Content
- 0.1 What temperature above zero can potatoes withstand?
- 0.2 What is the storage temperature
- 0.3 How to properly store in a vegetable store, cellar, refrigerator
- 0.4 What sub-zero temperature the culture can withstand, and at what freeze
- 0.5 At what temperature will potatoes freeze in the ground in spring?
- 1 Mulching potatoes
- 2 Watering potatoes
- 2.1 Watering features
- 2.2 Do I need to water the potatoes when planting
- 2.3 When to water after planting
- 2.4 Watering rules for a good harvest
- 2.5 How often potatoes are watered outdoors
- 2.6 Watering in the heat: how often to water
- 2.7 How to water so that the tubers are not covered with scab and other ailments
- 2.8 How many times to water potatoes per season
- 2.9 How to understand that you need watering
- 2.10 Signs of excess and lack of moisture
A key factor for high yields of potatoes is systematic watering during the growing season. It is important to keep the soil evenly moist from germination to the end of the season. Do not allow it to dry out completely, which can lead to unintended regrowth during watering and tuber overgrowth. Consider what temperature potatoes can withstand and the intricacies of mulching.
The culture prefers cool but frost-free conditions. The ideal temperature for growing the product, depending on the stages of the growing season, is as in spring: 8-25 ° C.
The origin of the culture from mountainous regions with cool climates has implications for the agrometeorological responses of the culture. Climatic features, physiological environment extremely important for the production of high yields with good quality tubers, in conditions typical for each specific site.

Potatoes have a fibrous root system, at best no more than 60 cm deep. As a result, the plant often cannot fully utilize nutrients and moisture within the soil profile.
What temperature above zero can potatoes withstand?
It is best to plant when the soil temperature is 7-10 ° C, daytime is in the range of 18 ° C, nighttime is 12-18 ° C. Optimal soil condition for root growth - from 10 to 35 ° C, the most active development occurs at 15 -20 ° C. Conditions are similar for the development of stolons.
For the growth of tops- from 7 to 30 ° C, the best mode is from 20 to 25 ° C. The appearance of tubers is caused by a short photoperiod and includes growth hormones. The cooler the soil temperature, from 15 to 20 ° C, the faster and more tubers are formed.
The process is favored by a low level of nitrogen and a high level of sucrose in the plant. High temperatures (35-40 ° C) reduce and actually stop the formation of tubers. Also, the long duration of the day delays the onset of tuber development.

- At 9 ° C there is a slight elongation of the seedlings, very slow at 6 ° C.
- At temperatures below 6 ° C, development practically stops.
- Exposing the tubers in the soil at 1-2 ° C for several days results in severe damage that affects the normal growth of the plant.
Potato prefers well-drained fertile soil with a high content of organic matter, with an acidity level of 5.0 to 5.5. As the soil becomes more alkaline, the size of the crop increases, but the incidence of scabs also increases - a condition that affects the skin but not the nutritional value of the product.
Temperatures between 12 and 18 ° C are considered the best for harvesting and processing tubers. Under cold and heat stress, when below 5 ° C and above 25 ° C, they are susceptible to disease, the risk of microbial rot.
What is the storage temperature
The storage area for potatoes must be suitable for the temperature conditions in order for the product to remain healthy and the natural decomposition process to slow down.
It is extremely important that it is dark, well-ventilated, for long-term storage of the seed variety, a mode of about 4 ° C is maintained.
For short-term storage, followed by cooking, an environment where 7-10 ° C is preferred.
Storage for long periods of time at temperatures below 4 ° C converts potato starch into sugar, which alters its taste and culinary qualities, it becomes bitter and is caused by an enzyme called invertase.
To maintain a low sugar content in the tubers, the culture is stored at intermediate temperatures of 8-12 ° C, although there is a risk of tuber sprouting.
In an adequate environment in commercial warehouses, potatoes are stored for ten to twelve months. At home the term is only a few weeks... If the tubers develop green areas containing glycoalkaloids, they must be trimmed before using the product.
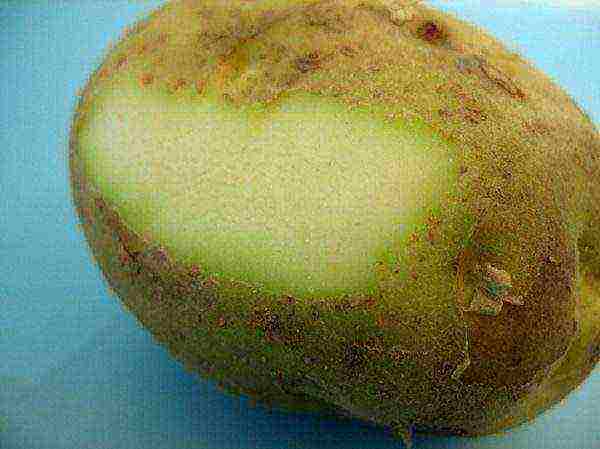

How to properly store in a vegetable store, cellar, refrigerator
Optimal conditions of temperature, humidity, aeration, oxidation state are the most important factors for storing potatoes. As a living organism, its quality decreases due to moisture loss and physiological decay. Deterioration is directly related to storage temperature.
Vegetable store
Before being placed in storage, the tubers must be cured at 7-15 ° C and 85-95% relative humidity for two weeks. During the curing process, the skin thickens and small cuts heal, minimizing the penetration of pathogens.
Most pathogens transported to the tuber storage facility increase population growth logarithmically at 5-26 ° C.
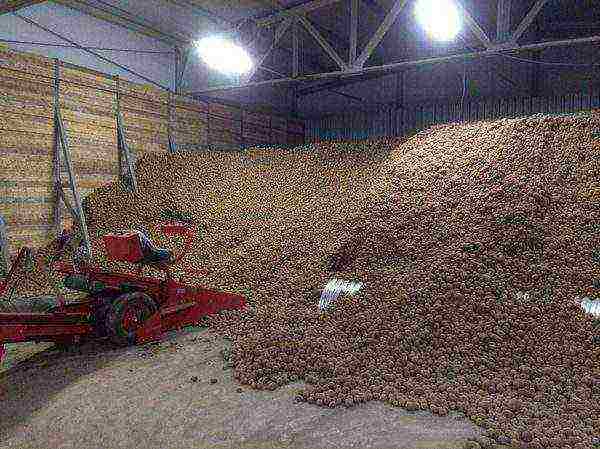

- Store potatoes in a dark place at 4-8 ° C and humidity 80-90%. Although it loses moisture through breathing, low humidity is the main cause of shrinkage during storage. In good conditions, the product lasts up to six months.
- At temperatures exceeding 8 ° C, the tubers germinate in two to three months.
- When stored under temperature conditions below 4 ° C potatoes acquire a sweetish taste. But the normal taste can be restored if it is left at room temperature for several days before use.
Potatoes must not be allowed to freeze.
Cellar
Most modern homes have several good storage areas for vegetables. The ideal place is a cellar in which tubers are stacked in heaps. Better to store in several small piles.
In stacked potatoes, the bottom layer is often damaged by pressure from the weight of the top layers. In addition, ventilation does not reach the center and the product becomes very hot, which reduces quality and shortens shelf life.

Can put tubers in small plastic buckets, which are overlaid with a layer of wet sand, boxes or baskets. Paper or perforated bags work well.The use of racks on which the tubers are stacked ensures good air circulation.
Refrigerator
Storage in the refrigerator (typically at 2 -5 ° C) undesirable... Cold temperatures convert starch to sugar, resulting in a sweet taste and discoloration during cooking. Warming the potatoes at room temperature for some time before cooking will reduce this effect.
Perforated plastic or paper bags in which the potatoes are placed provide an environment for extending shelf life in the refrigerator.

Losses are mainly caused by such processes as respiration, changes in the chemical composition and physical properties of tubers, damage at extreme temperatures. All mentioned losses depend on storage conditions.
Air circulation, atmosphere composition, relative importance (85-95%) are well controlled in the vegetable store, which is pretreated with germination inhibitors and equipped with mechanical ventilation.
What sub-zero temperature the culture can withstand, and at what freeze
Direct frost damage occurs when ice crystals form inside the protoplasm of plant cells (intracellular freezing). The extent of the damage depends mainly on how quickly the temperature drops. At a slower pace, ice formation is extracellular and the plant has a chance to recover.
The vapor pressure above ice is lower than that of water. As a result of extracellular ice formation, water evaporates, passes through semi-permeable cell membranes and settles on ice crystals outside the cells.
When water is removed from the cells, the concentration of the solute increases, which reduces the likelihood of freezing... But as the ice continues to grow, the cells dry out more and more. In damaged plants, extracellular ice crystals are much larger than the surrounding dead cells, which causes secondary stress to the surrounding cells.
With prolonged exposure to the freezing effect the plant dies completely... In an adult plant, the processes of biosynthesis (assimilation) stop at 2-4 ° C, as a result of which the tops turn brown. The plant freezes at a minus temperature of −2 ° C.
The slope of the ground affects the severity of the frost. Potatoes growing at high levels experience warmer temperatures and less frost damage. Conversely, when planted in a lowland, it finds itself in microclimatic conditions known as frost pockets that collect cold air.

At what temperature will potatoes freeze in the ground in spring?
Potatoes are planted in April, when the ground is thawed, dried and warmed up enough. When planted in soil with a temperature of less than 6 ° C, some of the tubers may rot and die. Unexpected late frosts can damage seedlingswhen the green foliage turns black.In the ground, the potatoes will not suffer, but only if the upper part survives. Early stands exposed to long periods of cold weather die for other reasons:
- cold and humid conditions delay germination and cause crushing of seeds;
- light frosts, around 0, -2, cause little harm to potato plants, but the difference between light frost and severe frost is only a few degrees;
- temperatures of -2.5, -3.5 cause serious damage to potatoes.
Mulching potatoes
Potatoes grow best in rich, loose soil. It helps to create it using organic mulch... Reasons for using mulch include preserving soil moisture, improving fertility and health, reducing weed growth and enhancing the visual appeal of the area.
What are the advantages of potatoes from being under mulch
In hot summers, mulching is a factor in plant survival. The practice of mulching has a huge impact on the moisture consistency of the soil. Potatoes are especially susceptible to excessive temperatures and irregular soil moisture.
A good thick layer of organic mulch helps to keep it in optimal condition in hot and cold weather.
By the beginning of the growing season mulch keeps the soil warm, which is especially important at night. As the potatoes grow, it stabilizes the temperature and moisture of the soil and prevents the growth of weeds.
The mulch effect is complex. It forms a layer between the soil and the atmosphere, preventing sunlight from reaching the surface, thereby reducing evaporation. On the other hand, it can prevent water from entering the soil by absorbing it.

How to plant potatoes under cut grass mulch
Cut grass for mulch best mixed with tree leaves or coarse compost to ensure aeration and decomposition of the material without rotting. Freshly cut grass can damage the plant, decomposing leads to a destructive accumulation of heat, blocking the circulation of air and moisture, so it is better to dry it before use.
Comparison of mulch, cut grass and straw
| Cut grass | Straw |
| Mixed with dried leaf litter makes good compost with a healthy balance of nutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium; this dramatically reduces the need for artificial fertilizers). | Controls humidity and reduces high-temperature stress to plants, but is more vulnerable to frost and wind. |
| Decomposes quickly due to the correct ratio of carbon and nitrogen, which also helps to avoid problems such as mold, unpleasant rotting smell. | Controls weedsbut at the same time there is a possibility of seed (weed) contamination. |
| Fresh grass has a relatively high nitrate content and most of it returns to the soil. Do not apply too thick a layer, as the cut grass decomposes into slimy cellulose, which is very hot and can burn the plant. | Mostly carbon. Dries nitrogen from soil and therefore should be mixed with grass, manure, compost to minimize losses. |
| Microbes can suck nitrogen and others nutrients from the soil in the process of decomposition, for this reason, a little fertilizer is added to it, compensating for the loss. | Ideal environment for slugs, attracts mice, voles. |
The benefit of any mulch is high yields and easier potato harvesting.

Growing potatoes under mulch
Any biodegradable material works. But the most preferred method for growing high-yield potatoes is with freshly cut grass or straw mulch. They keep the soil cool and moist while keeping out the Colorado potato beetle and other crawling insects.
Potato needs a thick layer, unlike other vegetable crops. Every few weeks it is checked for gaps and another layer is added.
To get the best results from mulching potatoes, you need to:
- Loosen the soil well.
- Prepare an area for planting. Dig a furrow about 10 centimeters deep and 25 centimeters wide four to six weeks before the last frost.
- Mix the garden compost thoroughly (it prevent soil compaction after landing).
- Plant seed tubers, cut side down (or whole), with eyes upward, about 30 cm apart. Whole tubers are pressed into the soil about 8 cm, cut - 2 cm deep.
- Fill the furrow with 15 cm of clean straw.
- When the plant breaks through the covering litter, add another layer 10 cm thick.

Water as needed, keeping the soil evenly moist, but not soggy. In this case, you do not need to remove the mulch.
Watering potatoes
Water is a vital ingredient in potato production, essential for both yield and quality. Irrigation at the beginning of the growing season minimizes common scab, stimulates the growth of the bush, and maximizes the number of tubers.
At the end of the season helps to harvest crops with minimal losses... But water must be applied in sufficient quantities and at the right time to achieve a good harvest.
Watering features
Regional climatic conditions, weather, soil conditions affect planting timing.

The depth of root formation of potatoes may vary, but optimal is usually 700 mm... Reduces the ability of the roots to find water in the soil in compacted soil, and accordingly affects the recommendations for irrigation planning.
Moderately acidic soil is preferred, but this is not essential as potatoes are adapted to a wide range. A furrow is dug 10 centimeters deep, where the tuber with the buds pointing up is placed and covered with soil.
If necessary, fertilizer can be scattered from above. So, when growing potatoes in an alkaline medium, sulfur is used after planting, which maximizes germination and eliminates common scab.
Do I need to water the potatoes when planting
Potato - moisture-loving culture, but when planting it is not watered. Planting is preferable in an open and well-lit position, in fertile, evenly moist, well-drained soil.
The need for water is provided by the mother tuber. On the contrary, additional watering can cause rotting.

When to water after planting
Potatoes need a steady, seasonal supply of water, but this is important 6-10 weeks after planting when the crop is developing tubers. The culture is usually supplied with water after germination.
Watering rules for a good harvest
Reliable watering schedule, cool soil temperatures will provide uniformly formed tubers... Both oversaturation of moisture and lack of water affect the yield, endangering the health of the plant.
The general rules are:
- to water potatoes once a week, taking into account possible precipitation, with a large amount of water, moistening the soil about 30 cm deep (minimum consumption of 50 liters per 1 square meter (or about 3-4 liters per bush), but in fact it all depends on the characteristics of the soil );
- a young plant is watered more often - once every 4-5 days;
- increase the frequency, once every 2-3 days, when the tubers begin to form (this happens almost simultaneously with the flowering of the plant);
- by the end of the growing season, when the tops turn yellow and begin to die off, watering is stopped, which will allow the tubers to dry out before harvesting.
Uneven watering causes growth and cracks in the tubers. This is due to the fact that with an insufficient amount of water, they do not develop, but with subsequent abundant irrigation, a second (new) growth occurs.
How often potatoes are watered outdoors
Potatoes need a lot of moisture, especially during the flowering period, when tubers begin to form. If Mother Nature is reluctant to provide the water needed, then some type of irrigation system may be needed (drip irrigation is a big advantage).
Watering in the heat: how often to water
In dry time, the plant it is advisable to water at least once a week... It is better to do this in the evening and in two sessions. An occasional heavy watering is sometimes better than a lack of frequent watering, which only moistens the surface layer of the soil, stimulating shallow rooting.
After watering, you can loosen the soil. Brings its effect and irrigation.

How to water so that the tubers are not covered with scab and other ailments
It is preferable to water the plant in the early morning hours. The afternoon sun evaporates the water. A plant that remains wet at night is susceptible to disease.
Warm, wet foliage encourages mushroom growth and weakens the structure of the plant as a whole... In addition, watering should be directed to the roots where it is needed the most, not to the top of the plant.
How many times to water potatoes per season
Moisture requirements in April-September vary depending on factors such as climatic conditions and soil type. Watering at certain stages of growth:
- Planting and watering up to 30 days: Pre-emergence watering is avoided if the soil is dry before planting (pre-irrigation should always be considered). Young plants (after germination) receive the first watering after about 5 days.
- 30-60 days: Moisture is critical for vegetative growth and tuber formation.
- 60-90 days: proper and thorough watering is necessary for the growth of tubers.
- 90-120 days: the tops turn yellow and die off. Watering about a week before harvest can still be continued, but in moderation.

How to understand that you need watering
The rate of moisture absorption by crops is highly dependent on the weather. Potatoes are a small-rooted plant, sensitive to even slight water deficiencies (in the root zone). Whenever it is exposed to moisture deficits, the growth rate is reduced.
The soil is stored with water with heavy rainfall after watering irrigation.Well-structured, porous soil, like loam, is capable of passing up to 100 mm of water per hour. Compacted heavy soil (clay) is limited to 5 mm per hour.
Signs of excess and lack of moisture
The consequences of the practice of improper watering lead to the fact that the plant is exposed to stress, which continues for several days after the problem is eliminated. An excess of moisture promotes decay and increases the risk of disease. On the contrary, a lack of moisture when the soil dries up completely stops the formation of tubers or leads to the development of various defects.

Potatoes are one of the healthiest vegetable crops. It grows easily, requires a little preparation, a little maintenance, and even pleasure at harvest time.


