Content [show]
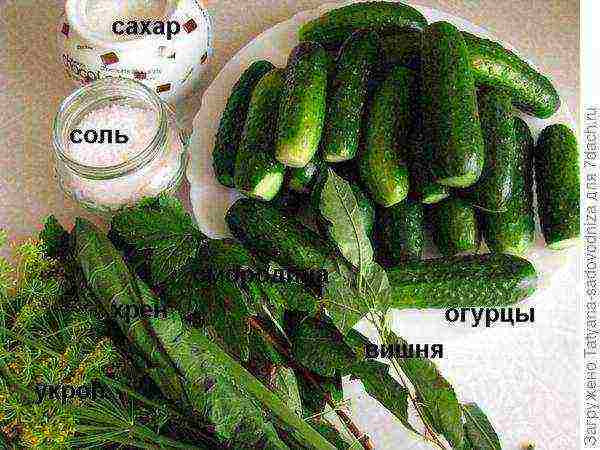
No, what are you, I do not swear at all! I solemnly swear that this post is dedicated to horseradish, but in its very plant meaning! =)) Yes, the "protagonist" of my article is a plant that you all probably know. The scope of its application is mainly canning vegetables and preparing a snack of the same name - horseradish. In addition, you can find table horseradish and even horseradish powder in stores)). I will not tell you the recipes (unless a little). I'll just tell you what kind of plant it is, where it grows, how it blooms, and what it is used for.
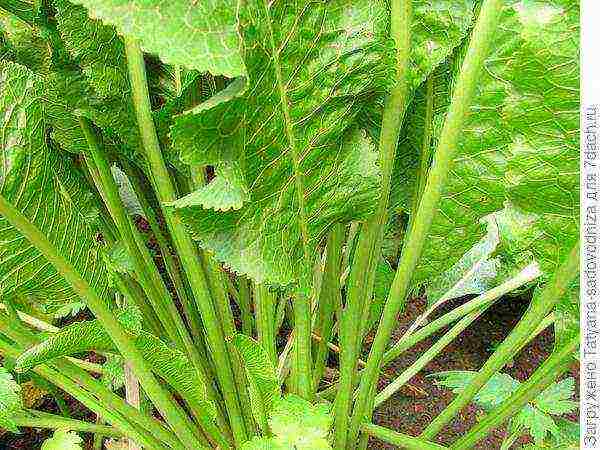

The name of the plant comes from the Old Russian "roll" - which means "smell". Remember the proverb that "horseradish is not sweeter than radish"? So, it is not unfounded, because horseradish really has a bitter-sharp vigorous taste. By the way, the taste and aroma are due to the content of mustard oil in horseradish and, as a result, a large amount of vitamin C and protein.

Planting horseradish
The first thing we do is choose a landing site. Fuck loves semi-shaded places. For example, here it feels great between cherry and plum. You should be very careful when choosing a soil. Horseradish does not like alkaline soils, it is much more comfortable for him to live on acidic wet ones.
Do not forget that horseradish can live up to 10 years in one place. Therefore, it is better to immediately allocate a suitable place for him. Consider also the fact that horseradish grows pretty well and in favorable conditions grows into a large lush "bush".
Excellent predecessors are grains and legumes. Remember that horseradish, although not very much, still clogs the site. The roots remaining in the ground will surely give rise to a "new life" =))
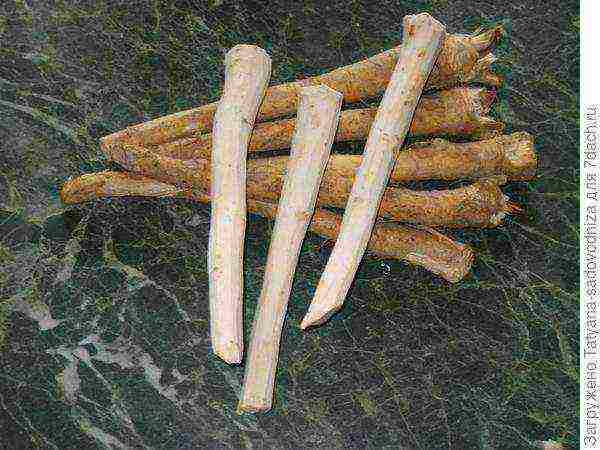

