Content
- 1 Japanese gladiolus (crocosmia): species
- 2 Japanese gladiolus (montbrecia): description
- 3 Growing conditions
- 4 Montbrecia in the garden
- 5 Planting and storing bulbs
- 6 Reproduction methods
- 7 Characteristic features of the plant
- 8 Choosing a place for planting a flower
- 9 Planting bulbs
- 10 Planting Japanese gladiolus seeds
- 11 Care advice
- 12 Bulb care in winter
- 13 Disease and pest control
- 14 And a little about secrets ...
- 15 Crocosmia: general description, varieties, photos
- 16 Crocosmia: planting and care in the open field
- 17 Reproduction of crocosmia
- 18 Diseases and pests
Japanese gladiolus is a beautiful garden plant of the iris family, characterized by orange-red bell-shaped flowers, collected in paniculate inflorescences, and a fan-like bundle of pointed hard leaves. A feature of montbrecia (as a garden plant is also called) is its similarity with iris and gladiolus; if on a gladiolus the flowers are quite densely clinging to a peduncle that looks like a huge ear, then in the Japanese gladiolus they grow branched.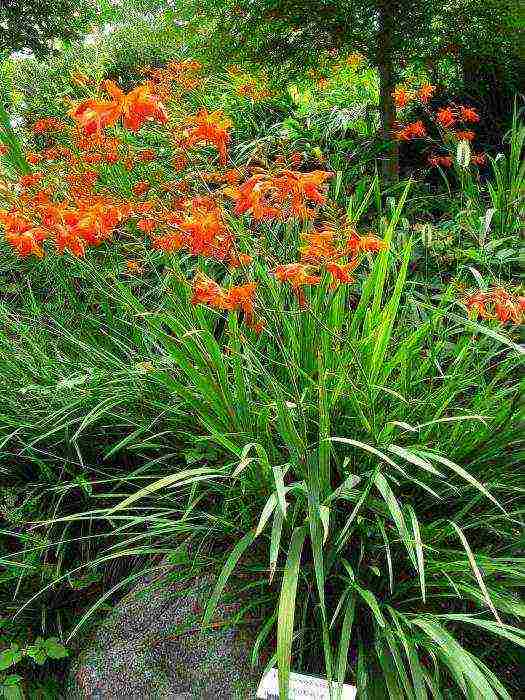
Japanese gladiolus, planting and caring for which give gardeners a real pleasure, has about fifty species, most of which are from South America, and has another name - crocosmia, derived from "crocos" and "osme" - smell.
Japanese gladiolus (crocosmia): species
- Crocosmia Panikulata is an early flowering tall plant with medium-sized bright orange flowers. Compared to the rest, it is the most frost-resistant species, tolerating wintering well, provided that a small shelter is provided.
- Crocosmia Lucifer is a hybrid created on the basis of Paniculat crocosmia. The flowers are coral-red. Frost resistance is relative.
- Crocosmia Golden. It is characterized by large (about 5 cm in diameter), yellow-orange flowers. Able to grow in small shade. The flowering period is autumn. Looks great when cut.
- Crocosmia ordinary. The most common hybrid of the Japanese gladiolus in culture, obtained by crossing the crocosmia Pottsi and Golden. Plant height is about 1.2 meters. Flowering occurs at the end of the summer period.
Montbrecia is characterized by high resistance to pests and diseases; needs minimal maintenance: watering, weeding, feeding and removing weeds.
Japanese gladiolus (montbrecia): description
Montbrecia has small corms (about 2 cm in diameter), covered in several layers with reticular membranes; one unit per season gives 3-4 beautiful peduncles and several replacement bulbs. The stem height is about 0.6-1.0 meters. The leaves are collected in a rosette, which gives the montbrecia a special appeal. Small flowers (about 3-4 cm in diameter) are funnel-shaped, with petals diverging to the sides. The blooming of the plant occurs gradually, one by one, from the base to the top, due to which, from the beginning of flowering (July-September) to late autumn, the Japanese gladiolus looks elegant. In the simultaneous flowering, about 10 flowers are revealed. The plant is not suitable for wintering in the open field.
The stem height is about 0.6-1.0 meters. The leaves are collected in a rosette, which gives the montbrecia a special appeal. Small flowers (about 3-4 cm in diameter) are funnel-shaped, with petals diverging to the sides. The blooming of the plant occurs gradually, one by one, from the base to the top, due to which, from the beginning of flowering (July-September) to late autumn, the Japanese gladiolus looks elegant. In the simultaneous flowering, about 10 flowers are revealed. The plant is not suitable for wintering in the open field.
