Content
- 1 Growing marrow seedlings
- 2 Sowing seeds and planting marrow seedlings in open ground
- 3 How to distinguish squash seedlings from pumpkin or cucumber
- 4 Outdoor zucchini care
- 5 Netherflower on zucchini - what to do?
- 6 Fertilizing zucchini in the open field
- 7 Dates for planting zucchini seeds in open ground
- 8 Proper preparation of beds and planting seed at home
- 9 Care during the growing season
- 10 How can you feed and fertilize zucchini?
- 11 Pests and the fight against them
- 12 Harvesting and storage
- 13 Preparing a place
- 14 Video "Tips for planting zucchini"
- 15 Selection and preparation of seeds
- 16 Landing
- 17 Seedling method
- 18 Zucchini care
In this publication, we will highlight the topical issues of growing zucchini. When, at what distance and at what depth to plant zucchini in the open field. Is it possible to plant them in June. How to feed zucchini after planting and how to water it correctly.
Zucchini is a guest from distant Mexico, which has taken root perfectly in our latitudes. At first, in Europe, only the seeds of this vegetable were eaten, then the Italians risked trying the pulp and were satisfied. And today, the most unusual zucchini dish is, perhaps, stuffed flowers, which are especially popular with the inhabitants of Provence.
Despite the unpretentiousness of the vegetable, there are still some planting and growing features that are important to consider if you want to get a rich harvest.
Growing marrow seedlings
To grow squash seedlings, you can buy soil at the store or mix 1 part sawdust, 2 parts turf, 2 parts compost and 6 parts peat. Some do not philosophize and use a mixture of sand and peat in a 1: 1 ratio for sowing seeds.
It is important to place the seed pots on a sunny windowsill, otherwise the seedlings may grow weak. Before the first shoots appear, it is desirable to maintain the room temperature at 18-25 ° C. After about a week, the first shoots hatch, and after 25-30 days the plants are planted in open ground.
Zucchini must be planted directly into the open ground with an earthen clod, since the roots of this plant do not like unnecessary anxiety. That is why many gardeners use peat pots when growing marrow seedlings.
There are early-growing zucchini, as well as varieties and hybrids of medium and late ripening. So that your table is not empty until autumn, you can choose several varieties for planting, or plant seeds of one variety every 10 days. After all, you can plant zucchini in June.
Sowing seeds and planting marrow seedlings in open ground
It is advisable to start preparing the soil for zucchini in the fall, digging to a depth of 20-25 cm and adding 30 g of superphosphate and 20 g of potassium sulfate to 1 square meter.
Zucchini should not be planted next to other plants of the pumpkin family, and it is also not recommended to grow them in the same place for several years in a row. But after potatoes, beets, cabbage, carrots, onions or greens, zucchini will feel very good.
In open ground, you can plant both seeds (early May) and seedlings (May-June) of zucchini if you want to get an earlier harvest. But it is still better to postpone the landing for a time when the threat of return frosts has passed.
First, it is necessary to choose a warm, sunny place in the garden and prepare the soil by loosening it to a depth of about 10 cm, as well as adding 15 g of ammonium nitrate per 1 sq. M.
When choosing and preparing a site for zucchini, it is necessary to take into account that the vegetable dislikes acidic soils with a high level of groundwater, and also reacts poorly to the introduction of chlorine-containing fertilizers.
When sowing, seeds (previously soaked in water without chlorine for several hours, and then germinated in a damp cloth) are buried 3-4 cm.
Zucchini are planted in open ground every 50-70 cm so that the plants do not experience nutrient deficiencies and do not interfere with each other. Some gardeners put 2-3 seeds in one planting hole, and after the emergence of seedlings, they thin out the plants, leaving one of the strongest and most well-developed in each hole.
How to distinguish squash seedlings from pumpkin or cucumber
Sometimes gardeners rearrange the seedlings from the windowsill to the windowsill, wanting to provide all the plants with a sufficient amount of light, and then ask themselves the question: "How to distinguish squash seedlings from pumpkins and cucumbers?" Unfortunately, this is not very easy, but there are some characteristic features.
At the zucchini the first true leaf is usually very thin and the stem is long and pale green.
By the pumpkin the stem is thicker and shorter. At the same time, he, as well as young leaves, are colored dark green. In addition, pumpkin leaves are usually slightly larger, denser and coarser in texture than those of a squash.
Cucumber the most conspicuous feature in the cotyledonous leaf phase is the thinner stem. When true leaves appear, the squash and pumpkin start to grow rapidly, and the cucumber tends to lag far behind.