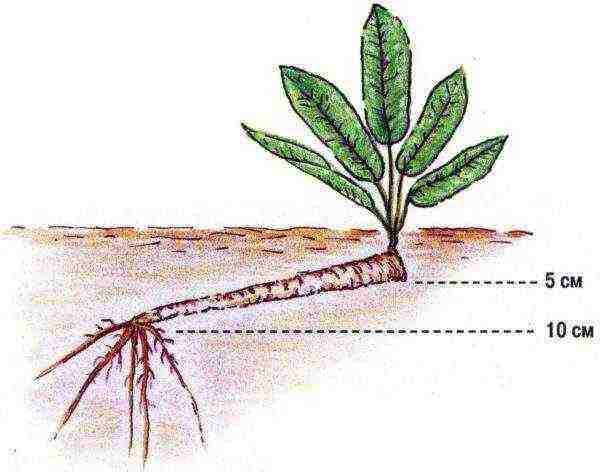
Having decided on the landing site, we prepare the planting material. By the way: these roots will serve them (photos below and above). You can use both a large spine and side ones. The side ones, however, are better suited for landing. From one plant, you can "get" 4-5 of these roots. We dig in the spine and cut it off. It is good if its diameter is about 1 cm, and its length is up to about 25 cm.
Then you should decide on the landing date. Horseradish is cold-resistant, so you can plant it even in early spring. It is possible in the fall. In the first case, the roots need to be prepared for wintering - so that in the spring the planting material is still vigorous and fresh.
Be sure to mark where the root is top and where the bottom is, so as not to plant it upside down in the spring. For example, you can make the bottom cut oblique and the top cut transverse. The main thing is not to forget which cut means what))). Until spring, the roots are stored in the basement or underground, sprinkled with 10-15 cm of earth. And don't forget to dig up a landing site in the fall. But this is ideal)).
Let's imagine that spring has already come and we are going to plant horseradish. We dig up the roots and clean them from the small roots that have grown over the winter. In this case, 1.5-2 cm should be retreated from the upper edge of the root, and 3 cm from the lower edge, since the leaves and roots of the new plant will form here.
I almost forgot: when planting several plants, the distance between them should be 30x70 cm, and the planting depth is such that the root is 4 cm covered with earth on top. The roots are buried obliquely, at an angle of 45 °.
This is how complicated it is if you do it according to the rules. I asked my mother how she planted, - she says: she dug it up and stuck it where it was necessary, and that's all =))) In general, you choose the method of planting.

Horseradish care
Horseradish is an unpretentious plant, but despite the fact that in the wild it grows by itself, some care is still required.
Watering Extremely fond of wet soils, so remember to water. If not watered, the horseradish leaves will be stingy and the roots will not grow large.
Weeding and loosening row spacing
It is necessary in order to let oxygen to the roots.
Fertilizer Optional, but desirable. The first feeding of potassium and nitrogen is especially important. It is done when the horseradish has taken root, and the first leaves have appeared.
Harvesting
Horseradish roots are harvested in the second half of October, however, if you do it earlier, it's okay. After all, don't wait until autumn to salt cucumbers or make shit. Horseradish leaves are also used for canning. I don't know about you, but we always canned cucumbers with horseradish. Some people are very fond of shit. Her taste is specific and vigorous. For some reason we don't do it, but we are very happy when someone treats it =)))

Classic pickles recipe:


Horseradish varieties
I really didn't know that there are different varieties of horseradish ... In my area, everything is done simply: I dug a root in the street or in someone's garden, stuck it in and that's it ... It turned out that there are horseradish seeds.
The most popular varieties are “Valkovsky" and "Atlant«.
I'll tell you a little about the first one. The variety is late ripening, with excellent taste. Suitable for canning. Grown in the open field. The root pulp is white and juicy.
Horseradish "Atlant" has the following characteristics: sandy pulp, dense, milky white. Mid-season, it is distinguished by excellent keeping quality and resistance to drought and frost. There are no external differences in the varieties. Used the same =)

