Content
- 1 Homemade lavender from seeds
- 2 Planting lavender seedlings outdoors
- 3 Propagation of lavender by cuttings and layering
- 4 How to care for lavender in the garden
- 5 Types of lavender with photos and names
- 5.1 English lavender
- 5.2 French lavender
- 5.3 Lavender real or English, spikelet, narrow-leaved Lavandula angustifolia
- 5.4 Broad-leaved lavender Lavandula latifolia
- 5.5 Lavender Dutch hybrid or lavender Lavandula intermedia
- 5.6 Pedunculate lavender Lavandula pedunculata
- 5.7 Lavender toothed Lavandula dentate
- 6 Benefits of lavender
- 7 Self-picking lavender seeds and choosing them for sowing
- 8 Pretreatment of lavender seeds
- 9 Sowing lavender in the ground
- 10 Soil and containers for sowing lavender seeds for seedlings
- 11 Sowing lavender seeds for seedlings
- 12 Conditions for seed germination
- 13 Growing plants
- 14 Diving seedlings and caring for young lavenders
- 15 Hardening lavender seedlings
- 16 Planting lavender seedlings
- 17 Key cultural features
- 18 Stage one. Stratification
- 19 Stage two. We prepare everything you need
- 20 Stage three. We sow the seeds
- 21 Stage four. We carry out the first pick
- 22 Features of transplanting into open soil
- 23 Rules for caring for lavender southerner
- 24 Types and varieties of lavender
- 25 Reproduction methods
- 26 Growing lavender from cuttings
- 27 Growing lavender from seeds
- 28 Planting lavender in open ground: choosing the best place in the garden
- 29 Outdoor lavender care
Lavender is a perennial evergreen semi-shrub plant of the Lamiaceae family. The height is 60-90 cm. The root is woody. The lower shoots branch well. The leaves are small: 1 cm wide and 2.5-6 cm long, located opposite. Lavender is notable for spike-shaped inflorescences of white, pink, blue, lilac, lilac-purple color. It blooms all summer long, exuding a pleasant aroma. By September, the fruits ripen - small brown nuts.
Lavender is native to the Mediterranean. The plant is thermophilic. Lavender is only able to winter outdoors in warm climates. In gardens, it becomes an adornment of alpine slides, rockeries, borders. In cold climates, they are grown in flowerpots - at the first hint of cold, move them indoors. Suitable for growing as a pot crop.
Homemade lavender from seeds

Photo lavender seeds
Growing lavender from seeds is a longer process.
In warm climates, seeds can be sown before winter - they will undergo natural stratification and sprout in spring. In the first year, the plant will grow its root mass, and flowering will come in the next season.
When to plant lavender seeds for seedlings
It is still preferable to plant lavender with seeds for seedlings: sow in late winter (February) in boxes or in early spring (March) for germination in a greenhouse on the street. Stratify the seeds beforehand: mix the seeds with sand, pour into a container, cover with plastic wrap and keep in the vegetable section of the refrigerator for a couple of months until sowing.
- The soil needs to be loose.
- Deepen the seeds by a few millimeters, keeping a distance of 1.5-2.5 cm.
- Moisten crops with a spray bottle.
- Germinate at 15-21 ° C. Maintain moderate soil moisture.

Lavender from seeds photo shoots
- Seedlings will appear in 2-4 weeks.
- Young plants will need 8 hours of daylight hours.
- With the appearance of 2 true leaves, transplant them into separate containers with a mixture of peat and perlite.
Transfer the grown plants together with an earthen lump. Fertilize the soil with granules of nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus. Carry out the next transplant with a growth of about 7.5 cm. Start hardening the seedlings - take them out for several hours in fresh air.
Planting lavender seedlings outdoors

How to plant lavender in the ground photo
Planting in open ground with the establishment of real heat without night frosts.
Seat selection
Find the right spot for good growth and flowering. An open area with bright sunlight is ideal. It will take root in the shade, but do not expect lush flowering. The root system of lavender reacts painfully to high soil moisture - avoid swampy areas, if the groundwater is close, you should build an elevated flower bed.
How to plant
- Dig up the area by adding compost. If the soil is acidic, be sure to add agricultural lime or ash.
- Make the holes corresponding to the size of the root system.
- Transfer lavender with full earthen coma.
- Keep a distance between the bushes equal to the maximum height of the bush (80-120 cm, depending on the species, variety).
- To make the landing look monolithic in the future, reduce this distance by half.
- Deepen the root collar by 5-7 cm. Water abundantly.
Propagation of lavender by cuttings and layering

How to plant lavender cuttings photo
The most popular is vegetative propagation (by cuttings, layering).
- Cuttings root quickly and easily. Do this in early spring or mid-summer.
- Green and lignified cuttings with at least 2 internodes can be rooted.
- Cut the leaves from the bottom, treat with a rooting stimulant and plant the cutting in loose soil, deepening a couple of centimeters, cover with a jar, cut with a plastic bottle or film.
- Air regularly, moisten the soil.
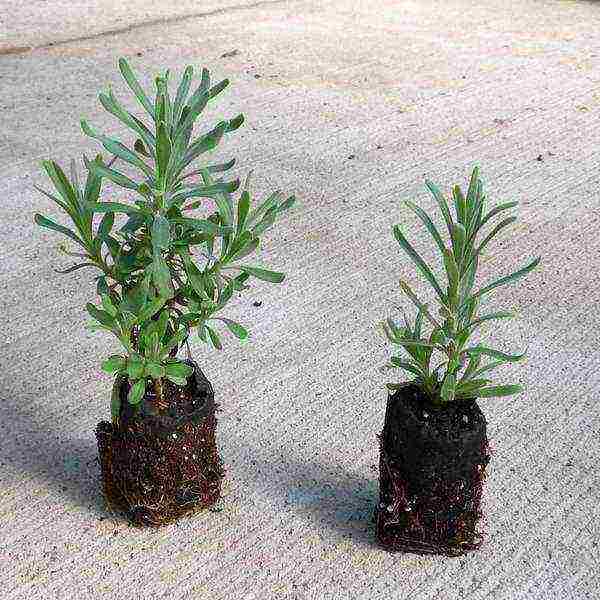