Outdoor zucchini care
Zucchini should be watered at the root as the topsoil dries up, usually no more than once every 10 days, on average, consuming about 10 liters of water per 1 sq. M. Excessive moisture can cause the zucchini tip to rot. But if the summer is dry and the zucchini is thirsty, their stems can crack and suffer from root rot. Therefore, it is always better to be guided by the weather conditions. Water for irrigation must be heated to 22 ° C or previously held in the sun, since cool water from a well or a column can become one of the causes of ovary decay.
Some gardeners advise to stop watering altogether 7-10 days before harvest, arguing that in this case, zucchini are less susceptible to rotting.
If you water zucchini abundantly in a greenhouse or greenhouse, do not forget about airing, because the plant does not like high humidity (more than 70%). It is also advisable to maintain the temperature at 24-26 ° C during the day and 15 ° C at night. If you do not follow these simple rules, plants can express their dissatisfaction by starting to shed the ovaries.
In order to ensure a decent harvest, it is necessary to attract as many pollinating insects as possible to the garden. This can be achieved in a variety of ways. For example, during flowering, some gardeners spray zucchini with a solution of sugar (100 g per 1 liter) and boric acid (2 g per 1 liter). Or leave between the beds containers with honey diluted in water (1 tsp for 1 glass of water). But there is an even easier way. Plant marigolds between the beds to attract pollinating insects, provide additional protection to the squash from root-infecting nematodes, and delight you with abundant flowering.
When the plants have 4-5 true leaves, the bushes must be earthed up in order to induce the growth of additional lateral roots. Also, before the leaves close, it is advisable to loosen the soil under the zucchini several times and weed it out as necessary.
Netherflower on zucchini - what to do?
Male flowers that are not able to form ovaries are popularly called barren flowers. However, this is not always a problem, because such flowers fertilize the flowers of the female type and soon fall off themselves. But sometimes the number of barren flowers significantly exceeds the number of female flowers. In this case, you should pay close attention to your green pets.
The reasons for the appearance of a large number of barren flowers can be:
- adverse weather conditions;
- acidic soil;
- improper planting or sowing of seeds;
- sowing fresh seeds, which are prone to the formation of barren flowers;
- excess nitrogen fertilizers;
- illness;
- insufficient number of pollinating insects.
To cope with unfavorable weather factors, in cold, wet weather, zucchini are sheltered at night, and the female flowers are also pollinated with a brush. In hot weather, pollen grains sometimes completely lose their ability to fertilize. To avoid this, plants are watered with clean warm water and sprayed with a solution of boric acid (10 g per 10 l of water).
But most often, the cucumber mosaic virus and powdery mildew become the cause of infertility in zucchini. Carriers cucumber mosaic virus there may be insects (aphids, ants, Colorado potato beetle), so it is best to treat the plantings with special preparations, for example, Aktara or Aktellik. It is also important to pickle the seeds before sowing and be sure to disinfect the garden tools.
To disinfect the instrument, you can use a dark pink solution of potassium permanganate, 5-10% solution of ferrous sulfate, Pharmayod, as well as various alcohol-containing products
For prevention powdery mildew it is important not to overfeed the plants with nitrogen fertilizers. And in case of signs of the disease, you need to quickly remove the affected leaves and spray the zucchini with a suitable fungicide (for example, Topaz or Fundazol).
To reduce soil acidity, you can use slaked lime (0.5 kg per 1 square meter - with significantly increased acidity, 0.3 kg - with an average degree of acidity, 0.2 kg - with slightly increased acidity).
Fertilizing zucchini in the open field
Feeding zucchini is possible both with ready-made fertilizers purchased in the store, and with folk remedies. To provide zucchini with the necessary trace elements, you can use a mixture of 5 g of superphosphate, 2 g of urea and 1 liter of water. The first feeding is carried out ten days after germination, the second - a week later.
You can also feed the zucchini with a mullein. To do this, dilute it with hot water (1:10), let it stand for 3-4 hours, then dilute it again (1: 5), after which you can water the plants at the root. Top dressing with a mullein is possible both at the stage of growing seedlings and after planting them in open ground. The plants must be watered abundantly beforehand.
Zucchini also respond positively to wood ash, which can be introduced when planting seedlings (about 1 tablespoon in each hole), as well as under digging (1 glass of ash per 1 sq. M).
As an alternative to ash when feeding zucchini, you can use eggshells
From folk remedies, yeast feeding has proven itself well, which also helps to attract some pollinating insects. 30 g of yeast and half a glass of sugar are poured into 3 liters of water and left in the sun until signs of fermentation appear. Then the infusion is diluted with 10 liters of water and watered with this composition of the plant. Sometimes instead of yeast, dried bread crusts are used, which are infused according to the same recipe.
