Content
Potatoes diseased with scab lose about 30% of starch, their taste becomes worse, and they are stored for much less time. Since the diseased potato is in the ground, it is impossible to immediately notice and cure the disease when the potato grows. Because of this, it is very important to carry out disease prevention activities.
Scab is a disease caused by a fungus, usually more common affects tubers, sometimes the roots and part of the stem that is underground.
How does it manifest on potatoes
Scab on potatoes is divided into 4 forms: ordinary, silvery, powdery and rhizoctonia (black scab).
Ordinary
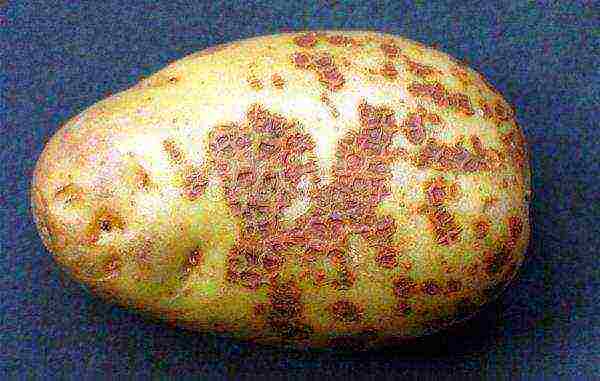
Fungal spores penetrate into tubers through cracks in the peel. During storage, potatoes do not become infected, since in unfavorable conditions the pathogens are dormant, but do not die.
Common scab mainly lies on potatoes with a scarlet or thin skin. If you plant potatoes deep in the ground, water intensively during the growth of tubers, then the risk of getting sick is reduced.
Symptoms: visible on tubers hard ulcers of irregular shape, ulcers can cover the entire potato, or cracks are visible on the sore spots on the peel.
Silvery
It often appears if potatoes are planted in sandy loam and loam, the optimum air temperature for the disease is 18-20 degrees, and the humidity is also increased - 85-100%.
The fungus enters the tubers through the ground, then spreads to the rest of the potatoes. The difference between this form and others - diseased tubers do not rot in storage, but only lose moisture.
Symptoms: the peel wrinkles, a silvery color appears on the diseased areas, this is especially clearly seen on varieties with a scarlet peel. Gradually, brownish-gray spots grow, sometimes they look depressed.

Powdery
She most common, it is a fungal pathogen that is able to move. The disease occurs on tubers, roots and the underground part of the stem.
When placed in storage, diseased potatoes dry out, but if there is excess moisture in the environment, then the potatoes rot. Often on sick potatoes, late blight and dry rot are added to the scab.
Sources - soil, diseased seed potatoes and manure (when feeding cattle with diseased potatoes, fungal spores do not lose activity even after passing through the digestion of a cow). The disease occurs on heavy lands with excess water, at a temperature of 12-18 degrees.
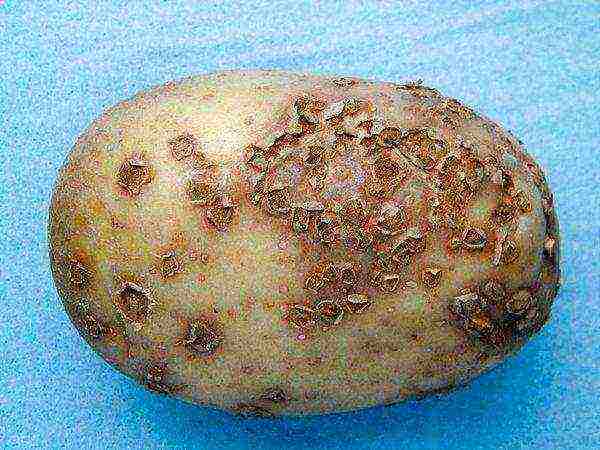