Does horseradish grow on your site? =)
Horseradish is traditionally grown in the Russian vegetable garden. It can be found in almost every site. For the needs of the family, it is not required to plant large areas with horseradish, three to five bushes are enough. Most often, he is not particularly looked after, but is remembered only during the summer harvesting period. But the cultivation of horseradish has its own subtleties, and they will be discussed in the article.
Horseradish - species and "relatives"
In our country, two types of this useful plant grow: horseradish (in the middle lane) and meadow horseradish (mainly in Siberia). Horseradish, or village, is a perennial from the cruciferous family, which in the modern classification has been renamed to the cabbage family. Plants belonging to this family contain vitamins and other substances useful for humans:
- essential oil,
- lysozyme (has antimicrobial activity),
- ascorbic acid (vitamin C),
- carotene (vitamin A),
- calcium, magnesium, iron.
Numerous "relatives" of horseradish:
- wild cabbage,
- radish,
- radish,
- carrot,
- beet,
- rape,
- mustard,
- rape,
- shepherd's bag,
- levkoy,
- mattiola (night violet).

Horseradish-related crops contain vitamins and other substances useful to humans
Horseradish varieties and their characteristics
There are not very many varieties of horseradish. The most famous among them are:
- Valkovsky (Wild) - variety for open ground, late ripening, white pulp, juicy;
- Atlant - frost-resistant, mid-season, with good keeping quality, milky-white pulp, grown in open ground; zoned in Siberia and the Far East;
- Suzdal - a variety of Vladimir selection, the leaves are dark green, does not have lateral processes, with even roots up to 30 cm long, with white, juicy, capacious pulp; only positive reviews;
- Latvian - cultivated for central Russia;
- Malinsky - bred in the Czech Republic.
There is a plant that looks like horseradish, but is not such - katran (it is also called Tatar horseradish). Nowadays, it is quite popular with gardeners due to its milder taste.
Photo gallery: horseradish varieties
Features of planting horseradish
Horseradish is a frost-resistant plant, it can grow in one place for up to ten years. It should be transplanted because the most succulent roots are obtained from young plants. No special preparations are required in order to plant horseradish. The plant is undemanding to growing conditions, and this is one of its advantages. As a place for planting, beds are suitable where early maturing crops grew, with loamy, sandy loam soil or chernozem. If the soil on the site is clayey, then it must be prepared before planting by adding a mixture of manure (10-12 kg / m2), peat and sand in the fall, and in the spring fill the soil with mineral fertilizers (potassium nitrate, ammonium nitrate and superphosphate) at the rate of 30 g / m2. At high soil acidity, ash is added: 40–500 g / m2. Horseradish likes to grow in a lighted or semi-shaded area. You can plant it by the fence, as it grows a lot.
Horseradish growing methods
Horseradish can be grown in different ways:
- on a raised bed,
- in a bucket,
- in a barrel,
- in a "sleeve" made of polymer film.
Method one: raised bed
Planting horseradish on a high bed has its advantages: it is easier to dig long roots in the fall, the plant does not flood with water in a rainy summer.
- First, the roots are prepared for planting. With the back of the knife blade, the lateral roots and buds are removed, leaving them only at the ends.
- The bed is lifted with a shovel above ground level, forming a ridge.
- Cuttings are planted at an angle of 30 ° at a distance of 30-40 cm so that there is 2-3 cm of soil above the cutting.
Video: planting horseradish in a raised bed
Method two: in a bucket
Horseradish tends to grow and is perceived by many gardeners as a weed. To limit its growth, gardeners have come up with a method of growing in buckets. The procedure is as follows.
- The old bucket is filled with a nutrient mixture (humus + earth).
- Bury a full bucket in the ground, leaving small sides raised.
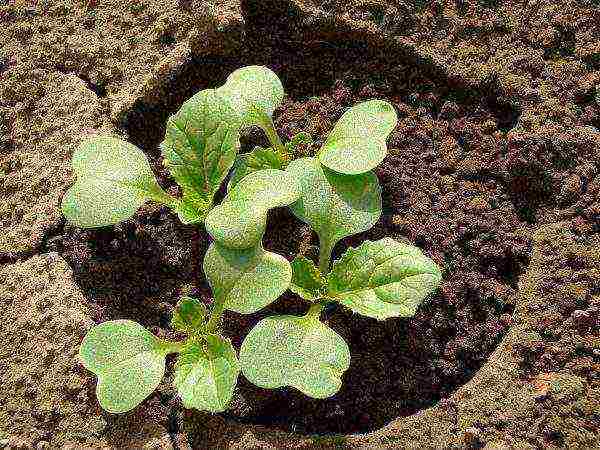

