Content
- 1 Terms for sowing peas in Ukraine, Moscow region, the Urals and Siberia
- 2 Preparing seeds before planting at home
- 3 Garden bed preparation and proper cultivation
- 4 Planting scheme in open ground in the country
- 5 Composition and useful properties
- 6 Landing
- 7 Features of plant care
- 8 Pea varieties
- 9 Pea planting technology in open ground
- 10 Outdoor pea care
- 11 Peas collection and storage
- 12 Peas in the open field: photo, video, planting, care and harvesting
- 12.1 Do I need to soak peas before planting in open ground
- 12.2 When is it better to sow peas
- 12.3 Soil and air temperature
- 12.4 Choosing a soil for planting peas
- 12.5 Preparation of beds and planting scheme
- 12.6 What can you plant peas next to?
- 12.7 Features of growing peas
- 12.8 Warmly
- 12.9 Light
- 12.10 Preparing for landing
- 12.11 Predecessors
- 12.12 Garden bed preparation
- 12.13 Seed treatment
- 12.14 Planting peas
- 12.15 Winter sowing
- 12.16 Pea care
- 12.17 Weeding
- 12.18 Pest control
- 12.19 Watering
- 12.20 Fertilizers
- 12.21 When to harvest
- 12.22 Pea cultivation technology features
- 12.23 Preparing soil and seeds for sowing
- 12.24 Planting in open ground, selection of varieties
- 12.25 Pea Care Tips and Harvesting
- 12.26 Ways to control pests and diseases
- 12.27 Know the enemies of your crop by sight!
- 12.28 Video about growing peas in the country
- 12.29 Soil and lighting
- 12.30 Sowing time
- 12.31 Landing features
- 12.32 Fundamentals of agricultural technology
- 12.33 Soil and seed preparation
- 12.34 Sowing
- 12.35 Video "About the benefits and cultivation of peas"
- 12.36 Care
- 12.37 Disease and pest control
- 12.38 Video "Pests of peas"
Peas have valuable properties that have a beneficial effect on the body. therefore the crop is grown in almost every vegetable garden... Despite the simplicity of care, it is not always possible to get a good harvest. This article reveals the basic rules of agricultural technology that need to be taken into account by novice gardeners, namely how to prepare the seeds, whether it is necessary to germinate and when to plant.
Terms for sowing peas in Ukraine, Moscow region, the Urals and Siberia
Peas are cold-resistant plants, young shoots can withstand night frosts down to minus 5-6 ° C. But this fact does not mean that you can start sowing in March. Cold resistance is short, the shoot will not develop at low temperatures... Therefore, you need to wait for the time when the night indicators will not fall below the 5-8 ° C mark.
 The timing of planting peas in open ground depends on the climate of the area.
The timing of planting peas in open ground depends on the climate of the area.
You can grow peas only using one method - seed. Seedling propagation method in this case is inappropriate.
When is the best time to plant peas at home? There is no specific time for sowing seeds, but many gardeners are guided by the lunar calendar and weather conditions. In Ukraine and the Moscow region, planting work in open ground begins in late April - early May, when the soil still retains the moisture accumulated over the winter. In the Urals and Siberia, the time is shifted by 10-15 days, depending on climatic features. But anyway experts recommend to complete the sowing of legumes by the end of May... The plant develops better, blooms and bears fruit during long daylight hours.
Preparing seeds before planting at home
Seed germination directly depends on the correctness of their preparation for planting. The peas should be calibrated first. - select the highest quality specimens from the total number, which have no traces of damage, black spots and other flaws. Spoiled seed will not give healthy shoots, and weak shoots are exposed to diseases and pests in the first place.
 Peas should be calibrated before planting
Peas should be calibrated before planting
Further preparation depends on the selected seeding method. There are only two of them: dry and with preliminary soaking. It is not customary to breed peas and beans with seedlings.
Stages of preparing seeds for planting:
- soak in a solution of boric acid (1 g. powder per 5 liters of water heated to 40 °) for 5-8 minutes;
- removal of excess moisture dry napkin;
- drying for 1-2 hours at room temperature;
- landing.
Treatment of seeds with a boric acid solution prevents damage to the root system by the larvae of the root weevil.
With the dry method, it is important to pre-water the groove with water and cover the bed with a film to create a greenhouse effect. This speeds up the germination process of the shoots.
As a preparation of peas for sowing, you can use the old grandfather's method.... To do this, the seeds are immersed for 1-2 days in a container with warm water (soaked), previously wrapped in a cotton napkin. For swelling and germination, a temperature regime of at least 20-23 ° will be required. As the fabric dries, it is wetted. Seeds are able to germinate in 3-5 days.
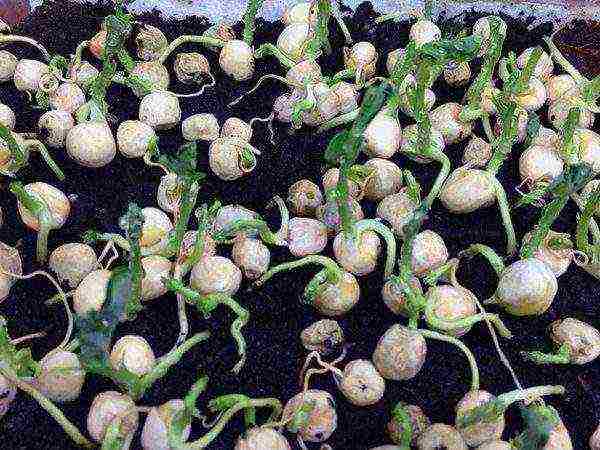 Sprouted peas
Sprouted peas
In order not to worry about the timing of germination, you can process the seed in a growth stimulator. How much seeds to soak? In such a solution, it is enough to soak the planting material for 2 hours, placing it on a home balcony or windowsill.
Garden bed preparation and proper cultivation
You need to start preparing the garden by choosing a place in the country or a personal plot. You need to give preference to well-lit areas on a hill... The roots of the plant penetrate deeply into the soil, with a high level of groundwater occurrence, there is a danger of their decay. Therefore, the flooded land is not suitable for planting legumes. Where is the best place to plant peas?
When choosing a place for a garden, take into account what was grown earlier. Ideal predecessors are: beets, potatoes, corn, zucchini, eggplants, etc. But after the peas, you can plant everything, the soil is enriched with nitrogen, it becomes looser and more fertile.
It is not recommended to organize a pea bed where perennial grasses, legumes, which can cause illness or pest infestations, grew.
 The site for peas is chosen sunny, with a deep bed of groundwater
The site for peas is chosen sunny, with a deep bed of groundwater
What kind of soil do peas like? Ideal soils for peas are non-acidic loams and light-textured sandy loams.... Chernozems, cultivated soddy-podzolic and other types of soil are also suitable. Sour, salty and raw are excluded. If acidity is noted on the site, then the introduction of dolomite flour or crushed lime will help to neutralize the environment.
Experienced gardeners advise, when preparing the garden, to fertilize the soil well, so that during intensive development the plant does not feel a deficiency of nutrients. However, feeding it is not worth it, you can provoke an increase in green mass. Even in the fall, during digging, organic matter is introduced (compost, humus, rotted manure). In the spring, when preparing the site, the soil is enriched with potassium (30 g) and double superphosphate (20 g) per 1 m2.
It is necessary to dig up the soil with the simultaneous introduction of fertilizer with immersion to 30-40 cm. It is better to perform the work itself before frost, so that insects and their larvae are frozen. From the garden, you should carefully select all plant debris in which pests can find refuge.
Planting scheme in open ground in the country
When choosing a planting scheme, you need to focus on the characteristics of the bush of an adult plant. If these are undersized and medium-sized crops, then the garden bed is planned with the following parameters:
- row spacing - 15-20 cm;
- the interval between seeds is 5-6 cm;
- immersion depth - 3-5 cm (if you make a powder of 1-2 cm, then the risk of eating peas by birds increases).
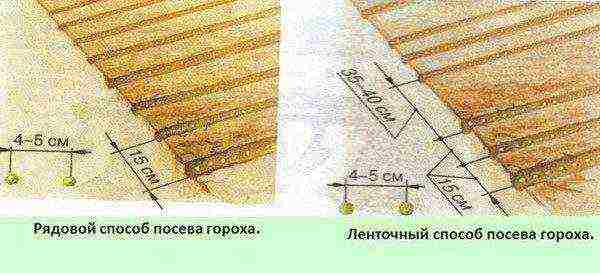 Pea planting scheme
Pea planting scheme
For tall plants (with a height of over 80 cm), it is recommended to use the scheme: 30x10 cm in two rows with a row spacing of 50 cm.
When planting, they consume about 15-17 peas per square meter.
The process itself involves sowing seeds into prepared grooves, followed by filling the soil. Before lowering the seeds into the ground, you need to pour it generously with warm water. The first shoots will appear a week and a half after sowing. For tall bushes, it's time to build a support. A plant spread on the ground will not bear fruit well.
Summarizing the above information, we can conclude that with the correct selection of the variety and the fulfillment of the growing requirements, a good harvest of peas is ensured. The main obligatory tasks: to feed the soil, prepare the beds, germinate and sow seeds, take care of the seedlings - a good harvest is guaranteed.Generous gifts of nature are suitable both for fresh consumption and preparations for the winter. The fruits retain their valuable qualities even when frozen.
Peas are one of the most popular plants to grow. It is appreciated for its excellent taste. In addition, peas are a healthy crop. Not surprisingly, he managed to win the love of children and adults.
How to properly sow peas in open ground and how to care for them later will be discussed in this article.
Composition and useful properties
Peas are self-pollinating annuals and belong to the legume family. This herb is comparable in protein content to beef. At the same time, vegetable protein is better absorbed.
In addition to protein, peas contain vitamins: A (carotene), B, C and PP; and trace elements: manganese, phosphorus, iron, potassium. From it, the body receives lysine - a deficient amino acid. This composition makes peas an important part of a therapeutic diet. It is especially necessary for people suffering from cardiovascular diseases.
Green peas saturate the earth with nitrogen, creating a breeding ground for beneficial microorganisms. The bacteria living in its roots recycle atmospheric nitrogen and contribute to its accumulation in the soil. Plants then use it.
Healthy! You can speed up the process of nitrogen enrichment of the soil. To do this, take some soil from the garden where the legumes grew before, and add it where you plan to sow peas. Together with the soil, you will carry the necessary bacteria.
Landing
Choosing a place for planting peas in the garden
Peas are a capricious vegetable. To grow peas outdoors, you need to carefully choose a place. When choosing a site, the following factors are taken into account:
- illumination;
- soil type;
- surrounding plants;
- climate.
Climatic conditions for growing
It is important to comply with the conditions for growing seed peas. In a humid environment, the plant develops well, gives friendly shoots. In regions with a lot of rainfall, it grows faster and gives a better harvest.
Peas especially need water during the flowering period: with a lack of moisture, they can shed their flowers. However, the plant will withstand short-term drought due to the strong roots that penetrate deep into the soil.
+ 5 ° C heat is enough for peas to germinate. To start flowering and fruiting, a stable temperature of + 15 ° C to + 22 ° C is required. The plant is frost-resistant and able to tolerate frosts down to -6 ° C.
Sowing time
The plant is sown in open ground early: at the end of April, 20-25. In summer, sowing of peas continues until July 10. It is worth giving preference to early ripening varieties.
Requirements for soil and illumination
Peas are not very picky about the composition of the soil. Loams, clayey soils, sandstones are suitable for cultivation. It is best to choose areas with light and fertile soils, rich in humus. It should be remembered that excess nitrogen destroys the plant.
Peas do not like acidic soils, so they are lime before planting. It is necessary to take 300 g of slaked lime (you can replace it with dolomite flour in the amount of 400 g) per square meter.
It is important to pre-dig well and moisten the soil, as well as apply fertilizers. The depth of groundwater should also be taken into account. Too high a level of occurrence will badly affect the sprouts.
One of the key conditions when planting peas is lighting. The more sun, the better for the plant. The site must be protected from the wind.
The best neighbors of peas
The yield of peas depends to a large extent on the plants that grew in the area before it. The best predecessors of peas:
- carrot;
- potato;
- beet;
- cucumbers;
- tomatoes;
- pumpkin.
The culture itself creates an excellent foundation for planting any other plants.
Important! You can not plant peas in places where other legumes were grown: beans, soybeans, peanuts, lentils. Including, you should not sow it on last year's garden. Better to skip 3-4 years. So you will protect the plant from diseases and pests that usually affect its family.
How to prepare the soil for planting
They begin to prepare the soil in the fall. The optimum digging depth is about 30 centimeters. The soil is fertilized with the following mixture:
- humus (compost is also suitable) - 4-6 kg;
- potassium salt - 15-20 g;
- superphosphate - 20-40 g.
The proportions are based on 1 square meter. When the time comes for sowing, wood ash is sprinkled on the ground.
It is good if the soil is fertilized regularly before sowing the peas. Large crops are harvested on such soils. Just do not feed the seedlings with fresh manure. In this case, the tops will grow, and the pods will be small.
Peas love flat, well-loosened soil. Before planting, the bed must be shed well.
Important! Although peas are a cold-resistant crop, experienced gardeners advise against rushing to sowing. Wait for a stable warm temperature.
Presowing seed treatment
The key to a good harvest is properly selected seeds. Only large, healthy specimens are suitable for sowing. Seeds of irregular shape, with spots and other defects, patients cannot be planted.
Did you know? It is very easy to calculate a good quality seed. For this, a saline solution is prepared at the rate of a tablespoon of salt per liter of water, and seeds are placed in it. The drowned ones can be safely planted, and the emerging ones are discarded.
To sprout faster, pea seeds are germinated. Soak them in warm water for 16 hours until they swell; change the water periodically. Dry the seeds before planting.
You can plant dry seeds right away. Before sowing, they are placed in a boric acid solution for several minutes. It is obtained by diluting 2 g of acid with 10 liters of water. The solution should be hot, about 40 ° C. Such pre-sowing treatment serves as a prophylaxis against one of the main pea pests - the larva of the nodule weevil.
Sowing process
There is nothing complicated and unusual in the technology of planting peas. In the prepared area with a hoe, they draw wide (20-25 cm) furrows at a distance of half a meter from each other. You can find out more precisely the distance between the rows by examining the seed packaging. It should be equal to the height of the plant. A mixture of soil and rotted compost or vermicompost is poured into the resulting furrows, leveled. The peas are laid out one at a time, no closer than 5 cm from each other. Normally, from 80 to 130 seeds are placed on one square meter. Then sprinkle with earth, compacting from above with the palm of your hand.
The planting depth depends on the type of soil. On average, it is 3-5cm. In sandstones - less, on clayey soils - more.Do not place peas too close to the surface - there they will be dug up and pecked by birds. To protect crops, you can cover the bed with a film.
Watch the video! Pea sowing process:
If the width of the beds allows, lettuce or radishes can be sown in the aisles. To save space, you can grow peas in the near-stem circle of the apple tree, but in this case, you need to make sure that the crops receive enough sunlight. A layer of fertile soil with a height of about 10 cm should be poured under the tree.
When sowing early, do not rely on the seed's natural frost resistance. It is better to play it safe and cover the bed with a film. Every 10 days, additional sowing is done, until the end of June, when the length of daylight hours is best suited for the development and fruiting of peas.
Reference! The first shoots will appear one and a half weeks after sowing, or even a little earlier.
Bait containing potassium and phosphorus will help to improve the taste of peas. Thanks to fertilizers, the fruits will be sweet.
Features of plant care
When planting work is over, all that remains is to provide proper care for the peas. It includes:
- compliance with the irrigation regime;
- top dressing;
- loosening;
- garter.
With proper care, yields increase.
First steps after sowing
First of all, peas need moisture. Regular watering makes up the bulk of your care. From the first day after sowing, care must be taken so that the soil does not dry out. Peas die from lack of water before they germinate.
Garter

