Content
- 0.1 Varieties
- 0.2 Aquatic plant
- 0.3 Rice countries
- 0.4 Land for landing
- 0.5 Cleaning
- 0.6 Video
- 0.7 Author of the publication
- 1 Indian sea rice - what is it?
- 2 Indian sea rice - composition
- 3 Indian sea rice - benefits and harms
- 4 What does sea rice cure?
- 5 Indian sea rice - cooking
- 6 Sea rice - application
- 7 Name
- 8 Botanical description
- 9 Spreading
- 10 Economic value and application
- 11 Classification and types of rice
- 12 Rice cultivation
- 13 Yield
- 14 Pests and diseases
- 15 Genetics
- 16 Research on cooking methods
- 17 see also
- 18 Notes (edit)
- 19 Literature
- 20 Links
From early childhood, people eat a food such as rice. But if, for example, we know almost everything about potatoes, then how does rice grow, what varieties are there and in which countries is it cultivated?

Varieties
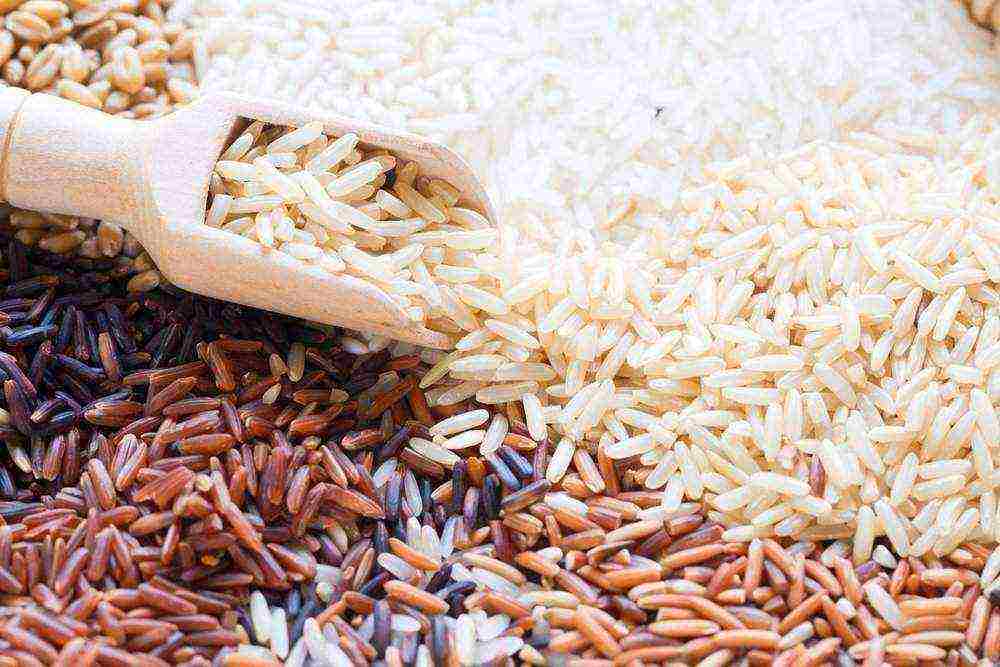
More than 20 types of rice are offered for sale: various varieties and degrees of processing. There are very cheap and quite expensive ones, but low price does not mean poor quality. Also, rice varies in color: from very white to black, brown rice and red - this depends on the cleaning of the shell of the grains. The darker the color, the more natural the product is and the more useful substances are stored in it.
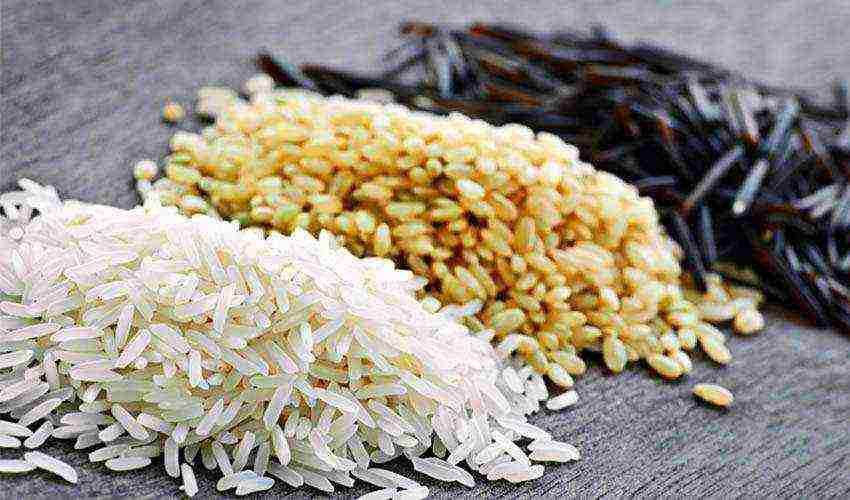

Also, grains are distinguished by their shape: round, medium and long grain. Wild rice is very interesting - marsh grass, up to 3 m high, akin to ordinary white. It is quite expensive as it is difficult to assemble and process. And such a "savage" grows in the North of America and in East Asia.

