Content
- 1 Varieties of Japanese spirea
- 2 How to care for Japanese spirea
- 3 Pruning Japanese spirea
- 4 Reproduction methods
- 5 Application in landscape design
- 6 Description
- 7 Growing conditions
- 8 Landing
- 9 Care
- 10 Growing tips, nuances
- 11 Spring flowering spireas and their varieties
- 12 Summer flowering spireas and their varieties
- 13 Spirea Bumalda (Spiraea x bumalda)
- 14 General characteristics and description of the plant
- 15 Varieties of Japanese spirea
- 16 Landing
- 17 Care and cultivation
- 18 Reproduction
- 19 Pests and diseases
- 20 Japanese spirea in landscape design
Content
- Varieties of Japanese spirea with photos
- How to care
- Pruning
- Reproduction methods
- Application in garden design
Japanese spirea (Spiraea japonica) is perhaps the most popular type of culture in gardening, native to Japan and some Asian countries. The plant is a dense, low deciduous, slow-growing shrub with tiny pink, ruby or white flowers, collected in flat corymbose inflorescences at the tops of the shoots. The flowering period usually lasts from late spring to mid-summer or early September.
The popularity of the Japanese spirea is due to its ease of care, high decorativeness, resistance to frost and drought, flowering time and availability in many varietal varieties. Ornamental-leafy varieties with lemon or light green foliage look especially great.
Varieties of Japanese spirea
Anthony Waterer characterized by narrow-lanceolate dark green leaves with a spectacular purple color with the onset of autumn. Intense pink flowers appear in mid-summer.

"Little Princess" - a compact, rounded bush a little more than half a meter in height. In late spring to mid-summer, it is covered with numerous pink inflorescences. The green leaves take on a gorgeous red hue in the fall.

"Macrophylla" - a large shrub about 1 meter high with large rounded leaves, which amaze with their decorative effect in the autumn, acquiring all shades of red, orange and purple.

Albiflora - compact shrub, reaching about 60-80 cm in height, characterized by white flowering.
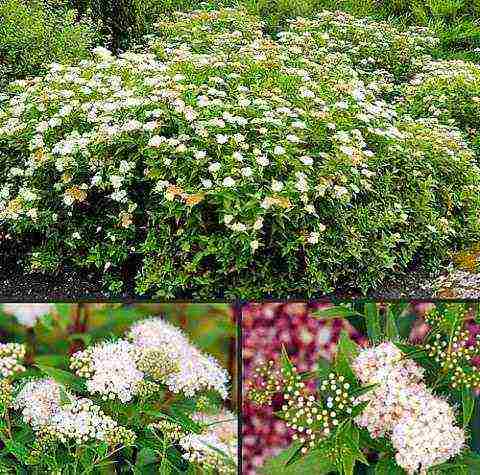

Miniature round-shaped variety "Golden Carpet" only 20-30 cm tall with creeping shoots. Attracts gardeners with amazing lemon-colored foliage.
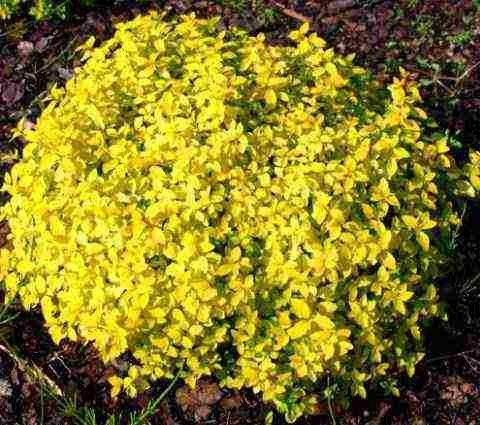

Spirea "Golden Princess" - a low compact bush that reaches 50 cm in height and 80 cm in width at the age of 10 years. Numerous small leaves of intense golden color retain their hue throughout the growing season. In summer, the ornamental value of the plant increases due to the abundant flowering.
Variety "Dart's Red" about 60 cm high. Leaves are light green lanceolate, flat ruby-pink inflorescences adorn a round bush from June to September.

Variety "Japanese Dwarf" or "Japanese gnome" - a compact dwarf shrub, about 40 cm in height. The annual growth is 5 cm. During the flowering period, the bush is covered with large pale pink inflorescences.

"Bullata" - the original variety, which is a low-growing bush with dark green wrinkled leaves. Its height is about 40 cm. Ideal for decorating rockeries and alpine slides.

"Crispa" - varietal form with serrated leaves and large pink inflorescences. It grows up to 60 cm. Leaves turn reddish-purple in autumn.

Walbuma, commonly sold under the brand name "Magic Carpet", was bred by an English breeder and is a ground cover and expanding shrub with small bright pink buds. Its young creeping shoots and leaves are initially orange-red in color, and as they grow, acquire a lemon color, which varies depending on the lighting. In full sunlight, mature leaves are golden, and in partial shade, golden green. Autumn color of foliage - red-pink, plant height 30-40 cm.

Variety "Goldflame" or "Golden Flame" got its name from the shoots, which seem to "burn" at the tips with an intense copper color - young leaves, first with a shade of brown and red, and in a later period turn yellow-green. Therefore, in the spring, this variety of Japanese spirea is one of the brightest shrubs. Dark pink flowers are formed on the shoots of the current year. The height of an adult bush is about 80 cm.
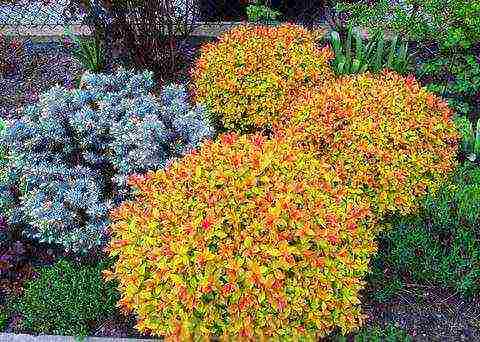
Varietal form "Goldmound"... A fabulous shrub with bright, sunny foliage, the color of which depends on the brightness of the light. When planted in the shade, it loses its decorative color as the foliage turns green. Easily withstands minus 30 degrees and even lower temperatures. Bloom from May to July. A beautifully rounded bush grows up to 60 cm in height.

