Content
- 1 Roses as they are
- 2 Preparing a place for planting garden roses
- 3 Spring planting dates
- 4 Dates of autumn planting
- 5 Selection of varieties of garden roses
- 6 How to choose the right rose seedlings
- 7 How to plant roses
- 8 Rose care
- 9 Diseases and pests
- 10 1 Description, types and varieties
- 11 2 Selection of seedlings
- 12 3 Landing
- 13 4 Care
- 14 5 Reproduction
- 15 6 Diseases and pests
- 16 7 Design
- 17 General information
- 18 Rose planting and care in the open field
- 19 Planting roses in open ground in spring
- 20 Watering roses
- 21 Fertilizers for roses
- 22 When to replant roses
- 23 Pruning roses
- 24 Preparing roses for the winter
- 25 Rose home care at home
- 26 Propagation of roses by seeds
- 27 Reproduction of roses by cuttings in summer
- 28 Propagation of roses by cuttings in potatoes
- 29 How to propagate a rose with cuttings from a bouquet
- 30 Propagation of roses by cuttings in a package
- 31 Reproduction of roses in the Burito way
- 32 Reproduction of roses in the Trannoy way
- 33 Propagation of roses by grafts
- 34 Reproduction of roses by dividing the bush is possible only for non-grafted species
- 35 Diseases and pests
- 36 How to grow roses: correct pinching (with photo and video)
- 37 How to grow beautiful garden roses: proper watering when leaving
- 38 How to grow roses in the garden yourself: the better to mulch the bushes
- 39 Growing and caring for roses: correct pruning in spring (with video)
- 40 How to grow roses on the site and how to cut bushes in the summer
- 41 How to properly prune roses in autumn (with video)
- 42 Caring for roses: how to properly cover bushes for the winter (with photo and video)
- 43 How and when to take shelter from roses in spring
- 44 Rose care: fertilization and feeding
- 45 How and what to feed and fertilize roses
Rose is a flower that will decorate any garden. However, these regal beauties are still fragrant in not all gardens. Inexperienced gardeners are afraid that the rose will require special care, great trouble and greenhouse conditions.
An experienced gardener certainly has at least a rose bush in his garden. It is known that this plant is quite unpretentious, withstands short-term frosts up to -5 degrees, perfectly takes root in our harsh climatic conditions and requires no more attention than any other flower.
And yet, this does not mean that you can plant a rose and forget about it.
In order for the beauty to delight every year with lush flowering, it is necessary to create conditions for her. And for this you need to find out in more detail what this magnificent flower is.
Roses as they are
There are many types and varieties of roses.
Roses are divided into:
- garden;
- climbing;
- park;
- bush;
- spray.
Garden roses
This plant comes from the common rose hips. Breeders have created a real queen of the flower world. A garden rose begins to bloom earlier than its counterparts by 2-3 weeks. Long-lasting, abundant flowering.
Unlike its ancestor, the garden beauty is more demanding in care, in choosing a planting site, and cannot hibernate without proper preparation.
If a garden rose is deprived of all this, it is capable of degeneration. The plant will survive by losing its best qualities - flower shape, splendor, number of buds. However, subject to all requirements, roses will delight for many - many years.

Climbing roses
Climbing roses are derived from rose hips. But unlike other roses, these plants have very long stems. Flowers can have various shapes: double, semi-double, simple.
Climbing roses are divided into:
- ramblers;
- claimings.
At first, ramblers were created. They immediately fell in love with flower growers. Now roses began to grow not as single bushes and played a major role in vertical gardening. Flexible trunks of ramblers began to climb trellises and arches, decorate the walls of houses and ennoble unsightly areas.
The flowers of this group do not differ in size, they are only up to 2.5 cm in size, but they are located along the entire length of the shoot. They are also good because they endure frost even under light cover.
But the breeders did not stop there. With the help of crossing ramblers with floribunda and hybrid tea roses, claimings appeared. These were roses, which had longer and stronger trunks than ramblers (the length of the trunk reaches 4 meters). And their flowers were larger. The size of the rose-laying is from 8 cm to 11 cm.
Claimings pay off for their beauty with a weaker resistance to frost. Their long lashes must be well covered. If the lashes are not preserved, the rose will not die, but it will not have time to build up full-fledged lashes, and all the charm of verticality will disappear.
Park roses
Park roses represent different types and varieties of cultivated rose hips.
These include vintage garden roses, wrinkled rose and modern breeding hybrids.
Plants of this group are unpretentious, flowering begins in May and lasts for a month. They are distinguished by good winter hardiness.
Canadian roses, a type of park roses, are especially resistant to frost. They were bred specifically for harsh climatic zones. These are exactly those roses that can withstand frosts up to - 35 and even up to - 45 degrees without shelter. At the same time, they endow their owners with abundant flowering, which occurs in waves. Re-blooming is not so lush, however, it has its own charms.
English roses - other representatives of park species, cannot boast of such frost resistance, they need to be sheltered from severe cold weather. However, their feature is the increased doubleness of the flower. The number of petals can be up to 100 pieces.

Bush roses
Another descendant of the wild rose is a bush rose. Already by the name it is clear that this rose grows as a bush. The shape of the bush can be spreading or pyramidal.
The height of such a bush can be different, it depends on the type of plant. There are roses, the bush of which rises only 25 cm, and there are those that are spread over a meter. The length of the peduncle is also different, it can reach more than 80 cm.
The flowers themselves can have different shapes and sizes. The flower can be up to 18 cm in diameter. At the same time, the flowers can be single, or they can be collected in large caps of inflorescences (up to 200 flowers). The doubleness of this species is also varied - from the simplest structure of a flower to many petals, the number of which reaches 120 pieces.

Spray
A group of spray breeders was introduced relatively recently at the end of the 20th century. Roses of this group originated from the famous floribunda. Their peculiarity is the small growth of the bush, but very abundant flowering.
The height of the bush rarely reaches 50 cm, but about 15 flowers bloom at the same time on one small shoot. At the same time, the bud itself is quite large for such a bush - up to 7 cm.
The flowers cover the branch so tightly that the stem itself is not always visible.
Because of this feature, designers are especially willing to use this type of roses in wedding bouquets. The rose is very decorative, resistant to frost, disease, damping and requires very little maintenance.

Preparing a place for planting garden roses
One of the main requirements for the long growth of the rose and the abundance of its flowering is the correct location of the bush.
Rose is a flower that has a very high need for sunlight.The plant itself will be able to survive in shade, however, in the shade, the lush beauty will definitely begin to reborn and very soon, instead of a bright, elegant bush, the owner will receive long, thin shoots that will bloom sparsely.
To prevent this from happening, you must fulfill a number of requirements:
- the place should receive sunlight throughout the day. Moreover, if several bushes are planted, tall ones should be planted in the background, and lower bushes should be placed in the foreground so as not to shade them;
- the rose should not be in a draft, however, it needs good air circulation. Otherwise, the flower will be susceptible to fungal diseases;
- groundwater should not be close to planted roots;
- swampy soil is not suitable for this plant;
- you should choose a soil that will be loose and saturated with minerals (the fertile layer should be at least 40 cm);
- the rose loves a lot of space, so overcrowding of plantings should be avoided.
Preparing the soil for planting
After the place for planting the bush is chosen, you can start preparing the place. This is a serious matter, it depends on him how long the entire bush will grow and develop, how quickly it will take root, how successfully it will endure the winter cold.
It is best to use a long preparation method.
Experienced flower growers do this: they do not dig up the sod at once, but cover it with several layers of newspapers (8-12 layers) and fix the newspapers so that it does not get carried away. Such a shelter is left for 2 months. All the weeds die under the newspapers, but the earth becomes soft, now it is easy to dig it up with a shovel or a rotary tiller.
After that, holes are prepared for each bush. If the plot of land has already been cultivated, it is necessary to add substances that improve the soil. In order to find out what the soil requires, it is best to check the soil for composition - a pH in the range of 6.0 to 7.0 is considered ideal for roses. If the soil is acidic, add lime.
When digging a hole for each plant, fertilizer is added to each hole.

In addition, about 250 g of bone meal are added to the planting pits. If superphosphate is added, care must be taken that the roots of the plant do not come into contact with it. It is necessary to pour superphosphate, then pour a layer of earth and only after that plant the bush.
Spring planting dates
In order to plant roses in spring, you need to wait until the ground is completely thawed and warmed up. It is believed that the best time for disembarkation is the period from the last decade of April to the second decade of May.
Too delay the landing is not good, even a very early landing is better than a late one. In this case, young plants will not begin to develop, but will not die, but will wait for the onset of favorable weather. But at a later time, the earth will dry out, the sun will already begin to warm up strongly, and under such conditions it will be extremely difficult for a young plant to take root, it may simply die.
Dates of autumn planting
Many gardeners strive to plant all plants in the spring. However, in the fall, you can easily plant rose bushes, they will have time to take root.
In autumn, you can plant a rose in open ground from mid-September to mid-October. At this time, the weather is still warm, the earth is warm and well saturated with moisture.
But flower growers who live in cooler regions (Siberia) cannot count on a long and warm autumn. Therefore, they are advised to plant roses from late August to late September.
The plant should be planted 21-30 days before the first frost.
Selection of varieties of garden roses
There are a lot of varieties of roses. Hardly anyone will be able to familiarize themselves with all of them.
Therefore, in order to choose a seedling, you need to decide in which direction to look for the most suitable variety for your own garden.
The best varieties for vertical gardening
For those who want to choose the best varieties for vertical gardening, we can recommend the varieties of semi-climbing and climbing roses:
- Variety "Hamburg" - the bush reaches a height of 2 m. Beautiful flowers of crimson color, slightly pointed shape, up to 9 cm in size. Has a delicate, unobtrusive aroma;
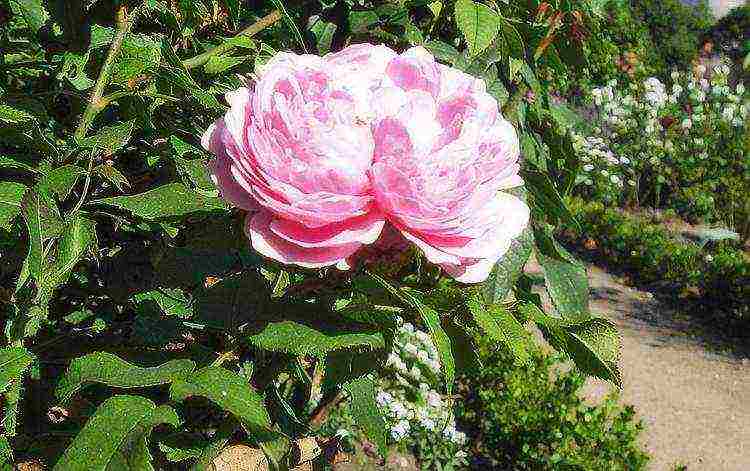

- "Berlin" is a bright scarlet flower up to 8 cm in size. The middle has a golden color. A very unusual rose. Scourges can reach 1, 5 m and more;

