Content
- 1 1 Description, types and varieties
- 2 2 Selection of seedlings
- 3 3 Landing
- 4 4 Care
- 5 5 Reproduction
- 6 6 Diseases and pests
- 7 7 Design
- 8 Autumn cuttings of roses - advantages and terms
- 9 How to cut rose cuttings
- 10 Planting a rose from a cut
- 11 Roses from cuttings at home
- 12 How to keep rose cuttings in winter
- 13 How to root a rose from a bouquet
- 14 Rooting cuttings of roses in potatoes
- 15 What is grafting?
- 16 The right time
- 17 Distinctive features of winter cuttings
- 18 Planting instructions
Today there are many rose hybrids that do not require a lot of attention when growing. Thanks to this, beginners in gardening art have the opportunity to choose a species according to their preferences and climatic conditions. Among the modern variety of varieties, along with thermophilic ones, there are frost-resistant representatives that take root without problems even in Siberia. For the best growing of roses, you must follow the basic rules.
1 Description, types and varieties
Rose is the generalized name for all representatives of this flower line, belonging to the genus of rose hips. In the process of growth, they form bushes, which differ in height depending on the species. Some do not exceed 30 cm, others can reach 2.5 m. By type, shoots are divided into uterine and annual. The standard classification also does not apply to the shape of the leaves, it all depends on the type.
The appearance, color and size of flowers vary. There are buds from 2–3 cm in diameter to 15–20 cm (with the number of petals from 5 to 100). The color scheme is striking in its variety, there are red, white, yellow, pink, black and even blue. Roses, which change their color during flowering, have become the pride of breeders. There is a conditional division of grades into classes. This helps to correctly navigate and choose the most appropriate option. The emphasis is placed not only on decorative indicators, but also on the place of intended cultivation - in the country, in the open field or at home.
Common varieties of roses often used in garden design, depending on the group belonging:
- Floribunda - Aprikola, Aspirin-Rose, Bengali, Black Forest Rose, Crescendo, Debut, Gebruder Grimm, Hermann-Hesse-Rose, Intarsia, Isarperle, Kosmos, Innocencia, Schone Koblenzerin.
- Groundcover Roses - Bluhwunder 08, Heidetraum, Sedana, Mirato, Schneeflocke, Stadt Rom, Mirato, Schneeflocke, Sorrento, Stadt Rom.
- Shrubs - Comedy, Goldspatz, Flashlight, La Rose de Molinard, Larissa, Medley Pink, Pink Swany, Shining Light, Yellow Meilove.
- Hybrid tea roses - Elbflorenz, Grande Amore, Eliza, La Perla, Pink Paradise, Schloss Ippenburg, Souvenir de Baden-Baden.
- Climbing large-flowered - Golden Gate, Hella, Jasmina, Kir Royal, Laguna.
The main groups of varieties of garden roses:
| Species name | Characteristic | Image |
| Park | Decorative representatives of roses. Endowed with increased winter hardiness, tolerate low temperatures well without shelter in regions of the middle climatic zone. Unpretentious to care, do not need annual pruning. They begin to bloom in late May - early June, the duration is from 2 weeks to 1.5 months. Bushes grow from 1 to 3 m in height |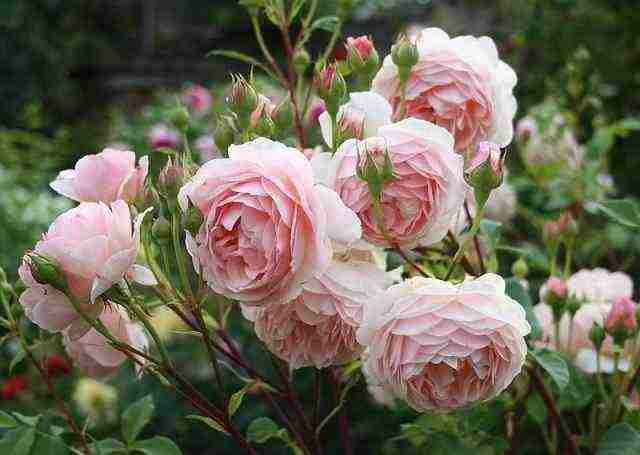  |
| Tea-hybrid | Bushes no more than 80 cm high. They are distinguished by long and spectacular flowering. The buds bloom once and last from June to autumn. The flowers are large, 10–15 cm in diameter. The varieties are frost-resistant, need a protective shelter in regions with cold winters |  |
| Polyanthus | Form numerous inflorescences on the shoots. Blossom from June until the first frost. Medium-sized flowers - 7-10 cm in diameter |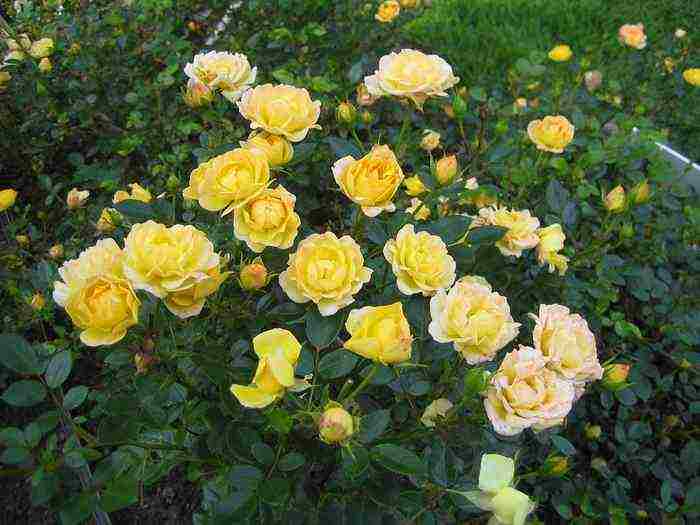  |
