Content
- 1 Lady's slipper: description of a species from the orchid family
- 2 How to choose a place and plant a lady's slipper?
- 3 Growing and caring for flowers in the garden
- 4 Wintering plants in the open field
- 5 Reproduction of Venus shoes
- 6 How to deal with diseases and pests?
- 7 The legend of the lady's shoe
- 8 We decorate open ground with shoes
- 9 Types of lady's shoes
- 10 What do they like?
- 11 Lady's Slipper - Landing
- 12 Spring Care for the Lady's Slipper
- 13 Bloom
- 14 Autumn winter
- 15 Reproduction
- 16 Diseases and pests
- 17 Place in design
- 18 Planting a Venus shoe - video
The real miracle growing in the garden is the Venus slipper orchid. In nature, flowers are listed in the Red Data Books of most states. Growing this capricious beauty in a flower bed is not so easy, but the effort is worth it. Beautiful delicate flowers bloom in late spring, delighting with the brightness of colors and the unusual shape of the inflorescences.
Lady's slipper: description of a species from the orchid family
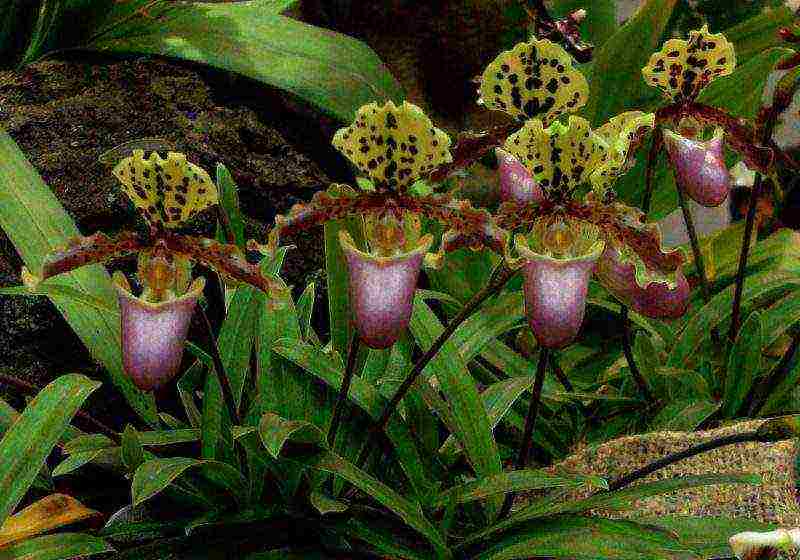
The name Lady's slipper of the Orchid family is used for 5 genera of orchids because of the similar flower shape. Indoor conditions mainly contain hybrids from the Pafiopedilum genus. It is impossible to calculate the total number of existing hybrids, it is so great.
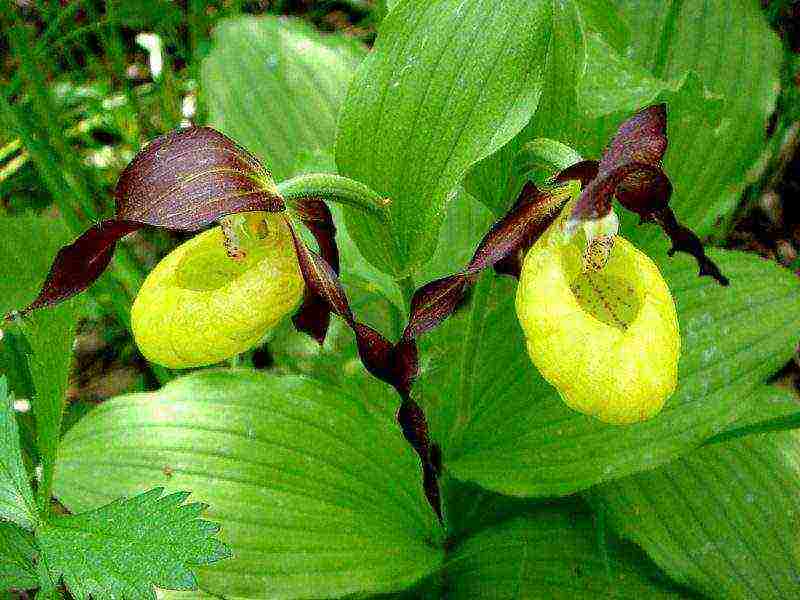

Among them, American polyploids with a very large flower and one rosette of leaves stand out. They rarely branch out and give additional rosettes. The indoor slipper blooms for a long time and can have different colors. Flowers are large and bright, last 2 or 3 months.
The shoe Cypripedium calceolus is grown on flower beds in the garden. According to the Royal Botanic Gardens, there are more than 50 species of this plant growing in various countries. The following description of the rules of planting and leaving is dedicated to them, cypripediums.
How to choose a place and plant a lady's slipper?
The soil for the shoes is prepared in advance - they will not grow in the garden black soil. To do this, mix peat, humus from fallen leaves, coarse sand and dolomite flour or limestone chips. The ratio of the components is 2: 1: 0.5: 0.5. To disinfect the substrate, use "Trichodermin" or "Baikal-EM".

The lady's slipper flower prefers shading, so it is better for him to choose a flower bed on the north side of the house or in a shady garden.
- For planting, holes are dug to a depth of about 40 cm, in width corresponding to the size of the rhizome of the plant.
- At the bottom, drainage from pieces of limestone is arranged and prepared soil mixture is poured into the holes.
- The plant, together with the earthen lump, is moved into the planting hole and covered with earth. The soil cannot be tamped from above.
- If the plant needs support, a peg is buried next to it.
For planting the shoe, a special soil mixture is prepared in containers.
It consists of:
- leaf humus;
- fibrous brown peat;
- sand;
- dolomite flour;
- charcoal up to 5 mm.
The ratio of the components of the mixture is equal, only dolomite flour and charcoal are taken twice less. Landing containers should have a large number of drainage holes and are twice as wide in volume as in height.
Growing and caring for flowers in the garden
In early spring, the shoes are freed from winter shelter, loosened the soil, remove weeds and water the beds. Cypripediums do not require much attention, but they need moderate, regular watering. Plants are fed in early spring, before flowering and at the end of June. Complex mineral fertilizer for garden flowers is diluted in half the recommended dose or special fertilizers for orchids are used.

