Content
- 1 Description and varieties
- 2 Outcome
- 3 Soil and lighting requirements
- 4 Landing time and scheme
- 5 Seedling selection and site preparation
- 6 How to plant currants correctly
- 7 Soil processing and watering
- 8 Top dressing
- 9 Pruning
- 10 Supports and preparation for winter
- 11 Biological features of currants
- 12 Different types of currants
- 13 Currant planting rules
- 14 Outdoor currant care
- 15 How can currant propagate
- 16 Diseases and pests of currants
Description and varieties
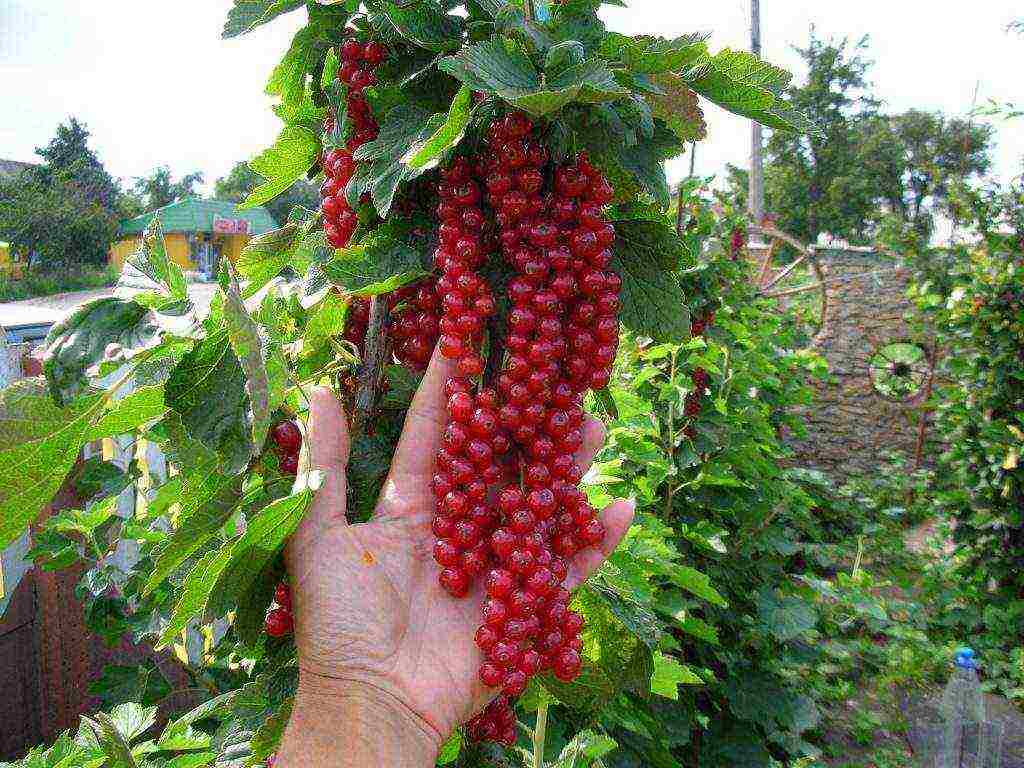
Currant is a berry shrub from the gooseberry family, of medium height (20-40 cm) with characteristic leaves. The currant belongs to a fast-growing shrub and begins to bear fruit one year after planting.

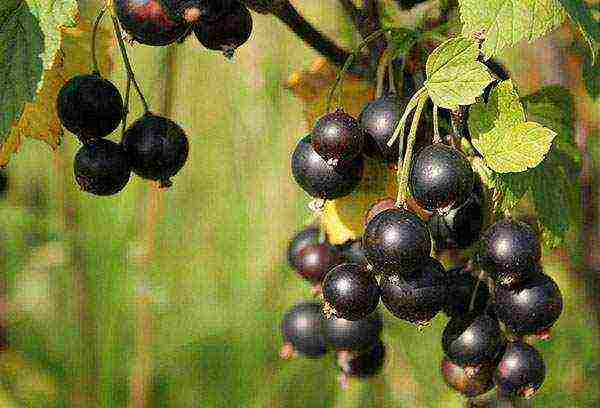
Its life span is 20 years for red currants, 15 years for black currants, however, the shrub is capable of multiplying rapidly. The main types of currants are black and red, differing from each other in the color of the berries and the characteristic smell inherent in black currants, due to the content of essential oils in it. However, there are other varieties: yellow currant, bred on the American continent, white currant and many crossed species.
Breeders have bred up to 700 species of various varieties of berries that are resistant to pests and diseases, resistance to powdery mildew, spotting, spring frost resistance and increased productivity, which allows it to be cultivated in various regions of the Russian Federation.
Currant, has a lot of useful qualities, which determines the use of the berry itself, its leaves, twigs for:
- Improving the elasticity of the vascular system.
- Reducing the concentration of sugar in the blood.
- Treatment of dermatitis and eye diseases.
- Therapy for atherosclerosis, lowering blood pressure; increasing the strength of the capillaries of the circulatory system.
- Treating sore throats and coughs.
- Therapy for colds and infectious diseases.
- Treatment of inflammation in the urinary tract area and as a diuretic.
How to properly plant currants in the open field
In general, the shrub is rather unpretentious to growing conditions, however, in order to obtain a high yield with the best vitamin and nutritional characteristics, a number of rules must be observed.

The shrub is sensitive to the water-air growth regime, since the length of its roots, up to 50 cm, is located in the upper soil layer and cannot consume moisture from the deep soil layers. This must be taken into account when choosing a place for planting, since too wet soil is a dangerous factor, and too dry requires frequent watering.
1. Site selection and soil preparation
The best conditions for growing currants is considered to be a well-lit area of soil, representing a lowland, slope or hill with an average degree of moisture. The degree of illumination is determined by a measure of how long during the day the currants are exposed to direct sunlight.
The duration of the illumination of the shrub by the sun's rays should be at least half a day for black currants; for red - at least 2/3 of the day.
The measure of the moisture content of the site is assessed by the level of groundwater in a nearby well, which should not be higher than 0.5-1 m. The requirements for the acidity of the soil are also clearly regulated; soils of a neutral and slightly acidic reaction are chosen for it. It is best to place currants in a place of some elevation of the relief, containing up to 0.5 m of a fertile layer with protection from both the direct effect of wind currents and from stagnant air.
2. Timing of boarding
The shrub can be planted in the spring from the onset of warmth to the period of bud opening with cuttings or grown cuttings and in autumn in September-October. The autumn planting method is considered the best, since when using it, the best conditions are created for plant survival and exit from the beginning of spring into the phase of rapid development.
3. Treatment and preparation of soil
It is better to plant shrubs with a distance of 1 m from neighboring bushes and at a distance of 1.5-2 m and 3-4 m from other shrubs and fruit trees. The required number of shrubs for planting is determined from the condition that, with normal care, currants give from 2 to 3 kg per bush.
4. Soil for currants and fertilizers

As a planting material, it is better to choose seedlings 15-20 cm long with a well-branched root system, no signs of pests and diseases. The dimensions of the pit for planting are 40 * 40 * 40 cm, it is better to dig up the pit either a few weeks before planting or in the fall of the previous year to create the necessary soil sediment.
It is necessary to prepare two layers of soil for planting a bush:
- The first consists of soil dug out of a pit, mixed with peat, compost or fertilizers with the addition of small doses of mineral additives and has a high biological value; serves to nourish the roots, located below them in level.
- The second one also consists of a fertile layer of soil removed from the pit without fertilizers.
5. The process of planting in open ground
The shrub, holding with one hand, is placed over the first layer of soil, so that the roots feel free. Further, sprinkle with a second layer of soil, given that the bush should protrude above the surface. The planted bush is watered abundantly with water, even if planting is done on a rainy day.
