Content
- 1 All about lilies: description and main characteristics
- 2 The most popular subspecies are:
- 3 The most popular varieties of hybrids:
- 4 Lilies care and growing at home
- 5 How to plant correctly
- 6 We plant in open ground
- 7 How to care for lilies
- 8 How to propagate and transplant
- 9 Pests and diseases
- 10 How to properly cover lilies before the onset of cold weather
- 11 Lilies care in spring after winter
- 12 Combination with other plants in landscape design
- 13 Planting lilies in open ground
- 14 Lilies - outdoor care
- 15 Reproduction of lilies
- 16 Lilies - pests and diseases
- 17 Shelter of lilies for the winter
- 18 WHERE TO BUY LILY BULBS
- 19 Lilies - Outdoor Planting and Care
- 20 Garden lilies: distinctive features, planting and care
- 21 Lilies - planting and care in the open field
- 22 Lily - planting in the fall in open ground: how and when to plant lilies, care in winter
- 22.1 When to plant lilies in the fall in the suburbs
- 22.2 When to plant lilies in the fall in the Urals
- 22.3 When to plant lilies in autumn in Siberia
- 22.4 Planting lilies in the ground before winter
- 22.5 Soil for lilies
- 22.6 How deep to plant lilies
- 22.7 How to plant bulbs in the fall
- 22.8 Lily care after planting
- 22.9 Lily care in autumn outdoors
- 22.10 Lily care in winter
- 22.11 Transplanting lilies in the fall to another place
- 22.12 How to store lilies before planting in the fall
- 23 Correct planting and care of lilies outdoors
- 23.1 How to grow lilies outdoors
- 23.2 Varieties, their advantages and disadvantages
- 23.3 Asian
- 23.4 Variety Candidum
- 23.5 Curly
- 23.6 Oriental hybrids (oriental)
- 23.7 The latest innovations from breeders
- 23.8 When to plant a flower in the country or in the garden: in autumn or spring?
- 23.9 Bulb planting rules, reproduction
- 23.10 How to care: care after planting, in the process of growing
- 23.11 Prevention of diseases and pests
- 23.12 Shelter for the winter
- 24 Lily in the open field: planting and care
- 25 Botanical description and distribution area
- 26 Types of lilies and their photos
- 27 Reproduction of lilies
- 28 Planting lilies in open ground
- 29 Care and transplant rules
- 30 Pests and diseases of lilies
A proudly standing blooming lovely lily immediately attracts all the attention. Her gorgeous flowers, whether large or miniature, always leave an unforgettable impression.
Lily belongs to the Lilia family, which includes perennial herbaceous plants with a bulb at the root. From 70 to 90 species belong to this genus. Many different hybrid varieties have been bred from them.

Yellow lily

Pink lily
Making your garden unforgettably beautiful is the dream of any gardener without exception. For this, a wide variety of flowers and plants are used, which are in perfect harmony with each other. Lily is a flower that will surely help you create a beautiful garden. The unusual shape and extensive palette of colors will make any person who is next to him enjoy its flowering.
There are many legends that tell about the appearance of a lily, and one of them says that the flower appeared thanks to the milk of an ancient Greek goddess. Of course, it is impossible to say that this is undoubtedly true, but you should not doubt the unforgettable beauty of the lily. According to its decorative properties, it can be placed next to the first beauty and garden queen, an unforgettable rose.
All about lilies: description and main characteristics
How to distinguish this culture from others:

Drooping lily
- All plants have a stem that can be 14 cm or up to 2.5 meters in height, completely covered with foliage. Exactly how long your flower will be depends on the variety you have chosen.
- Also, some varieties may differ in the stem, which is covered with leaves only in its lower part.
- There are plants with umbellate, conical and cylindrical inflorescences.
- You can find both single flowers and groups, the number of which varies from 5 pcs. and comes up to 15 pcs. Each inflorescence pleases the owner with its flowering for about 1-2 weeks.
- The flower has 6 petals, one pistil and stamens, which can be about 5-7 pcs.
- Among the numerous species, there are plants of the most original and unforgettable shapes and colors. But you will not be able to meet a blue or blue lily.
- Grows from bulbs, which can be of various sizes, depending on the selected variety. It can be either 1 cm or up to 27 cm.
Those who like to decorate their garden should remember that some types of lilies are quite difficult to breed. There are also plant varieties that even professional gardeners cannot cultivate. But this does not apply to hybrid varieties, since even the most inept florist can cope with their cultivation.
The size of the flower also depends on the variety chosen. Some can be around 250mm in circumference, while small flowering varieties reach around 40mm.
All currently available hybrids have been bred from several basic species. Let's see what kind of lilies are there?
The most popular subspecies are:
-
Asiatic lilies
The inflorescences resemble a bowl in their shape, and are also practically devoid of any aroma. The most spectacular and unforgettable among them Marlene variety... Sometimes the shoots and foliage of this variety are strongly influenced by climatic conditions, which is why they grow together to form a pyramid. This is what caused this variety to be called pyramidal lilies.

Asiatic lilies
Among the "Asians" it is worth highlighting:
- Cocktail
- Alaska or spotted lily
- Yeti
- London
- Tiger lily
These flowers are not demanding to care for, they are able to withstand frosts, various diseases and multiply without much difficulty. The height of this species reaches about 150 cm. It begins to delight the grower with its flowering from the end of July or the beginning of August. Also famous for their unsurpassed beauty are the bulbous lilies, which received this name because of the air bulbs located in the axils of the foliage.
-
American hybrids
They appeared due to the crossing of several species. These varieties are not afraid of frosts, but only they have a negative attitude towards transplants. Sometimes transplanting a plant leads not only to wilting, but also to its death. If you decide to grow this species, then you should choose well-drained, slightly acidic soil areas for it. American lilies love water and should be watered regularly.
-
Martagon hybrids
These are hybrids that appeared thanks to the curly lily. Like its predecessors, they easily cope with frost. They love partial shade, but they can survive in areas with direct sunlight. After planting in one place, they can grow for about 10 years, and sometimes even longer. This hybrid does not like transplanting, it is not picky about the composition of the soil.It begins to bloom at the end of June, but after planting it may not release buds for about 2 years. Plant height reaches 180 cm.
-
Candidum or snow-white lily

White lilies
This hybrid is based on the royal lily, which was crossed with European and Chalcedony lily varieties. In its natural environment, it occurs in humid climates, grows in rocky areas. You can grow this species in the garden anywhere, giving it, preferring sunny, protected from the wind areas. The shoot of this variety is very high and does not bend, so it can easily break in a strong wind. It has medicinal properties, therefore it is widely used in folk medicine. Includes a small number of varieties that differ in white or slightly yellowish flowers.
Snow-white Candidum (Lilium candidum) in pure translation means snow-white, like its giant inflorescences blooming in summer. The flower of the Madonna is also called, because the famous icon has an image of the Virgin Mary with a baby, in her hand she holds a white lily.
-
Longiflorum hybrids (Longiflorum)
Plants that love warmth very much. Growing them in cold climates is not easy as the flowers will need shelter to do this. It has rather large bell-shaped flowers, whose sizes can vary from 15 to 20 cm. Endowed with an unforgettable aroma, but very delicate and require special attention. Grown from bulbs in the house or in a greenhouse.
-
Tubular varieties
It is based on Asian lilies. These flowers are preferred by many gardeners as they require little or no maintenance. The plant blooms for about 3 months, but if it grows in the southern region, then it will delight you with its beauty until October.
These include popular varieties such as:
- Sunburst
- Pink
- Golden Showers
- Royal
- Hearts Desire
These hybrids are able to withstand the variability of the weather, reproduce with ease and cope with diseases caused by the activity of fungi and viruses. But only to grow these varieties, you need fertile land.
-
Oriental variety
It has rather large corrugated flowers, about 30 cm in diameter, and also has a rich aroma. The height of the lilies can vary from 40 cm and reach 120 cm. It pleases with its flowering in August and September.
Famous oriental hybrids:
- Mona lisa
- Sorbonne
- Golden lily
- Brazil
- Japanese
They have some disadvantages, among which it is worth noting poor reproduction, they are often attacked by various diseases, and are poorly resistant to frost.
Numerous crosses of different species among themselves, in order to obtain varieties with mixed qualities, marked the beginning of the emergence of new subspecies. The two most popular are OT and LA bands, but there are many more.
-
OT hybrids
Arose as a result of crossing the oriental and tubular lilies. Funnel-shaped and wide-bowl-shaped flowers are endowed with a strong unforgettable aroma, and are also famous for their original and bright colors. Basically, the height of the plant reaches 180 cm, but under favorable conditions for growing hybrids, they can grow up to 2.5 m in height.
-
La hybrids
These are all recently bred lilies, which have appeared thanks to the Asiatic and long-colored species. They do not have any aroma, they are endowed with large saturated flowers of various colors, which appear in the second half of July. They are able to cope with frost, and also do not require special care. In height they can reach from 80 to 120 cm.
The most popular varieties of hybrids:
Lilies OT-hybrids
Abbreviation for Oriental - Tubular

Terry lily
Pretty Woman - (Lilium Pretty Woman). It grows almost up to a meter in height. Large inflorescences creamy white with a delicate pink.
Anastasia (Lilium Anastasia) Intricately curved leaves of a rich emerald color. Countless flowers of a bright pink hue, with a white spot at the base and a greenish stripe on it.
Robina (Lilium Robina) In blooming vyde in a height of 1.5 m. Large green leaves with dark areas, Flowers purple-red with a yellowish core.
Scheherazade (Lilium Sheherazade). A giant variety of almost 2.5m. Multiple flowers of a reddish-burgundy hue, edging and at the core of a light cream color. Blooms in late summer.
Honeymoon Large but delicate slightly yellowish flowers.
Shocking Pure red flowers are edged with a rather thick golden yellow stripe.
Lilies LA hybrids

Burgundy lilies
The abbreviation stands for Longiflorum Asiatic longiflorum
Frey or Freya (Fray) beautiful golden yellow flowers.
Ercolano (Ercolano) delicate inflorescences of lemon shades with white splashes.
California (California) exquisite cherry color large flowers with green stems.
Brindisi is a tall subspecies, growing 1-1.3 m. Large flowers not of a solid pink color.
Fangio (Fangio) tall lilies up to 1.5-1.6 m. With a deep dark red beetroot color all over the petal.
Lilies A-hybrids
The abbreviation stands for Asiatic Lilies

Tiger
Tiger lily (Lilium lancifolium "Citronella".) Or lanceolate. On the purest yellow background, splashes of orange-brown color are scattered, petals fancifully twisted outward.
Red Twin. Terry red lilies are not clouded by a different tone of a pure shade, with stamens a little darker in color. Blooms early in June - July.
Fata Morgana from a row of yellow lilies. Terry soft yellow multiple flowers interspersed with brown dots in the neck. Blooms in late June or early July.
Ceres. The Asian lily is hybrid with a beetroot-crimson color, which is shaded in a light tone to the edge of a double petal.
Elodie. Double pink lilies. The pink tone lightens to the edge to pallor. In the center is a point of languid tone.
Lilies O-hybrids
The abbreviation stands for Oriental or Oriental Lilies.
Siberia white lily. Highly frost-resistant variety with snow-white inflorescences, with a slightly greenish center.
Lily Carolyn Tensen Huge snow-white inflorescences with a touch of some waxiness, looking slightly to the side. The foliage is light green.
Lilies LO-hybrids
The abbreviation stands for Longiflorum Oriental
Triumphator (White Triumphator), snow-white flowers with a crimson gradient in the center of swirling petals.
Lancon (lilium lankon). With drooping inflorescences of a beautiful pink shade with a large blotch on all petals of burgundy dots.
Lilies T-hybrids