How to care for Japanese spirea
After planting, caring for a Japanese spirea requires a minimal investment of time. This species feels equally well in the sun and in partial shade, but decorative leafy varieties need bright lighting to maintain the spectacular color of the foliage.
Fertile, loamy, well-drained soil with moderate moisture is best for the plant, but the culture also adapts well to poorer soil, and adult shrubs can tolerate short-term drought, but regular watering is necessary during long dry periods and during the first few weeks after planting. ...
It should be borne in mind that the shrub does not tolerate constantly damp soil and air humidity, which contribute to the formation of fungal diseases.
Japanese spirea, planted in fertile humus soil, does not really need additional feeding. A 2-3 cm layer of compost mulch allows you to enrich the soil around the plant with nutrients and retain moisture in the heat. The care of Japanese spirea also includes the timely removal of faded inflorescences, which contributes to a longer flowering.
Pruning Japanese spirea
When growing a shrub, it is advisable to carry out pruning, which rejuvenates the plant, stimulates abundant flowering and allows you to form a beautiful shape.
The flowers of this type of culture are formed on the shoots of the current year, therefore, pruning is carried out in early spring, even before the start of growth. Shoots are cut 5-20 cm, depending on the height of the variety. Remove dry, damaged and old branches, too thick bushes thin out a little.
Reproduction methods
Japanese spiraea propagates by dividing the bush, layering and cuttings in the open field. The first two methods are the simplest. Only adult 3-4 year old bushes are divided in mid-spring, carefully cutting the root system into 2-3 parts. Roots that are too long can be shortened. Delenki are planted in a permanent place and watered well for the first two weeks.

To obtain young plants with the help of layering, they take a well-developed lateral shoot, tilt it to the ground, laying it in a prepared groove, pin it and cover it with soil. At the end of the season, the shoot takes root and produces 2-3 young seedlings. The next year, the cuttings can be separated from the mother bush and transplanted to a new location.
Cutting is a more laborious method of propagation of the Japanese spirea.In late summer or early autumn, parts of shoots 10-15 cm long are cut off. The lower leaves are removed, the rest are cut to half and the cuttings are placed in water with the addition of "Kornevin" for about 2-3 hours. Then it is buried in a wet mixture of sand and compost (compost at the bottom, and a layer of sand on top) at an angle of 45 degrees, since this position stimulates the growth of the root system well. Cover the cuttings with a bag or jar. They monitor soil moisture and periodically ventilate the greenhouse. As soon as the plants grow, the cover is removed. For the winter, seedlings are covered with leaves, agrofibre or spruce branches.
Application in landscape design
Due to its high decorative qualities, this type of spirea fits into almost any style of landscape design. For example, undersized shrub varieties are an indispensable decoration for rockeries and alpine hills. Japanese spiraea looks great in composition with conifers and such decorative leafy and flowering shrubs such as barberry, euonymus, cotoneaster, Japanese quince, hydrangea, buddlea, roses.
Save
Save
Save
Save
Save
Save
Save
Save
Save
Save
Save
Did you like the article? Vote!
1 1 1 1 1 Rating 5.00
Japanese spirea is a unique plant that is useful on the site and as a hedge, and as a decorative ornament. Spirea can be grown in cool climates - it is quite unpretentious. We will learn the features of growing Japanese spirea in the open field, find out all the nuances of planting a plant and caring for it.
Description
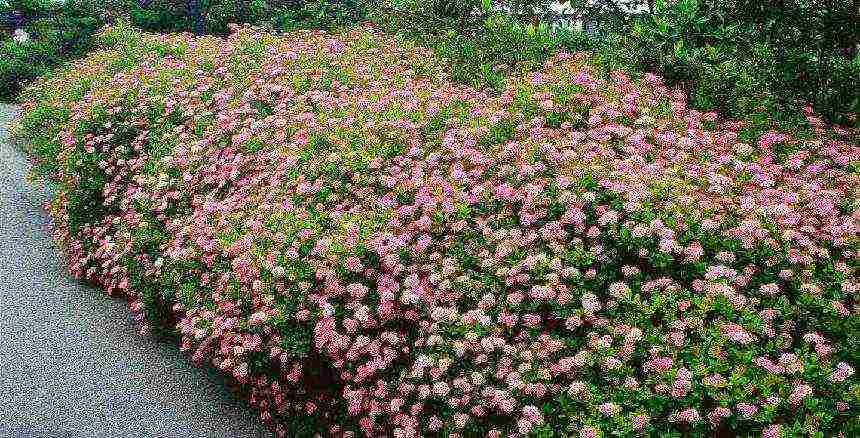

Japanese spirea is one of the representatives of the Rosaceae family. The shrub is compact, deciduous, and can be grown in various regions of our country. Pay attention to the photo spirales presented on our website.
An interesting feature of the color of the foliage of the spirea: only after blossoming in the spring, they are brown, then turn green by summer, and closer to autumn the foliage becomes red. Many landscape designers take advantage of this unique feature of the spirea, giving the site a great look.
Spirea flowers have a pinkish-red hue, small, but collected in rather lush and multiple inflorescences. The diameter of one inflorescence can be either 5 centimeters or 30, depending on the variety. In addition, this plant has very long flowering periods: from the end of June to the very fall.
All varieties of spirea are subdivided into:
- spring flowering;
- summer flowering.
The former begin to bloom from mid-late May, and the latter (there are more of them) from the end of June. Japanese spirea is a summer-flowering variety.
Varieties
Little princesses
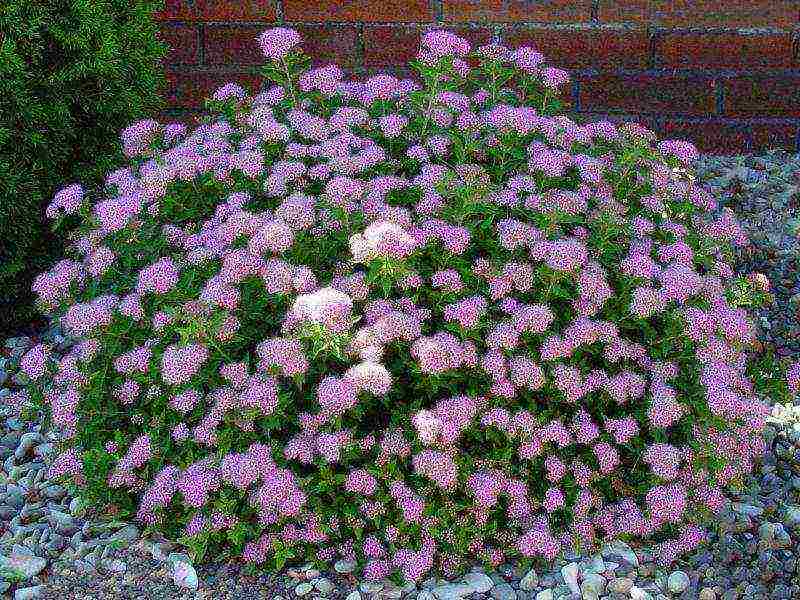

