Content
- 1 Distribution and habitat
- 2 Botanical description
- 3 History of domestication
- 4 Cultural biology
- 5 Method for extracting sugar from sugar cane
- 6 Production
- 7 Notes (edit)
- 8 Links
- 9 History
- 10 Description
- 11 Meaning and application
- 12 Sugar beet processing technology
- 13 Sugar beet producers
- 14 see also
- 15 Notes (edit)
- 16 Literature
- 17 Links
- 18 10. People's Republic of China - 8 million tons
- 19 9.UK - 9.4 million tonnes
- 20 8. Egypt - 11 million tons
- 21 7.Poland - 13.5 million tons
- 22 6.Ukraine - about 16 million tons
- 23 5.Turkey - 16.8 million tons
- 24 4. United States of America - 28.5 million tons
- 25 3. Germany - 30 million tons
- 26 2. Russian Federation - 33.5 million tons
- 27 1. France - 38 million tons
| Cultivated sugar cane | |||
 General view of a group of flowering plants, Mozambique |
|||
|
intermediate ranks
|
|||
|
Saccharum officinarum L. (1753) |
|||
Cultivated sugar cane, or Sugarcane noble (Latin Sáccharum officinárum) - plant; species of the genus Sugarcane (Saccharum) of the Cereals family. Used by humans, along with sugar beets, to obtain sugar.
Distribution and habitat
Cultivated sugar cane is a perennial herb cultivated in numerous varieties in the tropics, from 35 ° N. NS. up to 30 ° S sh., and in South America it rises in the mountains to a height of 3000 m.
Sugarcane comes from the Southwest Pacific. Saccharum spontaneum is found wild in eastern and northern Africa, the Middle East, India, China, Taiwan, and Malaysia and New Guinea. The center of origin is possibly northern India, where forms with the smallest chromosome set are found. Saccharum robustum is found along river banks in New Guinea and on some of the surrounding islands, and is endemic to the area. The cultivated sugarcane is most likely from New Guinea. This reed can only grow in tropical regions with a suitable climate and soil. Saccharum barberi may have originated in India. Saccharum sinense is found in India, Indochina, southern China, and Taiwan. Saccharum edule appears to be the pure form Saccharum robustum and is found only in New Guinea and the surrounding islands.
Botanical description
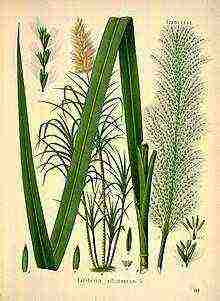
Rhizome perennial fast-growing plant up to 4-6 m high.
The rhizome is short-segmented, strongly rooted.
Stems are numerous, dense, cylindrical, glabrous, knotty, green, yellow, purple. The stem diameter is up to 5 cm.
The leaves are large, wide (from 60 cm to 1.5 m long and 4-5 cm wide), reminiscent of corn leaves.
The stem ends with an inflorescence - a pyramidal panicle 30-60 cm long; ears are small, monochromatic, collected in pairs and pubescent from below with hairs.
History of domestication
Sugar cane harvesting

The sugar cane culture began in ancient times. Sugar extracted from sugar cane is known in the Sanskrit language: "sarkura", in Arabic it is called "suhar", in Persian "shakar". Sugar is mentioned by ancient European writers under the name "saccharum" (by Pliny), but also as a very rare and expensive substance used only for medicine. The Chinese learned to refine sugar as early as the 8th century, and the Arab writers of the 9th century mention sugar cane as a plant cultivated along the coast of the Persian Gulf. In the 12th century, the Arabs brought it to Egypt, Sicily and Malta. In the middle of the 15th century, sugarcane appeared in Madeira and the Canary Islands. In 1492, sugarcane was transported from Europe to America, to the Antilles, and on the island of São Domingo, it began to be cultivated in large numbers, since by this time the use of sugar had become extensive. Then, at the beginning of the 16th century, sugarcane appeared in Brazil, in 1520 in Mexico, in 1600 in Guiana, in 1650 on the island of Martinique, in 1750 on the island of Mauritius, etc.In Europe, the cultivation of sugar cane has always been very small, since the sugar imported from the tropics was cheaper. Finally, after they began to make sugar from beets, the cultivation of sugar cane in Europe was completely abandoned.
The main modern sugarcane plantations are located in Southeast Asia (India, Indonesia, the Philippines), Cuba, Brazil and Argentina.
Cultural biology
Sugarcane is bred by cuttings.
Sugarcane cultivation requires a tropical or subtropical climate with a minimum of 600 mm of annual rainfall. Sugarcane is one of the most efficient plants for photosynthesis, capable of converting more than 2% of solar energy into biomass. In regions where reed is a priority crop, such as Hawaii, the yield is up to 20 kg per square meter.
Method for extracting sugar from sugar cane

