Content
- 0.1 The best varieties of lilies for the garden
- 0.2 Determine the type of lily on the bulb
- 0.3 Choosing a healthy bulb
- 0.4 When to buy bulbs
- 0.5 Buying lily saplings
- 0.6 Site selection
- 0.7 Soil preparation
- 0.8 Preparing the bulbs for planting
- 0.9 Planting lilies in the ground
- 0.10 Features of summer landing
- 0.11 Planting lilies in summer video
- 0.12 Watering
- 0.13 Loosening the soil
- 0.14 Top dressing in summer
- 0.15 Watering
- 0.16 Top dressing
- 0.17 Pruning
- 0.18 Protection of lilies from diseases and pests
- 0.19 Lily care after flowering video
- 1 Transplanting and dividing bulbs
- 2 Outcome
- 3 Choosing a site for growing lilies
- 4 Soil preparation
- 5 Dates of spring and autumn planting
- 6 Planting lilies
- 7 Lily care rules
- 8 How to cut flowers correctly
- 9 Transplant timing
- 10 Reproduction by scales
- 11 Features of cultivation after distillation
- 12 Correct fit
- 13 Features of different varieties
- 14 The incomparable beauty of lilies
- 15 A few more growing secrets
- 16 Care and fertilization
- 17 Garden lily care videos
Interspecific lily hybrid - Algarve cultivar
Lily is a decoration of many gardens and is very popular with flower growers all over the world. Everyone dreams of growing lily flowers in their garden, planting and caring for which is not difficult and affordable, but requires preliminary preparation.
Choosing a variety and bulbs of lilies
When choosing planting material, you need to make sure that it will match the selected variety, healthy, and suitable for growing in your area. In the issue of varietal compliance of lilies, one can only hope for the seller's conscientiousness, but the species and quality of the bulbs can be determined by their appearance.
The best varieties of lilies for the garden
The genus of lilies is represented by more than 80 wild and cultivated species around the world. Their varietal diversity is even more impressive - about 8000 varieties and hybrids, each of which is unique in its own way.
Throughout Russia, including Siberia and the Urals, summer residents practice the cultivation of lilies of Asian hybrids. These varieties are frost-resistant, grow quickly and are not demanding to care for. They bloom very profusely in June - July. The peculiarity of Asians is the lack of odor in flowers. The most famous varieties of this group are Marlene, Top Gunn, Lollipop, Yeti, Flore Pleno, Daira, Sorbet.
Popular Asian hybrid - Top Gunn variety
Oriental hybrids of lilies are more capricious when growing. They do not tolerate low temperatures poorly, therefore they prefer to grow them in the southern zone of Russia and in greenhouses of the Moscow region. They are distinguished by fragrant flowers of extraordinary beauty, up to 30 cm in diameter. The following varieties belong to the East: Casablanca, Barbados, Cassandra, Mona Lisa, Double Surprise, Magic Star.
Interspecific OT hybrid lily Brazil
Lily Kudrevataya (Martagon) is famous for its unpretentious cultivation. Martagon hybrids are widespread in the northern regions of our country, especially varieties such as Beyhouse, Markhan, Hyson, Gay Light. At the base, the leaves of this type of lily are collected in a whorl, and the high peduncle is strewn with many turban-shaped flowers.
The right variety is the key to easy care
That is why summer residents prefer tubular varieties.They are not affected by diseases and are unpretentious, and long, up to 1.5 m peduncles with many large flowers of various colors will become an exquisite decoration of your flower bed.
Determine the type of lily on the bulb
Experienced gardeners know that each group of lily hybrids has its own requirements for the composition of the soil, the illumination of the site and has its own frost resistance threshold. So, the cultivation of lilies in the open ground of the Asian group and LA hybrids is possible everywhere, and the oriental varieties do not tolerate wintering well; slightly alkaline soil is suitable for growing tubular lilies, and slightly acidic soil for OT hybrids.
The appearance of the bulb will help to determine which group the lily belongs to:
- White bulbs, sometimes with yellow and pink blotches, are characteristic of the Asian and Longiflorum (LA) groups;
- Oriental and Oriental (OT) lilies have large yellow, rarely purple bulbs;
- The bulbs of tubular lilies are purple in color.
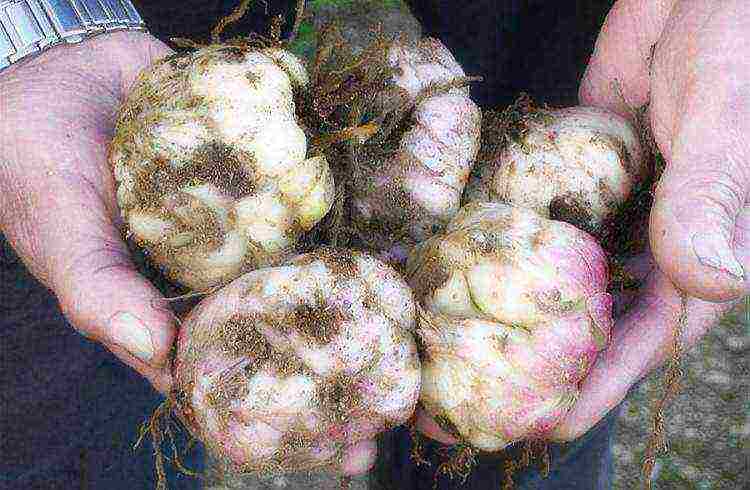
Choosing a healthy bulb
When buying lilies, it is important to correctly determine the quality of the planting material, since bulbs infected with fungal diseases will cause a lot of trouble and can infect flowers already growing in your flower beds.
Choosing the right lily bulbs
- The bulb must be firm, juicy, free from damage and signs of decay.
- Planting lilies, the bulbs of which are dry, do not have sprouts and root growth, will not bring the desired result. They need very careful care, and it is not known when flowering will come.
- Living roots must be at least 5 cm in size.
- Bulbs less than 3 cm in diameter will not bloom until two years after planting. The larger the bulb, the more luxuriant the lily color will be. The optimum diameter of the bulb is 12-16 cm.
When to buy bulbs
Lilies are planted both in autumn and spring. When choosing lilies that are planned to be planted in the fall, it is important to consider that they need to be planted as early as possible, leaving a sufficient time reserve before frost for rooting. Lilies, the cultivation and care of which was correct this year, begin to be dug up from the end of August. It is advisable to purchase bulbs during this period.
Healthy lily bulbs sprout and live roots in spring
Be careful when buying bulbs!
Look out for the sprouting bulbs that go on sale in the fall. Most likely, they were not planted in the spring in the ground, and they missed one life cycle. Once in the ground, they will immediately move to growth and freeze out at the first sub-zero temperatures on the ground.
Buying lily saplings
Planting lilies in the summer is possible, especially when it comes to Asian hybrids and Candidum. They are sold as seedlings with a clod of earth, often blooming. It is much easier to pick up a flower in this case - all its beauty is visible to the eye, and there is no likelihood of obtaining non-varietal planting material.
Lily seedlings for summer planting
Don't buy lily saplings after distillation!
Seedlings are often sold in June and July after forcing. In this case, the bulbs have passed the life cycle in artificial conditions. In the open field, they will hurt, and they will be able to bloom only after a few years. The cost of such planting material is not high, which is a temptation for many novice flower growers.
Preparation of soil and bulbs, rules for planting lilies
Choosing the right site, preparing the soil and planting the bulbs are critical to the successful cultivation of lilies. If you approach these stages responsibly, lilies will grow well and delight with flowering in the garden for more than one year.
Site selection
The choice of a site for growing largely depends on the type of lilies and their requirements for certain conditions:
- Asiatic, oriental, and pipe lilies prefer sunny areas with no through-winds. Partial shading will not affect the growth and flowering of these lilies.If the light in the garden is not the same throughout the day, it is preferable to plant the lilies on the east side so that they receive as much sunlight as possible before lunchtime.
- Curly lilies (Martagon) grow well and bloom in partial shade, especially when the leaf rosette is completely shaded and the flower stalks are in the sun.
To shade the bulbs during the summer, it is recommended to plant lilies near low-growing perennials (hosta, daylilies, daisies). In this combination, flowering lilies will stand out and look bright, and the bulb will remain in the shade, protected from overheating and drying out. In shady areas under trees and dense shrubs, lilies stretch out, their stem is thin, and flowering is scarce and belated. Such plants very often get sick, and the bulbs die.
Choosing a site for lilies in the penumbra of conifers
The best place to plant lilies
Preference for planting lilies should be given to elevated areas or plains. In the lowlands, the bulbs can get wet, be affected by fungal diseases, and in winter they are more likely to freeze.
Soil preparation
Lilies feel comfortable on garden or vegetable garden land, well-drained and without high groundwater. Peat or humus is introduced into sandy soils, and dense clay soil is facilitated by the introduction of coarse-grained river sand.
Preparing the soil for planting lilies
Lilies grow best when planted and cared for in moderately acidic soil.
- Moderately alkaline soil reaction (pH 7.0-8.0) is favorable for growing Snow-white and Curly lilies.
