Content
- 1 General information
- 2 Types and varieties of phlox
- 3 Phlox planting and care in the open field
- 4 Reproduction of phlox by dividing the bush
- 5 Reproduction of phlox by cuttings
- 6 Reproduction by layering
- 7 Seed propagation
- 8 Phlox pests and diseases
- 9 Use in landscape design
- 10 Description of the plant
- 11 Types and varieties
- 12 Reproduction
- 13 Landing features
- 14 Care
- 15 Pests and diseases
- 16 Types and varieties of phlox
- 17 How to plant phlox in open ground
- 18 Planting annual phlox in the ground
- 19 Planting phlox in open ground
- 20 How to sow phlox seeds
- 21 Outdoor phlox care after planting
- 22 Location and lighting for the plant
- 23 Fertilizing phlox
- 24 Watering phlox
- 25 Pinching phlox
- 26 Do not forget to loosen the soil under the phlox
- 27 Phlox transplant in the open field
- 28 How to prune phlox
- 29 Reproduction of phlox by dividing the bush
- 30 Reproduction of phlox by cuttings
- 31 Planting phlox in open ground and caring for them
- 32 Reproduction of phlox by dividing the bush
- 33 Phlox rejuvenation method
- 34 Reproduction of phlox by cuttings
- 35 Growing phlox from seeds
- 36 Phlox and powdery mildew What to do if phlox turn yellow
- 37 Types of phlox with photos and names
The genus Phlox belongs to the Polemoniaceae family and has more than 65 species. These plants are native to North America. All representatives of the genus are perennials, with the exception of the Drummond phlox, which is an annual plant.
The name of these beautiful flowers in translation from Greek means "flame". So the plant was named by Karl Linnaeus because of the fiery red color of flowers in wild species.
General information
Phlox, depending on the species, can have both erect and ascending or creeping stems. Their height ranges from 10-20 to 120-150 centimeters. Sessile leaves are located opposite, sometimes in the upper part of the stem can be arranged in the next order. Leaves can be oval-lanceolate, ovate-elongated or lanceolate with a solid edge.
The flowers have a diameter of 2.5 to 4 centimeters and form paniculate or corymbose inflorescences. Flowers delight the eye with a variety of colors: white, scarlet, blue, pink, lilac, red, with an "eye" in the center, etc. Phlox fruits are oval capsules with numerous small seeds.
Perennial phlox grown in the garden are derived from wild species as well as their hybrids. The appearance of phlox, like their botanical features, is very diverse and varies even within species. To systematize them, scientists have to resort to the methods of genetics.
Phlox are ubiquitous. They are also found in the harsh climate of Alaska and Canada, and in the southern regions, where winters never happen. They grow both in a dry desert climate and in a humid temperate climate.
The appearance of wild-growing phlox directly depends on the place of their growth. So, phlox, living on scree and bare rocks at an altitude of more than 3500 meters above sea level, undersized plants that form turf trees and, blooming, are covered with a cap of bright flowers. Phlox grow both in humid forests (for example, splayed phlox) and in dry mountain forests (stolon-bearing phlox).
They can also be found near rivers, in lowlands on moist soils, as well as in dry steppes, on sandy soils. Phloxes also differ in their relation to lighting. There are species that prefer to grow in the shade, and there are those that prefer growing in the bright sun and, with a lack of lighting, cease to please with their flowering.
Phloxes have a varied appearance. Most of the representatives have erect herbaceous stems, forming compact bushes with bright and lush inflorescences at the tops. In these species, only rhizomes with buds and the lower part of the stems overwinter. Phlox, forming dense turf, have creeping, branched stems with a large number of evergreen leaves.
These species bloom most often in spring and look like a solid carpet of pink, white, lilac or crimson-pink flowers. There are also phlox-shrubs with woody perennial stems creeping along the ground.
The phlox flower consists of 5 petals and has a tubular-funnel shape. The petals are bent at right angles to the tube and form a flat rim, which can have a star-shaped, wheel-shaped, deeply dissected, notched, saucer-shaped, and other shapes. Flowers come in a wide variety of colors - monochromatic, with "eyes", dots, strokes, shadows.
to the table of contents
Types and varieties of phlox
Depending on the morphological features, phloxes are divided into 3 groups:
- Shrub;
- Loose sod;
- Creeping.
Bush phlox forms are distinguished by 2 more subgroups. The first includes tall plants, strong erect stems which can reach 180 centimeters in height. By autumn, the base of the stems becomes lignified. Phloxes of this subgroup bloom in summer and early autumn with a large number of fragrant flowers that form large panicle inflorescences.
Representatives of the subgroup are smooth phlox, panicled phlox and spotted phlox. The second group included low-growing plants with straight or ascending strongly branching stems, ranging in height from 45 to 60 centimeters.
Phloxes of this subgroup form loose bushes with spherical-umbellate or corymbose inflorescences on the tops of the stems. Some representatives may have a shortened panicle or a sparse brush inflorescence. These bush phloxes delight with their flowering in late spring and early summer.
Representatives of this subgroup are hairy phlox, caroline phlox, oval phlox, adorable phlox and others. A characteristic feature of all bush phlox is the absence of grooves and cuts in the edge of the corolla petals.
Loose turf representatives of phlox have strongly branching creeping vegetative stems with multiple flowering shoots extending from them. They got the name due to the fact that their creeping stems form a loose turf.
These phlox bloom in late spring or early summer. The most common representatives of this group are stolon-bearing phlox and wide-spread phlox.
Creeping the phlox group is characterized by branching, creeping stems that sometimes rise at the ends and form sods and cushions of varying density. The leaves of such phlox are narrow and small, collected in bunches in nodes and are often evergreen.
Plants can be bare or pubescent. At the ends of the stems there are peduncles with one or more flowers. Creeping phlox bloom in spring. The most famous representatives are Hood's phlox, styloid phlox, Douglas phlox, snow phlox, dwarf phlox and star phlox.
During the period of introduction of phlox, a significant number of interspecific varieties and hybrids were bred, most of which form independent groups. For example, hybrids of Arends phlox were obtained as a result of crossing paniculata phlox with splay phlox. The first hybrid from such a cross was obtained in 1910 by the breeder J. Arends (hence the name phlox).
Over the next few years, 13 more varieties were obtained, almost all of which, unfortunately, have now been lost. The modern collection of Arends phlox hybrids consists of several varieties that combine the duration of the flowering of the paniculata phlox with the early flowering of the splay phlox.
to the table of contents
Phlox planting and care in the open field
Phloxes are unpretentious plants, but in order to achieve abundant and long-lasting flowering, it is necessary to choose the right place for their planting. It is best to plant the plants in a place protected from the wind.
Phlox can grow both in partial shade and in the sun. At the same time, in sunny places, the flowering of phlox is not long, and the flowers of some varieties may even fade and fade under the influence of sunlight.
Plants prefer soil that is loose, fertile, with a neutral or slightly acidic reaction and sufficient moisture, but without stagnant water. It is advisable to prepare the soil in the fall before the spring planting of flowers.
