Content
- 1 Characteristics and varieties
- 2 Where and how to plant lily bulbs
- 3 Lily care
- 4 Transplant and reproduction
- 5 Growing problems and their solution
- 6 Choosing a site for growing lilies
- 7 Soil preparation
- 8 Dates of spring and autumn planting
- 9 Planting lilies
- 10 Lily care rules
- 11 How to cut flowers correctly
- 12 Transplant timing
- 13 Reproduction by scales
- 14 Features of cultivation after distillation
Lily breeder workshop
These recommendations are primarily aimed at novice florists, but, perhaps, something will be of interest to experienced amateurs.
Thanks to the emergence of new highly decorative varieties of lilies, they have gained great popularity in recent years - they are loved by many flower growers, and the number of fans of these beautiful flowers is constantly growing. They are grown in flower beds, containers and on rocky hills, used for cutting and forcing during off-season.
Lilies are a wonderful decoration for homestead and summer cottages: they look great against the backdrop of green lawns, trees and shrubs. And during mass flowering (late June - early July), the period between the flowering of early summer flowers, summer flowers and late perennials is filled.
TIME OF BOARDING:
when is it better to plant lilies - in autumn or spring
The fact that lilies can be planted not only in autumn, but also in spring, now, probably, everyone already knows. Early fall planting is preferred for most lilies. However, the timing of the digging-transplant depends on the conditions of the summer season and requires annual clarification. The fact is that the flowering of lilies greatly depletes the bulb. The more unfavorable conditions are during the flowering period, the more nutrients they consume. After flowering, the bulbs need about 1-1.5 months to fully recover and prepare for winter. If the season was favorable, then recovery is faster and planting can begin earlier. If the summer was dry, then the accumulation of nutrients is slow and the bulb is formed later. In this case, it is better to delay the boarding a little. The condition of the bulb can be checked with a control dig. The elastic, dense bulb is suitable for transplanting.
The advantage of planting lilies in autumn is that its timing can change, because the bulbs are dormant and will not start growing.
The optimal time for planting lilies on the territory of Ukraine is September-October. Certain lily bulbs, especially Asian and LA hybrids, can be planted even in November, depending on terrain and weather conditions. I had to plant Asian and LA hybrids in November, even after frosts, when the ground was already frozen by a few centimeters and I was not sure that it would thaw. I removed a layer of frozen soil and planted the bulbs. They overwintered normally, but bloomed a little later than planted at the usual time.
Spring planting has both advantages and disadvantages. The advantage is that lilies can be purchased in fall, winter and spring (or dug up and stored until spring planting). By providing comfortable winter storage conditions, we avoid the influence of negative weather factors of wintering (freezing or soaking in the open field). When planting in spring, favorable conditions are created for the growth of roots and the survival of plants in a new place, it is preferable for late-flowering lilies (for example, oriental (oriental) hybrids). The disadvantage is that lilies usually go on sale from cold rooms where they are stored, and when they are transferred to heat, they grow rather quickly (especially early-flowering Asian hybrids), which means that there are restrictions on the timing of planting. You need to have time to plant the bulbs when the sprouts are not yet very large. If they have reached 10-15 cm, I recommend placing them sideways in the groove so that the sprouts lie almost horizontally. They will gradually take an upright position, and the plants will bloom in the current season, although they will not gain the height characteristic of the variety.But with this method of planting, you will get much more large children on the underground part of the stem than with a normal planting. This is especially true for LA hybrids and Asian hybrids when planted in spring. From my own experience, I can say that for the southern regions, spring planting can be harmful, especially if the spring is dry and there is no way to organize watering.
Such types of lilies do not tolerate spring planting: snow-white (candidum), Shovitsa, one-brother, Canadian, Hanson, curly.
Lilies can be planted or replanted in summer. Sometimes you have to do this within your garden, when you need to move a flowering plant to another place for some reason. For example, if an admixture of a different variety was found in the plantings and it needs to be planted or taken up an empty space in the flower bed after digging up daffodils, tulips, crocuses or other early flowering plants. To do this, you need to carefully dig out the plant with a lump of earth and transfer it to a previously prepared hole. Such a transfer is called transshipment. Lilies usually tolerate it well.
SELECTING A LAND: placement of lilies.
If you are a novice florist, then the choice of a site for lilies is not relevant for you. After all, you need to correctly place not hundreds or thousands of pieces, but only a few or tens of bulbs. You can, of course, place them on a separate bed in rows at a distance of 20-25 cm from each other (Asian hybrids and LA-hybrids) or 30-40 cm (oriental and OT-hybrids). With such a planting, care, protection from pests, diseases are facilitated. It is convenient to place large collections of lilies on the beds. But such plantings will not decorate your summer cottage or personal plot. We want to create beauty and enjoy it.
Lilies are not very suitable for arranging geometrically correct flower beds - flower beds and flower beds; it is better to place them according to the landscape principle - in groups, clumps, in mixed borders (mixborders). In this case, single-sorted group (3-5-7 or more lilies of the same variety) and mixed plantings of 2-3 varieties in one place or in combination with other plants - one- and perennial - are possible. When choosing lilies for a backyard or summer cottage, be sure to take into account the biological characteristics of different species and groups - winter hardiness, drought resistance, thermophilicity, etc.
Lilies of various varietal groups can be grown almost throughout the territory of Ukraine. Novice growers usually breed Asian species and hybrids, since they are the most resistant, winter-hardy and undemanding growing conditions. Tubular hybrids, as less winter-hardy, require shelter for the winter. The southern regions and Crimea are more suitable for them. An intermediate position is occupied by lilies of Caucasian-European origin - one-brother, Caucasian, snow-white (candidum), as well as North American lilies - Canadian, leopard and their hybrids. And finally, the most beautiful, but also more demanding to the growing conditions of the oriental lilies - beautiful, golden, Japanese and their hybrids. They need special attention, the high humidity of the air and soil is important for them, but they suffer greatly from rainy weather (they do not tolerate drops of moisture on the leaves). In terms of winter hardiness, they are close to tubular lilies, they also need shelter for the winter. They work best in greenhouses.
When choosing an assortment, the flowering time should be taken into account in order to have flowering plants for a longer time.
The earliest of the lilies are the Caucasian species (one-brother, Shovitsa), the violet lily and its hybrids (often bloom at the end of May). Quite early, namely in the first half of June, L. dwarf, Daurian and their hybrids. Most Asian and tubular hybrids bloom in July - early August.
And late, in August-September, the Henry lily and its hybrids, as well as oriental varieties and species, bloom.
The attitude of lilies to soil and climatic conditions is different.Winter-hardy Asian hybrids prefer slightly acidic soils. Tubular hybrids do not like acidic soils, moreover, they need to be covered for the winter. Oriental hybrids are very demanding on the soil, the plot for them is prepared separately.
Most lilies naturally grow among grasses and shrubs, that is, with little shade, and for some species shading is mandatory. Lilies that do not tolerate direct sunlight include all Caucasian species, Canadian lily, calloused, curly, Hanson, Sargent. Lilies should not be planted close to trees, because the soil under them is dry and heavily shaded.
Tubular and Orleans hybrids, Asian hybrids, species lilies grow well in open places: tiger, Daurian, bulbous, Wilmont, drooping and their hybrids.
The number of tubular lilies in a small garden should be limited due to their strong aroma.
PREPARATION OF THE SOIL: what kind of soil do lilies need
Asian hybrids of lilies are not particularly demanding on soil conditions, but they succeed better on loose nutritious permeable soils, clean of perennial weeds (wheatgrass, sow thistle, field bindweed). Therefore, it is desirable that the site for planting them be kept under black fallow for at least 1.5-2 months, which will help not only reduce the supply of weeds, but also accumulate the nutrients it needs.
The rates of pre-planting fertilization depend on the initial nutrient value of the soil. It must be remembered that an excess of organic and nitrogen fertilizers causes intensive growth of the aerial part to the detriment of flowering and the development of bulbs, reduces winter hardiness of plants and resistance to diseases. On poor podzolic soils, humus is applied at the rate of 8-9 kg / m2, on medium leached chernozems, 4-5 kg / m2. On rich chernozems, fertilizers can be omitted or limited to the minimum rate.
Asian and American hybrids of lilies develop better on soils with a slightly acidic reaction, therefore they respond well to the introduction of needles (it is better to take under large conifers - spruces, pines, etc.), peat chips or decomposed peat mixed with humus (in approximately equal parts) ...
Tubular lilies, Caucasian lilies, snow-white lily (candidum) do not tolerate the acidic reaction of the soil. On such a site, liming is preliminarily carried out (200-500 g of lime per 1 m2), adjusting the rates depending on the degree of acidity of the soil. Good results are obtained by the introduction of wood ash at the rate of 150-200 g per m2.
Some flower growers recommend applying fertilizers under the main pre-planting soil digging. Mineral fertilizers are added to organic fertilizers - 30-50 g of superphosphate and 20-30 g of potassium salt, trace elements, if necessary, lime. Lilies respond very well to bone meal (20-50 g per 1 m2).
ATTENTION! Do not use chlorine-containing fertilizers (for example, KCl), as chlorine negatively affects the growth and development of lilies. From nitrogen fertilizers, avoid ammonium nitrate - it is harmful to lily bulbs.
Since the roots of lilies absorb nutrients only when the soil has not yet cooled below 6-8 ° C, some lily growers do not recommend fertilizing when planting lilies in the fall. I plant bulbs in October. On my site there is sandy loam soil. To avoid leaching out of fertilizer, I generally use the following scheme. In autumn before planting - liming, application of needles, peat and granular hardly soluble fertilizers. After planting, I mulch the soil with humus and needles. In the spring, at the first loosening, I put mulch into the soil and apply mineral fertilizers.
You can recommend the application of fertilizers in liquid form in small doses (top dressing 10-14 days after early autumn planting on poor soils). In this case, the roots will have time to assimilate the fertilizers before the soil cools.
As you can see, the timing of fertilization can be different, depending on the specific conditions of the site, the timing of planting, etc.
LILY LANDING The bulbs prepared for planting are examined, the sick are discarded, rotten scales are removed, the lifeless are cut off and too long living roots are shortened. Young, healthy bulbs are preferred. Before planting, the bulbs are etched in a fungicide solution (for example, 0.2% foundationol or benomyl) or in an infusion of garlic (mince 30 g of garlic, pour 10 liters of water, leave for 1 day, strain and soak the bulbs for half an hour), and if necessary, in a solution of an insectoacaricide (for example, actofit or bazudin).
There are various guidelines for determining planting depth. And they are all, in principle, correct. It is important to remember the main thing:
- The planting depth of the bulbs depends on their size and the mechanical composition of the soil.
- on light sandy soils they are planted deeper, on heavy clay soils - shallower.
- for low-hardy lilies, the planting depth is increased.
I offer several ways to determine the planting depth, and you can choose the most convenient and rational.
Method I. Planting depth depends on the size of the bulb and the variety belonging to a particular group. It is determined using the table.
Method II. The depth of the groove or hole should be equal to the height of the bulb, multiplied by 3 or 4, that is, there should be 2-3 bulb heights above the top of the bulb to the soil surface. The exception is bulbs that do not have supra-bulbous roots, for example, white lily (candidum), which is buried 2-3 cm from the soil surface to the top of the bulb.
Method III. The bulbs can be planted 10 cm from the top of the bulb to the surface of the soil (no need to dig deep ditches and trenches). Shallow-planted bulbs will go deeper on their own to the depth they need.
After planting, the soil is mulched with peat chips, needles, leaf humus, rotted sawdust or other material.
I wish all flower growers, summer residents success in growing these wonderful flowers. Let them delight you with their bright bloom.
Graceful lilies are able to ennoble any suburban area. The flower is distinguished by a variety of varieties, relative unpretentiousness and ease of reproduction. Lily is also famous for its tart aroma. Correctly planted bulbs, attention to sprouts, moderate watering and timely replanting are all that is required for the successful cultivation of an exquisite beauty.