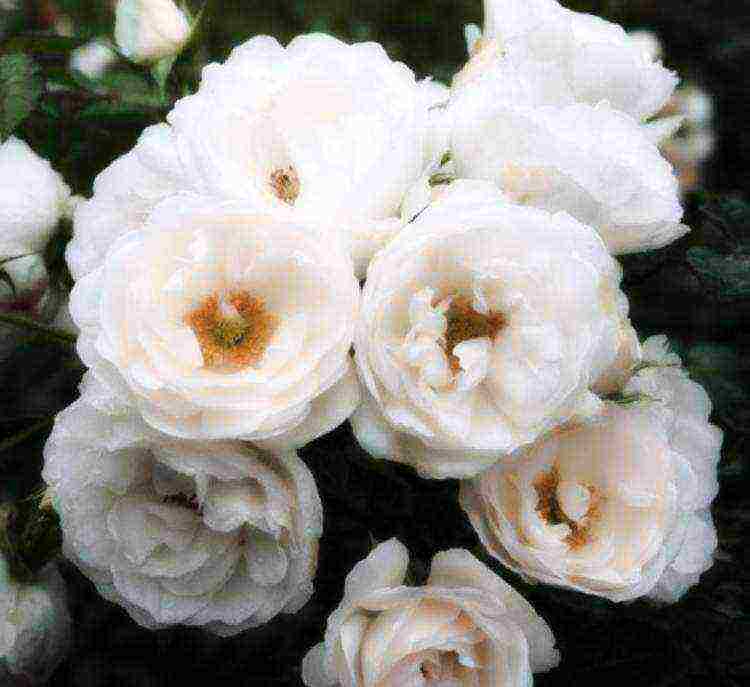
- "Gella" is a bush up to 3 m in size. The flowers are semi-double, collected in large brushes. The rose is creamy, with a light creamy shade;

- "Dorothy Perkins" is a bush that grows up to 5 meters. The flowers have a deep pink color. The shape of the flower is open, the flowers are collected in large baskets of inflorescences.
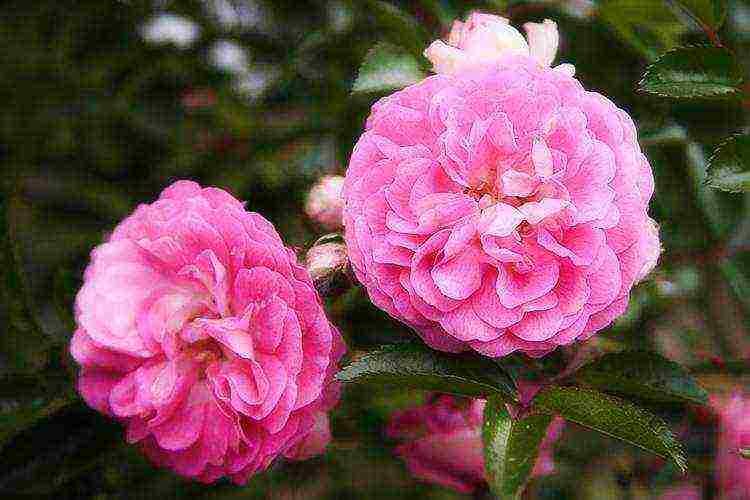

Frost-resistant varieties
There are no ugly roses. Therefore, it is especially important to pay attention not only to beauty, but also to other qualities. For example, resistance to harsh climates.
Canadian roses are the invincible leaders in this matter. They are able to hibernate without shelter and endure frosts down to -45 degrees.
Here are just a few varieties of this species:
- "Emily" (Emelie) - a variety with soft pink flowers, the bush reaches a height of 110 cm. Abundant flowering. A very grateful rose;

- "Gartentraume" - has not only large flowers, but also an incredibly pleasant aroma, and the height of the bush can grow up to 140 cm;
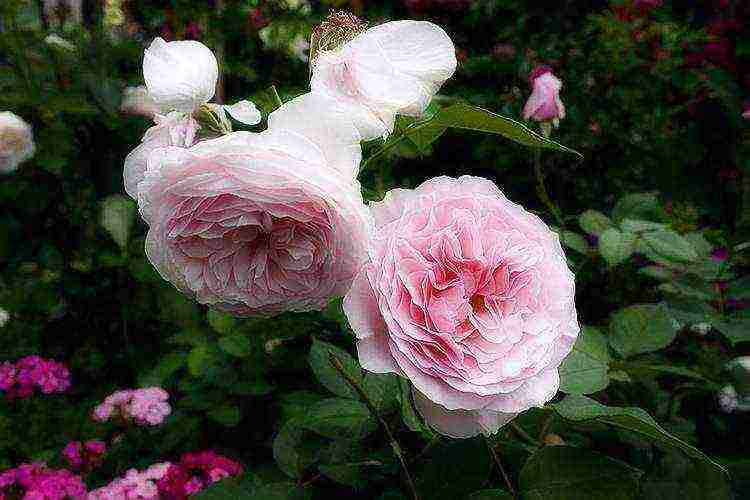

- "Midsummer" - besides the fact that it is the most hardy rose of all presented, its flower has an extraordinary color - the petals are bright red at the edges, and the center is fiery yellow. The shape of the flower is also beautiful - like that of old English roses;
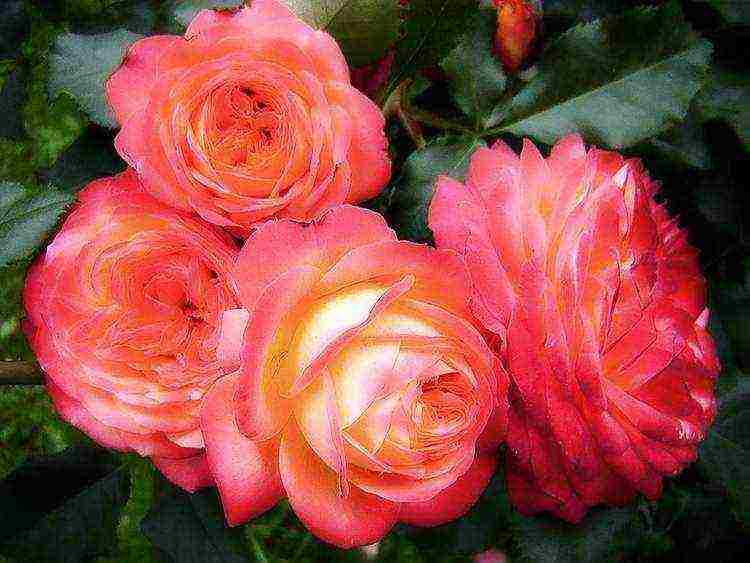

- "Piccolo" is a well-known variety with a red carmine color.
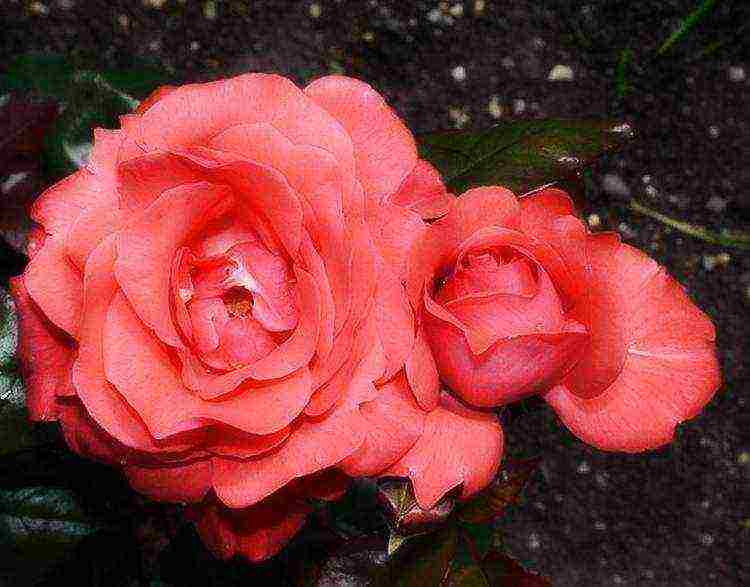

Miniature varieties
Roses are very interesting not only with huge flowers, but also miniature ones.
Here are a few varieties:
- Ferry is one of the most famous miniature roses. It has deep pink flowers, collected in rich inflorescence caps. Unpretentious enough;

- "Los Angeles" - bright yellow, almost orange flowers, up to 4 cm in size. The bush is not tall, up to 40 cm. It blooms very profusely;

- "Curlers" - a new variety in an unusual color - bright red with white veins.

Largest-flowered varieties
- Polka is one of the most famous varieties. Flowers can be up to 16 cm;

- "Paul Neyron" - the variety, which probably has the largest flower, reaches 18 cm;

- "Ashram" - flower up to 13-15 cm.

How to choose the right rose seedlings
Saplings should be chosen carefully. In retail outlets, roses can be sold both with a closed root system (in containers) and with an open one.
If possible, it is better to purchase a rose in a container, because the root system is preserved there better. However, if the rose was dug up recently, it's okay if you get a rose with open roots.
The seedling should have 2-3 cut and woody stems, which should be smooth, clean, without spots, sores and other signs of any disease.
The kidneys should be dormant.
There should be no leaves or flowers on the seedlings.
How to plant roses
For planting, you should dig a 40x50 hole, make a small mound in the middle of the hole. Plants are placed on this mound, and the roots are straightened and lowered from the mound into the planting pit.
It is necessary to make sure that the root collar of the bush is 5 cm below ground level. After that, the hole with the root system is buried.
For the convenience of watering around the plant, it is best to make a small side out of the ground, which will prevent water from spreading.
Water the plant after planting.
After planting, the bush is watered abundantly! If watering is missed, the plant may die.
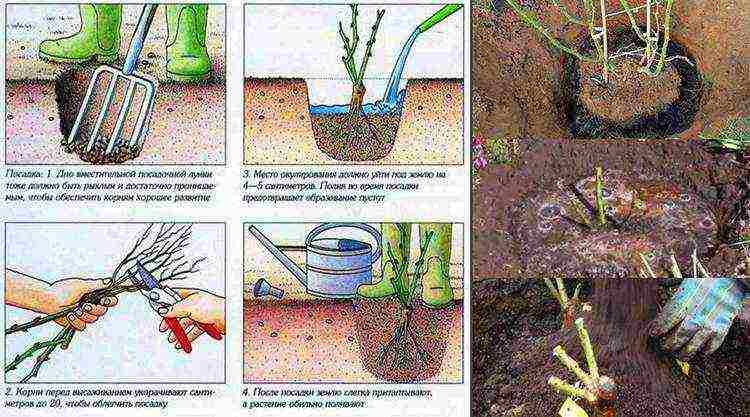
Pruning before planting
Few people know that seedlings need to be prepared for planting.
For this, it is necessary to consider the ratio of roots and shoots. It's okay if there are few shoots, and the root system is strong and well developed - the plant will grow and give new shoots.
But if there are many shoots, and the root system is weak, then you need to leave as many shoots as there are roots. Excess shoots are cut off.Otherwise, under the bright spring sun, the buds on all shoots will begin to bloom, and they will need a lot of moisture and nutrients. A weak root system is not able to feed a lush bush. Therefore, the plant may die.

Long shoots of the plant are not suitable for planting. Leave only hemp, 10 cm high, with two or three buds.
The dried ends of the roots are also neatly trimmed with pruning shears.
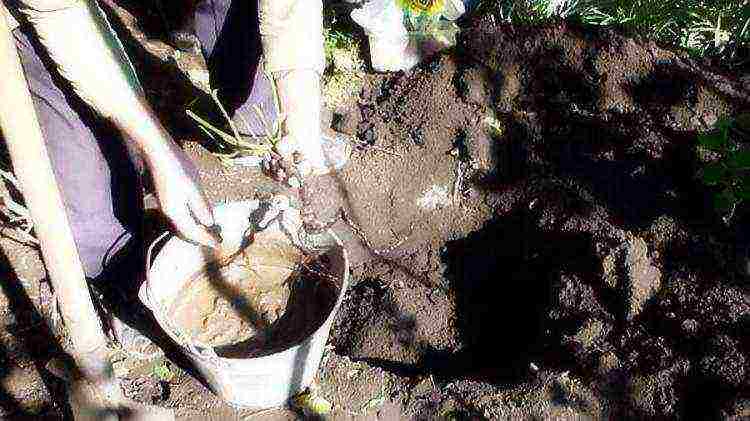
Clay root treatment
This treatment is done when the roots of a dug-out plant need to be preserved for some time (during transportation) or in order for the plant to better take root in a new place.
In order to prepare a chatterbox, you need to take 10 liters of water, add a little clay (so that after dipping the root a little clay remains on it), add 1 tablet of a root formation stimulator (heteroauxin, root), and stir. The resulting mixture should have the consistency of liquid sour cream.
Before planting, you need to dip the roots in a chatterbox and air dry them for about 30 minutes. After that, the plant can be planted.