The long, thin stems of peas cannot withstand the weight of the pods and drag along the ground. Air circulation and heat exchange are impaired. To prevent this from happening, the bushes must be tied up.
To make a support, you should stock up on wooden pegs or metal rods. They are placed along the beds one and a half meters apart. A rope is pulled between the rods (can be replaced with wire). Then the shoots are gently lifted, allowing them to catch their antennae on the support.
 Coarse mesh can be used instead of rope. It is fixed on two-meter stakes dug in along the edges of the garden. The net will serve as a support for plants for more than one year.
Coarse mesh can be used instead of rope. It is fixed on two-meter stakes dug in along the edges of the garden. The net will serve as a support for plants for more than one year.
Vegetable peas are inferior in grace to their decorative cousin, sweet peas. However, it can serve as an original decoration. Pea-stemmed gazebos, terraces, hedges, balconies and pergolas look fresh and elegant.
Protection of seedlings from birds
Birds love to peck not only peas, but also young sprouts. A fishing net or film will help save the crop. You need to use a translucent material, but make sure that the plants do not fade in the sun.
Watering
Peas do not tolerate drought. In the heat, you will have to spill the soil abundantly, using at least a bucket of water (10 liters) per square meter. Frequency - once a week. With the beginning of flowering and fruiting, peas need to drink especially a lot, otherwise they will throw off the ovaries. Drying out of the earth during this period is not allowed. The regularity of watering is increased up to twice a week.
Important! Peas love water, but should not be poured. Excessive diligence in watering increases the likelihood of disease.
Soil care: loosening, feeding features.
It is most convenient to combine watering and feeding. As the latter, it is good to use a tablespoon of nitroammophoska in a bucket of water. After watering, as well as after heavy rain, the soil around the plants should be loosened properly to avoid crusting. In order to prevent moisture from evaporating too quickly, the soil is mulched. For the entire growing season, it will take up to 3 loosening.
You should once again walk with a hoe between the beds in order to provide the microorganisms living there with oxygen. Such care is necessary when the plant has entered a phase of active growth. When the peas have formed 4 true leaves, it's time to harrow the ground. In order not to harm the roots, only dry soil is harrowed.
Nodule bacteria do not tolerate cold well. Therefore, in a cool spring, peas are fed with nitrogen fertilizers until the soil warms up. The solution consists of 1 kg of cow dung and a tablespoon of nitrophosphate per bucket of water.
Fertilizers are also applied during pea flowering to stimulate the formation of ovaries and increase yields. Good results are obtained from the use of mineral feeding. Before flowering, 25 g of dry fertilizers are applied per square meter. During the period of fruit setting, the beds are shed with a complex solution at the rate of 3 g per liter. Care must be taken not to get fertilizer on the leaves.
Pest and disease control
Not only summer residents love to feast on peas, but also pests. Young shoots should be secured from them in advance.
The most dangerous enemy of peas is the moth caterpillar. It hibernates in the soil, and in the spring, having turned into a butterfly, lays eggs on plants. Caterpillars hatched from eggs immediately attack the leaves and can chew them to such an extent that the sprout will die.
Spraying is used to combat the pea moth. Use decoctions and infusions of such plants as:
- wormwood;
- tobacco;
- garlic;
- tomato (greens);
- burdock (roots);
- celandine (leaves).
To prepare, for example, garlic infusion, pass through a meat grinder 20 g of garlic and leave to infuse in a bucket of water for a day. After that, the infusion is filtered and used for spraying. Processing is carried out in the evening. The garlic solution also helps in the fight against aphids.
The best way to deal with the moth is prevention. Therefore, spraying begins in advance. Additionally, you can sprinkle the beds with tobacco dust, ash, celandine ground into a powder. Digging up the site before winter, early sowing and pre-sowing treatment of peas will be an effective protection against the moth.
Peas are affected by powdery mildew. This unpleasant disease affects the entire plant and can ruin the entire crop. For treatment, a solution of field sow thistle is used. In 10 liters of water, 300 g of sow thistle leaves are insisted for 8-10 hours. Two sprays are carried out, the second - a week after the first.
Harvesting
A month or two after sowing, the peas begin to bloom. A month later, the first harvest ripens. After collecting the pods, the plant goes into growth. The fruits can be harvested several times at intervals of two days (in cool weather - 4 days) for a month and a half.
If you follow the cultivation technology, you can get up to 4 kg of crop per square meter. The ripening period of peas depends on the flowering time. The earlier the plant bloomed, the faster they start harvesting.
Interesting! The most delicious, delicate and sweet peas ripen one and a half weeks after flowering in the lower part of the plant. This applies to early ripening sugar peas.
The peas are harvested when the beans have not yet had time to overripe. The ready-to-harvest pod has bright green leaves, about 8 millimeters long. Fruits removed at the wrong time will prevent the rest from ripening. The best time to harvest is early in the morning; in the heat, the pods wither quickly.
 If you do not need the shoulder blades, that is, green peas, you should leave the crop on the bush until the lower pods are ripe. After harvesting, the plant must be cut at the root, tied peas in bunches and suspended for two weeks to ripen in a dry, well-ventilated place. The seeds will remain viable for two years.
If you do not need the shoulder blades, that is, green peas, you should leave the crop on the bush until the lower pods are ripe. After harvesting, the plant must be cut at the root, tied peas in bunches and suspended for two weeks to ripen in a dry, well-ventilated place. The seeds will remain viable for two years.
Thus, peas are useful in crop rotation, because they increase soil fertility, but they are not sown in the same place so as not to expose them to diseases.
Many gardeners do not know about the benefits of peas and therefore do not consider it a significant plant for the site. This approach is not correct. Peas are a valuable source of vitamins; a versatile vegetable that does not deplete the soil, but, on the contrary, enriches it. You should pay attention to it!
A delicious vegetable can be eaten straight from the garden, or can be used in the preparation of thousands of mouth-watering dishes.Enjoy growing peas on your property!
Watch the video! Pea growing technology:
Vegetable peas are one of those uncomplicated crops that you cannot do without in the country. It is remarkable in that, in terms of its nutritional value, it is an order of magnitude higher than all vegetables. In addition, it contains a special balance of vitamins, sugars, amino acids and trace elements. That is why you don't get fat and thin with it. In cultivation, peas are no more whimsical than any other early vegetable crop from the group of cold-resistant plants. In any case, even a novice summer resident who is addicted to this vegetable bean plant can grow it without problems. Read the recommendations for the technology of planting peas in open ground, with the features of proper care and proper collection for storage, and no difficulties will confuse you.