To do this, it is processed to a depth of 30 centimeters (there is no need for deeper, since the root system of phlox is in the upper ball of the soil) and wood ash, compost and superphosphate are added.
If the soil is clay, then it is necessary to add sand to it, in the amount of 1 bucket per square meter, and organic fertilizers. If the reaction of the soil is acidic, then lime is added.
Plant care consists in periodic feeding, loosening the soil and watering in the absence of rain. For the winter, the stems of the plant should be cut off near the ground.
to the table of contents
Reproduction of phlox by dividing the bush
This is probably the most popular of the methods. The time for such a transplant is either early spring, or after flowering in the fall, to allow the seedlings to take root before winter. In the summer, such a transplant is also possible, but it should be done in the evening and with good watering. But it must be borne in mind that the separated seedlings must be large and it is imperative to save an earthen lump at the root. After transplanting, ensure regular watering.
In the autumn period, we begin the division of the bush, with digging, it should be noted that this method of reproduction must be performed if the plant has already reached the age of six. Next, we completely remove the earth from the root system. After that, we carefully divide the roots that go to the stem. If the bush cannot be separated by hand, use a knife. Having divided the roots, we check that each one has shoots processes. The separated parts are immediately planted in the ground.
to the table of contents
Reproduction of phlox by cuttings
This breeding option involves three ways:
Reproduction of phlox stem cuttings, this method is not difficult and the best time for this is the period of active growth of the stems, before flowering, late May, early June. Choose good, healthy cuttings from an adult plant.
We divide the shoot so that there are several nodes on each handle. The leaves that are at the bottom of the cutting must be cut off completely, and the upper ones by half. We plant the cuttings in a container with loose nutrient soil and sprinkle with sand on top with a layer of several centimeters.
If the planting is carried out in open ground, then sprinkle with leaves or peat about 8 centimeters and a layer of sand on top of a few centimeters. We moisten the soil and plant the cuttings on the upper knot with leaves, pressing the soil against them. We plant at a distance of about five centimeters from each other.
After planting, we place a container with cuttings in a greenhouse and hide from direct sunlight for a period of up to 21 days with watering up to 3 times a day. After the cuttings are accepted and rooted, green leaves begin to appear on them, it is necessary to transplant to a more spacious place at a distance of up to 16 cm.This method can be propagated throughout the season.
The second way, the reproduction of phlox leafy cuttings... This method is best used at the beginning of July. Only with a blade you need to cut off a leaf with a bud and grab a little of the stem.
We plant the cutting in a container with loose soil and add a layer of one centimeter of sand. The distance between the plants is about five centimeters, we plant it deeply, taking into account that the bud and stalk are in the ground.
After disembarking, we cover the container with glass and leave it in a semi-dark place with a temperature regime of about 19 degrees. And we regularly moisturize, periodically airing, so that the cuttings do not get stuck. After rooting, we plant it in the ground.
The third way, the reproduction of phlox, root cuttings... This method is laborious, but it is sometimes used to get rid of stem nematode parasites. Can be planted in spring and after flowering. Having dug up the plant, select the strongest roots and cut into 6 cm pieces.
We plant in a container with earth and sprinkle with a layer of sand about 5 cm. Water abundantly and wait for new shoots. If in winter, we put it in a cool basement and water it, not letting the soil dry out, and in the spring we take it out and accustom it to heat and light gradually, rooted cuttings with shoots are planted in open ground in May.
to the table of contents
Reproduction by layering
A simple method available to anyone, even a novice amateur gardener. Sprinkle the bushes with earth, the higher the better. And after some period, roots appear on the shoots. And when the roots take root, you need to cut them off and plant them in the ground.
to the table of contents
Seed propagation
Subulate phlox reproduce by seeds, but often with such reproduction varietal traits do not always remain.
Before sowing, in order to improve the seedlings, you need to clear them from the boxes. Because of its fragility, it is better to sow immediately after harvest. You need to choose the largest seeds and in November sow in open ground or a box.
In winter, the seeds will undergo natural selection and the most hardened ones will delight you with good shoots. They appear in May, when several leaves appear, they must be planted at a distance of about 15 cm from each other. Following all the rules of planting and care, you will actively develop and bloom.
to the table of contents
Phlox pests and diseases
Phloxes can be affected by pests and fungal, viral and mycoplasma diseases. Most often, plants are affected by powdery mildew. This is due to improper care or growing in the shade.
Phloxes also often suffer from rust, verticillium wilting, white spot and mosaic.
The most dangerous of the pests is the stem phlox nematode. When a plant is damaged by this microscopic worm, the tops of the stems turn pale and twist, and the leaves become thinner.
The plant cannot be cured and must be dug up along with a large clod of earth and removed from the site so that other plants do not become infected.
to the table of contents
Use in landscape design
Phlox are excellent perennials for decorating flower beds. Their popularity among gardeners is due to their frost resistance, unpretentiousness, ease of care, as well as the splendor and brightness of flowering.
Phloxes can be used as representatives of cottage gardens, village front gardens, in rock gardens near water bodies, landscape, romantic or avant-garde style flower beds.
By choosing the right varieties of phlox, you can achieve flowering flower beds, starting in spring and ending in autumn. So creeping and loose-sourced phloxes will decorate the garden in spring and early summer, and spray ones - during summer and early autumn.
When planting plants, it is necessary to take into account their height and color of flowers so that the created compositions look harmonious.
You can also use fragrant phlox flowers to create bouquets. In this case, it is best to cut them off in the morning, having done the evening watering of the plant before that.
To ensure the formation of lush and dense inflorescences, it is recommended to leave no more than 7-8 stems in the bush.
to the table of contents
 Decorative bright phlox gardeners willingly grow on their plots because of the varied palette of colors and the long flowering from spring to autumn frosts. In addition, lush inflorescences can be cut off and made from them bouquets or compositions that will last a long time. How to grow phlox from seeds, you can learn about the features of their planting and care from our article.
Decorative bright phlox gardeners willingly grow on their plots because of the varied palette of colors and the long flowering from spring to autumn frosts. In addition, lush inflorescences can be cut off and made from them bouquets or compositions that will last a long time. How to grow phlox from seeds, you can learn about the features of their planting and care from our article.
Description of the plant
The first wild species flowers had a bright red color, for which they got their name - "phlox", which means "flame". Today the culture is spread all over the world and is very popular due to its unpretentiousness.
Most phloxes are perennials that differ in:
- compact bushy form;

- densely leafy creeping or straight stems from 10 to 150 cm high;
- a powerful root system that can easily withstand lush large bushes;
- oval-elongated, oppositely located sessile leaves;
- complex inflorescences located at the tops of the shoots, which consist of many small flowers, reaching a diameter of 3-4 cm;
- flower corollas, which can be dissected, star-shaped, saucer-shaped or other shape;
- numerous colors of buds, which can be both pale white and purple, red or even variegated.
Beautiful and spectacular phlox grow quickly and are winter hardy.