How much to deepen the vaccine, depending on the region
In regions with different climates and different soil composition, grafting in roses is deepened in different ways.
So, for example, in the steppe regions, where the winds are walking, and the snow cover is blown away, and the earth remains, sometimes, not covered, the vaccination is recommended to be buried by 5 cm.
In areas where the climate is damp and humid, it is recommended to leave the graft at the soil level, so it will not rot.
On average, it is believed that a rose graft should be buried 3-5 cm or left at soil level.
Rose care
Roses are not demanding plants. However, complete lack of care is unacceptable. For a rose, watering, timely feeding, spraying the bush from pests and treatment for diseases (if any) are important.
Overgrown bushes must be formed, that is, pruned. And also, you need to rejuvenate the bush, that is, cut out old and dried branches - to carry out sanitary pruning.
An important activity is preparing roses for winter.

Watering and feeding
Watering the flowers is necessary. Roses are watered abundantly - 10 liters per bush as the soil dries up.
Regular watering is especially necessary for spray and climbing roses. This is due to their large green mass.
Watering should be done in the evening, when moisture does not evaporate so quickly and the sun's rays do not burn the leaves.
On cold days (closer to autumn), you need to water the rose less. Dampness and cold can lead to fungal infections. But it should be borne in mind that without watering at all, even in the autumn period, roses will not be able to - the roots in the winter should go strong, and not dry.
In order for the plant to give huge caps of flowers, it needs strength. This requires top dressing.
It is believed that you need to feed 7 times per season:
- The first feeding is done immediately after thawing of the ground (mid-April). Ammonium nitrate is introduced (30-40g per 1 sq. M).
- 2 weeks after the first, feeding is repeated.
- When tying buds, it is better to feed with a complex fertilizer ("Kemira"), 30-40 g per 1 meter of kW.
- Before flowering, feed the mullein infusion prepared according to the scheme: the mullein is diluted with water in a ratio of 1:10, infused for 4-7 days and again diluted 1:10.
- After the roses bloom in the first wave (mid-July) - a complete complex fertilizer.
- Two dressings at the end of August and mid-September with potassium, for better ripening of shoots and resistance to diseases.
In no case should you fertilize roses with fresh manure! The roots of the plant will simply burn out. Poorly rotted manure is also not recommended.

Bush formation
After planting, the bush will take root, and increased growth of shoots begins. However, not all branches grow in the same way, there are some that are knocked up more than others. In order for the crown to retain its neat appearance, these branches need to be pinched.Such pinching not only stimulates the formation of new shoots, but also has a beneficial effect on the development of the root system. Therefore, it is recommended to pinch not only young bushes, but also old, weakened ones.
In order for the bush to be not too thick, summer pruning is done. With this pruning, diseased shoots, old, dried up, are removed. Too thick, shoots can be removed too. Roses do not like thickening.
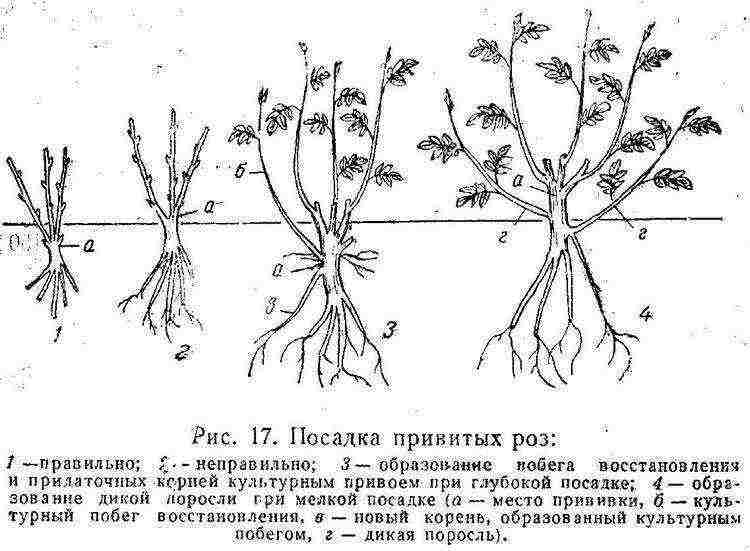
It often happens that new shoots begin to form below the graft. Such shoots must be removed. This is wild. Such shoots will not bloom, but will become an additional burden for the plant.
Preparing for winter
In order for the roses to winter safely, they need to be prepared for this.
Already since August, it is not recommended to cut flowers into bouquets - the bush can give new shoots that will not have time to turn numb by winter, which means they will not overwinter.
From mid-September, it is recommended to remove the lower leaves on the bushes. So the plant is made to understand that it needs to prepare for the cold.
You need to cover roses when the temperature is -5. Otherwise, covered roses can snuff.
Before the shelter, the shoots of roses are cut off.
In order for the wintering to be successful, the base of the bush is covered with humus or peat, and the tops of the shoots are bent to the ground and covered with spruce branches. After the snow falls, the shoots will not be able to freeze.
Experienced growers believe that it is not so important to cover roses for the winter as to open them in early spring.
Roses are strong enough to withstand light frosts. In some areas, they can even overwinter without shelter (if there is enough snow, and the frosts are not strong). But in spring, roses often die from overheating or from uneven thawing of the soil.
If the covered base of the bush (with which the roses have been warmed since autumn) is not dug out in time, the plant will overheat and sopreet. The rose will die.
However, such a situation often happens - the bush was freed from the covering material, green leaves went, and the rose suddenly wilted and died. This is due to the fact that the first rays awaken the buds, they grow, and the leaves unfold. But the ground has not thawed yet, the root system cannot fully work - it is in ice, and the plant does not receive nutrition. It dies.
In order to prevent this from happening, you need to do this: as soon as the topsoil thaws, you need to scoop the compost from the center of the bush, level the soil and cover the entire plant with covering material. Under this material, the temperature will be higher than without shelter, the ground will thaw faster. At the same time, bright sunlight will not be able to warm the bush with the same strength through the covering material, which means that the buds wake up longer, the leaves will not appear, the plant will wake up evenly.
Diseases and pests
For a rose to be strong and healthy, it is necessary to protect it from pests.
The main enemies of this plant are aphids, whiteflies, spider mites, caterpillars.
To combat them, there are many drugs on sale, if you regularly carry out preventive spraying of the bushes, then uninvited guests will not bother the rose.
Spraying is carried out in dry weather. If it rains after such an operation, it is better to spray again.
Spraying should take place in the morning or evening so that the solution does not burn the leaves of the plant.
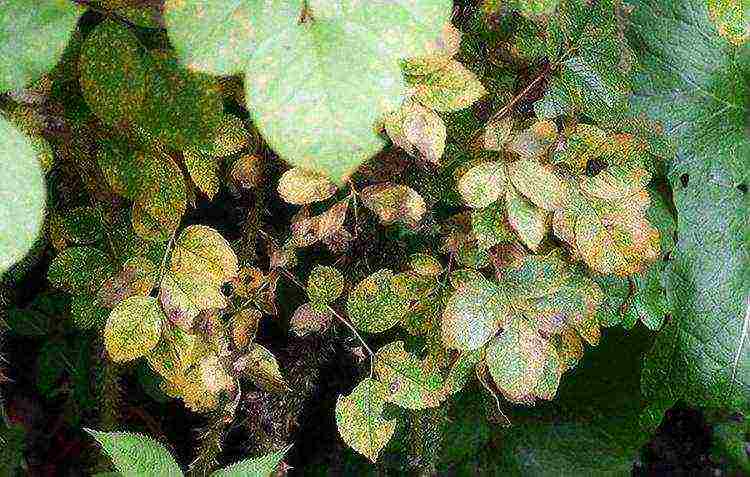

