Content
- 1 The best varieties of roses for Siberia
- 2 What roses should you choose for Siberia?
- 3 Features of planting roses
- 4 Siberian rose care basics
- 5 The choice of variety must be deliberate.
- 6 Difficulties in growing roses in a harsh climate
- 7 Where to plant
- 8 Soil preparation
- 9 How to preserve seedlings?
- 10 Propagation by cuttings
- 11 Rambler
- 12 Variety with fragrant flowers
- 13 Miniature climbing rose
- 14 Climbers
- 15 Shelter for the winter
- 16 Opening
- 17 Fertilizers
- 18 Diseases and pests
- 19 Black spot
- 20 Powdery mildew
- 21 1 Description, types and varieties
- 22 2 Selection of seedlings
- 23 3 Landing
- 24 4 Care
- 25 5 Reproduction
- 26 6 Diseases and pests
- 27 7 Design
With the advent of hardy and frost-resistant varieties, rose cultivation became available in the gardens of Siberia. Here the regional climate is somewhat harsh for culture, therefore, a good knowledge and adherence to agricultural technology is required from gardeners, careful selection of winter-hardy varieties and shelter for the winter.
The best varieties of roses for Siberia
This review presents the most hardy, frost-resistant varieties adapted to the climatic and soil conditions of Siberia. These plants are distinguished by strong immunity to major diseases and pests., do not lose their decorative effect during heavy rainfall.
Chippendale (Chippendale)
Roses Chippendale
A plant that forms a bush 80-120 cm high and 100 cm wide. Terry flowers in the old style, bright orange with a diameter of 10-12 cm... Recommended for planting in massive flower beds, as an accent in the background.
Queen Elizabeth (Queen Elizabeth)
Roses Queen Elizabeth
The bush is from 100 to 250 cm high. The flowers are double, goblet, pink, 10 cm in diameter. The plant forms a compact shrub suitable for planting in confined spaces... It grows well on poor soils.
Golden Celebration (Golden Celebration)
Roses Golden Celebration
A rounded bush with a height of 120-150 cm and a width of 120 cm. The flowers combine an old shape and an unusual copper-yellow color, differ in large sizes from 14 to 16 cm in diameter. Features of the variety - rapid growth of shoots, spicy-fruity aroma of flowers... Flowers do not open during heavy rains. An excellent option for decorating mixborders.
William Shakespeare 2000 (William Shakespeare 2000)
Roses William Shakespeare 2000
The variety is considered to be the best among red roses. The plant forms a lush bush 100-120 cm high and 100 cm wide... Differs in the rapid flowering of new shoots, the formation of large brushes that stay on the bush for more than 2 weeks. Flowers are densely double, bright purple, more than 10 cm in diameter with a characteristic aroma. Suitable for single and group plantings.
New Dawn (New Dawn)
Roses New Dawn
A climbing plant that, with a support, reaches up to 5 m in height, and without it up to 2 m. The variety is distinguished by continuous flowering from June to late autumn.... The flowers are pastel pink, 7-8 cm in diameter. The bush opens up most vividly when planted near a tree during free hanging of the lashes from the branches.
Westerland (Westerland)
Roses of Westerland
The variety is distinguished by its high (2 m) and wide bush (1.5 m). Terry flowers 10-11 cm in diameter with a pronounced aroma... They change color during the season: orange, apricot shades smoothly turn into pink. The plant can be used as a climbing and bushy plant. The variety is self-sufficient for single plantings.
Rosarium Utersen (Rosarium Uetersen)
Rosarium Uetersen roses
Lush shrub 200-350 cm high and 200 cm wide. Flowers 9-12 cm in diameter, densely double, deep pink shade with a light aroma... Suitable for decorating spacious lawns.
Plants of these varieties are distinguished by repeated or continuous flowering throughout the season. In rare cases, shrubs can be seen without a single flower. But even at this time, the bushes do not lose their decorative effect. Bright green glossy leaves, beautiful shoots and thorns are attractive in their own way.
What roses should you choose for Siberia?
The peculiarities of the Siberian climate are late spring, a small number of warm days, severe winters, hard Siberian frosts. Such conditions can only withstand plants zoned in the regional climate. therefore the first rule for gardeners is to purchase a seedling from local nurseries.
 The basis for breeding frost-resistant varieties of roses for Siberia is Canadian and some hybrid varieties.
The basis for breeding frost-resistant varieties of roses for Siberia is Canadian and some hybrid varieties.
It is much easier to take root and are distinguished by their endurance of roses grafted onto a rose hip. It is distinguished by strong immunity to diseases, the ability to adapt to any conditions and quickly recover from cold damage.
The scion should also have a good characteristic. The best indicators in all parameters are shown by the varieties of Canadian selection., derived taking into account the climate of this country, similar to the conditions of Siberia. Roses for planting in Siberia must have high frost resistance, disease and pest resistance.
Winter hardiness depends not only on the characteristics of the plant, but also on the efforts of the gardener - proper care during the season, regular feeding with minerals, proper preparation for winter.
Features of planting roses
Since spring is late in Siberia, the soil often does not have time to warm up to a comfortable temperature for the roots, it is recommended to plant them on the southern side of the site. To prevent bud burnout, it is advisable that the plants are in the shade during the hours of the very activity of the sun..
The climate of Siberia is characterized by cold north and west winds. Therefore, the rosary must have protection from these directions. These can be walls of buildings, bushy plants, gazebos or hedges. So that the barrier from the wind does not greatly shade the roses, they are planted at some distance.
For the rose garden, if possible, select elevated areas... In such places, the soil does not have time to freeze to critical temperatures and quickly thaws. This means that the roots will develop faster in the spring, less risk of rotting due to excessive moisture.
 The planting season of roses in Siberia begins in May, when the soil warms up to 10 degrees.
The planting season of roses in Siberia begins in May, when the soil warms up to 10 degrees.
In Siberia, roses are recommended to be planted in spring. Event are planned from May 15 to June 15... In this case, the air temperature should not be lower than + 10 ° С. The shoots of plants planted later than these dates do not have time to ripen, which becomes the cause of death in the very first winter season.
The rest of the planting of roses in Siberia differs little from warmer regions. A planting pit (50x50x50x) is formed on a pre-dug area for plants and the substrate is prepared. To do this, mix the components on a piece of film:
- humus 3 parts;
- peat 2 parts;
- weathered clay 1 part;
- river sand 1 part;
- wood ash 400 g.
The minerals superphosphate 300 g and potassium sulfate 30 g are added to the soil mixture.
The roots of the seedling, longer than 20 cm, are cut and immersed in a growth stimulator for 3-4 hours. The rose is planted with a deepening of the grafting site: for climbing roses by 10 cm, and for spray roses by 7 cm.
During planting, a hill is formed at the bottom of the pit, on which a seedling is placed and the roots are spread. After dusting the roots and compacting the trunk circle, pour 10 liters of warm water... After that, the bush is spud to a height of 10-15 cm, the soil under the bush is mulched with peat or humus. At first after planting, the seedlings should be protected from direct sunlight.
Siberian rose care basics
The roots of roses penetrate deep enough. Therefore, the plants do not need frequent watering. It is enough to carry out it once every 3-5 days, depending on the weather.... In this case, the earthen lump must be completely wetted, the rate is determined by the size of the bush from 10 to 20 liters.
 Stop watering roses in mid-August
Stop watering roses in mid-August
In the first year after planting, the plants do not need feeding. In subsequent seasons, it is important to feed the roses regularly.:
- in early spring: an aqueous solution of ammonium nitrate (20 g / 10 l);
- after 15 days repeated fertilization with ammonium nitrate, watering with mullein infusion (1: 10), 4 liters for each bush;
- at the beginning of budding calcium nitrate solution (1 tbsp. l / 10 l);
- a week after that are useful foliar feeding: solutions of double superphosphate, potassium nitrate, mullein or ash infusions, macronutrients to choose from;
- before flowering solutions of potassium magnesium or potassium humate;
- after flowering and sanitary pruning mineral complexes with an increased content of potassium and phosphorus (1 tbsp. l / 10 l);
- at the beginning of August organic solution, after 2 weeks with potassium-phosphorus complexes, and after another week with potassium sulfate.
