every day. Seven days later, the seedlings are checked and where the pepper has died, a new sprout is planted from the reserve. Reduce the amount of watering. This is called "thin" watering. It is important not to harm the plants with abundant watering. How to determine the water requirement of a vegetable? If the plant darkens, this is a sign that water is needed. Prolonged wilting of the plant should not be allowed. If the leaves are withered in the heat, this is not a reason for watering.
When the fruits ripen, watering is done once every 5-6 days. In the heat, watered in the morning or evening hours.

Watering young peppers should be regular
When to loosen the soil?
Sweet peppers grow comfortably in loosened ground. It should not be brought to the appearance of an earthen crust.
What is the use of loosening the soil?
- Air flow to the root is improved.
- The plant grows faster.
- The functioning of microorganisms is stimulated.
By weeding the ground, weeds are being fought.
You should be aware of the slow growth of pepper in the first 10-14 days, because the rhizome is strengthened and the soil does not need to be loosened.
The first loosening of the earth is done after the first "thin" watering. The root system is in the upper ball of the earth, so the loosening will be shallow, at a level of 5-10 cm.
If the soil is heavy, the first time it is allowed to loosen the soil deeper, destroying the soil crust. This way the soil warms up and ventilates better.
Further, loosening is carried out after each rain or watering, when the earth is dry, but there is still no crust.
Hilling is carried out during flowering.

Loosening the soil around the peppers should be done regularly.
Feeding
Pepper care will not bring the desired harvest if not fed.
Seedlings are well fertilized with nettle dressing. To do this, combine nettle with water, in a ratio of 1:10 and insist for two days. The last time the seedlings are fed 2 days before planting, increasing the dosage of fertilizers with potassium (7 g per 1 liter of liquid).
At least three dressings are done per season. The first time during the first plowing (after disembarkation in two weeks). Fertilize with slurry from manure, poultry droppings, mixing with phosphorus-potassium fertilizers or wood ash.
Manure is diluted with water in a ratio of 1: 4, bird droppings are diluted 1:10. It is good to alternate the chicken afterbirth with nitrophos (1 tablespoon per bucket of liquid).
It is effective to add 40-60 g of superphosphate and potassium chloride to a solution of organic fertilizer (manure, droppings) up to 20 g or wood ash in the amount of 150-200 g.
Mineral fertilizers are also used. To do this, add the following substances to 10 liters of water:
- ammonium nitrate - 15-20 g;
- superphosphate - 40-60 g;
- potassium chloride - 15-20 g.
This dressing is used for 8-10 seedlings.
During the formation of fruits, the need for pepper nutrition increases. At this stage, the third feeding is carried out. And the second time they feed at the beginning of fruiting, with an increase in the dose of ammonium nitrate.
If the fruits of the culture ripen small, they are fed for the fourth time.
It is important to know that when caring for peppers, they use fertilizing without chlorine or with a very small percentage.Pepper does not tolerate chlorine. But there is a good substitute for potassium chloride - this is ash from wood.

Superphosphate is one of the main fertilizers for pepper
How to protect peppers from frost?
Having planted pepper, you need to know how to protect the crop from frost and damage. Caring for a crop at the time of frost, forcing ingenuity.
Tents are built from scrap materials (pieces of wood, cardboard, fabric, etc.). They are made in the evening and removed in the morning. But when the cold snap lasts a long time, it is advisable to use a film.
Flowers and ovary fall off often. All due to the unfavorable temperature conditions for the vegetable (low or very high temperature). Growth stops at + 8-10 degrees. But if there is a heat of 30-35 degrees for several days, the buds also fall off.
The consequence of untimely watering is a lack of moisture. Dry soil also reduces crop growth.
Pepper cannot be shaded. In insufficient light, especially during a cold snap, flowers and ovary also fall off.

Bell pepper flowers may fall off due to lack of sunshine
Features of the care of bell pepper
There are some subtleties of caring for peppers, in order to better yield:
- It is imperative to pinch the pepper - removing the side and bottom stepsons. But in hot and dry weather, pinching is not recommended. Leaves protect the soil from evaporation. Professionals suggest, to increase the yield, cut the central flower that has grown from the first branch.
- During the growing season, long shoots are cut off a little so that there is no shading of other branches.
- Remove plant branches below the main branch and internal branches. Pruning is carried out every 10 days.
- Pollinating insects are useful for sweet peppers. They are attracted by spraying the plant, during the flowering period with a solution of sugar (100 g of sugar and 2 g of boric acid are diluted in 1 liter of hot water).
- Applying mulching of peppers with rotted straw (up to 10 cm of a layer), the frequency of watering will decrease.
- When leaving, it is important to tie up the crop immediately after hilling and mulching.