Growing conditions
Japanese gladiolus (the photo conveys all the charm and bright orange beauty of a garden plant) feels comfortable in loose, well-drained, humus-rich soil.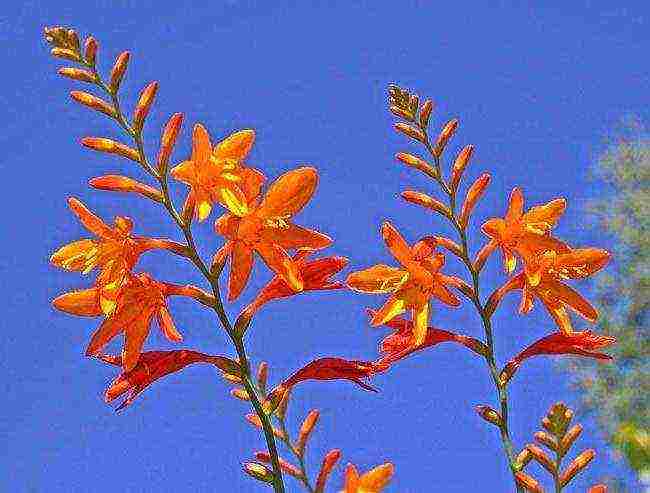  It is advisable to choose a place for landing that is well-lit, without drafts and sunshine on a summer afternoon. You should not plant the montbrecia in the shade, otherwise the plant will begin to stretch and will not bloom at all.
It is advisable to choose a place for landing that is well-lit, without drafts and sunshine on a summer afternoon. You should not plant the montbrecia in the shade, otherwise the plant will begin to stretch and will not bloom at all.
Since the fall, the site on which it is planned to grow Japanese gladiolus needs to be prepared by adding organic fertilizers to the soil in combination with slaked lime and superphosphate. Before budding, and then every 2-3 weeks, Japanese gladiolus, the cultivation of which is not too troublesome, is recommended to be fed with mineral fertilizers.
Montbrecia in the garden
Japanese gladiolus (photo can be seen in the article) is a flower that looks attractive in rock gardens and against the background of undersized flowers.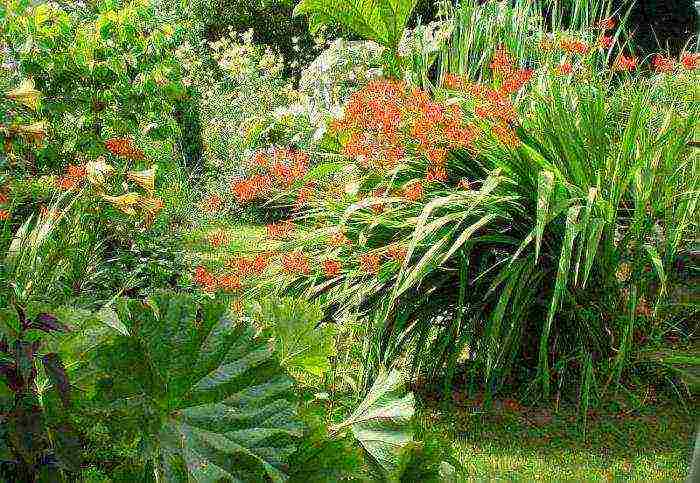  The plant is suitable for cutting, the inflorescences stand in water for about 10 days or longer. Dried flowers retain their color and shape well, therefore they can be used to decorate a winter bouquet.
The plant is suitable for cutting, the inflorescences stand in water for about 10 days or longer. Dried flowers retain their color and shape well, therefore they can be used to decorate a winter bouquet.
Planting and storing bulbs
Montbrecia bulbs are planted in April-May to a depth of 6-10 cm with an interval between plants of 10 to 12 cm.In the still rather cool ground, Japanese gladiolus will first form a root system, and as the soil warms up, it will actively begin to build up the aboveground part. When planted at a later date, the flower will immediately grow and will not have time to acquire good roots, which will negatively affect its appearance. The bulbs are dug up.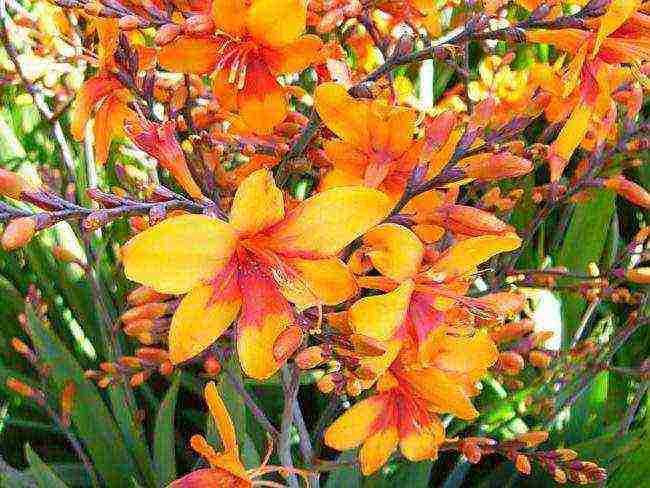  After digging out the bulbs, which is required after the leaves turn yellow (at the end of September-October), the stem is carefully trimmed, leaving 5 cm of its length at the root. Then the bulbs with children should be dried in a cool room (cellar or basement) at a temperature of 6-8 ° C for 1-2 weeks, folded in containers with dry peat, moss or sawdust. Before the spring planting, carried out in March, the bulbs are recommended to be kept at room temperature for several days, after which preparatory actions such as separating the children, peeling off the husks, pruning the roots and the remnants of the shoot are performed. Before planting, the bulbs should be held in a light solution of potassium permanganate for several hours. The plant must be planted in containers, and in May, transplanted to a permanent place of growth in open ground.
