Content
- 1 Types and varieties
- 2 Seat selection
- 3 Buying a seedling
- 4 Landing
- 5 Top dressing
- 6 Watering
- 7 Care
- 8 Reproduction methods
- 9 Some varieties of roses
- 10 1 Description, types and varieties
- 11 2 Selection of seedlings
- 12 3 Landing
- 13 4 Care
- 14 5 Reproduction
- 15 6 Diseases and pests
- 16 7 Design
- 17 Features of park roses
- 18 Classification of park roses
- 19 How to plant a park rose
- 20 Pruning and covering park roses for the winter
- 21 How to care for park roses
- 22 The best varieties of park roses for the Moscow region and the middle lane, which do not require shelter for the winter Photos and names
- 22.1 Park rose Martin Frobisher Martin Frobisher rose
- 22.2 Park rose Ferdinand Pichard rose Ferdinand Pichard
- 22.3 Rose Remy Martin park Canadian Remy martin rose
- 22.4 Park rose John Franklin John Franklin rose
- 22.5 Rose Pristine Pavement
- 22.6 Rose Chinatown
- 22.7 Rose park Red Diamond Rose Kordes Brilliant
- 22.8 Park rose Louis Odier Louise Odier Rose
- 22.9 Rose park Piano rose Piano
- 22.10 Rose park William Shakespeare rose William Shakespeare
- 22.11 Park rose Alexander Mackenzie rose Alexander Mc Kenzie
- 22.12 Rose park Louise Bugnet rose Louise Bugnet
- 22.13 Rose Canadian park Moden Fireglow Morden Fireglow
- 22.14 Park rose Crocus Crocus Rose
- 22.15 Rose climbing park Henry Kelsey Henry Kelsey Rose
- 22.16 Park rose Cuthbert Grant Rose
- 22.17 Park Rose J.P. Connell J.P. Connell Rose
- 22.18 Rose Champlain Rose Champlain
- 22.19 Rose park fluorescent Rose Fluorescent
- 22.20 Rose Canadian Park Adelaide Hoodless Adelaide Hoodless Rose
- 22.21 Rose black magic Rose Black Magic
- 22.22 Rose park Marchenland Rosa park Marchenland
Roses ... You can look at the flowers of these wonderful plants without taking your eyes off. If on a summer morning you want to see this enchanting beauty covered with dew drops like a scattering of diamonds in your country garden, then it's time to get down to business.

There are many types, species, groups of roses, but when buying, you should understand what you want to plant on the site: a tall spreading or miniature bush, a rose with drooping or strong erect shoots, a miniature plant that can fit in a flower pot.
Types and varieties
The difference is also observed in the shape of the flower:
- cruciferous,
- power socket,
- cupped,
- open bowl
- goblet (like hybrid tea roses),
- pompom, etc.
According to the duration and flowering periods, roses can be divided into single flowering (climbing, tea-hybrid), re-flowering (bush), constantly flowering (floribunda).
If you come to a garden center or a specialty store, then on the packing boxes or pots with roses, as well as in the online store, it will be indicated which group the plant belongs to: hybrid tea, floribunda, climbing, ground cover, miniature, bush, David Austin's English ...
Hybrid tea varieties of roses have erect bushes with straight, strong, rigid stems from 50 to 140 cm (depending on the variety). The flowers are large, single, goblet-shaped with a delicate or strong aroma, in which tea notes are always present. Hybrid tea roses require careful care and mandatory shelter for the winter.
Floribunda roses are characterized by small flowers collected in inflorescences, low bushes (from 50 cm to 1 m), long continuous flowering from summer to autumn.
Climbing roses differ in stem height: 2-4 m, abundant flowering, small flowers. They require an obligatory garter to strong supports: arches, pergolas, obelisks. Plants of this group do not bloom on the shoots of the first year, therefore, for successful cultivation, the bush must be laid on the ground and covered every year, and raised again in the spring and tied to supports.If the bush is powerful, then the lesson is quite laborious and it is better to cope with two people.
Groundcover, miniature, polyanthus, patio roses are compact floribunda roses with a bushy shape, numerous small flowers, almost odorless. Used for small flower beds, flower beds or container planting.
English bush roses from the David Austin nursery are gaining more and more popularity with amateur flower growers every year. You will be fascinated by the shape of the flowers, as if descended from the paintings of ancient masters: thick double, cupped, drooping under the weight of hundreds of petals. The aromas possessed by almost all varieties of English roses are so varied that at times they resemble exquisite French perfumes with different shades. Many varieties: Graham Thomas, Jubilee Celebration, Lady Emma Hamilton and others, have won awards and worldwide recognition from rose growers for their fragrance.
Seat selection
Decide on your landing site in advance. Roses prefer well-lit areas protected from cold northerly winds, but there are not so many such places on the site and many types of flowers, berries and vegetables claim to grow on them.

Find a place that gets direct sunlight for at least 5 or 6 hours a day - this kind of lighting is fine for a rose. If the lighting is limited to 3 or 4 hours a day, then such a place is considered partial shade. However, if this is a light partial shade from a tree with a thinned crown, then some varieties of roses will feel even more comfortable than being under the scorching sun all day long (for example, some varieties of English roses by David Austin with a delicate color: Mary Rose, Golden Celebration, single blooming roses, wrinkled rose hybrids, etc.). Usually, manufacturers indicate with icons on the packaging what the plant prefers: a sunny place or partial shade.
In areas that receive less than 3 hours of sun per day, roses will not be able to grow.
When choosing a place, it is also necessary to take into account the fact that some roses, especially for climbing ones, will have to be laid on the ground, and the shoots can reach a length of 2.5 - 3 m, so when planting, decide in which direction you will bend the lashes, so that for this enough space.
Soil requirements
For normal growth, light loamy soils, rich in humus, are required. Heavy clayey requires good drainage: sand, expanded clay, humus, peat are added to the planting pits. Light sandy soils require enrichment with humus, sod land, and organic fertilizers.
In one place, roses can grow up to 10 years, so the planting site is chosen carefully.
Buying a seedling
It is important to choose the right variety for your garden and buy a healthy, strong seedling from a trusted nursery or specialty store.
When choosing a group, be guided by the characteristics of your site: size, illumination, soil type, protection from winds, etc.
When choosing a variety, pay attention not only to the color and size of the flowers, the height and shape of the bush, but also the following indicators: disease resistance (powdery mildew, rust, black spot), flowering frequency, flower resistance: some do not tolerate bright sun (burn out) or rainy weather (drooping or rotting).
Now you can buy roses in tubes or bags, with an open root system (usually in nurseries) or closed (in containers with soil). It is better to buy roses in early spring (March, April) so that the buds do not open yet.
Closed-rooted plants can also be purchased in summer if they are in good condition. In this case, you will be able to see the selected variety in the flowering phase.

Saplings are grafted onto other varieties of roses, more winter-hardy, adapted to growing in your area or own-rooted, grown from cuttings.
When buying, you need to make sure that the plant is viable: with a live, undried root system (the roots are light yellow on the cut) and live shoots, and the grafted bush had at least three shoots.
It is best to store roses in tubes, boxes in refrigerators, in compartments intended for vegetables and fruits, having previously wrapped them in newspaper (provided that the buds have not yet started to grow). Seedlings with an open root system are stored similarly, but in this case, the roots must be wrapped in wet moss (sphagnum) and the plant should be placed in a perforated plastic bag. You can store seedlings in the cellar of a country house or on a cool glazed balcony.
Landing
The basic rule for growing roses is to apply a sufficient amount of organic fertilizer (rotted manure or compost).
The soil is preferable moderately acidic (pH 5.6-6.5). It is desirable to add ash or dolomite flour to acidic soil, you can use chalk or slaked lime.
Preparation of seedlings
Before planting, you should check the root system of the seedling, remove it from the packaging (tube, bag), prune broken, dry roots. Soak the seedling in a solution of rhizite (10 g per bucket of water), heteroauxin or epin for 2-4 hours. In some cases, nurseries carefully pack their products and the roots of the seedling are placed in a nutritious substrate - in this case, the dense self-decomposing wrapper does not need to be removed from the roots. The plant is planted in the same way as with a clod of earth.
Seedlings with an open root system can be placed in a clay mash with the addition of manure infusion in a 1: 1 ratio (clay, manure infusion and a little water; sour cream consistency solution) for a few minutes and let dry a little, then plant.
If the plant was purchased in a container, a pot (with a closed root system), try to carefully remove the seedling from the pot without damaging the earthen ball. Make sure fresh light roots are penetrating the soil and soak the roots in water for 2 to 3 hours.
In the event that the root system looks unimportant, soak it in a solution of rootite (10 g - per bucket of water), heteroauxin or epin for 2-4 hours.
Soil preparation
When preparing the soil for 1 m² of soil, 2 buckets of well-rotted manure or compost, 250-350 g of wood ash, 2 tbsp. spoons of superphosphate, 2 tbsp. spoons of nitrophosphate.