Royal
The abbreviation stands for Tubular Lilies
African Queen has strongly curled orange petals with darker spots on the outside. Dark emerald leaves.
Lily Royal Regale Album (Album) The flower is snow-white with a yellow core and richer in yellow stamens. They do not grow tall, only up to 1 meter.
Pink Perfection Smoky lilac-pink large tubular inflorescences.
Damson Pink flowers with an unexpected shade of fuchsia on tall peduncles.
Rare lilies
Black Beauty (lilium black beauty). Purple tall lily more than 1.5m tall. On the surface of each petal, burgundy dots are scattered.
Lily Henry (henryii). A multi-flowered lily with numerous small flowers (about 7 cm each), orange-apricot in color, with a brown speck. A short "beard" grows at the base of each petal.
Scarlet Delight. A rare beauty with burgundy flowers. A light green middle with a white edging comes out from each petal. The outer part of the petal is several tones lighter.
Dwarf lily
It also tolerates frost well, enchants with its miniature beauty and fragrant flowers.
Advice!
In order not to throw money down the drain, decide on the varieties that suit your region. For example, when choosing varieties of lilies for Siberia or for planting in the Urals, remember that Asian or LA hybrids will definitely be suitable, again with them at the base.
Lilies care and growing at home
Liliaceae include a wide variety of flowers, and you can probably choose the most suitable variety. But before deciding on a particular lily, you need to find out what exactly is needed to grow these flowers.
The first thing you need to know about is the variety and group to which your chosen plant belongs. From this will come the correct planting, growing and caring for the lily. Well, no less important is the onion, which should also be carefully selected.
How to plant lilies in spring video review:
How to choose bulbs
 When feeling the tubers, pay attention to the following:
When feeling the tubers, pay attention to the following:
- The onions should be firm, in no case soft or loose to the touch.
- Clean scales with no rot or mildew
- Developed roots about 4-5cm
- The nodule must have a certain weight, that is, it must not be dry and thinned
- The scales should not be thinned, they must fit snugly to the bulb
Lilies planted in spring may not produce inflorescences in the first year of their life.
The most suitable time to buy plants is August-September. Store purchased bulbs in the refrigerator in the spring. Remember to spray them to keep them dry while they wait to disembark.
Go through and take a good look at the tubers. If they are found sick or with any visible damage to the bulb, they should be removed. All the rest should be dipped in a weak solution of potassium permanganate and held in it for about 5-10 minutes, which will kill all harmful bacteria.
How to plant correctly
The main thing to remember is that the lily has been growing in a permanent place for a long time, so the choice of a place should be approached with all responsibility. You need a slightly elevated sunny place, but with protection from strong winds. It is preferable to plant on the southern sides of buildings or in front of perennial shrub-type plants, not trees. They create too much shading.
 In order for the plant to please you with its flowering, it is necessary to plant it correctly, observing some rules.
In order for the plant to please you with its flowering, it is necessary to plant it correctly, observing some rules.
- Remember, the larger the size of the planted tuber, the deeper the hole should be.
- If there are any rodent pests, shield the lilies with an iron net.
- In autumn, it is necessary to plant bulbs in deeper pits than in spring.
- Planting corms sideways will allow the plant to propagate faster.
- To avoid infection of the lily, sprinkle the ground around it with a small amount of ash or foundation.
 Depending on the species, there will also be an acidity that is needed for the selected lily. If your choice was stopped on American varieties, then they need acidic soil, an alkaline substrate is suitable for tubular. Other types of plants will feel great if the acidity of the soil is neutral.
Depending on the species, there will also be an acidity that is needed for the selected lily. If your choice was stopped on American varieties, then they need acidic soil, an alkaline substrate is suitable for tubular. Other types of plants will feel great if the acidity of the soil is neutral.
Fall-blooming lily species should be planted in March... Oriental and Asian plant varieties should be placed in the soil as soon as the snow melts. If your choice stopped at other types, then you can start planting them in the ground at the beginning of autumn, but do not forget to insulate them, protecting them from frost.
If you like Candidium, the Canadian and monotonous look, then you should not plant them in the spring, so this is the most inappropriate season for this procedure.
Based on the foregoing, it is worth concluding that the most suitable time for planting lilies in the garden is autumn. This will allow them to take root before the onset of the first frost, and also to get stronger by the beginning of the spring, constantly changing weather.
We plant in open ground

 You can determine the depth to which lilies should be planted by paying attention to its bulb. The fact is that the most suitable depth is the size of those bulbs, which is about 10-12 cm.Do not forget to take into account the quality of the soil, since it is worth planting the bulbs a little higher in heavy soil, while in soft light soil you need to slightly increase the depth pits.
You can determine the depth to which lilies should be planted by paying attention to its bulb. The fact is that the most suitable depth is the size of those bulbs, which is about 10-12 cm.Do not forget to take into account the quality of the soil, since it is worth planting the bulbs a little higher in heavy soil, while in soft light soil you need to slightly increase the depth pits.
LO- and TO- hybrids, which are based on oriental species, are very whimsical, therefore, when planting them, you should not dig a very deep hole, because germination will take away a lot of their strength and they will not be able to release flowers. The most suitable depth for a hole is about 7 cm. In autumn, these lilies should be well covered with dry foliage and a thin layer of soil. This will keep the area where the tuber hibernates dry.
Flowers planted in spring should be watered abundantly, but lilies planted in autumn should not be moistened.
How to care for lilies
 The first thing to consider is the correct watering of the plants. If summer and spring are dry, and there is too little snow in winter, then the lilies should be watered regularly. Under normal weather conditions, the flower is able to feed on the moisture that the tubers accumulated at the time of snow melting in the spring.
The first thing to consider is the correct watering of the plants. If summer and spring are dry, and there is too little snow in winter, then the lilies should be watered regularly. Under normal weather conditions, the flower is able to feed on the moisture that the tubers accumulated at the time of snow melting in the spring.- In the event that it becomes necessary to water the lily, then the water must be poured at the root.
- Be sure to loosen the soil and remove any weeds that appear around, as they take up all the nutrients.
- When cutting flowers, leave the leaves on the plant, which will allow it to accumulate nutrients necessary for the healthy life of the tuber in winter.
 Lilies planted in spring are rather weak, therefore, when they release the first flowers, they should be removed, which will allow them to grow better. Next year the plant will be stronger, which means that its flowers will be large, bright and beautiful.
Lilies planted in spring are rather weak, therefore, when they release the first flowers, they should be removed, which will allow them to grow better. Next year the plant will be stronger, which means that its flowers will be large, bright and beautiful.- As a rule, for about 4 years of their life, the flowers on the lily become smaller. In order for the plant to again begin to delight you with its inflorescences for 5 or 6 years, transplant it, not forgetting to divide the bulbs.
- Tall lilies need support.
- As soon as the flowering is completely completed and the shoot has dried up, it must be cut off, leaving a stump of about 15 cm above the ground.In late autumn, you have to carefully pull it out of the soil and cover the place where the tuber remained, thereby preparing it for wintering.
Do I need to fertilize lilies
It is imperative to feed the plant, no matter how fertile the soil is. For this, you can use both peat fertilizers and humus or rotted compost in a ratio of 1 bucket per 1 square meter. In the event that the land includes sandy impurities, then in order to improve its quality you will need phosphorus - potassium fertilizers. They must be used before planting the bulbs, using 100g of top dressing per square meter of soil.
How to propagate and transplant

- The easiest way is to divide the bulb. But it is very long, since it will take about several years to form a young large tuber. The bulbs are dug up and planted in the fall. After the bulbs have been dug up, they must be immediately placed in the area where they will grow in the future.
- The so-called babies that appear at the base of the shoot are used to reproduce almost all types of lilies. Remember, the deeper the bulb is planted, the more babies it will bring.

- The tubers have scales that are capable of forming bulbs. This method has its advantage, since only one scale can yield from 1 to 4 tubers. They are formed from 2 to 3 years. To propagate a lily in this way, the spring or autumn period is best suited. But you need to use only healthy scales from one third to half of the onion.
- In the axils of plants, the so-called air bulbs are formed, which are usually called bulbs. They usually appear after the lily has stopped blooming. As soon as their formation is complete, the bulbs will fall to the ground. Collect them and sow them in open ground or in a special container. But before you decide to breed lilies this way, make sure that the variety you choose is suitable for this purpose.
Pests and diseases
There are the following diseases and pests that can harm these plants:
- Lily beetle.

The leaves and buds of the plant can be affected not only by adults, but also by the larvae. In order to get rid of them, you need to manually remove them from the leaves. Treatment of lilies with karbofos, actelik or phytoverm will also be effective.
- Flies and aphids.
Fitoverm, Karbofos or Aktara will help you rid your flowers of these pests.
- Wireworm, Medvedka and May Beetles.
Preparations called grizzly, thunder and fly eater will save the plant from unwanted guests.
- Fusarium or as it is also called onion rot.

It is the most common lily disease. It can be easily identified as brown spots form on the leaves and flowers. Occurs due to abundant watering or temperature drops. Loosening the earth and spraying with copper-containing preparations will allow you to save the flower from such an ailment.
- Bacterial rot.
This disease occurs in the spring and is characterized by yellow spots on the foliage and stem. As a result of this attack, the leaves begin to rot and fall off. The reason may be an excess of nitrogenous fertilizer and moisture. To heal the plant, stop fertilizing it and water it much less often.
- Root rot.

If the upper part of the flowers turned yellow, then the plant was probably attacked by this ailment. Brown spots can be found on the roots. The reason for the occurrence can be both the purchase of a bad bulb and unfriendly soil. All you need to do is cut off the affected areas and cover them with brilliant green.
- Rust.
A disease that will attack the lily foliage. Small orange specks appear on the leaves, causing them to dry out. This disease is transmitted by purchased infected bulbs. In order to cure the plant, you need to process it using a 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid. Fungicides are also suitable as a drug.
How to properly cover lilies before the onset of cold weather
 Those plants that are planted slightly deep should be covered before the onset of the first frost. Flowers planted in deeper holes can be covered after the ground is slightly frozen.
Those plants that are planted slightly deep should be covered before the onset of the first frost. Flowers planted in deeper holes can be covered after the ground is slightly frozen.
In the autumn period, spruce branches and dry foliage are used to shelter lilies, which allows them not to freeze in winter and wake up in a timely manner in spring. Sheltered plants should not be opened in early spring after the onset of the first mild frosts. A little later, they will delight you with their active growth.
In order for the flowers not to start to rot in winter, they must be covered with a rainy autumn film, which will keep the site dry.
If there are late frosts in your region, which occur both in May and early June, then cover the place where the lily is planted with burlap or special covering material.
Important!
In our climate, Asian varieties, as well as LA hybrids, do not require any shelter before the onset of winter. But this cannot be said about oriental varieties and their varieties, since winter frosts can harm them.
Lilies care in spring after winter
The main care is to remove the cover, if you applied it - on time. Regularly weed out and loosen the soil around the sprouts that have appeared, you do not need to do this earlier, because of the risk, it is easy to cut off the beginning sprout. And then take care of it as described above. By regulating watering and fertilization.
Combination with other plants in landscape design

