Content
- 1 Features of growing climbing roses in the Urals
- 2 Review of varieties of climbing roses recommended for the Urals
- 3 General principles of caring for roses in the Urals
- 4 Typical mistakes of flower growers when growing roses in the Urals
- 5 Answers to topical questions of gardeners
- 6 A selection of tips for growing roses
- 7 Curly rose: planting and care, photo
- 8 Caring for planted bushes
- 9 Features of growing climbing roses in the Urals
- 10 Review of varieties of climbing roses recommended for the Urals
- 11 General principles of caring for roses in the Urals
- 12 Typical mistakes of flower growers when growing roses in the Urals
- 13 Answers to topical questions of gardeners
- 14 A selection of tips for growing roses
- 15 Curly rose: planting and care, photo
- 16 Caring for planted bushes
- 17 Where to begin?
- 18 The choice of planting material
- 19 Planting seedlings
- 20 Rose care
- 21 Preparing for winter
- 22 And a little about secrets ...
- 23 Features of growing climbing roses in the Urals
- 24 Review of varieties of climbing roses recommended for the Urals
- 25 General principles of caring for roses in the Urals
- 26 Typical mistakes of flower growers when growing roses in the Urals
- 27 Answers to topical questions of gardeners
- 28 A selection of tips for growing roses
- 29 How to plant roses in spring
- 30 BUY ROSE SEEDLINGS IN THE NURSERY
- 31 Where to begin?
- 32 How to plant roses in spring
- 33 BUY ROSE SEEDLINGS IN THE NURSERY
Let's find out in more detail what a climbing rose is. Planting and caring for this marvelous flower in the open field will be discussed in stages in this article. Summer residents and gardeners know that with the help of this type of roses, you can turn even the most modest plot into a beautiful romantic corner.
Climbing rose - description of the type and planting features
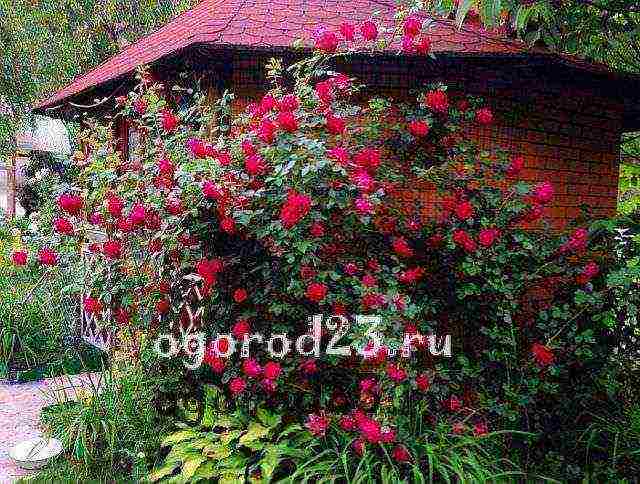

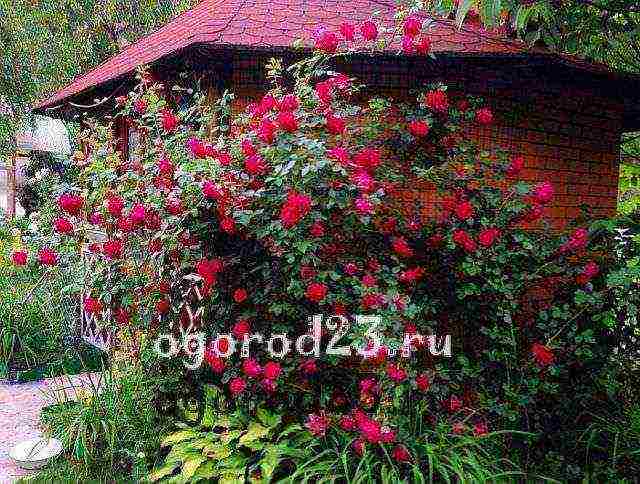
The shoots of climbing roses can reach several meters. Any support located in close proximity to the bush is quickly braided by its long and flexible branches. You have surely admired amazingly beautiful flower arches more than once. Floral columns, pyramids, trellises, well-disguised old buildings, part of a wall or roof - any garden structure can be decorated with a luxurious climbing rose. This type of plant is ideal for vertical gardening, but in order for everything to look harmonious and attractive, you should know the rules for planting, pruning, caring for and protecting bushes from pests.
The color scheme of this type of roses is as varied as that of their park or ground cover relatives. Buds range in size from 2.5 to 12 cm in diameter, climbing rose varieties bloom in June and continue to bloom as long as the warm season lasts (approximately 30-170 days, depending on the variety). There are many varieties of climbing roses, but they can all be divided into groups:
- Semi-plaited, whose height reaches 1.5-3 meters.
- Climbing - 3-5 meters.
- Curly - 5-15 meters.
The shoots of these roses are formed continuously, the phases of budding and flowering differ, again, depending on the variety.Among these representatives there are both single-flowering species and re-flowering species.
Climbing rose, photo:

The buds of some varieties can exude a pronounced aroma that can be heard from a distance, some smell slightly audible, subtle and gentle. This culture will feel great in sunny places with good ventilation. Wetlands are strictly contraindicated for it, as are sandstones and heavy clay soil. In general, loose loams or fertile soils with good soil permeability are most suitable for this type of roses. If your site is dominated by an unsuitable soil for a climbing rose, then be sure to dilute it with a suitable one. Thus, sand is added to the clay soil, and clay is added to the sandy soil (to a depth of about 30 cm), in addition to this, humus or humus should be added, as well as phosphorus additives.
All land adaptation procedures must be carried out six months before planting roses, or at least 2 months before that. Experienced gardeners recommend planting climbing roses where their counterparts have not previously grown. If it does not work in another way, then before planting you need to replace the top layer of the earth (by 50-70 cm). Ideally, the climbing rose should be planted on a small hill. The root system of these plants goes deep into the soil (up to 2 meters), so you should make sure in advance that the groundwater at the chosen place does not pass close to the top layer of the soil.
If you decide to "drape" a part of the house wall with a climbing rose, then the distance between the bush and the wall should be at least 60 cm (and at least half a meter from other plants). Most often, a climbing rose is planted in the last weeks of September or in the first half of October. Thus, before the onset of serious cold snaps, the roots will have time to take root in a new place. With the arrival of spring, all parts of the plant will enter a phase of active development and growth, and by the beginning of summer the rose will bloom in lush color. If a climbing rose is planted in the ground in spring, then by this time it should warm up to at least +10 ° C, catch the moment when the buds have not yet blossomed - this is important. The second half of April / first weeks of May is the most optimal time for spring planting.
↑ to the content ↑ Planting a climbing rose in the ground in spring
I will make a reservation right away that the rules for spring planting of seedlings are not much different from autumn ones. All stages described, as well as subsequent care, are applied both in spring and autumn. You should be prepared for the fact that roses planted in spring will lag a little in development, require increased attention from you to your person. Compared to their autumn counterparts, they can delay flowering by about 10 days.
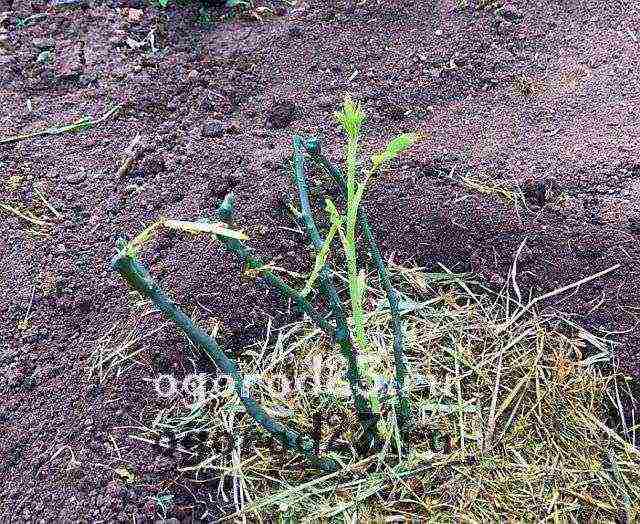
So, before planting, the seedling needs to shorten the branches, up to about 20 cm in length, the roots, too, up to 30 cm. Dig a spacious hole so that the roots have room to grow. The depth of the hole should be 60-70 cm.If you are planting several bushes, then the distance between them should be at least 100 cm. When immersing the seedling in the soil, make sure that the root collar is also buried 12-15 cm - this will protect it from frost in the cold season. The roots are gently straightened, covered with soil, slightly compacted with your hands. Make sure that all the roots are directed downwards and do not bend upwards!
Planting a climbing rose in spring provides for the introduction of nutritious soil into the hole. About 3-5 kg, for example, peat compost, will appeal to your rose. After planting, the soil is trampled down a little and watered abundantly. It will be very good if you add a preparation with beneficial bacteria that stimulates growth, for example, "Phosphobacterin" to the water for this first watering. The Heteroauxin phytohormone is also great.
In some cases, summer residents cover newly planted bushes with plastic wrap - this technique contributes to better adaptation of plants in a new place.It is up to you to decide whether to do it or not, if the weather conditions in your region push you to create greenhouse conditions for climbing roses, then do not forget to lift the film daily and gradually increase the airing time every day. After stable warm weather is established, remove the film and cover the ground around the bushes with leaf humus, peat, chopped bark or straw.
↑ to the table of contents ↑ How to plant a climbing rose in the spring, bought in a store?

Today in flower shops you can buy climbing rose seedlings with open or closed root systems. Representatives with open roots should be immediately planted in the ground. When choosing, pay attention to the presence of lignified shoots - there should be at least two of them. Such a shoot must be ripe (bend with a crunch), otherwise the rose may not withstand wintering. The bush as a whole should look healthy, have well-developed roots, strong, without dried out fragments. The length of the shoots should be at least 60-70 cm.
Climbing rose varieties with a closed root system are sold in pots, so you will not be able to immediately assess the condition of the roots. Carefully inspect the shoots, they should look healthy, not very elongated, if they have a light green color, then it is better to refrain from buying. The elongation of the shoots and their light shade indicate improper storage of seedlings - either in excessive heat or in insufficient lighting. Such a rose will be weak, painful, unlikely to survive the winter. Close attention should also be paid to the grafting sites; a properly grafted cutting should have callus tissue at the "joint" site, which promotes fusion. If the graft site is peeling and looks unhealthy, then with such a rose you will only have problems.
Planting a climbing rose in spring from the store, steps:
- A rose with a closed root system is carefully removed from the pot along with an earthen lump, and then planted in the chosen place. For representatives with an open root system, remove the film from the roots, place them in water. If there are buds or shoots below the grafting site, remove them. If there is wild growth, we also remove it, too long shoots can be pinched. Do not forget to powder the cut points with charcoal or activated charcoal.
- The roots should be in the water for 3-4 hours, thus, the plant will be saturated with moisture, the transport soil will become soft, it can be easily removed and carefully examine the root system. Stimulant "Kornevin" can be added to the water (according to the instructions).
- We take the roses out of the water, gently straighten the roots as possible and place the seedling in the dug hole. About what the hole should be and how to mix the soil (if the situation requires it), it has already been described a little higher. Water the rose well.
- After the water is absorbed, you can add more earth (spud). When re-filling the soil, the grafting site can be covered with a layer of soil, but not more than 3 cm.
- If the spring sun is shining too brightly, do not be too lazy to cover the young bush with a paper bag or a cloth of light shades - so it is guaranteed not to burn out. This protective coating can be left on for 5-7 days.
Further, you will need standard care for the climbing rose: hilling, watering, feeding, removing weeds, garter and forming a bush.
↑ back to content ↑ Climbing roses - care and cultivation
In hot and dry weather, rosebushes should be watered once every five days. After 20 days after planting, you need to carefully shake off the soil from the bush. By the way, roses planted in autumn are also opened after winter in the first weeks of April. For this procedure, it is advisable to choose a non-sunny day, so that later the plant does not experience stress during the night temperature drop.Make sure that the grafting site remains about 10 cm buried in the soil.
During the growing season, the climbing rose requires generous watering. After the buds appear, as well as after the formation of the bush, the plant should be watered every 10 days. At the same time, water should penetrate to the very roots and deeper, 10-12 liters per one bush will be quite enough. A couple of days after rain or watering, you need to loosen the soil around the rose. It can also be mulched. For roses, both waterlogging and lack of moisture are equally harmful, so observe the golden mean in this matter.
Climbing rose, photo:

↑ back to contents ↑ How to fertilize climbing roses
Fertilization is an important step in caring for a climbing rose, because this species is quite picky about feeding. Throughout the summer, nitrogen supplements should be alternated with complex fertilizers; it is recommended to apply them every 2-3 weeks. With the onset of spring, the plant is fed with a complex mineral fertilizer, for example - "Agricola-Rose" (according to the instructions). After two or three weeks, you can add organic matter - fertilizer "Ideal" or "Flower". You can also use the old proven method - 10 liters of mullein and 3 kg of wood ash, diluted in 50 liters of water. It is recommended to dilute one liter of this mixture in 10 liters of water, and then water the plant with the resulting composition at the very root. From about the second week of July, you can begin to slowly add phosphorus and potassium supplements in order to prepare the bushes in advance for the coming winter. Carefully read the dosage of drugs in the instructions, remember that by overfeeding the rose with chemistry, you can simply ruin it.
↑ to contents ↑ Care of a climbing rose in the first year
How does it differ from standard requirements? The further development and splendor of flowering depends on competent care in the first year of a plant's life. When new shoots appear, the soil is removed from the bushes (the one that was used for hilling). If there are sunny days, then at first light shading with coniferous spruce branches will not hurt. After 10-12 days after removing the hilling soil, you can start the first pruning of the central shoot. It should be shortened over the second or third sheet. A little later, with the lateral branches of the second order, you need to do a similar procedure, while the eyes "looking" inside the bush must be removed, and those eyes that are located on the outside are left for further correct formation of the bush.
Caring for a climbing rose in the first year also involves removing the buds, as odd as it sounds. From the beginning of flowering until the first weeks of August, it is recommended to leave only two flowers on each branch. With the arrival of autumn, these flowers will turn into boxes with seeds (fruits), and after the manipulations carried out, your rose will bloom especially magnificently next year.
In summer, preventive irrigation should not be neglected against the invasion of parasites, and with the onset of autumn, rose bushes should be covered. Lutrasil, spunbond or coniferous spruce branches are an excellent covering material for this plant. The bush is completely covered. When a new spring comes, young bushes are opened first, older representatives - later. In principle, all climbing rose bushes are sheltered for the winter. An old proven method is hilling with earth and sand (1: 1) to a height of about 30 cm, with the arrival of autumn, and a little later - full cover with the onset of the first frost.
↑ back to contents ↑ Pruning climbing roses or how to prune a climbing rose

Is the climbing rose pruned in the fall for the winter? If other types of roses can be simply spud, then the climbing one must be covered completely - this factor does not depend on your region of residence. You can choose one of the methods of thermal insulation, in the first case, the ground part of the bush is removed from the support, the foliage is removed, and all weak and old shoots are cut off.
Here you have to choose 10-12 of the strongest and healthiest branches (remaining after pruning), combine them into one bunch, rewind with twine and gently tilt them to the ground. With the help of metal brackets (we cut the wire into fragments and bend), the branches are fixed to the ground, and then they are covered with an appropriate protective material. If there are several shrubs, they are located in close proximity to each other, then they can be covered with one common covering canvas. In the second case, everything happens in a similar way, only in this case the plant is not removed from the support, but reliably wrapped in protective material directly on it. The base of the bush is spud in the way described above.
How to prune a climbing rose? This important agrotechnical care measure needs to be given special attention. Pruning helps to shape the crown of the plant, promotes generous and long-lasting flowering, and has a positive effect on the health and vitality of the climbing rose. Immediately after planting, all shoots are shortened by 20-30 cm, in the summer, faded buds and branches growing inside the crown (thickening it) are cut off.
Starting from the second year of the plant's life, the branches are pruned at the end of the flowering phase.
How to prune climbing roses after flowering? They fade around the end of August - September (depending on the climate in the region), at this time all diseased and dead branches should be removed. The oldest shoots (choose 1 or 2) are cut off completely, subsequently they will be successfully replaced by young basal processes. If these processes are absent, then the old branches should be measured about 40 cm from the base, and the rest should be removed - this procedure is aimed at activating the growth of replacing basal branches.
The rest (not very old) shoots are cut off in the place where a new powerful growth began to form, subsequently it will act as a conductor. Short peduncle branches are cut to 2 or 3 buds (about 15-17 cm from the base of the branch), weak stems are cut to 3 buds (we also measure from the base). The skeleton (base) of the crown should be formed from the strongest, correctly growing shoots (evenly directed), on which young branches will then form.
How to prune a climbing rose in the spring? You should pick up the pruner when the buds begin to swell on the branches from below (last weeks of April / early May), not earlier. If you start pruning too early, then with night frosts, the branches may simply freeze, as a result of which the rose will bloom much later than the due date. If you miss pruning time, then the plant will throw all its energy into the formation of new branches and foliage, and flowering will be poor.
Pruning climbing roses in the spring has one important point - removal, namely, cutting off (not cutting) wild shoots that have grown below the grafting site. Usually this situation becomes apparent after the spring opening of the bushes. Also, at this time, all sick, frozen branches are removed, all affected fragments are clearly visible in the spring, when the buds swell on the “living” branches.
↑ back to content ↑ Transplanting a climbing rose to another place
Sometimes, due to inexperience, the gardener chooses an unsuccessful place where the plant feels uncomfortable and sick. In such cases, the situation can be corrected by transplanting. The best time for this operation is autumn, September or the first weeks of October. It is not recommended to transplant later, since the rose needs time to adapt to a new place of residence before the onset of cold weather.
However, if circumstances require it, transplanting a climbing rose to another place is also possible. As soon as the ground thaws after the winter frosts, and the buds on the branches of roses have not yet had time to wake up, you can get down to business.To do this, the ground part of the plant is removed from the support, the bush itself is carefully dug in (moving in a circular manner), about 50-60 cm recede from the base of the plant.Do everything very carefully so as not to damage the root system of the rose, let the hole be deeper than necessary, but the roots will remain intact.
Next, the plant is removed from the ground, excess soil is removed from the roots, after which the climbing rose is immediately transplanted to a new place.
When replanting, the same rules are observed as with a standard planting - the roots are straightened and directed downward, the free space in the pit is filled with the appropriate soil mixture, the soil is lightly tamped and watered generously with water.
After 3-4 days, you should fill up the earth (it will settle slightly), spud your rose.
There is one interesting nuance associated with transplanting roses - their belonging to the climber and rambler groups. I will allow myself a small digression: all varieties of climbing roses can be figuratively divided into these two groups:
- climbers;
- ramblers.
Climbing varieties of climbing roses are called climbing, they form rough and thick branches that can reach 3-5 m in length. Climber shoots are not very flexible; when transplanting, they must be cut to half of their entire length!
Rambler are precisely curly roses with flexible and soft shoots-lashes, the length of which can reach 10 meters. Rumbler roses are characterized by active growth; when transplanted, they cut off all shoots that are more than two years old. All young branches are left intact, but at the end of the calendar summer they must be pinched tops - this technique accelerates the lignification of the branches.
↑ back to contents ↑ How to propagate a climbing rose?
There are four ways to propagate this rose: seeds, layers, cuttings and grafting. The most common and convenient option is grafting. Seed propagation is only possible if the seed is purchased at the appropriate store. As you know, self-collected seeds from climbing roses growing in your country house or in the garden do not carry the varietal characteristics of the mother plant.
↑ to content ↑ Growing a climbing rose from seeds
Pre-soak the seeds in 3% hydrogen peroxide for 30 minutes. Such disinfection creates a shield against the appearance of mold in the subsequent stages of plant growth. After we remove the seeds from the solution, put them on a thin layer of cotton wool, again soaked in hydrogen peroxide, cover it on top with a similar cotton layer, which is also saturated with peroxide.
Place the resulting "sandwich" in a plastic bag and hide it in the refrigerator, in the compartment for herbs and vegetables. We periodically inspect the seeds, change the cotton layers to new ones (also saturated with hydrogen peroxide).
After 40-50 days, the already germinated seed can be carefully transferred into peat tablets or small plastic cups with the appropriate soil mixture. Seedling cassettes are also fine.
Watering young shoots should be done as the soil dries up. For plants to develop properly, they need to be provided with daily light for 10 hours. If you do everything right, then a couple of months after planting the seeds in tablets or cassettes, the first buds may appear on young roses. With the arrival of spring, new livestock are planted in open ground.
↑ to the content ↑ Reproduction of a climbing rose by cuttings
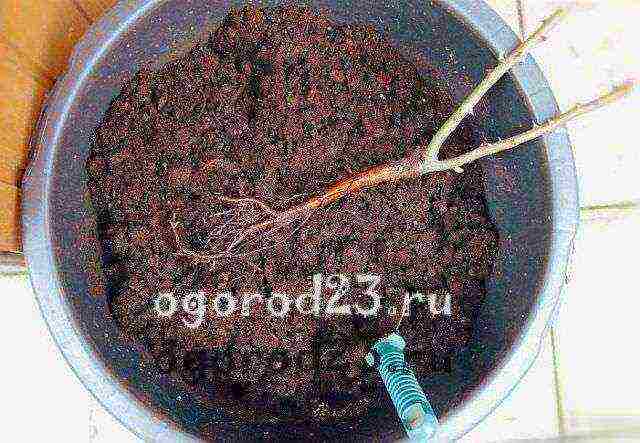