Characteristics and varieties
Lily is a perennial bulbous plant. This is one of the most beautiful and revered flowers. The height of the stem varies from 15 cm to 1.5 m. About 16 and sometimes up to 30 buds are formed on one cluster, each of which lives for about 9 days. The lily bloom lasts an average of 2 weeks. The buds are distinguished by a variety of shapes: there are cupped, tubular, stellate, funnel-shaped, etc. Each flower of almost all varieties has 6 petals.
There are about 80 types of lilies. Due to this diversity, all species and varieties are sorted into groups. Most Popular:
- Asiatic lily includes about 5 thousand varieties, this is the most diverse group of hybrids. Features: unpretentiousness, winter hardiness, no smell. A famous variety of this group is the Marlene lily: it has white-pink graceful petals.
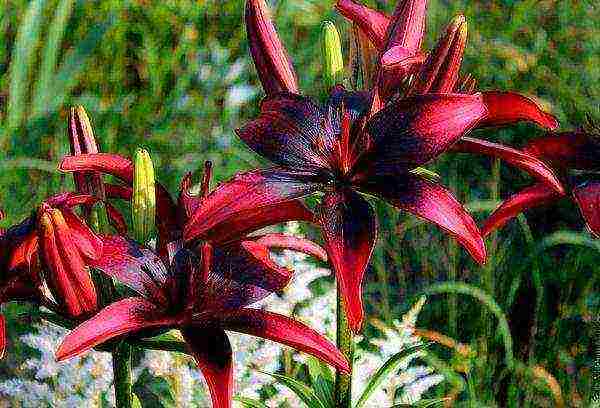

- Oriental lily (oriental) - a group of 1300 graceful varieties that are demanding for heat, susceptible to disease.

