Content
- 1 Preparing for landing
- 2 Planting process
- 3 Actinidia care
- 4 Harvesting
- 5 Wintering
- 6 Reproduction
- 7 Disease prevention
- 8 Pest control
- 9 How actinidia reproduces
- 10 Propagation of actinidia by cuttings
- 11 Actinidia from seeds at home
- 12 Planting actinidia in open ground
- 13 How to care for actinidia outdoors
- 14 How to distinguish male and female actinidia, we look at the video:
- 15 Diseases and pests
- 16 Harvesting
- 17 Wintering actinidia
- 18 Types and varieties of actinidia with photos and names
- 19 Useful properties of actinidia
- 20 When to plant
- 21 Landing technology
- 22 Care advice
- 23 Pruning rules
- 24 Reproduction methods
- 25 Diseases and pests
- 26 Organization of wintering
- 27 Types and varieties
An amazing liana from the Actinidiaceae family with small fragrant fruits that resemble kiwi in cut and taste like kiwi is not such a gimmick on personal plots.
However, the fruits of actinidia are delicious and are those exotic fruits that everyone calls kiwi.
Planting and caring for actinidia is no more difficult than for other garden perennials, and in the temperate zone, adult plants are able to endure winter even without shelter. It is necessary to work hard once, with a little effort and patience, until the plant gets stronger, then additional efforts will not be required in the future.
Ornamental greenery in summer and delicious unusual fruits in autumn will delight your family for at least half a century.
Preparing for landing

In our latitudes, species of actinidia are grown with smaller and less shaggy fruits than those of their historical ancestors, the Chinese kiwi.
The most popular species is kolomikta, which, due to its excellent winter hardiness, can be successfully cultivated both in the Moscow region and in the Leningrad region. Arguta, which has the largest fruits, is no less popular.
Landing dates

The best time for planting actinidia is early spring, when sap flow has not yet begun and the buds have not blossomed. Autumn planting dates are also permissible, but here it is important to guess the time of the onset of stable frosts, because the plants should be planted 2-3 weeks before this period.
Selection of seedlings
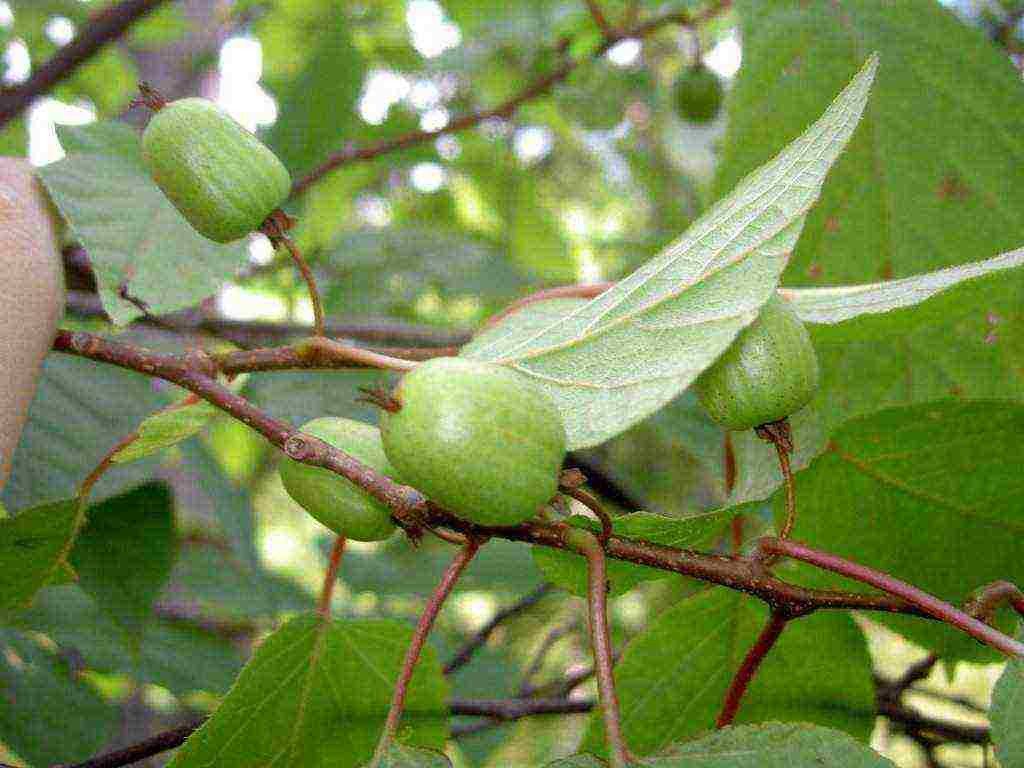

Actinidia has one feature that obliges us to take a responsible approach to the acquisition of planting material - the dioecious culture. This means that there are both female and male plants. And for successful pollination, and therefore, fruiting, it is important to plant both. However, the sex of the future vine can only be distinguished during flowering. With large planting volumes, one male plant is sufficient for pollination of 5-10 female plants.
Among the varieties, kolomikta and arguta are self-fertile, that is, they can be pollinated with the pollen of their own flowers. But this is very rare. The “Issaya” variety possesses such properties.

It is preferable to plant actinidia with material obtained by cuttings. Unlike the option with seedlings, the preservation of varietal qualities will be guaranteed.
Other advantages when choosing seedlings are:
- age not more than three years;
- container type of plants.
Older vines take root much worse, and the open root system is very capricious: exposure to sunlight and wind can be destructive.
Choosing a place on the site
When choosing a place for growing actinidia in the open field, you should remember about the natural growing conditions of vines in the wild. This is a native of warm countries, where in the openwork penumbra of rare neighbors, he finds support for his crown.

Domestic breeders have bred actinidia varieties that can successfully endure winter frosts in the middle lane, however, for the most part, the culture prefers calm, wind-protected places. The walls of houses, outbuildings, gazebos will be an excellent support at the same time. Otherwise, the installation of a trellis will be required.
"For the ripening of fruits, the sun is necessary, but the plant does not like direct sunlight."
They are especially destructive for newly planted babies, who shade with an excess of sun.
Constant flooding will also have a bad effect, therefore, when planting culture near houses or other buildings, it is necessary to notice where the drain passes. It is recommended to make the planting hole no closer than 0.6 m from the wall.
Neighbors

If, nevertheless, the vine is planted in the garden, currant or hazel bushes will become good neighbors for it, but friendship is unlikely to come out with an apple tree. Considering that the roots of actinidia grow in a horizontal plane, it will be correct to plant it a few meters from the fruit tree.
Soil preparation

It grows well on soils poor in organic matter, but it always responds to fertile land with more active growth. It is important that there is no alkaline reaction - this inhibits the seedling. Weakly acidic and close to neutral soil is best suited for growing.
For planting, the soil is prepared as follows: the top fertile layer extracted from the prepared planting pit is mixed with:
| humus (necessarily rotted, not fresh!) | 8-10 kg |
| superphosphate | 150-200 g |
| potash fertilizer | 70-80 g |
| ash | 250-300 g |
Such a "dressing" will provide adequate nutrition for a young plant for a long time. Open roots should not come into direct contact with the fertilizer granules, so the prepared composition is sprinkled with plain earth.
Planting process

Plant pits should be prepared in advance, at least two weeks before planting. So the soil can settle under the influence of natural conditions and in the best way ensure the fixation of the seedlings when planting. The pits will fit 50 x 50 x 50 cm.
At the bottom, drainage is laid with a layer of 10-15 cm from broken brick or expanded clay. Decide at what distance to plant plants from each other, based on the selected species:
- one meter is enough for kolomikta;
- for arguta it will be wider - 1.5-2 m, this species is larger;
- for the formation of a hedge, the distance is reduced to 0.5-0.7 m.
Attention! "The root collar must be above the surface of the ground, it cannot be buried."
After planting seedlings:
- poured abundantly with water (at least one bucket under each);
- the hole is mulched with bark or other material;
Plants are shaded from bright sunlight with a cloth or other breathable material.
Actinidia care

It is most important to properly care for the actinidia in the first years after planting, until the plant is strong and begins to bear fruit. Sustainable fruiting begins in the 7th year, but it lasts more than 30 years.
Support

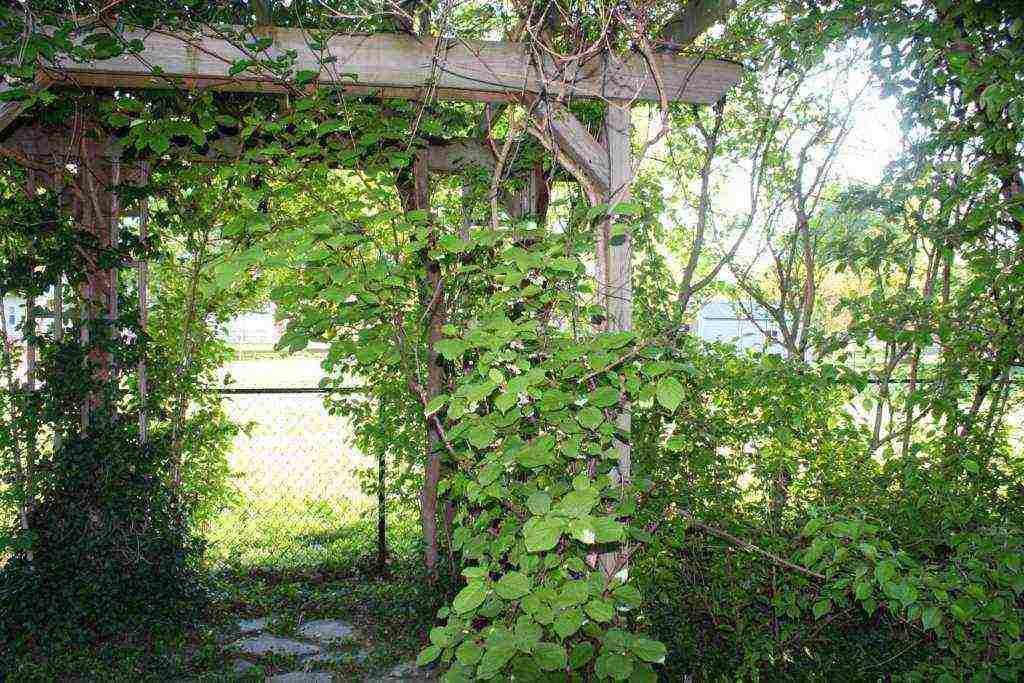
Based on the fact that all types of actinidia are woody vines, it is clear that when growing, you cannot do without a support. Without it, the plant is more difficult to care for, it develops more slowly, and the yield decreases.
"Any solid structure is suitable as a support: concrete, wood, metal."
The forms can also be different:
- arcuate. This is an excellent design solution that will allow you to easily harvest the crop, as the bulk of it is formed in the upper part of the vine;
- a trellis like a grape, when vertical pillars are crossed by horizontal elements;
- any wall or hedge. It should include details that allow the lashes to cling, because they have no air roots.
For varieties with poor frost resistance that need shelter, it is relevant to mount removable trellises that are inserted into metal pipes. For the winter, they can be pulled out together with the stems fixed to them and put on the ground, covering until spring.
Watering frequency

To reduce the frequency of watering in summer, root mulching of the soil will allow. It is very important that it does not dry out as the plant can shed its leaves. They grow back slowly, and this is fraught with problems with the future overwintering. On hot days, the vine is responsive to spraying. It is better to do it twice a day - in the morning and in the evening.
Top dressing
Like any garden plant, actinidia needs feeding. They promote the formation of new buds, increase yields and increase the winter hardiness of plants.
During the season, they must be carried out 3 times:
| In early spring | 35 g / sq. m of nitrogen fertilizers and 20 g / sq. m of phosphorus and potash |
| Before the formation of ovaries | 15-20 g / sq. m nitrogen and 10 g / sq. m of phosphorus and potash. |
| After harvest | phosphorus and potash 20 g / sq. m. |
Feeding is acceptable both in solid and dissolved in water. In the first case, you need to sprinkle the fertilizer with a layer of earth of at least 10 cm.
Actinidia pruning rules
Formative pruning of actinidia allows you to give it an attractive, well-groomed appearance, increase productivity by creating an optimal crown density. It must be carried out before the activation of the movement of the juice, otherwise, through the wounds, vitality will be depleted in the form of flowing juice.

