Content
- 1 Description of the plant
- 2 Useful properties of a flower
- 3 Reproduction and breeding
- 4 Choosing a landing site
- 5 Planting a plant
- 6 Peony care
- 7 Fertilization and feeding
- 8 And a little about secrets ...
- 9 Thin-leaved peony - garden savage
- 10 Variations on a theme
- 11 Caring for a thin-leaved peony - everything is like in nature
- 12 Wild peonies
- 13 Growing and caring for a thin-leaved peony
- 14 Reproduction
- 15 External description
- 16 Growing conditions
- 17 Reproduction
- 18 Landing
- 19 Care
- 20 Healing properties
- 21 Use in landscape design
The thin-leaved peony will become a decoration of the personal plot. The bright color of its flowers and delicate leaves will not leave anyone indifferent. Because of the original shape of the foliage, the British call the peony fern-leaved. The buds of the plant open in late spring, when other large-flowered species have not yet entered their flowering time. Even barely breaking through the ground, reddish-pink shoots look very beautiful against the background of sleeping nature. They grow literally before our eyes, gradually changing their color.
The thin-leaved peony will become a decoration of the personal plot. The bright color of its flowers and delicate leaves will not leave anyone indifferent. Because of the original shape of the foliage, the British call the peony fern-leaved. The buds of the plant open in late spring, when other large-flowered species have not yet entered their flowering time. Even barely breaking through the ground, reddish-pink shoots look very beautiful against the background of sleeping nature. They grow literally before our eyes, gradually changing their color.
Description of the plant
The thin-leaved peony belongs to the peony family. A wild perennial plant is found in the southeast of Russia, the Caucasus, Asia Minor and the Balkan Peninsula. It grows on rocky slopes, forest edges and clearings.

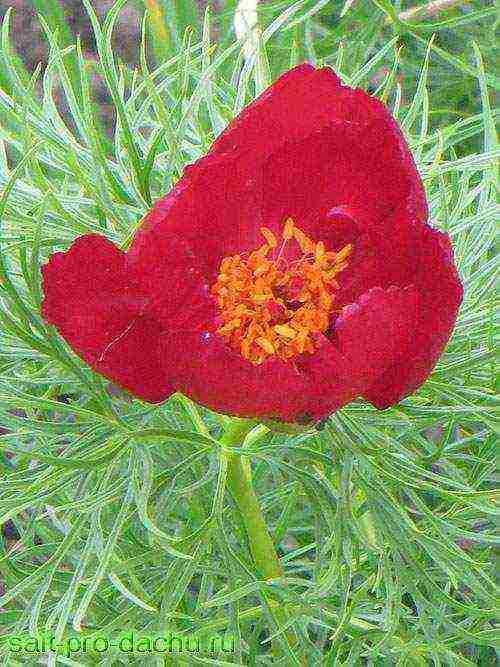
Shoots appear on the ground as soon as the last snow melts. Growing up to 40-50 cm, they form a dense spreading bush, resembling a ball in shape. Among the emerald greenery, buds appear on simple stems. They open in large flowers of a blood-red color with a satin sheen. The petals are bent-lamellar, obovate. Golden yellow anthers set off their brightness. The diameter of peony flowers reaches 8-10 cm. They have a delicate pleasant aroma.
 Clairvoyant Baba Nina named the signs of the zodiac, on which money will fall from the sky in May 2018 ...
Clairvoyant Baba Nina named the signs of the zodiac, on which money will fall from the sky in May 2018 ...
►
After a bright and lush flowering, which lasts for several days, the bush retains its decorative qualities for a long time. Its filamentous leaves are only 2 mm wide. They surround each flower like a fur trim. Leaflets may be glabrous or pubescent along the main veins.
Perennial blooms in late April - early May, simultaneously with late varieties of tulips. The terry type of thin-leaved peony is especially appreciated. Its flowers are so densely covered with petals that the yellow center is not visible. The flowering period of a terry plant lasts longer - up to two and a half weeks, even with minimal maintenance.

In one place, a plant can regularly bloom for more than 15 years in a row. Every year the bush increases in diameter and blooms more abundantly.
The frost-resistant flower has a short rhizome with pineal thickened edges. It looks a bit like elongated potato tubers.
Peony fruits appear in July - August. They represent a pubescent multifoliate, consisting of 2-5 leaflets. They contain brown-black shiny seeds, which gave the plant another name - raven.
Useful properties of a flower
Although the plant is considered poisonous, it is widely used in medicine as an expectorant, analgesic, bactericidal, protistocidal (antiparasitic) and antispasmodic agent. Preparations based on it are used to treat syphilis, anemia and cough. From rhizomes, infusions are prepared for the treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis and diseases of the cardiovascular system.

