Content
- 1 How to correctly determine the choice of cucumbers for greenhouses?
- 2 How to choose the right variety of greenhouse cucumbers for cooking?
- 3 When do greenhouse cucumbers ripen?
- 4 Variety selection
- 5 Varieties of greenhouse cucumbers and their descriptions
- 6 Hybrids or variety: making the right choice
- 7 Pollination and ripening dates
- 8 The use of cucumbers and conditions for them
- 9 Popular varieties of cucumbers for the greenhouse
- 10 Growing cucumbers in a greenhouse
Foreword
Cucumber is a worldwide annual herb belonging to the pumpkin family. When choosing varieties of cucumbers for greenhouses, you need to know the basic rules, following which you can get the largest harvest.
How to correctly determine the choice of cucumbers for greenhouses?
Breeders recommend planting new varieties of cucumbers along with proven old ones, which leads to higher yields of both types.
For growing cucumbers in greenhouses, their variety and method of pollination are of great importance.
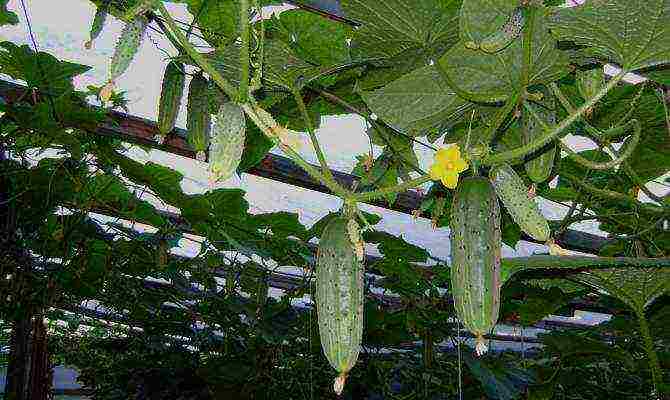

Growing cucumbers in a greenhouse
The most suitable for both varietal and hybrid greenhouse crops are parthenocarpic and self-pollinated varieties.
Parthenocarpic cucumber varieties have only female flowers and can be set without pollination. The fruits of such plants do not contain seeds. Best parthenocarpic cucumbers for greenhouses:
- Emerald City.
- Ant.
- Grasshopper.
- Okhotny Ryad.
- First grade.
- Buyan.
- Alphabet.
- Green wave.
- Ensign.
- Marina Grove.
- Dragonfly.
- Balalaika.
- Bouquet.
- Three tankers.
- Clean ponds.
- Focus.
- Anyuta.
- Heroic strength.
- Toddler.
- Matryoshka.
- Petrel.
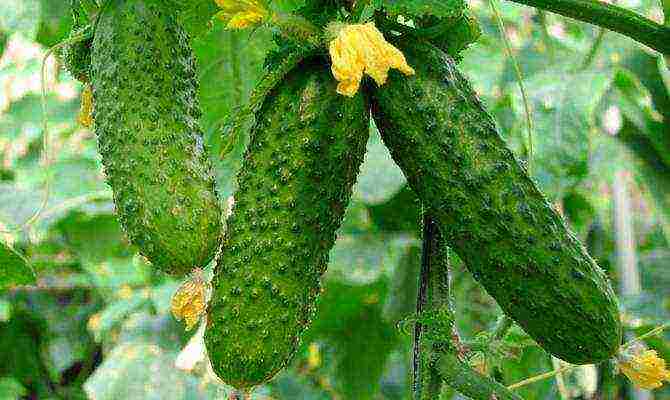

Parthenocarpic cucumber varieties
Self-pollinated varieties contain both female and male traits, so they can pollinate independently. The best varieties of cucumbers for greenhouses:
- Amur.
- Elegant.
- Dynamite.
- Ginga.
- Hermann.
- Zozulya.
- Orpheus.
- Muromsky.
- Competitor.
- Dawn.
- Son-in-law.
- Emelya.
- Surprise.
- Cheetah.
- Moscow greenhouse.
How to choose the right variety of greenhouse cucumbers for cooking?
When making choices among a variety of cultures, we first of all think about how we will use them in the future. Depending on this, you need to choose exactly the variety of cucumbers that suits you best. Here, preference should be given to both appearance, shape and texture.
According to the degree of suitability for food, the following types of greenhouse cucumbers are distinguished:
- salad;
- canned (suitable for pickling and pickling);
- universal.

Universal vegetables for pickling and pickling
When buying cucumber seeds, the packaging always indicates in what form it is best to eat them. For example, when fresh, it is better to eat high-yielding greenhouse salad cucumbers, which include:
- Anyuta.
- White angel.
- Athlete.
- Solar.
- Orlik.
- Courage.
- Masha.
- Vicent.
- Hercules.
- Danila.
- Crystal.
- Makar.
- Cartoon.
- Fawn.
- Martha.
- Tsarsky.

High-yielding greenhouse salad fruits of the "Danila" variety
Their flesh is more juicy and tasty, and the skin, on the contrary, is thicker. They are somewhat larger in size than the rest and have lighter spines on the surface.
For canning, pickling and pickling, it is necessary to choose varieties of cucumbers with thin skin and small sizes, then they are better amenable to heat treatment and will be very tasty.For example, the best varieties of greenhouse cucumbers are suitable for canning, pickling and pickling:
- Adam.
- Moscow dude.
- Blessed.
- Hector.
- Buran.
- Legend.

Small cucumbers with thin skin
If you want to eat fresh cucumbers and preserve them, the universal type is the best choice. Their skins are of medium thickness and lend themselves well to heat treatment, and they are also very pleasant to the taste. For example, according to gardeners, the best greenhouse varieties of universal cucumbers are:
- Annushka.
- Trump card.
- Sunrise.
- Three tankers.
- Petite.
- Thumb boy.
- Corporal.
- Moravian Gherkin.
- Blessed.
- Northerner.
When do greenhouse cucumbers ripen?
Greenhouse cucumbers can be enjoyed all year round.
To do this, you need to know which varieties ripen and at what time. Breeders involved in their cultivation and breeding distinguish 4 groups. Early ripening - wonderful cucumbers that ripen very quickly, in just 40 - 42 days. The best ones are:
- Emelya.
- Anyuta.
- Courage.
- Evita.
- Masha.
- Leandro.
Early ripening - one of the most favorite varieties of cucumbers for children. Their ripening period is 44 - 46 days. The most popular were:
- Balagan.
- Zozulya.
- Connie.
- Matilda.
- Marinda.
- Regia.
- Claudia.