- in September potassium magnesium.
In August, the application of nitrogen fertilizers is completely stopped.
The rest is seasonal maintenance consists of regular weeding and loosening of the trunk circle, shaping and sanitary pruning... To prevent diseases in spring and autumn, the bushes are sprayed with fungicidal solutions.
 Spring pruning of a rose grown in the Siberian region is carried out after the ground has completely thawed (in May)
Spring pruning of a rose grown in the Siberian region is carried out after the ground has completely thawed (in May)
To stimulate the ripening of shoots, watering is stopped since August. In the third decade of September, in dry weather, water-charging irrigation is carried out. Water norm for one bush 40-50 l... Soil moistened in deep layers freezes and thaws more slowly, retains heat longer.
During this period, the loosening of the trunk circle and the forming pruning are stopped. This is necessary to prevent the growth of new shoots.
Before sheltering, all leaves and petioles of plants are removed, unripe shoots are cut off.
Until the cold weather is below 0 ° C, the shoots of the rose are tied with twine and bent to the ground... It is important to avoid the contact of the branches with the soil, which leads to rotting of the stems, so they are fixed with a wire hook.
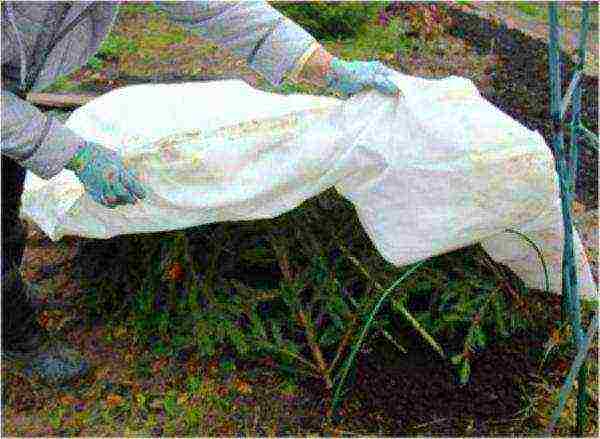 Cover roses as close as possible to the onset of frost to prevent debate processes
Cover roses as close as possible to the onset of frost to prevent debate processes
On top of the prepared shrub, wooden shields in the form of a roof are installed, securing them with pegs. The ends should be closed only after the temperature has been set below -7 ° C.... A dense plastic wrap is laid on top of the shelter and fixed.
The main cause of damage to roses in winter is the effect of moisture on the plant. Therefore, measures to shelter roses are carried out only in dry weather, and in winter they prevent humidification of the air inside the shields. To do this, during prolonged thaws, the ends of the shelter must be slightly opened.
Despite the whimsicality of plants, gardeners admit that the cultivation of roses in Siberia allows you to create a special atmosphere in the personal plot... Only the first 2 years are considered particularly difficult. As they grow older, properly cared for roses, they become much more resilient and do not require close attention.
The queen of gardens and parks, the rose, has long and deservedly been loved by flower growers around the world. This flower also adorns Russian landscapes. Its climbing types are ideal for vertical gardening. Is it possible to grow beautiful and healthy roses in Siberia? Planting and caring (photos and tips are presented in the article), correctly implemented, as well as recommendations for combating diseases will help you cope with this task.

The choice of variety must be deliberate.
Before you start breeding roses, you should get acquainted with the varieties. Take your time with the purchase. After all, you can purchase seedlings through the Internet, and this greatly expands the range and makes it possible to make a good choice. Explore the varieties, chat with rose growers on the forums, read the relevant blogs. With live communication with flower growers, you can learn a lot of valuable information. After all, beginners do not even always know what requirements plants must meet.
Often, only a flower is visible in photographs in store catalogs. Its smell, the shape of the bush, capriciousness in care or unpretentiousness are all very important. How long does the flowering last, how friendly is it, do the flowers fade, how they look after flowering? This information is not always available from the seller.
If a single flower is shown in the photo, but the entire bush is not shown, this may mean that the plant does not differ in abundant flowering or the bush is not able to boast of a decorative form.
Amateur gardeners who are just starting to master this plant always have many questions at first, for example: "Is it possible to grow roses in Siberia in the open field?" Certainly possible. And this is not at all as difficult as it might seem at first glance. The territory is huge, but severe frosts happen everywhere.
Difficulties in growing roses in a harsh climate
Beginners can be advised to pay attention to cold-resistant varieties. But growing roses in Siberia in a greenhouse is possible even in the northernmost regions.
In order for the undertaking to be crowned with success, and the noble plant endowed with lush flowering, you need to know and follow some rules. If you master them, and they are not at all difficult, then planting roses in Siberia will not disappoint, and perhaps even become a favorite hobby. The timing of the beginning and end of garden work is related to the ambient temperature and the degree of warming up of the earth. Since the climate has been unstable in recent years, this adds new questions for the care of the delicate flower.
For the most part, they all agree in determining the timing of planting, in taking care of a safe wintering, in the right fertilizer, providing long and abundant flowering, and in the fight against diseases. As for varieties such as Rambler or Claymer, which are quite common, unpretentious and well-mastered climbing roses by gardeners, planting and caring for these species in Siberia is not difficult. However, their cultivation is accompanied by other pleasant cares, such as decorating them in the landscape.
Where to plant
They are light-requiring. Planting roses in Siberia in the fall should be carried out with this feature in mind. By the way, it has been noticed that if the shrubs are provided with proper care - watering, feeding, etc., then they feel great and bloom even in partial shade.
If you want to decorate the wall of your house with plants, then roses are not the best choice. There is a high risk of unwanted temperature changes near the house. On the one hand - the cold air of the street, on the other - the warm wall of the house. Snow melting or drifts, icing during thaw periods are likely. Such contrasts are detrimental to delicate plants. Even good illumination of the south wall may not save the situation. You should not plant roses near the walls at all. For them, a well-lit place with partial shade in the center or on the outskirts of the site will be more comfortable. If you really want to decorate the house, then plant the bushes at a distance of at least a meter from the southern wall.
Soil preparation
Dig a hole about 40x40x40 cm, put complex fertilizer on the bottom. Roses are very sensitive to soil quality. If it is clayey, fluff it up by adding sand, wood ash, humus, some peat and leafy soil. If the soil is mostly sandy, then manure, humus and leafy soil. These components will make it nutritious enough and moderately weight.
Planting roses in Siberia is not a tricky business, and if you have a plant that is not grown on a rootstock, but is rooted, then you can not be afraid that in the spring, instead of a cultivated variety, you will have a well-wintered wild rose hip on the site. Try to choose just own-rooted varieties, and in any case deepen the root collar by at least 5 cm.It is also not recommended to deepen the root more deeply, since the rose will release new roots from the grafting site, and it will grow much weaker on the roots of the scion.

Half or a third of the prepared soil mixture should be placed on the bottom of the pit, under the roots. Then you should thoroughly moisten the substrate by pouring water into the pit. Powder the roots with ash before planting and place them neatly and evenly in the hole. Pour the remaining soil onto the roots from above, trying to tamp well so that there are no large voids between them. Water again abundantly.
How to preserve seedlings?
Autumn is more suitable for planting and replanting an adult rose. Planting and care in Siberia in spring is the best time for plants obtained from cuttings, as well as for roses sent by mail and overwintered in a cold room at home.