After digging out the bulbs, which is required after the leaves turn yellow (at the end of September-October), the stem is carefully trimmed, leaving 5 cm of its length at the root. Then the bulbs with children should be dried in a cool room (cellar or basement) at a temperature of 6-8 ° C for 1-2 weeks, folded in containers with dry peat, moss or sawdust. Before the spring planting, carried out in March, the bulbs are recommended to be kept at room temperature for several days, after which preparatory actions such as separating the children, peeling off the husks, pruning the roots and the remnants of the shoot are performed. Before planting, the bulbs should be held in a light solution of potassium permanganate for several hours. The plant must be planted in containers, and in May, transplanted to a permanent place of growth in open ground.
Reproduction methods
Japanese gladiolus, planting and caring for which does not require much effort, can be grown from seeds, babies and corms. In order to obtain seeds, the montbrecia bulbs are planted in March in a flower pot, all summer the flower is kept outdoors (without transplanting), in the fall it is again brought into the room. It is required to wait for the completion of its flowering and ripening of seeds, which are sown on seedlings in February. Young plants of Japanese gladiolus are recommended to be hardened before planting in open ground (in early June). The flowering of Japanese gladiolus grown from seeds begins in the third year. It is more convenient and less laborious to reproduce by children, of which the Japanese gladiolus produces 5-6 pieces per year. Montbrecia planted in this way bloom in the year of planting.
Planting and caring for montbrecia in the open field will not cause difficulties for amateur gardeners. The plant takes root easily. It is unpretentious and tolerates drought well. With minimal effort, you can enjoy the lush bloom of the original perennial. Bright, exquisite flowers will complement the landscape design. They will become the highlight of any type of flower bed. Dry inflorescences will delight you with a pleasant sweet-tart aroma with a slight bitterness, reminiscent of the smell of saffron. This similarity is due to the kinship of plants. Montbrecia and saffron belong to the Iris family.
Planting and caring for montbrecia in the open field will not cause difficulties for amateur gardeners. The plant takes root easily. It is unpretentious and tolerates drought well. With minimal effort, you can enjoy the lush bloom of the original perennial. Bright, exquisite flowers will complement the landscape design. They will become the highlight of any type of flower bed. Dry inflorescences will delight you with a pleasant sweet-tart aroma with a slight bitterness, reminiscent of the smell of saffron.This similarity is due to the kinship of plants. Montbrecia and saffron belong to the Iris family.
Characteristic features of the plant
Despite belonging to the Iris family, the montbrecia outwardly resembles a miniature gladiolus. Narrow pointed leaves of a xiphoid shape are collected in a basal rosette. Thin peduncles rise above them, reaching a height of 1.5 m. In late June-early July, the first buds appear on them. They bloom alternately, giving the plant an attractive appearance throughout the entire flowering period (July to September).
 Clairvoyant Baba Nina named the signs of the zodiac, on which money will fall from the sky in May 2018 ...
Clairvoyant Baba Nina named the signs of the zodiac, on which money will fall from the sky in May 2018 ...
►

4-5 colors similar to stars are revealed at the same time. They can be colored pink, white, golden yellow, juicy orange or scarlet. The diameter of the flowers reaches 5 cm. They are collected in dense paniculate inflorescences.
For its resemblance to the gladiolus, the montbrecia is called the Japanese (or Chinese) gladiolus. The plant is a bulbous hybrid obtained by crossing the Potts crocosmia and golden crocosmia. Flowers are native to South Africa.
The montbrecia has small flattened corms, similar to the roots of gladiolus. Their diameter is about 2-2.5 cm. The corms are covered with several layers of reticular membranes. During the warm period, several new replacement bulbs develop.

Plant care is not much different from the conventional gladiolus agricultural technology. Its corms are also recommended to be dug up and stored indoors during the winter under certain conditions.
Choosing a place for planting a flower
For montbrecia, you need to choose an open place, well-lit by the sun. You can plant the plant in areas that receive direct sunlight for only part of the day. It is better that the flower is not shaded in the morning. It tolerates partial shade well with diffused light.