Mulching Pepper Helps Reduce Watering Frequency
Pest control
Pepper is sensitive to diseases, therefore it requires special care.
But most pepper suffers from pests (scoop, whitefly, aphid, Colorado potato beetle, bear, slugs).
So that the plant is not damaged, pollination is carried out with wood ash (three times per season). To fight aphids, you can use a solution of serum with water (0.5 liters of serum per bucket of liquid). And sprinkle the leaves with wood ash on top.
With all the tips in hand, you can grow a great sweet pepper crop.
Subscribe Be aware of new products on our site
Pepper is a rather demanding crop, and you can only get a harvest with proper care. Experienced gardeners achieve excellent results without problems, but beginners often have difficulties in growing pepper. It often happens that strong healthy bushes give 2-3 fruits of not the best quality or the ovaries fall off for no apparent reason. But you really want to collect peppers in buckets, so that it is juicy, large, fragrant! In fact, it is not so difficult to achieve a good harvest, you just need to carefully study several important rules of agricultural technology of this wonderful culture.
Secrets of growing pepper
Variety selection
Bell pepper. Variety selection
When planning to grow peppers in the open field, first of all, you need to choose the right variety. The growing season for pepper is very long, and even in early varieties, the first fruits ripen 100 days after germination. Therefore, in order to have time to get a harvest, you need to pay attention only to early and mid-season varieties. In addition, you should take into account the climatic features of your region.For example, in the south of the country, peppers of different ripening periods are successfully grown, since the conditions there are the most favorable, and in the northern and eastern regions the best results are shown mainly by cold-resistant early maturing varieties.
Bulgarian pepper: variety selection
The shape and size of the fruit is also important. For stuffing and canning, it is worth choosing varieties with cone-shaped small fruits; for fresh consumption, large thick-walled cuboid fruits are more suitable.
Thick-walled sweet pepper
If you are going to grow peppers for sale, take a closer look at Dutch breeding hybrids: they are cold-resistant, ripen early and amicably, less often they are affected by diseases.
It is difficult for a novice gardener to understand the abundance of varieties, so below are the most popular and reliable ones:
- early cold-resistant varieties - Eroshka, Funtik, Yunga, Sorvanets, Cornet, Smile;
- early varieties with high yields - Ivanhoe, Marinkin Yazychok, Bonus, Coupon;
Ivanhoe
- mid-season varieties - Atlant, Bogatyr, Orange King, California miracle;
- productive hybrids - Gemini F1, Claudio F1, Salamander F1;
Claudio F1
- hot pepper varieties - Adjika, Hungarian yellow, Fiery bouquet, Ogonyok, Superchili.
Hot pepper - Hungarian yellow
Site preparation
You should choose and prepare a site for pepper in the fall. Well-prepared soil is a guarantee of normal growth and fruiting of plants for the next year. The ideal place is the beds on the south side of the house or outbuildings, which are in light shade in the afternoon. This arrangement provides protection from both wind and leaf burns in the July heat. Peppers should not be planted where tomatoes, potatoes, eggplants, and other nightshade crops have grown in the previous three years. The best predecessors of pepper are legumes and pumpkin crops, cabbage, melons, green manure.
Preparing a bed for pepper
The soil for the pepper should be neutral or slightly acidic. On beds with acidic soil, plants take root for a long time after transplanting, develop poorly, almost do not bloom and do not bear fruit.
Advice! It is very easy to check the acidity at home: you need to take a little earth and moisten it with ordinary table vinegar. If no reaction follows, the soil is acidic and needs liming, but if bubbles appear on the surface, this indicates neutral acidity.
How to determine the acidity of the soil
Plants-indicators of soil pH
So, if the soil in the selected area is acidic, slaked lime (1 glass per square meter) or wood ash (1.5-3 kg) is added during digging. If the soil is neutral, you need to add rotted organic matter (from 5 to 10 kg per m2) and dig up the beds to a depth of 20-25 cm.
Growing seedlings
Sowing pepper seeds in open ground is impractical, the plants will not have time to start fruiting before the cold weather. That is why both sweet and hot peppers are grown through seedlings. Mid-season and mid-late varieties are sown around early February, early ones - in early March. Please note that overgrown seedlings adapt for a very long time in the open field, especially if already flowering plants are planted.
Step 1. The seeds are immersed in warm water for 5-6 hours to swell. Then they are laid out on a damp cloth, wrapped and left in a warm place for 2-3 days until the sprouts hatch.
Soaking the seeds
Presowing seed treatment
Step 2. Mix 1 part of garden soil, 1 part of sand and 2 parts of rotted organic matter, heated in a microwave or conventional oven for disinfection. Then add a tablespoon of wood ash to 1 kg of the mixture and mix thoroughly.
Step 3. Take peat pots or disposable cups with a capacity of 0.5 liters for sowing and fill them with prepared soil.You can sow seeds in a common container, but as the seedlings grow, it will become cramped, and the pepper does not like picking.
Peat cups with soil
Step 4. The hatched seeds are laid out one by one in each pot, lightly sprinkled with earth, moistened through a spray bottle. Then the containers are covered with glass or foil and placed in a warm place. The temperature must be kept within 22-24 degrees.
Seedling care
Sprouts appear as early as 2-3 days after sowing. At this time, they need to provide at least 12 hours of lighting, so prepare phytolamps in advance. The film is removed from the pots so that the high humidity does not destroy the tender sprouts. Pepper seedlings are watered very sparingly, only when the substrate begins to dry out. Water is used only warm and separated, from cold water the development of seedlings slows down.
If the air in the room is too dry, the seedlings should be sprayed in the morning (also with warm water). When airing the room, be sure to cover the seedlings from drafts, avoid sudden changes in temperature. A week after germination, it is recommended to lower the night temperature to 15 ° C. The grown and matured seedlings should be hardened little by little. On warm days, when the temperature outside the window rises to 13 ° C, the pepper should be exposed to the open air, providing protection from the wind. For the first time, half an hour is enough, then the time spent in the air is increased daily. On cold days, seedlings are not tolerated, since plants can be damaged already at 10 ° C.
Growing pepper seedlings in peat pots
Pepper seedlings in cups
Landing in the ground
Before planting seedlings, the beds are weeded, loosened and leveled. The holes are made at a distance of 30 cm in a row, 60-70 cm are left between the rows. Peppers need to be planted in the evening or in cloudy weather, since the heat of the day is additional stress for the plant. About 5-6 hours before transplanting, the seedlings are watered abundantly so that the root system can more easily adapt to new conditions. Water for irrigation is also prepared in advance: it is collected in buckets or a large container and placed in the sun for heating.
Step 1. 2-3 liters of water are poured into each well and allowed to soak a little.
Step 2. Seedlings are carefully removed from the containers so that the earthen lump does not disintegrate. If peat pots were used, the peppers are planted with them.
The hole for planting pepper should be so deep that when planting, the root collar is at the level of the soil surface
Water and top up the soil abundantly
Step 3. Plants are lowered into the hole a little deeper than they grew in cups, sprinkled with earth on all sides, compacted with hands.
Advice! Peppers are easily pollinated, so if you plan on harvesting seeds, plant different varieties as far apart as possible. Additionally, you can intersperse them with tall crops, for example, corn, sunflower, Jerusalem artichoke and others. Hot and sweet peppers must also be planted at the maximum distance, otherwise all fruits will have a pungent taste.
Outdoor Pepper Care
Bell pepper seedlings a few days after planting
Watering and feeding
2 days after planting, the pepper is watered and the ground is sprinkled with fine straw, dry grass or sawdust. In the future, you need to water the plants once a week until the ovaries form, after which the watering is increased - 1 time per 5 days. In order not to water so often, you can increase the mulch layer to 10 cm.
Mulch the plantings with peat
The plantings are fed three times:
- for the first time, fertilizer is applied 10 days after planting. For this, bird droppings are used, diluted in a ratio of 1:10, with the addition of 200 g of ash and 40 g of superphosphate per 10 l of solution. The specified volume is enough for about 10 bushes;
- the second time the pepper is fed at the beginning of fruiting with a mullein solution in a ratio of 1: 5 or diluted bird droppings (1:10);
- the third time fertilization is applied during the mass formation of fruits, when the plants are most in need of replenishment of nutrients.
Sweet Pepper Care
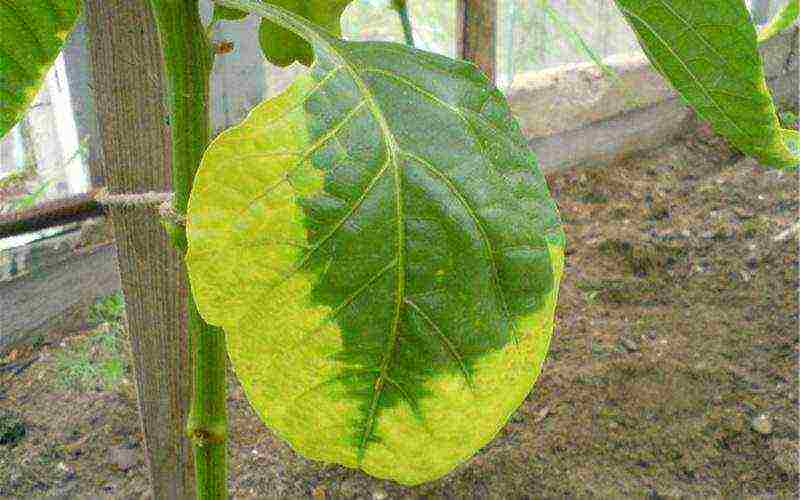
By the appearance of the pepper, it is easy to determine which substances it lacks. If the leaves dry out along the edge and then curl, this indicates a lack of potassium. Lack of nitrogen is expressed by the dullness of the leaves, the presence of a grayish tint. In addition, the leaves become small. But with an excess of nitrogen, ovaries and flowers begin to fall off. The deep purple color of the back of the leaves indicates a lack of phosphorus, a marble pattern occurs when there is a lack of magnesium. The use of mineral fertilizers helps to replenish all this, but do not forget to accurately observe the dosage, otherwise all the surplus will end up in the fruits.
If the autumn is warm, with the help of another top dressing, you can prolong the fruiting of early varieties. To do this, 50 g of superphosphate, 15 g of ammonium nitrate and potassium chloride are diluted in 10 liters of water.
Loosening
Loosen the ground around the peppers with a hoe to prevent weeds from growing
The soil between the rows must be regularly loosened to a depth of 10 cm. The formation of a soil crust slows down the development of pepper, causes oxygen starvation of the root system. It is best to loosen in the morning after watering while the ground is still moist enough. If mulch was not used, loosening is carried out under the bushes themselves, but very carefully, since the roots are located very close to the surface. During the period of budding and flowering, it is advisable to spud each plant to a height of 10-12 cm.
Bush formation
To get large ripe fruits, excess shoots (stepchildren) should be removed from the plant. All shoots located below the first branch are removed completely, since they only draw out the juices from the plant and interfere with fruiting. In addition, the crown should be thinned so that each branch receives enough air and light. Too dense bushes form few ovaries, small and thin-walled fruits grow on them.
Pepper picking
Sweet pepper bush formation
On average, pruning is carried out every two weeks, but if the summer is rainy, stepchildren will have to be removed more often - about once every 10 days. It is advisable to combine pruning with loosening the soil in order to disturb the plant less.
The shoots of the pepper are quite fragile, and any careless movement can damage the stems. To avoid this, it is recommended to tie tall varieties to supports.
Pepper garter
Diseases and pests
This culture is susceptible to late blight, white and apical rot, tobacco mosaic and some other diseases. The best way to deal with them is through prevention and proper care. Compliance with the planting scheme, timely thinning and pruning, proper watering, removal of diseased plants from the garden will help you keep plantings healthy and get a full harvest.
Dusting the bushes with wood ash is effective against pests. This should be done at least 5 times per season, preferably in the morning, while the leaves are wet. For spider mites and aphids, spraying pepper with garlic infusion also helps. Slugs that do not mind eating fresh leaves are collected using traps or scared away with salt, lime, mustard, pepper powder, scattered between the rows.
Video - Pepper: growing and care in the open field
Video - Planting pepper seedlings
Video - Formation of a pepper bush
.
How to properly cultivate peppers in the open field and create care? Bell peppers are a southern culture and require warmth and humidity. In the middle lane, peppers are grown in open soil through seedlings and greenhouses. To grow the desired crop crop, you need special care.

Pepper grows well in the open field of the middle lane
Soil preparation
Growing pepper in the open field requires competent preparation of the land.
Outdoor sweet peppers grow better in places with a mild climate and in an area where there is more sun and less wind. To protect from the wind, they make a shield from plants or erect a wattle fence.
To grow peppers in an open area, it is important to understand after which crops it is more effective to grow peppers.
Planting peppers is best done in the place where cabbage, pumpkin, cucumbers, legumes, table roots grew. In places with a previous harvest of tomato, eggplant, potatoes, planting peppers for three years is not recommended, since diseases of these vegetables spread through the ground.
The soil allocated for the pepper should be fertile and retain moisture. They begin to prepare the ground in the fall. Harvesting in the fall, you need to carefully collect the remains of the previous crop and dig up the ground. They also fertilize the soil, enriching the following substances (per 1 square meter):
- superphosphate in a volume of 30-50 g;
- wood ash - 50-80 g;
- humus - from 5 to 10 kg.
In places where fresh manure was fertilized, sweet peppers cannot be planted, since there is no need for organic fresh feeding. Excessive nitrogen in the soil causes the active growth of the vegetative parts of the pepper, and the ovary is so poorly preserved, which affects the yield.
In the fall, the place where they plan to place the pepper is dug deeply. In the spring, the soil is loosened and fed with fertilizers with phosphorus, potassium and nitrogen. The earth is slightly dug up and leveled before planting seedlings.

Pumpkin is a great precursor for pepper
How to properly plant seedlings?
Only when the frost is over is it recommended to plant peppers. This is in the second half of May. Planting is carried out according to the scheme 60-70 x 20-30 cm.
Before planting, it is important to water the seedlings well so that the pepper does not wilt. The withered pepper does not take root well, its growth is delayed, which leads to the dropping of the first buds. So the early harvest is lost.
If the weather is hot, it is best to plant in the evening. In gloomy weather, morning disembarkation is recommended.
Prepare the holes for planting and water. It is recommended to pour up to two liters of water (at least a liter) into each hole, which should be heated in the sun. The seedlings are planted deeper than they were planted in pots, like seedlings. On the stalk covered with earth, adventitious roots are formed that can feed the plant.

Pepper seedlings are planted in the holes, while ensuring sufficient watering
How to water bell peppers properly?
Sweet pepper seedlings require special care.
In order for the seedling to take root faster, it is necessary to water the root every 2-3 days. For one seedling, 1-2 liters of water are consumed. If the weather is hot, water it every day. Seven days later, the seedlings are checked and where the pepper has died, a new sprout is planted from the reserve. Reduce the amount of watering. This is called "thin" watering. It is important not to harm the plants with abundant watering. How to determine the water requirement of a vegetable? If the plant darkens, this is a sign that water is needed. Prolonged wilting of the plant should not be allowed. If the leaves are withered in the heat, this is not a reason for watering.
When the fruits ripen, watering is done once every 5-6 days. In the heat, watered in the morning or evening hours.

