Content
- 1 Landing dates
- 2 Landing distance
- 3 Features of growing potatoes in the Leningrad region
- 4 Potato varieties for cultivation in the Leningrad region
- 5 Landing dates
- 6 Landing distance
- 7 Features of growing potatoes in the Leningrad region
- 8 Potato varieties for cultivation in the Leningrad region
- 9 Features of planting potatoes
- 10 Growing potatoes in a greenhouse or greenhouse
- 11 The best potato varieties for the Leningrad region
- 12 Features of growing potatoes in the North-West region of Russia
- 13 The best varieties for the Northwest region
- 14 Potatoes for growing in the Leningrad region
- 15 New potato varieties for the Northwest region
The weather in the Leningrad region can change very much per day, there are sharp fluctuations in air temperature. Snow melts from mid-April. The average temperature in July is + 16-18 degrees. Besides, very poor soils in the Leningrad region, podzol and peat bog, therefore, when digging, a large amount of fertilizer should be applied. In this review, we will talk about the features of planting potatoes in this region.
Landing dates
Potatoes are planted in early May, at this time, buds burst on birches and leaves appear from them. It is required that the earth at a depth of 10 cm has a temperature of at least + 8-12 degrees.
Landing distance
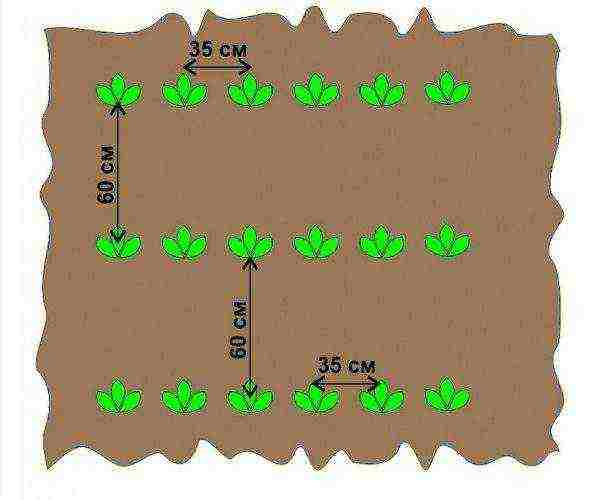 Potato planting scheme for ordinary beds
Potato planting scheme for ordinary beds
The distance between the bushes depends on the variety. For earlier varieties, holes are dug at a distance of 25 cm from each other, for later ones - 30-35 cm.
Features of growing potatoes in the Leningrad region
Choosing a landing site
 Potatoes are a very light-loving plant and the area for it should be sunny, as well as, if possible, protected from drafts.
Potatoes are a very light-loving plant and the area for it should be sunny, as well as, if possible, protected from drafts.
The place needs to be chosen sunny, but protected from northerly winds. It is necessary to observe the crop rotation. Potatoes are planted in the place where beans, beans, peas, cabbage, cucumbers grew last year... It is even better if rye or mustard grew on the site before. Rye makes the soil loose and breathable. She will enrich the land with nitrogen and potassium. It is not advised to plant potatoes in the place where tomatoes, peppers, eggplants, that is, nightshades and strawberries, grew before.The best soil acidity ph = 5-5.5.
Digging the soil
In autumn, scatter 5 - 10 kg of manure, 20 g of potassium sulfate and 20 g of double superphosphate per 1 m².
Then dig up the ground and make high ridges, then in the spring the earth will warm up faster. In addition, in the spring, after the snow melts and before planting, you can cover the ground with foil.
Landing rules in the Leningrad region
Sprouted tubers are planted.
A month before planting, select the healthiest tubers weighing 60-80 g, spread them on a flat surface in a warm place, illuminated by the rays of the sun, sometimes turn the tubers over. You can put the tubers in boxes filled with damp peat or sawdust, sprinkle them, sometimes sprinkle them with warm water. It is impossible for the sprouts to break, otherwise the potatoes will not sprout.
The rows are dug so that they are located from north to south.
Potatoes are planted in 3 ways:
- Digging on the site holes 8-9 cm deep.
- Forms high ridges and put potatoes in them to a depth of 10-12 cm.
- Plant tubers in trenches.
Summer in the region ends quickly, because of this, early and mid-season varieties are planted on the site. And potatoes of late varieties are planted in hotbeds and greenhouses.
Depending on the composition of the earth, holes are dug, less deepened holes are dug on denser and heavier soil. So, in clay soil, the depth of the hole is made 4-5 cm, and in sandy loam and sandy soil - 10-12 cm.
Also, if the ground is light, then make holes or furrows. A handful of ash is poured into each hole, a tuber is placed, and buried. The holes are dug, making an indent between them of 35 cm, and between the rows - 70 cm.
BUT if the ground is heavy, then plant potatoes in ridges about 12 cm high and about 0.65 m wide... Tuber crops on sandy loam soils are planted to a depth of 8-10 cm, and on loamy soils - 6-8 cm from the top of the ridge. Before planting, the ground is watered.
Care on the site
Watering
Before the buds appear, the soil is not watered, but when buds form and begin to bloom, the soil needs to be constantly moistened. Before watering, make sure the ground is dry to a depth of 6-8 cm. Water in the evening, pouring 2-3 liters of water under one bush. In drought, water the potatoes 3-5 times per season. Be sure to loosen the soil after watering.
Hilling
 Hilling beds with potatoes
Hilling beds with potatoes
First, spud the bushes that are 14-16 cm high, then spud them after 2-3 weeks when buds begin to form. Huddle after rain or watering.
Growing in a greenhouse
In the greenhouse, you can keep the ideal temperature and humidity for potatoes, it ripens a little earlier than on the site, and there are no diseases and harmful insects.
 Flowering potatoes in a greenhouse
Flowering potatoes in a greenhouse
You can plant potatoes in the greenhouse as early as April... Planting and grooming are the same as for a regular site. Fertilizers are poured onto the ground, dug up, dig holes, sprouted tubers are placed in each, covered with soil. The culture is loosened after watering, weeds are pulled out, hilled and watered.
To further reduce the growth period of the culture, plant seedlings. 3-4 weeks before planting, sprouted tubers are planted in peat cups, sprinkled with earth, watered and loosened the soil.
Landing in greenhouses
Arcs are placed on the garden bed and covered with film, securing the edges. This will save the culture from recurrent frosts and sudden temperature fluctuations. Sometimes in warm weather, when the sun is shining, remove the film so that the moisture evaporates, water the crop, fertilize it, loosen the soil and close the greenhouse again. In greenhouses, tubers can be harvested 14 days earlier than on the plot.