Pea varieties
Pea varieties are usually divided into 2 directions:
- Peeling (Atlant, Vera, Alpha, Premium, Avola, Voskhod, Viola, Adagumsky, Grasshopper, Early Gribovsky).

- Sugar (Oscar, Candy, Giant, Ambrosia, Bastion, President, Inexhaustible 195, Amicable, Swiss giant, Everest, Senator).

The external difference is that the peeling varieties are usually small bushes, while the sugar ones are quite tall.
Taste differences are that sugar varieties can be eaten with the shells (they are very sweet), while at shelling shells they are not eaten, but the peas themselves are much sweeter. Sugar varieties, for the most part, are grown in order to consume them immediately, while shelling is well suited for storage and preservation.
Pea planting technology in open ground
Sowing dates
Peas are very easy to grow. It tolerates frosts down to minus 5-8 degrees. Therefore, it should be planted as early as possible, as soon as the soil thaws, without even waiting for return frosts, of course, depending on the climatic characteristics of your region of residence. Peas are very fond of water, and the earth is wet at this time, and this just contributes to its better germination.
As for the specific optimal timing for planting peas in open ground, you can start sowing it from the second half of March or from the beginning of April. Accordingly, in the southern regions (in the Krasnodar Territory, in the Kuban) it is possible to plant as early as March, but in colder zones, for example, in the Middle Belt (Moscow Region), the Leningrad Region, in the Urals and in Siberia, it is better to postpone the planting of peas until April. May.
In general, you can plant peas in the garden in several stages, including in early summer and even in July. Of course, these must be early ripening varieties.

According to the lunar calendar in 2018, the following are auspicious days for planting peas in open ground:
- March - 20-23;
- April - 6-9, 19, 20, 23-26;
- May - 7-10, 19-24;
- June - 4-7.
In fact, it is not so scary if you plant peas on other dates, the main thing is not to plant on unfavorable days according to the lunar calendar, and this is in 2018:
- in March - from 1-3, 16, 30;
- in April - from 15-17, 29-30;
- in May - from 14-16, 28-30;
- in June - 12-14, 29.
Processing peas before planting
Before planting peas in open ground, it is recommended to pre-soak and germinate them for earlier germination.
If you are using your own seeds, then it is advisable to process such peas before planting by immersing them in a salt solution (at the rate of 30 grams of salt per 1 liter of water) for five to ten minutes. The seeds that float are most likely affected by the pea weevil, they should be thrown out, and those that sink to the bottom - rinsed with water and then soaked according to the instructions below.

Soaking peas is carried out as follows: pour peas into a deep plate, pour water about 1 cm higher than peas and leave until morning, that is, about 10-12 hours. Until the morning, the peas swell and collect water.Now they need to germinate for earlier germination. To do this, rinse the swollen peas under running water, and then wrap them in gauze or cloth bags and put them in a plastic bag until germination, that is, for about 2 days at a warm (room) temperature. It is advisable to take out the peas 1-2 times a day and rinse them with water so that mucus or decay does not form.
If suddenly the weather is not favorable for sowing, then such peas can be stored in the refrigerator for several weeks, and the sprouts will germinate, but not outgrow.
To disinfect the planting material, you can hold the peas in a weak solution of potassium permanganate for 15 minutes.
Note! There is also pelleted pea seeds, which do not need to be specially prepared or germinated, they have already been processed by the manufacturer, they must be sown immediately into the ground.
Video: soaking peas before planting to accelerate growth
Garden bed and soil
When choosing a place for a garden bed for planting peas in a summer cottage, it is recommended to choose the most sunny and most protected from the wind place.

Good precursors for planting peas are cucumbers, cabbage, potatoes and pumpkin, in other words, beds, where organic matter was previously abundantly applied, and even better - phosphorus-potassium fertilizers.
Note! It is advisable to plant peas in the same place no earlier than after 4-5 years.
Preparing a bed is quite simple: you need to remove all weeds, dig up and loosen all the soil, and then apply fertilizer. However, it is important not to overfeed the soil with fertilizers. When planting, only a little high-quality humus or compost should be introduced into the groove. If the soil is overfed, then you will receive an abundance of green mass to the detriment of the peas themselves.
If you have a heavy (clay) soil that cannot be called fertile, then it is still worth adding a little additional fertilizer to it. On fertile soils, peas are able to produce nitrogen themselves, accumulating it at the tips of their roots, but only after the formation of nodules.
In general, it is believed that the quality of the land for peas is not of fundamental importance. After all, this culture, according to experts of vegetable growers, is almost the best predecessor for absolutely all crops, except, of course, the legumes themselves. That is, if you want to revive or improve the soil, you are still thinking what kind of green manure to plant, then peas are the ideal option. You will not only enrich the soil with nitrogen, but you will also get delicious pea beans.
Landing in the ground
You need to plant peas according to the following scheme: the distance in the aisles is 50-60 centimeters (at least 30 centimeters if you have a lack of space in your summer cottage), between the peas themselves - 4-6 centimeters, the planting depth is up to 3 centimeters, depending on the soil: if it is light, then - 2-3 centimeters, if heavy (clay) - 3-4 centimeters.