This is the easiest breeding method, almost always giving 100% positive results. For cutting cuttings, already faded or still flowering branches are suitable for you, which are taken from a rose in the very middle of summer, on the 10th of July.
The cut fragment should have at least two internodes, the place of the lower cut (45º angle) should be located close to the kidney. The upper cut (flat) is carried out at a considerable distance from the kidney.
Further, all the lower leaves are cut off from the cutting, and the upper leaves are cut in half.A stalk is placed in a previously prepared container with sand or with a mixture of sand and soil, deepened by about 1-2 cm, covered with a glass jar on top and removed to a well-lit place.
Now you will need to periodically water the cutting (without removing the can) and make sure that it does not come into direct sunlight.
↑ to the content ↑ Reproduction of a climbing rose by layering
In the spring, from the shoots growing from below, we choose the most attractive one and make cuts on it, right under the buds. Next, we make out a small groove-bed about 10 cm wide, put a thin layer of humus on the bottom of the groove, sprinkle it on top with the same layer of soil. Now we carefully bend the shoot, put it in the groove and fix it with metal brackets. After that, we cover the shoot with soil, but leave the top looking out. Then, as usual, we take care of the bush, but do not forget to water and fertilize the place of the buried shoot. After a year, when spring comes, the layers can be cut off from the bush and planted in a separate place as a full-fledged plant.
↑ to the content ↑ Reproduction of roses by grafting (budding) on rose hips
A climbing rose can be grafted onto a rose hip bush - this technique is often used by gardeners and summer residents. The best time for this operation is the last weeks of July or the first half of August. Before budding, the dog rose should be watered generously with water.
Directly on the root collar of the bush, an incision is made in the bark in the form of the letter "T", after which the edges of the bark are slightly pulled back. This kind of "pocket" holds a peephole cut from a climbing rose. The peephole must be separated from the rose along with the bark and a small piece of wood.
Next, we tightly press the peephole to the neck of the stock and also tightly wrap this place with a special film for budding (freely sold in flower shops). After all the manipulations, the rose hip bush is earthed up, and so that the soil rises above the grafting site by 5 cm (this is the minimum). After two to three weeks, the film can be slightly weakened, and with the arrival of a new spring, it is removed for good.
↑ Back to Contents ↑ Climbing rose does not bloom - why?
This can also happen, at least on flower forums, gardeners often ask each other a similar question. Experimentally, 7 factors were found out that affect the absence of flowers in climbing roses.
- Diseases. The most dangerous diseases of climbing roses are bark cancer and ash (powdery mildew). Quite good results are given by preventive irrigation of the bushes with Bordeaux liquid (1%) at the stage of dormant buds. To reduce the risk of bark cancer, plants should be provided with potash fertilizers. At the beginning of autumn, you need to feed the climbing rose with potassium sulfate (potassium sulfate) and / or a nitrogen-phosphorus additive, for example, superphosphate. Careful inspection and timely removal of affected branches, as well as a competently carried out shelter of roses for the winter is a powerful shield against diseases that weaken the plant and can really cause the absence of flowers.
- Wild growth. Multiple shoots can often be seen near the root zone of the climbing rose. Of course, they should be removed in a timely manner, because they are not of any use, they only suck vitality from the bush. If you ignore them and allow them to grow further, your rose will gradually run wild and, naturally, will stop giving color. You should remove wild growth as soon as it caught your eye.
- The wrong shelter for the winter. A climbing rose needs careful shelter before the onset of cold weather.
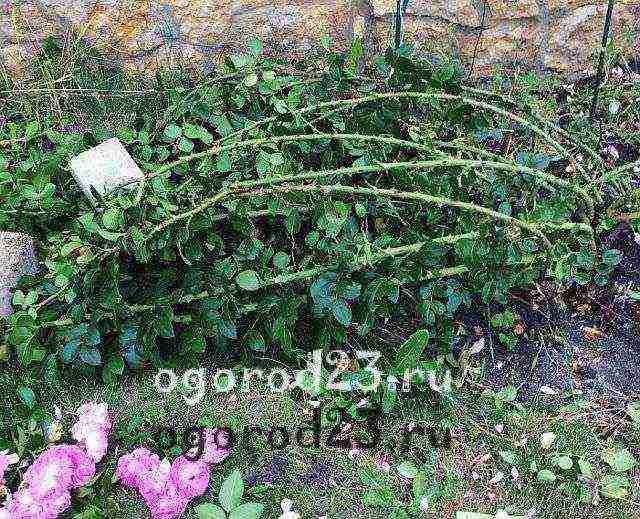 Correct wrapping of the bushes consists in creating an air cushion between the covering material and, in fact, the bush itself. Such an air gap will protect the plant from dampness during possible thaws, because dampness for a rose is as destructive as low temperatures.Proper preparation for winter also consists in limiting watering, starting from the first weeks of September. A ban is also imposed on loosening the soil. From this time on, the rose should not be given nitrogen fertilizing, only potash is allowed.
Correct wrapping of the bushes consists in creating an air cushion between the covering material and, in fact, the bush itself. Such an air gap will protect the plant from dampness during possible thaws, because dampness for a rose is as destructive as low temperatures.Proper preparation for winter also consists in limiting watering, starting from the first weeks of September. A ban is also imposed on loosening the soil. From this time on, the rose should not be given nitrogen fertilizing, only potash is allowed. - Too many nitrogen supplements. Everything is simple here - nitrogen fertilizers contribute to the growth of the green mass of the plant, which, in turn, negatively affects the setting of buds. If you overdo it with nitrogen, the climbing rose may not bloom.
- Inappropriate landing site. An incorrectly chosen place can cause not only a lack of flowers, the rose can simply die. Before choosing a site for planting a climbing rose, make sure that there will be no strong drafts and shade.
- Illiterate pruning. Everything should be in moderation, if you start pruning too actively and capture a lot of young shoots, the rose simply will not be able to recover and, of course, will not form buds. Prune the plant correctly, remove old and thickening branches, pay attention to wild growth.
- Unsuitable soil composition. The soil for growing climbing roses has already been mentioned above. The composition of the earth is an important factor, plus it must be fertile, loose, saturated with useful substances.
↑ back to content ↑ Climbing rose - diseases and pests
Prevention and control of disease or pest infestation is one of the aspects of climbing rose care. Spider mites, aphids, leafworms, thrips, rose sawfly - a list of the most active parasites of climbing roses.
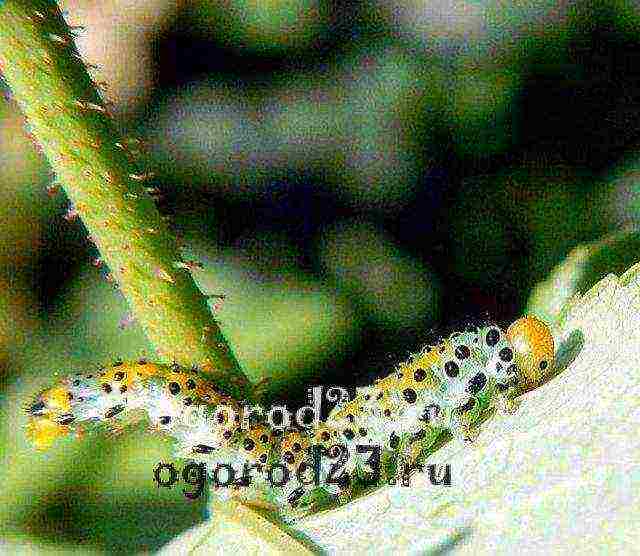 Caterpillar of a rose-cut sawfly on a rose
Caterpillar of a rose-cut sawfly on a rose Rose infested with spider mites
Rose infested with spider mites
At the initial stage, aphids can be manually removed from the branches, after putting on garden gloves, but as soon as it feels like a full owner, you will need the help of chemicals. Insecticides "Sharpei", "Aktara", "Inta-Vir", as well as the good old "Karbofos" are guaranteed to help you cope with this problem.
If you want to try the so-called folk methods of struggle, then grate laundry soap (1 tablespoon) and dissolve it in 1 liter of water. Irrigate rose bushes with this solution for a week, then remove all affected fragments - it should help.
A spider mite loves heat and drought, a silvery coating on foliage is a sign of the presence of an intruder. Old methods of struggle with the help of thick tobacco infusion or wormwood broth give very good results. Contact ascaricide "Neoron" is one of the best means of protecting roses from spider mites. One ml of the drug is dissolved in a liter of water, after which the bushes are irrigated. Sometimes it is enough to treat roses twice with this preparation for the tick to give up its positions. Bio-insecticide "Fitoverm" also proved to be excellent in this matter.
According to the reviews of experienced gardeners, the drug "Aktara" works great against the rose sawfly. The preparations "Aktellik" and "Phosbecid" (15 ml per 10 liters of water) also show a good result, which extends not only to the sawfly, but also to other "lovers" of climbing roses.
In addition to all of the above, I would like to remind you of the spring and autumn spraying of roses with Bordeaux liquid - this is important.
Among the diseases of climbing roses, the most dangerous are: bacterial cancer, gray mold, powdery mildew, coniotirium (burned bark).
 Powdery mildew
Powdery mildew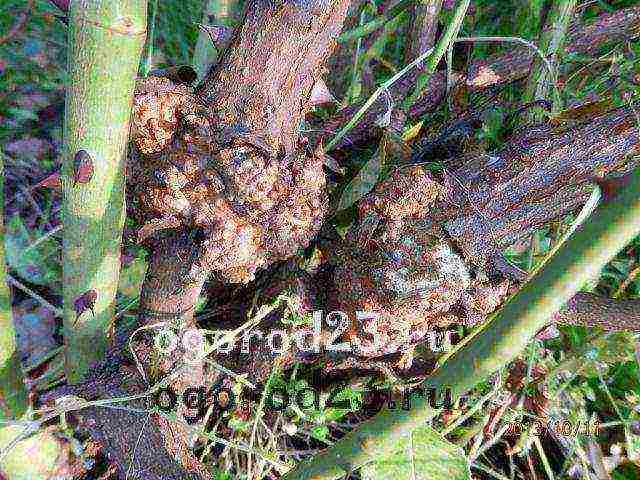 Bacterial cancer
Bacterial cancer
There is no cure for some diseases (bacterial cancer), but taking prevention seriously will minimize the risk of the disease.
Disinfection of the root system in a solution of 3% copper sulfate (before planting), removal of suspicious fragments and rapid irrigation of wound sites with the same copper sulfate are the most often recommended preventive measures.
The defeat of the coniotirium can be detected in the spring, as soon as the protective cover is removed from the roses.In this case, it is necessary to immediately cut off diseased branches (with the capture of healthy fragments) and burn them. Until the buds awaken, the plant can be treated with three percent iron sulfate, the ground around the bush must be watered too. The same Bordeaux liquid or the drug "Abiga-Peak" can also be involved in the case while the buds have not yet blossomed.
In principle, to combat other diseases of roses, the usual scheme works - the removal of the affected areas and their subsequent burning, abundant irrigation of the plant with a solution of ferrous sulfate (3%), copper sulfate (2%) or Bordeaux liquid (3%). Such spraying is often carried out in three stages (with a weekly interval), but sometimes, especially at an early stage, one treatment may be enough.
↑ to the content ↑ Climbing roses - photos and names of winter-hardy varieties
The dream of any gardener is that your favorite flowers delight the eyes with lush buds for as long as possible and endure wintering staunchly. It is simply unrealistic to mention all winter-hardy and long-blooming varieties of climbing roses, but I would like to highlight some of them, briefly describe their main qualities.
↑ back to contents ↑ Climbing rose "Iceberg"
It fully lives up to its name, its snow-white buds will bloom for a very long time (until autumn) and profusely. Repeated blooming is a distinctive feature of this rose, it grows rather quickly and in the shortest possible time can braid an arch or a wall of a building. The plant is unpretentious, cold-resistant, the aroma is weak.
Variety "Iceberg", photo:

↑ to contents ↑ Climbing rose "Lavinia"
It boasts cup-shaped flowers of a rich pink hue, undemanding to care, re-blooming, aroma with light Muscat notes. It grows up to 3 m in height, has good immunity to most rose diseases, blooms continuously until the first frost.
Variety "Lavinia", photo:

↑ back to content ↑ Variety "Polka"
It is characterized by undulating blooms, approximately five waves per summer. Terry buds, apricot shade, gradually turning into a creamy color. Loves sunlit places very much, has good disease resistance, can grow up to 3 m in height. This variety has powerful and spreading shoots with large thorns, weak aroma.
Photo of a climbing rose of the "Polka" variety:

↑ back to contents ↑ Climbing rose "Don Juan"
Luxurious double rose with large (12 cm in diameter) flowers of deep red color. It is an excellent option for decorating the walls of buildings and any vertical supports. It grows up to 3.5 m in height, loves the sun, but also blooms without problems in partial shade. These roses can be cut to make bouquets, they are very fragrant and keep fresh for a long time.
Variety "Don Juan", photo:

↑ back to content ↑ Sort "Flamentants"
This rose is considered one of the most attractive red climbing roses. Her buds are large (8 cm in diameter), double, multi-petal. Possesses increased frost resistance, powerful bushes can reach 2-3 m in height. With proper care, this variety can grow and bloom in one place for about 20 years. The aroma of the rose is very delicate, but not very pronounced.
Photo of roses "Flamentance":

↑ to contents ↑ Climbing rose "Handel"
The buds of this variety have a very interesting color - white-pink, with bright crimson edges and a slightly yellowish center. The buds are large, about 10 cm in diameter, the bush grows to 2.5-3 m in height. The rose is multi-blooming, disease resistance is average, one should beware of black spot and ash.
Variety "Handel", photo:

↑ back to content ↑ "Bobby James" variety
Small-flowered representative, but the most attractive in its category. Can reach 8 m in height, resistant to diseases, semi-double white flowers with a yellow center (about 4.5 cm in diameter), outwardly resemble cherry flowers.It has a pronounced musky aroma; during flowering, the branches are simply covered with buds, so that behind them you can hardly see the foliage. The buds themselves tend to open slowly over a period of about 10-12 days. A spectacular and incredibly luxurious variety
Photo of a rose variety "Bobby James":

↑ to contents ↑ Climbing rose "Golden Perfume"
A re-flowering variety whose flowers bloom slowly, to the delight of gardeners. Large buds (up to 10 cm in diameter) of this rose exude a very strong aroma that can be heard even from afar. Flowers of a rich bright yellow hue will adorn the bush until the arrival of the first frost. Shoots grow up to 2-3 m in height, foliage also looks very attractive - rich green, dense, creating a beautiful contrast with yellow flowers.
Variety "Golden Perfume", photo:

↑ back to content ↑ Variety "Parade"
One of the most winter-hardy re-flowering climbing roses, with large (10 cm in diameter) multi-petal buds of a juicy cherry shade or rich dark pink. Luxurious inflorescences are so large and heavy that the shoots literally bend from their weight. It blooms throughout the summer, blooms slowly, reaches 2-3.5 m in height, resistant to precipitation.
Roses of the "Parade" variety, photo:

↑ back to contents ↑ Climbing rose "Schwannensee"
Another variety with increased cold resistance. The multi-petal buds of this rose have a classic shape, medium size (7-9 cm in diameter) and a very delicate color - white, with a creamy pink core. Schwannensee blooms until the very frost, slowly blooming and spreading a delicate refined aroma. The variety is hardy, multi-flowering, rain-resistant. The bush can reach 3 m in height.
Variety "Schwannensee", photo:

↑ back to content ↑ Sort "Casino"
This rose is suitable for cutting into a bouquet, has a bright fruity aroma, lemon-colored buds are most beautiful when loose. A multi-petal variety, the diameter of a double flower reaches 9-11 cm, its color is darker inside, the outer petals are paler. The bush grows up to 3-4 m in height, blooms profusely, luxuriantly, repeatedly throughout the summer.
Climbing rose of the "Casino" variety, photo:

Of course, a climbing rose will require an investment of time and effort from you, but, you must admit, its luxurious beauty fully justifies such "sacrifices". Follow all the above recommendations, carefully consider the choice of a place of residence for a rose.
Do not plant it near bushes and trees with powerful roots, do not forget to feed it with appropriate fertilizers in time.
Provide her with reliable support, the types of which I will tell you about in the next article.
Let a climbing rose also settle on your site. Planting and care in the open field, the nuances of reproduction and transplanting, a rough idea of individual varieties - you now know all this and can apply my advice in practice.
The following videos will successfully complement the article:
Despite the harsh, sharply continental climate of the region, the dream of Ural gardeners about their own rose garden is quite realizable. The main thing is to choose a variety adapted to weather conditions, to study the peculiarities of planting and care.
Features of growing climbing roses in the Urals
The Ural region is characterized by difficult weather conditions for roses:

Climbing roses for the Urals. The Rosarium Uetersen rose bush reaches a height of 3.5 m, but it also perfectly withstands pruning up to two meters
- long frosty winters (down to -40 ° C);
- short summer;
- cold piercing winds;
- high snow cover;
- uneven distribution of precipitation;
- returnable spring frosts.
Moreover, on the plains of the Urals (west of the Ural Mountains), the climate is milder and humid. The natural conditions of the Trans-Urals (east of the Ural Range), where much less precipitation falls, is noticeably more severe, with pronounced features of the continental.Heat-loving climbing roses in such conditions do not fully reveal their varietal qualities: they do not reach the declared height, do not bloom again, do not fully open their buds. therefore adapted varieties of roses are chosen for growing in the Uralsadapted to the listed conditions: winter-hardy, unpretentious, with high immunity.
Review of varieties of climbing roses recommended for the Urals
The table contains a description of the varieties that are traditionally popular among the Ural gardeners:
| Variety | Description | Advantages |
| Flammentanz | One-flowering, deep red double buds up to 8 cm in diameter, collected in clusters of 3-7 pieces; sprawling bush, densely leafy, up to 2.5 m high; stems are tough, prickly, require strong support | Winter-hardy, disease-resistant, blooms profusely and for a long time (30-35 days) |
| Ilse Krohn Superior | Re-flowering; flowers are densely double, creamy white, 10-11 cm in diameter, appear one at a time or in brushes up to 3 pieces; the petals are large, curl as the bud opens | Winters well, strong immunity to diseases, flowers are resistant to precipitation |
| New Dawn | Re-flowering; flowers are semi-double, cupped, pearl pink with bright golden stamens in the center; tall bush, with long thin shoots | Frost-resistant, tolerates poor soils and partial shade, does not get sick |
| Rosarium Uetersen | Re-flowering; densely double (up to 100 petals) flowers of deep pink color appear one at a time or in lush brushes | Very winter hardy, resistant to rain and disease; unpretentious to the composition of the soil; suitable for cutting into bouquets |
| Super Excelsa | Re-flowering; double flowers of bright crimson color are collected in large brushes, appear throughout the summer; stunted bush (150-200 cm), spreading; suitable for vertical supports | Winter-hardy, while tolerating heat well; suitable for growing on a trunk; the bush is neat, the lashes fit easily for the winter |
| Westerland (Westerland) | Loose, large, fragrant flowers are grouped in inflorescences; the color of the buds varies from orange-yellow to salmon-apricot, depending on the stage of opening; sprawling bush, up to 1.7 m in height, suitable for single plantings | Winter hardy, resistant to powdery mildew and spotting; blooms early, blooms until late autumn |
All varieties presented in the table respond positively to decorative pruning of faded buds and tying. Moreover, some climbing roses in a short growing season show themselves better when grown in bush form.
Of all the varieties listed above, "Super Excels" is the most plastic. The bush is easily formed, the lashes are easily removed and bent down for the winter.
General principles of caring for roses in the Urals

The shoots of the "Super Excels" rose easily fall on the support of any configuration
It should be remembered that even the most weather-adapted variety requires proper care and adherence to agricultural practices... For climbing roses, the same top dressing is recommended as for other variety groups. During the season, you need to feed at least three times.
- In late May and early June, organic matter and mineral nitrogen fertilizers are applied.
- In July, they are fed with complex nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium fertilizers.
- In early August, they are fed with phosphorus and potassium (See also the article ⇒ Phosphorus fertilizers for garden roses).
Pruning is carried out as needed: cut shoots older than 3 years old, weak, damaged stems, growth not ripened by autumn. In the first wave of flowering, wilting buds with a part of the peduncle are removed in order to provoke the re-formation of flowers. Closer to autumn, this should not be done, since the plant must prepare for wintering.
The duration of bud formation of once flowering varieties is regulated by cutting off some of the freshly flowering branches.As a result, prolonged flowering is obtained on replacement shoots.