Around the planted bush, a near-stem circle is formed, with a diameter of 40-50 cm, a layer of mulch, peat or sawdust is applied, without affecting the planting itself.
After planting, the currant bush is pruned to a level of 7 cm above the ground. This measure is necessary to bring the aboveground part of the plant into conformity with the root system.
Currant care 1. Watering
The shrub is characterized by a fairly high moisture consumption, for which it competes, spending energy necessary to form the crop. For adult bushes, the maximum moisture consumption occurs during the growth of shoots, during the period of berry formation (June) and after harvesting to store moisture for the formation of the next harvest (September).
It is important to provide a sufficient amount of moisture during this period, since otherwise the berries will be small, and unripe berries will shatter.
To reduce the effect of drought periods on currants, it is necessary to maintain it by watering with 1.5-2 buckets of water per bush. It is also necessary to carry out measures to retain moisture in the soil, for which a layer of mulch, up to 10 cm thick, consisting of fallen leaves, weeded out weeds, and finely chopped thin twigs, is introduced around the circumference under the shrub.
2. Top dressing
In the case of correct planting of the shrub, fertilizing in the form of fertilizers is not required for several years.Further nutrition is carried out by introducing 4-5 kg of fertilizers or peat and 40 g of mineral fertilizers of a complex composition, superphosphate (100-150 g) and calcium chloride (30-40 g) under a bush in early spring or autumn before loosening.

In the absence of plant nutrition, the berries become small over time and contain fewer nutrients.
3. Pruning currants
The best time for pruning a shrub is considered to be the period of late autumn, after leaf fall, when sick and damaged shoots are clearly visible. Carrying out pruning for currant bushes begins with the removal of old and damaged shoots at ground level with a covering with a special decoction.
The next step in pruning is to remove young, poorly developed or disease-damaged branches. Further, the shrub is diluted by removing from 15 to 30% of shoots of various ages to direct moisture and nutrients not to the growth of young branches, but to the formation of a crop on mature cuttings. Ideally, after pruning, the bush should represent 12-15 healthy shoots of various ages.
When pruning, it must be borne in mind that excessive spreading of the bush is inconvenient and causes contamination of the berries during bad weather. To give the plantation a well-groomed and cultured look, props are made, trellises and stretched twine are used. However, the "matched" bush should not be overly tightened to exclude damage to the branches and disruption of sap flow.
4. Transplant

The transplant is carried out in cases of the need to rejuvenate the currant, the lack of necessary nutrients at the site of the previous growth for the growth and development of the plantation, the need to plant rooted young shoots, cuttings or cuttings. The rules for making a transplant in terms of time, choice of soil, watering and feeding do not differ from performing a normal planting.
5. Diseases and pests
- American powdery mildew, which poses a danger to young leaves and shoots of black currant, manifests itself in the appearance of white blooms on their surface, the leaves weaken, darken and deform. Treatment is carried out by removing and burning the affected leaves and shoots and applying autumn Topaz.
- Anthracosis, septoriasis, represent two types of a disease caused by the action of a fungus, as a result of which spots of dark and brown colors are formed on the surface of the leaves, which later turn into a brown shade. The affected shrub is more susceptible to frost, is characterized by a decrease in yield and early leaf fall. Treatment is carried out by removing the leaves with embedding in the soil, the plant before bud break, before and after flowering, it is recommended to treat with preparations based on copper.
- Terry, manifests itself in the deformation of young leaves, their acquisition of an elongated shape with a further deterioration in the appearance of flowers, the appearance of terry and the death of a shrub. The affected shrub must be dug up and burned.
- A kidney mite manifests itself in a strong swelling of the buds, which, together with the adjacent branches, are removed and burned before the shrub leaves the budding stage. The remaining bush before and immediately after flowering is sprayed with Aktellik, if there is no effect, the bush must be dug up and burned.
- Glass currant damages currant branches, which outwardly manifests itself in their lethargy, drying out and their increased fragility. It is possible to diagnose damage to the currant by the glass by examining the cross-section of the branch. In case of damage, there are quite wide passages-voids of a dark color on it. After the detection of the disease, all affected shoots are removed and burned, after flowering, the shrub is processed by Aktellik.
- Gooseberry shoot aphid is manifested in the fact that aphid larvae born during the period of bud swelling attack young shoots and leaves, sucking out juices from them. Aphid damage leads to a change in the shape of the leaves, increasing the risk of damage during wintering by cold. For the treatment of the disease, the shrub is treated with Aktellik during bud break.
- The red-headed aphid is expressed in the appearance of leaf swelling on the affected areas. The fight against aphids consists in the processing of currants with Aktellik before the period of bud formation, after flowering and in August-September.
Seasonal care and landing
Caring for shrubs includes periodically loosening the root area throughout the season. Insecticides, manual weeding and mulching are used to control weeds. Weed control is carried out twice a year in the fall, after harvest, or in the spring along with fertilization. Loosening is carried out to a depth of 8-10 cm using a pitchfork, shovel or hoe.
During the growing season, it is necessary to carefully monitor budding, where a sign of their defeat by a mite will be their swelling, but the absence of disclosure. If more than 3 buds are damaged by a pest, the entire branch is removed. During the season, it is necessary to spray the shrub 2-3 times with a 1-2% solution of Bordeaux liquid or copper sulfate.
Reproduction
Using cuttings, which are prepared as follows. A bush shoot with a thickness of more than 7 mm and a length of 20 cm, containing at least 4-6 buds on its body, is cut off from both sides. The lower cut is made at an angle of 45 °, the upper one should have a right angle, then the cutting is sent to a container of water overnight.
Then the cuttings are planted in the soil with a distance of 10-15 cm between them, so that at least 3-4 buds remain above the ground. The soil around the planted cutting is watered, compacted and mulched with peat or compost to a depth of 4-5 cm. This method of shrub propagation is well suited for the formation of hedges.
With the help of horizontal layering performed in the spring, during the ripeness of the soil. The soil near the plantation should be loose and provided with fertilizers. Young, healthy branches of currants are buried in pre-prepared grooves 5-7 cm deep.
The young vertical shoots that appeared after a while, 6-8 cm high from the ground level, are loosened and spud with a mixture of earth with humus, with a frequency of 2-3 weeks. In the fall, the rooted cuttings are transplanted, carefully separated from the planting and transplanted.
Answers to frequently asked questions
- When placing currants in place with a predecessor from vegetable, flower plants, the planting will be provided with nutrients for a sufficiently long time and will bear fruit better, since it will be located on unexhausted soils.
- It is not recommended to plant a shrub on the site of a previous cultivation of gooseberries or currants, since soils can get tired of monoculture for several years and produce an accumulation of toxins.
- For a more active pollination of currants with insects, it is recommended to spray during the flowering period with a solution of 1 liter of water from 1 tbsp. l honey.
- It is recommended to plant currants in groups of bushes next to each other, rather than individual bushes, since in the first case, better pollination of the bushes is ensured, which increases their fertility.
Great yield of black currants thanks to proper planting and care
Black currant is one of the favorite berries of gardeners. The secret of popularity: in the natural richness of vitamins and the undemanding culture of the growing conditions. Caring for black currants has its own characteristics, but it will not cause any particular difficulties if you choose and prepare a place for planting correctly, as well as cut and process the crop from parasites and fungal diseases in time.
Currant - planting and care in the country
Currants are planted in early spring or mid-autumn.Planting currants in the fall is preferable, since in the spring it is necessary to have time before sap flow begins and the buds bloom, while the soil may not have time to warm up enough and the plant will die.
A sunny place, protected from the wind with a well-drained non-acidic soil (pH value 6-6.5), is chosen for the currants. Fertile light loamy soil is ideal. To reduce the acidity of the earth, add up to 1 kg of lime, chalk or dolomite flour per 1 sq. m.