Step-by-step instructions for planting sprouted peas in open ground:
- Soak and germinate the planting material. Some growers planted with dry seeds. What to do - every gardener decides on his own through trial and error on his site.
- Prepare the bed and make grooves.
- Place a small layer of humus or compost into the grooves (optional or if you have very poor soil).
- Sow peas according to the recommended pattern. It is not forbidden if you plant the peas in one groove in a checkerboard pattern. With this planting, the peas will support themselves when they grow up.
- Cover with earth and be sure to slightly compact.
- Cover the bed with a covering material, for example, agril, otherwise all your plantings will be raked and pecked by birds.
Video: planting sprouted peas in the ground
Video: planting peas with dry seeds
Outdoor pea care
Important! It is advisable to prepare structures for the garter of future pea shoots immediately after sowing.To do this, you can drive in the pegs and pull the rope, or you can install a special metal mesh. If you do not tie it up, then the wind and rain will simply knock the bushes to the ground, and the yield will decrease.

Video: how to put supports for peas
The first friendly sprouts of peas, as a rule, you will be able to observe in 1-2 weeks.

The most important thing in caring for peas is watering. If you have dry weather, then the plant must be watered often and abundantly, at least once every 5-6 days. After each watering, do not forget to immediately loosen the ground, as well as periodically weed from weeds. Such a procedure will be good for the development of the peas. It is especially important to pay attention to watering during the flowering period and during the beginning of the appearance (setting) of the first fruits.

The most important secret to get large, sweet and soft peas is when the peas begin to bloom, feed them with wood ash (potash fertilizer). The solution can be made in this way: 1 kg of ash (this is about 2 liter cans) for 10 liters of water. You can also use green fertilizer for feeding.
Video: all about growing peas
Pest and disease control
The most vicious pest of peas is the pea moth (leafworm), which lays its eggs right on the green bushes, from which caterpillars then appear, which climb inside the pods and eat the peas. Also, your crops may be attacked by pea aphids.
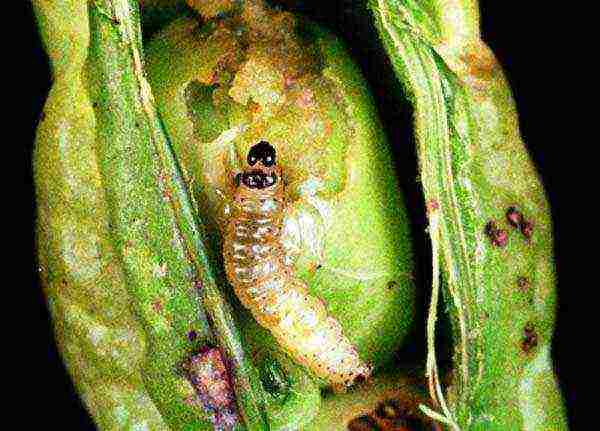

There are several ways to deal with pea pests:
- When planting peas, you can sow white mustard.

- It is also very good to pour a little hot red pepper into the grooves when sowing.
- If the pest has appeared, then it is worth trying to sprinkle the plant with an infusion of tomato tops (at the rate of 3 kg of tops per bucket of water, insist for 1-2 days).
- You can process pea plantings with garlic infusion (at the rate of 20 grams of grated garlic per bucket of water, insist for a day).
Peas collection and storage
It is customary to harvest peas about 2-4 weeks after flowering. The lower pods ripen earlier than the upper ones. The pods are removed every 2-3 days.

By the way! Harvesting on time can even help increase the yield of your peas. On the contrary, if you are late, it will slow down the ripening of the next pods, and the grains themselves will begin to coarse.

You can also leave the peas ripe for seeds. To collect peas for seeds, you should wait until the pods turn yellow, dry out a little and will "ring" in the pod.
Video: when and how to collect pea seeds for subsequent planting
There are several ways to store peas. Freezing and canning is great for this. Although you can just dry it.

Worth knowing! If you want pea grains not to lose their qualities (sugar, amino acids and vitamins), then immediately (within 2-4 hours) after harvesting, they must be dried, preserved or frozen.
It is advisable to store dried peas in glass jars, closed and in dark places. Storage in such conditions will prevent all kinds of worms and insects from appearing in peas.
Thus, if you are "sick" with such a respectable vegetable crop as peas, and strive to learn how to grow it correctly, use the tips and advice on progressive agricultural techniques for planting peas in open ground, collecting them for storage, and they will help even a novice summer resident, do not multiply mistakes, to achieve an exceptional harvest on your site.
Video: briefly about growing peas
Peas in the open field: photo, video, planting, care and harvesting

Peas in the open field: photo, video, planting, care and harvesting. Both adults and children love to feast on peas. It is also grown on an industrial scale, but the most delicious is early sweet green peas right from their garden.This culture is not difficult to care for, but first the peas must be planted correctly and on time.
Do I need to soak peas before planting in open ground
Vegetable peas are divided into two groups - sugar peas and shell peas. In summer cottages, sugar varieties are mainly grown, which do not have a hard parchment layer inside the pods, and the pods themselves are large and tasty, so they can be eaten whole without taking out the pea.
Sugar peas can be eaten with the pods
However, the preparation of any varieties for sowing and the sowing itself are practically the same.
You should not soak and germinate pea seeds before sowing, especially in the case of brain varieties, although many summer residents do this in the hope that soaking will accelerate germination:
- firstly, if it accelerates, then a maximum of a day, besides, when sowing in early spring, peas are still placed in wet ground;
- secondly, what is most terrible, if after sowing the cold returns and the soil temperature drops below +4 ° C, the roots of the peas will die, and the seeds themselves will disappear.
In early spring, sowing peas without soaking is more reliable.
Instead of soaking before sowing, do the following:
- It is better to sort the seeds into large and small ones, as well as discard those infected with pea weevils.
- It is inconvenient to do this manually, so the peas can be held in a solution of table salt (2-3 tablespoons per 1 liter of water) for five minutes, no more. During this time, non-viable and pest-affected peas will emerge.
- After treatment with a saline solution, the seeds must be washed well with clean water and dried to dryness by spreading them out on paper or cloth.
- You can warm up the seeds a little before sowing by placing them for an hour and a half next to the radiator. After such manipulations, the germination of the peas will be more friendly.
Note! At large agricultural enterprises, seeds are treated with formalin, in an effort to prevent the development of diseases, of which there are many in peas. Doing this at home is not worth it.
When is it better to sow peas
The growing season of different varieties of peas is very different, but in summer cottages, early sugar varieties are mainly sown. They are ready for use within a month and a half after sowing or a little later.
In central Russia, it is better to sow early varieties of peas
Focusing on the desired consumption period, it is easy to calculate the sowing date, because peas can be planted very early, as soon as the soil thaws.In central Russia, this time comes around the end, or even in the middle of April.
In the north, peas are sown in May, and in the south, the sooner the better: this crop does not like intense heat and must be harvested before it begins. Therefore, in such regions as Rostov or Astrakhan, peas must be sown in March.
To extend the harvest time, it is better to immediately sow both an early-ripening variety and a medium-ripening variety. And if there is a desire to feast on your favorite variety for a longer time, it is worth sowing it several times, with an interval of one and a half to two weeks.
Soil and air temperature
When sowing peas, one should be guided by the temperature not of the air, but of the soil. Any varieties of peas are extremely cold-resistant, seedlings can withstand severe frosts, but swollen, but not germinated seeds will simply rot at low temperatures in the ground.
Smooth-grain varieties germinate already at a soil temperature of + 1 ° C, and cerebral varieties - not lower than at + 4 ° C. Therefore, the first can be started to sow in open ground immediately after the snow melts, and the second - ten days later.
The last date for sowing peas is the end of June or a little later.
Peas are sown very early, when other plants have not yet woken up after winter.
During the growth of peas for the formation of green mass (stems, leaves), the optimum temperature of the air and soil is 12–16 ºС, of the generative organs (buds, flowers) - slightly higher (16–22 ºС).Too high a temperature during the flowering period, as well as the filling of the pods, has a negative effect on the quantity and quality of the crop.
Choosing a soil for planting peas
Peas are plants that accumulate nitrogen-containing organic matter on their roots and stems. But this does not mean that he is able to feed himself on any soil. On the contrary, he also needs various fertilizers containing, in addition to phosphorus and potassium, nitrogen.
On soils poor in nutrients, and besides, very acidic, it grows poorly - it will give out two or three pods on the plant and dry out prematurely. The best soils for peas are medium loamy and sandy loamy soils. Acidity - close to neutral or, better, slightly acidic. Strongly acidic soils must be calcified in advance by adding dolomite flour, chalk or lime.
It is best to plant peas in the place where tomatoes, pumpkin vegetables, cabbage, and potatoes grew before.
The beds are prepared in the same way as for most vegetables, from autumn, but the best option is when organic fertilizers (well-rotted manure or compost) were applied even earlier, under previous crops.
Note! Manure, especially fresh manure, causes a strong overgrowth of bushes, but at the same time prevents a high-quality harvest.
]
The amount of organic matter is about a bucket per square meter, to which you need to add a half-liter can of wood ash. Superphosphate and potassium salts (20-40 g per 1 m2) are desirable but not required. Peas are very fond of the presence of trace elements in the soil, especially molybdenum and boron, but this issue is solved by the introduction of wood ash.
Ash perfectly saturates the bed for peas with minerals and trace elements
To reduce the risk of disease, this plant cannot be planted on the same garden bed even for two years in a row, it is necessary to alternate with other vegetable crops.
Preparation of beds and planting scheme
A place in the country for sowing peas must be selected dry, open to the sun's rays. At first, it will be mostly cut off by children, so it is better to plant it in the beds located along the paths:
- for early ripening varieties, the ridge can be made no more than half a meter wide, so that children can freely reach the pods on both sides without trampling plantings;
- mid- and late-ripening pea varieties are best placed along the paths in very narrow beds, where you can sow it in 2-3 rows (then it will be easier to fill the bushes on the trellises).
For more convenient harvesting, it is better to plant peas in narrow beds.
Before sowing, transverse grooves are made on wide ridges, and longitudinal shallow grooves on narrow ridges. The distance between them depends on the variety of peas (how tall the bushes will grow), but on average it is from 15 to 30 cm. Seeds are laid out in grooves every 8-10 cm from each other.
What can you plant peas next to?
Peas saturate the soil with nitrogen, which, of course, will benefit any of its neighbors. Therefore, peas can be considered a useful companion for most vegetables. It is often planted simply in the aisles, not even for the sake of the harvest, but as a useful crop.
It is believed that the best neighbors of peas in the beds are cucumbers and carrots. The smell of tomatoes helps fight harmful insects, and corn planted next to it can be an excellent natural support for peas. Another "doctor" that scares the pea moth from planting is mustard. Peas normally coexist with salads, parsley, potatoes and any types of cabbage.
Peas normally coexist with most vegetable crops
But will all the neighbors benefit the peas themselves? Not all, but he does not have very many obvious antagonists. Peas do not like the neighborhood with garlic and onions - excellent healers of garden beds, with their phytoncides scaring away many pests. He does not live very well next to relatives - beans and any varieties of beans.