A significant amount of nutrients for your zucchini will be given by the infusion of weeds. It is not difficult to prepare it. To do this, you need a barrel, which is filled with weeds by 1/2 or 3/4, water is added and, covered with polyethylene, left in the sun for 1-1.5 weeks. Before use, the infusion must be diluted 1:10 with water.
Now that you have read our tips for planting zucchini in open ground (seedlings and seeds), and also learned about some of the features of caring for these plants, it's time to choose planting material. You will find the best varieties of zucchini with photos and descriptions in our previous materials.
This early ripening culture bears fruit throughout the summer. The plant is unpretentious, but requires care. Planting and cultivation is carried out in open beds; for an early harvest, seedlings are planted in greenhouses. In this article, we will look at how to properly plant a zucchini in open ground, as well as how to care for it at home and what to feed it during the entire growing season.
Dates for planting zucchini seeds in open ground
Start planting seeds in the ground when the soil warms up to +12 degrees, not earlier than mid-May. In cold ground, seeds will not germinate, will rot and die. Therefore, disembarkation is left until warmer weather. With late night frosts, tender sprouts will freeze. Planting zucchini seeds for seedlings is carried out at will, since the fruits have time to ripen and are planted immediately with seeds to the depth of the soil.
You can do this at the beginning of May (for the middle lane), after spilling the hole with warm water. The sowing site is covered with a plastic 5-liter transparent canister with a cut-off neck. It turns out a mini greenhouse for each plant. Do not forget that planting vegetables in the ground and in a greenhouse or greenhouse is significantly different.
After the onset of stable heat and the absence of night frosts, the canister is removed and the seeds can be grown further.
Proper preparation of beds and planting seed at home
The best way to prepare the ridges is in the fall. When digging, they add rotted manure or compost, a full range of fertilizers - superphosphate, potassium salt, ammonium nitrate. If necessary, they are preliminarily limed.
Where and which side to plant seeds? Zucchini can also be sown on compost heaps. Loose, humus-rich soil is a good place for this culture.
Do not plant zucchini next to the pumpkin. Over-pollination will reduce the yield of both crops.
It is enough to loosen a bed prepared in autumn in the spring and make holes in it. The zucchini bush is voluminous, planted at a distance of 0.5-0.8 meters. The seeds are treated with a 1% solution of potassium permanganate, ash or nitroammofoska, holding for 20 minutes. Then washed with water. This will protect the seeds from diseases and ensure friendly germination.
Place 2-3 seeds in the hole, in case one does not come up. When shoots appear, leave one seedling, pinch off the rest.
 Planting zucchini seeds in open ground in soil with ash
Planting zucchini seeds in open ground in soil with ash
Care during the growing season
Zucchini loves warmth and moisture. In dry weather, watered once a week with water, no colder than +22 degrees. With massive growth of fruits - every three days.Up to two liters of water are poured under each plant. Do not watered before harvesting so that the taste is not affected.
The culture does not tolerate moisture on the leaves. Watered under the root from a watering can without a spray. After that, they spud and mulch.
A large bush and large fruits require a lot of nutrition. Top dressing begins after the appearance of true leaves and continues the entire period of fruiting. Fertilizers are well applied in liquid form. Most of all he loves organic. Foliar dressing has a positive effect on the development of a vegetable. Spraying the bush every 10 days with a fertilizer solution can significantly increase the yield.
Weeds are only dangerous until they grow in the future, they simply will not be able to develop under a spreading crown.
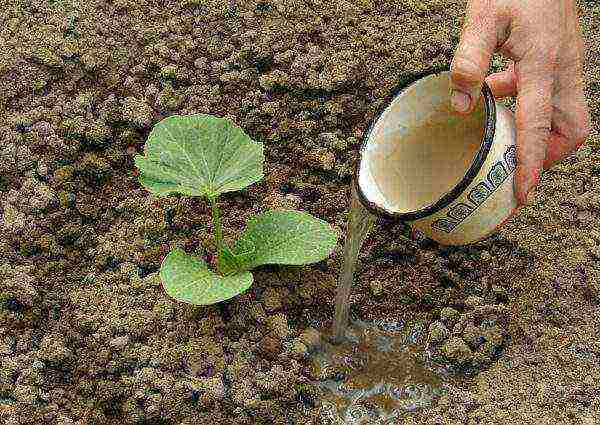 Watering a newly risen zucchini
Watering a newly risen zucchini
How can you feed and fertilize zucchini?
