Content
- 1 Features of ivy pelargonium
- 2 Landing and care rules
- 3 Reproduction of ivy pelargonium
- 4 The choice of planting material
- 5 Diseases of ampelous pelargonium
- 6 Beautiful cascades of delightful colors
- 7 Differences from ordinary geranium
- 8 Popular varieties
- 9 How to plant and propagate
- 10 Soil preparation
- 11 Complementary feeding and transplanting
- 12 Home care
- 13 How to prune ivy pelargonium
- 14 Possible diseases
- 15 Culture description and classification
- 16 Spectacular ampelous plant
- 17 Ivy Pelargonium varieties
- 18 Propagation by seeds and cuttings
- 19 Growing at home and care
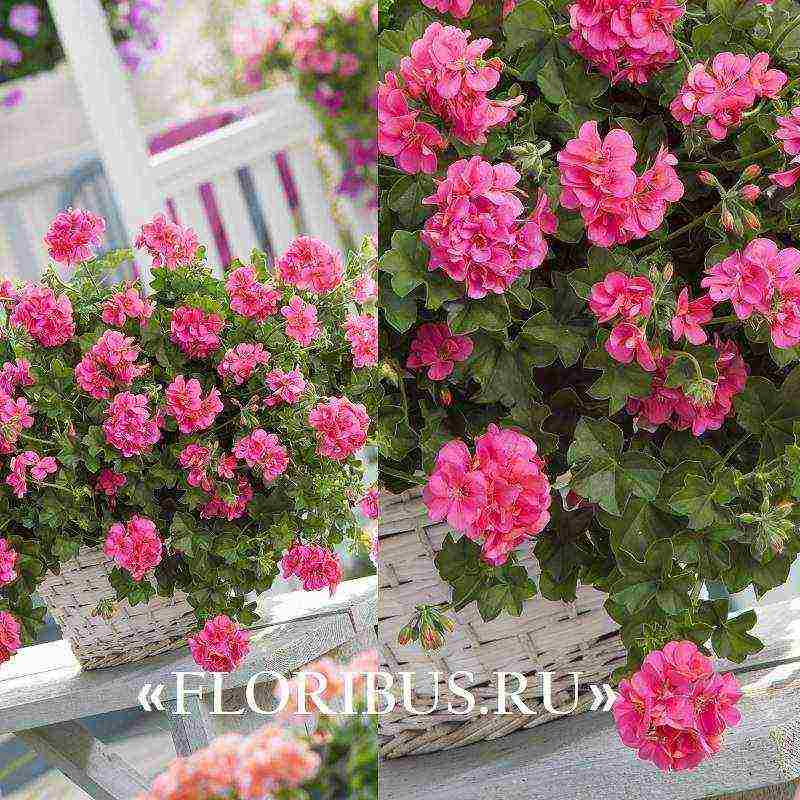
After the onset of the warm season, on city streets, in park areas, on the territory of personal plots, on balconies, loggias, you can observe a variety of decorative cultures. Among such plants, pelargonium ivy-leaved ampelous stands out, attracting the eyes with a multitude of falling shoots, on which magnificent bright inflorescences are formed.
Today, this representative of the geranium family is increasingly chosen by landscape designers, since it is considered one of the most popular plants used in landscaping activities.
Features of ivy pelargonium
 Under natural conditions, Pelargonium peltatum grows in South African territory. Today, numerous varieties, hybrids of the culture, bred by breeders, are in demand among flower growers in many countries, on various continents. Such plants, planted in hanging pots, used as a decor for balconies, loggias, window sills, look just great.
Under natural conditions, Pelargonium peltatum grows in South African territory. Today, numerous varieties, hybrids of the culture, bred by breeders, are in demand among flower growers in many countries, on various continents. Such plants, planted in hanging pots, used as a decor for balconies, loggias, window sills, look just great.
The cultivation of pelargonium in personal plots has proven itself well. This representative of geranium crops feels great if its lashes hang along a vertical plane, or when they form a blooming, dense carpet, gently settling along a flat area.
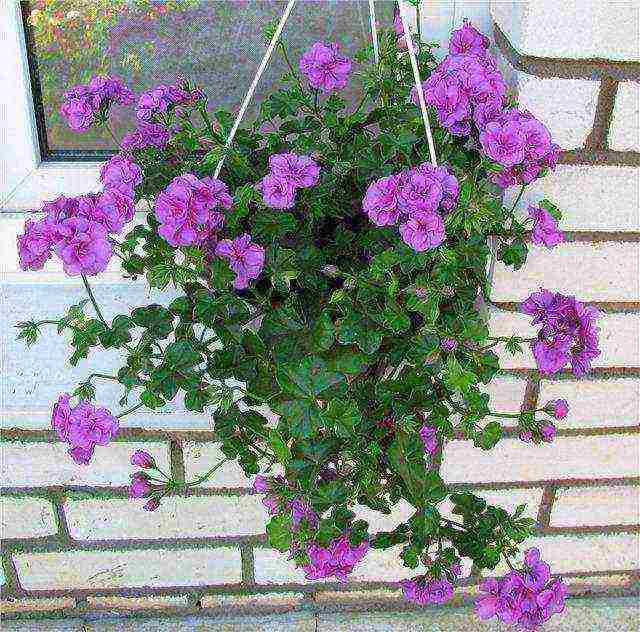 Pelargonium ivy got its name, thanks to its five-lobed, leathery, smooth leaves. They resemble the leaves of another climbing plant - ivy.
Pelargonium ivy got its name, thanks to its five-lobed, leathery, smooth leaves. They resemble the leaves of another climbing plant - ivy.
Pelargonium shoots are strong enough. They have the ability to cling to rocky ledges as they grow and climb upward to disperse seeds. Numerous varieties of ivy-leaved pelargonium, suitable for growing at home, are characterized by the presence of stems, the length of which is up to 1 m.
The culture has umbellate inflorescences uniting 6 - 15 flowers. Their formation occurs in the axillary depressions of the leaves, which have a green or variegated color. The varietal forms of the plant can have simple flowers with a uniform color. Terry ivy-leaved pelargoniums with petals decorated with contrasting spots, stripes, and a clear border look very impressive.
Landing and care rules
As practice shows, planting, caring for ivy pelargonium will not cause problems if the recommendations of specialists are correctly followed. Below are some tips for growing a crop that are sure to be helpful for budding florists.
What conditions are considered optimal for a plant?
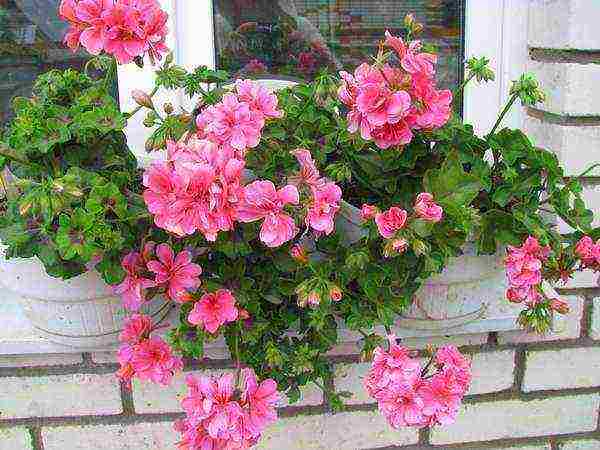 Pelargonium likes bright sunlight.She is able to grow rapidly, develop in good lighting conditions. At the same time, the bush tolerates drought without any problems. Pelargonium, planted in a balcony box, flowerpot, on a flower bed near the house, demonstrates excellent flowering in the warm season at temperatures of + 20 ... + 25 ° C.
Pelargonium likes bright sunlight.She is able to grow rapidly, develop in good lighting conditions. At the same time, the bush tolerates drought without any problems. Pelargonium, planted in a balcony box, flowerpot, on a flower bed near the house, demonstrates excellent flowering in the warm season at temperatures of + 20 ... + 25 ° C.
The plant, which will be provided with sufficient watering in the heat, will not lose its beauty, will delight with magnificent flowering for a long time. A culture that has undergone a hardening procedure calmly tolerates short-term cold snaps. Nevertheless, negative temperatures are contraindicated for her.
A plant grown in a flowerpot should be replanted every 2 years in the spring. In addition, such an event will be justified when the capacity becomes too tight for the bush.
Soil quality requirements
When choosing a soil for planting a culture, it is worth giving preference to moisture-absorbing, loose, nutritious soil.
 Planting pelargonium in soil with neutral, weak or medium acidity has proven itself well. When planting a plant in a flowerpot, you should purchase a special substrate in advance at a flower shop.
Planting pelargonium in soil with neutral, weak or medium acidity has proven itself well. When planting a plant in a flowerpot, you should purchase a special substrate in advance at a flower shop.
When deciding how to root pelargonium, you can start making your own potting soil. It should contain: peat, humus, sand, turf, leafy land in equal shares.
Preparing a flowerpot, drainage
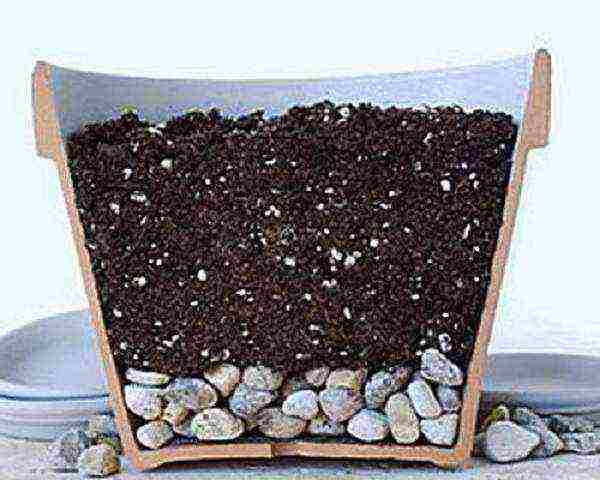 It is worth refusing to provide the plant with an oversized pot. It will be preferable to plant a culture in a container, the dimensions of which will exceed the size of the roots of pelargonium by an amount equal to the thickness of a finger (1 - 1.5 cm). Also, you can settle several bushes in one flowerpot, balcony box. Thus, the plants will constantly form new buds, which will not slow down to affect their splendor and beauty.
It is worth refusing to provide the plant with an oversized pot. It will be preferable to plant a culture in a container, the dimensions of which will exceed the size of the roots of pelargonium by an amount equal to the thickness of a finger (1 - 1.5 cm). Also, you can settle several bushes in one flowerpot, balcony box. Thus, the plants will constantly form new buds, which will not slow down to affect their splendor and beauty.
Since pelargonium is considered a mountainous "inhabitant", it needs to be equipped with drainage. For this purpose, pieces of expanded clay should be placed at the bottom of the flowerpot.
Periodic feeding
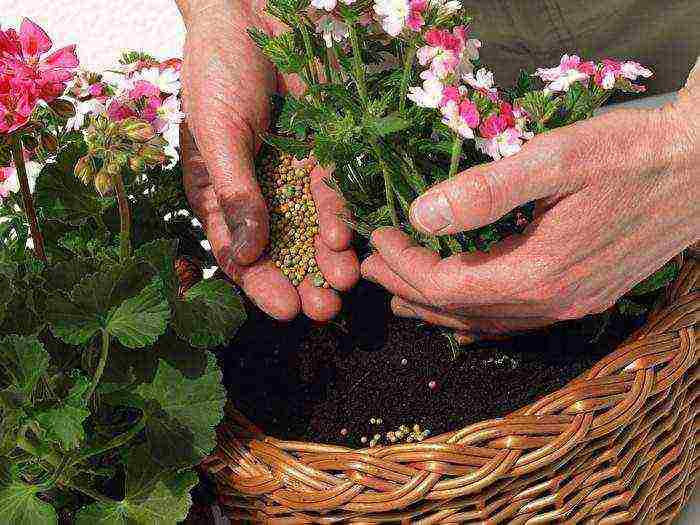 The culture needs periodic feeding. The bushes begin to develop actively in March, and their flowering lasts until the beginning of autumn. Plants growing in pots need to be fed weekly with mineral supplements. But fertilization with organic matter is not welcome.
The culture needs periodic feeding. The bushes begin to develop actively in March, and their flowering lasts until the beginning of autumn. Plants growing in pots need to be fed weekly with mineral supplements. But fertilization with organic matter is not welcome.
Experienced growers warn against the overuse of nutrient solutions containing nitrogen. Over-saturation of the soil with this component causes the rapid growth of stems and leaves, but negatively affects flowering. In a plant overfed with nitrogen, bud formation is inhibited altogether or occurs in a much smaller amount.
In order for the stalks of pelargonium to become covered with lush inflorescences, you need to give preference to potash, phosphorus fertilizers. The use of magnesium sulfate has proven itself well. Florists with experience to stimulate flowering often use a solution of iodine (1 drop) in water (1 liter). About 50 ml of such a product is applied under one bush at a time.
Pelargonium outdoors in summer
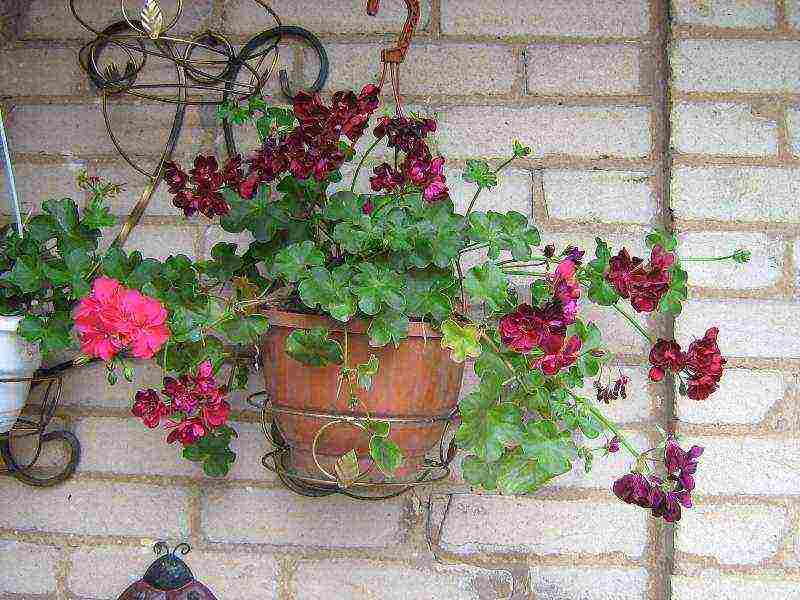 Permanently located in the room pelargonium zonal ivyleaf feels great. At the same time, plants exposed at the beginning of the warm season outside the window, into the garden, experience stress. In order for the acclimatization of a culture to be as painless as possible, it must be gradually accustomed to growing in conditions with constant changes in temperature, humidity, and illumination.
Permanently located in the room pelargonium zonal ivyleaf feels great. At the same time, plants exposed at the beginning of the warm season outside the window, into the garden, experience stress. In order for the acclimatization of a culture to be as painless as possible, it must be gradually accustomed to growing in conditions with constant changes in temperature, humidity, and illumination.
In May, after the frost pore has passed, the bushes are assigned to permanent places, where they will grow throughout the summer. In autumn, when temperatures drop to + 10 ... + 15 ° C, they should be taken back into the room. It is noteworthy that the formation of pelargonium, its flowering will occur faster if there is a nearby plant with petals of a contrasting color.
Organization of wintering of pelargonium
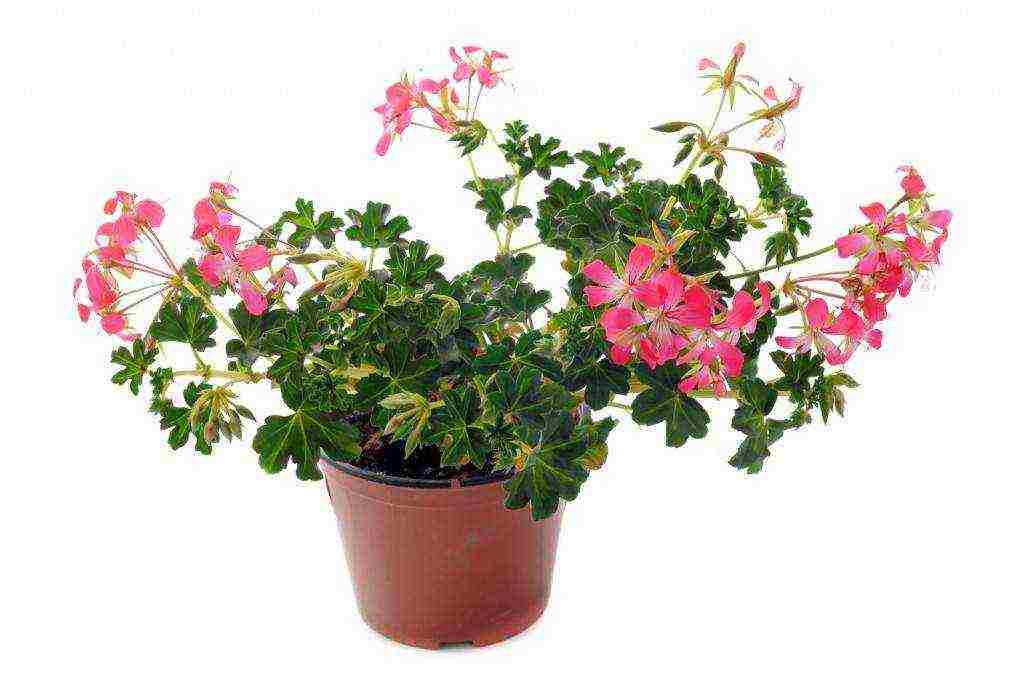 In order for ampelous pelargonium to overwinter indoors in the best possible way, it will need to be identified in a bright, cool, dry place. The recommended temperature range is + 7… + 15 ° C. At this time, watering is reduced. The plant has enough soil moisture, which excludes the death of the root system. Irrigation of leaves, stems is prohibited. It is advisable to complete the feeding in 30 days.
In order for ampelous pelargonium to overwinter indoors in the best possible way, it will need to be identified in a bright, cool, dry place. The recommended temperature range is + 7… + 15 ° C. At this time, watering is reduced. The plant has enough soil moisture, which excludes the death of the root system. Irrigation of leaves, stems is prohibited. It is advisable to complete the feeding in 30 days.
When studying information on how to cut pelargonium on the eve of wintering, you need to take into account that experienced florists prefer to remove all shoots, and dig the plant itself out of a flowerpot along with a lump of soil and determine its transparent plastic bag. The bush preserved in this way can be placed on an insulated balcony, loggia.
Reproduction of ivy pelargonium
It will not be difficult to reproduce ivy pelargoniums. For this purpose, grafting or seed method can be applied. The latter is more complex and painstaking. It is considered justified when it is necessary to obtain a large number of young plants.
Culture cuttings method
 According to most florists, cuttings of ivy-leaved pelargonium should be postponed to early March. This method is worth resorting to if you have access to planting material.
According to most florists, cuttings of ivy-leaved pelargonium should be postponed to early March. This method is worth resorting to if you have access to planting material.
It is necessary to prepare healthy, large cuttings of pelargonium - they are separated from the mother plant and left to dry for 2 days. For this, the apical sections of the vertical stems are used. The optimal choice will be the choice of shoots 7-10 cm long with 2 pairs of healthy leaves. Places of cuts are subject to processing with the use of carbon powder.
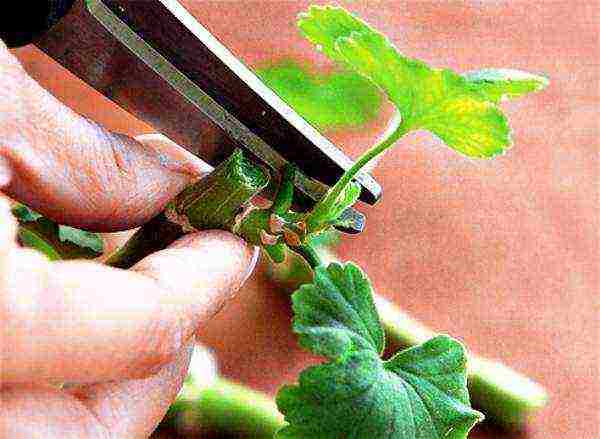 Having taken care of the solution to the problem: when to cut pelargonium, you should pay attention to the fact that you can start harvesting planting material not only in spring, but also in August. It is very important to get loose, disinfected soil in advance. Cuttings will be planted in it with an interval of 2 cm, deepening into the soil by 3 - 4 cm. It is advisable to equip the shelter above them not from a film, but from a non-woven material. It allows moisture to pass through well, does not allow the formation of condensation.
Having taken care of the solution to the problem: when to cut pelargonium, you should pay attention to the fact that you can start harvesting planting material not only in spring, but also in August. It is very important to get loose, disinfected soil in advance. Cuttings will be planted in it with an interval of 2 cm, deepening into the soil by 3 - 4 cm. It is advisable to equip the shelter above them not from a film, but from a non-woven material. It allows moisture to pass through well, does not allow the formation of condensation.
After a month, ivy-leaved pelargoniums will take root, after which they can be planted in flowerpots. You should count on the flowering of young bushes after they have overwintered.
Seed propagation of pelargonium
 As a rule, planting of pelargonium by sowing seeds is carried out during the period: February - mid-April. To stimulate the formation of a powerful root system in seedlings, you will need to fill pre-prepared pots with light, loose soil or use large peat tablets.
As a rule, planting of pelargonium by sowing seeds is carried out during the period: February - mid-April. To stimulate the formation of a powerful root system in seedlings, you will need to fill pre-prepared pots with light, loose soil or use large peat tablets.
Sowing of seeds is carried out with a depth of 5 - 10 mm. Next, you need to moisten the soil well by spraying from a spray bottle. The container with the seedlings is covered with foil and placed in a warm place with sufficient illumination. After a week, you can expect the first shoots to appear. After 3 to 4 weeks, the plants are placed in permanent flowerpots.
The choice of planting material
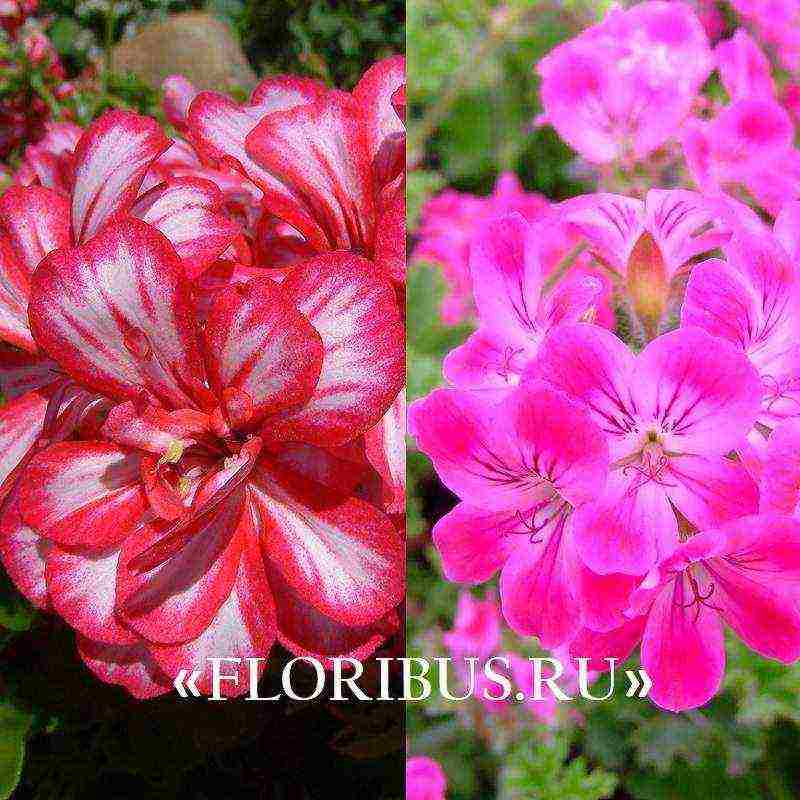
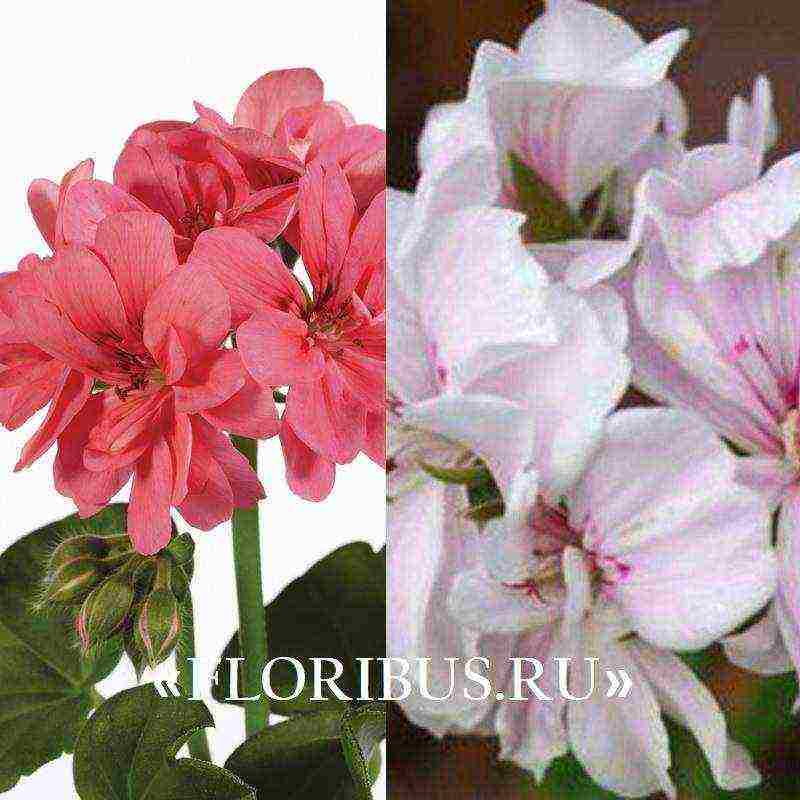
Modern flower shops offer for sale various varieties of terry pelargoniums, plants with simple inflorescences, among which it is worth choosing the most suitable planting material. In order not to be mistaken, it is advisable to study the information about the species of interest in advance. Below are descriptions of several varieties, crop hybrids, consistently receiving approving reviews from flower growers.
Pelargonium Crystal Queen f1
 Wonderful Pelargonium Crystal Queen f1 is a powerful plant that can easily be grown from seeds. The bushes of this hybrid in the amount of 1 - 2 pieces are allowed to be planted in a large hanging basket.
Wonderful Pelargonium Crystal Queen f1 is a powerful plant that can easily be grown from seeds. The bushes of this hybrid in the amount of 1 - 2 pieces are allowed to be planted in a large hanging basket.
Unpretentious pelargonium ampelous Crystal Queen f1 red is characterized by the presence of hard leaves, strong, shoots up to 30 cm long.It tolerates rainfall and wind. On one plant, about a hundred beautiful flowers can bloom at the same time. The culture is recommended for growing in hanging pots, balcony boxes, mixed containers.
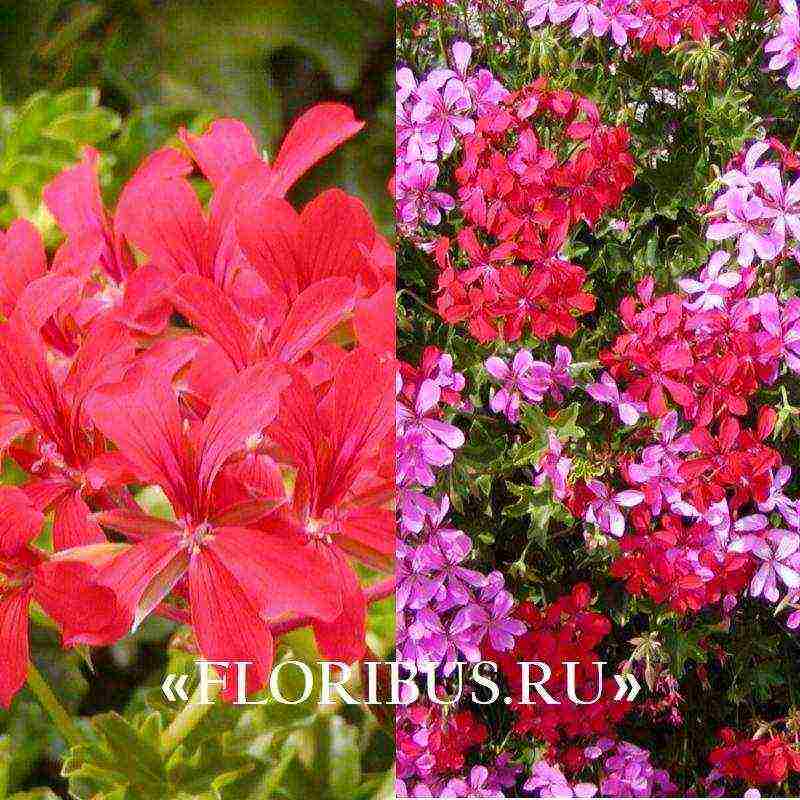
Pelargonium Tornado f1
 The magnificent Tornado f1 pelargonium is bred by Dutch breeders. European gardeners speak of the plant extremely positively. This red pelargonium with shoots of 30 cm or more looks great in hanging baskets and is often used for landscaping. The flowering of a crop that does not need the use of growth stimulants is likely to be long and abundant.
The magnificent Tornado f1 pelargonium is bred by Dutch breeders. European gardeners speak of the plant extremely positively. This red pelargonium with shoots of 30 cm or more looks great in hanging baskets and is often used for landscaping. The flowering of a crop that does not need the use of growth stimulants is likely to be long and abundant.
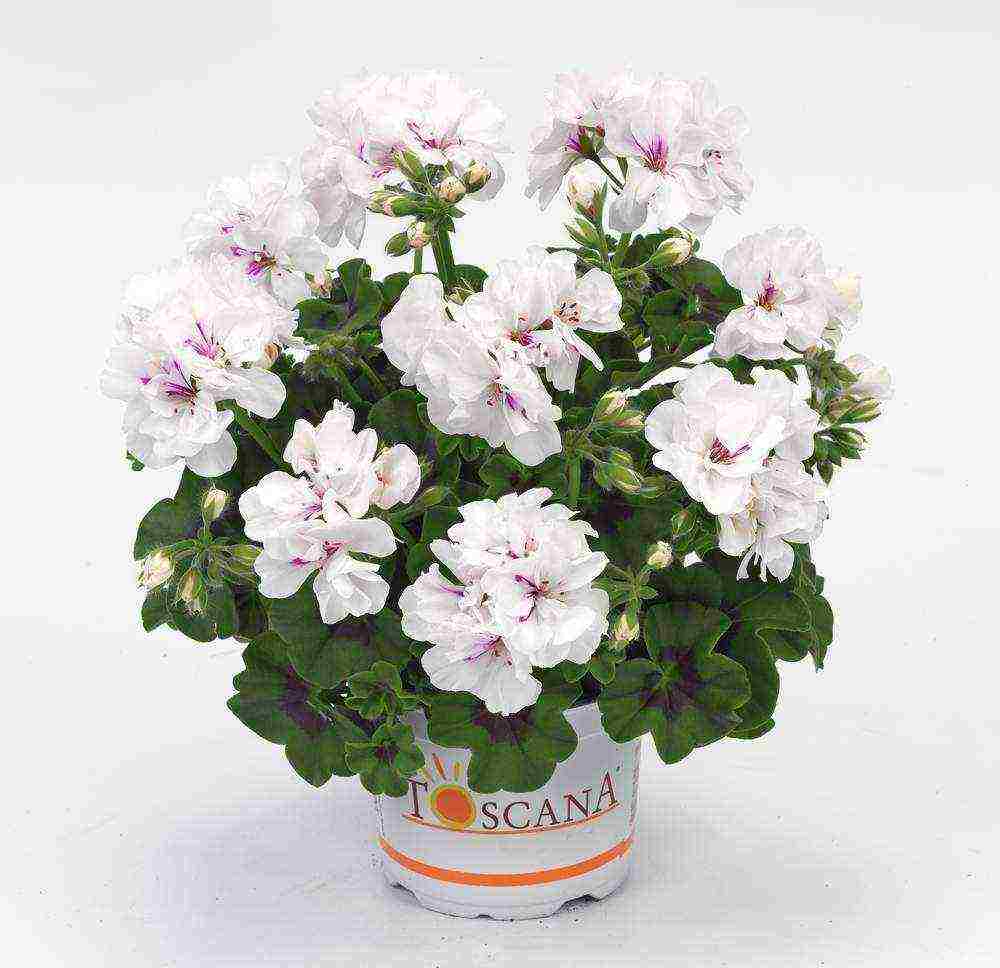 Pelargonium Tuscany
Pelargonium Tuscany
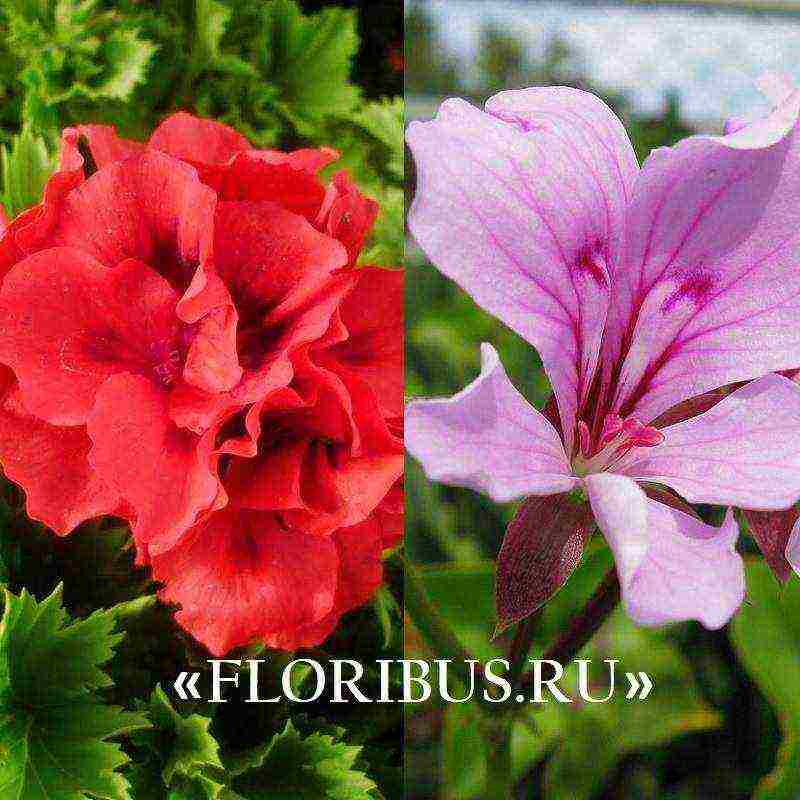
The popular Pelargonium Tuscany has many varietal forms. They all look extremely attractive. The ampelous pelargonium Toscana Eva is in particular demand, which delights florists with large white flowers blooming on hanging shoots about 50 cm long. The flowering of the culture starts in May and continues until frost.
Diseases of ampelous pelargonium
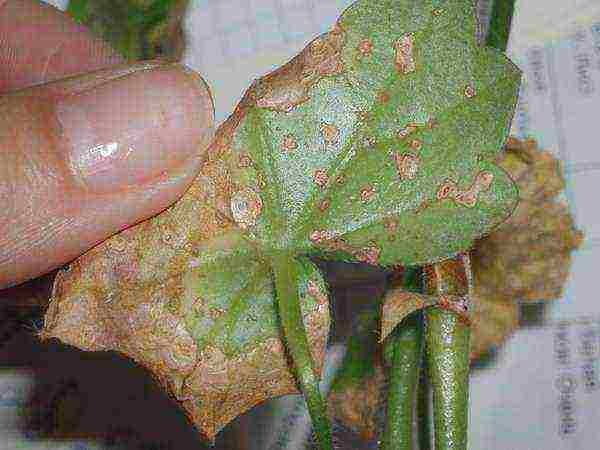 Since the plant spends a lot of time on the balcony or in the garden, it is exposed to negative environmental influences. High humidity, temperature extremes, mistakes in care often provoke pelargonium diseases, signals of which are the appearance of rusty, dry spots, light areas, and a yellow mosaic pattern on the leaves.
Since the plant spends a lot of time on the balcony or in the garden, it is exposed to negative environmental influences. High humidity, temperature extremes, mistakes in care often provoke pelargonium diseases, signals of which are the appearance of rusty, dry spots, light areas, and a yellow mosaic pattern on the leaves.
The greatest harm to the culture is caused by fungal infections, chlorosis, viral mosaic. To cope with ailments will help the treatment of bushes with the help of special tools, adjusting the schedules of watering, dressing. Effective preventive measures are: disinfecting the soil, loosening the soil, removing yellowed, fallen leaves, cutting off wilted inflorescences.
Thinning pruning of ivy-leaved pelargonium is necessary, which makes it possible to avoid excessive density of bushes, ensuring their ventilation.
Beautiful cascades of delightful colors
Correct implementation of planting measures, caring for pelargonium will be the key to obtaining a healthy, abundantly flowering plant, delighting during the season with beautiful cascades of delightful flowers. They will be able to admire not only households, but also neighbors, guests, and casual passers-by.
 The ampelous representative of the Geraniev family immigrated to us at the beginning of the 18th century from the south of the African continent.
The ampelous representative of the Geraniev family immigrated to us at the beginning of the 18th century from the south of the African continent.
Over the past decades, domestic breeders have managed to develop a variety of varieties that are most adapted to our climatic conditions.
Today pelargonium ivy ampelous is a common indoor flower that pleases with beautiful inflorescences and a pleasant aroma.
Differences from ordinary geranium
Often Pelargonium ivy is mistakenly called geranium, on many sites you will find the use of these two names as synonyms. Initially, the confusion arose due to the incorrect attempts of scientists to classify the plant in the distant 17th century. In order to fully appreciate the differences between two different flowers, it is worth considering the signs that indicate this:
 Geranium ivy is a low plant with an erect base. Pelargonium is an ornamental creeping dwarf shrub, the shoots of which grow up to a meter in length.
Geranium ivy is a low plant with an erect base. Pelargonium is an ornamental creeping dwarf shrub, the shoots of which grow up to a meter in length.- The leaves of the ivy geranium are tender and soft to the touch, while the leaves of the pelargonium are glossy and five-lobed.
- The inflorescences of the bright red color of the indoor plant are very decorative, which won the sympathy of gardeners. Common geraniums have symmetrical blue flowers.
- Native to the southern hemisphere, many varieties of pelargonium are thermophilic and suitable for indoor cultivation only. Geraniums can also be planted in gardens, because her homeland is northern latitudes and she can withstand cold temperatures
Popular varieties
Varieties to look out for:
- AMETHYST... A great option for a veranda or balcony.After planting, the plant develops rapidly, resulting in a decorative "living" basket. Inflorescences of large double flowers are characterized by dark pink, purple, bright crimson shades.
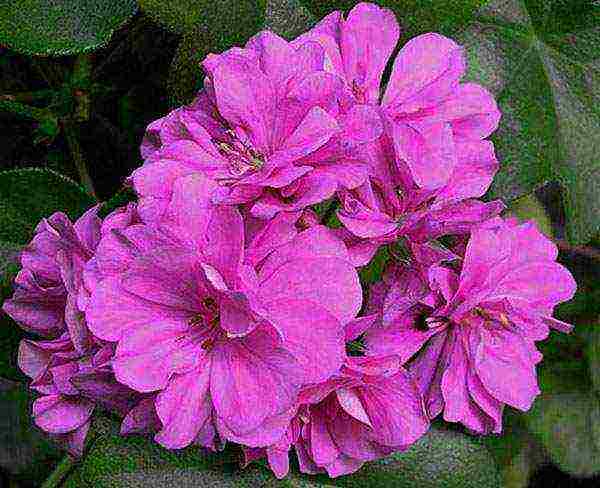