Types and varieties
The plant is divided into bush and ground cover species.
Low-growing perennial
Creeping or ground cover bushes can have stems from 5 to 40 cm long. They grow well in width, therefore they are often used to decorate an alpine slide. The most popular undersized phlox are the following varieties:
- Forked... A plant with slightly pubescent stems and an unusual shape of flowers. The petals of the buds are dissected, which makes it seem that this is not one, but several flowers. The color of the inflorescences is mainly blue and white.
- Douglas... A bush up to 10 cm high is distinguished by a dense cushion of flowers that are located on rigid stems. The color can be purple, white, lilac. Flowering lasts from May to June.
- Phlox subulate... Popular undersized plant with stems up to 18 cm long. When planted in open ground, subulate phlox covers a large area of soil with purple, white or pink inflorescences. The first flowering of the plant is in May-June, after which, in August and September, beautiful numerous flowers bloom again on the bush.
Gallery: phlox (25 photos)
Bush perennial
 Plant bushes are the most common and most commonly decorate flower beds in the garden... They are short - up to one meter high and tall - more than a meter high.
Plant bushes are the most common and most commonly decorate flower beds in the garden... They are short - up to one meter high and tall - more than a meter high.
Same
Low-growing varieties:
- Orange Perfection - a variety with salmon-colored buds that appear pink in the bright sun.
- Tiara - an unpretentious and beautiful plant with emerald greenery, against which the inflorescences stand out with their snow-whiteness.
- Sherbet Cocktail - a fast-growing shrub with olive-colored flowers.
Tall varieties:
- Magic Blue - a variety that blooms with scarlet, blue, lilac or white flowers that bloom in early summer and adorn the garden until September.
- Tenor - an abundantly flowering plant with bright purple-red inflorescences.
- Nicky - perennial bush up to 1.2 meters high. At the beginning of summer, dark saturated flowers bloom on it, which fade only in September.
- Natasha - a plant up to one and a half meters high with blue and white buds.
- Windsor - one and a half meter bush, distinguished by elongated oval-shaped leaves and inflorescence color from white to carmine.
Reproduction
 There are several ways to reproduce and grow perennial phlox:
There are several ways to reproduce and grow perennial phlox:
- seed;
- cuttings;
- dividing the bush;
- layering.
From seed
 A plant grown from seeds will be the most adapted to the climate of the region. Seeds are sold in the store, but if phlox are already growing on the site, planting material can be collected on your own. To do this, in the fall, when the leaves of the plant wither, they pluck the brown seed box and extract the seeds from it. They should be dark green and dense in structure.
A plant grown from seeds will be the most adapted to the climate of the region. Seeds are sold in the store, but if phlox are already growing on the site, planting material can be collected on your own. To do this, in the fall, when the leaves of the plant wither, they pluck the brown seed box and extract the seeds from it. They should be dark green and dense in structure.
Seeds are planted phlox in the fall. This is due to the fact that the planting material extracted from the seed pod quickly loses its germination and should be used as soon as possible.
For phlox, it is recommended to choose a windproof well lit place... In the lowlands, under the crowns of trees and in the shade, perennial flowering plants will feel uncomfortable.
It is recommended to plant phlox in November, having prepared a flower bed in advance for sowing seeds. Snow is cleared from it and seeds are laid out on the surface of the soil. Sprinkle them 1 cm layer of prepared or purchased potting soil and snow. With this method of planting, seed germination is about 70%.
You can sow seeds not in the ground, but in filled with soil mixture, humus and sand containers. Sowing is carried out to a depth of 1–2 cm. The container is left outside, sprinkled on top with foliage or snow. In the spring, it is brought into a warm room, where the seeds will begin to hatch and germinate.
Gallery: phlox in garden design (25 photos)
Cuttings
 Cuttings for planting can be cut from almost any part of the bush:
Cuttings for planting can be cut from almost any part of the bush:
- At the beginning of summer, leafy cuttings are harvested, which should be with an axillary bud and leaf. The bud deepens into the ground by 1–2 cm. Rooting should take place in a greenhouse at a temperature of +20 ° C to +30 ° C. Timely soil moistening is necessary. By autumn, leafy cuttings germinate, and in the spring they land in the open priming.
- Stem cuttings are cut in May-June or September. On a segment about 10 cm long, there should be at least two knots. The bottom cut is made just below the knot, and the top one is 2–3 cm above the knot. The lower leaves are removed from the cut, and the cuttings are placed in water for an hour. Sections should germinate in moist soil. Before planting, a small cut should be made at the bottom of the segment. The container with cuttings is covered with a film on top.
- Root cuttings are harvested in May-June... To do this, the bush is dug up, and healthy roots are cut into 5 cm long pieces. A container with sand and earth is prepared for them, where they are planted obliquely. Germination takes place for the first two weeks at an air temperature of 10 ° –15 ° С, after which the container with cuttings should be placed in a room with an air temperature of 20 ° –25 ° С. The soil must be moistened regularly. This method of growing phlox is used mainly when a shrub is infected with nematodes.
By dividing the bush
In the spring or early fall, you can dig up the bushes and divide them. For this, a healthy, mature four- or five-year-old plant is selected. Dig it out carefully so as not to injure the roots. When dividing into parts, the root collars are carefully separated. Delenki land on a new permanent place.
Layers
Layers are made from the lower shoots, which are bent and pinned to the ground, sprinkled with soil on top and moistened. After the layers take root, they are separated from the main bush and planted in a prepared place.
Landing features
You can plant phloxes almost at any time of the year:
- Bush planted in late April-early May
 will quickly take root, but bloom two weeks later than usual.
will quickly take root, but bloom two weeks later than usual. - In summer, phlox are planted already blooming.The inflorescence must be cut off, the plant should be shaded and watered well.
- In autumn, planting should be done in September. Before the cold weather, they must take root and stock up on nutrients for the winter. Phlox will bloom next summer.
The plant should be planted in a well-lit place with a deep location of groundwater. Although the culture loves moisture, excessive moisture in the soil can lead to various fungal diseases and root rot.
The soil should be fertile, loose, permeable and light. The best option is loam with neutral or slightly acidic acidity. Wood ash and compost are added to the planting hole. If the acidity of the soil is increased, then lime is added.
When planting plants, the distance between them should be:
- 60–70 cm for tall bushes;
- 50 cm for medium-sized bushes;
- 35–40 cm for ground cover phlox.
In pre-prepared holes, the seedling is placed vertically. The roots are straightened and covered with earth, which is compacted. Each planted bush must be watered well. It is recommended to mulch the soil around the plant with humus or peat.
In one place, under favorable conditions, the culture grows and blooms well for 10 years. But experienced florists advise replanting phlox every seven years. This is done to enhance flowering and rejuvenation of the shrub.
Care
 Growing a plant will not require a lot of effort and hassle. Phloxes are moisture-loving, therefore, first of all, it is necessary to monitor the soil moisture. Watering should be regular and abundant. But the culture also does not tolerate stagnant water in the ground.