| Floribunda roses | An intermediate variety between hybrid tea and polyanthus roses. The buds are large when opened and exude a pleasant aroma. Abundant flowering is observed for a long period. They endure the cold, staying for the winter in the open field |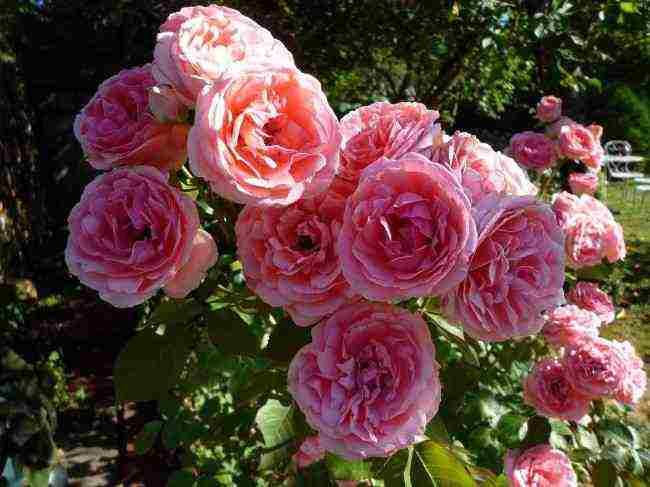  |
| Climbing | They are divided into 2 subspecies: small and large-flowered. The first variety is characterized by buds up to 4–5 cm in diameter; the second is from 5 to 10 cm.A distinctive feature is flexible long shoots, at the ends of which small group inflorescences are collected |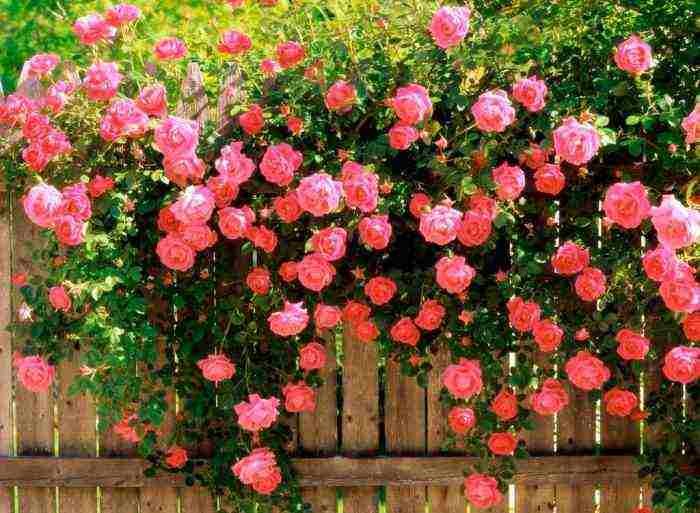  |
| Miniature | Compact bushes, abundantly strewn with small buds. Endowed with a long flowering period, right up to the first winter cold weather. In gardens, they are grown not only in flower-bed compositions, but also in suspended and stationary flowerpots or pots. |  |
| Ground cover scrubs | Roses of unusual decorativeness, which are planted as a continuous flowering lawn. Unpretentious to care, cold-resistant and with increased immunity to diseases |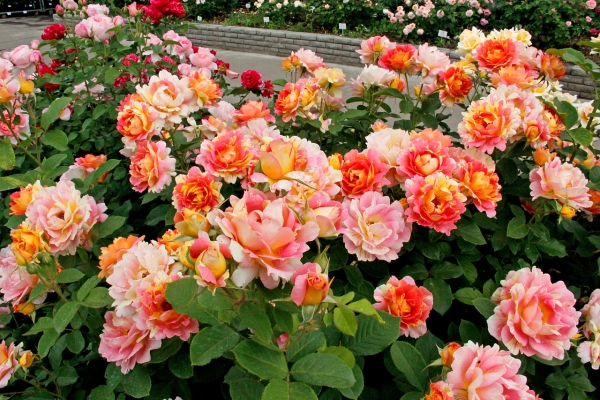  |
| Modern park | A group that includes hybrids of Cordes, musk rose, rugosa, shraba and moesi. In abbreviated form, all varieties are called scrubs. Includes all varieties that for some reason do not fall into other groups. They are characterized by the following features: buds of atypical configuration and different colors, they smell nice, the bushes are vigorous, strong and up to 2 m high. They have repeated flowering during the growing season. Plants are unpretentious, have strong immunity, frost-resistant |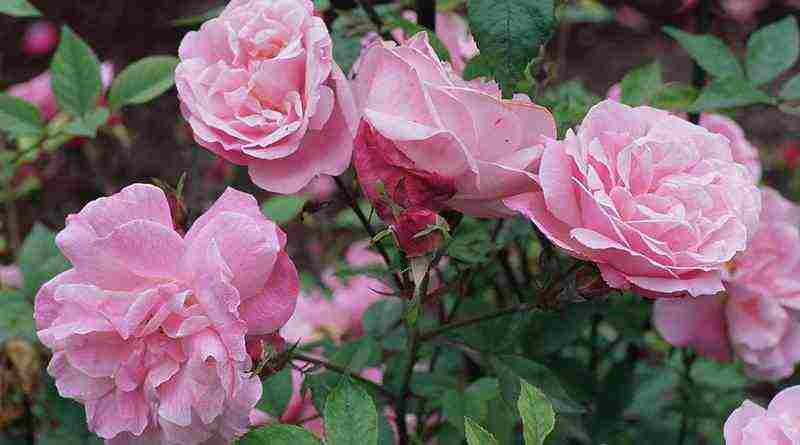  |
| Shrubs | The main difference is a large bush with shoots diverging on the sides. Even with minimal maintenance they grow up to 2.5–2.8 m in height. The following varieties are most popular among gardeners: Modern Shrab, Grandiflora. In landscape design, they are often used as hedges. |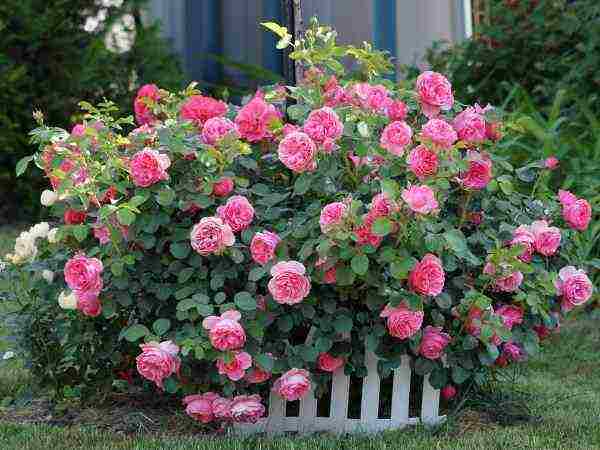  |
| Cascading | Rose hips with grafted climbing and ground cover roses at a height of 130–150 cm. The stems are long, sometimes drooping. The shape, size and color of the flowers vary and depend on the result of the vaccination |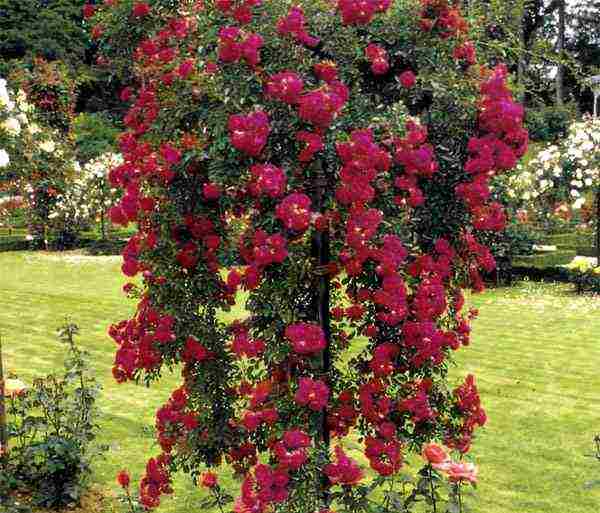  |
Rules for growing and caring for a climbing rose in the open field
2 Selection of seedlings
If you want to get lush roses in the garden, you should competently approach the choice of seedlings. First of all, attention is paid to the external state. Shoots and stems should be green in color, elastic structure, with bark free from defects and damage. The presence of live and healthy kidneys is imperative. The requirements for the root system are similar: no breaks, folds and rot. They try to touch the ground where the seedling is located, so that it is slightly damp. The foliage must be lively, green, without spots.
Important points to pay attention to when choosing seedlings:
- A sale tag is a must for a quality product. It contains all the necessary information: species, variety, selection.
- The presence of the ADR marking - a similar icon denotes varieties with increased resistance to diseases and the best decorative qualities.
- The most expensive seedlings have 3 or more shoots, 2 of which grow from grafting; the cheap ones have only 2, both from the vaccination site.
Roses come with open or closed roots, in containers. After buying seedlings with planting, it is not recommended to tighten it. This is usually done in the fall, before winter. However, in the regions of the middle zone, including in the Moscow region, planting is carried out in the spring. Otherwise, immature young roots do not have time to take root in a new place and die under the influence of frost. It is allowed to plant roses in summer, which is guaranteed to give a good result. This method can be more expensive.