Peas are a fast growing annual plant.At the dachas, "sugar" varieties are grown, from which you can eat unripe seeds and beans.
Grains and pods of these varieties do not contain coarse fibers, so they can be eaten fresh, canned and frozen.
Features of growing peas
Peas are a cold-resistant crop that tolerates a short-term drop in temperature to -4 ... -6 degrees. Some varieties of Afghan and Chinese origin at the germination stage withstand frost down to -12 degrees.
Any frost is destructive when the plants are in the phase of flowering, filling and green ripeness of beans.
Warmly
The culture is most thermophilic during the period from flowering to full maturation of seeds.
Temperature requirements:
| Phase | Temperature, ° С |
| Seed germination begins | 12 |
| Germination temperature | 25-30 |
| Temperature during stem growth | 12-16 |
| Temperature during flowering, bean formation, grain filling | 15-20 |
Peas prefer light sandy loam and loam, non-acidic, washed by rain, without stagnant water. On acidic moist soils, root nodule bacteria develop poorly, due to which the yield is reduced.
Nodule bacteria are microorganisms that live on the roots of legumes that fix nitrogen from the air.
Light
Peas are light-requiring. With a lack of light, it does not grow, does not bloom. It belongs to long-day plants, that is, it blooms and produces crops only in the middle of summer, when the daylight hours are long.
The rate of seed ripening also depends on the length of the day. In the north, daylight lasts longer in summer than in the south, so it will take less time from sowing to harvesting the first crop.
Peas bloom for 8-40 days, depending on the variety. Ultra-early ripening varieties ripen in 40-45 days, late-ripening in 120-150 days.
Features of culture:
- yield and harvesting time are highly dependent on the weather;
- in a humid cool summer, peas grow, but seed ripening is delayed;
- in a dry, warm summer, the stems grow more slowly, but the grains ripen 2 times faster;
- seeds ripen unevenly - in tall varieties, grains are simultaneously formed in the lower part of the stem and flowers in the upper part of the stem;
- the culture is strongly affected by pests and diseases;
- peas are less demanding on soil and moisture than other legumes - beans, soybeans, beans.
Preparing for landing
Preparatory operations consist of digging up the beds, filling the soil with fertilizers and pre-sowing manipulations with seeds, which increase their germination.
Predecessors
A good precursor to peas is a crop that leaves the soil free of weeds and does not tolerate much phosphorus and potassium.
Suitable predecessors:
- potato;
- sunflower;
- tomatoes;
- carrot;
- beet;
- pumpkins;
- onion.
You can not sow peas after other legumes, cabbage and any cruciferous plants, as well as next to them, since these crops have common pests.
Garden bed preparation
Peas are sown early, so it is better to dig up the soil in the fall, right after harvest. If the peas will be sown in place of potatoes, carrots or beets, the garden will almost not have to be specially dug up. In the spring, you can simply loosen it with a rake. Loosening will allow you to retain moisture in the soil and achieve a level surface, which is important for the uniformity of planting grains.
If the seeds are planted at different depths, the plants in the same bed will develop unevenly, making harvesting difficult.
Seed treatment
Peas are a self-pollinating plant. It does not need pollinating insects or wind to set seeds. Seeds of high-quality peas can be harvested and sown next year - they will retain all the characteristics of the parent plant.
Pea grains remain viable for a long time. Even after 10 years, half of the seeds will sprout.
The seeds are soaked according to the instructions for the preparation in any complex micronutrient fertilizer. Suitable "Green Lift", "Aquamix", "Aquadon", "Glycerol". In addition to micronutrient fertilizers, a little potassium permanganate or Maxim is added to the solution so that the grains are cleared of the spores on their surface.
If peas are sown on a site where legumes have never grown before, on the day of sowing, the seeds are treated with "Nitragin". This preparation contains spores of beneficial nodule bacteria. "Nitragin" increases the yield of peas by 2-4 times. The drug is useless if the peas will grow in dry conditions.
Planting peas
The culture is sown early, since its seedlings are insensitive to frost. Summer residents of the middle lane sow peas in late April-early May, as soon as the soil dries out. Sowing early saves plants from fungal diseases and summer drought. A 10-20 day delay in sowing reduces the pea yield by almost half.
Seeds are sown in rows in one or two lines with a row spacing of 15 cm. The seeding depth is 6-8 cm. The seeds are placed in the grooves evenly every 8-12 cm and covered with soil. Then the surface of the bed is compacted to ensure better contact of the seeds with the soil and pull them into the water from the lower layers. After that, the bed can be mulched with peat.
Peas are difficult to weed, so do not sow them on a clogged garden bed. It is best not to grow peas in a mixture with other crops, as clean crops yield the highest yields.
Peas can be grown in any soil. Medium nutrient content is most suitable. On humus-rich humus soils, peas do not ripen for a long time and are strongly affected by aphids. It is more profitable to take such beds for more demanding vegetables, for example, cabbage.
The culture loves phosphorus-potash fertilizers and lime. On lean sandy soils, yields will be low.
On acidic soil, lime must be added. If the acidity is 5.0 and below, the dose of fluff is up to a kilogram per square meter, and on heavy soils - up to 1.2 kg per square meter. It is better to lime the soil under the predecessor, but if you apply lime directly under the peas, there will be no significant harm.
Winter sowing
In the southern regions of Russia and the North Caucasus, peas are sown in winter. It overwinters well in the soil and gives a stable harvest of grain and green mass in the spring. Overwintered plants grow slowly in spring and do not lay fruiting organs until weather conditions become more favorable.
Peas do not have winter varieties. For sowing before winter, there is no need to look for special "winter forms". Normal varieties that can tolerate cold during the first phase of growth are suitable.
Wintering pea varieties:
- Neptune;
- Satellite;
- Phaeton;
- Seamus, Focus - varieties with a "baleen" type of leaf, resistant to lodging, can be grown without support;
- Legion - "two-handed", suitable for autumn and spring sowing, non-sprinkling.
Pea care
Plant care consists in weeding and timely installation of supports. Supports are installed as soon as the stems reach a height of 10 cm. Not all varieties need support. There are undersized standard varieties that are grown without trellises.
Weeding
The main technique in the care of crops is weeding. The pea bed must be kept in a weed-free state, which is not easy, since the plants intertwine, forming dense thickets from the ground, in which the weeds feel at ease.
On unweed beds, the yield is greatly reduced, since peas cannot compete with weeds. In addition, weed beds suffer from diseases and are damaged by pests.
Pest control
If you plan to use herbicides, be aware that peas are sensitive. Spraying must be carried out in strict compliance with the dosages indicated in the instructions, making sure that the herbicide does not fall into the same place twice. It is better to apply soil herbicides under the peas.
So that the plantings suffer less from diseases and pests, they are returned to their original place no earlier than after 3-4 years.
The main method of protecting peas from diseases is dressing the seeds two weeks before sowing with Maxim. The substance is a contact fungicide, available in ampoules and vials."Maxim" protects peas from fungal diseases.
To prepare a working solution, 10 ml of the drug is diluted in 5 liters of water. A liter of working solution is consumed per kilogram of planting material.
In addition to peas, you can soak potatoes, bulbs, tubers, flower bulbs and seeds of any vegetables in Maxim.
For the destruction of insects on crops, permitted preparations are used: "Karbofos", "Fury", "Karate", "Decis".
Watering
Peas need moderate watering. During the planting season, you will have to water at least 3 times.
When the beans are poured, the plants become especially susceptible to drought. It is very important that the soil is moist during budding, flowering and fruit formation. In dry summers, the plants ripen quickly, but some of the seeds remain underdeveloped, and the overall yield decreases.
Varieties with wide leaves are less drought-resistant than narrow-leaved varieties.
The peas are hosed over the soil. Do not use sprinklers, as diseases spread faster on wet leaves.
Fertilizers
Peas can use mineral fertilizers only at normal soil moisture. In dry soil, even with sufficient nutrient content, the yield decreases as mineral compounds become unavailable.
Organic fertilizers can only be applied under the previous crop. You can not bring fresh manure under the peas - the plants will develop powerful stems and leaves, but almost no beans will be tied. Peas will grow thin, the growing season will lengthen. In the same way as fresh manure, high doses of mineral nitrogen act.
Peas tolerate a lot of potassium. To compensate for the damage to the soil, it is necessary to apply so much potash fertilizers to the garden before sowing so that at least 30 grams returns for each square meter. pure potassium.
Phosphorus is required a little less - 10-20 grams. in terms of pure substance. The roots of peas have a great dissolving power, therefore, from phosphorus fertilizers, phosphorite flour gives a greater effect.
Phosphorus-potassium fertilizers are best applied in the fall. The exception is sandy and acidic soils. It is better to fertilize them in early spring, as they are heavily washed out by melt water.
The need for micronutrient fertilizers:
- The most essential micronutrient for peas is ammonium molybdate. The seeds are soaked in a dosage of 0.3 g of fertilizer per 100 g of seeds.
- On neutral soils, molybdenum fertilizers are not required, but the role of boron increases. Boron is introduced at sowing in the form of boric acid. A teaspoon of powder is poured onto 2 running meters of a row. To save money, it is better to apply fertilizer not to the whole garden, but to the row.
- If high doses of phosphorus have to be applied to the soil, zinc fertilizers become necessary. The seeds are treated with zinc sulfate at a dose of 0.3 g per 100 g of seeds.
- On alkaline soils with a Ph above 6.5, foliar fertilization with manganese will be required.
Peas react to foliar feeding with complex fertilizers. The procedure can be performed up to 3 times per season. Fertilizers include nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and sulfur. Foliar dressing gives an increase in yield by more than 20%.
Do not use only foliar feeding. The fact is that fertilizers that fall on the leaves will nourish the leaf plates, and the compounds absorbed by the roots from the soil evenly enter the entire plant, including the beans, and contribute to an increase in yield.
Pea fertilization rules:
- on neutral soils, phosphorus-potassium fertilizers are applied. They give a yield increase of 25-30%.
- on neutral soil, the introduction of boric, cobalt, copper and zinc micronutrients is effective, which are used when soaking seeds before sowing or in the form of foliar dressing on leaves.
- on acidic soils, where there was no liming, add urea in a dose of a tablespoon per running meter of a row. By applying more nitrogen, the yield will not increase as the plants will develop strong stems to the detriment of seed formation.
- of trace elements, molybdenum and zinc give good yield increases.
- during the formation and filling of beans, foliar dressing is carried out with complex fertilizer, which significantly increases the yield.
When to harvest
The paddles and grain are harvested as they form. The first crop ripens at the bottom of the bush.
In favorable conditions, up to 4 kg of green peas can be removed from a square meter of pea beds. Using different varieties, you can provide yourself with fresh produce within 25-40 days.
The blades are removed every day or every other day, starting the harvest in mid-June. If you do not allow the shoulder blades to set seeds, peas can re-harvest in August.
Cultivars grown for green peas should be harvested while the surface of the pods is still smooth and uniformly colored. As soon as the mesh forms, the seeds will become unsuitable for conservation. Green peas should be immediately canned or frozen until sugar begins to break down.