Growing a plant will not require a lot of effort and hassle. Phloxes are moisture-loving, therefore, first of all, it is necessary to monitor the soil moisture. Watering should be regular and abundant. But the culture also does not tolerate stagnant water in the ground.
The shrub should be watered at the root so that water does not get on the inflorescences and leaves. On very hot days, watering should be done in the morning and evening.
Around the plant, it is necessary to regularly remove weeds and loosen the soil. Will inhibit the formation of weeds and retain moisture in the soil with mulch (peat or humus) that can be spread around the plant.
It is recommended to feed bush phlox three times per season:
- As soon as the first shoots and leaves begin to appear on the plant, it must be fed with organic fertilizers. It can be wood ash or manure infusion (for 8 liters of water - 30 g).
- During the swelling of the buds, a second feeding is done with special mixtures for flowering plants or mineral fertilizers.
- At the end of summer, after flowering, the bushes are fertilized with phosphate and potassium. This will help the plant to bud for the coming season and give strength for root development.
Fertilizers are applied after watering the plant.
In the fall, after the bushes have faded, they need to be prepared for winter. This requires:
- Cut the shoots before the first frost to
 only 5–6 cm hemp remained.
only 5–6 cm hemp remained. - Cover the bushes with dry peat or fallen leaves. Leaves are harvested in spring, and peat can additionally serve as fertilizer.
- At subzero temperatures, when the ground is already frozen, pour one tablespoon of mineral fertilizer and a little ash under each bush.
In this form, phloxes will be able to winter well and will not freeze in snowless winters.
Pests and diseases
Under unfavorable growing conditions and improper care, plants can be affected by various diseases:
- Fungal diseases of the roots are indicated by the faintness of the color and wilting of the bush.
- Powdery mildew can be recognized by a whitish coating on leaves and shoots.
- With phomaosis, the stem cracks, and the leaves turn yellow and curl.
- Leaf spot can be recognized by brown spots that grow more and more.
All diseases must be treated with special drugs that can be bought in gardening stores.
Of the pests on phlox, caterpillars and butterflies, slobbering pennits, slugs, and nematodes can be found. You can get rid of them with folk remedies or insecticides.
Beautiful, long-blooming and showy phloxes can be propagated and grown independently.With the right planting and good care, the bright inflorescences will adorn the garden all summer.
Attention, only TODAY!
Phlox are rightfully considered one of the most beautiful garden plants. Their advantage is the abundance of flowers and a rather long flowering period. In nature, there are about 40 varieties of phlox, including wild ones. However, most of those that we can see in plots and gardens in the middle lane belong to the bush variety Paniculata, which includes many different hybrids.
The cultivated phlox is a perennial plant. Depending on the species, it can bloom at different times of the year - from May to September. A distinctive feature of phlox is their extremely rich color range - various shades of pink, red, white, purple.
Fresh articles about garden and vegetable garden
Types and varieties of phlox
Amethyst
Spectacular phlox of medium height with fragrant bluish-lilac inflorescences.
David
Luxurious snow-white phlox David received a prestigious award from British florists. This stately handsome man grows well both in the sun and in partial shade, practically does not get sick.
Delilah
A short plant with pinkish purple flowers. Phlox varieties Delilah are generally not capricious and resistant to various kinds of diseases, but sometimes they can be prone to spotting.
Candy Twist
Candy Twist is a paniculata phlox with a mischievous striped color that resembles candy. This phlox is very aromatic, does not fade in the sun, and is resistant to diseases.
Sandro Botticelli
A delightful variety of phlox, bred by Yuri Reprev, is deservedly named after the great Italian painter. Sandro Botticelli admires the delicate lilac-pink color. You might think that he came straight from the artist's canvas.
Spotted phlox
Spotted phlox is also often called meadow or pyramidal. It is a very close relative of the phlox paniculata. It is possible to distinguish the spotted phlox from its more popular "brother" by two features: small burgundy spots on the stem and the pyramidal shape of the inflorescences.
How to plant phlox in open ground
If you choose the right varieties of phlox and plant them, then you can admire the flowering from mid-spring to the end of September. Phlox can be planted in the ground in spring or autumn, regardless of their type.
Planting annual phlox in the ground
Annual varieties are sown directly outdoors in late autumn. In winter, the seeds undergo natural stratification and germinate better. But most often these flowers are grown as seedlings in the spring. Lush flowering is the result of timely planting of phlox in the ground and good.
Phlox are sown in boxes with earth, covered with polyethylene and watered regularly. Shoots appear in a week. When they have 4 leaves, they pinch the plants so that they branch better. In May, seedlings are planted in open ground at a distance of 20 cm from each other. Phloxes do not tolerate direct sunlight and fade quickly. The best place for them is light partial shade. The larger the shade, the longer the phlox bloom, however, the flowering intensity decreases. Phlox does not like heavy soils and grows best on fertile sandy loam soils.
Planting phlox in open ground
Seeds are sown in open ground before winter - in September - November, depending on the local climate. If we use our own achenes, we collect them in the fall, when the leaves fade, the capsules will compact, acquire a greenish-brown color and, when pressed, begin to crack.
How to sow phlox seeds
We plant directly into the garden. You can sow achenes directly into the ground, spreading them every 5 cm in rows 1 cm deep. Having distributed the achenes in rows, sprinkle them with soil.
We plant in seedlings. We grow the planting material in advance in a container, keeping a vessel with sown achenes for a couple of weeks in a cold place. We provide the seedlings with a warm place, good lighting, and timely watering.We plant the plants in the garden when 4 leaves appear.
Planting with seeds is good because the bushes are more powerful and healthy, but, unfortunately, they may lose some of the characteristics inherent in the variety.
Fresh articles about garden and vegetable garden
If you want to divide the bushes in the fall, we plant the separated bushes in early September, cutting off the stems by a third: rooting will be faster and easier. For the winter, we insulate the planting with mulch. The first shoots will appear in the spring as soon as the snow melts.
Separated bushes are planted as follows:
We dig in the bush to be divided, take it out of the ground and cut off the stems, leaving cuttings 15 cm long.
We divide the roots with a sharp knife: on each separated bush there should be 2-5 buds.
We make large holes, fill them with ash (a large handful) and compost (half a bucket), mix the additives with the soil.
Pour water into the holes, put a bush, sprinkle it with earth, covering the growth points by 4-5 cm.
We tamp the soil around the bushes, put a layer of compost and tamp it again.
At the end of planting, cover the soil around the plants with a ten centimeter layer of mulch using peat or straw.
Outdoor phlox care after planting
When caring for flowers, special attention should be paid to the choice of location, irrigation regime and fertilization. On these three whales the health of phlox is kept.
Location and lighting for the plant
If phlox are planted in a permanently shaded area, they will, of course, grow due to their endurance. But you will definitely not see beautiful bright colors! But take a look at the overly elongated painful stems, thin and deformed.