Deacidification of land for planting currants with dolomite flour
Propagate currants using cuttings or dividing the bush, by separating large shoots with roots from the main trunk. Cultivation of black currants will be successful if you choose two-year seedlings up to 40 cm high, with 3-5 skeletal branches at least 20 cm long, they take root best. Consider how the planting of currants is carried out in stages.
Soil preparation
The selected area is leveled 14 days before planting the seedlings, the rhizomes of the weeds are removed and the soil is left to shrink. After 2 weeks, the site is divided into circles with a diameter of 50-60 cm, which are dug to a depth of 40 cm.The distance between them is maintained at 1.5-2 m, when planting in rows - up to 3 m.
Three quarters of the pit is covered with a bucket of compost or other organic matter. Add 200 g of superphosphate, 60 g of potassium sulfate or 40 g of wood ash. A little black soil is poured on top of the fertilizers so that their concentration does not burn the roots, and then planting is carried out.
Planting black currant
The seedling is planted at an angle of 45 degrees, placing the root collar at a depth of 5 cm. This promotes the growth of basal buds and the further development of a powerful root system. If you plant a seedling directly, then the bush will be formed with a single stem.
Currant seedling planting scheme
Planting currants ends with watering 5 liters per hole and another 5 liters on a circular hole around it. After watering, it is necessary to loosen the soil: up to 8 cm in depth - directly under the plant, at a distance of 20 cm from it - up to 12 cm. Then the soil is sprinkled with fine peat or humus.
After completing the planting procedure, the seedling is cut at a height of 15 cm from the ground, leaving up to 5 buds on it. The cut branches can be stuck next to the main shoot, sprinkled with water with the addition of Kornevin and covered with a film or plastic container for rooting and engraftment. Pruning stimulates vigorous plant growth.
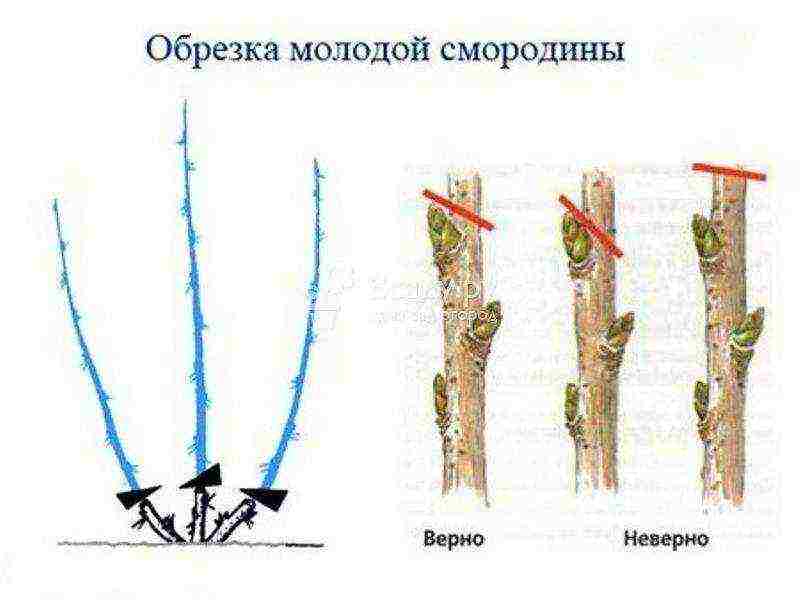 Scheme of cutting currant seedlings after planting
Scheme of cutting currant seedlings after planting
Planting currants in summer video
If the seedlings were not prepared in advance, it is possible to plant black currants in the summer. Most often this is necessary when propagating currants by layering in your garden. This planting is also called deposition or simply breeding. It is performed after the completion of fruiting: for early varieties - in July, and for late varieties - in mid and late August.
Black currant: growing and care
In order for berry bushes to develop well and bear fruit, it is necessary to provide proper care for black currants throughout the growing season.
Spring care for black currant
Before the appearance of buds, all old, dried or diseased branches are cut to a healthy stem, the wounds are covered with garden var. Nitrogen fertilizers are applied (up to 80 g of ammonium nitrate or 50 g of urea per plant) for two-year-old bushes. After feeding, the soil is dug up and watered.
Sanitary currant pruning
At the time of the formation of the ovary until the beginning of June, watering is carried out at the rate of up to 30 liters of water per bush, every 5 days. This is done in the evening using warm water (10-15 degrees Celsius) at the root. For watering, it is recommended to make circular grooves 15 cm deep at a distance of 30 cm from the seedling. Water ingress on leaves can lead to the development of powdery mildew.
Watering a young currant bush in spring
To improve the moisture resistance of the soil, mulching is desirable. You can use peat, straw or newspapers.It is important to do this during the green cone and bud formation phase to prevent moisture loss.
Summer currant care
In the first half of June, organic feeding should be carried out: up to 15 kg of humus per 1 bush, or liquid feeding (bird droppings diluted with water 1:10).
When there is no rain for a long time, timely watering is especially necessary. Usually a bucket of water a week is enough. Watering currants in summer becomes more frequent from late June to mid-July during the ripening of berries, and is done every 5 days.
Currant care in June also includes pinching the young stems of the tops by 2 buds to increase the number of side shoots. This procedure promotes the development of new shoots. The timing of the pinching is postponed to a later date in order to delay the fruiting of the bush.
During the ripening of the fruits, foliar dressing is applied: mixing 5 g of potassium permanganate, 40 g of ferrous sulfate and 3 g of boric acid. Dissolve them separately, and then mix together in a 10 L bucket of water. Spraying is carried out in the evening or on a cloudy, windless day.
Spraying and caring for currants in summer
After fertilizing or watering, it is recommended to remove weeds and gently loosen the soil up to 5 cm so as not to touch the root system of the plant located at a depth of 30 cm.The row spacing is loosened to a depth of 10 cm.
Harvesting berries must be done by the piece, and not plucked in a bunch. This is less likely to damage the plant. Watering and fertilization is completely stopped two to three weeks before harvest.
Care for currant bushes in autumn
After completing the harvest, starting in mid-August and throughout September, watering is carried out once a week, with loosening the soil to a depth of 5 cm. In dry autumn, preparation for winter includes increased soil moisture - half a meter deep.
At the end of September, organic matter (4-6 kg of poultry droppings) must be introduced, or fed with minerals: 20 g of potassium sulfate and 50 g of superphosphate. In any case, when fertilizing, add 200 g of wood ash. After that, the soil is dug up and mulched to increase fruiting for the next year.
Feeding currant bushes with organic matter
Before the onset of the first frost, it is necessary to prune underdeveloped and weak shoots, as well as those that grow in the middle of the bush and thicken it. Poorly developed young branches are also subject to removal, of which only 3-4 of the strongest are left. An adult bush usually consists of 15 shoots from different years of life.
Diseases and pests: prevention and treatment
With proper care, currants rarely get sick, there are such diseases: terry, anthracnose, gray rot, powdery mildew. Of the parasites, the kidney and spider mites, fruit sawfly, glass, and moth are dangerous for her.
Moth caterpillars on currant leaf
To protect the plant from diseases, preventive measures are used. In the spring, before the buds awaken, the bushes are watered with hot water at a temperature of plus 80 degrees. Celsius, at the rate of 3 liters per 1 plant for treatment against pests and diseases. They also carry out timely sanitary pruning of the bushes in order to prevent thickening and regularly dig up the soil to destroy pests.
Also, until the spring swelling of the buds, the currants and the soil under it are treated every 10 days. To do this, use a 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid, 2% solution of Nitrafen or Karbofos. These drugs are also used when signs of diseases or parasites are detected, in which case caring for black currants in summer includes spraying 3 weeks before picking berries. This will help protect the crop from septoria, brown spot, glassfly and aphids.