Thin-leaved peony contains tannins, anthocyanins (plant pigments of the glycoside group), flavonoids (plant pigments - phytoncides), vitamin C and fatty oil. All of its parts are used for the preparation of medicines. The flower is prized for its melliferous properties.
Peony is often used for decorative purposes, complementing landscape design. It goes well with brooms, wormwood, perennial flax and cereals in moderately dry mixborders. The plant is recommended to be planted in large rock gardens.
Reproduction and breeding
To decorate the backyard area with a bright steppe perennial, you can plant its seeds. They are harvested unripe and immediately sown in open ground. After collecting, you can put them in the refrigerator and plant them in the fall. Sometimes flowers appear only in the second or third year after sowing.
Store-bought seeds may appear shriveled. They lose moisture if stored for a very long time. The hardened shell can prevent the plant from hatching. To facilitate germination, the seeds are soaked in room temperature water before planting. After 2 days, the grains are immersed in the ground.

You can sow peony seeds in winter. Caring for them will take patience. River sand is poured into a flat wide dish. It is moistened and the planting material is immersed in it. The dishes are placed on a heating pad with a thermostat. In the daytime, the heating temperature must be increased to 30 degrees, and at night it must be lowered to 15 degrees. To maintain the moisture content of the sand, it must be regularly sprayed with water from a spray bottle.
Instead of a heating pad, you can use a central heating battery. A container with seeds is placed on it in the morning, placing a piece of foam plastic for insulation. In the evening, she is transferred to a cold windowsill.
When the first roots appear on the seeds, they are transplanted into fertile soil. You can use peat tablets. They are made from peat rocks with the addition of an antibacterial component. Nutrients and trace elements are in their composition in the amount necessary for the development of young plants.
Boxes with seeds are transferred to a cool room with an air temperature of 5-10 degrees. When the first leaves appear on the surface, the seedlings are brought into heat (18-20 degrees). After the development of 2-3 leaves, the sprouts dive. In the second half of August - early September, seedlings can be transplanted into open ground. In the fall, she will develop the root system. A young plant grown from seeds will bloom for 4-5 years.

It is much easier to propagate the thin-leaved peony by dividing the bush or dividing the rhizome. There should be 2-3 buds on the separated part of the root. You can divide the bush if its age exceeds 5 years. It is better to plant part of the rhizome or bush in late August - early September, as well as seedlings. But you can plant the bush in the spring, right after the snow melts before the buds develop.
Choosing a landing site
Before starting planting work, you need to find a suitable place for the plant on the site.
The narrow-leaved peony prefers slightly shaded places with diffused light. In such a place, it will bloom a little longer. It is advisable to choose a secluded corner, protected from drafts and cold winds. An ideal place would be a plot in the shade of garden trees.

Plants are not picky about the composition of the soil. If there is a lot of sand in it, the peony will develop well and will bloom earlier. But the brightness of the colors of his flowers will be moderate, and the flowering will end very quickly.In order for the peony to fully demonstrate its decorative qualities, it is better to give preference to areas with loamy soil, rich in nutrients. A peony planted in such a place will have a flowering period longer.
The crow, like other peonies, does not like acidic soils. You can find out where the areas with suitable soil are by looking at the weeds growing on them. For a peony, places where there is a shepherd's purse, quinoa, nettle (neutral soil reaction), in addition, poppy or bindweed (slightly alkaline reaction), are suitable.
When choosing a suitable place, you need to take into account the fact that in the middle of summer the peony foliage will lose its decorative qualities. Therefore, it should be planted in back rows or among lush plants that bloom between July and September.
You should not plant the narrow-leaved peony closer than 1.5 meters from the building, as well as in the root zone of trees and large shrubs. Stronger neighbors will take nutrients and moisture from the flower. For a plant, areas in the lowland, where a lot of water will accumulate, are not suitable.

If the groundwater on the site is less than 50 cm from the surface, you need to plant flowers in high ridges or create drainage ditches nearby.
Planting a plant
In the selected area, you need to dig a hole 70 cm deep and 60 cm in diameter. If several plants are planted, the distance between the holes should be at least 1 m. The excavated soil is carefully laid next to the hole. A small layer of broken brick and gravel (5-7 cm) is poured at the bottom of the funnel. With poor drainage, the plant can suffer from excess moisture. Even if good care is provided, soggy roots can die in the spring after frost returns.

Pour a mixture of 1 bucket of humus, 2 tablespoons of wood ash, 100 g of superphosphate and 50 g of potassium sulfate on top. If the soil is acidic, add 1 cup of dolomite flour or lime. The fertilizer layer, together with drainage, should occupy no more than half of the pit volume.
The previously dug earth is poured on top and a peony is planted on it. If part of a bush or root is planted, sprinkle the cut with river sand with the addition of 2-3 tablespoons of wood ash. This will help prevent rhizome decay.
The maximum planting depth is 10 cm. It is better not to submerge separated bushes deeper than 3-5 cm. Otherwise, they will not bloom luxuriantly. Do not allow the roots to touch the fertilizer layer. When the planting is finished, it is necessary to make an elevation from the soil with a height of 10-12 cm near the plant. Instead of earth, you can pour peat or humus.

Do not compact the soil at the planting site. This can damage the fragile roots of the plant.
Peony care
It is necessary to water the narrow-leaved peony regularly, avoiding strong drying out of the soil. An average of about 10 liters of water is poured onto one bush. It is especially important to regularly moisturize the roots during flowering. With sufficient watering, the flower will bloom longer. If the heat is intense, put a layer of mulch 5-10 cm thick from straw, grass cuttings, sawdust or bark under the bush.