You can start gardening immediately after the snow melts, when the shovel easily enters the ground. This usually happens in April. Old bushes can be replanted in spring, but this is less advisable than in autumn - prolonged habituation to a new place can negatively affect flowering, and you will think that the bush has degenerated or the place is not suitable. But cuttings in the spring always succeed perfectly well. Prepare the branches in the fall. Cut long shoots, bring home and disinfect in a weak solution of potassium permanganate. Store them in your basement in a sandbox. If there is no basement, then put it in the refrigerator, in the compartment for fresh vegetables. To prevent the shoots from drying out, wrap them in a damp cloth and then in plastic. In spring they will be fresh and green.
Propagation by cuttings
In April, when the snow melts, remove the thin upper parts of the shoots, cut the branches into 10-15 cm cuttings with buds on each, soak for a day in water with potassium permanganate and you can plant. Use a root root for guaranteed results.
To prevent spring frosts from destroying the plants, plant them in a sunny, wind-protected place with loose fertile soil. Cover each stalk with a plastic bottle: cut off the bottom, and use the upper part with a lid as a mini greenhouse. Keep the ground constantly moist. After a month, you can begin to ventilate the greenhouse bottles by removing the caps for a while. By doing this, you will gradually accustom the plants to the natural atmosphere. Do this very carefully. Root formation requires warmth, constant temperature, high humidity and lack of movement. Having got used to such conditions and being in the fresh air, a pampered plant can cope with a difficult adaptation and die.
It is believed that the appearance of the first leaves indicates that rooting has taken place. Don't be in a hurry to rejoice. You can completely remove the bottles only after a couple of months. In addition, all this year you will have to carefully take care of young plants - shade them from the scorching sun, fertilize, prevent the soil from drying out or stagnate water, and protect them from freezing.
Are there winter-hardy climbing roses? Planting and caring for many varieties of ramblers and claimings in Siberia does not cause any particular difficulties, since they are characterized as unpretentious and winter-hardy. If you are a beginner, then choose a self-rooted variety grown in a local nursery.
Rambler
I must say that growing roses in Siberia from cuttings is best done with ramblers. Doroty perkins, bobby james and excelsa have proven themselves most well in harsh climates. Cuttings can be practiced throughout the summer. For cuttings, twigs are collected from the third quarter of the lash - the one closer to the end. Sticks are cut into the size of a pencil. Rooting in the greenhouse takes place within a month.
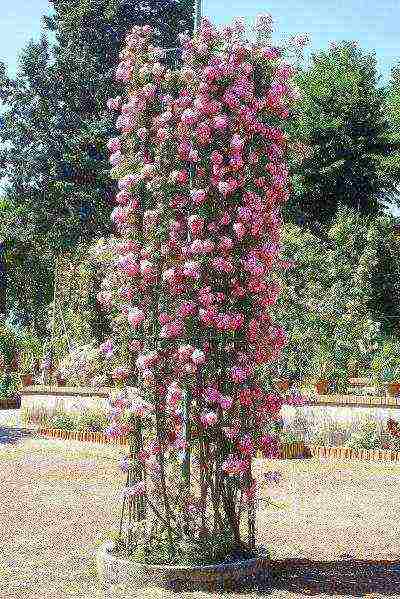

Rambler are very handy plants for decorating small areas. Their whips grow up to five meters, they are very flexible and plastic. They are twisted around the support clockwise, trying to keep the branch horizontally. This technique stimulates the regrowth of new flowering shoots of the rose. Planting and caring for the rambler variety in Siberia is suitable for novice gardeners. Its flowers are small, double, collected in lush inflorescences, which are very densely strewn with the entire bush. Flowering, although one-time, but very abundant, lasts almost a whole month. In order for flowers to decorate your garden longer, stop fertilizing with the beginning of flowering and watch the soil under the bush moisturize.
Variety with fragrant flowers
Musk roses are highly appreciated by many gardeners.Planting and caring for this variety in Siberia will be successful if you choose a place for them with loose neutral soil, well protected from cold winds and sufficiently illuminated. Traditional musk roses exude a strong amber scent. It does not come from the petals, as is the case with other varieties, but from the stamens, so even withered flowers continue to smell. However, they do not always have such a bright aroma. Many hybrids are more decorative than older varieties, but odorless. Musk roses produce flexible whips up to 2.5 meters long. This allows them to be used to decorate gazebos and arches. The best varieties are Mozart and Ballerina.
Miniature climbing rose
Another charming example of climbing roses is the pirouette variety. Since its branches do not grow more than one and a half meters, it is often planted as a scrub - a single bush. Small flowers of a slightly apricot shade are collected in a brush. They open very amicably and so abundantly that foliage is not visible behind them. Long flowering. The aroma is delicate, pleasant, sweet, albeit weak. "Pirouette", practically does not get sick with powdery mildew and black spot, which are often dominated by roses. Planting and caring for this variety in Siberia is also convenient because it is cold-resistant. A little cover is nevertheless necessary.
Climbers
These are, one might say, monumental climbing roses. Planting and caring for this variety in Siberia can be complicated by difficulties with shelter. Compared to ramblers, whose whips reach five meters in length, climbers are just babies. Their shoots do not outgrow the 2-meter mark. However, they are very thick and do not bend as easily as miniature ramblers. It is very difficult to wrap such an escape around a post or arch. If you run the branch vertically upwards, then it will bloom only at the upper end. Flowers are very abundant when the branch is horizontal. In a flower garden, they are placed in a fan on fences, trellises. This stimulates the regrowth of new flowering shoots. If you want the roses to bloom as long as possible, then stop feeding with the bud setting, and water daily in dry weather. And climbers bloom luxuriously! Large fragrant flowers adorn the bush for almost a month, and for remontants, twice a season. The best varieties are Elf, Rosanna, Pink Cloud and Pierre de Ronsard.
Shelter for the winter
How to keep roses in Siberia in winter? Planting and caring, watering and weeding, feeding and pest control - everything that you did in the spring, summer and autumn may be in vain, and next year you will have to start all over again, including the search for a good reliable bush if your bush is broken freezing.
Roses are covered after the first frost, on a dry day. This is important because sheltering wet bushes will create an unfavorable microclimate and the development of fungal infections. Shoots are removed from the supports and laid out neatly on the ground. If you bend down the thick branches of the climber, then use the forks to dig in the ground. This will make it easier to fold the bush. There is no need to spread it very low on the ground. Let it rise a little. Your goal is to dress the plants in a fur coat. Nonwovens such as lutrasil have proven themselves very well in severe winters. Take the thickest one and fold it in several layers. The bushes should be covered with a continuous blanket, and not in separate fragments. Press along the perimeter with bricks.
Opening
How does the cultivation of roses in Siberia begin? Spring is the time when new bushes are bought and old bushes are opened. Shelter should be removed in several stages. First they ventilate, then they open it slightly, increasing the time, and, finally, they completely remove it. This is done in order to accustom the flowers to new conditions. Having removed the covering material, they look through the lashes and cut off the damaged or dead ones to healthy tissue. At this time, it is very convenient to loosen the ground around the rose and pick out the roots of the weed.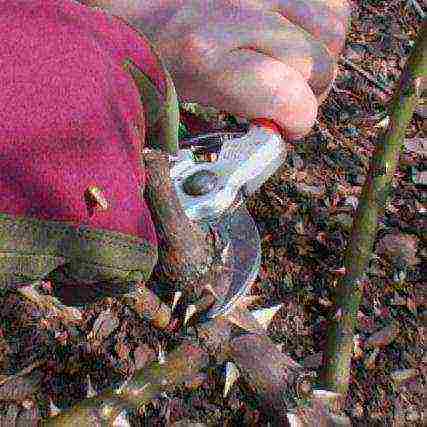
Fertilizers
Do roses require any special dressing in Siberia? Planting and care in this region is somewhat more time consuming than in Europe, but this is only due to protection from freezing in winter. The rest is the same. Plants require large amounts of nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus in spring. Roses are very dependent on the microbiological composition of the soil and are sensitive to the lack of one or another element. As for the acidity, the slightly acidic (pH 5.6) will be just right for them. From mid-July, nitrogen fertilizing, which enhances the growth of shoots, should be stopped. Otherwise, by winter there will be many young immature shoots on the bushes that will not withstand the difficult winter - the affected tissues of young shoots will become a breeding ground for infections, which can provoke the death of the entire plant.