There are also various diseases of roses. These are gray rot, rust, cytosporosis, fungal diseases. For their treatment, you should use special drugs. However, if you properly care for your plant, diseases can be avoided.
After all that has been written, it seems that growing a rose is difficult. But the rules described here apply to any plant. Everyone needs care and attention, and the rose is no exception. Performing these simple activities will give beautiful, strong and healthy plants that will delight lush flowering for many years.
Today there are many rose hybrids that do not require a lot of attention when growing.Thanks to this, beginners in gardening art have the opportunity to choose a species according to their preferences and climatic conditions. Among the modern variety of varieties, along with thermophilic ones, there are frost-resistant representatives that take root without problems even in Siberia. For the best growing of roses, you must follow the basic rules.
1 Description, types and varieties
Rose is the generalized name for all representatives of this flower line, belonging to the genus of rose hips. In the process of growth, they form bushes, which differ in height depending on the species. Some do not exceed 30 cm, others can reach 2.5 m. By type, shoots are divided into uterine and annual. The standard classification also does not apply to the shape of the leaves, it all depends on the type.
The appearance, color and size of flowers vary. There are buds from 2–3 cm in diameter to 15–20 cm (with the number of petals from 5 to 100). The color scheme is striking in its variety, there are red, white, yellow, pink, black and even blue. Roses, which change their color during flowering, have become the pride of breeders. There is a conditional division of grades into classes. This helps to correctly navigate and choose the most appropriate option. The emphasis is placed not only on decorative indicators, but also on the place of intended cultivation - in the country, in the open field or at home.
Common varieties of roses often used in garden design, depending on the group affiliation:
- Floribunda - Aprikola, Aspirin-Rose, Bengali, Black Forest Rose, Crescendo, Debut, Gebruder Grimm, Hermann-Hesse-Rose, Intarsia, Isarperle, Kosmos, Innocencia, Schone Koblenzerin.
- Groundcover Roses - Bluhwunder 08, Heidetraum, Sedana, Mirato, Schneeflocke, Stadt Rom, Mirato, Schneeflocke, Sorrento, Stadt Rom.
- Shrubs - Comedy, Goldspatz, Flashlight, La Rose de Molinard, Larissa, Medley Pink, Pink Swany, Shining Light, Yellow Meilove.
- Hybrid tea roses - Elbflorenz, Grande Amore, Eliza, La Perla, Pink Paradise, Schloss Ippenburg, Souvenir de Baden-Baden.
- Climbing large-flowered - Golden Gate, Hella, Jasmina, Kir Royal, Laguna.
The main groups of varieties of garden roses:
| Species name | Characteristic | Image |
| Park | Decorative representatives of roses. Endowed with increased winter hardiness, tolerate low temperatures well without shelter in regions of the middle climatic zone. Unpretentious to care, do not need annual pruning. They begin to bloom in late May - early June, the duration is from 2 weeks to 1.5 months. Bushes grow from 1 to 3 m in height |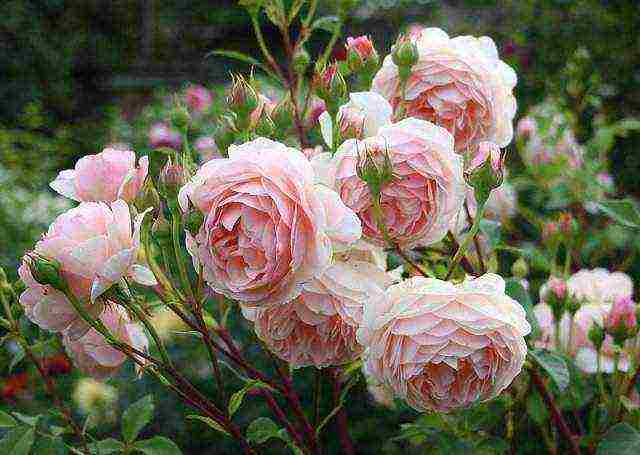  |
| Hybrid tea | Bushes no more than 80 cm high. They are distinguished by long and spectacular flowering. The buds bloom once and last from June to autumn. The flowers are large, 10-15 cm in diameter. The varieties are frost-resistant, need a protective shelter in regions with cold winters |  |
| Polyanthus | Form numerous inflorescences on the shoots. Blossom from June until the first frost. Medium-sized flowers - 7-10 cm in diameter |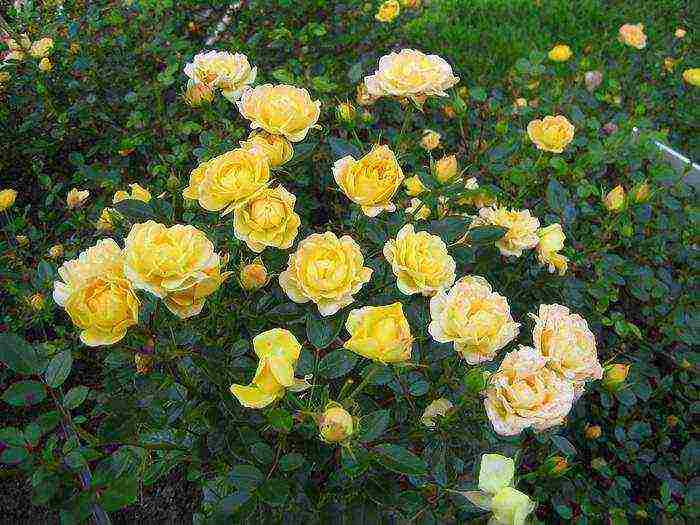  |
| Floribunda roses | An intermediate variety between hybrid tea and polyanthus roses. The buds are large when opened and exude a pleasant aroma. Abundant flowering is observed for a long period. They endure the cold, staying for the winter in the open field |  |
| Climbing | They are divided into 2 subspecies: small and large-flowered. The first variety is characterized by buds up to 4–5 cm in diameter; the second - from 5 to 10 cm. A distinctive feature is flexible long shoots, at the ends of which small group inflorescences are collected |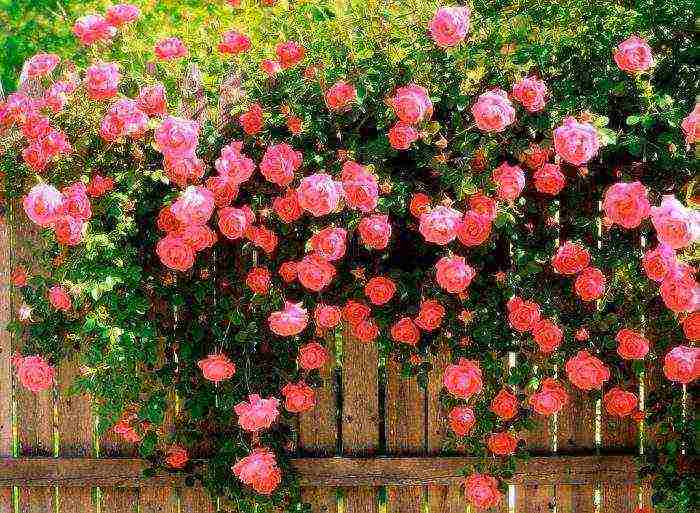  |
| Miniature | Compact bushes, abundantly strewn with small buds. Endowed with a long flowering period, up to the first winter cold weather. In gardens, they are grown not only in flower-bed compositions, but also in suspended and stationary flowerpots or pots. |  |
| Ground cover scrubs | Roses of unusual decorativeness, which are planted as a continuous flowering lawn. Unpretentious to care, cold-resistant and with increased immunity to diseases |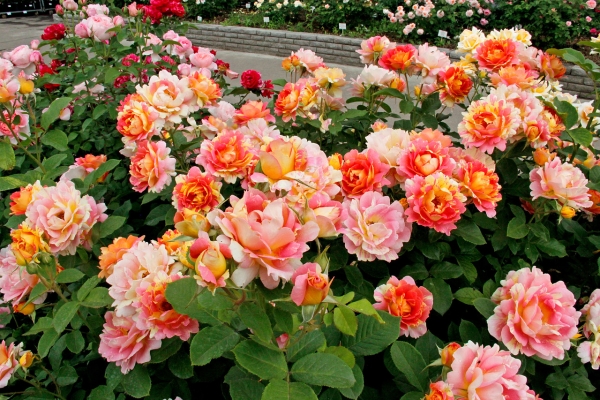  |
| Modern park | A group that includes hybrids of Cordes, musk rose, rugosa, shraba and moesi. In abbreviated form, all varieties are called scrubs. Includes all varieties that for some reason do not fall into other groups.They are characterized by the following features: buds of atypical configuration and different colors, they smell nice, the bushes are vigorous, strong and up to 2 m high. They have repeated flowering during the growing season. Plants are unpretentious, have strong immunity, frost-resistant |  |
| Shrubs | The main difference is a large bush with shoots diverging on the sides. Even with minimal maintenance they grow up to 2.5–2.8 m in height. Among gardeners, the following varieties are most popular: Modern Shrab, Grandiflora. In landscape design, they are often used as hedges. |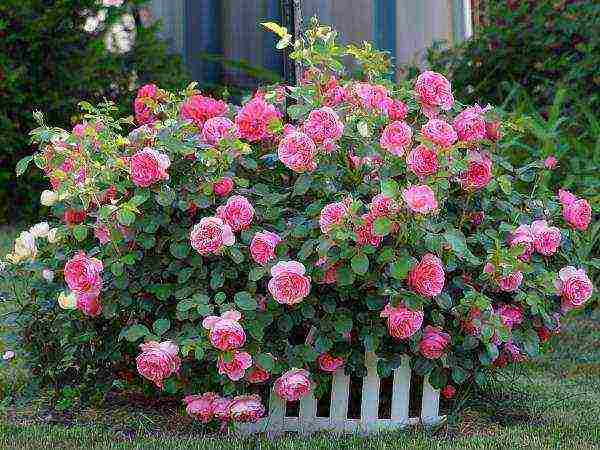  |
| Cascading | Rose hips with grafted climbing and ground cover roses at a height of 130–150 cm. The stems are long, sometimes drooping. The shape, size and color of the flowers vary and depend on the result of the vaccination |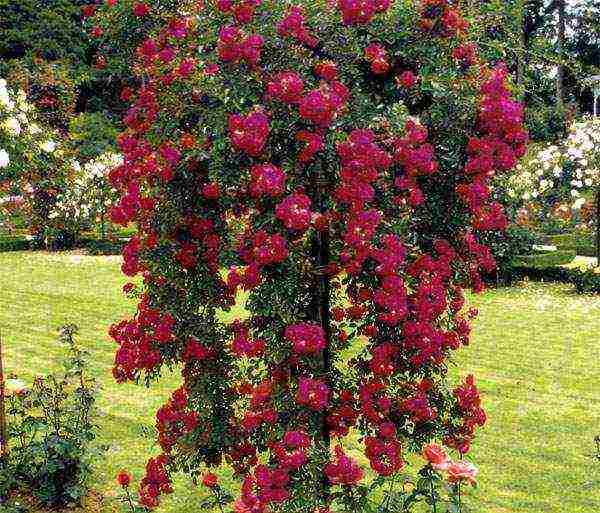  |
Rules for growing and caring for a climbing rose in the open field
2 Selection of seedlings
If you want to get lush roses in the garden, you should competently approach the choice of seedlings. First of all, attention is paid to the external state. Shoots and stems should be green in color, elastic structure, with bark free from defects and damage. The presence of live and healthy kidneys is imperative. The requirements for the root system are similar: no breaks, folds and rot. Try to touch the ground where the seedling is located, so that it is slightly damp. The foliage must be lively, green, without spots.
Important points to pay attention to when choosing seedlings:
- A sale tag is a must for a quality product. It contains all the necessary information: species, variety, selection.
- The presence of the ADR marking - a similar icon denotes varieties with increased resistance to diseases and the best decorative qualities.
- The most expensive seedlings have 3 or more shoots, 2 of which grow from grafting; the cheap ones have only 2, both from the vaccination site.
Roses come with open or closed roots, in containers. After buying seedlings with planting, it is not recommended to tighten it. This is usually done in the fall, before winter. However, in the regions of the middle zone, including in the Moscow region, planting is carried out in the spring. Otherwise, immature young roots do not have time to take root in a new place and die under the influence of frost. It is allowed to plant roses in summer, which is guaranteed to give a good result. This method can be more expensive.
Azalea - rules for growing outdoors and home care
3 Landing
Regardless of the variety, all roses prefer a loose, soft, fertile substrate with good drainage and a pH of 6–6.5. It is unacceptable to plant flowers on a plot where similar species have already grown for 8-10 years in a row... Such land is completely devastated, no fertilizers can restore the missing elements in its composition. At the same time, there is an accumulation of pathogenic microflora there.
Despite the love of light, the plant is not recommended to be planted in direct sunlight. This will not stop flowering, but the decorative appearance will change: the roses become faded and withered. Therefore, the place is selected with shading, which is important at noon. Ideal location - next to low garden trees or along fences.
Before planting, the seedlings are prepared: too long roots are cut with pruning shears, dry ones are removed completely. It is unacceptable to touch the filamentous roots. When planting in spring, the stems are shortened to 30–35 cm, leaving up to 4 buds on the surface. For 2-3 hours, the seedling is placed in a bucket of water.
If clay soil prevails on the site, river sand is introduced into the planting pit, sandstone is diluted with sheet compost. The sequence of agrotechnical measures:
- A hole is dug 2-3 times larger than the size of an earthen coma with roots. The bottom is well loosened.
- The seedling is buried at a level 4–5 cm higher than the grafting site.The extracted substrate is mixed with compost in a 1: 3 ratio and pure wood ash is added.
- The free space is carefully filled up, the surface is slightly compacted.
- At the end of the procedure, the planting site is abundantly moistened. To prevent the water from spreading, a furrow is made around the perimeter.
It is imperative to spud the root space not only immediately after planting, but in spring and autumn. In the first case, such a technique helps to exclude the rapid evaporation of moisture from the soil, and in the second, it protects the roots from freezing.
You can plant roses once with seeds. It is believed that they germinate for a long time, but it is possible to accelerate germination by preliminary keeping the material in the cold. When sowing before winter, it is advisable to treat the seeds with a stimulating solution. The garden bed is dug up, compost, peat and humus are introduced into it. Make parallel furrows about 4 cm deep, where the sowing is carried out. At the same time, an interval of 15–20 cm is observed. Sprinkle with soil on top. If winter is expected to be frosty, cover the bed with any suitable material for safety net. It is better to prepare a plot for spring sowing in the fall.
Another effective option for germinating seeds is seedlings at home. The favorable period for this is the beginning of February. Seed material is preliminarily placed in the cold for several months, then soaked in a growth stimulator. They are planted in separate pots, where the peat-sand mixture is poured. The seeds are deepened by 3-4 cm, sprinkled with sand and moistened with a spray bottle. With the appearance of 2-3 strong leaves, the seedlings dive separately. In May, they are transferred to a permanent place of growth - in the garden.
Planting and caring for Bartzella peony in the open field
4 Care
For full development and abundant flowering, roses must be looked after. Mandatory procedures are:
- Watering is carried out once every 7 days so that the soil is soaked to a depth of at least 25 cm. Otherwise, the plant puts out surface roots, which are easily damaged during subsequent loosening. Moisturize 2 times more often if the weather is hot. It is advisable to cover the root circle with humus or peat mulch. Then the moisture will evaporate less intensely.
- Before the onset of the first frosts (in October), the bushes are wrapped in burlap, and the roots are sprinkled with a mixture of earth and sand.
- Pruning plays a primary role in overall grooming. In the spring, they resort to formative. In the summer, wilted buds, drooping and diseased leaves are removed. In autumn, dry and damaged shoots are removed. Places of cuts are treated with garden pitch. Before the onset of winter, all weakened stems and shoots are pruned.
- Rotted horse manure is used as a top dressing, chicken and pork are contraindicated. This is due to their high acidity. Any fresh organic matter blocks nitrogen in the soil, thereby inhibiting the growth of flowers. The first time fertilizers are applied before laying the buds. Calcium nitrate is suitable (1 tablespoon per 10 liters of water). During the period of active growth, they are fed with infused liquid mullein, mineral supplements or herbal infusions. Frequency - once every 2 weeks.
From the middle of summer, all feeding is stopped, watering is minimized. The plant needs to go into a dormant state, which serves as a preparation for wintering.
5 Reproduction
Roses can be propagated by seed and vegetative methods. The first option is in little demand, since it does not retain varietal characteristics. Therefore, it is used more often in relation to wild representatives. The seeds are harvested when the fruit turns red. The raw material is preliminarily stratified in moist sand, kept until spring at a temperature of + 3 ... + 4 ° C. In the spring, the seeds are treated with a stimulant and planted in open ground. From above they mulch with humus. After some time, the plantings are thinned out, distributing the bushes at a distance of 10-15 cm from each other. In the summer, mineral dressings are introduced.Grown until next August, then used as a stock.
The most successful breeding method is by cuttings, along with grafting and dividing the bush:
| Method name | Description | Image |