Lateral shoots are removed at a distance of two internodes from the last berry. During the growing season, young shoots are cut at a distance of the 5-7th internode from the last ovary. An indicator of the required cutting point can be when the branch reaches the edge of the vertical support pillar.
The cut activates the formation of two new shoots, which, upon reaching the edge of the horizontal support, are also pruned. The next emerging shoots are allowed to go in opposite directions in order to cut them off again at the ends of the support.

Sanitary pruning is carried out in the second half of September in order to remove diseased and damaged parts. You can do this in the spring.
Rejuvenating pruning is carried out after 8-10 years of cultivation, leaving a stump with a length of 30-40 cm.
Harvesting

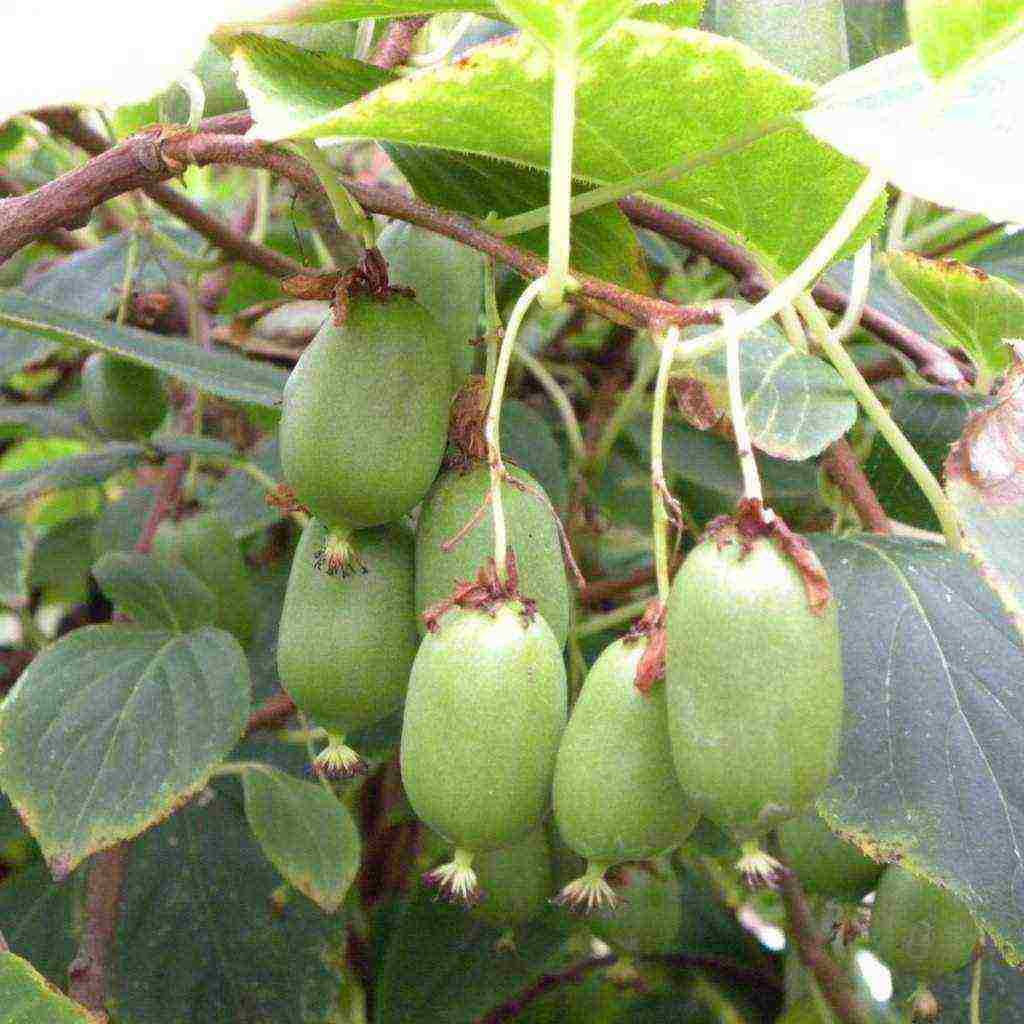
The long-awaited fruits may appear only in 5-7 years. Their ripening is extended in time and can occur from August to September. The size of the berries is much smaller than that of our usual kiwi, and the total yield varies depending on the variety and age of the plant. It can be from 5 to 40 kg per bush.
Attention! "After harvesting the fruits, the plant must be fed."
Wintering
The question of the need to shelter vines for the winter most often worries gardeners. For young plants that have not gained strength, the answer is unequivocally positive. Peat, spruce branches or just dry leaves are laid in a layer of about 20 cm.

It will not be superfluous to leave poison for rodents in such a hut. The plants themselves are not of interest to them, but the design is very tempting for arranging nests.
Breeders are constantly working to improve the winter hardiness of the varieties being bred. The greatest progress in this direction has been made for the actinidia kolomikta, the varieties of which are able to withstand severe winters without shelter.
Reproduction

The classic breeding methods of a liana-shaped beauty are cuttings, layers and seeds.A person interested in the result will not take risks and will get guaranteed good material in the nursery. When time suffers, and creativity is torn out, any tactic has a right to exist.
Lignified cuttings
This method is most familiar to summer residents. Such cuttings are harvested in the fall and, tied in a bunch, are sent until spring for storage in a cool, safe place, after placing them in the sand.
In the spring, they are planted in a greenhouse at a slight angle with a distance between the twigs of 5-6 cm. When signs of active growth appear, indicating the rooting of future plants, the covering material can be removed. They remain in this form until autumn. They need to be covered again for the winter. Overwintered seedlings are ready for planting in a permanent place.
You can also use green cuttings. They are prepared in June and, without any storage, are also planted under shelter in moist soil. Spray daily until roots appear, which usually appear after two weeks. The survival rate of such cuttings is even higher than that of lignified ones.
Seeds

The specimens that emerged from seeds are more resistant to climatic conditions, however, species characteristics may be lost. Full-fledged seeds selected in the fall must undergo stratification. The cultivation process is carried out as follows:
- In December, the seeds are soaked in water at room temperature and, after swelling, are placed in sand, after wrapping them in cloth.
- For two months they are kept at a temperature of 15-20 grams. C, and two more - at 3-5 gr. WITH.
- Placed in warmth for germination.
- The sprouted seeds are planted in fertile soil.
- With the onset of stable heat, the seedlings are transferred to the site.
- They are sheltered for the winter. It can be planted in a permanent place after two years.
Arc layering

This simple and reliable method includes the following steps:
- at the end of May, grooves under the bush are being prepared;
- the selected shoots are laid on the bottom and fixed in them;
- the shoots are pinched, the grooves are covered;
- the shoots that have emerged from the buds are separated by the next autumn.
Disease prevention

Among the possible diseases of actinidia, which occur extremely rarely, the following are known:
- phylosticosis;
- ramulariasis;
- powdery mildew;
- fruit and gray rot.
These diseases are associated with damage to green leaves and fruit pulp and require immediate treatment with fungicides such as Fozalon, Vertimek, Actellik. Treatment is carried out with folk remedies. Soap solution, calendula tincture, tobacco dust will do.
"For the purpose of prevention, a double treatment with a 1% solution of Bordeaux mixture is used in early spring with an interval of two weeks."
Pest control
To combat actinidia pests - leaf beetles, lacewings, bark beetles, moths - there is a wide range of effective and safe insecticides. They must be used according to the instructions attached to the drug.

Every gardener is interested in seeing the results of his efforts as soon as possible. New varieties of traditional perennials promise high yields and excellent fruits. Less common crops such as mini kiwi raise doubts and even apprehension, but in vain. Planting and caring for actinidia will not cause much trouble for the gardener, but in addition to exotic fruits that can surprise guests, your garden will acquire another decorative zest that lasts even in winter.
Actinidia (Actinidia) is a woody liana of the Actinidia family. The name of the plant is translated as a ray. In the natural environment, it is found in Southeast Asia, the Himalayas, and the Far East. China is considered the homeland.
It has been cultivated in European countries since 1958. Delicious actinidia is a plant whose fruit is the well-known kiwi. In the gardens of a temperate climatic zone, species are grown that give smaller fruits and are not so hairy.
Botanical description
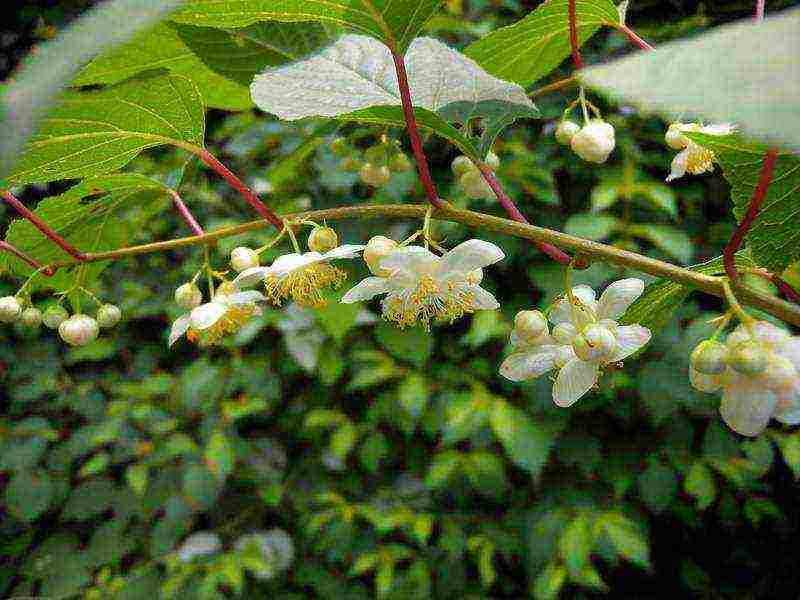
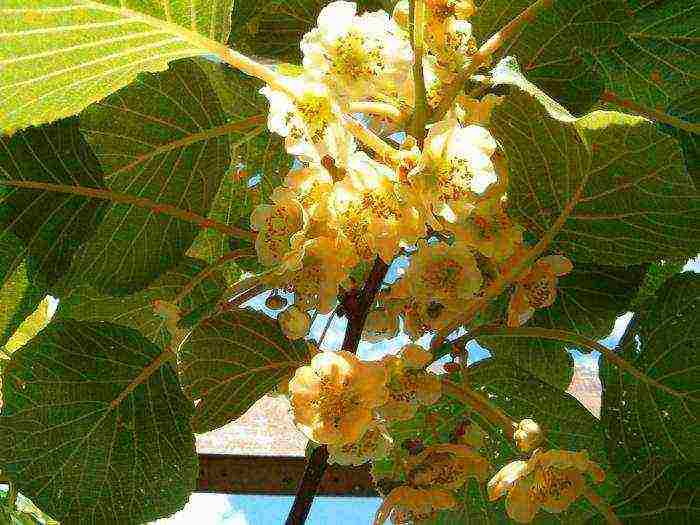
These are perennial deciduous vines. The stems need support.The leaves are whole, smooth or leathery, have a variegated color - the main reason for the decorativeness of the plant. In the axils of the leaves, flowers of white, golden yellow, orange color appear, they are located in 1-3 pieces. Flowers are fragrant only in some species.
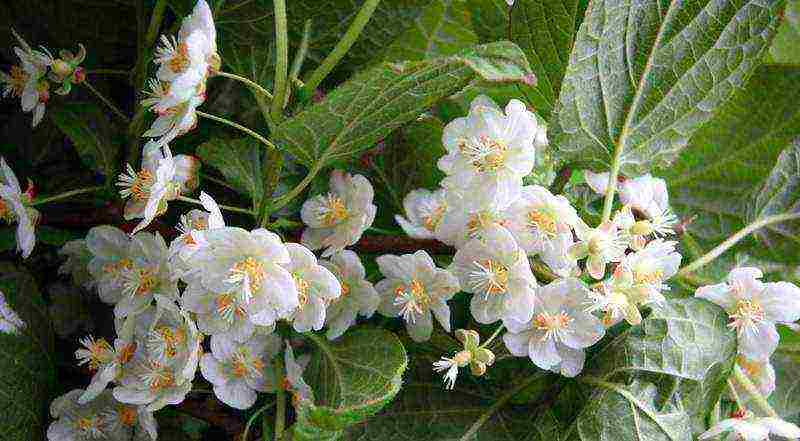