A compact shrub that grows 50-60 cm in height. The pink color of the inflorescences-scutes contrasts perfectly with the dark green dense foliage (see photo).
Goldflame

A variety that is characterized by a particularly noticeable change in foliage color. The flowers are small, pink, and look very decorative against the background of beautiful leaves.
Crisp
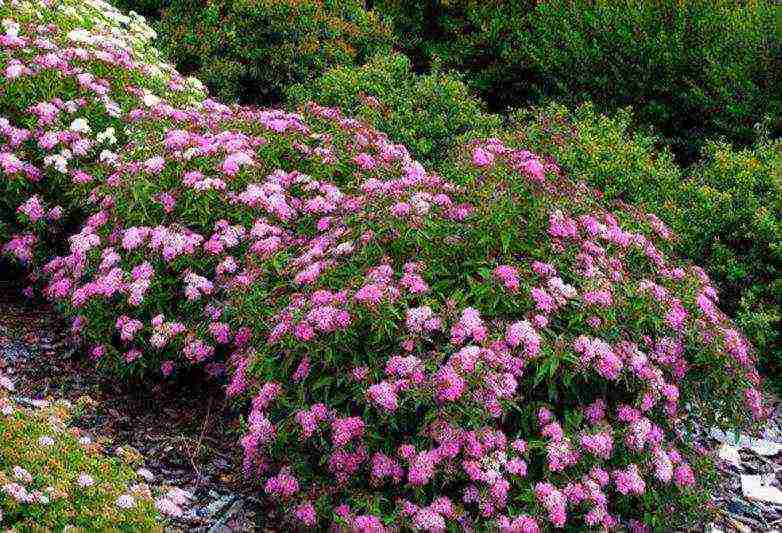

Low shrub, does not grow more than half a meter. The flowers are very delicate, light pink, collected in graceful umbrella inflorescences. Spirea Crispus is prized for its long-lasting flowering - the decorative period lasts about two months.
Macrophile

It features extremely decorative foliage that changes its color. So, in the spring the leaves of Macrophila have a purple hue, in the summer they are green, and in the fall the foliage becomes golden and orange.
Golden princesses

This Spirea reaches a meter in height, is distinguished by reddish-pink flowers and yellow foliage.
A variety such as Shirobana is also often planted. The variety boasts a compact bush and simultaneous flowering of both pink and white flowers on the same plant.
In landscape design, Japanese spirea is valued for its exceptional decorativeness. Various varieties of it are used to create hedges, and to decorate flower arrangements, alpine hills.
Growing conditions
We will find out what the requirements for the conditions of its content and location are imposed by the Japanese spirea.
Seat selection
Although the plant is unpretentious, however, it will best show its decorative qualities when planted in a sunny, well-lit area. By the way, the spirea can feel quite well in the shady corners of the garden, however, it cannot please with special decorativeness in this case: both the inflorescences will be smaller, and the color of the foliage is not so bright.
It is also important to know that the space allotted for the spirea should be quite extensive, since the roots of the plant grow underground to an area larger than the area of the shrub itself.
The soil
Japanese spirea will feel best in fertile, well-fertilized soil. Take care of this before planting by adding the necessary nutrients to the soil.
Planting time and seedling selection
Spirea should be planted in the open field in the spring. However, it is necessary to have time to carry out planting before the leaves bloom at the plant. Buy seedlings in proven nurseries, paying attention to the roots of the plant: it is important that they are not overdried. Otherwise, the spirea will not take root. When buying seedlings with open roots, choose specimens with live buds, but not yet started to grow. Bend the roots and shoots (without fanaticism) - they should be flexible and not brittle.
Preparing for landing
If the plant has damaged roots, remove them with a sharp, well-sanitized secateurs. If some of the healthy roots are too long, shorten them too.
Soak the roots of the plant in potassium permanganate water before planting. The procedure will simultaneously solve two problems at once: it will relieve the roots from drying out, and will provide disinfection.
Landing
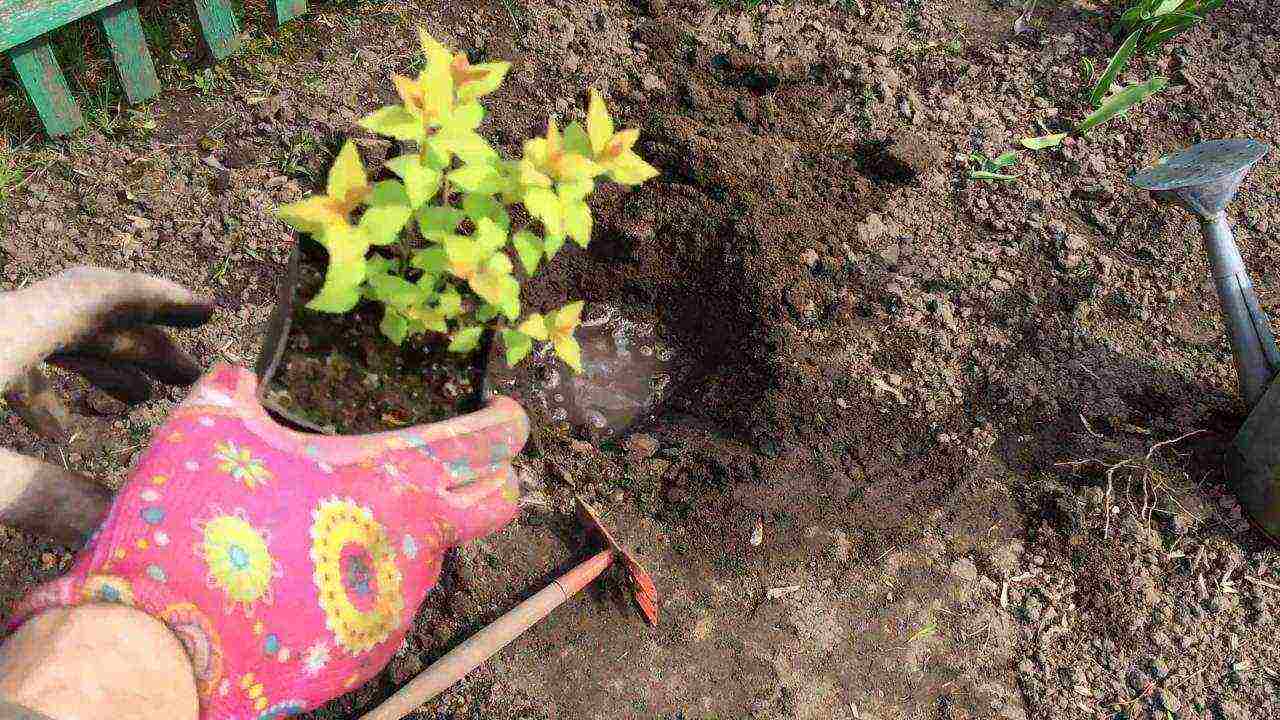