- CROCODILE... A characteristic feature is the original color of the leaves: the veins of a bright yellow color are clearly visible on a green background. Inflorescences are formed from coral or purple flowers.
- JAGKY GAULD... The semi-shrub develops rather quickly, is characterized by pomp and branching. Initially, double flowers are snow-white in color, but under the influence of ultraviolet radiation they can be repainted in purple or pink.
- ICEROSE... An adult shrub is completely covered with white double flowers. Outwardly, the plant is somewhat reminiscent of a rose bush.
- ROULETTA... The low shrub is characterized by its abundance. The highlight of the variety is the original color of the flowers: white petals at the edges are painted in bright pink.
- Mrs. MARTIN... The variety develops very quickly, an adult plant forms a decorative "living" basket. Inflorescences consist of double flowers of a light lilac or pink hue.
- RHAPSODY... The variety is a lush bush with glossy leaves and burgundy buds.
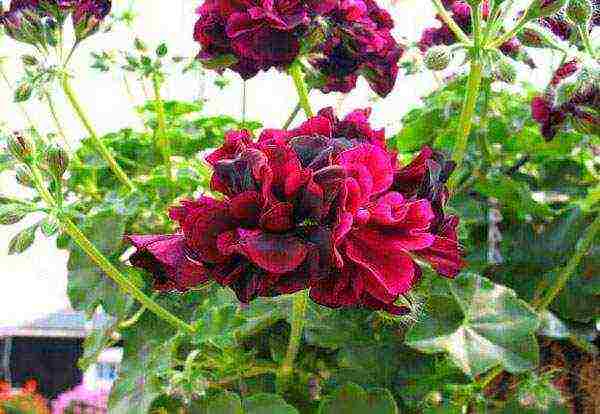