Actinidia kolomikta Dr. Shimanovsky Actinidia kolomikta ‘Dr Szymanowski’ in bloom photo
The actinidia fruit is a valuable food product. It is rich in sugars, ascorbic acid, and other biologically active substances. They are consumed fresh, they are used for making jam, wines, dried berries are similar to raisins. Actinidia is gaining more and more popularity in horticulture.
Male and female actinidia
The plant is dioecious, therefore, to obtain fruits, it is necessary to have male and female actinidia on the site. Sex is determined by the structure of the flower: males have many stamens, and the pistil is absent; female flowers have a large pistil surrounded by stamens with sterile pollen (not participating in pollination). Pollen from male plants enters female plants with the help of insects and wind.
How actinidia reproduces
Vegetative and seed propagation is possible. Actinidia grown from seeds are more hardy, but varietal traits are most often not transmitted, and you will only recognize the sex of the plant during flowering, which occurs in the 7th year of life. With vegetative propagation, flowering will occur in the 3-4th year.
Layers
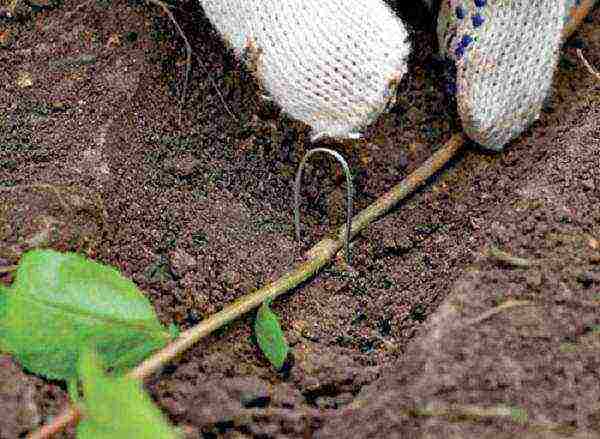

Reproduction of actinidia by layering photo
Reproduction by layering is a simple and reliable way.
- In the spring, when young leaves have already opened, a long, well-developed shoot should be chosen.
- Tilt it to the ground, pin and sprinkle with a layer of soil 10-15 cm thick, the top of the shoot should be above the ground.
- Mulch the mound with sawdust and humus.
- Water regularly, remove weeds, when a young shoot appears, spray it.
- In the fall, at least next spring, the young sprout will be ready to be separated from the mother plant and planted in a permanent place.
Propagation of actinidia by cuttings
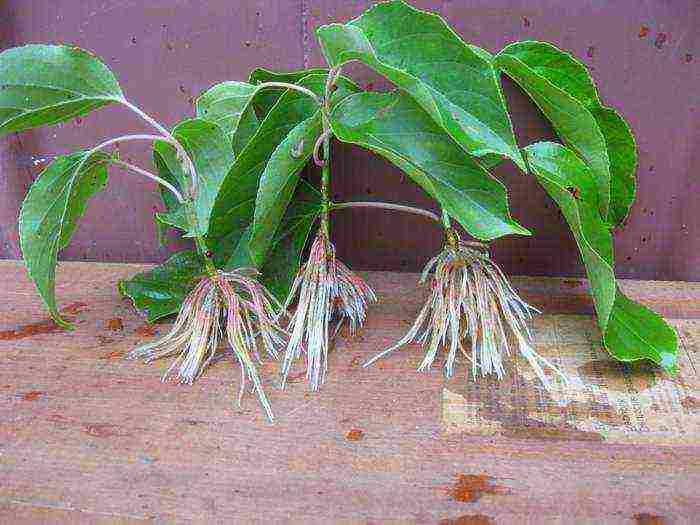

Actinidia cuttings rooted in water photo on the 25th day
Propagation by cuttings is the fastest and easiest way to propagate.
Green cuttings
- Root green cuttings in June. Select several annual branches 0.5-1 m long, cut 10-15 cm long pieces of them. Each stalk should contain 2 internodes and 3 growth buds.
- The cut under the lower kidney should be at an angle of 45º, the upper one should be straight, 4-5 cm above the kidney.
- Remove the lower leaves together with the petioles, and shorten the upper ones by half the length.
- Root in water, greenhouse, greenhouse, or right in your garden bed.
- In the latter case, the cuttings are covered with gauze in 2 layers: spray daily 3-5 times a day, in cloudy weather in the morning and in the evening, remove the gauze, completely get rid of it after a couple of weeks.
- The soil needs a neutral or slightly acidic reaction, into which humus, river sand and complex mineral fertilizer should be added (100 g for each m²).
- Position the stalk at a 60º angle with the middle bud remaining level with the ground. compact the soil, water well.
- Cover with fallen leaves for the winter. With the onset of spring (before bud break), transplant to a permanent growth site.
Lignified cuttings

Cuttings of actinidia photo
Woody cuttings can be rooted. Cut them in late fall, tie in bunches, place vertically in a box and store at 1-5 ºC air temperature until spring. Plant in spring for rooting.
We look at the rooting of lignified cuttings in the video:
Rooting of combined cuttings is possible: at the beginning of summer, select the shoot of the current year and separate it together with the heel (the part of the annual branch adjacent to it). Root outdoors or in a greenhouse. Water daily, shade out of direct sunlight.These cuttings are rapidly developing a root system and the next spring can already be transplanted to a permanent place of growth.
Actinidia from seeds at home

Actinidia seeds photo
Consider seed propagation. Seedlings should be grown.
- Collect seeds from ripe fruits: mash the berries, place in a mesh bag and rinse under running water. Then remove the seeds from the bag, spread out on paper and dry in the shade.
- Store until the first decade of December, and then soak the seeds for 4 days, change the water every day.
- Next, place the seeds in a nylon cloth and lower them into a box with wet sand, keep at an air temperature of 18-20 ºC.
- Remove the sandbag every week and ventilate for a few minutes, rinse the seeds under running water directly in the bag and return to the box again.
- The seeds should not dry out.
- In January, wrap the box with a cloth and move it to the garden, burying it deep in the snow for a couple of months. If there is no snow, store in the vegetable section of the refrigerator.
- After stratification, return to indoor and store at 10-12 ºC. At the same time, ventilate and rinse the seeds weekly.
- When the seeds are nailed, it is time to carefully plant them, being careful not to break the sprouts. Fill containers with a mixture of turf and river sand, spread the seeds over the surface less often and lightly sprinkle with sand.
- It will be necessary to moisten the crops with a spray gun and cover with a film to create a greenhouse effect. When the plants sprout, it is better to remove the film.
- Spray seedlings regularly, protect from direct sunlight.
- With the appearance of 3-4 true leaves, plant the actinidia seedlings in separate containers.
- Transplant outdoors in the 3rd year of life in the spring.
Planting actinidia in open ground
Rooted actinidia stalk ready for planting in spring photo
Actinidia grows well in one place for more than 30 years, but it is necessary to choose a suitable site and follow agricultural techniques.
Choosing a landing site
Actinidia is shade-tolerant, but the fruits will fully ripen only with access to sunlight: select an area under the bright sun with shade at midday. Not recommended to be planted next to apple trees. Suitable neighbors are currant bushes.
Priming
The soil is required to be moist, loose, well-drained. Does not tolerate clay and alkaline soils. Avoid areas with a close groundwater table (in this case, you will need to fill a hill). It is best to plant on hills or slopes - the water will drain naturally, without stagnating in the roots.
Support preparation
For actinidia, support is necessary, otherwise the stems will get tangled, it will become problematic to care for the plant, and the fruits in this case ripen unevenly.
- Vines do not have aerial roots, so plant them calmly near buildings, fences, frame gazebos.
- Use arches of classical form, pergolas (wooden, metal, concrete) as a support.
- You can stretch galvanized wire (3-4 rows) between two concrete posts according to the principle of a grape trellis: actinidia will grow vertically, tie up the shoots during growth.
- In areas with severe winters, it is better to use removable trellises in order to remove the vine for the winter, lay it on the ground with the construction of a shelter.
When and how to plant
Plant actinidia in early spring (before sap flow begins) or in autumn (2-3 weeks before frost starts). It should be noted that it is better to plant vines 2-3 years old in the fall, since older specimens are painfully tolerant of autumn planting.
- Prepare the planting hole 2 weeks before planting. Length, width and depth - 50 cm each.
- At the bottom, lay a drainage layer of small stones or broken brick.
- Move fertile soil with peat and compost, add fertilizers (250 g of superphosphate, 120 g of ammonium nitrate, 35 g of wood ash and potassium sulfate each) and fill the hole.
- Cut dry and broken roots on the seedlings, treat the sections with a fungicide, hold the seedlings in a clay mash.
- Pour a hill of soil without fertilization into the planting hole, place the seedling so that the root collar is flush with the soil surface.
- Cover the roots with earth, press the earth a little.
- Pour 10-15 liters of water under the bush, mulch with a layer of compost or peat 4-5 cm thick.
Maintain a distance between plantings of 1.5-2 m.To decorate the wall of a building, plant seedlings in a trench, retreating between plants 0.5 m.
The scent of the vine is attractive to cats - so protect the seedlings from their encroachment. Dig in a metal mesh that is at least 0.5 meters high around the plant.
How to care for actinidia outdoors
Watering and loosening the soil
Water the plant abundantly. During severe drought, add 6-8 buckets of water under each bush once a week. Spray actinidia in the morning and evening as well. This must be done so that leaves do not drop. Young leaves will not have time to get stronger in cold weather and will freeze in winter.
Loosen the soil, remove weeds.
Top dressing
It is important to feed regularly. In early spring, apply 20 g of potash and 35 g of nitrogen fertilizer per m². During the period of ovary formation, apply 10-12 g of phosphorus and potassium fertilizers and 15-20 g of nitrogen fertilizers per the same unit of area. After harvesting (about the second decade of September), add 20 g of potassium and phosphorus. Apply fertilizing in this way: embed the fertilizer granules into the soil around the plant to a depth of 10-12 cm, water abundantly.
Pruning
Sanitary pruning spend in mid-September: shorten the shoots by 1/3 of the length, remove the branches that thicken the crown.
Upon reaching the age of 3-4 years, it is necessary to carry out formative pruning lianas. Do this throughout the summer. Form a two-shoulder cordon along a horizontal trellis: direct two shoots of the same level in one plane in opposite directions and secure, cut off the remaining shoots. Next year, shoots of the second order will appear on them - it is on them that fruits are formed, they should be tied to a vertical guide.
Anti-aging pruning spend at the age of 8-10 years. Do it in the summer. Cut off the shoots completely, leaving a stump 30-40 cm high.
How to distinguish male and female actinidia, we look at the video:
Diseases and pests
Diseases and pests of actinidia are rarely disturbed.
Possible diseases: fungal diseases (powdery mildew, phylostictosis, etc.), green and gray mold, fruit rot. For prophylaxis, treat the plant with Bordeaux liquid after the buds appear and 2 weeks after the first treatment. When a disease appears, the affected areas should be removed and treated with a fungicide.
Pests: leaf beetles, moth caterpillar, lacewings, bark beetles. In spring and autumn, treat the vines and soil with Bordeaux liquid.
Harvesting
Fruiting begins at the age of 3-4 years. Full harvests can be harvested from actinidia from the age of 7 years: about 60 kg of berries from one plant with proper care. Fruit ripening is uneven, but they do not crumble for a long time. Harvesting time begins in mid-August and lasts almost until mid-October.
Wintering actinidia
Young plants (2-3 years old outdoors) will need shelter for the winter. Remove the branches from the supports, lay them on the ground, cover with peat, dry leaves, spruce branches (layer at least 20 cm thick). Mice can make nests there - use the poison. Adult specimens hibernate without shelter.
Types and varieties of actinidia with photos and names
In the natural environment, there are 70 species of plants, 3 of them are cultured with numerous varieties bred.
Actinidia arguta or acute Actinidia arguta
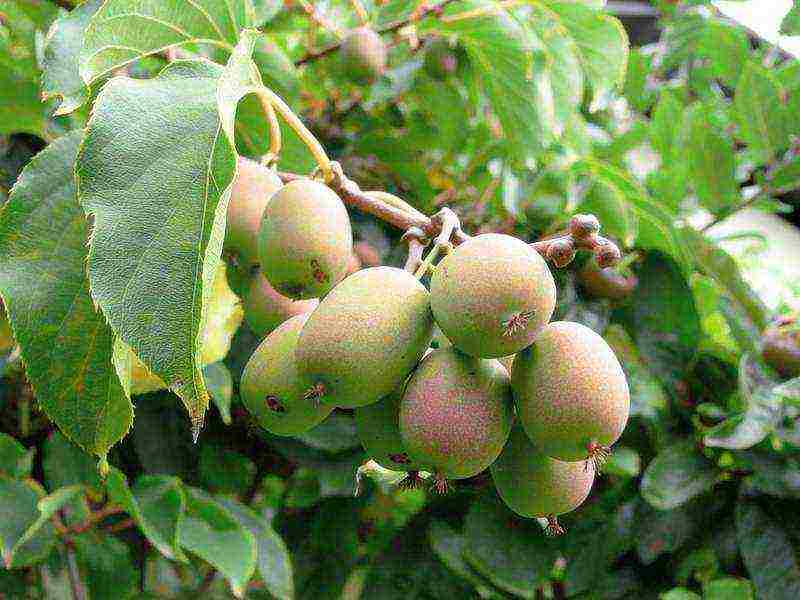