With appropriate pruning, "Flamentanz" blooms until the end of August
Expert recommendations: “The most difficult part of growing climbing roses is getting ready for winter. Before the shelter, the bushes are treated with iron vitriol for fungal diseases. Then the lashes are tied into one bundle and laid. Most of the bushes cannot be bent in one go without damaging the stems. You have to bend them in several passes. Laying roses on bare ground is not worth it, it is better to fix them on a dry substrate 20 cm from the ground. This creates the necessary air gap. At the end of the most crucial stage, a strong frame is built, on which Lutrasil-60 is laid and well fixed in 2 layers. "
Svetlana Aleksandrova is the chief agronomist of the Victoria gardening company (Magnitogorsk).
Tip # 1: It is convenient to use thick foam or plastic bottles stacked in a row as a substrate. And practical, and rodents "too tough", and the thawed snow will not flood.
A ventilation hole is provided in the shelter. Roses are fully wrapped when frost falls below -5 ° C
Spring awakening of a rose is a moment no less important than preparing for winter... Towards spring, the snow becomes dense and wet. The frame may not be able to withstand the weight of a snowdrift. A plant deprived of air will simply suffocate. Therefore, in March, the excess snow is raked, the shelter is ventilated if necessary. At the beginning of April, you can remove the second layer of covering material. It is not yet possible to fully open the rose, even if it is warm outside. The soil is still cold, the roots are dormant. The awakening of the root system and the aerial part of the plant should occur synchronously. At this time, you can carry out preventive treatment, sanitary pruning, after which the bush should be covered again. Finally, they remove the shelter after the soil has completely thawed (See also the article ⇒ When to remove the shelter of roses).
Advice number 2: To bring back to life a weakened rose that has difficult to endure wintering, immediately after leaving the shelter, stimulate the work of the root system. For this, the plant is fed with a solution of "Zircon" and "Tsitovita". In 10 liters of water, dissolve 1 ampoule of each drug, and water the bush under the root.
Typical mistakes of flower growers when growing roses in the Urals
- There is an opinion that roses planted in summer, in July-August, tolerate wintering better, since they manage to get stronger before the onset of frost. This is absolutely not true. About a month after planting, having exhausted the reserves of nutrients from its own root system, the seedling is actively moving into growth. Additional forces are required for the formation of growth. In the short Ural summer, there is not enough time for young growth to ripen. As a result, the plant leaves in the winter weakened, unripe stems vytryut, rot, become the cause of the death of the entire plant. The optimal time for an autumn transplant is the second half of September, for a spring one - the end of April.
- Novice gardeners often set up a flower garden according to the recommendations of landscape designers, taken from foreign magazines. For the Ural region, this approach is not acceptable. You need to plan the location of the rose garden according to the rules that take into account local climatic features (See also the article ⇒ DIY rose garden). Basic site requirements:
- protection from drafts;
- maximum solar illumination;
- southern or southeastern exposure;
- no stagnation of moisture (the depth of groundwater is at least 100 cm from the soil level).
It is categorically impossible to plant roses along the walls of houses, next to deaf fences, in the shade of other shrubs and trees, in flooded areas.
Answers to topical questions of gardeners

A healthy seedling has at least three smooth green shoots 20-30 cm long with developed buds
Question number 1: What seedlings to choose for the climatic conditions of the Urals: grafted or on their own roots?
In the Urals, it is recommended to plant grafted roses. Unlike their own rooted ones, they are more resistant to frost, bacterial and fungal diseases. The best stock for the Ural climate is the Kanin rose. Ultimate endurance is naturally built into this rosehip. Grafted cuttings take root from 2 to 4 weeks, and self-rooted seedlings form a full-fledged root system for more than three years. All this time, a rose grown on its own roots is vulnerable to adverse external factors and diseases.
Question # 2: Do I need to spud roses in front of the shelter?
Hilling bushes with sawdust, peat, soil, damp leaves and other materials in the climatic conditions of the Urals does more harm than good. Unlike other regions of Russia, the shoots do not have time to wood during the growing season, so they often undermine by the spring.
A selection of tips for growing roses
Presented the best tips in pictures for planting, care, pest and disease control in roses ⇓
Rate the quality of the article. We want to be better for you ⇓:
 You can decorate even the most unsightly corner of the garden and at the same time add a piece of light romance to it with the help of climbing roses. These extraordinary, beautifully flowering climbing plants please the owners with their flowering almost throughout the season. But for it to be flawless, climbing roses require proper planting and special care. We will tell you about all the intricacies and nuances of growing climbing plants in this article.
You can decorate even the most unsightly corner of the garden and at the same time add a piece of light romance to it with the help of climbing roses. These extraordinary, beautifully flowering climbing plants please the owners with their flowering almost throughout the season. But for it to be flawless, climbing roses require proper planting and special care. We will tell you about all the intricacies and nuances of growing climbing plants in this article.
Curly rose: planting and care, photo
Any plant in the garden or in the summer cottage requires care. Particular attention must be paid to some flowering crops, which include weaving roses.and with long branches... Abundant and long-lasting flowering of this beautiful plant can be achieved only with the exact fulfillment of all the rules for planting, careful care throughout the year, timely pruning and protection from winter frosts and pests.
Choosing a landing site
 Roses are photophilous, therefore, with a lack of sunlight, fresh stems will develop poorly and will bloom only in the next season. However, the midday sun can burn the plant. The place for planting roses should be such that in the hottest hours the bushes were in partial shade... The best option would be an area that the sun heats up in the morning. In the morning hours, the dew from the leaves will quickly evaporate, and the viral diseases of the roses will not be afraid.
Roses are photophilous, therefore, with a lack of sunlight, fresh stems will develop poorly and will bloom only in the next season. However, the midday sun can burn the plant. The place for planting roses should be such that in the hottest hours the bushes were in partial shade... The best option would be an area that the sun heats up in the morning. In the morning hours, the dew from the leaves will quickly evaporate, and the viral diseases of the roses will not be afraid.
Curly roses are also finicky. They do not tolerate drafts well, and therefore the corners of buildings are not suitable for planting them. Do not plant them in areas where roses have already grown and in wetlands. It is best to choose a bed with a slope so that water does not stagnate in the ground. The roots of the plant reach about two meters in length, so if the moisture of the soil is constantly very high, the flowers are planted on a hill.
Climbing shrubs for decoration can be planted along the walls of the building... So that their roots are not depleted, the distance from the wall should be at least 60 cm. In any case, the planting of climbing roses should take place near some kind of support. These can be fences, nets, pergolas, arches, walls, or specially crafted pillars or cones.
When to plant climbing roses?
In areas with a temperate climate, shrubs are planted in open ground in late September - early October. Within two weeks, they will give the first roots and before the onset of cold weather they will have time to get stronger. In the spring, the root and aerial parts will begin to grow actively, the bush will become lush, gain strength and bloom. However, in the northern regions, climbing roses are best planted in the spring, since the bushes planted in the fall will not have time to adapt, and can freeze out in winter.
Plants, which were planted in spring, are delayed in their development by about half a month and require increased attention. Before planting in the ground, such seedlings are cut into three buds.
Selection and processing of seedlings
Beautiful curly rosals can only be obtained in the presence of healthy seedlings... Their viability and quality are indicated by the appearance of the trunk. It should only be whitish green, not gray or brown. The acquired seedlings in open ground are not planted immediately. They must first be prepared:
-
 Soak the plant completely in water for a day.
Soak the plant completely in water for a day. - Shorten healthy roots by 15 cm, and cut off the crushed and weakened ones completely. A small bunch should remain.
- Shorten strong branches of roses by 15-20 cm, and remove weak ones completely.
- Sprinkle the cuts with crushed charcoal.
- Treat the roots with Heteroauxin or Kornevin.
Thanks to this preparation for landing the bushes will begin to actively grow, and during the flowering period, many buds are formed on them.
Soil preparation
Climbing roses love fertile, loamy, well-drained soil. Only heavy clay and sand are not suitable for growing them. Therefore, clay areas are diluted with sand, and sandy areas - with clay. More suitable in chemical composition and crumbly soil will become after adding a small amount of lime to it.
When digging, the fertility of the soil can be increased by adding to it:
- phosphate fertilizers;
- humus;
- humus;
- phosphorobacterin (special soil bacteria).
The soil is prepared for planting climbing shrubs in advance. It is necessary to dig it up several times at the end of summer, and then loosen it also in the spring.
Landing features
The roots of a young plant should not experience a lack of space, so the holes for them should be free enough. The optimal depth is considered to be 60-65 cm. In order for the root system to develop freely, the distance between plants must be at least one meter.
When planting roses in the hole, it is necessary observe the following recommendations:
-
 About five kilograms of the nutrient mixture is preliminarily introduced into each hole. You can use peat compost.
About five kilograms of the nutrient mixture is preliminarily introduced into each hole. You can use peat compost. - The roots of the roses should be free in the hole. The voids between them are necessarily filled up.
- The root collar of the plant is covered with soil by about 10-12 cm. This will help to protect it from frost in addition to insulation.
- The planted rose is watered with a bucket of warm water.
- The remaining space is filled with a mixture and lightly compacted.
The support to which the rose will be attached in the future should not interfere with the development of the root system. If the support is portable, then you can use special tripods, trellises or trellises. The pole and tripods can be made by yourself, knocking down for this wooden beams with a height of 2.5-3 meters... They will look gorgeous as arch supports, on both sides of which two bushes are planted. By the end of the second year, they will be completely entwined with curly roses with delicate flowers (pictured).
Caring for planted bushes
The main rules for caring for climbing roses include regular watering, timely feeding of plants, garter and pruning of shoots, sheltering bushes for the winter and protecting them from pests and diseases. Let's consider each point in more detail.
Watering and feeding
Climbing shrubs do not like excess moisture and tolerate drought without problems. It is recommended to water them once a week with a small amount of water, which should not be cold. Overmoistening plants can lead to viral diseases and poor appearance of the bushes.
Fertilizing roses is best manure or other organic fertilizers, alternating them with mineral dressings. It should be borne in mind that young plants at first will be sufficiently fertilized when planting soil. Therefore, it is not necessary to feed them too often.The next year after planting, caring for climbing roses will consist of fertilizing with fertilizers of the following composition:
- fresh black soil;
- humus;
- phosphorus complementary foods;
- humus.
With such a mixture, the soil in which the roses grow "revives" in spring and autumn. If it is not possible to prepare the composition yourself, then you can buy ready-made fertilizer for roses.
Pruning shoots
All climbing roses are divided into two types, each of which requires a certain pruning:
- In shrubs flowering from June to July, after planting, all shoots are shortened. There should be shoots 30 cm long. New stems that appear during active growth are cut off as needed to form a beautiful bush.
- Roses with a small number of basal shoots, which appear only on old branches, are shortened to 30 cm in the first year. The next year after planting, all old shoots are cut out completely.
Garter of climbing roses
After pruning, new branches will begin to grow, which need to be guided, giving the bush the intended shape. To form more buds, individual lashes are tied. At the same time, it is undesirable that they are directed only upward, since with this arrangement, the buds are formed only at the tops.
For lush flowering bushes there are several ways to tie:
- Shoots can be fanned out, leaving the side branches not tied up. They will not interfere with each other, freely extending to the sides and up.
- The main shoots are located horizontally, tied to the support. After a while, they will give new side branches, which will grow upward, forming a cloud of beautiful flowers.
- In order for the curly branches to braid an arch or a pillar, they are tied up in a spiral, twisting around the support.
Whichever way the bush is formed, one should not neglect the care of climbing roses and preparing them for winter.
Protecting roses from frost
 Before proceeding with the shelter, the bushes must be prepared. To do this, remove the leaves from them, cut out old loops and weak shoots. As a result there should be 11-12 healthy and strong shoots... All work is carried out in dry weather.
Before proceeding with the shelter, the bushes must be prepared. To do this, remove the leaves from them, cut out old loops and weak shoots. As a result there should be 11-12 healthy and strong shoots... All work is carried out in dry weather.
The way a climbing plant hides depends on the region in which it grows. In regions with a mild climate, the branches can not be removed from the support, covering them first with spruce branches, and then wrapping them in film.
In areas with severe winters, the plants are completely removed from the support. First, they are collected in a large bundle and tied. After the air temperature drops to -5C, they gently tilt to the ground, where they are fixed with wire or pegs. The base of the bush is sprinkled with a mixture of peat and soil, and the shoots are covered with spruce branches. From above everything takes cover thick film or agrofiber.
It is very important to remove the shelter on time in the spring. Otherwise, in a humid environment and without fresh air, the roses may suffocate and start to hurt. On open bushes, shoots are refreshed and tied to supports. The first feeding is recommended only after the appearance of young leaves.
Diseases of climbing roses
In case of errors in the care and incorrect arrangement of the bushes on the site, they may be affected by the following diseases:
-
 Black spot occurs on young shoots in warm weather and heavy rains. You can recognize it by the black and brown spots on the leaves, which have a yellow halo. All affected leaves are removed from the plant and burned. Feeding is done with phosphate and potassium.
Black spot occurs on young shoots in warm weather and heavy rains. You can recognize it by the black and brown spots on the leaves, which have a yellow halo. All affected leaves are removed from the plant and burned. Feeding is done with phosphate and potassium. - Powdery mildew progresses with increased humidity. If a white bloom appears on the leaves and stems, and the flowers do not bloom, then this indicates that the plant is sick. The bushes are treated with iron and copper sulfate, all the affected areas are cut out, the soil is dug up.
- Bacterial cancer can be recognized by the growths and bumps on the roots. They are soft at first, but darken over time. The plant begins to dry out and dies.The affected roots are cut out, and the remaining ones are treated with copper sulfate.
When treating climbing roses, it must be remembered that all cut off affected areas must be burned... Otherwise, they can infect other plants.
Proper planting and care is the key to the abundant and long-lasting flowering of these royal flowers. Those who decide to grow climbing roses on their site will never regret it.
Planting and caring for climbing roses

- Kind: Rosaceae
- Flowering Period: June, July, August, September
- Height: 30-300cm
- Color: white, cream, yellow, pink, orange, red, burgundy
- Perennial
- Hibernates
- Sun-loving
- Moisture-loving
If the lion is the king of beasts, then the rose is the unconditional queen of the garden. Since ancient times, this plant has been considered an object of admiration and worship. It was not for nothing that she was chosen as the symbols of love. The first mention of the rose can be found in the legends of the ancient Hindus. Legends about a beautiful flower are found in the annals of Ancient Iran. According to legend, Allah himself created a charming white Rose with very sharp thorns. She was supposed to become the mistress of flowers instead of the magnificent, but very lazy Lotus. Today this plant can become a real decoration for your gardens, but for this you need to learn how to choose and plant a seedling, what is the proper care for roses.
Planting and caring for roses is not as difficult as it seems. It's important to follow simple rules and your garden will be filled with gorgeous, fragrant shrubs.
To initially ensure your success in growing roses, you need to purchase high-quality planting material. It is better to choose plants whose root system will be closed. When planting such a seedling, the land around the root must be preserved.

Rose seedlings are best chosen with a closed root system: they take root more easily at the planting site and are less sick
Often in modern supermarkets you can see imported roses with a closed root system, which are sold in advance. Several seedlings can be stored in the refrigerator on the lower shelf at temperatures between 0 ° C and + 5 ° C. During storage, you will have to regularly monitor the condition of the substrate around the rhizome. It should not dry out completely, but too much moisture is also harmful for it.
Advice! A solution of root or heteroauxin promotes root growth, so you can water the seedlings with it several times.
It is recommended to plant roses in the middle lane in spring when the soil warms up to + 10 ° C. Usually, such conditions correspond to the period from late April to early May. Spring is chosen for planting standard roses.
Autumn planting is recommended for most of the roses. The preferred work period starts in mid-September and ends in mid-October. An earlier planting time is undesirable due to the fact that the rose can give fresh shoots in the warmth, which will not have time to get stronger and freeze in winter. Late planting is also dangerous, because the plant must take root before frost.

Most roses are planted in the fall. It is also convenient because when buying planting material on the market, you can see the flower itself
The place for planting roses should be sunny. In the shade, roses can get bored, they stop flowering, dark spots appear on the leaves of plants, blind shoots form. The plant can be affected by powdery mildew. Choose an area that is ventilated but protected from strong northerly winds.

Roses adorn the garden, regardless of their location, but the plants themselves need conditions for successful growth and flowering.
Roses have no particular preferences in terms of soil. They are not as capricious as they might seem. Any soil is suitable for them, except for heavy clay and light sandy loam. The landing site should not be located where groundwater comes close to the surface of the earth.
Planting holes need to be dug so deep and wide that the roots of the plant are spacious.If the soil is fertile, then half a meter of depth and the same width will be sufficient. For clay soil, with the same width of the hole, you need to dig 60-70 cm in depth.
It is necessary to prepare a nutrient mixture for backfilling into the pit. It contains humus or compost, rotted manure and soil. Fertilizers should not come into contact with the roots of the plant, so sprinkle them with a layer of soil.

The soil or substrate that covers the roots of the plant must be preserved: the rose adapts faster to new living conditions
Before planting the seedling, you need to pour water into the hole so that it is absorbed. If the root system of a rose is closed, it is not necessary to free the root from the ground. If the root is free, it must be cut to a third of its length and soaked in plain water or a root growth stimulator for two hours.
Shoots should also be pruned:
- in polyanthus and hybrid tea roses so that 2-3 buds remain on each of the shoots;
- for floribunda roses, leave 3-4 buds;
- for park roses, shoots are shortened by 10-15 cm;
- for a ground cover rose, only the cuts of the roots are cut (renewed, not shortened).
The seedling should be covered with earth so that the grafting site is about 5 cm below the ground. Wax should be removed from the burial site, if any. The earth should be tamped and watered again. In this way, air that may have remained around the roots is removed, and the closest contact between the plant and the soil is achieved. You can sprinkle the seedling by about 10-15 cm. The resulting slide must be removed in two weeks - the time during which the seedling should take root.
There are not so many ways to breed roses. But the desire to have as many of these undeniably beautiful and diverse plants as possible on the site is so great that gardeners strive to master them all and to the maximum extent. Here is a list of ways to propagate a rose:
- Budding. On the bark of the plant trunk, close to the ground level, a T-shaped incision is made, into which the bud of the cultivar is inserted, and then fixed with a film. The graft can use the developed root system of the rootstock. This operation is not difficult, but requires some experience.
- Seeds. This method is used extremely rarely due to the fact that the result has to wait a long time, and there is no certainty that it will turn out to be positive. And the germination of rose seeds leaves much to be desired.
- Layers. Shrub and climbing roses are propagated this way because they have long and strong stems. The shoot of the plant in the lower part is cut for 8 cm, a chip or a match is inserted into the cut. The cut part of the shoot is placed in the ground and fixed, and its free tip is tied to a peg. The rooted shoot is cut off from the parent bush.
- Cuttings. The method is good in that roses rooted in this way will not give wild shoots. The stalk is part of a strong shoot. It is cut next to the leaf bud and germinated using rooting stimulants. After the root appears, the rose can be planted in the ground.
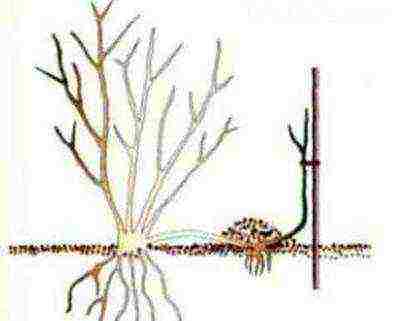
The layering method is good to use only for propagation of plants with long stems, which are used to create a new rose bush.
You can learn more about the propagation of garden roses by cuttings in this video:
In order for the rose to bloom and delight its owners for many years, you should pay attention to it, do not forget to feed it and protect it from viral diseases. Do not be afraid of difficulties: caring for different types of roses growing in the garden is not as difficult as it seems.
Manure is a natural fertilizer and, of course, preference should be given to it. Horse manure, which is at least six months old, is considered the best. Chicken and pork manure, especially fresh, can seriously harm the plant: it is sour and can simply burn young shoots. Fresh manure also badly affects the soil, because it blocks nitrogen.

Manure is a natural fertilizer, therefore the most acceptable.When choosing a top dressing, preference should be given to rotted horse manure or mullein
During the period of bud formation, you need to feed the plant with a solution of calcium nitrate at the rate of 1 tbsp. for 10 liters of water. During the active growth and development of the plant, it should be watered every 10-15 days with herbal infusion, a solution of mineral fertilizers, chicken droppings or infused mullein. To make the fertilizing better perceived by the plant, it is better to apply the same mineral fertilizers in dissolved form and after the next watering. When the first half of summer is already over, that is, in the second part of July, the feeding of the rose stops. The plant begins to prepare for winter.
Plants are also capable of dealing with stress. It is in this state that they stay during periods of extreme heat, cold or prolonged rains. To make it easier for roses to overcome difficult times in their lives, you need to spray them with zircon, epin, ecosil or sodium humate. Overfed roses produce abundant greenery, but bloom very sparingly.
Roses should be watered no more than once a week. If the summer is hot, then the frequency of watering can be doubled. The watering rate is a bucket of warm water for each bush. It is necessary to pour water at the root, trying not to get on the foliage. Water must penetrate into the soil to a depth of at least 20-30cm. Shallow watering can form superficial roots that are easily damaged.

A rose in dew is a magnificent sight, but nature has disposed so that the dew disappears with the first rays of the sun, otherwise its drops, like magnifying glasses, would enhance the energy of the sun and burn the petals: you need to water the roses at the root
If there is no one to water the roses for a long time (more than a week), the soil at the base of the plant should be covered with humus, cut grass or tree bark. Such a measure will not only retain moisture at the roots, but also prevent the growth of weeds.
With a lack of moisture, the flowers of the plant may become small, but roses should not be flooded either: this can lead to a reduction in the supply of oxygen to the roots. As a result, the leaves of the plant will turn yellow. To prevent this from happening, do not forget to loosen the soil after watering.
Of course, proper feeding and watering is important, but the process of caring for a garden rose is not limited to this. One of the most unpleasant diseases for a garden rose is powdery mildew. Preventive measures will help to take care of the health of the plant in advance. The rose must be sprayed directly over the leaves with a solution of ordinary baking soda at the rate of 40 grams of soda per liter of water. This should be done from spring 2-3 times every other week, as well as at the beginning of summer.