If there is an opportunity to feed the rose with manure, then do it in the spring, and it will repay you with excellent growth and flowering. Rotten manure and mullein are the best fertilizers for roses. Manure is a supplier of nitrogen, and the necessary potassium and phosphorus are found in wood ash. In addition, plants need calcium, magnesium, iron, boron, manganese and copper for proper growth and development. Therefore, do not neglect complex mineral fertilizers.
In September, it is recommended to add superphosphate or potassium nitrate for the last time under the bushes.
Diseases and pests
It's time to find out what roses are sick with. Planting and caring for these delicate plants in Siberia is not very difficult, but the harsh climate weakens the immune properties of roses and they can get sick. The most common diseases of climbing roses are black spot and powdery mildew.
Black spot
This misfortune is not as terrible as it seems, although it greatly spoils the appearance of the bushes. It occurs most often in the second half of summer. The leaves become covered with black spots, then turn yellow and fall off. It starts from the bottom of the bush and gradually rises upward. In severe cases, it leads to the complete fall of all foliage. At the onset of the disease, it is enough to cut off the affected leaves and burn them, and spray the bush with a weak solution of mullein (20 parts of water for one part of mullein). Two or three procedures are enough. If you can't find a mullein, buy drugs containing penconazole, triazole, or mancozeb from the store. It can be Topaz, Profit, Skor or Ridomil Gold.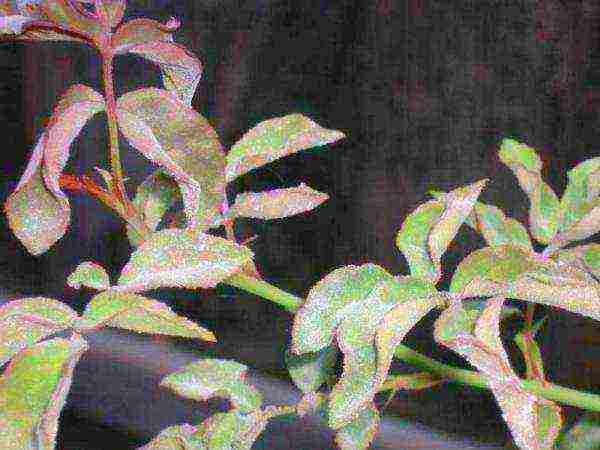
Powdery mildew
The disease often affects roses growing in a greenhouse. In climbing roses, it occurs as a result of damping as a result of too much watering in cool weather. It affects the young parts. They are covered with a white powdery coating. Spraying the bushes with an infusion of wood ash in this case is very effective. First, you need to remove the affected leaves, buds and shoots, cutting them to healthy tissue. All this must be burned so that the pathogenic microflora does not resume activity. The cleaned bushes should be sprayed with an ash solution, and after two hours rinse it off with clean water. In case of severe damage, drugs containing triazole are used - "Skor" and "Topaz".

- Kind: Rosaceae
- Flowering Period: June, July, August, September
- Height: 30-300cm
- Color: white, cream, yellow, pink, orange, red, burgundy
- Perennial
- Hibernates
- Sun-loving
- Moisture-loving
Siberians joke that weaklings do not survive in their harsh winters. We need a persistent character, and not only for people, but also for plants. So the criteria for selecting flowers for site design in Siberian conditions are much more severe than for the Moscow region or the southern regions of the country. And yet the inhabitants of the cold regions successfully grow even the thorny beauties of the rose. They have developed many interesting ways of sheltering plants, planting tricks in order to protect the root system in severe winters. We looked at the forums of Siberian gardeners and selected the most important information about frost-resistant varieties, shelter technology for the winter and what features are planting roses in spring in Siberia.
Rose varieties for cold climates
The Siberian climate is known to be characterized by late spring, short summers and severe winters.To withstand such conditions, plants must initially be regionalized in the local climate. Those. by the degree of survival rate, the seedlings grown in Siberian nurseries are in the lead. Gardeners give the second place to Canadian roses, because the climate of this country is similar to the Siberian one. But real Canadian roses, unfortunately, are rare. This category of plants is too attractive to buyers, so it is most often counterfeited. It is better to purchase Canadian varieties only from a reliable supplier, and, of course, not from hands or from the market.
The second selection criterion is vaccination. According to statistics, grafted varieties of roses in Siberia endure winters much easier and do not freeze, because they have higher immunity. The stock for a varietal rose is usually a rosehip, and its immune system is much more resilient than that of its own rose roots.
Here is what, according to Siberian gardeners, the five most unpretentious and winter-hardy varieties of roses look like:
First Place: Rosarium Uetersen
Belongs to the Climber group, i.e. large-flowered climbing roses. It can also be grown as a stem. It blooms in dark pink petals with gradual fading. The size of the flower can be up to 12 cm, but the colder the climate, the smaller the inflorescences will be. The approximate size of flowers for Novosibirsk is 5-6 cm. Rosarium Uetersen is loved for its resistance to fungal infections, repeated flowering (the first is the most abundant, and then - in waves). Powerful stems are not afraid of frost or wind. Gardeners can ruin this rose only if it is improperly laid for the winter, when the stems break from an unsuccessfully chosen direction of laying. The bush reaches up to 3 meters.

Rosarium Weathersen fits perfectly into arches, pergolas and other supporting structures, and if desired, it can be grown as a stem
Runner-up: Westerland
A German variety adored in Siberia for its continuous flowering. This rose wakes up and blooms very early, and after that it practically does not remain without flowers. The flowers change color from bright orange to apricot-salmon. In diameter - up to 10 cm. It is certified by ADR as one of the most unpretentious roses.

Timely removal of fading flowers from the climbing rose Westerland stimulates the bush to active growth and the formation of new flower buds
Third place: New Dawn
Descendant of American roses. It blooms with delicate pink, fragrant flowers almost all season. The gardeners of Siberia gave her the nickname "Very", that is. very frost-resistant, very unpretentious (grows everywhere), very prickly, very fragrant, etc. The only caveat: recently there have been copies of New Dawn, which bloom only once. Therefore, before ordering, check the number of blooms, otherwise you can see this beauty only once, at the beginning of summer.

Siberians believe that New Down lives under the motto "Everyone will be lost, but I will stay", because it survives in the most inhuman conditions
Fourth place: William Sheakespeare 2000
BUTNew generation English rose, grown by world renowned breeder David Austin. It blooms with velvety deep red flowers, gradually turning into a lilac hue. Fragrant, medium height (up to 110 cm), forms many flowering brushes on each branch. When buying, pay attention to the presence of the number 2000, since there is also an ancestor of this rose - William Sheakespeare, which is not so immune to fungal infections.

William Shakespeare 2000 - the result of selection of the English "ancestor" of the same name, which is distinguished by high immunity to diseases and excellent frost resistance
Fifth place: Golden Celebration
Another pet of David Austin. It blooms twice, with bright yellow large flowers, similar to balls, exuding a lemon-caramel aroma. In cold climates it grows up to one and a half meters in height. Practically not susceptible to diseases, except for black spot. Looks great in mixborders.

Golden Celebration's sunny, large inflorescences smell like lemon candy, so they are planted near recreation areas to enjoy the wonderful aroma.
Choosing a location: looking for the sunny side
Due to the fact that spring comes late in Siberia, and there are not very many sunny days in the year, they try to plant roses from the south. But a completely open area is not very profitable, since the flowering period is significantly accelerated, and the flowers fade in the heat. It is best to think over a light partial shade with the help of light-leaved shrubs or trees. The roses are planted near them so that in the hottest time of the day they are protected by the foliage of the "neighbors".