Aquatic plant
Why does rice grow in water? Plants are grown in the fields, which are completely filled with water and do not allow it to flow out until the cereals are fully ripe. Why do they need so much water all the time? It turns out that in this way, rice growers fight weeds, which greatly reduce the yield. And for the rice itself, such an amount of water is not at all a burden - it is hygrophilous.
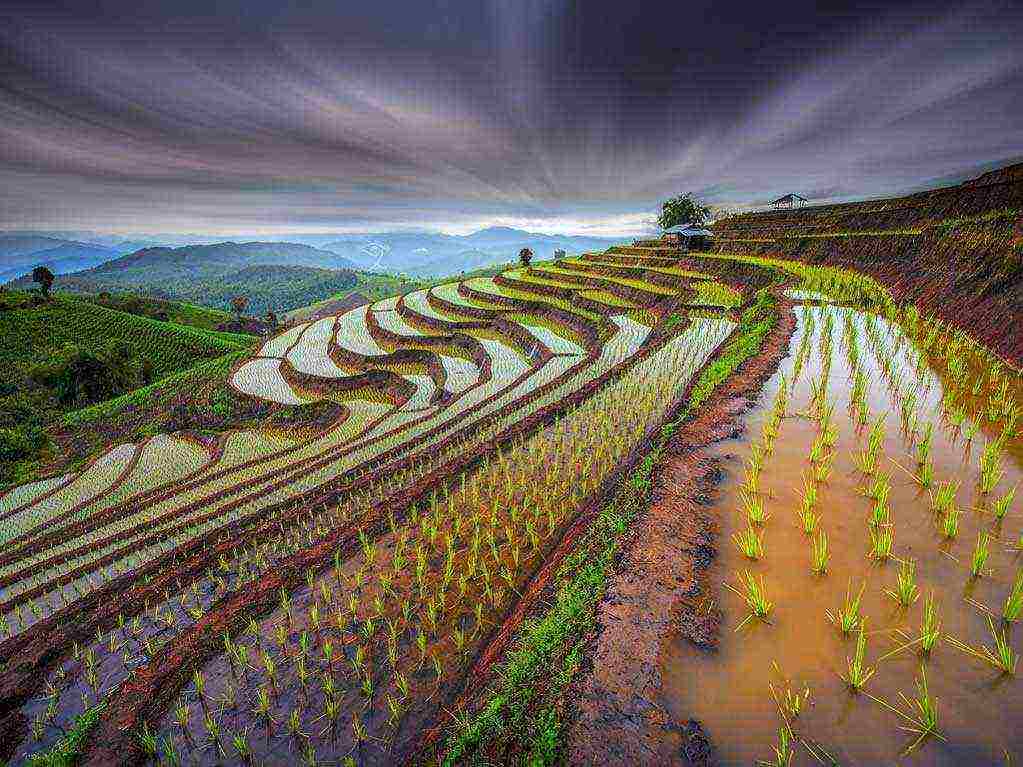

Plants are grown in plain fields and mountain terraces. By the way, in the mountains, such plantings look very beautiful - a photo of rice fields in a mountainous area. In countries where there is a lot of precipitation, grain is not grown in flooded areas.

What rice looks like when it grows not to everyone's liking. First, of course, fields of a beautiful green color, and during the ripening period of a dark brown hue. The rest of the time, in swampy places, bunches of plants of different heights stick out of the water. In some countries, rice is planted with seedlings, in others with seeds.
Rice countries
In which countries are these plants mainly cultivated?
- A lot of plantings are in China - almost 140 million tons are harvested every year from the fields of this country.
- It is followed by India, Indonesia, Vietnam.
- Rice is grown in the fields of South America and Australia.
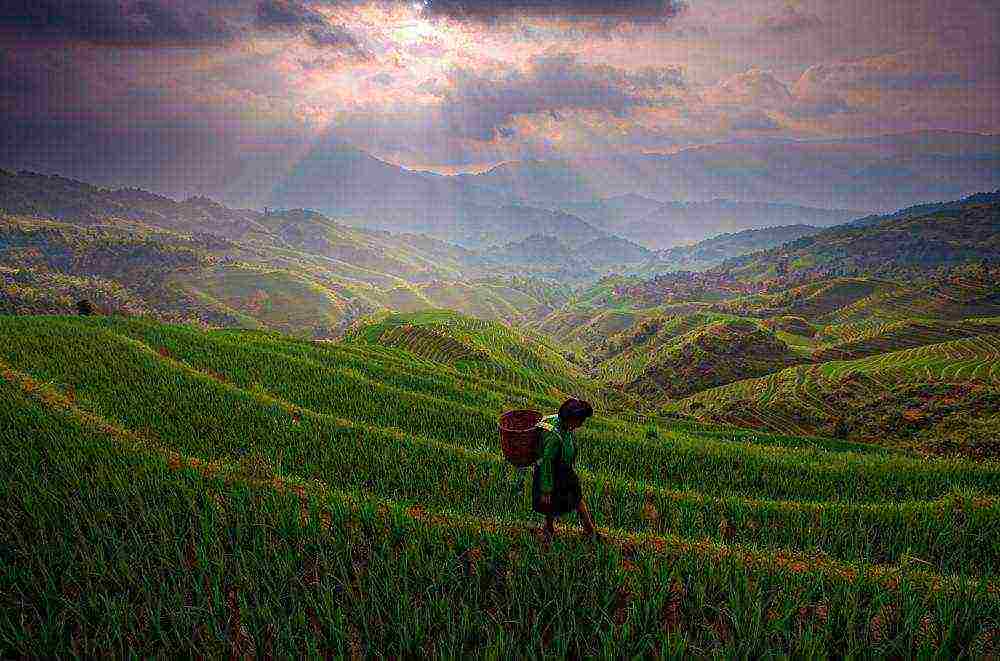