Plants, like all life on earth, can get sick. These are not random stains or fertilizer marks. It is powdery mildew and is easier to prevent than to cure.
Aphids are a big nuisance for roses. But you can overcome it. To do this, boil a bucket of water, put a piece of grated laundry soap and a couple of branches of wormwood in it, after which they boil for 10-15 minutes. Roses are sprayed with cooled and strained solution. After a week, the procedure should be repeated. If the aphid stubbornly does not want to leave the plant, you will have to use a systemic poison, for example, Aktara.
Aphids will not appear on roses at all if lavender or nasturtium is planted under them. And calendula and marigolds will help get rid of beetles. By the way, onions and garlic will add health to roses, as well as to people. In their environment, plants become more aromatic and less sick.
Spots on the leaves, cracks in the stems and the cessation of bud development indicate a disease. The affected branches should be removed. Prepare an infusion of horsetail, wormwood and nettle, and spray the rose with.
The shoots of the plant growing inward should be pruned. This stimulates the emergence of young shoots and active flowering. Withering flowers need to be removed, then the saved energy of the plant will be directed to a new wave of flowering, which will be more abundant.

Just look at what beauty! But all this splendor can be grown with your own hands.If someone succeeds, you will definitely succeed.
There are many pruning rules and this topic is undoubtedly worth a separate article devoted to it.
Let's find out in more detail what a climbing rose is. Planting and caring for this marvelous flower in the open field will be discussed in stages in this article. Summer residents and gardeners know that with the help of this type of roses, you can turn even the most modest plot into a beautiful romantic corner.
Climbing rose - description of the type and planting features

The shoots of climbing roses can reach several meters. Any support located in close proximity to the bush is quickly braided by its long and flexible branches. You have probably admired amazingly beautiful flower arches more than once. Floral columns, pyramids, trellises, well-disguised old buildings, part of a wall or roof - any garden structure can be decorated with a luxurious climbing rose. This type of plant is ideal for vertical gardening, but in order for everything to look harmonious and attractive, you should know the rules for planting, pruning, caring for and protecting bushes from pests.
The color scheme of this type of roses is as varied as that of their park or ground cover relatives. Buds range in size from 2.5 to 12 cm in diameter, climbing rose varieties bloom in June and continue to bloom as long as the warm season lasts (approximately 30-170 days, depending on the variety). There are many varieties of climbing roses, but they can all be divided into groups:
- Semi-plaited, whose height reaches 1.5-3 meters.
- Climbing - 3-5 meters.
- Curly - 5-15 meters.
The shoots of these roses are formed continuously, the phases of budding and flowering differ, again, depending on the variety. Among these representatives there are both single-flowering species and re-flowering ones.
Climbing rose, photo:

The buds of certain varieties can exude a pronounced aroma that can be heard from a distance, some of them smell slightly audible, subtle and tender. This culture will feel great in sunny places with good ventilation. Wetlands are strictly contraindicated for it, as are sandstones and heavy clay soil. In general, loose loams or fertile soils with good soil permeability are most suitable for this type of roses. If your site is dominated by an unsuitable soil for a climbing rose, then be sure to dilute it with a suitable one. Thus, sand is added to the clay soil, and clay is added to the sandy soil (to a depth of about 30 cm), in addition to this, humus or humus should be added, as well as phosphorus additives.
All land adaptation procedures must be carried out six months before planting roses, or at least 2 months before that. Experienced gardeners recommend planting climbing roses where their counterparts have not previously grown. If it does not work in another way, then before planting it is necessary to replace the top layer of the earth (by 50-70 cm). Ideally, the climbing rose should be planted on a small hill. The root system of these plants goes deep into the soil (up to 2 meters), so you should make sure in advance that the groundwater at the chosen place does not pass close to the top layer of the soil.
If you decide to "drape" a part of the house wall with a climbing rose, then the distance between the bush and the wall should be at least 60 cm (and at least half a meter from other plants). Most often, a climbing rose is planted in the last weeks of September or in the first half of October. Thus, before the onset of serious cold snaps, the roots will have time to take root in a new place. With the arrival of spring, all parts of the plant will enter a phase of active development and growth, and by the beginning of summer the rose will bloom in lush color. If a climbing rose is planted in the ground in the spring, then by this time it should warm up to at least +10 ° C, catch the moment when the buds have not yet blossomed - this is important.The second half of April / first weeks of May is the most optimal time for spring planting.
↑ to the content ↑ Planting a climbing rose in the ground in spring
I will make a reservation right away that the rules for spring planting of seedlings are not much different from autumn ones. All stages described, as well as subsequent care, are applied both in spring and autumn. You should be prepared for the fact that the roses planted in spring will lag a little in development, require increased attention from you to your person. Compared to their autumn counterparts, they can delay flowering times by about 10 days.
So, before planting, the seedling needs to shorten the branches, up to about 20 cm in length, the roots, too, up to 30 cm. Dig a spacious hole so that the roots have room to grow. The depth of the hole should be 60-70 cm.If you are planting several bushes, then the distance between them should be at least 100 cm. When immersing the seedling in the soil, make sure that the root collar is also buried 12-15 cm - this will protect it from frost in the cold season. The roots are gently straightened, covered with soil, slightly compacted with your hands. Make sure that all the roots are directed downwards and do not bend upwards!
Planting a climbing rose in spring provides for the introduction of nutritious soil into the hole. About 3-5 kg, for example, peat compost, will appeal to your rose. After planting, the soil is trampled down a little and watered abundantly. It will be very good if you add a preparation with beneficial bacteria that stimulates growth, for example, "Phosphobacterin" to the water for this first watering. The Heteroauxin phytohormone is also great.
In some cases, summer residents cover newly planted bushes with plastic wrap - this technique contributes to better adaptation of plants in a new place. It is up to you to decide whether to do it or not, if the weather conditions in your region push you to create greenhouse conditions for climbing roses, then do not forget to lift the film daily and gradually increase the airing time every day. After stable warm weather is established, remove the film and cover the ground around the bushes with leaf humus, peat, chopped bark or straw.
↑ to the table of contents ↑ How to plant a climbing rose in the spring, bought in a store?
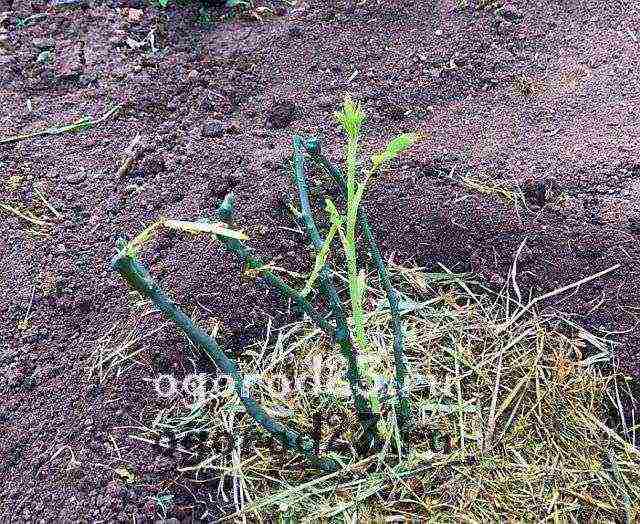

Today in flower shops you can buy climbing rose seedlings with open or closed root systems. Representatives with open roots should be immediately planted in the ground. When choosing, pay attention to the presence of lignified shoots - there should be at least two of them. Such a shoot must be ripe (bend with a crunch), otherwise the rose may not withstand wintering. The bush as a whole should look healthy, have well-developed roots, strong, without dried out fragments. The length of the shoots should be at least 60-70 cm.
Climbing rose varieties with a closed root system are sold in pots, so you cannot immediately assess the condition of the roots. Carefully inspect the shoots, they should look healthy, not very elongated, if they have a light green color, then it is better to refrain from buying. The elongation of the shoots and their light shade indicate improper storage of seedlings - either in excessive heat or in insufficient lighting. Such a rose will be weak, painful, unlikely to survive the winter. Close attention should also be paid to the grafting sites; a properly grafted cutting should have callus tissue at the "joint" site, which promotes fusion. If the graft site is peeling and looks unhealthy, then with such a rose you will only have problems.
Planting a climbing rose in spring from the store, steps:
- A rose with a closed root system is carefully removed from the pot along with an earthen lump, and then planted in the chosen place. For representatives with an open root system, remove the film from the roots, place them in water.If there are buds or shoots below the grafting site, remove them. If there is wild growth, we also remove it, too long shoots can be pinched. Do not forget to powder the cut points with charcoal or activated charcoal.
- The roots should be in the water for 3-4 hours, thus, the plant will be saturated with moisture, the transport soil will become soft, it can be easily removed and carefully examine the root system. Stimulant "Kornevin" can be added to the water (according to the instructions).
- We take the roses out of the water, gently straighten the roots as possible and place the seedling in the dug hole. About what the pit should be and how to mix the soil (if the situation requires it), it has already been described a little higher. Water the rose well.
- After the water is absorbed, you can add more earth (spud). When re-filling the soil, the grafting site can be covered with a layer of soil, but not more than 3 cm.
- If the spring sun is shining too brightly, do not be too lazy to cover the young bush with a paper bag or a cloth of light shades - so it is guaranteed not to burn out. This protective coating can be left on for 5-7 days.
Further, you will need standard care for the climbing rose: hilling, watering, feeding, removing weeds, garter and forming a bush.
↑ back to content ↑ Climbing roses - care and cultivation
In hot and dry weather, rosebushes should be watered once every five days. After 20 days after planting, you need to carefully shake off the soil from the bush. By the way, roses planted in autumn are also opened after winter in the first weeks of April. For this procedure, it is advisable to choose a non-sunny day, so that later the plant does not experience stress during the night temperature drop. Make sure that the grafting site remains about 10 cm buried in the soil.
During the growing season, the climbing rose requires generous watering. After the buds appear, as well as after the formation of the bush, the plant should be watered every 10 days. At the same time, water should penetrate to the very roots and deeper, 10-12 liters per one bush will be quite enough. A couple of days after rain or watering, you need to loosen the soil around the rose. It can also be mulched. For roses, both waterlogging and lack of moisture are equally harmful, so observe the golden mean in this matter.
Climbing rose, photo:
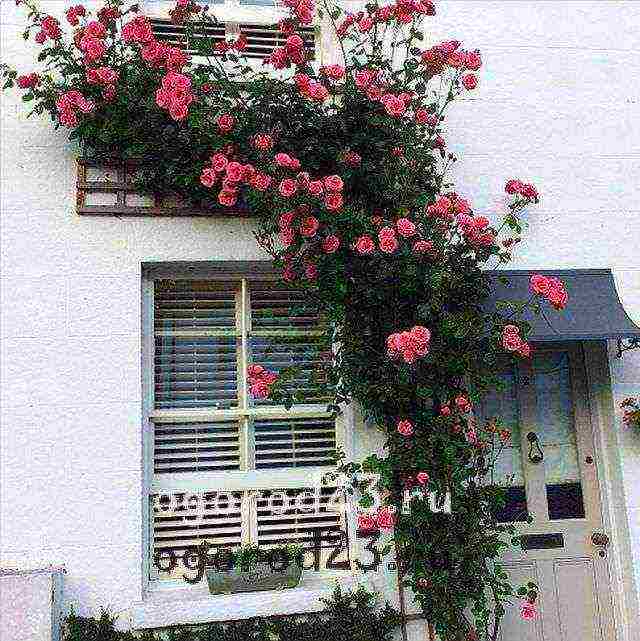

↑ back to contents ↑ How to fertilize climbing roses
Fertilization is an important step in caring for a climbing rose, because this species is quite picky about feeding. Throughout the summer, nitrogen supplements should be alternated with complex fertilizers; it is recommended to apply them every 2-3 weeks. With the onset of spring, the plant is fed with a complex mineral fertilizer, for example - "Agricola-Rose" (according to the instructions). After two or three weeks, you can add organic matter - fertilizer "Ideal" or "Flower". You can also use the old proven method - 10 liters of mullein and 3 kg of wood ash, diluted in 50 liters of water. It is recommended to dilute one liter of this mixture in 10 liters of water, and then water the plant with the resulting composition at the very root. From about the second week of July, you can begin to slowly add phosphorus and potassium supplements in order to prepare the bushes in advance for the coming winter. Carefully read the dosage of drugs in the instructions, remember that by overfeeding the rose with chemistry, you can simply ruin it.
↑ to contents ↑ Care of a climbing rose in the first year
How does it differ from standard requirements? The further development and splendor of flowering depends on competent care in the first year of a plant's life. When new shoots appear, the soil is removed from the bushes (the one that was used for hilling). If there are sunny days, then at first light shading with coniferous spruce branches will not hurt.After 10-12 days after removing the hilling soil, you can start the first pruning of the central shoot. It should be shortened over the second or third sheet. A little later, with the lateral branches of the second order, you need to do a similar procedure, while the eyes "looking" inside the bush must be removed, and those eyes that are located on the outside are left for further correct formation of the bush.
Caring for a climbing rose in the first year also involves removing the buds, as odd as it sounds. From the beginning of flowering until the first weeks of August, it is recommended to leave only two flowers on each branch. With the arrival of autumn, these flowers will turn into boxes with seeds (fruits), and after the manipulations carried out, your rose will bloom especially magnificently next year.
In summer, preventive irrigation should not be neglected against the invasion of parasites, and with the onset of autumn, rose bushes should be covered. Lutrasil, spunbond or coniferous spruce branches are an excellent covering material for this plant. The bush is completely covered. When a new spring comes, young bushes are opened first, older representatives - later. In principle, all climbing rose bushes are sheltered for the winter. An old proven method is hilling with earth and sand (1: 1) to a height of about 30 cm, with the arrival of autumn, and a little later - full cover with the onset of the first frost.
↑ back to contents ↑ Pruning climbing roses or how to prune a climbing rose

Is the climbing rose pruned in the fall for the winter? If other types of roses can be simply spud, then the climbing one must be covered completely - this factor does not depend on your region of residence. You can choose one of the methods of thermal insulation, in the first case, the ground part of the bush is removed from the support, the foliage is removed, and all weak and old shoots are cut off.
Here you have to choose 10-12 of the strongest and healthiest branches (remaining after pruning), combine them into one bunch, rewind with twine and gently tilt them to the ground. With the help of metal brackets (we cut the wire into fragments and bend), the branches are fixed to the ground, and then they are covered with an appropriate protective material. If there are several shrubs, they are located in close proximity to each other, then they can be covered with one common covering canvas. In the second case, everything happens in a similar way, only in this case the plant is not removed from the support, but reliably wrapped in protective material directly on it. The base of the bush is spud in the way described above.
How to prune a climbing rose? This important agrotechnical care measure needs to be given special attention. Pruning helps to shape the crown of the plant, promotes generous and long-lasting flowering, and has a positive effect on the health and vitality of the climbing rose. Immediately after planting, all shoots are shortened by 20-30 cm; in the summer, faded buds and branches growing inside the crown (thickening it) are cut off.
Starting from the second year of the plant's life, the branches are pruned at the end of the flowering phase.
How to prune climbing roses after flowering? They fade around the end of August - September (depending on the climate in the region), at this time all diseased and dead branches should be removed. The oldest shoots (choose 1 or 2) are cut off completely, subsequently they will be successfully replaced by young basal processes. If these processes are absent, then the old branches should be measured about 40 cm from the base, and the rest should be removed - this procedure is aimed at activating the growth of replacing basal branches.
The rest (not very old) shoots are cut off in the place where a new powerful growth began to form, subsequently it will act as a conductor. Short peduncle branches are cut to 2 or 3 buds (about 15-17 cm from the base of the branch), weak stems are cut to 3 buds (we also measure from the base).The skeleton (base) of the crown should be formed from the strongest, correctly growing shoots (evenly directed), on which young branches will then form.
How to prune a climbing rose in the spring? You should pick up the pruner when the buds begin to swell on the branches from below (last weeks of April / early May), not earlier. If you start pruning too early, then with night frosts, the branches may simply freeze, as a result of which the rose will bloom much later than the due date. If you miss pruning time, then the plant will throw all its energy into the formation of new branches and foliage, and flowering will be poor.
Pruning climbing roses in the spring has one important point - removal, namely, cutting off (not cutting) wild shoots that have grown below the grafting site. Usually this situation becomes apparent after the spring opening of the bushes. Also at this time all sick, frozen branches are removed, all affected fragments are clearly visible in spring, when buds swell on the “living” branches.
↑ back to content ↑ Transplanting a climbing rose to another place
Sometimes, out of inexperience, the gardener chooses an unfortunate place where the plant feels uncomfortable and sick. In such cases, the situation can be corrected by transplanting. The best time for this operation is autumn, September or the first weeks of October. It is not recommended to transplant later, since the rose needs time to adapt to a new place of residence before the onset of cold weather.
However, if circumstances require it, transplanting a climbing rose to another place is also possible. As soon as the ground thaws after the winter frosts, and the buds on the branches of roses have not yet had time to wake up, you can get down to business. To do this, the ground part of the plant is removed from the support, the bush itself is carefully dug in (moving in a circular manner), about 50-60 cm recede from the base of the plant.Do everything very carefully so as not to damage the root system of the rose, let the hole be deeper than necessary, but the roots will remain intact.
Next, the plant is removed from the ground, excess soil is removed from the roots, after which the climbing rose is immediately transplanted to a new place.
When replanting, the same rules are observed as with a standard planting - the roots are straightened and directed downward, the free space in the pit is filled with the appropriate soil mixture, the soil is lightly tamped and watered generously with water.
After 3-4 days, you should fill up the earth (it will settle slightly), spud your rose.
There is one interesting nuance associated with transplanting roses - their belonging to the climber and rambler groups. I will allow myself a small digression: all varieties of climbing roses can be figuratively divided into these two groups:
- climbers;
- ramblers.
Climbing varieties of climbing roses are called climbing, they form rough and thick branches that can reach 3-5 m in length. Climber shoots are not very flexible; when transplanting, they must be cut to half of their entire length!
Rambler are precisely curly roses with flexible and soft whip shoots, the length of which can reach 10 meters. Rumbler roses are characterized by active growth; when transplanted, they cut off all shoots that are more than two years old. All young branches are left intact, but at the end of the calendar summer they must be pinched tops - this technique accelerates the lignification of the branches.
↑ back to contents ↑ How to propagate a climbing rose?
There are four ways to propagate this rose: seeds, layers, cuttings and grafting. The most common and convenient option is grafting. Seed propagation is only possible if the seed is purchased at the appropriate store. As you know, self-collected seeds from climbing roses growing in your country house or in the garden do not carry the varietal characteristics of the mother plant.
↑ to content ↑ Growing a climbing rose from seeds
Pre-soak the seeds in 3% hydrogen peroxide for 30 minutes. Such disinfection creates a shield against the appearance of mold in the subsequent stages of plant growth. After we remove the seeds from the solution, put them on a thin layer of cotton wool, again soaked in hydrogen peroxide, cover it on top with a similar cotton layer, which is also saturated with peroxide.
Place the resulting "sandwich" in a plastic bag and hide it in the refrigerator, in the compartment for herbs and vegetables. We periodically inspect the seeds, change the cotton layers to new ones (also saturated with hydrogen peroxide).
After 40-50 days, the already germinated seed can be carefully transferred into peat tablets or small plastic cups with the appropriate soil mixture. Seedling cassettes are also fine.
Watering young shoots should be done as the soil dries up. For plants to develop properly, they need to be provided with daily light for 10 hours. If you do everything right, then a couple of months after planting the seeds in tablets or cassettes, the first buds may appear on young roses. With the arrival of spring, new livestock are planted in open ground.
↑ to the content ↑ Reproduction of a climbing rose by cuttings
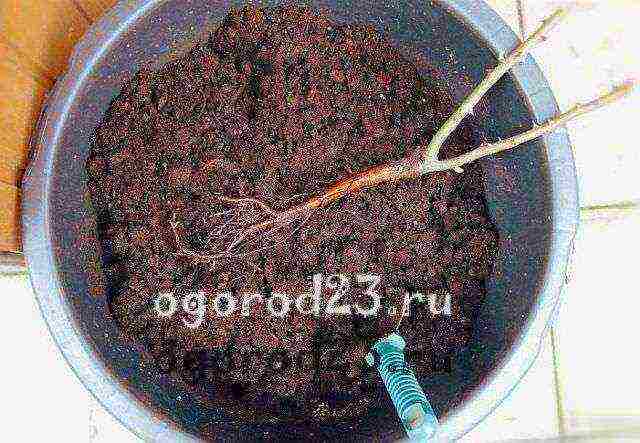