How to plant Japanese spirea in open ground.
The first step is to prepare the pit. Its volume should exceed the approximate volume of spirea roots by one third. Before planting, the pit should be allowed to settle for two to four days.
Planting should be done in cloudy weather or rain. Lay the crushed brick drainage on the bottom of the dug hole in a layer of about 15-20 cm.The soil should be as follows:
- sod land - 30 parts;
- humus - 2 parts;
- peat land - 1 part;
- river sand - 1 part.
Mix all ingredients.
Dip the roots of the plant into the hole, straighten them carefully, cover them with carefully prepared soil mixture. The root collar should be above the ground and not buried. When filling the hole with earth, immediately compact the soil during the process.
After planting, water the shrub with 1-2 buckets of water. Mulch the root circle with dry peat. Also make several depressions in the diameter of the root circle to retain water: this way you will provide better moisture for the plant roots.
A couple of days after planting, water the plant with water with ammonia dissolved in it. This substance acts on spirea like an anti-stress drug: it nourishes the roots while they have not yet completely taken root. In addition, ammonia will help you gain green mass faster. Feeding with ammonia, by the way, can be carried out later, when the plant has already taken root and will actively grow.
Care
The following is a description of the main points for caring for Japanese spirea growing outdoors.
Top dressing
To ensure long-term and abundant flowering of the spirea, it should be pampered with additional nutrition. Proper care involves feeding twice a season: after spring pruning and in July. Add mineral complex solution in spring and mullein solution in summer. Under one bush, it is supposed to pour from 1 to three liters of top dressing.
Loosening, mulching
Japanese spirea grows best in loose, well-permeable soil. Therefore, after watering and rains, it is advisable to loosen the soil in the root circle, at the same time removing weeds.The mulching procedure will help to retain moisture and get rid of weeds. Use dry compost or peat as mulch.
Drafts
The Japanese spirea is not afraid of the wind, so it can feel good in open areas. However, too strong gusts can negatively affect flowering, therefore, during the period of bud formation, it is better to protect the spirea from drafts.
Watering
The plant needs moderate watering. If it is hot outside, then the moisturizing procedure is mandatory. On average, in cool weather, 10 liters of water (bucket) are consumed per bush with one watering, in hot weather - 20 liters. Watering frequency is twice a month.
Irrigation and spraying
As for spraying, the spirea does not need this procedure. Irrigation is beneficial for its root system; foliage does not need to be irrigated.
Pest control
In general, this plant is resistant to diseases and pests. Nevertheless, although it is rare, sometimes aphids and spider mites attack the spirea. To cope with these pests, gardeners recommend using spraying with a solution of hot pepper, karbofos, tobacco. Against the spider mite, such remedies as Aktellik and Aktara have proven themselves well.
But it is better not to allow pests to be damaged initially. Carry out preventive spraying in advance - and then the spirea will always be healthy and strong. By the way, watering with water with ammonia serves not only as a top dressing, but also prevents many plant diseases.
Pruning, transplanting
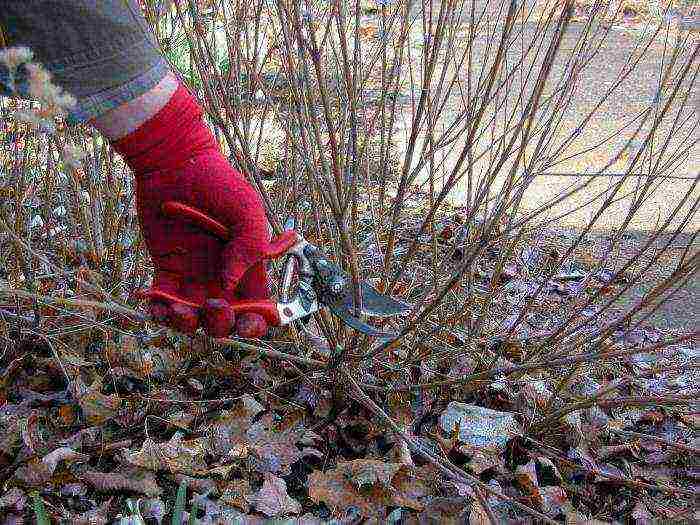