Rooted lavender cuttings ready for planting photo
Start reproduction by layering in the spring. Bend one of the lower shoots to the ground, fix it in place of contact with the soil and sprinkle it with earth, the top should remain on the surface. Water. After about 3 months of active growth, the new plant is ready to separate from the mother bush.
How to care for lavender in the garden
Watering and loosening the soil
Water the lavender as the topsoil dries. Waterlogging leads to yellowing of the shoots and rotting of the root system. Drought will not kill lavender, but bloom will not be as luxurious.
To maintain the optimum moisture level, cover the soil around the bush with decayed foliage, compost, and leave the base of the trunk uncovered.
It is important to regularly loosen the soil, remove weeds.
Top dressing
In the presence of mulch, top dressing can be omitted - the compost and leaves will gradually decompose, feeding the plant.
At the beginning of the growing season, feed with nitrogen fertilizers: dissolve 2 tablespoons of fertilizers in 1 bucket of water and pour around the perimeter of the bushes.
When flowering begins, feed with a complex mineral fertilizer. Also 2 tablespoons of fertilizer per 10 liters of water.
Pruning
Cropping is optional. After flowering, shorten the shoots a couple of centimeters. Be careful in your actions: shortening the shoots to the level of the lignified part can lead to the death of the bush.
Wintering
Lavender bushes overwintering outdoors can withstand temperatures as low as -25 ° C. A shelter should be built, but do not cover with leaves, otherwise the bushes will begin to rot. Better cover with spruce branches.
Diseases and pests
The plant is rarely exposed to diseases and pests.
From an excess of moisture, gray rot may appear - remove the damaged areas, treat with a fungicide. Be sure to adjust your watering.
The scent of the plant protects it from pests. Such a nuisance as pennies is possible - they lay their larvae, covering them with a substance similar to foam. It does not harm, but spoils the decorative effect. Just rinse them off with a jet of water.
Types of lavender with photos and names
There are 45 types. They are classified into 2 groups:
English lavender

English lavender photo
It has narrow leaf plates, elongated spike-shaped inflorescences. They winter hard in the open field.
French lavender

Lavender French French Lavender photo
Has wider leaves and shortened inflorescences. Most often grown as a pot crop. Withstands temperature drop down to -15 ° С.
Let's consider in more detail the popular types:
Lavender real or English, spikelet, narrow-leaved Lavandula angustifolia

Lavender real or English, spikelet, narrow-leaved Lavandula angustifolia ‘Elizabeth’ photo
The bush is 1 m high and wide. There are subspecies 30 cm high. The inflorescences are spicate. The most common type.
Broad-leaved lavender Lavandula latifolia

Lavender broadleaf Lavandula latifolia photo
On one stem there are 3 inflorescences, it has the brightest aroma.
Lavender Dutch hybrid or lavender Lavandula intermedia

Lavender Dutch hybrid or lavandin Lavandula intermedia grosso photo
The result of crossing the two previous species. The bush can reach dimensions of 2 m (height and width). The inflorescences are curved.
Pedunculate lavender Lavandula pedunculata

Pedunculate lavender Lavandula pedunculata photo
Has an unusual bright purple bloom.
Lavender toothed Lavandula dentate

