Content
- 1 Features of growing wisteria of different varieties
- 2 Wisteria planting rules
- 3 Wisteria care
- 4 Video tips for growing wisteria at home
- 5 Description of the plant
- 6 Types and varieties for the garden
- 7 Breeding features
- 8 Landing rules
- 9 Care secrets
- 10 Wisteria in landscape design
- 11 Description and types of wisteria
- 12 How to grow wisteria?
- 13 general description
- 14 Types and varieties
- 15 Wisteria propagation methods
- 16 Planting wisteria in the ground
- 17 Care for wisteria after disembarkation
- 18 Pests, diseases and possible problems
- 19 Wisteria in landscape design
- 20 What does wisteria look like
- 21 Types and varieties of wisteria
- 21.1 Chinese wisteria blue sapphire
- 21.2 Wisteria alba
- 21.3 Wisteria wisteria floribunda (profusely flowering, multi-flowered)
- 21.4 Wisteria macrostachia (large-walled)
- 21.5 Wisteria frost-resistant blue moon
- 21.6 Indoor wisteria
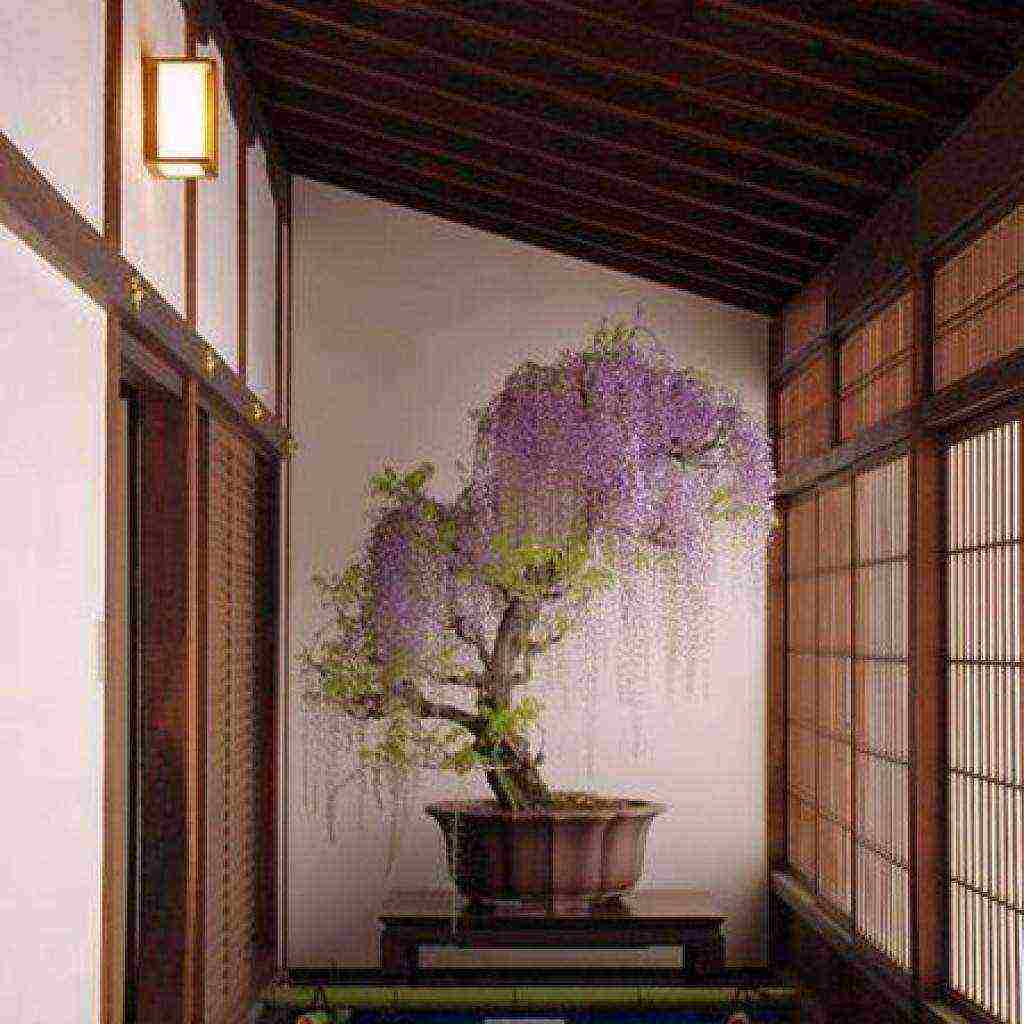
- 21.7 Wisteria bonsai
- 21.8 Beautiful wisteria
- 21.9 Shrub wisteria
- 21.10 Japanese wisteria
- 22 How to care for wisteria at home
- 23 How to prune wisteria for flowering
- 24 How wisteria reproduces
- 25 How to plant wisteria
- 26 Diseases and pests of wisteria
- 27 How poisonous is wisteria
 Wisteria is the true dream of every gardener. After all, this is the beautiful creeping plant in the world.