Early ripening variety "Zozulya"
Mid-season - ideal for canning, pickling and pickling. Their ripening period is 47 - 50 days. Among them, the most popular are:
- Droplet.
- Nezhinsky.
- Santana.
- Brownie.
Late ripening - ripen in 50 days and are also intended for all types of canning and pickling.
For greenhouses, you should choose special, most suitable varieties of cucumbers. Due to the different microclimate in the greenhouse, as well as the drop in humidity, diseases can occur in cucumbers. The most common among these are powdery mildew, gray or white rot.
The new varieties are the most resistant to diseases and are excellent for greenhouse conditions. They are distinguished by their high yield and unpretentious cultivation.

High-yielding unpretentious variety
Modern breeders recommend choosing exclusively climbing rather than bush varieties for planting in a greenhouse. This is due to the fact that cucumber whips are more convenient to form and tie in the greenhouse, moreover, they take up less space and let in more sunlight.
Cucumbers are thermophilic plants that thrive in warm greenhouses with moderate humidity. Caring for them does not require much effort, especially if your greenhouses are equipped with drip irrigation. It is necessary to irrigate them daily, but very carefully, because they have a weak root system, located almost on the surface, and it is easy to damage it.
During fruiting and flowering, cucumbers need additional organic feeding. It is better to feed the plant in the evening.
Rate the article:
(0 votes, average: 0 out of 5)
To choose for yourself 3-4 suitable greenhouse varieties of cucumbers, you must first clarify the selection criteria. To create the most complete classification of greenhouse cucumbers, you need to remember what they are.
The best varieties of cucumbers
Table. Classification of cucumbers according to various characteristics.
| Grade | • Varietal; • Hybrids |
| Pollination method | • insect pollinated; • Self-pollinated; • Non-pollinated (parthenocarpic). |
| Ripening rate | • Early maturing; • Mid-season; • Late ripening. |
| Dimensions (edit) | • Short-fruited; • Medium-fruited; • Long-fruited. |
| Method of use | • Salad; • Salting; • Universal. |
Varietal
Cucumbers from varietal seeds inherit the characteristics of the variety with further seed reproduction. From them you can collect seeds and sow again, continuing the tradition. Once every 5-7 years, the planting still needs to be completely renewed.
Why varietal cucumbers are good for a greenhouse
How to collect cucumber seeds
Hybrids
Derived from varieties, varietal characteristics do not transfer. For sowing, you need to purchase new seeds annually. Compared to varieties, they are more resistant to diseases, they are distinguished by a friendly and abundant yield in any weather and conditions.
Why hybrid cucumbers are good for a greenhouse
Greenhouse varieties of cucumbers
Insect pollinated
They are not often used for greenhouse cultivation, because in order to attract insects to the greenhouse, you need to work hard - plant attractive plants for them, arrange sweet baits, spray borage with honey syrup, open doors and windows, or temporarily remove shelter.
Pollination of cucumber
Insect pollinated cucumber varieties
Self-pollinated
They are the golden mean, since they do not need insects for pollination and do not need anyone at all. They have flowers with stamens and pistils (they combine male and female characteristics), so they cope with pollination on their own without assistance.
Hermaphrodite cucumbers
Non-pollinated
Parthenocarpic cucumbers are often confused and even called self-pollinated. But they are non-pollinated at all. Their female-type flowers are arranged in such a way that they can set fruits without pollination. One caveat, there are no seeds in the fruits of parthenocarpic varieties. That is, the situation with them for further reproduction is even worse than with hybrids.
Early ripe
Ripen in 40-45 days. They give the earliest harvest, which disappears quickly.
Mid-season
Ripen in 45-50 days. Fruiting takes longer, you can harvest fruits almost throughout the middle of summer.
Choosing cucumber seeds
Late ripening
Ripen within 50 days. Early autumn fruiting. In some areas, they may not have time to ripen, especially when sown in the ground. In greenhouses, they are grown from ready-made seedlings.
Short-fruited
These include two autonomous types of cucumbers - gherkins and pickles. They are characterized by the size of the fruits, the first - 4-9 cm, the second - 3-5. Some summer residents prefer to pick vegetables from borage at the stage of greenery, if they need short-fruited products. But this is impractical, since the yield of short-fruited varieties is much higher than zelents of normal size. The palatability of the original short-fruited varieties is also higher.
Short-fruited cucumbers
Medium-fruited
They are characterized by a size of 10-15 cm. The varieties with medium-sized fruits that fit into this range include the lion's share of all existing varieties.
Long-fruited
This category includes all cucumber plants, the fruits of which, at the stage of full consumer maturity, exceed the 15-centimeter line. There are varieties of long-fruited cucumbers, the fruits of which grow up to one and a half meters in length.
Long-fruited cucumbers
Salad
The method of consumption is usually indicated on the seed bag. And if the varieties for canning can still be somehow used in the stage of technical ripeness for fresh salads, salad cucumbers cannot be canned. When salted, they will become soft or empty, they will not stand for a long time.
Advice! If there is no information on the package, you can determine the purpose of the fruit by the color of the thorns and skin. White thorns, light dense skin - salad.
Salad cucumbers
Salting
Black, brown thorns, dark thin skin - salted. Salt hardly penetrates through the dense skin of salad cucumbers, so preservation fails.
Pickled cucumbers
Universal
There are varieties "both yours and ours." They are eaten fresh and can be preserved very well. Their skin is of medium thinness, the thorns are gray. They are designated as generic. You can safely purchase these seeds if you equally like to feast on fresh cucumbers and crunch pickled ones.
The best varieties of cucumbers for greenhouses
For growing in a greenhouse, the following are most suitable:
- hybrids;
- self-pollinated or not requiring pollination;
- universal use;
- early and medium ripening;
- medium-fruited or short-fruited.
Here it is - the perfect cucumber of our time.What varieties, suitable for these parameters, characterized by high resistance to diseases and good yields, do the breeders offer.
Variety selection
Every gardener, owner of a greenhouse, dreams of growing such cucumbers so that you can get a good harvest with minimal effort, time and material resources. With the right strain and care planning carefully, this is possible. There will be more time for other, more "capricious" cultures, or for a summer vacation.
Varieties of greenhouse cucumbers and their descriptions
"Courage"
Cucumbers Courage F1
The variety is classified as early maturing (ripening - 43-45 days). Self-pollinated, medium-fruited. On a borage with lashes of medium length, many fruits ripen, the size of which is 14 cm. This standard is in accordance with GOST. Highly commodity look. Aromatic taste. True cucumber crunch. The variety is versatile, protected from known diseases and stands out for its high yield.
Cucumber Courage F1
"Connie F1"
A bundle variety (flowers are arranged in bunches in the axils, and fruits subsequently grow in bundles). Perfect for plastic greenhouses. The shape of the fruit is not classical, but not typical, cylindrical. Medium and mid-season (about 47 days). Good taste. Versatile, suitable for salting and salads. Has a high yield.
Cucumber Connie F1
"Zozulya F1"
The variety came to us from the "old days" - it was bred during the heyday of the USSR. Nevertheless, it is still successfully grown in greenhouses. The variety has smooth fruits, it is considered long-fruited (cucumbers grow up to 30 cm). Mid-season and very productive. The record yield is 45 kilograms per square meter. High viral resistance. Zozuli has one drawback - it is a salad. Canning is not subject, no options. It is used only fresh.
Cucumber Zozulya F1
"Goosebump F1"
Early maturing (42-45 days) parthenocarpic hybrid. Bunch type, does not require pollination. Fruits with large tubercles and dark thorns, about 12 cm in size. This variety is loved for its genetic lack of bitterness. That is, cucumbers never taste bitter, even under bad weather conditions and non-compliance with growing conditions. The hybrid is versatile. It is equally used for pickling and fresh. The taste is high. There is immunity to some diseases, in particular, powdery mildew.
Goosebump F1
"Tom Thumb"
A favorite of the public. Begins to yield crops on the fortieth day - ultra early. Self-pollinated, medium-fruited (but 11-centimeter greens are used as gherkins). Salted variety, usually not grown for salads. Resistant to a whole range of viral diseases that cucumbers can be susceptible to.
Tom Thumb
"Benefit F1"
A mid-season hybrid with a 50-day fruiting period. Self-pollinated, with female flowers. Fruits - no signs of bitterness. The color is neutral green, the skin is covered with small tubercles. Begins to be used as greens, as soon as it grows to 11-12 cm. It is universal, used both for pickling and in salads. High resistance to rot and powdery mildew makes the hybrid popular.
Cucumber Benefis F1
"Alekseich F1"
Another favorite hybrid of summer residents. Super early, starts singing already on the 37th day. Full maturation - 43 days. Parthenocarpic, does not need pollination. Belongs to the gherkin types. The fruits are usually harvested when they reach the seven centimeter mark. The taste is very high. Virus resistance is present.
Alekseich F1, seeds
Alekseich F1
"Emelya F1"
Early maturing (40-43 days) parthenocarpic hybrid variety, which is used universally. Differs in thermophilicity and indeterminacy (the growth of lashes is unlimited, if it is not forced to restrict it). The ovary is bunchy. Fruit length - 15 cm. It is very tasty both in salads and preserved.
Emelya F1
"Hercules F1"
Also from the old varieties. Fruits are late (ripen for two months).Traditionally, it is pollinated by insects, in particular bees, which need to be attracted under the shelter.
Nevertheless, many summer residents nostalgically continue to grow it in greenhouses. The shape of the fruit is fusiform. Sizes - up to 20 cm. Tufted ovary.
Cucumber variety: Hercules f1
Advice! To attract the attention of flying pollinators to cucumber flowers, it is better not to place honey syrup in bowls throughout the greenhouse, as some gardeners do, but to spray the plant with it early in the morning. the fact is that the bee can take the syrup from the bowl and fly away without touching the flower. An even safer way is to plant flower plants attractive to bees around the perimeter of a greenhouse garden with cucumbers.
"Annushka F1"
Also from insects. Mid-season. The fruits are cylindrical. The skin is covered with light short stripes. Medium-fruited, cucumbers grow 12 cm long. The surface of the fruit is ribbed and tuberous. The yield and taste are high and stable. Disease resistance is available.
Cucumber Annushka F1
Dynamite F1
This early parthenocarpic is ideal for film growing. There is only one parameter to consider - it needs a lot of space. He scatters lashes and bushes to a great width. Cylindrical fruits grow up to 14 cm. It does not need pollination, drought and overheating are not terrible. An excellent greenhouse cucumber for a hot summer. It is more suitable for salads than for pickling.
Dynamite F1
"Berendey F1"
An excellent medium-growing variety that thrives in shade. Therefore, it can be grown in a greenhouse not on the sunniest side, giving a "warm place" to a crop that needs more sun. Ripening period is average (47 days). Fruits are cylindrical, with bright tubercles, up to 14 cm in length. It is versatile and has good taste.
Berendey F1
"Cucumber April F1"
White thorns and a rather thick skin indicate that this variety is classified as a salad in terms of use. Ripens early. It can be classified as long-fruited, since cucumbers on lashes grow much longer than 15 cm. Cold resistance is reflected even in the name of the variety. It tolerates cold, is resistant to viruses. It has excellent taste and high-quality appearance.
Cucumber April F1
Video - Cucumber Seeds "April F1"
Video - The best varieties of cucumbers
The best varieties of cucumbers for greenhouses
In greenhouses, it is best to grow cucumber hybrids with shortened lateral lashes, which do not require formation, that is, you do not need to pinch the lateral shoots. Usually, I form cucumbers in order to prevent thickening, due to which cucumber yields fall, in addition, the risk of stem rot and powdery mildew increases, which is not so easy to cure later.
All varieties and hybrids of cucumbers are divided according to the ripening period: early ripening (early), mid-ripening, late-ripening. And according to the method of pollination on: pollinated by insects and parthenocarpic (self-pollinating).
Self-pollinating cucumber varieties
If you want to have the earliest fresh cucumbers on the table, then opt for self-pollinated varieties. After all, we usually plant early cucumbers in a greenhouse, since there are no insects in April in the middle lane yet, that is, there is no one to pollinate the flowers.
Self-pollinating cucumber varieties give high yields. And the hybrids are unpretentious and practically not susceptible to diseases, moreover, there is no particular trouble with them with the formation of a bush.
Herman cucumbers are the best representative of Dutch hybrids