Actinidia arguta or acute Actinidia arguta photo
The most powerful plant among the cultivated species.The length of the liana reaches 25-30 m, the diameter of the trunk is 15 cm. The leaf plates are ovoid with finely toothed edges, their length is 15 cm. The flowers are fragrant, located singly or are collected in racemose inflorescences of 3 pcs. Fruits are spherical (diameter 1.5-3 cm), dark green, have a slight laxative effect, ripen at the end of September.
Varieties:
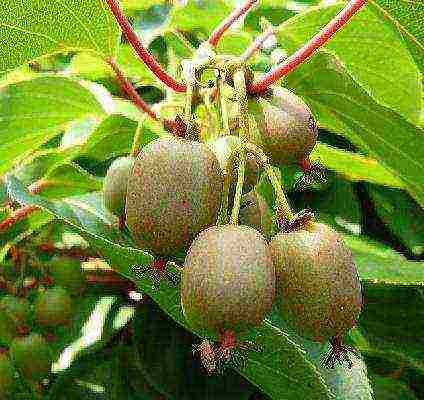

Self-fertile actinidia photo
Actinidia Self-fertile - fruiting begins in the second half of September. The weight of the elongated-cylindrical berry is about 18 g, it is colored bright green. Winter-hardy plant;

Actinidia arguta Actinidia arguta Primorskaya photo
Primorskaya - leaves of medium size, soft, oblong, green color. Fruits are elliptical, olive-colored, weight 6-8 g. Average winter hardiness;
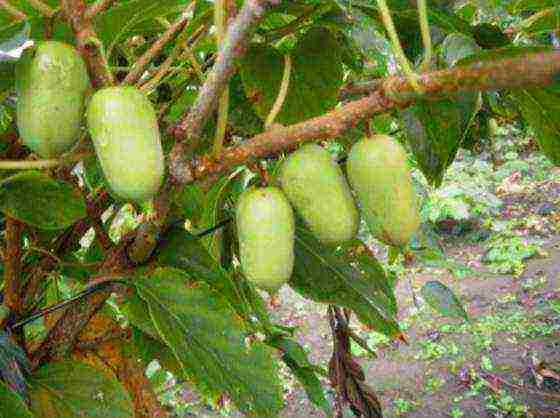

Actinidia arguta Large-fruited photo
Large-fruited actinidia is an elliptical fruit, painted in dark green color with a blush, weighing 10-18 g. Frost-resistant plant.
Other popular varieties: Mikhneevskaya, Relay, Golden Spit, Ilona, Vera, Lunnaya, September.
Actinidia kolomikta Actinidia kolomikta cultivar for Moscow region and Leningrad region
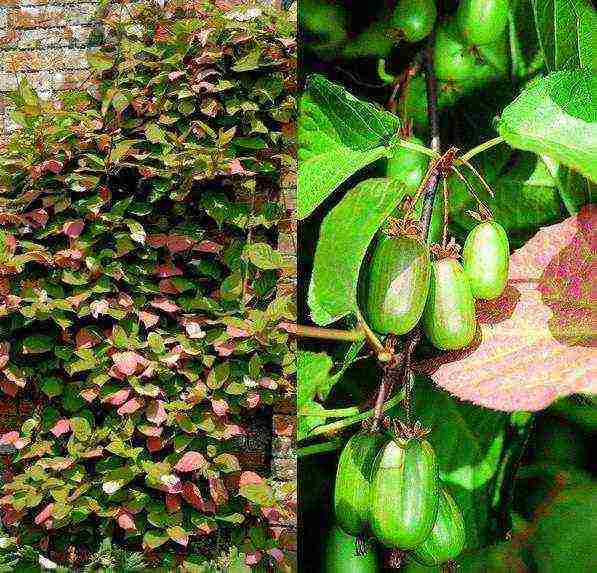

Actinidia kolomikta Actinidia kolomikta photo
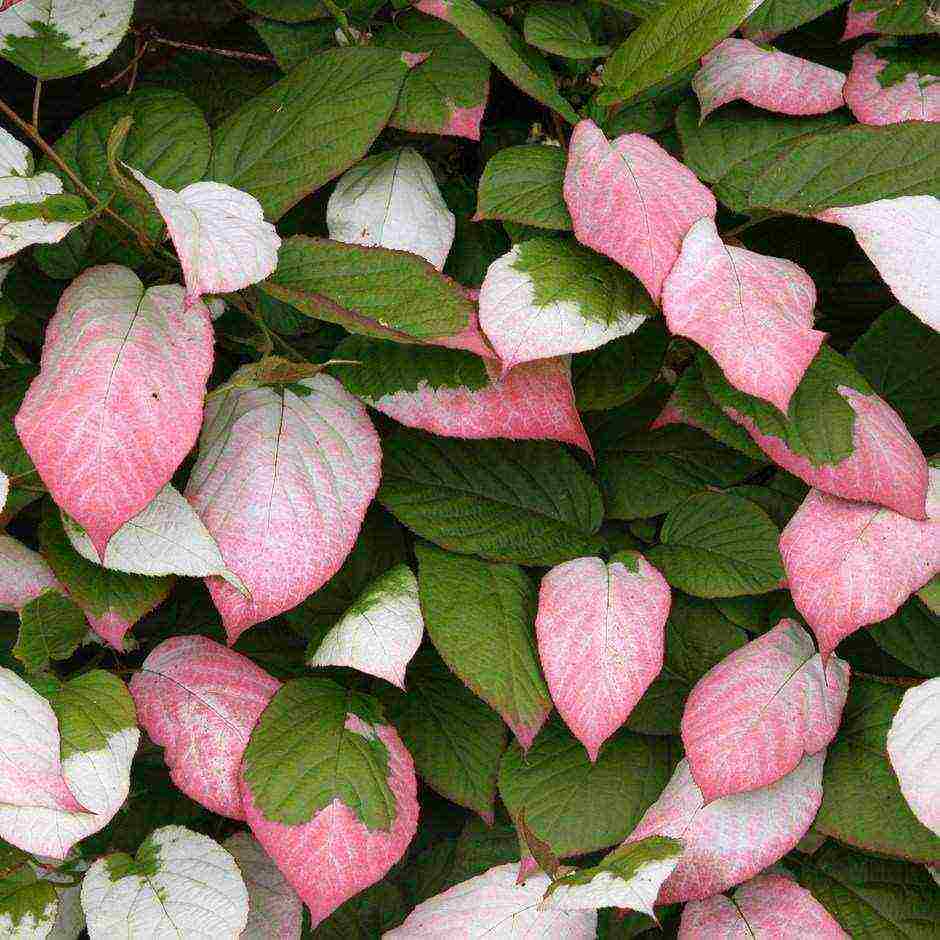
Very resistant to severe winter frosts. Plant height is 5-10 m, trunk diameter is 20 mm. The leaves are obovate, stretching 7-16 cm. They have sharp-edged edges, the veins are covered with orange-colored pubescence. in males, the leaves are variegated: in the fall they become yellow-pink, red-purple. Female flowers are arranged singly, male flowers - 3-5 pcs. Fruits are green in color, they acquire a bronze, reddish tint in the sun.
Varieties:
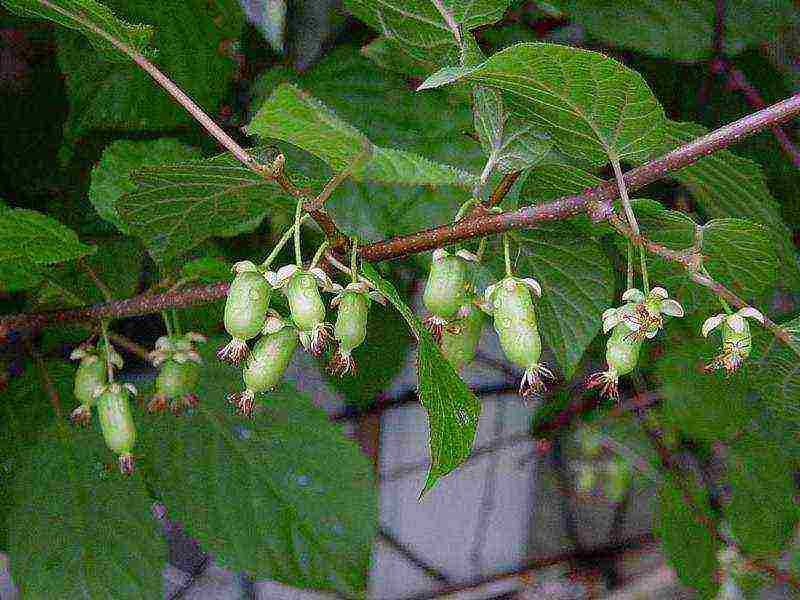

Actinidia kolomikta Actinidia kolomikta Grape photo
Actinidia Pineapple - a very productive variety. The oblong berries, 3 cm long, have a pineapple flavor;
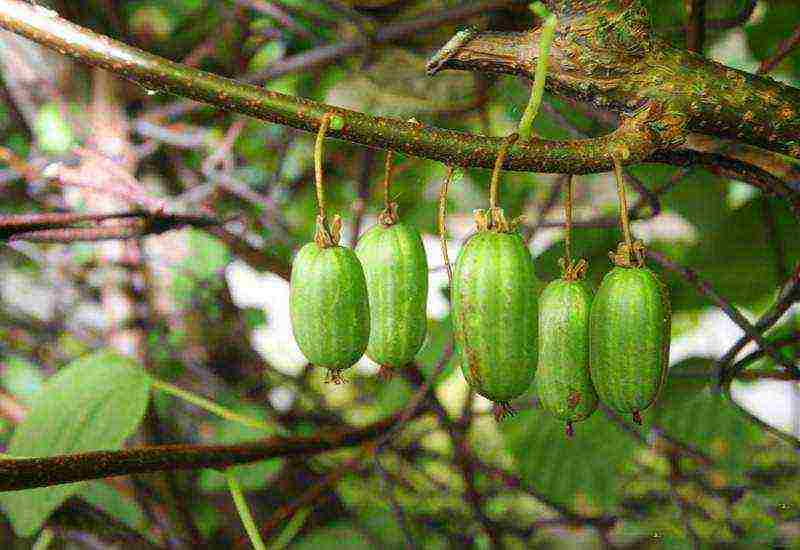