 Tall lilies are very often planted in separate islands in the same tone, or vice versa, mixing variegated varieties. Miniature subspecies will be favorably planted in the form of a low-growing curb.
Tall lilies are very often planted in separate islands in the same tone, or vice versa, mixing variegated varieties. Miniature subspecies will be favorably planted in the form of a low-growing curb.
A good solution would be to plant undersized violets or marigolds next to chic peonies or verbena, which will cover the roots of the lilies and help retain the necessary moisture, and after the lily has faded, they will cover the ugly wilting stems.
In the background, a good solution would be to plant astilba or evergreen juniper, fern or variegated hosta. All of these plants need partial shade that a growing lily can provide.
No one will dispute the opinion that any lily and any rose, for example a floribunda rose, will look great together in plantings.
All varieties of lilies have their own individual characteristics, both in decorative and climatic terms, and they just need to be taken into account when placing them in the landscape.After all, they differ not only in color, but also in height, flowering time and period, care and planting features.
OT hybrids of Santarello lily in the garden video:
 Lily is a flower of amazing, refined beauty. Lilies are very popular with gardeners for their unpretentiousness, bright color and large flowers. There are almost 80 varieties of lilies, from which breeders have bred many varieties. The most popular varieties grown in the Urals are described in THIS article. Lilies can become a real decoration of the garden only if they are provided with the necessary conditions for growth, therefore, planting and caring for lilies in the open field should be carried out according to certain rules.
Lily is a flower of amazing, refined beauty. Lilies are very popular with gardeners for their unpretentiousness, bright color and large flowers. There are almost 80 varieties of lilies, from which breeders have bred many varieties. The most popular varieties grown in the Urals are described in THIS article. Lilies can become a real decoration of the garden only if they are provided with the necessary conditions for growth, therefore, planting and caring for lilies in the open field should be carried out according to certain rules.
Planting lilies in open ground
 Almost all lilies love to grow in full sun, but can tolerate light shade. It is better if the lower part of the bush is in the shade, and the crown with flowers is in the sun. For this, lilies are planted between low perennials or lilies are planted with annuals. Better time to plant lilies in the Urals - mid-September. In cool weather and wet ground, lilies will root well and prepare for winter, and will begin to grow at full strength in the spring. You can plant lily bulbs in spring, but then they may not bloom in the first year, or the flowers will be small. In the spring for planting, you need to choose the time after the frost retreat (for the Urals - mid-May).
Almost all lilies love to grow in full sun, but can tolerate light shade. It is better if the lower part of the bush is in the shade, and the crown with flowers is in the sun. For this, lilies are planted between low perennials or lilies are planted with annuals. Better time to plant lilies in the Urals - mid-September. In cool weather and wet ground, lilies will root well and prepare for winter, and will begin to grow at full strength in the spring. You can plant lily bulbs in spring, but then they may not bloom in the first year, or the flowers will be small. In the spring for planting, you need to choose the time after the frost retreat (for the Urals - mid-May).
Choosing and preparing a place for planting lilies
Lily beds are prepared for many years, so you need to immediately choose the right place. Drafts, lowlands, shade, close groundwater - all this must be excluded when planting lilies. The ideal place is elevated sunny warm corners. For a lily to feel good, you need not only a sunny place, but also protection from the wind. You can make a flower bed on the south side of the house or garden house, or plant lilies in front of perennial ornamental shrubs.
The soil is well dug before planting, weeds are removed. Many lily species prefer neutral soils. Also, the land for planting should be light, airy and nutritious. It is good to add humus when digging, be sure to rotted. Mineral fertilizers can be successfully replaced by ash. The addition of fertilizers will help plants grow successfully for several years and delight you with flowering. Do not add fresh manure when planting lilies and other bulbs.
Planting lily bulbs in the ground
Before planting, you need to prepare planting material:
✿ Go through and carefully examine all the bulbs. Remove the sick and injured.
✿ Hold for 5-10 minutes in a weak solution of potassium permanganate. This will rid the bulbs of harmful bacteria.
The planting depth is based on the depth of the height of the three bulbs. This is about 10-12 cm. But for heavy soils, you need to slightly reduce the planting depth, and for light, sandy soils, increase.
It is better not to deepen the capricious LO-, OT-hybrids based on eastern ones when planting. So they spend a lot of energy in the spring to break through to the light. And then there is little strength left for flowering. Better to plant them at a depth of 6-7 cm and cover well in the fall. You can cover the bed in the fall with oilcloth so that the wintering site is dry. When dry with sufficient (20-25 cm) cover with spruce branches or leaves, the most whimsical types of lilies grow and bloom well.
When planting in spring, the soil must be shed well. It is not worth watering in autumn, but you need to cover the planting site with leaves for better wintering.
Lilies - outdoor care
Knowing and observing the basic rules for caring for lilies, you will achieve abundant flowering for many years:
✿ In a dry period, with dry spring and little snowy winter, you need to water the lilies, and in other cases, the lilies have enough moisture that the bulbs have accumulated in the spring, after the snow melts.
✿ If watering is necessary, water at the root.
✿ Watch out for weeds, weed and loosen crops in time.
✿ When cutting flowers, you should try to leave more leaves - they help accumulate nutrients for the bulbs for a successful winter.
✿ For spring planting in the first summer, the flowers are still weak, so it is better to remove the flowers for better growth. Fortified bulbs for the second year will delight you with all their beauty.
✿ After the fourth year, usually the flowers become smaller. For 5-6 years, lilies need to be transplanted and the bulbs need to be divided.
✿ For high peduncles, you need to make supports and tie up lilies.
✿ After flowering and complete drying of the stem and leaves, the lilies are cut off, leaving a stump of 15 cm above the ground. In late autumn, in front of the shelter, they also remove it, carefully pulling it out of the ground.
Reproduction of lilies
Lilies reproduce in different ways - the main one: dividing the bulbs. You can also grow new plants from scales and grow from small onion bulbs that form on the stem.
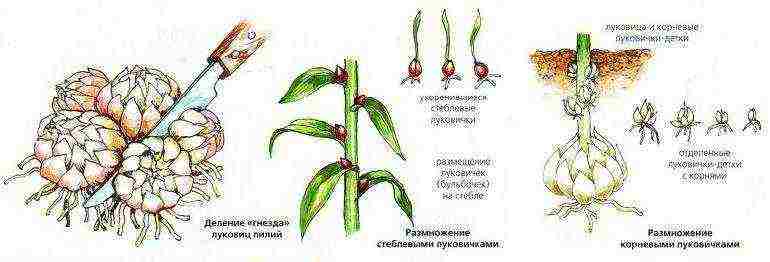 |
The division of the bulbs is carried out 5 years after planting. If lilies are grown in one place for a long time, then the bulbs become smaller, oppress each other and the flowering becomes not the same as the first years. The onions are separated from each other by hand or with a knife. Each is seated separately. They look after young plantings of lilies. Water, weed, loosen. Under favorable conditions, new bulbs bloom the next year.
Some varieties of lilies develop onion babies on a stem underground. They are separated and planted for growing in loose fertile soil.
In many lilies, bulbous babies are formed in the axils of the leaves. They can also be planted to produce full-fledged bulbs. When they are planted in spring and autumn, full-fledged bulbs will already grow.
When replanting old plantings, prepare a place for future plantings in advance. After digging up, do not expose the bulbs to the sun to prevent them from drying out. Try to plant right away. You can cover the onions with a sun cloth with a short wait. If it is not possible to immediately plant lilies, then wrap them in wet newspapers or wet moss and put them in a paper bag on the lower shelf of the refrigerator. This will keep the bulbs fresh for several days.
Lilies - pests and diseases
 The main pests of lilies are the onion root mite, onion leaf beetle, and purple scoop. The main methods of control are prevention. It is necessary to weed well the plantings from weeds, remove the remnants of the grass so that the pests do not have favorable conditions for reproduction. You need to collect beetles when they appear. Prevention of diseases and root mites is by dressing the bulbs in manganese or karbofos (keep 5 g per liter of water for 30 minutes). And warming up in hot water (so that the hand could endure a little) for 5 minutes. The bulbs are processed before planting.
The main pests of lilies are the onion root mite, onion leaf beetle, and purple scoop. The main methods of control are prevention. It is necessary to weed well the plantings from weeds, remove the remnants of the grass so that the pests do not have favorable conditions for reproduction. You need to collect beetles when they appear. Prevention of diseases and root mites is by dressing the bulbs in manganese or karbofos (keep 5 g per liter of water for 30 minutes). And warming up in hot water (so that the hand could endure a little) for 5 minutes. The bulbs are processed before planting.
With improper care, thickened plantings, lilies can be affected by fungal diseases: fusarium, rust, gray rot. The bulbs begin to rot, and the leaves turn yellow and wither. Prevention and treatment consists of spraying with fungicides.
Viral diseases are rare and incurable. Such plants are dug up and burned.
Shelter of lilies for the winter
 Lilies, planted shallow, are covered until frost. The rest can be covered after the ground freezes by 3-4 cm. By covering the lilies in autumn with leaves or spruce branches, we will not only save them from freezing in winter, but also help to wake up later in the spring so as not to get frozen. If you cover the lilies already on slightly frozen ground and do not open early in the spring, then in the spring they will later start growing. Lilies should overwinter in dry ground so as not to rot. To do this, during a rainy autumn, cover the area with lilies with oilcloth so that it is dry.
Lilies, planted shallow, are covered until frost. The rest can be covered after the ground freezes by 3-4 cm. By covering the lilies in autumn with leaves or spruce branches, we will not only save them from freezing in winter, but also help to wake up later in the spring so as not to get frozen. If you cover the lilies already on slightly frozen ground and do not open early in the spring, then in the spring they will later start growing. Lilies should overwinter in dry ground so as not to rot. To do this, during a rainy autumn, cover the area with lilies with oilcloth so that it is dry.
From late frosts, which may be in May-June, you can hide seedlings under covering material or bags.
Asian lilies and LA hybrids do not need shelter and winter well in our climate, but eastern lilies and their hybrids need warming for the winter.
WHERE TO BUY LILY BULBS
The Scientific and Production Association "Sady Rossii" has been introducing the latest achievements in the selection of vegetable, fruit, berry and ornamental crops into the wide practice of amateur gardening for 30 years. In the work of the association, the most modern technologies are used, a unique laboratory for microclonal reproduction of plants has been created. The main tasks of NPO Sady Rossii is to provide gardeners with high-quality planting material for popular varieties and novelties of world selection. Delivery of planting material (seeds, onions, seedlings) is carried out by Russian post.
We are waiting for you for shopping: NPO Sady Rossii
Lilies - Outdoor Planting and Care