Potato varieties for cultivation in the Leningrad region
It is best to plant elite varieties. They hardly get sick, they are not damaged by insects, in addition, their taste is better than that of other varieties.
Adretta
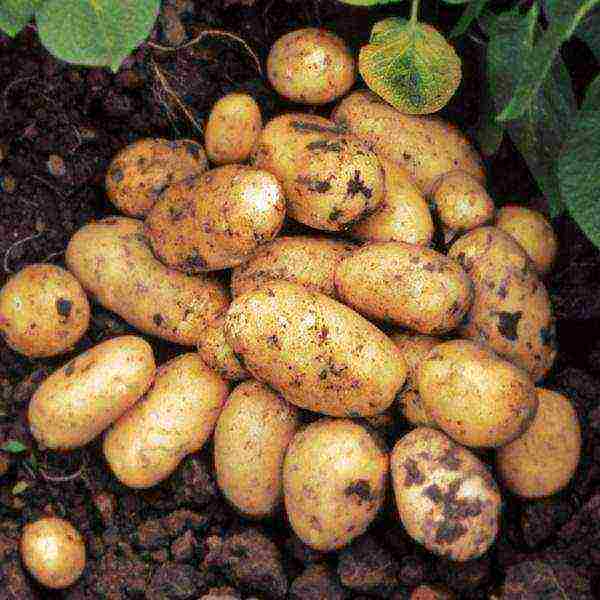 Adretta potatoes
Adretta potatoes
The variety is drought-resistant. Has a high yield - 45 t / ha. The peel is yellowish, rough.Adretta's potatoes are unpretentious to the composition of the land, which is very important for the poor soils of the Leningrad region. He was awarded a tasting taste assessment - 5 points. Tuber weight - 140 g.
Spring white
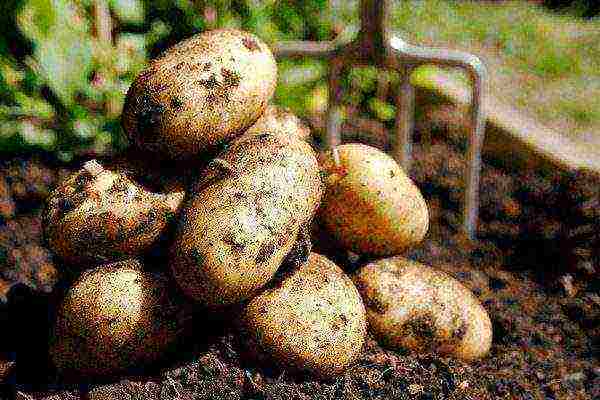 Spring white potatoes
Spring white potatoes
Tuber weight 80-140 g. The variety is moderately resistant to scab, Alternaria and viruses. But not resistant to late blight.
Aurora
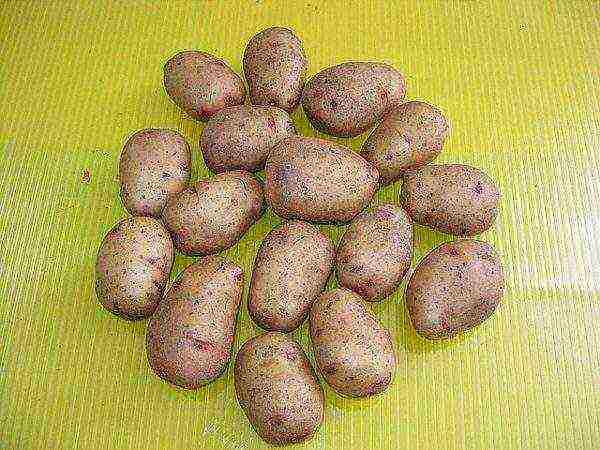 Potatoes Aurora
Potatoes Aurora
Productivity - 250-300 kg / ha. The weight of the Aurora variety tuber is 90-150 g.
Naiad
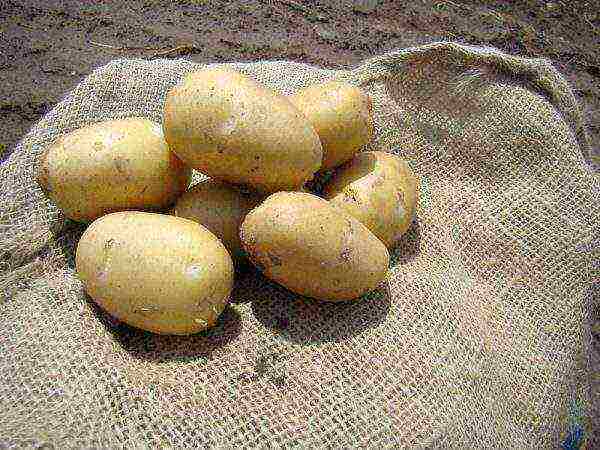 Naiad potatoes
Naiad potatoes
Productivity - 193-373 kg / ha. Tuber weight 72-126 g. The peel of the potato is yellow and the flesh is white. Resistant to nematodes and immune to cancer.
Pushkinets
 Potatoes Pushkinets
Potatoes Pushkinets
Productivity - 32 t / ha. Tuber weight - 103-106 g. The peel is beige, the flesh is snow-white. The cultivar is immune to cancer and resistant to nematodes. Moderately susceptible to scab and late blight. Tasting taste assessment - 4.0-4.7 points.
Latona
 Potatoes Latona
Potatoes Latona
The peel is yellow, the flesh is yellowish. Tuber weight 90-140 g. Productivity is one of the highest - 50 t / ha. The variety easily tolerates heat and dry weather, as well as constant rains. Taste score - 4.9-5 points. It is immune to scab, ring and dry rot of tubers, viral infections. Not susceptible to nematodes. Unfortunately, it is susceptible to late blight of leaves.
Impala
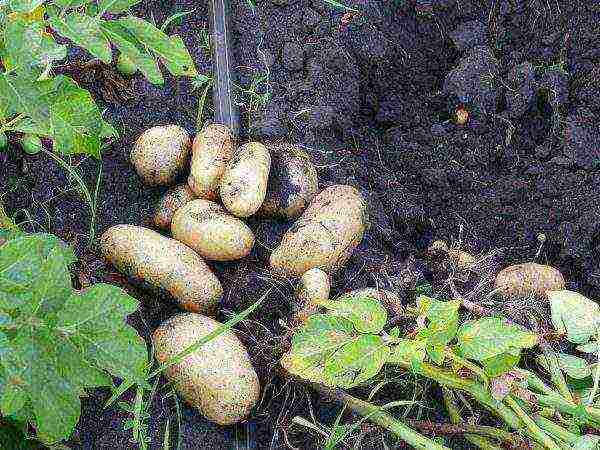 Impala potatoes
Impala potatoes
Tuber weight - 88-150 g. The highest yield - 367 c / ha. The peel is yellow, the flesh is creamy. Taste rating - 4 points. Impala variety Resistant to nematodes and immune to cancer, weakly susceptible to common scab and viruses. But it is susceptible to rhizoctonia, powdery scab and late blight. Has a high resistance to stress. Resistant to dry summer and mechanical damage.