| Summer cuttings | In the morning or in the evening, strong shoots with slight lignification are cut off. Cuttings 13-15 cm long are prepared. Several leaves and 2-3 living buds are left on each. The lower part is cleaned of foliage. The bottom is treated with a growth stimulant, the cutting is immersed in water, where rose petals are placed. They are planted directly into the ground, previously sprayed with potassium permanganate. Cover with a glass cover on top to create greenhouse conditions. The optimal temperature regime during the day is not lower than + 25 ° C, at night + 19 ... + 20 ° C |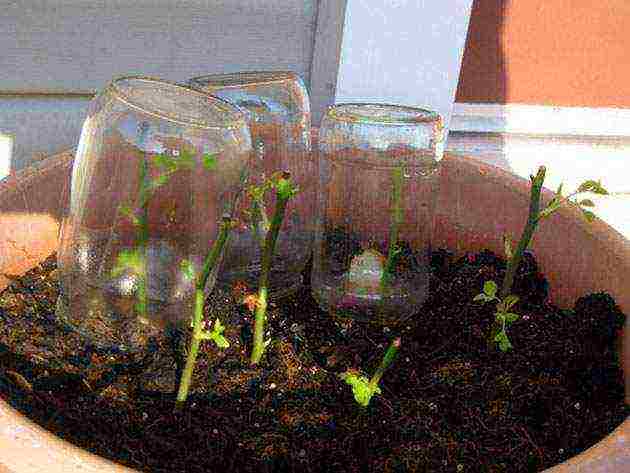  |
| Rooting in potatoes | The most popular and easy breeding method. Thus, the cuttings are saturated with carbohydrates and potato starch. In a bright area, a ditch is dug about 15 cm deep, filled with sand for a third of the volume. Cuttings are first stuck into the potatoes 10–12 cm and placed in the prepared recess. Further manipulations are standard: cover with a cap, after a while hardening is carried out. Pour sugar syrup every 5 days |  |
| Reproduction in a package | The bottom of the cuttings is moistened with aloe juice, then deepened into a lump of earth, laid in a plastic bag. It is hermetically closed, having previously released the air from the inside. Hang out for germination on the window. A month later, when young roots appear, they are planted in open ground |  |
| Rooting in water | Freshly cut stems, divided into cuttings, are immersed in distilled water. Before that, thorns are removed from the surface and other vegetation. The water is regularly changed until the cuttings take root |  |
| Vaccination | Reproduction by grafting is suitable for young rose hips. The procedure is carried out in the middle of summer. First, the lateral branches are removed from the stock, and the root collar is cleaned of the ground. An incision is made in the shape of the letter T, where the handle is placed. Fix it in place in any way. After 15–20 days, the kidney is checked: if it is swollen, then the vaccination was successful. If it is black, then the method has failed. Before the onset of winter frosts, the grafted roses are spud 5-6 cm above the grafting site. In the spring, the soil is raked. The plant is pruned over the graft. When pulling, pinch the top over the third leaf | 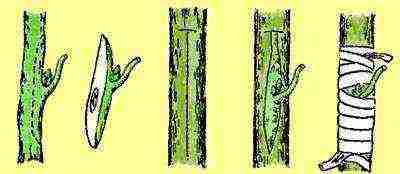 |
| By dividing the bush | Suitable for non-grafted varieties of roses. In the spring, before bud break, the bush is dug up and divided into parts. Each should consist of roots and a shoot. Bare areas are powdered with crushed coal. Then they are seated in separate places in the garden. |  |
| Layers | With the onset of the first spring heat, a low-lying shoot on a bush is chosen. They bend it to the ground and put it in a dug hole. An annular cut is made on the surface beforehand. Fix the shoot in place and cover it with earth. Further care is moisturizing until the cuttings take root. The next year, the baby is separated from the maternal source and planted separately. |  |
6 Diseases and pests
Most roses are endowed with stable immunity to many diseases, but this does not exclude the possibility of damage. The following diseases are most common:
- Rust - the peak of the disease is observed in the spring. Brown spots appear on the leaf surface, and from the inside - orange clusters of spores, which turn black towards the end of summer. Unauthorized leaf fall begins, the stems acquire a brown tint. The situation can be corrected by watering with a decoction of field ivy. The affected areas are removed.
- Black spot - appears in August, towards the end of the month. The leaves are instantly covered with black patches in a yellow frame. This gradually spreads to the stems. Leaves fall. If appropriate measures are not taken in time, the flowers die. Treatment is the same as for rust.
- Powdery mildew - a whitish bloom forms on the leaf component and shoots, then slugs form.The disease is characteristic of varieties that are grown in greenhouses and at home. The disease is characterized by rapid spread. Plants showing signs of damage are cut and destroyed. The earth is sprinkled with ash and dug up.
Of the insect pests, the most dangerous are aphids, spider mites. With few attacks, you can kill the first pest by hand or wash the leaves with soapy water. If there are a lot of insects, then treatment with insecticidal preparations helps. The mite is fought by applying tobacco or infusion of wormwood. With illiterate care, there are cases of attack by thrips, sawflies and cicadas.
With a lack of nitrogen in the soil, the plant turns yellow. It begins to spread from below and is accompanied by leaf fall. The same thing happens with the top. If the foliage is covered with yellowness only at the edges, this indicates a lack of potassium. Yellow streaks indicate a small amount of trace elements.
7 Design
Most people are used to planting roses in separate flower beds, but modern trends in landscape design have made their own adjustments. It is fashionable to combine them with perennial flowering crops or with low-growing shrubs.
For the design of mixborders, it is recommended to take varieties of musky representatives due to their brightness and proportional shapes of the bushes. Short varieties with small flowers are ideal. Then they do not dominate the neighbors, but harmoniously merge into a beautiful composition. It is better to place unpretentious varieties in unfavorable areas of the garden, and climbing roses will effectively decorate fences and terraces.
Rose is a plant belonging to the Rosehips. In the wild, these flowers mainly grow in the temperate climate of the Northern Hemisphere, but in our central Russia, roses are grown for planting and care in the open field, as well as at home.
General information
Roses are very attractive and are not only used as ordinary garden plants or houseplants. They are used in gardening, rose petal jam, and rose oil.
Growing up, roses form bushes with their shoots, the height of which differs depending on the type of plant. Some types of roses reach 30 cm in height, while others grow more than two and a half meters.
The branches of the plant are divided into uterine and annual stems. The shape of the leaf differs depending on the type of flower.
Peduncle size also varies from species to species. It can be short, or it can grow almost a meter. Rose flowers come in various shapes and colors, the size varies from a couple of centimeters in diameter to 15-20 cm. The number of petals in flowers is also different, from 5 to 120 pieces.
The colors of roses are of all possible colors - pink, black, white, even blue roses are bred. And the pinnacle of breeders' achievements are varieties that change color during flowering.
There is no way to describe the huge variety of roses. Among the cultivated roses, park and garden roses are distinguished; it is also worth remembering the indoor varieties. Most often, bush roses, climbing, miniature, floribunda and grandiflora roses are grown.
But the rather popular Chinese rose is actually hibiscus, and the desert rose is adenium.
A lot of varietal roses have been bred and it would take a very long time to list even a small fraction of varieties.
to the table of contents
Rose planting and care in the open field
Roses are quite demanding plants, so planting and caring for them requires knowledge of the characteristics of this flower.
Planting roses is best done in the fall, but no later than the middle of the season. It is also advised to purchase material for planting in the autumn, since in the spring they are often sold that were left over from last year.
Rosehips are photophilous and the place of growing for them should be chosen not shaded, but if you have climbing roses, it is better that the midday sun does not bake them.Drafts and northerly winds are bad for plants, and do not plant flowers in places where groundwater rises high to the surface.
To plant roses, you need to drain the soil, which should be slightly acidic (about 6 pH), fertility is not so important, but it affects the beauty of flowering, so fertile substrates are welcome.
Before planting roses, the seedlings are shortened to 20 cm and placed in water for a couple of hours. A hole for a rose is dug about 50 cm in, and the depth is made 10 cm deeper than its roots.
The soil from the pit must be mixed with compost. For three lobes of land, one share of compost is taken. It is also worth adding some ash to the substrate, and pouring a bucket of water with a tablet of heteroauxin into the hole.
The rose is planted so that the grafting site drops four centimeters into the soil, and for climbing roses - ten centimeters.
The flower must be placed in the hole and carefully covered with the substrate, trampling it down as the hole is filled. Young plants need to be hilled 15 cm and shaded for 15 days. Climbing roses spud 20 cm.
A distance of at least one meter must be observed between the landing sites.
Not far from the bushes, you need to warm up a small shaft from the soil so that the water does not spread during watering.
If groundwater is too high on your site, then you need to make an elevated flower bed for the roses, otherwise the roots will often rot.
Also, if the soil where you want to plant the plants is very clayey, then you need to dig it up with sand.
to the table of contents
Planting roses in open ground in spring
Young roses may not stand up to very cold winters and therefore, if you live in regions that are too frosty, plant flowers in the spring. The best period at this time is mid-April and almost all of May.
The planting process in spring is almost the same as in autumn. Right before planting, the seedlings need to be dipped in a clay mash, and after planting, the site is covered with mulch.
If there is a threat of frost, then the stems must be covered with a film, which must be removed for some time every day for airing. The time without film must be gradually increased, since the plants are hardened in this way. The film is completely removed when the frost is probably gone.
During the first year after planting, roses undergo a formation period. At this time, the main thing is to pinch the stems to improve bushiness. It is also important in the first half of the summer to remove the flower buds as soon as they begin to appear. In the second period of summer, the buds are also removed, but after formation. If you have a climbing rose, then it needs to be supported.
to the table of contents
Watering roses
It is not necessary to water the flowers often, but only as needed, when the soil dries up. Regular watering is needed only for the first year, which needs to be watered every couple of days.
During the growing season, watering is carried out a little more often so that the green mass develops better. And at the end of summer, watering, on the contrary, is reduced. It is preferable to carry out the procedure in the morning. Do not use cold water.
You need to water the bushes carefully, because water can erode the soil, it is best to use drip irrigation.
to the table of contents
Fertilizers for roses
As for fertilizer, the first years do not need to be fed at all. Further, fertilizers must be applied in this way.
In the spring, during the stage of active growth, a double dose of fertilizer is applied, then feeding is carried out during the appearance of buds, at the end of flowering and before the stems begin to grow stiff.
In the spring, for fertilization, take 20 grams of ammonium sulfate for each square meter of soil. After a couple of weeks, this fertilization is repeated. During the formation of buds, feeding is carried out using 20 g of ammonium nitrate, 30 g of superphosphate and 10 g of potassium salt per square meter.
At the end of flowering, the plant is fed with a complex fertilizer, and in the fall with potassium salt with superphosphate, about 30 grams per square meter.Among organic fertilizers, chicken droppings, ash, and manure are perfect. No fertilization is carried out during the flowering period.
For adult roses, fertilization is possible only with organic matter, but do not overdo it, otherwise the plant may give dense foliage, but not bloom.
to the table of contents
When to replant roses
Over time, roses grow and lose their beauty and when this happens, they need to be transplanted. Repotting is best done in April or October, but spring is still preferred.
Before starting the transplant, the bush is cut to 20 cm, and all the leaves are torn off. The bush must be removed from the soil along with an earthen lump. To facilitate its movement, the roots are placed on a piece of cloth. You can plant a rose with this fabric, it will rot over time.
Climbing roses are transplanted much less often, usually only if a bad place is chosen for growing and if the plant dies in the old place. When transplanting this variety of roses, you need to be more careful, since their roots are more sensitive than others.
to the table of contents
Pruning roses
In spring, summer and autumn, you need to prune the bushes. Spring pruning is carried out to form a bush shape, in summer it is carried out to clean the bushes from excess buds, dull flowers, and fruits. In the fall, bad stems are removed from the plant.
Pruning is carried out until the buds are swollen. Only strong branches should be left, of which the young are preferred.