Lilies - planting and care in the open field
Lilies are very loved by flower growers of all countries, but they are especially revered in France, it is not for nothing that the lily is a symbol of the royal power of this country. For one variety of lilies, royal status is official - the royal lily (L. regale). It originates from China and grows in the valley of a mountain river, has tubular flowers up to 15 cm in length and is famous for a very strong aroma.
Growing lilies in the garden has its own subtleties that you need to know if you want this flower to delight you with its beauty.
Different growers use their own tricks in growing lilies. But there are general principles that are best to follow if you want to achieve an excellent result.
How to choose lily bulbs for planting
When choosing bulbs in the market and in the store, make sure that the bulbs are healthy and large. Do not take lily bulbs with overdried scales.
If you bought your bulbs outside the planting season, it is important to know how to keep them safe and sound.
If the bulbs were bought in the spring, when it is too early to plant them in the ground, then you need to store them in the refrigerator tray. If your lily is in the package, but has already begun to sprout, then just cut a hole for the unhindered growth of the plant, otherwise the stem will be deformed and this will affect its further outlines.
When buying lilies in the fall, you can keep them in a dark room before planting. In the fall, you need to have time to plant the bulbs before mid-October.
Planting lily bulbs in the ground
The place for planting must be chosen carefully, since lilies do not like to be disturbed for 4 years. And then you will still need to plant them. It is best to plant lilies of the same variety in groups - this will make your flower bed look more attractive.
You should not buy one bulb of different varieties, it is best to buy at least three of the same varieties - the perception of flowers in the garden by the group will be more attractive.
Make a hole about 40 cm in size and 20 cm deep, on the bottom pour a layer of fertile soil about 5 cm. Put three onions at a distance of 20-25 cm from each other and cover with earth. As a rule, lilies are planted in the ground to a depth of two bulb heights.
Fertilizer for lilies
When planting lilies, mineral fertilizers should be applied, to which these flowers are very responsive. You can simply sprinkle the planting site with granular mineral fertilizers for bulbous. It is best to fertilize lilies at least twice a year - in the spring, when the sprouts are just beginning to break through, and in the fall, before wintering.
Do not add organic matter under the lilies! This can provoke a number of diseases, which, of course, we do not want.
It is best to choose a place for a flower bed with lilies in partial shade, so that the sun shines before lunch, and after lunch there is a shaded coolness. Plant the lily so that it is in the sun and its leg in the shade.
To do this, under the lilies, you can plant low plants, ground cover or medium-sized. Lilies with hosts that will cover the legs of lilies with their lush leaves will look very beautiful. It can also be astilbe, daisies, many short annuals.
In order for the lily to bloom well, it should have enough sunlight. Lilies do not need frequent watering, but in the summer heat, when there is no rain, they should be watered at least 2 days later.After the end of flowering, the plant should not be watered.
If you decide to cut lilies for a bouquet, then know that you should leave most of the stem, otherwise it will be difficult for the bulbs to develop.
In autumn
In October, cut the lily stems to a height of 12-15 cm and leave until spring. OT hybrids, LA hybrids, Asian hybrids are distinguished by very good frost resistance. More capricious - varieties of Oriental hybrids.
Follow these simple rules for planting and caring for lilies and they will delight you with their wonderful flowering!
This entry was posted in Flowers in the country. Bookmark the permalink.
Garden lilies: distinctive features, planting and care
Garden lilies have been popular among gardeners for many years.
And if a few years ago the choice of varieties was rather limited - in flower beds, the most common are Daurian and tiger lilies of orange color, now the variety of varieties of garden lilies is amazing.
It is difficult to say which lilies in the garden look more chic: snow-white royal, colorful oriental hybrids or graceful curly ones.
Introduction
Garden lilies have been popular among gardeners for many years.
And if a few years ago the choice of varieties was rather limited - in flower beds, the most common are Daurian and tiger lilies of orange color, now the variety of varieties of garden lilies is amazing.
It is difficult to say which lilies in the garden look more chic: snow-white royal, colorful oriental hybrids or graceful curly ones.
Different varieties are grown in separate groups or planted on one flower bed according to a certain pattern - such flower beds look very impressive!
Garden lily flowers are good because they feel great both in areas open to the sun and in the shade. The only thing that must be taken care of is that the soil is permeable, because with excessive moisture in the soil, these delicate flowers are affected by gray rot. Under natural conditions, wild lilies grow only in well-drained soil.
Garden lily flowers are good because they feel great both in areas open to the sun and in the shade.
Caring for lilies in the garden during the summer months consists in regularly loosening the earth, weeding weeds, protecting against diseases and pests, timely watering and feeding.
Autumn care is aimed at carefully preparing the plants for winter: after the lilies have faded, the dried foliage is cut off, and the plants themselves are covered for the winter or dug up and stored in bulbs in a cool room until spring.
Let's take a closer look at how best to place lilies in the garden, and how to care for garden lilies throughout the season.
about caring for garden lilies
Variants of using lilies in the garden
Whatever garden design you have in mind, lilies will always be in place, because you can make a low border from compact varieties of lilies, plant high varieties in the background of a flower garden or in the center of a multi-level flower bed.
A huge variety of shades of lilies (from pale pink to dark red, from golden to fiery red, from snow-white to almost black) allows you to beautifully combine flowers in a flower bed.
And if you skillfully choose varieties with different flowering periods, lilies will decorate your garden with their lovely flowers from the end of May until the very autumn frosts.
In flower beds of the correct geometric shape, garden lilies are usually not used; they are best suited for mixborders in combination with annuals and perennials. Garden lilies bloom especially well next to roses, for which such a neighborhood also only benefits. Many small varieties look great in containers, flowerpots and tubs exposed to fresh air during the summer.
In flower beds of the correct geometric shape, garden lilies are usually not used.
Despite the fact that the lily tolerates shade well, it is undesirable to plant it under trees or in deep shade from buildings - the flowers will be uncomfortable, hungry and dry in such conditions.
Planting garden lilies is recommended between low bushes, because this is how plants feel better in winter cold.
In the summer, in order to prevent the bulbs from overheating, ground cover plants can be planted under the lilies.
Features of planting garden lilies
In plants such as garden lily, planting necessarily involves preliminary preparation of the soil. Moreover, the composition of the soil for different types of lilies can vary significantly.
So, Daurian and tiger lilies normally tolerate acidified soil, curly, monochromatic, white and bulbous lilies are more comfortable to grow on slightly alkaline soil, and for the vast majority of varieties, neutral soil is preferable.
In any case, sandy or clay soil is not suitable for garden lilies - the soil must be loose, nutritious and drained.
If your land is heavy on your site, add sand, a little peat and humus to it 20 days before planting the lilies. Potash, nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizers are also applied for plowing the soil.
Everything is carefully dug up, leveled, watered and so left until the lilies are planted.
Sandy or clay soil is not suitable for garden lilies
The suitable timing and depth of planting of the bulbs is determined by the variety of lilies, as well as by the characteristics of the soil. Moreover, it is advisable to plant garden lilies in the fall, then the bulbs will have time to take root well. Having planted the bulbs in the pits using a one-line, two-line or three-line method, the beds are watered, mulched and left for the winter.
Garden lilies: care, transplant, preparation for wintering
In addition to the standard loosening of the soil, removing weeds and watering, you will need to feed the plants three times: with urea and complex fertilizer during the emergence of shoots, then potassium sulfate and superphosphate during budding, a solution of liquid mullein and nitrophoska during the flowering period.
Flowers are watered only at the root, since waterlogging of the leaves can lead to the appearance of gray rot
Caring for garden lilies has its own nuances:
- flowers are watered only at the root, since waterlogging of the leaves can lead to the appearance of gray rot;
- overheating and drying out of the top layer of the soil, in which the air roots of the garden lily are located, for this, the earth is mulched with peat or humus;
- after heavy rains, coniferous litter is added to the lilies in order to avoid exposing the bulbs;
- the buds are cut off from the bush grown to obtain planting material during the summer so that all the force is directed to the bulbs;
- flowers should be cut in the morning or in the evening, while it is cool; for normal growth of the bulbs, at least a third of the stem should be left when cutting.
about growing lilies
It is not recommended to grow garden lilies for a long time in the same place - they need to be transplanted about once every five years (the timing is different for different species). Thanks to transplantation, lilies are less likely to get sick, bloom more luxuriantly and feel better. You can familiarize yourself with the features of lily transplantation in the corresponding article.
As for the wintering of garden lilies, it all depends on the climate in your area and on the variety of lilies. For example, Daurian lily, Martagon, Asian hybrids, Russian frosts calmly endure without shelter.
It is recommended to cover the garden royal lilies.
Gentle American, tubular and oriental hybrids are best dug out of the ground in the fall and sent to the bottom shelf of the refrigerator for wintering, so that they can be planted in the ground with the beginning of the new season.
Lilies - planting and care in the open field

Lily is a beautiful and graceful flower that attracts with its bright colors and wonderful aroma. Many flower growers appreciate it and be sure to plant it in their summer cottage.
But not everyone knows that lilies, their planting and care in the open field require some knowledge, otherwise there is a high probability that the bulbs will simply not be accepted.
How to properly care for a plant? We will learn the answers to these questions from this article.
Lilies - planting and care in the open field
How to choose lily bulbs?
First of all, we note that the lily is a rather capricious flower that requires the creation of certain conditions for growing. But if you get bad planting material, you should not expect a good result.
Experts recommend giving preference to reputable markets or shops that sell quality bulbs grown and hardened in greenhouses.
Please note that the lily bulb itself should be large and fleshy, and the scales should not be overdried.
There are several opinions about growing times. Some growers insist that planting in the spring is considered the most successful, and some talk about autumn.
How to figure it out? The fact is that lily bulbs will sprout in spring and autumn, but if you plant them before winter, in summer you will definitely enjoy beautiful, bright, and most importantly healthy plants. The root system of such bulbs has time to develop well, get stronger and endure the March cold snaps.
The lily bulb will harden perfectly in winter and will be ready for any, even unpredictable conditions. Spring planting stock is often sick and rarely survives.
Planting lilies is best done in the fall.
If you purchased wrapped lily bulbs, immediately refrigerate them in a dark place to prevent sprouting.
Having decided to grow lilies in your summer cottage, you should know that each variety differs in the flowering period and care features.
For example, white lilies will bloom only if they are planted in mid-October, but Eastern or Asian hybrids can take place even in early spring.
Lilies - planting and care
The flower can grow without problems in one place for several years. Frequent replanting will certainly slow down its growth, so it is not advisable to move the plant from one place to another.
We have already determined that the most optimal and favorable time for planting lilies is autumn, but first, the planting material should be treated with special substances.
To do this, you need a foundationol solution, in which you need to leave the bulbs for about an hour. Planting a lily takes place in the following stages:
- To begin with, we pull out a small hole, 50 cm in diameter, 30 cm deep.
- A small drainage system is laid at the bottom, which will prevent rotting of the root system.
- A large layer of earth is poured on top and bulbs are laid out.
- The distance between the planting material should not be less than 5 cm.
- After the bulbs, the lilies are covered with earth and tamped.
Do not forget to put marks so that you do not forget about the planted flowers in the spring. Also important are mineral fertilizers, which are applied twice a year - in autumn and spring. In the fall, you can use a complex of mineral additives for flowers.
Important! It is forbidden to use organic fertilizers for lilies! It can cause a paradise of diseases.
The planting process is over. The plant does not need additional watering until spring.
Lily care rules:
- Watering. At the beginning of ripening, the flower really needs a lot of water, so regular watering should be organized.
- Fertilizers. Nutrition needs to be brought in already after the flower has faded.
- Spraying. Lily rarely suffers from pest attacks, but it is still necessary to process the plant several times.
As you can see, planting lilies and caring for them in the open field does not require much time and effort. We hope that our tips will help you grow beautiful, bright and healthy lilies on your site.
Lily - planting in the fall in open ground: how and when to plant lilies, care in winter