- Where is the plant spread in Russia? In our country, it grows in areas where there is a long and hot summer: in Krasnodar, Chechnya, Astrakhan and Primorsky Territories. Krasnodar Region is the largest rice supplier throughout Russia.
- An unusual red-brown variety "Devzira" is grown in Uzbekistan, which increases in size by seven times during cooking. Interestingly, the longer the grains are stored, the tastier they become. Naturally, the price of such rice is much higher than usual. And how long the variety should mature depends on the harvest. If a lot is grown, then it is possible to store for 2-3 years, periodically pouring water.

- Rice is also a main dish in Iran. It is boiled for food at any time and even used as a medicine.
- Round grain rice is grown in Ukraine and not only in the southern regions of the Odessa and Kherson regions.In recent years, attempts have been made to develop the northern regions of the country for planting this plant.
Land for landing
What soil does rice grow better in? These are chernozems and silty soil, rich in organic matter. In flooded fields, the yield increases several times due to the favorable ecosystem. Plants in such areas do not require feeding, all natural and useful substances are preserved for a long time. To do this, rice growers, after harvesting, burn the remains of rice stalks and mix with the ground.

Cleaning
But how are rice plants harvested? On large plantations with a special harvester on a caterpillar track to make it easier to drive through swampy fields. The machine collects and threshes (that is, it does the same work as combines harvesting wheat, rye and other grain crops).

Small areas for personal use are cleaned in a different and rather original way. For example, the Chinese gather with the whole family and cut the stems, collecting them in sheaves. And then the whole crop is simply laid on the roads, where cars drive and people walk. The wheels of the machines seem to knock out the grain and clean it from dirt. Then everything is collected and taken away for storage. Before cooking, of course, the rice is washed.
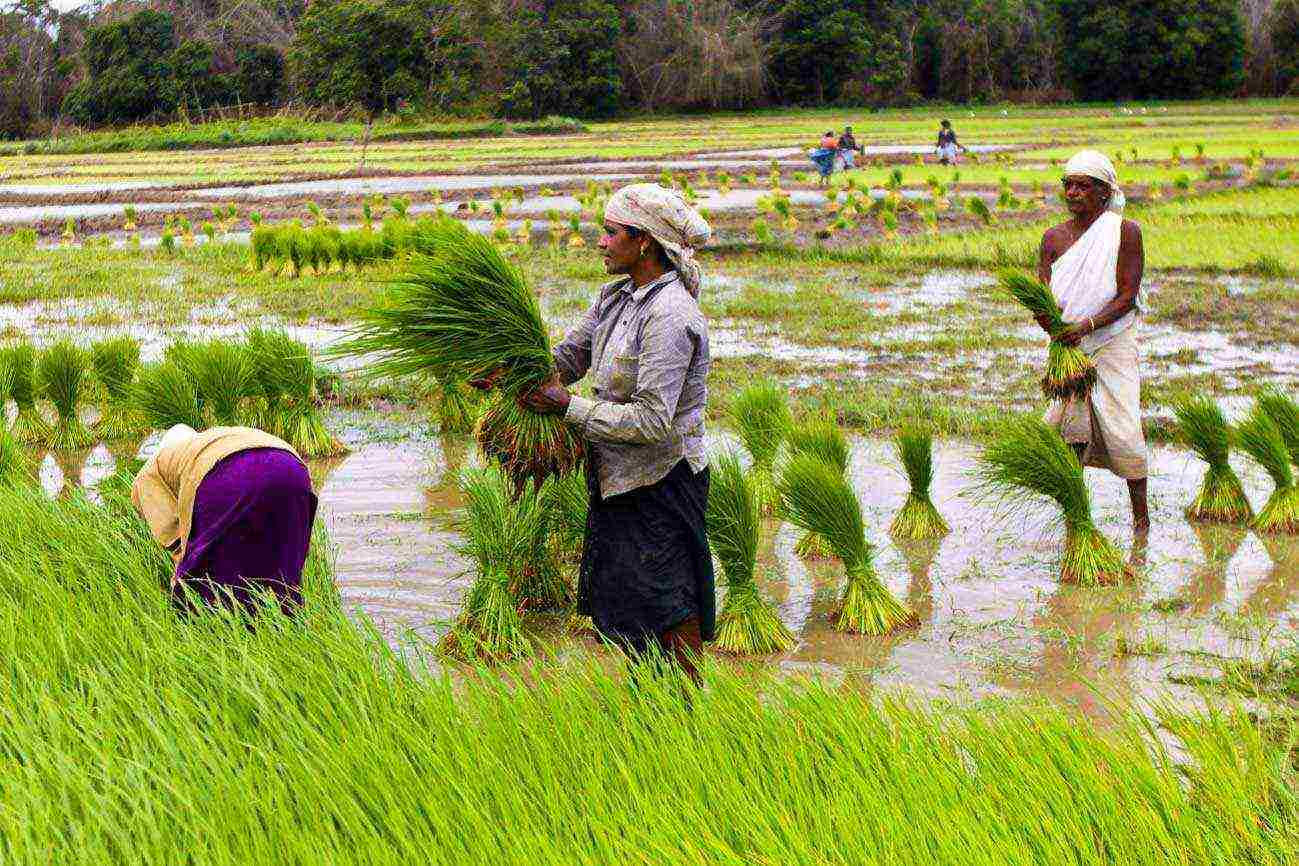