Experienced growers advise not to pull out weeds that have accidentally grown next to the shoes, but to cut them at the root so as not to damage the delicate root system of flowers.
For planting in a flower bed in spring or autumn, it is better to buy adult, already flowering plants in pots. Cypripediums tolerate frost and slight shading well.
When grown in a flower bed, flowers are transplanted 1 time in 4 years, it is best to do this in August, after the leaves turn yellow. It is undesirable to mulch plants, this can lead to acidification of the soil.
Container crops are replanted annually in the spring, increasing the size of the planting capacity. Plants begin to bloom in the second decade of May, flowering stops in summer.
Wintering plants in the open field
Perennial cypripediums hibernate in the open field. After the foliage turns yellow and withers away, it is cut off. The rhizomes are protected from frost with fallen leaves, raking it on the ridges, or with a layer of mulch.

Containers with flowers hibernate buried in the ground, with foam insulation at the edges and on top. Many hybrid varieties tolerate temperatures as low as -35 ° C.
Reproduction of Venus shoes

Cypripediums reproduce by vegetative division of an adult bush. Adults, 3-year-old plants are planted in early spring or autumn. Planting holes are prepared in advance. The lady's slipper plant is divided with a sharp disinfected tool, the sections are treated with charcoal.
How to deal with diseases and pests?
Most shoe diseases are associated with improper care or fit.
Frequent watering is harmful to plants, especially in the evening.
Water trapped in the leaf outlet can cause rotting if the air is cold at night, so the plants are watered only in the morning.
Cypripediums can be affected by rot and pests.
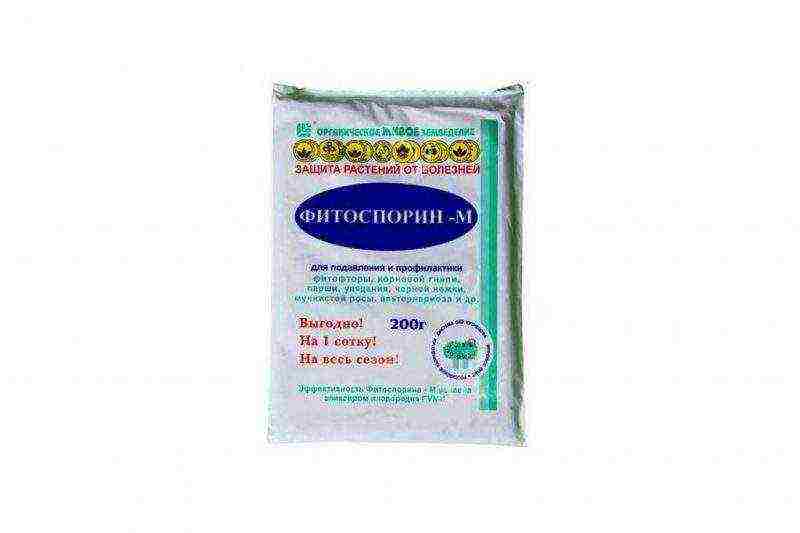
- To combat fungal rot, flowers are treated with fungicides - "Fitosporin" or "Trichodermin".
- Numerous insects, which are especially activated during flowering, are destroyed with biologically active drugs or conventional insecticides and acaricides. You can use "Bona-Forte", "Bitoxiballicin-P", "Fitoverm".
- The cause of damage to plants in a flower bed may be a violation of quarantine, the purchase of a low-quality seedling. Therefore, you need to pay attention to the absence of suspicious spots and cobwebs on the purchased specimen and in any case treat it for prophylaxis with a mixture of fungicide and insecticide.
The legend of the lady's shoe
The lower petal of the shoe has a bulging, unusual shape. It is thanks to this structure that the legend about the origin of the flower appeared.

There is a legend that once a beautiful orchid grew thanks to the goddess of love and beauty Venus. The goddess interceded for the mortal, showing love and sympathy for him. For this she was overthrown from Olympus. In a hurry to return back, Venus lost her shoes. In place of her shoe, a flower of amazing beauty grew, which even today resembles an elegant shoe with a bow.
We decorate open ground with shoes
Cypripedium is suitable for growing in a shady flower bed and it is not easy to find neighbors for it.

Shoes grow well in the same area with ferns, as they have the same requirements for soil and flower bed illumination. You can plant them with hosts and ground cover flowers.
It is undesirable for fast-growing ornamental crops and shrubs to be near the shoes - they will interfere with the development of orchids. It is possible to create a beautiful mono plant from cypripediums of various colors. But it must be borne in mind that the shoe blooms only 2 weeks a year, and at the end of August its leaves dry up completely. Annuals growing nearby can increase the decorative effect of the flower bed.
The large-flowered lady's slipper looks beautiful in a mixborder - a mixed flower garden of an elongated shape, where annual and perennial herbaceous plants, small trees grow side by side. The shoe does not like direct sunlight, a slight shading from the tree will be to its benefit.The flower has a superficial root system, which can reach half a meter in diameter, so dense plantings should be avoided.
The beautiful northern Cypripedium orchids will become the pearl of the garden. Exotic, delicate flowers will decorate shady flower beds, where they will not have worthy competitors.
There are plants with unusual flowers in the Orchidaceae family. The lower petal (lip) of a zygomorphic flower so skillfully repeats the Dutch wooden slipper that a separate genus Slipper (Cypripedium) was isolated in the family, and the scientific name was assigned to the plant, singled out as a type species, cypripedium real (Cypripedium calceolus L.typ) or in Russian translated, the slipper is real, the slipper is small.
It should be noted that the special shape of the lower petal of the corolla in the flower is characteristic of 3 more genera of this family, which are also called "Slipper" - Paphiopedilum, Phragmipedium and Selenipedium. Once upon a time it was 1 genus, but botanists divided it, according to some botanical characteristics, into 4 and left one name "Lady's slipper".