When asked when it is better to plant lily bulbs in the ground, there are many reasoned answers.On one site, readers are trying to convince that the best time for planting lilies is early spring, another source suggests taking their time and waiting until May. The third claims that the autumn planting of lilies is more reliable than the spring one.
And from our point of view, this is an absolutely fair statement. During the fall, the bulbs have time to take root, hibernate under cover, and in the spring they grow quickly and bloom earlier than the lilies planted in the ground in the spring. It remains only to decide when to plant lilies before winter and how to do it correctly.
In this article, we will tell you about when to transplant lilies in the fall to a new place.
Lilies are planted in the fall with such a margin of time so that before the frost begins, their root system has time to develop and get stronger, then the sprouts that appear in the spring will withstand the spring frosts without any problems. First, the bulbs of white lilies are planted - they have the shortest dormant period.
After the white ones, you can start planting the Caucasian and North American species of lilies, and in the last turn, plant tubular, oriental and Asian hybrids, as well as tiger and Tibetan lilies, which, in fact, are best planted in early spring.
When exactly to plant lilies in the fall in open ground, in what month is it best to plant lilies? The timing of planting lilies in the ground primarily depends on the climatic and weather conditions of the region.
The main requirement of agricultural technology is to plant bulbs when the air temperature drops to 10 ºC and no longer rises, but in different regions this happens at different times.
How to plant tulips in autumn and care after planting
When to plant lilies in the fall in the suburbs
For example, when asked when to plant lilies in the fall in the Moscow region, we can answer that in the middle lane it is better to plant bulbs in the ground from the beginning of October to the beginning of November, so amateur gardeners of the central regions of Russia and the Leningrad region can start preparing the site already in mid-September. When to plant lilies before winter in Ukraine, Moldova and southern regions of Russia? In warm climates, planting bulbs is carried out until mid-November.
When to plant lilies in the fall in the Urals
When to plant lilies in the fall in the Urals? In the Ural climate, planting of lilies is possible from early September to early October. But if suddenly a cold snap begins immediately after planting, you need to cover the area with bulbs for the winter.
When to plant lilies in autumn in Siberia
You should know that only domestic varieties adapted to the climate of the area are planted in the fall in the ground, and Dutch planting material should be planted in the spring. Moreover, when it comes to planting flowers in the harsh Siberian climate. When to plant lilies in autumn in Siberia? Planting lilies in August or September in the Siberian climate will be absolutely justified.
Planting lilies in the ground before winter
Soil for lilies
The choice of the site on which you will grow lilies must be taken responsibly, because in this place they will grow from 3 to 5 years. The site should be sheltered from the wind, well warmed up, sunny, but light shading is acceptable.
Under natural conditions, lilies usually grow in neutral loose soil, covered with a layer of organic matter, therefore, in the garden, it is necessary to provide them with conditions close to natural. Flowers need soil that is well-drained, sandy loam or loamy - in heavy soils, lilies do not develop well, and stagnant water can lead to rotting of the bulbs.
Some types of lilies tolerate a small amount of lime in the soil, while others are harmful.
Before planting the lilies, the site should be dug up to a depth of 40 cm. A bucket of sand and peat is added to the heavy soil for digging for 1 m², and only peat is added to the light soil.
It is also necessary to add 5-10 kg of humus or compost, 100 g of superphosphate and 50 g of potassium sulfate for each square meter of flower beds.
If you are going to grow white lily, martagon or tubular hybrids in acidic soil, add wood ash, limestone or chalk to the soil at the rate of 200-500 g per m².
How deep to plant lilies
The planting depth of lilies depends not only on the composition of the soil and the size of the bulbs, but also on the type of lily. For example, stem-root lilies should be planted to a depth of at least 25 cm, lilies with roots - to a depth of 12-15 cm.On average, bulb varieties are divided into:
- – undersized: large bulbs of these varieties are planted to a depth of 10-12 cm, small ones - by 7-8 cm, the distance between bulbs in a row is observed from 15 to 20 cm;
- – medium-sized: large bulbs are buried by 12-15 cm, small ones - by 10 cm, the distance between bulbs in a row is 20-25 cm;
- – tall: large bulbs are immersed in the soil by 15-20 cm, small ones - by 12 cm, the gap between plants is 25-30 cm.
It is important to know that a bulb deeply buried in the ground will germinate longer, but subsequently it will give more babies than with a shallower planting.
How to plant bulbs in the fall
Coarse sand is poured onto the bottom of the dug holes, an onion is placed at the required depth, its roots are straightened, sand is poured around it from all sides, and soil is on top.
The surface of the plot with the planted bulbs is compacted and watered abundantly. A flower bed with oriental, Asian and LA hybrids is mulched with a layer of peat or sawdust 5 cm thick, thus increasing the acidity of the soil.
The planting of the lily marchagon, snow-white and tubular hybrids is mulched with humus with wood ash.
We are often asked how beautifully to plant lilies on the site.
Given the limited area, it is advisable to place lilies in group plantings, growing several lilies of the same variety side by side - if you plant bulbs of different varieties next to each other, they will grow over time, and it will be difficult to separate one variety from another with a mandatory transplant.
Tall lilies are very effective as a background strip along the fence. In mixborders, species and varieties of lilies are planted, which bloom at different times, so the flower bed does not lose its attractiveness from early summer to autumn.
A flower bed with lilies growing literally from a green carpet looks very impressive, with which ground cover or undersized plants cover the soil - sedum, saxifrage, violets or daisies. In addition to the decorative effect, such an arrangement of plants on the site creates protection for lily stems and soil from overheating.
Lily care after planting
Lily care in autumn outdoors
Lilies in the fall will not require much attention from you. If you have applied all the necessary fertilizers before planting in the ground, there is no need to make additional fertilizing.
There is still nothing to treat against pests and diseases - seedlings will appear only in spring. You will have to water the lilies, but only if the autumn is abnormally dry, and remove weeds from the site.
Towards the end of autumn, you need to prepare a site with lilies for wintering.
Lily care in winter
The condition of lilies in the cold season depends on their variety and the region in which they are grown. Under a layer of snow 10 cm thick, lilies feel great in the ground in winter, but if there is no snow cover yet, and the frosts are already cracking, you need to cover the area with dry peat, pine needles or fallen leaves.
Needles are preferable to other mulching materials, since they do not allow slugs to get under the cover, which will begin to destroy lily shoots in the spring. But keep in mind that the mulch needs to be removed on time - as the snow melts.
If you remove the mulch too early, the quickly emerging lily sprouts can destroy the frost, and if it is too late, the seedlings that have not received the necessary lighting due to the coverage will be thin and weak.
Transplanting lilies in the fall to another place
Lilies are transplanted once every 4-5 years.If you do this less often, the bulbs form nests - they are heavily overgrown with children who are cramped and lacking in nutrition. Asian and LA hybrids are planted once every three years. When to replant lilies - in spring or autumn? Lilies are transplanted after the end of the growing season, after waiting a month for the bulbs to recover after flowering.
In the north of Russia, the best time to divide the bulbs and transplant them to a new place is early autumn - late August and early September. In the middle lane, it is better to do this in mid-autumn - all September and early October, in the south of Russia, in Ukraine and Moldova - in October-November. Actually, the timing of dividing the bulbs and transplanting them to a new place coincide with the timing of the primary autumn planting of lilies.
Lily bulbs are dug out of the ground, divided, processed, stored until the right moment, and then planted in the ground in the way we have already described.
How to store lilies before planting in the fall
After flowering, remove the seed pods from the lilies, but do not cut the leaves and stems - they continue to feed the bulb and are still needed by the plant for photosynthesis.
When it is time to dig up and transplant the lily, cut off its ground part and remove the bulb with children from the ground, clean it from soil, inspect for mechanical damage, insect gnawing, rotten roots, dry scales and other defects, rinse under running water, carefully separate those children who are ready to leave, place the planting material for half an hour in a 1% solution of Karbofos or in a strong solution of potassium permanganate, then dry it in the shade and plant it in the ground in a new place or put it in storage.
Where and how best to store lily bulbs? Put a layer of peat in a plastic bag or box, put a layer of onions on it, cover it with a layer of peat, on which again put a layer of onions, the last layer in the container should be made of peat. Now consider the options for storing containers with bulbs. The basic requirements for storing lilies are as follows:
- - the storage should not be too dry so that the bulbs do not dehydrate and shrivel;
- - it is also impossible to store bulbs in a room with high humidity - bulbs can become moldy and rot;
- - the temperature of the content should be such that the bulbs do not freeze and at the same time do not start growing;
- - there must be good ventilation in the storage, otherwise there may be a risk of damage to the planting material by rot or mold.
Based on these recommendations, you can put the lily bulbs in a plastic bag filled with peat and place them in the vegetable drawer of the refrigerator at a stable temperature (0 to 5 ºC), which allows the bulbs to remain dormant. But the disadvantage of a refrigerator as a storage is that fruits can be stored there simultaneously with the bulbs, which release ethylene into the air, which makes it difficult for lily bulbs to breathe.
You can put the bulbs in the cellar or basement until spring, if there is a suitable temperature and humidity for them.
Or place the planting material in cardboard boxes, heat chambers or other containers with good thermal insulation and keep them on a balcony, loggia or garage.
Just do not forget that in a room with large windows on sunny days the temperature even in winter rises to the "plus" mark, from which the lilies can sprout.
A detailed article on growing lilies in the garden
It is advisable to store the bulbs so that in the middle of winter you can check several times in what condition they are.
If you find dry roots or scales on them, spray the bulbs with water, and if you find mold, rotten roots or areas, place the planting material for half an hour in a potassium permanganate solution, dry it and put it in storage in another place where the air humidity is not so high. ...
Correct planting and care of lilies outdoors
Bouquets of blooming lilies leave no one indifferent.Delicate and refined, they fascinate with their beauty and make you want to try to grow them yourself. Having learned about the main features of planting and the nuances of care, growing lilies in the open field will not cause any particular difficulties.
How to grow lilies outdoors
When growing lilies in the open field, it is necessary to take into account the characteristics of the variety and their ability to grow in a given region.
Varieties, their advantages and disadvantages
The most common varieties for cultivation in garden plots are the following:
Asian
The most popular and favorite among flower growers lilies with increased winter hardiness, unpretentious, disease-resistant.
These hybrids varied in shape and color of flowers... Having picked up varieties with different flowering periods, you can admire the luxurious flowers from the end of June to the whole of July.
Plants can grow in any soil, tolerate light shading, reproduce well. The disadvantage of hybrids can be considered lack of flavor.
Asiatic lilies
Variety Candidum
Plants with white and yellow tubular flowers. Flowers have a strong scent... The disadvantage of this hybrid is susceptibility to fungal diseases.
Variety Candidum
Curly
Lilies with drooping heads. They have good winter hardiness, tall, not demanding of light, grow on any soil and at the same time are unusually gentle and graceful.
Curly lily
Oriental hybrids (oriental)
Fascinate with their beauty have the largest flowers and strong aroma... Luxurious flower petals often have wavy edges and are varied in color.
Plants are demanding on growing conditions: they grow only in places protected from wind and sunny places, are highly susceptible to fungal and viral diseases, they winter poorly in open ground (they do not tolerate frost), therefore they are suitable for cultivation in the southern regions.
In the conditions of the middle lane, you need to dig it up for the winter or warm it well. Reproduction is very difficult to reproduce.
Oriental hybrids (oriental)
The latest innovations from breeders
LA hybrids - are distinguished by increased resistance to frost, grow in Siberia, the Urals, the Far East. They bloom first among lilies, are unpretentious, easily multiply.
LA hybrids
OT hybrids - not demanding plants that winter well in the open field, have large fragrant flowers up to 25 cm in diameter.
OT hybrids
When to plant a flower in the country or in the garden: in autumn or spring?
It is best to plant plants at the end of August and September., in the southern regions, planting can be carried out in October, the plants are dormant during this period.
They tolerate well the violation of the integrity of the root system; in the cool and humid autumn period, the bulbs take root well. In the spring, they immediately start growing and drive out the flowering bud.
Autumn planting of lilies:
Oriental and late-flowering varieties (OT-hybrids, Tubular, etc.) are planted only in spring, in the autumn they are forming a bulb.
If flowers are planted in spring, then they do this as soon as the soil has thawed and warmed up, but the heat has not yet begun.
When planting in spring, an unrooted plant spends energy on forcing a peduncle, flowering. By the fall, such a bulb is severely depleted and may die without enduring the winter frosts.
Bulbs purchased in spring are mostly sold with sprouts hatching., since the dormant period ended and she started to grow. These shoots often break during transportation, and the planted plants may not bloom.
Such bulbs grow a little and stop in development, but this does not mean that she died. It builds up the root system, enlarges and will give abundant flowering next summer.
Asiatic lilies are planted even in summer at the stage of budding and flowering, they tolerate transplantation well.
How to plant lilies in spring:
Bulb planting rules, reproduction
Lilies do not like frequent replanting (it slows down the development of the bulbs), the bushes are planted after about 5 years, so the place for planting is carefully selected.
Choose a sunny place protected from cold winds. In the shade, plants do not bloom well and develop, lose winter hardiness.
In areas for planting lilies, water should not accumulate after rains and close occurrence of groundwater is contraindicated for them. When the soil is waterlogged, the bulbs rot and die.
Lilies should be planted in areas that are exposed to the sun in the morning, and in the midday summer heat, they should be in shade.
Lilies love loose, loamy, organic-rich soils... Before planting, mineral fertilizers are applied to the soil at the rate of 100 g of superphosphate and 50 g of potash fertilizers per 1 m2.
For planting, they choose sunny places protected from cold winds, with loose, loamy soil.
Before planting, the bulbs are examined, rotten and dry scales are removed, dry roots are cut off, and live ones are shortened to a length of up to 5 cm.
For the prevention of fungal diseases, before planting, the bulbs must be etched in a 0.2% solution of foundationol or soaked in the "Maxim" preparation.
You can hold it in a dark manganese solution for 20-30 minutes, and then rinse under water. If the purchased bulbs are sluggish, they need to be soaked for 12 hours in the growth stimulator Epin, Zircon.
When planting, follow the rule: large lilies Ø 8-12 cm are planted to a depth of 25 cm, small ones - to a depth of 3 bulb diameters.
If the soil in the country or in the garden is heavy, then the planting depth is reduced to 2 bulb heights, on light, sandy soils, on the contrary, they are buried by 2-4 cm.
Oriental, LO-, OT-hybrids, when planting, are planted shallowly to a depth of 6-7 cm, so that in the spring they ascend faster, spending little effort
At the bottom of the planting hole, a 2 cm layer of sand is poured, an onion is laid, straightening the roots, in no case should they be bent, sprinkled with a layer of soil, watered and mulched.
The distance between them when landing is:
- for powerful, high varieties - 0.4-0.5 m;
- for lilies of medium height - 0.25-0.3 m;
- for low - 0.1-0.15 m.
Lay the onion, straighten the roots, sprinkle with a layer of soil, water and mulch
If you want to multiply your favorite variety as soon as possible, planting should be done deeper and the bulbs should be laid on their side.
How to care: care after planting, in the process of growing
Further care for lilies consists in:
- Watering... Since waterlogging of the soil is contraindicated for lilies, watering should be abundant during the budding period and dry periods.
- Top dressing... Plants are fed with mineral fertilizers four times per season:
- in the spring - nitrogen fertilizers, scattering them over the soil after the snow melts - 1 tbsp. l. for 1 m2;
- when forming buds, nitroammofoska is introduced at the rate of 50 gr. for 10 liters of water;
- during flowering give potassium-phosphorus fertilizers 2 tbsp. l. for 10 liters of water;
- after flowering again potassium-phosphorus fertilizers.
During the growing season, it is necessary to apply ash 4-5 times under the plants at the rate of 100 g. per 1 m2, which increases the size of flowers and gives brightness to the color.
- Regular loosening of the soil under the plants for better oxygenation of the roots.
- Garter tall stalks lilies to the supports to avoid breaking and lodging under the weight of flowers.
Pruning discolored flowers and wilting inflorescences: at the same time, at least 2/3 of the length of the stem should remain, since after flowering the bulb is forming, it is gaining nutrients and lays a flower bud.
The longer the stem left, the larger the bulb will be. Make the cut obliquely, in order to avoid the accumulation of water on the stem.
Processing lilies after flowering:
Prevention of diseases and pests
Lilies are affected by the root onion mite and the onion leaf beetle (for prevention and control, the dressing of the bulbs before planting and the spilling of the soil during the growing season with a solution of karbofos is used - 5 gr.for 1 liter of water).
If the lily is planted in the spring, then it is natural that it is still weak, poorly rooted and, in order not to deplete the bulb, it is better to remove the peduncle and let it gain strength over the summer to bloom magnificently next year.
With thickened plantings and during rainy periods, plants can be exposed to fungal diseases such as fusarium, gray rot and rust.
In diseased plants, the bulbs rot, and the leaves turn yellow and wither. For prevention and treatment, fungicides are used.
Lily pests:
Shelter for the winter
In autumn, plant stems must be cut to a height of 6-8 cm so that in winter they do not serve as a conductor of cold to the bulb. Lilies harbor for the winter sawdust, spruce branches, fallen leaves, cut branches.
In hiding do not need Asiatic lilies and LA hybrids.
Observing the basic rules of how to plant and care for lilies, everyone can plant and grow them on their site, even a novice florist.
Due to their unpretentiousness, they will not take much of your time., but they will delight with their flowering for many years.
Lily in the open field: planting and care
Lilies are perennial bulbous, very delicate and beautiful flowers that are very common among amateur flower growers. Planting garden lilies is not particularly difficult: the plant does not require special conditions.
In order for a lily to bloom beautifully in the open field and look great, proper care for it and adherence to the rules of planting, reproduction and sometimes transplantation is required.
Views
When choosing a lily, you must be guided by 2 principles:
- she should be liked externally;
- correspond to the climatic conditions in which it is planned to grow.
Today there is a wide range of species of this plant, and to make it easier to navigate in it, the main varieties are considered below:
- Asiatic lilies and their hybrids are the largest and most common variety. This is due to a number of advantages: the plant has frost-resistant qualities, and reproduction and caring for it usually does not cause any significant difficulties. This species is very unpretentious and can normally do without transplanting for several years. The average height is about 70-110 cm, but to date, miniature varieties have been bred, which reach only 40 cm.There are species with both upward and downward-looking flowers.
- Forest lilies and their hybrids include only groups of varieties, the flowers of which are directed downward. Due to their unpretentiousness, they are well suited for growing in the middle lane. This variety does not really like transplants and this is one of its main advantages, the plant can grow in one place for decades. The height usually reaches 120-160 cm, the flowering period begins at the end of June.
- Tubular lilies and their hybrids it is often more difficult to grow, since many varieties are very whimsical and can die due to spring cold snaps or snowless winters. They are also more susceptible to various diseases than other species, therefore, it is recommended to plant and grow this variety for more experienced growers.
- Other hybrid varieties of lilies... Traditionally, they have an abbreviation of two letters in the name, which denote from the crossing of varieties of which groups these species were obtained. Each species can have its own unique characteristics.LA Londan Hart
Buying bulbs
The process of acquiring bulbs requires the same responsible approach as transplanting, propagating or caring for. In particular, when making a choice, you need to know the following rules in order to avoid possible mistakes:
- The main and mandatory requirement is obtaining information about which specific group the favorite and purchased variety belongs to, since in the future all other processes will depend on this, including planting, leaving or preserving for the winter. If it is not possible to obtain such information, then it is recommended to choose a different type of lily.
- If the purchase of oriental hybrids is carried out, then it is necessary to clarify the flowering period, since it can vary significantly between different varieties included in this group.
- Check the bottom of the bulb for damage before purchasing.
- Bulb size also matters since the largest specimens form rather large flowers already in the first season. In this case, the diameter does not matter at all, since the size is usually measured exclusively in height.
- The purchase process itself is recommended to be carried out before the start of the planting season. This is due to many factors, including at this time a wide range of bulbs are available that have not yet been damaged by buyers at the time of selection.
- After making a purchase, it is recommended to carry out the processing of the bulbs, to protect them from various sucking parasites.
Site selection and soil preparation
Choosing a landing site is another process that needs to be taken as seriously as possible.
First of all, it is necessary to remember some of the features of lilies, which are the determining factors when choosing their location:
- Plant height is one of the main criteria that influences the choice of a landing site. Tall lilies look good in the back of a flower garden or individually, low varieties are more suitable for planting on an alpine slide.
- Flower color, size and shape also have an impact on the determination of the planting site, it is important that the lily blends harmoniously with other surrounding plants.
- The ideal spot for a lily is where partial shade reigns. These plants tolerate being in sunny places well, but there is a risk of drying out from an excess of heat and lighting without regular and abundant watering.
After the most suitable planting site has been chosen, it is necessary to start preparing the soil:
- The land at the planting site must be dug to a depth of 25-30 cm. If lilies are planned to be planted in the spring, then the soil goes through a preparation process in the fall. If the planting is carried out in the fall, then the land is dug up in the summer.
- There are certain varieties that have supra-lucid roots; for them, the depth of digging the soil increases to 40 cm.
- Layers that turned out to be turned upside down during the digging process must be left in this position for the entire winter.
- Under the dug layer, it is necessary to put manure humus, it takes about one bucket for each square meter. In addition, about 50 grams is relied on the same area. superphosphate and 0.5 liters of wood ash. It is important that the manure applied to the soil is completely rotted, otherwise the lily bulbs may die.
Landing in open ground
When planting lilies, you must follow the following detailed instructions:
- Make holes on the soil prepared in advance, each of them should have a diameter that is twice the size of the onion.
- Lilies are planted at a distance of about 15-45 cm from each other, the exact value depends on the size of the plant, as well as on the type of planting. Quite miniature varieties are allowed to be planted at a distance of 10-15 cm from each other.
- The depth to which the bulbs are buried depends on the individual characteristics of the root system of each group or variety. There are varieties with stem roots, they require a significant depth, which can be up to 20 cm.If the selected variety forms root processes only at the bottom, then a small depth of 5-7 cm is quite enough for such a plant.
- The planting depth also depends on the type of soil: on heavy varieties, it is recommended to bury the bulbs by 20-25 cm, on more nutritious species, 15-20 cm is enough.A number of growers are guided by the rule that the depth should be equal to two or three sizes of the bulb itself, an exception is made only for varieties that do not have aboveground root shoots, since it is in any case not recommended to bury them to a depth exceeding 5-7 cm.
- At the bottom of the seat, it is necessary to place a drainage layer, which can consist of sand with a coarse fraction, small varieties of gravel or expanded clay. The drainage height is usually about 5 cm.
- When placing the bulb inside the hole, carefully straighten the roots and slightly press it into the soil layer.
- The hole with the bulb is covered with soil, after which its layer is additionally compacted and subject to abundant watering.
- From above, the planting site is mulched with peat.
Care
Lily belongs to perennial bulbous plants, and the process of caring for them is usually simple and does not cause any problems. This is mainly due to the fact that these types of plants do not need to dig deep holes, thinning, frequent spraying or pruning.
However, some care measures will still need to be taken, among them the following are the main ones:
- Regular removal of weeds from the flower garden as soon as they begin to appear there.
- Systematic loosening of the soil at the growing site. This procedure is usually carried out in dry weather; it is also not necessary to loosen the soil directly near the plants, in this place it is mulched with compost or peat.
- Watering the soil if hot and dry weather is established without precipitation. Once the roots have started to grow, it is very important to prevent them from drying out. It is also extremely important to avoid getting moisture on the leaves of the plant, watering is carried out exclusively at the root.
- Top dressing, it is best to use liquid fertilizers.
- Some varieties of lilies, which are of considerable height, require mandatory tying.
Reproduction and transplantation
After some time, the lilies will need to be transplanted; when implementing this process, the following rules must be followed:
- The first transplant will be required only after 4-5 years, since by this time the plants have grown significantly and they become cramped in their old place.
- The timing of the transplant depends on the climatic conditions; in the middle lane, this procedure is carried out in late summer or early September.
- It is not allowed to transplant if less than 1-2 months have passed after the end of flowering, since during this period the plant is weakened.
- If by the time of transplantation the plant has already begun to turn yellow, then it must first be cut off, leaving only small hemp from the stems.
- The digging process depends on the characteristics of the root system of the variety: in some species, the bulbs crumble like potatoes, in others they must be dug up and cleaned of the earth by hand.
Reproduction of lilies becomes possible after a few years, when their first transplant will be carried out. There are several ways to do this:
- Dividing bulb nests is the simplest option. This procedure is also important for the plant itself, since it avoids possible thickening, as a result of which the lily begins to bloom poorly. With this method, the separated bulbs will start to bloom within a year.
- Certain varieties can form baby bulbs directly on the stem itself, slightly above the main planted bulb. They must be carefully separated during the transplanting process, and then planted separately so that the children can go through the growing process. Flowering with this method of reproduction will come in 2-3 years.
- A distinctive feature of some varieties is the ability to form a stem variety small bulbs in the axils of the leaves, which are located on the stem of the plant. The collection is carried out at the very end of summer, when small root shoots form and the bulbs fall off themselves. After that, they need a separate planting, while the depth should not exceed 3-4 cm. In winter, the planting site is additionally covered to maintain heat, flowering occurs in 2-3 years.
- Reproduction by scales is the most difficult of the possible ways to implement this process. Some loose scales are very easy to separate, after which the place of their separation is required in additional processing, wood ash or a solution of potassium permanganate is best suited for these purposes. For planting scales, you need to prepare a trench with a shallow depth, a layer of sand pours out on the bottom. The scales are stuck into the sand at a distance of about 5 cm from each other. Planting is best done in the spring, then by the fall it will already be possible to get small bulbs.
Pests and diseases
There are a number of pests that can harm lilies, among the main species are:
Onion leaf beetle potato scoop
- Onion leaf beetle eats foliage, and its larvae skeletonize it. Outwardly, it looks like an oblong orange beetle with red legs.
To combat it, it is necessary to eliminate all weeds, as well as collect all noticed pests.
- Potato scoop Are caterpillars eating stalks. To prevent the appearance, it is necessary not only to eliminate weeds, but also to remove their remnants from the flower garden.
- Onion hoverflies - these are greenish flies with a metallic sheen of the body, its larvae feed on bulbs. To combat them, it is necessary to discard the infected bulbs and process them with a 30% solution of karbofos.
The susceptibility to disease depends on the variety of lilies, but they are all susceptible to the following ailments:
-
Penicillosis on lilies
Rust, expressing in colorless spots on the foliage, which then lead to yellowing.
- Gray rot, capable of affecting any part of the lily, outwardly manifests itself in the appearance of round brown spots.
- Penicillosis expressed in the appearance of a green bloom and decay of the plant.
All of these diseases are of the fungal type; they are controlled both by agrotechnical methods and by treating plants with fungicides.
Lilies, which are easy to plant and care for outdoors, are widespread throughout the world. Moreover, you can always pick up a variety or hybrid that will feel great in the Caucasus mountains or in the harsh Siberia.