Cut sugarcane stalks
To extract sugar, the stems are cut before they bloom; the stem contains up to 8-12% fiber, 18-21% sugar and 67-73% water, salts and protein substances. The cut stems are crushed with iron shafts and the juice is squeezed out. The juice contains up to 0.03% protein substances, 0.1% granular substances (starch), 0.22% nitrogen-containing mucus, 0.29% salts (mostly organic acids), 18.36% sugar, 81% water and a very small amount of aromatic substances that give the raw juice a peculiar smell. Fresh lime is added to the raw juice to separate proteins and heated to 70 ° C, then filtered and evaporated until the sugar crystallizes.
Production

Combine KTP-1 for mechanized harvesting of sugar cane, developed on
Lyuberetskiy
agricultural engineering plant named after A. V. Ukhtomsky in the second half of the 1970s to work on
Cuba
and subsequently licensed in the city
Holguin 
Up to 65% of the world's sugar production is obtained from sugar cane.
Sugarcane is one of the main export items in many countries.
Until 1980, India was the leader in the production of sugar cane, since 1980 - Brazil. Until 1992, Cuba steadily occupied the third place, where its production fell sharply since the beginning of the 1990s due to the termination of the existence of the USSR.
Notes (edit)
Links
- Sugarcane // Brockhaus and Efron Encyclopedic Dictionary: in 86 volumes (82 volumes and 4 additional). - SPb., 1890-1907.
- FAO production figures

Sugar beet (beet) - a group of varieties of common root beet (Latin Beta vulgaris); industrial crop, the roots of which contain a lot of sucrose.
History
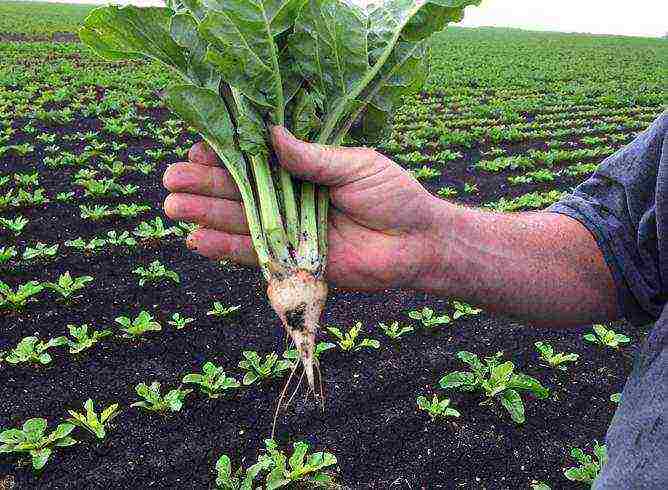
Sugar beets are the result of the work of breeders. In 1747, Andreas Marggraf found out that sugar, which was previously obtained from sugar cane, is also contained in beets. At that time, the scientist was able to establish that the sugar content of fodder beets was 1.3%. In the current varieties of sugar beets, bred by breeders, it exceeds 20%.
The discovery of Marggraf was appreciated and for the first time practically used by his student Franz Karl Achard, who devoted his life to obtaining beet sugar and in 1801 equipped a factory in Lower Silesia where sugar was produced from beets.
Sugar beet appeared on the territory of modern Russia and Ukraine in the first half of the 19th century. The leading sugar refiners of the Russian Empire were first Count A. A. Bobrinsky and his heirs, then Leopold Koenig, at the beginning of the 20th century - Tereshchenko, Kharitonenko, Khanenko and Brodsky. See the sugar industry for details.
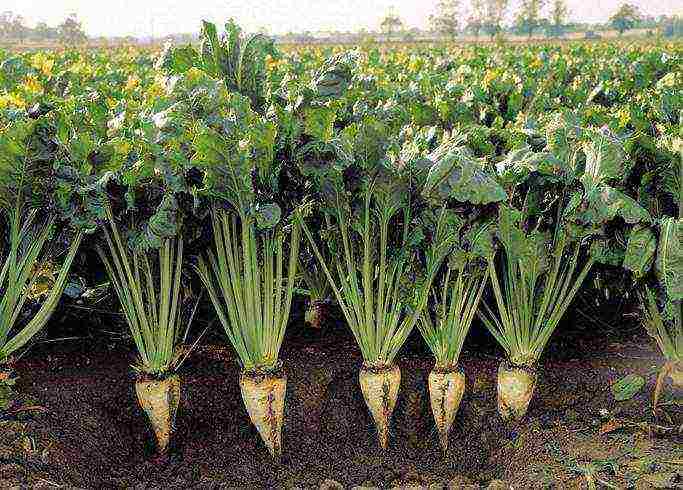
Description
Sugar beet is a biennial root vegetable that is cultivated primarily for sugar, but can also be cultivated for animal feed. In the first year, the plant forms a rosette of basal leaves and a thickened fleshy root crop, in which the sucrose content usually ranges from 8 to 20%, depending on growing conditions and variety.
Sugar beets love warmth, light and moisture. The optimum temperature for seed germination is 10-12 ° C, growth and development 20-22 ° C. Seedlings are sensitive to frost (they die at -4, -5 ° C). The amount of sugar in fruits depends on the number of sunny days in August-October. A particularly good harvest is harvested on chernozems.
Meaning and application
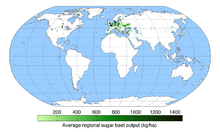
Sugar beet growing areas

Sugar beet is the most important industrial crop providing raw material for the sugar industry.
Waste production:
- pulp: used as livestock feed
- molasses: food product
- defecation mud: lime fertilizer.