Watering young peppers should be regular
When to loosen the soil?
Sweet peppers grow comfortably in loosened ground. It should not be brought to the appearance of an earthen crust.
What is the use of loosening the soil?
- Air flow to the root is improved.
- The plant grows faster.
- The functioning of microorganisms is stimulated.
By weeding the ground, weeds are being fought.
You should be aware of the slow growth of pepper in the first 10-14 days, because the rhizome is strengthened and the soil does not need to be loosened.
The first loosening of the earth is done after the first "thin" watering. The root system is in the upper ball of the earth, so the loosening will be shallow, at a level of 5-10 cm.
If the ground is heavy, the first time it is allowed to loosen the soil deeper, destroying the soil crust.This way the soil warms up and ventilates better.
Further, loosening is carried out after each rain or watering, when the earth is dry, but there is still no crust.
Hilling is carried out during flowering.

Loosening the soil around the peppers should be done regularly.
Feeding
Pepper care will not bring the desired harvest if not fed.
Seedlings are well fertilized with nettle dressing. To do this, combine nettle with water, in a ratio of 1:10 and insist for two days. The last time the seedlings are fed 2 days before planting, increasing the dosage of fertilizers with potassium (7 g per 1 liter of liquid).
At least three dressings are done per season. The first time during the first plowing (after disembarkation in two weeks). Fertilize with slurry from manure, poultry droppings, mixing with phosphorus-potassium fertilizers or wood ash.
Manure is diluted with water in a ratio of 1: 4, bird droppings are diluted 1:10. It is good to alternate the chicken afterbirth with nitrophos (1 tablespoon per bucket of liquid).
It is effective to add 40-60 g of superphosphate and potassium chloride to a solution of organic fertilizer (manure, droppings) up to 20 g or wood ash in the amount of 150-200 g.
Mineral fertilizers are also used. To do this, add the following substances to 10 liters of water:
- ammonium nitrate - 15-20 g;
- superphosphate - 40-60 g;
- potassium chloride - 15-20 g.
This dressing is used for 8-10 seedlings.
During the formation of fruits, the need for pepper nutrition increases. At this stage, the third feeding is carried out. And the second time they feed at the beginning of fruiting, with an increase in the dose of ammonium nitrate.
If the fruits of the culture ripen small, they are fed for the fourth time.
It is important to know that when caring for peppers, they use fertilizing without chlorine or with a very small percentage. Pepper does not tolerate chlorine. But there is a good substitute for potassium chloride - this is ash from wood.

Superphosphate is one of the main fertilizers for pepper
How to protect peppers from frost?
Having planted pepper, you need to know how to protect the crop from frost and damage. Caring for a crop at the time of frost, forcing ingenuity.
Tents are built from scrap materials (pieces of wood, cardboard, fabric, etc.). They are made in the evening and removed in the morning. But when the cold snap lasts a long time, it is advisable to use a film.
Flowers and ovary fall off often. All due to the unfavorable temperature conditions for the vegetable (low or very high temperature). Growth stops at + 8-10 degrees. But if there is a heat of 30-35 degrees for several days, the buds also fall off.
The consequence of untimely watering is a lack of moisture. Dry soil also reduces crop growth.
Pepper cannot be shaded. In insufficient light, especially during a cold snap, flowers and ovary also fall off.

Bell pepper flowers may fall off due to lack of sunshine
Features of the care of bell pepper
There are some subtleties of caring for peppers, in order to better yield:
- It is imperative to pinch the pepper - removing the side and bottom stepsons. But in hot and dry weather, pinching is not recommended. Leaves protect the soil from evaporation. Professionals suggest, to increase the yield, cut the central flower that has grown from the first branch.
- During the growing season, long shoots are cut off a little so that there is no shading of other branches.
- Remove plant branches below the main branch and internal branches. Pruning is carried out every 10 days.
- Pollinating insects are useful for sweet peppers. They are attracted by spraying the plant, during the flowering period with a solution of sugar (100 g of sugar and 2 g of boric acid are diluted in 1 liter of hot water).
- Applying mulching of peppers with rotted straw (up to 10 cm of a layer), the frequency of watering will decrease.
- When leaving, it is important to tie up the crop immediately after hilling and mulching.

Mulching Pepper Helps Reduce Watering Frequency
Pest control
Pepper is sensitive to diseases, therefore it requires special care.
But most pepper suffers from pests (scoop, whitefly, aphid, Colorado potato beetle, bear, slugs).
So that the plant is not damaged, pollination is carried out with wood ash (three times per season). To fight aphids, you can use a solution of serum with water (0.5 liters of serum per bucket of liquid). And sprinkle the leaves with wood ash on top.
With all the tips in hand, you can grow a great sweet pepper crop.
Subscribe Be aware of new products on our site
Perhaps,
bell pepper
belongs to the most common vegetables among domestic gardeners. It is actively planted both in open ground and in greenhouses. Caring for him cannot be called scrupulous, however, some basic principles and agrotechnical features still need to be considered in more detail. By being ready for the process of growing bell peppers at home, you can achieve visible results.
Land preparation
Very often, it is the choice of the optimal land plot for planting bell peppers that becomes a whole problem. Many farmers believe that a vegetable garden is also suitable for this purpose: the land is regularly fertilized, while it is rather loose. However, there is one significant drawback. As a rule, a vegetable garden is an open area, there are constantly blowing winds, and there is no way to protect the plants from it. These conditions are not considered optimal in the case of bell peppers. Therefore, try to plant this vegetable in a place protected from strong drafts. It is also very important that it is well lit.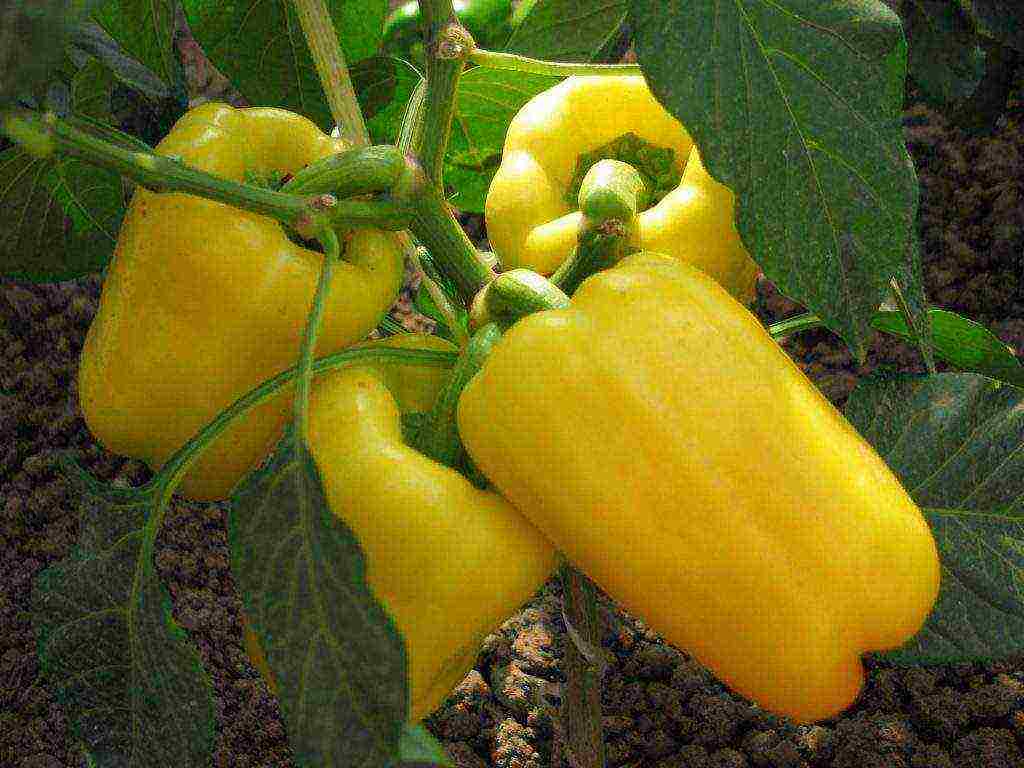
Before planting bell peppers in the open field, you should carry out some soil preparation procedures. What exactly does the farmer need to do:
- it is necessary to prepare for planting this culture, however, like most vegetables and root crops, in the fall. To do this, the land in the garden or garden plot is plowed and then loosened. The final stage of the autumn soil preparation is its fertilizing with mineral fertilizers. In particular, it is worth paying attention to mixtures containing potassium and phosphorus - these are the substances most necessary for pepper;
- in the spring, before you start planting vegetables, it is worth re-feeding the soil. Ammonium nitrate is added to the soil at the rate of 40 g per square meter;
- the final stage of soil preparation is saturation with a solution of copper sulfate. You must add 1 tbsp. l. of this substance in a bucket of water.
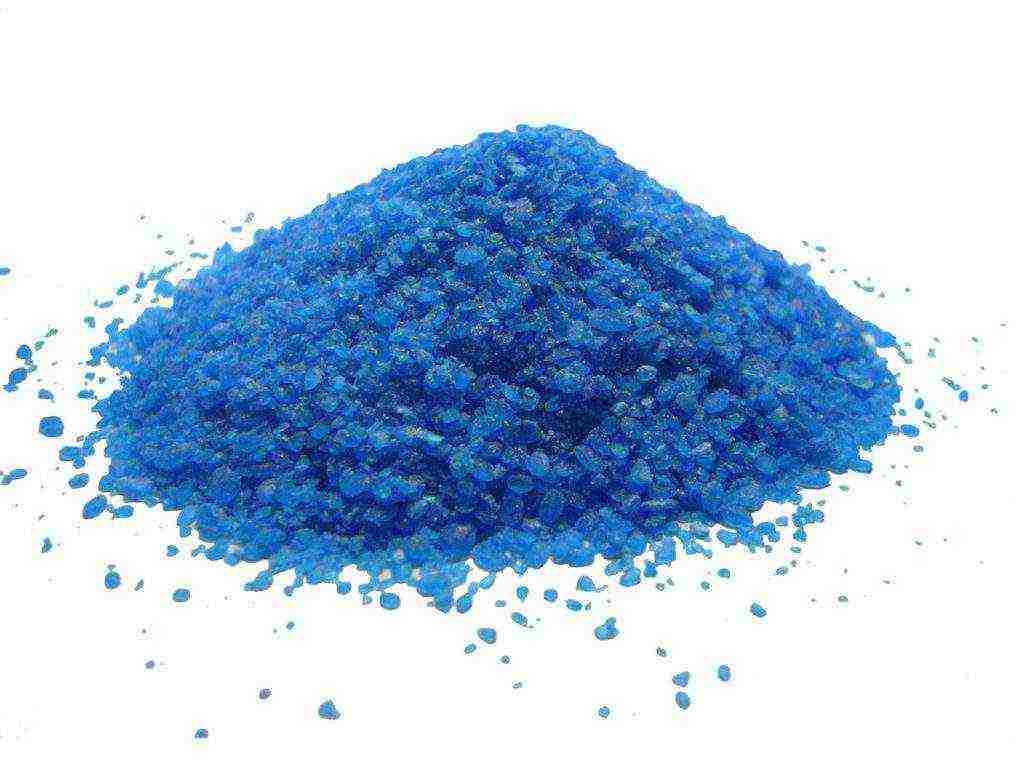