They loosen the soil near the bush to a depth of 5-7 cm.At a distance of 20-25 cm from it, you need to deepen by 10-15 cm.
In the first 2 years after planting the peony, weak buds should be removed with garden shears. Such care will help strengthen the root system of the flower. After the foliage withers, it must be cut off at the root. If there is a need for seeds, you can leave one flower.
At the end of autumn, 5-10 cm of peat should be poured onto the cut bush to protect it from severe frosts.
If comfortable conditions are created for the plant, it will not suffer from pests and diseases. It is extremely rare for a peony to be attacked by aphids. Soap spraying will help get rid of it. 300 g of solid brown laundry soap is grated and dissolved in 10 liters of water. Instead, you can take 125 ml of liquid soap or 100 g of tar. Spray the plant daily until the aphids disappear.

Ash solution helps to get rid of aphids well. 250-300 g of ash is added to 10 liters of water, then boiled for 30 minutes. When the liquid has cooled, 40 g of laundry soap is dissolved in it.
Fertilization and feeding
When the plant grows, it is necessary to apply 50 g of nitrogen-containing fertilizers to the soil. You need to carefully feed the thin-leaved peony with nitrogen. An excess of it can lead to poor flowering, lodging of shoots and infection with fungal diseases.
When the first buds appear, the bush is fed with phosphorus (15-20 g) and potassium (10-15 g per 1 bush). It is also advisable to pour it with mullein solution, which must be prepared in advance. Half a bucket of mullein is bred with 3 buckets of water and the liquid is left for 10 days. While it is fermenting, it must be stirred daily. The finished product is diluted in half with water and poured over the root soil. Watering the root collar of the plant should be avoided. Fertilizer can burn it.
Starting from the second year after planting the peony, it needs to be fed foliarly. In the spring, immediately after the emergence of shoots, the plant is sprayed with a solution of urea (40-50 g per 10 l of water). After 2 weeks, the procedure is repeated by adding 1 tablet of microelements to the liquid. After another 14 days, 3 spraying is carried out with water with 2 tablets of microelements dissolved in it (per 10 l). Spraying is best done in the evening.
Starting from the third year after planting, care must be carried out depending on the amount of precipitation. During the heat, the amount of fertilizer is reduced, and with an abundance of precipitation, it is increased.
And a little about secrets ...
The story of one of our readers Irina Volodina:
I was especially depressed by the eyes, surrounded by large wrinkles plus dark circles and swelling. How to remove wrinkles and bags under the eyes completely? How to deal with swelling and redness? But nothing makes a person look older or younger than his eyes.
But how to rejuvenate them? Plastic surgery? Recognized - not less than 5 thousand dollars. Hardware procedures - photorejuvenation, gas-liquid pilling, radiolifting, laser facelift? Slightly more affordable - the course costs 1.5-2 thousand dollars. And when to find all this time? And it's still expensive. Especially now. Therefore, for myself, I chose a different way ...
Read the article >>