- Asiatic and Oriental lilies grow well on soils with neutral acidity.
- Tubular lily also has preferences - its varieties with pink flowers bloom brighter and more beautifully on slightly acidic soils (pH 6.0-6.5).
How to regulate acidity
Lime, chalk, ash or dolomite flour are added to lower the pH level. Heather earth, peat, acetic acid or colloidal sulfur will help increase the acidity.
The soil for lilies is prepared in advance: in autumn - for spring planting, in summer - for autumn planting. They dig it to a depth of 35-40 cm, turning over the layers. For digging into the soil, fertilizers are applied per m²:
- 1 bucket of humus, rotted manure or compost. The introduction of fresh manure is not permissible, since lilies in such soil will rot;
- 1-2 tbsp. spoons of superphosphate, urea, nitroammophoska;
- 1 liter of wood ash solution, except for those areas where Martagon and Candidum lilies are planned to be planted.
Applying this amount of fertilizer to the soil will provide the lilies with the nutrients they need for good growth and abundant flowering.
Preparing the bulbs for planting
The pre-planting preparation of lilies is necessary to minimize the damage to the bulbs by fungal diseases. Dried onions are pre-soaked in water at room temperature for several hours.
Preparing lily bulbs for planting
The onions are etched for 15-20 minutes in one of the solutions:
- pink solution of potassium permanganate;
- 2 g karbofos per 1 liter of water;
- 2 g of foundation per 1 liter of water;
- a special preparation for dressing bulbous plants before planting Maxim or Vitaros.
After processing, the bulbs are dried in the shade.
Planting lilies in the ground
Early autumn planting of lilies in open ground is considered the most successful. Planted during this period, they will have time to take root well before frost and are guaranteed to bloom next year. The exceptions are Oriental lilies and OT hybrids. They bloom late, by September the bulbs are not yet ready for planting, and during the October planting they will not have time to take root. Therefore, they are planted in the spring when the soil warms up well.
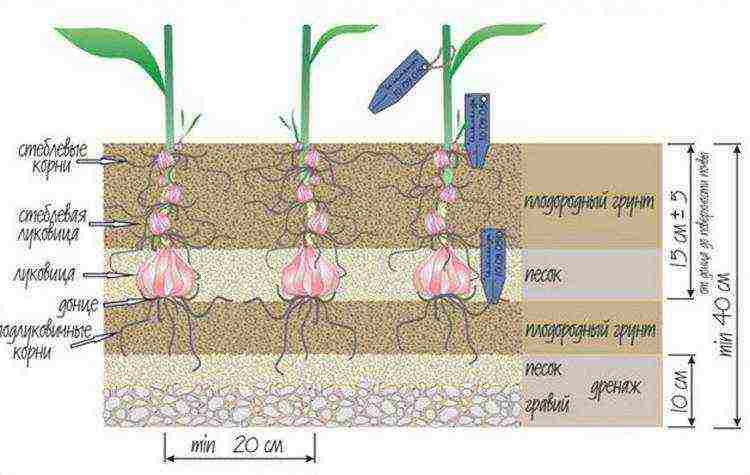
The planting depth of the bulbs depends on several factors:
- Bulb size. The larger the bulb, the deeper it needs to be planted. The minimum depth is 10 cm. Lily bulbs should not be embedded in the ground deeper than 25 cm.Bulb babies are sown in furrows 5-7 cm deep.
- Soil composition. On heavy soils, the bulbs must not be deeply deepened.
- Lily variety. For undersized plants, the planting depth is about 10 cm, for tall ones - 15-20 cm.
Planting lilies in the fall
A distance of 20 cm is maintained between the bulbs. Lilies of the Asian group grow rapidly, therefore, when planted, they stand at least 30 cm between them. Pictures of multi-colored lilies, planted in 5-7 bulbs in one wide hole, look beautiful.
Lilies are planted in autumn and spring in pre-prepared holes, on a 5-7 cm "pillow" of river sand. The roots are evenly distributed, after which the bulbs are covered with earth and watered abundantly.
Spring planting material can often be found with a twisted sprout. There is nothing terrible in this, but you need to place the bulb in the hole so that the top of the sprout is vertically above the ground. The bulb itself will take the desired position as the lily grows.
If for the reproduction of lilies it is necessary to obtain a large number of children, the bulbs are planted "on the side". In this position, the nest of bulbs will form faster and the number of daughter bulbs will increase.
It is advisable to mulch the planting of lilies, but a separate mulch is used for each varietal group:
- Asian, Eastern, LA and OT hybrids are mulched with peat, sawdust, pine needles;
- Plantings of Snow-White, Tubular and Curly varieties are mulched with leaf humus, cut grass, and ash is also added.
Features of summer landing
Asian and LA hybrids can be planted in summer. This also applies to the Snow White Lilies, the bulbs of which are dormant in July-August. Lilies are planted in July using the transshipment method.
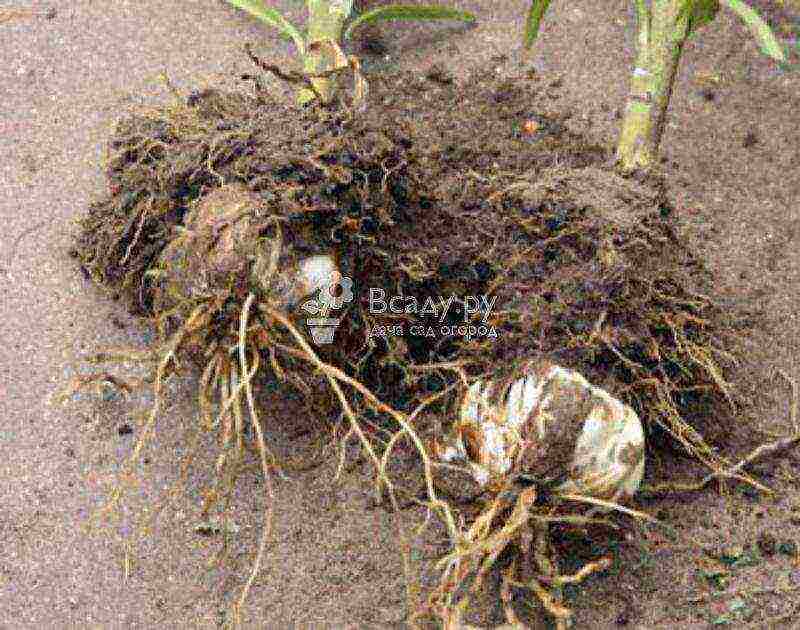 Planting lily bulbs in summer
Planting lily bulbs in summer
Bulbs must be dug out with a clod of earth. A volumetric hole (50x50x50 cm) is prepared in advance, to which 1 tbsp is added. spoon of superphosphate and mix it with the ground. The bottom of the hole is covered with river sand with a layer of 5-7 cm, after which a seedling is placed and sprinkled with earth mixed with humus or rotted manure. The seedling is watered abundantly and, if it is tall, tied to a support. The existing buds and flowers are cut off so that the lily spends all its strength on rooting.
Planting lilies in the summer video
Summer Lily Care
Growing lilies in the country is not burdensome. Caring for them comes down to regular moistening and loosening of the soil, as well as periodic application of top dressing.
Caring for lilies in the summer, at the stage of bud formation
Watering
The soil under the lilies should be moderately moist throughout the growing season. Moisture stagnation will lead to decay of the bulbs, while lilies tolerate short-term drought painlessly. Lack of watering for a long time will lead to wilting of the lower leaves and poor development of the peduncle.
Drying of the lower leaves of lilies due to insufficient watering
The basic rule of watering lilies
Lilies experience the greatest need for moisture in the spring, during active growth. In summer, they are not watered so abundantly, moistening the soil to the depth of the bulbs. Surface watering will not be beneficial. In this case, the plant will feel thirsty, and a crust will form on the surface of the soil, which does not allow air to pass through well.
Watering lilies during budding and flowering
It is advisable to water the lilies before lunch at the root, avoiding water getting on the leaves. During flowering, the amount of watering can be reduced. It is enough to shed the soil 25-30 cm deep, once every two weeks.
Loosening the soil
Garden lilies, care and planting of which are done correctly, need constant access to air to the root system. Loosen the soil very carefully, taking care not to damage the additional stem roots located at the surface of the soil. At the same time, weeds are removed.
During heavy rains, sand is washed out of the soil, it clogs and hardens. In this case, river sand is poured under the lilies, which, during loosening, mixes with the earth and makes it lighter.
Mulching the plantings with straw or wood shavings will help to facilitate the care of lilies in the summer. Also, you can maintain constant soil moisture and protect the bulbs from overheating by planting low-growing perennials near the lilies.
Mulching lilies with wood chips
Top dressing in summer
If you have an automatic irrigation system set up, as well as planting has been made in the prepared soil, and care for the lilies is practically not required - in the first year the plants need a one-time application of fertilizers.
Complex fertilizing is poured under the flowers during budding, using equal amounts of ammophoska and nitroammophoska, at the rate of 30g / m². Dissolving them in 10 liters of water.
Caring for lilies after flowering
Many gardeners have a question about how to care for lilies after flowering. It was during this period that the plant is most susceptible to diseases, since all the forces went to the peduncles.
Watering
After flowering, the watering rate is increased, trying to ensure constant soil moisture at a depth of 25-30 cm. From the second half of August, watering is completely stopped, since the soil must be dry for successful wintering of the bulbs.
Most of all, this applies to Oriental and OT hybrids. After flowering, the soil is thoroughly dried. In September, the flower beds should be covered with plastic wrap to keep it dry during prolonged autumn rains and thaws in winter. The shelter is removed in early spring after the snow melts, during fertilization.
Top dressing
After flowering, lilies need phosphorus-potassium fertilizers. Superphosphate and potassium sulfate are used as top dressing at 10 and 30 g per m², respectively. Dilute them in 10 liters of water and water the lilies with this solution under the root, after preliminary watering with clean water.
Feeding lilies with organic matter
Feeding lilies with organic
Lily bulbs do not have a protective shell, like tulips and other bulbs, so organic fertilizers must be applied very carefully. Nutrient solutions based on manure or slurry are prepared in low concentration: 0.3-0.5 liters per bucket of water. Over-saturation of the soil with organic fertilizers will lead to rotting and subsequent death of the bulb.