Give the phlox as much light as possible to get healthy, beautiful plants with a sturdy, sturdy stem that holds the voluminous caps of dense inflorescences. In partial shade conditions, the flowers will appear later than the due date and will be pale and friable. Air humidity
Phloxes tolerate heat and arid atmosphere well, especially with sufficient moisture in the soil. But in the absence of rain, they should be periodically sprayed from above from a spray bottle. The procedure can be carried out only in the evening, when the sun reduces its aggressiveness.
Fertilizing phlox
Fresh manure cannot be applied under phlox, various rot may occur. The land intended for planting phlox must first be fertilized.
If the soil is clay, then coarse river sand, gravel, wood ash, peat, compost are added. To fertilize 1 square meter of soil requires 7 kg of peat, about 300 grams of wood ash, about 5 kg of humus or compost. All components are thoroughly mixed, river sand or fine gravel, 30 grams of nitrophoska, 30 grams of potassium sulfate and the same amount of Agricola-7 are added to them.
Then the fertilized soil is dug up again. Phlox also like coniferous compost, although it is not available to everyone.
During the summer, it is required to feed phlox three times. If the summer is rainy, then the top dressing is done dry, if there is not enough rain, liquid top dressing is carried out.
The first feeding is done when the stems grow back. Liquid top dressing consists of 10 liters of water and 2 tablespoons of urea diluted in it. The dry top dressing includes: one bucket of compost or humus and two tablespoons of urea. The components are thoroughly mixed and scattered next to the plants. This amount can feed three phlox bushes.
Watering phlox
Growing phlox is not complete without watering. Phloxes simply adore him. During the growth and development of buds, watering is simply necessary for phlox. It must be firmly remembered that phloxes need to be watered at the root, but not over the plants themselves, especially with cold water. This can provoke such a common fungal disease as powdery mildew. In hot weather, the watering hose can be left under the bush for a while. This method of watering for phlox is the most comfortable.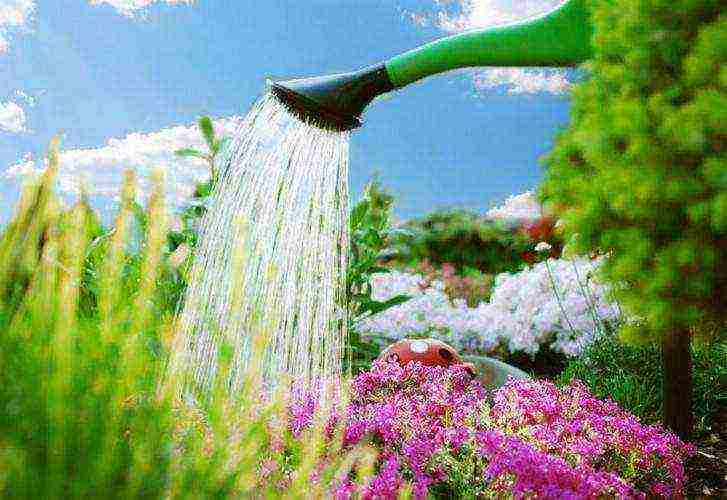
Pinching phlox
In many cases, summer residents in mid-spring take care of perennial phlox by thinning - pinching. Thus, it is possible to achieve an extension of the life of the bush by several weeks. It should be noted that up to 3 shoots can develop on a pinched stem. All pinched stems allow the growth of small inflorescences that can acquire an exceptional decorative appearance. In addition, this method of caring for phlox allows you to achieve rapid development of shoots and increase the flowering time of the bush until the last days of August. On summer days, we pinch the fifth pair of leaves on top of the phlox bushes. Thanks to this procedure, the plants will grow more branchy and voluminous. In addition, this achieves their fastest tillering. It should be noted that, preferably, after four seasons of flowering, it is better to divide the rhizomes into parts.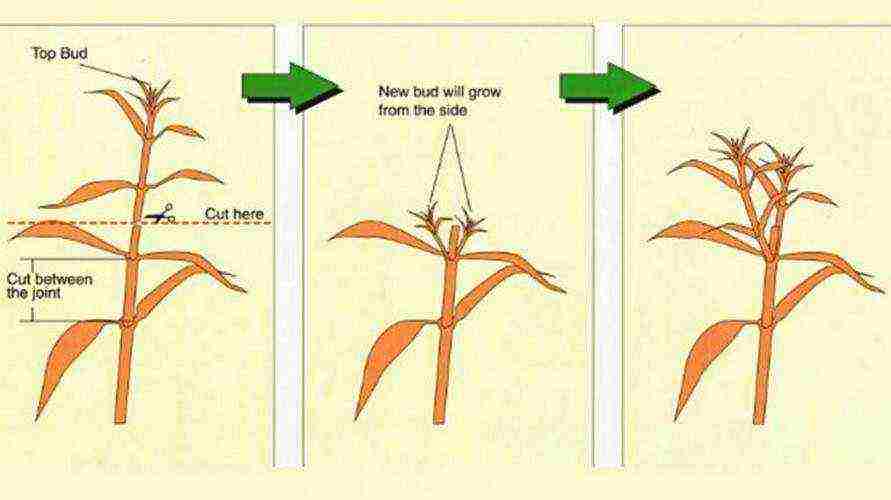
Do not forget to loosen the soil under the phlox
While loosening the soil, we strive not to harm the immature roots of plants. Therefore, we carefully cultivate the soil, since there is a considerable risk of affecting young roots in the upper layers of the soil (about 3-4 cm). Systematic and frequent feeding of flowers without proper water supply to the grown phlox is strictly prohibited. It should be taken into account that perennial phloxes develop optimally not only on soil rich in minerals, but also on sufficiently moisturized soil.
Phlox transplant in the open field
The most favorable time for transplanting is the end of April and the beginning of May. If the transplant is scheduled for the fall, then it should be completed by mid-August. In the autumn, phloxes are transplanted with the trimmed upper part of the plant for better rooting. In a flowering state, transplantation is also possible if the seedling is carefully dug up and subsequently watered regularly. If the root system dries up, phlox will not be able to fully take root and in the future will often get sick and will not be able to fully grow and develop. How to care for a cotoneaster, read on this page. When choosing a phlox planting site, you need to take into account its variety. Since some varieties of Drummond phlox reach half a meter in height, forming a lush bush, you need to choose a place where it will not interfere with neighboring plants.