Shoots of thin-leaved peony shoot out of the ground that has not yet thawed rapidly, declaring their right to be the first to start the season. It is their appearance that arouses anxious understanding - indeed spring has come
For 18 years we have become accustomed to a spherical wild peony bush with openwork, heavily dissected, almost threadlike leaves. As if it should be so: from year to year the bush grows, occupying an ever larger area. Grows in partial shade, on the south side of the stem of a rather old apple tree. I cannot say that this neighborhood can be recognized by experts as correct. But in the conditions of the harsh Ural winters, such a dense planting does not interfere with either the peony or the apple tree.
Reddish pink shoots peony (Paeonia tenuifolia) nimbly reach for the sun, changing their color with growth.
Admire their decorativeness and desire to become the first among blooming brothers. In the spring bustle, you will not have time to blink an eye, as the recent stalwarts of the wild peony have already formed a low, up to 60 cm, neat bush of a beautiful, rounded-spreading shape. And this form is filled with emerald leaves: carved, amazingly delicate, delicate, cut into thin thread-like parts. Everything is just waking up, and the thin-leaved peony is already standing in all its glory: a little more, and the buds will bloom, decorating the already charming bush with bright lights.
In the conditions of Siberia and the Urals, the awakening of the thin-leaved peony can begin in the second half of April, and flowering in the second half of May, when the bulbous ones have faded: tulips, daffodils, muscari. At this time, the shoots of herbaceous peonies are just beginning to sprout from the ground.
Isn't it a hurry ?! But he also comes out of the growing season first. The seeds begin to ripen in mid-June, depending on weather conditions, and the foliage gradually loses its emerald color, which reduces the decorative effect of the plant. But not enough to upset….
See also: Peonies - planting and varieties (photo)
Thin-leaved peony - garden savage
Until recently, one did not have to hear much about species peonies. We hear more garden peonies, which can be found almost everywhere. The number of their varieties increases many times over from year to year.
And very few are mentioned wild forms of peonies. It turns out that P. thin-leaved was quite widespread in the second half of the last century. The changing fashion for plants has removed it from the gardens, replacing it with varietal ones. But interest in natural savages is constantly growing, as is the price of planting material. And not surprising, because  fine-leaved peony is a flowering herb of the peony family, has the status of a rare species, is listed in the Red Book.
fine-leaved peony is a flowering herb of the peony family, has the status of a rare species, is listed in the Red Book.
Thus, a specially protected natural area was created near the village of Tersinka, Volgograd region. Such territories are of particular value for the preservation of flora and fauna listed in the Red Book. They are created in order to preserve the unique growing places of valuable, scarce, rare and endangered plant species, including the fine-leaved peony.
Undoubtedly, it is imperative to protect rare plants from barbaric plundering (and, as a result, destruction) for the sake of the ubiquitous garden fashion. But, on the other hand, the gradual introduction of wild species into culture, careful care and reproduction of them by gardeners will contribute to the expansion of the distribution area of these plant rarities.
ON A NOTE
This amazing peony often gets popular names in the area where it grows. As soon as he is not called: narrow-leaved peony, azure flower, funnels, greenery, raven, red lazoric. It is sometimes called the steppe peony. but steppe peony (Paeonia hybrida) and n. thin-leaved - these are two completely different plants.
According to information from the World Wide Web and printed sources, the fine-leaved peony is now considered one of the most expensive and very popular plants in some countries of Western Europe, the United States and Canada. And this is not surprising, because now natural gardens are in vogue. And any rare plant becomes the highlight and pride of the gardener.
The thin-leaved peony has become more in demand in Russia. Few of the guests of our garden are not surprised at the sight of its delicate bushes. It does not stop gardeners who strive at all costs to bring this type of peony into the garden, and the fact that the plant is poisonous.
Reference by topic: Unusual varieties of peonies (photo) - speckled double and semi-double
The peony bush is extremely decorative. Especially during flowering. Not very large flowers of a raspberry-cherry shade with a yellow center, exuding a delicate aroma that garden peonies do not have, open in the morning and close in the evening. This reaction to the change of day and night is especially touching. Blooming lasts several days, during which the peony is a stunning sight.
Variations on a theme
Special attention is drawn to itself and pleases with decorativeness of the item thin-leaved with double flowers. An unusual combination of extremely delicate foliage and double flowers, in which the yellow middle is not visible, cannot leave anyone indifferent. Experts do not categorically claim that this is a wild natural specimen. There is an opinion that he can be a man-made brainchild. It seems that great opportunities are opening up for scientists in breeding using species peonies. No less attractive and even less common is the thin-leaved p. Blooming with amazing white flowers.
Propagation of a peony thin-leaved by seeds After flowering, a seed box with small black seeds is formed.If there is a desire to propagate a peony with seeds, they should be harvested slightly unripe. Since they quickly lose their germination, it is better to sow immediately after harvest or in late autumn, but in this case, after harvesting, they must be able to be preserved. A refrigerator is suitable for this. Seedlings may appear next spring, or in a year or two. Not fully ripe seeds sprout much more amicably. Self-sowing germinates and seeds not harvested on time. True, rarely and in small quantities. It remains only to wonder how, despite the fact that in nature the seed method of reproduction is the main one, these unique plants could not disappear. However, no one knows how many of them have been irretrievably lost over the past millennia.
Thin-leaved peonies grown from seeds do not bloom soon, in contrast to those propagated vegetatively (by dividing the bush). It is worth noting that by dividing the bush, you can rejuvenate an adult plant, the flowering of which is deteriorating.
A distinctive feature: the thin-leaved peony can be propagated by pieces of rhizomes, which are formed in abundance when dividing or transplanting a bush. The short roots are very fragile and break easily, and the buds that have awakened on them give life to new plants. We were convinced of this by replanting our peony bushes that have grown over time.
When planting a delenka, it is better not to deepen: the renewal buds should be at a shallow depth. It will not be superfluous if you put drainage at the bottom of the planting pit. Thin-leaved peonies do not tolerate excessive waterlogging, the rhizomes can rot. So it is better not to abuse it by watering.
See also: Tree peonies or peonies in science
Caring for a thin-leaved peony - everything is like in nature
We can say that planting and feeding a wild species practically does not differ from the agricultural technology of garden peonies. Potassium and phosphorus are important in nutrition, but overfeeding with nitrogen is risky: and the bush fattens, loses its decorative effect, and flowering ceases
be abundant. This happens with other plants: why bother about procreation, if there is more food than necessary. Easier to expel vegetative mass. But you need to take into account the fact that this peony is wild, from the natural environment, or rather, you need to take into account the specific features of its habitat.
The thin-leaved peony grows both in the sun and in partial shade. It is noticed that in places of natural growth, the soils are alkaline, which must be ensured when planting in your garden. A simple and affordable deoxidizer will help - wood ash, the constant companion of the gardener. Of course, for some time the peony will try to survive in acidic soil, but this struggle is unlikely to end in victory over genes, getting used to unnatural conditions.
In nature, the peony has enough nutrition, and no one with a generous hand adds either phosphorus or potassium. Everything is formed by itself.
By dividing the bush, you can rejuvenate an adult peony, the flowering of which has noticeably deteriorated over time.
One has only to accept the rules for obtaining fertile soil and not interfere with the mechanism that has been working for centuries to work miracles. And that's all: do not dig furiously the earth, take mulching of the soil with any organic materials as a prerequisite for the comfortable growth of plants.
If you believe the experts, with proper mulching, a centimeter layer of humus can be formed over a season, and in natural nature this will take more than one decade.
But many gardeners to this day do not believe that mulching the land at their summer cottage helps not only create healthy soil, but also significantly reduce labor costs when growing many plants. Moving a little away from the topic of growing peonies, we note that thanks to mulching, you do not need to worry about endless loosening of the soil after the rain. Also, this technique makes it possible not to worry about watering.
The most important action of mulch is weed control. It is much more difficult for them, and often it is simply impossible to break through it.We, out of habit, fight weeds, like Don Quixote with windmills, trying to make the soil surface spotlessly clean. Forgetting that keeping the ground bare is simply unacceptable and destructive.
Wild peonies
A wide circle of gardeners is also unfamiliar with a small fraction of wild peonies that survived natural disasters and have survived to this day. Slightly more than 20 representatives of this unique genus of shrub and herbaceous peonies are found in our time. Some of them, to the great chagrin, can be counted on one hand. Others were more fortunate. One of them is the root often found in the culture of Maryin, or, in botanical terminology, evading peony (Paeonia anomala).
No less interesting and valuable is Wittmann's peony (Paeonia wittmanniana). It has many names, including depending on the variation in color and shape of the flower, leaf pubescence, and the habit of the whole plant. So, the Litvinskaya peony has a white flower with a pink bottom. There are many subtleties, but this is for narrow specialists, and for amateurs - just Wittmann's peony, a rare and beautiful representative of wildlife.
According to the collector of wild plants Oleg Budkeev from Altai, rare plants are very decorative and capable of decorating any flower garden with their magnificent flowering and unusual appearance. They allow the creation of gardens of continuous flowering in the most difficult climatic zones. This enthusiastic enthusiast's collection of rare natural plants already has more than 2 thousand items. Most of them require artificial reproduction. However, his efforts help to replenish the population of rare plants, introduce them into garden culture, and also preserve species from the Red Book for future generations.
Below are other entries on the topic "Cottage and garden - do it yourself"
Division and transplantation of peonies: Peonies: divide and transplant August-September -… Calendar of peonies care: Caring for peonies - when ... Varieties of yellow peonies - care and photo, name and description: Yellow peonies - the best varieties ... Peonies: planting and leaving in spring in open ground: Planting and caring for peonies ... Tree peonies or peonies in science: Tree peonies - features of growing ... Peonies and flower care in questions and answers: How to care for peonies - ... How to cut shrubs correctly: Cutting and shaping shrubs - ...
Subscribe to updates in our groups.
Let's be friends!
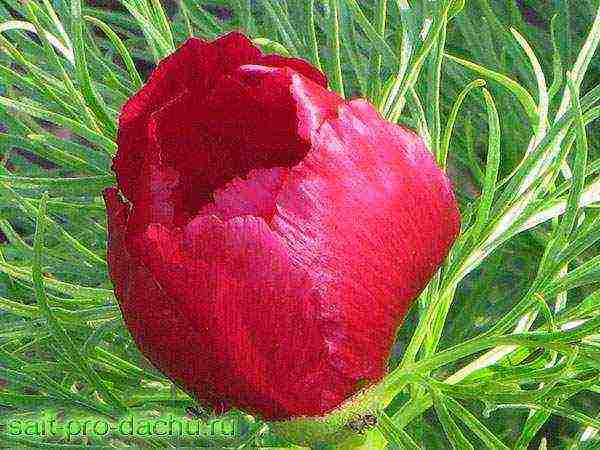