During flowering and the appearance of the first leaves, additional treatment with fungicides is necessary: Alirin-B, Gamair, Prognoz, Topaz, Glycoladin - from rust and anthracnose.
You can read about how to get rid of a kidney mite on currants in our article.
Preparing currants for winter
Proper care of black currants includes preparing for winter. The soil under the bushes is weeded and the fallen leaves are removed.
Scheme of strapping a currant bush for the winter
After the onset of the first frost, the bush is pulled together in a spiral upward with a rope, at the top clamping it with a clothespin. The ground is covered with mulch. After a large amount of precipitation falls at the base of the bush, a snow pillow 10 cm high is made, and then the bush is completely covered with snow.
Outcome
Growing currants on the site will only bring pleasure, since the culture is not demanding and bears fruit perfectly. Carefully monitor the behavior of the plant so that you always know what it needs, do not forget about timely watering, fertilizing and preventive treatments. Then the black currant, which is taken care of according to all the rules, will thank you with a magnificent harvest and a large berry.
There are many types of berry bushes found in summer cottages. But in the list of preferences of their owners, black currant is in the first place: its planting, like caring for plants, does not cause difficulties, it is not afraid of harsh winters, it begins to bear fruit early and thanks the owner for years for taking care of generous harvests. It is easy to propagate it, and you can do it in different ways. And everyone knows about the benefits of its berries and leaves.

Soil and lighting requirements
Black currant is one of the most viable crops. It can grow almost anywhere. On the sand, in thick shade or in flooded lowlands, its bushes will turn out to be less lush, but even in such conditions they will not die. The plant will be most comfortable in areas open to sunlight with moderately moist soil, protected from wind and drafts.
A shrub is also planted in light partial shade. But in this case, expectations about the harvest should be reduced: a lack of light will make black currant berries more acidic and reduce their number. To understand whether the chosen place is suitable for the plants, their appearance will help. In favorable conditions, they branch well, and their leaves are rich in color and look healthy.
Planting currants in fertile loose soil will be productive. It should freely allow air to flow to the plant roots and retain moisture. Light loam is an ideal option for a shrub. In dense soil, its development will slow down and yield will decrease. It is important to consider the reaction of the soil. It should be slightly alkaline or neutral. Currants do not like sour soil. Such soil will have to be limed before planting.
The culture is hygrophilous, but it grows and bears fruit poorly in swampy soil. It is best to plant shrubs on gentle slopes. It will be unsuccessful to place it in closed lowlands or on sand, as well as on lawns. The distance to groundwater should be at least 0.5-1 m.

Landing time and scheme
Black currants are planted in spring and autumn. Basically, summer residents prefer the second option. Bushes placed on the plots in the spring begin to grow quickly, so it is more difficult for them to root. There is one trick in which planting black currants at this time will be successful. For her, you need to choose plants whose root system is closed. They take root easier and faster in the open field if they are watered abundantly. You can place them in summer cottages at almost any time.
Autumn planting in the middle lane is usually carried out in early October, at the latest in the middle of the month. Under the weight of the snow, the earth around the currant bushes will be compacted in a natural way. In the spring, they wake up early and show rapid growth.
Planting black currants in a row has already become a tradition. This placement makes it easier to care for her bushes and saves space on the site. 1-1.25 m are left between neighboring plants. Some summer residents increase this distance to 2 m. It is important to take into account the proximity of other shrubs and trees when planting. At least 1.5-2 m retreat from the first, 3-4 m from the second. Currants grow quickly.When only 3-4 years have passed, the seemingly bare area will be unrecognizable.
Advice
If you want to get the harvest earlier, you can leave less space between the bushes (70-80 cm). With a dense planting, they will begin to bear fruit after 2-3 years, but fewer berries are formed on them, and they will grow old faster.
Having decided to place the currants near the fence or walls of buildings, you need to leave enough space for it. The minimum distance to them is 1.2 m. It will not be possible to harvest from the branches pressed against the fence.

Seedling selection and site preparation
Preparing a place in the country for currant bushes will not take much time. If earlier this site was used for growing vegetable or flower crops, it is simply dug well, going deeper by 1 bayonet of a shovel and picking out the roots of perennial weeds from the soil. Deep depressions or pits are covered with soil, carefully leveling the surface.
Planting black currants correctly means taking into account the peculiarities of crop rotation. In order for the plants to have enough nutrients and they are less sick, the culture is returned to the previous site only after 3 years. The same recommendation is adhered to if gooseberry bushes used to be at the planting site.
For those who don't have time to wait, there are 2 options:
- find another site;
- deviate from the old at least 1 m.
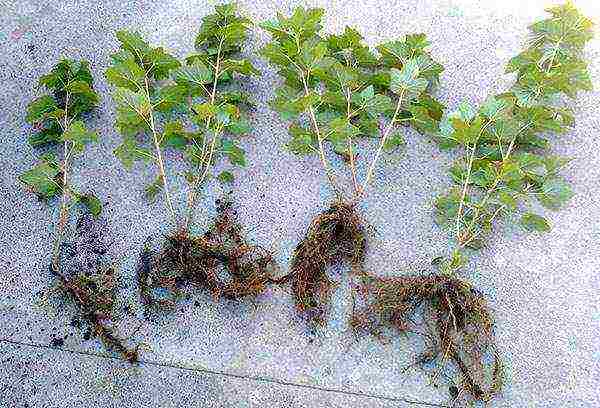
When choosing a seedling, they carefully examine it. A viable plant has lignified and branched roots. 3-5 of them should be skeletal and reach a minimum length of 15-20 cm. A high-quality seedling has 1-2 (or more) 30-40 cm branches. The plant should look fresh and free from signs of infection and pests.
Pay attention to the specific characteristics of the variety:
- its compliance with the climate of the area;
- the presence of immunity to diseases;
- frost resistance.
The harvest will be more plentiful, and the berries will be larger if you plant several varieties of crops in the country. This rule applies even to self-fertile blackcurrant species. Planting in areas of plants with different flowering periods will help to insure against recurrent frosts. So even in a cold spring, it will be possible to get a harvest from at least a few bushes.

How to plant currants correctly
Planting currants begins with the preparation of the pit. It is usually made shallow (35-40 cm) and wide (50-60 cm in diameter). If the soil in the country is poor, the size of the pit is increased so that it can be filled with a nutritious substrate. Lay it out in 2 layers. Fertile soil is poured at the bottom, adding the following components to it:
- compost;
- rotted manure (peat can be used instead);
- wood ash or potassium sulfate;
- superphosphate.
About ¾ of the pit volume is filled with this mixture. It should be under the roots of the seedling. The rest of the deepening will be occupied by simple fertile soil without fertilizers. Having sprinkled a nutritious substrate with it, they begin to plant a plant.
Its roots are examined. If damaged or dry areas are identified, they are trimmed to healthy tissue. With proper planting, the bush will be 5 cm below the mark at which it grew up to it. The root collar should be underground (at a distance of 6-8 cm from the surface). This will give an impetus to the intensive formation of basal buds, and the bush will grow lush.
The next step is abundant watering. ½ a bucket of water is brought into the pit itself and the same amount into the hole, which is made at the landing site. Then the soil under the bushes is mulched without covering the plants themselves.
As mulch, you can use:
- peat;
- compost;
- straw;
- sawdust.
The recommended thickness of a mulching layer made of organic materials is 5-8 cm. If they are not at hand, use dry soil. It is poured in a thinner layer (1-2 cm). Planting ends with pruning of the plant. Only a stump is left from it, which should rise 7 cm above the soil surface.Do not spare the seedling. Already next year it will turn into a small but branched bush. Without pruning, it will take a season longer to wait.