For wintering lily bulbs, the same feeding as in summer is done in spring when the snow melts. Fertilizers are applied dry on the crust of thawed ice and get to the roots of the bulb gradually, stimulating its awakening, growth and development.
Pruning
Withered flowers are cut off from the peduncle. It is impossible to hesitate with this, since seed boxes will begin to form on the peduncle, and the plant will spend all its strength on their development.
Caring for lilies after flowering includes pruning the stem. It is carried out only after the leaves and peduncle have completely dried out, since they are a conductor of nutrients to the bulbs. In September, the stem is cut "on a stump" 10-15 cm long. In late autumn, in October or November, this stump is carefully pulled out so that cold air does not enter the bulb through it.
After the stem of the lily has dried, it is cut off
You need to cut flowering lilies for bouquets correctly!
The cut of the peduncle is made at an acute angle so that the remaining leaves completely or partially cover it. An oblique cut is necessary for water to drain off when it rains. If the cut is made even, a large amount of moisture through it will get to the bulb, which will provoke its rotting.
Protection of lilies from diseases and pests
Lilies can be affected by pests, the most dangerous of which are:
- Onion root mite. Prevention and protection - planting healthy material; pickling the bulbs before planting with karbofos (5 g / 1 l of water for 30 minutes); heat treatment of bulbs in water of 50 ºС for 5 minutes.
- Onion leaf beetle. Fighting - timely weed harvesting; collecting beetles; chlorophos treatment (10 g per bucket of water)
- Purple scoop. Fighting - timely removal of weeds and plant residues.
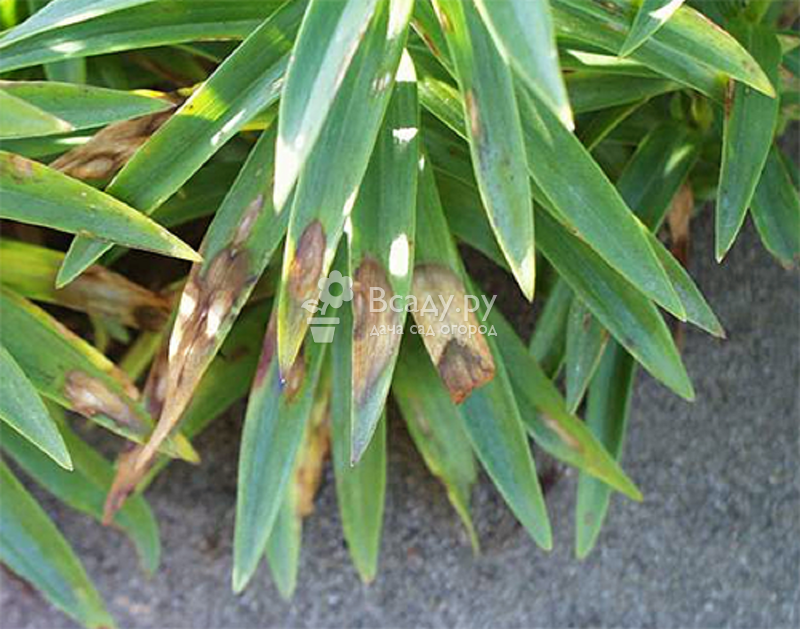 Signs of fungal diseases on lily leaves
Signs of fungal diseases on lily leaves
Often, lilies, planting and caring for which were carried out in violation of the rules of agricultural technology, are affected by fungal diseases such as fusarium, rust, gray rot. In this case, the bulbs begin to rot, and the leaves become stained and wither. If the development of fungi is allowed to take its course, the plant will die.
To combat fungal diseases, the bulbs are etched with fungicides before planting: Fundazol, Topsin, Euporen, Bavistin. Plants are sprayed with the same preparations during the growing season, if the first signs of diseases appear.
Viral diseases of lilies are much less common, but there are currently no effective means to combat them. Infected plants are removed and destroyed outside the site.
Lily care after flowering video
Features of caring for lilies in Siberia and the Urals
Today lilies are successfully grown in Siberia and beyond the Urals. Asian and LA hybrids, Martagon lilies and tubular hybrids are cultivated there. Some varieties of OT hybrids and oriental lilies are able to winter in these regions under cover. Planting and caring for the Urals and Siberia is not much different from growing lilies in regions with a warm climate.
Shelter of lilies for the winter in Siberia and the Urals
A feature of caring for lilies in Siberia and the Urals is their shelter for the winter. The beds are insulated with humus, a layer of at least 7 cm, or fallen leaves - about 20 cm. Oriental lilies and OT hybrids are additionally covered with plastic wrap or agrofibre so that the soil remains dry in winter. Curly lilies calmly endure winters in Siberia without shelter.
The lily shelter is removed immediately after the snow melts so that the sprouts do not appear early and do not freeze during late frosts. If, nevertheless, the lilies have sprouted, and the threat of frost has not passed, they are covered with spruce branches or straw.
Transplanting and dividing bulbs
In order for a lily, planting and caring for which in the open field does not require special skills, to develop well and bloom, its bulbs must be regularly transplanted to a new place. Otherwise, their stems become lethargic, and the flowers become smaller. The frequency of the necessary transplant depends on the type of lily grown:
- Curly and American lilies without transplanting are grown up to 15 years.
- Oriental and Long-flowered lilies, OT and La hybrids are transplanted every 3-5 years.
- Asiatic and Tubular lilies can be replanted every year as they grow intensively.
Transplant in the fall
The optimal time for transplanting a lily, the care of which was organized according to all the rules, is early autumn. The bulbs are dug up in August or early September, a month and a half after flowering. By this time, they have accumulated a sufficient amount of nutrients and quickly take root in a new place. With late autumn planting, there is a high probability that the bulbs will not have time to take root and will die in the frozen ground.
Children are separated from the bulbs dug out for transplantation. Often they fall off on their own, but if the daughter bulbs are tightly collected in the nest, they are cut off with a clean knife, making sure to keep a part of the bottom on each bulb. Dividing the bulbs is the easiest and most reliable way to reproduce lilies, in which all the maternal qualities of the variety are preserved.
Dry and rotting scales are removed from the bulbs, and too long roots are cut off. They are treated with antifungal drugs: 1% solution of potassium permanganate, 2% iodine, 1% ferrous sulfate, foundation. Then they are dried in a shaded, well-ventilated place.
It is advisable to plant lilies in a new place within a week after digging so that the bulbs do not dry out. Small daughter bulbs are planted separately for growing to a depth of 5-7 cm and after a year or two, they are again transplanted to a permanent place.
Spring transplant
Oriental and OT hybrids of lilies are transplanted in the spring, since they fade only by the end of August.Their bulbs are dug up in late autumn, dried and stored in a cool place. Place them in plastic bags or plastic containers with ventilation holes and sprinkle with wet sawdust or moss to keep them from drying out. The bulbs are planted in a permanent place when the threat of recurrent frosts has passed.
Dividing the nest of lily bulbs in spring
Spring transplanting is also permissible when growing other types of lilies, before the emergence, or at the very beginning of the development of sprouts. It is important to take into account that during spring transplantation, lilies develop rapidly and the appearance of early shoots can lead to their death due to late frosts.
Transplanting lilies in summer
Snow-white lilies need a summer transplant, the vegetation cycle of which has its own characteristics. They enter the resting phase in July-August, and by September they are already beginning to form a new rosette. When transplanting, you do not need to cut off the stem, but it is advisable to shorten the long roots to 7-10 cm. Water the lilies after the completion of the procedure should be abundant, stimulating the growth of new roots.
Lily transplant in summer
Dividing and planting lilies in July is also possible when growing Asiatic lilies. The dug nests are divided into separate stems with a bulb and immediately planted in a new place. In this case, the buds and existing flowers are cut off.
Outcome
Growing lilies in the country is possible even for a novice florist, provided that he follows the rules for caring for them. It is important to remember that, depending on the species, lilies need different conditions, the observance of which will be the key to abundant and colorful flowering.
Lilies are perennial, bulbous plants of the Liliaceae family, common in Asia, Europe and the American continent. The popularity of the plant is associated with beautiful flowering and varietal diversity, but lilies require special care. Let's consider the process of growing lilies in the open field in more detail.
Choosing a site for growing lilies
The choice of the site depends on the varietal affiliation of the lily. For example, Asian varieties grow well in sunny areas, although in partial shade they can feel quite comfortable. Asian lilies are frost-resistant, easy to care for, and grow rapidly.
Japanese, Gorgeous, Reddish and Callous lilies are suitable for partial shade. These varieties prefer the upper part of the stem to be in the sun and the lower part in the shade, and cannot tolerate even the slightest frost. For this reason, ornamental grasses or low flower bed flowers are often planted with lilies of these varieties as a border. They are common in the southern regions. In the middle lane, they are grown in greenhouses.
Tubular types of lilies are unpretentious in care. It is they who are preferred by summer residents. Tubular species practically do not get sick, are not damaged by insects and adapt to any climatic conditions.
If the lily bulbs are from a garden nursery, be sure to consult with experts about the intricacies of care.