This shrub grows quickly, so regular shaping is essential. Every spring, before the onset of the growing season, shorten the regrown shoots up to the first strong and strong buds. In addition, after each winter, remove weed shoots: weak, sick, frozen.
When the shrub is four years old, you can prune it more, removing up to 30 cm of the length of the shoots. Keep in mind that the more you shorten the spirea shoots, the more lush and abundantly flowering the bush will be.
Reproduction
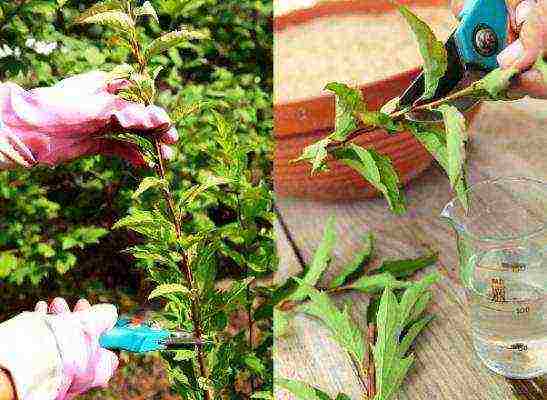

The plant can be propagated in four ways:
- seeds;
- dividing the bush;
- layering;
- cuttings.
In amateur gardening, the cuttings or layering method is usually used. Dividing a bush already requires a more professional approach, not to mention seed reproduction - long and painstaking. In addition, there is a risk of buying the wrong seeds that you need: for example, hybrid varieties of spirea, in principle, are not derived from seeds.
Care at different times of the year, wintering
In spring and autumn, the plant only needs pruning, while the spirea tolerates winter quite well. However, if you live in an area with snowless and frosty winters, it is best to cover the roots of the plant for the winter. And even if you live in an area with a temperate climate, it is advisable to cover for the winter the roots of those plants that have not yet turned four years old. Young spirea tolerates cold worse. As a shelter, you can use spruce branches or fallen leaves - a layer of 15-20 cm is quite enough.
Growing tips, nuances
Keep in mind that for the first time spirea blooms only in the third year after planting. You should be patient - the decorative spectacle of the flowering shrub is worth it.
It is also important to know that the root system of the plant is superficial, therefore, it cannot take moisture from deep layers of soil. Therefore, do not allow the roots to dry out, and be sure to regularly water the spirea, in the heat - twice as much.
The spirea bush lives for about 17 years, but if, upon reaching the age of four, it did not please with abundant flowering, it is better to replace it with a higher quality specimen.
Japanese spirea is a real decoration of the garden, striking with a unique combination of delicate flowers and bright color of leaves. In addition, the shrub is unpretentious, so novice gardeners can also grow it. And our advice will definitely help you with this.
Spirea is prominent among the ornamental shrubs.For lush flowering, unpretentiousness and frost resistance, she won the love of summer residents, landscape designers and breeders. But some types and varieties of spirea are held in high esteem.
The name of this shrub, translated from Latin, means "bend": the branches of the plant form a graceful arc. People sometimes call spirea a meadowsweet, but this is not true. Meadowsweet and spirea have similar inflorescences, but they are different plants.
Spirea is a shrub of the Rosaceae family, which has almost a hundred species. All of them are undemanding to growing conditions, multiply easily, grow quickly, bloom for a long time, tolerate a haircut well and have many other advantages. Today, spirea is widely used to decorate summer cottages and city parks.
Spirea can live on the site for tens of years
The height of the spirea can vary from 50 cm to 2.5 m. The flowering time - depending on the species - occurs in spring, summer or autumn. The shape of the crown is spherical, weeping, pyramidal, cascading or erect. In addition to flowers, spireas also decorate the site with decorative foliage. Many varieties have been bred with an openwork leaf shape. In autumn, they change color to bright red, yellow, orange.
All types of spirea are divided into two large groups: spring-flowering and summer-flowering.
Spring flowering spireas and their varieties
Spring species of spirea form inflorescences of predominantly white and cream shades. Flowering is usually very lush, at this time the bush becomes like a white cloud. Due to this, spring spireas are sometimes called May snow. Let's list some of the most common types of this type.
Spirea Wangutta (Spiraea x vanhouttei)
This hybrid spirea is a medium to tall shrub, which at the end of May is covered with a dense cascade of white flowers. Tall varieties look great singly, while lower varieties look great in mixed plantings. Spirea Wangutta is also suitable for hedges.
The most popular variety is Pink Ice, with variegated leaves and creamy buds.
Spirea Wangutta Pink Ice is an ideal plant for specimen planting
Spirea oak-leaved (Spiraea chamaedryfolia)
One of the first to bloom - in early or mid-May. The shrub grows up to 1.5 m, sometimes slightly taller. This species reproduces well with root shoots, so it is often planted in city parks. Also, the oak-leaved spiraea easily tolerates a haircut, therefore it is excellent for hedges.
Spiraea oak-leaved - not only an ornamental plant, but also a good honey plant
Spirea nippon (Spiraea nipponica)
It is a lower ball-shaped shrub. Its height usually does not exceed 1 m. It blooms very profusely in late May and June. The varieties Snowmound and Halvard Silver are especially effective.
Spirea Nipponskaya varieties Snowmound (left) and Halvard Silver (right)
Spirea Thunberg (Spiraea thunbergii)