If there is not enough light, the plant will stretch excessively, lose its brightness and bloom poorly. In deep shading conditions, it will not release inflorescences.
There should be undersized plants or lawn near the Japanese gladiolus. Montbrecia needs additional space, as it is spreading. Its inflorescences will hang above the ground, taking up additional space. You need to plant a plant at a distance of at least 40-60 cm from the path.
Flowers should not be in a draft. It is desirable that they be protected from prevailing winds, especially cold ones. At the same time, there must be good air circulation in the area.
You should not plant such a flower in a lowland, where rain and melt streams will collect. You should also avoid places where groundwater is close to the surface of the earth. Like other bulbous plants, montbrecia does not tolerate stagnant moisture. However, choosing the highest section is also not recommended. The soil will dry out quickly on it. Although the plant is drought tolerant, it feels most comfortable in moist soil.
Montbrecia loves loose acidic soils with a pH of 5.8-6.4. You can determine the area with acidic soil by the plants growing on it. Among them will be horsetail, horse sorrel, moss, sedge and wood lice.

If you plan to plant several types of plants, you need to select different areas for them. The minimum distance between specimens of different varieties is 80 cm. With a closer planting, the flowers will become pollinated and lose their decorative qualities.
Planting bulbs
Prepare the soil in the selected area in the middle of autumn. It must be dug up and fertilized (20 g of potassium chloride, 100 g of slaked lime, 2 buckets of humus and 40 g of superphosphate per 1 m²).

The easiest way to plant Japanese gladiolus is with bulbs. They are immersed in open ground when it warms up to a temperature of + 6 ... + 7 ° C (in late April or early May).Before planting, the bulbs must be brought into a warm room, the children must be separated from them and the layers of dried shells must be removed. 2-3 hours before placing in the ground, they must be soaked in a warm (+ 25 ... + 30 ° C) solution of potassium permanganate. The concentration of potassium permanganate should not exceed 0.1%. Soaking is necessary to disinfect the bulbs and to stimulate root and stem growth.
Until the soil warms up well, the plant will form a root system. After that, it will begin to build up the ground part. If the bulbs are planted too late, the montbrecia will immediately begin to grow upward, without spending resources on the formation of the root system. Plants with poorly developed roots have low decorative qualities.
Before planting in the ground, you need to apply nitrogen fertilizers (30 g per 1 m²). The soil must be loosened, breaking up large clods, and moistened. Large bulbs need to be deepened into the ground by 8-10 cm. Small planting material is placed at a depth of no more than 4-5 cm.

It is necessary that there is a distance of at least 6-12 cm between the plants. The rows should be placed at a distance of 25 cm. The more space there is, the more magnificent the bush will be and the higher the peduncles. They can be cut to create stunning bouquets. The planted flowers should be watered and protected from direct sunlight for 2-3 days.
For Chinese gladiolus to bloom earlier, the bulbs can be planted in pots. The sprouts are transferred to open ground in May or June. Babies will bloom only in the second year.
Planting Japanese gladiolus seeds
You can plant the seeds of montbrecia. Large grains with a brownish-red tint are found in the seed capsule. They need to be collected when the fruit dries up and opens. But it is better to purchase planting material in the store. Plants grown from self-collected seeds may not have the decorative qualities of a hybrid.

It is recommended to pre-prepare the seedlings, as in the open field the seeds may not germinate.
In the last days of February or early March, planting material should be soaked in water at room temperature. It must be changed every 6 hours. After a day, the seeds are planted with a substrate at a distance of 2-3 cm. The soil should contain leafy earth, peat, humus and sand. The components of the mixture must be taken in equal parts.
The container with soil is covered with foil and placed in a well-lit place. When the first shoots appear, the film is removed. The sprouts need to be watered as the soil dries and loosened. So that the plants do not become infected with fungal diseases, and their roots do not rot, the earth should be slightly moistened.
When 2-3 leaves appear on the sprouts, they are dived (moved to separate pots). The last 10-14 days before planting, containers with seedlings should be taken outside daily, gradually increasing the duration of their stay in the fresh air. This will allow the plants to more easily adapt to new conditions after planting in open ground.
You need to plant seedlings at the same time as the bulbs (in late April-early May). For each plant, you need to dig a hole 5-7 cm deep. It should be wide enough to fit the entire earthen sprout. Do not remove soil from the root system. She will help protect her from damage.
Plants grown from seed will bloom only in the second or third year.
Care advice
You need to water the flower 2-3 times a week. On hot days, the frequency of moisture is increased, not allowing the soil to dry out excessively. So that a crust does not form after it, the earth must be loosened regularly. Weeds must be removed at the same time. Regular weeding and loosening will provide oxygen to the roots of the plant.

