Content
Feeding and caring for turkeys at home
You won't surprise anyone with the presence of turkeys in the poultry yard now. They are grown for dietary meat. Low cholesterol levels, a range of vitamins and amino acids ensure that turkey meat is easily digestible. An adult is gaining live weight up to 20-30 kg. However, they are still not as popular as chickens or geese. Why?
The reason is that turkeys are more susceptible to disease than other poultry, in the need to provide them with a large area for walking. And the turkeys themselves are large in size. Many, especially housewives, are afraid to take care of them due to fear of being pecked by these "monsters".
This article will talk about proper care, feeding, treatment of possible diseases of turkey poults at home.
Keeping turkeys in industrial production and at home
Taking into account the fact that turkeys are a large, wide-breasted bird, their keeping at home has its own specifics. In industrial production sometimes they use the cellular method of breeding them. At home - almost always prefer walking.
Cellular way
Applies only to poultry of light breeds. This is directly related to their live weight. No more than two heads are kept in one cage. The males are separated from the females. Grow turkeys up to a maximum of 4 months of age... It is also advisable to keep young growth in cages for sale up to the age of one and a half months.
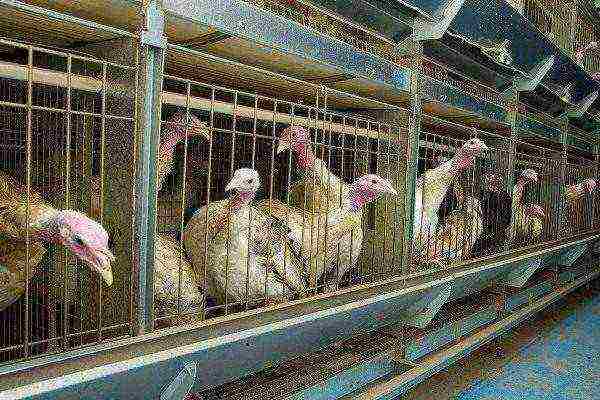

Its advantages:
- saves space due to the possibility of keeping in 2 tiers. With this method, the cages are placed along the aisles. The efficiency of using the area is doubled;
- by saving space livestock in one poultry house can be increased by 1.7-1.8 times;
- the bird is easier to service, the labor productivity of the service personnel increases.
The disadvantages of such content are much more.... This is the reason that this method has not found widespread use:
- the intensity of growth decreases young animals after one month of age;
- reproduction is declining in males and females;
- there is a weakening of the leg muscles due to limited space. Since the bird is heavy, the muscles need periodic physical exertion;
- wings break, since their scope is large, and the area of content is limited;
- Turkeys and turkeys are more stressed, and become shy, from a sharp knock they raise a general hysteria, beat in cages and often, breaking doors, fall to the floor, receive bone injuries;
- Unnecessarily fat is stored in the liver.
Walking way
With this method of breeding, the bird feels better. It is not much different from keeping chickens or geese. Open walking and open-air cage method are used.
Outdoor walking
This is the best content option. But it requires the constant presence of a person. With this method, in the daytime, a herd of turkeys is released into the street to grazing areas unsuitable for agriculture. A slowly chased bird finds food for itself, which is not limited only to plants. Turkeys will peck almost everything that comes their way: insects, including those harmful to agricultural crops, vole mice, and other small animals. When the heat comes (if walking is carried out in summer), the herd hides in the shade of trees or abandoned buildings. With the onset of puberty, males are separated from females and grazed separately. The bulk of the diet consists of grasses and grains. You can release a bird for open walking when it has reached one and a half months of age.
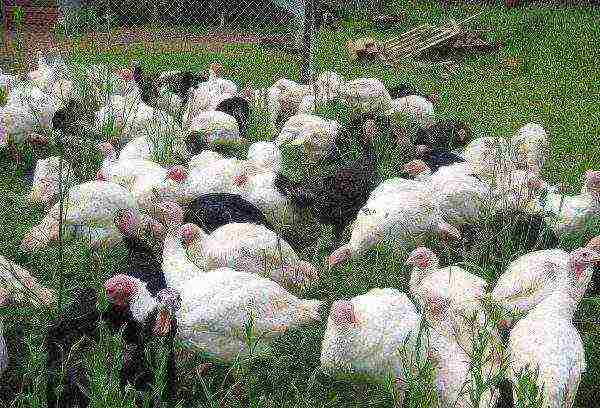

The advantages of this method of keeping:
- overall reproduction;
- disease susceptibility decreases by strengthening immunity;
- lower feeding costs by eating green mass;
- poultry health improves, since there is a daily exercise and a systematic load on the muscles;
- growth intensity increases chickens;
- not required no additional investment.