Soil processing and watering
Legends can be made about the unpretentiousness of black currant. But so that the plantings do not overgrow, and the yield does not fall, you still have to take care of them. The shrub does not like the neighborhood of weeds. They are its main competitors in the fight for moisture and nutrients. Best of all, currants feel on a soil clean from any other plants.
It is impossible to spray herbicides near currant plantations, so there are 2 ways to remove weeds:
- weeding;
- mulching.
"General cleaning" of competing plants is carried out twice a season: in spring, when fertilizers have already been applied, and in summer, when the last berries are harvested.
Black currant responds well to soil loosening. Any garden tools are used for him: a hoe, a shovel, a pitchfork. Near the root collar, the soil is cultivated to a depth of 6-8 cm. Under the bushes, loosening is made more intense, affecting a 10-12-centimeter layer of earth. If the trunk circle is mulched, the soil remains moist longer and the frequency of loosening is reduced.
The roots of the shrub are located shallowly - only 50 cm from the soil surface. Therefore, currants cannot do without watering for a long time. Saplings and young bushes especially suffer from lack of water. Adult plants need regular moisture in June, when shoots are actively growing and berries are poured, and in late summer-early autumn, when flower buds of the next season are laid. Drying out of the soil during this period will lead to shedding of unripe berries and crushing of the remaining ones. It will also negatively affect the harvest of the next year.
If the summer is dry, the plantings are watered often (at intervals of 7-10 days) and abundantly. For each plant, they spend 1.5-2 buckets of water. It is more convenient to water in the grooves. They are dug around the bush, stepping back 20-25 cm from the tips of its shoots. If it rains periodically, 4-5 waterings per season will be enough for adult plants. Loves currants and leaf spraying. On hot days, it is better to spend them more often.

Top dressing
With the correct preparation of the planting pits, the cultivation of black currants on the site in the first 2 years does without top dressing. When this milestone is passed, the plants will have to be fertilized annually. Some summer residents feed the plantings less often - once every 2 years. Currant reacts equally well to mineral and organic compounds. They are brought in mainly in the fall or early spring. Spreading humus or compost (4-5 kg per plant) and complex mineral fertilizer (about 40 g) under the bushes, they loosen the soil.
Closer to the end of spring (but before the beginning of summer), when the currant bushes enter the phase of active growth, one more root dressing is carried out. To do this, it is good to use one of the following means:
- manure diluted with water in a ratio of 1: 8;
- poultry manure solution (1 part fertilizer per 10 parts water);
- infusion of herbs.
The nutrient composition is poured into the grooves, immediately sprinkling them. Each plant takes 1.5-2 buckets. The introduction of complex mineral fertilizers at this stage will be less useful, but you can use it as well.
With the onset of flowering, currant bushes are watered with infused potato peel. The starch contained in it will increase the productivity of plants. A solution is prepared from dried potato peelings. They are added to boiling water (in a ratio of 1:10), covered with a lid and, having wrapped the container well, left to cool completely. For each currant bush spend 1 liter of the resulting composition.
Advice
In September, plantings are fed with phosphorus-potassium preparations. They will help plants survive the winter with minimal damage.

Pruning
Growing black currants in the country involves regular pruning. It is most convenient to carry them out in the fall, when the bush is completely naked, exposing old and unnecessary branches. Young (less than 5 years old) shoots are left on an adult plant. Old branches are cut strictly at the level of the soil, leaving no stumps. The wound is treated with garden varnish.
Young shoots are disposed of only in extreme cases - if they:
- injured;
- are sick;
- poorly developed;
- thicken the bush.
Young plants also need pruning. In the first years of life, a bush is formed in a permanent place, shortening its shoots to 10-15 cm. After the procedure, 2 to 4 developed buds should remain on them. The next year, they get rid of small shoots, simultaneously removing weak branches. The skeleton of the bush begins to form, leaving a maximum of 4 well-developed zero-order shoots.
A year later, the main focus is on the branches of the first order. Of these, the 5 most powerful are kept on the plant, and the rest are removed. By the age of 4-5, the currant bush should have 15-20 skeletal branches. In the future, the task of the gardener becomes their sanitary and rejuvenating pruning, which is carried out annually.
Supports and preparation for winter
In many varieties of currants, the bushes grow sprawling. This makes it difficult to care for them and leads to the fact that part of the crop is soiled in the ground. It is convenient to place supports under such bushes. You can buy ready-made in stores or make them yourself. The easiest option is to drive stakes around the plant and pull off the branches with twine. But here it is important not to overdo it. Currant shoots should not be pressed against each other. That's right, if there is a lot of free space between them.
After the autumn feeding, the planting is spud. If the soil in the area is heavy, it is better to dig it to a shallow depth without breaking lumps. This will keep more moisture in the ground. Light and loose soil in the near-trunk circles can simply be loosened well by 5-8 cm. But you cannot do without digging the row spacing (by 10-12 cm). Watering is also required at this time, especially if the autumn is dry. Under each plant, add 20-30 liters of water.
Before the onset of cold weather, it is advisable to tie the bushes with a rope or twine so that the branches do not break and do not bend to the ground under the weight of the snow. You can build a kind of fence of stakes around them. In winter, the bushes are covered with a thick layer of snow.
With the arrival of heat, the plants should be carefully examined. Frost-beaten branches are cut out, and the remaining ones are treated with Bordeaux liquid (1%). It is worth paying attention to the swelling kidneys. They can be infected with a tick. Signs of its presence are a strong enlargement of the kidneys, their inflated, rounded shape. You cannot leave such shoots on the bush; they must be removed immediately and burned.

Agrotechnology of black currant is simple, but its observance will allow you to get rich yields of tasty and healthy berries. From planting this particular shrub on the site, inexperienced summer residents should start their experiments. Currants, like no other culture, are tolerant of the mistakes of the owner. Neither overflow, nor lack of nutrition and moisture, nor frosty winters, nor improper pruning will be able to ruin it.
Shrub reproduction will not bring trouble either. 6-year-old plants are the most productive, therefore, professionals in summer cottages do not allow plantings to grow old. When the currant bush reaches 3 years of age, cuttings are cut from it or the branch is bent to the ground and added dropwise to obtain layering. They are deposited in a separate area. By the time the yield of the mother plant decreases, the first berries will already be tied on young bushes.
Currants are good for everyone: they are beautiful, tasty and do not require special care. Know yourself, remove the weeds, and put the berries in your mouth. For which gardeners love it, growing almost everywhere, from the Kuban to Siberia. But, you can significantly increase the yield, provide yourself with berries, and sell the surplus. True, for this it is necessary to select suitable varieties and strictly observe agricultural technology. Read our article and find out how to surprise yourself and your neighbors with rich currant crops.
There is a rule: "To fix something, you need to know how it works." This also applies to the cultivation of currants: in order to achieve high yields, you need to know the biological characteristics of the plant. There are three types of currants:
- black;
- red;
- golden.
The species are similar in principles of agricultural technology and biological characteristics. As part of the article, we will consider black currants, and we will tell you the nuances of growing red as necessary.
Biological features of currants
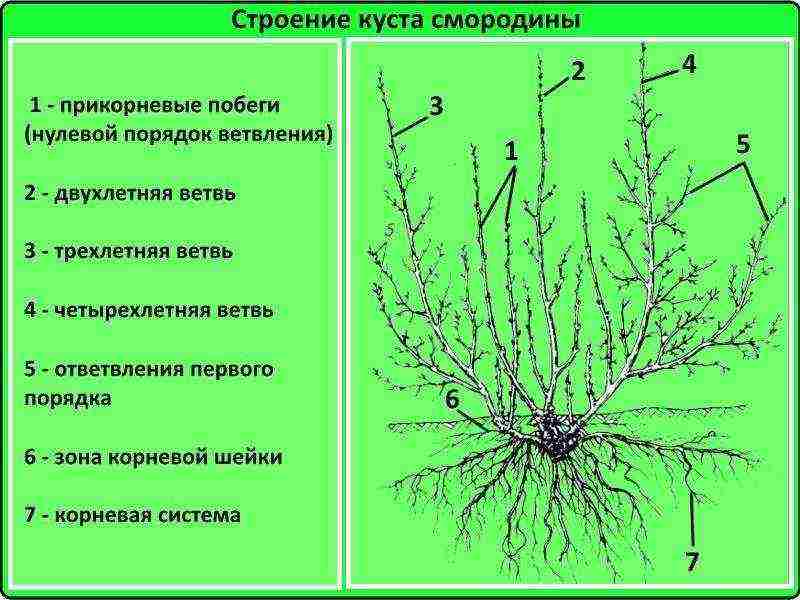 Currant is a perennial shrub, the height of which does not exceed 1.5-2 m. A feature of the plant is the absence of buds on the roots.