It is advisable to select high places of the site for the rose garden. There, the degree of soil freezing is always less, which means that the roots will wake up faster. This will save the plant from high humidity, which is typical for lowlands. Too much moisture provokes the development of rot and fungal infections.
Strong winds are not uncommon in Siberia, with a cold front coming from both the north and the west. From these directions (north, north-west and north-east) roses need protection in the form of buildings, gazebos, living coniferous hedges, etc. But the wall should be at such a distance that no shadow is cast on the bushes.
Landing rules: light earth + depth
For the Siberian climate, spring plantings are desirable, and their period is much shorter than in other regions. The planting season begins in May, when the soil warms up to 10 degrees. Gardeners determine the optimal time for dandelions: as soon as they bloom, it is time to plant rose bushes. The grafted seedlings are planted first, because the rose hips are not afraid of sudden late frosts. Own-rooted roses - not earlier than May 15th. The maximum landing date is June 15th. If you are late, the rose will not have time to grow stronger in a short summer and will leave for the winter without a lignified trunk. This means that it will freeze easily.
The Siberian planting of roses is not very different from the rest of the areas. Thorny beauties like slightly acidic soils with a high humus content. The base of the soil can be loam. It is good when planting to lay on the bottom of the pit and sprinkle with earth the rotted horse manure, which will warm the roots. Bushes are not planted directly into the manure so as not to burn the young roots.
The optimal composition of the earth: 1 part clay + 1 part sand + 3 parts humus + 2 parts peat + 0.5 parts wood ash. It's not bad if you immediately apply a special fertilizer for roses.
Landing rules:
- The depth of the landing pit is at least half a meter.
- Purchased seedlings are dipped in a solution of water with a growth stimulator for 3-4 hours so that they are saturated with moisture.
- Too long roots (above 20 cm) are shortened, stimulating the growth of lateral roots.
- Paraffin is removed from the aerial part and branches are slightly pruned (to a green healthy color).
- Most important point: a slightly recessed fit.
Many gardeners in Siberia have found that tea, English varieties and floribundas survive better in cold weather if the grafting site is not 5 cm below the soil level, but 7-8 cm, i.e. a little deeper. Accordingly, for climbing roses you need 12-15 cm. Such plantings can be less sheltered, and some owners have completely abandoned shelter, having bought varieties with high frost resistance.

When planting deeply, the rose can release roots above the graft site, developing its own root system, which is weaker than that of the rose hips, so the "wrong" roots must be removed
When planting, the roots of the rose are straightened so that they only go from top to bottom, and not wrap themselves in a ring. A planting mound can help this arrangement: a fertile soil is poured onto the bottom of the pit, a seedling is placed on top, the roots are straightened along the mound and sprinkled. When planting with a mound, watered after the rose is planted. With a normal planting, you can first shed the roots, and then cover with soil.
After planting, the bush is invariably spud to a height of 15 cm.This is necessary so that the water does not quickly evaporate.The earth will also protect delicate branches from the scorching sun, because at the time of engraftment they dry out very quickly. In the northernmost areas, plantings are covered with lutrasil to protect them from night frosts.
Siberian ways to hide such roses
So that the cultivation of roses in Siberia does not end with the freezing of the bushes in the very first winter, gardeners have come up with many different options for shelter. Their similarity is that for roses in cold climates it is necessary to create a dry shelter, i.e. protect each seedling on top with a waterproof material. It will protect the plant from moisture, which instantly turns into ice.
Shelter options:
- "Snow blanket"... If your area has stable snowy winters, then throwing snow on each bush is the best option for shelter. Indeed, in Siberia, snow both falls and lies until spring, so that under it there is always a stable temperature.
- "Frame made of plastic arches". A frame is made of two intersecting arcs, placed over a rose, the bush is covered with half-dry earth or leaves, covered with a double layer of spunbond or lutrasil on top, on top of which the film must be spread so that it captures part of the soil. Sprinkle the edges of the film with earth. Before the onset of a stable frost, the film should be slightly opened so that the stems do not come out.
- "House made of polycarbonate". Instead of plastic arches, two pieces of polycarbonate are placed over the rose, fastened at the top with twine. It turns out a house. Cover with lutrasil and film from above. But at the ends, the film is closed only after the onset of frost.
- "From plastic buckets." Each bush is spud up to a height of 20 cm, covered with spruce legs and covered with plastic containers without holes on top.
This is how it all looks like:

It is impossible to cover roses only with lutrasil without using film, since during the thaw moisture accumulates inside, and at the first frost it will settle on ice on the plants

Covering roses with spruce paws is recommended for those owners who have a lot of mice, as they like to build nests in lutrasil
With any type of shelter in early spring, many Siberians repeatedly shed soil with epin in order to revive their pets. Grateful roses give their owners abundant and fragrant flowering, although nature has given them very little time for this.
Rate the article:
(11 votes, average: 3.8 out of 5)
Today there are many rose hybrids that do not require a lot of attention when growing. Thanks to this, beginners in gardening art have the opportunity to choose a species according to their preferences and climatic conditions. Among the modern variety of varieties, along with thermophilic ones, there are frost-resistant representatives that take root without problems even in Siberia. For the best growing of roses, you must follow the basic rules.
1 Description, types and varieties
Rose is the generalized name for all representatives of this flower line, belonging to the genus of rose hips. In the process of growth, they form bushes, which differ in height depending on the species. Some do not exceed 30 cm, others can reach 2.5 m. By type, shoots are divided into uterine and annual. The standard classification also does not apply to the shape of the leaves, it all depends on the type.
The appearance, color and size of flowers vary. There are buds from 2–3 cm in diameter to 15–20 cm (with the number of petals from 5 to 100). The color scheme is striking in its variety, there are red, white, yellow, pink, black and even blue. Roses, which change their color during flowering, have become the pride of breeders. There is a conditional division of grades into classes. This helps to correctly navigate and choose the most appropriate option. The emphasis is placed not only on decorative indicators, but also on the place of intended cultivation - in the country, in the open field or at home.
Common varieties of roses often used in garden design, depending on the group affiliation:
- Floribunda - Aprikola, Aspirin-Rose, Bengali, Black Forest Rose, Crescendo, Debut, Gebruder Grimm, Hermann-Hesse-Rose, Intarsia, Isarperle, Kosmos, Innocencia, Schone Koblenzerin.
- Groundcover Roses - Bluhwunder 08, Heidetraum, Sedana, Mirato, Schneeflocke, Stadt Rom, Mirato, Schneeflocke, Sorrento, Stadt Rom.
- Shrubs - Comedy, Goldspatz, Flashlight, La Rose de Molinard, Larissa, Medley Pink, Pink Swany, Shining Light, Yellow Meilove.
- Hybrid tea roses - Elbflorenz, Grande Amore, Eliza, La Perla, Pink Paradise, Schloss Ippenburg, Souvenir de Baden-Baden.
- Climbing large-flowered - Golden Gate, Hella, Jasmina, Kir Royal, Laguna.