In the 20th century, sugar beets are grown mainly in temperate countries. As of 2015, 12% of all sugar produced in the world is produced from sugar beets, 88% from sugar cane.
Russia
In 2008, Russia produced 29.1 million tons of sugar beet.
In 2011, a record harvest of sugar beet was harvested in Russia (46.2 million tons), thanks to which the country switched to the export of beet sugar in significant volumes (more than 200 thousand tons per year).
In 2016, the gross harvest of sugar beets amounted to 51.4 million tons, which became an absolute record.
Sugar beet processing technology
- The beets are accumulated in the storage room, where they can be kept for up to 90 days;
- Root crops are washed and turned into shavings;
- Getting diffusion juice with hot water (+75 ° C);
- The juice is purified in several stages using calcium hydroxide and carbon dioxide;
- The resulting juice is boiled down to a syrup with a dry matter concentration of 55-65%, decolorized with sulfur oxide and filtered;
- From the syrup in a vacuum apparatus of the 1st stage, massecuite of the 1st crystallization (7.5% water) is obtained, which is centrifuged, removing the "white" molasses. The crystals remaining on the centrifuge sieves are washed, dried and packaged.
- "White" molasses is again thickened in vacuum apparatus of the 2nd stage and, with the help of centrifuges, most often of continuous action, they are divided into "green" molasses and "yellow" sugar of the 2nd product, which, after having previously dissolved in pure water, is added to the syrup entering the 1st stage vacuum apparatus;
- For additional sugar extraction, a 3-stage boiling and desugarizing is sometimes used;
- The molasses obtained at the last stage of crystallization is molasses - a waste of sugar production, which contains 40-50% sucrose and is 4-5% by weight of the processed beet
Sugar beet producers
| 1 | Russia, Russia | 33,5 | 51,4 |
| 2 | France France | 37,8 | 33,8 |
| 3 | USA USA | 28,4 | 33,5 |
| 4 | Germany Germany | 29,7 | 25,5 |
| 5 | Turkey Turkey | 16,7 | 19,5 |
| 6 | Ukraine Ukraine | 15,7 | 14,0 |
| 7 | Poland Poland | 13,5 | 13,5 |
| 8 | Egypt egypt | 11,0 | 13,3 |
| 9 | PRC PRC | 8,0 | 8,1 |
| 10 | United Kingdom United Kingdom | 9,4 | 5,7 |
| 11 | Iran Iran | 4,7 | 5,5 |
| 12 | Netherlands Netherlands | 6,8 | 5,5 |
| Total | Peace | ||
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) |
|||
see also
- Sugar cane
Notes (edit)
Literature
- Beet // Safflower - Soan. - M.: Soviet Encyclopedia, 1976. - (Great Soviet Encyclopedia: / Ch. Ed. A. M. Prokhorov; 1969-1978, vol. 23).
- Lebedev S.V., Chekhov V.P. Biological changes in sugar beet // Izv. Siberian chemical-technol. in-that. - 1931. - No. 1.
- Lebedev S.V., Parfatskaya M.P. Heat of thawing of sugar beet // Izv. Siberian chemical-technol. in-that. - 1931. - No. 1.
- Keys to harmful and beneficial insects and mites of sugar beet in the USSR. - L., 1986.
Links
- Sugar beet (English): Information on the GRIN website.
- Ecological Center Ecosystem: A Guide to the Cultural Plants of the World: Sugar Beet (Beta vulgaris var. saccharifera)
- Detailed description

Sugar is one of the most important components of life. With him, people make tea or coffee, prepare various dishes: cakes, pies, cookies and much more. Sugar is made from sugar cane, which grows mainly in Cuba.
In addition to this plant, there is another way. Sugar beets provide the most valuable sugar in cooking, according to many chefs in the world. The production of this type of sugar is directly related to the cultivation of beets. There are countries that not only do an excellent job of this, but are also leaders in the production and export of beet sugar. Some countries practically do not do this at all, and some of them are very good at growing this plant. We represent 10 leading countries.
10. People's Republic of China - 8 million tons

China is generally one of the leaders in agriculture. It is in the last place in the ranking and grows eight million tons of sugar beets. Sugar is very much needed in China, as Chinese tea and sweets are especially popular in this country.
There are few sugar beet fields in China.This is not due to the fact that the population density in China is off scale, but to the fact that this country grows everything a little bit.
9.UK - 9.4 million tonnes