Older plants need to be pruned more carefully, as they are worse at restoring the crown, the same applies to flowers planted on poor soil. After the operation, the cut sites must be treated with garden varnish.
In autumn, these rose hips do not require watering and special supervision, in addition to weeding and loosening the soil.
to the table of contents
Preparing roses for the winter
Before winter, they need to be spud with a mixture of peat and sand. Hilling is carried out with the onset of the first frost, and the site is covered with a film to prevent precipitation from falling on them.
Before wintering, the leaves are cut off from the plants and burned. It is also advisable to treat the bushes with a 1% solution of copper sulfate. When the night temperature drops to -6ºC, roses are warmed with spruce branches.
To prevent rodents from disturbing your plants in winter, you need to scatter poison baits around the flower bed.
If you covered the area with insulation and oilcloth, then from time to time it will need to be ventilated so that the bushes do not bump.
Climbing roses must be removed from the supports before winter and lowered to the ground. Old roses do not fit well and therefore, it will be necessary to bend them to the ground gradually. This procedure must be carried out at positive temperatures, otherwise the bushes will break. Before wintering, a climbing rose is pinned in the soil, and insulated in the same way as an ordinary one.
to the table of contents
Rose home care at home
If you want to have a room rose, then remember that they do not like cold water and too hot temperatures in the summer.
When buying a plant, you should not rush to transplant it; first you need to wait for the rose to get used to the new conditions.
During the period of growing green mass, you need to water the rose well, and during the rest of the time, watering is carried out a little less often, but make sure that the water does not stagnate in the pot.
A rose transplant is carried out by transshipment in the waxing moon phase. It is necessary to carry out the operation if the plant has filled the entire pot, if the soil in the container with the plant is depleted or the plant has aged and needs to be rejuvenated.
We recommend fertilizing indoor roses with a mullein once every 15 days, and during the flowering period every 7 days. If the plant is sick or has recently been transplanted, feeding is not necessary, and it is also better not to fertilize the flowers in gloomy and cold weather.
In summer, moving it to the balcony will benefit a room rose. You can start to take out the flower after the night temperature becomes warm. At first, the rose needs to be kept in the shade so that it adapts, and then it is moved to diffused light.
For the winter, the stems need to be cut so that there are 4 buds on each branch.Pruning can also be done in the spring, before the plant begins to develop. In winter, the flower is watered every three days and sprayed.
Roses are very sensitive to drafts and plant protection with a paper cylinder would be a good solution to this problem (the height of the cylinder is about half a flower).
to the table of contents
Propagation of roses by seeds
Reproduction of roses is carried out by seeds and vegetatively. Seed propagation is usually used only for wild roses, and not all of them can produce full-fledged seeds.
The material is taken at the stage when the fruit turns red. This usually happens in August or a little earlier.
Then stratification is carried out in wet sand at a temperature of about 3 ºC. With the onset of spring, the seeds are treated with stimulants for better root formation and sown to a depth of two centimeters, and then covered with humus mulch.
When a pair of true leaves appears in sprouted roses, they are transplanted so that the seedlings are at a distance of 7 cm from each other, and the gap between the rows is 20 cm. In the summer, the area with young roses must be fertilized with mineral fertilizer.
Until next August, you need to take care of the bushes, and then they are taken as a stock.
to the table of contents
Reproduction of roses by cuttings in summer
Usually, the best results are obtained by propagation by cuttings, which can be carried out in different ways.
For a simple, natural way to root shoots in summer, you need to cut the stems in the evening or early in the morning. Slightly woody shoots or those that are about to bloom or have recently faded are preferred.
You can find out that the stem is ready for reproduction by breaking off a thorn on it. If it breaks off easily, then you can use the shoot as a cutting.
The length of the cuttings should be about 14 cm, and each of them should have a pair of leaves and buds without flowers. Excess leaves are plucked.
The incision is treated with a root growth stimulator and placed in water, to which are added pieces of rose leaf.
Cuttings are planted directly into the ground, having previously treated the pits for planting with a solution of potassium permanganate.
The branches need to be covered with jars that will serve as greenhouses for them. Young cuttings are very sensitive and the daytime temperature should not drop below 25 ºC and the night temperature 19ºC until rooting has passed.
to the table of contents
Propagation of roses by cuttings in potatoes
An interesting way is to root cuttings in potatoes. To do this, in the spring, you need to dig a shallow trench, about 15 cm and fill it 5 cm with sand.
Twenty-centimeter cuttings are stuck into potatoes, from which you need to cut out all the eyes, and then they will simply be thrown into your little ditch with sand. At first, the seedlings can be kept under glass jars.
It is important to constantly water the cuttings, and once every 5 days, water it with sweetened water (2 tea boats of sugar per glass of water).
to the table of contents
How to propagate a rose with cuttings from a bouquet
If you were presented with a bouquet of domestic roses, then they can be used for propagation. Imported flowers will not work as they are treated with preservatives.
All flowers, thorns, buds are removed from the cuttings, and the leaves are removed from below and shortened from above. The stem itself is cut to 20 cm. Then it is simply placed in distilled water, which is changed until roots appear.
Further procedures do not differ from those described above for conventional cuttings.
to the table of contents
Propagation of roses by cuttings in a package
The finished cuttings are placed in a bag with moist soil, inflated and tied well, and then placed on the windowsill. In about a month, roots should form and the cuttings can be planted.
Transplanting cuttings is done before winter, if you want to plant cuttings in spring or later, you have received the desired cutting and it seems difficult to keep it.
Just dig the shoot into the soil and arrange a dry shelter for it so that the cold does not reach it, and plant the cuttings in the spring.
to the table of contents
Reproduction of roses in the Burito way
Burito's method is completely unreliable, since root formation does not occur even in 50% of cases. But sometimes it does happen.
The cuttings should be treated with a root-growth agent and then placed in a damp newspaper in a dark, warm place (about 17 ° C). You will have a chance that after 15 days the cuttings will form roots, but let's be honest - this chance is scanty.
to the table of contents
Reproduction of roses in the Trannoy way
To reproduce with this type, you need to cut off the top of the shoot with a limp flower and a few small leaves. Further, it is observed until the kidneys from below begin to swell. This indicates that the stem is ready for growing.
At this time, the cuttings need to be cut to 20 cm, remove all the leaves except the top two and plant in a well-lit area, several copies at once in one hole. Cover the cuttings with a large plastic container, which is not removed until the cold weather. Seedlings will sometimes need to be watered and loosened up next to them.
This method is also quite unreliable, but still better than the previous one.
to the table of contents
Propagation of roses by grafts
They need to be grafted onto young rose hips. The dog rose and its varieties are considered the best for this, but others can be used. The vaccine is usually done in the middle of summer.
To do this, remove the lateral stems from the stock and clean its root collar from the soil. A T-shaped incision is made on it in which the cutting is placed. Check the kidney after 20 days. If it is swollen, then everything is fine, but if it turns black, then the grafting failed. Before wintering, grafted roses are spud 5 cm above the grafting level.
In the spring, the earth is raked, and the plant on which the grafting was carried out is cut one centimeter above the grafting site. When the flower begins to grow, it will need to be pinched over the third leaf.
to the table of contents
Reproduction of roses by dividing the bush is possible only for non-grafted species
For such reproduction, it is necessary in the spring, even before the buds begin to bloom, dig up a rose and cut it in such a way that on each division there is a part of the root and a shoot. The places of the cuts are powdered with coal and then parts of the bush are simply planted like ordinary roses.
To propagate a rose by layering, in early spring you need to make an annular cut on the stem that grows from the root collar, and then bend it into the hole, fix it and sprinkle it with moist soil. Further, the soil will need to be moistened until autumn, when the cuttings take root. It will be possible to separate the cub from the mother next spring.
to the table of contents
Diseases and pests
The worst pests for roses are aphids and spider mites... In the early stages, aphids can be fought by simply cutting off the leaves or crushing the aphids, you can also wash the leaves with soap, but if this does not help, you need to buy an insecticide "for roses and grapes" in a specialized store.
WITH spider mite you can fight with an infusion of wormwood or tobacco, but if the pest has spread too much, it is better to buy a means to combat it. This pest affects the rose if it grows in dry conditions and lacks moisture.
Also, the rose can be attacked thrips, cicadas, rose sawfly, but if you take proper care of the plant, they will not appear.
One of the diseases dangerous for the rose is bacterial cancer, which can be recognized by the growths that gradually harden. This disease cannot be cured and the plant will die.
Examine the material before buying, and also carry out pest control before planting with a three percent Bordeaux liquid. If you notice growths on the plant, try removing the leaves and treating the cuts with copper sulfate, but there is no guarantee that you will have time to help the flower.
Coniotirium it is a disease that affects the bark of plants. It appears as brown spots that darken over time and “ring” the stem. These shoots must be cut off and burned immediately.Also, if this ailment is found, before winter it is necessary to stop fertilizing the rose with nitrogen, and replace it with potassium fertilizing.
Powdery rose represents white spots. Sick areas should be immediately removed and burned, and the plant should be treated with iron (3%) or copper (2%) vitriol.
Brown spots on the leaves and the falling off of the latter indicate black spot... To prevent the development of the disease, you need to fertilize the rose with potassium-phosphorus dressings in the fall, as well as treat the plant and the area where it is grown with Bordeaux liquid (3%).
Also, the rose can get sick gray mold, after which the plant is most often burned. But, if the fungus has not entered into force, then you can try to cure it with a Bordeaux solution diluted in water (100 grams per bucket). In this way, a diseased plant will need to be processed 3-4 times every seven days.
- If your rose is not blooming, then you may just have acquired a weak plant or a variety that rarely blooms. This also happens if the flower lacks light or nutrients. The absence of flowering can be caused by freezing in winter. But the most dangerous reason for the lack of flowering, in which the rose loses its varietal properties, is the wildness of the plant.
- If you notice shoots with small leaves and an abundance of thorns, then immediately cut them off (usually such stems appear from the very bottom of the bush). If you do not fight them, then over time these shoots capture the entire bush and it runs wild.
- The leaves of roses can fall off if they are struck by pests or a disease, and besides this, the reason is often hidden in the roots of the plant. The root can rot, and there are also cases of damage by bears or May beetle larvae, mice and moles.
- In addition to diseases, the leaves of a rose can turn yellow from an elementary lack of nutrients such as nitrogen, iron and manganese, as well as potassium.
With a lack of nitrogen, the leaves turn yellow alternately. First, this happens with the bottom layer, which falls off after yellowing. Further, such a fate awaits the middle leaves, and then the whole bush. With a lack of potassium, the leaves begin to turn yellow from the edge, and then dry out. With a lack of trace elements, the veins on the leaves of the plant begin to turn yellow. Another cause of yellowness is excess moisture in the soil.
to the table of contents
How to grow roses: correct pinching (with photo and video)