Poor soil should be fertilized regularly. As soon as the first leaves appear on the surface, they need to be watered with nitrogen fertilizers every 2 weeks (2 g per 1 liter of water). Top dressing will enhance plant growth. In the summer, it is better to fertilize the soil with mullein diluted in water in a ratio of 1:10.When the first buds appear on gladioli, fertilizers rich in potassium should be applied to the soil.
When Japanese gladioli have faded, their stems and foliage should be cut off. Then flowers will spend all their resources on the development of bulbs.
Bulb care in winter
In the southern regions of the middle belt, the montbrecia can not be dug out for the winter. The plant must be mulched with fallen leaves, bark, spruce branches, straw, grass cuttings or sawdust. The layer of mulch should be at least 15-20 cm. It is covered with a film on top. In the spring, after the temperature is above zero, the film and mulch must be removed so that the sprouts appear safely on the surface. The leaves of the plant that will winter in the ground must be cut off.

If the Japanese gladiolus tolerates the winter well, it should be dug up once every 3-5 years to separate the babies from the bulb. If this is not done, the plants will be too close to each other. They will become small and bloom sparsely.
In regions with colder winters, the bulbs should be dug out of the soil in mid-October, before the first frost, when the leaves of the plant turn yellow. If you do this earlier, the kids will not have time to mature. A stalk is cut off a dug plant at a height of 5 cm from its base. The bulbs are dried together with an earthen clod in the open air in the shade or in a well-ventilated room at a temperature of 10 ° C.
They should be stored in boxes with sawdust, moss or dry peat in cool rooms at an air temperature of + 5 ... + 8 ° С. A basement or cellar is best suited for this purpose. If it is not possible to keep the bulbs in such a room, they can be put on the lower shelf of the refrigerator, wrapped in a clean cotton cloth or paper.
The bulbs are removed a few days before planting. They are warmed indoors at room temperature.
Experienced gardeners recommend leaving some of the bulbs in the ground, even in relatively cold climates. Some of them can spend the winter safely. The surviving specimens become more hardy and resilient. They throw out powerful peduncles, bloom longer and more abundantly. In case of failure, you can plant the planting material dug out for the winter.
Disease and pest control
Chinese gladioli are affected by diseases common to gladioli. If the leaves of a plant dry up, the stems are bent, the flowers are deformed and their color changes, it is affected by fungal organisms that cause fusarium. For the treatment of the disease, fungicides (agents with an antifungal effect) are used.

Yellowing and drying foliage can be a sign of grassiness. This viral disease is spread by leafhoppers. Such a plant must be dug up and burned.
With an excess of water, the montbretium can be attacked by bacteria that cause gray rot. A sign of the disease is a gray bloom on the bulbs and an unpleasant odor. You can cure the plant by reducing the frequency of watering.
If the castings dry up, the stems bend, and the flowers fall off, the Japanese gladiolus can be attacked by thrips. Pests leave colorless streaks or spots on it. They are fought with Karbofos, Confidor or Agravertin.
Bears can destroy flowers. They eat their bulbs. To get rid of insects, they dig a hole 50 cm deep and fill it with manure. Towards the end of autumn, a hole is dug up and the bear that has settled in it for the winter is removed.
Falling leaves can be caused by the activity of a spider mite. The pest sucks out the juices of the plant, causing its death. It can be killed by any insecticide.
And a little about secrets ...
The story of one of our readers Irina Volodina:
I was especially depressed by the eyes, surrounded by large wrinkles plus dark circles and swelling. How to remove wrinkles and bags under the eyes completely? How to deal with swelling and redness? But nothing ages or rejuvenates a person as much as his eyes.
But how to rejuvenate them? Plastic surgery? Recognized - not less than 5 thousand dollars. Hardware procedures - photorejuvenation, gas-liquid pilling, radiolifting, laser facelift? Slightly more affordable - the course costs 1.5-2 thousand dollars. And when to find all this time? And it's still expensive. Especially now. Therefore, for myself, I chose a different way ...
Read the article >>
 A surprisingly beautiful crocosmia plant will be able to compete with many bulbous plants. The flower, whose homeland is South Africa, has long been grown in the gardens of our country. Its bright green leaves appear at the very beginning of spring, and in summer crocosmia adorns the garden with its beautiful flowers with a warm range of shades. The plant is unpretentious in care, but its planting and growing requires adherence to some recommendations.
A surprisingly beautiful crocosmia plant will be able to compete with many bulbous plants. The flower, whose homeland is South Africa, has long been grown in the gardens of our country. Its bright green leaves appear at the very beginning of spring, and in summer crocosmia adorns the garden with its beautiful flowers with a warm range of shades. The plant is unpretentious in care, but its planting and growing requires adherence to some recommendations.