Lavender toothed Lavandula dentate photo
It has soft leaves of a green-silver color. Differs in larger flowers.
Benefits of lavender
In addition to decorating gardens, lavender is used for medicinal, perfumery, and culinary purposes.
Lavender water is found in many cosmetics.
Lavender oil has an antiseptic effect and can be used to lubricate burns. Lavender syrup is used to treat migraines. Infusions are used to treat diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Brew lavender tea or take a bath with dried buds - it soothes, helps to cope with insomnia.
Lavender can cause allergic reactions.
In cooking, lavender is used as a spice for fish, meat, dry petals are added to sauces, salads, and confectionery is decorated with flowers. Sugar with a lavender aroma is popular in European countries.
Lavender honey is very useful.
Lavender is one of the indispensable perennials that is considered both luxurious and versatile at the same time. Despite its Mediterranean origin, lavender has long taken root in our country. And although only one species can boast of sufficient winter hardiness, it is impossible to imagine a single modern garden without lavender. But the popularity had little effect on the rather high price of planting material, because of which more and more gardeners decide to grow a plant on their own. The most affordable way - growing lavender from seeds - is not quite rightly called the most difficult.
Lavender during flowering
Lavender (Lavandula) in the middle lane and to the north is represented by only one frost-hardy species - English lavender, or narrow-leaved lavender (Lavandula angustifolia). It is a perennial shrub with numerous woody shoots in the lower part, densely covered with opposite, sessile silvery-grayish leaves. Small blue or lilac lavender flowers are collected in whorls in slender spikelets of inflorescences crowning leafless shoots. Fragrant, bright, textured, unusually elegant, lavender is recognizable at first sight.English lavender traditionally blooms in mid to late summer.
In reproduction, both narrow-leaved and other types of lavender are almost the same. Regardless of the degree of winter hardiness, representatives of the genus Lavandula retain common features and differ only in details - in the size of leaves and flowers. Without exception, all lavenders are easiest to propagate vegetatively.: Plants give a large number of shoots, and cuttings and cuttings root well in them. But in this way you can only get lavender of the variety and type that you already have or are on the market (and rare varieties with an interesting color and unusual species, as a rule, are rare). And the number of "offspring" will always be more or less limited. If you want to grow a new variety of lavender and get a large number of seedlings, significantly saving both time and money, then you can use the less popular, notoriously difficult, method - to grow lavender from seeds. In practice, seed propagation of lavender is not at all tricky, since the only difficulty - stratification - is overcome quite simply.
Self-collection of lavender seeds and their selection for sowing
When choosing lavender seeds, pay special attention to price and manufacturer. Buy lavender only from trusted companies and suppliers you trust, with a wide palette of ornamental plants and a representative collection of not only summer seeds, but also other perennials. Remember that lavender seeds cannot be readily available: cheap seeds can be unpleasantly surprised by “substituting” one type for another. Make sure that information about the manufacturer, plant characteristics, planting characteristics is presented in full.
You can also collect the seeds yourself, by buying or collecting fully blossoming inflorescences, making bouquets of lavender and, after drying, preserving the small and fragrant seeds that have spilled out.
Lavender seeds remain viable for an astonishingly long time. It is not at all necessary to use them fresh, even after 5 years they will grow together, subject to all the rules of agricultural technology. And the main condition is proper storage of seeds: they must be kept in hermetically sealed containers.
Pretreatment of lavender seeds
Lavender seeds need stratification, or rather cold stratification. Without cold treatment, they will not rise, and the effect of low temperatures should continue for a long time. Depending on the method and timing of processing, there are two options for growing lavender from seeds:
- Artificial stratification, cold exposure before sowing.
- Natural stratification, sowing before winter to pass the cooling period already in the soil.
The minimum period for stratification of lavender seeds is 1.5 months (or at least 30-40 days). If stratification takes longer, this will only have a positive effect on the number of seedlings and the rate of germination.
Artificial stratification it is better to carry out not in bags, but by mixing lavender seeds with sand or substrate. After filling the container with the prepared mixture, it is wrapped with foil or covered with a lid (you can also fill hermetically sealed plastic bags with the mixture). The seeds are sent for cooling for 6-8 weeks at a temperature of about 5 degrees Celsius. There is no need to freeze lavender seeds: they just need to be placed in the refrigerator to pass through the cooling phase.
In addition to the usual stratification, you can experiment with other processing methods:
- scalding lavender seeds sown in the ground;
- treatment with a growth stimulant or phytohormones (for example, gibberellin at a concentration of 100 to 200 ml per 1 liter of water).
But such methods may not work at all.
Sowing lavender in the ground
Sowing lavender before winter is not a difficult task and differs little from growing any perennial and annual plant that prefer stratification.Sowing is carried out at the end of October, trying not to bury the seeds too much in the soil and be sure to mulch the ridge for protection for the winter. You should not be afraid that lavender does not sprout in early spring: the plant will release the first shoots no earlier than May, or even on the eve of summer, when temperatures at night will rise significantly.
Sowing in the soil in spring is carried out in May.when the threat of strong returnable frosts disappears. In this case, the seeds are subjected to artificial stratification.
Seed-grown lavender seedlings
Soil and containers for sowing lavender seeds for seedlings
For lavender, universal loose substrates with a high proportion of nutritional value are used. For this plant, it is preferable to use ready-made soil mixtures (universal for indoor plants or special for seedlings and summer plants). Before planting, it is advisable to ignite or spill the substrate with potassium permanganate.
When choosing containers for sowing lavender seedlings, you should give preference to shallow, but large and wide containers, boxes and bowls. Lavender is not sown in cassettes. The maximum depth of the container is 7 cm.
Sowing lavender seeds for seedlings
Sowing for seedlings is carried out at the end of winter, in the second half of February or the first half of March.... It is customary to sow lavender in large boxes quite rarely, laying out the seeds literally one at a time, because despite the fact that the plants are not afraid of transplants, they have powerful roots and primarily grow long roots, which are easy to damage with dense sowing. The rest of the landing rules are quite simple:
- The containers are filled with soil and carefully, without tamping, level it.
- The soil is moistened from above with a spray bottle.
- Lavender seeds are planted one at a time at a distance of 1.5-2 cm.
- Cover from above with 2 - 3 mm of soil (preferably sifted), without deepening deep.
- Immediately after sowing, the containers are covered with glass or foil.
Conditions for seed germination
For lavender, there are two main factors to ensure:
- bright lighting;
- restrained room temperature in the range from 15 to 21 degrees Celsius.
During the entire period before the emergence of lavender shoots, it is necessary to maintain a light but stable soil moisture, carefully spraying the soil in the morning and airing the "greenhouses". Waterlogging is very dangerous, but without constant, at least light humidity, it will be difficult to achieve friendly shoots.
Lavender usually takes a long time to germinate. The first shoots can appear in 2 weeks, friendly shoots - on average, after 1 month.
Growing plants
After the emergence of friendly shoots of lavender, glass or film is removed from the containers as soon as possible, but they continue to maintain a light soil moisture. Young shoots should be placed in the brightest place (preferably on a sunny southern windowsill). If there is not enough sunlight, lavender is supplemented with light, increasing daylight hours to 8-10 hours.
Transplanted lavender seedling grown from seed
Diving seedlings and caring for young lavenders
Lavender dives only when the plant forms one pair of true leaves and the third or fourth full-fledged leaf begins to develop... As a rule, even young seedlings of lavender first of all grow roots, and at this stage rather powerful roots are formed, which will not have enough space in a shallow bowl.
The lavender is transplanted carefully, but this procedure is easily tolerated by the plants. It is advisable to dive into individual pots or cups with a diameter of 5-6 cm, but large boxes can also be used, leaving a similar distance between the plants. For lavender seedlings, you can use a peat-sand mixture or a lighter substrate for indoor plants with the addition of perlite and sand. Long-term fertilizers can be added to the soil.
Lavender is transferred to new containers, trying not to destroy the earthen ball, carefully crumbling the ground around the seedlings to speed up rooting.
Hardening lavender seedlings
Lavender seedlings will need to be hardened for at least 1 week to adapt to new conditions. Plants are taken out gradually, starting at 1 hour per day and increasing the time spent outdoors every day.
Planting lavender seedlings
Lavender grown from seeds blooms only the next year after germination. For the entire first year, the plant does not develop very rapidly: first, lavender grows roots, and only then shoots. But on the other hand, well-rooted plants develop very quickly in the second year and delight with their fragrant inflorescences.
For planting lavender seedlings, they choose sunny places with light soil, to which organic fertilizers have been added. Stony, sandy-clayey soils are more suitable for this perennial. The optimum pH for this plant is 6.5 to 7.5. For planting, it is better to prepare a special soil mixture by mixing the soil removed from the planting hole with sand, humus and mineral fertilizers or completely replacing the soil with a mixture of leafy soil, sand and humus in a ratio of 3: 1: 2.
The distance when planting lavender is from 30 to 40 cm.This plant is planted in individual, rather large planting holes with a depth and diameter of about 30 cm.
Lavender will gratefully respond not only to abundant watering, but also to mulching immediately after planting (it is advisable to keep the mulch layer constant, but never bring it directly under the base of the bushes).
Seed-Transplanted Lavender Bush
In the first year after planting seedlings or sowing in the ground, despite all its drought resistance, it is advisable for lavender to provide regular watering. Watering is carried out only in drought. But weeding and protection from weeds are needed in the first year regular. In the first year of flowering, you should not let the lavender bloom violently and, even more so, form seeds: it is advisable to cut off the inflorescences as soon as the first flowers bloom. In the second year of flowering, the inflorescences are cut off as soon as a third of the flowers open and leaving about a third of all inflorescences on the plant. In subsequent years, such tricks will not be needed.
In the first wintering in the soil, it is advisable to protect lavender grown from seeds with an additional high layer of mulch from dry leaves or spruce branches.