For residents of many countries, rice is the second bread. How many dishes consist of rice grains: porridge, pilaf, pies and much more. This plant contains a lot of carbohydrates, proteins and useful vitamins.
Video
We have shown the cultivation of rice in pictures in this article. By the way, those who want to plant it in their summer cottage can easily do this. The main desire!
Author of the publication
0 Comments: 0Publications: 258Registration: 12-04-2017
Indian Sea Rice is a unique bacterial culture that is a living laboratory where bacteria synthesize sugar and a combination of vitamins and organic acids. The fungus is known for its beneficial properties and has gained popularity among fans of healthy eating. With regular use, it has a positive effect on all body systems and helps to get rid of many ailments.
Indian sea rice - what is it?
People who first encountered an overseas product are interested in the question: sea rice - what is it? Culture came to Europe from India more than a century ago. In fact, this is not rice, but a milky fungus, so named because of its resemblance to cereals. It does not grow in the sea, it just came from afar and used to be called "overseas". The closest relatives of rice are tea and kefir fungi (Tibetan milk mushroom). The cultured product lives in sweetened water. You can grow it at home like the infamous Kombucha. Sea rice tincture has medicinal properties.
Indian sea rice - composition

Externally, sea rice looks like whitish gel-like balls, only vaguely resembling cereals (heavily digested). The special state in which bacteria reside is called zooglea (from the Greek gloios - "sticky substance"). The microorganisms secreting mucus stick together. But later the mass breaks up into separate granules - "rice". Zooglea absorbs nutrients from the water, due to which bacteria grow. They are acetic acid and ferment, in the process they form useful acids.
Indian sea rice - benefits and harms
The healing properties of a living fungus have been known for a long time, but it is less common than other similar crops. Informal medicine uses Indian sea rice as a natural living medicine, the beneficial properties and contraindications of which are much more extensive than those of its relatives. For the first time its influence was tested by the Polish doctor Shtilman in the 19th century. Having corrected his health with the help of the fungus, he revealed its amazing qualities to the whole of Europe.
Indian sea rice - beneficial properties

Alternative medicine uses natural benefits to get rid of all kinds of ailments: plants, inanimate and living organisms.Sea rice is suitable for treating many diseases and improving well-being; its benefits are obvious. Drinking a drink made from milk fungus brings not only pleasure, but also a positive result. Bacteria and microorganisms saturate the liquid with acids, each of which contributes to the baggage of useful properties:
- coumarovaya has a bactericidal effect;
- folic acid plays an important role in the synthesis of immune cells;
- pyruvic is a link in the conversion of proteins, carbohydrates and lipids;
- lemon juice stimulates metabolism.
Many people believe that a living fungus that grows at home can replace many medicines. If you regularly eat sea rice, the beneficial properties will have a beneficial effect on the body. The drink stimulates metabolic processes, a tonic and immunomodulatory effect is achieved. Bad cholesterol and toxins are eliminated from the body. Indian sea rice has other positive qualities:
- breaks down fats;
- improves intestinal motility;
- helps to lower blood pressure (including due to the diuretic effect);
- prevents the deposition of salts;
- fights headaches and stress;
- relieves fatigue;
- prevents the development of cancer.
Indian sea rice - contraindications
Sometimes, after consuming milk fungus, negative manifestations can occur. Due to the abuse of the drink and addiction to it, diarrhea and discomfort in the respiratory tract appear (especially in asthmatics). Allergy sufferers experience adverse skin reactions when using rice for cosmetic purposes. Not everyone can use sea rice, the contraindications to consumption are as follows:
- diabetes;
- a number of gastrointestinal diseases;
- increased acidity of the stomach.
It is not recommended to self-medicate with rice when it comes to serious pathologies. It is really useful, but you need to consult a specialist who will tell you how to correctly combine the intake of essential medicines and mushroom kvass. As a multicomponent preparation, Indian rice can enhance, speed up or weaken the effects of certain medicines.
What does sea rice cure?
There is no evidence that the Indian milk fungus can cure many diseases. It is allowed to be taken in order to prevent various ailments, as well as in combination with drug therapy. Even healthy people, for general strengthening of the body and raising immunity, should regularly consume sea rice, the properties of which make it indispensable for other pathologies and diseases. The list of ailments is wide. The mushroom infusion is taken when:
- rheumatism;
- deposition of salts;
- arthritis (rheumatoid);
- atherosclerosis and arrhythmias;
- colds;
- bronchitis;
- pharyngitis;
- pneumonia;
- tuberculosis;
- periodontal disease and stomatitis;
- constipation;
- hemorrhoids;
- sorry, enuresis;
- neurasthenia;
- epilepsy;
- violations of the cardiovascular system;
- weakened immunity.
Indian sea rice - cooking