Today it is the most popular cucumber variety on the Russian market. Early maturing, high-yielding. The authors of this hybrid are Monsanto Agrofirm. In 2001, German F1 was included in the state register of the Russian Federation (approved for use in all regions of Russia). Suitable for both greenhouses (greenhouses) and open ground. The period from full germination to fruiting is 40–45 days.
Push: there is no bitterness at all. An early hybrid, very hardy.When the temperature drops to +9, it feels great, only slightly "inhibits" the growth of zelents. Cucumbers grow 10-12 cm long. I use it for salads and for canning.
Zozulya cucumbers, excellent early hybrid
Cucumber Zozulya F1 - early maturing (45-50 days from germination to fruiting) hybrid with fruits with thin skin. Known since 1977.
Cylindrical cucumbers with slight tuberosity, dark green color with slightly pronounced light stripes, light thorns. Zelentsy reach a size of 14-22 cm, with an average weight of a ripe fruit of 140-300 grams. With good care, the harvest for the first month per square meter is 8-12 kg.
Push: I have been growing for 10 years. Never let me down. Cucumbers up to 25 cm long are very good for pickling in a barrel. Always amicable ripening, resistant to various rot. Suitable for both greenhouses and open ground.
Cucumbers Dynamite, photo
Cucumber Dynamite F1 - parthenocarpic, salad, canning, pickling hybrid. It starts bearing fruit 40-43 days after full germination.
The plant is indeterminate, vigorous, medium-branched, female flowering type, with bundled ovaries. The leaf is medium-sized, green, smooth, irregularly serrate along the edge.
Cucumbers are cylindrical, green with smeared stripes up to 1/3 of the length, medium-sized tubercles, sparse, brown pubescence. The average weight of a cucumber is 100-120 grams, length 12-14 cm, diameter 4.0-4.5 cm. Taste qualities of fresh and canned fruits are excellent.
Yield: 15-18 kg of fruits per 1 sq. meter of planting (in the presence of watering and dressing).
Push: climbing, therefore requires freedom. It goes well in salting, and in pickling, and in salads.
Cucumbers Zyatek, description, characteristics