The prepared plantation is dug to a depth of 40-50 cm for self-rooted seedlings and at least 50-60 cm for grafted ones.
If you are planning single plantings, it is better to dig a planting hole, the depth and diameter of which will correspond to the size of the plant's root system, about 40-60 x 40-50 cm, on heavy clay soils it can be deeper - about 65 cm, because the roots need to be aerated (breathable).
Please note that the grafting area should be 2-5 cm below the soil level, so the depth of the hole should be previously measured with a tape or stick.
The soil at the bottom of the pit must first be loosened. Expanded clay or large crushed stone is poured at the bottom. Then, next to the pit, a mixture is prepared (you can first spread a film for this) from sand, well-rotted manure, peat, garden soil in the ratio: 1: 1: 1: 2, add 150-200 g of ash and a handful of complex fertilizer for roses or flowering garden plants (or 2 tablespoons of superphosphate and potassium sulfate).
Instead of the specified mixture, you can fill the planting hole with special soil for roses: throw about 60 g of complex fertilizer for roses at the bottom of the hole and mix another 80 g of the same fertilizer with the ground, which you will fill the planting hole with the seedling placed in it.
How to plant
Part of the prepared mixture is poured onto the bottom of the pit, a rose seedling with an open root system is placed in the center, the roots are straightened, the level of the grafting site is checked again and the hole is filled with the prepared soil mixture, the soil is slightly tamped with feet so that the plant does not sway with the wind and there are no air pockets around the roots.
If the rose was sold in a tube or box, then you need to pull the plant out of it, leaving only the inner packaging for the roots. Place the seedling in the center of the planting pit, check the planting depth: the grafting site should be 2-5 cm below the soil level. Water with the prepared solution of the root formation stimulator. The plant, similar to the previous version (with an open root system), is covered with prepared soil mixture, tamped down.
Roses with a closed root system are also planted; before planting, they must be carefully removed from the pot (container). It should be borne in mind that the diameter of the planting hole should be approximately 2-2.5 times the diameter of the pot, and the depth should be slightly greater than the height of the pot (container).
Leaving immediately after planting
After planting, the roses are watered with warm settled water at the rate of 10-15 liters under the seedling and the soil is mulched with peat, humus, mown grass, and large shavings.
At first, the plants should be shaded from the sun (set arcs and put on a thin covering material of 17 g / m²), watered abundantly in time and saved from pests. When planting in early spring, return frosts occur, because you may have to shelter from frost. In this case, the density of the non-woven covering material should not be less than 30 g / m².
If, when planting, the root collar is above the soil level, then during the winter the plant may not survive.
When to plant
In spring, it is advisable to plant roses in cold ground, as soon as it has thawed and can be dug ("cold start"). But you need to make sure that the ground is not frozen or waterlogged. At the same time, the seedlings of roses should be still dormant, i.e. with buds but no leaves.
Seedlings with a closed root system can be planted from spring to autumn (the main thing is to shade and water abundantly in time). With an open root system - in addition to spring, they are also planted in autumn until mid-September, because the plant must take root before frost. However, roses planted in autumn do not always winter safely.
Top dressing
Without a sufficient amount of fertilizers, roses will not be able to develop and bloom normally, especially they are partial to organic fertilizers. Therefore, it is advisable to have an infusion of mullein or bird droppings for feeding: 1 kg of fresh manure is poured with a bucket of water (10 l) and allowed to brew for 5-7 days.
Organic mullein-based feeding is prepared as follows: 1 liter of infused mullein (7-10 days) is diluted in 10 liters of water (1:10), based on bird droppings: 0.5 liters of infused chicken manure (7-14 days) is also bred in 10 liters of water (1:20).
In a similar way, you can prepare an infusion of fermented nettle (dandelion, celandine, chamomile, etc.): chop 1 kg, pour a bucket of water, let it brew for at least 5 days. For top dressing, dilute 1 liter of infusion in 10 liters of water.
For foliar feeding, you can use preparations designed specifically for roses or prepare yourself. Ash infusion: pour boiling water over one glass of ash, let it boil a little, after it cools down - strain, dilute in 5 liters of water. Double superphosphate does not dissolve quickly in cold water, so 50 g of superphosphate is poured into 0.5 liters of hot water, infused for about 5 hours, filtered and diluted in 5 liters of water. Foliar dressing is carried out only in the evening, with a freshly prepared solution. They cannot be carried out in cold, damp weather.
The main chemical elements that roses need:
- Nitrogen - for the growth and build-up of green mass (urea, ammonium nitrate - at the rate of: 1 tbsp. L. Per 10 l of water).
- Potassium - for successful flowering, ripening of shoots, resistance to diseases (potassium nitrate, potassium magnesium (1 tbsp. L per 10 l of water), potassium sulfate (30 g per 10 l of water), potassium sulfate.
- Phosphorus - for the normal development of the root system, successful wintering, abundant flowering (superphosphate, double superphosphate, ammophos).
- Trace elements: manganese, magnesium and boron increase the immunity of plants to diseases, iron does not allow chlorosis to develop.
How often and when to feed
During the season, an average of 6-7 dressings are carried out with organic and mineral fertilizers.
It is especially important to feed the roses in early spring, when the buds begin to bloom and in the middle of summer after the first wave of flowering. At this time, the plants are gaining strength for the second wave of flowering.
During flowering, roses are not fed, so as not to accelerate the process of their flowering.
As soon as the ground thaws, after spring pruning (April - early May), and the plant grows, it is necessary to feed it with a full complex fertilizer: sprinkle fertilizer for roses or another universal (Kemira (1 tablespoon per bush), Agricola for roses or flowers, etc.) in the form of powder or granules around the bush, with a hoe or scoop, they bury it in the soil and water it abundantly. If the spring is cold, then it makes sense in May to feed the roses with nitrogen-containing fertilizers (ammonium nitrate or urea, 1 tablespoon per 10 liters of water), as well as pour 3-4 liters of organic fertilizer under the plant or spread well rotted under each bush manure.
In early June, when the plants lay buds, they are fertilized with mineral fertilizer (potassium sulfate or calcium nitrate: 1 tablespoon per 10 liters of water) and a solution of organic fertilizer (mullein, chicken droppings) or green fertilizer (nettle, calendula, dandelion) ...
In June-July, it is recommended to carry out foliar dressing with potassium nitrate with superphosphate, infusion of ash, mullein, nettle or trace elements.
If aphids overpower, and she always loves to feast on young juicy leaves, then treat the bush as a foliar top dressing with a solution of urea (30 g per 10 liters of water). By the way, urea will also serve as a prophylactic agent against fungal diseases.
In sunny weather, feeding cannot be done in order to avoid burns to the stems and leaves. It is better to use a fine diffuser to keep the droplets small so they stay on the plant longer. It is necessary to spray the bush from all sides, that is, the leaves must be processed from the lower side.
In July, after the first wave of flowering, roses are fed with a full complex mineral fertilizer (Kemira, Agricola), a solution of organic fertilizers, mulch is laid out under the bushes (peat, rotted manure, etc.)