In the wild, Thunberg spirea is found on mountain slopes and in valleys. The bush reaches a height of no more than 1.5 m. Its dense branches are covered with graceful leaves, which change their color from green to orange in autumn. Lush white inflorescences adorn the spirea from May to June. The plant prefers sunny places and in the middle lane it can freeze slightly in severe winters.
The most popular varieties are Fujino Pink (with pale pink inflorescences on drooping branches) and Ogon (with golden-green willow-like leaves and white inflorescences).
Spirea Thunberg Fujino Pink (left) and Fire (right)
Spirea crenate (Spiraea crenata)
Spectacular shrub up to 1 m in height with a loose crown and obovate leaves of a grayish-green color with a characteristic crenate edge and protruding veins. Yellowish-white flowers are collected in corymbose inflorescences.
Thanks to the well-developed root system of the spirea, the crenate is not afraid of frost or drought.
Spirea gray (Spiraea x cinerea)
It is a hybrid of Spiraea hypericifolia and whitish-gray spirea (Spiraea cana).The plant is a shrub up to 2 m high with branched shoots, gray-green pointed leaves and white flowers, collected in loose inflorescences-shields. This spirea blooms in May - early June.
The Grafsheim variety is especially interesting. It is a small densely branched shrub with arched drooping branches, narrow leaves and large white double flowers.
Grafsheim is not only a very beautiful, but also a perfect unpretentious variety. The bush grows very quickly, tolerates a haircut well, is not afraid of the cold and does not need good lighting
Summer flowering spireas and their varieties
In spring spirits, flower buds are formed on two-year-old shoots, and in summer spirits, on the shoots of the current season. Therefore, they are often cut off. Summer-flowering spireas are distinguished by inflorescences, as a rule, of different shades of red and pink. Here are the most famous species.
Spirea willow (Spiraea salicifolia)
It usually grows from 1 to 2.5 m. From the end of June, the upright shrub is covered with light pink inflorescences. Light foliage, similar in shape to willow, takes on a red tint in the fall.
Willow spirea is most often grown in hedges.
The most popular in gardens is the large-flowered form of willow spirea (f. Grandiflora) - with more lush light pink flowers.
White-flowered spirea (Spiraea albiflora)
It is named so because it is one of the few summer species with white flowers. It blooms for a long time from the second half of summer, exudes a pleasant aroma. The bush is usually low - 1-1.5 m.
Of the bred varieties, it is worth noting Macrofila. Its foliage changes color twice: young leaves are red, gradually they turn green, and in autumn they turn yellow.
Spirea white-flowered variety Macrofila is famous for its large leaves
Japanese spirea (Spiraea japonica)
This is the most common spirea. It has a small height (usually about 50 cm), blooms for one and a half to two months, starting in mid-summer. Looks good in curbs and group plantings.
Among the many varieties, one of the most spectacular is Shirobana. On one bush, flowers of white, pink and red shades are found at the same time. Also good varieties are Golden Princesses (distinguished by golden foliage), Gold Mound (leaves are also golden, but darker and with a pink tip).
Spirea Japanese varieties Shirobana, Golden Princesses and Gold Mound (from left to right)
Spirea Douglas (Spiraea douglasii)
Shrub up to 1.5 m high with straight, reddish-brown, pubescent shoots, oblong-lanceolate silvery-green leaves and dark pink flowers, collected in narrow pyramidal or paniculate inflorescences. The plant blooms from July to August for approximately 45 days.
Spirea Douglas is often used to strengthen slopes and slopes
Spirea Bumalda (Spiraea x bumalda)
This hybrid of Japanese and white-flowered spirits is found in gardens even more often than its "parents". Spirea Bumalda is a short shrub (up to 75 cm) with a spherical crown, erect branches, ovate-lanceolate leaves and pink or crimson flowers.
The most popular varieties:
- Gold Flame (pink flowers, leaves when blooming are bronze-orange, later - golden-yellow, in summer - greenish-yellow, and in autumn - copper-orange);
- Darts Red (inflorescences are deep crimson, leaves are pinkish when blooming, in summer they are dark green, and in autumn they are red).
Spirei Gold Flame (left) and Darts Red (right)
Spirea Billard (Spiraea x billardii)
This is a winter-hardy hybrid of Douglas spirea and willow spirea. The bush grows up to 2 m in height, differs in broadly lanceolate leaves and pubescent bright pink inflorescences that adorn the plant in the second half of summer.
The most popular variety is Triumfans (with purple-pink spike-shaped inflorescences).
Spirea Billard Triumfans is suitable for creating hedges, as well as for group and single plantings in gardens and parks
Spirea goes well with other plants. It can be flowering shrubs and strict conifers. Planting a spirea allows you to cover the leafless part of the lilac and other shrubs and trees bare from below. Miniature varieties will find their place among stones on an alpine slide or in a rockery. And from tall spirits beautiful hedges are obtained. Select a corner in the flower garden for a charming spirea - and you will not regret it!