Sugar is grown quite well in England. As you know, in this country it rains very often (rain and heat are needed, at times). This is what sugar beets need to grow properly. For export, of course, not very much, if we talk about mass trade, but for our own citizens it is quite enough.
The state is not very big, and growing 9,400,000 tons is not bad at all, and agriculture is not particularly a priority there.
8. Egypt - 11 million tons

You can often find various vegetables from Egypt on supermarket shelves. Many people think that this country has a very hot climate and there is nothing to grow there. However, this is not the case. Egypt is one of those countries where agriculture can easily become more developed than in other states. For example, Egyptian potatoes can often be found in supermarkets in Russia. The Egyptians grow eleven million tons of sugar beets, which are exported almost all of them.
7.Poland - 13.5 million tons

In Poland, as in many other European countries, many cultivated plants are grown. Usually Poland does not export beets, but finished products of its production. Polish sugar is rarely found on the shelves of Russian stores. Poland grows thirteen and a half million tons of sugar beets, which is quite impressive for a small European state.
6.Ukraine - about 16 million tons

Despite the tense political situation in the country, sugar beets are grown very well. The climate allows, there is enough territory, so that nothing prevents Ukrainians from growing and selling. The functionality of agriculture in Ukraine is very similar to that in Russia. Reached the sixth place in the ranking of world leaders. Most likely, Ukraine will leave the top five, as the state of agriculture, the economy as a whole, is greatly deteriorating.
5.Turkey - 16.8 million tons

The state produces goods related to almost all branches of production. Including, of course, sugar beets. Just like in Ukraine: a good climate, there is where to grow. They export mainly the beets themselves. Turkey has bypassed Ukraine as it grows almost seventeen million tons. The country is hot, and for growing large beets, just such climatic conditions are needed.
4. United States of America - 28.5 million tons

For a very long time, the United States has been involved in agriculture. Back in the days of cowboys, Americans cultivated many cultural goods. Endless corn plantations, wheat fields are shown in films shot in the studios of this country. A little later, America began to grow sugar beets, and the success of this business remains the same. This is done here by both corporations and the most ordinary farmers - amateurs. 28 and a half million tons of beets. The United States is still in fourth place in the ranking.
3. Germany - 30 million tons

In third place is Germany, which has long been famous for its work and its high-quality results. In recent years, the Germans have grown a fairly significant amount of sugar beets, both for themselves and for sale to other countries. Both beets and sugar, including refined sugar, are exported.
Germany, in addition to growing beets, is similarly engaged in other cultivated plants. Also, Germany has a large number of equipment, which greatly helps both sowing and harvesting. Also, many people often notice that German citizens are not only good at work, but also like to work.
2. Russian Federation - 33.5 million tons

Our country took second place, since both the climate and the presence of a large amount of territory allow us to do this.Sugar beets grown in Russia are mainly exported, and about a third of the extracted beets are used for sugar production.
In this state, sugar beet does not enjoy the advantage, since at all times cereals were a priority here. Many people think that Russia is the world leader in sugar beet growing, but alas. The territory, of course, is large, including enough land suitable for beets. Almost no one can guess the country that took first place in this rating.
1. France - 38 million tons