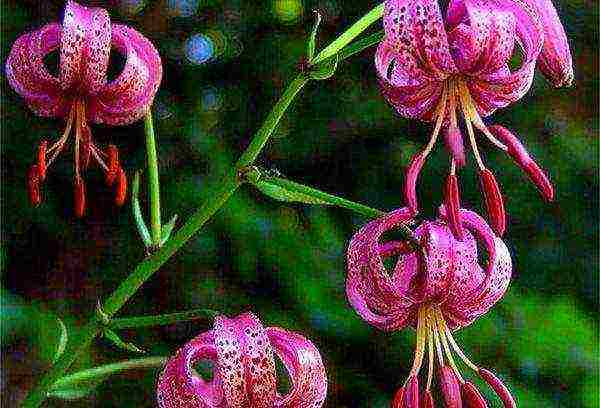
- Lily martagon is a group of curly hybrids, distinguished by their multicolor (sometimes up to 50 flowers). These curly flowers take root well on the site, but they do not differ in the resistance of the corms, which complicates their reproduction. They prefer partial shade, do not like transplants, they can grow in one place for 10 or more years.

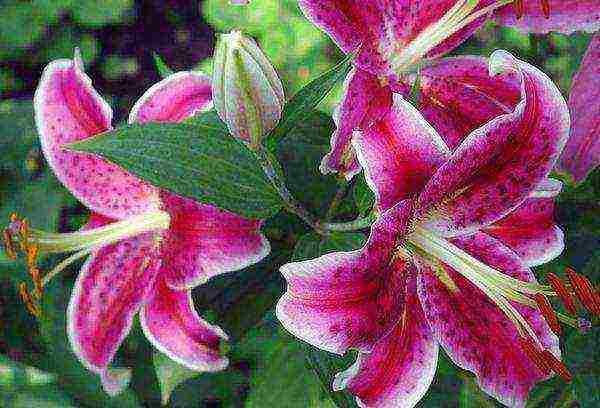
- Candidum is a group of snow-white hybrids with a pleasant aroma. They require careful care, as they are more prone to disease than other hybrids.
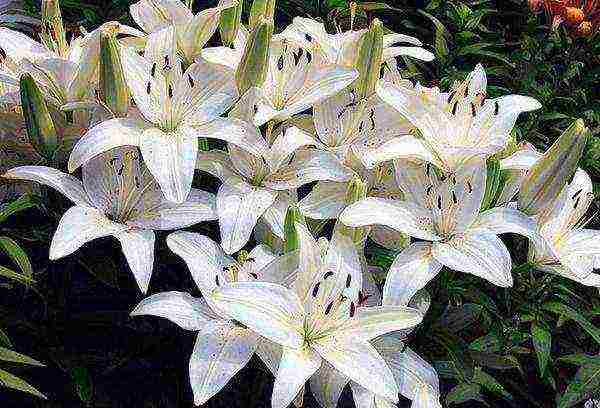

- Tiger lilies, or lanceolate lilies, are a special species loved by many gardeners. The flowers of these lilies are yellow, orange or red-orange, decorated with purple spots. Popular varieties - Yellow-flowered, Splendis, Pink Tiger (pink flowers), Fortuna.

Where and how to plant lily bulbs
Planting determines the further growth and beauty of flowering, so it is important not to make mistakes at this stage. Several rules for placing lilies on the site:
- Tall flowers will look good in clusters. These plantings serve as a good backdrop for lower plants.
- Low-growing varieties are combined with other flowers, such as roses, peonies.
- The growing area should be well lit, but partial shade is also allowed.
- Lilies do not like drafts, so they need to be settled in a place protected from the winds.
- The soil is dug up and fertilized with humus and peat. This will allow the bulbs to develop actively. All roots and weeds must be removed. Lilies love well-drained soil, so you need to add river sand.
- The soil for most varieties is neutral, but some species prefer slightly alkaline (candidium) or slightly acidic soils (tiger, Asian). Many varieties do not tolerate salt marshes and heavy loams.
- You can prepare the soil for filling the planting holes yourself. For this, sand, fallen needles, peat and sod land are mixed in equal proportions.
- If the soil is too acidic, it is neutralized with wood ash, chalk and limestone. These additives also provide additional drainage.
- The optimal distance between bulbs in group plantings is 15 cm.

Operating procedure:
- Planting lilies in open ground is carried out in early spring, before a sharp warming (otherwise the bulbs will not be able to take root). This time is considered optimal for many varieties. Spring planting is preferable, since the root system has time to develop, and the risk of freezing the bulb in winter or drying out in the heat is significantly reduced. Summer and autumn planting is possible. Autumn (usually in October) is good because in conditions of low temperature and sufficient humidity, the bulb normally adapts and takes root.
- The bulbs need to be prepared before planting. To begin with, all planting material is examined, all damaged units are removed. The optimal size of the bulbs is 2-3 cm (if it is not a tall variety), the smaller ones are unlikely to bloom in the first years of life. The healthy bulb is dense to the touch, the scales hold tightly, there are no spots and cracks. You also need to pay attention to the roots: they should not be dry and with signs of rot, the optimal length is 5 cm. Bulbs suitable for planting are freed from flower scales. It remains to rinse them in a strong solution of potassium permanganate or foundationol to disinfect, then soak the onions for half an hour and dry them.
- How to determine the planting depth of the bulb: you need to measure its diameter and dig a hole three times deeper than this value. Important: if the soil is sandy, then the bulb is placed deeper, and vice versa, the bulb should not be deeply buried in heavy soil. In loose soils, deep planting will provide frost protection.
- A mixture of ash and sand is poured into the bottom of the planting pits.
- The bulbs are placed on top. They need to gently straighten the roots, then lightly press them to the bottom of the pit.
- The holes are covered with earth and watered abundantly.
- If planting is carried out in the fall, the bulbs must be additionally covered with dry leaves and another layer of soil. This measure will protect the material from freezing.
Advice
To save the bulbs for planting, they are placed in a bag filled with peat or sawdust and left in a cool room (cellar, on the bottom shelf of the refrigerator). If the bulbs begin to germinate prematurely, you will have to plant them in a pot as seedlings.
Lily care
Growing lilies on the site is not difficult.These graceful flowers are unpretentious, but leaving them to the mercy of fate would be the wrong decision. To see a lush bloom in the garden and feel the tart aroma, you have to track the growth of the lilies, starting from the bulb stage.
How to properly care for garden lilies:
- Flowers are moistened as the soil dries. In dry summers, lilies require regular water input, although these flowers usually do not need an abundance of moisture. Additional water is not required during the rainy season. Watering is done strictly at the root. Water should not fall on the leaves, otherwise the sun's rays will cause evaporation and burns.
- In summer, it is advisable not to allow the soil to overheat, otherwise the lily bloom will not be lush. To retain moisture in the soil, it is mulched with sawdust, straw and cut grass.
- Fertilizers are applied three times a year. In the spring - to strengthen the roots; a solution is prepared from 40 g of ammonium nitrate and 10 liters of water. The second feeding is done during the formation of buds, the third - after flowering. Lilies will love peat fertilization, humus, and rotted compost. If the soil is sandy, then its composition will be improved by phosphorus-potassium dressing before planting the bulbs.
- For tall varieties of lilies, you need to install supports, since the stems can break off under the weight of the buds and their own weight.
- Immediately after the lilies have faded, you need to cut the flower stalks.
Advice
In the first year of life, lilies are rather weak, flowering can drain them, and in winter they will die. Gardeners recommend cutting off all the buds as soon as they form. But in the second year, the plant will delight with abundant flowering.