Zhukovsky early
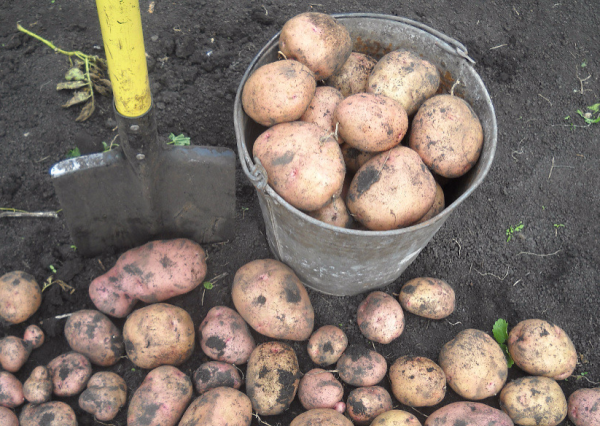 Potatoes Zhukovsky early
Potatoes Zhukovsky early
The variety is not susceptible to cancer, nematodes, Alternaria, and black scab. Drought-resistant. The rind is pink and the flesh is white. Tuber weight - 100-120 g. Productivity - 400-450 kg / ha. Tasting taste assessment - 5 points out of 5 possible.
Bullfinch
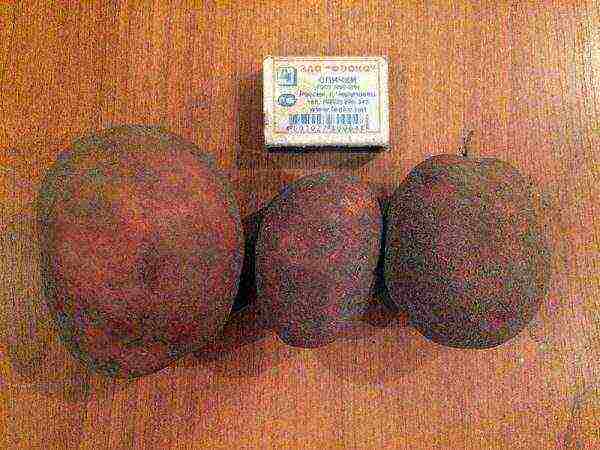 Potato bullfinch
Potato bullfinch
Tuber weight - 60-90 g. Average yields 350-450 c / ha. It is immune to cancer, scab and viruses, late blight and macrospore of tubers. But it can be attacked by a nematode.
Luck
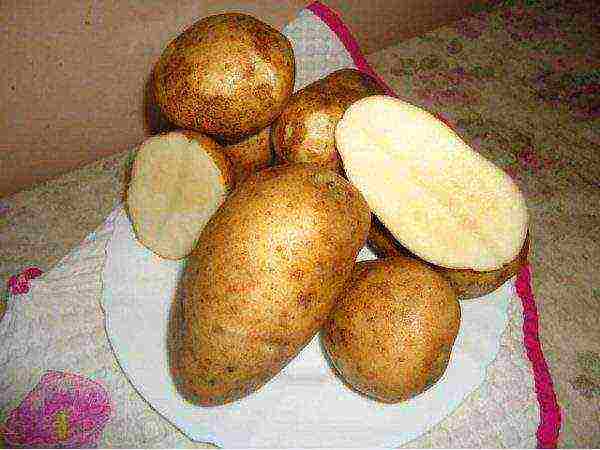 Potato Luck
Potato Luck
Tuber weight - 120 g. Productivity 42 t / ha. Variety Luck is resistant to rhizoctonia, scab, cancer, wrinkled mosaic, viral diseases. The variety is susceptible to late blight.
Which ones are early varieties
Early varieties include Adretta, Zhukovsky early, Pushkinets, Latona, Impala.
When growing potatoes in the Leningrad Region, do not forget that the soils there are usually depleted, therefore add fertilizer when digging. For growing late varieties of potatoes, use greenhouses, hotbeds, plant seedlings.
Correct planting of potatoes in the Leningrad region
Rate this post
The weather in the Leningrad region can change very much per day, there are sharp fluctuations in air temperature. Snow melts from mid-April. The average temperature in July is + 16-18 degrees. Besides, very poor soils in the Leningrad region, podzol and peat bog, therefore, when digging, a large amount of fertilizer should be applied. In this review, we will talk about the features of planting potatoes in this region.
Landing dates
Potatoes are planted in early May, at this time, buds burst on birches and leaves appear from them. It is required that the earth at a depth of 10 cm has a temperature of at least + 8-12 degrees.
Landing distance
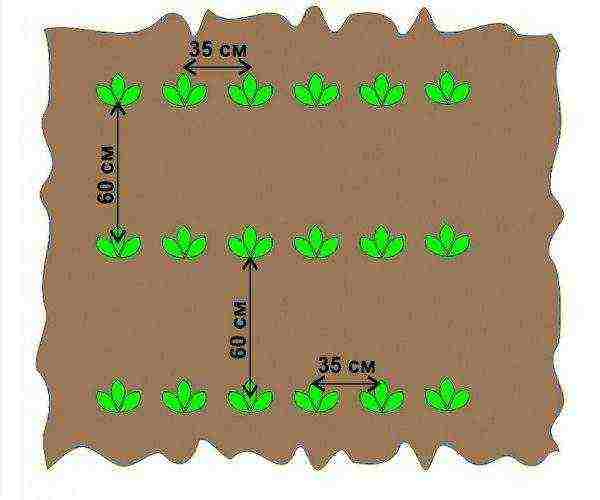 Potato planting scheme for ordinary beds
Potato planting scheme for ordinary beds
The distance between the bushes depends on the variety. For earlier varieties, holes are dug at a distance of 25 cm from each other, for later ones - 30-35 cm.
Features of growing potatoes in the Leningrad region
Choosing a landing site
 Potatoes are a very light-loving plant and the area for it should be sunny and, if possible, protected from drafts.
Potatoes are a very light-loving plant and the area for it should be sunny and, if possible, protected from drafts.