Planting horseradish in a bucket prevents the plant from spreading too much in the garden
- Several horseradish rhizomes are planted in each bucket.
In summer, plantings should be watered and fed. And in the fall, you can pull out the bucket or turn it over to its side. In this case, the roots will remain intact. They only need to be shaken off the ground.
Method three: in a barrel
Similarly, you can grow horseradish in an old barrel. It will hold more plants than a bucket.
Video: how to grow horseradish in a barrel
Method four: "sleeve" made of polymer film
Methods for limiting horseradish overgrowth can be even more modern. So, another way is to use a polymer film with a thickness of 100 microns. The diameter of the "sleeve" is 4–5 times larger than the diameter of the seedling. The planting stalk is placed in it so that the upper part protrudes by 1 cm, and the lower one by 2 cm, the sleeve is placed in the soil at a slight slope. The upper part gives a rosette of leaves, and the lower one - roots, lateral branches are not formed, since the film isolates the plant from the soil. With this method of planting, the plant does not branch at all, and in the fall it is easy to extract it from the ground.

The polyethylene film for the sleeve must be dense, at least 100 microns thick
Horseradish breeding
Horseradish cultivars rarely produce seeds. For this reason, it is propagated in other ways, most often vegetatively - by dividing the rhizomes.
Rhizome cuttings
As a planting material, cuttings of overwintered plants are harvested immediately after the soil thaws. Better if they come from annual roots. They are cut to a length of 25 to 30 cm. Be sure to mark the top (cut straight) and bottom (obliquely) so as not to plant the cuttings upside down. The thickness of the handle is at least 1 cm.For one m2, you will need 4–6 such cuttings. Before planting, all lateral buds from the cutting are removed, leaving only the lower ones, from which the roots and leaves will develop... To do this, wipe the middle part of the cutting with a thick cloth (burlap) or the blunt side of a knife. This process is called "blinding."
Cuttings are planted with a peg obliquely: the upper (straight) part - to a depth of 3-4 cm, and the lower (beveled) - to a depth of 10-12 cm. The planting scheme is 30 × 70 cm. Cuttings can be planted both in spring and in summer , and even in early autumn.
When horseradish propagates by rhizomes, cuttings are planted at an angle
Apical kidneys
Cut off the hatched apical buds (these are the buds at the ends of the main or lateral shoot) with pieces of rhizome, place them in a fertile substrate, and after rooting, they are seated in individual containers. And in order to develop "not tops, but roots" in the future, the extra rosettes of leaves should be removed, leaving no more than two. Planted in the spring to a permanent place.

Pieces of horseradish rhizome together with apical buds are planted as seedlings in fertile soil
Seeds
Growing horseradish from seeds can be considered a curiosity. In stores, there is a katran, which is called a horseradish substitute. It is a very similar perennial plant from the cabbage family. If, nevertheless, you have the opportunity to grow horseradish with seeds, then you can try to do it in the same way as sowing seeds of other cold-resistant crops... Seeds are planted before winter or early spring. No stratification is required, nor is it necessary to grow through seedlings.