ADVICE! Almost all varieties of ampelous pelargonium develop very quickly. It only takes a few weeks to grow a lush bush, while the rhizome fully performs its functions even in tight containers. Ivy-leaved pelargonium sheds leaves and flowers if the root system still lacks space.
How to plant and propagate
Reproduction of pelargonium can be in two ways: seeds and cuttingsand. The first method is more painstaking and is used only by experienced gardeners. For convenience, the planting process should be divided into several stages:
- Seed preparation... Large pelargonium seeds are protected by a thick shell, therefore, it is recommended to scarify them before planting them in the ground with a sharp object or sandpaper. Under no circumstances should the inner seed be damaged.
- Soil preparation... The easiest option is to use a store-bought compound. If you are used to doing everything yourself, you need to mix three main ingredients, taken in equal proportions: turf, sand, peat.
 Direct landing... Previously, the earth is abundantly watered from a spray bottle. The depth of seeding the seeds into the soil should not exceed 0.5-1 cm. Containers with future vegetation are covered with a transparent film and placed in a place with temperatures of + 22-25 ° C.
Direct landing... Previously, the earth is abundantly watered from a spray bottle. The depth of seeding the seeds into the soil should not exceed 0.5-1 cm. Containers with future vegetation are covered with a transparent film and placed in a place with temperatures of + 22-25 ° C.- Watering and further care... The soil with seeds is watered once every 5-6 days. For airing, the film is periodically opened for several hours.
ADVICE! After scarification, it is advisable to treat the soil and sorted seeds with a solution of potassium permanganate.
How to root pelargonium? Here is a step-by-step instruction for propagation by cuttings:
- the best period for spending is the beginning of spring;
- so that pelargonium multiplies well, only large and healthy shoots are selected, cut off and dried throughout the day;
- the plants are transplanted to a permanent place after a month.