Between the main dressings continue foliar infusion of ash and double superphosphate with potassium nitrate.
In the first decade of August, we feed the roses with phosphorus-potassium fertilizers (autumn fertilization - 1 tbsp. L. Under the bush), excluding nitrogen. This top dressing will be the last of the season.
An excess of fertilizers negatively affects the roses, they begin to actively increase the green mass, stop blooming or, on the contrary, stop growing. Read and follow the recommendations on the fertilizer packaging carefully.
Watering
Roses must be watered in dry, hot weather, especially for young seedlings. It is better to water rarely 2 times every 6-7 days, but abundantly: one bush requires at least 10 liters of water. Watering should be done in the evening from a watering can with a gentle stream under the root, the water should be warm and settled.
Do not use a hose with cold water - this can lead to serious fungal infections.
Sprinkling in the evening should be carried out if the weather is very dry and an infestation of spider mites is observed on the shoots.
From September, watering should be stopped, since the roses should stop growing and prepare for winter: the wood needs to ripen. An exception is possible if the weather is very dry.
Care
Remove weeds in time. Fight insect pests and diseases common to roses. The soil in the rose garden should be loose and moderately moist, so it is important to water the plants on time and abundantly, and after rains and watering, carefully loosen the soil to a shallow depth so as not to damage the roots.
Mulch the soil with humus, peat, large shavings, grass cuttings - this will serve as protection against weeds and keep the soil moist longer.
Pruning roses
To prune roses you will need: heavy-duty garden gloves, a pruner, a delimber and a garden saw.Tools after or before working with roses must be processed to avoid introducing infections.
In the spring, when the buds have already woken up, but the foliage has not yet blossomed, they begin spring pruning. It is necessary to remove frozen, damaged, old, diseased, weak shoots to soil level or to healthy wood. For scrubs, shorten the left shoots by 1/3, and cut the branch to the first large outer bud, i.e. the one from which the shoot will grow, directed not inside the bush, but outward (where it is oriented). Cut off above the bud itself, leaving no more than 0.5-0.7 cm of the shoot above it, at an angle of 45 °, so that moisture does not accumulate in this place. Also remove those branches that thicken the bush, because all shoots must have adequate lighting and good air exchange. Sections are treated with Rannet, garden var, etc.
In the summer, we remove wilted flowers (or the entire brush to the outer bud of the first ordinary leaf - a five-leafed leaf) and wild growth (applies only to grafted roses), pinch strongly growing shoots, and this is undesirable for climbing roses. At the end of summer, pruning should be stopped in order to exclude the growth of new shoots, the wood of which will not have time to ripen before winter.
In the fall, in our climate, it is better to refuse pruning. We do not remove the withered flowers, since the fruit setting promotes the ripening of the wood at the shoots, we only cut off the withered petals.
The only exception is pruning to the height of the shelter, if it is not possible to bend the shoots to the ground under arcs (floribunda, tea-hybrid, some varieties of scrubs).
Shelter for the winter
Try to cover roses in dry weather in late September - early October (because it is not always possible to go to the country house during the rainy season, and sometimes winter comes already in the first ten days of October). If you live outside the city, next to your roses, then you can wait for the moment when the temperature drops to 0 ° С and below (roses must withstand frosts down to -5 ° С). Newly planted roses that have not yet acclimatized should be especially carefully covered.
Before hiding from the bushes, you should remove the foliage from the bottom of the shoots, gently slowly bend each shoot to the ground and fix them in this position. If necessary: pour a little dry humus under each bush, treat with copper-containing preparations (3% Bordeaux liquid, 1% copper sulfate solution). Stick arcs over the shoots, on which to throw covering material with a density of at least 60 g / m² (preferably in 2 layers), secure the edges of the shelter with stones, bricks and other improvised materials (ie, a closed tunnel is obtained). It is also possible to use coniferous spruce branches for the construction of a shelter.
For tall climbing roses, especially if the bush is powerful enough, the shelter can be built as follows: put several long dry boards on the ground, put some spruce branches on them, then lay roses on the boards, a little more spruce branches on top, cover with roofing material or old covering material , leave small "windows" on the side, lay the old slate on top (it is quite heavy and the whips will not be able to straighten up again under its weight.
If roses (hybrid tea, English) cannot be bent, there is another way: hammer three strong pegs around the rose in the form of a triangle, higher than the plant, away from the roots, tilt them towards each other, you can pull them off with a rope to make the frame of the hut. The structure must be strong to withstand the drifts. On top, put on a cone-shaped cover made of covering material (it can be on sale for conifers or you can sew it yourself). If the material of the cover is not dense enough, then with the onset of frost, cover it with a second one of the same cover.
In winter, throw snow to the roses and trample it down, because this is the best insulation.
Opening roses in spring
In the spring, after the snow melts, the soil thaws and the weather is warm (April), it is necessary to check the condition of the roses: carry out spring pruning and, if necessary, treat with copper-containing preparations (3% Bordeaux liquid or 1% copper sulfate solution). Remove the top layer of the covering material, leave only lutrasil with a density of 60, 42 or 30 g / m² until the danger of severe frosts has passed and the roses start to grow (May). Covering non-woven material is good for air and light, so it will serve as a good protection against spring frosts. It is advisable to completely remove the shelter in the evening or in cloudy weather.