The place needs to be chosen sunny, but protected from the northerly winds. It is necessary to observe the crop rotation. Potatoes are planted in the place where beans, beans, peas, cabbage, cucumbers grew last year... It is even better if rye or mustard grew on the site before. Rye makes the soil loose and breathable. She will enrich the land with nitrogen and potassium. It is not advised to plant potatoes in the place where tomatoes, peppers, eggplants, that is, nightshades and strawberries, grew before. The best soil acidity ph = 5-5.5.
Digging the soil
In autumn, scatter 5 - 10 kg of manure, 20 g of potassium sulfate and 20 g of double superphosphate per 1 m².
Then dig up the ground and make high ridges, then in the spring the earth will warm up faster. In addition, in the spring, after the snow melts and before planting, you can cover the ground with foil.
Landing rules in the Leningrad region
Sprouted tubers are planted.
A month before planting, select the healthiest tubers weighing 60-80 g, spread them on a flat surface in a warm place, illuminated by the rays of the sun, sometimes turn the tubers. You can put the tubers in boxes filled with wet peat or sawdust, sprinkle them, sometimes sprinkle them with warm water. It is impossible for the sprouts to break, otherwise the potatoes will not sprout.
The rows are dug so that they are located from north to south.
Potatoes are planted in 3 ways:
- Digging on the site holes 8-9 cm deep.
- Forms high ridges and put potatoes in them to a depth of 10-12 cm.
- Plant tubers in trenches.
Summer in the region ends quickly, because of this, early and mid-season varieties are planted on the site. And potatoes of late varieties are planted in hotbeds and greenhouses.
Depending on the composition of the earth, holes are dug, less deepened holes are dug on denser and heavier soil. So, in clay soil, the depth of the hole is made 4-5 cm, and in sandy loam and sandy soil - 10-12 cm.
Also, if the ground is light, then make holes or furrows. A handful of ash is poured into each hole, a tuber is placed, and buried. The holes are dug, making an indent between them of 35 cm, and between the rows - 70 cm.
BUT if the ground is heavy, then plant potatoes in ridges about 12 cm high and about 0.65 m wide... Tuber crops on sandy loam soils are planted to a depth of 8-10 cm, and on loamy soils - 6-8 cm from the top of the ridge. Before planting, the ground is watered.
Care on the site
Watering
Before the buds appear, the soil is not watered, but when buds form and begin to bloom, the soil needs to be constantly moistened. Before watering, make sure the ground is dry to a depth of 6-8 cm. Water in the evening, pouring 2-3 liters of water under one bush. In drought, water the potatoes 3-5 times per season. Be sure to loosen the soil after watering.
Hilling
 Hilling beds with potatoes
Hilling beds with potatoes
First, spud the bushes that are 14-16 cm high, then spud them after 2-3 weeks when buds begin to form. Huddle after rain or watering.
Growing in a greenhouse
In the greenhouse, you can keep the ideal temperature and humidity for potatoes, it ripens a little earlier than on the site, and there are no diseases and harmful insects.  Flowering potatoes in a greenhouse
Flowering potatoes in a greenhouse
You can plant potatoes in the greenhouse as early as April... Planting and grooming are the same as for a regular site. Fertilizers are poured onto the ground, dug up, dig holes, sprouted tubers are placed in each, covered with soil. The culture is loosened after watering, weeds are pulled out, spud and watered.
To further shorten the growth period of the culture, plant seedlings. 3-4 weeks before planting, sprouted tubers are planted in peat cups, sprinkled with earth, watered and loosened the soil.
Landing in greenhouses
Arcs are placed on the garden bed and covered with film, securing the edges. This will save the culture from recurrent frosts and sudden temperature fluctuations. Sometimes in warm weather, when the sun is shining, remove the film so that the moisture evaporates, water the crop, fertilize it, loosen the soil and close the greenhouse again. In greenhouses, tubers can be harvested 14 days earlier than on the plot.
Potato varieties for cultivation in the Leningrad region
It is best to plant elite varieties. They hardly get sick, they are not damaged by insects, in addition, their taste is better than that of other varieties.
Adretta
 Adretta potatoes
Adretta potatoes
The variety is drought-resistant. Has a high yield - 45 t / ha. The peel is yellowish, rough. Adretta's potatoes are unpretentious to the composition of the land, which is very important for the poor soils of the Leningrad region. He was awarded a tasting taste assessment - 5 points. Tuber weight - 140 g.
Spring white
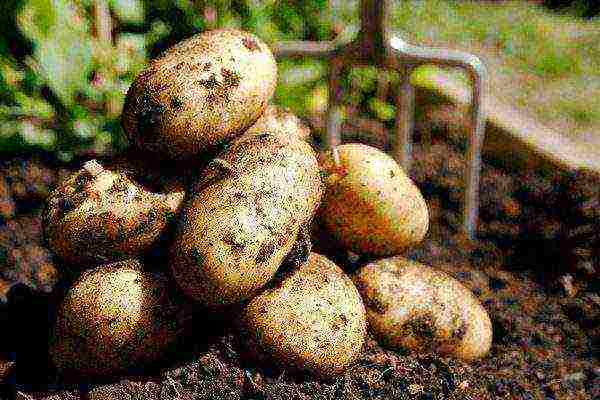 Spring white potatoes
Spring white potatoes
Tuber weight 80-140 g. The variety is moderately resistant to scab, Alternaria and viruses. But not resistant to late blight.
Aurora
 Potatoes Aurora
Potatoes Aurora
Productivity - 250-300 kg / ha. The weight of the Aurora variety tuber is 90-150 g.
Naiad
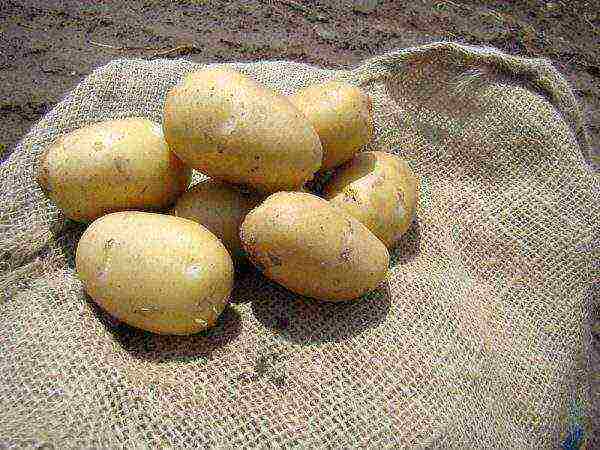 Naiad potatoes
Naiad potatoes
Productivity - 193-373 kg / ha. Tuber weight 72-126 g. The peel of the potato is yellow and the flesh is white. Resistant to nematodes and immune to cancer.