What fertilizers are used for the plant, we list them:
- Mineral.
- Organic.
- Fertilizers from improvised means.
Mineral fertilizers
For the development of this culture, a complete complex fertilizer is used in the following composition: 1 tbsp. spoon of potassium sulfate, double superphosphate, urea dissolves in 10 liters of water. After complete dissolution, watered under the root system by 1.5 liters per plant.
Nitrogen cause the growth of the green mass of the plant. Used in spring and summer. Closer to autumn, their use is undesirable. These are urea, ammonium, calcium and sodium nitrate, ammonium sulfate.
Phosphoric help fruits ripen faster, reduce the growing season. These are superphosphate, double superphosphate, phosphoric flour.
Potash increase the resistance of plants to lack of moisture and heat. Increases resistance to diseases and pests. Distinguish between potassium sulfate, potassium chloride, potassium salts.
Magnesium and iron-containing ones include magnesium oxides, boron, and iron. They increase the yield of fruits and their quality. Magnesium contributes to soil deoxidation. It is better to fertilize in the fall according to a certain scheme, as indicated in the instructions.
It is very convenient to use ready-made complex fertilizers. They contain the necessary chemical elements as a percentage. Azofoska, nitrophoska, diammophos include phosphorus, nitrogen and potassium in a state of easy assimilation for plants.
Microadditives are very important for the development of plants: boric, molybdenum, manganese, copper. They require a small amount, they are added to the complex.
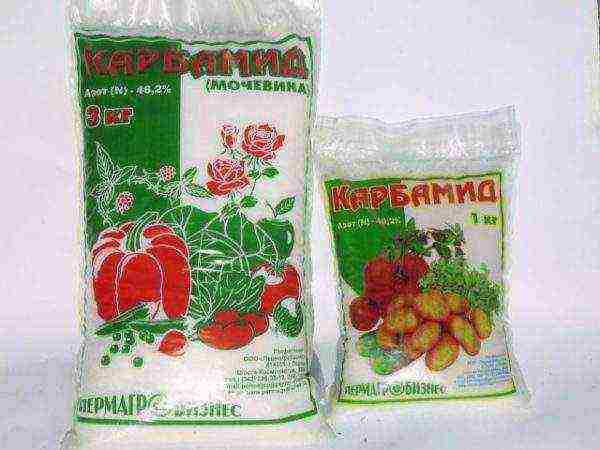 Urea is a mineral fertilizer used for feeding zucchini
Urea is a mineral fertilizer used for feeding zucchini
Organic fertilizers
Organic - an important component in the nutrition of zucchini. They include the main elements - nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, trace elements, vitamins. All this is easy to digest. So you can feed the zucchini at any time.
Manure. Organics of animal origin. Not very nutritious feeding. Improves soil structure. The simultaneous application of mineral fertilizers and manure improves the assimilation of mineral fertilizers.
Humus. Rotted manure. Improves the condition and composition of the soil. Assimilated after application under the bush in a short time.
Compost. It is obtained after the decomposition of vegetable and kitchen waste. Its ripening lasts at least three years. Used for feeding, mulching.
Bird droppings... Contains all the necessary components, the most valuable manure fertilizer. It takes time to be ready for application under crops. When fresh, it is caustic and can burn roots and leaves.
Peat... Makes the soil lighter, nourishes. Not all peat is healthy. Sour peat is used in composts.
 Bird droppings for soil fertilization
Bird droppings for soil fertilization
Other organic fertilizers and fertilizing
For food use grass and leaves, yeast, ash, food waste.
Green grass, nettle is especially good, is soaked in a barrel of water, kept for 10-15 days, and get herbal infusion. Strain it and get a fertilizer that is easily absorbed in a short time.
Green herbal dressing is obtained by digging and embedding in the ground grown in a garden bed.
Stimulates the growth and development of zucchini, yeast additives. Yeast can be added to herbal infusion or diluted in warm water with sugar.
Folk infusion of wood ash contains many trace elements, reduces the acidity of the soil. Does not contain nitrogen, it must be added.
Pests and the fight against them
Zucchini are subject to the following diseases:
- White rot
- Gray rot.
- Powdery mildew.
- Fusarium wilting.
White and gray rot covers leaves, stems and ovaries with bloom, they soften and dry out. It's a fungus. Appears in cold, wet weather in dense plantings. Spores persist in the ground. To destroy the disease, spray with copper sulfate, sulfuric zinc, urea solution. Do not thicken the planting, water with warm water.