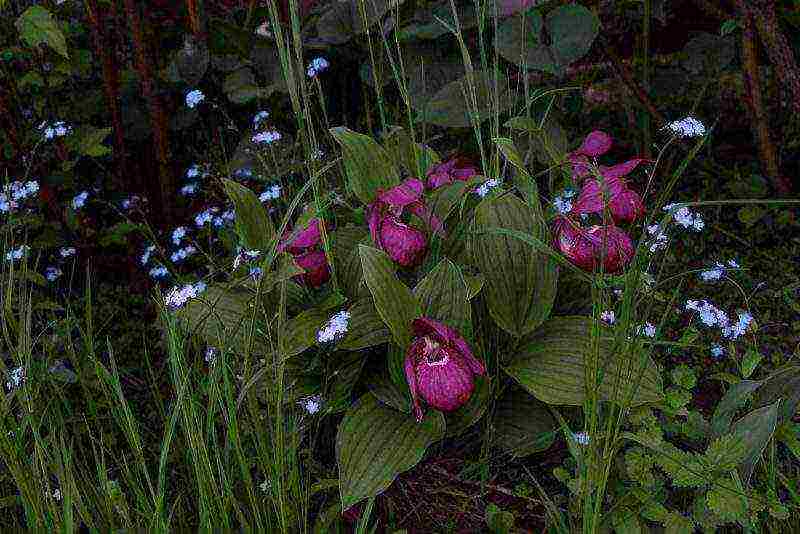
Queen's slipper (Cypripedium reginae)
A huge list of synonyms accompanies Venus's slippers in almost every state where the plant grows in natural conditions. In Europe it is called the lady's shoe, Venus's shoe, ladies' shoe, in America - moccasins. In Russia, there are cuckoo shoes, a lady's shoe, Mary's shoe, the boots of the Mother of God, Adam's head, cockerels, boots, a limestone shoe.
The lady's slipper so fascinated the sedate Norwegians that in the Norwegian province of Nur-Trøndelag it was depicted on the coat of arms of the commune of Demolition.
Features of the orchid family and the genus slipper
All orchids are herbaceous, flowering perennials. According to the requirements for living conditions, orchids are epiphytes. They settle on living large perennial trees, which they use as a support, that is, the place of attachment, which is always well illuminated by the rays of the sun. They do not harm trees, since food is obtained from the surrounding atmosphere.

Lady's slipper (Cypripedium acaule)
Most orchids have a thick, short rhizome. There are species with a thin long branched rhizome. The rhizome is located in the upper soil layer. The replacing vegetative buds develop secretly for 3-4 years, and then a young sprout appears on the surface. Real roots extend from the rhizome to the sides. Orchid roots, depending on the function performed, can be dark to dark brown and twisty light, covered with numerous hairs. In orchids, the roots perform 2 functions: anchoring and assimilating.
- The fastening function is performed by the fastening roots. They securely attach the plant to the bark of the tree. They are coarser and darker in color.
- Assimilatory is performed by thinner silvery-gray roots, which with numerous hairs absorb water from precipitation of any kind. They are satisfied with the scarce reserves of organic matter in the water, in the cracks in the bark on the branches of trees.
Orchid leaves are simple. The leaf blade is whole with a very short petiole. The arrangement of the leaves is alternate or two-row. The flowers are located on a high peduncle, usually in racemose or spike-shaped inflorescences. Single flowers rarely form. The flowers are accompanied by bracts. The flower itself has a very bizarre shape of a shoe, a hanging jug, sometimes in the form of insects or arachnids.
For the genus of slipper, the vegetative organs are similar in external structure and function to the family. The bizarre shape of the flower is characteristic. The corolla petals are arranged in 2 circles: 3 petals in the outer circle and 3 in the inner. The lower petal of the inner circle of the corolla resembles a swollen pouch or the toe of a shoe, more often a shoe. The two lateral ones are narrower, sometimes twisted into a spiral, spread out to the sides like unfolded or semi-lowered wings.Of the three upper petals of the outer circle, one is always bent and plays the role of an umbrella, and the other two fused together usually hide behind or under the lip (shoe). The lip is brightly colored to attract pollinating insects. This arrangement of trap flowers guarantees pollination.
The fruit is a capsule in which up to 4 million dusty seeds are formed. Insects are the main pollinators.

Lady's slipper spotted (Cypripedium guttatum) or speckled
Distribution area
The genus Slipper (Cypripedium) includes about 50 species. Plants are most widespread in America (South and North), in Europe and Asia, where they grow in natural conditions from the forest-tundra to the tropics. On the territory of Russia, 5 species of the genus Cypripedium are widespread and are found in Karelia (they are called the northern orchid), on the Volga, in Kamchatka, in the southern regions of Siberia, in the Far East, and occasionally in Alaska. Most often, orchids grow in deciduous, mixed forests, sometimes in conifers. Some species prefer steppe forests, their edges, forest meadows and shrubs.
Types or Russian shoes
Of the 50 species of the genus Cypripedium, distributed around the world, 5 grow on the territory of Russia, of which 3 are the most promising for garden design.
Swollen slipper (C. ventricosum Sw.) Is considered the most beautiful orchid found in the temperate zone of the European regions, in Siberia, in the Far East. Ornamental plants with a slightly pubescent stem up to 40-45 cm tall. On the stem there are 3-5 broad-oval 12-15 cm dark green leaves with pointed ends. Single flowers have 2 leafy bracts. The color of the flower is white, brownish-red, lilac-light. Highly ornamental plant, can be used in garden plantings.