Is there a place for a small garden on your site? Then plant sweet peas. It does not require much space, it can even be dropped along the fence. And the fresh fruits of this plant are very fond of children, moreover, peas will help to complement many dishes for adults.
Today we'll talk about how to grow a vegetable garden in the country in the open field and consider the agricultural technology of this tasty and healthy crop.
Pea cultivation technology features
Peas are herbaceous plants of the legume family. A cute curly annual will decorate your garden during the flowering period, and when the time of fruiting comes, it will provide a sweet, juicy product rich in vitamins and nutrients.
Despite the apparent simplicity, peas are a rather finicky plant. But growing it can be pretty easy if you follow certain rules.
Properly prepared soil is the key to a good harvest
First of all, peas should be sown in the spring, when the soil has already warmed up sufficiently. The best time for planting is the second half of April and early May.
Since the roots of peas grow deep into the soil, the soil must first be dug up. It is good if you do this in the fall, while simultaneously applying complex fertilizers.
Nutrient-poor, too hot soil will not produce a good, succulent crop. But in addition, you still need to decide on the varieties and classification of the type of peas. It can be garden or pod, round, wrinkled, tall, dwarf. There are superearly, mid-early and basic varieties.
Pea agrotechnology can be imagined as follows:
- time from the moment of sowing to the appearance of the first shoots - 5-8 days;
- the likely yield from a row of 3 running meters is about 5 kg;
- the estimated time from sowing before winter to harvest is 32 weeks;
- estimated time from spring sowing to harvest is 12 weeks;
- cultivation and care are complicated.
Do not plant peas in cold soil with high moisture and low fertility. As it grows, the crop will require protection from birds and spraying from insects and diseases if necessary. Pea care will include combating weeds, regular watering, top dressing and loosening the soil.
Preparing soil and seeds for sowing
Peas love warmth and good lighting, so for planting you need to choose a quiet, windless and warming area. Do not get too carried away with fertilizing the soil, it can harm the plantings, "burn" the roots of the plant.
It is enough to add a little organic and mineral fertilizers. Soil treatment with lime, about 250 g / m2 and additional application of 20 g of double superphosphate and 30 g of potassium will have a good effect on germination and subsequent harvest.
Prepare your seeds correctly before planting
It is very important to get the correct seed placement during sowing.For example, in heavy, clayey soil, peas are grown closer to the surface, and in light soil, they are planted much deeper.
- Before starting planting work, carefully sort out the seeds, throwing away spoiled and broken ones.
- Warm good seeds a little and soak for 10 minutes in a solution of boric acid. The ratio of the solution is 1 g of acid per 5 liters of water. You need to plant seeds after they swell a little and dry out.
- You can use special growth stimulants for processing. But is it worth it to spend if you can prepare seeds at home with the help of improvised means to achieve a good result?
Planting in open ground, selection of varieties
Sow peas in mid-spring when the soil is already well warmed up by the spring sun. At the same time, observe the sowing density: undersized varieties should be planted denser, and tall ones less often.
Prepare a seedbed. Make several furrows, each 5-7 cm deep, at a distance of 50-60 cm from each other. It is advisable to prepare the furrows a few days before sowing, after adding a mixture of ash and compost to them, sprinkling it with earth from the garden. After that, the depth of the grooves will be up to 5 cm. Remember the peculiarities of the soil composition, which we talked about above.
Be sure to provide props for the peas in advance
For each meter of the groove, 15-17 peas should be sown, that is, 1 piece approximately every 6 cm. The soil of the bed must be well moistened before planting the peas. Sprinkle soil over the crops and tamp lightly to retain moisture. After a maximum of 2 weeks, you will already see young shoots.
If you want to harvest your peas at different times, choose a variety that suits your needs. Both landing and leaving in this case have a number of some differences.
Sow peas in mid-March for a harvest in June and July. Smooth-grain and very early wrinkled varieties, such as Kelvedon Wonder or Early Onward, are well suited for this. They are more resistant to cold weather.
Planting in April and May will yield a crop in August. Wrinkled varieties of the main crop work well. If you are growing tall pea varieties, pay attention to the spacing6 between the rows. For example, the popular Alderman would require a distance of about 2 meters. If space is limited, select the Senator variety.
To harvest in early fall, September and October, sow ultra-early wrinkled peas in June or July.
Pea Care Tips and Harvesting
Now you have to take care of the peas. It needs to be taken very seriously if you want a healthy, bountiful harvest.
Young pea shoots especially need protection
- First of all, protect crops from birds immediately after planting. Stretch a fine mesh or film over the bed, securing it at a height of 10-15 cm so that the birds cannot get inside.
- Loosen the soil around them 2 weeks after sprouting. You can even carry out hilling if the seedlings are already sufficiently entrenched and have grown well.
- When the plant reaches 8-10 cm in length, feed it. After that, you can feed the peas no more than once every 2 weeks, and then if necessary. But watering is needed regularly, especially during the hot dry season.
- During the growing period, it is very important not to flood the peas, as the root system can rot. But during flowering and fruit formation, watering should be more thorough, at the rate of 1 bucket of water per 1 sq. beds.
- It is very important to properly secure the pea garter, and this must be done before the flowering period. Install the pegs every one and a half meters and run a rope or wire horizontally along them in several rows. Thus, the plant will not lie on the ground, it will be well ventilated and warm.
- After the plant has faded, young peas can be tasted in 2 weeks. Tear off the pods very carefully.
- The daily collection of ripe peas will help you to increase the yield. In this case, overripe and dried pods must be removed.
- You can completely remove the plant from the garden when the lower pods are ripe and dry. Cut the plant, collect in several bunches and hang in a dry, dark room, where the peas finally ripen.
Ways to control pests and diseases
When growing peas, it is very important to prevent the effects of diseases and pests that can ruin both young shoots and the future harvest.
Among insect pests, the most common are:
- weevil;
- aphid;
- moth;
- pea weevil.
The nodule weevil is especially dangerous for young shoots. It eats leaves, cotyledons and apical point of growth. The larvae that emerged from the eggs feed on the nodules on the roots. To combat the weevil, seedlings need to be pollinated with DDT dust 12% (1.5 g per 1 sq.m.) or hexochlorane dust 12% (1 g per 1 sq.m.). sometimes pollination needs to be repeated.
Pea aphid is the largest of the aphids. Winters on perennial legumes. It develops well in humid warm weather. It settles at the beginning of the flowering period on the tops of the stems, sucks the sap from the plant and covers it with a sticky layer. From this, the flowers and ovaries crumble, and the stems wither.
Spraying with a solution of anabazine sulfate and a soap emulsion (15 g of anabazine sulfate and 40 g of soap per 10 liters of water) or anabazine sulfate and thiophos (10 g of anabazine sulfate and 5 g of thiophos per 10 liters of water) will help to cope with aphids. Solution consumption 60-70 cm3 per 1 m2. Dusting crops with 12% hexachlorane dust (1.8-2 g per 1 m2) or spraying with a soap solution (250-300 g of soap per 10 liters of water) is also used.
The moth moth lays eggs on the plant during its flowering period. The larvae emerging from them penetrate into the pod and damage the peas. Early sowing, timely loosening of the soil, as well as spraying with hexachlorane dust (1.5-2 g per 1 m2) will help to get rid of it.
]
Pea weevil larvae also harm the pods. To avoid this, spray the crops with hexachlorane dust 12% (2 g per 1 sq. M.) The first time at the beginning of flowering, and the second time after 8-10 days.
To get a good harvest of peas, eliminate pests and diseases in a timely manner.
The most common diseases are ascochitis, rust and bacteriosis.
To avoid infection with ascochitis, plant only healthy seeds and provide the sprouts with good, tall supports. Pickle seeds 2-3 weeks before planting with granosan (3-5 grams per 1 kg of seeds).
Rust more often affects late varieties of peas. Bordeaux liquid 1% helps from its development. Perform the first spraying as soon as you notice signs of illness, the second after 10 days.
Bacteriosis can develop on any part of the plant, and humid weather contributes well to this. Thorough autumn tillage and seed dressing with granosan will help to save peas from it.
Know the enemies of your crop by sight!
Video about growing peas in the country
Peas are good not only fresh, they can be prepared for the winter for cooking various dishes. We hope that our tips will help you grow this wonderful crop on your site. If you have any experience and secrets of growing, share with us in the comments. Good luck!
Source