Pushkinets
 Potatoes Pushkinets
Potatoes Pushkinets
Productivity - 32 t / ha. Tuber weight - 103-106 g. The peel is beige, the flesh is snow-white. The cultivar is immune to cancer and resistant to nematodes. Moderately susceptible to scab and late blight. Tasting taste assessment - 4.0-4.7 points.
Latona
 Potatoes Latona
Potatoes Latona
The peel is yellow, the flesh is yellowish. Tuber weight 90-140 g. Productivity is one of the highest - 50 t / ha. The variety easily tolerates heat and dry weather, as well as constant rains. Taste score - 4.9-5 points. It is immune to scab, ring and dry rot of tubers, viral infections. Not susceptible to nematodes. Unfortunately, it is susceptible to late blight of leaves.
Impala
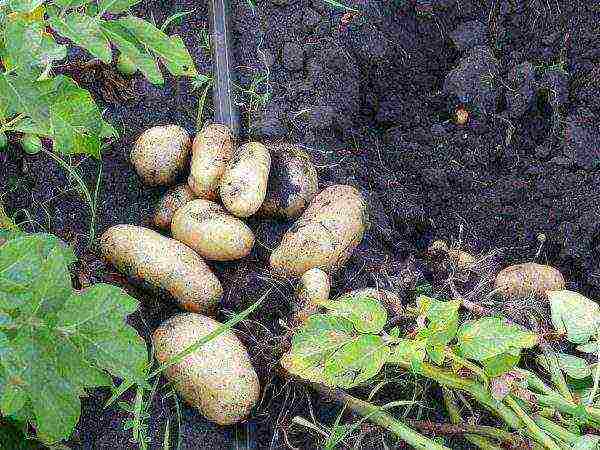 Impala potatoes
Impala potatoes
Tuber weight - 88-150 g. The highest yield - 367 c / ha. The peel is yellow, the flesh is creamy. Taste rating - 4 points. Impala variety Resistant to nematodes and immune to cancer, weakly susceptible to common scab and viruses. But it is susceptible to rhizoctonia, powdery scab and late blight. Has a high resistance to stress. Resistant to dry summer and mechanical damage.
Zhukovsky early
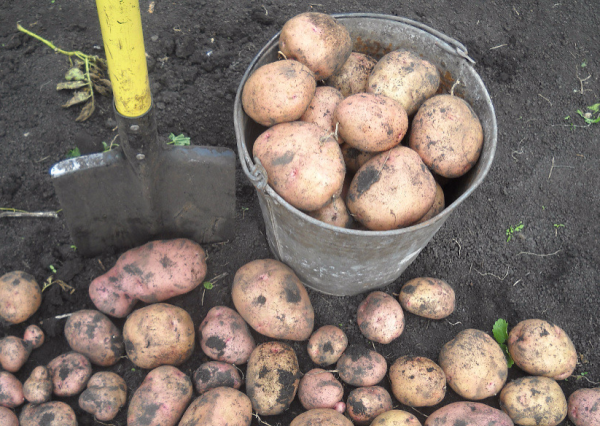 Potatoes Zhukovsky early
Potatoes Zhukovsky early
The variety is not susceptible to cancer, nematodes, Alternaria, and black scab. Drought-resistant. The rind is pink and the flesh is white. Tuber weight - 100-120 g. Productivity - 400-450 kg / ha. Tasting taste assessment - 5 points out of 5 possible.
Bullfinch
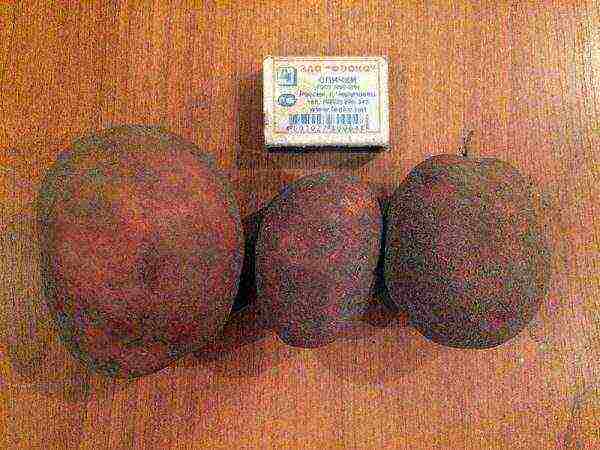 Potato bullfinch
Potato bullfinch
Tuber weight - 60-90 g. Average yields 350-450 c / ha. It is immune to cancer, scab and viruses, late blight and macrospore of tubers. But it can be attacked by a nematode.
Luck
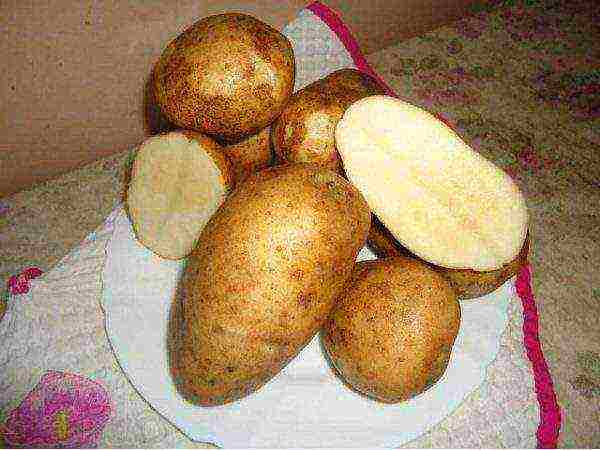 Potato Luck
Potato Luck
Tuber weight - 120 g. Productivity 42 t / ha. Variety Luck is resistant to rhizoctonia, scab, cancer, wrinkled mosaic, viral diseases. The variety is susceptible to late blight.
Which ones are early varieties
Early varieties include Adretta, Zhukovsky early, Pushkinets, Latona, Impala.
When growing potatoes in the Leningrad region, do not forget that the soil there is usually depleted, therefore add fertilizer when digging. For growing late varieties of potatoes, use greenhouses, hotbeds, plant seedlings.
Record Correct planting of potatoes in the Leningrad region first appeared About the farm.
It seems that potatoes are grown in almost all of Russia. Although it is considered an unpretentious plant, its yield depends on the weather conditions of the area. In ideal conditions, a very good harvest can be harvested, and if the summer is cold and rainy, then without additional care and special fertilizers, the potatoes will grow small and rare.
Unfortunately, in the Leningrad region, warm and slightly rainy weather all summer is a real rarity. In one day, the weather can change several times from a shower to a scorching sun. The air temperature in the middle of summer is kept at +15 degrees. The land in the northern region of Russia is peat bog, so summer residents definitely need to fertilize their own beds.