Narrow-leaved peony (Paeonia tenuifolia) or funnels, azure flower, red lazoricum is a flowering herb of the Peony family, a rare species listed in the Red Book. Under natural conditions, the flower can still be found in the south of Russia: in the Tambov, Voronezh and Belgorod regions. It has been cultivated in culture since the end of the 18th century.
As soon as the last snow melts, delicate pink shoots appear from the ground, which very quickly begin to grow, reaching a height of 50 cm. The narrow-leaved peony blooms at a time when many small-bulbous plants and daffodils with tulips have already faded. At this time, the shoots of herbaceous peonies are just beginning to sprout from the ground.
Bushes of narrow-leaved peony have a spherical shape and openwork strongly dissected filamentous leaves. At the tops of the shoots, buds are formed, which turn into not very large (up to 8 cm in diameter), not double flowers of a bright crimson color. In the middle of the flower are golden yellow anthers, beautifully in harmony with the color of the petals. The most delicate aroma emanates from the petals, which cannot be compared with any artificially created one. Blooming lasts several days, during which it is a stunning sight.
There are also known double varieties of narrow-leaved peony (P. tenuifolia Plena, P. tenuifolia Rosea) with oval flowers and anthers, which are hidden between the petals. In these varieties, flowering lasts up to 2.5 weeks. After flowering, a seed capsule with small black seeds is formed in place of the flower.
Growing and caring for a thin-leaved peony
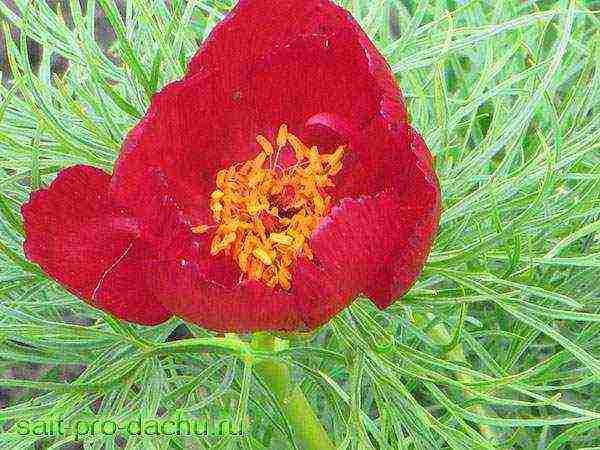

