Content
- 1 How to properly deal with late blight of potatoes
- 1.1 How to fight
- 1.2 Three-fold processing scheme for landings
- 1.3 Late blight disease
How to properly deal with late blight of potatoes
Late blight occurs on green parts of plants: stems, leaves, peduncles, and also affects tubers. The disease affects potatoes more intensely in high humidity and moderately warm weather. Of course, vegetable growers want to get rid of the disease in a short time and save plantings in the future.
How to fight
You can fight the disease in various ways: this and chemical means of protecting potatoes and folk... Consider what are the main methods of combating and preventing the appearance of late blight.
Preparations and processing times before planting
The soil may contain vegetation contaminated with fungal spores. In order not to spread the infection, in the spring, before planting, the soil is watered with Bordeaux liquid or a solution of copper sulfate (1-3%), then the earth is dug up.
The composition is prepared on the day of planting., and mix it before spraying. Place the solution in a sprayer and spray the sprouted potatoes, wait 1-2 hours, then plant the tubers. It is advised to deliver tubers to the planting site in closed bags.
You can instead of him treat with Maxim.
- Copper sulfate
- Maxim drug
What to process - seeds or tubers
Usually, when planting, it is the tubers (and not the seed for planting) that are sprayed with a drug for late blight.
How to protect potatoes from late blight after planting
To protect the culture from disease, formulations with copper are used, for example, Bordeaux mixture 1% (it is prepared by pouring 100 g of copper sulfate, 100 g of lime into a ten-liter bucket of water).
The intervals between sprays are 7-10 days. The last spray is 21 days before harvest.
Simultaneously with spraying with Bordeaux mixture, no other fungicides can be used.

Means of preventing potatoes from late blight
Then:
- Isolate healthy bushes from the sick, including collecting garbage, pulling out weeds, this will delay the appearance of the disease on the stems and leaves until the time of bud formation.
- Pick only healthy potatoes for planting.
- Treat seed tubers with fungicides.
- Observe the crop rotation: potatoes are planted a year, after 2 years lupines, beans, beans, and then again potatoes.
- If you huddle the bushes high, this will partially protect them from secondary infection.
- Sanitary measures - moisture stagnation is unacceptable; do not water the potatoes by sprinkling in the evening, otherwise dew will appear in the morning; pull out weeds in a timely manner.
- Avoid excess nitrogen.
- Mow the tops a week before harvestif you plan to use potatoes, and 10 days in advance if you plan to plant tubers in the future.
- Harvest when there is no rain, then dry the potatoes for 5 hours. Dig up the aisles 5 days before harvest. This makes it easier to harvest potatoes and removes weeds.
Fungicides for potatoes
Contact fungicides
Should remain on the plants, when the pathogen comes into contact with them, it will die.
Table 1... Contact fungicides against late blight and application rate
| Fungicide | Rate kg / ha |
| penncoceb | 1.1—1.6 |
| Bravo | 2—2.3 |
| novozir | 1.6 |
| Cupricol, copper oxychloride | 2.4—3.2 |
| cuprosat | 5.0 |
| utan | 1.2—1.6 |
| shirlan | 0.3—0.4 |
| bordeaux mix | 3.0 |
| abiga peak | 2.9—3.8 |
- Penncoceb
- Cupricol
- Cuproxat
- Shirlan
- Abiga Peak
Translaminar
They spread only in places of irrigation, penetrating the tissue of leaves. This is the Acrobat, Kurzat.
Systemic
Already after 2-6 hours from the time of treatment, the rains will not diminish the effect of their action. And they clean the pathogen for 2-3 weeks. But pathogens develop resistance to them.
Therefore, it is advised apply them 2 times per season... And if more spraying is needed, then you can use contact preparations or a systemic fungicide with a completely different composition.