Agricultural technology for growing roses in the open field in the photo
Agricultural technology for growing roses in the open field involves the timely pinching of strongly growing shoots - this way you can adjust the shape of the bush. Sometimes only one peephole under the pruning site gives rise to a shoot that grows very long, which spoils the appearance of the whole plant, especially in the standard rose. When such a shoot appears in May, it is likely that the first early flower may soon appear at the end of it.
Nevertheless, it is better to donate to them, and pinch the young shoot, leaving 3-4 eyes, from which new stems will go, suitable for the formation of a beautiful crown of the plant. A pinched rose in the same year will give more than one flower, although somewhat later.
Sometimes the shoot of a rose ends in a single leaf without an eye. The flower is no longer formed here. In order to properly grow roses, as practice shows, such a so-called "blind" shoot must be cut over the nearest leaf, where there is a healthy eye, and then a new shoot that can bloom will later grow out of it.
If the rose was improperly planted and was not properly cared for, it can give rose hips below the budding site. The leaves of these shoots, in contrast to the leaves of cultivated varieties, are lighter, of different sizes and with a different number of leaves. They have others and thorns.
To grow beautiful roses like in a nursery, you need to remove these wild shoots. To do this, open the root collar of the bush and part of the roots, carefully cut the shoots at the very root. Sometimes an escape is enough, if it is young, just pull it out.However, by cutting it off at the surface of the ground, as is often done, the gardener thereby, on the contrary, awakens the shoot to more intensive growth and branching.
These photos of growing roses and caring for them show how to do the correct pinching:
And a few more recommendations on how to grow garden roses:
- Novice gardeners often have problems - they planted a rose, and after 2-3 years it turned into a "wild". Know that a rose bush cannot be reborn into a rose hip. You just did not cut out the wild root growth in a timely manner, and it “strangled” the cultivated part of the plant. Watch out especially for roses in the first years after planting, later the root is older and less wild growth is formed on it.
- When growing self-rooted roses, there is no need to remove wild growth and the cost of planting material is significantly reduced.
Watch a video on how to grow roses in your garden:
How to grow beautiful garden roses: proper watering when leaving
The role of watering in the care of roses is not as great as for other garden plants. Since they put their roots deep into the ground and from there get themselves the necessary moisture, the bushes look fresh and healthy even when the leaves on other bushes wither due to the prolonged heat.
But how to grow healthy roses on the site if the summer drought has dragged on? This often happens in the southern region in June, July and August. In this case, it is very desirable for roses to be watered at least once a month. The norm is 20-30 liters per plant or per 1 m2 of rose garden area. More often, self-rooted roses need watering, as well as those growing on too light or sandy, permeable soil that does not retain moisture well.
Proper watering of roses is performed only in the morning and evening hours. The best way of watering is by overflow (the hose is placed directly to the bush itself and water is let in under low pressure so that it flows out slowly). Short watering with a strong pressure of water will not help, because the moisture will not reach the roots of the plant, it will remain only in the upper layer of the soil and quickly evaporate, without bringing any benefit to the bushes.
For better preservation of moisture and air exchange in the soil, loosening is necessary after each watering and rain.
When watering roses, remember that the less water gets on the leaves, the better, it is advisable not to water them at all. Foliage that remains moist for a long time is more exposed to the threat of infection with fungal diseases (black spot, powdery mildew, botrytis - gray rot, etc.).
Despite the fact that roses often grow well without watering, be aware that with sufficient soil moisture, more powerful and abundantly flowering bushes develop.
Next, you will find out the best way to mulch roses in your garden.
How to grow roses in the garden yourself: the better to mulch the bushes
Mulching plays an important role in the cultivation of roses - covering the soil around the bush with a 3-5-centimeter layer of peat and sawdust. How else to mulch roses in the garden? For this purpose, you can use humus, compost or lawn mowed grass. Mulch in the spring, right after loosening and pruning bushes or loosening the soil around uncovered varieties.
In order to grow roses on your own, as practice shows, the mulching material in late autumn, together with the soil, will also be a good material for sheltering (hilling) bushes. In one or two years, sawdust and mowed grass will grind and become a good organic fertilizer, like humus, compost and partially peat.
With proper care during the cultivation of roses in the garden in mulched areas, the soil structure is significantly improved. The soil becomes looser, does not compact when watering, does not form a crust, the number of weeds is significantly reduced, the harmful effect of overheating of the soil on the root system is excluded, the roots develop better, and also less wild growth (rose hips) appears, on which most varieties are grafted.Mulching is especially effective in areas where watering is not possible.
Growing and caring for roses: correct pruning in spring (with video)
Pruning bushes is one of the most important garden rose maintenance techniques. The decorativeness of plants, the splendor of their flowering, the intensity of damage by pests and diseases, and, finally, longevity depend on pruning.
Pruning roses when caring for plants is done at least three times a year (spring, summer and autumn). The most important pruning is spring.
After removing the shelter, when the buds swelling on the shoots are clearly visible, the bushes are thinned out. Such pruning of roses in spring is to remove dying and unnecessary branches and shoots that are not important for flowering. As a result of the removal of excess shoots, the plant will send more nutrients to those shoots that can use them with great effect for flowering.
At the same time, with proper pruning of roses, in the spring, shortening of the remaining shoots is carried out in order to awaken the lower buds to growth, ensuring flowering. In this case, we give the plant the opportunity to direct nutrients to the development of flowers to achieve their highest quality.
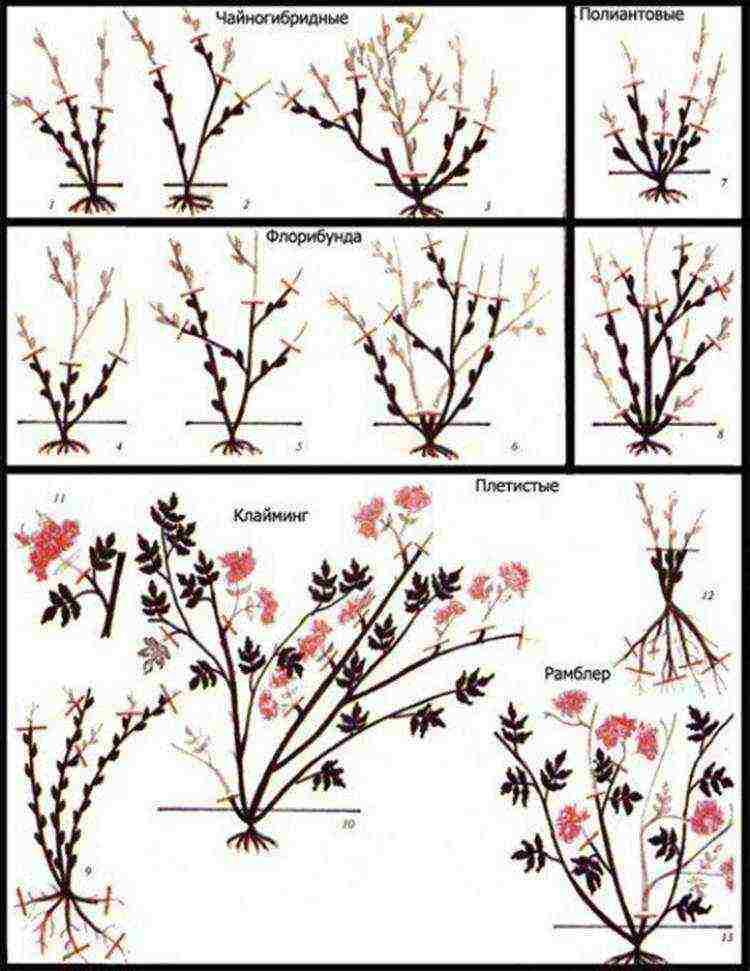
When shortening, depending on the group of roses, the pruning is short, medium and long. The cut is made above the peephole looking outward of the bush. For the plant to form correctly, young shoots should not grow inside the bush.
How to prune roses correctly to form a beautiful bush? The cut should be perfectly smooth and run 0.5 cm above the kidney with a slight slope in the opposite direction from it. The sections must be immediately covered with garden pitch, then moisture will not linger on them, the risk of various infections entering through fresh wounds will decrease. While working, avoid flattening and traumatizing plant tissues, do not allow the bark to break.
With short pruning, most of the shoot is removed, leaving a hemp with about 2-3 eyes. With medium or less short pruning, 4-8 eyes are left. With long pruning, only the tip of the shoot is removed, and the number of eyes can be of an indefinite number. In this case, the thickness of the shoots plays a role.
Most of the varieties grown by gardeners need short pruning. They endure strong pruning without any damage to their life.
When leaving during the cultivation of garden roses, hybrid tea varieties are subjected to short pruning - small-flowered and large-flowered polyanthus and undersized varieties of other groups.
Medium and less short pruning is sufficient for remontant varieties (with the exception of undersized ones, which are also pruned short) and some vigorous varieties of tea hybrid and other groups.
When pruning for all roses, thinning of the bushes is mandatory. At the same time, weak, deformed (unnaturally curved), broken, dying shoots, as well as those with signs of disease or pests, are completely removed. They are cut off at the very base, leaving no stumps. Damaged stems are shortened to healthy tissue (with a white core).
There are four types of spring pruning of roses: preventive, thinning, shaping and rejuvenating. Preventive pruning is done in early spring to eliminate fungal diseases. Thinning is carried out in spring and summer, removing old shoots with dying growth and branches growing inside the bush. This pruning promotes abundant flowering. It is also used to rejuvenate old bushes of park and climbing roses.
There are three types of formative pruning: strong, medium, and weak.
With strong pruning, 1-2 well-developed buds are left on the shoot, with medium - 3-6, with weak - only the tops of the shoots are removed.
As a rule, strong pruning is used for polyanthus and miniature roses, medium - for hybrid teas, floribunda and grandiflora roses, weak - for park and climbing roses.
Immediately after spring pruning, prophylactic spraying against harmful organisms is carried out, if the buds are dormant, with copper or iron sulfate (100-150 g per 10 l of water), if a green cone has formed (the buds have started to grow) - 3% Bordeaux liquid or its substitutes ("Abiga-Peak", "Oxyhom", "Copper oxychloride", etc.).
The video "Leaving, growing and pruning roses" clearly demonstrates how the spring shaping of the bush is performed:
How to grow roses on the site and how to cut bushes in the summer
All roses tend to develop a lot of extra weak shoots. Among them are the "blind" who do not carry a flower. Leaving all the shoots on the bush in the summer is useless and even harmful, since they lead to excessive thickening of the bush. How to prune roses in the summer correctly? To do this, it is necessary at the beginning of summer to cut into a ring (to the base) shoots directed inside the bush, underdeveloped and "blind". And then carry out summer pruning depending on the purpose for which you grow roses: for flower decoration of a garden or summer cottage or for obtaining commercial flowers for cutting.
Many varieties of hybrid tea roses form several buds on the shoots. To get a large flower, only one bud is left, the most developed is the central one, the others are removed. A lush and long-flowering bush will turn out if the buds on it are not touched, but only fading, fading and crumbling flowers are removed.
At the same time, remember that excessive removal of flowering shoots leads to a general weakening of the aerial part, as a result of which root growth (rose hips) develops.
The flowering of the bushes and the quality of the flowers when caring for garden roses directly depend on how correctly the cut is made. You cannot cut more than two flowers from a bush at the same time. At the base of the peduncle, it is necessary to leave 2-4 nodes and cut over a well-developed bud, looking outward. Then you can hope for a quick resumption of growth and re-flowering.
The photo "Growing and caring for roses in the garden" shows how summer pruning is performed:
How to properly prune roses in autumn (with video)
Since most of the roses in the winter have to be covered (with the exception of ground cover and park), autumn pruning comes down to shortening and removing part of the shoots so that a shelter can be installed above the bushes. Even if we limit ourselves to hilling roses for the winter, their long branches must still be cut off, leaving no more than 40-45 cm. Otherwise, wet snow or icing may cause the bushes to break (fall apart) at the base.
Roses are pruned to rejuvenate and keep the bush in good shape, so that the plants bloom more luxuriantly and the flowers are larger. Weak, dry and old shoots are removed by pruning. In grafted roses, root shoots and shoots on the stem of the stock are completely removed, if possible.
For each group of roses, there are specific pruning rules, but there are general provisions that are inherent in all groups to one degree or another.
Roses are pruned in spring for flowering, in summer for re-flowering and maintaining the shape of the bush, in autumn for winter shelter.
Before pruning roses correctly in the fall (however, this is also true in other seasons), prepare a good sharp garden pruner, preferably with two blades, since the cut should be even and smooth. Water gets into a torn or uneven cut, and with it pathogens.