The green pods, densely packed with juicy and sweet peas, are always eye-catching and appetizing. Knowing how to plant peas, you can enjoy your favorite treat since childhood, plucked straight from the beds.
Even the lack of a land plot will not be a problem. The culture is able to grow and bear fruit at home: on a windowsill, a glazed loggia or a balcony.
The technology of its cultivation is quite simple, but it is still necessary to provide some conditions for its bushes.
Soil and lighting
Peas are an unpretentious plant.Due to the minimum requirements of the crop for the quality, structure and type of soil, it can be successfully cultivated in almost any vegetable garden.
Only soils with a high level of acidity and those that contain a lot of salts are contraindicated for peas. It is sown in such land only after preliminary liming.
The correct technology for growing a crop, leading to its high yield, provides for compliance with crop rotation.
Peas develop well in areas where last season were placed:
- cucumbers;
- tomatoes;
- pumpkins;
- cabbage;
- potato;
- perennial cereals or forage grasses.
The worst predecessors for him will be plants from the legume family. From the moment of their harvesting, 4 years should pass, only then it will be possible to sow peas on this place.
Fertile loose soils of loamy or sandy loam type are preferred for culture. But even in not very nutritious soil, growing peas will bear fruit if you put a little effort and prepare it for planting.
This is done during the autumn digging, before which superphosphate is scattered over the site.
By the time sowing begins, the fertilizer has been distributed in the soil and decomposed into compounds that will be easily absorbed by the pea roots.
It is permissible to postpone the preparation of the site and in the spring. But in this case, it is better to enrich the soil with organic compounds:
- humus;
- rotted manure;
- mullein;
- infusion of bird droppings.
Experienced gardeners advise in the spring, during sowing, to fertilize the beds with mineral preparations, which include trace elements: copper, boron, molybdenum. You can also soak the peas in their solution before placing them in the soil.
The roots of the plant are powerful, their length reaches 1 m.Therefore, when cultivating a culture on the balcony, planting is correctly carried out in deep pots. If the groundwater is close to the surface of the site, growing peas on it will be difficult.
We'll have to build high ridges for him.
For plantings to bring a good harvest, they need a lot of light. In dense shade, both on the street and on the balcony, the peas will wither away, so it is better to choose the sunniest place for it. The beds can be made separate or mixed. In the first case, it will be more convenient to place them along the garden paths.
This will make harvesting easier. When organizing mixed beds, it is important to remember that peas should not be planted next to other legumes, as well as with onions, cabbage, tomatoes, potatoes. Many summer residents prefer to sow it near the walls of various buildings or fences.
With this method of placing the peas, there will be no need to worry about the supports.
Sowing time
The timing of planting crops in open ground depends on the climate of the area and on when it is planned to harvest. The earliest sowing is carried out in the second half of April. By this time, in most regions, the snow has already melted, and the earth dries out and warms up.
Pea seedlings are not afraid of cold weather. They can easily tolerate spring frosts if the temperature does not drop below -6 ° C. In order for the pea pods to ripen in June or early July, the seeds are sown again after 15-20 days.
And if you carry out the third planting in the last days of May, you can feast on juicy fruits in the middle of summer.
Peas can be grown in any soil. Medium nutrient content is most suitable. On humus-rich humus soils, peas do not ripen for a long time and are strongly affected by aphids. It is more profitable to allocate such beds for more demanding vegetables, for example, cabbage.
It is advisable to germinate the seeds before placing them in the ground. They are placed in a cloth, and the resulting bundle is placed in water. After a couple of hours, they take it out and leave the peas to peck. For this they need from 3 to 5 days. As it dries, the fabric is moistened.
Some gardeners prefer to soak their seeds with room temperature water. It must completely cover them.Planting material is kept in liquid for 12-18 hours. The water is often changed (every 2-3 hours).
Peas can be grown in any soil. Medium nutrient content is most suitable. On humus-rich humus soils, peas do not ripen for a long time and are strongly affected by aphids. It is more profitable to allocate such beds for more demanding vegetables, for example, cabbage.
Dry planting material is also used. But the result will be better if you prepare it first. The technology is very simple. Only two components are needed for seed treatment:
- boric acid;
- water heated to 40 ° C.
The peas are dipped into the prepared solution and kept in it for 5 minutes. This procedure is a good prophylaxis against the root weevil, whose larvae often damage delicate seedlings in spring. If the seeds did not germinate, they need to be planted in moist soil. Then young shoots will appear from the soil in a week. Dried earth will need to be thoroughly moistened.
Landing features
The seeding pattern depends on how the peas are planted - in rows or along fences. In the first case, the seeds are laid out at intervals of 5-7 cm. The optimal row spacing is 15-20 cm.
If the peas will grow near the fence, it is better to plant them in 2 rows. 10-12 cm of free space is left between them. The seeds are placed in the ground at a distance of 5 cm from each other.
The planting depth should not be great; it is enough to cover the peas with a 2–2.5 cm layer of soil.
Sowing is completed by mulching the beds. A layer of compost or dry foliage will protect the seedlings that have not yet matured from pests and retain moisture in the soil, which is necessary for seed germination. Supports for pea bushes are best installed in the spring.
Its lashes develop rapidly, and if they have nothing to cling to, the plantings will turn into a continuous carpet that cannot be untangled without damaging the shoots, or they will entwine neighboring plants.
They don't need too high supports, meter ones are enough.
You can grow peas on a heated balcony all year round. They plant it not only for the sake of the fruit. The tops of young plants are rich in vitamins and are added to salads. To get it, it is better to purchase seeds of low-growing varieties of culture, their greens are more juicy.
Peas can be grown in any soil. Medium nutrient content is most suitable. On humus-rich humus soils, peas do not ripen for a long time and are strongly affected by aphids. It is more profitable to allocate such beds for more demanding vegetables, for example, cabbage.
After a while, young and juicy shoots will appear on it.
Fundamentals of agricultural technology
Growing peas in the country is a fascinating and not at all complicated process. After landing, you need to take care of it minimally:
- weed;
- watering;
- loosen;
- protect from pests.
Young pea shoots are a delicacy for birds. You can protect the planting from ruin by them if you cover the beds with a fishing net. Peas do not like heat.
If the summer is dry, the plantings will have to be moistened often and abundantly. It is correct to spend 9-10 liters of water on 1 m² of the surface of the garden.
Simultaneously with watering, fertilizing is carried out, diluting 1 tbsp in the specified volume of liquid. l. nitroammophos. After moistening the planting, the soil is mulched.
Peas can be grown in any soil. Medium nutrient content is most suitable. On humus-rich humus soils, peas do not ripen for a long time and are strongly affected by aphids. It is more profitable to allocate such beds for more demanding vegetables, for example, cabbage.
The soil under them is periodically loosened, preventing the formation of a crust, and the bushes can also be hilled. In dense soil, their growth and development slow down. When cultivating peas on the balcony, loosening is also indispensable.
It will be correct to carry them out after each watering.
On any site, peas, planting and caring for which will allow you to harvest a useful crop, will have to be in place. It is unpretentious and grows quickly.While other vegetable crops are just forming ovaries, its ripe pods are already delighting adults and children with their sweet seeds. After the peas, you can plant any plants; on nitrogen-enriched soil, they will be powerful and bear many fruits.
The technology of its cultivation has been known to mankind since ancient times. They will benefit from planting even when the last pods are collected from them. Having cut the tops of peas, they send it to compost, and the roots extracted from the ground are finely chopped and buried. This is how a natural and effective fertilizer is obtained, which also improves the structure of the soil.