Systemic contact
table 2... Systemic contact fungicides and their dilution rate
| Fungicide | Norm |
| Thanos | 0.6 l / ha |
| Acrobat Mts | 50gr. for 10 liters of water |
| Tattu | 100 ml. for 10 liters of water |
| Ridomil Gold | Not more than 2.5kg / ha
50gr. for 10 liters of water |
- Thanos
- Acrobat MC
- Tattu
- Ridomil Gold
Folk remedies
Trichopolus
Purchase the medicine at the pharmacy, dissolve 1 tablet in 1 liter of water. Spray the bushes every 2 weeks.
Wood ash
When the potatoes come up, sprinkle the aisles with ashes. When the potatoes bloom, then repeat.
Milk with iodine
Pour 1 liter of skim milk into a ten-liter bucket of water, add 15 drops of iodine. Solution spray the bushes every 14 days.
- Trichopolus
- Wood ash
- Milk with iodine
Means for fighting homemade
Infusion of garlic with potassium permanganate
Spray the bushes with the solution every 2 weeks. Pour half a liter onto the bush.
Milk serum
Add the same amount of water to the whey from sour milk and spray the bushes every 2-3 days.
Three-fold processing scheme for landings
It means that plantings are processed 3 times:
- From the emergence of seedlings to the closing of the tops in a row, they use - Shirlan, Tattu.
- From the closing of the tops to the blooming of the buds, they use - Ridomil Gold, Infinito.
- From the appearance of flowers to the wilting of the tops - Acrobat Mts.
Late blight disease
What is potato late blight
Potato late blight is a dangerous disease arising from the spread of the fungus, it develops very quickly, and as a result, yields are greatly reduced.
Signs of late blight
With precipitation, spores from the leaves fall on the ground, then on the tubers, secondary damage occurs.

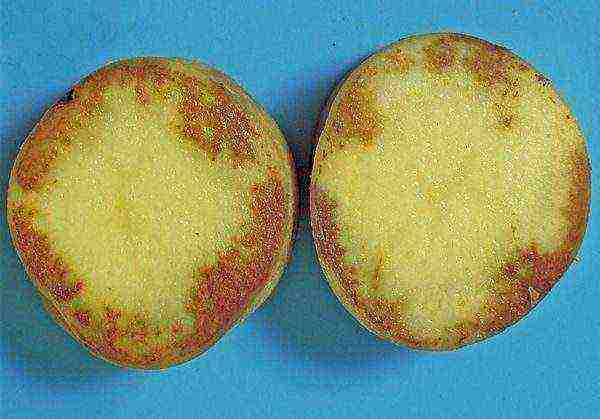
Phytophthora on tubers, primary lesion: small gray spots are visible, they grow and merge into darkish areas of the pulp, the peel becomes reddish-brown.
Secondary damage to tubers: they rot, decompose, have an unpleasant odor, then become soft. The disease can affect the very center of the tuber and in winter, when the fungus begins to multiply, it becomes visible.
What is the causative agent of late blight
Causative agent — pathogen oomecitis of the species Phytophthora infestans. It is assumed that he originally from mexico.
There are 2 strains of the disease: A1, it does not form spores capable of overwintering; A2 has spores that are frost resistant. When crossing oomecytes, new strains appear that are resistant to frost and fungicides.
Late blight and late blight - is there any difference
From late blight mushrooms, the disease itself appears - late blight. She can have tomatoes, peppers, potatoes, eggplants, buckwheat, strawberries.
- Late blight of tomatoes
- Peppers with late blight
- Eggplant affected by late blight
Why fight late blight
Late blight spoils every year 10—15% of harvested tubers, in the years of epitaphs — up to 70%.
The smallest temperature at which the disease is observed — 1.3 ° C, the biggest is + 30 ° C. The incubation period lasts depending on the air temperature 3—16 days.
Fungal spores multiply more intensively at a temperature of + 10 ° C and ambient humidity 75%. Spores of the fungus are transferred by wind and rain from one plant to another. The wind carries the spores 2-3 km from the initially affected plant, this has been proven.
And remember that it is better to carry out preventive measures so that the plants do not get sick with late blight, than to eliminate the disease and eliminate the consequences!