Crocosmia: general description, varieties, photos
Japanese gladiolus, montbrecia, crocosmia are all names for one attractive bulbous plant with long stems and lily-like flowers. Depending on the variety crocosmia reaches a height of 60 to 150 cm. Its leaves resemble iris leaves, and paniculate inflorescences consist of yellow-orange or red flowers.
To compose compositions in garden plots, the following varieties of montbrecia are used:
- Crocosmia golden in nature grows in the forests of tropical regions. The plant grows up to 70-100 cm in height and is distinguished by basal xiphoid or linear leaves. Flowers are yellow-orange in length up to 5 cm. Since montbrecia is a golden forest plant, it is recommended to grow it in slightly shaded areas. It blooms in autumn, used for making bouquets.
- Crocosmia masonorum grows up to 60–80 cm, has large bulbs and corrugated xiphoid leaves. It blooms for a long time with small flowers blooming in summer.
- Montbrecia Posta adapts to almost any unfavorable conditions. In nature, it grows in wetlands and along the banks of the rivers of South Africa. Differs in smooth narrow leaves and small flowers.
-
 Crocosmia Panikula blooms with small orange flowers in early summer. Differs in corrugated leaves and frost resistance.
Crocosmia Panikula blooms with small orange flowers in early summer. Differs in corrugated leaves and frost resistance. - Montbrecia Lucifer is a hybrid species that has a wide variety of colors. They can be bright or pastel colors. The species is widely used to decorate flower beds, flower beds and create compositions in the garden.
Crocosmia: planting and care in the open field
Growing Japanese gladiolus is identical to planting and care of many bulbous plants in open ground... However, there are some differences. So, for example, the planting material of montbrecia is prepared a few days before disembarkation:
- Bulbs stored in a cool room in the winter season must be peeled, dried and kept warm for several hours.
- The dried planting material is soaked in a solution of potassium permanganate for two hours.
- In late April - early May, depending on the region, the bulbs are planted outdoors. Since the plant is thermophilic, the minimum soil temperature during planting should be at least + 5C. It is checked at a depth of 10 cm.
Depending on the weather conditions of the region, crocosmia can be planted directly in open ground or first grown at home.
Planting montbrecia in open ground
Japanese gladioli love open sunny areas... They can be planted on unprotected hills, since they are not afraid of the wind.
The soil for planting a plant must be prepared in the fall. The soil is dug up shallowly and fertilized with superphosphate. Per square meter of land you should take 30-40 grams of fertilizer. Potassium chloride and nitrogen can also be added to nutrient-poor soils. Clay soil is lightened by small pebbles and sand.
 Since crocosmies do not like moisture stagnation, the following is added to the soil in equal proportions:
Since crocosmies do not like moisture stagnation, the following is added to the soil in equal proportions:
- peat;
- sand;
- compost.
Everything is mixed and placed in the prepared holes with a layer of 15 cm. The planting material is distributed over the laid out "pillow", sprinkled first with sand, and then with an earthen mixture from the site.
Large bulbs should fall into the holes by about 10 cm, and small ones - by 5 cm. The distance between them depends on the size and can be 5-15 cm. Distance between gladioli of different varieties should be at least 80 cm, otherwise they can become overdusted and lose their varietal qualities.
Growing crocosmia seedlings
Planting bulbs for seedlings should be carried out in large containers, which are filled with moist peat or sawdust. At a short distance from each other planting material is laid out on a layer 4-5 cm thick... The containers are covered from above with glass or polyethylene. Seedling care consists of daily airing the bulbs and keeping the soil moist.
Crocosmia flower
In order not to remove polyethylene from the boxes every day, small holes can be made in it for ventilation. Watering the bulbs is not recommended; it is best to moisten them by spraying with water at room temperature.
As soon as sprouts appear, the bulbs are planted in separate pots filled with earthen mixture. In them Crocosmia seedlings will grow within two to three weeks. In open ground, seedlings are planted from mid-May to early June, when the threat of frost passes and the soil warms up.
Care features
Montbrecia is unpretentious and does not require special care. During the season her  need to be watered regularly, but so that there is no stagnant water in the soil.
need to be watered regularly, but so that there is no stagnant water in the soil.
Three times a month, Japanese gladioli are fed with mineral fertilizers, which alternating with watering plants with infusion of bird droppings or cow dung... The first feeding is done when the leaves appear. In autumn, montbrecia is fed with potash fertilizers.
When caring for a tall plant, it is recommended to tie up long peduncles to pegs, otherwise they may break under the weight of spike-shaped inflorescences. To ensure the flow of nutrients to the rhizomes, it is recommended to cut out the faded inflorescences in a timely manner.
Crocosmia in winter
Depending on the type and variety of plants, montbrecia can remain outdoors for the winter or be dug up and stored indoors. Are not afraid of frost mainly small-flowered forms, which, with good shelter, do not freeze even in the middle lane. They are first covered with foliage or sawdust, which are covered with a film from above.