Large-flowered lady's slipper (Cypripedium macranthon)
Large-flowered slipper (C. macranthum Sw.) Is distinguished by a strongly shortened thick rhizome and thin winding roots. On a 45 cm stem there are 3-4 large long (up to 16 cm) simple leaves. The leaves are stalk-enveloping, slightly hairy along the veins and edges. The flowers are solitary, like the bloated shoe. Behind the lip is a two-toothed petal, fused from two perianth petals. Coloring of the perianth from lilac to violet-pink. There are pure white colors with a delicate delicate aroma, yellowish with a yellow-green mesh, with a yellow-reddish tint. Bloom in June-July. Uncommon plant, but promising for introduction into horticultural culture.
Spotted slipper or speckled (C. guttatum Sw.) distributed in the same regions as the previous 2 species. In addition, it is found in the eastern and central regions of the European part of the Russian Federation, where it forms large clumps in the grass cover.
Low plant (stem up to 30 cm). The rhizome is long, creeping. The leaves are smaller (6-12 cm), simple, elliptical, hairy along the veins and edge. Blooms in May-June. The flower is distinguished by a spotted purple-white pattern.
The species is able to grow on any soil. Decorate an alpine slide, a stone garden. Does not form dense curtains. Unpretentious care. As an ornamental deciduous and flowering plant, it is recommended for use in landscape gardening culture.
Photo gallery of species Cultivation and care Selection of planting material
A healthy rhizome suitable for planting has a large number of white, light-colored roots and healthy living buds. It is best to purchase three-year-olds. Brown roots, a large number of black, broken roots, black rhizomes indicate the unsuitability of the material.

Swollen slipper (Cypripedium x ventricosum)
Choosing a landing site
Plants are light-loving, but cannot stand direct hot rays of light, so the north side near the fence, other buildings or the openwork shade of deciduous trees is suitable for them. The place should not be hot and calm (like in a forest, on the edge).
Soil requirement
For shoes, soil is needed that is depleted in organic matter, loose, air and water permeable, with a well-drained bottom layer. A potting soil mixture is best suited for growing a lady's shoe, which is prepared from the following components:
- local garden land,
- peat (2 parts),
- sheet land (1 part),
- neutral baking powder: sand, flint gravel, crushed brick, expanded clay (2-3 parts),
- limestone chips, finely crushed shells (1 part) to neutralize acidification,
- dust from oak, on which honey agarics grew (2 parts), coniferous litter for mulching planting.
Stir the mixture thoroughly.
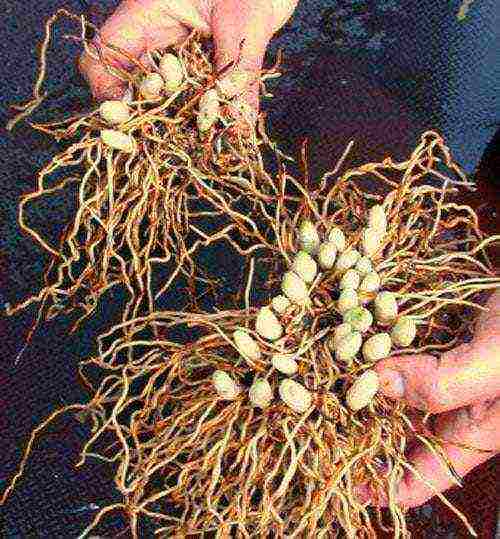

Healthy roots with vegetative buds
Landing
- The best period for planting shoes is spring before the start of growth and autumn, when the foliage withers. The purchased material is checked before planting. Cut off the blackened roots.
- Pits prepared for planting should be 30-40 cm deep, filled with prepared soil mixture and correspond in width and length to the habit of the planting material. It is good to add a few soft limestone stones to the bottom of the pit (under the soil mixture).
- The rhizome is laid horizontally in the prepared place. The roots are gently spread to the sides.
- The planting depth should cover the vegetative bud by 1.0-1.5 cm. Deepening will lengthen the onset of flowering, sometimes by several years.
- A layer of soil mixture is poured on top and watered.
- Cover with a layer of moss mulch, pine needles, rotted healthy leaves.
With proper planting and caring for venereal shoes, in the first 4 years, plants form a root system on an area of 50-70 cm, deepening the roots up to 30 cm.

Root laying when planting a lady's shoe
Care
In the spring, with the onset of warm weather (April, May), the shoes are freed from the winter shelter (if any). Spring feeding of species shoes can be limited to the autumn rotten leaf left over from the winter shelter, the introduction of a thin layer of mulch of matured vermicompost. During this period, it is good to plant purchased rhizomes or cuttings.
In the second half of May, you can carry out the first feeding of only varietal shoes with full mineral fertilizer, using flower fertilizers in a half dose. Dilute 1 tablespoon of Kemira-Lux in 10 liters of water and add 2 ampoules of Epin. Sprinkle the plants. Better only weakened - with yellowed or light green leaves.
Remember! Orchids do not like to overeat. Flowering begins in late May and early June and lasts 2-3 weeks.

Shoots of Venus's shoe
In mid-June (at the end of flowering), repeat the feeding of varietal shoes and all weakened plants, including last year's plantings of type species.
The soil is kept clean throughout the growing season. Weeds are not pulled out, but cut off above the soil surface. The soil is not loosened so as not to damage the roots and not break their symbiosis with soil fungi.
Watering is moderate, carried out when the topsoil dries up.
At the end of August-September, the dead above-ground mass is cut off. Shoes are prepared for vegetative propagation, planting, transplanting.
With the onset of a cold snap (October-November), they mulch (cover) plantings for the winter. Sprinkle mulch on the buds above the ground with pine needles, moss, mature compost.