The leader in the cultivation of sugar beets in the world. It may seem surprising, but France, in fact, specializes in this. The warm climate and the presence of endless fields make it possible to take first place. This applies primarily to the province Champagne... This province is the southernmost in France, where a variety of crops are grown, such as grapes for the production of the famous French wines. The French grows the most sugar beet, its amount is about 38 million tons.
Sugarcane is an annual cereal plant with a long history of cultivation. It is the only source of sugar production in Africa and some Asian countries. India is considered to be the ancestral home of sugarcane; the soldiers of Alexander the Great were the first to taste the honey plant, when, in the process of conquest, the locals introduced them to sugarcane.
Rational use of the sugar plant is waste-free. Sugar, drinks and sweets are just a few of what can be obtained from sugar cane processing. The processed sugar cane products are in great demand in the domestic and foreign markets.
The content of the article:
- Sugar made from sugar cane
- How to plant sugar cane properly
- Growing sugar cane
- Sugar cane harvesting
- Sugarcane seeds: collection, storage
- Sugar cane processing
- Cane sugar: good or bad?
Sugar made from sugar cane
Brown cane sugar is considered to be a more natural product than beet sugar. Crystalline Sweet Nibs are obtained from cane through multi-level processing. Cane sugar is considered one of the most ancient sweets of the East.
Glucose from brown cane sugar, of higher quality, it feeds the brain and liver activity of the body and contributes to an energy surge in general. Such sugar is considered less harmful, due to the content of plant fibers in it.
One of the distinguishing features of cane sugar is its high content of glucose and sucrose, which in total constitutes up to 2% of the weight of the stem. This fact implies cleaning without a lot of lime, and without a bleaching agent, thereby increasing the competitive component of the naturalness of brown cane sugar over white beet sugar.
The main production of cane processing plants is raw sugar. Only a few industrial factories bring cane sugar to a refined state. But in both cases, the primary processing of raw sugar is the same, the only difference is that raw sugar undergoes additional processing in the form of recrystallization, the same raw sugar.
The processing of raw sugar begins with the fact that before pressing, panicles and leaves must be removed, that is, only the stem gets under the press to extract juice. Then the juice is evaporated to a concentrated syrup. The syrup, in turn, undergoes cooking and crystallization. After full processing, cane sugar is packaged and supplied to the sales markets.
One cup of coffee or tea with cane sugar will charge you with energy and positive mood for the whole day, in addition, cane sweetness contains trace elements and B vitamins in its composition.
How to plant sugar cane properly
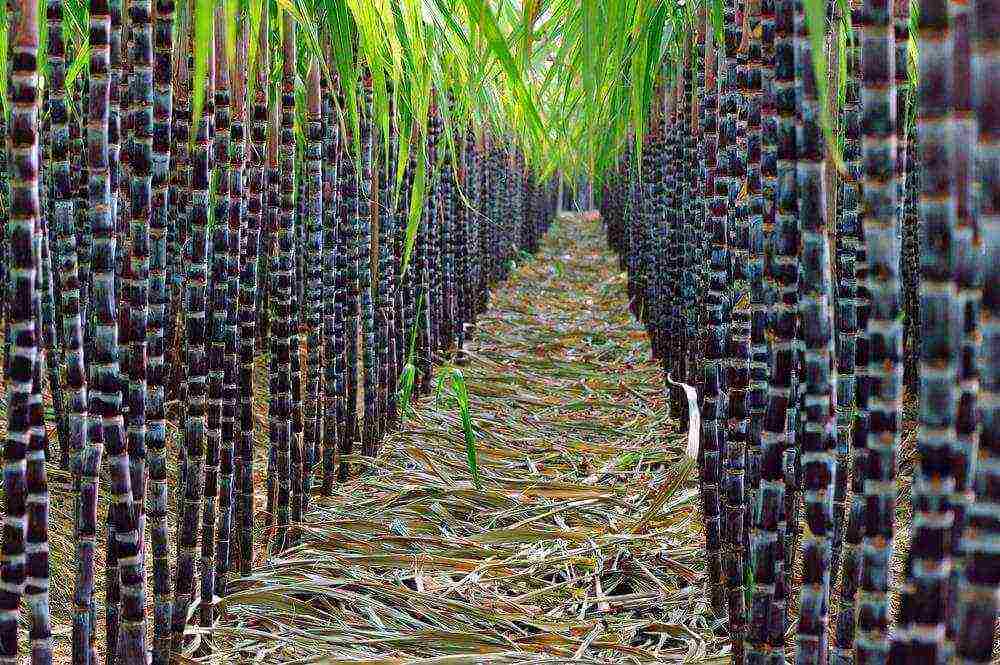 Unpretentious sugarcane, similar to bamboo and wild cane, grows vertically upward with a stem covered with long leaves. Sweet reed, waste-free unique plant. From its pulp, cardboard and paper are obtained, and biofuel is obtained from it, used as fertilizer.
Unpretentious sugarcane, similar to bamboo and wild cane, grows vertically upward with a stem covered with long leaves. Sweet reed, waste-free unique plant. From its pulp, cardboard and paper are obtained, and biofuel is obtained from it, used as fertilizer.