Botanical description and distribution area
Lilies are bulbous perennial herbs of the Lílium genus of the Liliaceae family. Liliaceae also include tulips, lilies of the valley, asparagus, onions, hazel grouses.
The genus of lilies is distinguished by a variety of species that have differences in the structure of bulbs, leaves, stems, flowers, fruit:
- The bulbs are hollow, oval, ovoid or spherical. More often they consist of contiguous lobules-scales. They can have a loose or dense structure. In several North American varieties, the bulbous tubers are attached to a powerful rhizome. The size of the bulbs varies from 1 to 30 cm. Strong, developed roots extend from the bottom of the bulbs. In several species, small airy bulbs (bulbs) arise in the leaf sinuses, suitable for reproduction.
- The lily stem is erect, 40 to 400 cm long. The shape is round, tetrahedral, flat, ribbed.
- Leaves are usually sessile, devoid of cuttings, elongated and shaped like a lancet or ellipse, egg or heart, from 2 mm to 8 cm wide, up to 20 cm long.The leaf surface is smooth, matte, glossy, sometimes pubescent, but always on the leaf parallel veins are clearly expressed.
- Flowers in the form of a funnel, bowl, cup, turban. Single or grouped in umbellate inflorescences, brushes, whorls. Some lilies have up to 100 flowers in the inflorescence cap.The diameter of the flower is from 2 cm to 25 cm. The color range is different: snow-white, all shades of red, orange, yellow, pink. There are purple, violet, lilac varieties. The petals are often decorated with specks, streaks, small spots. The flower consists of 6 lobes, 6 stamens and a pistil. There are many species with a double-flowered type of flowers.
- In the capsule fruit light, flat, triangular small seeds ripen, carried by the wind over considerable distances.

On the territory of the country, lilies are also found in the wild.
Liliaceae grow in North, East and Asia Minor, the Himalayas, North America, Europe, the Philippine Islands. On the territory of the Russian Federation, wild lilies are found in Kamchatka, the Far East, Western Siberia, the Urals, the Central region, and the Caucasus mountains. In total, about 18 species of lilies grow on the territory of the Russian Federation.
Important. Lovers mistakenly classify rhizomatous plants (belladonna, daylily) very similar to them as lilies, which do not have bulbs. Some bulbous plants do not belong to liliaceae. These are hippeastrum, amaryllis, daffodil, clivia. Called water lilies, the water lily and egg capsule belong to the buttercup family.
Types of lilies and their photos
Botanists have described about 85 species of lilies and 250 hybrids. In the modern classification used by the largest flower growing companies, lily species are grouped into seven main sections.
Martagon
Section Martagon combines plants common in Europe, North and East Asia. For lilies, which are also called Asian, are characterized by:
- underground location of the bulbs;
- delayed awakening, germination and formation of a bulbous nest and daughters;
- erect, tall, strong stems;
- shiny leaves collected in whorls;
- medium-sized flowers with smooth petals curved in the form of a turban.
Subspecies are distinguished in the section:
- Martagon or curly lily... In the Urals and Siberia, it is known under the names of locust and royal curls. In nature, there are white, lilac, pink and purple locusts. Among the famous varieties: the snow-white Album with speckless petals, the white Albiflorum with flowers decorated with pink specks, the wine-red tall Cattani lily (Dalmatian).

Lily Martagon
- Lily Hanson... Originally from Korea. It is famous for its fragrant yellow-orange flowers with spectacular red-brown specks and dense thick petals. Differs in long flowering. In Asia, the bulbs and petals of this lily are used for food.
- Graceful (synonymous with honey lily). In the wild, it grows in the Far East, Korea and China. Low-growing species (40-80 cm) with pink, orange flowers without a pronounced aroma, collected in shortened umbrella inflorescences.
- Tsingtau (Qingdao, Asian lily). A low (up to 90 cm) plant with umbellate inflorescences of orange speckled flowers that have an unpleasant odor.
- Double row lily... Differs in yellow-orange flowers, collected in a brush at the top of the stem.

Lily double row
Important. On the basis of Asian lilies, many varieties have been bred, united under the general name Martagon Hybrids. Popular Russian, Dutch, Canadian varieties: Valdai bell, Unexpected, Arabian Night, Ivorine, Manitoba Fox, Maroon King, Rosalinda, Guinea Gold.
Pseudolirium
The section includes more than two dozen species of lilies common in North America, including:
- leopard;
- Canadian;
- Philadelphia;
- Colombian;
- lilies of gray;
- Michaud;
- Perry;
- Humboldt;
- Bolander;
- Kellogg;
- Kelly.
American lilies do not tolerate harsh winters. In Russia, they are grown mainly in the southern regions.

In the photo leopard lily
Liriotypus
The homeland of Liriotypus lilies is Europe and Western Asia. This species includes snow-white, one-brother, multi-leaved lilies. White bulbs of plants belonging to this section germinate above ground and slowly.
Archelirion
This group includes Japanese and Chinese types of lilies:
- golden;
- Japanese;
- beautiful;
- reddish.
Bulbs with white scales, slow germination type. The flowers are tubular, in lilies of golden and beautiful appearance, the flowers look like a wide funnel. All species form supra-luminal roots.
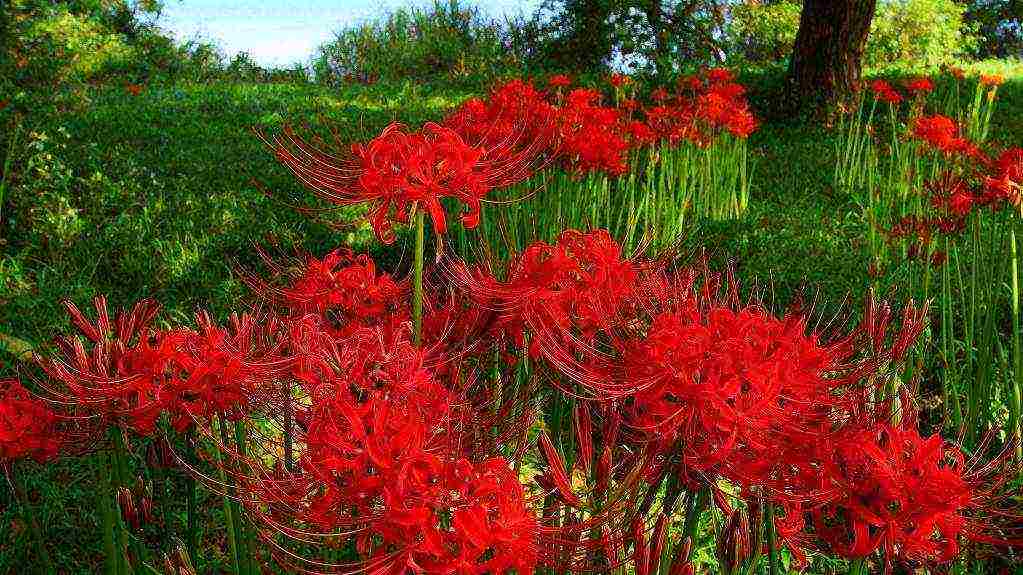

Japanese lily "spider"
Sinomartagon
East Asians. The group includes:
- onion-bearing;
- drooping;
- lily of David;
- lily Leuchtlin;
- Henry's lily and more than a dozen and a half rare plants.
Most species in this section have a fast, aerial type of germination. Plants form supra-luminal roots. The flowers are shaped like a turban.
Leucolirion
The section contains 6 West Asian species. This is:
- long-flowered;
- Taiwanese;
- Filipino;
- Willich's lily;
- Wenshanense;
- Рuerense.
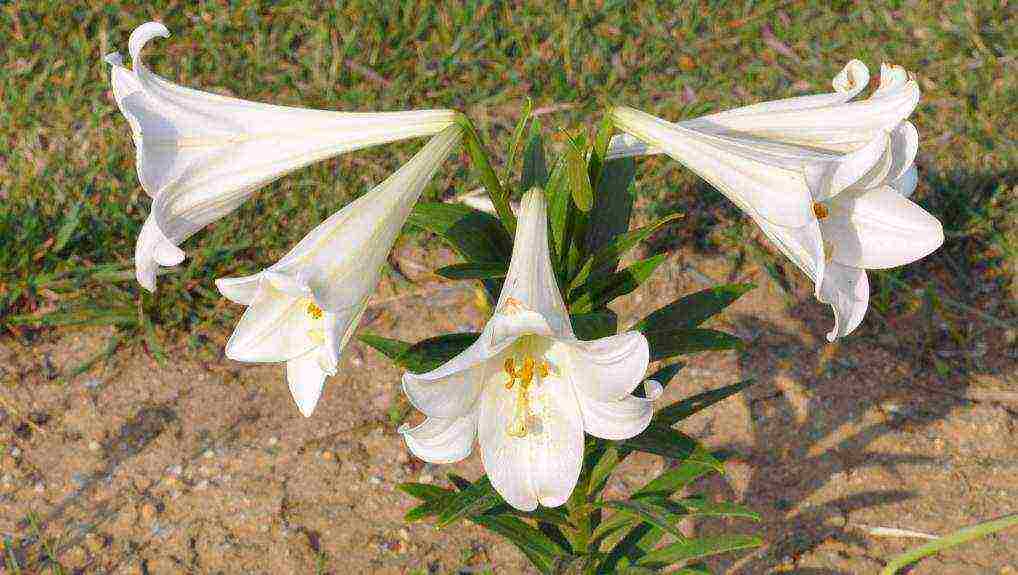

Long-flowered lily
Germinate aboveground, quickly. Leaves are alternate, sessile type. The flowers are tubular.
Daurolirion
The smallest section, including one species from Northeast Asia, is the Daurian lily, often referred to as Penselvan. Plant with a height of 60 to 120 cm. Flowers in a cup handicraft: red, orange, yellow. Blooms early, hardy.
Reproduction of lilies
Lilies reproduce in two ways.
- Seeds... Suitable for sowing are full-weight seeds that have been stored for no more than two years. Plants bloom, depending on the species, for 3-4 years. The seed propagation method is used mainly by breeders to develop new varieties and hybrids.
- Vegetatively... More productive breeding method than seed. Lilies bloom for 1-3 years, retain varietal characteristics better. There are several types of vegetative propagation: stem bulbs, babies, dividing bulbs, stones, scales, leaves and stems.
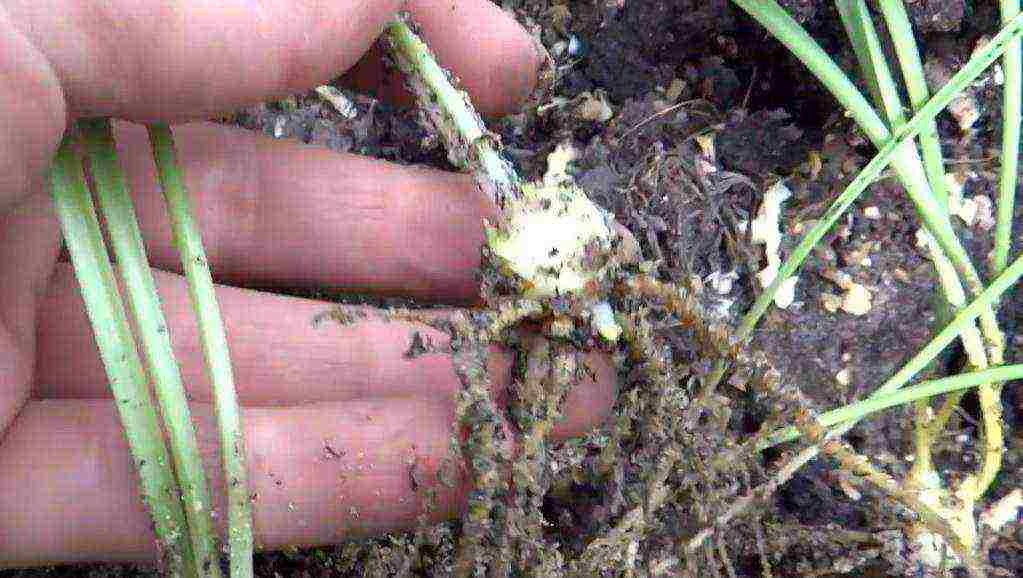

Lily can be successfully propagated with bulbous scales.
Important. The most popular way to plant lilies is by dividing the bulbs. The formed nest is divided 4-5 years after planting.
Planting lilies in open ground
First of all, they choose a variety, study its characteristics, determine the timing of planting, select a place, prepare the soil and planting material, and only then proceed directly to planting.
Optimal planting dates and recommended species
Depending on the type and variety, lilies are planted in spring or autumn, less often in summer. In Russia, it is preferable to plant in open ground in the autumn. The timing depends on the region and climatic conditions:
- Almost all types of lilies take root in the southern regions, and the best planting time is mid-October.
- For the Moscow region and the Central regions of Russia, all types of lilies are suitable, except for the North American ones. Planting period from mid-September to mid-October.
- In the Urals and Siberia, unpretentious lilies from the Asian sections and Martagon hybrids grow well. Planting begins from August 10-15, ends at the end of September.

When planting a lily, it is necessary to take into account its variety and the recommended timing.
For some varieties, spring planting is preferable (tiger and long-flowered lilies, Dutch hybrids). Planting in spring reduces the risk of bulbs freezing and wetting.
Spring planting dates depend on weather conditions. It should be noted that in our climatic conditions, bulbs do not always ripen during spring planting.
Choosing a landing site
There are varieties whose wild ancestors grew in shaded areas, among tall grasses or bushes. But, nevertheless, it is not worth planting lilies under the trees, since in the dense shade the plants will stretch and weaken.
The site should be sunny, sheltered from the winds and located on a hill. Good neighbors in a flower garden for lilies will be low perennial plants (hosts, daylilies), which protect the bulbs from overheating with their foliage.
Preparing the soil and bulbs
Before planting, the earth is carefully dug up, removing roots, pebbles, weeds. When planting, take into account the type of soil, characteristics of the variety. Some lilies require calcareous soils, others acidic ones.In any case, do not plant in heavy loamy or brackish areas.
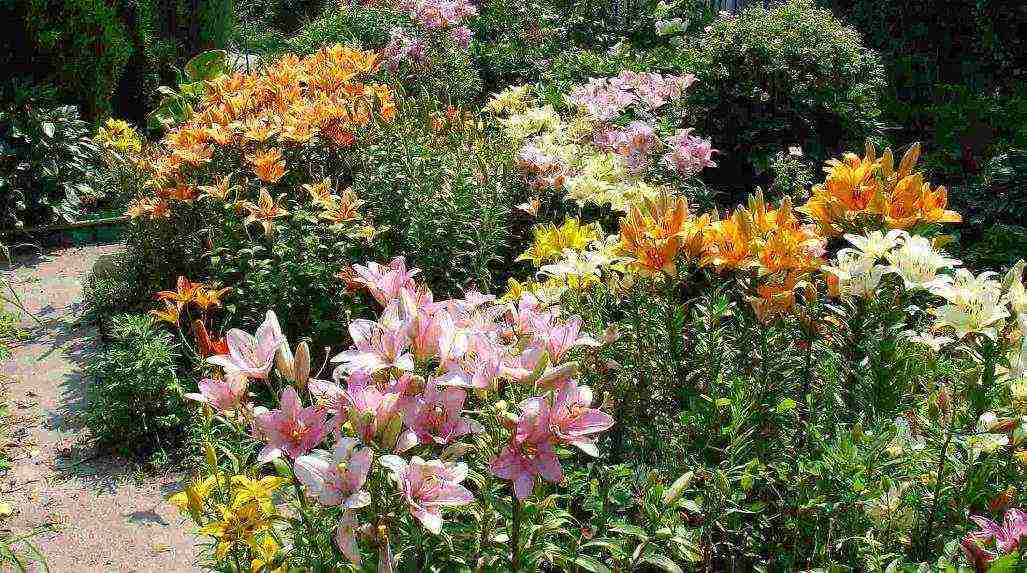

Lilies are quite picky about the type of soil
Depending on the type of soil, it should be prepared.
- Peat, humus, rotted compost will improve sandy soils.
- Wood ash will lower excess acidity.
- Loamy soil will become more air and moisture permeable after the introduction of coarse river sand.
The algorithm for preparing the bulbs is as follows:
- autumn digging of bulbs;
- pre-planting sorting and sizing;
- culling of non-viable, damaged bulbs;
- removal of flower scales;
- washing in a weak manganese solution.
Important. Dry bulbs can be "saved" by placing them in water at room temperature for several hours.
Landing
The bulbs are laid out in pre-prepared holes, on the bottom of which 5-7 cm of river sand are poured. The planting depth and the distance between the holes depends on the type of soil, the size of the bulbs, the variety:
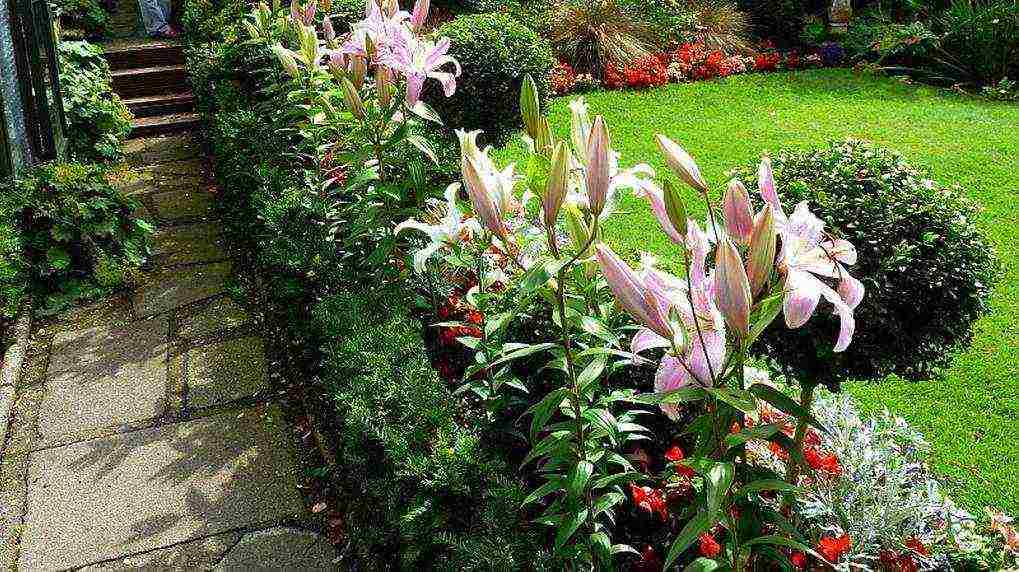

When planting bulbs, you must follow the recommendations for depth and distance.
- in heavy soils, the depth of the hole for large bulbs is 15-16 cm, for small ones - 5-6 cm;
- in soils of medium severity, large bulbs are buried to a depth of about 20 cm, small ones are enough to be instilled by 5-6 cm;
- planting material is planted in light, loose soils 2-4 cm deeper than in medium-heavy ones, i.e. 22-24 cm and 7-11 cm, respectively;
- the distance between the holes for tall, large varieties is 25-30 cm, for small ones - 10-15 cm.
The bulbs are placed in the holes, the roots are carefully straightened, sprinkled with earth, spilled abundantly, fed, mulched. When planting in autumn, the flower garden is covered with leaf litter, spruce branches or covering material.
Care and transplant rules

Caring for a lily is no different from caring for other garden flowers.
Outdoor lilies are easy to care for. They need:
- Timely and regular watering... Plants are watered at the root to a depth of 25-30 cm. Watering is carried out in the morning or in the evening. During the flowering period, the intensity of watering is reduced, and in the second half of August, they stop altogether.
- Top dressing.
- Loosening.
- Removing buds in the first year after planting and withering flowers from adult plants, otherwise the formation of a fruit with seeds will begin and the plant will weaken.
- Anchoring tall and abundantly flowering plants on supports.
- Pruning stems after flowering and complete withering away of leaves and peduncles. In early autumn, the stem is cut off, leaving 10-15 cm above the ground. Before wintering, the remainder of the stem is removed completely.
To make the bulbs easier to winter, they are sheltered from the rains in the fall.
The need for transplanting plants usually arises 4-5 years after planting. Although white, long-flowered, tiger and some other species require division and transplantation as early as the 3rd year, and the Ganson variety lilies grow well in one place for up to 10 years.
Lilies are transplanted mainly in the fall. Transplanting in the spring often leads to the death of bulbs, a decrease in the size and number of flowers, and a weakening of the plant.
Digging begins in August-September, when the last flowers wither. The scheme is as follows:
- the bulbs are carefully dug up, the earth is shaken off;
- children who do not come off on their own are separated with a sterilized sharp knife, leaving part of the bottom;
- daughter bulbs are cleaned of damaged scales, long roots are cut off;
- the planting material is treated with an antifungal agent and laid out to dry under a canopy for 5-7 days.
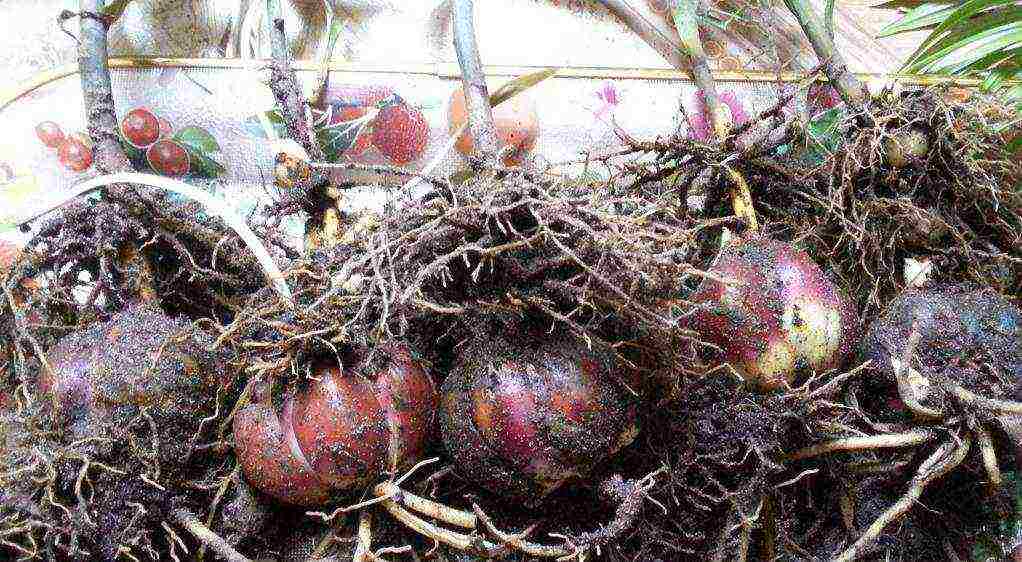

Dug bulbs from lilies around August - September
The prepared bulbs are planted in a permanent place in accordance with the recommendations for the variety.
Pests and diseases of lilies
Lilies often suffer from pests and diseases. Mice, shrews, moles, common and water rats inflict great damage to flowers. Rodents are eliminated with the help of mousetraps, traps, mole traps, poisoned bait.
To scare away animals and make it difficult to access the bulbs, in the fall, the flower garden with lilies is covered with thorny spruce branches. In winter, snow is trampled down between the rows.
Insect pests can also cause significant harm to plants. They damage plants and carry dangerous diseases. Most often, lilies are annoyed by:
- spider, root and onion mites;
- squeak beetle, larvae of the May (Khrushch) beetle and the click beetle (wireworm), onion leaf beetle;
- thrips;
- stem and root nematodes;
- lily flies, onion hover flies;
- lily and greenhouse aphids;
- bear;
- caterpillars of the onion scoop.

Periodically, lilies need to be examined for diseases and pests.
To combat insects, spraying with soapy water, acaricidal and insecticidal preparations is used. To prevent the reproduction of insects, damaged buds, leaves, shoots are removed from plants, and weeds are regularly destroyed. During pre-planting digging, larvae and adult insects hidden in the ground are collected.
Effectively autumn mulching of a flower garden with peat. Dusting the bulbs before planting with Bazudin helps from flies.
Many insects are attracted by dampness, increased acidity of the soil. In such areas, the land is limed, wood ash is added.
Ignoring the rules of agricultural technology, too dense planting, excessive moisture in the earth, damp weather, weediness of the site lead to the occurrence of various rot caused by fungi. Most often, lilies are affected by:
- gray (botrytis), sclerocial (rhizoctonia) rot;
- blue mold;
- fusarium, cercospora, leaf spot (anthracnose);
- phytium;
- penicellosis (rust).

Lilies are often affected by rot
There are no drugs that can 100% destroy the fungus in the flower garden. In order not to ruin plantings, it is most effective to take proactive measures:
- soaking the planting material in disinfectants;
- soil treatment with solutions of copper sulfate and formalin;
- spraying plants with biologically active drugs (Fitosporin-M, Alirin), fungicides (Fundazol).
Aphids, thrips, ticks, infected garden tools, poor-quality planting material are carriers of deadly viral diseases:
- cucumber and tobacco mosaics;
- variegation of tulips;
- rosette disease.
It is necessary to monitor the cleanliness of gardening tools, destroy suspicious plants and insect pests, pickle the bulbs in special means before planting. In cases of significant damage to the flower garden by viruses and fungi, the aboveground and underground parts of the plants are removed and burned. The soil is disinfected with bleach or ash. In the affected areas, the plants are re-planted no earlier than 3-5 years later.
We invite you to get acquainted with the features of planting lilies. Happy viewing!



Cut off the stem at a height of 10 cm, so it will be easier for the bulb to recuperate. No need to dig.