This is what a lady's slipper looks like at the peak of flowering.
Wintering
The hybrid varieties of shoes, offered in specialized stores, perfectly withstand frosts of -35 ... -37 * C. If the snow layer is 5-6 cm, the plants do not need another shelter. But in more southern regions, where there is little snow, the plants need to be insulated, as mentioned above.
Reproduction
Orchids are propagated by seeds and vegetatively by dividing the rhizomes. They are rarely propagated by cuttings, as well as by seeds. Growing a lady's shoe from seeds is very difficult, although the number of seeds formed is huge. The main difficulty is associated with the development of plants due to symbiosis with the fungus, especially the first 4 years. The lady's slipper plant, grown from seed, blooms at 12-17 years.
In garden culture, orchids are propagated mainly by cuttings, which are obtained by cutting the rhizomes into several parts. Each part should have 2-3 buds. The bud on the rhizome develops 3-4 years underground, and then appears on the surface. Therefore, the breeding of Venus shoes is carried out by divisions only 3-4 years old. Places of cuts are immediately disinfected, and the cut is planted in a prepared place. Further care is described above.
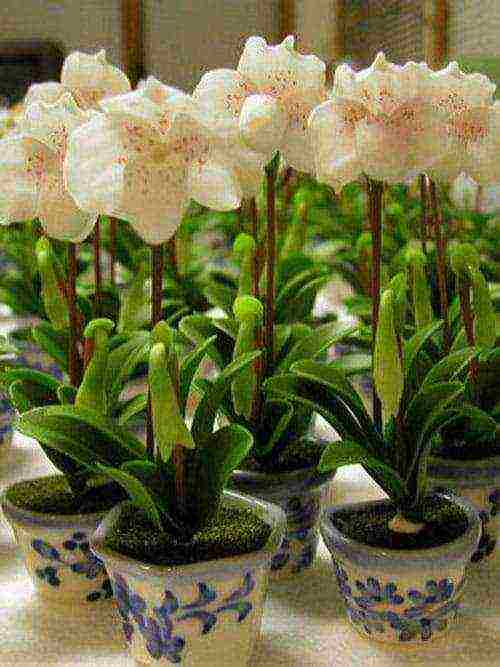

Shoes in flowerpots
Diseases and pests
Diseases of the shoes are mainly associated with a violation of agricultural cultivation techniques:
- excessive watering causes root rot due to fungal rot,
- when used in planting infected diseased plants,
- when working with non-dezenified toolkit.
Diseased plants are treated with biofungicides: phytosporin, trichodermin, alirin-B and others according to the instructions in the recommendations.
Pests that cause noticeable harm to plants are mealy worms and spider mites, aphids, scale insects, slugs, snails. There are chemicals for the fight, but they are harmful to the health of residents and animals. Therefore, it is possible to recommend processing plants only with biological products such as bitoxibacillin-P, vertilillin, Bona-Forte and others. Moreover, bioinsecticides can be used in tank mixtures, which will reduce the number of treatments for diseased and pest-affected plants.

Lady's slipper in the garden
Use in outdoor decor
Orchids need special care conditions for normal growth and development. Given their peculiarity, orchids are best used in mono-plantings, choosing shady areas (for example, resting corners). Some types can be used in decorating rock gardens, stone gardens.
The lady's slipper of the genus Cypripedium looks decorative in combination with low ferns, hosts, ground cover plants. The lady's slipper gets along well with slowly growing grasses and shrubs that cannot drown them out quickly. Orchids are easy to care for and vegetative propagation. They will provide a positive result even in the areas of novice florists.