Azalea - outdoor growing rules and home care
3 Landing
Regardless of the variety, all roses prefer a loose, soft, fertile substrate with good drainage and a pH of 6–6.5. It is unacceptable to plant flowers on a plot where similar species have already grown for 8-10 years in a row... Such land is completely devastated, no fertilizers can restore the missing elements in its composition. At the same time, there is an accumulation of pathogenic microflora.
Despite the love of light, the plant is not recommended to be planted in direct sunlight. This will not stop flowering, but the decorative appearance will change: the roses become faded and withered.Therefore, the place is selected with shading, which is important at noon. Ideal location - next to low garden trees or along fences.
Before planting, the seedlings are prepared: too long roots are cut with pruning shears, dry ones are removed completely. It is unacceptable to touch the filamentous roots. When planting in spring, the stems are shortened to 30–35 cm, leaving up to 4 buds on the surface. For 2-3 hours, the seedling is placed in a bucket of water.
If clay soil prevails on the site, river sand is introduced into the planting pit, sandstone is diluted with sheet compost. The sequence of agrotechnical measures:
- A hole is dug 2-3 times larger than the size of an earthen coma with roots. The bottom is well loosened.
- The seedling is buried at a level 4–5 cm higher than the grafting site. The extracted substrate is mixed with compost in a ratio of 1: 3 and pure wood ash is added.
- The free space is carefully filled up, the surface is slightly compacted.
- At the end of the procedure, the planting site is abundantly moistened. To prevent the water from spreading, a furrow is made around the perimeter.
It is imperative to spud the root space not only immediately after planting, but in spring and autumn. In the first case, such a technique helps to exclude the rapid evaporation of moisture from the soil, and in the second, it protects the roots from freezing.
You can plant roses once with seeds. It is believed that they germinate for a long time, but it is possible to accelerate germination by pre-keeping the material in the cold. When sowing before winter, it is advisable to treat the seeds with a stimulating solution. The garden bed is dug up, compost, peat and humus are introduced into it. Make parallel furrows about 4 cm deep, where the sowing is carried out. At the same time, an interval of 15–20 cm is observed. Sprinkle with soil on top. If winter is expected to be frosty, cover the garden bed with any suitable material for safety net. It is better to prepare a plot for spring sowing in the fall.
Another effective option for germinating seeds is seedlings at home. The favorable period for this is the beginning of February. Seed material is preliminarily placed in the cold for several months, then soaked in a growth stimulator. They are planted in separate pots, where the peat-sand mixture is poured. The seeds are deepened by 3-4 cm, sprinkled with sand and moistened with a spray bottle. With the appearance of 2-3 strong leaves, the seedlings dive separately. In May, they are transferred to a permanent place of growth - in the garden.
Planting and caring for Bartzella peony in the open field
4 Care
For full development and abundant flowering, roses must be looked after. Mandatory procedures are:
- Watering is carried out once every 7 days so that the soil is soaked to a depth of at least 25 cm. Otherwise, the plant puts out surface roots, which are easily damaged during subsequent loosening. Moisturize 2 times more often if the weather is hot. It is advisable to cover the root circle with humus or peat mulch. Then the moisture will evaporate less intensely.