How to prepare bulbs for wintering:
- At the end of flowering, the number of waterings is reduced. Phosphorus-potassium fertilizers are applied to the soil.
- In autumn, with the onset of cold weather (no need to rush), the stems need to be mowed, as they will conduct cold air to the bulb.
- For protection, a shelter is being prepared from foliage, spruce branches, sawdust. Early flowering varieties of lilies are well kept in the ground. Late-flowering flowers are best dug up and kept in a cool place until spring.
Transplant and reproduction
At 4-5 years of age, the flowering of lilies becomes less beautiful or stops altogether. This means that it is time to transplant and reproduce by division. A bush is dug out some time after the end of flowering, so that the bulbs have time to ripen. The most suitable tool is a pitchfork, they will not damage the roots.
Then the bulb should be washed with water, dried and carefully divided into mother and daughter. Before planting, they are soaked in a solution of potassium permanganate for 20 minutes. After that, the material is dried, the roots are trimmed and seated separately from each other. Care is carried out according to the rules described above. Blossoming of the cut begins in a year.

Growing problems and their solution
Outdoor care includes protection from pests and diseases. More often than others, the flower is affected by the onion leaf beetle, onion root mite, and purple scoop. The attack of many insects will be prevented by spraying with a special solution: 1 tbsp. l. soda, ammonia and copper sulfate per 9 liters of water. The risk of insects is higher with spring planting in open ground. If the bulbs are added to the site in the fall, small rodents are dangerous. The way of protection is to place the bulbs in special metal nets before planting.
In the absence of proper care, a fungus appears on the lily: fusarium, rust, gray rot. Favorable conditions are excessive moisture, thickened plantings, weeds. It is easy to identify the fungus by the appearance of the plant: the leaves turn yellow and wither, and the bulbs rot. Treatment is carried out with fungicide preparations.
Growing garden lilies is a worthy task for both the beginner and the experienced florist. The variety of varieties allows you to choose a task of any complexity. Particularly capricious varieties of lilies on the site will be an occasion for a demonstration of skill.
Lilies are perennial, bulbous plants of the Liliaceae family, common in Asia, Europe and the American continent. The popularity of the plant is associated with beautiful flowering and varietal diversity, but lilies require special care. Let's consider the process of growing lilies in the open field in more detail.
Choosing a site for growing lilies
The choice of the site depends on the varietal affiliation of the lily. For example, Asian varieties grow well in sunny areas, although in partial shade they can feel quite comfortable. Asian lilies are frost-resistant, easy to care for, and grow rapidly.
Japanese, Gorgeous, Reddish and Callous lilies are suitable for partial shade. These varieties prefer to have the upper part of the stem in the sun and the lower part in the shade, and cannot tolerate even the slightest frost. For this reason, ornamental grasses or low flower bed flowers are often planted with lilies of these varieties as a border. They are common in the southern regions. In the middle lane, they are grown in greenhouses.
Tubular types of lilies are unpretentious in care. It is they who are preferred by summer residents. Tubular species practically do not get sick, are not damaged by insects and adapt to any climatic conditions.
If the lily bulbs are from a garden nursery, be sure to consult with experts about the intricacies of care.

All varieties of lilies have general requirements for growing conditions:
- area with light, nutritious soil;
- lilies should not be located in the shade of trees;
- the site must be drained, without moisture stagnation;
- it is advisable to enclose the lilies with a barrier from drafts.
The barrier can be natural or artificial. Artificial barriers include walls of residential and utility buildings, natural ones - garden trees or other tall plants.

Soil preparation
It is necessary to approach the preparation of a site for lilies responsibly, because these flowers grow without transplanting for 3 to 5 years. Lilies prefer light black soil, therefore, when preparing the site, it may be necessary to adjust the soil structure.
Heavy soils are facilitated by the introduction of a peat-humus mixture with sand. All components are taken in equal amounts and added during digging. For depleted soils, 4 kg of humus / 1 m2 will be needed, for podzolic soils - 8 kg / 1 m2.
Basically, lilies prefer neutral soils, but there are species that require slightly alkaline or acidified soil. Before purchasing a particular variety, consult with a specialist on this matter.

If the soil is rich in humus, organic fertilizers can be replaced with mineral additives: 30 ml of superphosphate / 30 ml of urea / 15 ml of nitroammophoska / 1 m2.
Digging is performed to a depth of 40 cm (shovel bayonet). The soil for the lilies is prepared in advance. If you plan to plant in spring, you need to apply fertilizer in the fall, and, conversely, for a winter planting, fertilizer is applied in the spring.
Dates of spring and autumn planting
Even experts are not able to say unequivocally when it is better to plant lilies. In the spring, as well as in the autumn planting, there are advantages and disadvantages.
Spring planting
The advantage of spring planting is the safety of the planting material. The risk of bulbs getting wet, rotting and freezing is minimal. Oriental varieties and tubular hybrids are planted in early spring in March, just after the snow melts. Tibetan and tiger species are planted in the last week of March, and terry hybrids in the first week of April, but, of course, the timing depends on the growing region.
Autumn planting
Autumn planting is preferred by most flower growers, as it has its advantages:
- lack of summer heat;
- no need for regular watering;
- pests are not a threat;
- lilies bloom earlier;
- saving time in spring, when there is a lot of work on the site.
In the fall, planting dates can be adjusted. The bulbs are planted in late September - mid-October.The main thing is that before the onset of frost there must be at least a month so that the bulbs have time to take root.
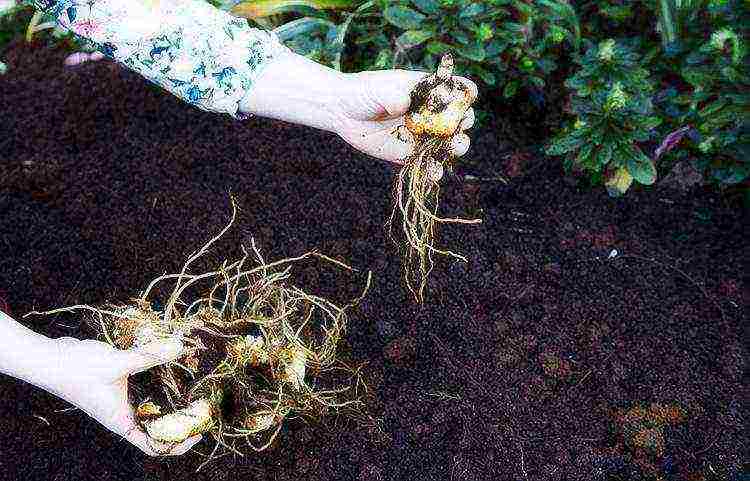