It is recommended that you pay attention to one more nuance before you finally plant a pepper in your garden. Let's say you want to breed several varieties of pepper at once. In this case, it is better to plant the sprouts away from each other. The thing is that this crop can get dusty during the ripening process. There is a risk that as a result you will not get the result you expected. However, there is a way out of the situation. Divide your home plantation of several varieties of peppers with taller plants (corn, tomatoes, or sunflowers). Thus, you can easily grow several varieties of bell peppers in the garden at once.
Video "Growing and caring for pepper"
From the video you will learn how to properly grow and care for peppers.
Top dressing of seedlings
It is necessary to feed the pepper, but you need to clearly understand what kind of soil you are dealing with. Your choice of fertilizers should also depend on its features. Let's say you decide to plant a pepper in a greenhouse and take in the usual garden land. In this case, be prepared for the fact that it will be necessary to recharge the soil every 10 days. If you approached this issue more thoroughly, using a specially prepared earthen mixture for planting bell pepper seedlings in it, it will be enough in the future to carry out no more than three stages of fertilization.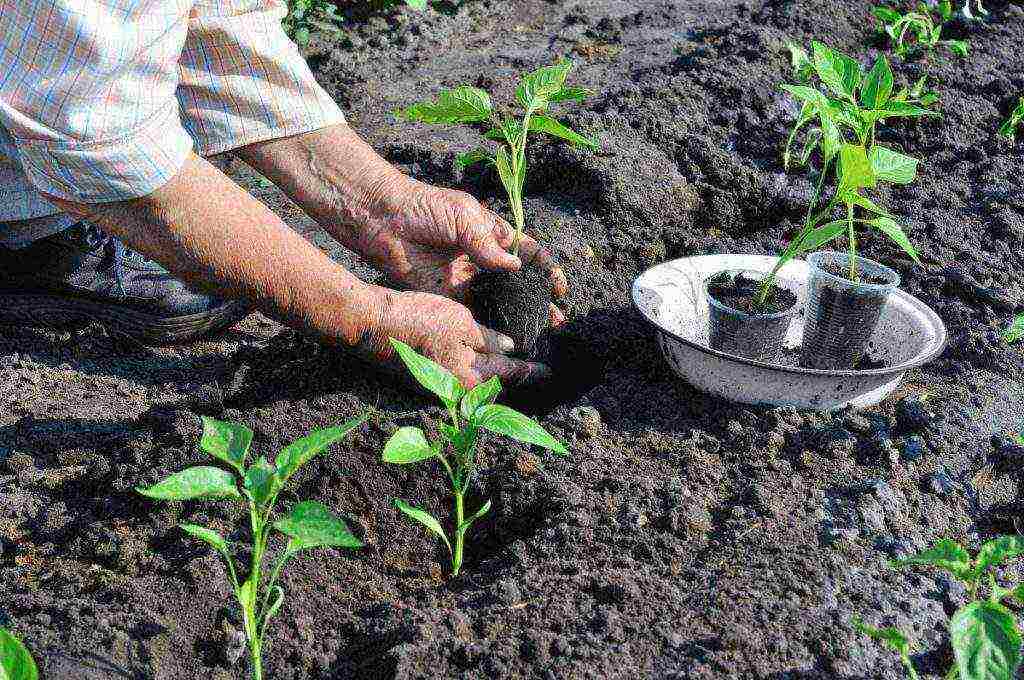
How do experienced gardeners-gardeners get out of the situation?
Many people prefer exclusively natural feeding. Shallow trenches are dug between the rows with seedlings, into which manure or bird droppings are poured. When can this kind of procedure be carried out? It is advisable to do this after 2-3 leaves bloom on the sprouts.When the seedling of bell pepper grows noticeably, it must be dived, and then the next stage of fertilizing the soil is carried out. You can use both special complex mixtures and dry ash or compost tea.
Top dressing after planting
You can endlessly determine the optimal place for planting bell peppers. But your efforts to grow a bountiful harvest of peppers shouldn't end there. Particular attention should be paid to the regular replenishment of the soil with mineral fertilizers. Moreover, this must be done not once, but during the development of the plant, ripening the fruits. What kind of fertilizers are suitable for bell pepper, and in what proportions should they be added to the soil?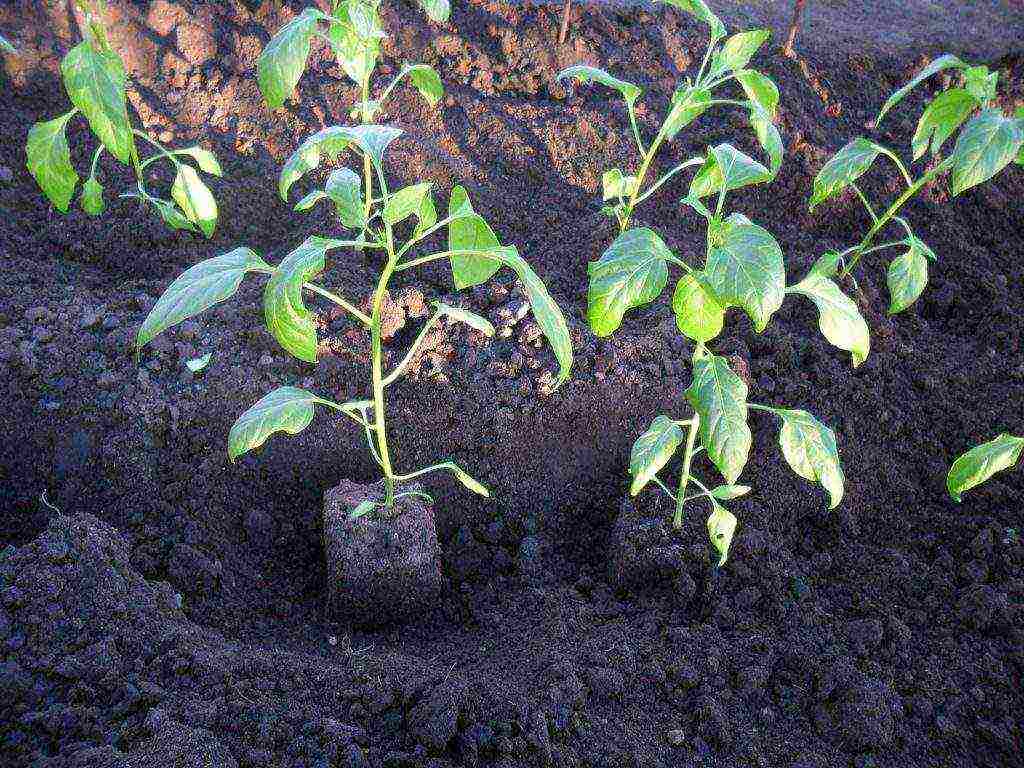
Among the variety of modern fertilizers, urea and phosphates are most distinguished for this agricultural crop. But that's not all.
Today, many summer residents use potash and phosphorus fertilizers for feeding, as well as folk remedies (cow dung or bird droppings). It is best to feed the pepper with natural mixtures.
For example, cow dung is recommended to be diluted with water in a ratio of 1:10. As for poultry droppings, the proportions here are 1:12. These types of dressings are considered the most versatile for bell peppers.
If you prefer to feed a vegetable plant as a preventive measure for diseases and in order to strengthen the vegetative part of agriculture, you can safely use universal fertilizers. However, if for some reason you did not feed the soil in advance, or did it, but noticed certain deterioration in the appearance of bell pepper seedlings, you must act immediately. First, identify the problem and then quickly fix it. For example, if your plant is not sufficiently saturated with nitrogen, over time, the vegetative mass begins to turn yellow. In the case when burns appear on the edges of the leaves of seedlings, the cause is in most cases a deficiency of potassium in the soil. It happens that the bell pepper bushes acquire a purple hue: this means that it is necessary to apply phosphorus fertilizers to the substrate.
Stimulation of fruiting
In order to prevent the occurrence of such problems, it is worth supporting the seedlings at all stages of their development. For this, there are universal natural fertilizers, among which nettle tea stands out. How to cook it? It is necessary to grind the stems of this plant, and then fill them with some barrel or container (about 2/3). The greens are filled with water. It is advisable to leave the resulting mixture in a dark place for effective fermentation. At the end of the process, and it will take about a week, the solution is used to fertilize the soil, before diluting it with water in a ratio of 1:10. If you wish, you can feed the soil to obtain a more generous yield of bell peppers using a high concentration of nettle solution. To do this, you need to add dandelion, woodlice, plantain and other herbal plants to it.
Stimulating fruiting is a good thing, however, it is undesirable to overdo it with it. With excessively large amounts of fertilizer and too frequent feeding, the branchy part of the bell pepper can become stiff. In addition, sometimes you can get the opposite result: when the soil is oversaturated with fertilizers, the fruits grow almost empty inside, falling off long before the end of the ripening period.
Watering features
Outdoor varieties of bell peppers do not require too much maintenance. However, with regard to moisturizing, oversights in this matter are unacceptable, as they can cost you dearly. Interestingly, it is recommended to water the pepper seedlings regularly, it is impossible for the soil to dry out. But it is also not worth breeding excessive dampness.
What rules should be followed about watering pepper:
- after planting seedlings in open ground, it is undesirable to water it immediately.It is necessary to give her a few days to adapt and only after that carry out the first phase of watering. Next, try to observe the established intervals until the seedlings begin to actively sprout;
- as soon as the sprouts are green, it is recommended to water them daily;
- be sure to use warm and pre-settled water for irrigation - non-observance of such recommendations is fraught with the occurrence of diseases in the plant;
- it is important that water does not fall directly on the leaves of the pepper;
- drainage must be present at the bottom of the seedling container. Thus, excess moisture will evaporate in a timely manner.
If you follow the key recommendations, the bell pepper harvest will certainly delight you. In addition, caring for him does not require huge investments and efforts.
Video "Growing pepper in a greenhouse"
From the video you will learn how to effectively grow peppers in a greenhouse.
Bell pepper also called sweet, it is rich in nutrients and vitamins, in various colors, juicy and tasty.
Process growing sweet peppers has its own characteristics, as pepper is a heat-loving vegetable. To get a good harvest of peppers, you need to have knowledge and certain skills.