- Before the onset of the first frosts (in October), the bushes are wrapped in burlap, and the roots are sprinkled with a mixture of earth and sand.
- Pruning plays a primary role in overall grooming. In the spring, they resort to formative. In the summer, wilted buds, drooping and diseased leaves are removed. In autumn, dry and damaged shoots are removed. Places of cuts are treated with garden pitch. Before the onset of winter, all weakened stems and shoots are pruned.
- Rotted horse manure is used as top dressing, chicken and pork are contraindicated. This is due to their high acidity. Any fresh organic matter blocks nitrogen in the soil, thereby inhibiting the growth of flowers. The first time fertilizers are applied before laying the buds. Calcium nitrate is suitable (1 tablespoon per 10 liters of water). During the period of active growth, they are fed with infused liquid mullein, mineral supplements or herbal infusions. Frequency - once every 2 weeks.
From the middle of summer, all feeding is stopped, watering is minimized. The plant needs to go into a dormant state, which serves as a preparation for wintering.
5 Reproduction
Roses can be propagated by seed and vegetative methods. The first option is in little demand, since it does not retain varietal characteristics. Therefore, it is used more often in relation to wild representatives. The seeds are harvested when the fruit turns red. The raw material is preliminarily stratified in moist sand, kept until spring at a temperature of + 3 ... + 4 ° C. In the spring, the seeds are treated with a stimulant and planted in open ground. From above they mulch with humus. After some time, the plantings are thinned out, distributing the bushes at a distance of 10-15 cm from each other. In the summer, mineral dressings are introduced. Grown until next August, then used as a stock.
The most successful breeding method is by cuttings, along with grafting and dividing the bush:
| Method name | Description | Image |
| Summer cuttings | In the morning or in the evening, strong shoots with slight lignification are cut off. Cuttings 13-15 cm long are prepared. Several leaves and 2-3 living buds are left on each. The lower part is cleaned of foliage. The bottom is treated with a growth stimulant, the cutting is immersed in water, where rose petals are placed. They are planted directly into the ground, previously sprayed with potassium permanganate. Cover with a glass cover on top to create greenhouse conditions. The optimal temperature regime during the day is not lower than + 25 ° C, at night + 19 ... + 20 ° C |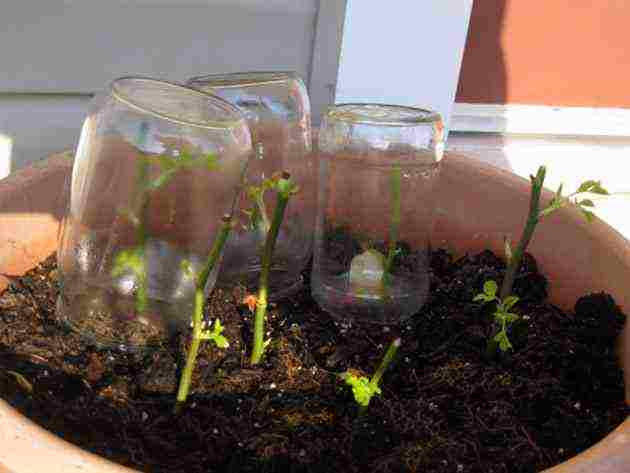  |
| Rooting in potatoes | The most popular and easy breeding method. Thus, the cuttings are saturated with carbohydrates and potato starch. In a bright area, a ditch is dug about 15 cm deep, filled with sand for a third of the volume. Cuttings are first stuck into the potatoes 10–12 cm and placed in the prepared recess. Further manipulations are standard: cover with a cap, after a while hardening is carried out. Pour sugar syrup every 5 days |  |
| Reproduction in a package | The bottom of the cuttings is moistened with aloe juice, then deepened into a lump of earth, laid in a plastic bag. It is hermetically closed, having previously released the air from the inside. Hang out for germination on the window. A month later, when young roots appear, they are planted in open ground |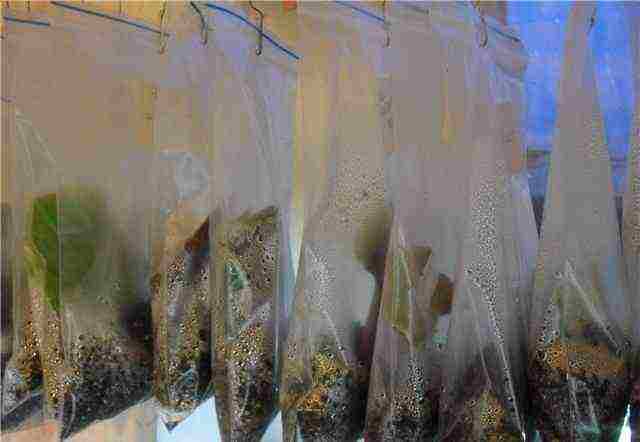  |
| Rooting in water | Freshly cut stems, divided into cuttings, are immersed in distilled water. Before that, thorns are removed from the surface and other vegetation. The water is regularly changed until the cuttings take root |  |
| Vaccination | Reproduction by grafting is suitable for young rose hips. The procedure is carried out in the middle of summer. First, the lateral branches are removed from the stock, and the root collar is cleaned of the ground. An incision is made in the shape of the letter T, where the handle is placed. Fix it in place in any way. After 15–20 days, the kidney is checked: if it is swollen, then the vaccination was successful. If it is black, then the method has failed. Before the onset of winter frosts, grafted roses are spud 5-6 cm above the grafting site. In the spring, the soil is raked. The plant is pruned over the graft. When pulling, pinch the top over the third leaf | 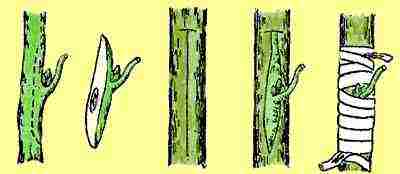 |
| By dividing the bush | Suitable for non-grafted varieties of roses. In the spring, before bud break, the bush is dug up and divided into parts. Each should consist of roots and a shoot. Bare areas are powdered with crushed coal. Then they are seated in separate places in the garden. | 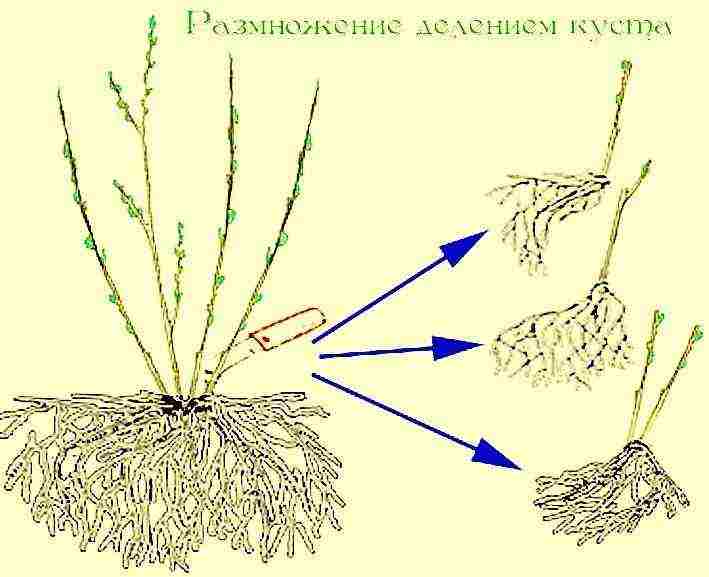 |
| Layers | With the onset of the first spring heat, a low-lying shoot on a bush is chosen. They bend it to the ground and put it in a dug hole. An annular cut is made on the surface beforehand. Fix the shoot in place and cover it with earth. Further care is moisturizing until the cuttings take root. The next year, the baby is separated from the maternal source and planted separately. |  |