Zyatek F1 is a parthenocarpic hybrid of early ripening (42-48 days from germination to fruiting), bred in the Russian breeding and seed company Gavrish (Moscow). In 2007, the variety was entered into the state register of plants in Russia. Designed for growing in protected ground, but also suitable for open ground.
Plants are indeterminate, medium branched, female flowering type, with bundle ovaries. In one node, an average of 3 - 4 cucumbers are formed (maximum - 6-8 pieces). The leaves are green, medium in size.
Fruits are medium lumpy, cylindrical, 10–12 cm long, weighing 90–100 grams. The skin is soft, green, with short light stripes. Frequent pubescence. The thorns are white. The pulp is dense, good taste, sweetish, without bitterness. Long-term fruiting - throughout the summer season.
Yield - 13.2 kg / sq.m. One plant produces 5 - 7 kg of fruits.
Push: I planted it for the first time last year, this year I will definitely plant more. Very tasty at the stage of milky ripeness (gherkins). The harvest is high, the ripening period is up to 48 days. Cucumbers up to 10 cm long, with pimples.
Early varieties of cucumbers for greenhouses
Early varieties of cucumbers are a real find for residents of the northern regions and the middle zone, since every summer day is valuable for us, and especially early, early ripening and ultra-ripe varieties of cucumbers and other vegetables.
Cucumber Elegant, description, photo
A bee-pollinated variety, it produces a large number of male flowers and this property allows it to be used as a pollinator for other varieties. Cucumber variety Graceful is intended for cultivation in open field and spring film greenhouses. Plants are medium-growing, form up to 5-6 lateral shoots.
Cucumbers are leveled, elliptical, with small tubercles, 9-12 cm long, weighing up to 150 grams. The skin is thin, light green in color, with white stripes and a white top. The pulp is juicy, crispy, sweetish, without bitterness. Low yield: 5-7 kg / square meter. A variety of salad type, but it is also used for canning.
Push: I think one of the best in this category. Its fruits have a wonderful aroma and the first cucumbers can be removed already 38 days after germination.
Cucumber Muromsky 36, characteristic of the variety
An old bee-pollinated early ripening variety of cucumber. Designed for growing in open ground and under temporary film shelters. The period from full germination to fruiting is 32 - 42 days. The length of the central whip is 100–160 cm. Plants are well leafy.
Cucumbers are oval-elongated or ovoid, almost round in cross-section, with very small, sparsely located tubercles, 6 - 8 cm long, weighing 50–70 grams. The skin is light green with well-defined longitudinal white stripes. The pubescence is mixed. The thorns are black.
Yield small - 2-3 kg / sq.m.
Push: very early variety. Many gardeners like it because the more often you collect it, the more fruits grow.
Cucumbers Competitor - out of competition
An old bee-pollinated variety of medium-early cucumber (the period from germination to fruiting with spring planting is 45-50 days, with summer planting - 29-30 days).
In 1980, the variety was added to the state register of the Russian Federation. Plants of this variety are powerful, slightly branched, with a long main stem. The length of the stalk is 5–7 cm, which makes harvesting easier.
Fruits are oval-cylindrical, ribbed, large tuberous, small (9-12 cm long, weighing 70-100 grams). The skin is green, with blurred white stripes of medium length. Frequent pubescence. The thorns are black. The pulp is dense, crispy, aromatic. Average yield - 3-5 kg / square meter.
These cucumbers are very good in salted and pickled form, which is confirmed by numerous reviews of gardeners, however, fresh and in salads, they are just as highly valued.
Push: excellent in preservation - tasty, crispy. Fruits are only 10 cm long. There are no problems with diseases, the main thing is not to create stagnant moisture.
If you have additions to the article, please write in the comments. What varieties of cucumbers do you grow? What are the best varieties of cucumbers at the end of 2016? What new varieties of cucumbers have you already purchased for 2017?
Your reviews and additions will help many gardeners choose the best varieties of cucumbers for planting.
The choice of varieties depends on what cucumbers you plan to cultivate and what expectations you have for the future harvest. There are many such varieties on the seed market now. Some are ideal for outdoor cultivation, others at home, and others in greenhouses, including those made from polycarbonate. Today we will find out what are the best varieties of cucumbers for polycarbonate greenhouses.
The variety of varieties is so great that among them you can choose exactly those that suit you in terms of their taste, size, type, growth rate and other parameters.

The best varieties of cucumbers for polycarbonate greenhouses
Hybrids or variety: making the right choice
Novice summer residents, most likely, at first will confuse these two concepts - hybrid and variety. However, there are fundamental differences between them.
The most important difference between a variety and a hybrid is the possibility of inheritance by a plant that has grown from seeds of one type or another, hereditary genetic traits. Crops grown from the seeds of the varieties will yield seeds from which you can get exactly the same plant as the mother one next year. This plant will inherit all the characteristics and qualities of the parent species. And the seeds obtained from hybrid cucumbers will either give completely different plants, unlike their parents, or even refuse to grow at all. The qualities, properties, features of the hybrid will not be preserved in the offspring.