It is best to dig up Japanese gladioli with large flowers for the winter. It is recommended to do this in the second half of October, since the children need to be given time to mature. Planting material is dried in a well-ventilated area and is laid in peat, sand or sphagnum. Babies are not separated from the mother's bulb, otherwise they may dry out. Bulbs are stored at a temperature not exceeding + 10C. If there is no such room, then you can use the vegetable section of the refrigerator.
Reproduction of crocosmia
The bulbous plant reproduces both by seed and vegetative means.
 Large seeds of montbrecia are sown in containers filled with earthen mixture and placed in a warm place for germination. When the first seedlings appear, they must be transferred to a well-lit place. Seedling care consists in the timely moistening of the soil and planting the grown seedlings in separate pots. Seedlings are planted on the beds in mid-May. Plants grown from seeds will bloom in the second or third year.
Large seeds of montbrecia are sown in containers filled with earthen mixture and placed in a warm place for germination. When the first seedlings appear, they must be transferred to a well-lit place. Seedling care consists in the timely moistening of the soil and planting the grown seedlings in separate pots. Seedlings are planted on the beds in mid-May. Plants grown from seeds will bloom in the second or third year.
When crocosmia is multiplied by bulbs, babies are separated from the mother bulb in the spring and planted in open ground in wells prepared in advance. In the second year after planting, they will bloom.
Diseases and pests
Montbrecia is most often affected by thrips and bears. When found on shoots and leaves of thrips, the plant must be treated with special chemicals, from which the solution is prepared according to the instructions.
Medvedki cause great harm to crocosmia. Pests love to gnaw on bulbs, as a result of which the plant starts to hurt, its leaves wither, and corms rot. To combat the bears, special preparations are used:
- "Thunder";
- "Grizzly";
- "Medvetox".
But the use of only such means will not completely eliminate pests, since they constantly fly from one area to another. Isolate a special repeller will help from the bearwhich can be purchased at garden stores.
The refined and graceful crocosmia inflorescences will decorate the summer and autumn flower beds of the garden plot with bright colors. They are will look spectacular as in a single landingand among chrysanthemums, echinacea, dahlia, cannes and daylilies.
Although this plant is rarely seen in gardeners, we can say that montbrecia with their graceful inflorescences are excellent ornamental plants for a summer-autumn flower garden. They can be planted separately and in a group with other flowers. They look very impressive against a green lawn background. Bouquets of montbrecia with one or two sprigs of asparagus are incomparable in their beauty and elegance. How to grow an unrecognized gladiolus in the garden, we will tell you in the article.
Crocosmia (montbrecia)
Content:
- Botanical description of the plant
- Growing requirements - in brief
- Features of care for Montbrecia (Crocosmia)
- Landing of Montbrecia (Crocosmia)
- Reproduction of Montbrecia (Crocosmia)
- Diseases and pests
Botanical description of the plant
Montbrecia, or Crocosmia, Latin name - Crocosmia, folk - Japanese gladiolus.
In the genus Montbrecia (Crocosmia), from the iris family, 50 species of these corms are known to be native to South Africa. Plants are very similar to miniature gladioli, only flowers and peduncles are more graceful. For which they are also popularly called the Japanese gladiolus. In floriculture, commonMontbrecia crocosmic and the hybrid form - garden montbrecia, obtained by the French breeder Lemoine in 1980 as a result of crossing Montbrezia golden and Montbretia Potts.
The names Montbrecia, or Crocosmia, are used approximately equally. The third name - Tritonia is used much less often. Name Montbrecia (Montbretia) is given to a plant named after botanist Ernest Cockber de Montbre and is considered obsolete. More modern nameCrocosmia comes from the Greek words "krokos" - "crocus" and "osme" - "smell", because the flowers smell like crocus (saffron).
The corms of the montbrecia are small, covered with 2-3 layers of mesh membranes. Narrow xiphoid leaves, 40-60 cm long, are collected in a fan-shaped basal rosette. 3-4 peduncles grow from 1 corm. The graceful thin stem can reach a height of 100 cm, very branched.
Paniculate inflorescences, consisting of small (3-5 cm in diameter) star-shaped and funnel-shaped graceful orange-red or yellow flowers. Flowering is abundant and long, summer-autumn - from July to September.
Growing requirements - in brief
Location: light-requiring, requires an open location, otherwise flowers may not appear.
The soil: prefers humus-rich, fairly moist soil. Stagnant water is unacceptable. The soil is prepared in the fall. For 1 m2, 2 buckets of humus, 40 g of superphosphate, 20 g of potassium chloride, 100 g of slaked lime are added. In the spring, nitrogen fertilizers are given (30 g / m2).