Horseradish seeds are propagated very rarely.
How to care for horseradish
Horseradish care is reduced to weeding, regular loosening. The first time is loosened a week after planting to a depth of 3-4 cm, after the emergence of seedlings, the depth of loosening is increased to 6–8 cm, at the third stage it is brought to 10–12 cm. A total of 5–7 loosening is carried out per season. Watering is necessary in dry weather with a water consumption of 3-4 l / m2.
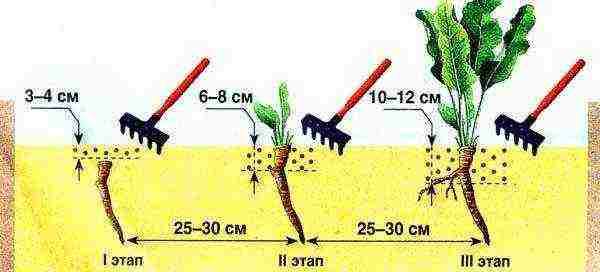
Loosening horseradish is done carefully, at a short distance from the plant, so as not to damage the roots.
Top dressing and loosening
Horseradish is not picky about fertilizers, it grows well without them. You can feed the plantings once a month: 50 g of complex fertilizers per 10 liters of water. At the same time, loose soil is very important for horseradish, as for all root crops. Loosening the ground should be done carefully, taking care not to damage the roots.
Pest and disease control
Horseradish is used in salads and preparations. Unfortunately, not only people love it, but also insects, despite the sharp and even bitter taste, which greatly harm the plant. How can you help him?
Table: horseradish pest control measures
Photo gallery: horseradish pests
Horseradish is a useful and unpretentious plant, it is used not only for food, but also in the treatment of many diseases, but sometimes it can itself be affected by diseases.
Table: horseradish diseases
Reviews
In order for horseradish to please you with a harvest of juicy and vigorous roots, you need to take care of it. If you plant it and forget it, you may end up with a problem of how to get rid of the horseradish. Let you get the first option!
My name is Natalya. I am a teacher of the Russian language and literature by profession. Rate the article:
(1 vote, average: 5 out of 5)
Agricultural technology, varieties, planting scheme, blank recipes
Horseradish is an amazing culture. Some consider her to be almost a weed that does not have the right to permanent residence in a decent garden, others adore and take care in every possible way. Having studied the experience of FORUMHOUSE participants, we will tell you about how to care for horseradish, how to easily remove it from your site, about popular varieties of horseradish and recipes for delicious preparations from it.

Content:
- Popular horseradish varieties
- Preparing the soil for planting horseradish
- Preparing horseradish cuttings
- Horseradish planting scheme
- Horseradish planting methods
- How to remove horseradish from the site
- Horseradish in the garden and in the kitchen
FORUMHOUSE participant Elena Miss complains: horseradish refuses to grow in her garden, although the soil is fertile and the place is moist. The leaves are barely enough for pickling cucumbers. And it turns out that this is not such a rare occurrence.
Elena MissFORUMHOUSE member
Maybe there are modern varieties, otherwise I have a bush from neighbors ... It's already two years, but it grows 5-6 leaves and does not multiply ... And I really want to make grated horseradish!
Good horseradish grows only from good planting material.
Popular horseradish varieties
Despite the fact that in Russia there are several excellent varieties of horseradish, semi-wild or wild horseradish grows in almost every first vegetable garden. Some grow horseradish of Polish selection, but many consider it not vigorous enough.
kan74FORUMHOUSE Member
Polish horseradish - it's bad, too sweet.
A FORUMHOUSE member has compiled a list of varieties that are grown by true lovers of this crop.
Suzdal - this variety of Vladimir selection has only good reviews.
Valkovsky - late-ripening variety, dug out 200 days after planting, with a one-year cultivation, the rhizome reaches 3 cm in diameter. Resistant to flea beetles.
Tatar - this variety is grown in the southern regions.
Tolpukhovsky - common in Central Russia. This is a late-ripening variety, the rhizome is large, weighing up to 250 grams.
Atlant - mid-season variety, can be dug out on 85-120 days of average size.
Alpo - a variety of Polish selection, medium-sized rhizome with bright white pulp.
Malinsky - a variety of Czech selection.
How to grow horseradish
Despite the fact that horseradish is considered an aggressor, which, after an unsuccessful move by the cultivator of one bush, spreads throughout the garden, it is a rather whimsical plant. Horseradish becomes an uncontrollable weed when they stop caring for it and, without digging it, leave it to grow in one place for more than three years.
So that horseradish does not creep around the site, they dig it up in the fall, and in the spring they plant it again with cuttings.