Flaws:
- with this method of walking constantly human presence is required.
Aviary method
An aviary for turkeys is made in the same way as for keeping chickens or geese. The main difference - the size of the enclosure must be large. It is built at the rate of 10 square meters per head. I.e, to contain 20 heads, you need to fence a plot of 200 square meters.

If possible, two equal sections are fenced off. They are periodically changed for grazing and walking. If there is no free area, then it is advisable to leave the walking area of 10 m2 per head, and not reduce, divide into two parts for the sake of rotation of the site. In this case, the bird is fed with freshly cut grass. During daylight hours, in hot weather, turkeys are driven either indoors, or equipped with sheds to create shade. Feeders and drinkers are also placed there.
Small turkeys: how to feed and care for healthy offspring
Caring for turkeys is no more difficult than caring for other poultry. There is no need to build special premises for their maintenance. The poultry houses left after chickens and geese are used. Main condition - the room should be spacious. At a height of 70-80 cm from the floor, we install perches from thick wooden beams. At a height of 50-60 cm, we make nests for turkeys in remote places of the poultry house. Feeders and drinkers are being installed.
For offspring first we build turkey nests from hay and straw. We put small branches on the bottom to give the rigidity of the wreath shape. If there are several nests, be sure to fence them off from each other as high as possible. We do not allow turkeys to the nests. If the turkeys have left their eggs for eating, make sure that they do not cool down. To do this, lightly cover with straw.
Turkey poults do not hatch in one day. Therefore, we remove the newborn chicks from the nest in a separate box. If necessary, illuminate with a lamp. We create the necessary microclimate using the heater, since the birth of chicks occurs in the spring, less often in the fall... After all the turkeys have hatched, they are returned to the turkey.
We make sure that there are no drafts in the room, that it is light, temperature regime in summer time - not higher than + 25, in winter - not lower than +5 degrees. To lower the air temperature, we use ventilation, ventilation. To maintain warmth in winter, we insulate windows and doors. In very cold winter periods, we additionally heat the room.
Feeding turkeys, diet tables, daily allowance and proper diet
Due to the set of large live weight (up to 20-30 kg) during his life turkeys need a lot of feed... First of all, turkey poults that have just been born need a balanced diet.
In order to grow healthy offspring, you can feed ad libitum, or you can feed it according to the norms, but the normalized type of feeding is more suitable for feeding with ready-made balanced feed.
Standards for feeding turkey poults:
| Age, weeks | Feeding rate, gr |
| 1 | 10 |
| 2 | 25 |
| 3 | 40 |
| 4 | 60 |
| 5 | 75 |
| 6 | 90 |
| 7 | 110 |
| 8 | 130 |
| 9 | 155 |
| 10 | 175 |
| 11 | 200 |
| 12 | 220 |
| 13 | 235 |
| 14 | 250 |
| 15 | 260 |
| 16 | 280 |
| 17 | 285 |
| 18 | 290 |
| 19 | 295 |
| 20 | 295 |
| 21 | 300 |
| 22 | 305 |
| 23 | 310 |
| 24 | 310 |
| 25 | 300 |
| adult females | 260 |
| adult males | 500 |
In the early days
In the first hours of hatched turkey poults it is necessary to drink clean water with added glucose. After 8-10 hours day old chicks are fed with finely chopped boiled eggs. Make sure that no large lumps remain. Corn flour or wheat bran can be added to reduce moisture in the feed. It is better to put the food on a rag bed so that it draws out excess moisture. Up to one week of age turkey poults are also fed with grated low-fat cottage cheese, with the addition of a large amount of herbs to the diet: dandelion, woodlice, milkweed, finely chopped green onion feathers. Gradually we move on to feeding with mash of millet, wheat turf. Make sure that the food is not too wet. Otherwise, the turkey poults will have an upset stomach, which is dangerous at their age. We give barley and oatmeal as an independent feed. At such an early age, food for turkeys is given at intervals of every three hours. For the mash we make a separate feeder, for dry food there should be one. We make sure that there is constantly fresh water in the drinkers.