Powdery mildew. The leaves are affected first, then the disease damages the whole plant. Absorbs plant nutrition, reduces yield. It spreads with temperature fluctuations, excess nitrogen. It is treated by spraying with colloidal sulfur, manure infusion, potassium permanganate solution.
Fusarium wilting affects the roots. With further development, it passes to the stem, and it dies. It can only be destroyed by completely replacing the soil.
All these diseases persist on plant debris and in the soil. Their appearance can be prevented by careful preparation of the ridges, burning plant residues, post-harvest processing, and observing crop rotation.
Insect pests for squash:
- Melon aphid.
- Spider mite.
- Whitefly.
Larvae melon aphid hibernate on plant debris, multiply rapidly in spring. They damage stems and leaves, after which they dry out. Autumn cleaning of ridges and burning of plant debris will help to prevent the invasion of insects. In summer, plants are sprayed with infusion of hot peppers, onions, potato tops, and powdered with tobacco dust.
Spider mite small invisible pest. Occurs in the lower part of the leaf. Causes leaf spotting and drying out. Control measures are the same as with aphids.
Whitefly forms a sticky sugar coating on the back of the leaves. This is the environment for the formation of various fungi and plant diseases. The pest can be washed off with water, not allowing them to remain on the ground after that. In case of a large number of insects, treat the soil after harvesting with the Komandor insecticide.
Harvesting and storage
The most delicious and healthy are green fruits up to 25 cm long. They have a thin skin and small unripe seeds. By removing zucchini on time, we help the formation and growth of new ovaries. In this case, we will have fresh greens all summer. From the end of August, we begin to make a blank for storage for the winter. We harvest fruits with hard skin and a long stalk for better storage. We collect the harvest until the frost.
Well-ripe zucchini can be stored in a cool room for 4-5 months until March.
Zucchini is an early ripening culture, we get the first harvest 20 days after flowering. An early harvest allows you to get fresh vitamins already at the beginning of summer. Their wide range of uses makes zucchini a popular crop among gardeners.
 Zucchini is a garden culture that has taken root well in many household plots. It is "respected" for its ease of cultivation, dietary properties and delicate taste. Planting zucchini is a matter that does not require much difficulty. With a little physical effort and agrotechnical knowledge, you can serve a delicately aromatic dish on the table or prepare excellent preparations for the winter.
Zucchini is a garden culture that has taken root well in many household plots. It is "respected" for its ease of cultivation, dietary properties and delicate taste. Planting zucchini is a matter that does not require much difficulty. With a little physical effort and agrotechnical knowledge, you can serve a delicately aromatic dish on the table or prepare excellent preparations for the winter.
Half of the success is the thoughtful planting. Therefore, we will pay special attention to the question of how to plant zucchini.
What seeds for zucchini to choose?
Work on the future harvest begins with the selection of zucchini seeds. They can be collected from your own plot or bought at market ruins or in the store. How to skillfully collect from zucchini grown on your own plot, you can see here.To choose purchased seeds - consider a number of important points:
- The manufacturer must be well known. It is advisable that this was a company whose products you or your friends have tested in practice.
- Quality seeds are sold full-bodied and heat-treated.
- Zucchini hybrids are not suitable for removing seeds from their fruits.
- Most of the imported seeds are hybrid.
- Most of the domestic varieties are superior to foreign ones in frost resistance.
- Foreign zucchini varieties are characterized by a longer growing season.
- They retain their presentation for a long time, which is beneficial when grown for sale.
- They have a thinner skin, which is good for quick eating.
- Zucchini of domestic varieties are better stored in their natural form, retain their taste well with any type of processing and preservation.
- The shelf life of domestic seeds is 5-8 years. But the good ones can come up later.
Zucchini seed varieties
The whole variety of seeds can easily fit into three large groups:

Early ripening varieties. For early planting of zucchini, the varieties White Swan, Anna, Zebra, Gribovsky, White bush, Zolotinka, Beloplodny and some others are suitable. Many gardeners are especially fond of the Tsukesh variety - for its refined taste and thin skin. It ripens for about two months, bush shape, cylindrical fruits, up to 40 cm long, weighing from 0.5 to 1 kg, slightly greenish color.
Mid-season. Allocate Macaroni (Spaghetti), Jade, Black handsome (zucchini), Kuand and others. The first is especially surprising - when boiling the pulp, it turns into separate fibers that outwardly resemble spaghetti.
Late ripening. Tivoli F1, Walnut, Long-fruited. Some hybrids. Their ripening period is three months or more. Perfect for long-term storage and preparation for the winter.