Having decided to experience the miraculous properties of the Indian fungus, people are trying to cultivate it at home. The question arises: how to cook Indian sea rice yourself? The fungus is unpretentious in care, everyone can start breeding at home. To grow rice, you need a minimum of ingredients, but the most important thing is to get the fungus. Indian sea live rice is sold in online stores. The cost is low - 50 rubles per tablespoon, four of these will be required for breeding.
How to Grow Indian Sea Rice?
To cultivate the fungus, only three things are required: a three-liter glass jar, gauze covering its neck, and purified water. The main thing to consider before growing Indian sea rice is in what environment the fungus will develop. Water must be filtered, not piped. To grow rice, you need a warm, dry place (a window sill or wall cabinet, on which the sun's rays fall), liquid and top dressing. After the tincture is ready, the beans can be poured over again.Kvass is recommended to be consumed within the next 5 days.
Sea rice - recipe

When all the preparations are ready, you can start cultivating the fungus. How to cook sea rice? The classic scheme of action is as follows:
- Put 4 tablespoons of mushroom in a clean jar - live Indian sea rice.
- Add top dressing: a few raisins or other dried fruit (dried apricots, figs, etc.). You can put 2 croutons from black and white bread.
- Pour sweetened water - at the rate of 3 tbsp. tablespoons of sugar per liter of water. It is allowed to breed a mushroom in milk.
- The neck of the jar is closed with gauze and placed in a warm place. Fermentation takes place actively at 21-25 degrees.
- The fungus is infused for two days, then the liquid is filtered through cheesecloth and drained into several drinking containers.
- Rice is washed under cold water and put back. You can prepare a new batch of rice kvass.
How to store Indian Sea Rice?
Sea rice, which is easy to clean and prepare, must be stored properly. When the temperature drops to 20 degrees and below, reproduction stops, and if it drops to 16-18 degrees, the grains become smaller and may die. How to store Indian Sea Rice? Live fungus (not cultivated) is not afraid of the cold and should be stored in glass containers. It is recommended to have two servings of live granules, one of which should prepare the drink, and the other should lie in the refrigerator at this time - but not longer than 5 days. Then they replace each other.
Sea rice - application
Indian rice is not used live, only its derivative. A drink from a medicinal fungus is consumed internally to get rid of various ailments and prevent them. The course of administration depends on the disease and its severity: from 20 to 120 days. But the product obtained from the fungus can be used in other ways:
- Like nasal drops from a runny nose.
- For gargling with colds.
- As rubbing and compresses. With the help of the infusion, bruises, sprains, and back problems can be cured.
- For the treatment of hemorrhoids, rice kvass is diluted with water (in the ratio of 2 tablespoons of the drink to 100 ml of water) and poured into an enema.
- Indian sea rice is used in cosmetology as part of lotions and masks.
- Use the product as a bath salt by adding the fungal milk to the water.
Indian sea rice for weight loss
A natural and safe remedy for losing weight is Indian Sea Rice. Lipase - a special enzyme in its composition - breaks down fats, fighting against accumulated deposits. Regular use of medicinal kvass returns to normal the metabolic processes of the body, which are disturbed by poor ecology, harmful food and other factors. How to take sea rice for weight loss? The intake rate is 150-200 ml of kvass twice a day. Preferably 15 minutes before meals.
Indian sea rice for face