This is the easiest breeding method, almost always giving 100% positive results. For cutting cuttings, already faded or still flowering branches are suitable for you, which are taken from a rose in the very middle of summer, on the 10th of July.
The cut fragment should have at least two internodes, the place of the lower cut (45º angle) should be located close to the kidney. The upper cut (flat) is carried out at a considerable distance from the kidney.
Further, all the lower leaves are cut off from the cutting, and the upper leaves are cut in half. A stalk is placed in a previously prepared container with sand or with a mixture of sand and soil, deepened by about 1-2 cm, covered with a glass jar on top and removed to a well-lit place.
Now you will need to periodically water the cutting (without removing the can) and make sure that it does not come into direct sunlight.
↑ to the content ↑ Reproduction of a climbing rose by layering
In the spring, from the shoots growing from below, we choose the most attractive one and make cuts on it, right under the buds. Next, we make out a small groove-bed about 10 cm wide, put a thin layer of humus on the bottom of the groove, sprinkle it on top with the same layer of soil. Now we carefully bend the shoot, put it in the groove and fix it with metal brackets. After that, we cover the shoot with soil, but leave the top looking out. Then, as usual, we take care of the bush, but do not forget to water and fertilize the place of the buried shoot. After a year, when spring comes, the layers can be cut off from the bush and planted in a separate place as a full-fledged plant.
↑ to the content ↑ Reproduction of roses by grafting (budding) on rose hips
A climbing rose can be grafted onto a rose hip bush - this technique is often used by gardeners and summer residents. The best time for this operation is the last weeks of July or the first half of August. Before budding, the dog rose should be watered generously with water.
Directly on the root collar of the bush, an incision is made in the bark in the form of the letter "T", after which the edges of the bark are slightly pulled back. This kind of "pocket" holds a peephole cut from a climbing rose. The peephole must be separated from the rose along with the bark and a small piece of wood.
Next, we tightly press the peephole to the neck of the stock and also tightly wrap this place with a special film for budding (freely sold in flower shops). After all the manipulations, the rose hip bush is earthed up, and so that the soil rises above the grafting site by 5 cm (this is the minimum). After two to three weeks, the film can be slightly weakened, and with the arrival of a new spring, it is removed for good.
↑ Back to Contents ↑ Climbing rose does not bloom - why?
This can also happen, at least on flower forums, gardeners often ask each other a similar question. Experimentally, 7 factors were found out that affect the absence of flowers in climbing roses.
- Diseases. The most dangerous diseases of climbing roses are bark cancer and ash (powdery mildew). Quite good results are given by preventive irrigation of the bushes with Bordeaux liquid (1%) at the stage of dormant buds. To reduce the risk of bark cancer, plants should be provided with potash fertilizers. At the beginning of autumn, you need to feed the climbing rose with potassium sulfate (potassium sulfate) and / or a nitrogen-phosphorus additive, for example, superphosphate. Careful inspection and timely removal of affected branches, as well as a competently carried out shelter of roses for the winter is a powerful shield against diseases that weaken the plant and can really cause the absence of flowers.
- Wild growth. Multiple shoots can often be seen near the root zone of the climbing rose. Of course, they should be removed in a timely manner, because they are not of any use, they only suck vitality from the bush. If you ignore them and allow them to grow further, your rose will gradually run wild and, naturally, will stop giving color. You should remove wild growth as soon as it caught your eye.
- The wrong shelter for the winter. A climbing rose needs careful shelter before the onset of cold weather.
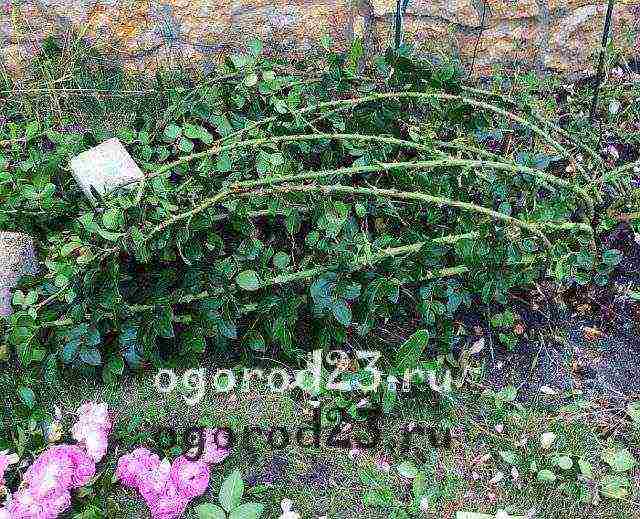 Correct wrapping of the bushes consists in creating an air cushion between the covering material and, in fact, the bush itself. Such an air gap will protect the plant from dampness during possible thaws, because dampness for a rose is as destructive as low temperatures. Proper preparation for winter also consists in limiting watering, starting from the first weeks of September. A ban is also imposed on loosening the soil. From this time on, the rose should not be given nitrogen fertilizing, only potash is allowed.
Correct wrapping of the bushes consists in creating an air cushion between the covering material and, in fact, the bush itself. Such an air gap will protect the plant from dampness during possible thaws, because dampness for a rose is as destructive as low temperatures. Proper preparation for winter also consists in limiting watering, starting from the first weeks of September. A ban is also imposed on loosening the soil. From this time on, the rose should not be given nitrogen fertilizing, only potash is allowed. - Too many nitrogen supplements. Everything is simple here - nitrogen fertilizers contribute to the growth of the green mass of the plant, which, in turn, negatively affects the setting of buds. If you overdo it with nitrogen, the climbing rose may not bloom.
- Inappropriate landing site. An incorrectly chosen place can cause not only a lack of flowers, the rose can simply die. Before choosing a site for planting a climbing rose, make sure that there will be no strong drafts and shade.
- Illiterate pruning. Everything should be in moderation, if you start pruning too actively and capture a lot of young shoots, the rose simply will not be able to recover and, of course, will not form buds. Prune the plant correctly, remove old and thickening branches, pay attention to wild growth.
- Unsuitable soil composition. The soil for growing climbing roses has already been mentioned above. The composition of the earth is an important factor, plus it must be fertile, loose, saturated with useful substances.
↑ back to content ↑ Climbing rose - diseases and pests
Prevention and control of disease or pest infestation is one of the aspects of climbing rose care. Spider mites, aphids, leafworms, thrips, rose sawfly - a list of the most active parasites of climbing roses.
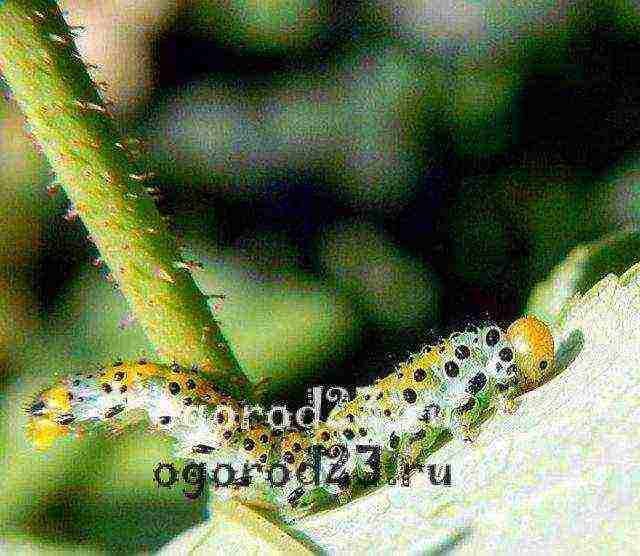 Caterpillar of a rose-cut sawfly on a rose
Caterpillar of a rose-cut sawfly on a rose Rose infested with spider mites
Rose infested with spider mites
At the initial stage, aphids can be manually removed from the branches, after putting on garden gloves, but as soon as it feels like a full owner, you will need the help of chemicals. Insecticides "Sharpei", "Aktara", "Inta-Vir", as well as the good old "Karbofos" are guaranteed to help you cope with this problem.
If you want to try the so-called folk methods of struggle, then grate laundry soap (1 tablespoon) and dissolve it in 1 liter of water.Irrigate rose bushes with this solution for a week, then remove all affected fragments - it should help.
A spider mite loves heat and drought, a silvery coating on foliage is a sign of the presence of an intruder. Old methods of struggle with the help of thick tobacco infusion or wormwood broth give very good results. Contact ascaricide "Neoron" is one of the best means of protecting roses from spider mites. One ml of the drug is dissolved in a liter of water, after which the bushes are irrigated. Sometimes it is enough to treat roses twice with this preparation for the tick to give up its positions. Bio-insecticide "Fitoverm" also proved to be excellent in this matter.
According to the reviews of experienced gardeners, the drug "Aktara" works great against the rose sawfly. The preparations "Aktellik" and "Phosbecid" (15 ml per 10 liters of water) also show a good result, which extends not only to the sawfly, but also to other "lovers" of climbing roses.
In addition to all of the above, I would like to remind you of the spring and autumn spraying of roses with Bordeaux liquid - this is important.
Among the diseases of climbing roses, the most dangerous are: bacterial cancer, gray rot, powdery mildew, coniotirium (burned bark).
 Powdery mildew
Powdery mildew Bacterial cancer
Bacterial cancer
There is no cure for some diseases (bacterial cancer), but taking prevention seriously will minimize the risk of the disease.
Disinfection of the root system in a solution of 3% copper sulfate (before planting), removal of suspicious fragments and rapid irrigation of wound sites with the same copper sulfate are the most often recommended preventive measures.
The defeat of the coniotirium can be detected in the spring, as soon as the protective cover is removed from the roses. In this case, you must immediately cut off diseased branches (with the capture of healthy fragments) and burn them. Until the buds awaken, the plant can be treated with three percent iron sulfate, the ground around the bush must be watered too. The same Bordeaux liquid or the drug "Abiga-Peak" can also participate in the case while the buds have not yet blossomed.
In principle, to combat other diseases of roses, the usual scheme works - the removal of the affected areas and their subsequent burning, abundant irrigation of the plant with a solution of ferrous sulfate (3%), copper sulfate (2%) or Bordeaux liquid (3%). Such spraying is often carried out in three stages (at weekly intervals), but sometimes, especially at an early stage, one treatment may be enough.
↑ to the content ↑ Climbing roses - photos and names of winter-hardy varieties
The dream of any gardener is that your favorite flowers delight the eyes with lush buds for as long as possible and endure wintering staunchly. It is simply unrealistic to mention all winter-hardy and long-blooming varieties of climbing roses, but I would like to highlight some of them, briefly describe their main qualities.
↑ back to contents ↑ Climbing rose "Iceberg"
It fully justifies its name, its snow-white buds will bloom for a very long time (until autumn) and profusely. Repeated blooming is a distinctive feature of this rose, it grows rather quickly and can braid an arch or a wall of a building in the shortest possible time. The plant is unpretentious, cold-resistant, the aroma is weak.
Variety "Iceberg", photo:
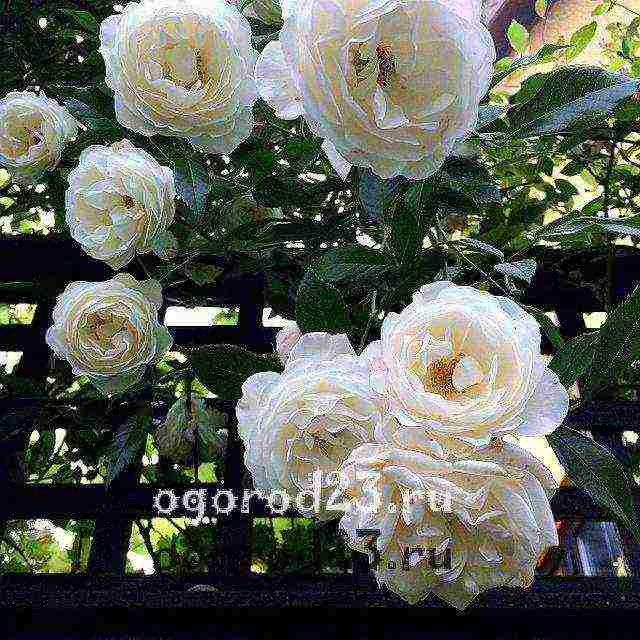

↑ to contents ↑ Climbing rose "Lavinia"
It boasts cup-shaped flowers of a rich pink hue, undemanding to care, re-blooming, aroma with light Muscat notes. It grows up to 3 m in height, has good immunity to most rose diseases, blooms continuously until the first frost.
Variety "Lavinia", photo:
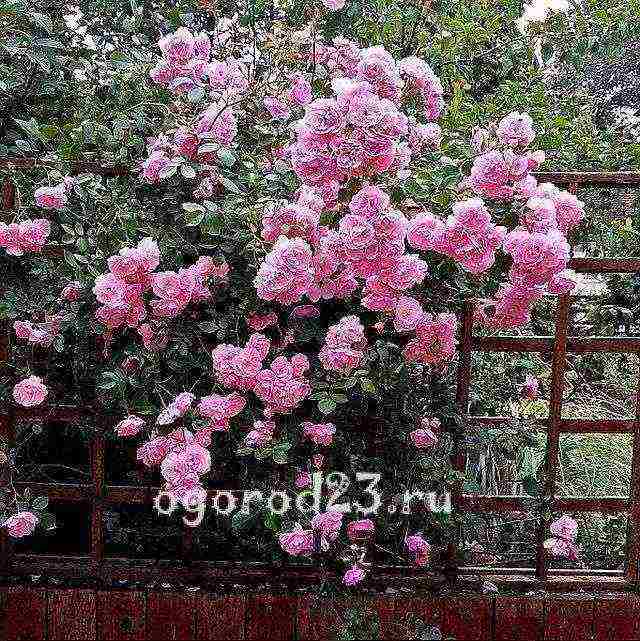

↑ back to content ↑ Variety "Polka"
It is characterized by undulating blooms, approximately five waves per summer. Terry buds, apricot shade, gradually turning into a creamy color. Loves sunlit places very much, has good disease resistance, can grow up to 3 m in height.This variety has powerful and spreading shoots with large thorns, weak aroma.
Photo of a climbing rose of the "Polka" variety:
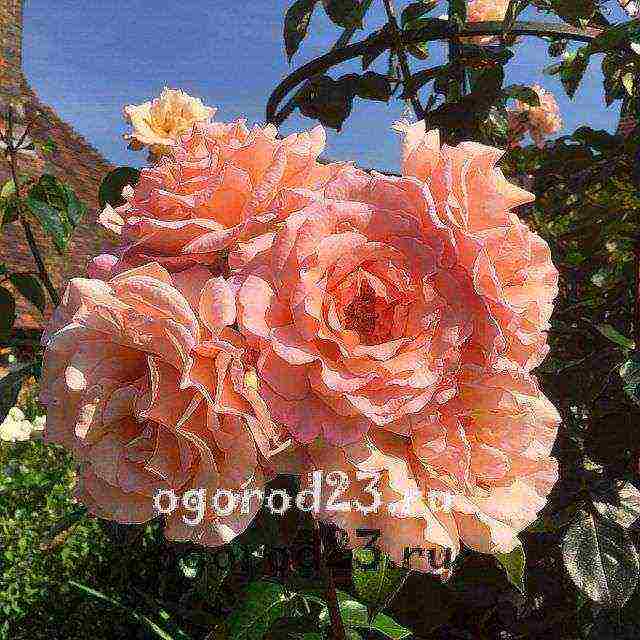

↑ back to contents ↑ Climbing rose "Don Juan"
Luxurious double rose with large (12 cm in diameter) flowers of deep red color. It is an excellent option for decorating the walls of buildings and any vertical supports. It grows up to 3.5 m in height, loves the sun, but also blooms without problems in partial shade. These roses can be cut to make bouquets, they are very fragrant and keep fresh for a long time.
Variety "Don Juan", photo:
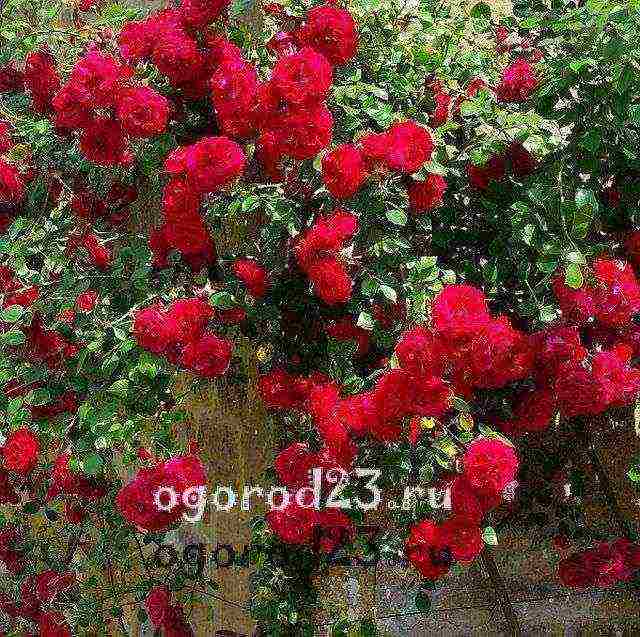

↑ back to content ↑ Sort "Flamentants"
This rose is considered one of the most attractive red climbing roses. Her buds are large (8 cm in diameter), double, multi-petal. Possesses increased frost resistance, powerful bushes can reach 2-3 m in height. With proper care, this variety can grow and bloom in one place for about 20 years. The aroma of the rose is very delicate, but not very pronounced.
Photo of roses "Flamentance":

↑ to contents ↑ Climbing rose "Handel"
The buds of this variety have a very interesting color - white-pink, with bright crimson edges and a slightly yellowish center. The buds are large, about 10 cm in diameter, the bush grows to 2.5-3 m in height. The rose is multi-blooming, disease resistance is average, one should beware of black spot and ash.
Variety "Handel", photo:

↑ back to content ↑ "Bobby James" variety
Small-flowered representative, but the most attractive in its category. Can reach 8 m in height, resistant to diseases, semi-double white flowers with a yellow center (about 4.5 cm in diameter), outwardly resemble cherry flowers. It has a pronounced musky aroma; during flowering, the branches are simply covered with buds, so that behind them you can hardly see the foliage. The buds themselves have the ability to slowly open over about 10-12 days. A spectacular and incredibly luxurious variety
Photo of a rose variety "Bobby James":

↑ to contents ↑ Climbing rose "Golden Perfume"
A re-flowering variety whose flowers bloom slowly, to the delight of gardeners. Large buds (up to 10 cm in diameter) of this rose exude a very strong aroma that can be heard even from afar. Flowers of a rich bright yellow hue will adorn the bush until the arrival of the first frost. Shoots grow up to 2-3 m in height, foliage also looks very attractive - rich green, dense, creating a beautiful contrast with yellow flowers.
Variety "Golden Perfume", photo:

↑ back to content ↑ Variety "Parade"
One of the most winter-hardy re-flowering climbing roses, with large (10 cm in diameter) multi-petal buds of a juicy cherry shade or rich dark pink. Luxurious inflorescences are so large and heavy that the shoots literally bend from their weight. It blooms throughout the summer, blooms slowly, reaches 2-3.5 m in height, resistant to precipitation.
Roses of the "Parade" variety, photo:

↑ back to contents ↑ Climbing rose "Schwannensee"
Another variety with increased cold resistance. The multi-petal buds of this rose have a classic shape, medium size (7-9 cm in diameter) and a very delicate color - white, with a creamy pink core. Schwannensee blooms until the very frost, slowly blooming and spreading a delicate refined aroma. The variety is hardy, multi-flowering, rain-resistant. The bush can reach 3 m in height.
Variety "Schwannensee", photo:

↑ back to content ↑ Sort "Casino"
This rose is suitable for cutting into a bouquet, has a bright fruity aroma, lemon-colored buds are most beautiful when loose. A multi-petal variety, the diameter of a double flower reaches 9-11 cm, its color is darker inside, the outer petals are paler. The bush grows up to 3-4 m in height, blooms profusely, luxuriantly, repeatedly throughout the summer.
Climbing rose of the "Casino" variety, photo:

Of course, a climbing rose will require an investment of time and effort from you, but you must admit that its luxurious beauty fully justifies such "sacrifices." Follow all the above recommendations, carefully consider the choice of a place of residence for a rose.
Do not plant it near bushes and trees with powerful roots, do not forget to feed it with appropriate fertilizers in time.
Provide her with reliable support, the types of which I will tell you about in the next article.
Let a climbing rose also settle on your site. Planting and care in the open field, the nuances of reproduction and transplanting, a rough idea of individual varieties - you now know all this and can apply my advice in practice.
The following videos will successfully complement the article:
Despite the harsh, sharply continental climate of the region, the dream of Ural gardeners about their own rose garden is quite realizable. The main thing is to choose a variety adapted to weather conditions, to study the peculiarities of planting and care.
Features of growing climbing roses in the Urals
The Ural region is characterized by difficult weather conditions for roses:

Climbing roses for the Urals. The Rosarium Uetersen rose bush reaches a height of 3.5 m, but it also perfectly withstands pruning up to two meters
- long frosty winters (down to -40 ° C);
- short summer;
- cold piercing winds;
- high snow cover;
- uneven distribution of precipitation;
- returnable spring frosts.
Moreover, on the plains of the Urals (west of the Ural Mountains), the climate is milder and humid. The natural conditions of the Trans-Urals (east of the Ural Range), where much less precipitation falls, is noticeably more severe, with pronounced features of the continental. Heat-loving climbing roses in such conditions do not fully reveal their varietal qualities: they do not reach the declared height, do not bloom again, do not fully open their buds. therefore adapted varieties of roses are chosen for growing in the Uralsadapted to the listed conditions: winter-hardy, unpretentious, with high immunity.
Review of varieties of climbing roses recommended for the Urals
The table contains a description of the varieties that are traditionally popular among the Ural gardeners:
| Variety | Description | Advantages |
| Flammentanz | One-flowering, deep red double buds up to 8 cm in diameter, collected in clusters of 3-7 pieces; sprawling bush, densely leafy, up to 2.5 m high; stems are tough, prickly, require strong support | Winter-hardy, disease-resistant, blooms profusely and for a long time (30-35 days) |
| Ilse Krohn Superior | Re-flowering; flowers are densely double, creamy white, 10-11 cm in diameter, appear one at a time or in brushes up to 3 pieces; the petals are large, curl as the bud opens | Winters well, strong immunity to diseases, flowers are resistant to precipitation |
| New Dawn | Re-flowering; flowers are semi-double, cupped, pearl pink with bright golden stamens in the center; tall bush, with long thin shoots | Frost-resistant, tolerates poor soils and partial shade, does not get sick |
| Rosarium Uetersen | Re-flowering; densely double (up to 100 petals) flowers of deep pink color appear one at a time or in lush brushes | Very winter hardy, resistant to rain and disease; unpretentious to the composition of the soil; suitable for cutting into bouquets |
| Super Excelsa | Re-flowering; double flowers of bright crimson color are collected in large clusters, appear throughout the summer; stunted bush (150-200 cm), spreading; suitable for vertical supports | Winter-hardy, while tolerating heat well; suitable for growing on a trunk; the bush is neat, the lashes fit easily for the winter |
| Westerland | Loose, large, fragrant flowers are grouped in inflorescences; the color of the buds varies from orange-yellow to salmon-apricot, depending on the stage of opening; sprawling bush, up to 1.7 m in height, suitable for single plantings | Winter hardy, resistant to powdery mildew and spotting; blooms early, blooms until late autumn |
All varieties presented in the table respond positively to decorative pruning of faded buds and tying. Moreover, some climbing roses in a short growing season show themselves better when grown in bush form.
Of all the varieties listed above, "Super Excels" is the most plastic. The bush is easily formed, the lashes are easily removed and bent down for the winter.
General principles of caring for roses in the Urals

The shoots of the "Super Excels" rose easily fall on the support of any configuration
It should be remembered that even the most weather-adapted variety requires proper care and adherence to agricultural practices... For climbing roses, the same top dressing is recommended as for other variety groups. During the season, you need to feed at least three times.
- In late May and early June, organic matter and mineral nitrogen fertilizers are applied.
- In July, they are fed with complex nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium fertilizers.
- In early August, they are fed with phosphorus and potassium (See also the article ⇒ Phosphorus fertilizers for garden roses).
Pruning is carried out as needed: cut shoots older than 3 years old, weak, damaged stems, growth not ripened by autumn. In the first wave of flowering, wilting buds with a part of the peduncle are removed in order to provoke the re-formation of flowers. Closer to autumn, this should not be done, since the plant must prepare for wintering.
The duration of bud formation of once flowering varieties is regulated by cutting off some of the freshly flowering branches. As a result, prolonged flowering is obtained on replacement shoots.