The group of zucchini marrows stands apart, which can be of different ripening periods, but are equally valued for high yields, compact plantings, long-term preservation of fruits and a whole "bouquet" of useful properties. Some varieties: Aeronaut, Zolotinka, Tsukesha, Zebra.
Interesting varieties that have the ability to self-pollinate - Zucchini white-fruited, Apollo, White Swan, Belogor and others.
It is clearly seen even from the examples given that the choice of varieties and their characteristics is very diverse, you just need to understand which zucchini should be planted on your site.
Seeds and seedlings - how to prepare for planting?
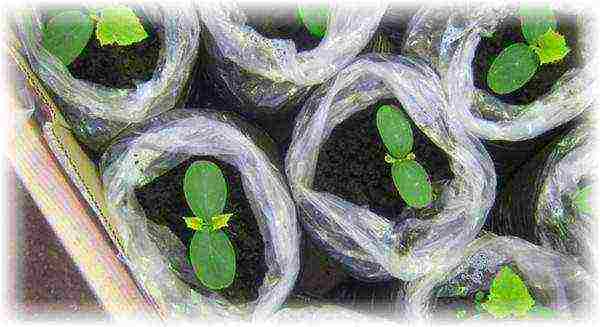
Zucchini are usually planted in open ground with seeds or seedlings. Before "entrusting" the future vegetable to the land allotment, the planting material must be prepared. Work begins with checking the germination of seeds. All of them are soaked in a 1% solution of potassium permanganate or growth stimulant for 20 minutes, then washed and placed in damp and warm gauze.
When the zucchini seeds are swollen (but have not yet taken root), they are slightly frozen to zero and kept in this state for 2 days. Then they warm up for a week in a well-lit place. After that, germination can be continued. When the hatched root takes up to one third of the length of the seed, it is planted in a container for seedlings or open soil, if it is not colder than 12 degrees Celsius.
Soil and containers for seedlings at home
At home, sowing zucchini for seedlings is available in almost any container. These can be crates, empty dairy bags, or paper cups. Best of all, seedlings will rise in peat pots, at least 10 x 10 cm in size.

A mixture of soil from a store is placed in a container or compiled independently. To do this, add one part of sawdust to six parts of peat and two parts each of wood ash and compost, mix well. Add ammonium nitrate (6 g), half a glass of ash, potassium sulfate (10 g) and a little more superphosphate to this. When it is not possible to prepare the mixture, ordinary earth is added to the container.
To exclude the preservation of the black rot larvae, the mixture or the earth is thoroughly frozen or spilled with a hot infusion of strong potassium permanganate.
Before planting the squash, the soil should be warm (but not hot) and well loosened.
Sowing seedlings at home - the main types of work
Prepared zucchini seeds are planted each in a separate container or pot. In light soils, they are buried by 5-6 cm, more dense - 3-4. Identify two germinated seeds, the weak sprout is then harvested. The surface above the planting is mulched with peat or humus so that there is no crust formation.
Decide when to plant zucchini for seedlings in different climates in different ways. In warm regions to the Volga region, seeds are planted in the ground under a film in early May, in the middle lane and the Urals - in early June, and in Siberia and the Far East they can be planted even in July. Accordingly, a month before the expected removal into the ground, the seeds are "determined" in pots.
Until the sprout rises, the temperature is kept at 20-22 degrees of heat, then for 5-6 days it is lowered to 13-15 in the daytime (up to 18 at night) and again the degree is increased to the original values.
Standard watering once a week. A lot of sunlight is important so that the seedlings do not weaken and do not stretch out.
Fertilizing the soil at the stage of growing seedlings. Good gardeners fertilize the soil under the squash seedlings in two stages during cultivation. They begin 7 days after the "emergence" of the sprouts - they are usually diluted with a large spoonful of urea and superphosphate per 5 liters of water, watered with a glass for each plant. A week later - a glass of nitrophoska mixture (1 teaspoon per liter can of water) for one sprout. If two stages are impossible, it is imperative to fertilize at least 1 time a week before taking it out for planting in open soil.
Preparing the land for planting zucchini in open ground

Before planting zucchini in open ground, the soil must be prepared and dug up.
You cannot plant where pumpkin seeds grew in the last season, in lands where groundwater runs high. Best of all, zucchini "master" light loamy soils or chernozem.
Fertilizers are applied to the rest of the soils. After feeding and digging up the earth, it is spilled with hot fertilizer (40 degrees), for example, Ross or water. Warm under the film.