Mushroom kvass is a natural lotion with tonic properties. With its help, you can cleanse pores, eliminate bacteria, refresh your face, remove dead cells. The Indian sea rice mushroom produces a healing drink, which is usually consumed on the second or third day. For cosmetic purposes, a weekly infusion is used. To prepare a rejuvenating mask 1 tbsp. kvass is mixed with 1 tsp. honey and 1 tsp. vegetable oil (pomegranate, sea buckthorn, etc.). The mask is applied to the face with a thin layer for 15-20 minutes, washed off with cool water.
Sea rice for hair
Sea rice in milk or water, infused for a long time (6-7 days), is used in hair care. Mushroom kvass is added to shampoos or used independently:
- To prepare natural shampoo, a tablespoon of rice tincture is mixed with egg yolk, a tablespoon of vegetable oil, diluted with 0.5 cups of warm water.
- A compress of warmed vegetable oil mixed with rice kvass is applied to dry and brittle hair. It is rubbed into the scalp, wrapped in a towel and lasts for 1-2 hours.
- It is recommended to wipe oily curls every two days with a mixture of infusion of fungus (2 tablespoons) and vodka (half a glass).
- If the hair is very oily, the scalp also needs attention. You can dilute ¼ glass of alcohol and a tablespoon of weekly kvass. Nutritious carrot juice is sometimes used instead of vodka.
- A remedy made from mushroom kvass, castor and burdock oil, mixed in proportions of 2: 1: 1, will help restore strength to damaged and colored curls. The mixture should be rubbed into the scalp daily.
Indian sea rice is a real treasure of beneficial properties. You can find a use for a drink made from a fungus in many areas. They are supplemented with therapy for a variety of diseases, including heart pathologies, gastrointestinal problems, joints, respiratory tract, neurological diseases. It is useful to drink mushroom infusion for prophylaxis, to improve general well-being, in addition, to use it to improve hair and skin.
Rice (lat. Orýza) - a genus of annual and perennial herbaceous plants of the Cereals family; cereal culture.
Very picky about growing conditions, can be destroyed by frosts. Rice loves moisture very much, and its shoots grow directly from the water. Seeds germinate at 10-12 ° C.
Name
The word "rice" appeared in Russia only at the end of the 19th century, being a derivative of it. Reis, Netherlands. rijs, from Romanesque: ital. riso, Art. rîs... Prior to that, rice was called "Saracen grain" or "Saracen wheat", then the name was transformed into "Sorochin millet".
Generic name lat. Oryza comes from ancient Greek. ὄρυζα, which in turn goes back to the Sanskrit vrihi.
Botanical description
Rice stems reach up to one and a half meters in height, its leaves are rather wide, dark green and rough along the edge. A panicle of spikelets appears at the top of the stem. Each spikelet contains four scales (spinous or awnless) covering the flower; in the flower, unlike other grasses, 6 stamens and a pistil with two feathery stigmas. The caryopsis is densely covered with scales.
Spreading
It grows mainly in the tropics and subtropics of Asia, Africa, America, Australia.
Origin
As an agricultural crop in the tropics, subtropics and warm regions of the temperate zone, an annual sowing rice (Oryza sativa), which is one of the oldest food crops. Its domestication took place about 9 thousand years ago in East Asia. In South Asia (Rakhigarchi) rice was completely domesticated separately from this process in China and the ancestor of this rice was most likely a wild-growing species Oryza nivara.
Also grown in Africa African, or naked rice (Oryza glaberrima), which was domesticated 2-3 millennia ago on the banks of the Niger River. Nowadays, it has practically been supplanted as an agricultural crop by Asian rice varieties and can be grown in some places for ritual use. The local population in Africa also eats grains from a number of wild rice species, most notably rice point (Oryza punctata) and short tongue rice (Oryza barthii).
Rice fields are flooded with water before the seeds ripen to protect them from direct exposure to sunlight, and as one of the means of weed control. The fields are drained only at the time of harvest.
Economic value and application

Rice is rich in carbohydrates and relatively poor in protein. The share of the former in dry matter reaches 70%, while the latter, as a rule, does not exceed 12%. Rice ash is rich in phosphoric acid.
It is considered the main (national) food product in the countries of Southeast Asia and China. Since peeled caryopses are low in vitamins, the popularity of rice has led to a widespread prevalence of beriberi disease. Rice grains are used to produce cereals and starch, and oil is obtained from rice germs. Rice flour without any other admixture is not very suitable for making bread, mainly porridge or pies are made from it; in large quantities it goes to cosmetic factories, for processing into powder.There are many rice-based dishes, the most famous of which are pilaf, risotto and paella. In Japan, it is used to make mochi cakes and special sweets for the tea ceremony.
In America, Africa and Asia, rice is used to prepare various alcoholic beverages, and in Europe, alcohol is obtained from it. Traditional rice wine is popular in China; in Japan, national alcoholic drinks of various strengths are produced from rice - sake, shochu, avamori. In Korea, rice and its wastes are the basis of many traditional drinks such as Sikh and Sunnun.
Puffed rice is also produced, similar in consistency to popcorn, only smooth and round. It is sometimes molded into caramelized slabs like kozinaki.
Rice straw is used to produce rice paper, cardboard, and wicker products. Rice straw is thick and soft; it is most often used for bedding in the barn and, in general, is of little use for making wicker items. The straw hats sold for rice straw are actually fabricated from very thin stalks of rye and wheat.
The bran left over from rice cleaning is good food for poultry and domestic animals; poultry feeds on kurmak in Central Asia, and rice chaff, with an admixture of broken grains, serves as an excellent food for pets.
In Islamic countries, there is a measure of weight equal to the weight of one grain of rice - aruzza.
Some species of the genus, especially Oryza rufipogon, litter crops of cultivated rice.
Classification and types of rice

Genus Rice includes 18 types, grouped into 4 sections:
- Oryza sect. Australiensis
Oryza australiensis Domin
- Oryza sect. Brachyantha
Oryza brachyantha A. Chev. & Roehr.
- Oryza sect. Oryza
- Oryza sect. Oryza ser. Latifoliae
Oryza eichingeri Peter Oryza grandiglumis (Döll) Prodoehl Oryza latifolia Desv. Oryza minuta J. Presl Oryza officinalis Wall. ex Watt Oryza punctata Kotschy ex Steud. - Point rice
- Oryza sect. Oryza ser. Oryza
Oryza barthii A. Chev. - Short-tongued rice Oryza glaberrima Steud. - African rice, or Naked rice Oryza longistaminata A. Chev. & Roehr. Oryza rufipogon Griff. Oryza sativa L. - Sowing rice typus
- Oryza sect. Padia
- Oryza sect. Padia ser. Meyerianae
Oryza meyeriana (Zoll. & Moritzi) Baill. Oryza neocaledonica Morat
- Oryza sect. Padia ser. Ridleyanae
Oryza longiglumis Jansen Oryza ridleyi Hook.f.
- Oryza sect. Padia ser. Schlechterianae
Oryza schlechteri Pilg.
Rice cultivation
| 2014 | 2016 | |
| PRC PRC | 206,5 | 209,5 |
| India | 157,2 | 158,8 |
| Indonesia Indonesia | 70,8 | 77,3 |
| Bangladesh Bangladesh | 52,3 | 52,6 |
| Vietnam Vietnam | 44,9 | 43,4 |
| Myanmar myanmar | 26,4 | 25,7 |
| Thailand thailand | 32,6 | 25,3 |
| Philippines Philippines | 18,9 | 17,6 |
| Brazil brazil | 12,2 | 10,6 |
| USA USA | 10,1 | 10,2 |
| Cambodia Cambodia | 9,3 | 9,8 |
| Japan japan | 10,5 | 8,0 |