How to prune phlox
It is recommended to prune phlox bushes in the fall, after flowering ends, approximately from the end of September to the end of October, when all the nutrients accumulated in the plant will go to the root and the soil will begin to freeze. Pruning must be completed before the onset of constant cold weather, in different zones it is different: it can be both in October and in November.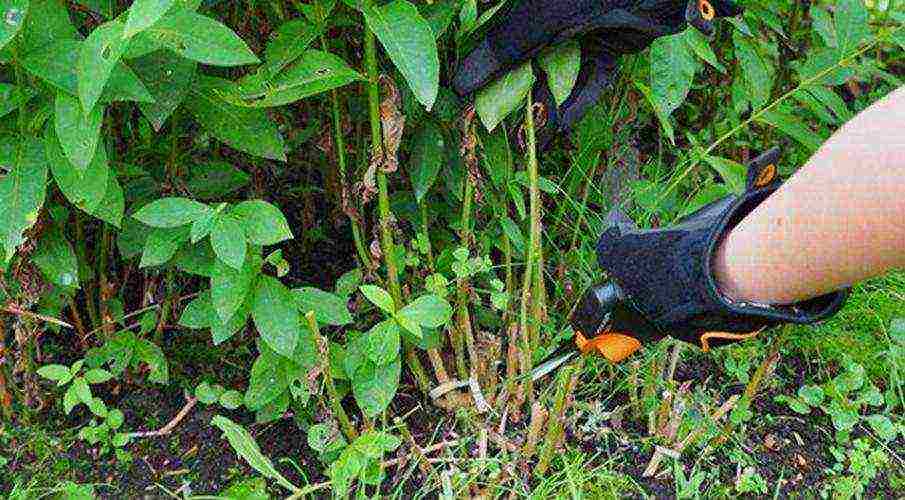
Some gardeners recommend pruning in early spring, (especially in areas with little snow in winter), since the ground part of the bush (stems) will be needed in order to collect snow over phlox in winter, because in the northern regions it is the best protection against frost, and in the south it helps to increase soil moisture. In such cases, snow near the bushes cannot be tamped.
Fresh articles about garden and vegetable garden
The process of autumn pruning consists of pruning itself, feeding and mulching the land around the bush, differing only in the materials used.
There are several options for trimming phlox:
- level with the ground - to avoid the preservation of infections and pests;
- leaving 5-10 cm above the ground - for trapping snow, in poor snow conditions or when landing in a windy area.
After pruning, all residues (stems, leaves) should be collected and burned, as they may contain fungal spores, foci of diseases and insect pests. The base of the bush and the soil around it should be treated with fungicides against diseases.
Reproduction of phlox by dividing the bush
Phlox can be planted in spring and autumn.In early spring, when young sprouts appear with a sharpened shovel, about 70% of the bush is carefully separated right in the ground. The dug out part is divided with a knife into five or more parts. The resulting plots are planted in a new place, and the old bush grows intensively over the summer and forms new stems. Even if there is no need to multiply phlox for every second year, it is recommended to update the plantings in this way, and excess plots can be given or destroyed.
The flowering of the transplanted plots occurs in the first summer. The part of the bush left in the old place blooms more abundantly, delighting its owners with large flowers.
The autumn division of the bush begins at the end of the growing season. For these purposes, bushes with 20 cm in diameter and more than 10 stems are chosen. These are, as a rule, three to four-year-old plants. Before dividing, the bushes are cleaned of old roots and planted. For 2-3 years of intensive growth, full-fledged bushes are formed.
Reproduction of phlox by cuttings
Phlox can be propagated quite easily by cuttings taken from various parts of the plant. At the same time, there are quite a few opportunities for those wishing to propagate the desired variety. The soil for all types of cuttings is prepared in the same way. A cutter, that is, a bed for grafting, is best arranged in partial shade.  The soil should be loose, fertile, moist and healthy, 1/3 of good garden or sod land, 1/3 of leaf humus or weathered peat and 1/3 of washed river sand. If the soil on the bed is fertile, then you can pour a mixture of sand and peat, sifted compost or leaf humus on its surface and mix with a rake with the top layer of earth. The surface of the ridge is leveled, compacted or watered abundantly, and washed sand is poured on top with a layer of 2–2.5 cm. The sand prevents mosses and crust from forming on the soil surface. The edges of the bed are well edged with boards 25-30 cm wide, which makes it easier to maintain the microclimate in the bed, more even temperature and humidity.
The soil should be loose, fertile, moist and healthy, 1/3 of good garden or sod land, 1/3 of leaf humus or weathered peat and 1/3 of washed river sand. If the soil on the bed is fertile, then you can pour a mixture of sand and peat, sifted compost or leaf humus on its surface and mix with a rake with the top layer of earth. The surface of the ridge is leveled, compacted or watered abundantly, and washed sand is poured on top with a layer of 2–2.5 cm. The sand prevents mosses and crust from forming on the soil surface. The edges of the bed are well edged with boards 25-30 cm wide, which makes it easier to maintain the microclimate in the bed, more even temperature and humidity.
Phlox are beautiful bright flowers from the cyanotic family, which are very decorative, used in the formation of flower beds. Beautiful plants have advantages, for which gardeners are fond of - unpretentiousness in care, the ability to grow in conditions of different lighting conditions, survival on any soil. Cut phloxes stand for a long time - they can often be found when decorating the interiors of living rooms.
Phlox grows in flower beds for many years, surviving the winter, severe frosts. Breeders have bred many varieties that differ in shades, plant height, endurance, and other indicators. This genus of plants is one of the best in the flowerbed for the duration of flowering, the ability to survive frost.
You can get your own plant by taking out seeds or a stalk. In both ways, it quickly turns out to grow an adult plant, which begins to bloom in the shortest possible time.
Planting phlox in open ground and caring for them
Phlox can be grown on almost any soil - they are unpretentious. But the most ideal ones are loamy. It is recommended to add a little lime to the soil to improve the growing conditions of the plant.
They begin to prepare the site in the fall: they arrange a thorough digging of the earth on it, during which the rhizomes of weeds and pebbles are removed, since in the early years the bushes are weakly opposed to wild vegetation.
They choose the most illuminated areas of the flower beds, since phloxes love the sun. The exception is hybrids, the petals of which can quickly burn out in the sun.
If phlox has dark petal colors, it is better to plant them interspersed with light ones, so that both in the evening and in the afternoon the flowerbed looks as profitable as possible.
How to plant phlox in the ground, we look at the video:
Taking care of phlox is easy. It is necessary to regularly keep the soil loose, remove weeds in time. In order for the flower bed to please with exuberant flowering, it is periodically necessary to apply fertilizers.
For paniculate phlox, it does not matter where to grow - in the shade or in the sun. But undersized varieties need more sun. Those and other forms of plants need to be fertilized in time so that they grow quickly and in a timely manner to the desired forms.
Watering should be sufficient, but sparse. The exception is the weeks when it is very hot outside and the air humidity is minimal. Then the soil very quickly loses water, so you need to water the plant more often. This procedure is performed in the afternoon, in the late afternoon.
Some phlox varieties naturally form seeds. But this is not a 100% guarantee. In order for the plant to give seed, the required optimal air temperature, proper growing conditions, and proper care. Therefore, do not worry if there are no seeds - this is quite a frequent occurrence.
Phlox care in autumn
Before winter, all phloxes must be protected from frost by covering them with earth or humus, manure. The recommended layer thickness is 8-12 cm, which is sufficient to protect the underground buds from frost. A mandatory procedure is for young plants 1 year old.
Phloxes that have suffered from fungal diseases need fungicide treatment, which is carried out in October, when most of the shoots have faded.