In the spring, infectious burns may occur, therefore, if they are detected, wounds should be treated with drugs such as: Hom, Gamair, Ranet, copper-containing preparations, garden var.
Pests
- spider mite - spraying with water, Fitoverm;
- aphid - Spark KE, 5 ml per 5 liters of water; Biotlin, 5 ml per 10 liters of water; infusion of garlic, nettle; urea, 20 g per 10 l of water; scare away aphids by nasturtium and lavender;
- rose leaf roll - Spark EC, 5 ml - for 5 liters of water; we collect by hand;
- rose sawfly - Aktara;
- rose leafhopper - Aktara, Conform;
- thrips - Fitoverm, 2-4 mg per 1 liter;
- caterpillars - Iskra KE, 5 ml per 5 liters of water; Herald, infusion of garlic, nettle.
Diseases
- powdery mildew - white bloom on shoots and leaves (powder the leaves with wood ash and wash it off after two days), Skor (2 ml per 10 l), Pure flower (2 ml per 5 l of water);
- black spot - collection and burning of infectious shoots and treatment of plants (Fitosporin, Skor (2 ml per 10 l), Topaz (4 ml per 10 l), mullein infusion (1:20) - once a week, 1% solution of copper sulfate or ferrous sulfate (10 g per 1 liter of water), Bordeaux liquid (30 g per 1 liter of water);
- rust - collection and burning of infectious shoots and treatment of plants (Fitosporin, Skor (2 ml per 10 L), Hom (40 g per 10 L), Topaz (4 ml per 10 L), mullein infusion (1:20) - 1 time per week), 1% solution of copper sulfate or iron sulfate (10 g per 1 liter of water), Bordeaux liquid (30 g per 1 liter of water);
- onions and garlic planted next to roses increase disease resistance.
Reproduction methods
- Cuttings: small ground cover, polyanthus, miniature roses reproduce successfully. Others take root in this way very reluctantly, it is advisable to propagate them by grafting.
- By seeds: most often plants with simple flowers grow from seeds, while the seeds need stratification, i.e. they are kept in the refrigerator for some time.
- Layers: before the buds dissolve, the shoot is bent to the loose earth, fixed and poured on top with loose earth. Separate from the mother plant after a year.
- Grafting on a winter-hardy rose: this method is most common for growing hybrid tea roses, English scrubs, etc.
Some varieties of roses
- Floribunda: Leonardo da Vinci, Botticelli, Angie, Pig Honey, Freifrau Carolina, Josie Whitney, Apricot, Carol Kitting Rose, Abracadabra;
- climbing: Flemintans, Pink Heidelberg, Aloha, Polka, Galia, Jasmine, Elf;
- tea-hybrid: Ena Hackness, Betty Apriichard, Virgo, Britain, Souvenir de Baden-Baden, Empress Farah, Dolce Vita, Double Delight, Cherry Lady, Bolshoi Theater, Russian Beauty, Botero, Vivaldi;
- English: Graham Thomas, Claire Austin, Lady of Shallot, Alan Tichmarsh, Teasing Georgia, Abraham Derby, Golden Celebration, Pat Austin;
- polyant: Snow Queen, Saint Exupery, Rumba, Allotria, Pink Queen;
- groundcover: Bentheiner Gold, Swanee, White Meijandina, Gartnerfroyde;
- miniature: Mandarin, Roxy, Watertag, Dorola, Gold Symphony, Baby Maya, Schneekusschen 2016, Simend.
Today there are many rose hybrids that do not require a lot of attention when growing. Thanks to this, beginners in gardening art have the opportunity to choose a species according to their preferences and climatic conditions. Among the modern variety of varieties, along with thermophilic ones, there are frost-resistant representatives that take root without problems even in Siberia.For the best growing of roses, you must follow the basic rules.
1 Description, types and varieties
Rose is the generalized name for all representatives of this flower line, belonging to the genus of rose hips. In the process of growth, they form bushes, which differ in height depending on the species. Some do not exceed 30 cm, others can reach 2.5 m. By type, shoots are divided into uterine and annual. The standard classification also does not apply to the shape of the leaves, it all depends on the type.
The appearance, color and size of flowers vary. There are buds from 2–3 cm in diameter to 15–20 cm (with the number of petals from 5 to 100). The color scheme is striking in its variety, there are red, white, yellow, pink, black and even blue. Roses, which change their color during flowering, have become the pride of breeders. There is a conditional division of grades into classes. This helps to correctly navigate and choose the most appropriate option. The emphasis is placed not only on decorative indicators, but also on the place of intended cultivation - in the country, in the open field or at home.
Common varieties of roses often used in garden design, depending on the group belonging:
- Floribunda - Aprikola, Aspirin-Rose, Bengali, Black Forest Rose, Crescendo, Debut, Gebruder Grimm, Hermann-Hesse-Rose, Intarsia, Isarperle, Kosmos, Innocencia, Schone Koblenzerin.
- Groundcover Roses - Bluhwunder 08, Heidetraum, Sedana, Mirato, Schneeflocke, Stadt Rom, Mirato, Schneeflocke, Sorrento, Stadt Rom.
- Shrubs - Comedy, Goldspatz, Flashlight, La Rose de Molinard, Larissa, Medley Pink, Pink Swany, Shining Light, Yellow Meilove.
- Hybrid tea roses - Elbflorenz, Grande Amore, Eliza, La Perla, Pink Paradise, Schloss Ippenburg, Souvenir de Baden-Baden.
- Climbing large-flowered - Golden Gate, Hella, Jasmina, Kir Royal, Laguna.
The main groups of varieties of garden roses:
| Species name | Characteristic | Image |
| Park | Decorative representatives of roses. Endowed with increased winter hardiness, tolerate low temperatures well without shelter in regions of the middle climatic zone. Unpretentious to care, do not need annual pruning. They begin to bloom in late May - early June, the duration is from 2 weeks to 1.5 months. Bushes grow from 1 to 3 m in height |  |
| Hybrid tea | Bushes no more than 80 cm high. They are distinguished by long and spectacular flowering. The buds bloom once and last from June to autumn. The flowers are large, with a diameter of 10-15 cm. The varieties are frost-resistant, need a protective shelter in regions with cold winters |  |
| Polyanthus | Form numerous inflorescences on the shoots. Blossom from June until the first frost. Medium-sized flowers - 7-10 cm in diameter |  |
| Floribunda roses | An intermediate variety between hybrid tea and polyanthus roses. The buds are large when opened and exude a pleasant aroma. Abundant flowering is observed for a long period. They endure the cold, staying for the winter in the open field |  |
| Climbing | They are divided into 2 subspecies: small and large-flowered. The first variety is characterized by buds up to 4–5 cm in diameter; the second - from 5 to 10 cm. A distinctive feature is flexible long shoots, at the ends of which small group inflorescences are collected |  |
| Miniature | Compact bushes, abundantly strewn with small buds. Endowed with a long flowering period, right up to the first winter cold weather. In gardens, they are grown not only in flower-bed compositions, but also in suspended and stationary flowerpots or pots. |  |
| Ground cover scrubs | Roses of unusual decorativeness, which are planted as a continuous flowering lawn. Unpretentious to care, cold-resistant and with increased immunity to diseases |  |
| Modern park | A group that includes hybrids of Cordes, musk rose, rugosa, shraba and moesi. In abbreviated form, all varieties are called scrubs. Includes all varieties that for some reason do not fall into other groups. They are characterized by the following features: buds of atypical configuration and different colors, they smell nice, the bushes are vigorous, strong and up to 2 m high. They have repeated flowering during the growing season. Plants are unpretentious, have strong immunity, frost-resistant |  |
| Shrubs | The main difference is a large bush with shoots diverging on the sides. Even with minimal maintenance they grow up to 2.5–2.8 m in height.Among gardeners, the following varieties are most popular: Modern Shrab, Grandiflora. In landscape design, they are often used as hedges. |  |
| Cascading | Rose hips with grafted climbing and ground cover roses at a height of 130–150 cm. The stems are long, sometimes drooping. The shape, size and color of the flowers vary and depend on the result of the vaccination |  |
Rules for growing and caring for a climbing rose in the open field
2 Selection of seedlings
If you want to get lush roses in the garden, you should competently approach the choice of seedlings. First of all, attention is paid to the external state. Shoots and stems should be green in color, elastic structure, with bark free from defects and damage. The presence of live and healthy kidneys is imperative. The requirements for the root system are similar: no breaks, folds and rot. They try to touch the ground where the seedling is located, so that it is slightly damp. The foliage must be lively, green, without spots.
Important points to pay attention to when choosing seedlings:
- A sale tag is a must for a quality product. It contains all the necessary information: species, variety, selection.
- The presence of the ADR marking - a similar icon denotes varieties with increased resistance to diseases and the best decorative qualities.
- The most expensive seedlings have 3 or more shoots, 2 of which grow from grafting; the cheap ones have only 2, both from the vaccination site.
Roses come with open or closed roots, in containers. After buying seedlings with planting, it is not recommended to tighten it. This is usually done in the fall, before winter. However, in the regions of the middle zone, including in the Moscow region, planting is carried out in the spring. Otherwise, immature young roots do not have time to take root in a new place and die under the influence of frost. It is allowed to plant roses in summer, which is guaranteed to give a good result. This method can be more expensive.
Azalea - rules for growing outdoors and home care
3 Landing
Regardless of the variety, all roses prefer a loose, soft, fertile substrate with good drainage and a pH of 6–6.5. It is unacceptable to plant flowers on a plot where similar species have already grown for 8-10 years in a row... Such land is completely devastated, no fertilizers can restore the missing elements in its composition. At the same time, there is an accumulation of pathogenic microflora there.
Despite the love of light, the plant is not recommended to be planted in direct sunlight. This will not stop flowering, but the decorative appearance will change: the roses become faded and withered. Therefore, the place is selected with shading, which is important at noon. Ideal location - next to low garden trees or along fences.
Before planting, the seedlings are prepared: too long roots are cut with pruning shears, dry ones are removed completely. It is unacceptable to touch the filamentous roots. When planting in spring, the stems are shortened to 30–35 cm, leaving up to 4 buds on the surface. For 2-3 hours, the seedling is placed in a bucket of water.
If clay soil prevails on the site, river sand is introduced into the planting pit, sandstone is diluted with sheet compost. The sequence of agrotechnical measures:
- A hole is dug 2-3 times larger than the size of an earthen coma with roots. The bottom is well loosened.
- The seedling is buried at a level 4–5 cm higher than the grafting site. The extracted substrate is mixed with compost in a ratio of 1: 3 and pure wood ash is added.
- The free space is carefully filled up, the surface is slightly compacted.
- At the end of the procedure, the planting site is abundantly moistened. To prevent the water from spreading, a furrow is made around the perimeter.
It is imperative to spud the root space not only immediately after planting, but in spring and autumn.In the first case, such a technique helps to exclude the rapid evaporation of moisture from the soil, and in the second, it protects the roots from freezing.
You can plant roses once with seeds. It is believed that they germinate for a long time, but it is possible to accelerate germination by pre-keeping the material in the cold. When sowing before winter, it is advisable to treat the seeds with a stimulating solution. The garden bed is dug up, compost, peat and humus are introduced into it. Make parallel furrows about 4 cm deep, where the sowing is carried out. At the same time, an interval of 15–20 cm is observed. Sprinkle with soil on top. If winter is expected to be frosty, cover the garden bed with any suitable material for safety net. It is better to prepare a plot for spring sowing in the fall.
Another effective option for germinating seeds is seedlings at home. The favorable period for this is the beginning of February. Seed material is preliminarily placed in the cold for several months, then soaked in a growth stimulator. They are planted in separate pots, where the peat-sand mixture is poured. The seeds are deepened by 3-4 cm, sprinkled with sand and moistened with a spray bottle. With the appearance of 2-3 strong leaves, the seedlings dive separately. In May, they are transferred to a permanent place of growth - in the garden.
Planting and caring for Bartzella peony in the open field
4 Care
For full development and abundant flowering, roses must be looked after. Mandatory procedures are:
- Watering is carried out once every 7 days so that the soil is soaked to a depth of at least 25 cm. Otherwise, the plant puts out surface roots, which are easily damaged during subsequent loosening. Moisturize 2 times more often if the weather is hot. It is advisable to cover the root circle with humus or peat mulch. Then the moisture will evaporate less intensely.
- Before the onset of the first frosts (in October), the bushes are wrapped in burlap, and the roots are sprinkled with a mixture of earth and sand.
- Pruning plays a primary role in overall grooming. In the spring, they resort to formative. In the summer, wilted buds, drooping and diseased leaves are removed. In autumn, dry and damaged shoots are removed. Places of cuts are treated with garden varnish. Before the onset of winter, all weakened stems and shoots are pruned.
- Rotted horse manure is used as a top dressing, chicken and pork are contraindicated. This is due to their high acidity. Any fresh organic matter blocks nitrogen in the soil, thereby inhibiting the growth of flowers. The first time fertilizers are applied before laying the buds. Calcium nitrate is suitable (1 tablespoon per 10 liters of water). During the period of active growth, they are fed with infused liquid mullein, mineral supplements or herbal infusions. Frequency - once every 2 weeks.