In the "reduced version" of soil preparation - fertilizers can be applied before planting zucchini directly into the holes. They take humus, add a small spoonful of complex fertilizer and a large spoonful of ash, put it in holes and cover it with earth, in which seedlings or seeds are planted.
Planting zucchini in open ground

Open planted zucchini begin to be planted from the last days of May and, depending on local temperatures, this process can take place until July. So that the fruits can be removed for longer, sowing is done several times with a period of 5-6 days. For the middle lane, planting in early June is more suitable. The southern regions of the country can To to plant the second "wave" of zucchini in August.
Zucchini is grown in lighted dry places, excluding planting next to any pumpkin seeds. Planting seeds or seedlings in the morning or in the evening closer to sunset in cloudy weather.
Sowing seeds
Zucchini is planted with "dry" or sprouted seeds. You can raise small beds or plant seeds directly into the ground at a distance of 50-70 cm between holes and 1 m or more between rows. Seeds in ordinary soil deepen by 5-7 cm, in more humid lands - by 3-4. Place 2 seeds in each hole. When the shoots sprout to the first leaf, the weaker planting is removed, carefully plucking it out of the ground.
For warmth, zucchini seeds are covered with foil or large plastic bottles (one per well). Plants are good at "catching up" seedlings to real warmth, and if the temperature rises, it is convenient to open the cork in the bottle.
Experienced gardeners believe that if you plant zucchini with seeds, their fruits will retain their useful and taste qualities longer.
Planting seedlings
Zucchini seedlings are planted together with the soil from the pot, and if it is peaty - without getting it. In this case, you need to slightly raise the edges of the pot above the soil level.
Zucchini are planted with seedlings in well-fertilized and watered soil.
The distance between plants is slightly greater than when planting with seeds. It is planted to a depth of 5 cm. After planting, the soil is leveled, watered (directly under the root) and mulched. It is closed with a covering material and pressed along the edges with "sinkers" so that they are not carried away by the wind.
Planting zucchini by seedling method gives a greater yield of fruits, due to the early maturity of them.
Now you know how to choose the right seeds, germinate and plant the squash for an earlier or later harvest. Half of the work has been completed and now all that remains is to learn how to preserve and increase what the forces were spent on during landing.
Growing and planting zucchini, annual herbaceous plants of the pumpkin family, is probably one of the most uncomplicated activities in the garden. A variety of shapes, colors, sizes of vegetables will decorate not only the beds, but also your table. Zucchini in the garden love light, warm weather, timely watering, as well as a large space for free growth. Like pumpkins, zucchini thrive on suspended soils, practically do not require careful fertilization and easily survive fruiting, creating a large number of seeds for the next year.
Preparing a place
Planting zucchini every year requires preliminary site preparation. The better you arrange the beds, the less problems you will have with growing a vegetable. So, you need a well-lit open area where the wind is not raging. It is advisable that pumpkins or cucumbers did not grow in the chosen place last year, ideal predecessors would be: carrots, beets, onions, potatoes. The fact is that pumpkins and zucchini are susceptible to fungal diseases, which take root in the soil and, when re-grown in the same place, actively progress and infect pumpkin plants. Therefore, every year you need to transplant pumpkin plants to a new place.
Prepare the soil before planting. This is usually done in two stages every year: in the fall and in the spring. At the end of autumn, level the ground with a rake, dig it up. Right now, it is better to add manure or compost with superphosphate and potassium to the soil. For fertilizing 1 sq. m. you will need 30 g of superphosphate, 15 g of potassium, 1 bucket of organic raw materials. In the spring, the procedure with fertilizing the soil is repeated: after loosening the soil, add 20 g of ammonium nitrate (per 1 sq. M.) To it.
Also, it will not be superfluous to use soil mixtures, for example, mix sand with peat. A good fertile cocktail is obtained by mixing sawdust, turf, humus and peat, by itself it will provide squash and pumpkin with the necessary "credit" for good growth.
Video "Tips for planting zucchini"
Demonstration video with tips for planting zucchini.
Selection and preparation of seeds
Zucchini (like pumpkins) is conveniently propagated by seeds, moreover, the culture is replete with varieties, both early and late. You can pick up for every taste. If you do not want to delve into the intricacies of selection, then you should opt for hybrid varieties that grow and reproduce well without undue attention from the gardener. You should not take seeds that are a year or two old for cultivation - they will give a large number of male flowers, but they will be extremely poor in female inflorescences.