6 Diseases and pests
Most roses are endowed with stable immunity to many diseases, but this does not exclude the possibility of damage. The following diseases are most common:
- Rust - the peak of the disease is observed in the spring. Brown spots appear on the leaf surface, and from the inside - orange clusters of spores, which turn black towards the end of summer. Unauthorized leaf fall begins, the stems acquire a brown tint. The situation can be corrected by watering with a decoction of field ivy. The affected areas are removed.
- Black spot - appears in August, towards the end of the month. The leaves are instantly covered with black patches in a yellow frame. This gradually spreads to the stems. Leaves fall. If appropriate measures are not taken in time, the flowers die. Treatment is the same as for rust.
- Powdery mildew - a whitish bloom forms on the leaf component and shoots, then slugs form. The disease is characteristic of varieties that are grown in greenhouses and at home. The disease is characterized by rapid spread. Plants showing signs of damage are cut and destroyed. The earth is sprinkled with ash and dug up.
Of the insect pests, the most dangerous are aphids, spider mites. With few attacks, you can kill the first pest by hand or wash the leaves with soapy water. If there are a lot of insects, then treatment with insecticidal preparations helps. The mite is fought by applying tobacco or infusion of wormwood. With illiterate care, there are cases of attack by thrips, sawflies and cicadas.
With a lack of nitrogen in the soil, the plant turns yellow. It begins to spread from below and is accompanied by leaf fall. The same thing happens with the top. If the foliage is covered with yellowness only at the edges, this indicates a lack of potassium. Yellow streaks indicate a small amount of trace elements.
7 Design
Most people are used to planting roses in separate flower beds, but modern trends in landscape design have made their own adjustments. It is fashionable to combine them with perennial flowering crops or undersized shrubs.
For the design of mixborders, it is recommended to take varieties of musky representatives due to their brightness and proportional shapes of the bushes. Short varieties with small flowers are ideal. Then they do not dominate the neighbors, but harmoniously merge into a beautiful composition. It is better to place unpretentious varieties in unfavorable areas of the garden, and climbing roses will effectively decorate fences and terraces.
A novice florist may have a question as to whether it is possible to grow roses from cuttings in the fall? As practice shows, reproduction at this time of the year is more effective than what is carried out in the spring.
Reproduction of roses by cuttings in autumn
Loading …
The rose is called the queen of the garden. The flower decorates the garden and fills it with an amazing aroma. In order for them to actively bloom and not encounter certain ailments, they will need appropriate care.
The most common method for propagating a rose involves growing it from a cuttings. It is better to cultivate a flower in the fall. Such work will not require serious time expenditures. How can I do this? Let's figure it out.
Autumn cuttings of roses - advantages and terms
If we compare grafting with grafting, then the first has a larger list of advantages:
- Flowers that are grown this way do not form a wild root cavity, so they will need serious maintenance.
- Flowers from cuttings are highly resistant to winter weather conditions. If their upper part is destroyed by frost, the plant will recover from dormant buds.
- To acquire planting material, you just need to take a stem from a flower from a gift bouquet.
Autumn cuttings of roses
Reproduction and pruning are carried out in the same period - in late October and early November. If you are thinking about this method of plant propagation, you need to find out which varieties are suitable for this:
- All varieties of polyanthus and miniature roses;
- Almost all varieties of semi-climbing roses;
- Climbing roses from the rambler group (Rambler);
- Excelsa roses;
- Large-flowered variety Flammentanz;
- Iceberg and Rosalind from the floribunda group;
- Hybrid tea (do not confuse with tea) roses take root in the shortest possible time, but in the future their root system is not developing so actively. That is why it is recommended to vaccinate them.
reproduction and pruning are carried out in the same period
As for the remontant and park varieties, their propagation by cuttings is a complex process, which only an experienced florist can master.
How to cut rose cuttings
Reproduction is carried out according to the following scheme:
- Take ripe shoots without signs of disease. Their thickness should be 4-5 mm.
- Divide them into segments (each of them should have 3-5 developed buds).
- Make straight cuts at the top, obliquely at the bottom. This way you will know exactly which part to plant the cutting. Use a well-sharpened tool for work. Be sure to disinfect it by scalding it with boiling water or treating it with alcohol.