Planting rice seedlings on the island
Java
, in Indonesia

Rice is one of the most important grain crops, as more than half of the world's population feeds on it. Its culture has been known since ancient times. In a solemn ceremony established by the Chinese emperor as far back as 2800 BC. BC, rice is already playing an important role. The reigning emperor had to sow it himself, while four types of other plants could be sown by the princes of the imperial family. No less classical country of rice cultivation is India, where the rice culture may not be as ancient as in China, nevertheless it occupies vast areas, and the grains of this plant constitute the main food of the population.
Rice is also sown in significant quantities in Bangladesh, Indonesia, Sri Lanka, central and eastern Africa, Polynesia, Melanesia and other countries lying between the equator and 45 ° latitude. In Europe, rice cultivation is found in Spain (the Moors introduced it here), Italy (the first rice fields near Pisa date back to 1468), Greece and Turkey, in America it is mainly cultivated in the USA and Brazil. In Russia, it is grown in relatively small quantities in the Krasnodar Territory, the Rostov Region and in the south of Primorye. Due to its thermophilicity, rice has a limited distribution in the countries of the temperate zone. For its full development at an average summer temperature of 22-30 ° C and with a growing season of 150 days, it takes from 3300 to 4500 ° C (the number of days of the period of the entire growth of the plant until it ripens is multiplied by the average temperature of this period. So, 4500 = 150 × 30; 3300 = 150 × 22). Another reason lies in the special conditions of rice cultivation, which, like a marsh plant, requires a lot of stagnant water, why rice fields, being under water for a long time (90-100 days), easily become waterlogged, which can lead to the spread of intermittent fevers, and also causes large consumption of water, a scarce resource for some countries. Water or wet rice especially requires a lot of water, the main variety of this plant, cultivated in most countries. Each hectare planted with wet rice requires twice as much water as winter grain and five times as much as spring dzhugara. Of the European and American varieties, common rice, Caroline, Piedmont, and others are more or less known.There are more numerous varieties of rice cultivated in the East, their grains are also variably colored; there are red, black and purple; of these, red rice is considered the most nutritious. In Japan, Java, Sumatra and Cochin, many more varieties of rice with fine grains are cultivated. Along with wet rice, mountain or dry land rice is also bred in the East. At home, this rice grows wild on the slopes of the mountains of southern China and manages to complete its growth without artificial irrigation during the tropical rains. The practice of the cultivation of dry land rice in Northern Italy has shown, for example, that although it certainly cannot grow there without artificial irrigation, the amount of water required to irrigate this rice variety is almost half that required for ordinary wet rice. Commercial rice varieties: Caroline (grains are oblong, odorless, white and transparent); Piedmontese (grains with a yellowish tint, shorter and more rounded, opaque); Indian (grains are oblong, with a well-defined transparency); Japanese (grains are very small, but white and of good quality).
Rice is cultivated on rice paddies, which can be permanent or only temporary. The first are busy from year to year with rice crops and constantly remain under water; the latter, after 2-3 years of rice sowing, usually engage in some other kind of bread. The best soils for rice are clay and loamy. Rice fields are surrounded by low rollers and are flooded. Usually, sowing is carried out in water, standing in a layer of 6-8 cm, in the month of March-April. Sometimes, however (as is most often the case in China, India, Japan, Java and in some places in the Transcaucasus) rice is not immediately sown on plantations; first it is incremented and allowed to rise to a height of 15-20 cm, and then it is transplanted into the ground, preferably in rows spaced 20-30 cm apart. a sufficient supply of nutrients is brought in. As it grows, rice requires careful maintenance. You have to constantly monitor, immediately after the sowing, the state of the air and water temperature, and if these drop significantly, then it is necessary to drain some of the inflated water until the sun warms up the soil well. When the first leaves of rice appear on the surface of the water, the layer of water is increased, and if the arriving water is cold, then it is warmed, previously with the help of the sun, in special containers. Then, from time to time, all the water that fills the rice plantations has to be drained clean and released again; in different localities, this operation is performed at different intervals - every third, fourth or tenth day, and sometimes even longer. In general, the water layer should not cover more than half of the plant; it always suffers from excess water. Before harvesting, the water is finally drained. The enemies of the rice crop, in addition to the lack of heat and water, are also weeds. To remove them, weeding was used - in the past, a very difficult job, usually lasting about three weeks. Among the weeds, the most harmful Leersia oryzoides (rice wheatgrass), Panicum Crus galli, reed, sedge, susak, Alisma plantago and others. Of the fungi, it is most often found on rice Pleospora oryzaeproducing the so-called white and black disease on rice. Rice is considered ripe when its stem turns completely yellow, and the grain itself turns white, which happens in Central Asia in late August and early September. It is considered risky to be late for harvesting, since