Soil preparation
As mentioned above, in order for the flowers to successfully root, it is enough to buy a universal primer in the store... But you can prepare it yourself.
Ingredients you will need for self-cooking the soil:
- sod land;
- leafy land;
- humus;
- peat;
- sand.
The proportions of the components must be equal. Small planters can be used as a pot.
Complementary feeding and transplanting
Ampel plant needs feeding only in the spring-summer period, namely, nitrogen fertilizers after winter dormancy and pruning to restore the volume of the green crown and compositions containing a large amount of potassium and phosphorus for exuberant flowering. The frequency of feeding is once every 10 days.In autumn and winter, the flower does not require additional organic and mineral nutrition.
 Pelargonium ivy is transplanted in the spring.
Pelargonium ivy is transplanted in the spring.
To make rooting more successful, a number of simple procedures are performed:
- the flower is removed from the old container along with a lump of soil on the rhizome, only those layers of earth that are easily removed are removed;
- the roots are partially removed - only the part that has grown into the drainage;
- the pots are thoroughly washed, a plant is placed in it, and new soil is poured.
Advice! Dwarf varieties of ivy pelargonium are transplanted every year or every other year.
Home care
Unlike many ornamental indoor plants pelargonium does not need painstaking care thanks to which she won the sympathy of gardeners. But still, in order for the flower to fully develop and please the eye, it is important to adhere to certain nuances:
- ampel representative of the Geranievs - light-loving plant, therefore, it is advisable to place flower pots on the south side;
- the optimal temperature in summer is + 22-25 ° C, in winter, when pelargonium goes into a state of dormancy - + 15 ° C;
- the plant practically does not suffer from drought, but excessive humidity can adversely affect development;
- the recommended frequency of watering is once every 10-14 days, for this it is better use a spray bottle.
How to prune ivy pelargonium
Ampelous pelargonium needs substantial circumcision for the purpose of rejuvenation... On the eve of winter, only two lower leaves with axillary shoots are left, otherwise the stem will be completely bare, acquiring a non-aesthetic appearance.