There are plants in the orchid family with unusual flowers.
Their lower petals so skillfully repeat the shape of the Dutch antique shoes that the word "slipper" was included in the name of the plants.
Types of lady's shoes
Three types of Venus slipper are the most promising for garden design.
The swollen lady's slipper is considered the most beautiful orchid found in the European part of Russia, Siberia, and the Far East. These are elegant plants with a slightly pubescent stem up to 40-45 cm in height. The color of the flower is white, brownish-red, lilac-light. Such a highly decorative plant can be used in garden plantings.
The large-flowered lady's slipper is distinguished by a strongly shortened thick rhizome and thin winding roots. The height is the same as in the previous species. Colors - from lilac to violet-pink. There are pure white tones, yellowish with a yellow-green mesh, with a yellow-reddish tint. Bloom in June-July. Uncommon  plant, but promising for introduction into horticultural culture.
plant, but promising for introduction into horticultural culture.
A healthy rhizome of the Venus shoe, suitable for planting, has a large number of white, light roots and healthy living buds. It is best to purchase three-year-old plants. Brown roots, a large number of black, broken roots, black rhizomes indicate the unsuitability of the material.
Spotted or speckled slipper - a low plant (stem up to 30 cm). The rhizome is long, creeping. The leaves are smaller (6-12 cm), simple, elliptical, hairy along the veins and edge. Blooms in May-June. The flower is distinguished by a spotted violet-white pattern. The species is able to grow on any soil. Decorate an alpine slide, a stone garden. Does not form dense curtains. Unpretentious care.As an ornamental deciduous and flowering plant, it is recommended for use in landscape gardening culture.
See also: Growing Venus shoes (orchid) at home and in the garden
What do they like?
Venus shoes are light-loving, but they cannot stand direct hot sunlight, so the north side near the fence, other buildings or the openwork shade of deciduous trees is suitable for them. The place should be cool and calm. These plants require soil that is depleted in organic matter, loose, air and water permeable, with a well-drained bottom layer.
A soil mixture is best suited for growing a Venus shoe, which is prepared from the following components: local garden soil or peat (2 parts), leaf soil (1 part), neutral disintegrants: sand, flint gravel, crushed brick or expanded clay (2-3 parts ), limestone chips or chalk, finely crushed shells (1 part). And to neutralize acidification, add dust from oak (2 parts). The mixture must be thoroughly mixed.
Lady's Slipper - Landing
The best period for planting shoes is spring, before growth begins, and autumn, when the foliage withers. Before this, the blackened roots are necessarily cut off from the plants. Pits prepared for planting with a depth of 30-40 cm are filled with soil mixture, and in width and length they must correspond to the size of the planting material. It is good to add a few chalk stones to the bottom of the hole (under the soil mixture). The rhizome is laid horizontally in the prepared place. The roots are gently spread to the sides. The planting fur coat should cover the vegetative bud by 1-1.5 cm. Deepening will lengthen the onset of flowering, sometimes by several years.
A layer of soil mixture is poured on top and watered. Then they are covered with a layer of mulch made of moss, pine needles, rotted healthy leaves. With proper planting and caring for venereal shoes, in the first 4 years, the plants form a root system on an area of 50-70 cm, deepening the roots to 30 cm.
Spring Care for the Lady's Slipper
In the spring, with the onset of warm weather (April, May), the shoes are freed from the winter shelter (if any). Spring feeding of species shoes can be limited to the autumn rotten leaf left over from the winter shelter, the introduction of a thin layer of mulch of matured vermicompost. During this period, it is good to plant rhizomes or delenki. In the second half of May, you can carry out the first feeding of only varietal shoes with full mineral fertilizer, using flower fertilizers in a half dose. You can dilute 1 tbsp. l. "Agricola" in 10 liters of water and add 2-3 ampoules of "Epina-extra". Orchids do not like to be overfed.
On a note
Species plants include those that occur in nature. Varietal - bred as a result of human selection.
Bloom
 Flowering begins in late May - early June and lasts 2-3 weeks. In mid-June (at the end of flowering), you need to repeat the feeding of varietal shoes and all weakened plants, including last year's plantings of typical species. During the entire growing season, the soil is kept clean. Weeds are not pulled out, but cut off above the soil surface. The soil is not loosened so as not to damage the roots and not break their symbiosis with soil fungi. Watering should be moderate, it is carried out when the topsoil dries up.
Flowering begins in late May - early June and lasts 2-3 weeks. In mid-June (at the end of flowering), you need to repeat the feeding of varietal shoes and all weakened plants, including last year's plantings of typical species. During the entire growing season, the soil is kept clean. Weeds are not pulled out, but cut off above the soil surface. The soil is not loosened so as not to damage the roots and not break their symbiosis with soil fungi. Watering should be moderate, it is carried out when the topsoil dries up.
Autumn winter
At the end of August - September, the dead aboveground mass is cut off. Shoes are prepared for vegetative propagation, planting, transplanting. With the onset of a cold snap (October-November), they mulch (cover) plantings for the winter. Sprinkle the buds above the ground with pine needles, moss, and mature compost. Hybrid varieties of shoes perfectly withstand frosts down to minus 25-30 degrees.
On a note
If the snow layer is 10-20 cm, the Venus shoes do not need another shelter. But in more southern regions, where there is little snow, the plants should be insulated.
Reproduction
Orchid cultures are propagated most often by dividing the rhizome. Cuttings and seeds are rarely used.The main difficulty is associated with the development of plants due to symbiosis with the fungus, especially the first 4 years. The lady's slipper, grown from seed, blooms only in the 10-12th year.
Therefore, in garden culture, orchids are propagated mainly by divisions, which are obtained by cutting the rhizomes into several parts. Each part should have 2-3 buds. They develop on the rhizome for 3-4 years underground, and then appear on the surface. Therefore, only 3-4-year-old venereal shoes are propagated by divisions. Places of cuts are immediately disinfected, and the cut is planted in a prepared place.
Diseases and pests
Diseases of shoes are mainly associated with a violation of agricultural cultivation techniques. Fungal rot lesions occur with excessive watering, causing root rot, using infected diseased plants in planting, and working with non-disinfected tools. Diseased plants are treated with biofungicides: "Fitosporin-M", "Trichodermin", "Bactofid", etc.
Pests that cause significant harm to plants are mealybugs, spider mites, aphids, scale insects, slugs, snails. To combat them, the chemicals "Biotlin", "Actellik", "Iskra" are used.
Place in design