Alternative breeding methods for lavender:
- separation of bushes (planting overgrowth);
- rooting of cuttings;
- cuttings of annual shoots.
Few people think about growing lavender at home due to the "self-breeding" of this crop. When lavender seeds ripen, they independently lie on the surface of the earth, stratify themselves and reproduce. Although if you want the plants to grow in the right place, you still have to work hard. In the absence of such a need, you can simply forget about any worries regarding the cultivation.
Lavender: growing and care
It is quite another matter if these beautiful flowers are grown indoors - in this case, it will take not only strength, but also certain knowledge. For example, lavender Southerner grows from seeds at home well, but efforts still need to be made.
Lavender Southerner in a pot
Key cultural features
Lavender Yuzhanka is a perennial shrub with a fairly large (up to two meters in length) and fibrous root. Shoots are numerous, can reach up to 60 centimeters in height. The inflorescences can have a wide variety of shades - from lilac to blue-violet - and are collected in large ears.
Photo of blooming lavender
On a note! Lavender is known primarily for its diuretic effect, moreover, it has a calming effect on frequent palpitations and neurasthenia.
The culture grows in sunny and sheltered places from the wind, mainly on light soil, blooms in July-August.
When growing South lavender, you need to observe certain conditions, consider them.
- Lavender should be grown in a well-lit place, since in partial shade flowering will weaken and, as a result, the aroma of flowers. Daylight hours should be at least six hours, otherwise flowering will not occur at all. In short, ideally, lavender should be located on the south side of the building.
Lavender grows well in sunny areas
- The temperature when germinating seeds should fluctuate between 15-21 degrees.
- Seeds should be sown in late February or early March to a depth of at least 0.3 centimeters.
- Watering should be done regularly and abundantly, especially during the first months of cultivation, but stagnant water should not be allowed (the bushes may dry out). In the future, the frequency and abundance of watering can be reduced.
- Drainage is another prerequisite for growing lavender. Without it, the water will stagnate, which, as we have already found out, is unacceptable.
Correct drainage
Drainage bark
- The soil must be breathable. But there is no need for fatty and nutritious soils, since the plant feels great in poor soil.
- Mulching is unacceptable for Yuzhanka lavender. Therefore, even if you had to cover the plants for the winter, hurry up to open them when spring comes to prevent the moisture level at the base from rising.
If you take into account all these agrotechnical requirements, then you can grow a culture at home without any problems.
Growing lavender
Stage one. Stratification
Usually lavender is bred by cuttings, but if desired, this can be done using seeds. The second method - even if it is slow and not effective in all cases - is good because it is much cheaper than purchasing planted bushes or cuttings, and if a number of requirements are met, it gives the same beautiful plants.
Lavender angustifolia southerner - seeds
Set for growing plants "Lavender"
What is the main difficulty in growing with seeds? And it lies precisely in stratification. More precisely, this is not even a difficulty, but the need for additional time for the preparation of planting material.
On a note! Stratification means simulating the impact of natural winter conditions on the seeds, making it easier for the seeds to germinate. The procedure increases germination and accelerates germination.
Seed stratification - timing
Lavender seeds are characterized by the fact that they may not germinate at all, without first being in the cold for a certain time. The stratification process is not difficult: take a not very deep container, pour sand into it, and put the seeds on top. Then sprinkle the seeds with a little more sand and place in the refrigerator (basement) about a month and a half before the expected sowing date. In this case, it is necessary that the temperature during storage is approximately 5 degrees. Actually, this completes the stratification procedure, we proceed to further actions.
Stratification Tanks Stratification Tanks
Perforation
River sand will be needed
We take seeds. It is advisable to soak them in water in advance.
Mix 1 part of seeds with 3 parts of sand, moisten, put in a cool place
The temperature is set from 0 to +5 degrees
Also, for stratification, instead of sand, you can use perlite.
Stage two. We prepare everything you need
Immediately before sowing, you need to prepare the container. It should be deep and wide. If you are using a pot, then its diameter should be at least 30 centimeters. The fact is that the lavender root grows over time to a decent size, and if the pot is small, then at one "fine" moment it will simply stop growing.
Remember to rinse the pot with soap
Another important point is soil preparation.Lavender Yuzhanka, as noted earlier, needs only loose soil when grown. You can use a store-bought substrate or, alternatively, mix peat with sand yourself (ratio - 1: 1). If you wish, you can further increase fertility by adding eggshells or perlite.
Stage three. We sow the seeds
When sowing, adhere to the following algorithm of actions.
Table. Sowing lavender seeds Yuzhanka
| Step 1 | Take a prepared container and fill it with soil. It can be not only a pot, but also, for example, a wide container, not divided into cells, or a seedling tray. |
Fill a container with planting seed mixture |
| Step 2 | Moisten the surface of the soil slightly, then sow the seeds. If using a split seedling container, place one grain in each cell. If the container is not divided, then sow the seeds at a distance of 1.2-2.5 centimeters from each other. |
Sow seeds. Sprinkle the soil from above |
| Step 3 | Sprinkle the seeds with a layer of soil approximately 0.3 centimeters thick. This is for protection. In this case, the layer should not be too thick, because the seeds require sunlight to germinate. |
Sprinkle the seeds 1/3 cm |
| Step 4 | Place the container with seeds in a warm room (the temperature should be about 21 degrees). |
Keep seeds warm |
| Step 5 | Water the soil lightly. The humidity should be medium (if you overdo it, a fungus will begin to develop, which will destroy all the seeds). It is better to water in the morning so that the soil dries up by the evening. |
Watering |
| Step 6 | Wait a while, watering the soil regularly. Typically, lavender seeds will germinate after two to four weeks. |
Seedlings |
| Step 7 | When the first shoots appear, make sure they get enough sunlight. If there is no suitable place, provide artificial lighting with fluorescent lamps (seedlings should be illuminated for at least eight hours a day). |
Lighting |
Growing lavender at home
Stage four. We carry out the first pick
When a few true leaves appear on the shoots, make the first transplant. The leaves must be "correct", that is, fully developed. At that time, the roots will grow so much that they will not be able to develop further in a not very deep container (for example, the same seedling tray).
Grown lavender, about 2 months
Potted lavender
Prepare larger containers and fill them with soil (not the one used for germination, but another - preferably consisting of perlite, peat and earth). If you are using a tray, keep in mind that the distance between plants in it should be about 5 centimeters.
Preparation for a dive, transfer
On a note! Never use vermiculite. The fact is that it may contain asbestos, even if the manufacturer does not indicate this on the label.
Add some granular fertilizer containing nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus to the soil. Then make a hole in the soil of the new container to the desired size. Gently remove the lavender from the old container along with the soil, place it in the hole and compact the surface around it (the plant needs to be well fixed).
Preparing the soil for seeds. Lavender loves alkaline soil
Fill the pots with soil
Apply fertilizer
Transplant the sprouts gently into the pots
The next transplant will be required when the plant height reaches at least 7.6 centimeters (this can take from one to three months), and until then, gradually "accustom" the lavender to natural conditions - take the containers out into fresh air for several hours every day. After a week, lavender should adapt to new conditions.
Plants must reach a height of 7.6 cm before replanting them again.
Lavender sprouts
Lavender - planting and care
Features of transplanting into open soil
If you are planning to transplant plants outdoors, start by choosing a suitable location. The site should be lit, because in shaded areas the soil is damp, which, again, can cause fungus to develop.
Loosen the area by mixing the soil with compost. Check the pH level: if it is below 6.5-7.5, then add agricultural lime.
Transplant the plants carefully, 30-60 centimeters apart. To do this, dig holes with a depth corresponding to the depth of the containers in which the bushes are located. Remove the plants and transplant to a new location.
Transplant lavender
Watering lavender
Rules for caring for lavender southerner
For lavender to thrive at home, it needs constant care and attention.
- Water the plants daily in the morning using only settled water. When watering, try to get on both the green mass and the soil. In summer, the soil should always be slightly damp, while in winter it is advisable to minimize watering.
Do not forget to water your bushes with settled water in the early morning or evening.
Lavender doesn't like over-watering
- Lavender Southerner needs an annual transplant. New containers, of course, must be larger than old ones.
- The containers should be located in a well-lit place. If there is a lack of lighting (for example, in winter), additionally equip an artificial backlight, as mentioned above.
- When the flowering period is over (approximately in the second half of summer), cut off the lavender - remove the dry stems entirely, and trim the bushes themselves a little.
Correct pruning of lavender
- In winter, the air temperature should be between 15 and 20 degrees, which will allow plants to develop and provide healthy inflorescences. However, this only applies to the growing season, since the rest of the time the lavender must be kept cool.
- Within 35-40 days after sowing, apply liquid flower food (about twice a month). By the way, when grown by cuttings, such fertilizer does not need to be applied.
- In some cases, plants are deficient in moisture due to nearby heating radiators. In this case, the problem can be solved either by spraying the bushes or using a humidifier.
In principle, these are all tips for growing and caring for the described crop. If you grow these plants at home, they will delight you with beautiful flowering and unsurpassed aroma not only in summer, but also in winter. Of course, a lot of hassle, but the result is really worth it.
In France, lavender is called "blue gold"
Video - Growing lavender using seeds
Lavender is a completely unique ornamental and medicinal plant that won endless love two thousand years ago for its pleasant spicy aroma, traditional purple or lilac fluffy beauty and wonderful culinary qualities. Nowadays, lavender is widely used to create borders and ridges, it is advantageous to place it in pots, and it is also indispensable as a background plant. In addition, experienced gardeners will confirm that the smell of lavender is hateful to the Colorado potato beetle and moth. For this purpose, it is important to place the plant not only in the flower bed, but also in the garden. However, in order for the sea of these delicate and cheerful spikelets to take root in your summer cottage, you need to keep in mind some of the features of their reproduction and proper planting in open ground. Read about all this in our material.