Currant is a perennial shrub, the height of which does not exceed 1.5-2 m. A feature of the plant is the absence of buds on the roots.
Take a look at the image. The growth of basal shoots (1) begins from the zone of the root collar (6). It is in this way that a currant bush is formed, because it does not give growth. The next year, after the emergence of zero-order shoots, two-year branches appear (2), then three-year branches (3).
This feature of the currant must be taken into account when planting a bush.
Root collar
should be about 10 cm below the soil surface.
In this case, many shoots of the zero order appear, the bush is easier to form, and over time it is possible to rejuvenate without problems. Most gardeners do not know about this, and many Internet resources do not provide such information. Meanwhile, the correct location of the root collar of the bush is the key to the strength of the plant and a bountiful harvest.
Features of the development of stems
Currants differ in the nature of the development of the stem. Conventionally, the plant can be divided into three groups:
- Many annual branches, but few perennial ones. In the currants of this group, the fruits live for a year or two, then they die, and new ones are formed in their place. After 4-5 years, new fruit branches stop forming and yield decreases. The situation can be corrected by pruning branches older than 4 years "per ring". The most famous black currant of this species is September Daniel.
- There are few basal shoots, but perennial stems branch well. Fruits on such bushes live for a long time, on average 4-5 years, therefore the bush bears fruit for 6-7 years. If the branch is older, the fruits on it become smaller, the yield decreases. The solution to the problem is the annual cutting of 2-3 perennial branches. This stimulates the growth and development of basal shoots, the bush is renewed in a timely manner, the yield does not decrease. A variety of this type is Pamyat Michurin.
- In this group, the varieties occupying an average "position" between the previous ones. In other words, both the number of basal shoots and the degree of their branching have an average value. The fruiting period is 5-6 years. It can be increased by shortening the branches to the first strong bud. One of these varieties is Success.
In the figure, you can see how fruits are formed on branches of different ages in black currant.

As for the red currant, it has more durable fruits. Subject to agricultural technology, red currants give a greater yield than black currants for 8-10 years. Pruning is mainly aimed not at rejuvenating the bush, but at reducing the degree of thickening.
Currant morphogenesis
If you are scared and decide to quickly scroll through this item - we hasten to reassure you. We will not tell you all the biological subtleties. But knowing the timing of the morphogenesis of currants and what it affects will help to take the necessary measures in a timely manner to increase yields.
Scientists have found that the process of laying a crop begins a year before fruiting. This year, the yield will depend on how the currant developed in the last season. And it is morphogenesis (kidney differentiation) that is the most important stage. The timing of the process is different, depending on the following factors:
- type and variety of currants;
- air temperature;
- the amount of precipitation;
- the number of sunny and cloudy days;
- other conditions.
It was found that in dry and sunny weather, morphogenesis proceeds faster than in cloudy and rainy ones. According to the timing, we can only say for sure that the beginning of kidney differentiation is from July 12, and the end is in the spring of next year. In some years, morphogenesis can begin in early August.
Surprisingly, it is during this period that most inexperienced gardeners calm down and limit themselves only to weeding and waiting for the harvest. In the meantime, efforts must be redoubled and the observance of agricultural practices must be monitored.
Currant bushes should receive the required amount of nutrients, water, light. It is necessary to pay attention to the condition of the leaves. Disease-damaged or underdeveloped leaves do not provide high-quality photosynthesis. The significance of this process for plant life is known from the school course in biology.
Different types of currants
Check out the main modern currant varieties of different types. You can enlarge the photo by clicking and view everything in more detail. The varieties listed below are approved by VNIISPK and zoned.
Smolyaninovskaya currant
One of the few modern varieties that have white fruits. As a result of selection, scientists have obtained a shrub that not only possesses such unusual berries, but also has a high resistance to diseases.
The Smolyaninovskaya variety is easy to care for, it is not afraid of frost, the berries are juicy, with a characteristic sourness. At the same time, a good yield was achieved: if you follow agricultural technology, then you will receive up to 5 kg of harvest from one bush! It is possible to grow this variety in open ground in the Urals, the Volga region and in the central regions of Russia.
Currant varieties Karaidel
The variety is intended for cultivation in the Urals, but is also suitable for other regions of Russia. The bush is compact, it is not difficult to care for it. Of the amenities - a low degree of infection with fungal diseases, winter hardiness.
The berries are large enough, fragrant, with dense pulp. There are few seeds, you can safely use it for making jams. The only drawback is that it requires regular pruning due to the strong growth of basal shoots.
Dutch red currant
One of the oldest currant varieties. It is known that it was grown in Europe as early as the 17th century. The currant bush is high, the crown density is increased, but at the same time not very spreading. Fruits are dense, with a characteristic sour taste. The seeds are dense, large, therefore the main purpose of the variety is processing and conservation.
Dutch red currant has excellent resistance to fungal diseases. The plant is suitable for growing outdoors in the North-Western regions of Russia, but it does not take root well in the Urals or Kuban.
Currant Krasa Altai
Are you looking for a variety of currants that can be grown outdoors in the Urals and Siberia? Pay attention to the Beauty of Altai. The plant is susceptible to powdery mildew and some pests, but, with timely preventive treatments, it will delight you with yield.
The variety perfectly tolerates severe frosts, self-pollinates. A pleasant addition - the berries are firmly adhered to the branches and, after ripening, do not crumble. At the same time, the taste of currants is pleasant, with a slight sourness. Suitable for food both fresh and for preservation.
Currant Ural beauty
Despite the fact that the variety is zoned for Western Siberia, it is successfully grown in the Urals, in the Moscow region and in other regions of Russia. The variety attracts gardeners with its high yield and large, sweet berries. The Ural beauty tolerates severe frosts well, and the medium-sized bush facilitates the process of caring for the plant.
Among the shortcomings, one can single out a weak resistance to some pests. You can fight them, and successfully. Subject to the recommended agricultural practices, the variety will delight you with regular and abundant harvests.
We have described for you only some of the modern varieties of currants. If you are interested in earlier breeding, which were cultivated in the USSR, see the table.
| Belarusian sweet | Average | Black, large, weighing 1-1.2 g | High | 2.5-3 kg / bush |
| Grape | Early | Black, large, weight 1.3 g | Excellent | 3-6 kg / bush |
| Leningrad giant | Average | Black, with a thin skin, weighing 1.2-2.2 g | Good | 3-5 kg / bush |
| Stakhanovka Altai | Average | Black, dull, do not crumble, weight 0.7-0.9 g | High | 1.5-3 kg / bush |
| Chulkovskaya | Early | Red, small, weighing 0.4 g | Average | 4-6 kg / bush |
| Sugar red | Early | Juicy, sweet, weighing up to 1 g | High | 4 kg / bush |
| Versailles white | Average | Yellow, transparent, large, weight up to 1.5 g. | Average | 3-4 kg / bush |
Remember that you need to buy currant seedlings of any kind in nurseries. Buying at the market or from a "familiar gardener" is fraught with unpleasant consequences. The fact is that some pathogens and parasites of currants have an incubation period of 1-2 years. Outwardly, the seedling may look healthy, but after a while the disease will manifest itself. When buying planting material in nurseries, there is no such risk.