All varieties of lilies have general requirements for growing conditions:
- area with light, nutritious soil;
- lilies should not be located in the shade of trees;
- the site must be drained, without moisture stagnation;
- it is advisable to enclose the lilies with a barrier from drafts.
The barrier can be natural or artificial. Artificial barriers include walls of residential and utility buildings, natural ones - garden trees or other tall plants.

Soil preparation
It is necessary to approach the preparation of a site for lilies responsibly, because these flowers grow without transplanting for 3 to 5 years. Lilies prefer light black soil, therefore, when preparing the site, it may be necessary to adjust the soil structure.
Heavy soils are facilitated by the introduction of a peat-humus mixture with sand. All components are taken in equal amounts and added during digging.For depleted soils, 4 kg of humus / 1 m2 will be needed, for podzolic soils - 8 kg / 1 m2.
Basically, lilies prefer neutral soils, but there are species that need slightly alkaline or acidified soil. Before purchasing a particular variety, consult with a specialist on this matter.

If the soil is rich in humus, organic fertilizers can be replaced with mineral additives: 30 ml superphosphate / 30 ml urea / 15 ml nitroammophoska / 1 m2.
Digging is performed to a depth of 40 cm (shovel bayonet). The soil for the lilies is prepared in advance. If you plan to plant in spring, you need to apply fertilizer in the fall, and, conversely, for a winter planting, fertilizers are applied in the spring.
Dates of spring and autumn planting
Even experts are not able to say unequivocally when it is better to plant lilies. In the spring, as well as in the autumn planting, there are advantages and disadvantages.
Spring planting
The advantage of spring planting is the safety of the planting material. The risk of bulbs getting wet, rotting and freezing is minimal. Oriental varieties and tubular hybrids are planted in early spring in March, just after the snow melts. Tibetan and tiger species are planted in the last week of March, and terry hybrids in the first week of April, but, of course, the timing depends on the growing region.
Autumn planting
Autumn planting is preferred by most flower growers, as it has its advantages:
- lack of summer heat;
- no need for regular watering;
- pests are not a threat;
- lilies bloom earlier;
- saving time in spring, when there is a lot of work on the site.
In the fall, planting dates can be adjusted. The bulbs are planted in late September - mid-October. The main thing is that before the onset of frost there should be at least a month so that the bulbs have time to take root.