Types and varieties of lavender
The most popular types of lavender are as follows:
Reproduction methods
You can propagate lavender in the following ways:
- stem layering;
- dividing the bush;
- cuttings;
- seeds.
We will briefly talk about the essence of each of the breeding methods, and we will talk in more detail about how to grow lavender from cuttings and seeds.
Stem layering
The easiest way to propagate lavender in the garden is with cuttings.
Step-by-step instructions for propagating lavender with stem layering are as follows:
- In the spring, it is necessary to lay one of the bush branches in a small depression, and then sprinkle it on top with soil with compost and water it.
- It will take several months for the cuttings to take root. During this time, you should constantly keep the soil moist.
- Once the cuttings are fully rooted (usually in the fall), they should be cut from the mother bush. Remember to treat the cut to prevent it from starting to rot (for example, with crushed charcoal).
- Transplant the rooted cuttings to a new location in the garden the following spring, along with the earthy clod.
Video: propagation of lavender by stem layering
By dividing the bush
In order to propagate lavender by dividing the bush, you need to do the following manipulations:
- After pruning in the fall, spud the lavender bushes well, filling the space between the stems with soil.
- Next spring, it will be necessary to huddle the shrub again well (although the reproduction procedure can be carried out already during this period).
- In the fall, you should divide the bush into several parts, planting the plant together with an earthen lump in a previously dug hole in a new place.
- Fill the hole with soil and tamp lightly, then water liberally.
Important!The root system of lavender can reach a length of several meters, so it is advisable to replant with small bushes.
Growing lavender from cuttings
Propagating lavender by cuttings is considered the most economical and efficient way. It is suitable both for breeding at home and for open ground.