The properties of hybrid cucumbers are not preserved in the offspring
On a note! It is easy to distinguish a hybrid from a variety at the stage of buying seeds - all hybrids have the F1 marking in the name.
Table. The main differences between hybrids and varieties in comparison.
| The price of such seeds is lower. | Hybrids tend to be more expensive. |
| You will be able to collect seeds yourself in the fall and plant them for seedlings the next year without spending additional funds. | Seeds collected from hybrids in the fall will not produce good offspring. A rare exception is the first generation.You will have to buy them again in the store. |
| Varietal plants are resistant to diseases declared on the packaging for several generations. | In general, hybrids are resistant to plant diseases only in the first generation. |

Outwardly, the fruits of hybrids do not differ from the fruits of ordinary varieties.
Why are hybrids so good and why are they recommended to buy (especially for beginners)? Why are they more expensive than varietal seeds? It's simple - they have a number of advantages.
So, hybrid cucumbers:
- not afraid of temperature changes;
- they are not afraid of most plant diseases, have excellent immunity (whoever is not afraid of this hybrid is usually indicated on the package with the seeds);
- tolerate adverse weather conditions well and perfectly adapt to different climates;
- as a rule, high-yielding (this indicator is about 40% higher in hybrids);
- give larger and tastier fruits;
- bear fruit earlier, and the fruits ripen faster and are well stored.
That is why many people prefer to buy hybrids instead of conventional varieties.
Advice! When buying seeds, stop at Russian, accustomed to specific natural conditions, cucumbers. Of course, Dutch seeds have long been popular in the same way as German seeds, but you must agree that the climate in those countries is milder than in Russia, and you will have to provide more comfortable conditions for the plants obtained from such hybrids.

Give preference to domestically produced seeds adapted to the natural conditions of the country
By the way, what does the F1 marking that accompanies the name of the hybrid mean? It's simple: F is the initial letter of the Italian word for "children", and 1 indicates that generation is the first. Translating, we get the phrase "children of the first generation." Hybrids are obtained by crossing two different varieties with specific characteristics.

F1 is the designation for first generation hybrids
By the way, hybrids and varieties of cucumbers also differ in care. It even matters how you pinch the bushes. For example, as soon as varietal cucumbers grow 4-5 leaves, their top is pinched. Then the lateral shoots will go into active growth, on which the female (necessary for the formation of fruits) flowers are mainly formed. In this case, there will be more of the latter, which will have a positive effect on the volume of the harvest. And in hybrids, on the contrary, the lateral shoots are pinched.

Cucumber Connie F1
Growing eggplants in a polycarbonate greenhouse
In this article, you'll find everything you need to know about growing eggplant in a polycarbonate greenhouse! We also recommend reading the article on why tomatoes crack when ripe.
Pollination and ripening dates
Those who first decided to grow cucumbers on their own should definitely know that the seeds of this culture are not only divided by hybrids, varieties, species, but also differ in terms of fruiting times and the way they are pollinated.
There are three types of pollination:
- self-pollinated;
- parthenocarpic;
- pollinated by insects.
How are they different? The latter type is capable of pollinating, as the name implies, only through the transfer of pollen from flower to flower with the help of insects. Man can also pollinate such varieties manually. The second, parthenocarpic, have flowers of a mostly female species, and in order for them to have greens, they do not need pollination at all.
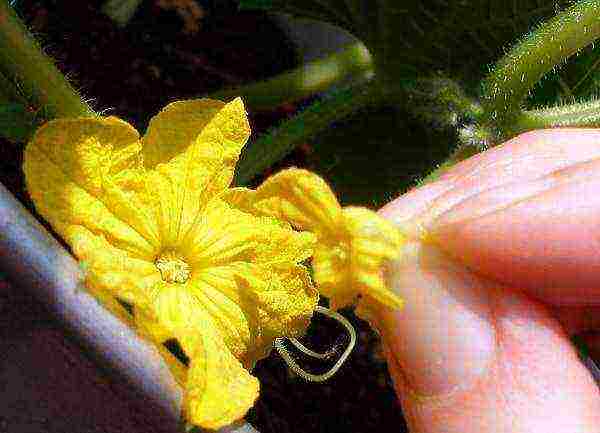

Insect-pollinated varieties can be manually pollinated
On a note! In fruits obtained from parthenocarpic cucumbers, seeds are often completely or partially absent.
But self-pollinated cucumbers have bisexual flowers, which have pistils and stamens. Such plants are capable of pollinating on their own.
Advice! It will be extremely difficult to drive pollinators in the required quantity into the greenhouse, therefore, parthenocarpic cucumbers or self-pollinated species are traditionally grown in it. Pollinated by insects are usually grown outdoors.
Cucumbers can be divided according to the time it takes for them to grow, develop before the start of fruiting, into:
- super early;
- early;
- medium early;
- mid-season;
- late ripening.
The first two types are the species from which the harvest can be obtained as quickly as possible. Some begin to bear fruit just 40 days after sprouting. Mid-early ones give the first cucumbers about 47 days, and from mid-season ones, you will wait for them no earlier than 51-52 days. Late ones bear fruit in 55-56 days.
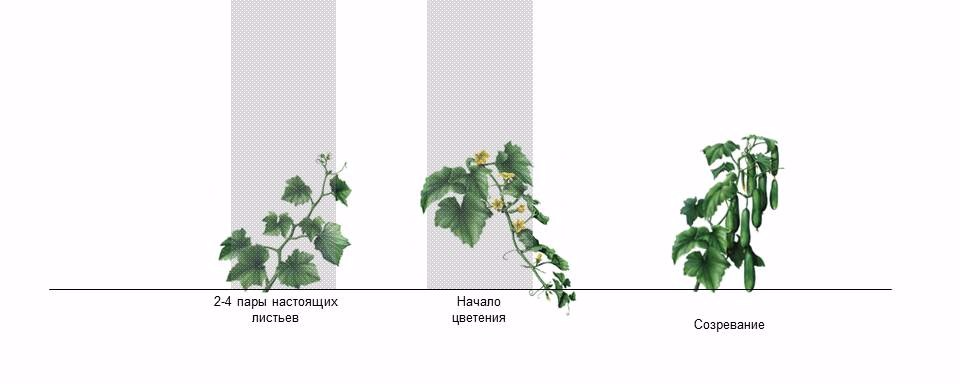
Cucumber growth phases
Advice! In order for fresh cucumbers to appear on your table as long as possible, it is best to cultivate several different varieties in a greenhouse that differ in the ripening time of the greens.
The use of cucumbers and conditions for them
In order to choose the right variety of cucumbers for cultivation in greenhouses or greenhouses, you will have to decide what you need the fruits of this culture for. You can make salads, blanks from them, and you can also sell them.
By type of use, cucumbers are divided into:
- salad;
- salting;
- universal.