Often, plants increase the seed, but do not have time to do this before the frost. To obtain seeds, the bushes are removed from the flower bed along with the soil and planted in pots, which are kept in the building until the seeds are fully ripe.
Autumn is a great time for phlox rejuvenation and transplantation, which will be discussed later.
When to transplant phlox
Panicled phlox is a plant that does not require frequent transplanting. It feels comfortable up to 15 years old in one place. But due to the growth of lateral shoots and the aging of the center of the plant, it is recommended to do rejuvenation and transplantation at least every 5-7 years.
Than when and how to feed phlox
Phloxes are fed several times per season:
- In spring, in May, before flowering - with nitrogen and potassium. Potassium nitrate is great.
- In early June, feeding is repeated by adding superphosphate to potassium nitrate, which will stimulate budding and flowering.
- In early July, they feed the third time, reducing the dose of nitrogen.
- At the end of July, they are fed only with phosphorus and potassium salt.
- The last time phloxes are fed in August, and then if they are still in bloom. They use phosphorus and potash fertilizers.
The consumption of each fertilizer is calculated as follows: a matchbox of loose or granular fertilizer (or their mixture) for 10 liters of water. This solution is consumed per square meter.
An excellent fertilizer for phlox is fermented bird droppings, which are applied before the phlox begins to bloom. Introduce 0.5 liters. thick turbulence on a bucket of water and pour 1-2 liters of solution under the bush.
Reproduction of phlox by dividing the bush
Any phlox should be divided into separate bushes so that they develop normally and have a neat appearance. The procedure is carried out at least once every 5-7 years, but it can be done more often - once every 3-4 years. They do not choose a special season for this, the division is carried out at any warm time.
In a circle, the bush is dug in, it is taken out of the soil and the shoots are shortened up to 10-15 cm long. Then, with an ax, a shovel, a knife, they divide the bush into parts with 2-5 renewal buds in each. There is no need to worry about the roots: they are long and developed.
The pits where the plant will sit must be prepared in advance, that is, in the fall they are prepared for spring, and in the spring for summer. The distance between the pits is 60 cm for tall phlox and less for the rest.
The pit is filled with compost (0.5 buckets), mineral fertilizer, ash as a source of potassium. If the pH of the soil is acidic (that is, less than 5-7), you need to pour a glass of lime into each hole. Before planting phlox, all the ingredients in the pit are thoroughly mixed in order to prevent root burns.
Water is poured abundantly into the pit and a seedling is placed.They cover it with a substrate, making sure that the renewal buds are covered with earth only by 5 cm. Then they tamp the earth, adding compost if necessary.
The final planting layer is a mulch made of peat, leaf litter or humus, the thickness of which is 10 cm.This layer is needed to create optimal conditions in the ground and accelerate the rooting of new plants, because they must have time to do this before frost.
Phlox rejuvenation method
There are other ways to rejuvenate plants. They take a narrow pointed shovel, with which they cut out the center of the bush, process the cut site with a weak solution of potassium permanganate and pour humus on top. The resulting section of the plant can be planted in another place or divided.
Reproduction of phlox by cuttings

Reproduction of phlox cuttings photo
Cuttings for propagation are used green, which are harvested when the plant reaches a height of 15 cm. This is the ideal time when the cuttings take root best, and then their vitality decreases throughout the year.
Cutting off young shoots, make sure that the mother plant remains with at least two developed buds. Young cuttings are kept in water for an hour to protect them from wilting during planting and to speed up the rooting process. It is not worth keeping greens in water longer, so as not to cause the opposite process.
- Before setting the stalk in the ground, cut off the peduncle, pinch off the lower leaves, and partially cut off the rest to reduce evaporation.
- The length of an ideal planting stalk is 6-10 cm.

Cutting phlox photos
A mature stalk can be planted in the shade on a flower bed or held on a windowsill. The survival rate of phlox increases when they are covered with wet paper. The stalk is inserted only 2-3 cm deep into the ground, lightly tamping the soil around. Be sure to monitor the moisture content of the soil, you can cover the stalk with a cut plastic bottle and remove the cap from the neck for airing. Rooting occurs 6-14 days after this operation.
Using autumn cuttings for phlox propagation
Autumn cuttings are ideal planting material for phlox propagation. August-September is suitable for harvesting, although before that you can also harvest shoots by rooting them in shady places in the garden. When the plant overwinters on its own, it will bloom profusely in the spring.
It is important to plant the cuttings deeply, placing a large number of buds under the ground, which will provoke excellent wintering and vigorous growth in the spring.
Growing phlox from seeds

Phlox seeds photo Grow phlox from seeds
Phlox seeds have excellent germination, so they are sown directly into the ground in spring. Many people prefer to sow phlox seeds before winter using seedling boxes. They leave them for the winter in the garden and, at the first warmth, bring them indoors to get early seedlings.
Seeds sprout amicably, so you need to sow them as little as possible to avoid picking. However, for dense crops, it is better to plant the plants in separate cups in order to get powerful seedlings. They are planted in the ground in May, after hardening the plants.
The video will tell you about growing phlox from seeds:
Phlox and powdery mildew What to do if phlox turn yellow
Phloxes are not very susceptible to disease, but powdery mildew is a frequent guest of this plant. It is unpleasant because green foliage and flowers are covered with a white unpleasant bloom, which is difficult to get rid of. The peak of the development of the disease occurs in July-August. When damaged, the leaves curl - the plant loses them. It is necessary to immediately begin to fight the disease.
Preventive measures consist in treating flowers with copper sulfate or Bordeaux liquid at a concentration of 1% in late autumn, and fungicides are also added to the complex in summer, with which the entire flowerbed is treated twice a year (foundation, topaz, green soap, fast).
If the disease is actively manifested again, you need to change the therapy and treat the foliage with soda ash at a concentration of: 2 tbsp. l. soda is mixed with 50 g of soap and a bucket of water.Bordeaux liquid (1%), a solution of copper with soap (20-30 g of vitriol and 200-300 g of soap) also work well. But when the plant stops blooming, diseased and dried residues are removed, after which the phlox is again treated with fungicides.
Phloxes have a pleasant external, noble flowering, therefore they will become a pleasant addition to any garden, without requiring special cares and growing conditions.
Types of phlox with photos and names
Consider the most popular varieties and types of phlox, which are especially in demand in ornamental gardening.
Phlox paniculata or Phlox paniculata

Phlox paniculata or paniculata Phlox paniculata planting and care Variety Apple color photo
The most popular type of plant. Blooms in the last month of summer - early autumn. Differs in large inflorescences, collected from multi-colored fragrant flowers - white, pink, various shades, lilac, purple. The yellow color of the petals is absent. Breeders have bred varieties that have multi-colored stripes on the petals.
The height of the bushes is 0.4-1 m. They are filled with leaves and lush greenery. The bushes themselves can consist of more than 20 shoots, growing as widely as possible.