Consider cultivation of bell peppers from seeds, from seedlings, especially care when growing in open ground, pest and disease control, when harvesting.
Content:
Growing bell pepper seedlings
Choosing a place for planting bell peppers
- Video - Peppers, the secret of a rich harvest
Outdoor Pepper Care
Top dressing of peppers in the open field
- Video - HOW CORRECTLY TO FORM PEPPER !!! CARE AND FEEDING !!!
Pepper pruning
Pests and diseases of bell pepper
Harvesting bell pepper
- Video - 10 ERRORS when growing sweet peppers
Pepper is a plant of short daylight hours, and if the daylight hours are less than 12 hours, the pepper begins to bear fruit earlier.
Planting pepper seeds in open ground is impractical even in the southern regions, because it is necessary to wait until the soil warms up, the pepper will begin to bear fruit later and not for long. Therefore, mainly sweet peppers are grown in seedlings.
Growing bell pepper seedlings

When growing seedlings at home, pepper seeds are sown in February, so that the plants are 90-100 days before transplanting into the ground. Peppers do not tolerate diving well, so try to immediately sow seeds in separate peat pots with a diameter of 8-10 cm.
There is no need to use large pots due to the slow development of the root system of the peppers.
Seedling soil
A light and loose substrate consisting of humus mixed with 1 part earth and 1 part sand is suitable. Add 1 tbsp for 1 kg of substrate. l. wood ash.

Before sowing, carry out the processing of pepper seeds - soak the seeds in hot water + 50 degrees for 5 hours. Then place the seeds in a damp cloth for germination for 2-3 days, the room temperature should be + 20 degrees. After such pre-sowing preparation, seedlings appear the very next day after sowing.
Seeds sown in cups, pour and cover with plastic wrap or glass. Until the emergence of shoots, keep the pots in a warm place with a temperature of + 22 degrees. After the emergence of seedlings, remove the film and transfer the seedlings to a room with a temperature of 26-28 degrees during the day and 10-15 degrees at night.

When caring for seedlings of peppers, do not allow the soil to dry out, but we do not recommend excessive watering.
Watering with warm water +30 degrees, cold water will grow frail seedlings, the plants can get sick. The indoor air should not be too dry, protect the plants from drafts and spray the plants.
In winter in February, the seedlings require additional lighting so that the daylight hours are from 7 am to 9 pm.
First feeding carried out in the phase of appearance of 2 true leaves with the following solution: dilute 5 g of ammonium nitrate, 10 g of potassium fertilizers, 30 g of superphosphate in 10 liters of water.
Second feeding carried out 14 days after the first mineral fertilizers in 2 times greater proportion than the first.
Third feeding carried out 2 days before planting seedlings in the ground. The dose of potassium fertilizers in the solution is increased to 70 g per 10 liters of water.
A few weeks before planting pepper seedlings, the plants are hardened, taking them out into the fresh air for several hours. Make sure that the air temperature is not lower than +13 degrees, the seedlings may die.
Choosing a place for planting bell peppers

Pick up a plot in the garden where cucumbers, onions, pumpkins, carrots, cabbage, zucchini, and various siderates grew before. Pepper does not grow well and bear fruit if planted on a site where potatoes, eggplants, tomatoes, peppers had previously grown.
Pepper grows best on light soils. Prepare the site for planting in advance, in the fall add 50 g of phosphorus and potash fertilizers per m2, dig deep. In the spring, add 40 g of ammonium nitrate per m2 of the plot to the topsoil.
Before planting seedlings in open ground, decontaminate the soil with such a solution: dilute 1 tbsp of copper sulfate in 10 liters of water.
At the end of May, pepper seedlings are planted in open ground with a distance of 40x40 cm between plants. Seedlings are planted in a film greenhouse at the end of April.
Seedlings should be planted at the same depth as the plants grew in cups or boxes. Do not expose the roots, but also try not to drop in the root collar.
Peppers do not like cold soil, arrange for peppers in tall beds, raised 25 cm to get a good harvest of peppers.
Attention: peppers are susceptible to over-pollination, so plant different varieties of peppers as far away from each other as possible or separate them using tall plantings of tomatoes, corn, sunflowers.
Video - Peppers, the secret of a rich harvest
Outdoor Pepper Care
It is necessary to carry out watering, fertilizing, garters and weeding of pepper plantings in a timely manner.

Top dressing of peppers in the open field
During the season, it is necessary to carry out 3-4 feeding with chicken manure diluted with water 1 x 10. Alternate such feeding by foliar, using spraying with nitrophos (1 tbsp. L. Per 10 l. Water).
Lack of potassium will lead to curling of the leaves, the appearance of a drying border. But pepper does not tolerate an abundance of potassium chloride.
At lack of nitrogen pepper leaves become smaller, acquire a matte grayish tint. If there is an excess of nitrogen, flowers and ovaries are shed.
Lack of phosphorus - the leaves on the lower side become deep purple, nestle against the plant stem and rise up.
At lack of magnesium leaves become marbled in color.
Video - HOW CORRECTLY TO FORM A PEPPER !!! CARE AND FEEDING !!!
Pepper care
Carry out pinching in hot and humid weather, removing side shoots, especially the lower ones. Conversely, when the hot and dry weather is not the peppers, the leaves during this period protect the plants from evaporation of soil moisture.

Pepper pruning
During the growing season, the longest shoots are pruned, especially all the shoots below the fork of the main stem, as well as all the branches that go inside the plant, are removed. Prune every 10 days and after harvesting.
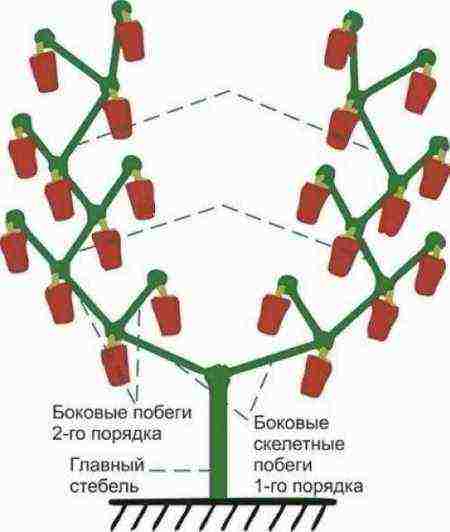
To attract pollinating insects, spray the planting of pepper with a sugar or honey solution: 100 g of sugar, add 2 g of boric acid, dilute everything in a liter of hot water.
Mulching the pepper with rotted straw (10 cm layer) will reduce the frequency of watering to 1 time in 10 days.
Timely carry out the garter of plants, it is better to do this after hilling.
Pepper pests and diseases

Pests such as slugs, scoops, aphids, whitefly, bear and Colorado potato beetle can harm plants. It is necessary to pollinate the pepper with wood ash 3 times per season.
Common Bell Pepper Diseases - late blight, Septoriasis, macrosporiosis, apical rot, white rot, black leg.
In the fight against the bear, before planting in the ground, fill the planting holes with onion water (insist 500 g of onion husks in 10 liters of water for 3 days).
If aphids are damaged, treat the plants with a solution: dilute 1.5 liters of milk whey in 10 liters of water. After processing, shake with ash.
Harvesting bell pepper

When the peppers are maturing in size and color, start harvesting by cutting off the stalked vegetables. Ripening of pepper begins from the beginning of August and lasts until the first frost.
Video - 10 ERRORS when growing sweet peppers
Big harvests of sweet pepper!
To get a good harvest of bell peppers, it is important to create the necessary conditions for it. High humidity and high temperature are those indicators that have a positive effect on this vegetable. But such a plant can be grown not only in warm regions. It is often found in vegetable growers' beds. In order for the pepper to produce a crop, it is important to know how to plant peppers in open ground, what to put in the holes, as well as what should be the distance when planting peppers in open ground, and how to properly care for sweet peppers in open ground.
Seed handling technique
Outdoor cultivation of bell peppers begins with proper seed preparation. The technology for preparing bushes for planting is to calculate the timing, because the sowing should be carried out so that by the required date the pepper is ready for planting in the ground.
There are several seed treatment techniques for successfully maintaining and improving planting stock. With their help, you can increase guarantees for a successful harvest.