Growing peas from seeds is not difficult, in some ways even pleasant. Despite the increased requirements for care and maintenance, the technology of this process is not sophisticated.
The first step is to take care of the composition of the soil.
When planting sprouted peas in the ground on the site, you should evaluate how hot it will be in the beds - peas do not tolerate heat, preferring a warm, but shaded place.
Soil and seed preparation
Preparing the soil for both germinating seeds and planting on the site is a very important stage. It is best to fertilize the soil with lime, potassium and double superphosphate. How much fertilizer do you need? Take 5-7 g of each per 1 square meter. meter. The application of organic fertilizers should be carried out in late autumn when digging a site.
Keep in mind that the root system of peas grows deep enough; care should be taken not to be damaged by insects, for example, a bear or yourself when loosening the earth.
Planting peas is best after cucumbers, pumpkins, potatoes or cabbage. At the same time, after green peas, absolutely any crops can be planted - they will automatically receive nitrogen-rich soil for rapid growth.
Initially, the seed preparation technology consists in the selection of peas. Throw away spoiled, broken, too small peas - nothing good will grow out of them.
Heat quality material in the oven (temperature should be 40-50 ° C) for 2-3 minutes. Dilute 1 g of boric acid in 5 liters of warm water, place in the pea solution for 6-8 minutes.
Peas can be grown in any soil. Medium nutrient content is most suitable. On humus-rich humus soils, peas do not ripen for a long time and are strongly affected by aphids. It is more profitable to allocate such beds for more demanding vegetables, for example, cabbage.
Another option for preparing seeds is sprouting peas. To do this, preheated seeds are wrapped in a damp cloth moistened with a solution of boric acid or potassium permanganate.
Seed pretreatment helps plants more easily resist disease and insect pests.
Sowing
Wait for stable warm weather, when the temperature does not drop below + 12-14 ° C, and the soil is warmed up enough so that the seeds and sprouts of peas do not die from the cold. For example, the planting of green peas in Ukraine begins in mid-April.
Form furrows 6-7 cm deep on the bed so that the distance between them is about 45-50 cm. About a week before planting, place rotted manure in the furrows, mixing it with wood ash so that the depth of the bed becomes 34 cm.
When growing undersized peas, 40-50 peas per 1 square meter are placed in the furrows. meter. If you chose a tall variety, then reduce the number of peas to 18-20 pieces. Sprinkle soil over the beds, water liberally, and then cover with foil.
Peas can be grown in any soil. Medium nutrient content is most suitable. On humus-rich humus soils, peas do not ripen for a long time and are strongly affected by aphids. It is more profitable to take such beds for more demanding vegetables, for example, cabbage.
Fill the boxes with loose, fertilized soil, place the peas in it, deepening by 3 cm and keeping the gaps of 5 cm.In the first two weeks, you can feed the peas with a nitrogen solution. The rest of the time, peas grow well with moderate watering and a sufficient amount of light and heat. Equipment that will be needed during cultivation - net or ropes to tie the peas.
Video "About the benefits and cultivation of peas"
This video is about the beneficial properties of peas, as well as how to grow a crop on your land.
Care
You need to take care of the peas from the first minutes of planting in the ground and do it right. The technology is simple: cover the beds or container with plastic wrap to create a greenhouse effect.
A stable temperature is very important for the peas. So the plant will quickly grow, actively increasing the green mass. Prepare a grid or posts ahead of time; pea shoots will need to be tied to them. This way, you will prevent the plant from rotting and tangling of the shoots.
From the very first days, keep the beds covered with a loose cloth or film, then cover the tied bushes with it, so as not to attract birds who like to feast on peas.
Peas can be grown in any soil. Medium nutrient content is most suitable. On humus-rich humus soils, peas do not ripen for a long time and are strongly affected by aphids. It is more profitable to take such beds for more demanding vegetables, for example, cabbage.
It is best to use a mixture of potassium and phosphorus to enhance vegetative processes in stems and leaves. If the summer is dry, you can use a yeast solution that will help the plant not only actively develop, but also cope with the high air temperature.
As soon as the first blades are formed, this usually happens one and a half to two weeks after flowering, they need to be cut off. The fact is that the longer they stay on the bush, the less new ovaries will form. Tear off the pods carefully, holding the shoots and being careful not to take away the live part of the peas.
Carefully make sure that there are no weeds in the beds - they clog the soil and prevent the roots of green peas from eating normally. Moreover, weeds are very often home to harmful insects and pathogens.
Disease and pest control
How many plants - so many diseases. Green peas are susceptible to many diseases, and also often become a delicacy for a variety of insects. Therefore, before growing it on your site, you should learn how to protect or cure the plant.
Great harm to plantings is caused by the pea moth. Small caterpillars easily survive the winter cold, and then turn into butterflies, laying a large number of eggs on the lower part of the plant's leaves.
The cycle repeats annually, especially if you are not following the crop rotation or removing residues from the beds. The favorite plants of the moth are mid-ripening and late-ripening pea varieties.
Peas can be grown in any soil. Medium nutrient content is most suitable. On humus-rich humus soils, peas do not ripen for a long time and are strongly affected by aphids. It is more profitable to take such beds for more demanding vegetables, for example, cabbage.
To combat the pea moth, insecticides are used, which are used to treat the soil in autumn. In the spring, the beds are sprayed with infusion of tobacco, burdock and celandine.
Another pest is the pea weevil. The insect lives in the seeds, gnawing at itself a cozy rookery inside the pea. It is quite easy to determine which seeds are spoiled: soak the peas in a strong salty solution, mixing 30 g of salt with 1 liter of water. Floated peas - are struck by a weevil, they need to be thrown away, and those that have settled to the bottom - rinse, dry and prepare for planting.
Pea cyst nematode leads to slower growth of peas, a general slowdown of vegetative processes.In a sick plant, the leaves turn yellow and fall off, the roots develop poorly and wither.
Peas can be grown in any soil. Medium nutrient content is most suitable. On humus-rich humus soils, peas do not ripen for a long time and are strongly affected by aphids. It is more profitable to allocate such beds for more demanding vegetables, for example, cabbage.
To combat the nematode, insecticides, soap solution, infusion of tobacco ash and wood ash are used. It is important to tie the peas as soon as they reach 14-15 cm in length.
Among the pathogens to which green peas are susceptible, the most to be feared are downy mildew, gray and root rot, olive mold, mosaic.
Downy mildew is one of the most common fungal diseases in plants.
Peas can be grown in any soil. Medium nutrient content is most suitable. On humus-rich humus soils, peas do not ripen for a long time and are strongly affected by aphids. It is more profitable to allocate such beds for more demanding vegetables, for example, cabbage.
To cope with downy mildew, it is necessary to remove the infected parts of the plant (or the entire plant), treat it with fungicidal preparations, for example, Topsin-M. It is worth using a soap and yeast solution.
Gray rot affects the entire plant, covering them with dark green spots, on which a gray bloom develops, and then black spots. Over time, the affected parts of the peas dry out, acquiring a brown color.
Dry weather contributes to the spread, and high humidity and watering with cold water contribute to active reproduction.
To prepare a working solution, 10 ml of the drug is diluted in 5 liters of water. A liter of working solution is consumed per kilogram of planting material.
The disease of root rot leads to the fact that the leaves of the peas turn yellow, within a few days they curl up into a tube and die off. The vegetative processes in the plant slow down, it withers and, if untreated, dies. With high humidity, yellow spots on the leaves are covered with a pale pink bloom. It is necessary to treat root rot with the preparations "Zircon" and "Fitosporin".
When infected with olive mold, the peas become covered with a dark olive-brown bloom. Very often, the disease enters the plant, forming black ulcers throughout the stem. For treatment, a solution of Bordeaux liquid is used, as well as the drug "Zircon".
Ordinary mosaic appear mainly on pea leaves - light streaks form, from which yellow spots "spread" soon. Leaves stretch in length, vegetative processes slow down. For treatment on the site, a solution of Bordeaux liquid is used, as well as the fungicidal preparation "Topsin-M".
Video "Pests of peas"
This video shows what pests can be found on pea plantings and how much harm they cause.