Currant planting rules
The yield of any kind of currant depends on the conditions in which it grows. The landing site must meet the following requirements:
- the site is flat, or a small slope (no more than 50);
- planting on hills or depressions is not recommended: in the first case, the plant will suffer from cold wind, in the second - from the accumulation of cold air;
- any soil, but their acidity is not lower than 4.5 pH;
- the depth of the groundwater is at least 1 m.
Having found a suitable place, proceed to the next stage. Remove all weeds, apply fertilizers to the soil according to the following scheme:
- manure or compost - a bucket per square meter;
- lime - 2-6 kg / m2 (dosage depends on the pH level);
- superphosphate - 500-700 g / 10 m2;
- potassium salt - 200 g / 10 m2.
After fertilizing, dig up the soil onto the bayonet of the shovel. Remember that soil preparation should be done approximately 2 months before planting.
The size of the planting pits depends on the quality of the soil. The optimal values are 40x40 cm, if the land is scarce in nutrients - do not be lazy and dig large holes. The currant will thank you with enhanced growth and high yields.
You can see the layout schemes in the table.
| Single | 1 | 1,8-2 |
| Tape | 0,6-0,8 | 2 |
The belt scheme has an advantage over the single one: already in the first years, the yield increases significantly. The disadvantage of this method is that fungi and viruses are actively developing in a thickened environment, which requires additional care. The choice of the currant planting scheme is up to you.
Plants can be planted in the fall, but the best survival rate is obtained with spring planting. The seedlings need to be prepared. How to do it?
Cuttings must be kept in water at a temperature of 460C for 13-15 minutes. The purpose of this procedure is to kill the currant kidney mite. Be careful about the water temperature, lower values will not give the desired result, higher ones will ruin the cuttings.
Purchased seedlings need to be pruned, if this was not done in the nursery. Leave 3-4 buds on the branches, remove the rest. This activity stimulates the development of the bush in the first years of life. See the photo for an example, the branches to be removed are marked in red.
Now you can start planting currants. Make a soil mixture using the following recipe:
- a bucket of soil;
- humus bucket;
- 200 g of phosphate fertilizers;
- 40 g of potassium preparations.
Mix well and pour on the bottom of the planting hole. To protect the roots of currants from burns with fertilizers - make a small mound of clean earth on top of the mixture. As a result, you should have a mound at the bottom of the hole.
Now you can proceed directly to planting:
- Pour a bucket of water into each well to form a liquid mud.
- Place the seedlings. An important condition: they should be located at an angle, and the root collar is 8-10 cm below the soil surface. This planting stimulates the rapid development of basal shoots. We wrote about this at the beginning of the article. If your site has loamy soils, then the depth of the root collar should be no more than 5 cm.
- Spread the roots, make sure that they do not bend upwards, this will worsen the survival rate.
- Fill in the soil and compact it so that there are no voids around the roots.At this stage, it is important not to overdo it, so control yourself. Just tug lightly on the seedling: it should not be pulled out, but also not "sit" firmly in the ground.
Water the plant well for the first 5 days after planting. The norm is 3-5 liters per bush. If the weather is rainy, there is no need to water.
Outdoor currant care
Pay special attention to weed control, they must be removed regularly. For the development of beneficial soil microorganisms, loosening must be carried out. Do this carefully so as not to damage the roots. The depth of loosening at a distance of 30 cm from the bush is 4-6 cm, further 30 cm - up to 12 cm. This technique, in addition, will not allow weeds to multiply. In the early years, you can grow lettuce or dill between rows.
Don't forget about mulching. It will help to retain moisture, protect against weeds, and increase yields. Use humus, peat, foliage, or plastic wrap. The width of the mulched circle in the first years of the life of the currant is 50-70 cm, later - 1.25 m. The thickness of the mulch is 4-5 cm.
As for watering, it is necessary during dry periods, during the growth of the bush, and after harvesting. The norm is 30 l / m2. Remember, if the year is rainy, you do not need to water the currants.
Fertilizers and fertilizers for currants
Do you want to increase the yield of currants by 30%, or even 50%? This is possible if fertilizers and feeding are applied correctly. In the first year, if you planted the plant according to the rules, the seedlings do not need to be fertilized. Enough application of urea, in a concentration of 0.3% - this will improve the development of the seedling in the growth phase.
Starting from the second year of the currant's life, begin to apply fertilizers. Remember that in early summer, the plant requires nitrogen fertilization to stimulate leaf growth and increase ovary formation. Towards the end of summer, especially after harvest, when morphogenesis is most active, currants need potash fertilizers. For drugs and their dosage, see the table.
| 1-3 years | Ammonium nitrate | 100-100 |
| Superphosphate | 200-300 | |
| Potassium nitrate | 100-150 | |
| 4 years and older | Ammonium nitrate | 200-400 |
| Superphosphate | 300-600 | |
| Potassium nitrate | 150-300 |
Ammonium nitrate is a nitrogen fertilizer, superphosphate is a phosphorus fertilizer. This information will help you determine when to apply. These substances can be added both in dry form and in solutions; the method will not affect the effectiveness.
Important:
Try not to use potassium salts: currants react badly to them. For red currants, it is generally better to replace mineral potash fertilizers by adding wood ash in the same dose.
Organics can also be used as root feeding:
- slurry - dilute with water 5-6 times;
- bird droppings - diluted with water 10-12 times.
Not only dosage and timing affect the effectiveness of fertilizer use. What matters is how they are entered. For example, if you just dig up the soil along with the preparations, they will remain in the top layer of the soil. Roots that are deeply located will not receive nutrients. Therefore, this method can be used with a single landing pattern.
Better results are obtained by the method that our grandfathers used. Dig circular holes along the projection of the bush. They should be narrow, but at least 25 cm deep. After top dressing - fill the holes with earth.
A good result when growing currants in the open field is given by foliar dressing, which is carried out by spraying. We recommend using one of two recipes:
- 1.3 g of potassium permanganate and boric acid per bucket of water - spray the plants in the flowering phase.
- 30 g of ammonium and 25 g of potassium nitrate, 100 g of superphosphate, 10 liters of water - for spraying bushes.
Top dressing is done early in the morning, it is desirable that the leaf is wet. You cannot hold such events at lunchtime: you can burn the foliage.
Mineral fertilizers are good, but don't forget about organics.The introduction of humus, peat, compost as top dressing will not only provide the plant with the necessary substances, but also enrich the soil with beneficial bacteria. Such feeding should be carried out every two years, in late autumn.
Currant pruning
We already spoke about the technique partly at the beginning of the article, now in more detail. The purpose of pruning is sanitary and bush formation. The yield of the plant largely depends on how correctly the currant pruning was done. What do you need to pay attention to?
- You have already pruned the branches when planting. Now you need to choose and leave two or three powerful root shoots every year, remove the rest. This will create a strong and productive shrub.
- Cut the left branches to ¼ of the original length.
- Cut branches that are more than 5 years old. It is easy to outstrip them: the tops of the shoots dry out, the growths are weak.
- Prune diseased branches in time.
For red currants, the pruning technique is the same. The exception is on two-year-old shoots and older, the tops cannot be cut off.
How can currant propagate
Have you bought currants, got your first harvest and thought about how to propagate the bushes? Use a vegetative method, it is he who allows you to preserve the parental qualities of the plant.
- Woody cuttings.
- Green cuttings.
- Green apical cuttings.
- Layers.
Each method has its own nuances, we will tell you about them, and you choose the method at your discretion.
Propagation by woody cuttings
The method impresses with its simplicity and worthy results. The main thing is to strictly adhere to the technology. Read carefully and memorize.