From the middle of summer, all feeding is stopped, watering is minimized. The plant needs to go into a dormant state, which serves as a preparation for wintering.
5 Reproduction
Roses can be propagated by seed and vegetative methods. The first option is in little demand, since it does not retain varietal characteristics. Therefore, it is used more often in relation to wild representatives. The seeds are harvested when the fruit turns red. The raw material is preliminarily stratified in moist sand, kept until spring at a temperature of + 3 ... + 4 ° C. In the spring, the seeds are treated with a stimulant and planted in open ground. From above they mulch with humus. After some time, the plantings are thinned out, distributing the bushes at a distance of 10-15 cm from each other. In the summer, mineral dressings are introduced. Grown until next August, then used as a stock.
The most successful breeding method is by cuttings, along with grafting and dividing the bush:
| Method name | Description | Image |
| Summer cuttings | In the morning or in the evening, strong shoots with slight lignification are cut off. Cuttings 13-15 cm long are prepared. Several leaves and 2-3 living buds are left on each. The lower part is cleaned of foliage. The bottom is treated with a growth stimulant, the cutting is immersed in water, where rose petals are placed.They are planted directly into the ground, previously sprayed with potassium permanganate. Cover with a glass cover on top to create greenhouse conditions. The optimal temperature regime during the day is not lower than + 25 ° C, at night + 19 ... + 20 ° C |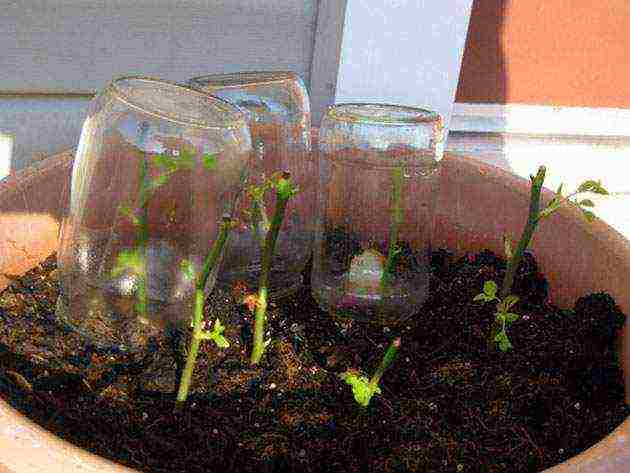  |
| Rooting in potatoes | The most popular and easy breeding method. Thus, the cuttings are saturated with carbohydrates and potato starch. In a bright area, a ditch is dug about 15 cm deep, filled with sand for a third of the volume. The cuttings are first stuck into the potatoes 10–12 cm and placed in the prepared recess. Further manipulations are standard: cover with a cap, after a while hardening is carried out. Pour sugar syrup every 5 days |  |
| Reproduction in a package | The bottom of the cuttings is moistened with aloe juice, then deepened into a lump of earth, laid in a plastic bag. It is hermetically closed, having previously released the air from the inside. Hang out for germination on the window. A month later, when young roots appear, they are planted in open ground |  |
| Rooting in water | Freshly cut stems, divided into cuttings, are immersed in distilled water. Before this, thorns are removed from the surface and other vegetation. The water is regularly changed until the cuttings take root. |  |
| Vaccination | Reproduction by grafting is suitable for young rose hips. The procedure is carried out in the middle of summer. First, the lateral branches are removed from the stock, and the root collar is cleaned of the ground. An incision is made in the shape of the letter T, where the handle is placed. Fix it in place in any way. After 15–20 days, the kidney is checked: if it is swollen, then the vaccination was successful. If it is black, then the method has failed. Before the onset of winter frosts, grafted roses are spud 5-6 cm above the grafting site. In the spring, the soil is raked. The plant is pruned over the graft. When pulling, pinch the top over the third leaf | 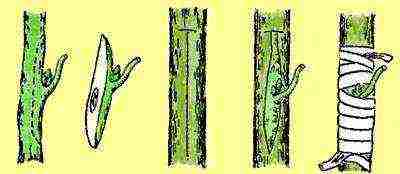 |
| By dividing the bush | Suitable for non-grafted varieties of roses. In the spring, before bud break, the bush is dug up and divided into parts. Each should consist of roots and a shoot. Bare areas are powdered with crushed coal. Then they are seated in separate places in the garden. | 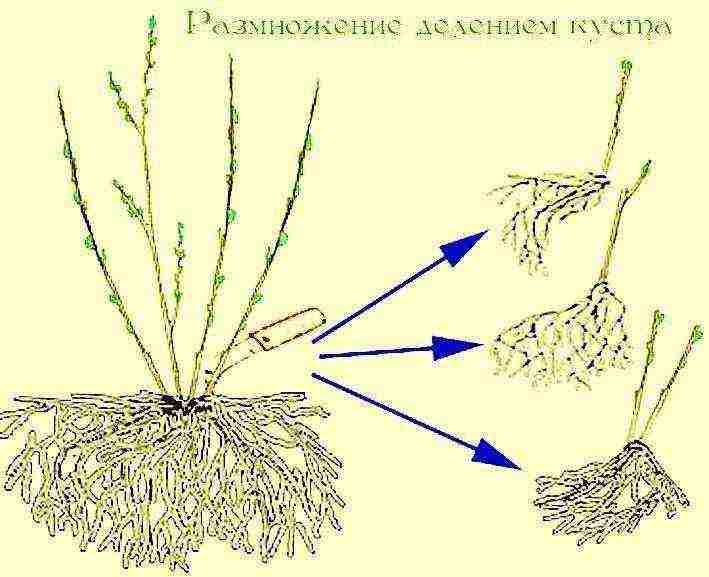 |
| Layers | With the onset of the first spring heat, a low-lying shoot on a bush is chosen. They bend it to the ground and put it in a dug hole. Preliminarily, an annular cut is made on the surface. Fix the shoot in place and cover it with earth. Further care is moisturizing until the cuttings take root. The next year, the baby is separated from the maternal source and planted separately. |  |
6 Diseases and pests
Most roses are endowed with stable immunity to many diseases, but this does not exclude the possibility of damage. The following diseases are most common:
- Rust - the peak of the disease is observed in the spring. Brown spots appear on the leaf surface, and from the inside - orange clusters of spores, which turn black towards the end of summer. Unauthorized leaf fall begins, the stems acquire a brown tint. The situation can be corrected by watering with a decoction of field ivy. The affected areas are removed.
- Black spot - appears in August, towards the end of the month. The leaves are instantly covered with black patches in a yellow frame. This gradually spreads to the stems. Leaves fall. If appropriate measures are not taken in time, the flowers die. Treatment is the same as for rust.
- Powdery mildew - a whitish bloom forms on the leaf component and shoots, then slugs form. The disease is characteristic of varieties that are grown in greenhouses and at home. The disease is characterized by rapid spread. Plants showing signs of damage are cut and destroyed. The earth is sprinkled with ash and dug up.
Of the insect pests, the most dangerous are aphids, spider mites. With few attacks, you can kill the first pest by hand or wash the leaves with soapy water. If there are a lot of insects, then treatment with insecticidal preparations helps. The mite is fought by applying tobacco or infusion of wormwood. With illiterate care, there are cases of attack by thrips, sawflies and cicadas.
With a lack of nitrogen in the soil, the plant turns yellow. It begins to spread from below and is accompanied by leaf fall. The same thing happens with the top. If the foliage is covered with yellowness only at the edges, this indicates a lack of potassium. Yellow streaks indicate a small amount of trace elements.
7 Design
Most people are used to planting roses in separate flower beds, but modern trends in landscape design have made their own adjustments. It is fashionable to combine them with perennial flowering crops or undersized shrubs.
For the design of mixborders, it is recommended to take varieties of musky representatives due to their brightness and proportional shapes of the bushes. Short varieties with small flowers are ideal. Then they do not dominate the neighbors, but harmoniously merge into a beautiful composition. It is better to place unpretentious varieties in unfavorable areas of the garden, and climbing roses will effectively decorate fences and terraces.
Roses are planted in a permanent place for 10-15 years and longer, so the soil must have good physicochemical properties. Basically, in the conditions of the Moscow region, the following soil mixtures are used.
Sod land is prepared like this. Sod is cut in the spring. Pile it (grass to grass), moisten it with feces, season it and then use it. The land can be taken from the garden. Sawdust is soaked 3-4 weeks before planting with a solution of fertilizers and kept under a film. For 3 buckets of sawdust, 1 bucket of solution.
Various solutions are possible (per bucket of water): garden fertilizer mixture 2.5 tbsp. spoons and 1 tbsp. spoon of urea; 1.5 tbsp. spoons of urea; slurry from the toilet, diluted with water 10 times; 3 tbsp. tablespoons of ammonium sulfate; fresh mullein - 3 liter jar.
Humus can be taken from greenhouses or from a two-year pile. You should not use fresh manure - a burn of the roots is possible (especially for self-rooted roses). Peat is taken not fresh, but lying in the pile for at least one year. You can replace TMAU (any fertilizer number).
The reaction (acidity) of the soil mixture should be close to neutral or neutral. The acidity of the soil is checked as follows. They take a handful of the mixture, dry it, grind it and sift it. Pour up to the 2nd division into a bottle for baby food and fill it with water up to the 5th division (take rainwater). Fall asleep (from a piece of paper) 1/2 teaspoon of crushed chalk and immediately put a long nipple rolled up with a snail on the neck.
Wrap the bottle with a towel in 2-3 layers and shake the contents vigorously for 3-5 minutes. If the nipple is completely straightened, then the substrate is acidic; the nipple is straightened in half - medium acid; the nipple is not straightened - neutral. Acidic soil is neutralized with lime, chalk, furnace ash.
I plant roses in pits, trenches, and in damp places on ridges. A hole for planting is dug 60X60X50 cm in size. The soil mixture is poured at the bottom with a slide so that when planting, the grafting site (for self-rooted roses - the root collar) is 5-10 cm below the soil level.
Then the roots are spread along the hill, the depth of the grafting site is checked and the roots are covered with soil. Carefully compact the earth, starting from the edges of the pit, and water the seedling abundantly, and when the water is absorbed, they spud it to a height of 10-15 cm so as not to dry out. After 10-15 days, when the seedlings take root and start to grow, they will be uncooked.
Successful wintering of roses depends on the planting depth. New growth buds in roses and rose hips are most often formed in the area of the root collar when they are illuminated by the sun. Subsequently, the most powerful shoots grow from them. With a high planting, the grafting site is above the soil level and new shoots will grow in abundance from the stock (rosehip). To avoid this, the inoculation site is deepened. At the same time, it was noticed that a rose bush, planted deeply (8-10 cm), lags behind in its development, is less productive, therefore, in the summer, the soil is raked away from the root collar, and in the fall, in September, it is returned to its place. It is convenient to water and feed the plants through the formed hole.
If there are a lot of bushes, then it is advisable to plant them in rows in trenches, and with a close standing of groundwater - on ridges. The distance between plants depends on the group of roses. Hybrid tea and Floribuida are planted every 40-60 cm, Polyanthus - 30-50 cm, Miniature - 20-30, and park plants - at a distance of no less than 1 m from each other. This planting pattern makes it easier to care for roses. Distances can be reduced or increased depending on the growing area.
After planting, the plants must be pruned:
- in varieties with small flowers (Miniature and Polyantovye), 2-3 lower buds are left;
- in Hybrid and Floribunda - 3-4;
- curly (climbing) and parks are shortened by 1/3 of their length.
In the year of planting, with well-filled planting pits, I do not feed roses. Only by keeping the soil moist, preventing it from drying out, weeding and fighting pests and diseases. On some bushes, buds appear in the first year. They are cut off, since the root system is not yet able to feed the flowering plant. When the buds reach the size of a pea, pinch the tops of the shoots above the last well-developed leaf.
Particularly powerful shoots are pinched at a height of 50-60 cm from the soil level, the rest are lower and repeatedly until it is possible to cause the growth of strong shoots from the lower part of the stem.
The best flowers are formed from buds located in the axils of medium leaves (with 5-7 leaves). Therefore, when cutting, 2-3 lower five-leaf leaves are left on each shoot.
Young plants often suffer from pests and diseases. To combat a number of them, a soap-oil emulsion is used. 5 tbsp. spoons of any washing powder are dissolved in 1 liter of hot water and 5 tbsp. tablespoons of diesel fuel or engine oil. The oil quickly dissolves when stirred and a whitish, cloudy liquid is obtained. It is diluted with cold water to 10 liters (1 bucket). The emulsion can be stored for quite a long time.
A fresh 2% infusion of onions, garlic, pyrethrum works well against ticks, aphids and thrips.
Powdery mildew is the most common fungal disease. To combat it, in addition to removing and burning dry leaves and twigs, plants are regularly sprayed with colloidal sulfur (0.6-0.8% - 6-8 g per 1 liter of water), as well as washing (soda ash) soda (0.3 -0.5%) with the addition of soap (0.3-0.4%).
Fresh manure is also used. For this, 1 part of manure is diluted with a double amount of water and kept for 3-4 days, then the infusion is diluted to a concentration of 1:20 - a liquid of the color of sleeping tea is obtained. It is filtered and used for spraying.
It is extremely important to remember to control wild growth, which can be recognized by the leaves. The grafted rose bush consists of a rootstock (rosehip) and a scion (cultivar). The part of the root above the skeletal ramifications is called the root collar. The vaccination site is located on it. At the very surface of the soil there is a thickened part - the "head". Several shoots of different ages depart from it. The branches growing from these shoots and above the grafting site are always cultivated. Those growing below the graft site and from the root are wild. They must be removed in a timely manner, without leaving hemp (close to the bark). It is useful to cover the wounds with crushed coal so that the root does not rot.
We often hear from flower growers talk about the "wildness" of the bush. A rose bush cannot "be reborn" into a wild rose, but simply through an oversight of the owner, who did not remove the wild root growth in a timely manner, the cultivated part of the plant dies. So you need to be especially careful about the rose in the first two years of cultivation. Later, the root grows old and less wild growth is formed on it.
Park roses have one common advantage: incredible endurance and ease of maintenance. And all because the ancestors of this group of roses are wild rose hips, which were cultivated and passed a long selection selection, due to which varieties unique in beauty and endurance were obtained.
Park roses have subgroups:
- Vintage garden rose varieties
- All kinds of wrinkled rose
- Hybrid groups
Park roses also differ in that they have a one-time flowering period, lasting about a month. Hybrid forms can bloom for up to two months. Flowering starts around late May-early June and lasts until early-late July. All kinds of colors: white and pastel colors, bright red, purple, pink, orange and yellow, as well as many variegated colors that are very popular among gardeners. The flower shape is also varied, but mostly double.
Features of park roses