To plant sugarcane, you need to pay due attention to the planting material and soil. The thicker the trunk of the reed, the more suitable the plant is for planting.
The top and side leaves are removed, and the cane itself is divided with a knife or secateurs into pieces of about 35 cm.
A furrow up to 20 cm deep, watered abundantly and fertilized with compost, then the cuttings are laid horizontally and covered with soil. The first "sugar" shoots will appear in two weeks. Shoots grow from the formed reed stem nodes and require regular watering.
It takes about 4 months for a sugar plant to reach maturity. Caring for the plant is important only at first, while the seedlings are young, when the reed reaches maturity, it will clog the weeds itself and be able to tolerate drought.
Planting sugar cane with seeds implies early agrotechnical measures for preparing the soil with the introduction of nitroammophos, compost and selection of seeds.
And in the spring, when the soil warms up, planting is carried out in holes 2 cm deep, care for the plantings is carried out according to the schedule and as needed. In July, the plant begins to grow actively, adding 3 cm per day to its growth. Moderate feeding, regular watering and breaking off panicles are a must for growing sugarcane. Watering with superphosphate with reddening of the cane leaf is required.
The reed reaches a height of 2 or even 3 meters at maturity, and three months after germination, when the seeds turn brown, you can start harvesting. Every day of delay in harvesting sugar cane, leads to a loss of up to 3% of sugar in the plant.
Growing sugar cane
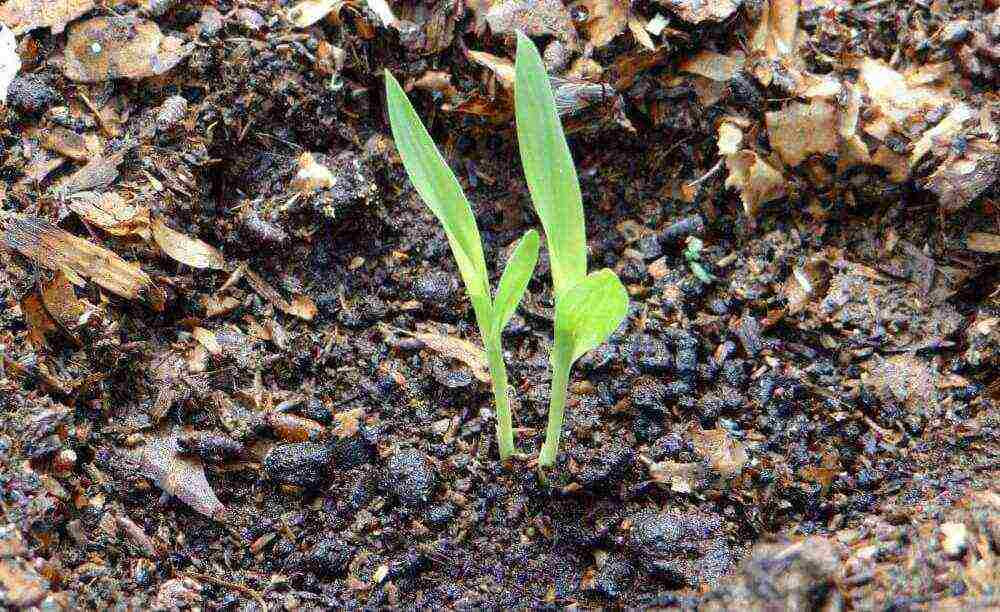 Oddly enough, the cultivation of sugar cane in Russia on an industrial scale is recognized as inexpedient. However, many gardeners do not deny themselves the pleasure of watching the growing process of this plant and even make homemade sugar.
Oddly enough, the cultivation of sugar cane in Russia on an industrial scale is recognized as inexpedient. However, many gardeners do not deny themselves the pleasure of watching the growing process of this plant and even make homemade sugar.
In order for the reed to grow, a well-lit place must be allocated to it on the site. Before planting, you need to prepare the site, dig it up, apply mineral fertilizers, and organic matter is introduced in the fall.
A simple method of planting is seed, today there is a sufficient amount of seed for sale, for any needs of the summer resident. When the soil warms up to 12 degrees, you can start sowing. Seedlings will appear in two weeks.
When reed is grown in favorable conditions, it is disease-free and grows rapidly. It is better to cut the reed in a timely manner so that the trunk is strong and thick, and planting should be done at a distance of at least 35 cm between plants and half a meter between the rows.
It is enough to water the cane three times a week, and weed as needed, until the plant reaches half a meter in height, after which the sugar plant will be able to get rid of weeds on its own, taking nutrients from the soil and clogging other vegetation.
Aerated soil has a good effect on the growth rate of reeds, so do not neglect the hilling of young plants. After three to four months, the sugar cane will begin to ripen and throw back the panicles with grains, during this period you should start collecting the cane for sugar.