Venus shoes, given their characteristics, are best used in landscape architecture and open ground decor, in the form of mono-plantings in shady areas, for example, recreation areas. Some types can be used in decorating rock gardens, rocky gardens.
The lady's slipper looks very decorative in combination with low ferns, hosts, astilbe, ground cover plants, it also gets along well with slowly growing grasses, grasses and shrubs that cannot drown it out quickly.
See also: Pafiopedilum flowers or Venus shoes - care and features of orchids
Planting a Venus shoe - video
Lady's slipper. Pafiopedilum (landing)
Below are other entries on the topic "Cottage and garden - do it yourself"
Papiopedilum transplant - question and answer: Venus's shoe needs a transplant. Urgent Acquaintance ... How to cut shrubs correctly: Cutting and shaping shrubs - ... Growing a lady's slipper (orchid) at home and in the garden: How to grow a lady's slipper plant Ah, ... Growing and caring for shoe orchids (cypripediums) - believe it, it's simple! : Orchid shoes: planting and care. Tips ... Rare plant - Lady's slipper: Orchids of Russian forests Orchids are unambiguously associated ...
Subscribe to updates in our groups.
Let's be friends!
There are plants with unusual flowers in the Orchidaceae family. Lower petal (lip)
zygomorphic flower so skillfully repeats the Dutch wooden slipper,
that a separate genus Slipper (Cypripedium) was allocated in the family, and behind the plant
the scientific name was fixed, allocated to the type species, the cypripedium is real
(Cypripedium calceolus L.typ) or in Russian translation real slipper, slipper
small.
The content of the article
Features of the orchid family and the genus of slipper Distribution area Species or Russian slippers Photo gallery of species Cultivation and care Choice of planting material Choice of planting site Requirement for soil Planting Care Wintering Reproduction Diseases and pests
Use in outdoor decor
It should be noted that the special shape of the lower petal of the corolla in the flower is also characteristic of
3 genera of this family, which are also called "Slipper" - Pafiopedilyum
(Paphiopedilum), Fragmipedium (Phragmipedium) and Selenipedium (Selenipedium). Once upon a time
it was 1 genus, but botanists divided it, according to some botanical characteristics,
on 4 and left one name "Lady's slipper".
Queen's slipper
(Cypripedium reginae)
A huge list of synonyms accompanies Venus
shoes in almost every state where the plant grows in
natural conditions. In Europe it is called the lady's shoe, the slipper
Venus, a lady's shoe, in America - moccasins. In Russia - cuckoo
slippers, lady's slipper, Maryin's slipper, boots of the virgin, adamova
head, cockerels, boots, limestone slipper.
The lady's slipper so fascinated the sedate Norwegians that in the Norwegian province
Nur-Trøndelag he was depicted on the coat of arms of the commune of Demolition. Features of the orchid family
and the genus slipper All orchids are herbaceous flowering perennials.
According to the requirements for living conditions, orchids are epiphytes. They settle for the living
large perennial trees that are used as a support, that is, a place of attachment,
necessarily well lit by the rays of the sun. They do not harm trees, since food
extracted from the surrounding atmosphere.
Lady's slipper (Cypripedium acaule)
Most orchids have a thick, short rhizome. There are species with a thin long
branched rhizome. The rhizome is located in the upper soil layer. Substituting
vegetative buds develop secretly for 3-4 years, and then a young one appears on the surface
sprout. Real roots extend from the rhizome to the sides. Orchid roots depending on
the function performed can be dark to dark brown and twisty light,
covered with numerous hairs. In orchids, the roots perform 2 functions:
and assimilating. The fastening function is performed by the fastening roots. They are reliable
attach the plant to the bark of a tree. They are coarser and darker in color. Assimilating
perform thinner silvery-gray roots, which have numerous hairs
absorb water from precipitation of any kind. Satisfied with scarce organic supplies
in the water, in the cracks in the bark on the branches of trees.
Orchid leaves are simple.
Sheet
whole plate with very short petiole. The arrangement of the leaves is alternate or two-row.
Flowers are located on a high peduncle, usually in racemose or spike inflorescences
... Single flowers rarely form. The flowers are accompanied by bracts. The flower itself has
t a very bizarre shoe shape, hanging jug, sometimes insect-shaped
or arachnids. For the genus slipper, the vegetative organs are similar in external structure and
performed function with the family. The bizarre shape of the flower is characteristic. Corolla petals
arranged in 2 circles: 3 petals of the outer circle and 3 inner ones. The lower petal of the inner
the circle of the corolla resembles a swollen bag or the toe of a shoe, more often a shoe. Two side
narrower, sometimes twisted into a spiral, spread out to the sides as unfolded or
semi-lowered wings. Of the three upper petals of the outer circle, one is always bent
and plays the role of an umbrella, and the other 2 fused are usually hidden behind or under the lip (shoe).
The lip is brightly colored to attract pollinating insects. Such a structure of trap flowers
guarantees pollination. The fruit is a capsule in which up to 4 million dusty seeds are formed.
Insects are the main pollinators. Lady's slipper spotted (Cypripedium guttatum)
or speckled distribution The genus Slipper (Cypripedium) includes about 50 species.
Plants are most widespread in America (South and North), in Europe and
Asia, where in natural conditions grow from forest tundra to the tropics. On Russian territory
5 species of the genus Cypripedium are widespread and are found in Karelia (they are called the northern orchid),
on the Volga, on Kamchatka, in the southern regions of Siberia, in the Far East, and occasionally in Alaska. Most often
orchids grow in deciduous, mixed forests, sometimes in conifers. Some species prefer
steppe forests, their edges, forest meadows and shrubs
... Types or Russian shoes
Of the 50 species of the genus Cypripedium, distributed around the world, 5 grow on the territory of Russia,
of which 3 are the most promising for garden design.
Swollen slipper (C. ventricosum Sw.) Is considered
the most beautiful orchid found in the temperate zone of the European regions, in Siberia, in the Far East.
Ornamental plants with a slightly pubescent stem up to 40-45 cm tall. On the stem 3-5 broadly oval
12-15 cm dark green leaves with pointed ends. Single flowers have 2 leafy bracts.
The color of the flower is white, brownish-red, lilac-light. Highly ornamental plant, can
used in garden plantings.
Large-flowered lady's slipper (Cypripedium macranthon)
Large-flowered slipper (C. macranthum Sw.) Is distinguished by a strongly shortened thick rhizome
and thin winding roots. On a 45 cm stem there are 3-4 large long (up to 16 cm) simple
sheet. The leaves are stalk-enveloping, slightly hairy along the veins and edges. The flowers are single, like a shoe
bloated. Behind the lip is a two-toothed petal, fused from two perianth petals.
Coloring of the perianth from lilac to violet-pink. There are pure white colors with a thin
delicate aroma, yellowish with a yellow-green mesh, with a yellow-reddish tint. Bloom in June-July.
Uncommon plant, but promising for introduction into horticultural culture.
Spotted or speckled slipper (C. guttatum Sw.) Is distributed in the same regions as the previous