What is the difference between park roses flower photos
Bushes can reach a height of one and a half meters. When planting, they need to leave more space, since the bushes are spreading, quite voluminous. The buds of the park rose are distinguished by their fullness, these are chic double flowers containing up to 150 petals per bud, which no other type of roses can boast of.
Many beautiful varieties of park roses require shelter when grown in the middle lane and the Moscow region. Hybrid forms, varieties of Canadian selection, as well as wrinkled and gray roses, are able to withstand frost, provided that they are properly deep-planted. For wintering without shelter, you need to withstand the conditions:
- Landings are made in places well protected from the wind.
- There should be no groundwater close to the surface
- High-quality care in warm weather, allowing the plants to gain enough strength for successful wintering
- An abundance of sunlight so that the site warms up well
However, with a high-quality shelter, a park rose is capable of more abundant flowering, because the buds are formed mainly on the branches of the last year. Frozen or drastically cut, park roses do not fully reveal their beauty.
It is better to show a little patience, bend the branches and cover them for the winter, in order to admire the magnificent splendor of the regal beauties in the spring and summer.
Classification of park roses
Park roses are classified according to the principle of flowering rate:
- Blooming once
- Re-blooming
Once flowering varieties are categorically impossible to cut off, because they can bloom only on last year's shoots. However, this is their advantage: the branches do not require bending, they winter well without shelter. This is a group of vintage roses that are cultivated rose hips. Among them, the most common varieties are Wasagaming, Minette, Poppius.
Re-blooming park roses, in turn, are further subdivided into subgroups:
- Frost-resistant hybrids, rugoses
- Frost resistant canadian park roseswintering without shelter subject to agricultural technology
- A group that does not hibernate without shelter, and requires bending of branches
Rugoses delight with their frost resistance, however, they cannot boast of a variety of shapes and colors, remotely resembling each other. Some hybrids are beautiful, but require shelter for the winter.
The Canadian rose group has gained particular popularity, the most prominent representatives being the Morden Centennial and Prairie Joy varieties.
Among the covering varieties, there is a huge variety of shapes and colors. One cannot fail to note the work of the English breeder David Austin, who presented the world with the Fisherman's Friend variety of covering park roses, enchanting with its unique beauty. Popular varieties of work of breeders Meiyana, Cordes, Tantau. This group also includes old remontant and Bourbon varieties.
How to plant a park rose
When to plant
Autumn planting is preferable, so the bushes take root better and in spring they already begin to bloom. When planting in autumn, a park rose is immediately spud. It is also possible to plant in the spring, but the bushes planted in the spring will noticeably lag behind the autumn ones.
How to plant correctly
To prevent a park rose from freezing in winter, it must be slightly deepened when planting below ground level: the grafting site should be covered with a layer of earth of 8-12 cm.This measure will protect the grafting site from premature aging and peeling of the bark, and also stimulate the growth of young shoots. A properly planted rose will stay healthy for a long time without expelling wild rose hips.
When planting a hedge, leave more distance between the bushes, about 80-100 cm, and for bushes above a meter - 1.2-1.5 m.If you plant individual bushes in a flower bed, keep a distance of 1.5-3 m. varieties are planted according to the scheme 50x50 - 70x70 cm.
- The planting pit is made spacious, up to 60 cm in diameter, 40-50 cm in depth. Garden soil can be mixed in half with humus to lay the foundation for future lush blooms. It is also good to add a handful of wood ash to the ground when planting.
- A seedling with a closed root system is simply rolled over, filling up the earth.
- If the root system is open (rose out of the box), examine the roots well so that there are no rotten ones. Cut off all suspicious parts of the root. Plant with roots spread out so they don't bend. It is better to make a mound and spread the roots of the rose on it. Top up and level the ground, press lightly.
- Water abundantly, in a bucket of water under the bush.
- After watering, it is better to mulch the soil in order to retain moisture for longer and create a microclimate in the soil that favors the reproduction of beneficial microorganisms and earthworms.
In the future, it will be enough to keep the soil moist by watering the roses in the morning or in the evening abundantly at the root.
Tips for planting roses correctly, look at the video:
Pruning and covering park roses for the winter
A park rose is cut minimally, cutting out only old, damaged or frozen branches. After flowering, the faded buds are cut off. Pruning is completely stopped in August. In autumn, the branches are freed from the leaves, bent down, pinned with metal staples and covered. It is difficult to bend especially powerful bushes to the ground, then you will need to dig them up on one side until the root begins to bend and tilt the bush. The root collar must be piled up to a height of 20-30 cm. The rose is covered with spruce branches from above; non-woven material can be used. The main condition is that the shelter breathes, and the branches do not come out in wet, damp weather.
In the spring, when the snow melts, the structure is dismantled, straightening the bush before the start of sap flow. Old 4-5-year-old branches are cut at the root. It is advisable to treat the cut points with garden pitch so that the rose does not get sick. Young branches are not cut. The remaining branches can be cut into two buds so that the shoots on them are more powerful. Make sure that when pruning, all the upper buds look outward of the bush, and not inward.
How to prepare roses for wintering, the video will tell:
Properly covered for the winter, park roses will delight the owners with a lush flowering waterfall. It is worth trying for such splendor!
How to care for park roses
How to water properly
The rose loves water, so water it abundantly 2-3 times a week. It is important that the earth is soaked deeply, so it is better less often and more abundantly than a little every day. You should be guided by the weather: the soil should be constantly slightly damp. By the end of summer, watering is stopped, the roses should start preparing for wintering and stop growing young shoots.
How to feed
You will have to feed from the second year after planting, when the organic matter in the soil will gradually be used. You can use organic fertilizers or special complex fertilizers for roses. They are inexpensive, and when foliar top dressing is carried out on the leaves, they give an amazing result. It is advisable to feed it 1-2 times a month. The procedure is very simple and does not take much time, and the flowering will increase immediately.
The best varieties of park roses for the Moscow region and the middle lane, which do not require shelter for the winter Photos and names
Park rose Martin Frobisher Martin Frobisher rose