Actinidia kolomikta Dr Szymanowski photo
Actinidia Dr. Shimanovsky variety description- Curly liana, lashes reach a length of 3 m. The annual growth is about 1.5 m. Young leaves have light green spots, but quickly become pink in color. Liana loves warm, sunny, wind-protected places. A bisexual species. Flowers are white, fragrant, bloom in June. The fruits are edible, sweet, ripen in August.
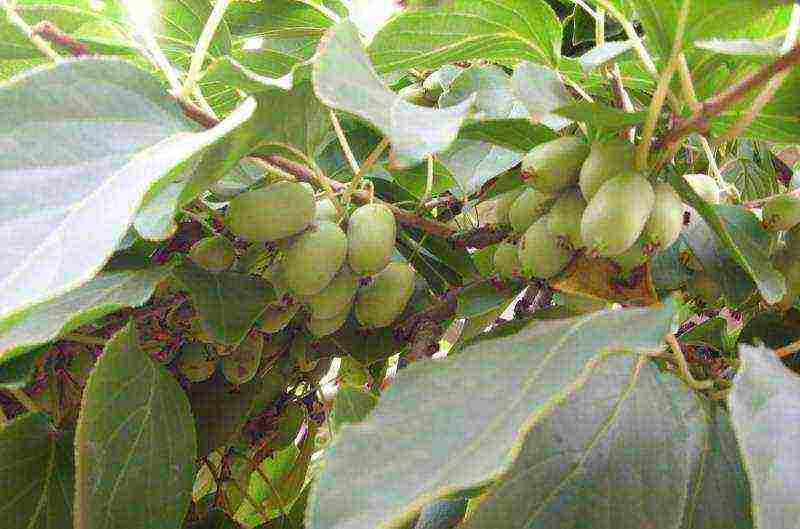

Actinidia kolomikta variety Lakomka photo
Gourmet - has fruits 30 mm long and weighing 4-5 g, taste: sweet and sour with a hint of pineapple.
Other varieties: Festive, Sweet, Waffle, Narodnaya, Moma, Household.
Actinidia polygama Actinidia polygama

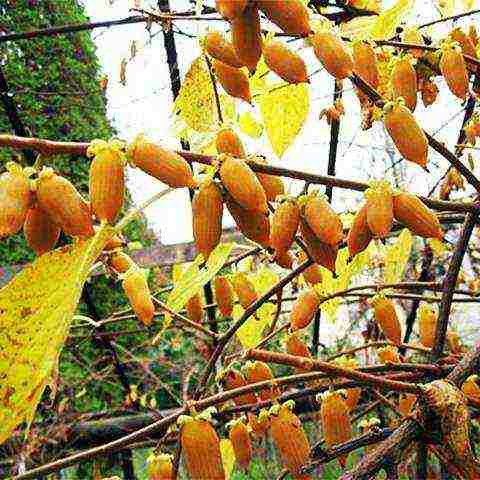
Actinidia polygama Actinidia polygama photo
Liana 4-5 m high. Elliptical leaf plates with pointed tops and serrated edges, painted green with silvery spots, leaves turn yellow in autumn. Fruit weight - 3 g.
Varieties:

Actinidia polygamy Apricot (female) photo
Actinidia polygamous Apricot - moderate winter hardiness, fruits ripen late. The berries are slightly flattened, weighing about 6 g, have a sweet and sour taste;
The beauty is a winter-hardy plant. Fruits are yellow-green in color, sour taste;

Actinidia Polygamum Patterned Photo
Patterned - fruits of a cylindrical shape, colored orange with longitudinal stripes. It has a fig-pepper flavor.
Actinidia giraldii Actinidia giraldii
A species listed in the Red Book. Similar to actinidia argut, but with larger fruits.
Varieties:
Juliana - berry weight 10-15 g, sweet taste;
Alevtina - berries weighing 12-20 g, sweet;
Native - berry weight 7-10 g.
Actinidia purpurea Actinidia purpurea
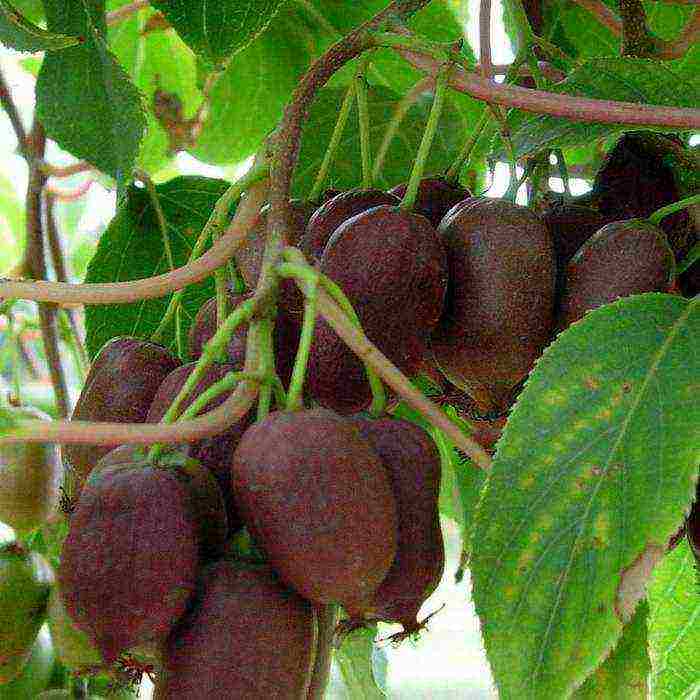

Actinidia purpurea Actinidia arguta cultivar ‘Ken’s Red’ photo
Shade-tolerant vine, low cold resistance. The fruits are purple in color. Their weight is 5.5 g. They taste sweet.
Actinidia hybrid
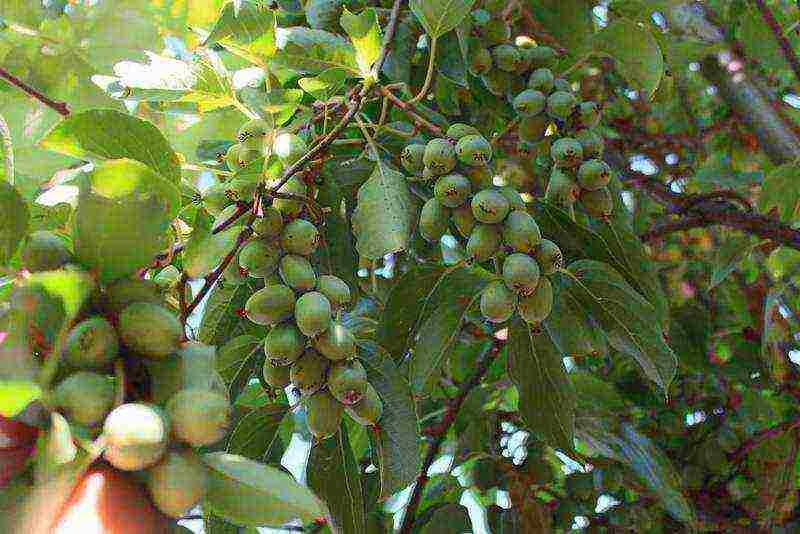