Wisteria is the true dream of every gardener. After all, this is the beautiful creeping plant in the world.
The flowering of multifaceted flower clusters can be compared with the most beautiful of the waterfalls, only this waterfall emits a surprisingly delicate and pleasant aroma. Most often, a plant is grown with the purpose decorating the walls of a house, gazebo or arches.
Description of the plant
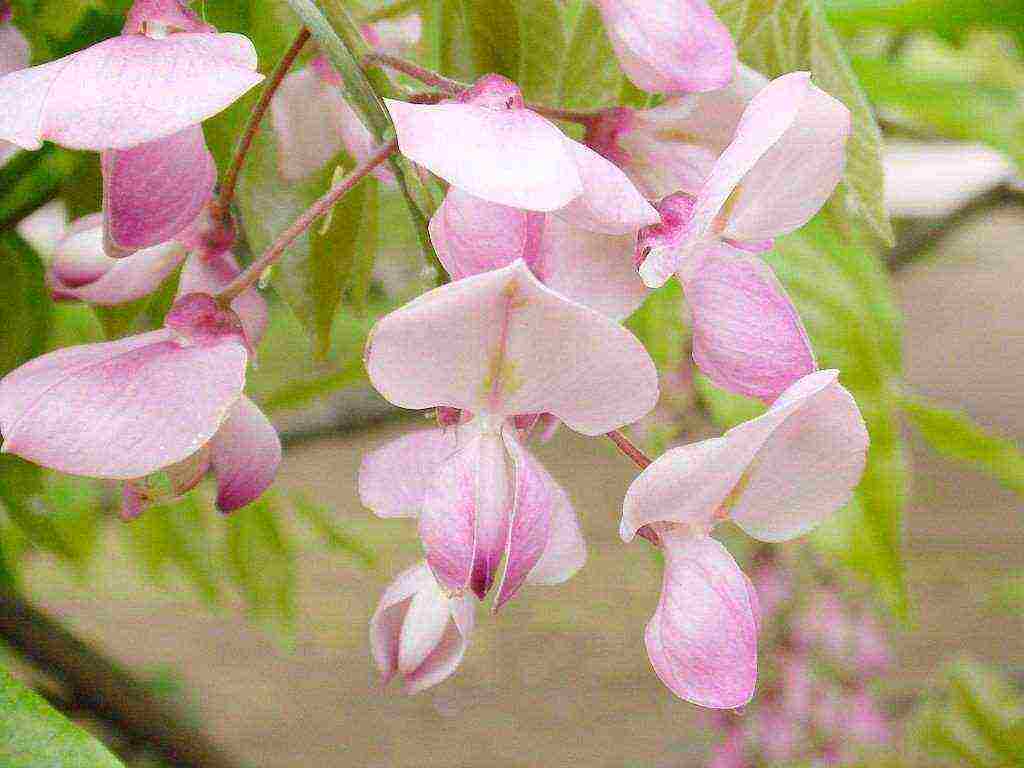
 Wisteria or, in other words, wisteria - This legume tree... This plant belongs to liana-like and has amazingly beautiful cluster-shaped flowers of lilac, pink or white.