The Japanese spirea is one of the most popular landscaping plants. It has high decorative parameters both in the flowering and vegetative state. Doesn't have any special requirements for planting, soil and care.
General characteristics and description of the plant
Spirea Japanese, or Japanese meadowsweet (Latin Spiraea japonica) is a perennial deciduous shrub or shrub belonging to the Pink family. Shoots are erect, with dense tomentose pubescence; young shoots have soft, adpressed pubescence. Leaves are simple, petiolate, pubescent. Very appreciated for its flowers - panicles or shields collected in inflorescences.
 The peculiarity of this plant is that it is very hardy and can easily adapt to various natural conditions.
The peculiarity of this plant is that it is very hardy and can easily adapt to various natural conditions.
Depending on the variety, flowers can be white, red, pink, etc. Also, depending on the variety, flowers can be located both at the top of the stems and almost along the entire length of the shoot.
Japanese varietal spirea is usually divided into summer-flowering and spring-flowering.
Varieties of Japanese spirea
Japanese spirea has about 100 species and hybrids. The most popular are:
Little Princesses
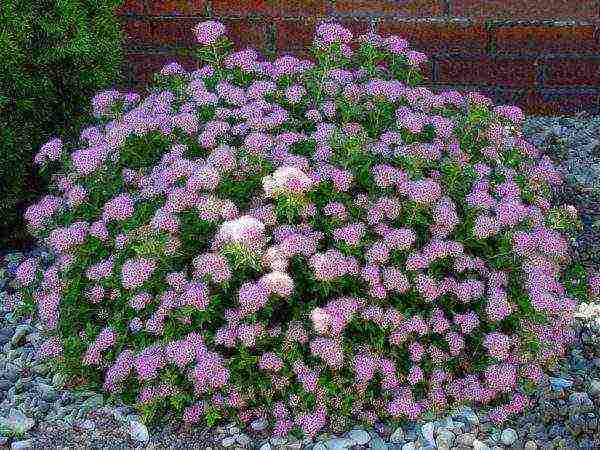 Spirea Japanese Little Princess
Spirea Japanese Little Princess
Forms a small shrub about half a meter high. Prized for its vibrant foliage and panicles of pale pink flowers. Blooms in the middle of summer... Well suited both for single planting and for decorating hedges, alpine slides, flower beds.
Golden Princesses
 Spirea Japanese Golden Princess
Spirea Japanese Golden Princess
It is shrubby and reaches a height of 80-100 cm and giving almost a meter span. It got its name for the golden color of the foliage, which appears closer to flowering. The flowers are large, dark pink, well shaded with leaves.
Shirobana
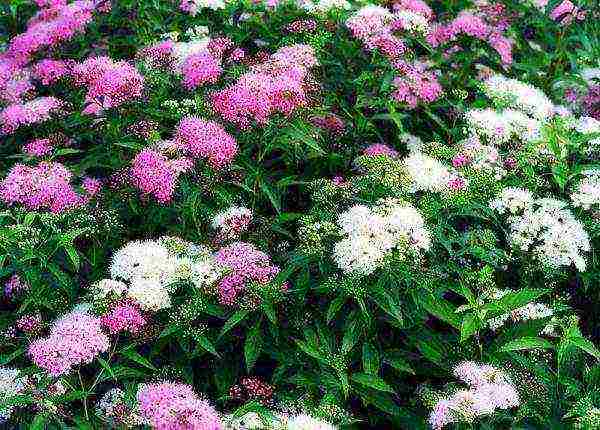 Spirea Japanese Shirobana
Spirea Japanese Shirobana
It is summer flowering. Tall shrub up to a meter. It differs from others in narrow elongated dark green leaves. Shades of flowers range from white to almost red... Needs a haircut, since the crown is formed very chaotically during the growth process. The variety is notable for the fact that inflorescences are often formed on it, resembling a heart in shape.
Albiflora
 Spirea Japanese Albiflora
Spirea Japanese Albiflora
Differs in white flowers. Low shrub or shrub blooming in late summer... It has a strongly growing crown, needs regular trimming and removal of faded peduncles.
Goldflame
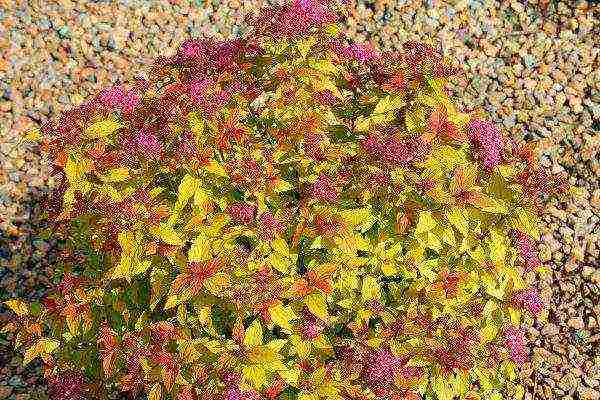 Spirea Japanese Goldflame
Spirea Japanese Goldflame
They are loved for their fast growth and powerful flowering. One of the most powerful varieties of Japanese spirea. Reaches heights up to 1 meter... During the season, the foliage changes color from orange in spring and bright yellow in summer to copper in autumn. The flowers are bright pink, clearly visible on the contrasting foliage. The variety takes root very well in urban conditions.
Landing
The most optimal time for planting spirea is autumn after leaf fall. Less often, the spirea is planted in early spring, immediately after the snow melts before the first buds open. The plant is not demanding on the soil, but light-requiring... Some varieties are more shade-loving, and the planting site comes from the characteristics of the variety itself.
The seedling is cut too long, unhealthy, damaged roots. The branches are shortened by an average of one third, diseased and damaged branches are cut at the root.
 It is necessary to plant spirea in cloudy weather, ideally in the rain
It is necessary to plant spirea in cloudy weather, ideally in the rain
If the roots have been overdried, immediately before planting, they are soaked in a bucket of water.
The planting pit should be twice the size of the root system and have strictly vertical walls. The bottom of the pit is laid with peat or turf, sheet soil. After disembarkation, the earth is slightly crushed and shed well. If the soil is clayey, a drainage layer in the form of broken bricks is added to the bottom of the pit.
The landing pit is prepared in 2-4 days.
Care and cultivation
Spirea is loved for its unpretentiousness, resistance to frost and disease, to the neighborhood with other ornamental plants. However, almost all varieties have certain content requirements. Due to the peculiarities of the root system spirea does not tolerate drought well, needs regular weeding and loosening to improve oxygen access to the roots. Some varieties need regular crown shaping for the neat appearance of the bush.
Watering
The weak root system of the spirea requires regular watering, especially during dry seasons. Spring varieties are more tolerant of lack of moisture, summer ones, especially during flowering, absorb large amounts of water.
 Spirea should be watered in moderation.
Spirea should be watered in moderation.
An excess of moisture, like a lack of it, is harmful to the plant. With an excess of moisture in the soil, the roots will begin to rot, which will inevitably lead to the death of the plant.
In a drought, each bush is spilled with 1.5 buckets of water every two weeks. The plant needs good watering in the spring after planting and after pruning to restore vitality.
Top dressing