Planting lilies
Planting lilies can be carried out according to several schemes, in addition, planting material requires careful selection and some preparation.
How to choose healthy bulbs
The pre-planting preparation of the bulbs begins with their inspection and careful selection. Rotten specimens or bulbs on which fungal foci are visible are removed.
Healthy bulbs have:
- cover scales of a uniform color, white or creamy shade, without visible spots and blotches;
- well-developed roots 3 cm - 5 cm long.
If there is not enough seed, you can try to treat the bulbs with the preparations "Fundazol" and "Karbaphos", after cleaning the affected areas. These bulbs are planted in a separate group so as not to infect healthy lilies.

Before planting, the selected material is kept for 20 - 30 minutes in a warm solution of potassium permanganate for disinfection. Before soaking, the upper scales are carefully removed from the bulbs.
If the spring planting of lilies is carried out, the bulbs are pre-germinated in containers, which are filled with disinfected fertile soil from the site or an industrial soil mixture especially for lilies.
Bulb planting
Planting lilies with bulbs is carried out according to several schemes: single-line ribbon planting, two-line and three-line.
- In the first version, the bulbs are planted in one row with a distance between holes of 10 cm - 15 cm and a distance between rows of at least 50 cm.
- The two-line scheme assumes two ribbons of bulbs with a distance between them and the holes for the bulbs of at least 15 cm - 25 cm. The row spacing must be at least 70 cm. This method is used for tall lilies.
- According to the three-line scheme, they are left between the holes for the bulbs and between the lines of 15 cm, and in the aisle 70 cm.The scheme is chosen depending on the variety, the size of the plot and the general flower arrangement.
How to make a hole and plant an onion correctly:
- The depth of the hole is twice the diameter of the bulb to be planted.
- On heavy soils, a little fine gravel or expanded clay is poured at the bottom of the hole for drainage.
- On sandy loam and sandy soils, a mixture of humus and fertile soil is laid.
- The bulb is placed in the hole, slightly pressing the roots into the ground.
- The hole is filled up and tamped so that a small depression remains for fertilizing and watering.
To protect against pests and diseases, the hole is dusted with a small amount of wood ash.
In the autumn planting, the bulbs are buried a few centimeters lower and protected with a special plastic sheath from rodents. Heat-loving varieties can be protected from frost with a layer of mulch 30 cm high from hay, foliage or straw. It is not recommended to use sawdust, as wood acidifies the soil.
Planting lily seeds
No disease is transmitted through seeds. This breeding method is safer, but much longer. It will take 3-4 years on average to grow flowering lilies from seeds.
The seeds are harvested from healthy flowers or bought at the store. Before planting, it is necessary to determine which type of seeds are: fast or slow germinating. The fast germinating ones will emerge in the first year. Slowly growing by autumn give only a small bulb.
The planted seeds germinate unevenly, some can sprout in the first year, some - only in the next season.
You can sow in open ground, but sowing in containers increases the germination of seeds.

If the seeds are planted directly into the ground, it is important to choose an area where no bulbous crops have been planted before. Sowing is carried out in a tape manner. The distance between the lines should be at least 15 cm. A thickened planting will lead to the development of infections and the death of immature seedlings.
Slow growing varieties are planted before winter immediately after collecting the seeds. Humus is applied to the garden a month before planting, and before the onset of frost, the soil is mulched to keep warm with foliage or hay. With the beginning of the growing season, lilies will need standard care: watering, loosening, weeding and feeding.

Seeds are laid in containers in the last days of February - the first ten days of March. Expanded clay is placed at the bottom of the containers, on it is a soil mixture for lilies: peat, humus and fertile soil in equal amounts. Humus can be replaced with rotted plant compost.
At home, the seeds germinate after about 20 days, the optimum temperature for lily seedlings is + 18 ° C - + 25 ° C. The seedlings are looked after until September, after which the resulting bulbs are planted in unprotected soil.
Lily care rules
Lush buds in lilies can be achieved by following the usual care rules:
- In the first year, lilies do not need spring feeding.
- Fertilizers are applied once per season, after flowering. But this is only if fertilizer was applied before planting.
- Before flowering, tall varieties are recommended to be tied up.
- After flowering, dried buds are removed.