The main groups of varieties of garden roses:
| Species name | Characteristic | Image |
| Park | Decorative representatives of roses. Endowed with increased winter hardiness, tolerate low temperatures well without shelter in regions of the middle climatic zone. Unpretentious to care, do not need annual pruning. They begin to bloom in late May - early June, the duration is from 2 weeks to 1.5 months. Bushes grow from 1 to 3 m in height |  |
| Hybrid tea | Bushes no more than 80 cm high. They are distinguished by long and spectacular flowering. The buds bloom once and last from June to autumn. The flowers are large, 10-15 cm in diameter. The varieties are frost-resistant, need a protective shelter in regions with cold winters |  |
| Polyanthus | Form numerous inflorescences on the shoots. Blossom from June until the first frost. Medium-sized flowers - 7-10 cm in diameter |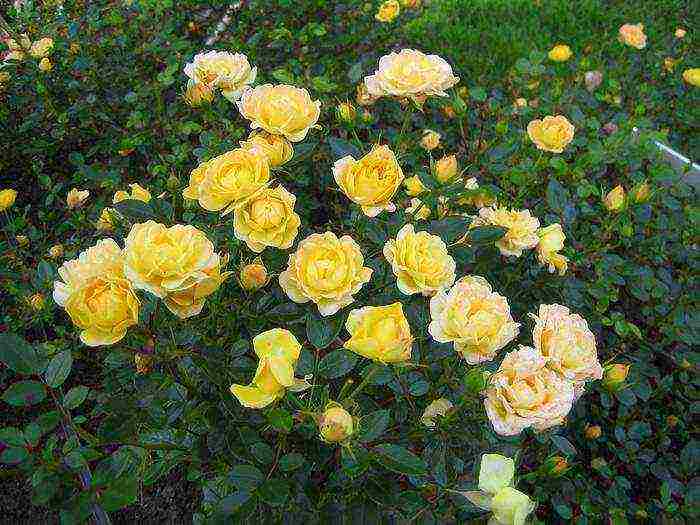  |
| Floribunda roses | An intermediate variety between hybrid tea and polyanthus roses. The buds are large when opened and exude a pleasant aroma. Abundant flowering is observed for a long period. They endure the cold, staying for the winter in the open field |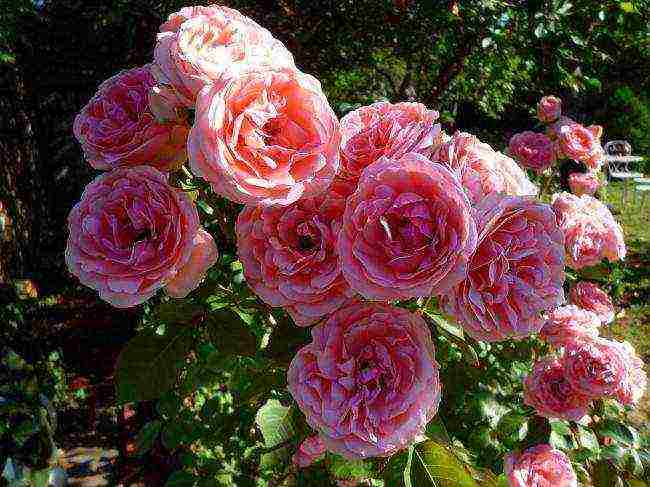  |
| Climbing | They are divided into 2 subspecies: small and large-flowered. The first variety is characterized by buds up to 4–5 cm in diameter; the second - from 5 to 10 cm. A distinctive feature is flexible long shoots, at the ends of which small group inflorescences are collected |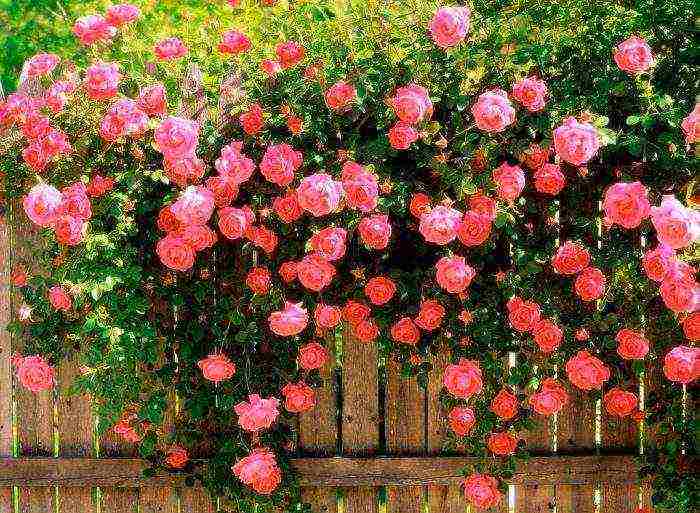  |
| Miniature | Compact bushes, abundantly strewn with small buds. Endowed with a long flowering period, right up to the first winter cold weather. In gardens, they are grown not only in flower-bed compositions, but also in suspended and stationary flowerpots or pots. |  |
| Ground cover scrubs | Roses of unusual decorativeness, which are planted as a continuous flowering lawn. Unpretentious to care, cold-resistant and with increased immunity to diseases |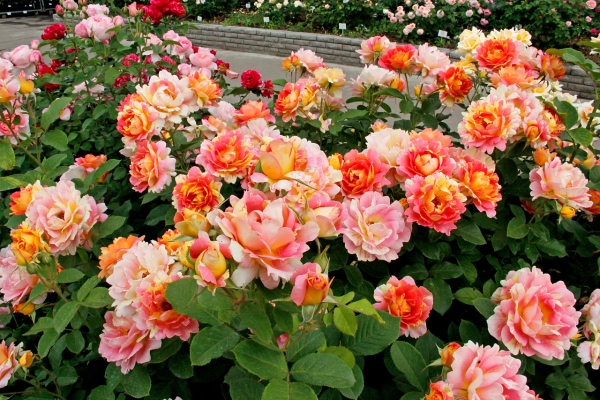  |
| Modern park | A group that includes hybrids of Cordes, musk rose, rugosa, shraba and moesi. In abbreviated form, all varieties are called scrubs. Includes all varieties that for some reason do not fall into other groups. They are characterized by the following features: buds of atypical configuration and different colors, they smell nice, the bushes are vigorous, strong and up to 2 m high. They have repeated flowering during the growing season. Plants are unpretentious, have strong immunity, frost-resistant |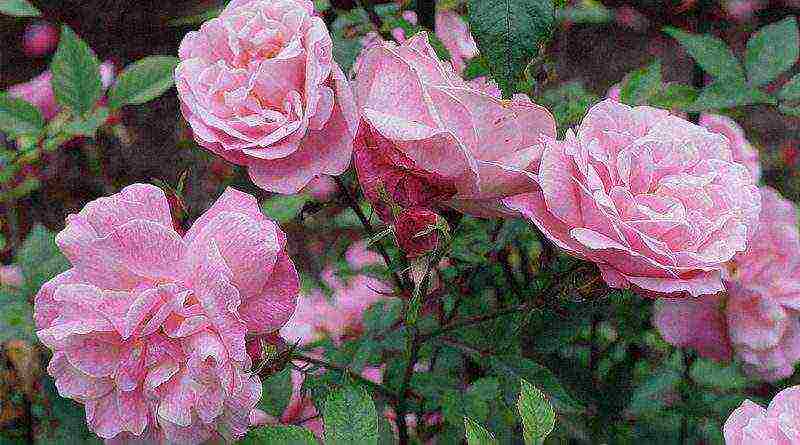  |
| Shrubs | The main difference is a large bush with shoots diverging on the sides. Even with minimal maintenance they grow up to 2.5–2.8 m in height. Among gardeners, the following varieties are most popular: Modern Shrab, Grandiflora. In landscape design, they are often used as hedges. |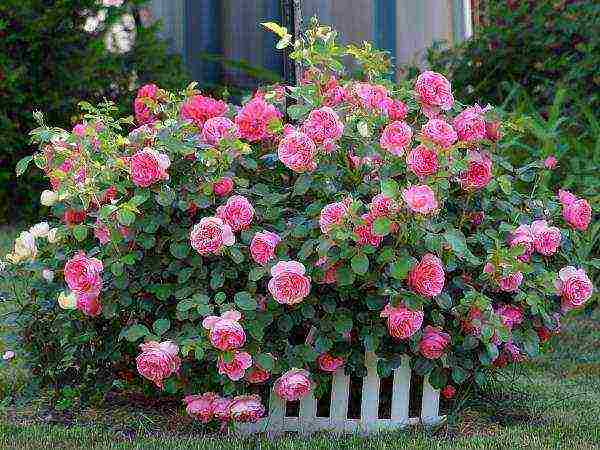  |
| Cascading | Rose hips with grafted climbing and ground cover roses at a height of 130–150 cm. The stems are long, sometimes drooping. The shape, size and color of the flowers vary and depend on the result of the vaccination |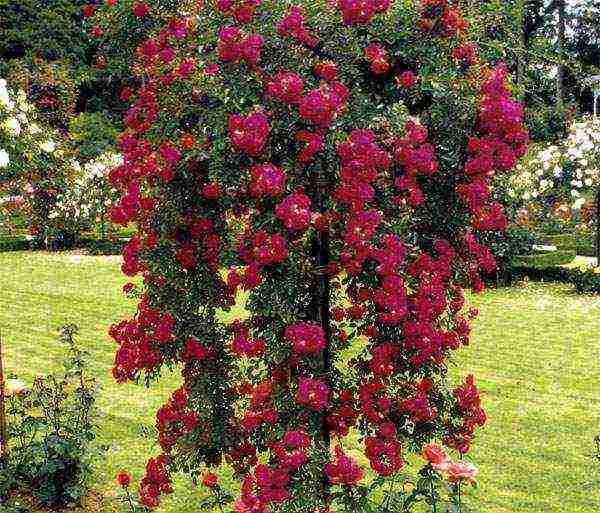  |
Rules for growing and caring for a climbing rose in the open field
2 Selection of seedlings
If you want to get lush roses in the garden, you should competently approach the choice of seedlings. First of all, attention is paid to the external state. Shoots and stems should be green in color, elastic structure, with bark free from defects and damage. The presence of live and healthy kidneys is imperative. The requirements for the root system are similar: no breaks, folds and rot. They try to touch the ground where the seedling is located, so that it is slightly damp. The foliage must be lively, green, without spots.