- Make the upper cut 2-3 cm above the upper kidney, the lower one - under the one below.
Use a well-sharpened tool for work
Important! If you do not plan to root the plant right away, do not pluck all the leaves, you will have to leave a few pieces in order for it to be supplied with food. Leaves growing from below must be trimmed.
Planting a rose from a cut
Once you have cut the cuttings, you will need to assign the plant to a permanent location. This way it will not be stressed. Autumn rooting is carried out according to the following scheme:
- Trim the cuttings and apply a root former to them.
- Dig a hole, the depth of which will be 30 cm, fill it 2/3 with grass, and put a layer of compost on top of it.
- Plant the shoots at a 45-degree angle. Leave 1/3 of the cuttings above the surface, or 1-2 buds above ground level.
- Water the plantings.
Planting a rose from a cut
Not every grower is aware of how to properly cover cuttings in late autumn so that they can survive after wintering. For shelter, you can use plastic or glass bottles. Punch holes for air in them or raise them above ground level. Cover the bottle with leaves and lay a non-woven cloth over them. Drive the pegs into the places where the landings are. A straw shelter is suitable for insulation.
Roses from cuttings at home
Those who grow roses at home or in the country can resort to this breeding method. Its principle is as follows:
- In early November, after the arrival of the first frost, prepare cuttings with 2-3 buds. Their length should be within 20 cm. Please note that the buds may bloom at the wrong time. To prevent this, dip the top of the cuttings in melted wax and then in cold water.
- Place a layer of expanded clay (5-6 cm) in a plastic bucket and a soil for flowers, combined with perlite or vermiculite.
- Water the soil, dip the bottom of the cutting into water. Then treat them with "Kornevin" and stick them into the hole. A container with a diameter of 30-40 cm can hold about 30 petioles.
- Cover the bucket with cellophane or a bag, wrap with rope. Secure the top of the bag with clothespins. You can also cover the plantings with glass jars (never leave them in the sun).
- Wrap the bucket in a blanket and place it on the glazed loggia. If the balcony has a cement floor, boards or foam must be placed under the container.
Preparing cuttings
Important! If serious frosts are coming at night, remove the pots in the apartment.
How to keep rose cuttings in winter
If it was decided to postpone the breeding of roses until spring, make sure that they can survive the winter. Proceed as follows:
- Dig a hole 15 cm deep in the garden. Lay covering material at the bottom. Cotton fabric is ideal as the latter.Place the cuttings on top of it.
- To make it easier for you in the spring to find shoots that were hidden for storage until spring, drive wooden pegs along the edges of the hole.
- Remove the leaves and place the cuttings evenly apart.
- Cover with a cloth and place a small layer of earth on top of them.
- After the snow melts in the spring, dig up the cuttings and inspect them. The fact that they have taken root will be evidenced by the appearance of callus - a growth with roots. After removal, they must be immediately planted in the cuttings or in a permanent place.
Saving rose cuttings for the winter
Advice. If it is not possible to plant immediately, dip the cuttings into a container with water, to which a few drops of plant growth regulator (for example, "Epin") have been added.
How to root a rose from a bouquet
How do you want to extend the life of a presented bouquet of fresh flowers. This is impossible to do, but if you try, you can grow a rose out of them in your flower bed. Slice the flower stems into cuttings. You can root them at any time. To do this, you can use flower pots or cellophane bags filled with moss or fibrous peat. For watering the earth, aloe liquid is suitable. For 9 tsp. water will need 1 tsp. juice of this plant. Inflate the bags slightly and hang them from the window frame. Soon, a greenhouse effect will appear in this environment, and roots will appear on the cuttings.
Remember to pay attention to watering the soil in pots
Remember to pay attention to watering the soil in the pots. Cut fresh sprouts and leaves by half. Thus, the plant will be able to maintain strength before planting it in an open area.
Rooting cuttings of roses in potatoes
There is another effective way of rooting cuttings. For this you need potatoes. Process the freshly cut cuttings in a solution of potassium permanganate, then soak them in water mixed with equal proportions of aloe juice. After 12 hours, insert the cutting into the potato tuber. Dip it in a pot, fill it 2/3 with earth and pour it with a strong solution of potassium permanganate. In the future, you will need to water the planting as the topsoil dries up. Use standing water for this. Water the plant every 5 days with water diluted with sugar (2 teaspoons per 200 ml of water).
Growing cuttings of roses in potatoes
Loading …
To create a greenhouse effect and activate rooting, cover the planting with a jar. We do not give a 100% guarantee that this method will be effective. Experiment, you may be able to propagate the plant using potatoes.
As for other growing options, roses planted in the fall take root well and take root and soon delight the eye with their gorgeous flowering. Good luck with this difficult task!
What is grafting?
Cutting is an artificial method of vegetative propagation of plants, in which parts separated from the mother plant are used - cuttings. When cuttings, young plants with their own root system are obtained, which retain all the characteristics and properties of the parent specimen.
reference... The following varieties of roses can be perfectly grown from cuttings: all miniature and polyanthus, most semi-climbing and climbing, hybrid tea varieties, excelsa roses, Iceberg and Rosalind varieties. Repair and park roses are cut with great difficulty.
The right time
Roses can be cut at any time of the year. Florists often root cuttings cut in the summer. But autumn is considered the most successful season for propagation by cuttings: cuttings cut from rose bushes during autumn pruning are planted in the ground for rooting.
But there are situations when such copies fall into the hands of a lover of these flowers, the acquisition of which he has long dreamed of. And it's already winter outside, and there can be no talk of a full-fledged rooting of the plant. Therefore, it makes sense to save the harvested shoots until spring.
Distinctive features of winter cuttings
 The meaning of the production of cuttings before winter is to preserve the cuttings until spring in a state capable of vegetation and rooting. This is tantamount to keeping the roses alive until spring. There are several options for saving:
The meaning of the production of cuttings before winter is to preserve the cuttings until spring in a state capable of vegetation and rooting. This is tantamount to keeping the roses alive until spring. There are several options for saving:
- preservation of cuttings in the basement;
- in the fridge;
- on the glazed balcony;
- on a cold windowsill.