Sugar cane harvesting
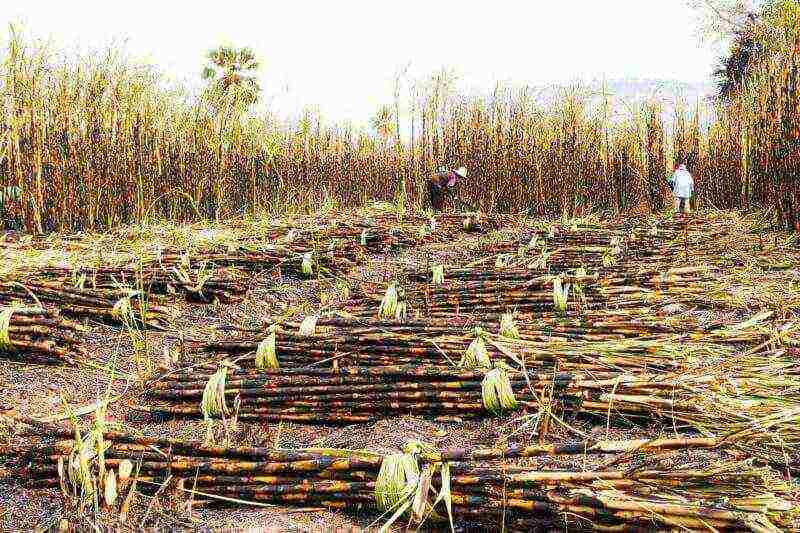 Sugarcane harvesting should start four months after germination.On an industrial scale, harvesting is carried out with specialized equipment, and small acreage of reed is harvested by hand. Sugar stalks before flowering are cut with special knives or cutting devices, at the root and cleaned of foliage.
Sugarcane harvesting should start four months after germination.On an industrial scale, harvesting is carried out with specialized equipment, and small acreage of reed is harvested by hand. Sugar stalks before flowering are cut with special knives or cutting devices, at the root and cleaned of foliage.
Crop sugar cane, when properly processed, can yield a much higher sugar yield than sugar beet. About 70% of the world's sugar reserves are derived from cultivated sugar cane.
In order to obtain high-quality sugar in the processing process, the harvesting time must be accurately calculated. Every day the harvest is delayed, the percentage of sugar in the cane is reduced. Another thing is when sugarcane is planted for forage purposes.
For harvesting sugar cane, they use: reed harvesters and machines, and it is also possible to use sorghum harvesting equipment, with their help, by direct mowing, the harvest (safra) takes place.
Sugarcane seeds: collection, storage
 Sugarcane seeds are short-lived, their viability lasts up to six months. Collecting sugar cane can be done when the cane has released its panicles, and they turn brown. However, in central Russia, it is difficult to achieve full maturation of reed seeds due to inappropriate climatic conditions. And in the southern regions of our country, with the usual planting, without additional agrotechnical measures, sugarcane seeds rarely fully ripen.
Sugarcane seeds are short-lived, their viability lasts up to six months. Collecting sugar cane can be done when the cane has released its panicles, and they turn brown. However, in central Russia, it is difficult to achieve full maturation of reed seeds due to inappropriate climatic conditions. And in the southern regions of our country, with the usual planting, without additional agrotechnical measures, sugarcane seeds rarely fully ripen.
One "sugar" panicle, with proper care, brings about 600 seeds, when planted, it is quite enough for one hundred square meters of land. When collecting seeds, the panicles are broken off, threshed and sifted, you can pick the panicle with your hands, and then dry the seeds. Due to the fragility of the seeds, they can be stored in a tissue bag, no later than until next year.
Sugar cane processing
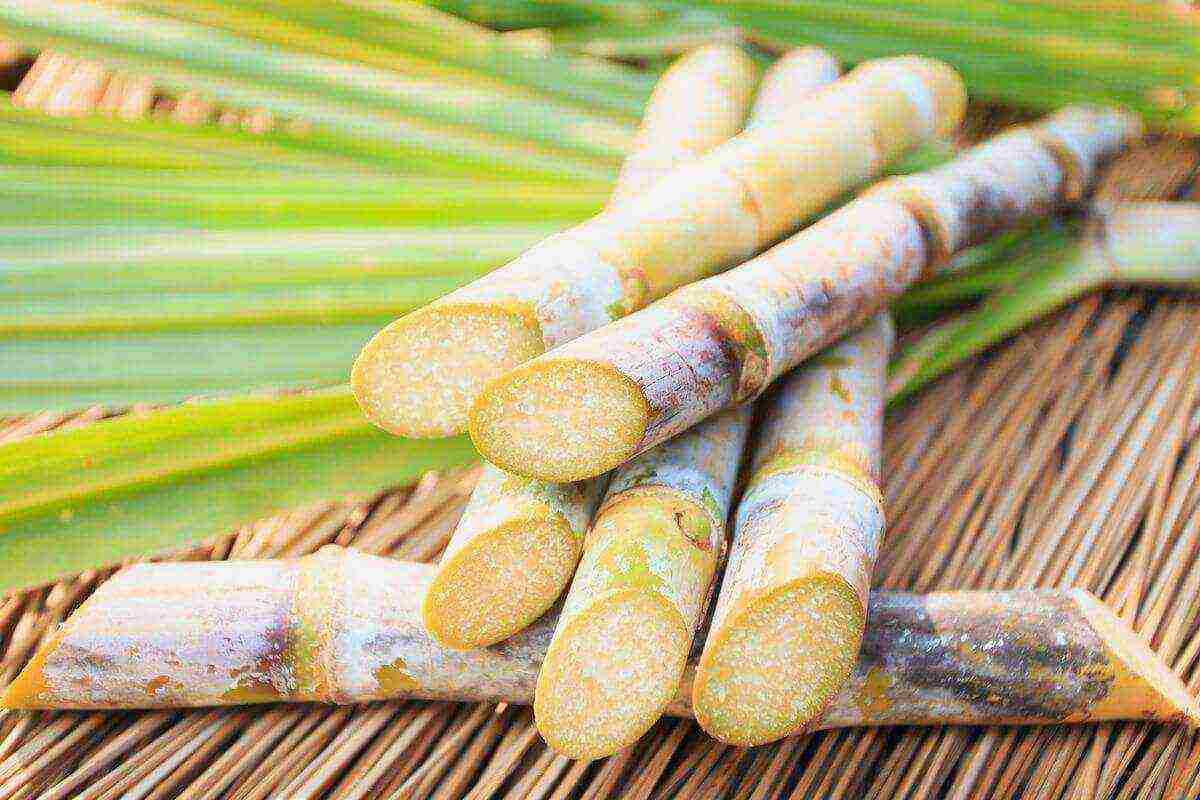 Cane sugar without additional processing, unsuitable for consumption and further storage. Therefore, additional processing or refining is considered the optimal cycle to complete the production of cane sugar.
Cane sugar without additional processing, unsuitable for consumption and further storage. Therefore, additional processing or refining is considered the optimal cycle to complete the production of cane sugar.
The technology for producing sugar from cane is similar to the method for producing sugar from sugar beet. Both raw material processing technologies include several identical steps:
- Grinding the product
- Getting juice from a processed product
- Purification of juice from additional impurities
- Concentration of juice to the concentration of syrup by evaporation method
- Crystallizing the concentrate and converting it into sugar