Care: during the summer, feed every 10 days with mullein infusion (1:10) and full mineral fertilizer (2-3 g / l), starting from the appearance of the 2nd leaf. During the budding period, potash fertilizers (2 g / l) are added. Plants are watered abundantly once a week and the soil is periodically loosened.
Features of care for Montbrecia (Crocosmia)
In central Russia, the species, relatively small-flowered montbrecia winters safely under a shelter of dry leaves or shavings with a layer of at least 20 cm with a film on top to protect it from dampness during thaws. Moreover, the montbrecia overwintered in the soil is more powerful, blooms earlier and blooms longer. In the south of Russia, it hibernates even without shelter. But varietal large-flowered montbrecia is still better to dig up for the winter, and cover in the south.
Crocosmia (montbrecia)
They dig up the corms as late as possible - if serious frosts have not burst out, then in the second half of October, since they grow precisely at the end of the season. In dry weather, corms are dug with the baby formed over the summer and, having shaken off the entire “nest” from the ground, the stems and leaves are cut off at a height of 5 cm, then dried for several days.
The corms prepared in this way are sprinkled with dry peat, placed in boxes or paper bags and stored in a cellar at a temperature of + 5-7 ° C.
Landing of Montbrecia (Crocosmia)
In March, a month before planting, the planting material is taken out and kept in room conditions for several days. Then the montbrecia is prepared for planting: the “nests” are disassembled, the baby is separated, the roots and the remains of the stems with leaves are cut off, the dry shells are removed.
Before planting, the corms and the baby are poured with a warm 0.1% solution of potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate) for several hours. In addition to the disinfecting effect, the drug stimulates the germination of corms and the formation of roots.
The montbrecia wintering in the ground are dug up and divided every three years.
Reproduction of Montbrecia (Crocosmia)
The plant propagates by corms, children and seeds.
Every year, 5-6 babies are formed around one adult bulb, which bloom the next year. At the same time, the mother bulb continues to bloom and form a new baby, and, thus, the plant reproduces rather quickly. Montbrecia is planted at the end of April, when the soil warms up to 6-10 ° C: large corms - to a depth of 6-8 cm (the distance between plants is 10-12 cm); baby - to a depth of 3-5 cm (5-6 cm).
Before planting, it can be grown in pots and then planted with a lump of earth in open ground in May-June. The babies are separated in the spring and used for breeding. They reproduce easily by seeds. Sowing fresh, pre-washed seeds is desirable. With early spring sowing in greenhouses, flowering occurs in the second year.
Diseases and pests
Montbrecia is affected by the same diseases as gladiolus.
Fusarium (it manifests itself in different ways and has several names: desiccation, yellowness of gladiolus, rot of the core, dry rot). Fusarium is most characterized by yellowing of the tips of the leaves, which progresses before or during flowering. The yellowness spreads between the veins, the leaves become striped, turn brown and die off. With a strong defeat, the whole plant dries up. Spores of the fungus penetrate into the vessels of the roots and corms. Plants are easily pulled out of the soil.
In infected plants, the shape, size and color of the flower change, leaves and peduncles are bent. The baby is almost not formed. Affected bulbs darken and shrivel. Most often, the defeat begins from the bottom. The development of fusarium is promoted by both drought and excessive moisture, thickened plantings and disturbances in agricultural technology.
Herbiness, or jaundice... With early infection of gladiolus, the disease manifests itself in the yellowing of the tips of the leaves, which gradually spreads to the entire plant. The leaves turn straw yellow, the plant dies prematurely. With lesions at a later date, no external signs of the disease are observed. By the time of planting, many buds appear on an apparently healthy bulb. After planting, chlorotic filamentous shoots are formed. These shoots do not develop and die after a while.The bulb becomes hard and stays in the soil for a long time without decaying.
The disease is carried by cicadas. Heat treatment of slightly diseased bulbs at a temperature of 45 ° C for 15-20 minutes completely destroys the pathogen.
Thrips - a small sucking insect with an elongated body (its length is 1-1.5 mm). Thrips parasitizes gladioli both during their growth and during storage. Sometimes, during flowering, thrips affects the flowers so much that the latter are not able to bloom. Larvae and adult insects, piercing tissue, suck sap from leaves, flowers and bulbs.
At temperatures below + 12 ° C, thrips goes under the covering scales of the bulbs and hibernates there. Bulbs affected by thrips are covered with a sticky bloom of juice in winter and mummified. With a strong defeat, they do not sprout.
Medvedka - an insect up to 5 cm long, dark brown with a chitinous coating. Medvedka damages the roots, bulbs and stems of gladioli. It settles most often on wet soils, near water bodies, on peat bogs and humus-rich soils. Leads mostly underground life.
Those who nevertheless decide to grow a montbrecia will be amazed at the beauty and grace of this flower and will become its constant adherents. And the appearance of montbrecia on the flower market will bring real pleasure to lovers and connoisseurs of beauty.