Features of planting potatoes
A place for growing potatoes is always selected sunny, closed on all sides by bushes from the harsh northerly winds. A soil richly fertilized with nitrogen and potassium is suitable for potatoes, so it is best to plant it in the area where legumes, cabbage, rye, mustard and cucumbers grew last year, which made the soil loose and breathable. But it is not recommended to choose the garden where eggplants, strawberries and tomatoes grew. Every four years, you should change the place for planting potatoes so that pests do not start in the soil.
The soil for planting potatoes must be prepared in the fall, scattering manure, potassium sulfate, double superphosphate over the beds. Then all this needs to be dug up and the beds made high so that the soil warms up faster in spring. And in the spring, after the snow melts, to help the earth warm up faster, you can cover the entire soil with a film that is removed before planting.
A month before planting, you need to carefully check the potatoes that are set aside for planting, since during storage some of the vegetables can get sick. If such a tuber is thrown for planting, then it will either decompose in the ground, infecting neighboring bushes, or it will give a very weak harvest. Therefore, if you see even a small speck of rot on the potato, in no case put it next to others for planting.
If you come across large tubers weighing about 100 grams, then you can cut them in half and plant these halves in different holes. However, it should be borne in mind that one half will give a lower yield than a whole tuber.
After checking and rejecting, the potatoes must be placed in a warm place so that the sprouts hatch, since only sprouted tubers are planted. If possible, place them in a sunny place. From time to time, the tubers can be turned over, but carefully so as not to break the fragile shoots, otherwise there will be no harvest from it. It will be ideal if you select several varieties of potatoes for planting at once, since they do not give an excellent harvest every year and a large number of them will save you from a complete lack of potatoes.
Tanks for sprouting tubers:
- Low boxes made of any material.
- Transparent containers that can be stacked on top of each other are the most ideal container.
- In a warm room on the floor, window sills, shelves.
- In 5 liter plastic bottles with ventilation holes.
- In canvas bags.
If there is very little time left before planting, no more than a week, and there are no sprouts on the tubers, then you can resort to wet germination. This requires a dark room with high humidity up to 70%. Potatoes in one or two layers are placed in plastic boxes with holes. The boxes themselves are placed on a layer of peat or sawdust up to 6 centimeters thick, pre-moistened with a solution of copper sulfate.
Then a small layer of peat or sawdust, also dipped in the same solution, is poured onto the potatoes. If there is no peat in that amount, then you can get by with sawdust alone. Throughout the week, you need to monitor the humidity, water if necessary. By the end of the week, it is important not to miss the moment when the roots grow to such a length that they do not get confused. Otherwise, tubers with long sprouts will be difficult to plant.
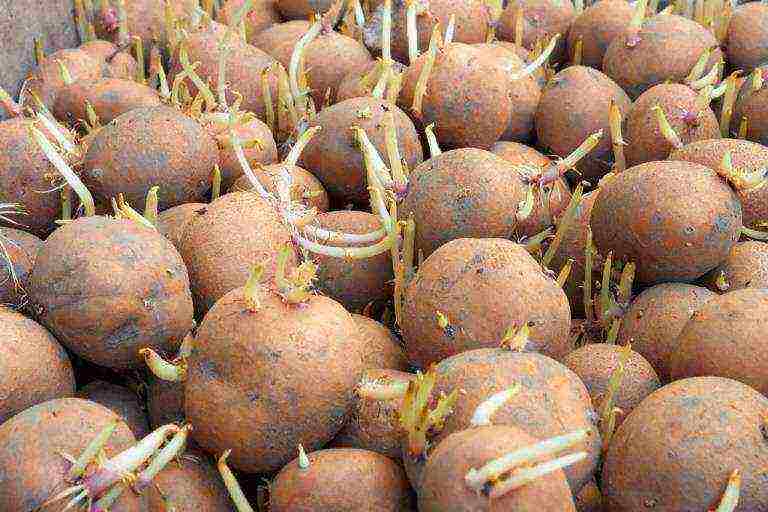

If the weather deteriorates sharply on the day of planting, and the sprouted vegetable is already ready, in order to stop the growth of its sprouts, you need to slightly lower the room temperature.
In order to protect potatoes from fungal diseases and increase their yield, the day before planting, they are moistened for about a minute in a solution of copper sulfate.
In this northern area, it is recommended to plant tubers in early May, so that they have time to ripen by the end of August. Of course, if the weather is favorable for planting. Therefore, only an early potato variety is suitable for this area. Late varieties are planted a little later and only in greenhouses.
First, choose one of three landing methods that are convenient for you:
- Trenches up to 10 centimeters deep are made if the ground is light.
- If the soil is dense and heavy, then dig out separate holes 7-9 cm deep for each vegetable.
- In order for the earth to warm up properly, high beds are made, where potatoes are placed at a depth of 10 cm.
It should be remembered that planting tubers in the ground deeper than 11 cm or less than 4 cm in the northern regions reduces the yield of potatoes. The distance between the rows should be from 60 to 70 centimeters, and between the tubers themselves about 35-40 centimeters.
First, the soil must be watered if there was no rain the day before. Before you throw the tuber into the hole and bury it, you need to throw a pinch of ash or chicken droppings for fertilization. After the potatoes are planted, you need to loosen the soil above them with a rake so that the water does not evaporate from the ground. The land is not watered after planting.
As soon as the first buds appeared and began to bloom, then the soil should be watered regularly, but try not to overflow it. In order not to kill the beds for weeding all summer, try to huddle the beds more often. Hilling should be done after the crop has been watered.
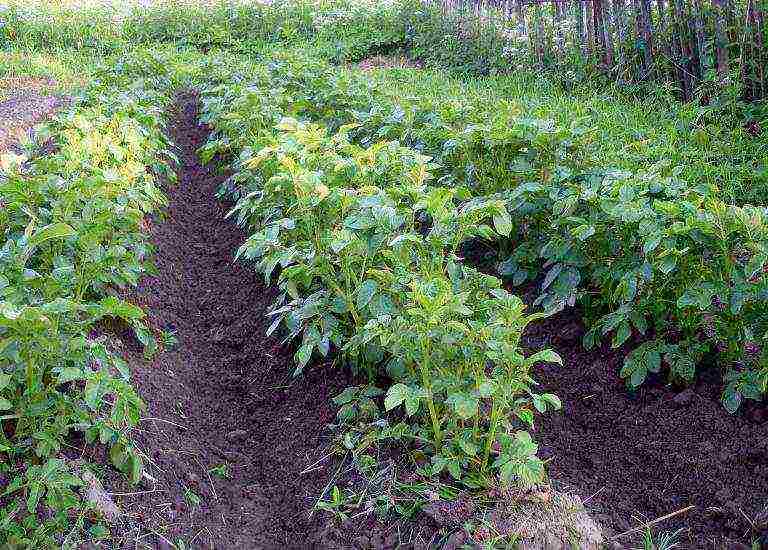

Growing potatoes in a greenhouse or greenhouse
This method is suitable for very northern places where warm summer days are very rare. Planting tubers in a greenhouse and a greenhouse has many advantages:
- Ideal air temperature.