The flowering time of paniculate phlox is the entire season. The number of varieties, their diversity is so great that you can choose summer and autumn varieties, increasing the total flowering period of the flower bed by several months.
Phlox subulate or subulum Phlox subulata
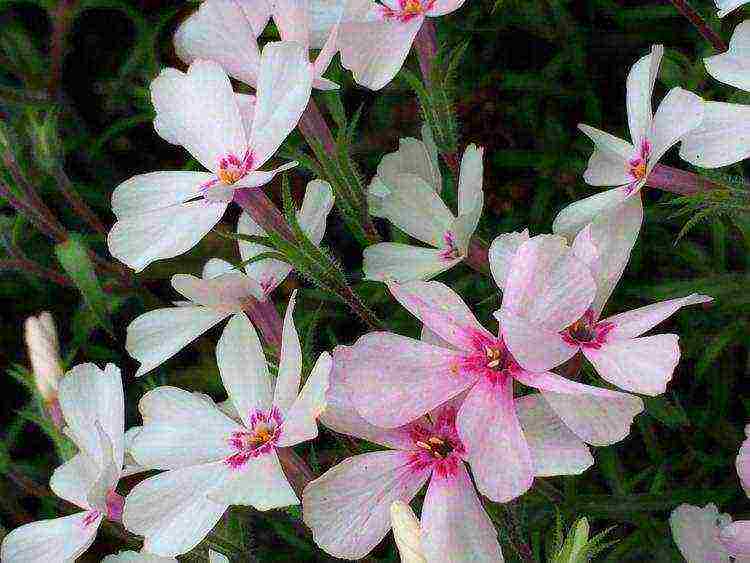

Phlox subulate or subulata Phlox subulata photo
The herbaceous plant is very short (no more than 15 centimeters), with pale lilac or lilac-pink flowers in the amount of 2-4 pieces per inflorescence. Each stem contains a lot of branches that end in inflorescences. Thus, the phlox of the subulate forms a whole carpet covered with delicate flowers, under which there is a dense soddy bush. Therefore, it is also called sod phlox. Flowering time is May-June.
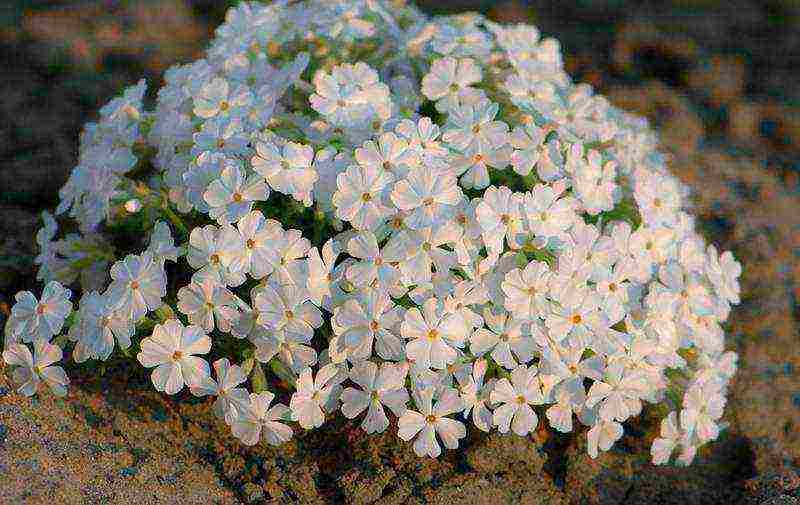

Phlox subulate White Delight White Delight photo of flowers
The species is distinguished by interesting leathery leaves, which, due to their small width and pointed end, resemble needles.
A subulate phlox is grown as a border flowering plant, used for ridges, perennial clumps, planted in flower baskets, flowerpots. It can be cut, trying to form an interesting flower arrangement.
Douglas phlox Phlox douglasii

Phlox Douglas Phlox douglasii planting and care photo
The plant is even smaller in height (5 cm), which spreads like a carpet over the surface of the flower bed. It blooms twice a year, which makes it especially popular. The first falls in May-June, and the second falls in the fall. The leaves are gray-green, small in width. It blooms in white, pink, pale lilac and blue.
Creeping ground cover phlox

Phlox ground cover planting and care photo in the garden
Also a small plant that blooms very early. The height is only 15-20 cm. It is characterized by no less strong branching than other similar plants. Flowers are united in umbrellas, of which some individuals may have up to 10. Flowering time - May-June. Possible colors of the petals are pink, purple, red.
Phlox canadensis or splayed Phlox divaricata
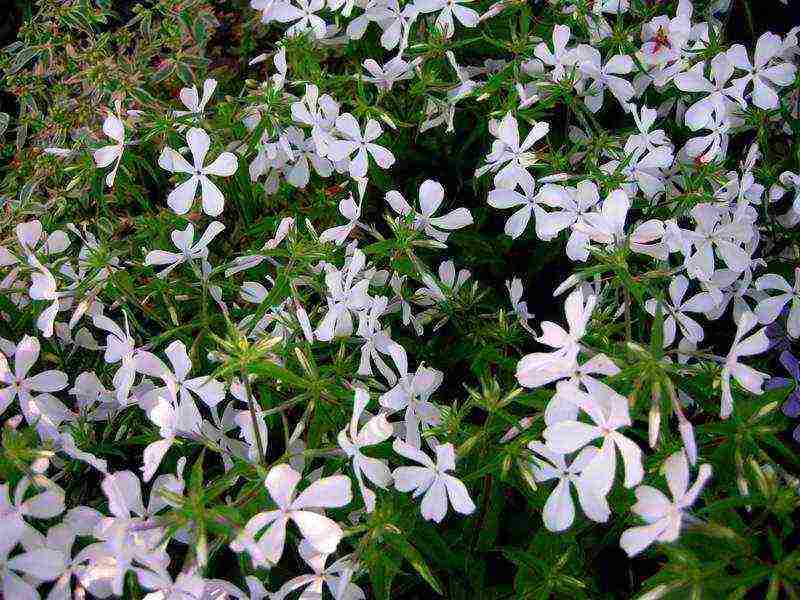

Phlox Canadian or splayed Phlox divaricata in the photo, cultivar May Breeze
The plant is already taller, the height of the stem of which is in the range of 15-40 cm. With the increase in size, the plants became larger and the size of the flowers - they are larger than the rest, have a white, lilac color, shades of gray. The diameter of the main inflorescence - the umbrella - is 10 cm. Seeds after flowering, the time of which is May-June, are not formed.
This species is more sensitive to soil composition than others. On peat, acidic forest soils, it will wither, but soils based on humus and various light components will be ideal. You should not add peat, leaves, fresh manure to them.
As already mentioned, paniculata phlox is the most popular species, but this does not mean that other options should not be considered.If you plant low-growing phlox, which bloom early in May-June, it will be an excellent flower bed decoration in spring. The taller species will continue to bloom in late summer and fall. Thus, there will be a blooming carpet on the site all the time, which can be used to decorate an alpine slide and rockery.