Watering
Lilies need moderate watering. Stagnant water will lead to rotting of the bulbs, a lack - to drying out of the leaves and improper development of the peduncle.
The greatest amount of moisture is needed in the spring, at the beginning of the growing season, when the plant grows green mass.
In summer, watering is reduced. Water to the depth of the bulbs as the soil dries up at the lower leaves. To extend the flowering period, watering is again reduced to 1 - 2 times a week. After the end of flowering, watering is increased again so that the bulbs can store food for the winter.
Top dressing
In annual plants, the only feeding is performed after flowering with complex fertilizers or with the use of potassium-phosphorus agrochemicals.
For plants aged 2 - 4 years old, the first feeding is performed after the snow melts in March with nitrogen fertilizers, for example, ammonium nitrate: 20 g / 1 m2 of a flower garden.
You can use a low concentration mullein infusion so as not to harm the bulbs.
The second feeding falls on the period of bud formation.It is convenient to use complex compositions of ammophoska or nitroammophoska at the rate of 30 ml of fertilizer / 10 l. The third top dressing - after flowering: 30 g superphosphate / 30 g potassium salt / 1 m2.
How to cut flowers correctly
Usually, lilies are not cut and left to bloom in the flower bed to strengthen the bulbs and ensure abundant flowering next year. But sometimes you want to make a bouquet and decorate a room or living room with lilies.
To reduce the negative impact of pruning, you need to learn how to cut flowers correctly:
- cut lilies only in the morning hours or with the onset of dusk; during the day, you can cut flowers only in cloudy weather;
- use a sterile tool for cutting; alcohol or a pharmacy iodine solution is used to process the knife;
- do not cut off the stem at the very base, leave a third of the stem and adjacent leaves for proper nutrition of the bulbs;
- cut at an angle, after watering or rainfall, the water will not stagnate on the stem.

Transplant timing
Most lilies will need to be transplanted approximately once every 3 to 5 years. But some varieties, for example, Martogon, are transplanted once a decade. And the common varieties of Tubular, as well as Asiatic lilies are planted in a year, these hybrids grow so quickly.
Thickened plantings are planted in spring or at the end of the growing season in autumn, it all depends on the climate and varietal affiliation of the grown lilies. Florists are more fond of an autumn transplant, when the bulbs are practically in a state of complete dormancy.
But what to do with Asian and Tubular hybrids, which fade a month before the onset of the first frost and simply do not have time to take root? In this case, replanting is carried out in the spring, when the soil warms up to a temperature of + 10 ° C, and the average daily air temperature will be at least + 15 ° C.
The growing region is also taken into account when planting. In the middle lane, autumn transplantation is carried out at the end of August - the first half of September, in the southern regions, work can be postponed to October, and in the northern regions, it is carried out immediately after flowering.
Asian varieties are completely unlimited in terms of spring transplantation. They are transplanted from the beginning of spring until the time of flowering. Water the lily abundantly after transplanting and tear off the buds to improve survival.

Reproduction by scales
The most common breeding method for lilies is vegetative - bulbs. Growing from seeds is less common. But there is another non-standard method - reproduction by scales, when the bulb is divided into scales and planted in the ground. Abundant watering promotes germination and development of a full-fledged plant.
Features of cultivation after distillation
There may be several reasons why lilies do not bloom. Scorching sun, insufficient watering, irregular feeding, disease-damaged bulbs for planting. All these problems can be corrected by replanting the plant, increasing watering and applying fertilizers on time.
It should be noted that in the first year, lilies may not bloom at all or form a small number of buds. This is normal and is caused by insufficient rooting and development of the bulbs.
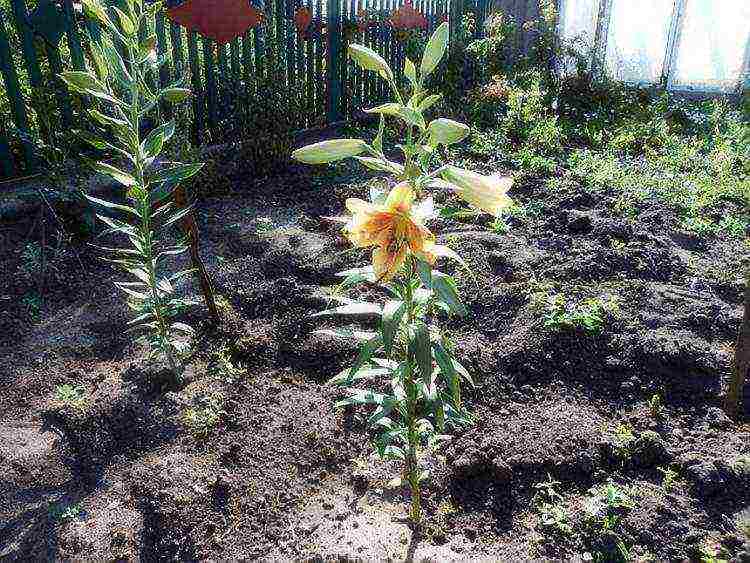