Planting lilies
Planting lilies can be carried out according to several schemes, in addition, planting material requires careful selection and some preparation.
How to choose healthy bulbs
The pre-planting preparation of the bulbs begins with their inspection and careful selection. Rotten specimens or bulbs on which fungal foci are visible are removed.
Healthy bulbs have:
- cover scales of a uniform color, white or creamy shade, without visible spots and blotches;
- well-developed roots 3 cm - 5 cm long.
If there is not enough seed, you can try to treat the bulbs with the preparations "Fundazol" and "Karbaphos", after cleaning the affected areas. These bulbs are planted in a separate group so as not to infect healthy lilies.
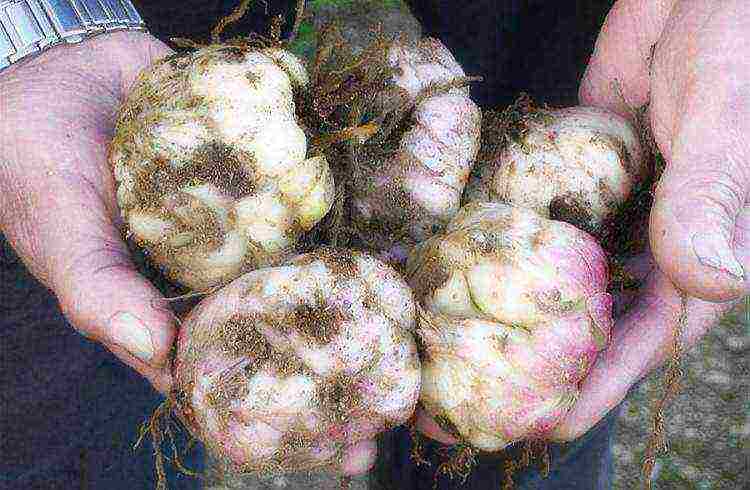

Before planting, the selected material is kept for 20 - 30 minutes in a warm solution of potassium permanganate for disinfection. Before soaking, the upper scales are carefully removed from the bulbs.
If the spring planting of lilies is carried out, the bulbs are pre-germinated in containers, which are filled with disinfected fertile soil from the site or an industrial soil mixture especially for lilies.
Bulb planting
Planting lilies with bulbs is carried out according to several schemes: single-line ribbon planting, two-line and three-line.
- In the first version, the bulbs are planted in one row with a distance between holes of 10 cm - 15 cm and a distance between rows of at least 50 cm.
- The two-line scheme involves two ribbons of bulbs with a distance between them and the holes for the bulbs of at least 15 cm - 25 cm. The row spacing must be at least 70 cm. This method is used for tall lilies.
- According to the three-line scheme, they are left between the holes for the bulbs and between the lines of 15 cm, and in the aisle 70 cm.The scheme is chosen depending on the variety, the size of the plot and the general flower arrangement.
How to make a hole and plant an onion correctly:
- The depth of the hole is twice the diameter of the bulb to be planted.
- On heavy soils, a little fine gravel or expanded clay is poured at the bottom of the hole for drainage.
- On sandy loam and sandy soils, a mixture of humus and fertile soil is laid.
- The bulb is placed in the hole, slightly pressing the roots into the ground.
- The hole is filled up and tamped so that a small depression remains for fertilizing and watering.
To protect against pests and diseases, the hole is dusted with a small amount of wood ash.
In the autumn planting, the bulbs are buried a few centimeters lower and protected with a special plastic sheath from rodents. Heat-loving varieties can be protected from frost with a layer of mulch 30 cm high from hay, foliage or straw. It is not recommended to use sawdust, as wood acidifies the soil.

Planting lily seeds
No disease is transmitted through seeds. This breeding method is safer, but much longer. It will take 3-4 years on average to grow flowering lilies from seeds.
The seeds are harvested from healthy flowers or bought at the store. Before planting, it is necessary to determine which type of seeds are: fast or slow germinating. The fast germinating ones will emerge in the first year. Slowly growing by autumn give only a small bulb.
The planted seeds germinate unevenly, some can sprout in the first year, some - only in the next season.
You can sow in open ground, but sowing in containers increases the germination of seeds.

If the seeds are planted directly into the ground, it is important to choose an area where no bulbous crops have previously been planted. Sowing is carried out in a tape manner. The distance between the lines should be at least 15 cm. A thickened planting will lead to the development of infections and the death of immature seedlings.
Slow growing varieties are planted in the winter immediately after harvesting the seeds.Humus is applied to the garden a month before planting, and before the onset of frost, the soil is mulched to keep warm with foliage or hay. With the beginning of the growing season, lilies will need standard care: watering, loosening, weeding and feeding.

Seeds are laid in containers in the last days of February - the first ten days of March. Expanded clay is laid at the bottom of the containers, on it is a soil mixture for lilies: peat, humus and fertile soil in equal quantities. Humus can be replaced with rotted plant compost.
At home, the seeds germinate after about 20 days, the optimum temperature for lily seedlings is + 18 ° C - + 25 ° C. The seedlings are looked after until September, after which the resulting bulbs are planted in unprotected soil.
Lily care rules
Lush buds of lilies can be achieved by following the usual care rules:
- In the first year, lilies do not need spring feeding.
- Fertilizers are applied once per season, after flowering. But this is only if fertilizer was applied before planting.
- Before flowering, tall varieties are recommended to be tied up.
- After flowering, dried buds are removed.
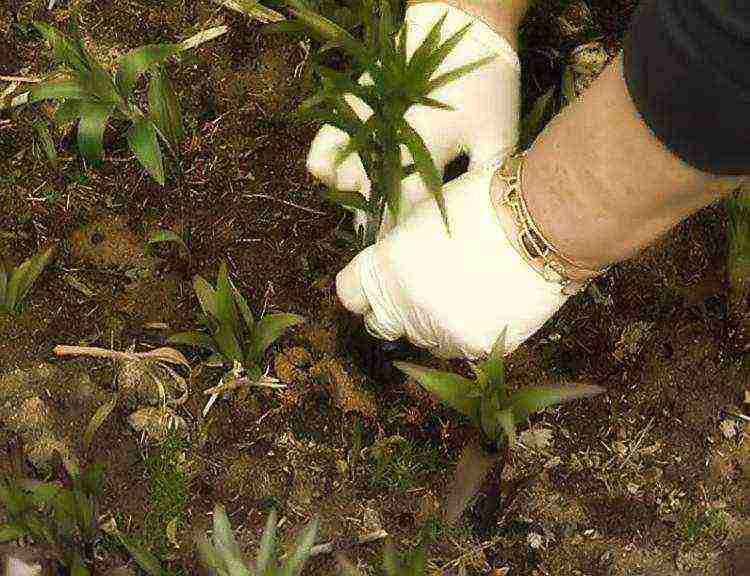