The narrow-leaved peony grows well under the sun and in partial shade. Loves fertile earth with an alkaline reaction. In the wild, it is often found on calcareous slopes. He does not like acidic soil, does not grow on it for a long time, dies over time. If the soil is acidic, it is recommended to add a glass of dolomite flour or lime into the planting hole, 2 tbsp. wood ash, mineral fertilizers (superphosphate - 100 g, potassium sulfate - 50 g). This nutrition will be sufficient for several years.
With poor drainage and planting in lowlands during winter thaws or spring floods, the flower can get wet. During spring return frosts, there is a possibility of damage to flower buds. The narrow-leaved peony is quite winter-hardy, therefore it is cultivated without any shelter. It is resistant to many diseases, but it can sometimes be damaged by aphids.
Plant care consists in regular watering, top dressing with carbamide and ammonium nitrate (about 50 g per bush) over spring snow. During flowering, it is fed with mineral fertilizer, and at the beginning of autumn with phosphorus-potassium fertilizer.
By the month of July, the bush becomes an adult and disintegrates. By the end of summer, all of its terrestrial part dies off, new shoots will appear only next spring.
Reproduction
The narrow-leaved peony is propagated by seeds, cuttings or root cuttings.
Delenki
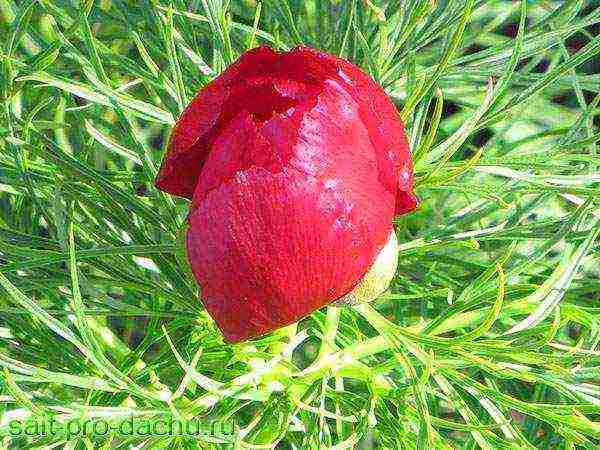

A good cut is a pair of adventitious roots 1 cm thick, about 5-6 cm long, and with 3-4 developed renewal buds. Such a division has an optimal supply of nutrients, which are sufficient for rooting and primary growth.
It is worth noting that dividing a bush is not only a method of reproduction, but also a rejuvenation of an adult plant.
Planting pits are located at a distance of 60-70 cm. Organic matter is placed at the bottom of the pit. Delenki during planting do not deepen. Renewal buds should be no more than 5 cm from the ground.
Seeds