Horseradish loves fertile soil and grows best on loams: on sandy roots there is not enough moisture, and they become "wooden"; heavy soil is also not suitable, it is in it that the horseradish roots become branched and rough.
Horseradish loves good watering, but can die from excess moisture.
Horseradish grows poorly on acidic soils.
Horseradish: three ways of planting
The soil for planting horseradish is prepared as follows: they dig up the soil to a depth of about 40 cm, into which fertilizers have already been applied for the autumn digging.
For 1 square meter - 5-9 kilograms of compost or rotted manure, 25 grams of urea, 50 grams of superphosphate and 35 grams of potassium chloride. If necessary, horseradish is grown on bulk beds.

Horseradish is propagated only by cuttings. Cuttings for planting material are prepared in the fall, when the horseradish crop is dug up. All small branches, which are cut off from the rhizome, go to the cuttings. Requirements for cuttings:
- For the southern regions - the length is about 25 cm, the thickness is at least 0.5 cm.
- For the Central, Northwestern regions and Siberia - about 25 cm long, at least 1 cm thick.
Since the planting material will have to be stored until spring, the lower part of the cutting is marked so as not to confuse it with the upper one later. The easiest way to mark is by making an oblique cut. Cuttings are stored in a cellar or basement, covered with any available material or digging into a box with earth. About a month before planting, the cuttings are brought into a bright room. To awaken the dormant buds, the middle of the roots is covered with burlap, and the top and bottom are left open. When the cuttings germinate, they are "blinded" just before planting in a prepared place.
The "blinding" procedure consists in removing all the buds from the middle of the cutting, which was under the burlap - both dormant and growing. "Blinding" is done with a hand, wearing a mitten, or a piece of burlap. The buds that have begun to grow in the lower and upper parts of the cutting are not removed.
Blinding helps prevent the lateral branching of the rhizome, so that in the fall we get cylindrical, even roots.
Now you can start planting cuttings, which is carried out using planting pegs. A peg is stuck into the prepared loose soil, which is about 5 cm longer than the cutting, and the cutting is planted into the hole that remains after the peg is removed. Here we need an oblique cut made in the fall - it should be at the bottom. The cuttings are sprinkled with earth, the layer thickness is 3-5 cm, depending on the composition of the soil, the lighter it is, the thinner the layer should be. Distance between cuttings 30 cm, between rows -70 cm.
We told you about vertical planting of horseradish; there are two more planting methods: horizontal and inclined.
MihkelFORUMHOUSE Member
For biennial cuttings, the maximum yield is for inclined cuttings. For annuals (planted in spring - harvested in autumn), the maximum yield is from horizontally planted ones.
But horizontal planting has a big drawback - a lot of extra buds awaken, the root will turn out to be branched, sloppy and inconvenient for storage.
Immediately after planting, you can "postpone the tambourine" until autumn - horseradish will not require any more dances from us, you will only need to weed it a couple of times a season and water it several times.
How to remove horseradish from the site