From early maturing varieties, the following have proven themselves well: “White Swan”, “Anchor”, “Zebra”, “Kavili”, “Helena”. Mid-season ones lag behind in diversity, but they pay off with a stable harvest already in July: “Macaroni”, “Jade”, “Black Beauty”.Late-ripening varieties "Nut" and "Dlinnoplodny" will give you a fresh harvest in the fall, just in time for the beginning of the canning season. Among the hybrid varieties are self-pollinated "Belogor", "Aeronaut", "Black zucchini", "White".
Having decided on the variety and seeds, proceed to the stage of preparing the plant material for planting. Of course, you can do without preparation at your own peril and risk, but then the crop will also be at risk - diseases and pests are not asleep! Seed pretreatment consists of three steps:
- Hardening against fungal infections. Place the seeds in water with a temperature of 45-50 ° C, leave them for 5 hours, and then put them in cold water for 3-4 minutes. Treat them with one of the fungicidal preparations, suitable - "Gamair", "Alinir-B", "Fitosporin-N". The procedure should take place at room temperature for at least 8 hours. If you hate chemicals, you can use aloe and Kalanchoe juices.
- Seed soaking. Wrap the planting material in a damp cloth and leave it there until they swell or begin to hatch.
- General hardening. If sprouts have already begun to hatch, then it is too late to harden them. But before the growth begins, you can place the seeds wrapped in a damp cloth in the refrigerator for 12-13 hours, and then leave them in a room with an air temperature of at least 18 ° C.
Thus, you can prepare seeds not only for marrow, but also for cucumber, pumpkin, squash.
Landing
The next stage is planting in open ground or boxes. Here it is important to understand how to plant zucchini correctly in order to get a healthy plant that will regularly bear fruit. The ideal time for planting zucchini outdoors is late May or early June. The latest planting time is in July, but only early-maturing hybrid varieties are ready for this.
You can grow zucchini and pumpkins in two ways by seedlings (more reliable option) and using seeds (less reliable option). When choosing between them, pay attention to climatic, weather, soil conditions, and also think about how soon you want to get a crop. For planting seeds in open ground, you will need a lot of space: there should be about 60-70 cm of distance between the holes. It is more convenient and practical to grow zucchini seedlings in cups or tubs.
Seedling method
You can start growing seedlings from seeds at the end of April, so that at the beginning of June you already have vigorous seedlings ready for transplanting. Optimal soil composition: peat, humus, sod land. You cannot do without fertilizers, here you can use a mixture of 8 g of carbamide, 10 g of potassium, 15 g of superphosphate. It is better to calcine the soil in the oven, and also treat it with a solution of potassium permanganate for disinfection. After that, you can start planting seeds.
Each seed is placed flat in the soil to a depth of 2 cm. If planted in tubs or flower pots, keep at least 15-20 cm between the seeds. It is much more convenient to grow in separate cups. After planting the seeds, cover them with foil to maintain a stable temperature up to 25 ° C. As soon as the first leaves hatch, you need to lower the temperature by 5-6 ° C.
Seedlings need a lot of light, so if you do not have a sunny side, then turn on the fluorescent lamps for 10-12 hours, otherwise the seedlings will grow frail. After 35-40 days, the seedlings will be ready for moving to open ground, but to be sure, wait about 50 days for the plant to get stronger. Recall that the ideal planting date is late May - early June, when the ground temperature is high enough and frosts are not expected.
Zucchini care
It is a pleasure to take care of zucchini, because apart from standard actions, nothing really needs to be done. Every year you will repeat the same care procedures, over time without even thinking about what and why you are doing. It is imperative to loosen the soil to ensure the permeability of moisture and heat, because zucchini are very thermophilic.Combine loosening with weeding the beds, as the proximity to the weed will harm the vegetable by taking nutrients from the soil.
Zucchini love abundant, but rare watering. About 10 liters of cool, but not cold, water should be poured into open ground once every 8-10 days. At the end of June and in July, you can slightly increase watering so that the plant receives enough moisture to gain green mass. However, do not pour in the zucchini - this will lead to root rot, and will also awaken fungal diseases such as powdery mildew and root rot.
Zucchini should be fertilized 2-3 times a year, adding mullein solution, yeast solution or mineral fertilizers to the soil. The first application should be in early June, the second in July. It is especially worth paying attention to plants during flowering and, subsequently, during fruiting. Also, do not forget, for preventive purposes, to treat the plantings with fungicides or iodine solution, so as not to give diseases a chance. The pollination technique, if your plant has problems with insect access (for example, in a greenhouse), is the same as for pumpkins or cucumbers: you should gently shake off the pollen, trying to get it on the female inflorescences.