Despite the absence of buds, it is necessary to carry out the usual care of the lilies: feed at the end of the growing season, water and loosen the soil in time. With proper care for the second year, the lily will certainly delight you with beautiful buds.
Newcomers to floriculture find lilies a difficult flower to grow. You can see that caring for lilies is no more difficult than for other bulbous plants. Pick up several varieties with different flowering times and a beautiful lily will be decorating your garden all summer long.
Garden lilies are gardeners' favorite flowers. Their beauty is difficult to compare with other flowers, and the scent can melt the coldest heart! This plant will decorate a flower garden, garden, park, home flower bed.It is not surprising that garden lilies, their planting and caring for them are of interest to many owners of summer cottages.
Correct fit
Garden lilies usually grow in one place for several years. And this place should be chosen so that for the next 5 years not to disturb the plant, because too frequent transplants significantly slow down the development of the lily.
- Most often, lily bulbs are planted during September, when they are dormant. Before planting, treat each bulb: for 20 minutes, dip it in a 0.2% solution of foundationol, and then for an hour in a growth biostimulator.
- Remove the dead scales from the bulbs, and shorten the roots to 5 cm. Try to choose when buying bulbs with intact bottoms.
- Dig a small hole under the bulb - 40 cm in diameter and 25 cm deep. Cover the bottom with a layer of gravel, on which spread fresh, fertile soil in a layer of 5 cm.Place the bulbs and cover them with the same soil, covering the top of each bulb and tamping slightly.
- Make a small indentation with your finger where the onion is planted and add some granular fertilizer.
- If you purchased the bulbs in the spring, store them at the bottom of the refrigerator until planting, at a temperature slightly above 0. Place them in a perforated plastic bag filled with dry peat.
- Plant these lilies in a greenhouse, plastic bottles or pots. Only after the spring frosts are over, can they be transplanted into open ground along with a lump of earth.
- If a lily bulb purchased in spring has a large sprout - more than 5 cm, then it must be planted obliquely.
- If you are going to transplant a lily, then wait 1-1.5 months after it has faded. The flowering period is very depleting for the bulbs, they need to gain strength, become larger and denser.
- Remember that the death of the lily stem indicates fungal diseases. If this happens, dig up the bulbs and carefully remove the affected stems from them. If the plant is healthy, green, then before transplanting, cut the stems close to the ground, leaving a stump.
The most convenient scheme for planting lily bulbs
Lilies, not transplanted for more than 5 years, begin to form large nests of bulbs of different sizes and ages around them. Typically, such a nest will disintegrate itself when excavated, but sometimes manual separation may be required.
Features of different varieties
There are many varieties of this beautiful flower. Only in our latitudes there are about 100 of them! And among our gardeners, species such as Asian hybrids, oriental hybrids and tubular hybrids have become very popular. Each species has its own characteristics and many varieties. The most popular Asian hybrids are:
- Deep yellow with red - Grand Cru;
- coffee ones with scarlet tips - Lollipon;
- pink and white - Marlene, Ventu Marseille, Vermeer, Kentucky;
- yellow - Kansas;
- yellow with red - Gitana.
Popular varieties of oriental hybrids include:
- raspberry white - Barbados;
- white with yellow - Time out;
- white with pink and yellow - Star Class;
- white with pink - Set Point;
- tricolor - Arena.
Among the tubular hybrids are the following:
- apricot Bestseller;
- lemon aerobics;
- pink and coffee Royal Club;
- red Royal Parade;
- apricot swing.
Tubular lilies are very sensitive to frosts in May. They will need nutritious, loose soil with good drainage, in a sunny, wind-protected area.
Asian varieties of lilies are the most unpretentious
Among the oriental hybrids, there are varieties that are not well tolerated in winter. Plant their bulbs to a depth of 15-20 cm to prevent them from freezing. It is these flowers that have the most magnificent scent, but also require good care.
Asiatic lilies are hardy and hardy, so you can choose a site for them both on the sunny side and in the shade.The soil is slightly acidic or neutral, well fertilized. Such flowers do not exude a scent at all, but this is compensated by the ease of caring for them.
The incomparable beauty of lilies
A few more growing secrets
Dig up the bulbs very carefully to avoid damaging them. A garden pitchfork is best suited for this. Shake off the ground and carefully examine, remove scales with brown or rusty spots from the bulbs. Rinse in running water and place in a solution of karbofos (10 liters of water - 1 tablespoon) for 20 minutes.
Pay close attention to the condition of the bulbs
Clean, unaffected bulbs with roots are enough to pickle for half an hour in a 0.1% solution of potassium permanganate. After rinsing and dressing is complete, dry the bulbs in a shady place, trim the roots 5 cm and plant in prepared soil. On the eve of disembarkation, in dry weather, water the soil to the desired depth. If the soil is already moist enough, water it directly into the furrow when planting.
The soil for all types of lilies should be nutritious, loose, with good water permeability. These include sandy loam soils, light loams, garden lands, which are well fertilized. Damp, heavy soils cause rot and death of the bulbs as moisture collects between the flakes. To fix this, add sand, perlite, or other baking powder to the soil.
The size of the bulbs, the type of lily, and the composition of the soil directly affect the planting depth. The most common option is that the depth of the hole should be 3 times the diameter of the bulb itself. In light sandy soil, planting is done deeper than in heavy soil.
The depth to which lilies should be planted:
- large bulbs of undersized varieties - 10-12 cm;
- small bulbs of undersized varieties - 7-8 cm;
- large bulbs of medium-sized varieties - 12-15 cm;
- small bulbs of medium-sized varieties - 8-10 cm;
- large bulbs of high varieties - 15-20 cm;
- small bulbs of high grades - 10-12 cm.
The depth is indicated to the bottom of the bulb. The distance between the lilies also depends on the height. For example, large lilies need 20-25 cm, medium lilies 10-15 cm. Make grooves or holes for bulbs 10 cm deeper than they should be, if they have roots. Pour a mound of river sand on the bottom of the hole, place the onion and straighten the roots, and then cover the hole with earth.
Care and fertilization
Lilies are very fond of mineral fertilizers, in spring - with nitrogen content, in autumn - without it. Purchase these fertilizers in granular form, specially formulated for bulbous flowers. It is necessary to fertilize the area with lilies in the spring, with the appearance of the first shoots, and in October, before the plant, having completed the flowering period, falls into a dormant period.
Organic fertilizers are categorically not suitable for lilies, as they cause fungal diseases. Never add manure or compost! But wood ash introduced into the soil will help protect flowers from pests. To prevent the development of diseases, spray the plants with a solution of Bordeaux liquid three times a year.
The best option for the location of the lily is the top with flowers in the sun, and the leg in the shade. This will prevent the bulb from overheating. In order for lilies to grow well, you need to plant undersized plants near them, for example, hostu, flax or bell. You can also alternate between types of lilies of different heights. This way the bottom of the stem is shaded and the bulb is protected from overheating.
Try to plant the lily so that the top is in the sun and the bottom of the stem is in the shade.
Lily care is mainly about weeding thoroughly and watering well, especially during the flowering period. Abundant watering is required only in drought, and after flowering it can be completely stopped.
You need to cut the lilies obliquely, leaving most of the stem with leaves, about 8-18 cm, so that the bulb continues to develop.If the cut is straight, then rainwater will enter the core of the stem and cause rotting.
Before wintering, sprinkle a handful of peat on each lily and cover. To do this, you can use:
- sawdust;
- spruce branches;
- plastic wrap;
- dry leaves.
The ground must be completely dry. In the spring, the shelters are removed before the first shoots sprout.
Garden lily care videos
We hope our tips will help you decorate your garden with these gorgeous flowers. Share in the comments your experience of growing lilies or ask your questions. Good luck!
 Lilies are very delicate and beautiful flowers that are very popular among amateur flower growers. Planting garden lilies is not difficult: this perennial plant is very unpretentious.
Lilies are very delicate and beautiful flowers that are very popular among amateur flower growers. Planting garden lilies is not difficult: this perennial plant is very unpretentious.
In order for the lily to delight us with its beauty and feel good in the open field, proper care is required, and of course, follow the rules of reproduction and planting.
Lily: characteristics of the species
Lily (Lilium) is a perennial flowering crop that belongs to the Liliaceae family. The stems of the plant are straight and tall (some varieties reach 1.5 m in height), with small glossy leaves. Flowers can be of different shapes: cup-shaped, funnel-shaped, star-shaped or bell-shaped. However, they always consist of 6 elongated petals and the same number of stamens.
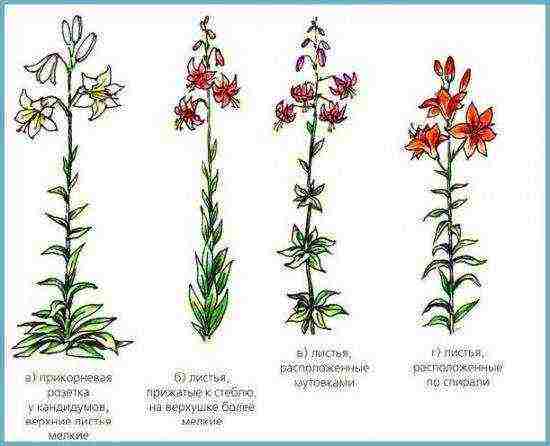
Scheme: types of lilies according to the structure of the stems
Although the word "lily" literally means "completely white", the flowers of modern varieties can have different shades: yellow, orange, red, lilac, lilac, pink. Varieties with a combined color are very popular among summer residents.
The underground part of the plant is a single-tiered (less often two-tiered) root system and a bulb. It is the bulb that is the source of nutrients for the culture, as well as the reproductive organ of the species. About the cultivation of other types of bulbous plants - hyacinths, tulips.