And it is possible, as the long-term experience of flower growers shows, to create a kind of storage for cuttings right in the ground in the open air. They can simply be dug into a specially dug hole, and you can also create a special structure - a cuticle ("cold greenhouse").
The essence of the method of storing cuttings in the refrigerator is to place the cut cuttings in a damp cotton cloth or paper (as an option - sphagnum moss), in which they are wrapped, and then packed in a plastic bag. Storage place - a section in the refrigerator for vegetables.
reference... Cuttings can also be placed in a moist peat and sand substrate that is poured into a box and stored in the basement room.
You can store cut cuttings on the balcony:
- put them in a bucket;
- put on a plastic bag on top;
- warm well with blankets and jackets;
- putting packing foam under the bucket, leave to winter.
Planting instructions
- Preparation of inventory and materials... To carry out cuttings, you will need a sharp, alcohol-disinfected garden knife or pruner, iron arcs, covering material (agrofibre, lutrasil), plastic wrap.
- Soil preparation... For the cuticle, it is necessary to dig a pit or trench 30 - 70 cm deep. The soil that was taken out must be mixed with peat and sand in equal proportions. Peat will provide looseness of the soil, its air permeability, sand will facilitate drainage (outflow of excess water).
Humus, compost can be added to this mixture. The bottom of the cuticle must be covered with a layer of coarse sand (5 - 10 cm). As an option: the bottom is filled with dry branches, grass (20 cm), then a layer of peat (20 cm), then a layer of compost soil (20 cm).
- Cutting cuttings... The stems from which the cuttings will be cut must be straight, strong, without visible damage and infectious diseases.
 Their thickness is about the size of a pencil (4 - 5 mm in diameter). Each of the stems is cut into 20 - 25 cm long pieces.
Their thickness is about the size of a pencil (4 - 5 mm in diameter). Each of the stems is cut into 20 - 25 cm long pieces. An important condition: on each of these segments there should be 3 - 5 developed kidneys. It is better not to take the upper part of the shoot, as it may be immature.
The upper cut - straight - is made 2 - 3 cm above the upper kidney, and the lower one - at an angle of 45 degrees - right below the lower kidney. All leaves and thorns must be removed.
Attention! The plant can lose moisture through the leaves and thorns, which jeopardizes the successful rooting process.
- Processing cuttings... It is desirable if the cuttings are treated with root stimulants (Kornevin, Ukorenit, Heteroauxin) before planting. Some flower growers recommend preliminarily placing the shoots of roses for a day in water with a stimulant diluted in it.
- Rooting... The substrate in the cuttings must be well moistened before planting cuttings. Each stalk is buried 2/3 into the ground, 1/3 of the surface remains above the surface. Deepening is carried out at an angle of 45 degrees to increase the contact area of the cutting with the ground. The substrate around the seedlings is well crushed in order to exclude the flow of air to the cut. The distance between the planted shoots is 10 - 15 cm.
- Landing... In the spring (May), rooted cuttings must be transplanted to a permanent place. The best place for a rose is an open, light area, without drafts and groundwater close to the surface of the earth.Seedlings must be carefully removed from the cuttings together with an earthen lump formed around the roots and planted in a prepared planting pit.
Cutting technology will allow the gardener to grow healthy and fragrant roses, and cuttings can be extracted from a bouquet, using the potato method or by the method of autumn cuttings. By choosing the appropriate method and properly organizing the care of the planted cuttings, the gardener will be able to create a colorful flower bed.
The content of the article:
- What is grafting?
- What are the benefits of cuttings?
- Turning a cutting into a seedling
- Cuttings from a bouquet
- Potato cuttings method
- Autumn cuttings
- Care of planted cuttings
The easiest and most reliable way to create a rose garden in the garden is to use ready-made seedlings purchased on the market or directly from a specialized flower nursery for planting. But experienced gardeners know that this is far from the only way to expand their collection. Seedlings do not have to be bought, they can be grown independently from cuttings.
What is grafting?
A stalk is a part of the stem of an adult plant, devoid of roots, but having 2-3 buds. Knowing how to grow a rose from a cutting, you can turn this small part of the stem into a full-fledged seedling, from which a rose bush will soon grow.
For cuttings, the middle or upper part of the stem of a strong, healthy plant is used. Moreover, it is recommended to cut a stalk from a semi-woody shoot that is about to bloom or is about to fade. With the help of a pruner, a stick about 10-15 centimeters long, containing three buds, is cut from such a stem. Moreover, the lower and upper sections (they are made at an angle of 45 degrees) should be located, respectively, directly under the lower and above the upper kidney. So that the stalk does not lose moisture through evaporation, the lower leaf is removed completely, and the two upper ones are shortened by one or two thirds.
What are the benefits of cuttings?
Although grafting is a longer and more troublesome process than planting seedlings, it has its advantages:

- Cheapness. Depending on the variety, the cost of one seedling ranges from several hundred to several thousand (and even tens of thousands) rubles. Instead of spending a fortune on creating a rose garden, you can buy just a few seedlings (you can even have one) and multiply them by cuttings in a few years. In addition, having figured out how to grow roses from cuttings, you can easily exchange planting material with friends or neighbors at no cost at all.
- Roses from a bouquet. A flower bouquet, at its best, can last for a couple of weeks, and most often only for a few days. If the presented flowers are very dear to you and you want to extend their life so that they will continue to be a living reminder of a happy day, you can also make cuttings from a bouquet. And then the very roses that turned out to be so dear to you will delight you for many years, and not 4-5 days.
Turning a cutting into a seedling
Before a 15-centimeter section of a rosebush stem turns into a full-fledged plant, it must go through two stages - rooting (that is, turning into a seedling) and planting the seedling itself. Only then will the formation of a normal rose bush begin.