Actinidia hybrid Kiev large-fruited Arguta Kievskaya photo
The work of the breeder I.M. Shaitan. This is a cross between actinidia argut and actinidia purpurea. The fruits are large, purple in color.
Varieties:
Kievskaya Large-fruited - oval berries of green color, weight - 10 g, taste - sweetish;
Candy - fruits ripen late, have a sweet taste and candy-fruity aroma;
Souvenir - greenish-red fruits weighing about 8 g, sweet.
Useful properties of actinidia
The fruits of the plant are excellent remedies for belching, heartburn, and other digestive disorders. They are also recommended to be taken for anemia, rheumatism, lumbago, gonorrhea, colitis.
Other parts of the plant also have medicinal properties. Infusions, decoctions, ointments are prepared from them.
Polygamol is a drug based on actinidia with a tonic effect.
Contraindication to the use of drugs is varicose veins, thrombophlebitis.
 How many amazing plants can be found in the wild! But many of them freely take root in indoor conditions or on personal plots. Among the rather simple and incredibly beautiful representatives of the exotic flora is actinidia, which has found a response in the hearts of many summer residents. Despite the subtropical origin, connoisseurs of bright vegetation practice the cultivation of actinidia in the Urals and Siberia, which is explained by the plant's endurance and unpretentiousness.
How many amazing plants can be found in the wild! But many of them freely take root in indoor conditions or on personal plots. Among the rather simple and incredibly beautiful representatives of the exotic flora is actinidia, which has found a response in the hearts of many summer residents. Despite the subtropical origin, connoisseurs of bright vegetation practice the cultivation of actinidia in the Urals and Siberia, which is explained by the plant's endurance and unpretentiousness.
It is known that this vine has a very ancient history... It is believed that it appeared in the era of the dinosaurs and freely survived the ice age. It is not excluded that it is due to this "vitality" that it still grows in an extreme environment, including the Siberian regions. Today we will deal with all the features of growing actinidia in Siberia and other regions with a harsh climate. You can't even imagine how you can transform your site with the correct arrangement of the flower near the gazebos and balconies.
Actinidia - species description
In addition to its delightful decorativeness, actinidia attracts many gardeners with its practical benefits - its edible fruit has excellent flavoring properties... Naturally, over the years of its existence, the species has gone through many changes, therefore, the characteristic features of modern actinidia are presented as follows:
 the plant belongs to the bisexual group. To see the fruits of the vine, it is enough to plant a "male bush", which will act as a pollinator. There is a variant of planting and self-fertile actinidia, however, its yield is not as abundant as in the first case;
the plant belongs to the bisexual group. To see the fruits of the vine, it is enough to plant a "male bush", which will act as a pollinator. There is a variant of planting and self-fertile actinidia, however, its yield is not as abundant as in the first case;- actinidia is a deciduous plant. In autumn, its leaves turn crimson or yellow, which only increases the decorative appeal. The shape of the leaves is slightly elongated and heart-shaped. The edges of the leaves are both smooth and slightly jagged;
- during the flowering period, the vine is strewn with excellent white flowers, which emit a delightful aroma. True, the duration of flowering is very short, so you can not enjoy such a sight for long;
- actinidia fruits have a slightly pubescent surface. Varieties with smooth fruits and sweet and sour taste are sometimes grown. By the way, the berries contain several times more vitamin C than black currants. Harvesting begins at the end of summer;
- in the Urals, the fruits of actinidia are considered incredible value. To maintain a high content of ascorbic acid, it is enough to follow some rules. For example, you can let ripe fruits hang until the autumn cold. In this case, the storage time will increase significantly. Many people cook fruit-based jams, jams, compotes and other delicacies;
- actinidia has found its application in folk medicine. For centuries, it has been used as an excellent tool for lowering blood cholesterol levels and supplying the body with all kinds of vitamins and minerals. The culture is credited with the ability to get rid of problems with the digestive, respiratory and cardiovascular systems. To prepare a highly effective remedy for the prevention or treatment of common ailments, almost all parts of the plant are used, including bark, roots and flowers;
Varieties and varieties of actinidia for the Urals
 By its nature, actinidia is considered a heat-loving culture, therefore, if you want to plant a plant in the harsh Siberian conditions, pay attention to suitable varieties with good cold-resistant characteristics and endurance to any weather changes. Experienced growers are sure that the best solution for growing in the Urals is the actinidia Kolomikta. By the way, this species is represented by many popular varieties and hybrids, which expands its decorative and practical properties. Let's highlight the most popular varieties: -"Doctor Shimanovsky"... They are a very interesting hybridization that has an excellent appearance in the form of whitish-green leaves and a slightly pinkish color in summer. Ripe fruits turn yellow and fall off immediately after ripening. Liana is characterized by a very rapid annual growth, up to 1.5 meters. In most cases, the height of the culture reaches 4 meters;
By its nature, actinidia is considered a heat-loving culture, therefore, if you want to plant a plant in the harsh Siberian conditions, pay attention to suitable varieties with good cold-resistant characteristics and endurance to any weather changes. Experienced growers are sure that the best solution for growing in the Urals is the actinidia Kolomikta. By the way, this species is represented by many popular varieties and hybrids, which expands its decorative and practical properties. Let's highlight the most popular varieties: -"Doctor Shimanovsky"... They are a very interesting hybridization that has an excellent appearance in the form of whitish-green leaves and a slightly pinkish color in summer. Ripe fruits turn yellow and fall off immediately after ripening. Liana is characterized by a very rapid annual growth, up to 1.5 meters. In most cases, the height of the culture reaches 4 meters;- grade "Adam". It is very popular among the flower growers of the Urals, which is explained by the unusual color of the foliage, which can change annually. With proper care, the variety grows up to four meters in height. Can be planted both in a pot and in open soil;
- "Queen of the garden"... The variety is characterized by an early ripeness of fruits, which reach 3.5 grams of weight. The fruits have an oval shape and a characteristic greenish color. Representatives of the variety belong to the group of medium-sized vines;
- "Waffle"... The variety conquered the hearts of flower growers from the Urals with sweet fruits reaching 3.2 grams of mass. Differs in an average degree of ripening and relatively short growth - up to 2.3 meters. The crown of Waffle actinidia is not very thickened;
- "Narodnaya"... The fruits of this variety have a wonderful strawberry aroma and a compressed cylindrical shape. The shoots are characterized by a beautiful brown color, which emphasizes the contrasting color of the crown;
- "Hope"... The variety is represented by a beautiful bush form and belongs to the group of tall ones, because the maximum height of an adult reaches 6 meters. Due to its unpretentious nature, it is considered an invaluable find for novice gardeners. A good advantage of the variety is the early ripening of fruits and high taste properties of ripe berries;
Features of planting and caring for actinidia in the Urals
 An important stage in the successful planting of crops in the Ural conditions is in choosing a suitable seat... Do not forget that the plant can grow normally for many years in the same place, because it is considered a long-liver. However, it is important to provide him with enough room to grow, both in width and height. Before choosing a place for planting, consider the estimated size of the future bush, paying attention to varietal characteristics. Also consider setting up a suitable actinidia support.
An important stage in the successful planting of crops in the Ural conditions is in choosing a suitable seat... Do not forget that the plant can grow normally for many years in the same place, because it is considered a long-liver. However, it is important to provide him with enough room to grow, both in width and height. Before choosing a place for planting, consider the estimated size of the future bush, paying attention to varietal characteristics. Also consider setting up a suitable actinidia support.
As a soil composition, it is better to choose neutral or slightly acidic compositions based on sandy loam or loam with a high content of nutrients, including humus.
Despite its need for abundant moisture, liana does not react well to stagnant water near the roots... For this reason, it is best to grow it in higher elevations or in areas with a good drainage layer.
To harvest a tasty and rich harvest, the plant needs to provide an abundance of sunlight. Representatives of some varieties have excellent shade tolerance, but still cannot develop normally without abundant lighting. The method of planting actinidia near other garden trees, which will play the role of partial shade, has proven itself very well.
When to plant actinidia in open ground in the Urals, care after planting
 It is better to start growing actinidia Kolomikt in springsince the high risk of frost in autumn does not allow planting in autumn.In turn, in order not to waste time, in the autumn time it is necessary to start choosing a suitable place for planting and preparing the landing pit. Experienced gardeners are advised to start planting in early May, when the threat of too severe frosts and temperature changes will finally disappear.
It is better to start growing actinidia Kolomikt in springsince the high risk of frost in autumn does not allow planting in autumn.In turn, in order not to waste time, in the autumn time it is necessary to start choosing a suitable place for planting and preparing the landing pit. Experienced gardeners are advised to start planting in early May, when the threat of too severe frosts and temperature changes will finally disappear.
When choosing a suitable planting material, you need to be extremely careful. Do not forget that some seedlings may not be of high quality, so they simply will not take root in the soil. The decorativeness and state of the future culture depend on the right choice. To avoid mistakes it is enough to follow some selection rules and follow the recommendations of experienced gardeners:
 do not buy planting material of actinidia Kolomikt "off hand", because in this case you will not have a 100% guarantee of the quality of planting material. Also, you will not be able to find out whether this variety is winter-hardy or not, but it is the cold resistance indicators that occupy a key place in the search for suitable seedlings for growing in the Urals. For a successful purchase, contact specialized nurseries or experienced florists who attach certain documents or return guarantees to their products;
do not buy planting material of actinidia Kolomikt "off hand", because in this case you will not have a 100% guarantee of the quality of planting material. Also, you will not be able to find out whether this variety is winter-hardy or not, but it is the cold resistance indicators that occupy a key place in the search for suitable seedlings for growing in the Urals. For a successful purchase, contact specialized nurseries or experienced florists who attach certain documents or return guarantees to their products;- it is known that actinidia Kolomikt has a very fragile root system, which can be damaged at the slightest mistake during transportation. For this reason, it is better to buy specimens with a carefully closed rhizome;
- do not pay attention to the size of the seedlings. Buy specimens at the age of 1 year, because older seedlings may have a dry earthen lump, which will aggravate further rooting in the open field;
- many gardeners buy actinidia Kolomikta for home cultivation, not only in order to decorate the backyard area. Many of them start growing the plant for an excellent harvest. If you wish to receive a “shock” dose of vitamin C on the site, purchase 1 “male” for every 3 “female” seedlings;
Features of soil preparation for actinidia Kolomikta
As mentioned above, you can start preparing the soil composition in the autumn, and the planting itself is best done in the spring, paying attention to a number of recommendations of experienced professionals.
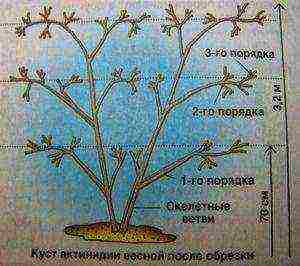 Before proceeding with the preparation of the planting pits, you need to correctly create a scheme for their placement, provided that you intend to engage in mass crop cultivation. It is better to place planting pits in an ordinary way, which is directed from north to south. This arrangement will allow the vine to receive the maximum amount of sunlight. A minimum distance of 1.5-2 meters must be adhered to between two plants. When planting crops in several rows, leave about four meters of free space between the rows;
Before proceeding with the preparation of the planting pits, you need to correctly create a scheme for their placement, provided that you intend to engage in mass crop cultivation. It is better to place planting pits in an ordinary way, which is directed from north to south. This arrangement will allow the vine to receive the maximum amount of sunlight. A minimum distance of 1.5-2 meters must be adhered to between two plants. When planting crops in several rows, leave about four meters of free space between the rows;- If there are a lot of planted plants, and you plant them in a row, arrange a trench 50 centimeters deep and 40-50 centimeters wide. The optimal size of the planting pit varies within 50x50 centimeters. When growing larger individuals - 60x60 cm;
- At the bottom of the planting pit, it is better to lay out a drainage layer created from pebbles, chipped bricks or small stones;
- The next step is to prepare the nutrient soil composition. For this purpose, it is enough to add 9-10 kilograms of humus, 200 grams of superphosphate and 80 grams of potassium salt to the excavated earth. Similar proportions will be effective for one planting pit;