With appropriate pruning, "Flamentanz" blooms until the end of August
Expert recommendations: “The most difficult part of growing climbing roses is getting ready for winter. Before the shelter, the bushes are treated with iron vitriol for fungal diseases. Then the lashes are tied into one bundle and laid. Most of the bushes cannot be bent in one go without damaging the stems. You have to bend them in several passes. Laying roses on bare ground is not worth it, it is better to fix them on a dry substrate 20 cm from the ground. This creates the necessary air gap. At the end of the most crucial stage, a strong frame is built, on which Lutrasil-60 is laid and well fixed in 2 layers. "
Svetlana Aleksandrova is the chief agronomist of the Victoria gardening company (Magnitogorsk).
Tip # 1: It is convenient to use thick foam or plastic bottles stacked in a row as a substrate. And practical, and rodents "too tough", and the thawed snow will not flood.
A ventilation hole is provided in the shelter. Roses are fully wrapped when frost falls below -5 ° C
Spring awakening of a rose is a moment no less important than preparing for winter... Towards spring, the snow becomes dense and wet. The frame may not be able to withstand the weight of a snowdrift. A plant deprived of air will simply suffocate. Therefore, in March, the excess snow is raked, the shelter is ventilated if necessary. At the beginning of April, you can remove the second layer of covering material. It is not yet possible to fully open the rose, even if it is warm outside. The soil is still cold, the roots are dormant. The awakening of the root system and the aerial part of the plant should occur synchronously. At this time, you can carry out preventive treatment, sanitary pruning, after which the bush should be covered again. Finally, they remove the shelter after the soil has completely thawed (See also the article ⇒ When to remove the shelter of roses).
Advice number 2: To bring back to life a weakened rose that has difficult to endure wintering, immediately after leaving the shelter, stimulate the work of the root system. For this, the plant is fed with a solution of "Zircon" and "Tsitovita". In 10 liters of water, dissolve 1 ampoule of each drug, and water the bush under the root.
Typical mistakes of flower growers when growing roses in the Urals
- There is an opinion that roses planted in summer, in July-August, tolerate wintering better, since they manage to get stronger before the onset of frost. This is absolutely not true. About a month after planting, having exhausted the reserves of nutrients from its own root system, the seedling is actively moving into growth. Additional forces are required for the formation of growth.In the short Ural summer, there is not enough time for young growth to ripen. As a result, the plant leaves in the winter weakened, the unripe stems vytryut, rot, become the cause of the death of the entire plant. The optimal time for an autumn transplant is the second half of September, for a spring one - the end of April.
- Novice gardeners often set up a flower garden according to the recommendations of landscape designers, taken from foreign magazines. For the Ural region, this approach is not acceptable. It is necessary to plan the location of the rose garden according to the rules that take into account local climatic features (See also the article ⇒ DIY rose garden). Basic site requirements:
- protection from drafts;
- maximum solar illumination;
- southern or southeastern exposure;
- no stagnation of moisture (the depth of groundwater is at least 100 cm from the soil level).
It is categorically impossible to plant roses along the walls of houses, next to deaf fences, in the shade of other shrubs and trees, in flooded areas.
Answers to topical questions of gardeners

A healthy seedling has at least three smooth green shoots 20-30 cm long with developed buds
Question number 1: What seedlings to choose for the climatic conditions of the Urals: grafted or on their own roots?
In the Urals, it is recommended to plant grafted roses. Unlike their own rooted ones, they are more resistant to frost, bacterial and fungal diseases. The best stock for the Ural climate is the Kanin rose. Ultimate endurance is naturally built into this rose hip. Grafted cuttings take root from 2 to 4 weeks, and self-rooted seedlings form a full-fledged root system for more than three years. All this time, a rose grown on its own roots is vulnerable to adverse external factors and diseases.
Question # 2: Do I need to huddle roses in front of the shelter?
Hilling bushes with sawdust, peat, soil, damp leaves and other materials in the climatic conditions of the Urals does more harm than good. Unlike other regions of Russia, the shoots do not have time to wood during the growing season, so they often undermine by the spring.
A selection of tips for growing roses
Presented the best tips in pictures for planting, care, pest and disease control in roses ⇓
Rate the quality of the article. We want to be better for you ⇓:
 You can decorate even the most unsightly corner of the garden and at the same time add a piece of light romance to it with the help of climbing roses. These extraordinary, beautifully flowering climbing plants please the owners with their flowering almost throughout the season. But for it to be flawless, climbing roses require proper planting and special care. We will tell you about all the intricacies and nuances of growing climbing plants in this article.
You can decorate even the most unsightly corner of the garden and at the same time add a piece of light romance to it with the help of climbing roses. These extraordinary, beautifully flowering climbing plants please the owners with their flowering almost throughout the season. But for it to be flawless, climbing roses require proper planting and special care. We will tell you about all the intricacies and nuances of growing climbing plants in this article.
Curly rose: planting and care, photo
Any plant in the garden or in the summer cottage requires care. Particular attention must be paid to some flowering crops, which include weaving roses.and with long branches... Abundant and long-lasting flowering of this beautiful plant can be achieved only with the exact fulfillment of all the rules for planting, careful care throughout the year, timely pruning and protection from winter frosts and pests.
Choosing a landing site
 Roses are photophilous, therefore, with a lack of sunlight, fresh stems will develop poorly and will bloom only in the next season. However, the midday sun can burn the plant. The place for planting roses should be such that during the hottest hours the bushes were in partial shade... The best option would be a site that the sun heats up in the morning. In the morning hours, the dew from the leaves will quickly evaporate, and the viral diseases of the roses will not be afraid.
Roses are photophilous, therefore, with a lack of sunlight, fresh stems will develop poorly and will bloom only in the next season. However, the midday sun can burn the plant. The place for planting roses should be such that during the hottest hours the bushes were in partial shade... The best option would be a site that the sun heats up in the morning. In the morning hours, the dew from the leaves will quickly evaporate, and the viral diseases of the roses will not be afraid.
Curly roses are also finicky. They do not tolerate drafts well, and therefore the corners of buildings are not suitable for planting them. Do not plant them in areas where roses have already grown and in wetlands.It is best to choose a bed with a slope so that water does not stagnate in the ground. The roots of the plant reach about two meters in length, so if the moisture of the soil is constantly very high, the flowers are planted on a hill.
Climbing shrubs for decoration can be planted along the walls of the building... So that their roots are not depleted, the distance from the wall should be at least 60 cm. In any case, the planting of climbing roses should take place near some kind of support. These can be fences, nets, pergolas, arches, walls, or specially crafted pillars or cones.
When to plant climbing roses?
In areas with a temperate climate, shrubs are planted in open ground in late September - early October. Within two weeks, they will give the first roots and before the onset of cold weather they will have time to get stronger. In the spring, the root and aerial parts will begin to grow actively, the bush will become lush, gain strength and bloom. However, in the northern regions, climbing roses are best planted in the spring, since the bushes planted in the fall will not have time to adapt, and can freeze out in winter.
Plants, which were planted in spring, are delayed in their development by about half a month and require increased attention. Before planting in the ground, such seedlings are cut into three buds.
Selection and processing of seedlings
Beautiful curly rosals can only be obtained in the presence of healthy seedlings... Their viability and quality are indicated by the appearance of the trunk. It should only be whitish green, not gray or brown. The acquired seedlings in open ground are not planted immediately. They must first be prepared:
-
 Soak the plant completely in water for a day.
Soak the plant completely in water for a day. - Shorten healthy roots by 15 cm, and cut off the crushed and weakened ones completely. A small bunch should remain.
- Shorten strong branches of roses by 15-20 cm, and remove weak ones completely.
- Sprinkle the cuts with crushed charcoal.
- Treat the roots with Heteroauxin or Kornevin.
Thanks to this preparation for landing the bushes will begin to actively grow, and during the flowering period, many buds are formed on them.
Soil preparation
Climbing roses love fertile, loamy, well-drained soil. Only heavy clay and sand are not suitable for growing them. Therefore, clay areas are diluted with sand, and sandy areas - with clay. More suitable in chemical composition and crumbly soil will become after adding a small amount of lime to it.
When digging, the fertility of the soil can be increased by adding to it:
- phosphate fertilizers;
- humus;
- humus;
- phosphorobacterin (special soil bacteria).
The soil is prepared for planting climbing shrubs in advance. It is necessary to dig it up several times at the end of summer, and then loosen it also in the spring.
Landing features
The roots of a young plant should not experience a lack of space, so the holes for them should be free enough. The optimal depth is considered to be 60-65 cm. In order for the root system to develop freely, the distance between the plants must be at least one meter.
When planting roses in the hole, it is necessary observe the following recommendations:
-
 About five kilograms of the nutrient mixture is preliminarily introduced into each hole. You can use peat compost.
About five kilograms of the nutrient mixture is preliminarily introduced into each hole. You can use peat compost. - The roots of the roses should be free in the hole. The voids between them are necessarily filled up.
- The root collar of the plant is covered with soil by about 10-12 cm. This will help to protect it from frost in addition to insulation.
- The planted rose is watered with a bucket of warm water.
- The remaining space is filled with a mixture and lightly compacted.
The support to which the rose will be attached in the future should not interfere with the development of the root system. If the support is portable, then you can use special tripods, trellises or trellises. The pole and tripods can be made by yourself by knocking down for this wooden beams from 2.5-3 meters high... They will look gorgeous as arch supports, on both sides of which two bushes are planted. By the end of the second year, they will be completely entwined with curly roses with delicate flowers (pictured).
Caring for planted bushes
The main rules for caring for climbing roses include regular watering, timely feeding of plants, garter and pruning of shoots, sheltering bushes for the winter and protecting them from pests and diseases. Let's consider each point in more detail.
Watering and feeding
Climbing shrubs do not like excess moisture and tolerate drought without problems. It is recommended to water them once a week with a small amount of water, which should not be cold. Overmoistening plants can lead to viral diseases and poor appearance of the bushes.
Fertilizing roses is best manure or other organic fertilizers, alternating them with mineral dressings. It should be borne in mind that young plants at first will be sufficiently fertilized when planting soil. Therefore, it is not necessary to feed them too often. The next year after planting, caring for climbing roses will consist of fertilizing with fertilizers of the following composition:
- fresh black soil;
- humus;
- phosphorus complementary foods;
- humus.
With such a mixture, the soil in which the roses grow "revives" in spring and autumn. If it is not possible to prepare the composition yourself, then you can buy ready-made fertilizer for roses.
Pruning shoots
All climbing roses are divided into two types, each of which requires a certain pruning:
- In shrubs flowering from June to July, after planting, all shoots are shortened. There should be shoots 30 cm long. New stems that appear during active growth are cut off as needed to form a beautiful bush.
- Roses with a small number of basal shoots, which appear only on old branches, are shortened to 30 cm in the first year. The next year after planting, all old shoots are cut out completely.
Garter of climbing roses
After pruning, new branches will begin to grow, which need to be guided, giving the bush the intended shape. To form more buds, individual lashes are tied. At the same time, it is undesirable that they are directed only upward, since with this arrangement, the buds are formed only at the tops.
For lush flowering bushes there are several ways to tie:
- Shoots can be fanned out, leaving the side branches not tied up. They will not interfere with each other, freely extending to the sides and up.
- The main shoots are located horizontally, tied to the support. After a while, they will give new side branches, which will grow upward, forming a cloud of beautiful flowers.
- In order for the curly branches to braid an arch or a pillar, they are tied up in a spiral, twisting around the support.
No matter how the bush is formed, one should not neglect the care of climbing roses and preparing them for winter.
Protecting roses from frost
 Before proceeding with the shelter, the bushes must be prepared. To do this, remove the leaves from them, cut out old loops and weak shoots. As a result there should be 11-12 healthy and strong shoots... All work is carried out in dry weather.
Before proceeding with the shelter, the bushes must be prepared. To do this, remove the leaves from them, cut out old loops and weak shoots. As a result there should be 11-12 healthy and strong shoots... All work is carried out in dry weather.
The way a climbing plant hides depends on the region in which it grows. In regions with a mild climate, the branches can not be removed from the support, first covering them with spruce branches, and then wrapping them with foil.
In areas with severe winters, the plants are completely removed from the support. First, they are collected in a large bundle and tied. After the air temperature drops to -5C, they gently tilt to the ground, where they are fixed with wire or pegs. The base of the bush is sprinkled with a mixture of peat and soil, and the shoots are covered with spruce branches. From above everything takes cover thick film or agrofiber.
It is very important to remove the shelter on time in the spring. Otherwise, in a humid environment and without fresh air, the roses may suffocate and start to hurt.On open bushes, shoots are refreshed and tied to supports. The first feeding is recommended only after the appearance of young leaves.
Diseases of climbing roses
In case of errors in the care and incorrect arrangement of the bushes on the site, they may be affected by the following diseases:
-
 Black spot occurs on young shoots in warm weather and heavy rains. You can recognize it by the black and brown spots on the leaves, which have a yellow halo. All affected leaves are removed from the plant and burned. Feeding is done with phosphate and potassium.
Black spot occurs on young shoots in warm weather and heavy rains. You can recognize it by the black and brown spots on the leaves, which have a yellow halo. All affected leaves are removed from the plant and burned. Feeding is done with phosphate and potassium. - Powdery mildew progresses with increased humidity. If a white bloom appears on the leaves and stems, and the flowers do not bloom, then this indicates that the plant is sick. The bushes are processed with iron and copper sulfate, all the affected areas are cut out, the soil is dug up.
- Bacterial cancer can be recognized by the growths and bumps on the roots. They are soft at first, but darken over time. The plant begins to dry out and dies. The affected roots are cut out, and the remaining ones are treated with copper sulfate.
When treating climbing roses, it must be remembered that all cut off affected areas must be burned... Otherwise, they can infect other plants.
Proper planting and care is the key to the abundant and long-lasting flowering of these royal flowers. Those who decide to grow climbing roses on their site will never regret it.
Planting and caring for climbing roses

- Kind: Rosaceae
- Flowering Period: June, July, August, September
- Height: 30-300cm
- Color: white, cream, yellow, pink, orange, red, burgundy
- Perennial
- Hibernates
- Sun-loving
- Moisture-loving
If the lion is the king of beasts, then the rose is the unconditional queen of the garden. Since ancient times, this plant has been considered an object of admiration and worship. It was not for nothing that she was chosen as the symbols of love. The first mention of the rose can be found in the legends of the ancient Hindus. Legends about a beautiful flower are found in the annals of Ancient Iran. According to legend, Allah himself created a charming white Rose with very sharp thorns. She was supposed to become the mistress of flowers instead of the magnificent, but very lazy Lotus. Today, this plant can become a real decoration for your gardens, but for this you need to learn how to choose and plant a seedling, what is the proper care for roses.
Planting and caring for roses is not as difficult as it seems. It's important to follow simple rules and your garden will be filled with gorgeous, fragrant shrubs.
To initially ensure your success in growing roses, you need to purchase high-quality planting material. It is better to choose plants whose root system will be closed. When planting such a seedling, the land around the root must be preserved.

Rose seedlings are best chosen with a closed root system: they take root more easily at the planting site and are less sick
Often in modern supermarkets you can see imported roses with a closed root system, which are sold in advance. Several seedlings can be stored in the refrigerator on the lower shelf at temperatures between 0 ° C and + 5 ° C. During storage, you will have to regularly monitor the condition of the substrate around the rhizome. It should not dry out completely, but too much moisture is also harmful for it.
Advice! A solution of root or heteroauxin promotes root growth, so you can water the seedlings with it several times.
It is recommended to plant roses in the middle lane in spring when the soil warms up to + 10 ° C. Usually, such conditions correspond to the period from late April to early May. Spring is chosen for planting standard roses.
Autumn planting is recommended for most of the roses. The preferred work period starts in mid-September and ends in mid-October. An earlier planting time is undesirable due to the fact that the rose can give fresh shoots in the warmth, which will not have time to get stronger and freeze in winter.Late planting is also dangerous, because the plant must take root before frost.

Most roses are planted in the fall. It is also convenient because when buying planting material on the market, you can see the flower itself
The place for planting roses should be sunny. In the shade, roses can get bored, they stop flowering, dark spots appear on the leaves of plants, blind shoots form. The plant can be affected by powdery mildew. Choose an area that is ventilated but protected from strong northerly winds.

Roses adorn the garden, regardless of their location, but the plants themselves need conditions for successful growth and flowering.
Roses have no particular preferences in terms of soil. They are not as capricious as they might seem. Any soil is suitable for them, except for heavy clay and light sandy loam. The landing site should not be located where groundwater comes close to the surface of the earth.
Planting holes need to be dug so deep and wide so that the roots of the plant are spacious. If the soil is fertile, then half a meter of depth and the same width will be sufficient. For clay soil, with the same width of the hole, you need to dig 60-70 cm in depth.
It is necessary to prepare a nutrient mixture for backfilling into the pit. It contains humus or compost, rotted manure and soil. Fertilizers should not come into contact with the roots of the plant, so sprinkle them with a layer of soil.

The soil or substrate that covers the roots of the plant must be preserved: the rose adapts faster to new living conditions
Before planting the seedling, you need to pour water into the hole so that it is absorbed. If the root system of a rose is closed, it is not necessary to free the root from the ground. If the root is free, it must be cut to a third of its length and soaked in plain water or a root growth stimulator for two hours.
Shoots should also be pruned:
- in polyanthus and hybrid tea roses so that 2-3 buds remain on each of the shoots;
- for floribunda roses, leave 3-4 buds;
- for park roses, shoots are shortened by 10-15 cm;
- for a ground cover rose, only the cuts of the roots are cut (renewed, not shortened).
The seedling should be covered with earth so that the grafting site is about 5 cm below the ground. Wax should be removed from the burial site, if any. The earth should be tamped and watered again. In this way, air that may have remained around the roots is removed, and the closest contact between the plant and the soil is achieved. You can sprinkle the seedling by about 10-15 cm. The resulting slide must be removed in two weeks - the time during which the seedling should take root.
There are not so many ways to breed roses. But the desire to have as many of these undeniably beautiful and diverse plants as possible on the site is so great that gardeners strive to master them all and to the maximum extent. Here is a list of ways to propagate a rose:
- Budding. On the bark of the plant trunk, close to the ground level, a T-shaped incision is made, into which the bud of the cultivar is inserted, and then fixed with a film. The graft can use the developed root system of the rootstock. This operation is not difficult, but requires some experience.
- Seeds. This method is used extremely rarely due to the fact that the result has to wait a long time, and there is no certainty that it will turn out to be positive. And the germination of rose seeds leaves much to be desired.
- Layers. Shrub and climbing roses are propagated this way because they have long and strong stems. The shoot of the plant in the lower part is cut for 8 cm, a chip or a match is inserted into the cut. The cut part of the shoot is placed in the ground and fixed, and its free tip is tied to a peg. The rooted shoot is cut off from the parent bush.
- Cuttings. The method is good in that roses rooted in this way will not give wild shoots. The stalk is part of a strong shoot. It is cut next to the leaf bud and germinated using rooting stimulants. After the root appears, the rose can be planted in the ground.
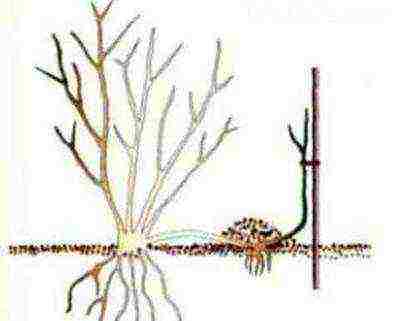
The layering method is good to use only for propagation of plants with long stems, which are used to create a new rose bush.
You can learn more about the propagation of garden roses by cuttings in this video:
In order for the rose to bloom and delight its owners for many years, you should pay attention to it, do not forget to feed it and protect it from viral diseases. Do not be afraid of difficulties: caring for different types of roses growing in the garden is not as difficult as it seems.
Manure is a natural fertilizer and, of course, preference should be given to it. Horse manure, which is at least six months old, is considered the best. Chicken and pork manure, especially fresh, can seriously harm the plant: it is sour and can simply burn young shoots. Fresh manure also badly affects the soil, because it blocks nitrogen.