Symptoms: whitish growths are visible on the roots, having a varied shape, they gradually turn brown. On a sick tuber, warts and various spots are visible. After some time, the diseased areas dry up, after which ulcers burst and appear, a gray-brown substance is visible in them - spores. More potatoes will rot.
Rhizoctonia (black scab)
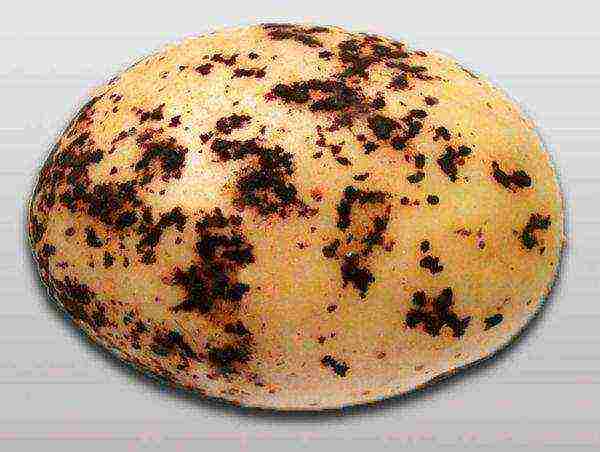
It can hit potatoes with high humidity and an air temperature of 17 degrees, if precipitation often occurs in spring, and cold weather. Harvest losses from black scab - 20—25%.
Symptoms: black spots on tubersresembling earth, they cannot be washed off the tubers and are difficult to scrape off, but they do not harm the tuber. Sick bushes wither during the day, grow low, they have twisted leaves. If it rains and it is warm, then a "white leg" is visible on the stem.

Where does the disease come from and how it develops
Reasons for the appearance:
- Affected land.
- Sick tubers, on which the disease is not visible, but the fungus is located, since it is not visible during the initial spread.
- An excess of nitrogen in the earth stimulates the development of scab.
- If you plant potatoes in one place from year to year, then diseases will accumulate in the ground.
- High ground temperature.
- The earth has acidic properties.
- Fertilizing the soil before planting potatoes fresh manure.
How to fight
Fungicides
Maxim Is a contact fungicide. By killing the fungus, Maxim preserves the useful microflora of the earth. Add 4 ml of Maxim to 0.05-0.1 l of water. Use when processing 10 kg of tubers.

To get rid of the disease, tubers are sprayed before planting:
- 13 g of Agata25K is added to 1 liter of water, this composition is enough for 100 kg of potatoes;
- 10 g of Fitosporin M is dissolved in 5 liters of water, this rate is used for 20 kg of tubers;
- 10 drops of Crezacin drip into 2 liters of water, use this composition for 40 kg of potatoes.
Bushes are sprayed with phytosporin 3 times per season, add 3 liters of water to 1 package of the drug, then spray it.
Take 25-50 g of Cuprosat, add to a ten-liter bucket of water, spray the bushes. The bushes are treated the second time after 10 days, but no later than 20 days before digging the bushes.
Bushes are also sprayed with drugs Albit, Kolfugo, Acrobat MC, Mancozeb, Profit Gold, Fenoram super, Ordan.
-

- Mancozeb - Chinese development for spraying scab bushes
-

- Ordan - Russian fungicide
Prophylaxis
- For planting, select absolutely healthy tubers... Treat the tubers with special compounds before planting.
- Change the place of planting of potatoes every year, plant potatoes after beans, peas, beans. Do not use fresh manure as fertilizer.
- If you have alkaline soil, make it more acidic by adding a solution of 2 tbsp. tablespoons of ammonium sulfate in a ten-liter bucket of water and spill the area. When flowering under one bush, pour 0.5 l of the solution.
- 14 days before digging up potatoes mow the tops.
- The potato storage room should be dry and cool.
Which potato varieties are considered highly resistant to disease
-

- Alena - early scab resistant variety
-

- Variety Snow White - medium early, not subject to infection
- Alyona - early variety. The tubers are oval, they have a scarlet rind and snow-white flesh. Potatoes are resistant to scab, cancer, drought. But it is not resistant to late blight, it will have to be fought with.
- Snow White - mid-early grade. Good and long-term storage. Has resistance to scab and late blight. Oval tubers have a yellowish peel and snow-white flesh, tiny eyes.
- Resource - mid-season. Resistant to drought and heat. Almost not susceptible to viral diseases, scab. Resistant to mechanical damage. Oval tubers with beige skin.
- Lasunok (Lasunak) - medium late, introduced in Belarus. He has excellent taste, high yield. It is resistant to scab, it is practically not affected by the Colorado potato beetle.
- Pace - late. Large, round-flat in shape with a creamy peel and creamy pulp, it tastes great. Scab resistant.
In order for the potatoes not to be affected by scab, it is worth choosing special varieties for planting that are resistant to this disease, and also not to neglect prevention.