- 1 third of the planting pit should be filled with nutrient composition;
- If the purchased plant has an open rhizome, the roots are gently spread over the mound during planting. If the root system is closed, then the earthen lump is pre-moistened before planting, after which the rest of the earthen soil is compacted;
- It is important not to deepen the root collar and water the garden abundantly after the successful planting of the seedling;
- Also, after watering, it is necessary to mulch the upper layers of the earth, which will allow moisture to remain in the soil for a long time. In the process, it is better to apply leaves, peat or humus;
Conclusion
Despite the unpretentious nature and hardy immunity, actinidia Kolomikta can be exposed to some diseases and problems. Among them:
- Philostiktosis;
- Ramulariasis;
- Fruit affections;
It is very pleasant and easy to grow a culture in the harsh conditions of the Urals. With patience and desire, you will be pleasantly surprised by the amazing appearance of the vine, and the excellent yield indicators. True, you should understand that the success of such cultivation is determined by your responsibility and willingness to select the right care.
>
 The actinidia plant, leading the genus of woody lianas of the Actinidiaceae family, appeared in European garden culture relatively recently - in the late 60s of the last century, and a little later the exotic beauty settled on the household plots of Russia. Many gardeners mistakenly call this outlandish culture "garden kiwi", but this opinion is only partly true: everyone's favorite shaggy fruit is the fruit of delicacy actinidia, which, unfortunately, is not grown in temperate climates. But don't be discouraged! Adapted to the harsh conditions of mid-latitudes, crop species produce excellent yields of edible berries, albeit not as large and fluffy as kiwi.
The actinidia plant, leading the genus of woody lianas of the Actinidiaceae family, appeared in European garden culture relatively recently - in the late 60s of the last century, and a little later the exotic beauty settled on the household plots of Russia. Many gardeners mistakenly call this outlandish culture "garden kiwi", but this opinion is only partly true: everyone's favorite shaggy fruit is the fruit of delicacy actinidia, which, unfortunately, is not grown in temperate climates. But don't be discouraged! Adapted to the harsh conditions of mid-latitudes, crop species produce excellent yields of edible berries, albeit not as large and fluffy as kiwi.
Actinidia fruits are not only tasty, but also a healthy delicacy. They are used to make jam, compotes, jams, make wine, prepare marmalade and all kinds of medicinal drugs. Dried berries are similar in appearance and taste to raisins. In addition, a tall liana with lush foliage looks great in the landscape. Having such a productive beauty on the site is a pleasure even for a sophisticated gardener.
When to plant
Liana is planted in open ground in April, before the active movement of juices begins. Actinidia is a dioecious plant, so you need at least two seedlings on the site to harvest. You can easily determine the sex of actinidia by flowers. In the male plant, the flowers are devoid of a pistil, but are decorated with many stamens. The female pistil flower also has stamens, but their pollen is absolutely sterile.
Autumn planting of actinidia is also possible, but plants younger than 2-3 years old are suitable for it, older specimens may not tolerate such stress.
Landing technology
In one place actinidia grows and bears fruit for 30-40 years, so before planting, go around the garden and determine for it a suitable area on an elevation with drained moist soil of a neutral or slightly acidic reaction. Clayy, dense soils are not suitable for culture. An exotic liana with black currant adjoins well, but categorically cannot stand the proximity of apple trees. For the ripening of the fruits of actinidia, the sun is needed, so choose a well-lit place, but with the condition that the plant is slightly shaded in the sultry midday hours. The recommended distance between adjacent specimens is about 1 m, when decorating walls - 0.5–0.6 m. Planting works are carried out in stages:
- Dig holes at a distance of 0.5? 13-15 days before planting. 0.5? 0.5 m, on the bottom of which pour a layer of pebbles or broken brick for drainage. Not construction crushed stone! Lime is destructive for actinidia.
- Examine the root system of the seedlings, cut off dry and damaged shoots, and then dip the roots in a clay mash.
- Fill the soil extracted from the pit with humus or peat and mineral fertilizers - ammonium nitrate (120 g), superphosphate (250 g), wood ash or potassium sulfate (35 g). In no case do not add chlorine-containing fertilizers, this element is certain death for the plant. Pour the resulting fertile mixture into the pit on the drainage layer, and on top of it form a low mound of soil without fertilizers.
- Set the seedling on a mound, leaving the root collar flush with the soil surface, straighten the roots and dig in.
- Thoroughly compact the soil under the young liana, pour 2-3 buckets of water under the root and cover the tree trunk with a five-centimeter layer of compost or peat.
Like all vines, actinidia needs good support. The lack of a reliable design will lead to tangled shoots and a decrease in yield, and caring for a dense "ball" will be much more complicated. Any support is suitable for your pet - trellis, pergola, arch. Since actinidia has no aerial roots, it can be safely used to decorate the walls of residential and utility buildings.
Note! Cats are not indifferent to the scent of actinidia, and so that the mustachioed-striped ones from all around do not go scratching their claws against your vine, install a fence made of metal mesh with a height of 50-60 cm around the stem.
Care advice
There is absolutely no need to care for actinidia incessantly. Caring for her includes the following vital procedures for any plant:
- In extreme heat, the vine is moistened daily by sprinkling. The foliage should be sprayed twice a day - in the morning and in the evening. If the dry weather lingered in your area, it is necessary to pour 6-8 buckets of water under the root of actinidia every 7-10 days. In no case should the soil be allowed to dry out for a long time, otherwise the vine will shed its foliage, and the regrown young leaves will not have time to form before the cold weather and will freeze.
- The culture is fed three times per season. In early spring for every m? make 35-40 g of nitrogen-containing and 20 g of potash and phosphorus fertilizers. During fruit setting, food is served in the same composition, but the amount of fertilizer is halved. After picking berries, in the second or third week of September, actinidia is fed only with phosphorus and potassium (20 g / m2 each). The work is carried out as follows: nutrient granules are embedded in the soil to a depth of 10–12 cm, after which the near-trunk circle must be generously watered.
- Periodically, the soil under the liana is shallowly loosened, at the same time eliminating weeds.
The first harvest of actinidia will delight you at the age of 3-4 years, but it will start bearing fruit stably only in the seventh year of life. The berries ripen unevenly and stay on the plant for a long time. They begin to be removed from the second half of August and harvested until mid-September. With quality care, you are guaranteed an annual harvest of 50-60 kg of tasty fruits.
Pruning rules
From the age of three to four years of age of actinidia, annual pruning is indicated. During the summer, all unnecessary branches are removed from it, and the remaining shoots are evenly spread in the desired direction. You should not neglect the procedure: vines with an overly dense crown are less winter-hardy and more susceptible to disease. The most successful way to form a bush is in 2 lashes. Spread 2 first-order shoots in opposite directions and fix, and tie the branches of the next year, on which the berries will be tied, to a vertical support. To help the wood ripen better, periodically pinch the tops of young branches. At the age of 8–10 years, for the renewal of skeletal shoots, a radical pruning of the vine is carried out - the actinidia is shortened to a height of 35–40 cm. Important! In no case, do not cut the plant in early autumn or early spring, otherwise your vine, flowing out with juice, will simply die.
Reproduction methods
If you decide to breed actinidia, then keep in mind that the sex and varietal qualities of plants are inherited only during vegetative propagation, with generative reproduction it is impossible to determine the sex and characteristics, but vines grow stronger and more hardy from seeds. The advantages of each method are obvious, but which one to choose is up to you:
- Cuttings are the fastest way, thanks to which you get a large number of viable seedlings.In June, cut off several 0.5–1 m long annual branches from an adult actinidia and cut each of them into 10–15 cm pieces. Each cutting should have 3 healthy buds and 2 internodes. The lower cut is made at an angle of 45 °, and at the top, the shoot is cut off 4–5 cm above the bud. The finished material is rooted in a greenhouse, moist, well-fertilized soil, sprinkling with water 3-5 times a day. For the winter, plantings are covered with dry leaves, and with the onset of spring heat, they are planted in the garden.
- Layering is a very convenient and reliable way. After actinidia finishes sap flow and leaves leaves, outline a strong healthy shoot and bend it to the ground, fix it and sprinkle it with moist soil in the place of attachment. Sprinkle the resulting bump with peat and water it regularly. Spray the young shoot every day after regrowth. In the fall, the cuttings can be separated from the maternal vine and transplanted.
- Seeds are not a way for the lazy. Ripe actinidia fruits are kneaded with a fork, the pulp is placed in a gauze knot and thoroughly washed under running water. After drying, the seeds are poured into a bag made of nylon stocking and buried in wet sand. Seeds are taken out of the sand every week and washed and ventilated right in the stocking. In the middle of winter, a pot of sand and seeds is placed in the refrigerator for a two-month stratification. Over time, the pot is arranged at a temperature of + 10–12 ° C and the same manipulations are repeated - rinsing, airing. When the seeds are baked, they are sown in a sand-sod mixture to a depth of 0.5 cm and kept on the windowsill until 3-4 leaves appear. In June, seedlings are planted for growing in a greenhouse. In the third or fifth year of life, the seedlings will enter the first flowering, and then, having determined their sex, you can plant them in open ground.
Actinidia grown vegetatively will begin to bear fruit at the age of three to four years, and vines from seeds will give the first berries only after 6-7 years.
Diseases and pests
High resistance to diseases and pests is another characteristic feature of actinidia. Subject to the norms of agricultural technology, she rarely experiences health problems. However, in a rainy summer with frequent and sharp temperature changes, the fruiting liana can be struck by such ailments as powdery mildew, phyllosticosis and other fungal infections, which you can recognize by yellow or brown spots on the leaves. Actinidia arguta is also vulnerable to fruit rot, gray and green mold. The sooner you start treatment, the more chances the plants have for early recovery - first of all, absolutely all damaged leaves, shoots and fruits should be removed, and then the plantings should be treated with potent fungicides (Khom, Topaz, Horus, Fundazol "). Against powdery mildew, actinidia is sprayed twice with a weak (0.5%) solution of soda ash, the interval between procedures is 10-12 days.
The worst enemies of culture are leaf beetles, moth caterpillars, lacewings and bark beetles. So that all these gluttonous parasites do not disturb your vine, pay special attention to preventive measures. In spring and autumn, treat actinidia and the soil under it with Bordeaux liquid, which will destroy pests and their larvae.
Organization of wintering
In autumn, young (no older than 2-3 years) lianas are removed from the supports and reliably insulated. Spruce paws, peat, or dry foliage can be used as cover. Be sure to put poison for mice in the winter "dwelling" of actinidia. Fluffy rodents, of course, will not eat the plant, but they will pretty much damage it by arranging nests in the shoots. Adult specimens successfully winter in the ground without shelter, but before winter they need sanitary pruning - the branches thickening the crown must be removed, and the liana itself must be shortened by 35-50%.
Types and varieties
Of the great variety of natural varieties of actinidia, only 3 of them are suitable for garden cultivation - arguta, purple and kolomikta, as well as interspecific forms of culture - polygamy, hybrid, Geraldi. Having studied their characteristics, you can choose the fruiting vine that is right for you:
- Actinidia arguta is a native inhabitant of the Far East. Powerful dioecious liana, growing in length up to 25-30 m, with ovoid serrated leaves. In the place of white fragrant flowers, single or collected in a brush, dark green medium-sized berries (from 1.5 to 3 cm in diameter) form in September. Popular varieties of actinidia arguta: Ilona, September, Vera, Primorskaya, Relay, Golden Spit, Samoplodnaya, Lunnaya, etc.
- Actinidia purpurea is a shade-tolerant high-yielding treelike vine native to China. Of the shortcomings, it is worth noting only low frost resistance. Among gardeners, the Purple Garden variety is very popular, whose burgundy berries ripen at the end of September and have an exquisite marmalade taste.
- Actinidia kolomikta is the most cold-resistant of the cultivated species. It is a dioecious plant, reaching a length of 5–10 m. The ovate serrate leaves on reddish petioles are softly pubescent along the veins. The male specimens of the species are incredibly beautiful: in the middle of summer, the tops of the leaves turn white and, gradually turning pink, acquire an intense crimson hue. The actinidia kolomikta berries, green with a bronze or red tint, begin to ripen in August. The best varieties: Household, Slastena, Moma, Pineapple, Gourmet, Wafer, Narodnaya, Doctor Shimanovsky.
- Actinidia polygamy looks very similar to the previous species. Liana 4–5 cm high with elliptical silvery-green leaves that turn yellow by autumn. Fruits weighing about 3 g have a pleasant sour taste. Varieties: Apricot, Patterned, Beauty.