Manure is a natural fertilizer, therefore the most acceptable. When choosing a top dressing, preference should be given to rotted horse manure or mullein
During the period of bud formation, you need to feed the plant with a solution of calcium nitrate at the rate of 1 tbsp. for 10 liters of water. During the active growth and development of the plant, it should be watered every 10-15 days with herbal infusion, a solution of mineral fertilizers, chicken droppings or infused mullein. To make the fertilizing better perceived by the plant, it is better to apply the same mineral fertilizers in dissolved form and after the next watering. When the first half of summer is already over, that is, in the second part of July, the feeding of the rose stops. The plant begins to prepare for winter.
Plants are also capable of dealing with stress. It is in this state that they stay during periods of extreme heat, cold or prolonged rains. To make it easier for roses to overcome difficult times in their lives, you need to spray them with zircon, epin, ecosil or sodium humate. Overfed roses produce abundant greenery, but bloom very sparingly.
Roses should be watered no more than once a week. If the summer is hot, then the frequency of watering can be doubled. The watering rate is a bucket of warm water for each bush. It is necessary to pour water at the root, trying not to get on the foliage. Water must penetrate into the soil to a depth of at least 20-30cm. Shallow watering can form superficial roots that are easily damaged.

A rose in dew is a magnificent sight, but nature has disposed so that the dew disappears with the first rays of the sun, otherwise its drops, like magnifying glasses, would enhance the energy of the sun and burn the petals: you need to water the roses at the root
If there is no one to water the roses for a long time (more than a week), the soil at the base of the plant should be covered with humus, cut grass or tree bark. Such a measure will not only retain moisture at the roots, but also prevent the growth of weeds.
With a lack of moisture, the flowers of the plant may become small, but roses should not be flooded either: this can lead to a reduction in the supply of oxygen to the roots. As a result, the leaves of the plant will turn yellow. To prevent this from happening, do not forget to loosen the soil after watering.
Of course, proper feeding and watering is important, but the process of caring for a garden rose is not limited to this. One of the most unpleasant diseases for a garden rose is powdery mildew. Preventive measures will help to take care of the health of the plant. The rose must be sprayed directly over the leaves with a solution of ordinary baking soda at the rate of 40 grams of soda per liter of water. This should be done from spring 2-3 times every other week, as well as at the beginning of summer.

Plants, like all life on earth, can get sick. These are not random stains or fertilizer marks. It is powdery mildew and is easier to prevent than to cure.
Aphids are a big nuisance for roses. But you can overcome it. To do this, boil a bucket of water, put a piece of grated laundry soap and a couple of branches of wormwood in it, after which they boil for 10-15 minutes. Roses are sprayed with cooled and strained solution. After a week, the procedure should be repeated.If the aphid stubbornly does not want to leave the plant, you will have to use a systemic poison, for example, Aktara.
Aphids will not appear on roses at all if lavender or nasturtium is planted under them. And calendula and marigolds will help get rid of beetles. By the way, onions and garlic will add health to roses, as well as to people. In their environment, plants become more aromatic and less sick.
Spots on the leaves, cracks in the stems and the cessation of bud development indicate a disease. The affected branches should be removed. Prepare an infusion of horsetail, wormwood and nettle, and spray the rose with.
The shoots of the plant growing inward should be pruned. This stimulates the emergence of young shoots and active flowering. Withering flowers need to be removed, then the saved energy of the plant will be directed to a new wave of flowering, which will be more abundant.

Just look at what a beauty! But all this splendor can be grown with your own hands. If someone succeeds, you will definitely succeed.
There are many pruning rules and this topic is undoubtedly worth a separate article devoted to it.
Once upon a time, growing roses in the Urals seemed impossible. The weather conditions of these places create problems for the cultivation of even less fastidious crops. But breeders work tirelessly, and now lemons, grapes and roses are growing in the Urals.
Once upon a time, growing roses in the Urals seemed impossible. The weather conditions of these places create problems for the cultivation of even less fastidious crops. But breeders work tirelessly, and now lemons, grapes and roses are growing in the Urals.
Where to begin?
It is necessary to start in winter. The first task is to choose varieties for the future flower garden. There are incredibly many varieties. The classification of roses by attribute into 8 groups is accepted. Each group takes into account the height, winter hardiness, flowering features, etc.
- 1Tea-hybrid roses - the hobby of gardeners with these flowers began with them. Very beautiful, with a wonderful aroma, they are very capricious, very thermophilic and susceptible to many diseases. Nevertheless, in the Urals, they grow thanks to specially bred varieties. Here are just a few of them: Gloria Day, Blue Moon, Double Delight, Rose of the World title holder, Ashram.
- 2 Floribunda roses - this variety appeared by breeding hybrids from the tea rose. The most beautiful rose gardens are obtained from the flowers of this variety. We managed to breed varieties that have good winter hardiness: Arthur Bell, Deja Vu, Jack Forst, Rosie Mittermeier, Sunsprite, Evelyn Fison.
- 3 Canadian roses are just beginning their history in Russia. Received by hybridization in Canada, they have excellent properties. They withstand frosts down to -40 ° C, are resistant to diseases, and tolerate temperature extremes well. And at the same time, they are beautiful, they bloom for a long time. Varieties: David Thompson, Moden Blanche, etc.
- 4Miniature roses. Adorable babies, not reaching half a meter in height. Outwardly, they look like hybrid tea roses. They are distinguished by long flowering. They can hibernate under the snow with a little cover. There are quite a few varieties: Baby Masquerade, Mandarin, etc.
- 5 Ground cover roses. They are still rare. Long shoots grow on the bushes, which create an amazing carpet of flowers on the ground. They are resistant to weather disasters. Varieties: Fairy, Ondela, etc.
- 6Park roses are cultivated wild-growing roses. They are easy to grow. They tolerate winter well. Varieties: Robusta, Grothendorst, etc.
- 7 Shrub roses - have a delightful strong scent and bloom for a long time. Varieties: Charles Austin, Graham Thomas, etc.
- 8 Climbing roses are distinguished by a strong aroma and exuberant flowering several times per season. They have whips up to 5 m long. Plants need props. Varieties: Dorothy Perkins, New Doon, Schwannensee, etc.
Clairvoyant Baba Nina named the signs of the zodiac, on which money will fall from the sky in June 2018 ...
►

The choice of planting material
Having decided on what you will plant, you can go for seedlings. On sale can be both own-rooted and grafted seedlings.On which graft the seedling is grafted, its winter hardiness depends. You need to get this information from the seller. Rosa Kanina is the best rootstock for the conditions of the Urals.

The seedling must have at least 3 shoots, on which well-developed buds are well defined. The stem should be 20-30 cm long and green and smooth. When you buy a plant with open roots, it is possible to inspect them well. Living healthy roots are immediately visible. Such roots should be wrapped in a damp cloth during transportation. If you buy a plant whose roots are covered with a lump of earth and a film, then it does not need to be unpacked until planting. Open roots should be disinfected in a solution of copper sulfate or phytosporin. If the roots are dry, place them in a bucket of water for 24 hours.
Seedlings purchased in the fall can be stored underground in wet sand.
If the planting is not immediate, you can store the seedlings by digging them into a trench and compacting the ground well. Or leave in a damp cloth, wrapped in plastic.

Planting seedlings
Roses in the Urals can be planted in spring or autumn.
In autumn, this is done when the temperature reaches + 4 ° C. It is important here that the plant does not start growing. The root system will waste energy and leave weakened in the winter.
In spring, the time is chosen according to the condition of the soil. If the ground has warmed up to 10 ° C, you can plant. This usually happens by the end of April.
When choosing a site, one must remember that a rose is a delicate plant. You can not plant it in a lowland, where severe freezing and waterlogging of the soil is possible. The place should be well lit, but shaded. Otherwise, in hot weather, the flowers will dry out and fall off, the flowering time will be greatly reduced. You should also protect roses from drafts.
Roses love slightly acidic and humus-rich soils. Before planting, you need to dig a hole about 50 cm deep and fill it with a specially prepared mixture: equal parts of sand and clay, 3 parts of humus, 2 parts of peat and 0.5 parts of wood ash.
If you put manure on the bottom of the pit, preferably horse manure, then the roots will receive additional heat.
Before planting, seedlings must be kept in a growth stimulator. Then trim the roots if they are longer than 25 cm.

Fill the hole with a nutrient mixture, making a mound on which to place the straightened roots. Then cover with the rest of the potting mix. Deepen the root collar by 7-8 cm. You can water it with the addition of mineral fertilizer for roses. Spud the seedling, adding soil 10-15 cm.
Rose care
The Ural is an area of risky farming. Such a whimsical plant requires a lot of strength to endure all the vicissitudes of the weather. This is ensured by proper care.
Watering roses should be done once a week. But if it's a dry summer, then you need to do it more often. Watered at the root. Do not water with cold water - the roots will not develop and may get sick. Roses are very good at mulching. Watering should be deep, at least 30 cm. Otherwise, the plant will release surface roots that will constantly dry out. If you pour the bush, the root can rot. It is necessary to loosen the soil regularly.

It is important to properly fertilize the rose garden. The first feeding is needed at the beginning of the growing season, when the plants have started to grow. This is the middle of May in the Urals. It is best and easiest to use complex fertilizers, for example Kemiru. But traditional ammonium nitrate or urea will also be used. If you use dry fertilizer, then top dressing must be combined with watering, scattering the drug around the bush at a distance of at least 15 cm from the plant trunk. If the summer is unfavorable, it is necessary to help the plants to survive the weather disasters. For this, foliar feeding is performed with zircon or epin.
During the period of bud formation, water with a solution of calcium nitrate at the rate of 1 tbsp. l. 10 liters of water. During the period of active growth, fertilizing is required every 10 days until the end of July. Do not overfeed your roses. In this case, they will give lush greenery and few flowers.From the second half of July, the plant begins to prepare for winter. No more fertilizer is required.
Roses are susceptible to disease and pest attacks. To protect them from the most common disease, powdery mildew, it is necessary to spray the bush with a solution of soda, 40 g per 1 liter of water. This should be done from the beginning of active growth until the first decade of June, once a week. If the disease appears, HOM or Topaz should be used.

Rose pests are spider mites and rose aphids. Folk remedies are not very helpful here. The fight against these insects must be persistent and persistent. The drugs Iskra, Fufanon, Confidor, etc. are used.
If you plant nasturtium and marigolds among the roses, the likelihood of a pest attack will be much less.
Preparing for winter
Watering stops from mid-August. No need to cut fresh and wilting flowers or pluck buds. This will prevent the formation of new shoots. Spud the bush to a height of 15 cm and cover with mulch from dry leaf humus or cover with a film so that moisture does not get on the roots.
In the fall, before the onset of frost, the plants must be cut off. Then process with copper sulfate and spud. Climbing roses are removed from the supports and laid on the ground, pressing the lashes with hairpins.
In the Urals, sheltering roses for the winter is a responsible business. It is important to keep the bushes dry and cover in dry weather. There is no rush to do this work. Roses tolerate frosts well down to -7 ... -8 ° С. If you cover it early, then during warming, the shoots can sprout, and in winter it is harmful to the plant. There are many ways to hide. You can make a frame from scrap materials, fill it with spruce branches and close it with polyethylene on top. A very reliable cover with a bag, more precisely, a sleeve. A bag without a bottom is put on a bush, filled with dry foliage, grass or spruce branches. Then a bag is tied on top. For a climbing rose, they make a shelter from boxes or shields, filling it with the same spruce branches and covering it with polyethylene.
In the spring, there is no need to rush to open the roses. With the seeming warmth, the ground is still frozen. It is necessary to open the shelters from time to time for a short period so that there is no excess moisture. Then gradually begin to remove the elements of the shelter. And finally, by the end of April, roses are freed from winter "clothes".
And a little about secrets ...
The story of one of our readers Irina Volodina:
I was especially depressed by the eyes, surrounded by large wrinkles plus dark circles and swelling. How to remove wrinkles and bags under the eyes completely? How to deal with swelling and redness? But nothing makes a person look older or younger than his eyes.
But how to rejuvenate them? Plastic surgery? Recognized - not less than 5 thousand dollars. Hardware procedures - photorejuvenation, gas-liquid pilling, radiolifting, laser facelift? Slightly more affordable - the course costs 1.5-2 thousand dollars. And when to find all this time? And it's still expensive. Especially now. Therefore, for myself, I chose a different way ...
Read the article >>
Despite the harsh, sharply continental climate of the region, the dream of Ural gardeners about their own rose garden is quite realizable. The main thing is to choose a variety adapted to weather conditions, to study the peculiarities of planting and care.
Features of growing climbing roses in the Urals
The Ural region is characterized by difficult weather conditions for roses:
 Climbing roses for the Urals. The Rosarium Uetersen rose bush reaches a height of 3.5 m, but it also perfectly withstands pruning up to two meters
Climbing roses for the Urals. The Rosarium Uetersen rose bush reaches a height of 3.5 m, but it also perfectly withstands pruning up to two meters
- long frosty winters (down to -40 ° C);
- short summer;
- cold piercing winds;
- high snow cover;
- uneven distribution of precipitation;
- returnable spring frosts.
Moreover, on the plains of the Urals (west of the Ural Mountains), the climate is milder and humid. The natural conditions of the Trans-Urals (east of the Ural Range), where much less precipitation falls, is noticeably more severe, with pronounced features of the continental.Heat-loving climbing roses in such conditions do not fully reveal their varietal qualities: they do not reach the declared height, do not bloom again, do not fully open their buds. therefore adapted varieties of roses are chosen for growing in the Uralsadapted to the listed conditions: winter-hardy, unpretentious, with high immunity.
Review of varieties of climbing roses recommended for the Urals
The table contains a description of the varieties that are traditionally popular among the Ural gardeners:
| Variety | Description | Advantages |
| Flammentanz | One-flowering, deep red double buds up to 8 cm in diameter, collected in clusters of 3-7 pieces; sprawling bush, densely leafy, up to 2.5 m high; stems are tough, prickly, require strong support | Winter-hardy, disease-resistant, blooms profusely and for a long time (30-35 days) |
| Ilse Krohn Superior | Re-flowering; flowers are densely double, creamy white, 10-11 cm in diameter, appear one at a time or in brushes up to 3 pieces; the petals are large, curl as the bud opens | Winters well, strong immunity to diseases, flowers are resistant to precipitation |
| New Dawn | Re-flowering; flowers are semi-double, cupped, pearl pink with bright golden stamens in the center; tall bush, with long thin shoots | Frost-resistant, tolerates poor soils and partial shade, does not get sick |
| Rosarium Uetersen | Re-flowering; densely double (up to 100 petals) flowers of deep pink color appear one at a time or in lush brushes | Very winter hardy, resistant to rain and disease; unpretentious to the composition of the soil; suitable for cutting into bouquets |
| Super Excelsa | Re-flowering; double flowers of bright crimson color are collected in large brushes, appear throughout the summer; stunted bush (150-200 cm), spreading; suitable for vertical supports | Winter-hardy, while tolerating heat well; suitable for growing on a trunk; the bush is neat, the lashes fit easily for the winter |
| Westerland (Westerland) | Loose, large, fragrant flowers are grouped in inflorescences; the color of the buds varies from orange-yellow to salmon-apricot, depending on the stage of opening; sprawling bush, up to 1.7 m in height, suitable for single plantings | Winter hardy, resistant to powdery mildew and spotting; blooms early, blooms until late autumn |
All varieties presented in the table respond positively to decorative pruning of faded buds and tying. Moreover, some climbing roses in a short growing season show themselves better when grown in bush form.
Of all the varieties listed above, "Super Excels" is the most plastic. The bush is easily formed, the lashes are easily removed and bent down for the winter.
General principles of caring for roses in the Urals
 The shoots of the "Super Excels" rose easily fall on the support of any configuration
The shoots of the "Super Excels" rose easily fall on the support of any configuration
It should be remembered that even the most weather-adapted variety requires proper care and adherence to agricultural practices... For climbing roses, the same top dressing is recommended as for other variety groups. During the season, you need to feed at least three times.
- In late May and early June, organic matter and mineral nitrogen fertilizers are applied.
- In July, they are fed with complex nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium fertilizers.
- In early August, they are fed with phosphorus and potassium (See also the article ⇒ Phosphorus fertilizers for garden roses).
Pruning is carried out as needed: cut shoots older than 3 years old, weak, damaged stems, growth not ripened by autumn. In the first wave of flowering, wilting buds with a part of the peduncle are removed in order to provoke the re-formation of flowers. Closer to autumn, this should not be done, since the plant must prepare for wintering.
The duration of bud formation of once flowering varieties is regulated by cutting off some of the freshly flowering branches. As a result, prolonged flowering is obtained on replacement shoots.
 With appropriate pruning, "Flamentanz" blooms until the end of August
With appropriate pruning, "Flamentanz" blooms until the end of August
Expert recommendations: “The most difficult part of growing climbing roses is getting ready for winter. Before the shelter, the bushes are treated with iron vitriol for fungal diseases. Then the lashes are tied into one bundle and laid. Most of the bushes cannot be bent in one go without damaging the stems. You have to bend them in several passes. Laying roses on bare ground is not worth it, it is better to fix them on a dry substrate 20 cm from the ground. This creates the necessary air gap. At the end of the most crucial stage, a strong frame is built, on which Lutrasil-60 is laid and well fixed in 2 layers. "
Svetlana Aleksandrova is the chief agronomist of the Victoria gardening company (Magnitogorsk).
Tip # 1: It is convenient to use thick foam or plastic bottles stacked in a row as a substrate. And practical, and rodents "too tough", and the thawed snow will not flood.
A ventilation hole is provided in the shelter. Roses are fully wrapped when frost falls below -5 ° C
Spring awakening of a rose is a moment no less important than preparing for winter... Towards spring, the snow becomes dense and wet. The frame may not be able to withstand the weight of a snowdrift. A plant deprived of air will simply suffocate. Therefore, in March, the excess snow is raked, the shelter is ventilated if necessary. At the beginning of April, you can remove the second layer of covering material. It is not yet possible to fully open the rose, even if it is warm outside. The soil is still cold, the roots are dormant. The awakening of the root system and the aerial part of the plant should occur synchronously. At this time, you can carry out preventive treatment, sanitary pruning, after which the bush should be covered again. Finally, they remove the shelter after the soil has completely thawed (See also the article ⇒ When to remove the shelter of roses).
Advice number 2: To bring back to life a weakened rose that has difficult to endure wintering, immediately after leaving the shelter, stimulate the work of the root system. For this, the plant is fed with a solution of "Zircon" and "Tsitovita". In 10 liters of water, dissolve 1 ampoule of each drug, and water the bush under the root.
Typical mistakes of flower growers when growing roses in the Urals
- There is an opinion that roses planted in summer, in July-August, tolerate wintering better, since they manage to get stronger before the onset of frost. This is absolutely not true. About a month after planting, having exhausted the reserves of nutrients from its own root system, the seedling is actively moving into growth. Additional forces are required for the formation of growth. In the short Ural summer, there is not enough time for young growth to ripen. As a result, the plant leaves in the winter weakened, unripe stems vytryut, rot, become the cause of the death of the entire plant. The optimal time for an autumn transplant is the second half of September, for a spring one - the end of April.
- Novice gardeners often set up a flower garden according to the recommendations of landscape designers, taken from foreign magazines. For the Ural region, this approach is not acceptable. You need to plan the location of the rose garden according to the rules that take into account local climatic features (See also the article ⇒ DIY rose garden). Basic site requirements:
- protection from drafts;
- maximum solar illumination;
- southern or southeastern exposure;
- no stagnation of moisture (the depth of groundwater is at least 100 cm from the soil level).
It is categorically impossible to plant roses along the walls of houses, next to deaf fences, in the shade of other shrubs and trees, in flooded areas.
Answers to topical questions of gardeners
 A healthy seedling has at least three smooth green shoots 20-30 cm long with developed buds
A healthy seedling has at least three smooth green shoots 20-30 cm long with developed buds
Question number 1: What seedlings to choose for the climatic conditions of the Urals: grafted or on their own roots?
In the Urals, it is recommended to plant grafted roses.Unlike rooted ones, they are more resistant to frost, bacterial and fungal diseases. The best stock for the Ural climate is the Kanin rose. Ultimate endurance is naturally built into this rose hip. Grafted cuttings take root from 2 to 4 weeks, and self-rooted seedlings form a full-fledged root system for more than three years. All this time, a rose grown on its own roots is vulnerable to adverse external factors and diseases.
Question # 2: Do I need to huddle roses in front of the shelter?
Hilling bushes with sawdust, peat, soil, damp leaves and other materials in the climatic conditions of the Urals does more harm than good. Unlike other regions of Russia, the shoots do not have time to wood during the growing season, so they often undermine by the spring.
Rate the quality of the article. Your opinion is important to us:
A selection of tips for growing roses
Presented the best tips in pictures for planting, care, pest and disease control in roses ⇓
 To survive the harsh Ural winters, a persistent character is needed, and not only for people, but also for plants. Therefore, the criteria for selecting flowers for gardens in the middle lane are more stringent than for the southern regions of the country. Despite this, gardeners of cold regions successfully grow even capricious thorny rose beauties. The Ural climate is known to be characterized by late spring, short summers and severe winters.
To survive the harsh Ural winters, a persistent character is needed, and not only for people, but also for plants. Therefore, the criteria for selecting flowers for gardens in the middle lane are more stringent than for the southern regions of the country. Despite this, gardeners of cold regions successfully grow even capricious thorny rose beauties. The Ural climate is known to be characterized by late spring, short summers and severe winters.
To withstand such conditions, plants must initially be regionalized in the local climate. By the degree of survival rate, the seedlings grown in the Ural nurseries are in the lead. Gardeners give the second place to Canadian roses, because the climate of this country is similar to ours. But real Canadian roses, unfortunately, are rare. This category of plants is too attractive to buyers, so it is most often counterfeited. It is better to buy Canadian varieties only from a reliable supplier, and not on the market.
The second selection criterion is vaccination. According to statistics, varieties of roses grafted in the Urals tolerate winters much easier and do not freeze due to increased immunity. The stock for a varietal rose, usually, is a rose hip - its immune system is much more hardy than that of a rose. The best varieties of roses for growing in the Urals are listed HERE
How to plant roses in spring
The choice of planting material
 Having decided on the variety of roses, you can go for seedlings. Both self-rooted and grafted seedlings can be on sale. On which graft the seedling is grafted, its winter hardiness depends. “Rosa Kanina” is the best rootstock for the conditions of the Urals. The seedling must have at least 3 shoots, on which well-developed buds are well defined. The stem should be 20-30 cm long and green and smooth.
Having decided on the variety of roses, you can go for seedlings. Both self-rooted and grafted seedlings can be on sale. On which graft the seedling is grafted, its winter hardiness depends. “Rosa Kanina” is the best rootstock for the conditions of the Urals. The seedling must have at least 3 shoots, on which well-developed buds are well defined. The stem should be 20-30 cm long and green and smooth.
When you buy a plant with open roots, it is possible to inspect them well. Living healthy roots are immediately visible. Such roots should be wrapped in a damp cloth during transportation. If you buy a plant whose roots are covered with a lump of earth and a film, then it does not need to be unpacked until planting. Open roots should be disinfected in a solution of copper sulfate or phytosporin. If the roots are dry, place them in a bucket of water for 24 hours. Seedlings purchased in the fall can be stored in a cool place in wet sand. If the planting is not immediate, you can store the seedlings in a damp cloth, wrapped in plastic.
Choosing a landing site
 Due to the fact that spring comes late in the Urals, they try to plant roses from the southern side. But a completely open area is not very profitable, since the flowering period is significantly accelerated, and the flowers fade in the heat. It is best to think over a light partial shade with the help of light-leaved shrubs or trees. The roses are planted near them so that in the hottest time of the day they are protected by the foliage of the "neighbors".
Due to the fact that spring comes late in the Urals, they try to plant roses from the southern side. But a completely open area is not very profitable, since the flowering period is significantly accelerated, and the flowers fade in the heat. It is best to think over a light partial shade with the help of light-leaved shrubs or trees. The roses are planted near them so that in the hottest time of the day they are protected by the foliage of the "neighbors".
It is advisable to select high places of the site for the rose garden. There, the degree of soil freezing is always less, which means that the roots will wake up faster.This will save the plant from high humidity, which is typical for lowlands. Too much moisture provokes the development of rot and fungal infections. The Urals are characterized by strong winds, with a cold front coming from both the north and the west. From these directions (north, north-west and north-east) roses need protection in the form of buildings, gazebos, living coniferous hedges, etc. But the wall should be at such a distance that no shadow is cast on the bushes.
When and how to plant roses in spring
 For the Ural climate, spring plantings are desirable, and their period is somewhat shorter than in more southern regions. The planting season begins in May, when the soil warms up to 10 ° C. Gardeners determine the optimal time for dandelions: as soon as they bloom, it is time to plant rose bushes. The grafted seedlings are planted first, because the rose hips are not afraid of sudden late frosts. Own-rooted roses - not earlier than May 15th. If you are late with planting, the rose will not have time to grow stronger in a short summer and will leave for the winter without a lignified trunk. This means that it will freeze easily.
For the Ural climate, spring plantings are desirable, and their period is somewhat shorter than in more southern regions. The planting season begins in May, when the soil warms up to 10 ° C. Gardeners determine the optimal time for dandelions: as soon as they bloom, it is time to plant rose bushes. The grafted seedlings are planted first, because the rose hips are not afraid of sudden late frosts. Own-rooted roses - not earlier than May 15th. If you are late with planting, the rose will not have time to grow stronger in a short summer and will leave for the winter without a lignified trunk. This means that it will freeze easily.
Thorny beauties like slightly acidic soils with a high humus content. The base of the soil can be loam. It is good when planting to lay on the bottom of the pit and sprinkle with earth the rotted horse manure, which will warm the roots. Bushes are not planted directly into the manure so as not to burn the young roots. The optimal composition of the earth: 1 part clay + 1 part sand + 3 parts humus + 2 parts peat + 0.5 parts wood ash. It does not hurt to immediately apply a special fertilizer for roses. Landing rules:
♦ The depth of the planting pit is at least half a meter.
♦ Purchased seedlings are dipped in a solution of water with a growth stimulator for 3-4 hours so that they are saturated with moisture.
♦ Too long roots (over 20 cm) are shortened, stimulating the growth of lateral roots.
♦ Remove the paraffin from the aerial part and slightly prune the branches (to a healthy green color).
♦ An important point: a slightly recessed landing. Many gardeners of the Urals argue that tea, English varieties and floribundas survive better in frosts if the grafting site is not 5 cm below the soil level, but 7-8 cm, i.e. a little deeper. Accordingly, for climbing roses you need 12-15 cm. Such plantings can be less sheltered, and some owners have completely abandoned shelter, having bought varieties with high frost resistance.
♦ When planting, the roots of the rose are straightened so that they only go from top to bottom, and not wrap themselves in a ring. A planting mound can help this arrangement: a fertile soil is poured onto the bottom of the pit, a seedling is placed on top, the roots are straightened along the mound and sprinkled.
♦ When planting a mound, watered after the rose has been planted. With a normal planting, you can first shed the roots, and then cover with soil.
♦ After planting, the bush is invariably spud up to a height of 15 cm. This is necessary so that the water does not quickly evaporate. The earth will also protect delicate branches from the scorching sun, because at the time of engraftment they dry out very quickly.
Rose care
 The Ural is an area of risky farming. Such a whimsical plant like a rose takes a lot of strength to endure all the vicissitudes of the weather. This is ensured by proper care. Watering roses should be done once a week. But if it's a dry summer, then you need to do it more often. Watered at the root. Do not water with cold water - the roots will not develop and may get sick. Roses are very good at mulching. Watering should be deep, at least 30 cm. Otherwise, the plant will release surface roots that will constantly dry out. If you pour the bush, the root can rot. It is necessary to loosen the soil regularly.
The Ural is an area of risky farming. Such a whimsical plant like a rose takes a lot of strength to endure all the vicissitudes of the weather. This is ensured by proper care. Watering roses should be done once a week. But if it's a dry summer, then you need to do it more often. Watered at the root. Do not water with cold water - the roots will not develop and may get sick. Roses are very good at mulching. Watering should be deep, at least 30 cm. Otherwise, the plant will release surface roots that will constantly dry out. If you pour the bush, the root can rot. It is necessary to loosen the soil regularly.
It is important to fertilize the roses correctly. The first feeding is needed at the beginning of the growing season, when the plants have started to grow. This is the middle of May in the Urals. It is best and easiest to use complex fertilizers, for example, "Kemiru". But traditional ammonium nitrate or urea will also be used.If you use dry fertilizer, then top dressing must be combined with watering, scattering the drug around the bush at a distance of at least 15 cm from the plant trunk. If the summer is unfavorable, it is necessary to help the plants to survive the weather disasters. For this, foliar feeding is performed with zircon or epin. During the period of bud formation, water with a solution of calcium nitrate at the rate of 1 tbsp. l. 10 liters of water. During the period of active growth, fertilizing is required every 10 days until the end of July. Do not overfeed your roses. In this case, they will give lush greenery and few flowers. From the second half of July, the plant begins to prepare for winter. No more fertilizer is required. Roses are susceptible to disease and pest attacks. To protect them from the most common disease, powdery mildew, it is necessary to spray the bush with a solution of soda, 40 g per 1 liter of water. This should be done from the beginning of active growth until the first decade of June, once a week. If the disease has appeared, you should use the drugs "HOM" or "Topaz". Rose pests are spider mites and rose aphids. Folk remedies are not very helpful here. The fight against these insects must be persistent and persistent. Use drugs "Iskra", "Fufanon", "Confidor", etc. If you plant nasturtium and marigolds among the roses, the likelihood of attack by pests will be much less.
BUY ROSE SEEDLINGS IN THE NURSERY
 The Scientific and Production Association "Sady Rossii" has been introducing the latest achievements in the selection of vegetable, fruit, berry and ornamental crops into the wide practice of amateur gardening for 30 years. In the work of the association, the most modern technologies are used, a unique laboratory for microclonal reproduction of plants has been created. The main tasks of NPO Sady Rossii is to provide gardeners with high-quality planting material for popular varieties of various garden plants and novelties of world selection. Delivery of any planting material (seeds, onions, seedlings) is carried out by Russian post. We are waiting for you for shopping: NPO "GARDENS OF RUSSIA"
The Scientific and Production Association "Sady Rossii" has been introducing the latest achievements in the selection of vegetable, fruit, berry and ornamental crops into the wide practice of amateur gardening for 30 years. In the work of the association, the most modern technologies are used, a unique laboratory for microclonal reproduction of plants has been created. The main tasks of NPO Sady Rossii is to provide gardeners with high-quality planting material for popular varieties of various garden plants and novelties of world selection. Delivery of any planting material (seeds, onions, seedlings) is carried out by Russian post. We are waiting for you for shopping: NPO "GARDENS OF RUSSIA"

Once upon a time, growing roses in the Urals seemed impossible. The weather conditions of these places create problems for the cultivation of even less fastidious crops. But breeders work tirelessly, and now lemons, grapes, and roses grow in the Urals.
Once upon a time, growing roses in the Urals seemed impossible. The weather conditions of these places create problems for the cultivation of even less fastidious crops. But breeders work tirelessly, and now lemons, grapes, and roses grow in the Urals.
Content
- 1. Where to start?
- 2. The choice of planting material
- 3. Planting seedlings
- 4. Caring for roses
- 5. Preparing for winter
Where to begin?
Similar publications
 To survive the harsh Ural winters, a persistent character is needed, and not only for people, but also for plants. Therefore, the criteria for selecting flowers for gardens in the middle lane are more stringent than for the southern regions of the country. Despite this, gardeners of cold regions successfully grow even capricious thorny rose beauties. The Ural climate is known to be characterized by late spring, short summers and severe winters.
To survive the harsh Ural winters, a persistent character is needed, and not only for people, but also for plants. Therefore, the criteria for selecting flowers for gardens in the middle lane are more stringent than for the southern regions of the country. Despite this, gardeners of cold regions successfully grow even capricious thorny rose beauties. The Ural climate is known to be characterized by late spring, short summers and severe winters.
To withstand such conditions, plants must initially be regionalized in the local climate. By the degree of survival rate, the seedlings grown in the Ural nurseries are in the lead. Gardeners give the second place to Canadian roses, because the climate of this country is similar to ours. But real Canadian roses, unfortunately, are rare. This category of plants is too attractive to buyers, so it is most often counterfeited. It is better to buy Canadian varieties only from a reliable supplier, and not on the market.
The second selection criterion is vaccination. According to statistics, varieties of roses grafted in the Urals tolerate winters much easier and do not freeze due to increased immunity. The stock for a varietal rose, usually, is a rose hip - its immune system is much more hardy than that of a rose. The best varieties of roses for growing in the Urals are listed HERE
How to plant roses in spring
The choice of planting material
 Having decided on the variety of roses, you can go for seedlings. Both self-rooted and grafted seedlings can be on sale. On which graft the seedling is grafted, its winter hardiness depends. “Rosa Kanina” is the best rootstock for the conditions of the Urals. The seedling must have at least 3 shoots, on which well-developed buds are well defined. The stem should be 20-30 cm long and green and smooth.
Having decided on the variety of roses, you can go for seedlings. Both self-rooted and grafted seedlings can be on sale. On which graft the seedling is grafted, its winter hardiness depends. “Rosa Kanina” is the best rootstock for the conditions of the Urals. The seedling must have at least 3 shoots, on which well-developed buds are well defined. The stem should be 20-30 cm long and green and smooth.
When you buy a plant with open roots, it is possible to inspect them well. Living healthy roots are immediately visible. Such roots should be wrapped in a damp cloth during transportation. If you buy a plant whose roots are covered with a lump of earth and a film, then it does not need to be unpacked until planting. Open roots should be disinfected in a solution of copper sulfate or phytosporin. If the roots are dry, place them in a bucket of water for 24 hours. Seedlings purchased in the fall can be stored in a cool place in wet sand. If the planting is not immediate, you can store the seedlings in a damp cloth, wrapped in plastic.
Choosing a landing site
 Due to the fact that spring comes late in the Urals, they try to plant roses from the southern side. But a completely open area is not very profitable, since the flowering period is significantly accelerated, and the flowers fade in the heat. It is best to think over a light partial shade with the help of light-leaved shrubs or trees. The roses are planted near them so that in the hottest time of the day they are protected by the foliage of the "neighbors".
Due to the fact that spring comes late in the Urals, they try to plant roses from the southern side. But a completely open area is not very profitable, since the flowering period is significantly accelerated, and the flowers fade in the heat. It is best to think over a light partial shade with the help of light-leaved shrubs or trees. The roses are planted near them so that in the hottest time of the day they are protected by the foliage of the "neighbors".
It is advisable to select high places of the site for the rose garden. There, the degree of soil freezing is always less, which means that the roots will wake up faster. This will save the plant from high humidity, which is typical for lowlands. Too much moisture provokes the development of rot and fungal infections. The Urals are characterized by strong winds, with a cold front coming from both the north and the west. From these directions (north, north-west and north-east) roses need protection in the form of buildings, gazebos, living coniferous hedges, etc. But the wall should be at such a distance that no shadow is cast on the bushes.
When and how to plant roses in spring
 For the Ural climate, spring plantings are desirable, and their period is somewhat shorter than in more southern regions. The planting season begins in May, when the soil warms up to 10 ° C. Gardeners determine the optimal time for dandelions: as soon as they bloom, it is time to plant rose bushes. The grafted seedlings are planted first, because the rose hips are not afraid of sudden late frosts. Own-rooted roses - not earlier than May 15th. If you are late with planting, the rose will not have time to grow stronger in a short summer and will leave for the winter without a lignified trunk. This means that it will freeze easily.
For the Ural climate, spring plantings are desirable, and their period is somewhat shorter than in more southern regions. The planting season begins in May, when the soil warms up to 10 ° C. Gardeners determine the optimal time for dandelions: as soon as they bloom, it is time to plant rose bushes. The grafted seedlings are planted first, because the rose hips are not afraid of sudden late frosts. Own-rooted roses - not earlier than May 15th. If you are late with planting, the rose will not have time to grow stronger in a short summer and will leave for the winter without a lignified trunk. This means that it will freeze easily.
Thorny beauties like slightly acidic soils with a high humus content. The base of the soil can be loam. It is good when planting to lay on the bottom of the pit and sprinkle with earth the rotted horse manure, which will warm the roots. Bushes are not planted directly into the manure so as not to burn the young roots. The optimal composition of the earth: 1 part clay + 1 part sand + 3 parts humus + 2 parts peat + 0.5 parts wood ash. It does not hurt to immediately apply a special fertilizer for roses. Landing rules:
♦ The depth of the planting pit is at least half a meter.
♦ Purchased seedlings are dipped in a solution of water with a growth stimulator for 3-4 hours so that they are saturated with moisture.
♦ Too long roots (over 20 cm) are shortened, stimulating the growth of lateral roots.
♦ Remove the paraffin from the aerial part and slightly prune the branches (to a healthy green color).
♦ An important point: a slightly recessed landing. Many gardeners of the Urals argue that tea, English varieties and floribundas survive better in frosts if the grafting site is not 5 cm below the soil level, but 7-8 cm, i.e. a little deeper. Accordingly, for climbing roses you need 12-15 cm.Such plantings can be less sheltered, and some owners have completely abandoned shelter, having bought varieties with high frost resistance.
♦ When planting, the roots of the rose are straightened so that they only go from top to bottom, and not wrap themselves in a ring. A planting mound can help this arrangement: a fertile soil is poured onto the bottom of the pit, a seedling is placed on top, the roots are straightened along the mound and sprinkled.
♦ When planting a mound, watered after the rose has been planted. With a normal planting, you can first shed the roots, and then cover with soil.
♦ After planting, the bush is invariably spud up to a height of 15 cm. This is necessary so that the water does not quickly evaporate. The earth will also protect delicate branches from the scorching sun, because at the time of engraftment they dry out very quickly.
Rose care
 The Ural is an area of risky farming. Such a whimsical plant like a rose takes a lot of strength to endure all the vicissitudes of the weather. This is ensured by proper care. Watering roses should be done once a week. But if it's a dry summer, then you need to do it more often. Watered at the root. Do not water with cold water - the roots will not develop and may get sick. Roses are very good at mulching. Watering should be deep, at least 30 cm. Otherwise, the plant will release surface roots that will constantly dry out. If you pour the bush, the root can rot. It is necessary to loosen the soil regularly.
The Ural is an area of risky farming. Such a whimsical plant like a rose takes a lot of strength to endure all the vicissitudes of the weather. This is ensured by proper care. Watering roses should be done once a week. But if it's a dry summer, then you need to do it more often. Watered at the root. Do not water with cold water - the roots will not develop and may get sick. Roses are very good at mulching. Watering should be deep, at least 30 cm. Otherwise, the plant will release surface roots that will constantly dry out. If you pour the bush, the root can rot. It is necessary to loosen the soil regularly.
It is important to fertilize the roses correctly. The first feeding is needed at the beginning of the growing season, when the plants have started to grow. This is the middle of May in the Urals. It is best and easiest to use complex fertilizers, for example, "Kemiru". But traditional ammonium nitrate or urea will also be used. If you use dry fertilizer, then top dressing must be combined with watering, scattering the drug around the bush at a distance of at least 15 cm from the plant trunk. If the summer is unfavorable, it is necessary to help the plants to survive the weather disasters. For this, foliar feeding is performed with zircon or epin. During the period of bud formation, water with a solution of calcium nitrate at the rate of 1 tbsp. l. 10 liters of water. During the period of active growth, fertilizing is required every 10 days until the end of July. Do not overfeed your roses. In this case, they will give lush greenery and few flowers. From the second half of July, the plant begins to prepare for winter. No more fertilizer is required. Roses are susceptible to disease and pest attacks. To protect them from the most common disease, powdery mildew, it is necessary to spray the bush with a solution of soda, 40 g per 1 liter of water. This should be done from the beginning of active growth until the first ten days of June, once a week. If the disease has appeared, you should use the drugs "HOM" or "Topaz". Rose pests are spider mites and rose aphids. Folk remedies are not very helpful here. The fight against these insects must be persistent and persistent. Use drugs "Iskra", "Fufanon", "Confidor", etc. If you plant nasturtium and marigolds among the roses, the likelihood of attack by pests will be much less.
BUY ROSE SEEDLINGS IN THE NURSERY
 The Scientific and Production Association "Sady Rossii" has been introducing the latest achievements in the selection of vegetable, fruit, berry and ornamental crops into the wide practice of amateur gardening for 30 years. In the work of the association, the most modern technologies are used, a unique laboratory for microclonal reproduction of plants has been created. The main tasks of NPO Sady Rossii is to provide gardeners with high-quality planting material for popular varieties of various garden plants and novelties of world selection. Delivery of any planting material (seeds, onions, seedlings) is carried out by Russian post. We are waiting for you for shopping: NPO "GARDENS OF RUSSIA"
The Scientific and Production Association "Sady Rossii" has been introducing the latest achievements in the selection of vegetable, fruit, berry and ornamental crops into the wide practice of amateur gardening for 30 years. In the work of the association, the most modern technologies are used, a unique laboratory for microclonal reproduction of plants has been created. The main tasks of NPO Sady Rossii is to provide gardeners with high-quality planting material for popular varieties of various garden plants and novelties of world selection. Delivery of any planting material (seeds, onions, seedlings) is carried out by Russian post. We are waiting for you for shopping: NPO "GARDENS OF RUSSIA"