Terms of cuttings
Many summer residents carry out the lavender cuttings procedure throughout the year. But it is still optimal to choose exactly those seasons when the plant has the most green and young (not yet lignified) shoots, that is, it is better to do this in spring or autumn.
Preparing cuttings
To cut and prepare a lavender stalk for planting, you must:
- Take a secateurs (or a sharp knife, but not scissors!), Choose the most suitable tops and cut them off (the length should be about 10-15 cm). If the shoot is flowering, then its upper part with flowers must be cut off.
- Now you need to clean the lower part of the shoot from the leaves by about 3-4 centimeters. The upper leaves are left to feed the cutting. If you leave too much greenery, then the plant will spend all its energy on it, although we need it to grow roots.

Planting cuttings in pots
Before planting, you need to pick up planting containers, for example, small pots, 0.5 liter cups and soil mixture. Prepare the shards for drainage. There are several ways to prepare soil for planting lavender cuttings: 1. mix universal soil and perlite in equal proportions; 2. compost and perlite are also in equal proportions; 3. turf land, leaf land and sand again in equal proportions.

Step-by-step planting of lavender cuttings in a pot:
- Prepare planting containers, drainage and potting soil.
- Lay drainage and some moistened sand at the bottom.
- Fill the pot with earth, tamp it from the ends, and then spill it with water (you can use a phytosporin solution to disinfect it).
- Pour some sand on the surface of the soil.
- Before planting, it is recommended to treat lavender cuttings with root growth stimulants (for example, the same "Kornevin"), and then burrow into the pot with the peeled tip down to the very leaves (you can plant 2-3 cuttings or even more in one pot).