Interesting! If the seed is left untreated, the seeds will sprout fourteen days after planting. When processing, the result will be visible on the third day.
First of all, it is necessary to determine which of the seeds are healthy. To do this, they must be filled with a 3% solution of baking soda and water at room temperature. Healthy seeds will remain at the bottom of the pot in five minutes, and empty and unsuitable for planting will float to the surface. After the check, the seed is rinsed out of salt and prepared for processing.
The inoculum is disinfected using various solutions. These can be Albit, Fitosporin, Alirin-B, or Trichodermin. You can also use your grandmother's recipe and treat the swollen pepper seeds with a solution of potassium permanganate. 30 minutes will be enough for the treatment to give a result.
Such preparations as Ecogel, Novosil or Epin increase the immunity of the plant and accelerate its growth. They are applied according to the instructions attached to them. To improve the effect, such preparations can be used after the ascent of the sprouts.
In order to make the seeds strong and strong, special fertilizers are used that strengthen the seeds. To do this, it is enough to soak the seeds in diluted fertilizer for 12 hours.
Growing pepper seedlings

Seedlings are grown in the ground three months after sowing the seeds. Therefore, it is necessary to prepare since February. It is important to complete all the necessary procedures before proceeding with sowing seeds. First of all, it is necessary to process and disinfect the seeds. Then they are hardened and soaked. After that, they are ready to disembark.
Sowing seeds
In order for the pepper to grow faster, you must first wrap the seeds in a damp cloth and hide in a warm place for two days. After that, you can plant them in pre-prepared soil (in boxes, pots or other containers). The distance between the peppers when planting in the ground should be 1.5 cm, after which the container is covered with glass or plastic wrap until the seedlings rise.

Important! For planting bell peppers, you need a light soil, which consists of sand, black soil and humus.Water the seedlings with water, which is infused for one day.
It is important to regularly apply fertilizers of organic and mineral origin to the soil. The first complementary feeding occurs after the first leaves on the seedlings bloom.
Growing pepper seedlings
You can prepare soil at home using the following components:
- sod land;
- peat;
- humus;
- sawdust.
All components are mixed in a 2: 4: 1: 1 ratio. Then ash and sand are added to the formed soil, adhering to the following dosages: three tablespoons of ash and 0.5 liters of river sand per bucket. The resulting consistency is poured with potassium permanganate.

There are two ways to grow bell peppers:
Using a pick
It is important to carry out a pick on time so that the plant takes root better. As soon as the seeds germinate, the grower counts 20 days and makes a pick. Since the root of the pepper is poorly restored, it is not touched, but other parts of the plant are used.
Without using a pick
This technique is more common. It is only necessary to move the seedlings from a smaller container to a larger one. Then the root system does not touch and the plant takes root faster.
Growing pepper on a windowsill

When growing bell pepper on a windowsill, you need to know a few subtleties and nuances. First of all, you need to choose the right time for planting the seeds. Since bell peppers at home often lack warmth and sufficient moisture, they will sprout longer than the allotted time. Therefore, it is recommended to plant seeds in late February - early March.
For the plant to grow normally, it needs to be provided with 12 hours of light. To do this, it is enough to keep the windows in constant cleanliness, since dirty windows take away some of the light.
Do not forget about the humidity in the room. For bell peppers, it should be 70%. For this, a humidifier is installed in the room. Of course, you can spray plants with a spray bottle, but a humidifier will be more rational and safe.
For planting seeds, two-hundred-gram cups are used, which are replaced by liter cups after one month has passed after planting.
Bell pepper, cultivation and care in the open field

The technology for growing peppers outdoors is similar to growing tomatoes. It is important to water the plant on time, feed, shape, and, if necessary, remove stepchildren. Do not forget about protection from various pests and diseases.
It is necessary to water sweet peppers as soon as they are planted in open ground, then after five days. After each watering, it is necessary to loosen the soil so that there is no hardened soil. Plant feeding is carried out three times per season. For this, nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus are used.
Don't forget about heat protection. To prevent pollen from losing its ability, it is necessary to make screens that will darken the plant.
You may be interested in:
Bell pepper growing in a barrel
You can also grow a culture in a barrel. To do this, you need to take the barrel and remove the bottom from it. In order for oxygen to enter the barrel, holes must be made in its walls, 1 cm in diameter at a distance of 20 cm from each other.
Then the following components are laid out in layers: faded (layer thickness 10 cm), soil mixture (turf and ordinary soil, compost).
In early May, one pepper bush is planted and covered with a film. After three hours, cut off all the lower leaves and cover the plant 10 cm with soil mixture. After the plant grows up, repeat the procedure. Do this until the barrel is completely filled with earth (this will be the beginning of June). Then the barrel can no longer be covered with foil.
Features of agricultural technology

The agricultural technology for growing sweet peppers in the open field consists of the following processes:
- Irrigation. It is necessary to water the seedlings with settled water every day. You need to be careful not to overdo it with water.
- Prevention.Spray the plants periodically with a spray bottle to maintain moisture.
- Temperature. It should not exceed 22 ° С during the daytime and 15 ° С at night.
- Top dressing. To increase the immunity of pepper, it is necessary to feed it with minerals.
The principles of growing on the site
Bell peppers are a plant that requires care and attention. Therefore, an experienced gardener prepares all the necessary tools for caring for him in advance. Outdoor maintenance for sweet peppers consists of the following steps:
- seedling preparation;
- planting a plant in the ground;
- watering;
- feeding.
Preparing bushes
Before planting seedlings in open ground, they must be hardened. For this, the plant periodically needs to be exposed to the sun for adaptation. This will make the pepper weather resistant and strong. Hardening begins two weeks before disembarkation.

The process of planting plants in open soil
To get a good harvest of pepper, you need to choose the right place for the beds. This area should not be in direct wind streams, be sunny and protected from drafts. Since the fall, it is important to prepare the necessary site for planting, having previously dug it up and fertilized it. It is necessary to plant bell peppers in open ground by impregnating the soil with potash and phosphorus substances.
When planting, it is important to remember that bell peppers do not like direct sunlight and too hot air. Therefore, care must be taken to keep the seedlings in the shade.

Depending on which variety is planted, a scheme for planting bell peppers in open ground is being developed. The holes should be at a distance of 35 cm from each other, and 45 cm between the rows.If the pepper is planted in the ground in two, then the distance increases to 60 cm.
There is also a square-nest method of planting pepper. Its essence is that each hole has the same sides, which do not exceed 60 cm.
Peppers are transplanted into the ground in late spring or early June, depending on weather conditions. It is recommended to do this on a cloudy day or in the late afternoon, so that there are no direct rays of the sun on the ground.
Planting pepper in open ground begins with the fact that the seedlings are first watered and carefully, without damaging the root of the plant, removed from the container along with a lump of soil. In this case, it is important to know at what depth it is necessary to plant pepper seedlings in the hole. The stem of the plant is placed under the ground up to its first lower leaves. After the planting of sweet pepper in the open ground has been completed, it is recommended to insert pegs next to it, to which it will be tied in the future.
Watering features

Bell pepper does not require regular watering and moisture in the open field. Initially, it must be watered during planting, then after 5 days and then watered once a week. About one pepper bush will need one liter of water.
During flowering, the water for irrigation should be about 20 ° C. Do not forget, after each watering, loosen the ground around the bush so that a crust does not form. To keep moisture stored longer, bell peppers are advised to mulch. Pepper mulching in the open field is carried out using re-matured straw or grass.
Top dressing of pepper
It is necessary to fertilize the soil three times during the whole season. In order for plants to develop and grow normally, they need nitrogen. Therefore, the first feeding is preparations with a nitrogen content. It is done after 2 weeks after planting the bushes in the ground.

The next feeding is carried out during the flowering period of the pepper. The plant needs potassium to form fruit. It is found in wood ash. And the last feeding occurs when the first fruit is formed. For this, potassium salt and superphosphate are used. Two teaspoons of each component are added to a bucket of water and the plants are watered with the resulting solution.
Potential diseases and pests and their control
The following pests can often be observed on pepper:
- aphid;
- slugs;
- Colorado beetle;
- whitefly;
- bear.

These pests are collected by hand, and a solution of wood ash is used for aphids.
The most popular diseases are:
- Yellowing of the leaves. This means that the pepper is deficient in nitrogen. For treatment, it is necessary to add 1 teaspoon of urea to 10 liters of water and spray the bushes with the resulting solution.
- Falling ovaries. A boric acid solution will solve the problem (1 spoon per bucket of water).
- Fruits develop poorly. It is treated with superphosphate or wood ash.
- Blackleg. Arises from an excess of moisture.

Growing greenhouse peppers
Planting a culture in open ground under a film is considered the most convenient, as it brings the culture closer to normal conditions. The seedlings can be planted in the greenhouse in April. To do this, holes are made in the greenhouse, keeping the correct distance.
It is important to fertilize the hole before planting seedlings. A solution based on chicken manure or manure is perfect for this (for 10 liters of water, half a glass of fertilizer). After planting, the bushes are watered with 1 liter per one bush. And to support the plant, you can make a support from the pegs, so that later you can tie the pepper to it.
Collection and storage
Bell peppers are harvested as the fruit ripens. Some growers can pick unripe fruits to relieve weight from the bush. This vegetable is used in many recipes fried, stewed, or baked. The fruits can be peeled and frozen or preserved.