Seeds quickly lose their germination, so they are sown mainly immediately after harvest or in late autumn, but in the latter case they are stored in the refrigerator all summer. Seedlings will appear next spring, but the seeds can germinate in 1-2 years. A good result can be obtained by sowing incompletely ripe seeds.
It is effective to sow seeds in boxes with a nutritious substrate or "before winter" in open ground. With such a planting in the spring, you can get high-quality planting material. But gardeners rarely resort to seed reproduction, since it takes 5-6 years from sowing to flowering plants.
You can propagate by cuttings, but this method is relatively long and not always effective.
In the flower garden, the thin-leaved peony goes well with wormwood, eremurus, perennial flax, and numerous cereals.
One of the common garden plants in many European countries is the narrow-leaved peony. In Russia, this plant is less common. It is mainly cultivated by experienced gardeners.
External description
A feature of this plant is its unusual leaves. Unlike other garden peonies, they have a shape dissected into needle-like lobes and resemble a fern. The bush is dense, compact, grows no more than 50 cm in height. The flowering period begins in late spring. Around the end of May, large single flowers appear with one row of bright red petals and yellow anthers in the middle, which look like a flash in a spring garden. On one bush, more than a dozen flowers can be located, which emit a unique aroma. Flowering lasts a little more than a week.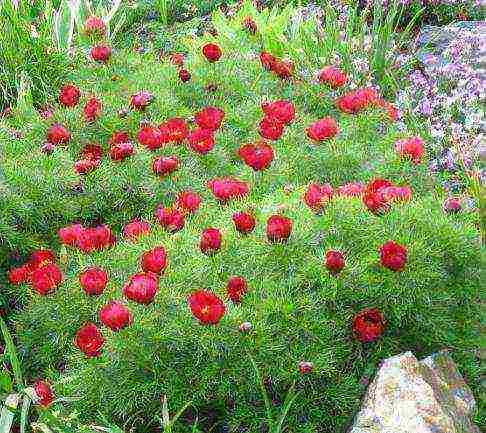
But even after the narrow-leaved peony has faded, it does not lose its decorative effect due to the airy light green foliage.
Growing conditions
This plant is quite unpretentious and can easily tolerate small frosts or droughts. Even a beginner grower is quite capable of growing a narrow-leaved peony.However, some conditions should be observed in order for the plant to be a decoration of the garden for as long as possible.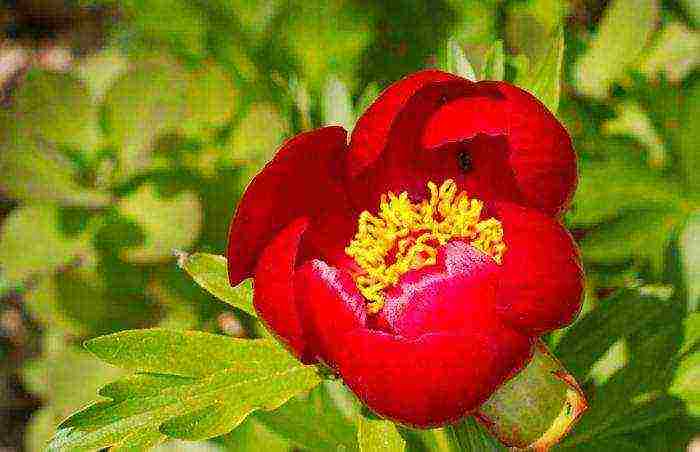  A peony needs well-lit places; with a lack of light, flowers may simply not appear on it. The soil should be moderately moist. Excessive waterlogging leads to decay of the root system. Good watering is required only during the bud ovary period. It is not recommended to plant the narrow-leaved peony on sandy soils. Decreased flowering can cause overuse of fertilizers.
A peony needs well-lit places; with a lack of light, flowers may simply not appear on it. The soil should be moderately moist. Excessive waterlogging leads to decay of the root system. Good watering is required only during the bud ovary period. It is not recommended to plant the narrow-leaved peony on sandy soils. Decreased flowering can cause overuse of fertilizers.
Reproduction
Usually the peony is propagated by dividing the bush, but sowing seeds can also be used. In early September, when the days are no longer so hot, they plant these flowers by dividing the rhizome. For this, old bushes are used, which are at least 5 years old. The rhizome is divided into several parts so that each has 3 or 4 renewal buds.
For propagation of peony seeds, you must first prepare them. Boxes with this planting material are collected a little unripe, until they are fully opened.  Sowing is carried out at the end of September, so the seeds are carefully packed and stored in the refrigerator until autumn. This method is used mainly for selection, since in this case it is possible only after 3, or even after 4 years, to observe how the narrow-leaved peony blooms.
Sowing is carried out at the end of September, so the seeds are carefully packed and stored in the refrigerator until autumn. This method is used mainly for selection, since in this case it is possible only after 3, or even after 4 years, to observe how the narrow-leaved peony blooms.
Landing