- Drizzle with water.
- As soon as the water is absorbed, it is necessary to create greenhouse conditions for the plant, namely: cover with a bag or film.
- Place in a warm place for rooting.
Caring for planted cuttings
The basis of caring for lavender cuttings is keeping the soil moist, in other words, regular watering. The soil should not dry out.
Landing in open ground
Typically, it takes about 4-6 weeks for lavender to take root. The signal for transplanting into separate containers (suitable for both growing at home and for a garden) or planting in open ground is the appearance of young roots that are trying to crawl out through the drainage holes of the planting container.
Seedlings must be carefully removed from the planting containers. To do this, they should be turned over, then holding the upper part of the plant, lightly knock on the bottom of the container and pull out together with a lump of earth.
Depending on the growing method, plant the seedlings in larger pots (which you can again put in the fresh air or leave at home) or in the ground in the garden.
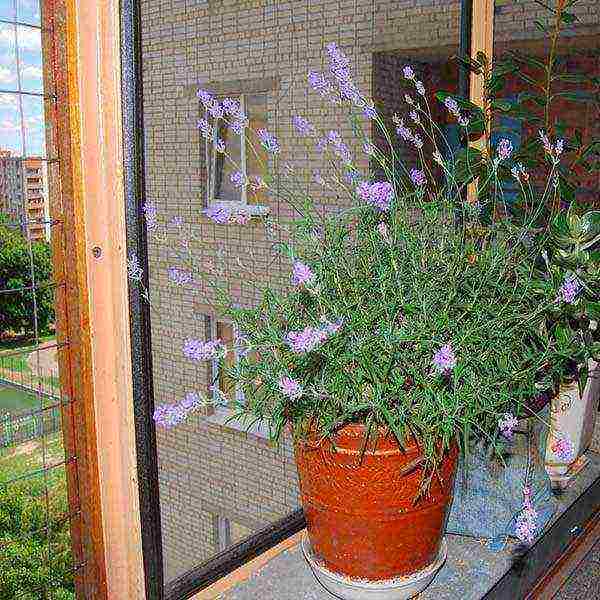

Recommendations for choosing a place for planting in a garden can be found below.
Video: planting lavender cuttings
Growing lavender from seeds
It is not so easy to grow lavender from seeds, moreover, it will take a lot of time. Therefore, you first need to decide on the timing of planting and lay the seeds for stratification.

Important! Often, problems with growing lavender from seeds are due to the fact that only fresh lavender seeds germinate well, so when buying, you should first of all pay attention not to their expiration date, but to the date of collection.
Sowing dates
You can sow lavender for seeds both in spring and in autumn, just calculate the time for stratification in advance. For example, plant seeds for stratification in January so that they can be sown in pots in March, and in May to plant lavender seedlings in open ground.
Stratification
Lavender seeds require mandatory stratification, in other words, the seeds must be kept for some time at a low temperature and in a humid environment. This is done, firstly, in order to create natural conditions under which the seeds germinate. Secondly, this triggers embryonic sleep, that is, when the temperature drops, the seeds fall asleep, and as soon as it starts to rise, they immediately wake up. Thirdly, this is a kind of shock therapy.
Methods for stratification of lavender seeds:
In wet sand

- Take the sand, then you need to sift it, rinse and bake it in the oven for 30-40 minutes.
- Pour sand into a bowl and moisten it from a spray bottle (water should preferably be thawed or settled).
- Sprinkle lavender seeds onto the wet sand.
- Sprinkle a little dry sand on top.
- Place the bowl in a bag and wrap it around the container.
- Place the container in the lower drawer of the refrigerator (where the temperature ranges from + 3 ... - + 5 degrees) for 1-2 months.
On cotton pads

- Take a small lid and a couple of cotton pads.
- Place 1 cotton pad on the lid and moisten it from the spray bottle.
- Sprinkle the seeds onto a damp cotton pad.
- Cover with a second cotton pad and spray again with a spray bottle.
- Put moistened cotton pads with seeds inside in a plastic bag (it is convenient to do this with a ZIP bag), which should be disinfected with hydrogen peroxide beforehand.
- Place the bag with cotton pads in the lower drawer of the refrigerator (where the temperature ranges from +3 ..-. + 5 degrees) again for 1-2 months.
On a wet wipe
- The method is identical to the previous one, only instead of two cotton pads, you use one napkin, which you just need to fold in half.
In a pot of soil
- Take a pot or any other small container, fill it with universal soil (or coconut substrate) and sand in equal proportions.
- Pour an additional small layer of sand on top.
- Moisten the surface with a spray bottle.
- Sow the seeds and sprinkle lightly with sand on top.
- Put the pot in a bag and tie it or secure it with an elastic band.
- Place the pot in the lower drawer of the refrigerator (where the temperature ranges from + 3 ... - + 5 degrees) also for 1-2 months.

Important! It is necessary to ventilate containers at least once a week.We just open the bags and let the fresh air go inside! First for 5 minutes, and then gradually increase to 15-20 minutes. For the same time, after airing, we leave it at room conditions. At the end of stratification, about 1-2 weeks before sowing, after airing, we begin to leave the seeds in room conditions for 30-60-120-180 ... minutes and so on until the whole day in the room, and at night in the refrigerator.
This stratification treatment will help the lavender seeds germinate faster.
Sowing seeds
When the stratification is over (the seeds will sprout), and the time comes to sow lavender seeds in a pot, you will need to do the following:
- Pick up small planting containers with drainage holes.
- Prepare a soil mixture, for example, take a universal soil for seedlings and mix it with sand in equal parts. Or take garden soil, humus and river sand in a ratio of 3: 2: 1.
- Sow seeds on the surface of the soil (you can together with sand, if you used method 1 of stratification) and lightly sprinkle with sand.
- Moisten with a spray bottle with warm water.
- Cover with foil and put on a light and warm windowsill, where the temperature is about + 18-22 degrees.
Video: growing lavender seedlings from seeds
By the way!If you live in the south, you can sow lavender seeds right away. in the fall in open ground, in which during the winter (especially if the winter is snowy) they will undergo natural stratification, and in the spring the first shoots will appear. In this case, the seeds should be buried 3-4 cm into the soil.
This method is not suitable for the Middle zone (Moscow region), Siberia and the Urals!
Seedling care after sowing
After about 2-3 weeks, the first sprouts of lavender seedlings will begin to appear.

Further care consists in regular watering (light spraying at first. When you grow up more you can water from a watering can) and maintaining temperature and light conditions.