In spring, bare branches and stems are pruned, leaving the healthiest and youngest parts... For the preservation of decorativeness, the plants promptly remove dried leaves and wilted inflorescences, get rid of old woody shoots. It is recommended to resort to grafting every 2-3 years.
This video details how to form a lush pelargonium bush by pruning:
Possible diseases
Common problems that can affect a potted flower:
- fungal disease, manifested by spotting on the leaves;
- root rot, which is the result of an excess of moisture;
- a bacterial disease provokes the wilting of the plant;
- rust on the leaves, usually characterized by a yellow spot.
To prevent the further development of this or that disease, it is necessary to normalize the care, in some cases it will be necessary to resort to the treatment of pelargonium with special means.
Ampel ivy-leaved pelargonium can become a real decoration of your home, balcony, garden plot, if you follow the simple rules of care.
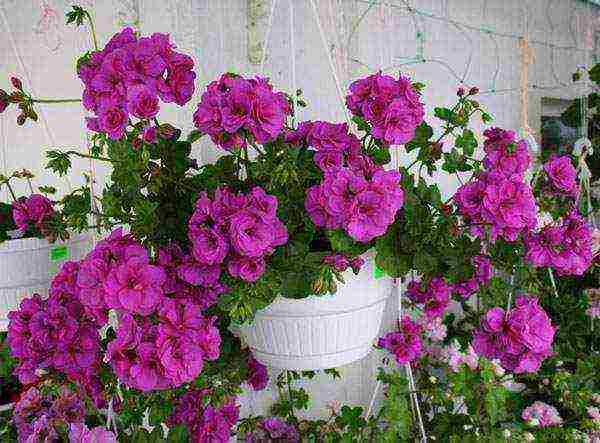

Like any other beautiful house plant, ivy-leaved pelargonium deserves special attention, since its prevalence rightfully overshadows the popularity of all other cultures for decorating interiors.
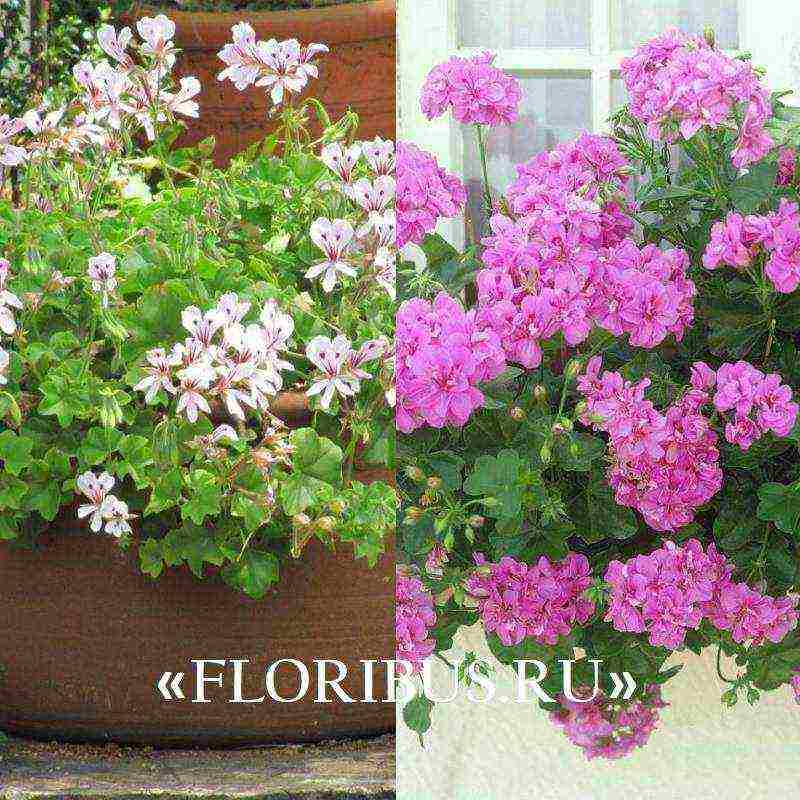
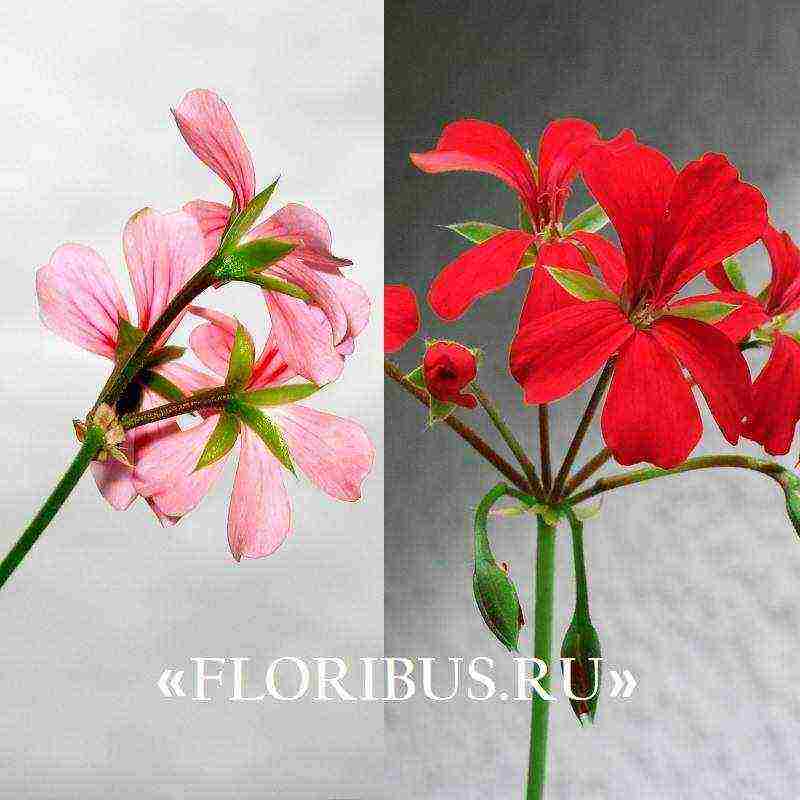
A very beautiful outdoor and indoor plant is Pelargonium peltatum, it has not been forgotten for a minute by breeders and flower growers after its discovery. Neat, long shoots hang down and form a beautiful ampelous bush or cover soil curtain. In this issue we will learn about the variety in more detail, see a photo of ivy-leaved pelargonium and try to grow it at home. Moreover, the rules for growing and organizing crop care are quite simple and do not require a lot of experience and special knowledge.
Look at the ivy-leaved pelargonium in the photo of the plant, where the culture is presented in different phases of its vegetative development: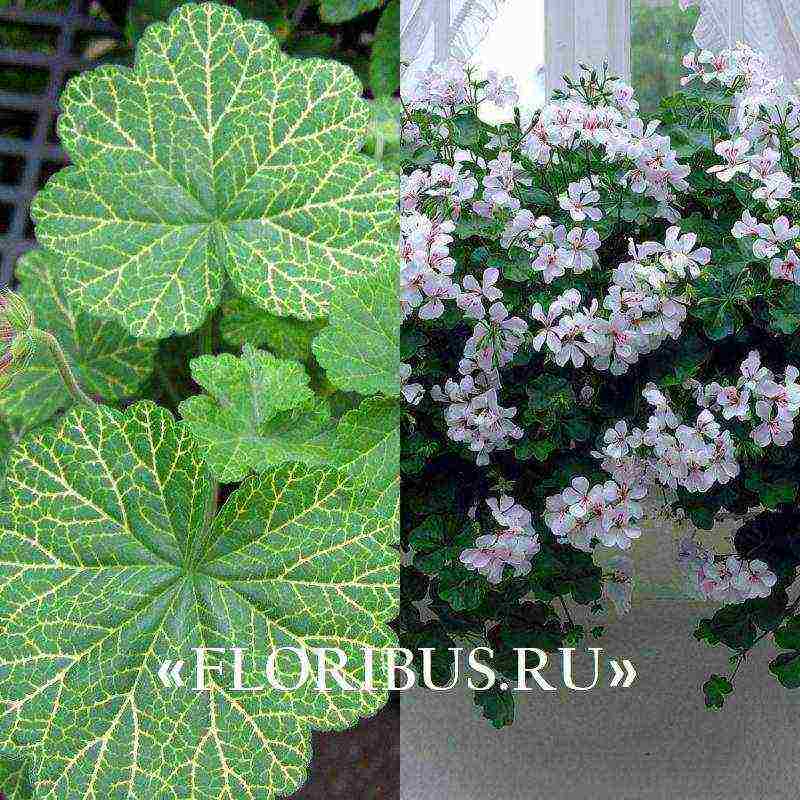