In order to get fresh pepper before December, you can transplant the flowering bush together with the earth into any container and leave it on the windowsill in the house.
Conditions for growing sweet peppers

Growing sweet pepper in the photo
Of all the variety of types of pepper in the culture, the most common pepper is annual, or capsicum. It is to this species that the so-called sweet (or bulgarian) pepper, widely known and popular among amateur gardeners, belongs.
There are two groups of pepper varieties - vegetable and spicy (hot). In the former, the fruits are used unripe as a vegetable, in the latter they are very spicy and used as a spice.
Pepper fruits are very different in shape - from rounded to elongated-cone-shaped with a two-, four-chambered middle. In technical ripeness (before the seeds ripen), the color of the fruit, depending on the variety, is dark green, green, light green, cream, yellow. When the seeds ripen, the fruit turns red, in some varieties - orange.
The homeland of pepper is the tropics, so it is distinguished by increased requirements for heat, moisture, soil fertility; is, along with cucumbers and tomatoes, a fruitful greenhouse crop.
In the southern regions it grows and gives a good harvest outdoors. In the central (middle) lane, it is grown in glazed greenhouses.
Pepper belongs to the nightshade family, like tomatoes and eggplants. Therefore, the agricultural technology for growing peppers and other nightshade crops is largely the same. The best predecessor in a garden bed can be cabbage, beets, carrots, radishes, radishes, cucumbers, onions, garlic and green crops.
The fruits become edible 25-45 days after flowering, at which time they are green or white in color.
Ripe green fruits are considered ripe. It doesn't make sense to wait for them to turn red - they won't taste better.
Pepper is a light-loving plant; it grows poorly in the shade. The optimum temperature for development and fruiting is + 18 ... + 25 ° С. At + 15 ... + 20 ° C, plant growth slows down, and at + 13 ° C, it stops. Prolonged cold snap negatively affects flowering and the formation of generative organs. Sharp daily temperature drops cause massive dropping of flowers and ovaries.
The culture cannot stand even short-term frosts. Plants die when the air temperature drops to -0.5 ° C. Therefore, it is necessary to create optimal conditions for growing pepper.
Sunny, warm days are necessary for pepper during the fruiting period. He also does not tolerate high humidity. At a temperature of +35 ° C, buds and flowers fall off.
Pepper plants grow slowly at the beginning of the growing season, the root system grows longer than the leaf mass. Flower buds begin to form on the plant when the fourth leaf unfolds. The ripening phase begins 15-45 days after the appearance of the first bud.
According to the technology of growing pepper in the open field, plants are not stepchild, only the first bud is removed. Fruits are formed where the stems are branching, therefore well-developed plants with a large number of branches tend to produce more fruits.
When caring for peppers in the open field, regular watering at the root is required. Optimal soil moisture enhances fruit formation, promotes the yield of high-quality products. With a lack of moisture, the fruits become smaller, deformed, they are often affected by apical rot.
The correct technology for growing pepper does not allow mixed planting of sweet and bitter species, since cross-pollination will occur, and in appearance, sweet forms will taste bitter.
Next, you will learn how to grow a good crop of peppers using the seedling method.
Agrotechnics growing pepper: planting seeds for seedlings
The growing season for the culture is long (150-200 days). Therefore, even in the southern regions, the cultivation and care of peppers is carried out through seedlings. Growing seedlings for open ground begins in the second half of February. Sow in boxes or bowls with drainage holes.
The seeding depth when planting pepper seeds for seedlings is 1.5-2 cm. Until the seeds germinate, the crops are kept at a temperature of +25 ... + 28 ° C. After the emergence of mass shoots for a week, the crops are transferred to a cool room (+ 17 ... + 20 ° С) so that the seedlings do not stretch out. In the future, the seedlings grow at room temperature + 20 ... + 24 ° С.

Bell pepper seedlings in the photo
Seedlings dive after about 20 days into 7 x 7 cm pots, one plant at a time. Weak seedlings are discarded. The pots are filled with nutritious soil. Mineral fertilizers are not added to the soil when growing seedlings. After planting seeds for seedlings for growing peppers with a small volume of pots, plants do not need fertilizer. On the garden bed, they are brought into the hole.
When growing pepper seedlings from seeds, the seedlings are looked after in much the same way as tomato seedlings. But given that peppers begin to grow a month earlier, it is necessary to lengthen the daylight hours with the help of backlighting to 12-14 hours.
Watch the Planting Pepper Seeds video for a better understanding of this farming technique:
How to grow a good crop of peppers outdoors
Here are some tips on how to grow peppers outdoors and get a good harvest:
- Do not use seeds purchased from a random source for sowing. The basis for obtaining high-quality seedlings, and therefore a good harvest, is high-quality seeds. Purchase seeds from specialized stores. The seed bag must clearly indicate the variety, the number of seeds and the expiration date.
- Do not sow seeds in a dense, heavy potting mix of unknown origin. The best mixture is garden soil plus store-bought seedling soil. Do not forget to water the soil in the boxes first before sowing the seeds, otherwise the seeds with water will be pulled deep into the soil and the germination period will be extended.
- Do not thicken the crops of seeds; always sow the rate, otherwise the plants will stretch out, be weak, and may be affected by the "black leg".
- Do not put containers with seeds on the radiator - the soil instantly dries up and the seeds that have hatched die. Crops are placed only next to the battery and must be covered with foil.
- Do not use bowls or other containers without drainage holes for seeding. Stagnant water leads to the death of seeds, as well as seedlings in the initial stage of germination.
- Do not be late with picking seedlings. For most vegetable crops, this should be done after one or two true leaves appear. After picking, the plants are watered and shaded for 1-2 days.
- Remember to harden the seedlings before planting them in their permanent place. 7-10 days before planting plants, containers with seedlings are taken out for 2-3 hours on loggias, verandas, windows in the room are opened. The time spent for seedlings in the open air is gradually increased. Seedlings are planted in the evening or in cloudy weather.
The video "Growing pepper with seedlings" shows how to plant seeds and care for seedlings correctly:
Planting sweet pepper seedlings in open ground
Planting pepper seedlings in open ground is carried out at the age of 55-60 days. By the time of planting, it should be strong, have a height of 16-20 cm, 8-10 developed leaves, buds and form a well-developed root.
Seedlings are planted in double rows (ribbons) with a distance of 60 cm between ribbons, 30 cm between rows and 20 cm between plants.Wide aisles are made for passage during harvesting and plant care, and grooves are made in narrow ones for irrigation.
Low-growing varieties of this culture can be planted thicker, tall ones - to give more distance. The main thing is that adult plants should be closed with crowns.
When planting in open ground, pepper seedlings are not buried, since no additional roots are formed above the root collar on the stem, as in eggplant. Buried plants grow poorly and do not give a good harvest. For the same reason, growing peppers never huddle.
Proper care of sweet peppers in the open field: watering and feeding
When caring for peppers, you need top dressing and regular watering.
Watering. From an early age and throughout the growing season, pepper needs frequent watering and the obligatory loosening of the soil after each watering or rain.
Excess moisture, like its lack, is contraindicated in pepper. Excessive watering reduces air access to the roots, leaves turn pale green and plants wither.
Insufficient watering of sweet peppers inhibits the growth of plants, leading to the shedding of flowers, ovaries and the formation of small fruits. The frequency of watering depends on the weather conditions and the phase of plant development, but generally at least 1-2 times a week.
Correct watering of the pepper is carried out only with warm water. From wells and wells, water for irrigation must be preheated in the sun in containers for 2-3 days.
Fertilizing and feeding. Pepper needs fertile soil. It grows successfully on light loamy and black soil, well supplied with nutrients, including nitrogen. Solonetzic and heavy loamy soils are not suitable for pepper.
Peppers, like tomatoes, need phosphorus. He needs both organic and mineral fertilizers. For feeding peppers in the open field when planting seedlings, a tablespoon of superphosphate is added to each hole in a mixture with humus or just with earth.
During the period of budding, flowering and fruiting, every two weeks they give fertilizing with complex water-soluble fertilizers ("Sudarushka", "Agrolux", "Aquarin", "Solution" or "Zdraven", etc.). They are alternated with organic fertilizers.
In the second half of summer and autumn, sweet pepper is fed by "Kaliyphos".
Harvesting is carried out selectively when the fruits reach consumer (technical) maturity (green). Collection - weekly, preventing the formation of seeds in them, as this will slow down the appearance of new ovaries. Remove the fruits carefully with both hands, so as not to break off the plant shoots with the pepper.
The video "Growing Pepper" demonstrates how to properly water and fertilize a crop:
Pests and diseases of pepper: photos and control measures
In this section of the article, you will learn about pests and diseases of pepper, as well as measures to combat them in your personal plot.

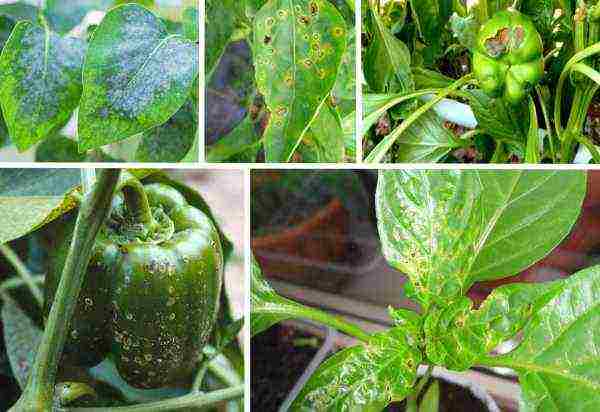
Stolbur (small-leaved) pepper leaves in the photo
Stolbur (small-leaved) - a viral disease is manifested by chlorotic leaf color, internodes are shortened. The leaves then wither, droop and fall off. Stolbur is not tolerated either with the juice of a diseased plant or with seeds. The leafhopper is the main vector of the disease.
Planting high-quality seedlings in the ground, systematic watering followed by loosening the soil, and weed control are the basis for the prevention of this disease.
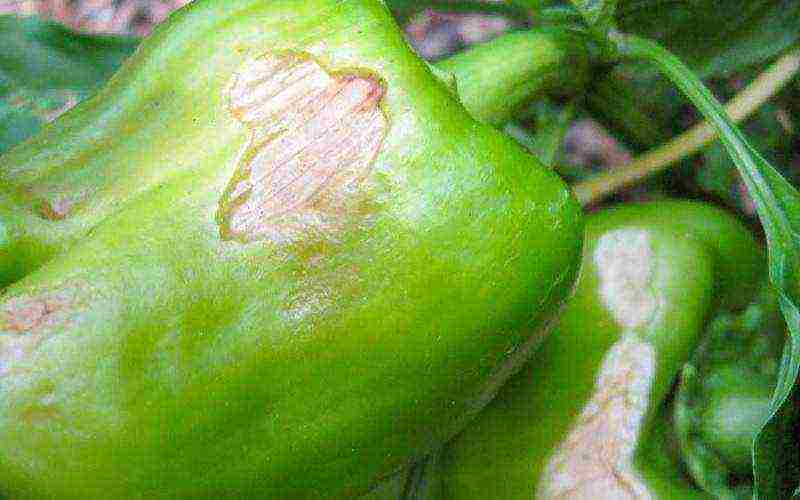