From one week to one month old
During this period, turkey poults grow intensively and gain weight.... They are active, run, willingly eat whatever they are given. We gradually increase the share of green mass in the total composition, bringing it to 30% of the total feed. Greens can be finely chopped by mixing with dry food. They also give pure greens. Better during this period to feed a balanced composition of feed. At two weeks of age add chalk, bone meal to the feed. Add potassium permanganate to the water so that the solution is not pink. During this period, the poults are fed every 4 hours. With good feeding, by the age of one month, the young gains up to two kilograms in weight.
From a month to two
During this period, young animals are fed only three times a day. This is due to the fact that their activity decreases. In order not to accumulate fat, stop adding compound feed to the diet.... The main emphasis is placed on grain and grain waste, green mass, bran, crushed corn, dry residues of animal origin. Give wet mash, increasing the amount of protein feed: minced meat from meat waste or inexpensive fish, etc. By the onset of hot weather, turkeys reach two months of age and gain a decent mass.
After two months before slaughter
The diet during this period of life does not differ from the previous one. We increase the share of grain and grain waste in the total mass... We transfer the bird to a walking method of keeping. It is described above. Adult turkeys for reproduction are kept up to two and a half years old, turkeys for breeding chicks - up to three years old. If the goal of growing is the sale of meat, it is advisable to fatten the livestock up to five months of age. With the onset of autumn, the natural growth of herbs decreases. For replenishment it is necessary to increase the proportion of grain. The economic effect of growing is decreasing.
Feeding rations
Sample rations for feeding turkeys are shown in table. 1-3.
Table 1. Approximate ration for feeding turkeys, g per head per day (1st option)
| Stern | Age, days | ||||||
| 1-5 | 6-10 | 11-20 | 21-30 | 31-40 | 41-55 | 56-70 | |
| cottage cheese | 3 | 10 | 10 | 10 | — | — | — |
| curdled milk | 20 | 20 | — | — | — | — | — |
| corn grits | 40 | 38 | 20 | 20 | 10 | — | — |
| wheat | 15 | 20 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 35 | 25 |
| barley | 12 | 14 | 21 | 21 | 27 | 30 | 35 |
| millet | 10 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| penny bran | — | — | 20 | 20 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| fish flour | 12 | 15 | 10 | 10 | 13 | 14 | 20 |
| meat and bone meal | 5 | 5 | 2 | 5 | 5 | — | — |
| oats | — | — | — | — | 10 | 30 | 30 |
| wheat | — | — | 10 | 10 | 20 | 15 | 20 |
| crushed corn | — | — | 10 | 10 | — | — | — |
| barley | — | — | — | — | 20 | 15 | 40 |
| greens | 5 | 30 | 60 | 50 | 70 | 100 | 100 |
| shell, chalk | 2,5 | 2,5 | 2,5 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4,5 |
| fish fat | 2 | 2 | 2 | — | — | — | — |
| salt | 0,1 | 0,2 | 0,3 | 0,5 | 0,7 | 0,8 | 1 |
Table 2. Approximate ration for feeding turkeys, g per head per day (2nd option)
| Feed | Age, days | ||||
| 1-5 | 6-10 | 11-20 | 21-30 | 31-40 | |
| boiled egg | 2 | 1 | — | — | — |
| skimmed milk | 5 | 10 | 10 | 15 | 10 |
| fat-free cottage cheese | 2 | 5 | 10 | 5 | — |
| whole grain (corn) | 5 | 7 | 152 | 208 | 3015 |
| wheat bran | 4 | 5 | 8 | 12 | 15 |
| cake | — | — | — | — | 5 |
| greens | 3 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 30 |
| shell, chalk | — | 0,5 | 1 | 1,5 | 3 |
| total | 21 | 38 | 61 | 81 | 108 |
Table 3. Approximate ration for feeding turkeys, g per head per day (3rd option)
| Stern | Age, days | |||||||||
| 1-5 | 6-10 | 11-15 | 16-20 | 21-30 | 31-35 | 36-40 | 41-50 | 51-60 | 61-70 | |
| grain of two types | 5 | 8 | 20 | 30 | 50 | 60 | 80 | 15 | 145 | 175 |
| wheat bran | 4 | 5 | 5 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 15 | 15 | 25 | 25 |
| fresh greens | 3 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 100 | 100 |
| return | 5 | 10 | 10 | 15 | 10 | — | — | — | — | — |
| cottage cheese | 2 | 10 | 10 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| boiled egg | 3 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
Diseases of turkeys: symptoms, treatment and prevention of diseases
In the process of life, turkeys need not only a room, food, but also protection from disease.