2 types. In addition, it is found in the eastern and central regions of the European part of the Russian Federation, where it forms in
large clumps of grass. Low plant (stem up to 30 cm). The rhizome is long, creeping.
The leaves are smaller (6-12 cm), simple, elliptical, hairy along the veins and edge. Blooms in May-June.
The flower is distinguished by a spotted purple-white pattern. The species is able to grow on any soil. Will decorate
alpine slide, stone garden. Does not form dense curtains. Unpretentious care. How decorative
-leaf and flowering plant is recommended for use in landscape gardening culture.
Photo gallery of views
Kentucky slipper
Lady's slipper (Cypripedium calceolus L)
Californian Cypripedium (Cypripedium californicum)
Cypripedium ram-headed (Cypripedium arietinum)
Slipper Yatabe (S. yatabeanum Makino)
Large-flowered slipper (C. macranthum Sw.)
Lady's slipper is real
Tibetan slipper (Cypripedium tibeticum)
Large-flowered slipper (Cypripedium macranthos)
Cultivation and care Selection of planting material A healthy rhizome suitable for planting has a large number of white, light roots and healthy living buds. It is best to purchase three-year-olds. Brown roots, a large number of black, broken roots, black rhizomes indicate the unsuitability of the material.
Swollen slipper (Cypripedium x ventricosum)
Choosing a planting site Plants are light-loving, but cannot stand direct hot rays of light,
therefore, the north side near the fence, other buildings, or the openwork shade of deciduous trees will suit them.
The place should not be hot and calm (like in a forest, on the edge). Soil requirement For shoes
a soil depleted in organic matter is needed, loose, air- and permeable, with well-drained
bottom layer. The best soil for growing a lady's shoe is a soil mixture that
prepared from the following ingredients: local garden soil, peat (2 parts), leaf soil (1 part), neutral
baking powder: sand, flint gravel, crushed brick, expanded clay (2-3 parts), limestone chips
, finely crushed seashells (1 part) to neutralize acidification, dust from the oak on which they grew
honey mushrooms (2 parts), coniferous litter for mulching planting. Stir the mixture thoroughly. Healthy roots
with vegetative buds Planting The best period for planting shoes is spring before growth and autumn,
when the foliage is dry. The purchased material is checked before planting. Cut off the blackened roots
... Pits prepared for planting should be 30-40 cm deep, filled with prepared soil
the mixture and in width and length correspond to the habit of the planting material. To the bottom of the pit (under the soil
mixture) well add a few stones of soft limestone. The rhizome is placed in the prepared
the place is horizontal.
The roots are gently spread to the sides. Planting depth should be 1.0-1.5 cm
cover the vegetative bud. Deepening will lengthen the onset of flowering, sometimes by several years.
A layer of soil mixture is poured on top and watered. Cover with a layer of moss mulch, pine needles,
rotted healthy leaves. With proper fit and care of venereal shoes, in the first 4
Years, the plants form a root system on an area of 50-70 cm, deepening the roots up to 30 cm.
when landing a Venus shoe Leaving Spring with the onset of warm weather (April, May) shoes
freed from winter shelter (if any).
ny feeding of species shoes may be limited
with an autumn rotten leaf left over from a winter shelter, the introduction of a thin layer of mulch of ripe vermicompost.
seedlings
carry out the first feeding only varietal shoes with full mineral fertilizer, using flower
fertilizer in a half dose. Dilute 1 tablespoon of Kemira-Lux in 10 liters of water and add 2 ampoules of Epin.
Sprinkle the plants. Better only weakened - with yellowed or light green leaves.
Remember! Orchids do not like to overeat. Flowering begins in late May-early June and lasts 2-3 weeks.
Shoots of the Venus shoe In mid-June (at the end of flowering), repeat the feeding of varietal
shoes and all weakened plants, including last year's plantings of type species. The entire growing season
the soil is kept clean. Weeds do not pull out, but are cut off above the soil surface. The soil
do not loosen, so as not to damage the roots and not break their symbiosis with soil fungi. Watering is moderate,
carried out when the topsoil dries up.
At the end of August-September, the dead aboveground mass is cut off
... Prepare shoes for vegetative reproduction, planting, transplanting. With the onset of a cold snap (October-
November) mulch (cover) plantings for the winter. Sprinkle the buds with mulch above the ground with pine needles
, moss, mature compost. This is what a lady's slipper looks like at the peak of flowering Wintering Hybrid varieties
shoes, offered in specialized stores, perfectly withstand frosts -35 ... -37 * С.
If the snow layer is 5-6 cm, the plants do not need another shelter. But in more southern areas where
there is little snow, the plants need to be insulated, as mentioned above. Reproduction Propagated by orchid seeds
and vegetatively by dividing the rhizome. They are rarely propagated by cuttings, as well as by seeds. Cultivation of venereal
a shoe made of seeds is very difficult, although the number of seeds formed is enormous. The main difficulty
associated with the development of plants due to symbiosis with the fungus, especially the first 4 years. The plant is a lady's slipper,
grown from seed blooms in 12-17 years. In garden culture, orchids are propagated mainly by delenks,
which are obtained by cutting the rhizomes into several parts. Each part should have 2-3 buds. Bud
develops on the rhizome for 3-4 years underground, and then appears on the surface. Therefore, the breeding of Venus shoes is carried out by divisions only 3-4 years old. The places of the cuts are immediately disinfected, and the cut
planted in a prepared place. Further care is described above. Shoes in flowerpots Diseases and pests
Diseases of shoes are mainly associated with a violation of agricultural cultivation techniques: excessive watering
causes rotting of the roots due to the defeat of fungal rot, when used in planting infected
diseased plants when working with non-desensitized tools. Diseased plants
treated with biofungicides: phytosporin, trichodermin, alirin-B and others, respectively
the directions in the recommendations. Pests that cause significant harm to plants - mealy worm and
spider mites, aphids, scale insects, slugs, snails. There are chemicals to fight, but they are harmful
for the health of residents and animals. Therefore, it is possible to recommend processing plants only with biological products.
such as bitoxibacillin-P, vertilillin, Bona-Forte and others. Moreover, bioinsecticides can be used
in tank mixtures, which will reduce the number of treatments for diseased and pest-affected plants.
Lady's slipper in the garden
Use in outdoor decor
Orchids need special care conditions for normal growth and development. Given their peculiarity
orchids are best used in mono-plantings, choosing shady areas (for example, resting corners)
... Some types can be used in decorating rock gardens, stone gardens. Lady's slipper
the genus cypripedium looks decoratively in combinations with low ferns, hosts,
ground cover plants. Lady's slipper gets along well with slowly growing herbs
and shrubs that cannot drown them out quickly. Orchids are easy to care for and vegetative
reproduction. They will provide a positive result even in the areas of novice florists.