Salad cucumbers
Advice! Usually, the seed producer indicates the purpose of each variety on the packaging. But if it happened that you lost the packaging and forgot which variety it was, then the purpose of the fruit will help determine the color of the thorns on them. If they are white, then they are salad cucumbers, since pickles have darker thorns.
Salad cucumbers are not recommended to be salted, as they lose all their taste - their skin is too thick, through which salt cannot penetrate in sufficient quantities. And pickles do not crumble into salads, as they will be too tough. But on the other hand, their thin skin perfectly passes the brine inside the fruit, and pickles from such varieties in winter will delight you very much.
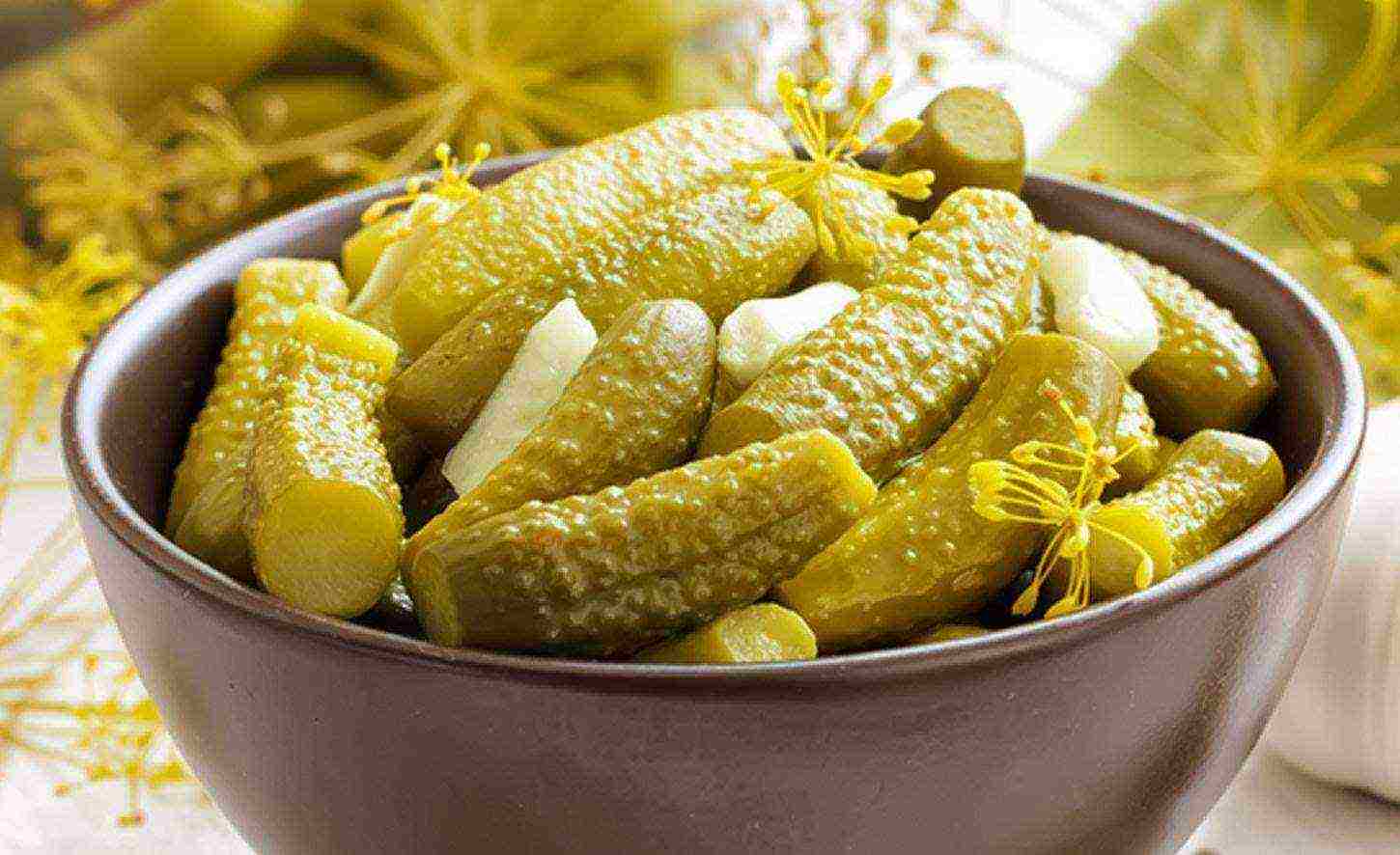

Pickled cucumbers cannot be crumbled into a salad
There are cucumbers and versatile. They are best suited for those new to the gardening business. The fruits of these varieties are used for the preparation of salads, as well as for all types of culinary processing, including pickling and pickling. Zelentsy do not lose their taste in any of the cases.
By the way, varieties are also divided according to growing conditions. There are types for open and closed ground. Of course, some can be cultivated in any conditions, but it is still better to take note of what is written on the packaging with seeds: "street" cucumbers cope better with winds, cold weather, dry air, but greenhouse cucumbers are usually better protected from the effects of pests and diseases , since they have undergone the appropriate processing. It is better not to change their places - there is a great risk that heat-loving greenhouse plants on the street will simply wither and die.
Cucumbers can also vary in size - this is what often depends on how they will be used.
Table. Types of cucumber fruits by size.
|
Pikuli |
The tiniest cucumbers, ranging in length from 3 to 5 cm, are a common type of short-fruited. |
|
Gherkins |
Slightly larger fruit than pickles. The length of one cucumber varies from 4 to 9 cm. Also belongs to the general type of short-fruited. |
|
Medium-fruited |
Any cucumbers, the dimensions of zelents in which range from 10 to 15 cm. The diameter is about 55 mm. |
|
Long-fruited |
These are the largest cucumbers, the fruits of which can be 15 cm, and even giant 1.5 m. |

And this, although not the largest, but certainly the most unusual of the cucumbers
On a note! Short-fruited cucumbers can be obtained by collecting growing greens of the required size from absolutely any bush. But specially bred varieties of gherkins are still tastier.

Spiny gherkins
As for the height of the bush, in greenhouses, by and large, you don't have to worry about it too much. In a greenhouse, low bushes should be grown, and in a greenhouse structure, you can afford not only medium-sized varieties, but also very tall bushes.
Popular varieties of cucumbers for the greenhouse
What varieties of cucumbers for polycarbonate greenhouses are the most popular and have already proven themselves on the good side? Of course, experienced summer residents know about this, but if you are a beginner, then we will try to share this valuable information with you.