The main ones are:
- Smallpox: an infectious disease, manifested in the refusal of the bird to eat and drink, turkeys become inactive, feathers ruffle, wings hang down. Infected from other sick birds, flies, mosquitoes. Infected individuals should be destroyed and burned, and healthy ones should be vaccinated with an embryo vaccine. As a prophylaxis, turkeys in the sixth week of life are vaccinated with this drug.

- Worms: pests that settle inside the individual, affecting the digestive organs and respiratory tract. The bird begins to lose weight. Sources of infection: soil, other infected poultry, feed. Control methods: use of piperazine sulfate, phenothiazine. Preventive measures: processing of the premises with sanitary and hygienic means.
- Respiratory mycoplasmosis: bacteriological disease covers the respiratory tract, the mucous membrane of the eye becomes inflamed. Turkeys lose their orientation, walk, staggering. Individuals may die without treatment. The disease infects healthy birds through contact with sick birds. The occurrence is facilitated by a decrease in immunity due to unbalanced feeding and improper maintenance (hypothermia of individuals, high humidity and dirt in the room). Ways to fight: chlortetracycline or oxytetracycline is added to the diet for a week at the rate of 4 grams per 10 kg of feed. Antibiotics erythromycin, chloramphenicol and streptomycin are also saved. Prevention: balanced nutrition, the room is kept clean, constant ventilation.
- Tuberculosis: the most dangerous disease due to the scale of the defeat of the livestock. All respiratory organs are affected. The bird practically does not eat, sits in one place, vilifies. Dirty water is the source of infection.inventory and bedding infected with tubercle bacillus. It is recommended to urgently destroy the infected bird. The best way to fight - the presence of direct sunlight and fresh air. The house is left unoccupied and open. The livestock is transferred to another location.
- Histomoniasis: the cecum in birds and other digestive organs are affected. Symptoms: turkeys begin to vilify, rapidly lose their weight. It is urgent to separate the infected bird from the healthy one. The room is cleaned and disinfected. Furazolidone, osarsol or phenothiazine are added to the feed. The cause of the disease - in a dirty room and lack of disinfection after the previous inhabitants.
- Hard goiter: the reason lies in an unbalanced diet, the composition of which is limited to solid food. It is necessary to add chalk, pebbles of gravel and shells to the diet so that the grain in the crop is better processed. The poultry is slaughtered for meat. It is not contagious.
- Hypovitaminosis: in sick birds, eyes become inflamed, rickets develops. The body lacks vitamins... When a disease occurs, injections are made from a complex of vitamins.
- Diarrhea: the cause of the occurrence is viral diseases, direct contact with parasites, as well as the consumption of foods of insufficient quality. If the diarrhea is brown, then some food product is not suitable for young turkeys. If the color of the excrement is white - these are signs of an infectious disease of pullorosis. Ways to fight: drinking chamomile decoction or potassium permanganate solution, if this does not help, they are treated with antibiotics.
- Diseases of the feet: occur due to the keeping of birds in a confined space (in cages, small poultry houses). It manifests itself in the fact that sick turkeys fall to their feet. Another cause of the disease is a lack of calcium-containing foods in the diet. Prevention: egg shells, chalk, shells are added to the feed, less soybeans, fats, a limited amount of corn. Arthritis in turkeys occurs as a result of an overabundance of protein in the feed.

- Newcastle disease: infection. The result is paralysis of the lower extremities. Vaccination is carried out against this disease. But it does not always help. Prevention: adding mineral and vitamin supplements, fresh herbs, cottage cheese (for turkey poults) to the diet.
- Runny nose (rhinitis): its main causes are hypothermia, lack of vitamins. The exceptions are vitamins A and D. Also, the cause of rhinitis in turkeys can be a poorly ventilated room in which they are kept. Treatment and prevention: there are cases when a runny nose in turkeys quickly passes if they are placed in a warm, dry room and continue the treatment of turkeys with infusion or decoctions of dill (seeds). You can also give them an infusion made from violets, or from the leaves and berries of strawberries. But it is recommended to wipe the beak and nostrils with a feather soaked in salt water. For this solution, you need to take a glass of water and one teaspoon of salt. After this procedure, you should smear the beak with boron fat.
Turkey farming as a business is still underdeveloped. But after all together with dietary meat we get an egg, fluff, feather... With a competent approach to business, a dozen heads of such a bird will be enough to provide a family with meat and its sale in order to compensate for material costs. An increase in livestock leads to a good net profit.