Watering
Lilies need moderate watering. Stagnant water will lead to rotting of the bulbs, a lack - to drying out of the leaves and improper development of the peduncle.
The greatest amount of moisture is needed in the spring, at the beginning of the growing season, when the plant grows green mass.
In summer, watering is reduced. Water to the depth of the bulbs as the soil dries up at the lower leaves. To extend the flowering period, watering is again reduced to 1 - 2 times a week. After the end of flowering, watering is increased again so that the bulbs can store food for the winter.
Top dressing
In annual plants, the only top dressing is performed after flowering with complex fertilizers or with the use of potassium-phosphorus agrochemicals.
In plants aged 2 - 4 years, the first feeding is performed after the snow melts in March with nitrogen fertilizers, for example, ammonium nitrate: 20 g / 1 m2 of a flower garden.
You can use a low concentration mullein infusion so as not to harm the bulbs.
The second feeding falls on the period of bud formation. It is convenient to use complex compositions of ammophoska or nitroammophoska at the rate of 30 ml of fertilizer / 10 l. The third top dressing - after flowering: 30 g superphosphate / 30 g potassium salt / 1 m2.
How to cut flowers correctly
Usually, lilies are not cut and left to bloom in the flower bed to strengthen the bulbs and ensure abundant flowering next year. But sometimes you want to make a bouquet and decorate a room or living room with lilies.
To reduce the negative impact of pruning, you need to learn how to cut flowers correctly:
- cut lilies only in the morning hours or with the onset of dusk; during the day, you can cut flowers only in cloudy weather;
- use a sterile tool for cutting; alcohol or a pharmacy iodine solution is used to process the knife;
- do not cut off the stem at the very base, leave a third of the stem and adjacent leaves for proper nutrition of the bulbs;
- cut at an angle, after watering or rainfall, the water will not stagnate on the stem.

Transplant timing
Most lilies will need to be transplanted approximately once every 3 to 5 years. But some varieties, for example, Martogon, are transplanted once a decade. And the common varieties of Tubular, as well as Asiatic lilies are planted in a year, these hybrids grow so quickly.
Thickened plantings are planted in spring or at the end of the growing season in autumn, it all depends on the climate and varietal affiliation of the grown lilies. Florists are more fond of an autumn transplant, when the bulbs are practically in a state of complete dormancy.
But what to do with Asian and Tubular hybrids, which fade a month before the onset of the first frost and simply do not have time to take root? In this case, replanting is carried out in the spring, when the soil warms up to a temperature of + 10 ° C, and the average daily air temperature will be at least + 15 ° C.
The growing region is also taken into account when planting. In the middle lane, autumn transplantation is carried out at the end of August - the first half of September, in the southern regions, work can be postponed to October, and in the northern regions, it is carried out immediately after flowering.
Asian varieties are completely unlimited in terms of spring transplantation. They are transplanted from the beginning of spring until the time of flowering. Water the lily abundantly after transplanting and tear off the buds to improve survival.

Reproduction by scales
The most common breeding method for lilies is vegetative - bulbs. Growing from seeds is less common. But there is another non-standard method - reproduction by scales, when the bulb is divided into scales and planted in the ground. Abundant watering promotes germination and development of a full-fledged plant.
Features of cultivation after distillation
There may be several reasons why lilies do not bloom. Scorching sun, insufficient watering, irregular feeding, disease-damaged bulbs for planting. All these problems can be corrected by replanting the plant, increasing watering and applying fertilizers on time.
It should be noted that in the first year, lilies may not bloom at all or form a small number of buds. This is normal and is caused by insufficient rooting and development of the bulbs.
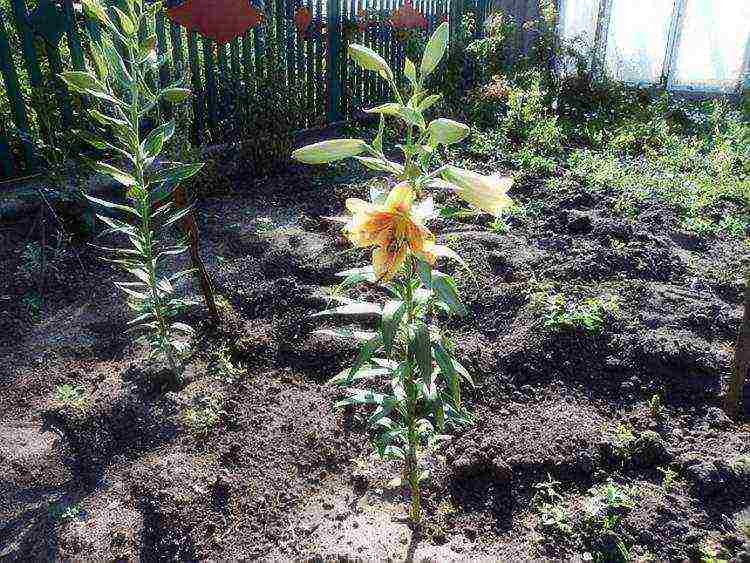

Despite the absence of buds, it is necessary to carry out the usual care of the lilies: feed at the end of the growing season, water and loosen the soil in time. With proper care for the second year, the lily will certainly delight you with beautiful buds.
Newcomers to floriculture find lilies a difficult flower to grow. You can see that caring for lilies is no more difficult than for other bulbous plants. Pick up several varieties with different flowering times and a beautiful lily will be decorating your garden all summer long.

- Type: lily
- Flowering Period: May, June, July, August, September, October
- Height: 20-250cm
- Color: white, yellow, orange, red, spotted, two-colored
- Perennial
- Hibernates
- Sun-loving
- Moisture-loving
Lily is an amazingly beautiful flower with a pleasant aroma that has been revered in many cultures. The Greeks attributed divine origin to her, believing that the lily grew from the milk of Juno - the mother of the gods. And when literally translated from Greek "li-li" sounds like "white-white". The Romans revered her as the main flower at festivities celebrating the goddess of spring Flora. Christians and Jews adorn their sacred altars with it, considering the lily a symbol of purity. This flower can be found on the coats of arms of noble families of different countries. Today, lilies adorn many parks and suburban areas, acting as a bright accent in any flower garden. One of the prerequisites for the lush flowering of these marvelous plants is the correct planting of lilies and their care.
- The main groups and popular varieties of lilies
- The choice of planting material
- Choosing a seat for landing
- Correct soil preparation
- Planting material processing
- Choosing the planting time
- Subtleties in the care of an exotic beauty
- Daylily - lily for the lazy
The main groups and popular varieties of lilies
According to the international classification, these flowering perennial bulbous plants are divided into 9 groups:
- Asian - include 5 thousand varieties. They are characterized by unpretentiousness and winter hardiness, flowers do not smell.
- Curly - there are 200 varieties. It got its name from the inflorescences that resemble a candlestick with drooping heads.
- Snow white - include 30 varieties. They have a wonderful aroma, they can have a pale yellow color. They are very moody.
- American - there are 140 varieties. The flowers are very original in bright exotic colors, often decorated with two-tone black specks. Quite finicky.
- Longiflorum - have an elongated bud shape with a direction to the side or downward, Extraordinarily fragrant. In garden conditions, they often suffer from viral diseases, they are mostly grown as greenhouse crops.
- Tubular - have a characteristic flower shape, reminiscent of an elongated gramophone, collected from dense wax petals. Capricious, in need of shelter for the winter.
- Oriental (oriental) - a large group of 1300 varieties. They are capricious, demanding for warmth, often affected by diseases.
- Interspecific hybrids - combine the best qualities of individual groups. Extremely beautiful and exotic. Among the varieties obtained as a result of crossing, the most popular are LA hybrids, OT hybrids and LO hybrids with large flowers up to 25 cm in diameter for forcing.
- Natural species - play a key role in the creation of new varieties.
Under natural conditions, these herbaceous plants are ubiquitous in the temperate latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere: in the Mediterranean, southeastern Central America, Japan, and China. Asian lily hybrids are most widespread in mid-latitudes.

Lilies are one of the most beautiful representatives of the bulbous genus. They belong to the daylily family and are relatives of onions, hazel grouses, tulips.
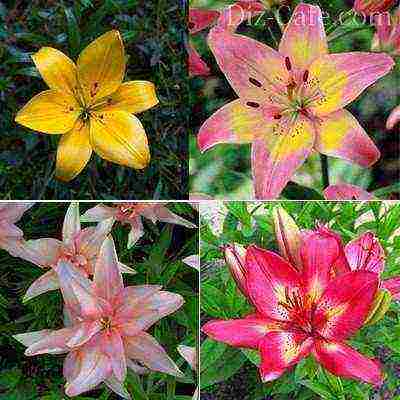

Asians come from natural species of Siberian lilies, such as Daurskaya and Tigrovaya, and therefore the most winter-hardy and adapted to not so favorable climatic conditions. Other groups of lilies, such as oriental, tubular or curly lilies, require more careful maintenance.
Among Asian hybrids, varieties are distinguished by the greatest decorativeness:
- "Marlene" - petals of a delicate pink hue. It is famous for its abundant flowering.
- "Landini" is a spectacular maroon beauty over a meter high.
- "Aphrodite" is a double flower with pink petals.
Of the old and time-tested varieties, it is also worth highlighting: "Inchantment" with flowers of a rich red-orange hue, "Destin" with delicate lemon-yellow petals, "Peprike" with bright red flowers.

Worthy representatives of the Orientali group can be considered: "Mona Liza" with graceful pale pink flowers, "Tiber" with lilac flowers framed by a white border, snow-white beauty "Siberia"
The choice of planting material
When choosing planting material, it is important to take into account the climatic features of the area, since not all lilies are able to painlessly tolerate temperature fluctuations.
When purchasing planting material, carefully examine the bulb: there are no spots and traces of rot on it. These signs indicate the defeat of the plant by diseases. The bulb should be evenly colored, the scales should adhere tightly to each other.
The marking will help to determine the varietal affiliation of the plant:
- The first Roman numeral denotes a lily group;
- The second digit indicates the position of the flower ("a" - directed up, "b" - to the side, "c" - down);
- The letter through the fraction denotes the shape of the flower ("a" - tubular, "b" - cupped, "c" - flat, "d" - turban).
It is best to store the bulbs in a cool place until planting, sprinkling with sand, sawdust or damp moss. Some adapt the bottom shelf of the refrigerator for this purpose.

For spring planting, choose bulbs on which sprouts have already hatched and short white roots have begun to grow
In the case when the bulb begins to germinate ahead of time, it is advisable to plant it in a flower pot, leaving it in a warm room. It is worth replanting into open ground after frost.
Choosing a seat for landing
When planning where to place an exotic beauty on a site, you should focus on her group affiliation.Tubular, Asian and Eastern lines show the greatest decorative effect only in well-lit areas.
They feel comfortable in the partial shade of lilies, which have adventitious roots on the underground part of the stem. These include varieties of the group of curly lilies. It is advisable to place them so that the root part is shaded, and the inflorescence is illuminated by the sun's rays.

Lily is a heat-loving plant that prefers well-lit areas, reliably covered with a "screen" of green foliage from gusts of wind
Lilies with large flowers look spectacular in solo performance. When planting small-flowered lilies, in order to obtain an expressive aesthetic effect, it is better to form small groups, placing them at a distance of 10-15 cm from each other. Against the background of the lush foliage of other perennials, bright graceful flowers will stand out favorably, creating a magnificent picture.
Sites located on a small hill are ideal for planting flowers. This prevents stagnation of rainwater, which often causes damage to plants by pathogens. Swampy soils are destructive for fastidious beauties. It is possible to improve the conditions on clay and heavy loamy soils by arranging drainage. For this, ditches are laid, placing them at a slight slope. The bottom of the ditches is lined with a layer of crushed brick or fine gravel, sprinkled with river sand on top and covered with earth.
So that the soil near the root area of the flower is in the shade and does not overheat under the sun's rays, it is better to plant daylilies, bells and hosts in the immediate vicinity. Their spreading foliage will cover the surface of the earth, creating optimal conditions for the development of fastidious beauties.
Correct soil preparation
Correct soil is 80% of success in growing lilies. Regardless of the group belonging of the bulbous, they all prefer to grow on rich soils.

On enriched and well-drained peat soils, varieties of the American group and oriental hybrids thrive.
Humus is considered the best fertilizer for lilies. But it should be introduced with caution: with an excess of nutrition, the plants begin to "fatten". This provokes their slowdown in development, a decrease in disease resistance and a decrease in frost resistance. The optimal ratio of the introduced humus is 7-8 kg per 1 sq. M.
The introduction of poorly decomposed manure containing pathogenic microflora with pathogenic plants can have a detrimental effect on plants.
The soil under these flowering herbaceous plants must contain a sufficient amount of nutrients, because a plant can live in one place from 3 to 5 years. When digging the soil, it is filled with mineral fertilizers, which include nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus. They are brought in at the rate of 100 grams per square meter.

Since the roots of plants go quite deep, they dig up the soil before planting, deepening 30-40 cm.To drain heavy clay soil, sand is added to its composition
Most members of the daylily family do not tolerate acidic soils, preferring slightly alkaline and slightly acidic soil compositions. On acidic well-drained soil, only varieties of the eastern group feel comfortable. Asians and LA hybrids are more fond of neutral and humous soils, and tubular lilies show the greatest decorative effect on poor, slightly alkaline soil with admixtures of ash and sand.
Help reduce the acidity of the soil:
- Wood ash - it is brought in at the rate of 150-200 gr per 1 sq. M;
- Chalk - during digging, 300-500 gr. Per square meter.
Planting material processing
The bulbs are examined before planting, discarding diseased specimens: they remove damaged tissues, cut off rotten scales and dead roots.
The examined material is washed under pressure for 20-30 minutes.Then, in order to prevent the development of fungal diseases, they are first kept in a solution of potassium permanganate, prepared in a proportion of 5 g per 10 liters of water, and then in a solution of the drug foundation. If necessary, they can be etched in an insecticidal solution based on chlorophos and 1% phosphamide.

The root system of these plants dries quickly enough. Therefore, after soaking, there is no need to dry them.
Choosing the planting time
The optimal planting time is after the plants have faded. This is the period from late summer to mid-autumn. If the bulbs are purchased in early spring, planting can be done as soon as the soil thaws and dries up. Late spring planting is risky in that young shoots can be damaged.
Spring planting is also more suitable for late-flowering varieties, the bulbs of which are slowly formed. These include LO hybrids and varieties of the eastern group: Rio Negro, White Haven, Rialto, Marco Polo.
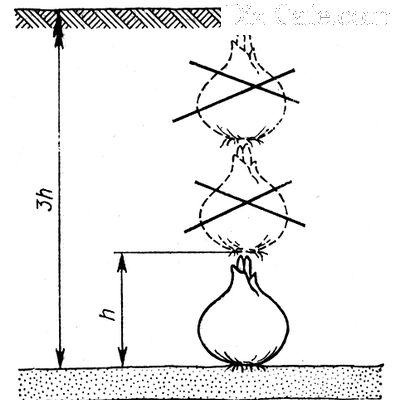
When planting plants, you should be guided by the rule that large bulbs with a diameter of 8-12 cm are planted to a depth of 25 cm, and small ones - to a depth three times the size of the bulb itself
The only exceptions are Chalntcedony, Snow White and Testaceum. They form a root rosette of leaves, and therefore the soil layer above them should not exceed 2-3 cm.
When planting bulbs in heavy soil types, the bottom of the planting pits is covered with a 5 cm layer of sand. To protect them from voles, wire mesh is laid along the inner walls of the planting pit.
The bulb is laid out on the bottom of the pit, placed on an impromptu sand "pillow", and the roots are straightened. They cannot be wrung and bent upwards. The landing site is marked with a peg and sprinkled with earth, lightly tamping. The well is poured abundantly with settled water and covered with bark mulch.
Lilies are very sensitive to root drying. To prevent the bulbs from weathering while the hole is being prepared, it is better to wrap them in a wet napkin or hide them in a box with wet peat. Tender young sprouts are afraid of temperature extremes
To protect young shoots, the planted bulbs are covered with plastic bottles with cut-out bottoms. For this purpose, it is better to use bottles with wide walls with a volume of 2-3 liters.
Subtleties in the care of an exotic beauty
How to care for lilies? To minimize the care of these flowering plants, a number of recommendations must be followed:
- During the season, feed the plants with complex fertilizers and ash at the rate of 50 grams per square meter. Top dressing is carried out in three stages: in early spring, at the stage of bud formation and after flowering. Suitable for spring root feeding: ammonium nitrate (40 g per 10 l), nitroammophosphate (50 g per 10 l), a solution of fermented mullein in a ratio of 1:10.
- Provide timely watering. Although the lily does not like excessive moisture, especially dry days need frequent watering. You need to water at the root, trying not to moisturize the leaves. Accidentally falling water droplets can act as a kind of lens, causing sunburn.
- Mulching the soil. Very harmful to bulbous plants and soil overheating, which disrupts the course of biological processes. This can be prevented by mulching the soil with natural materials of light shades (cut grass, straw, sawdust).
- Pest control. The lily beetle and lily fly are dangerous for the aboveground part of plants. You can get rid of pests by collecting the larvae by hand and spraying the stems with preparations such as "Thunder", "Grizzly", "Mukhoed".
- Garter stalks. Tall varieties with thin stems must be tied to supports, thereby preventing them from breaking off and lodging.
- So that wilted inflorescences after flowering do not spoil the picture, they should be removed in a timely manner. The peduncles are removed at the end of the season.
- After the end of the growing season, the stems of the plants must be cut and burned so that in winter they do not serve as a conductor of cold to the bulb.
- For the winter, it is advisable to cover garden lilies with leafy soil, sawdust or spruce branches of conifers. Only Asian and LA hybrids do not need shelter.
Lilies are planted, separating the daughter bulbs, every three years, one and a half months after the end of flowering. By this period, they had built up mass and gained the greatest strength.

Lilies are planted, separating the daughter bulbs, every three years, one and a half months after the end of flowering. By this period, they had built up mass and gained the greatest strength.
Slowly growing varieties of Caucasian origin are best planted only after 5-6 years. Asian varieties can be replanted even in summer. The main thing is to dig up the plants with a garden pitchfork along with a lump of earth, while preserving the root system.
> When transplanting, baby bulbs are carefully separated from the stem and planted in seedling beds for growing. Immediately after planting, they are sprinkled with compost or manure humus, forming a layer 3-4 cm thick. They will form full-fledged bulbs in the second or third year.
Daylily - lily for the lazy
No wonder the breeders called these unpretentious and disease-resistant perennials "lilies for the lazy." And the statement that the more beautiful the flower, the more capricious it is, is not applicable to this plant. Daylily grows well in any garden soil, feeling comfortable both in the bright sun and in partial shade.
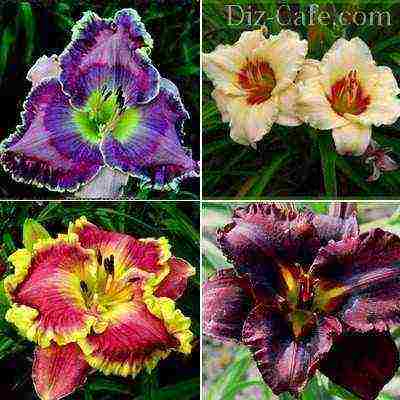

Not inferior in beauty to garden lilies and their closest "relatives" - daylilies, but unlike fastidious beauties, they are very easy to care for
Planting and caring for daylilies takes a minimum of time and effort. And the plant begins to delight with flowering already in the first year of planting. These perennials prefer neutral or slightly acidic soil. They are able to grow on depleted soils, but they show the greatest decorative effect on loose loams rich in organic matter. They are tolerant of infrequent watering, but, like lilies, do not tolerate stagnant water.

Perfectly combined with ornamental grasses and flowering annuals, they perfectly mask the slow disappearance of spring-flowering bulbs.
Daylilies can become a bright decoration of any flower garden. With the right selection of species with different flowering periods, the flowering of daylilies will not be difficult to stretch for the entire season.
>