Wild lily - the predecessor of hybrid varieties
When to plant a lily
As you know, lilies can be planted both in spring and in the middle of autumn - it all depends on the wishes of the grower.
Autumn planting is considered the most favorable. A low temperature and a sufficient amount of moisture will allow the plant to adapt and take root normally - thus reducing the stress level of the crop. That is why it is better to plant lilies in the southern regions of Russia in October.

Preparing for planting lilies in open ground
However, it is worth noting that most varieties of lilies require exactly spring planting - study the characteristics of the variety you have chosen.
Choosing a place for planting lilies
Before planting a crop in open ground, carefully select a place to grow it. The plant grows well in sunny places that are protected from the wind (if you want to plant a lily near the house, observe which side of it the sun is for most of the day).

Any sunny spot on your backyard is suitable for planting lilies.
When the site is selected, dig up the soil and remove any remaining roots of other plants (especially weeds). Lilies can be planted in the same flowerbed with other flowering plants - the culture will not feel bad from this. The main thing is that the "neighbors" are not too tall and do not create the shadow of a lily. For this reason, you should not plant under trees or bushes.
Soil preparation
Lily does not tolerate drought well, so the soil in which it is planted should be good at allowing moisture to pass through. Most lily varieties like fertile soils with high moisture permeability. Although breeders have also developed varieties that safely tolerate dry and even swampy areas. However, heavy loamy soils and salt marshes should be avoided when cultivating crops.

The optimal soil for planting lilies should consist of layers of gravel, sand and fertile soil.
Whatever the type of soil, it should be remembered that fertilizing the lily is still necessary. Peat fertilizers, humus or rotted compost (1 bucket per 1 m2) are suitable for feeding. If the soil is dominated by sandy impurities, then a good option for improving the quality of the soil would be phosphorus-potassium dressing, which is applied before planting the plant (100 g per 1 m2).
Important! Having well fertilized the soil when planting plants, you will provide them with comfortable conditions for growth and development for the next 2 - 3 years.
By the type of environment, the soil for lilies should be alkaline or slightly acidic. Too acidic environment is not suitable for the plant, therefore it is neutralized with wood ash (also ensures proper drainage of the soil), limestone or chalk (200-300 g per 1 m2).
Planting lilies in open ground
If you decide to plant lilies in the spring, then you should do this when the frosts have already receded, but the dry period has not yet begun. For each region of the country, the optimal time for planting lily bulbs in the ground will be different.
Prepare lily bulbs for planting as follows:
- sort the bulbs, removing spoiled planting material;
- the most viable specimens are completely cleaned of flower scales;
- rinse the bulbs in a solution of potassium permanganate or foundation (this will get rid of harmful bacteria).

Lily sprout
The planting depth of the bulb is determined depending on the type of soil:
- in heavy soils, small bulbs should be planted to a depth of 5-6 cm, large planting material - at 13-16 cm.
- if the soil is loose, it should be planted 2-4 cm deeper than in the previous example.
Important! Only good quality bulbs with an intact root system can be planted.
After planting is complete, the plants should be fed with organic and mineral fertilizers. If you planted lilies in the fall, then cover the flower bed with dry leaves and an additional layer of soil. This will allow the planting material to avoid freezing.
Care principles
Maintaining optimum soil moisture is the first thing you need to watch out for. Watering is carried out as the soil dries up (accordingly, in dry periods, watering is done more often, and in rainy periods, watering can be excluded altogether). Use the root watering technique (called strip irrigation): surface irrigation can harm lilies. If necessary, fertilizing can be applied along with watering.

If the summer is rainy, then the lily need not be watered.
In the first year of life, the plants are rather weak. Therefore, in order to improve their development, remove all the buds: the lily will spend too much energy on flowering and, having weakened, will not be able to endure the winter frosts. But in the second and third years after planting, the plant will bloom profusely. Usually, in the fourth year, the flowering intensity decreases - this means that the crop needs feeding. Closer to the fifth year, flowers are divided and transplanted.
Advice! Do not forget to create support for the lilies: these crops often break under the weight of their own stems.
Reproduction and transplantation of lilies
Lilies are propagated by dividing the bulbs. The procedure is carried out at 4-5 years of growth of the lily: the thickening of the bulbous nests by this time is fraught with the cessation of flowering. The lily bulb is split and each part is planted separately. Care for transplanted bulbs is required the same as for plants in the first year of life. Under favorable conditions, the divided bulbs will bloom within a year.

Schematic: breeding species of lilies
Some varieties of lilies produce baby bulbs. They are attached just above the base of the main bulb. Such bulbs should be carefully separated and planted for growing. These plants will bloom only 2-3 years after planting.
There is also a more complex method of reproduction of lilies - with the help of scales. Small loose growths are carefully separated from the base of the mother bulb and planted in a special sandy mat.If the planting of scales was carried out in the spring, then by the fall, bulbs are formed from them.
Popular groups of lilies
When choosing lilies for planting in the country or in the courtyard of a private house, you should pay attention to the following groups of hybrid plants:

Asiatic lily (left) and Candidum lily (right)
- Asian hybrid lilies. Unpretentious winter-hardy varieties, have cup-shaped flowers of white, pink, orange, yellow, as well as multicolored colors.
- Candidum. These varieties are capricious to growing conditions. Flowers have a funnel-shaped or tubular shape, the color is snow-white or yellow. Unlike the previous group, the flowers of these varieties have a strong aroma.

American lily (left) and oriental lily (right)
- American hybrid lilies. The varieties are well suited for breeding in central Russia. They are distinguished by moderate demands on growing conditions. The flowers are turbid with pink or lilac color and bright red dots.
- Oriental hybrid lilies. The varieties are quite resistant to external factors, but at the same time they are highly susceptible to viral and fungal diseases. Flowers of various shapes and colors. Suitable for breeding in the middle lane and southern regions of Russia.
Each of the four groups of lilies includes many varieties with similar characteristics. Choose a group based on the planting conditions and climate in your region. The variety is determined solely at the discretion of the gardener.
How to plant lilies: video
Lily varieties: photo