- Desired percentage of moisture.
- Absence of various diseases and harmful insects.
- Early harvest.
Unlike open ground, which depends on weather conditions, sprouted tubers are planted in the greenhouse at the beginning of April. The very process of planting and subsequent care occurs in the same way as in an open garden.
In order to get an early harvest in the greenhouse, not sprouted tubers can be planted in the soil, but its seedlings, previously grown in peat cups.
The greenhouse method is more suitable for large beds. After the potatoes are planted in the ground, you need to put special arcs on all sides of the garden and cover them with a special film, securing the edges well. Thus, the plants will be protected from bad weather conditions. As soon as the sun appears and the air temperature rises, you need to ventilate the beds by removing the film from them. It is undesirable to leave the bed open at night. Do not forget to water and fertilize the crop, huddle the beds. Thus, potatoes in a greenhouse will ripen two weeks earlier than in open soil.
The best potato varieties for the Leningrad region
First you need to decide what you are growing potatoes for. If for cooking or mashed potatoes, then you need to choose varieties with a high starch content. And for fried potatoes or salads, they are suitable with a low starch content, they will not boil over. If for long storage, then you need to choose those varieties that do not deteriorate until next spring. It is imperative to take into account what diseases are common in your area so that the entire crop does not die immediately.
Luck
An early maturing table potato variety, whose tops with a lot of foliage reach a medium height. The potato itself is white, large oval in shape. Differs in a very high yield, can be stored for a long time. The taste is amazing. It is considered the best variety for the Leningrad region.
Detskoselsky
Medium early variety, resistant to various diseases such as late blight, scab, cancer. Medium-sized potatoes are light pink in color with white flesh. The taste is excellent, does not deteriorate during storage until the end of spring.
Visa
Differs in undersized tops and resistance to viral diseases. It almost always produces a large harvest. Potatoes with a red skin and white flesh, are both oval and round. In storage, it showed itself from an excellent side.
Fresco
Early ripe oval-shaped potatoes, resistant to all types of diseases, have excellent taste. Its rind is yellow and the flesh is light yellow and tastes great.
Kholmogorsky
It is resistant to late blight, belongs to the early maturing variety, gives the maximum yield.Oval-shaped potatoes with red skin and yellow flesh. Stored for a long time.
Spring white
Oval or round potatoes have a yellow rind and white flesh. It is affected by late blight, but viruses bypass it.
Latona
It has not only a yellow skin, but also a pulp. Produces a very high yield, ideal for the weather conditions of the Leningrad region, as it withstands endless rain and drought. In terms of taste, this variety received the highest score. Although this variety is immune to viruses, scab, it can get late blight.
Impala
Average tuber weight is about 100 grams. Not resistant to all viruses, it can get scab, late blight. Possesses high stress resistance, easily tolerates drought, does not deteriorate in case of mechanical damage. The peel of the potato is yellow, the flesh is creamy.
Potatoes are a plant that requires warmth and light. How to grow it in conditions of frequent changeable weather and excessive abundance of natural precipitation.
Features of growing potatoes in the North-West region of Russia
The climate in the Northwest region of Russia is influenced by Arctic, Atlantic and continental air masses. Winter here lasts from November to February. March is the sunniest of all months of the year, while April is foggy and cloudy. The hot period of summer is no more than two weeks, all other days are cloudy and precipitation. Autumn begins in mid-August. Not every potato variety is suitable for growing in this region.
There are many factors to consider when choosing a potato variety.
Landing time
Potatoes are planted, as a rule, in early May, when leaves bloom on birches. The specific date is determined using the lunar calendar. An important rule is to warm up the soil at a depth of 10 cm to no less than 8-12 degrees Celsius.
Potatoes are planted only in well-heated soil.
Site selection
A plot for potatoes is chosen sunny and protected from free winds. It cannot be planted in the same place every year. The best predecessors are cabbage, cucumbers, legumes. But best of all, in the fall, in the place where you plan to grow potatoes, plant rye or mustard. Rye planted in winter will enrich the soil with nitrogen, potassium, and organic matter. It is a wonderful green manure that makes the ground loose and breathable.
Rye enriches the soil with nutrients useful for potatoes
Podzolic and peat bog soils, which require large amounts of fertilizers, prevail in the North-West region of the country. They need to be applied in autumn and spring, before plowing. The most suitable are poultry droppings and manure, in the fall you can apply fresh, but in the spring - only in a rotted state.
The soil for planting potatoes must be fertilized
In order for the soil to warm up faster in spring, in the fall it needs to be loosened or high ridges formed. Also, to speed up the process, you can cover it with a film after the snow melts.
Rules for planting potatoes in the northwest
In order to obtain an early harvest, only germinated tubers need to be planted. To do this, about a month before sowing, they are taken out of storage, the healthiest ones, weighing 60–80 grams, are selected, and germinated: laid out on a flat surface and kept in a warm, well-lit place, periodically turning over. You can put the tubers in boxes with wet peat or sawdust, sprinkle them, not forgetting to sprinkle with warm water from time to time. You need to be very careful with the sprouts, you cannot damage them, otherwise there will be no seedlings.
For planting potatoes, you need to use only sprouted tubers.
Potatoes are planted in three classic ways:
- Smooth - digging holes on a flat surface.
- Ridge - laying potatoes into formed ridges.
- Trench - planting tubers in trenches.
For each type of site, the method must be selected individually.For example, in waterlogged soil, growing in ridges is well suited. The soil in them dries out faster, and the roots of plants are better enriched with oxygen, which has a very good effect on the speed and quality of the fruits formed. Optimal planting depth for medium-sized potatoes — 8-9 cm, in the ridges — 10-12 cm. The basic rule for any method of planting potatoes is that the arrangement of the rows must be observed strictly from north to south.
For waterlogged soils, growing potatoes in ridges is well suited
Features of growing late varieties
Summer in the Northwest region is rather short, so only early and middle type potatoes can be grown in the open field. To fully form their fruits late varieties, you need to use hotbeds or greenhouses.
Growing potatoes in a greenhouse
In the greenhouse, the optimal air temperature and humidity are created for the plants, they ripen earlier than in unprotected soil, and there are no diseases and various pests.