If you don’t dig up the horseradish every year, it is really difficult to control it. Before you have time to look back, he captured half of the site.
kan74
Previously, when they dug under a shovel and chose the roots, everything was done manually - it did not grow much. Now I'm plowing everything with a motor-cultivator, so he flooded.
A member of FORUMHOUSE alike figured out how to keep the hell in a frame - for this she literally strictly limited it to a frame.
AlikeFORUMHOUSE Member
I plant it only in a cistern dug into the ground without a bottom, only have time to harvest the crop, and does not creep into the beds.
If horseradish has already grown, and you are thinking of how to remove it from the garden, use the advice of a member of our portal Svail, whose garden already resembled a horseradish plantation. She harassed this culture with cut 1.5 liter plastic bottles.
Svail
In the spring, you put the trimmed one and a half on the root and sprinkle it with earth so that the air does not pass. Over the summer, everything burned down, and the roots too.
Horseradish in the garden and in the kitchen
For some reason, many do not know that horseradish leaf infusion is an effective remedy for aphids. It is enough just to pour the leaves with water, stand for three days and spray cabbage or cucumbers with infusion. After this treatment, the aphids will not have the slightest chance.

Horseradish leaves are indispensable when roasting meat on charcoal. You can wrap each piece of meat in a horseradish leaf and bake on a wire rack (eaten with the leaves), or you can put horseradish leaves on the wire rack, put the meat on top, tomatoes and onions on top, and the horseradish leaves on top again. Bake until the leaves turn brown. Such meat is never charred, it turns out juicy and tasty.
At FORUMHOUSE you will find the best recipes for horseradish with honey and various horseradish preparations that do not lose their pungency and odor for up to six months, you can share your experience in growing vegetables, watch a video dedicated to spicy aromatic crops.
 Horseradish is a very popular plant, it is successfully used for conservation, in cooking, and its medicinal properties are appreciated. What are the varieties of horseradish, how to grow it correctly, propagate it, care for it, prepare it for planting in open ground - you will find out later in the article.
Horseradish is a very popular plant, it is successfully used for conservation, in cooking, and its medicinal properties are appreciated. What are the varieties of horseradish, how to grow it correctly, propagate it, care for it, prepare it for planting in open ground - you will find out later in the article.
Description: varieties and varieties of horseradish
Horseradish is a perennial with large oval leaves and a massive root system. If you grow it not only for the sake of leaf mass, but also use rhizomes, then it is better to update it annually, periodically replanting it to new places.Such manipulations are done due to the fact that by the second year the roots grow stiff, thinner, become branched, and such a plant is no longer suitable for food.
Delicious spices, additives, sauces are prepared from horseradish roots, for meat, fish, liquid dishes, they are added to pickles-marinades.
Horseradish is a pantry of useful substances: it contains vitamins B (2,6,8,9), C, PP, carotene, mustard oil (it is because of it that horseradish is so "vigorous" and smells in a special way). Many folk recipes contain horseradish - for example, to get rid of tonsillitis, sciatica, etc.

Horseradish roots and leaves are both used in cooking.
There are several varieties of plants for growing outdoors:
- Atlas is lying, ripens in mid-summer, the root is smooth, white inside, dense, weighs up to 420 g, up to 45 cm in length, fragrant, does not bloom. The variety is drought-resistant, tolerates frost and heat.
- Valkovsky - late ripening, zoned, resistant to pests.
- Tolpukhovsky - late ripening, with white root pulp.
Planting plants in open ground. Fertilizers and horseradish feeding
Before planting horseradish, the soil is flavored with compost (manure). We find a semi-shaded place, it's great if legumes or grain plants were planted there before. Horseradish loves moist acidic soils.
Important! Horseradish is a rather tenacious and tenacious culture, it grows quickly under suitable conditions. Therefore, if you do not limit the space for him, he can begin to clog the area. And the small roots left after "poor-quality" weeding germinate easily.
The place of planting in open ground has been chosen, it is necessary to prepare the planting material: in principle, you can use both the main root and the shoots (although it is better to take the shoots, one main root can have 4-6 roots). It is necessary to dig up the spine and cut it off, it is desirable that the diameter of the material is about 1-1.5 cm, and the length is up to 20 cm.
Planting outdoors is done in spring or autumn. Horseradish is not afraid of the cold, so both early spring and late autumn are suitable. If the roots are to fall into open ground in the spring, then they must be properly preserved in the winter so that they remain fresh, not sluggish. Keep the material in a cellar or basement, covered with earth.
Important! It should be noted where the spine has the upper part, where the lower one, so as not to be confused when landing.
When planning to plant horseradish, we clean the root cuttings from small processes, without affecting the areas above and below the root, where roots and leaves are then formed. It is better to bury it obliquely, the distance between the roots is from 30 cm, sprinkle with earth on top by about 4-5 cm.
An important stage in growing a crop is feeding. Fertilizers are applied even on rich soils, only the dose varies. In autumn, before digging, organic matter is introduced (up to 10 kg / m2) or in the spring (up to 8 kg / m2). At the same time, it is fertilized with superphosphate and potassium chloride. Such a mixture of fertilizers improves the structure of the soil, microorganisms in the soil work more actively, which increases acidity and adds nutrients. If the soil is too acidic, liming is carried out in autumn (up to 0.8 kg / m2). In the spring, mineral fertilizers are used with the addition of potassium, nitrogen, phosphorus.