The best varietal cucumbers
Table. The best hybrid cucumber varieties for polycarbonate greenhouses.
|
Goosebump F1 |
Parthenocarpic, super early, medium height | Very high-yielding variety, lateral shoots do not actively branch. Produces fruits of medium size (up to 12 cm), covered with black thorns. Excellent for salting, but also used raw. Absolutely not afraid of powdery mildew. |
|
Suomi F1 |
Super early, cold-resistant, parthenocarpic | A species with excellent immunity, not afraid of bad weather conditions, root rot. Fruits up to 6 cm long appear as early as 38 days after the first shoots. A distinctive feature is that green plants cannot outgrow their sizes declared by the seed manufacturer, and therefore there will be no overgrown cucumbers. Free from bitterness. Perfectly salted and delicious fresh. |
|
Emelya F1 |
Parthenocarpic, early maturing, vigorous | A hybrid that produces fruits that are great for all kinds of pickles and salads. Zelentsy are oval or cylindrical, up to 15 cm. White thorns. Suitable for greenhouse cultivation only. |
|
Valaam F1 |
Super early, fast growing, parthenocarpic | Not afraid of low temperatures, ideal for growing in greenhouses in regions with cold climates. Produces fruits in the form of a cylinder up to 6 cm with large tubercles. Such cucumbers do not taste bitter and do not outgrow, but bear fruit for a very long time. Suitable for salads, pickling. |
|
Alekseich F1 |
Medium-sized, self-pollinated, early maturing | An excellent universal hybrid of cucumbers, producing medium-sized fruits up to 8 cm long with a high quality taste. Not afraid of powdery mildew. |
|
Sarovskiy F1 |
Parthenocarpic, super early | Not afraid of harsh climatic conditions, bears fruit for a long time. Cucumbers are beautiful, have the shape of an elongated oval, up to 13 cm long, with white thorns. The skin is thin. The pulp tastes great. Can be preserved and used for salads. |
|
Real Colonel F1 |
Partenocarpik, vigorous, early maturing, high-yielding | Zelentsy resemble a spindle in shape, up to 15 cm long, weighing up to 120 g, almost not ribbed, with large tubercles. Delicate in taste, not bitter, but, on the contrary, a little sweet. |
|
Benefit F1 |
Self-pollinated early maturing | Produces tasty fruits about 12 cm long, not bitter. They are universal, therefore they are used in any culinary recipe. The hybrid is not afraid of rot, powdery mildew. |
|
Finger Boy F1 |
Super early, parthenocarpic | Produces non-prickly fruits up to 11 cm and weighing up to 65 g. This variety is perfect for those who love gherkins. Not afraid of most common plant diseases. |
Recommended varieties of cucumbers
Growing cucumbers in a greenhouse
So, you have chosen a type, maybe even several, and are ready to start growing cucumbers in a new polycarbonate greenhouse.
Step 1. To begin with, you must grow seedlings from seeds. When is it to be done? You will have to calculate everything yourself, depending on the climatic conditions of the region of residence. Cucumbers love warmth, they can be moved to the greenhouse no earlier than the soil temperature in it will be +15 degrees. For example, if this figure reaches the desired level at the end of May, then plant the seeds at the beginning of this month 3 weeks before moving to the greenhouse.

Calculate the time of planting seeds based on the climatic characteristics of your region
Attention! Seeds that are planted too early can cause your seedlings to outgrow.
Step 2. Prepare the seedling soil. It should be fertile and contain peat, humus, or compost. Mix, for example, turf, peat, humus and sawdust in a 1: 1: 1: 1 ratio. It is better to steam the soil so that it is disinfected.

Preparing the soil for seedlings
Step 3. Prepare containers for cucumbers - plants do not like transplants, so plant them immediately in separate pots. Take the latter at least 10 cm in diameter. Wash and disinfect the containers well, drain at the bottom so that there is no waterlogging.
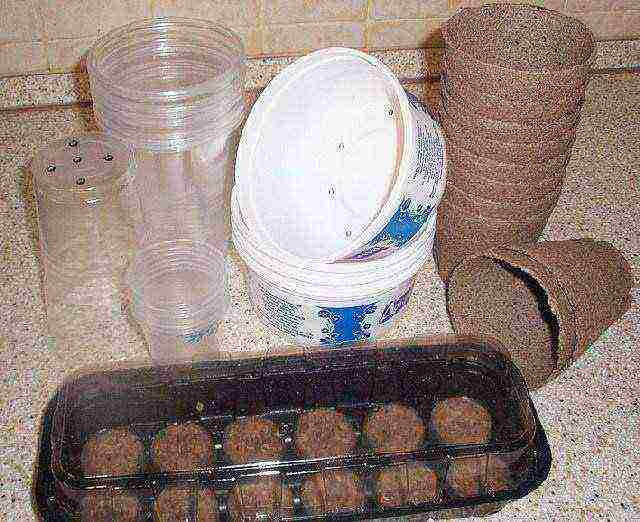

Preparing seedling containers
Step 4. Prepare your seeds. Wrap them in a damp cloth for 2-3 days. As soon as the first shoots appear, the seeds can be planted.
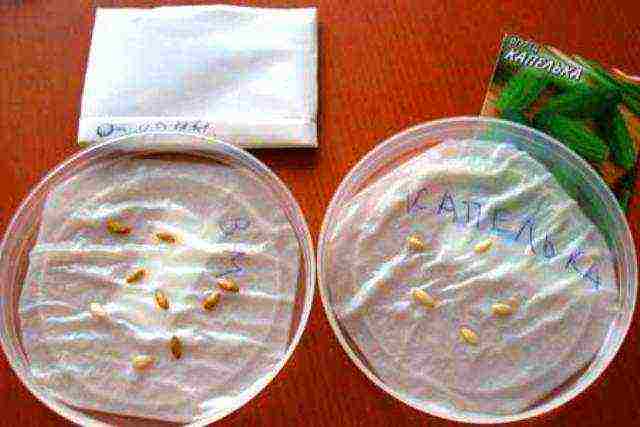

Germinating seeds
Step 5. Fill containers with ready-made soil, place a seed in each, sprinkle with a thin layer (about 1 cm) of earth, lightly compact. Watering is necessary 2 times every 7 days.
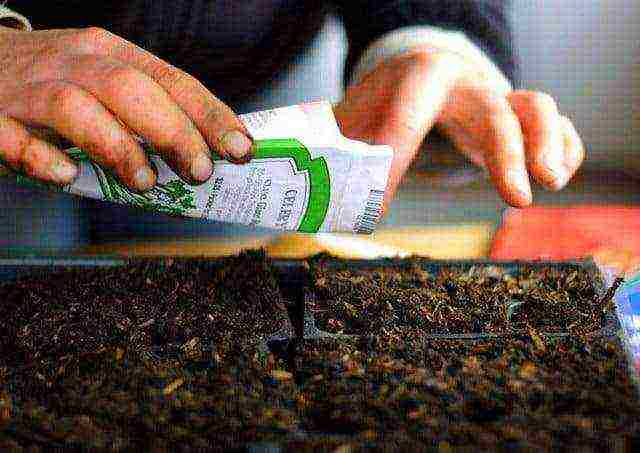