There are several options for how to grow a tea rose from a cuttings:
- In the ground. In the garden or vegetable garden, a small weed-free plot of land is allocated, in which a special bed is made. In order for the plants to root better, it is better to mix the original soil with peat and sand. The cuttings are placed on the bed at an angle of 45 degrees so that the lower bud is underground. The aboveground part of the cutting is covered with a glass jar to create a greenhouse effect. The cuttings should be watered, but not very hard, so that excess moisture does not lead to decay.When the stalk begins to sprout, the jar can be removed for a short time during the day so that the young plant is tempered. After a couple of weeks of such hardening, you can get rid of the "greenhouse" for good.
- In a pot. This method is generally similar to the first, but instead of a vegetable garden or garden, even a window sill in a city apartment can serve as a rooting platform. This method is relevant if you decide to do cuttings during the cold season, or do not have your own country house. Using this method, you can easily grow a rose from a cuttings at home.
- In water. If desired, instead of a vegetable garden or a pot of soil, you can even use a jar of water (preferably boiled). The container with the handle should be placed in a moderately lit place (it is not necessary to put it on the windowsill), and the water in it should be changed with some regularity. When, after three weeks, the cuttings acquire thin roots, they can be planted in pots with normal fertile soil and allowed to ripen to a full-fledged seedling.

One of the main conditions for growing roses from cuttings is a fairly warm ambient temperature (+ 23-25 degrees), good lighting and moderate watering. You should also warn that if buds appear on cuttings, they should be pinched immediately.
Cuttings from a bouquet
As a whole, we figured out how to grow a rose from a cut cuttings. Now let's look at a more unusual option - cuttings from a bouquet.
If for some reason you really want the roses presented to you to live for more than a week, make cuttings from their stems and try to root them. And although in general this process occurs according to the same principles as the grafting of ordinary rose bushes, there are still several features. So that the cuttings from the bouquet are viable, you need to adhere to the following rules:

- change the water in the vase where the bouquet stands daily;
- at night, immerse the bouquet "with the head" in a bucket or basin with clean water;
- cut the cuttings from the stems only after the petals begin to fall from the buds;
- if cuttings from a bush must contain three full-fledged buds, then bouquet cuttings are weaker by default, and therefore can give life only if there are a maximum of two (or better one) buds; in addition, this way more cuttings will turn out from the bouquet, which will increase the overall chances of survival of the bouquet;
- bouquet cuttings should be stuck into the ground vertically, and not at an angle; while one kidney must be above ground level.
For the rest, care for cuttings from a bouquet is carried out according to the same scheme as for shoots taken from living rose bushes. That is, in more detail, see the general recommendations on how to properly grow a rose from a cutting.
Potato cuttings method
In recent years, a somewhat extravagant method of rooting cuttings has been gaining popularity. Not all growers recognize it, but if you have a progressive outlook on the world, you can also try the potato technique. It is equally suitable for rooting cuttings taken from a bouquet as well as those taken from a normal rose bush.

The preparation of the cuttings themselves is carried out in exactly the same way as if you were preparing to root them using traditional methods. The garden bed should be either an indoor greenhouse / greenhouse, or a pot of soil placed indoors. Next, you need to take young medium-sized potato tubers, carefully remove all the eyes with a knife (try to damage the potatoes as little as possible) and stick one cutting into each tuber. We add the resulting structure to the garden bed (potatoes down, of course) or in a pot. In this case, the potatoes are laid on a layer of sand and covered with soil. Cuttings should be planted no closer than 10-15 cm apart. The aboveground part should traditionally be covered with a glass jar to create the most comfortable conditions for the shoots.
Immediately after planting, the cuttings should be watered with water with potassium permanganate dissolved in it to a light pink color. In the future, watering is carried out with water and sugar (one spoon per liter) every five days. When it becomes obvious that the cuttings have survived and have begun to sprout, the cans can be gradually removed to harden the young plants. In general, cuttings should be kept under glass protection for no longer than 15 days.

The main advantage of the potato method is the optimal combination of moisture and nutrients that pink cuttings provide potato tubers. As a result, rooting is faster, and the survival rate of plants is higher.
The technique is suitable for most varieties. So, if you do not know how to grow a climbing rose from a cutting, you can try this method.
Autumn cuttings
As mentioned above, in order for the cuttings to root normally, they need approximately room temperature and good illumination. That is why cuttings on open ground are carried out in late spring and summer, and in winter only in heated rooms. But if the cuttings were at your disposal on the eve of winter, and you have nowhere to root them in pots, or you simply don’t want to, they can be “preserved” until spring.
Autumn cuttings just allow you to keep the shoots alive and healthy until spring, without allowing them to take root (which would lead to the death of a plant that did not have time to get stronger). With the arrival of spring, cuttings "preserved" in the ground will be fully ready for planting and rooting under normal conditions.

This method is very popular, because in the fall, growers prune rose bushes, as a result of which there are many cuttings that are simply a pity to throw in the trash.
To preserve the cuttings until spring, they need to be dug into the ground completely, leaving nothing above the ground. In this case, the garden bed should not be placed where it is convenient for you, but where the most snow is swept in winter. Usually such a place is the north side of the fence or one of the blank walls of the house / shed. It is advisable to sprinkle dry peat on top with a small layer and, if possible, cover the garden bed with dry leaves or spruce branches. We have already described how to grow a climbing rose from a cuttings that have wintered in such conditions.
Care of planted cuttings
To get strong viable seedlings and reduce the likelihood of death of cuttings, in the process of rooting, you should adhere to simple rules for caring for a bed with cuttings:

- Water the shoots regularly, but not too abundantly, because in the waterlogged soil, the underground part of the shoot will begin to rot.
- In hot weather, instead of excessive watering, it is better to spray the shoots with a spray bottle.
- Provide the cuttings with the most comfortable temperature conditions. So, if a jar protects the plant from a sudden summer cold snap, then only artificial shade and the temporary removal of the jar will save it from the 30-degree heat. Otherwise, the cutting will simply be baked.
- After the cuttings show signs of life, they can be fed with complex fertilizers.