- Actinidia hybrid is an artificially bred species obtained by the Kiev breeder I.M.Shafran as a result of crossing of Arguta and purple actinidia. The best qualities of the hybrids are high cold resistance, large fruit size, exquisite taste and aroma of berries. Sorts: Candy, Souvenir, Kiev large-fruited, Hybrid Sausage.
- Actinidia Geraldi is a very rare species in nature, in some sources referred to as a subspecies of arguta actinidia. Large juicy fruits have a pleasant taste and delicate pineapple aroma. Varieties: Tuzemka, Juliania, Alevtina.
There are legends about the many beneficial properties of actinidia fruits. Due to the high content of starch, fiber, sugars, pectins, organic acids, mineral salts and alkaloids, the fruits of the culture are recommended to be eaten for anemia, rheumatism, colitis, scurvy, caries, diseases of the respiratory and digestive systems. There is much more vitamin C in actinidia berries than in oranges and black currants. Decoctions from the roots and leaves of creepers are indicated for joint pain, gout and sciatica. The peel of the fruit is used to heal wounds, and regular consumption of actinidia juice increases appetite.
Note! Excessive enthusiasm for sweet and sour healthy berries can provoke a serious intestinal upset, and actinidia is also contraindicated in thrombophlebitis, varicose veins and increased blood clotting.
Materials:
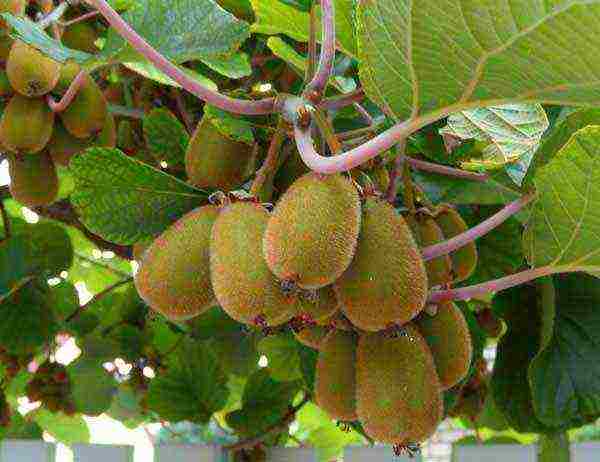
Self-fertile actinidia is quite an interesting ornamental plant. Its fruits are extremely beneficial for human health, tasty and aromatic. It is not difficult to grow and care for a plant. In addition, actinidia produces high and stable annual yields. The fruits are marketable and have excellent transportability; they can be stored for a long time in a cool place. Detailed information on growing actinidia and keeping it at home is provided below.
 The above plant has several names.This is actinidia holly, and self-fertile actinidia, and kiwi, and pineapple atinidia. The plant is, first of all, a spectacular tree-like liana, which is characterized by a beautiful decorative appearance and edible fruits. The latter are distinguished by an extremely high content of useful trace elements and vitamins.
The above plant has several names.This is actinidia holly, and self-fertile actinidia, and kiwi, and pineapple atinidia. The plant is, first of all, a spectacular tree-like liana, which is characterized by a beautiful decorative appearance and edible fruits. The latter are distinguished by an extremely high content of useful trace elements and vitamins.
This plant is characterized by stable, high yield, sufficient frost resistance, unpretentiousness to growing conditions, resistance to diseases and pests.
It should be noted that self-fertile actinidia does not require a male plant: it is well pollinated by itself. This monoecious plant begins to bear fruit as early as 4 years after planting. From one bush, you can get up to 9 kg of berries.
Actinidia fruits can be stored in the refrigerator for up to 2 months, but it is imperative to observe a strict temperature range for this: from 0 to 2 degrees Celsius.
 The above plant has the following characteristics:
The above plant has the following characteristics:
- has a height of up to 25 m (sort of argut), up to 6 m (type of kolomikt);
- trunk up to 5 cm in diameter;
- high growth rate of plant shoots (up to 2 m per season);
- fibrous root system, with skeletal roots;
- the maximum minus temperature that the actinidia plant can withstand is -30 degrees Celsius;
- kiwi that has entered fruiting is more frost-resistant than non-fruiting;
- mid-August - fruit ripening period;
- the fruits of the plant are distinguished by a round or oblong shape, from light to dark green in color;
- fruit taste - from sweet and sour to freshly sweet;
- light-loving plant;
- the culture loves moisture, but does not tolerate excessive amounts of it;
- spring pruning is strongly discouraged.
It should be noted that the actinidia plant can grow and bear fruit well for about 30 years.
The fruits of the above plant are extremely beneficial for the human body. They contain in their composition:
- carotene, niacin, ascorbic acid, vitamin B5;
- polyphenols;
- minerals: salts of potassium, magnesium, calcium, phosphorus;
- dry matter;
- organic acids;
- pectins.
It should be noted that the fruits of this plant contain 5 times more vitamin C than black currant and 10 times more than citrus fruits.
These fruits significantly strengthen the immune system of hypertensive patients, people with diabetes mellitus, the elderly and children. Especially useful fruits of kiwi for patients with vision problems.
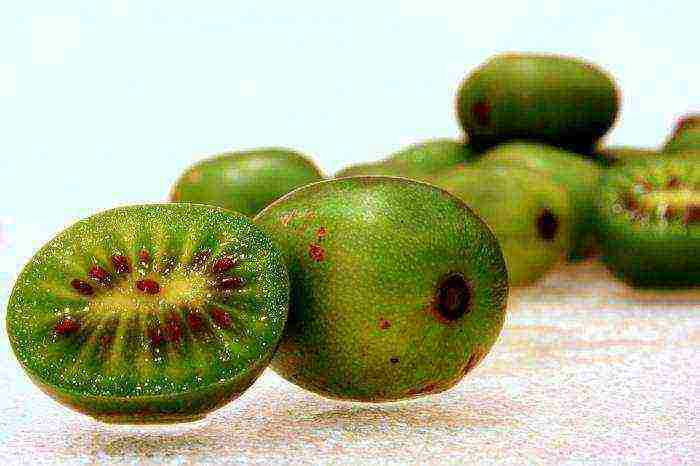 Perennial tree lianas have about 30 plant species in the genus. All varieties of actinidia are distinguished by high annual fertility and beautiful decorative appearance. On the territory of Russia, the following types of the above plant are known:
Perennial tree lianas have about 30 plant species in the genus. All varieties of actinidia are distinguished by high annual fertility and beautiful decorative appearance. On the territory of Russia, the following types of the above plant are known:
- Hybrid;
- Kiev large-fruited;
- Curly;
- September;
- Actinidia Argut is self-fertile.
Pollination of this plant occurs with the help of wind or insects. It is interesting that this process can be carried out at fairly large distances: up to half a kilometer. For example, some species of colomicts and interspecies are pollinated independently. In this case, the harvest comes out small.
In one place, woody lianas can grow for more than 70 years.
The yield of a vine depends on its type. Argut trees give the largest amount of fruits - up to 250 kg, colomic ones - only up to 3 kg. The weight of the fruits themselves is also different: for example, polygamous ones have fruits weighing 6 grams.
Recently in America, breeders have introduced a new variety of actinidia called Kiwi. So he is capable of producing fruits weighing up to 330 grams.
As for the harvest, the Giralda variety and all the colomicty fruits are harvested at the end of August, the rest until mid-September. Although, if you want more sugars to accumulate in the fruit, remove the kiwi closer to frost.
If the crop was harvested at sub-zero temperatures, it will not last long in the refrigerator.
 The above plant propagates both by cuttings and seeds.Seed stratification is carried out for 2 months. Before this process, the seeds are steamed. Then they are mixed with sand and slightly moistened. After that, the seeds are wrapped in a cloth and placed in a refrigerator, where a temperature of about +5 degrees Celsius must be maintained. It is recommended to ventilate them daily for fifteen minutes at room temperature.
The above plant propagates both by cuttings and seeds.Seed stratification is carried out for 2 months. Before this process, the seeds are steamed. Then they are mixed with sand and slightly moistened. After that, the seeds are wrapped in a cloth and placed in a refrigerator, where a temperature of about +5 degrees Celsius must be maintained. It is recommended to ventilate them daily for fifteen minutes at room temperature.
After the above stratification process, the seeds are planted in light soil, which is pre-steamed. Seedlings appear early enough: after two weeks. They grow slowly during the first year. But it is not recommended to feed them with anything.
Young seedlings of actinidia in the first winter are best kept in a cool place. It is advisable to plant it only in early spring.
If actinidia is propagated by cuttings, then it is recommended to cut them with two or three buds. One upper shortened leaf is also left. It is recommended to put the cuttings in a glass of distilled water for a day. Only then can they be planted in a container with a substrate. As the latter, you can safely use peat or sand. Important: do not cover the bud with a leaf with a substrate! After planting the cuttings, they need to be watered and covered with foil.
In order for the cuttings to take root well, it is necessary to provide them with a temperature regime (+18 degrees Celsius), humidity above average and access to sunlight. Once a day, it is recommended to spray the cuttings with a spray bottle.
Saplings that are grown from cuttings will begin to bear fruit in two to three years.
Actinidia seedlings prefer a variety of soils, with the exception of floating clay soils, near which groundwater is located. Breeders recommend making good drainage for the plant. Therefore, tree lianas are best placed on slopes with water drainage, in elevated areas. This will prevent stagnation of water in the roots of the plant.
Intensive growth of actinidia is observed on acidic and slightly acidic soils fertilized with organic mixtures. But in no case should they contain lime. The plant does not tolerate this feeding. Also, it is not recommended to add calcium chloride under actinidium.
It should be noted that it is strictly forbidden to plant actinidia after actinidia. An undesirable neighbor for the above plant is the apple tree. Better to plant actinidia near black currants.
In no case is it allowed to dig up the soil around the tree-like liana. The most that can be done is to carry out shallow loosening.
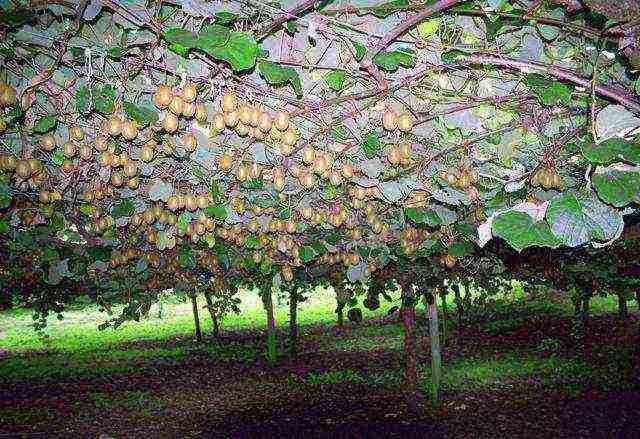 Plants are planted in spring to a depth of 70 cm. Gardeners are advised to add a little fertilizer to each hole: about 10 kg of ordinary humus and 100 grams of superphosphate. It should be noted that the planting of actinidia is carried out in early spring.
Plants are planted in spring to a depth of 70 cm. Gardeners are advised to add a little fertilizer to each hole: about 10 kg of ordinary humus and 100 grams of superphosphate. It should be noted that the planting of actinidia is carried out in early spring.
At the very bottom of the pit, you first need to place drainage, which can be stones, expanded clay or broken brick.
Plants are planted at a distance of up to 2.5 m. Before planting a tree liana, its roots are moistened in a clay mash.
In addition, breeders recommend planting one male for 10-15 female plants - for better pollination.
Actinidia care is carried out as follows:
- Before flowering, the tree liana is fertilized with phosphorus.
- In the fall, actinidia is fed with humus, potassium salt, superphosphate and ammonium nitrate.
- For a plant, it is useful to mulch the soil with humus, sawdust or peat with a layer of 12 cm.
- In addition, actinidia takes shelter for the winter to prevent young plants from freezing.
The above plant is unpretentious, but still requires some attention. The tree-like liana prefers to grow in the sun, although it feels good in the shade.
The conditions for keeping actinidia are as follows:
- It is important to build supports for the plant.
- Provide her with additional watering in hot weather.
- During the fruiting period, the soil around the tree-like liana is kept under black fallow.
This action cannot be performed:
- in early spring;
- during the period of intensive sap flow (due to the loss of juice, the plant becomes weak);
- at the end of summer (can cause awakening of the buds on the shoots of the current year).
The ideal time for pruning is the period after the plant has flowered. Actinidia is also pruned in late autumn. At this time, you can thin out plants, cut out weakened branches, remove frozen tips on the shoots.
The above plant is highly resistant to various diseases. Breeders note the following diseases that can affect actinidia:
- phyllostictosis of the leaves (brown spots);
- fruit rot on berries.
It should be noted that in order to combat the above infections, the affected fruits and leaves are collected and destroyed.
A dangerous pest for actinidia is cats that like to gnaw off young shoots and dig in the roots of the plant. Therefore, it is important to fence the woody liana with a wire mesh, and cover the top.
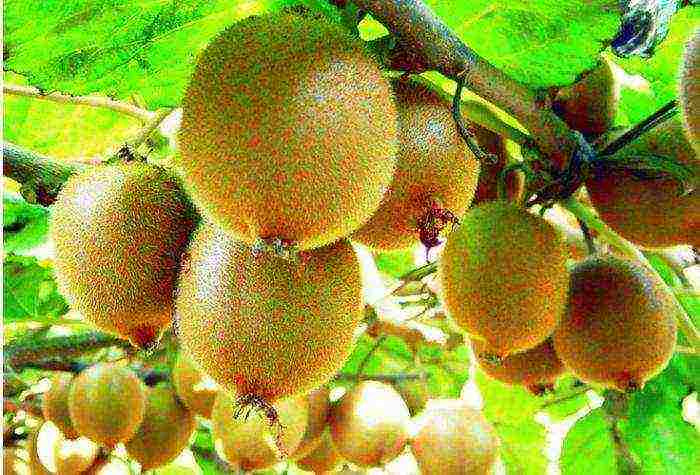 In order for the plant to grow intensively and bear fruit well enough, it is important to carry out the necessary work on time for the care and maintenance of actinidia:
In order for the plant to grow intensively and bear fruit well enough, it is important to carry out the necessary work on time for the care and maintenance of actinidia:
- In April, shelters are removed from young tree-like lianas. This is the time when the actinidia is planted.
- In May, gardeners are advised to feed the tree liana with organic fertilizers. Also this month it is recommended to loosen, weed the soil around the actinidia. If the weather is too dry in May, gardeners are advised to water the plant and mulch the soil.
- In June, it is desirable to ensure that the plant receives the required amount of moisture. It is also important to do a little loosening and weeding of the soil. At this time, cutting of green cuttings is also carried out.
- In July, in addition to weeding, loosening and watering, it is important to tie up the plant. It is also necessary to remove excess shoots.
- Harvested in August. After harvesting the fruits, it is recommended to feed the plant with minerals and organic fertilizers.
- The harvest is also in September.
- In October and November, actinidia is pruned to form a bush. Although the above plant is also distinguished by high frost resistance, it is all just important to have time to cover young tree-like vines for the winter to sub-zero temperatures.
Do you know that:
- in terms of the content of ascorbic acid, only wild rose can compete with the fruits of the above plant;
- 1 or 2 actinidia berries provide the body with a daily need for vitamin C;
- about 700 berries of the above plant cover the annual need for ascorbic acid for humans;
- for a family of 4, it is enough to have just one bush of a tree liana to provide each of its members with an annual intake of vitamin C.
 The fruits of the above plant are actively used in cooking. They are also harvested for the winter: canned and dried.
The fruits of the above plant are actively used in cooking. They are also harvested for the winter: canned and dried.
Jam is made from actinidia fruits, juice is squeezed out, cocktails are made. The above fruits are also used for decorating cakes and other sweets, for making desserts.
Dried actinidia or raisins are especially popular, which resembles dried grapes (raisins) in their appearance.
When preserving actinidia fruits, experts recommend adding citric acid, since already processed, they have a taste with mild acidity.
Self-fertile actinidia is a plant that can not only decorate a personal plot, but also give extremely tasty and healthy fruits. This is just a godsend for an enterprising summer resident.
Materials:


