Content
- 1 Keela cabbage and other most common diseases and pests
- 1.1 The most common cabbage diseases
- 1.1.1 Keela cabbage what to do to protect the plant
- 1.1.2 Prevention of Alternaria
- 1.1.3 White rust
- 1.1.4 How to treat powdery mildew
- 1.1.5 Peronosporosis
- 1.1.6 Rhizoctonia drugs
- 1.1.7 Late blight
- 1.1.8 How to save seedlings from a black leg
- 1.1.9 Leaf spots or fusarium wilting
- 1.1.10 How to deal with bacteriosis
- 1.2 Insect pests of cabbage in the open field
- 1.3 Protection of cabbage from diseases and pests
- 1.1 The most common cabbage diseases
Keela cabbage and other most common diseases and pests
The agricultural technology of cabbage is not much different from the rules for growing other vegetable crops, but getting a good harvest of heads with healthy leaves is very difficult. The plant is literally attacked by various pests and diseases, including such as: keela, powdery mildew, late blight, peronosporosis and many others, which is explained by its moisture and thermophilicity. How to deal with them in order to protect the plant from death and grow a good harvest, you will learn from the article.
The most common cabbage diseases
The article will discuss the diseases that affect cabbage beds. Having become familiar with the characteristic signs and methods of treatment, the gardener can, if necessary, quickly localize the problem and prevent the virus or infection from spreading to other plants. Each disease is dangerous in its own way, so it is not worth delaying the treatment. Otherwise, you can not only receive less harvest, but also completely lose it.

Keela cabbage what to do to protect the plant
The disease is also known as root cancer. The first signs of the disease appear on the wilting leaves, which acquire a yellowish tint. But the biggest changes occur in the root system, which is found only after digging up the bush. Growths are formed on the kocherezhki, outwardly, the impression is made of swollen roots. The danger of the keel is incurable and it will not be possible to save the affected plant, it should be removed from the garden and disposed of, and the soil should be treated with Bordeaux liquid for disinfection.
The cause of the development of root cancer is a fungus that actively develops in a humid environment. Cabbage needs moisture, but watering rates should be carefully monitored to avoid stagnant water in the soil.
As a preventive measure, it is necessary to enrich the soil with calcium-containing fertilizers, colloidal sulfur, wood ash.
Prevention of Alternaria
The disease affects seedlings and adult culture, manifests itself in the form of necrotic stripes and black spots that can appear on the cotyledons and hypocotyledonous knees. On the formed head of cabbage, the spots densely cover the outer leaves, on which a soot deposit can be found, indicating the sporulation of the fungus.
When Alternaria is detected, colloidal sulfur and other sulfur and copper-containing agents are used. As a preventive measure, the rules of crop rotation are observed, seeds are disinfected before planting with planriz, TMTD.
- Powdery mildew of cabbage
- Alternaria on a head of cabbage
- White rust
White rust
High humidity and low temperature can provoke the development of the disease. When mushrooms mature, a powdery white coating appears on the outer leaves of cabbage.If detected, spraying with Ridomil Gold should be carried out.
How to treat powdery mildew
The disease can be recognized by the white bloom on the cabbage leaves, which eventually turns light brown. Affected foliage deforms and dries out. An infected plant lags behind in development. In some types of cabbage, taste may deteriorate (for example, Peking cabbage and white cabbage).
To prevent the development of powdery mildew in the fall, all plant residues are carefully removed from the beds, they plan to dig the earth closer to frost so that harmful microorganisms die. With a massive defeat of cabbage, they are treated with special preparations: Bayleton, Quadris, Tilt, Topaz, Fundazim, Fundazol.
Peronosporosis
Another better known name for the disease is downy mildew. The causative agent, the parasitic fungus Peronospora brassicae Guum, comes into an active phase of development in high humidity and warm weather. The disease can even affect seedlings. Typical signs are gray and yellow spots on the leaves, whitish bloom can be observed on the reverse side. Over time, the leaves dry out completely and crumble. You can also notice the problem by the weak development of the shoot.
To protect the crop from death, it is necessary to process the beds using special preparations: Ridomil Gold, Fitoftorin. At the initial stage of development of downy mildew, you can spray the culture with Bordeaux liquid, repeating the procedure after 10 days.
- Head of cabbage affected by late blight
- Rhizoctonia of cabbage
- Peronosporosis and its consequences
Rhizoctonia drugs
The disease can be determined by the rapid thinning of the root collar and darkening. Young shoots and adult plants are susceptible to infection. Even in the harvested crop, mushrooms continue to develop, which manifests itself in breaking off leaves and signs of rot.
If symptoms are found, it is necessary to spray the beds with Fitolavin-300. It is necessary to prepare the solution taking into account the growing season (the larger it is, the higher the concentration of the agent).
Late blight
The disease is characterized by rapid development, the affected areas on the stem quickly spread to the leaves. A characteristic feature is brown spots, rapidly increasing in size.
How to save seedlings from a black leg
A fungal disease caused by high soil moisture and poor air circulation. It appears on the stem near the root zone in the form of blackening and thinning of the neck. At the startled stage, the stem part of the bush completely rots, the lesion spreads to the entire plant.
Before planting, the seeds are processed with granosan (for 100 g of seeds, 0.4 g of the product). The soil is also disinfected with a special preparation TMTD (50%) at the rate of 50 grams. per 1 m2.
If signs of a black leg are found on cabbage seedlings, it is recommended to water the bushes with a weak solution of potassium permanganate (0.5 g of potassium permanganate per 1 liter of water).
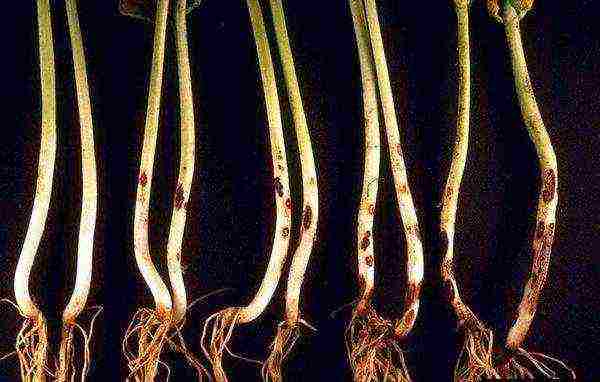
Leaf spots or fusarium wilting
A fairly common fungal disease that affects almost all cruciferous crops. Fusarium can be identified by the following signs:
- yellow spots on the leaves, their drying and withering away;
- a small head of cabbage, which is formed with various deformations.
Initially, the plant becomes lethargic, the leaves fade noticeably.
- Slimy bacteriosis on cabbage
- Fusarium wilt of cabbage
How to deal with bacteriosis
There are two types of bacteriosis: mucous and vascular. In the first case, the disease can occur in two variants, which differ in the initial zone of damage (decay starts from the stump or from the leaves).
Signs of mucous bacteriosis:
- the smell of rot;
- brown watery spots appear on the surface of the leaves;
- primary signs can be found in the stump.
The disease is transmitted by insects or through plant debris. The soil is not contaminated.
Vascular bacteriosis is recognized by the leaves turning yellow from the edges, forming a black net. The taste of cabbage changes, the shelf life is significantly reduced.
It is possible to prevent the development of bacteriosis by treating seeds before planting TMTD, observing the rules of agricultural technology and crop rotation, and thoroughly cleaning the beds at the end of the season.
Insect pests of cabbage in the open field
The humid environment and the ability to hide between the leaves of the forming head attracts insects, among which there are many pests. In just a few days, parasites can spoil the presentation of the crop, or even deprive it. Timely prevention and fast processing will help to solve the problem.
How to get rid of a cabbage fly
The pest outwardly practically does not differ from an ordinary fly. The danger is not the insect itself, but the larvae that adults lay in warm soil. As a food, parasites choose young shoots, or rather their root system. The eaten bush becomes stunted, easily removed from the soil due to the eaten roots. The lower leaves change color to gray lead.
If a pest is found, it is necessary to process the beds with Thiofos or Chlorophos. The preparations are diluted with water to the concentration indicated on the label. When spraying, it is worth observing the norms of the working solution per plant.
- Cabbage fly
- Cabbage fly larvae
- Leaf beetle babanukha close up
Fighting babanukha
A very voracious leaf beetle that activates in early June. The insect is easy to recognize - it is a black beetle with a green tint. His paws are brown. It hibernates in the soil along with plant debris.
Control measures:
- glue traps;
- collecting bugs manually;
- dusting the beds with wood ash;
- insecticide treatment.
How to protect cabbage from whitefly
It is easy to recognize an insect - it is a small butterfly with white wings. The culture is eaten by both adults and larvae.
Control measures:
- glue traps;
- spraying with garlic solution;
- processing with dandelion infusion;
- the use of special drugs (Aktara, Fitoverm, Aktellik, Confidor).
- Whitefish larvae
- White butterfly
- Whitefly on cabbage
Methods of dealing with whites
In fact, the insect is a large moth. It is activated in the daytime when it lays eggs on cabbage leaves (up to 100 eggs at a time). After about a week and a half, caterpillars are obtained from the eggs, which gnaw at the vegetable in a matter of days.
Control measures:
- processing cabbage with calcium arsenate (1.2 g per 10 m2);
- spraying the beds with chlorophos (65%);
- spraying with entobacterin (concentration 0.1-0.4%).
Fire
A small moth with brown wings becomes active in early June. Caterpillars tolerate wintering well in the soil, so gardeners recommend digging up the ground in late autumn. Pests deprived of shelter will freeze out at the first frost.
The moth lays eggs in cabbage, from which caterpillars appear en masse in a few days. Thanks to their excellent appetite, they intensively damage cabbage leaves, even internal ones.
Control measures:
- treatment with drugs (bitoxibacillin 1%, gomelin 0.5%, dendrobacillin 0.1%);
- spraying culture with ambush, bolofos, rovikurt and other means.

Protection of cabbage from diseases and pests
To prevent the development of plant diseases and the invasion of pests, it is possible, first of all, by preventive measures. The basic rules for protecting cabbage consist of the following points:
-
- seeds for planting would have to be selected in specialized stores or nurseries;
- before sowing, the planting material must be decontaminated (by soaking in a weak solution of potassium permanganate);
- a plot for a garden bed has been prepared since the fall (it is thoroughly cleaned of plant residues and dug up with the simultaneous introduction of fertilizers);
- before planting, the soil must be disinfected (watering with hot water, a solution of potassium permanganate or copper sulfate);
- timely application of fertilizers will provide young shoots with nutrients, which will strengthen their immunity and resistance to diseases;
- the soil should be not only fertile, but also loose so that water does not stagnate in it (this will prevent fungal diseases);
- if signs of a disease are found, it is necessary to remove the diseased part of the plant or the entire bush so that microorganisms do not spread throughout the garden;
- when planting and after it, the temperature regime and irrigation rates should be observed;
- if the cultivation of the culture is carried out in a greenhouse, then the surfaces of the structure must be disinfected at least 2 times a year, the soil is periodically replaced with a new fertile layer (after infection of the cabbage, the soil is completely replaced).
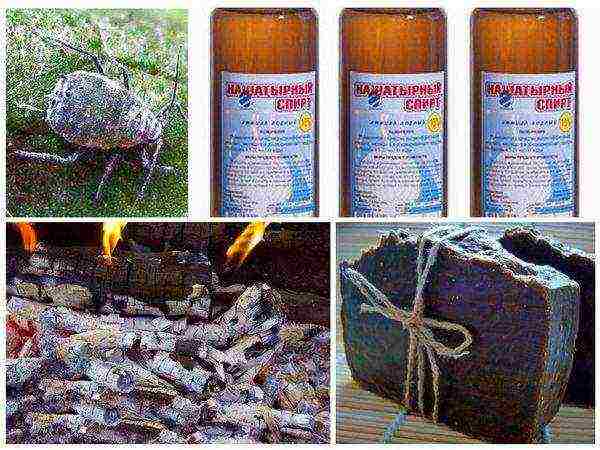

Folk ways to combat cabbage pests - For the prevention of diseases, the following means are used:
- spraying with an ash solution, an infusion of chamomile, onion husks, a decoction of tomato tops, wormwood and other plants;
- dusting with wood ash, crushed chalk, lime;
- treatment of the garden with Bordeaux liquid, colloidal sulfur solution, Hom, Energen, Fitoflavin, etc.
Chemicals are used only for extensive plant damage. When choosing a product, preference should be given to options developed on biological substances.Cabbage is an incredibly healthy and delicious vegetable. To get a good, and most importantly healthy harvest, it is worth spending time and effort, then in winter the body will not suffer from a deficiency of vitamins and minerals.