Culture description and classification
Due to the similar appearance and the reason that geranium and pelargonium belong to the same Geranium family, after the plants were brought to Europe from Africa in the 17th century, it was assumed that this is the same perennial.This was the reason for the fact that there are still disputes between breeders and experienced botanists. A novice florist can easily confuse geranium with pelargonium, especially if these genera contain species similar in appearance and names. In this issue we will talk about ivy-leaved pelargonium, which is mistakenly called Geranium. The difference between representatives of the two Geraniev clans can be seen in the description of the culture in numerous photos.
The fact is that according to the classification of these genera of Geranium plants, there is no variety of ivy geranium. This is the name of the proud plant Pelargonium, native to South Africa. In home floriculture, the substitution of concepts most likely occurs because perennials are not just similar to each other, but also our grandmothers called the plant Geranium for convenience. Most novice florists are not inclined to become closely acquainted with the seemingly insignificant nuances of biology and classification of plant taxa. Even such great minds as Karl Linay confused plants with each other and called them mixed - "Geranium (Pelargonium)" and vice versa, and believed that they were one and the same genus. The most important difference between these two species is their habitat. Pelargonium grows mainly in hot parts of Africa, when, like some species of Geranium or Crane, they are found in the forests of our country and are common in regions of Eurasia with a temperate climate.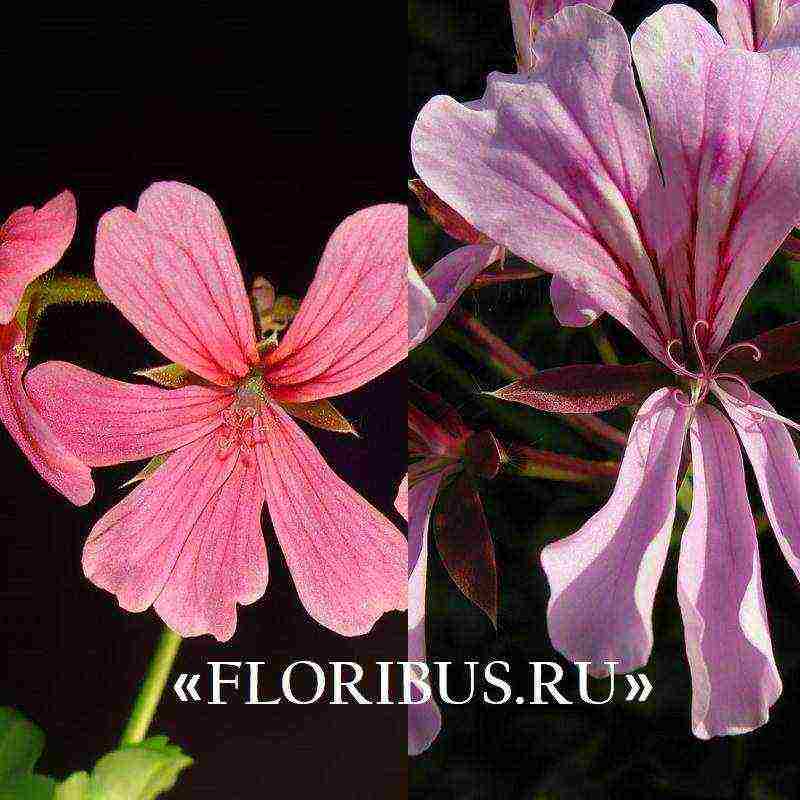
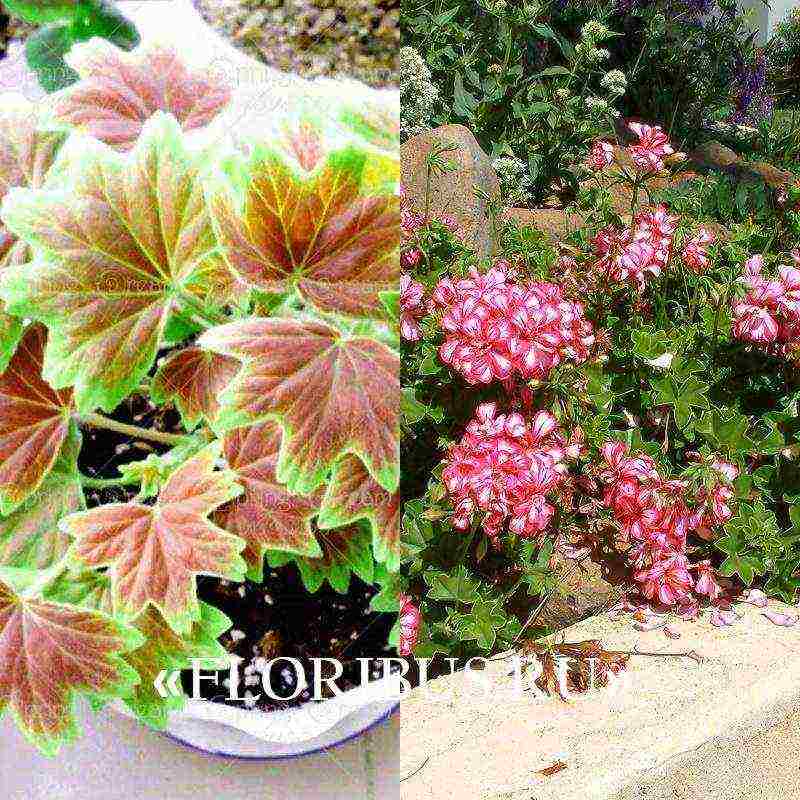


Spectacular ampelous plant
Ivy Pelargonium is a very effective ampelous plant with abundant and very long flowering. It has not yet become widespread in home and garden floriculture, as it is mistakenly considered a very whimsical herbaceous perennial. Ampel pelargonium, in fact, is extremely unpretentious and requires minimal maintenance, which we will talk about a little later.
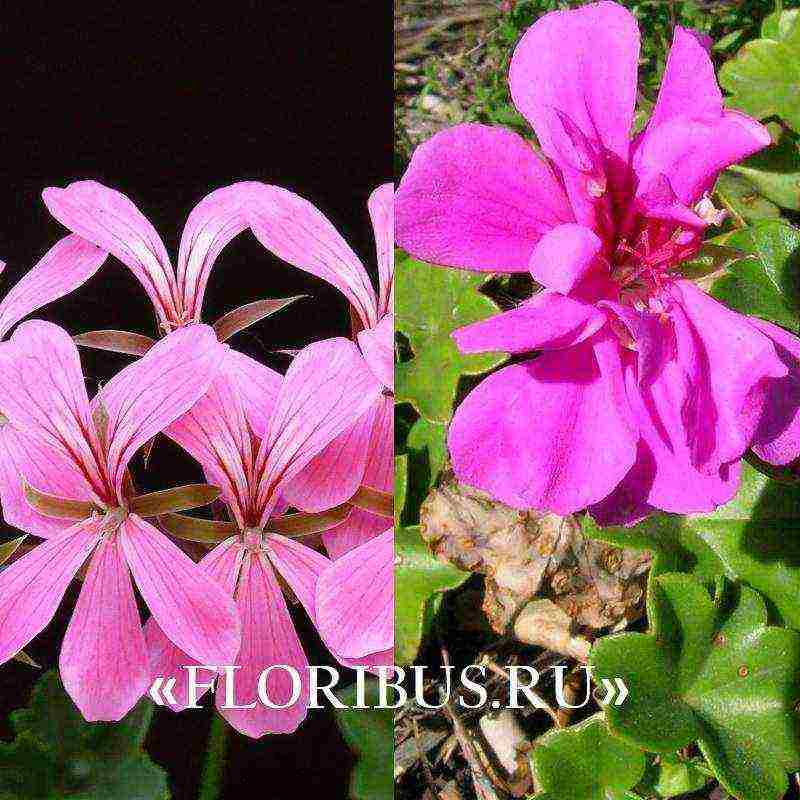
Long stalks of pelargonium creep along the ground or hang from a hanging planter. Shoots reach 80-90 cm in length, curl a little and can intertwine with each other. The surface of the stems is smooth, elastic. The stems are not brittle, they are able to form several lateral processes, which helps the plant to form a dense bush. The leaf plates are smooth and cool to the touch. The smooth surface is slightly glossy and reaches a maximum of 5-6 cm in width. Due to the similarity of the leaf to ivy, the variety is called ivy. There are varieties with beautiful decorative leaves.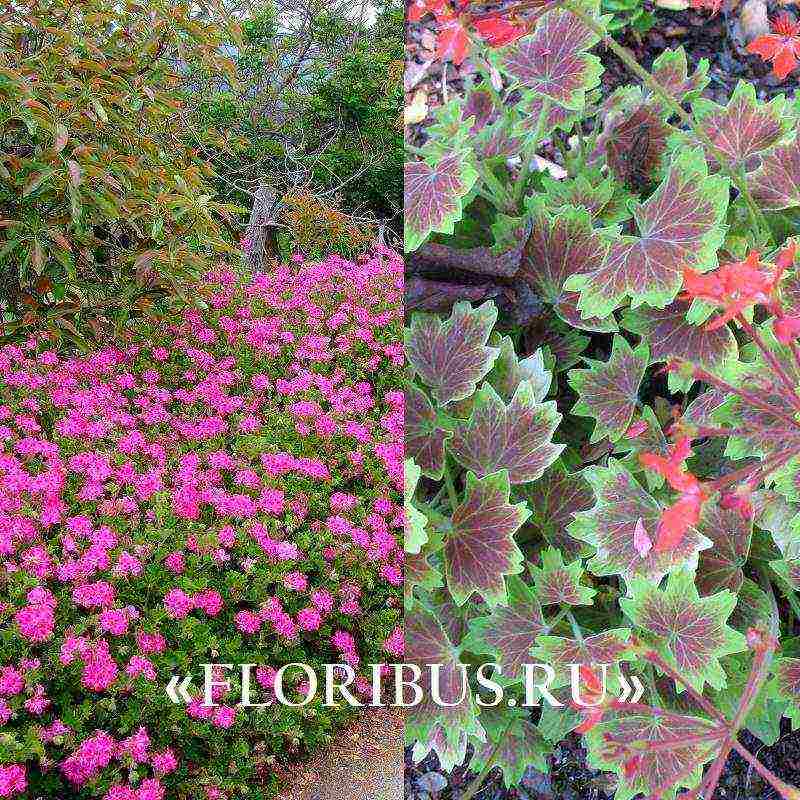
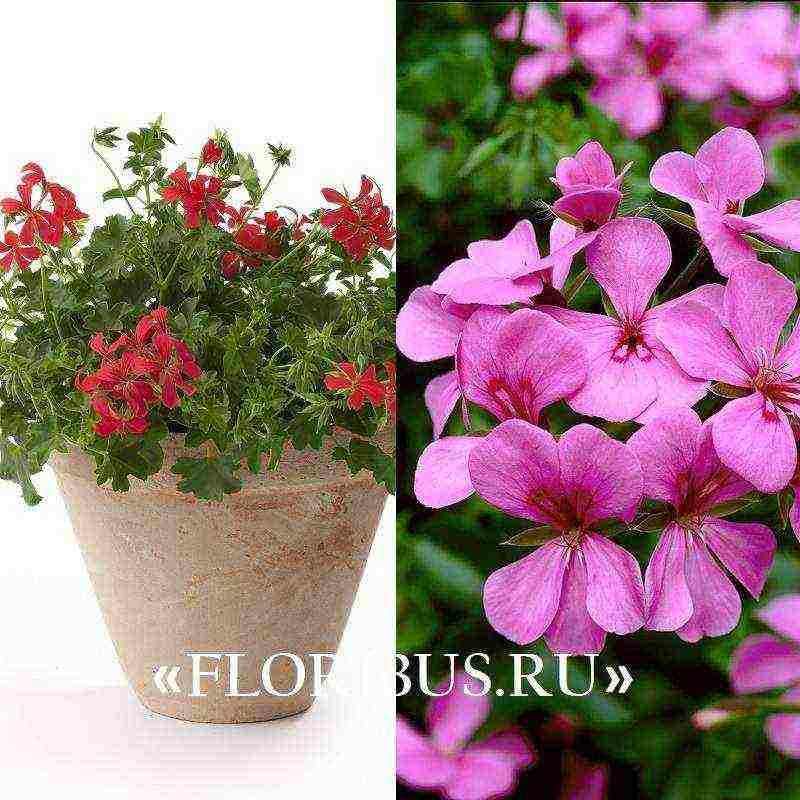


The flowering of the variety is long-lasting. At this time, large flowers are formed, collected in spherical inflorescences - apical umbrellas. There are varieties with double buds similar to tulips or roses. Perennials can have semi-double and simple flower petals that form a bud similar to a carnation. Umbrellas are almost always brightly colored. It can even be two-tone.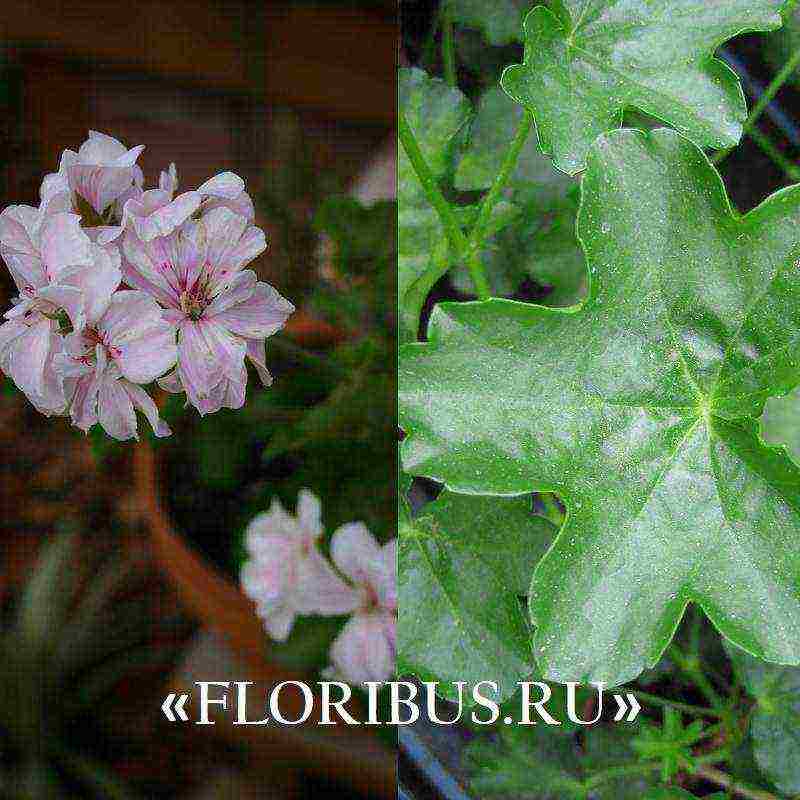


Ivy Pelargonium varieties
There are many interesting varieties that distinguish Pelargonium ivy from other varieties. The brightest group of hybrids is Toskana. It was bred on the basis of crossing ivy and zonal pelargonium. The hybrid cultivar includes the following popular ampelous cultivars:
- "Malaika" - recently bred. The variety has beautiful deep pink flowers of large size, collected in an umbrella inflorescence. Semi-double buds;
- "Marlen" - semi-double purple or lilac flowers;
- "Teske" - long stems with large inflorescences of lilac flowers;
- "Nixe" - lush semi-double flowers, two-color: cherry and white.
There are many more interesting varietal groups. One of them is the Ivy Pelargonium "Crystal Queen F1". Large plants with long hanging shoots, up to 30-40 cm long, are easily grown as garden annuals or home crops.Flowering is very abundant and long, one bush can have up to 100-150 small buds, collected in umbellate inflorescences.
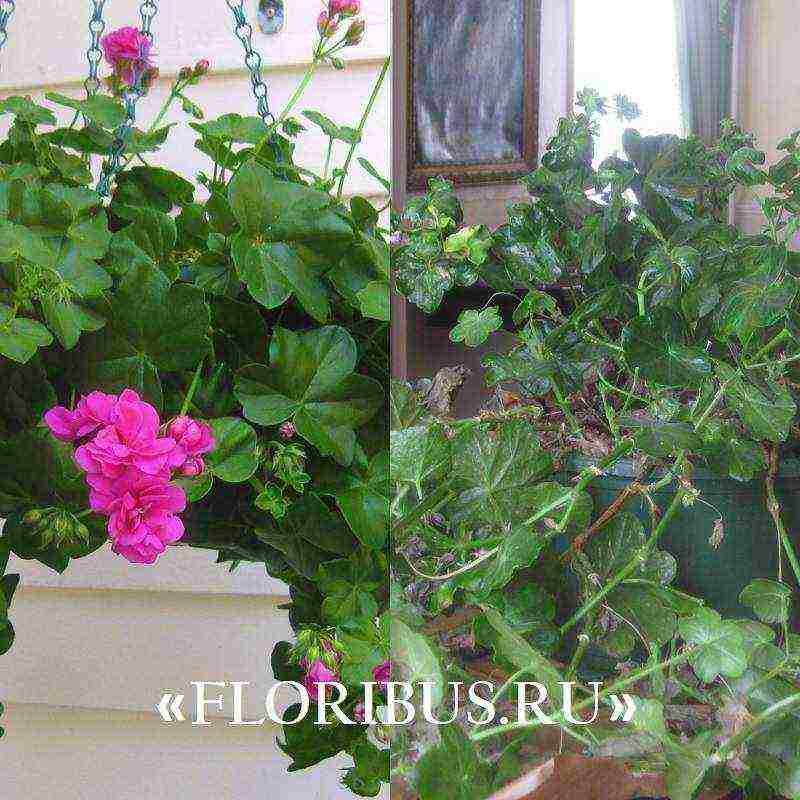


The hybrid group of Tornado varieties is popular in home floriculture. These are perennials with long stems (up to 40 cm) and dense paniculate inflorescences of various shades. Flowering is long and plentiful, usually lasts up to 5-6 months in a row.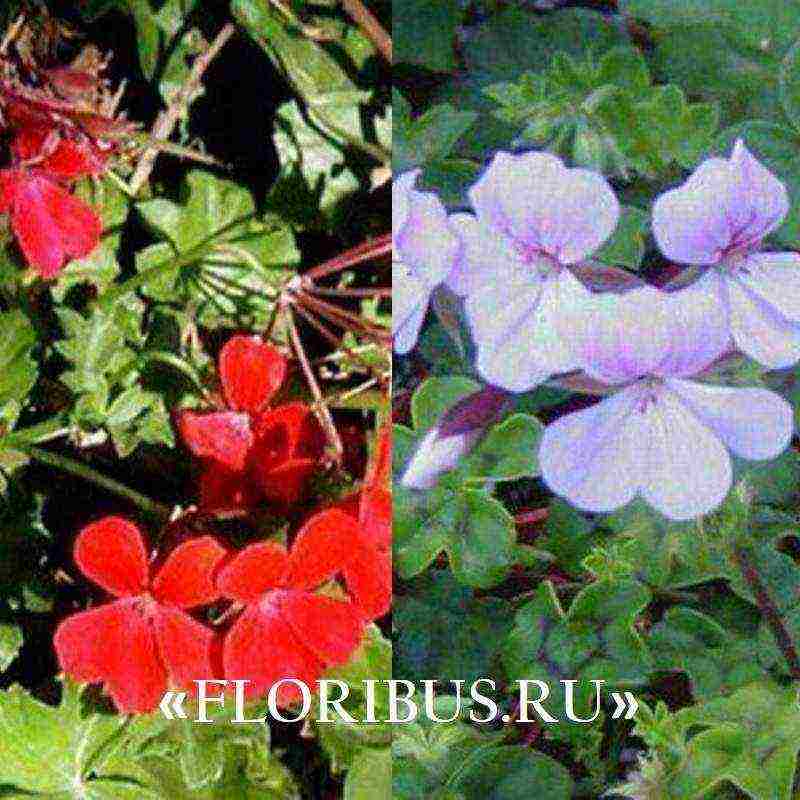


Propagation by seeds and cuttings
If you know all the rules for the reproduction of ampelous pelargonium, then this process will not be particularly difficult. Some growers, during this process, face some problems. Most often, inexperienced botanists meet with the fact that the seeds do not germinate, as they are collected from home crops. Some hybrids produce this type of sterile planting material. Many of the ivy pelargonium varieties produce seeds that do not retain their parental properties. In order to maintain the same appearance as the mother bush, we will use cuttings.
Apical stems can be cut into cuttings in the spring (in March) or by the end of flowering (in August). The stems are cut under the nodes of the leaves, so that a shoot remains, 7-12 cm long with 3-4 healthy leaves (usually taken with two pairs of plates). We process the sections with crushed charcoal - wood or activated. While we are drying the cuttings at room temperature or in the fresh air for two days, you can start preparing a nutrient substrate for their rooting. A light mixture with a high content of nutrients will do. You can take compositions based on peat and sand (instead of sand, perlite is often used). The most important thing is that the soil allows moisture and air to pass through well.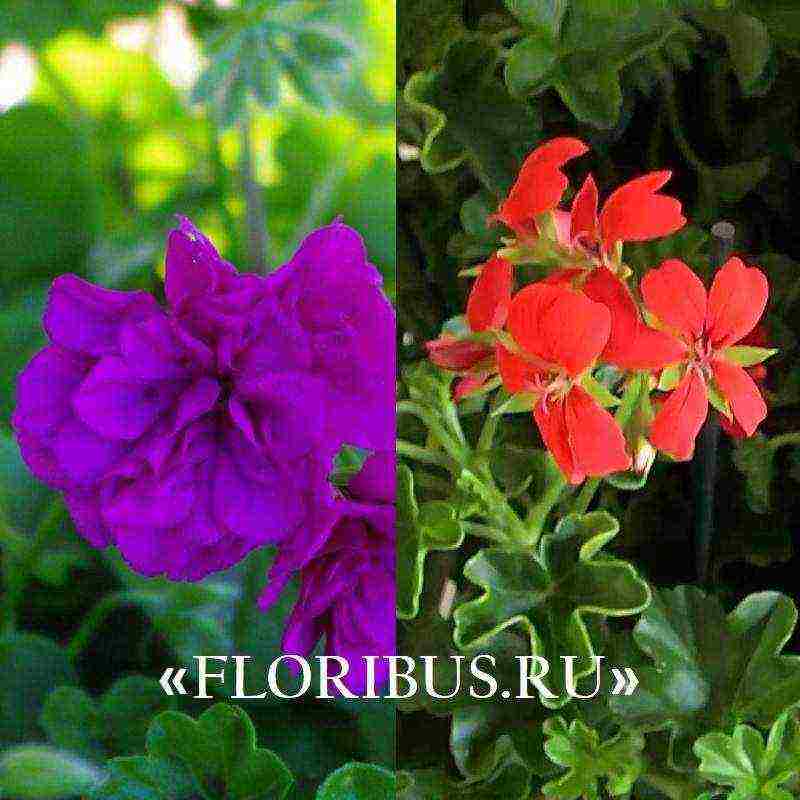


After the cuttings are dried, you can plant them in a rooting substrate. We deepen the shoots into the ground to a level of 3-4 cm, maintain a distance of 2 cm between them, this is necessary so that the young roots do not intertwine with each other. Cover with a non-woven fabric that will allow moisture to pass through until its own root planting system appears. This is to avoid condensation. The formation of excess moisture leads to the fact that the leaves begin to rot and the plant dies. If you covered the planting with polyethylene, then watch the condensation yourself, constantly airing the cuttings.
Pelargonium cuttings take root within 30-40 days. After this period, shoots can be planted in permanent places. The perennial will begin to bloom in the next summer season, after it survives the first wintering in special conditions (reducing watering and lowering the temperature to 12 degrees Celsius).
Seed reproduction
Seed propagation is recommended for those who are new to pelargoniums. This method is suitable for novice growers, since from a very young age the plant will grow and get used to constant conditions. Seeds are sown in seedling containers with a light moisture-absorbing substrate in February and until mid-April. The planting material is deepened into the ground by a maximum of 0.5-1 cm. Next, you need to water the substrate or spray it with water from a spray bottle so as not to wash out the top layer. Seedlings, until the first shoots appear (7-10 days), are kept under a plastic cap in a warm, well-lit place. 3-4 weeks after germination, young pelargoniums can be transplanted in permanent pots.
Growing at home and care
Many growers are afraid to grow the ampelous form of ivy-leaved pelargonium, as they believe that it is very whimsical. In fact this is not true. The fact is that difficulties can arise only if houseplants are taken out into the street. Living in indoor conditions, getting into the fresh air, pelargonium experiences severe stress, which leads to serious illnesses and consequences.Therefore, perennials begin to adapt to the content outside the window or in the garden from the beginning of May, when warm days come. This is done gradually: every day in the morning, they take out pelargonium to fresh air, accustoming it to new conditions for several minutes, and then several hours. Growing pelargonium ivy at home does not require special care for the crop.


The air temperature for indoor ivy pelargonium does not really matter, since the variety easily adapts to home conditions and air humidity in the house. Another thing is if the plant grows in a garden or on a balcony. In this case, the air temperature ranges from 15 to 25 degrees. An increase to 30 does not affect decorativeness, but a decrease to 10 degrees Celsius stops the growth and development of flowers. Pelargonium loves fresh air and warm weather, many varieties and varieties easily tolerate precipitation and are not subject to brittleness under the influence of strong winds. The main thing is that rain moisture does not accumulate on the leaf blades, as it can cause rot. Short-term exposure to a powerful flow of icy air, for example, when ventilating in winter, is detrimental to the plant.
Lighting for both indoor and balcony plants should be bright. Pelargonium loves direct sunlight. Often, the sun can leave burns in the form of yellow streaks, usually this happens on diseased plants. In this case, pelargonium needs to be shaded and thought about its health, intervention may be required. Strong darkening leads to the fact that the plant does not bloom and its foliage becomes smaller, and the bush itself stretches out its shoots and loses its decorative effect.

Transplanting, feeding and watering
For transplanting ivy pelargonium, a pot with a volume of 1.5-2 cm larger than the diameter of the root system is always chosen. In too large a container, the perennial stops blooming and grows wide, stretching out the shoots. The transplant procedure is performed every two years. If the plant has become cramped (for example, this can be determined by the roots that have emerged from the drainage holes), then you need to transplant it into a more spacious container. You can plant different varieties in group plantings in large hanging pots. When planting pelargonium ivy, there should be a powerful drainage layer, which is ¼ or 1/5 of the pot. Use broken brick or expanded clay as drainage.
Pelargonium quickly consumes nutrients, so you need to constantly feed the plant. It is not recommended to use organic and nitrogen-containing fertilizers. Apply mineral formulations weekly from early March to fall. During the flowering period, focus on potassium and phosphorus. An excess of nitrogen prevents the perennial from budding.
In autumn, as soon as the air temperature drops to 10-15 degrees Celsius, the perennial must be brought home for wintering. At this time, sanitary pruning of ivy-leaved pelargonium is carried out, since next year the buds will appear only on young shoots. The plant hibernates at a temperature of 12-15 degrees Celsius in a well-lit place. It is advisable to stop feeding 30 days before the start of wintering. Some gardeners, outdoor pelargoniums, so that they do not get used to home conditions and easily adapt to the street for the next year, store it differently. They take out the perennial along with the rhizome with an earthen clod, cut off the ground part and place it in a plastic bag. It must be tightly closed and placed in a warm room with good lighting for the winter.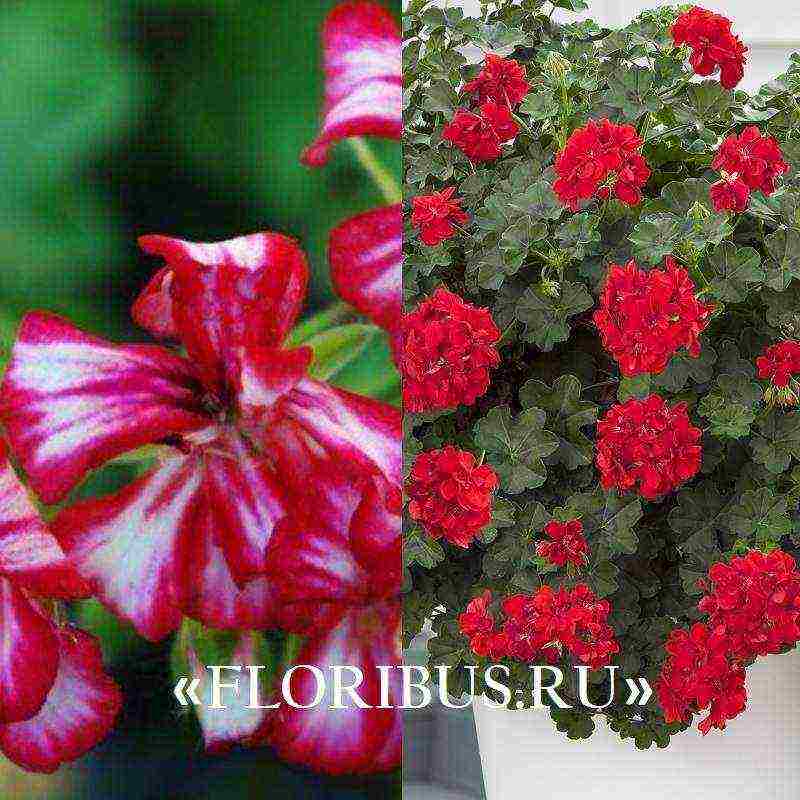


It is possible to water ivy-leaved pelargonium no more than 1 time 10-14 days in order to avoid waterlogging of the soil. Excess moisture and the appearance of water on the leaves leads to the formation of rot and the plant begins to ache. In winter, watering is reduced even more to 1 time in 20-25 days.
Pests often attack the plant.It is loved by aphids, spider mites and whiteflies. You can get rid of them with soapy water or insecticides. With an excessive density of the bush, perennials are infecting a fungus and a mosaic virus. To avoid such a problem, constantly cut through bushes and cut off old, elongated shoots. One of the unpleasant diseases of ivy pelargonium is chlorosis, it occurs when the plant is under severe stress, for example, in the fresh air.