Planting cucumber seeds
Step 6. Spill over with water and cover with foil to create a mini greenhouse. Place where it is warm and light.
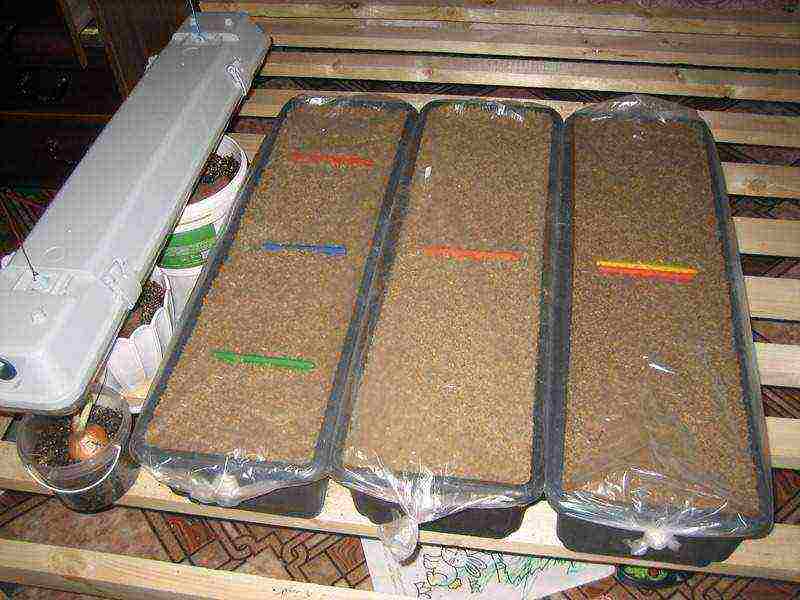

The containers are covered with foil
Attention! The air temperature in the first days should be at least 25 degrees. As soon as the cucumbers rise, lower it to 22 degrees during the day and 17 at night.
Step 7. The grown seedlings, when they get stronger, can be rearranged in the greenhouse if the structure is heated.
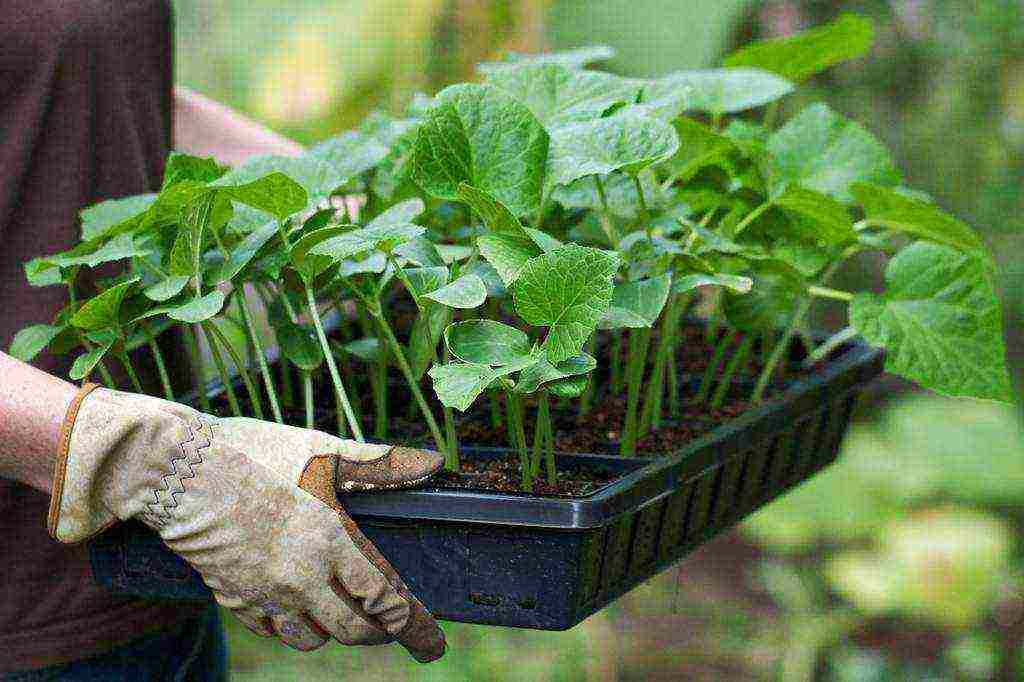

The grown seedlings can be transferred to a heated greenhouse
Step 8. It's time for the seedlings to move to the greenhouse, which means it's time to start preparing. The soil in your greenhouse should be prepared in the fall, so just loosen it slightly, spill it and make holes in a checkerboard pattern at a distance of 60 cm from each other. The holes should have a depth equal to the height of the pot in which the seedlings are located.

Seedling holes in a greenhouse bed
Step 9. Spill each well with organic fertilizer, carefully remove the seedlings from the pots and place in them. Sprinkle with earth lightly. Now, subject to careful and proper care, the cucumbers will quickly grow and will soon delight you with the first greens.
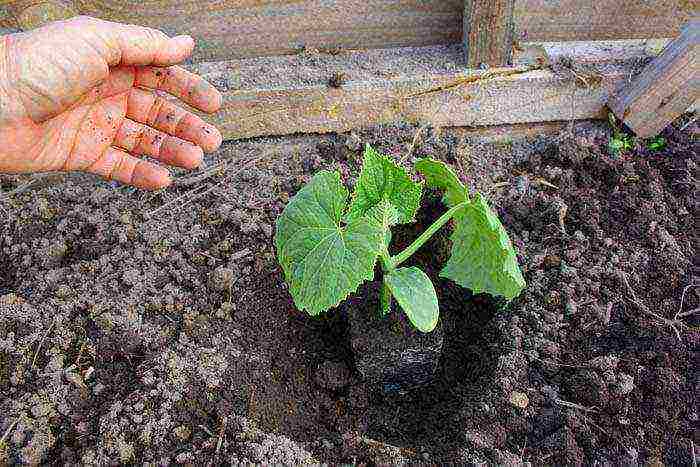

Planting seedlings in a greenhouse

Growing cucumbers in a greenhouse
Fertilizer dosage table for feeding cucumbers
It is very easy to grow cucumbers in a greenhouse, especially in one made of polycarbonate (minimum of cracks, there are practically no drafts). And if you choose the right variety or hybrid that is right for you, then the harvest will definitely not disappoint you.
Video - Cucumber varieties for greenhouses
Video - Choosing varieties of cucumbers