Important points to pay attention to when choosing seedlings:
- A sale tag is a must for a quality product.It contains all the necessary information: species, variety, selection.
- The presence of the ADR marking - a similar icon denotes varieties with increased resistance to diseases and the best decorative qualities.
- The most expensive seedlings have 3 or more shoots, 2 of which grow from grafting; the cheap ones have only 2, both from the vaccination site.
Roses come with open or closed roots, in containers. After buying seedlings with planting, it is not recommended to tighten. This is usually done in the fall, before winter. However, in the regions of the middle zone, including in the Moscow region, planting is carried out in the spring. Otherwise, immature young roots do not have time to take root in a new place and die under the influence of frost. It is allowed to plant roses in summer, which is guaranteed to give a good result. This method can be more expensive.
Azalea - rules for growing outdoors and home care
3 Landing
Regardless of the variety, all roses prefer a loose, soft, fertile substrate with good drainage and a pH of 6–6.5. It is unacceptable to plant flowers on a plot where similar species have already grown for 8-10 years in a row... Such land is completely devastated, no fertilizers can restore the missing elements in its composition. At the same time, there is an accumulation of pathogenic microflora.
Despite the love of light, the plant is not recommended to be planted in direct sunlight. This will not stop flowering, but the decorative appearance will change: the roses become faded and withered. Therefore, the place is selected with shading, which is important at noon. Ideal location - next to low garden trees or along fences.
Before planting, the seedlings are prepared: too long roots are cut with pruning shears, dry ones are removed completely. It is unacceptable to touch the filamentous roots. When planting in spring, the stems are shortened to 30–35 cm, leaving up to 4 buds on the surface. For 2-3 hours, the seedling is placed in a bucket of water.
If clay soil prevails on the site, river sand is introduced into the planting pit, sandstone is diluted with sheet compost. The sequence of agrotechnical measures:
- A hole is dug 2-3 times larger than the size of an earthen coma with roots. The bottom is well loosened.
- The seedling is buried at a level 4–5 cm higher than the grafting site. The extracted substrate is mixed with compost in a 1: 3 ratio and pure wood ash is added.
- The free space is carefully filled up, the surface is slightly compacted.
- At the end of the procedure, the planting site is abundantly moistened. To prevent the water from spreading, a furrow is made around the perimeter.
It is imperative to spud the root space not only immediately after planting, but in spring and autumn. In the first case, such a technique helps to exclude the rapid evaporation of moisture from the soil, and in the second, it protects the roots from freezing.
You can plant roses once with seeds. It is believed that they germinate for a long time, but it is possible to accelerate germination by preliminary keeping the material in the cold. When sowing before winter, it is advisable to treat the seeds with a stimulating solution. The garden bed is dug up, compost, peat and humus are introduced into it. Make parallel furrows about 4 cm deep, where the sowing is carried out. At the same time, an interval of 15–20 cm is observed. Sprinkle with soil on top. If winter is expected to be frosty, cover the bed with any suitable material for safety net. It is better to prepare a plot for spring sowing in the fall.
Another effective option for germinating seeds is seedlings at home. The favorable period for this is the beginning of February. Seed material is preliminarily placed in the cold for several months, then soaked in a growth stimulator. They are planted in separate pots, where the peat-sand mixture is poured. The seeds are deepened by 3-4 cm, sprinkled with sand and moistened with a spray bottle.With the appearance of 2-3 strong leaves, the seedlings dive separately. In May, they are transferred to a permanent place of growth - in the garden.
Planting and caring for Bartzella peony in the open field
4 Care
For full development and abundant flowering, roses must be looked after. Mandatory procedures are:
- Watering is carried out once every 7 days so that the soil is soaked to a depth of at least 25 cm. Otherwise, the plant puts out surface roots, which are easily damaged during subsequent loosening. Moisturize 2 times more often if the weather is hot. It is advisable to cover the root circle with humus or peat mulch. Then the moisture will evaporate less intensely.
- Before the onset of the first frosts (in October), the bushes are wrapped in burlap, and the roots are sprinkled with a mixture of earth and sand.
- Pruning plays a primary role in overall grooming. In the spring, they resort to formative. In the summer, wilted buds, drooping and diseased leaves are removed. In autumn, dry and damaged shoots are removed. Places of cuts are treated with garden pitch. Before the onset of winter, all weakened stems and shoots are pruned.
- Rotted horse manure is used as top dressing, chicken and pork are contraindicated. This is due to their high acidity. Any fresh organic matter blocks nitrogen in the soil, thereby inhibiting the growth of flowers. The first time fertilizers are applied before laying the buds. Calcium nitrate is suitable (1 tablespoon per 10 liters of water). During the period of active growth, they are fed with infused liquid mullein, mineral supplements or herbal infusions. Frequency - once every 2 weeks.
From the middle of summer, all feeding is stopped, watering is minimized. The plant needs to go into a dormant state, which serves as a preparation for wintering.
5 Reproduction
Roses can be propagated by seed and vegetative methods. The first option is in little demand, since it does not retain varietal characteristics. Therefore, it is used more often in relation to wild representatives. The seeds are harvested when the fruit turns red. The raw material is preliminarily stratified in moist sand, kept until spring at a temperature of + 3 ... + 4 ° C. In the spring, the seeds are treated with a stimulant and planted in open ground. From above they mulch with humus. After some time, the plantings are thinned out, distributing the bushes at a distance of 10-15 cm from each other. In the summer, mineral dressings are introduced. Grown until next August, then used as a stock.