The greenhouse is the perfect place for potatoes
Potatoes are planted in a greenhouse earlier than in open ground, because the soil there warms up faster. In the Northwest region, this period usually begins in April. The cultivation process is the same: the soil is dug up and fertilized, a hole is dug, a sprouted tuber is put, sprinkled with earth, the plants are loosened, weeded, spud, watered.
Potatoes are planted in the greenhouse earlier than in open ground
To shorten the growing season of potatoes, which is important when growing late varieties, the seedling method is used. To do this, 3-4 weeks before planting, sprouted tubers are planted in peat, plastic pots, or cut bottles, sprinkled with soil or sand, watered and loosened in a timely manner. Plants obtained in this way take root better in the soil.
Seedling method of growing potatoes shortens the growing season
Growing potatoes in greenhouses
If the greenhouse is occupied for planting more thermophilic crops, then potatoes in the open field can be covered with foil or agrofibre, and it is better to make a greenhouse. To do this, you need to install arcs on a garden bed with potatoes and cover them with a film, securing the edges well. This shelter will help protect plants from temperature extremes. From time to time, in good sunny weather, the greenhouse will need to be opened to weather the excess accumulated moisture, water, fertilize the plants, loosen the soil and close it again. In greenhouses, potatoes ripen at least 2 weeks earlier, and the quality of the crop is much higher than that grown in the open field.
Greenhouse allows you to get an earlier harvest of potatoes
Care
The gardeners of the North-West region are constantly experimenting. They grow potatoes in barrels, buckets, bags, wooden boxes, under straw and hay, in the Dutch, Chinese way. Someone eventually switches to these alternative planting methods completely, while someone grows, as they say, the old fashioned way. But whichever method you choose, the potatoes definitely need full care, otherwise there will be no high yields. It includes weeding, hilling, loosening the soil, watering and fertilizing, protecting against diseases and pests.
Most often, potatoes are watered with natural precipitation, but two weeks after germination, as well as during the beginning and end of flowering, plants need additional watering with top dressing. A good fertilizer is diluted mullein or nettle infusion. Thus, the potatoes are watered and fertilized at least three times during the entire growing period. This number increases during dry seasons.
Over the entire period of growth, potatoes must be watered at least three times.
Hilling plants, you save them from cold snaps, remove weeds, saturate the roots with oxygen, and stimulate the growth of green mass. The first time hilling is carried out at the emergence of seedlings, and then after watering and rains.Flowering signals the beginning of the formation of tubers, therefore, during this period, air access is especially necessary.
Hilling oxygenates the plant roots
Plants in the North-West region are most often protected from late blight, the development and widespread distribution of which is provoked by increased moisture in the air and soil. Ash is a good helper in this, the plants are watered with its solution, and the tops are showered in a dry form.
Late blight is a consequence of increased soil and air humidity
Of the pests in the North-West region, shrews are especially common, which are especially gluttonous. The benefit of these animals is that they eat a huge number of insects. Harm - the destruction of root crops.
The shrew is one of the most common potato pests in the Northwest region.
Potato pests of the Northwest region table
The best varieties for the Northwest region
Potato planting material directly affects the harvest. The best option is elite varieties. They practically do not get sick, and pests bypass them, in addition, their quality and taste are higher than other varieties. Among other things, they do not degenerate longer, but they are an order of magnitude higher than other varieties, and not every gardener has the opportunity to purchase them.
Elite varieties are the best option for growing potatoes
It is better to plant several types of potatoes at once, with different growing periods, because it is not known what kind of weather this summer will please and what variety can grow and give a harvest.
Types of potatoes
Potatoes are divided into three types:
- Early - 50-60 days from the moment of germination - ripens quickly, is very poorly stored.
- Mid-season - 70–90 days - has a long shelf life, has a good taste.
- Late ripening - more than 100 days - a lot of starch, good taste and shelf life.
Early varieties
Early potatoes ripen early, before late blight begins to spread. This is its undeniable advantage. The disadvantage is that it is very poorly stored, so it is most often grown in small quantities, and having dug it out, they try to cook it right away.
For the North-West region, many varieties of potatoes have been zoned. Basically, gardeners are guided when choosing their yield.
Best of early table
The best of the early varieties of potatoes photos
Mid-season potato varieties
Mid-season potatoes are the preferred type for the Northwest region, with an optimal growing season, good taste and shelf life.
The best mid-season varieties table
The best mid-season potato varieties photo
Late varieties
Due to the long growing season in the North-West region of the country, late varieties of potatoes are not grown outdoors. But because of their good taste and ability to store for a long time, some gardeners make a choice in their favor and grow in greenhouses and greenhouses.
The best among the late varieties table
The best of the late varieties of potatoes photos
Potatoes for growing in the Leningrad region
In the area under consideration, gardeners are also preferred to early potato varieties due to the short and humid summer.
Potato breeding common in the Leningrad region - table
The main requirements of gardeners for potatoes are the tolerance of adverse weather conditions, a short growing season, resistance to late blight and high yield.
Common varieties of potatoes in the Leningrad region - table
Photo gallery of common varieties
New potato varieties for the Northwest region
Despite the abundance of varieties, breeders are constantly breeding new potatoes, with good resistance to diseases and pests, beautiful and tasty fruits. For the Northwest region, such ones as Charoite, Manifesto and Damaris are suitable.
Manifesto is a mid-early variety. Tubers are oval, elongated, red, weight 100-130 grams, amber pulp, excellent taste.The yield is high (160-460 kg per one hundred square meters), depends on fertilizers, keeping quality is good. Resistant to golden nematode and leaf roll virus. Medium susceptible to late blight.
Manifesto - a variety without flaws
Charoite is an early potato variety, you can start digging tubers after 60 days from the moment of germination. For the rapid formation of fruits, it is popularly called the Rapid Ripening of Peter. Tubers are elongated, oval, yellow, weighing 100-140 grams. The taste is excellent, the yield is high (230–320 kg per one hundred square meters). Stores well. Resistant to cancer. Susceptibility to late blight is average. It is affected by the golden nematode.
Charoite is the best variety for the North-West region of Russia
Damaris is a medium early variety, with beige oval tubers of good taste, weighing 90–130 grams. A productive variety (180-450 kg per one hundred square meters), well stored. Resistant to diseases such as cancer, scab, mosaic, black leg. Medium susceptible to late blight. Not affected by golden nematode.
Damaris
Take a note of the variety you like and plant it on the site. Experiment additionally: look for and plant new varieties, apply new growing methods. Search directly for yourself, the best potatoes for your taste.
Rate the article:
(10 votes, average: 3.6 out of 5)