Picking

Diving lavender is not difficult at all. The procedure is more than standard. When the lavender seedlings have 2-3 true leaves, you will need to do the following:
- To begin with, water the plantings abundantly so that the seedlings are easily accessible. And also the soil in containers where you will dive.
- Make indentations in new sapling houses.
- With your hands or with the help of special tools, carefully take out the seedling and deepen it to the cotyledon leaves.
Video: picking lavender seedlings
Further care is no different. Water and wait for the lavender seedlings to grow old enough. Then plant it in pots or open ground when weather conditions permit.

Worth knowing! Typically, perennial lavender grown from seed,does not bloom in the first yearbecause she is gaining strength and growing green mass. And already in the 2nd year, she will certainly delight you with her beautiful flowers. Although there are some varieties of lavender that can bloom in the first yeareg annuals.
Planting lavender in open ground: choosing the best place in the garden
Landing dates
Planting lavender outdoors, as a rule, occurs in the last spring month of May. This applies both to the method in which the seedlings are grown from cuttings and from seeds.
Place and soil
Choose a sunny location for planting lavender. If you plant it in the shade, then the flowering will be less abundant and bright. When choosing a place, it is also worth considering that it is optimal to plant a plant in high clubs, wet lowlands will not suit it. Moreover, it is impossible for groundwater to pass close by.

The optimal soil for planting lavender is sandy loam, sourness. - 6.5-7.5 pH. But just in case, before planting in the ground, it is still advisable to add wood ash (or lime), because the plant does not tolerate acidic soils.
You can successfully grow lavender on loams, but you have to make good drainage and improve the soil (loosen it up) by adding compost to it.
As for landscape design, blooming lavender will look great next to garden paths (as borders), on alpine slides and rockeries.

As for the distance between plantings, if you want to get a hedge, plant 1/2 of their intended height, otherwise the distance between flowers should be equal to their height.
By the way! Lavender is a great attraction for beneficial pollinating insects and repels harmful ones such as aphids. Therefore, it would be nice to sit her next to with roses.

Outdoor lavender care
Lavender cannot be called a completely unpretentious plant, which every novice gardener can cope with growing, but you cannot refer to it as particularly demanding.
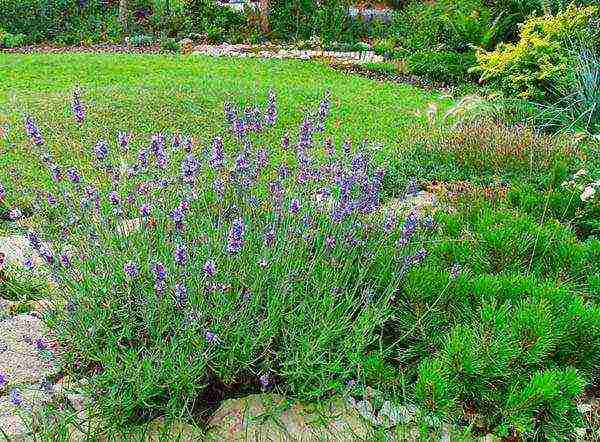

Thus, further care for lavender after planting in open ground consists in the following garden manipulations: watering, weeding and loosening, hilling, fertilizing, pruning and shelter for the winter.
Watering lavender must be carried out strictly as the soil dries. The plant does not like when the soil is excessively moist, but it should not be overdried either, otherwise it will negatively affect its flowering.

Weeds are an unwanted guest in a lavender flower bed, so from time to time it is necessary loosen and weed, and even better to take care of its protection from weeds in advance. This is perfect for this mulch (grass, peat, bark, compost). But only the trunk circle should be mulched, the trunk itself should not be covered with mulch, otherwise the plant may rot.
To stimulate the growth of new young shoots, lavender is needed in spring and autumn.spud.
Feed lavender follows in several stages. Spring feeding should include nitrogen fertilizers for building up green mass, for example, urea (at the rate of 1 tbsp. Spoon for 1 bucket of water). During the budding period and during flowering, the plant requires a lot of potassium, which means you need to perform potassium fertilization, for example, with potassium sulfate or potassium nitrate. A weaker, but much more popular potash fertilizer is a solution of wood ash (100 grams per bucket of water).
By the way! If you use compost as a mulching material, then you most likely will not need additional fertilizing.
After the lavender has faded, its peduncles should be promptlyprune.
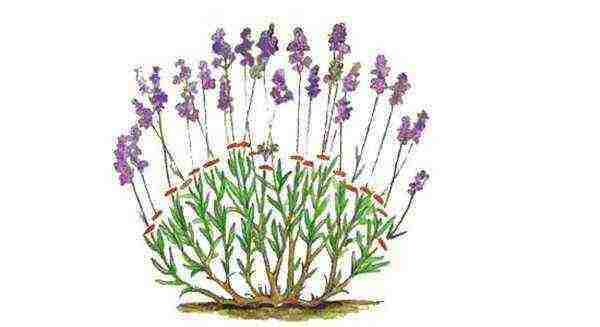
Video: breeding, planting and caring for lavender
Preparing lavender for winter
English lavender is quite frost-resistant, which cannot be said about its French variety, which it is desirable to grow in a pot, and take it to a warmed loggia or to a windowsill for the winter.

Important! For detailed information on the method of preparing lavender for winter (pruning, shelter) read in this article.
Video: preparing lavender for winter
If it is a hundred times more interesting for you to grow lavender yourself, to put your soul into a wonderful flower, then please be patient and love, as well as our proven methods of proper planting and caring for the plant, set out above.
Video: breeding and planting lavender