when the spikelets dry out, part of the crop is lost. Sarts often put rice in green; such rice, dried in the sun, is considered, in their opinion, the best for pilaf. Cleaning is done by cutting or pulling; the harvested ear is dried for 2-3 days, and then it is threshed. The upland rice culture is simpler.It is usually sown from March to July, and harvested in June-November, depending on the conditions and height of the area where this rice is cultivated. As an exception, in Sumatra, it is sown in September or October and removed in February or March; in Cochin, sowing is done in December or January and the harvest in April or May. This variety does not require such regular irrigation as water rice. Threshed grain (shala or brown rice) is cleaned of awns and impurities, then goes to the millstones, where the film is separated. The final finishing of cereals is done in a polishing machine or in mortars. On average, 100 kg of rice, when converted into cereals, give: coarse grain - 60 kg, medium - 15 kg, fine 15 kg, flour - 10 kg; and from 100 parts of unrefined rice it turns out: pure grain 74 parts, waste (shell, skin, embryos) - 26 parts.
Yield
The average yield is about 60 c / ha (6 t / ha or 600 t / km²), but in traditional rice-growing countries rice is harvested several times a year. The maximum rice yield is up to 150 c / ha (15 t / ha or 1500 t / km²).
Pests and diseases
Rice pests are organisms and microbes that have the ability to reduce the profitability or yield of rice fields (or rice seeds). Rice pests include weeds, pathogens, insects, nematodes, rodents and birds. A number of factors can contribute to pest outbreaks, including pesticide abuse, inadequate irrigation and excessive nitrogen fertilization rates. Weather conditions also contribute to pest outbreaks. For example, the mass appearance of rice gall midge and grassworm caterpillars (Spodoptera frugiperda), as a rule, follow at the beginning of the rainy season after the first heavy rainfall, while the appearance of thrips is associated with drought.
Rice crops also affect several types of nematodes, causing diseases such as ditylench stem (Ditylenchus dipsaci), rice apilench (Aphelenchoides besseyi) and gallic disease (Meloidogyne graminicola). Some types of nematodes such as Pratylenchus spp. pose the greatest danger to dry land rice in all parts of the world. Rice root nematodes (Hischmanniella spp.) is caused by migratory endoparasitis, this disease at later stages of crops leads to the complete destruction of the rice crop. In addition, obligate parasites also reduce plant vigor and increase the susceptibility of rice seedlings to other pests and diseases.
To protect plants, scientists are trying to develop rice pest control methods that would help create sustainable agriculture. In other words, control crop pests so that they do not threaten crop production in the future.
Effective pest control is based on four principles: biodiversity, host resistance (HPR), landscape ecology, and landscape hierarchy - from biological to social. Currently, rice pest control includes the development of pest-resistant rice varieties and the use of pesticides (as well as insecticides). However, more and more evidence is accumulating that the use of pesticides by farmers is often unnecessary and even unwittingly promotes pest reproduction, reducing the population of natural enemies of rice pests, so the misuse of insecticides can actually lead to outbreaks of pest breeding. In 1993, the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) demonstrated that an 87.5% reduction in pesticide use can lead to an absolute reduction in the total number of pests. In 1994 and 2003, the institute also conducted two campaigns during which rice growers were educated about the dangers of insecticide abuse and effective methods for controlling rice pests in Vietnam.
Genetics
Molecular genetics
- Deposited nucleotide sequences in the database EntrezNucleotide, GenBank, NCBI, USA: 4 497 096 (accessed March 15, 2015).
- Deposited protein sequences in the database EntrezProtein, GenBank, NCBI, USA: 315,790 (accessed March 15, 2015).
Most of the deposited sequences belong to sowing rice (O. sativa) Is the genetically most studied representative of this genus.
Genomics
Complete sequencing of the rice seed genome (Oryza sativa) was completed in 2005. The genome is organized on 12 chromosomes and contains 37,544 genes. At the same time, sowing rice became the second type of plants (after Tal's rezukhovidka - Arabidopsis thaliana), for which there is a complete genomic sequence serving as a "reference" (eng.reference genome) to study other genomes and compare with them. In 2009-2014, kind of Oryza six other species were also fully sequenced and six more species were partially sequenced.
Research on cooking methods
Most people use a 2: 1 ratio when cooking rice. However, oddly enough, this is the wrong way to cook it. Such rice can even develop health problems in a person, for example, diseases of the cardiovascular system, diabetes and cancer. According to scientists, rice contains arsenic due to air emissions and pesticide residues in the ground. To get rid of the poison, you need to increase the amount of water: either add twice as much water, or soak the rice in water overnight before cooking. In a programme BBC "Trust Me, I'm a Doctor" Professor Andy Meharg of Queens University in Belfast, compared three ways to cook rice:
- Add 2 cups of water and 1 cup of rice and let the water evaporate while cooking (the arsenic level is still quite high)
- Add five cups of water and 1 cup of rice and at the end pour out the excess (this method reduced the level of arsenic by half)
- The professor left the rice in the water overnight and found that the arsenic content in the product was reduced by 80%.
see also