Control the plant, it can spread strongly over the site
Proper horseradish care and combination with other plants
- Watering crops in the open field. Horseradish loves moist soil, so regular watering is a must. Otherwise, the leaf mass will dry out, and the roots will not have enough moisture for growth.
- Loosening, weeding - helps to deliver oxygen to the roots.
- Fertilizer. In principle, you can not fertilize horseradish planting, but it is advisable to make at least the first nitrogen-potassium fertilizing. Its term comes when the plant has already taken root and the first leaves have opened.
- Chemical processing. Everyone who has been involved in horseradish cultivation knows: any plant can suffer from pests and diseases, in this case, processing is carried out with special compounds or folk remedies.But after using chemicals, horseradish leaves can no longer be eaten.
Advice. If they want to get even beautiful roots, then somewhere in July they are freed from the ground (not completely) and the lateral processes are removed, then they are again covered with earth.
When growing horseradish as an annual, it is advised to alternate it with cucumbers, legumes, potatoes, tomatoes, root crops. To remove horseradish steams, after harvesting, perennial herbs are planted, clogging up young horseradish shoots.
Plant propagation. Horseradish diseases and pests
Horseradish propagates by root shoots (cuttings). To separate the shoots, two-year-old rhizomes are taken, which are planned for processing. Intact, healthy processes are cut from them. If this is a summer cottage, then it is optimal to do cuttings of spring roots. It is best to take the lower processes - there will be fewer flower shoots, and the roots will be of higher quality. Proper watering is important.
Diseases:
- Black rot - occurs on flower stems and roots.
- White rust - light yellow spots on the leaves.
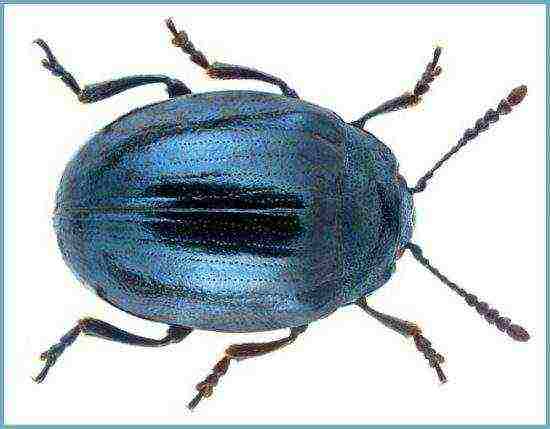

Babanukha
Pests:
- Babanukha (horseradish leaf beetle) - beetles that eat leaves and lay larvae there.
- Cabbage White - caterpillars can eat horseradish leaves to the very veins.
- Rapeseed beetle - reddish beetles with a black stripe, damage the leaf mass.
- Horseradish flea - spends the winter under the remains of last year's plants and affects young leaves in early spring
And in conclusion, it remains to add that growing horseradish is an easy task, and there are quite a lot of benefits from these roots, so the labor costs and the time spent will more than pay off. Horseradish will delight you with snacks on the table and healing properties for ailments.
How to plant horseradish root: video
Growing horseradish root: photo