- Select the bottom or middle part of the annual branch. The length of the harvested cutting should be 15-20 cm, thickness - 6 mm. The number of buds on the handle is 4-5 pcs. Material procurement time is the second half of September.
- Place the cut material in a container with wet sand and put it in the basement. If possible, the cuttings can be kept under the snow, this method of wooding is preferable.
- Treat the cuttings with root growth promoters before planting in spring. Use "Kornevin" - 5g / 5L or heteroauxin - 100-150 g per liter of water. Keep the cuttings in the solution for a day, while they should be 2/3 immersed in the liquid. The air temperature should not be lower than 230C.
- Transplant the cuttings into potting soil. After about 12 days, seals will appear on the bottom, which signal that the cuttings can be planted in a permanent place in the open ground.
- While the cuttings are in the pots, prepare the soil at the planting site. To do this, add 8 kg of compost, 40 g of superphosphate and 15-20 g of wood ash for each square meter. Dig up and moisten the soil.
- Cuttings should be planted in early spring at an angle of 450, leaving one bud on the surface. This planting contributes to the rapid growth of the root system. The distance between the cuttings in a row is 10 cm, the row spacing is 25 cm.
- An important condition is abundant irrigation after planting in the amount of 30 liters of water per square meter.
A good result is obtained by planting cuttings under a film. To do this, spread the material over the garden bed, dig in the edges. The planting pattern with this method is 8x15 cm. To get rid of weeds that can grow under the film, sprinkle the aisles with earth in the summer.
With this method of propagation, the bush is obtained with one stem. To get several branches - pinch the top as soon as it grows 8 cm. You will get 2-3 shoots.
Propagation by green cuttings
One of the simple and reliable breeding methods, which is suitable for both a novice hobbyist and an experienced gardener. Cutting is carried out as soon as the desired shoots reach a length of 20 cm. This usually happens by the middle of summer, but the timing for each region is different. To have a clear idea of the method - see the schematic image.
- Select branches that are 2 years old with developed second-order shoots (1).
- Cut the cuttings according to the scheme, the lower leaves can be removed.
- Remember that there should be a small patch of 2-year-old wood on the bottom.
- Plant in the ground (3), the distance between the cuttings is 5 cm, in the row spacing is 15 cm. The planting depth is 3-7 cm, but the longer the cutting, the greater the value.
- Water abundantly, about 3-4 times at knocks. In case of heat - 5-7 times.
Further care of cuttings consists in timely weeding, loosening and fight against diseases.
An interesting way is used by some gardeners, we hasten to share it with you. The technology is the same, but the cuttings are grown not outdoors, but indoors under plastic wrap stretched over arcs. Gauze is pulled from above to protect the plant from sunburn. Before closing the bed, it is watered abundantly.
Now you can rest for 15 days. Watering the cuttings is carried out by means of condensation, and the increased air temperature contributes to the rapid rooting of the cuttings. A month after planting, remove the film and continue to grow young bushes in the usual way.
Propagation by green apical cuttings
The method is rather complicated; special equipment is required. For its implementation, a greenhouse or greenhouse and a fogging installation are required. This technology is available to specialized gardens and nurseries, so let's talk about it briefly.
Cuttings are planted in a specially prepared substrate consisting of soil and peat in a 1: 1 ratio. Then, using the installation, a fog is created, the humidity of the air must be at least 90%. With this method, the cuttings take root after 2 weeks.
Reproduction by layering
The method is simple, it is often used. It is based on the ability of currants to "put down" roots from shoots. The technology is simple:
- In early spring, bend annual shoots to the ground, fix them with wooden spears, as shown in the figure.
- As soon as the shoots grow 10 cm, make the first hilling 4 cm thick. The soil must be moist.
- After 20 days, repeat the hilling, the layer thickness is 10 cm.
- In the fall, cut off the shoot from the base of the bush, select the strongest shoots and transplant to a permanent place. Do not touch weak shoots, let them grow.
The survival rate of cuttings is high, you can easily propagate the variety you like.
Diseases and pests of currants
Even modern varieties of currants of different types can be damaged by diseases or diseases.
See tables for signs and treatments.
Currant pests
| Currant kidney mite | The kidneys enlarge, become rounded. In the spring they are deformed, take the form of a head of cabbage. Leaves and inflorescences are not formed. | 1. Wood cuttings are disinfected with hot water (read in the article), green cuttings with black tea. 2. Before flowering treatment of buds with karbofos (30g / 10 l of water). 3. Spraying the bushes with garlic infusion (100 g / 10 l). 4. To destroy heavily affected bushes. |
| Spider mite | Damages foliage, which first brightens, then turns brown and falls | Treatment, as in the case of a currant mite. Prevention - timely cleaning of fallen leaves |
| Gooseberry shoot aphid | The leaves on the tops of the branches curl, the young shoots are curved. | Spraying with nitrafen (300g / 10 l). Infusion of tobacco 400 g / 10 l. |
| Willow shield | Larvae appear and firmly attach to the bark. As a result, the branches weaken and can dry out. | Nitrafen treatment 300 g / 10 l. |
| Leafy currant gall midge | The parasite larvae eat the leaves. Damages appear, the leaves turn brown and dry. | Prevention: mulching with peat and autumn digging of the soil. Treatment: 0.3% karbofos emulsion. |
| Stem currant gall midge | The parasite larvae destroy branches and young shoots. | The measures are the same as for leaf gall midge. Re-processing after harvest is needed. |
| Currant kidney moth | The caterpillars of the parasite are red or green in color, the head is black.They bite into the buds of the currants and eat them away from the inside. | Timely cutting of dry branches and stumps, followed by burning. Treatment of the bush with a nitrafen solution (300 g / 10 l). |
| Gooseberry moth | Caterpillars of the butterfly are dark green in color, the head is black. They parasitize on black currant fruits. | Hilling currants in the fall with a layer of soil up to 10 cm. Spraying with infusions of wormwood or tobacco. |
Currant diseases and their treatment
| Powdery mildew | A light white bloom appears on the shoots and fruits. Further, it thickens, changes color to brown. Leaves and shoots stop growing and die. | Spraying before flowering with a solution of copper sulfate (300 g / 10 l) After flowering, 4-fold treatment of the bushes with a solution of soda ash and soap (50 g / 10 l each). In case of severe damage, spraying with colloidal sulfur 1% (50 g / 10 l). |
| Terry black currant | The leaves lengthen, become asymmetrical, and the number of veins decreases. The inflorescences become purple in color. The bushes are thickened. | Purchase planting material from nurseries. Destroy diseased bushes. There are no effective control measures. |
| Anthracnose | Yellow spots appear on the leaves and shoots, which change color to brown. Over time, the lesions grow and merge. The leaves take on the appearance of burnt and fall off. Brown bumps may appear on the berries. | Prevention: timely collection and destruction of fallen leaves. Treatment of planting material with a solution of copper sulfate (100 g / 10 l). For treatment, spray the bush with Bordeaux liquid 1%. Double processing: before flowering and after harvesting. |
Red currants are not affected by the described pests and are less sick. But, if suddenly a disease has arisen, the control measures are the same.
Conclusion
Now you know not only how to plant currants, but also the basics of proper care for a high yield.
Note that many modern varieties may have slightly different requirements for agricultural technology, so check the nuances of care when buying seedlings.
When writing the article, the following literature was used:
- Shaumyan K.V., Kolesnikov E.V. 'Yagodniki' - Moscow: Rosselkhozizdat, 1981 - p. 64.
- Glebova E.I., Dankov V.V., Skripchenko M.M. 'Berry Garden' - Leningrad: Lenizdat, 1990 - p. 205
If you still have any questions - ask in the comments, we will answer them. Did you like the article? Share it with your friends on social networks.