- Drying the finished product
Juice is obtained by crushing, pressing and further pressing the raw cane. Thanks to a special technology for treating cane with water, using a press, almost one hundred percent of the juice is extracted from the raw material. The juice goes through the cleaning procedure through a mash trap and accumulates in the measuring tanks.
The pulp, in turn, returns to the press, and carries out a secondary pressing together with the primary mass of the supplied raw material. After cleaning, the juice undergoes a procedure of cold or hot lime defecation. In this way, organic acids are neutralized and a neutral, soluble lime salt is formed. In the process of cold defecation, the juice is mixed with milk of lime, mixed and placed in sedimentation tanks. In order for the sugar to settle, the settling tanks are heated, and a thick concentrated mass is obtained at the bottom, with juice on top.
The thick mass is subjected to a filter press, and the juice is drained. In another method, the thickened syrup is fed into a vacuum apparatus and boiled into massecuite. The resulting cooked mass is placed in the master massecuite for crystallization and cooling. After that, the sugar is whipped in the centrifuge.The fine sand obtained in the production of sugar is re-loaded into the crystallizer and undergoes the procedure for re-melting the product and placed in the vacuum apparatus of all massecuite for boiling subsequent syrups.
The production of cane sugar described above is somewhat different from the production of sugar from beets. The first difference is that the cane is pressed on roller presses, and the beets are extracted in a diffusion battery. The second difference is the stages of juice purification, and processing with the least amount of lime, rather than in the production of granulated sugar from beets.
Cane sugar: good or bad?
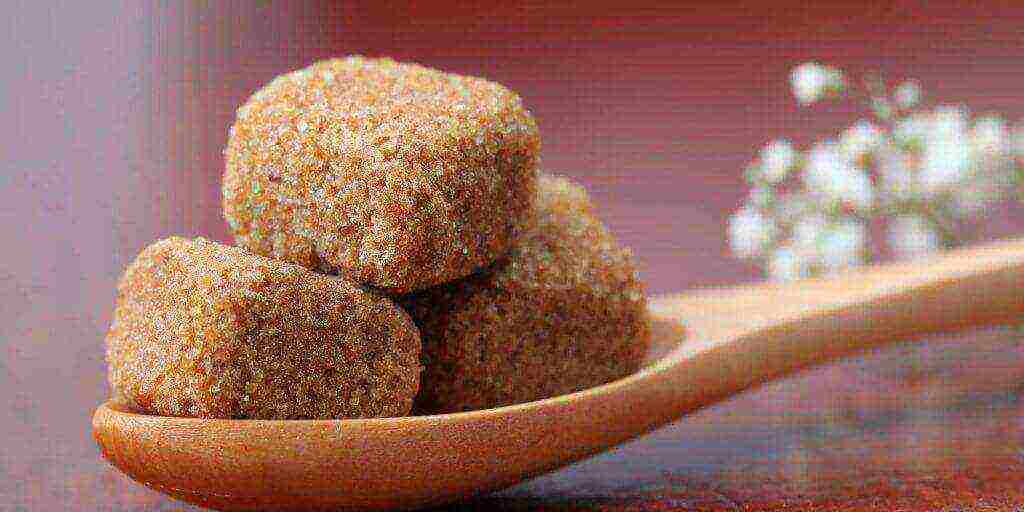 Cane sugar is 90% sucrose and is absorbed faster. In addition, it also contains trace elements: potassium, calcium and iron. It is better to use unrefined cane sugar, it is more natural. It is better to give preference in the store to cane sugar in transparent packaging in order to closely examine the product, this will help to distinguish natural cane sugar from colored beet sugar.
Cane sugar is 90% sucrose and is absorbed faster. In addition, it also contains trace elements: potassium, calcium and iron. It is better to use unrefined cane sugar, it is more natural. It is better to give preference in the store to cane sugar in transparent packaging in order to closely examine the product, this will help to distinguish natural cane sugar from colored beet sugar.
The first distinctive feature of cane sugar is its loose appearance and strong molasses aroma, incomparable with the smell of white sugar. In addition, natural cane sugar is brown in color, but there is also white cane sugar. How can you tell them apart? To distinguish a fake from a natural product, a cup of water will help by dissolving a brown lump of sugar in it, the water should remain unchanged, but if staining has occurred, then you have a fake.
Cane sugar goes through fewer processing cycles than beet sugar, so there is an opinion that it retains more nutrients.
Cane sugar improves brain activity, improves mood, gives a boost of vigor, by replenishing the body's energy reserves. Cane sugar is contraindicated for people suffering from diabetes and intolerance to glucose and galactose.