On fertile soil, spirea does not need additional feeding. It is allowed to feed the plant with peat or compost once a season in autumn or spring after the snow melts. Spirea must be fed with mineral fertilizers immediately after planting.
 In order for the spirea to delight you with lush and long flowering, it is useful to pamper it with liquid dressings twice during the summer
In order for the spirea to delight you with lush and long flowering, it is useful to pamper it with liquid dressings twice during the summer
In the process of growing on nutrient-poor soils, top dressing is carried out in the spring before flowering, after flowering and after pruning, as well as in autumn. In the middle of summer, the plant can be fed with a mullein solution with the addition of superphosphate.
Pruning
Pruning is an important part of spirea care. Bushes tend to grow and overgrow. Pruning is carried out to form the crown, to rejuvenate the shoots, to heal the bush as a whole.
 The more you cut the plant, the more powerful and magnificent the bush will grow.
The more you cut the plant, the more powerful and magnificent the bush will grow.
Preventive pruning is carried out before bud break... The frozen tops are pruned, dried and diseased trunks are pruned. The rejuvenation of the bush is carried out when the plant begins to age and produce fewer flowers. The entire bush is completely cut off at the root in the fall. In the spring, young shoots will go from the root.
It is permissible to rejuvenate the bush by cutting out only old and thick shoots, leaving thin young ones.
Spring varieties are pruned immediately after flowering, summer varieties - in the spring of next year. During flowering, drying stalks are cut off so as not to waste the vitality of the plant.
Reproduction
The plant can be propagated by dividing and planting an old bush, as well as using seeds, using cuttings and layering.
Seeds
 Seed shoots of Japanese spirea
Seed shoots of Japanese spirea
Only non-hybrid species can be propagated by seeds, since the seeds do not retain the varietal qualities of the parent plant. Seeds are sown in spring in boxes with fertile soil, pre-well moistened. Seedlings are planted in open ground after 3 months.
Cuttings
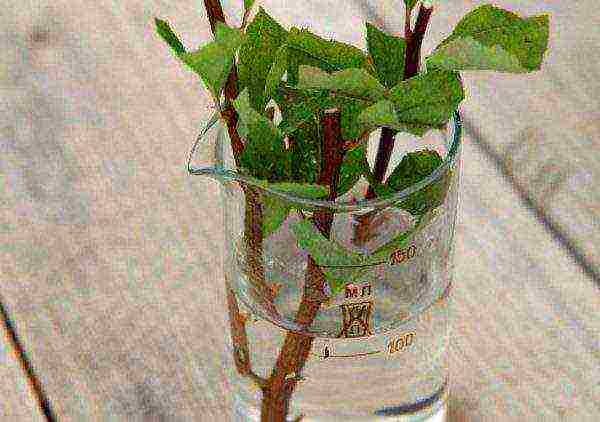 Reproduction of Japanese spirea by cuttings
Reproduction of Japanese spirea by cuttings
Cuttings can be carried out starting from the third decade of June. The shoot is cut into several equal parts, which are planted in a mixture of peat and river sand. Cuttings require high soil and air moisture - watering is carried out up to four times a day, spraying up to eight.In winter, the cuttings are covered, and in the spring they are planted in a new place.
By dividing the bush
 Reproduction of Japanese spirea by dividing the bush
Reproduction of Japanese spirea by dividing the bush
The division of the bush is carried out only on young plants not older than three years. Old plants will not tolerate transplanting well and will not give good shoots. The division is carried out in the fall after leaf fall or in the spring before the first buds open.... The bush is dug up and divided into several daughter ones. One daughter bush must have at least five mother trunks. Further, the daughter bushes are transplanted to a new place.
Layers
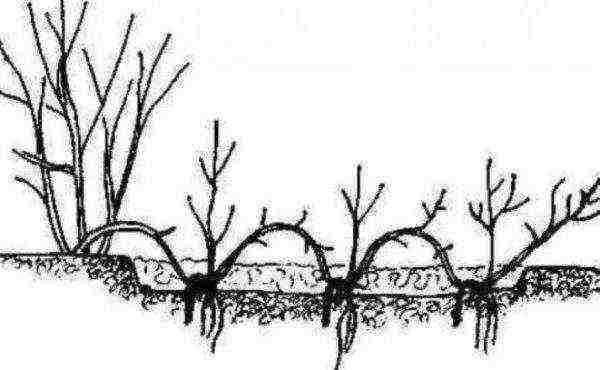 Reproduction scheme of Japanese spirea by layering
Reproduction scheme of Japanese spirea by layering
One of the most effective methods of reproduction is propagation by layering - such seedlings have a fairly high survival rate. The vegetative branch is not cut off from the main bush, but pressed to the ground with staples and covered with soil or peat-soil mixture. The branches take root well, and the daughter seedlings can be transplanted to a new place without much difficulty.
Pests and diseases
In general, spiraea is resistant to various pests and diseases. The spider mite is considered the most unpleasant and dangerous for spirea.whose eggs are reasonably resistant to most chemicals. Spider mite treatment is carried out several times to completely destroy all possible eggs and individuals.
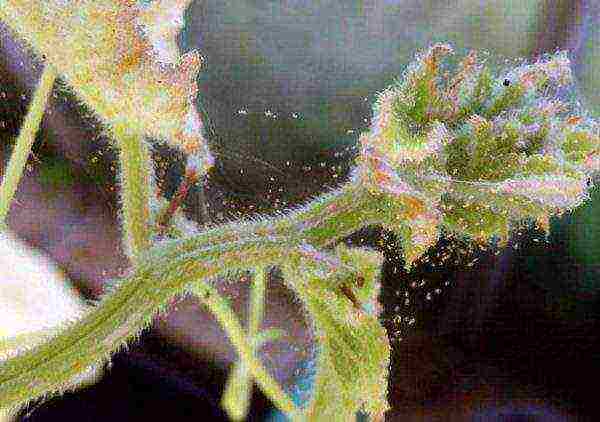 The plant is affected by spider mites
The plant is affected by spider mites
In summer, ants can drag aphids onto bushes, especially if the anthill is located near the bushes. Aphids eat inflorescences and suck out the juice, from which the plant loses its attractiveness and becomes withered in appearance. Another such pest is the rose leafworm.
Japanese spirea in landscape design
Due to its high decorative effect, unpretentiousness and frost resistance, it is used in many household plots. In spirea, both flowers and leaves are decorative, since in many varieties they change their color depending on the season. We can safely say that this type of shrub is one of the most popular among landscape designers. It is used in the design of hedges, alpine slides, for the design of artificial ponds, in flower beds... Looks good as a single shrub. It successfully tolerates the neighborhood with most other ornamental plants.
 The use of Japanese spirea in the design of the garden
The use of Japanese spirea in the design of the garden
Spirea does not cause problems in care, is unpretentious, resistant to cold weather. It grows quickly and gives a large area coverage. Even a novice gardener will cope with pruning and feeding, and in response, the plant will delight the eye with its bright leaves and fragrant flowers from the first warm days to leaf fall.