Top rot of peppers in the photo
Top rot - a disease of a physiological nature. It manifests itself at high temperatures and low relative humidity.
Regular even watering. Root and foliar dressing with calcium nitrate, as well as superphosphate during the period of intensive fruit growth, allows you to get a full harvest.
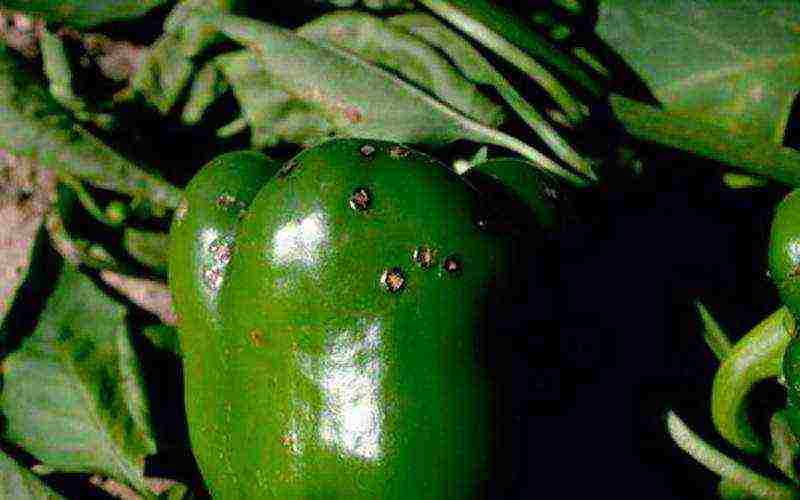

Black bacterial spot of pepper in the photo
Black bacterial speck of pepper. Not only fruits are affected, but also leaves and stems. On the leaves, the spots are small, at first watery, and then blackening, the tissue around the spots turns yellow. The disease is transmitted with seeds and plant debris. Preventive spraying with a copper-containing preparation "Abiga-Peak", starting from seedlings, allows you to get healthy fruits of pepper.
During the harvest season, to contain the spread of the disease, use the biological preparation "Gamair", which has a therapeutic effect.
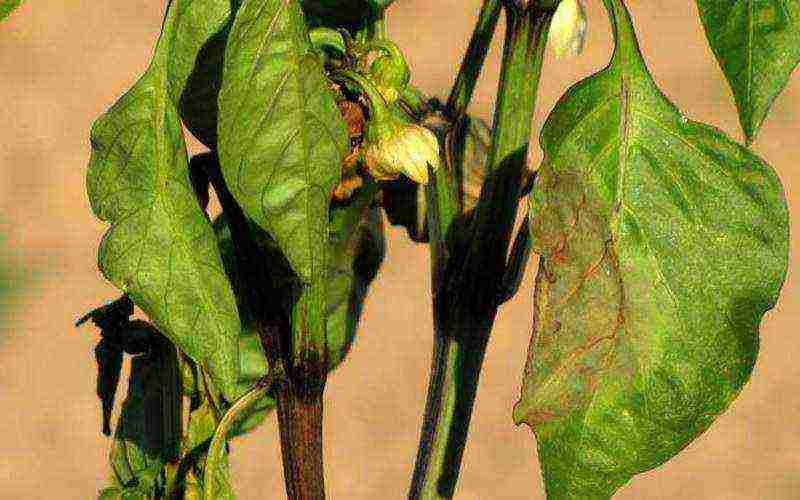

Fusarium wilting of peppers in the photo
Fusarium wilting. Symptoms first appear as slight yellowing of the leaves and wilting of the upper leaves. As wilting progresses, the leaves may turn dull green to brown in color and remain on the plant. When the stem or roots are cut, reddish-brown streaks are visible in the conductive tissues. Diseased plants must be removed.
Look at a selection of photos "Diseases of pepper and measures to combat them":
Spider mite. In the steppe zone, pepper plants are often colonized by spider mites. When a pest appears, treat the plants with Iskra-M or Fufanon. If the crop is on its way, use Tuoeum Jet, colloidal sulfur or Bitoxibacillin.
Aphid. This pest can also create problems when growing a crop. To fight, use the "Iskra Zolotaya" or "Confidor", "Commander" with a waiting period of at least 20 days. During the harvest period - Fitoverm, Iskra Bio, Akarin (waiting period 2-3 days).
Here you can see photos of diseases and pests of photos that threaten the crop:
Below you can read the description of the varieties of peppers, suitable for growing in the open field, and see their photos.
The best varieties of sweet peppers for open ground: photo and description
Traditional sweet peppers combine excellent fruit set, large fruit size and excellent taste. They differ in ripening period, fruit color, their weight up to 200 g, with a fleshy, juicy wall. They are characterized by a friendly return of the harvest.
These varieties include:
"Gift of Moldova",
"Martin",
"Belozerka",
"Winnie the Pooh",
"Venti",
"Caramel",
"Golden Jubilee"
"Yaroslav",
"Alesha Popovich".
Early ripe sweet pepper hybrids.
Latino F1 - from germination to technical ripeness of fruits 97-110 days. Plants up to 100 cm high. The fruits of this variety of pepper for open ground are cuboid, 3-4-chambered. In technical ripeness it is dark green, in biological it is bright red.
"Peresvet" F1 - from germination to technical ripeness 92-105 days, to biological - 120-135. The plant is medium-sized, 50-60 cm high, compact, standard.
"Sonata" F1 - from germination to technical ripeness 95-100 days. The plant is up to 100 cm high. The fruit is cuboid, 3-4-celled, glossy, dark green in technical ripeness, bright red in biological ripeness, weighing 180-200 g.
"Orange Miracle" F1... Hybrid for open and protected ground (100-110 days) Plants 90-110 cm high. Fruits are large, cuboid, bright orange in color.
"Jubilee Semko" F1 - hybrid for open and protected ground (90-100 days).The plant is a standard plant, medium-sized, 50-60 cm high, compact, slightly spreading and low-leafed. Fruits are light green in technical ripeness and red in biological ripeness.
Montero F1 - 90-108 days pass from germination to technical ripeness of fruits. The fruits are long, prismatic, green in technical ripeness, and bright red in biological ripeness.
"Snowfall" F1 - fruits are cone-shaped, up to 15 cm long, creamy white at the technical stage, red at the biological stage.
High yields also give hybrids
"Grenada",
Sevilla,
"United" with large cuboid fruits.
Among the best varieties of pepper, a special mixture of Siesta hybrids is distinguished.
Original color sweet pepper hybrids:
"Cardinal" F1 with large purple cuboid fruits.
Aries F1 - with large dark red fruits weighing up to 300 g, prismatic.
Fidelio F1 - with silvery white fruits.
Large-fruited sweet pepper hybrids include:
"Russian size" F1... Giants over 20 cm long grow without much additional effort.
"Yellow Bull-NK" F1 - fruits are elongated, large, up to 200 g, 9x20 cm in size, consist of 3-4 lobes, green, when ripe they are yellow.
"Red bull-NK" F1 - fruits are large, weighing up to 200 g, elongated shape 8 x 20 cm, consist of 3-4 lobes, light green, when ripe - red.
"Black Bull-NK" F1 - it is distinguished by a defiant brilliant black color. Fruits weighing up to 400 g.
Indalo F1 - mid-early hybrid. From germination to technical ripeness of fruits 110-120 days. Plants 110-120 cm high. This is one of the best varieties of sweet peppers with large cuboid fruits, beautiful bright yellow color, weighing 280-300 g. Wall thickness up to 10 mm.
Flamenco F1 - early maturing, high-yielding. The variety has cuboid, thick-walled fruits measuring 10 x 14 cm, consisting of 3-4 lobes. Fruits are light green in color; when ripe, they acquire an intensely bright red color. The variety is suitable for various types of indoor and outdoor ground.
Such hybrids also deserve attention: Minotaur F1, Sevilla F1, Athena F1, Flamenco F1.
Check out the best varieties of pepper in the photos below:
Using sweet peppers
The authority of pepper as a food and medicinal plant is high. Its beneficial effect on the human body is explained by the richness of its vitamin composition.
In terms of vitamin C content, sweet pepper ranks first among vegetable crops. Its fruits in technical ripeness contain 100-150 mg% of vitamin C per 100 g of fresh weight, and in biological ripeness - 250-480 mg%. Vitamin P (rutin) gives a special value to pepper, its fruits are 70-380 mg% per 100 g of raw weight. Contains sweet peppers and vitamin A - 0.5-16 mg%. It contains from 2 to 6% sugars and starch, about 1.5% proteins, fat, fiber, ash compounds.
Sweet pepper contains carotene, valuable for the body (red pepper is especially rich in it), vitamins B1, B2, E, PP, as well as minerals, including sodium and potassium. It is also rich in glucose, fructose, useful organic acids and mineral salts.
The use of all varieties of sweet peppers in food is permissible at the onset of technical ripeness. These are already fully formed fruits of at least 6-8 cm, with thick fleshy walls, light green or green color and with a characteristic peppery aroma.
Red, yellow, orange, pinky yellow, black, lilac or green peppers are great in all varieties. Fresh fruits decorate dishes with bright colorful colors, taste and aroma. You can also use pepper leaves in the preparation of soups, green cabbage soup, borscht. They contain vitamin C.
Bell peppers are eaten raw, fried, baked, stuffed, pickled, pickled and even dried. Ripe fruits can be chopped and dried. The dried fruits of this culture and the powder from them are a vitamin product used as a seasoning for main dishes and for making sauces.
Bell peppers can also be kept fresh.To do this, the fruits are cut carefully together with the stalk. Each fruit is wrapped in paper, placed in a cardboard box in 1-2 layers, placed on a shelf in a dry cellar. The fruits harvested at the stage of technical ripeness gradually ripen, and their vitamin C content increases.
Rate the article:
(0 votes, average: 0 out of 5)