The most successful breeding method is by cuttings, along with grafting and dividing the bush:
| Method name | Description | Image |
| Summer cuttings | In the morning or in the evening, strong shoots with slight lignification are cut off. Cuttings 13-15 cm long are prepared. Several leaves and 2-3 living buds are left on each. The lower part is cleaned of foliage. The bottom is treated with a growth stimulant, the cutting is immersed in water, where rose petals are placed. They are planted directly into the ground, previously sprayed with potassium permanganate. Cover with a glass cover on top to create greenhouse conditions. The optimal temperature regime during the day is not lower than + 25 ° C, at night + 19 ... + 20 ° C |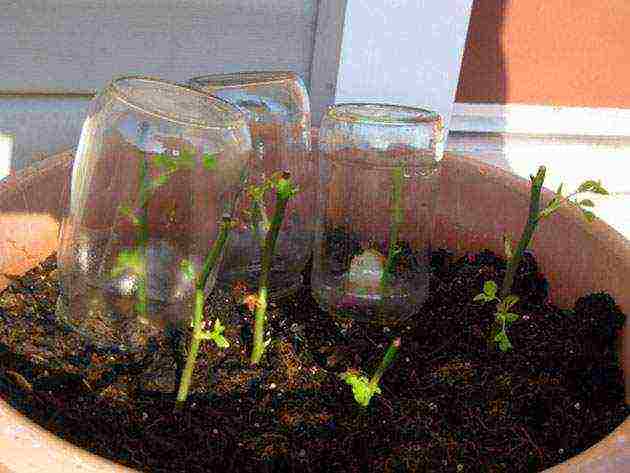  |
| Rooting in potatoes | The most popular and easy breeding method. Thus, the cuttings are saturated with carbohydrates and potato starch. In a bright area, a ditch is dug about 15 cm deep, filled with sand for a third of the volume. Cuttings are first stuck into the potatoes 10–12 cm and placed in the prepared recess. Further manipulations are standard: cover with a cap, after a while hardening is carried out. Pour sugar syrup every 5 days |  |
| Reproduction in a package | The bottom of the cuttings is moistened with aloe juice, then deepened into a lump of earth laid in a plastic bag. It is hermetically closed, having previously released the air from the inside. Hang out for germination on the window. A month later, when young roots appear, they are planted in open ground |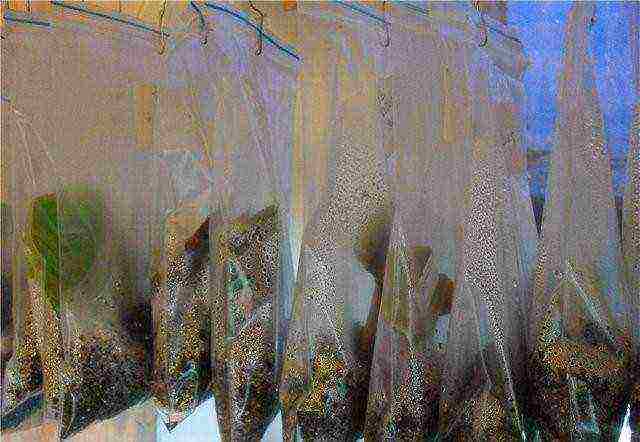  |
| Rooting in water | Freshly cut stems, divided into cuttings, are immersed in distilled water. Before that, thorns are removed from the surface and other vegetation. The water is regularly changed until the cuttings take root |  |
| Vaccination | Reproduction by grafting is suitable for young rose hips. The procedure is carried out in the middle of summer. First, the lateral branches are removed from the stock, and the root collar is cleaned of the ground. An incision is made in the shape of the letter T, where the cutting is placed. Fix it in place in any way. After 15–20 days, the kidney is checked: if it is swollen, then the vaccination was successful. If it is black, then the method has failed. Before the onset of winter frosts, grafted roses are spud 5-6 cm above the grafting site. In the spring, the soil is raked. The plant is pruned over the graft. When pulling, pinch the top over the third leaf | 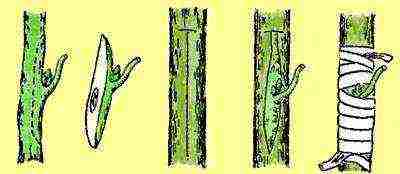 |
| By dividing the bush | Suitable for non-grafted varieties of roses. In the spring, before bud break, the bush is dug up and divided into parts. Each should consist of roots and a shoot. Bare areas are powdered with crushed coal. Then they are seated in separate places in the garden. | 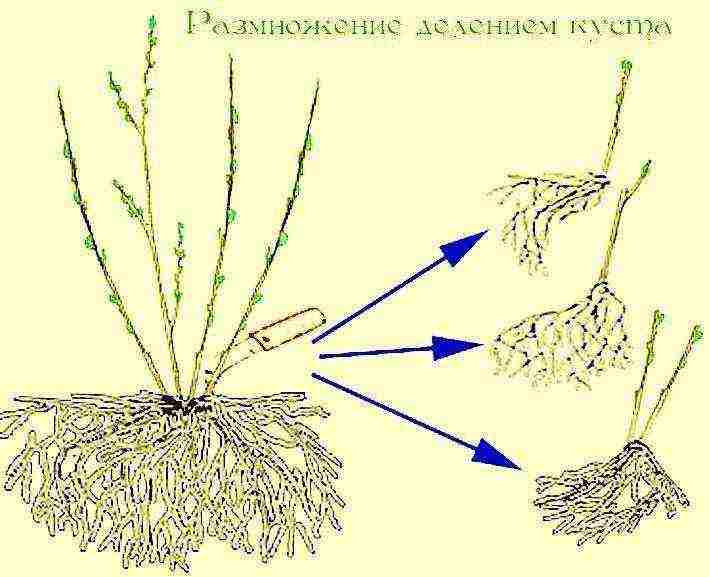 |
| Layers | With the onset of the first spring heat, a low-lying shoot on a bush is chosen. They bend it to the ground and put it in a dug hole. Preliminarily, an annular cut is made on the surface. Fix the shoot in place and cover it with earth. Further care is moisturizing until the cuttings take root. The next year, the baby is separated from the maternal source and planted separately. |  |
6 Diseases and pests
Most roses are endowed with stable immunity to many diseases, but this does not exclude the possibility of damage. The following diseases are most common:
- Rust - the peak of the disease is observed in the spring. Brown spots appear on the leaf surface, and from the inside - orange clusters of spores, which turn black towards the end of summer. Unauthorized leaf fall begins, the stems acquire a brown tint. The situation can be corrected by watering with a decoction of field ivy. The affected areas are removed.
- Black spot - appears in August, towards the end of the month. The leaves are instantly covered with black patches in a yellow frame. This gradually spreads to the stems. Leaves fall. If appropriate measures are not taken in time, the flowers die. Treatment is the same as for rust.
- Powdery mildew - a whitish bloom forms on the leaf component and shoots, then slugs form. The disease is characteristic of varieties that are grown in greenhouses and at home. The disease is characterized by rapid spread. Plants showing signs of damage are cut and destroyed. The earth is sprinkled with ash and dug up.
Of the insect pests, the most dangerous are aphids, spider mites. With few attacks, you can kill the first pest by hand or wash the leaves with soapy water. If there are a lot of insects, then treatment with insecticidal preparations helps. The mite is fought by applying tobacco or infusion of wormwood. With illiterate care, there are cases of attack by thrips, sawflies and cicadas.
With a lack of nitrogen in the soil, the plant turns yellow. It begins to spread from below and is accompanied by leaf fall. The same thing happens with the top. If the foliage is covered with yellowness only at the edges, this indicates a lack of potassium. Yellow streaks indicate a small amount of trace elements.
7 Design
Most people are used to planting roses in separate flower beds, but modern trends in landscape design have made their own adjustments. It is fashionable to combine them with perennial flowering crops or undersized shrubs.
For the design of mixborders, it is recommended to take varieties of musky representatives due to their brightness and proportional shapes of the bushes. Short varieties with small flowers are ideal. Then they do not dominate the neighbors, but harmoniously merge into a beautiful composition.It is better to place unpretentious varieties in unfavorable areas of the garden, and climbing roses will effectively decorate fences and terraces.