Park rose pink Martin Frobisher Martin Frobisher rose photo
Hybrid rugosa, a super frost-resistant park rose of Canadian selection, which does not require shelter in the middle zone and the Moscow region, in severe snowless winters, it may be submerged. The bush practically does not have thorns, large double flowers of milky pink color abundantly cover the bush, gathering in inflorescences up to 10-15 pieces. Flowering is continuous throughout the warm season until the very frost. The petals fade and turn brown, so you need to cut off the faded buds in a timely manner.The bush is powerful, spreading, with many shoots. The variety is resistant to all diseases, sometimes it is affected by black spot.
Park rose Ferdinand Pichard rose Ferdinand Pichard

Rose park striped Ferdinand Pichard rose Ferdinand Pichard photo
A variety of old garden roses, a remontant re-blooming hybrid, with a striped pink color. Terry buds, loose, up to 25 petals. Pronounced fragrant aroma. The height of a powerful bush is 1.2-2.4 m, its width reaches 90-120 cm. It can withstand frosts up to -31 ° C without shelter. It is very resistant to all types of diseases. Requires annual pruning of old branches and bending of young shoots.
Rose Remy Martin park Canadian Remy martin rose
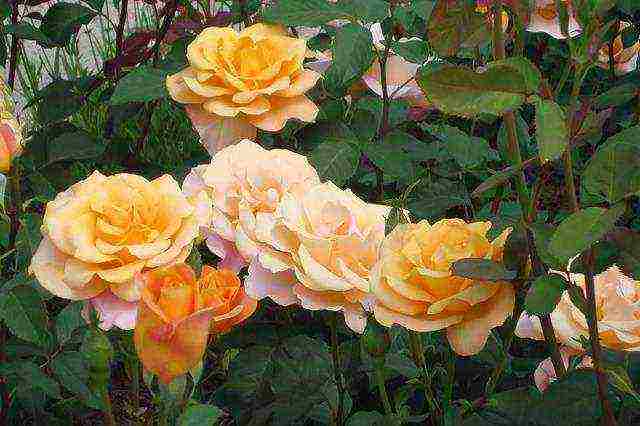

Rose park canadian yellow Remy Martin Remy martin rose photo
A re-blooming frost-resistant variety of Canadian selection. The height of the bush is 1-1.5 m. The width of the bush is up to 100 cm. Soft-apricot large flowers of a classical shape, up to 25 petals. Resistant to powdery mildew.
Park rose John Franklin John Franklin rose

Park rose red John Franklin John Franklin rose photo
Rose of Canadian selection of the Explorer series. Frost resistance is weak, freezes above the snow level, but if the shoots are bent to the ground, it hibernates successfully. It is resistant to powdery mildew, but can be affected by black spot in wet weather. A very beautiful variety with large semi-double flowers of bright red color, gathering in inflorescences of 3-5 pieces, and with intensive care - up to 30. Diameter of flowers up to 6 cm, petals up to 25 pieces. The leaves are dark green, rounded, with a glossy sheen. The bush is densely leafy, with many shoots, erect.
Rose Pristine Pavement

Rose park white Pristan Pavement Rose Pristine Pavement
A very frost-hardy re-blooming hybrid of the wrinkled rose that does not require shelter for the winter. Semi-double large loose flowers are collected in inflorescences up to 3-5, blooms profusely, resistant to diseases. The height of the bush is 0.9-1.5 m. The color is white with a slight pink tinge, which brightens when blooming.
Rose Chinatown Rose Chinatown

Rose park yellow Chinatown Rose Chinatown photo
Powerful, branched, erect shrub with large flowers of a pale cream with a pink tint. The shape of the bud is classic with pointed petals, the diameter of the flower is up to 10 cm. There can be up to 9 flowers in an inflorescence. Winter-hardy scrub up to 1 m high, slightly remontant. The variety is resistant to diseases, prefers shade and partial shade, flowers fade in the bright sun. The leaves are dark green, shiny, large. For the winter, it requires bending the branches.
Rose park Red Diamond Rose Kordes Brilliant

Rose park red Red Brilliant Rose Kordes Brilliant photo
Frost-resistant variety, withstands frosts without shelter down to -25 ° С. In severe winters without snow, it freezes over, requires bending of branches. It blooms profusely with bright scarlet flowers gathering in dense inflorescences. The shape of the bud is classic, the flowers are loose, a delicate weak aroma. Planting density - 3 bushes per square meter. The height of the bush is 1.2 m, the width is 60 cm. The shape of the bush is erect. There are a lot of branches, densely leafy, with dark green shiny leaves.
Park rose Louis Odier Louise Odier Rose

Park rose pink Louis Odier Louise Odier Rose
The Louis Audier variety is classified as a French bourbon rose. Large bright pink flowers up to 8 cm in diameter are collected in inflorescences up to 3 pieces. The buds are dense, double, about 40 petals. The bush is tall, on average up to 1.5 meters, in France it can reach 3 meters. The rose is remontant, it blooms in waves throughout the warm season. The bush is densely leafy, the leaves are large, light green. The variety requires bending the branches for the winter. Little susceptible to disease.
Rose park Piano rose Piano

Rose park red Piano rose Piano photo
A repairing variety of high winter hardiness up to 60-80 cm high and about 60 cm wide. Large double flowers up to 11 cm in diameter of scarlet-pink color are collected in inflorescences of 5 pieces. The bush blooms profusely several times per season, and is not susceptible to disease. The rose belongs to the group of romantic ones: a beautiful spherical shape of a flower, when blooming, transforms into a cup-shaped one, with petals tightly adjacent to each other.
Rose park William Shakespeare rose William Shakespeare

Rose park burgundy William Shakespeare rose William Shakespeare 2000 photo
A powerful spreading bush reaches a height of 1-1.2 meters. Numerous branches are covered with large leaves and large double flowers, collected in inflorescences of 5 pieces.The aroma of an old rose, pronounced, strong, with hints of violet. The velvety crimson-red color of the buds becomes burgundy purple when blooming. Withstands frosts down to -26 ° С, during severe winters it requires bending of branches.
Park rose Alexander Mackenzie rose Alexander Mc Kenzie

Rose park red Alexander Mackenzie rose Alexander Mc Kenzie photo of flowers
A very frost-resistant variety, withstands frosts down to -39.9 ° C. A tall, erect bush with drooping branches. It reaches 1.5 m in height and width. Large two-tiered red-pink flowers with numerous, tight-fitting petals, have a spherical shape. The leaves are large, dark green, dense, with a glossy sheen. Strong strawberry aroma. The variety is not susceptible to disease. Blooms profusely from late spring to late summer.
Rose park Louise Bugnet rose Louise Bugnet

Rose pink park Louise Bugnet rose Louise Bugnet photo
Rugosa hybrid of Canadian selection with high frost resistance, withstands frosts without shelter up to -34 ° C. There are variations with pearl pink, white, pastel pink tones, as well as changing color when blooming. The aroma is light, the flowering is wave-like all season. Disease resistant. Flowers are large, double, collected in inflorescences up to 5 pcs.
Rose Canadian park Moden Fireglow Morden Fireglow

Rose red Canadian park Moden Fireglow Morden Fireglow
Very hardy remontant variety with orange-red flowers. The bush is 80-100 cm high, powerful, erect, blooms in early spring, again - at the end of summer. Withstands frosts down to -37 ° С. It is better to cut it in early spring, you can not cover it for the winter, but it is advisable to huddle. The pleasant scent of a rose attracts butterflies and bees to the garden. The shape of the bud is goblet, the flowers are large, up to 5 pieces per inflorescence. Responds positively to fertilizing, prefers humus-rich soils.
Park rose Crocus Crocus Rose