The place where the peonies will grow is being prepared in advance. To do this, dig a landing hole measuring 60x80 cm or even more. When planting several plants, it is required to maintain a distance between them of at least 1 meter. Drainage is laid at the bottom of the pit, which is covered from above with compost with mineral fertilizers and wood ash. After that, a small mound is formed from ordinary garden soil at the bottom of the pit, on which the rhizome is located. Before planting, it is recommended to treat the cut site with a solution of wood ash for disinfection purposes. It is necessary to bury the peony in such a way that the apical bud is 6 cm above the soil surface.
Seed propagation allows you to get a large amount of planting material. At the end of September, seeds are sown to a depth of 5-6 cm on a prepared bed or in a special container. At the same time, a certain part of coarse river sand is added to the soil.
Care
Like all garden plants, the narrow-leaved peony needs watering, feeding and timely weeding. Excessive moisture for this plant is detrimental, so it needs to be watered only when the soil begins to dry out. In dry summers, you need to regularly moisten the soil. During the rainy period, the plant does not need watering.
Fertilizing with mineral fertilizers should be carried out only 3-4 years after planting. If the soil is poor in composition, then this can be done after 2 years. At the same time, it is important not to overdo it, since an excess of nitrogen, for example, can lead to decay of the rhizome, and also affect the quality of flowering.
So that the thin-leaved (narrow-leaved) peony does not lose its decorative appearance even after flowering, it is pruned at the level of the upper leaf. Thanks to this, the plant acquires a more compact form, and the seed pods do not spoil its appearance.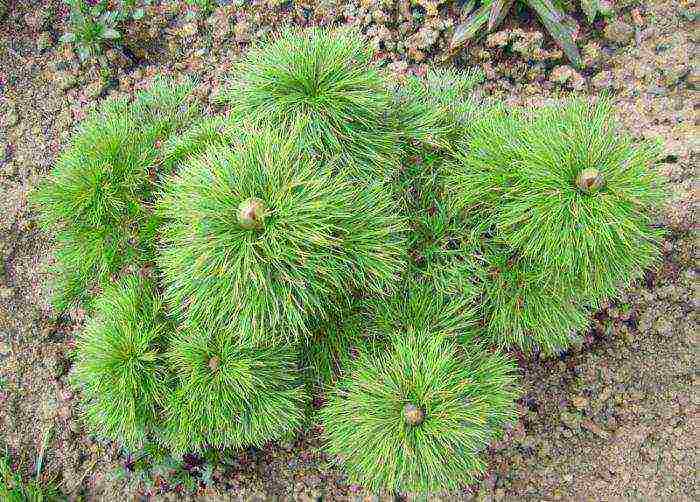
Pests bypass the peony. And only aphids can sometimes attack him. To combat it, it is enough to spray the plant with a specially prepared solution of tobacco and soap infusion. Excess moisture can cause various fungal diseases. For prophylactic purposes, the peony can be sprayed with Bordeaux liquid.
The peony is able to tolerate frost well, therefore it does not require shelter for the winter. But in regions with severe winters, you can cover it with spruce branches, paying special attention to the fact that the roots are not exposed.
Healing properties
Narrow-leaved peony, which is usually grown for decorative purposes, is also used to treat a number of diseases.Its diuretic, antispasmodic and sedative effect has been known in folk medicine for a long time. Peony rhizome is used to prepare various home remedies that are used to treat gout, anemia, and nervous diseases. The decoction of the root also helps with pain in the heart, stones in the bladder and kidneys, concussion.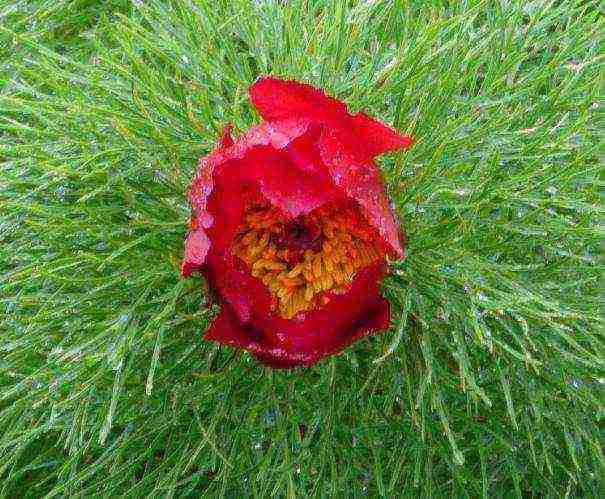
It should be remembered that when using funds based on this plant, it is very important to observe the dosage, since in the roots of the peony there is an increased content of a poisonous substance called neonin. Therefore, it is better to consult your doctor before use.
Use in landscape design
Human activities (plowing the steppes, grazing, etc.) have led to the fact that the wild peony now belongs to plants in need of conservation. Breeding in parks and gardens helps preserve this species by promoting its distribution.
In landscape design, the narrow-leaved peony has excellently proven itself, the double variety of which is especially good in combination with broom bushes, cereals and perennial flax. It looks good on slides, rock gardens, mixborders. These flowers are planted both in composition and individually.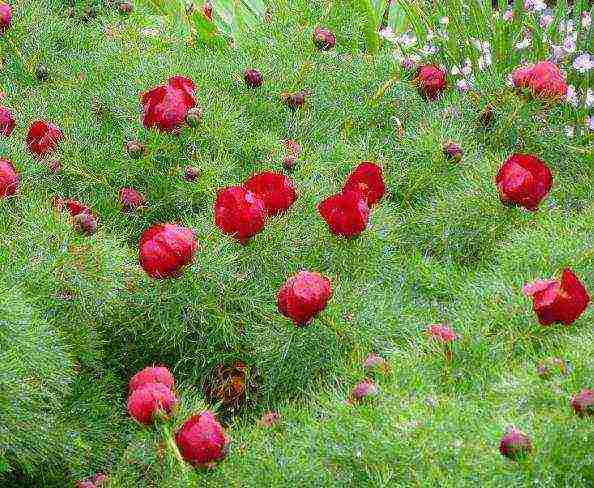  You can place several different varieties of peonies on the same flower bed, blooming at different times. The narrow-leaved peony, planted among stones or against the background of a talus, looks very beautiful. Photos of all kinds of compositions with this plant show how many options for using its decorative properties exist.
You can place several different varieties of peonies on the same flower bed, blooming at different times. The narrow-leaved peony, planted among stones or against the background of a talus, looks very beautiful. Photos of all kinds of compositions with this plant show how many options for using its decorative properties exist.