In the process of pruning roses in the fall, it is important to observe the shape of the bush and the position of the buds, from which new shoots will go. The bud should look outward, then the bush will be beautiful and not thickened in the center, it will hurt less, since it is well illuminated by the sun and blown by the breeze.
It is important to choose the right cutting site: not too close to the kidney or too far from it. Cut off very close, the bud may dry out or the bud will be weak.When cut too far, ugly stumps remain, during the growing season they dry out, however, they can be cut out later, but this is additional work. Even the slope of the cut matters.
When pruning and growing and caring for roses, remember to remove dry, damaged and thin branches first, leaving only a few good, strong shoots. They are shortened to the 3rd, 4th or 5th kidney. The result should be stems from 10 to 25 cm in height.
The formation of a young, first-time blooming rose bush requires special attention. The flowering of the bush in the first year should be minimal. Leave no more than 1-2 flowers per plant. Remove the rest in the bud phase. Flowering shoots should be arranged symmetrically, alternating with non-flowering ones. Only in this case is an even distribution of nutrients achieved and, therefore, uniform development and formation of the bush.
Watch the video on how to prune roses to get a better understanding of how to shape the bushes:
Caring for roses: how to properly cover bushes for the winter (with photo and video)
Winter hardiness of rose bushes depends on the physiological state of the plants and their successful preparation for winter. There are two preparatory periods. The first one takes place in the second half of summer, active growth stops, starch accumulates in plant tissues, and the consumption of carbohydrates is reduced. It is necessary to significantly reduce the intensity and frequency of watering, remove nitrogen from the dressings, and carry out foliar dressing with phosphorus-potassium fertilizers.
In September, you need to stop cutting flowers, and starting from the second half of the month, do not water or loosen the soil around the bushes. Weeds must be removed without fail. Then the shoots will ripen better and wintering will be successful. Even before the first frost, it would be good to slightly spud the roses with loose earth. That's all the preparatory operations.
With the onset of stable cold weather, before covering the roses for the winter, you need to remove all the leaves from the bushes, then cut off the diseased, weak and immature shoots and shorten the healthy ones to 40 cm.
The second period falls on late autumn - the beginning of winter, when the air temperature is set in the range of -2 ... -3 ° С. At this time, plant cells are dehydrated, starch is converted into sugars and fats, which helps to reduce the freezing point of plant tissue.
When caring for roses in front of shelter, the bushes are sprayed with 2% iron sulfate from fungal infections.
In the southern region, it is quite enough to cover the roses with loose soil, making mounds 15-20 cm high.
Hilling more than 20 cm is impractical, since in winters with frequent thaws it impairs air access to the stems of the bushes.
Most gardeners, when hilling roses, take the land right there, near the plants. In this case, pits and grooves are formed with a depth on the bayonet of a shovel, the most active part of the root system is damaged and exposed. This ultimately leads to inhibition of growth and weak flowering of the bushes, since food does not come from the most fertile soil layer.
You should know that the root system of traditional bush roses grafted on rose hips develops mainly in the surface horizon to a depth of 50-60 cm.And in the upper soil layer (8-10 cm), horizontal roots extend to the sides of the bush by 80-100 cm. There are, of course, vertical roots that go down to 1.5 m, but they mainly supply water.
In addition to mechanical damage to the roots, in the pits formed around the bushes in the autumn-winter months, water stagnates and freezes, which causes further damage to the roots. Therefore, the roots of roses should not be exposed.
As shown in the photo, in order to cover roses for the winter, the soil for hilling must be taken elsewhere or the bushes must be covered with humus, peat, compost, leafy soil, finally, with sand, sawdust or leaf litter, and on top with agrotex-type material:
In the central zone of Russia, all groups of roses without special shelter for the winter suffer greatly, and sometimes freeze completely.
To the south of the central strip of Russia, the most winter-hardy are park roses, which do not need shelter for the winter. Then there are polyanthus and hybrid-polyanthus roses, which require moderate cover, and then hybrid tea roses, which need the most careful cover.
How to cover roses correctly so that they overwinter successfully? For this, on top of the hilling, another layer of woody foliage or spruce branches is applied, and sometimes a film or roofing material, so that the shelter does not get wet.
When covering roses for the winter, do not use plastic wrap, as condensation forms on it, which increases humidity and contributes to the development of fungal diseases. The film does not allow fresh air to pass through, the heat stagnates under it in the sun, and the next cold snap affects the plants even more severely.
- Wild roses and once-blooming shrub roses do not need any special winter protection. They are hardy enough to withstand all bad weather. Even if any of the shoots dies from frost, just cut it off in the spring as low as possible.
- Newly planted bushes, as well as roses that bloom again, should be sheltered for the winter (sprinkle with earth by 15-20 cm).
- Sudden changes in temperature during the winter months are more dangerous for roses than just extreme cold.
The video "How to cover roses for the winter" shows how to protect the bushes from frost:
How and when to take shelter from roses in spring
Many novice florists are interested in when to take shelter from roses in spring. You do not need to do this right away. As soon as the soil thaws and shakes out, the hilling hill that has compacted during the winter is slightly loosened. This will provide better air access to the plants and will help dry out the cover layer. With the onset of warm weather, rose buds quickly swell and start growing. It is not necessary to break the roses immediately, but in parts, in order to retard the development of roses as much as possible, and most importantly - to protect them from recurrent night frosts.
In order to prevent fungal infection at this time, spray the bushes with Bordeaux liquid (3% if the buds are dormant, or 1% if they have already started to grow). This spraying will help keep the shoots moldy over the winter, but still alive.
If you know when to remove the shelter from roses in spring, keep in mind that it is also dangerous to be late with the opening of the bushes, because the tender shoots sprouted without access to light will immediately fall under the influence of direct sunlight, wind and may die.
In such cases, sunburns of the bark are obtained, it turns brown, cracks and begins to peel off; shoots dry up, the plant dies. Therefore, it is necessary to finally undo the roses on a cloudy day, and if the sun appears, shade the bushes that have moved into growth with non-woven material (agryl, agrotex, green-tex, etc.). Keep this material ready in case you want to cover your bushes at night in the event of an unexpected freeze.
It is known that hybrid tea roses have an increased ability to restore damaged shoots, since the bushes have a large number of "dormant" spare buds in the lower part of the shoots, from which new shoots develop. From spring, such bushes should be given 1-2 fertilizing with nitrogen fertilizer (carbamide - 20-25 g per 1m2 with an interval of 12-15 days), keep the soil moist (in the absence of precipitation - regular watering of at least 10 liters of water per bush). This will contribute to the restoration of vital activity and the rapid regrowth of young shoots in roses.
Heavily affected, especially in harsh winters, do not rush to throw out rose bushes in the spring, even if others nearby have already started to grow, and these are still without signs of life. If they were planted correctly (the place of budding is 5-7 cm below ground level), water the bushes several times with Kornevin or Kornerost, spray with Epin - the roses can leave in late May - early June.
Rose care: fertilization and feeding
An important part of caring for roses is feeding, it is needed to ensure proper nutrition of the bushes. Roses have a good "appetite". For optimal growth and development, roses need mineral and organic fertilizing. Mineral fertilizers should contain nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and magnesium.
Fertilizing with nitrogen when caring for roses stimulates the growth of new powerful shoots with beautiful dark green foliage, so it is applied at the beginning of the season. In autumn, roses are not fed with nitrogen, otherwise the young tender shoots that have grown by winter will die at the first frost. It is best to apply nitrogen fertilizers immediately after pruning roses, that is, in April-May. If necessary, nitrogen fertilization can be repeated at the end of the first wave of flowering.
Fertilization with phosphorus when caring for roses is necessary for the development of new roots, the formation of buds, flowers. Considering that superphosphate acts slowly, for its maximum effect it is better to apply in early spring.
Potassium also plays a large role in the health of roses. Its lack reduces the resistance of plants to diseases. This element is applied under the roses in the form of a ready-made potash fertilizer, best of all in early July. From potash, choose fertilizers containing magnesium - another element important for roses (potassiummag or potassium-magnesia). Yellow leaves with green veins are a sign of magnesium deficiency.
How and what to feed and fertilize roses
Usually, it is enough for roses to be fed three times a year: at the end of October, compost or humus is applied under the bushes, in April - nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizers, and at the end of flowering - potash fertilizers.
Before feeding roses, carefully study the information on the estimated doses of fertilizers per 1 m2, which is indicated on the packaging of each dressing.
It is necessary to alternate fertilizing with mineral fertilizers with organic fertilizing. Organic fertilizers do not contain mineral salts. They consist of rotted animal or vegetable waste. The effect of such fertilizers is based not only on supplying plants with nutrients, but also on activating biological processes in the soil and thereby enriching it with humus.
Organic fertilizers must first interact with soil microorganisms and are brought into a form that can be better absorbed by plants. Therefore, unlike mineral fertilizers, which are usually very quickly assimilated, organic fertilizers take time to assimilate.
Organic fertilizers are applied in larger quantities than mineral fertilizers (up to one bucket per bush). But this source of nutrients lasts longer.
How to fertilize roses with manure? It is introduced into the ground in advance, even before planting the seedlings. Manure is filled into the topsoil, applying about 8-10 kg / m2 on light soils and about half of this rate on heavy soils.
The best dung is cow dung. Equine - more caustic, it should be used with caution, and in a well-decomposed form (humus).
A good organic fertilizer is not only humus, but also rotted compost and leafy soil from old forest belts, where the top layer of soil up to 10-15 cm thick is removed for fertilization. This layer is light and very nutritious, it consists of perennial leaf litter.
In the selection of photos "How roses are grown", it is shown what fertilizers are used for these plants:
Roses during the summer need foliar dressing with solutions of mineral fertilizers (Agro Lux, Zdraven, Solution, Potassium Humate and other water-soluble compounds in turn). Such fertilizers contain nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, magnesium and trace elements: boron, copper, iron, manganese, molybdenum, zinc, etc. These substances give not only good growth and development of roses, but also increase their resistance to diseases and pests.
In dry years, fertilizers are applied less than in a year with heavy rains, nitrogen is used especially carefully.
As a rule, it is necessary to finish feeding no later than August, so that the shoots of roses can ripen well before winter arrives.
In the first year after planting, roses are not fed. Knowing how and with what to fertilize roses, remember that mineral fertilizing begins only from the second year and then it is done regularly. In the spring, when the buds open, shoots are formed, leaves appear and the first flowers are formed - at this time the plants have a great need for nitrogen. In summer, roses need to be fed with potassium and phosphorus for the second and subsequent flowering.
Rate the article:
(1 vote, average: 5 out of 5)