Rose beige park Crocus Crocus Rose photo in the garden
English park rose by David Austin. Large creamy white buds have the shape of an old rose, up to 10-12 cm in diameter. A powerful erect bush reaches a height of 1.2 m and a width of 1 m. The variety is very hardy, resistant to diseases. Prefers brightly lit areas and fertile, well-drained soils. Has a light tea rose scent. Withstands frosts up to -31 ° C without shelter, in conditions of harsh winters it requires bending the shoots. Remontant rose, blooms profusely in July and September.
Rose climbing park Henry Kelsey Henry Kelsey Rose

Rose red park Henry Kelsey Henry Kelsey Rose photo
It is a climbing form of the Canadian park rose that requires support, a frost-resistant hybrid Kordesii from the popular Explorer series. Withstands frosts up to -26 ° C without shelter, requires bending of shoots at lower winter temperatures. Shoots with numerous sharp thorns, branches are flexible, drooping, up to 4 meters in length. Leaves are small, dark green, numerous. Semi-double dense flowers are collected in inflorescences of 5-15 pieces, abundant flowering. The color is bright scarlet, the petals fade to pink in the sun. The variety is resistant to diseases, extremely rarely affected by black spot. A remontant variety, blooms in July and again in September.
Park rose Cuthbert Grant Rose

Rose park Canadian Cuthbert Grant Cuthbert Grant Rose and pink park rose Mary Rose photo
A very beautiful Canadian variety of the Explorer series of park roses. High frost resistance, withstands frosts without shelter up to -37 ° C. Large cup-shaped dense flowers are collected in inflorescences of 5-9 pieces. The bush is powerful, erect, with gracefully drooping branches. The variety is resistant to diseases, re-blooming: the first wave in early spring, the second - at the end of summer. The color is velvety, crimson red with a burgundy tint. Does not require shelter for the winter and bending down the shoots.
Park Rose J.P. Connell J.P. Connell Rose

Park Rose J.P. Connell J.P. Connell Rose
A very hardy variety that can withstand frosts down to -37 ° C, is not affected by powdery mildew, and is affected by black spot.This is the most beautiful yellow rose of the Explorer series. A powerful upright bush completely covered with large double cupped flowers, in brushes up to 7 flowers. The rich yellow buds become creamy when they open up. The bush grows slowly, it cannot be cut off, after a few years it is gaining full strength. A remontant variety, blooms in late spring-early summer, the second wave of flowering occurs after rest, towards the end of summer. Does not require shelter for the winter.
Rose Champlain

Rose Champlain Rose Champlain photo
The Canadian park rose, which can withstand frosts down to -35 ° C without shelter, recovers well after freezing. The bush is upright, up to 1-1.2 m high. The diameter of the dense double flowers is 5-6 cm, they are collected in inflorescences of 5-10 pcs. The color of the buds is bright red, does not fade in the sun. Blooms continuously throughout the warm season. Prefers sunny areas and drained slightly acidic soils, rich in humus.
Rose park fluorescent Rose Fluorescent
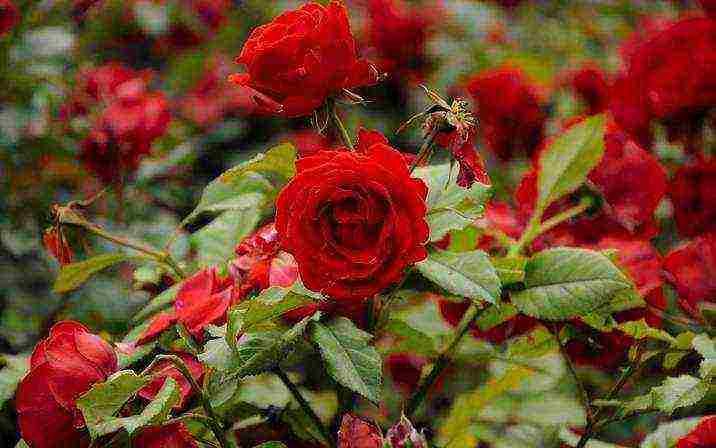

Rose park fluorescent Rose Fluorescent photo
Winter hardiness is low, withstands frosts without shelter up to -20 ° C, requires bending branches and shelter in snowless winters. Blossoming is one of the most beautiful among the red park roses. The upright erect bush is entirely covered with flowers of a classical form, in a cluster of up to 5 flowers. Full buds, 30-40 petals. The color is deep red. Blooms continuously all summer until frost, flowers do not crumble and do not fade. The variety recovers well after freezing, perfectly cuttings. Medium disease resistance.
Rose Canadian Park Adelaide Hoodless Adelaide Hoodless Rose
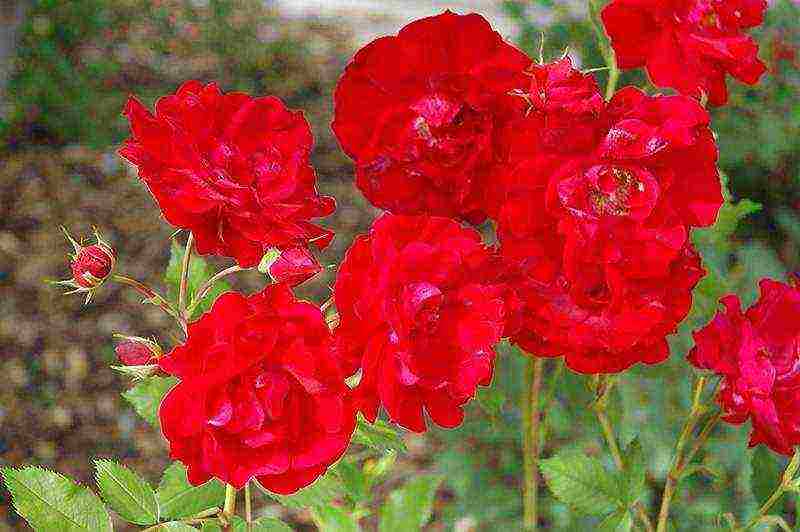

Rose canadian park Adelaide Hoodless Adelaide Hoodless Rose photo
Stunning beauty scarlet Canadian rose. The bush is powerful, erect, up to 2 m high, grows and recovers very quickly, requires support. High winter hardiness, up to -42 °, does not require shelter for the winter. Semi-double loose flowers are collected in inflorescences of 5-15 pieces, the first spring flowering is very abundant, which is why the branches droop beautifully. The second wave comes later, not so abundant. The leaves are small and dense. The variety is resistant to diseases, tolerates hot summers well.
Rose black magic Rose Black Magic
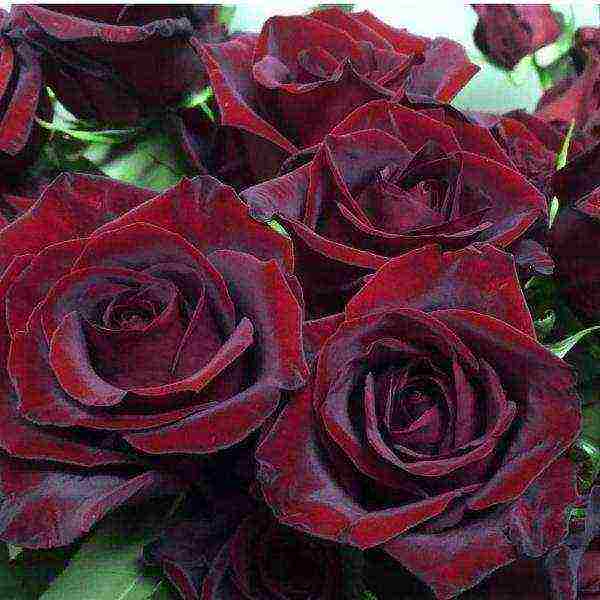

Park rose Black magic Rose Black Magic photo
This German-bred park rose has a classic appearance of buds and shoots, very good in cutting. The stunningly rich black and burgundy velvet color makes the variety very popular among florists and gardeners. A tall, powerful bush (up to 1-1.5 m, width 1 m) blooms profusely, in the clusters there are up to 4 flowers with beautifully bent pointed petals. The leaves are dark green, large, with a glossy sheen. Disease resistant. Flowers are cut for up to two weeks. Winter hardiness is small, withstands frosts down to -20 ° C, requires bending branches and shelter for the winter.
Rose park Marchenland Rosa park Marchenland

Rose park Marchenland Rosa park Marchenland photo
This variety conquered with its tenderness, classic appearance and unique delicate colors: a mixture of pastel-apricot and salmon tones. The flowers are large, up to 8 cm in diameter, with a slight aroma. There can be up to 40 flowers in a brush. Leaves are numerous, large, dark green, with shine. A powerful bush reaches a height of 0.8-1.5 m, blooms very profusely, continuously throughout the summer until frost. Disease resistant, does not require pruning (sanitary only). Winter hardiness is very high. Prefers sunny areas with fertile, well-drained soils.