Wisteria or, in other words, wisteria - This legume tree... This plant belongs to liana-like and has amazingly beautiful cluster-shaped flowers of lilac, pink or white.
The wisteria genus contains more than 9 varieties of vines... They are all common in countries with a subtropical climate. But other varieties of wisteria are also known, which are distinguished by resistance to a drop in temperature.
They are successfully grown in conditions of the middle zone and perfectly tolerate temperature extremes. True, after a harsh winter, the beauty will no longer bloom. She'll just freeze out. But wisteria can often be found on the windowsills of apartments or offices in the form of a small tree - bonsai.
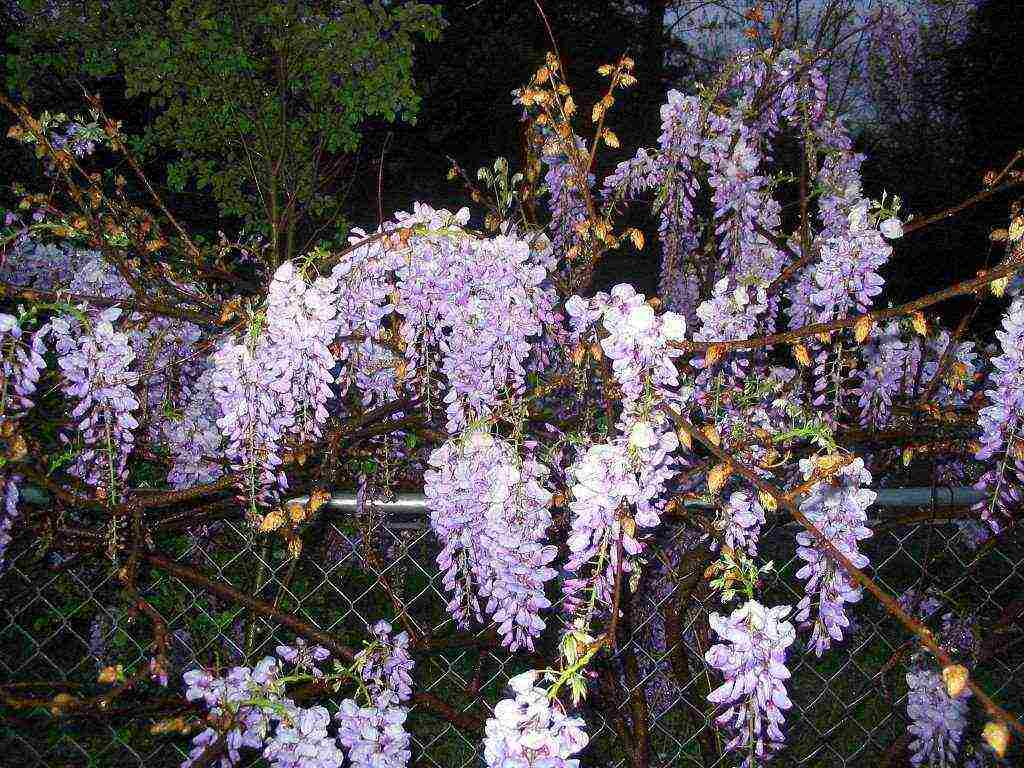
Chinese wisteria, as the name implies, grows in China. In the wild, it is found almost everywhere in this country. The plant has a fairly dense foliage. Each leaf of the plant can grow up to 30 cm, and wisteria shoots grow so large and long that they can completely cover tree trunks, house walls and other fences.
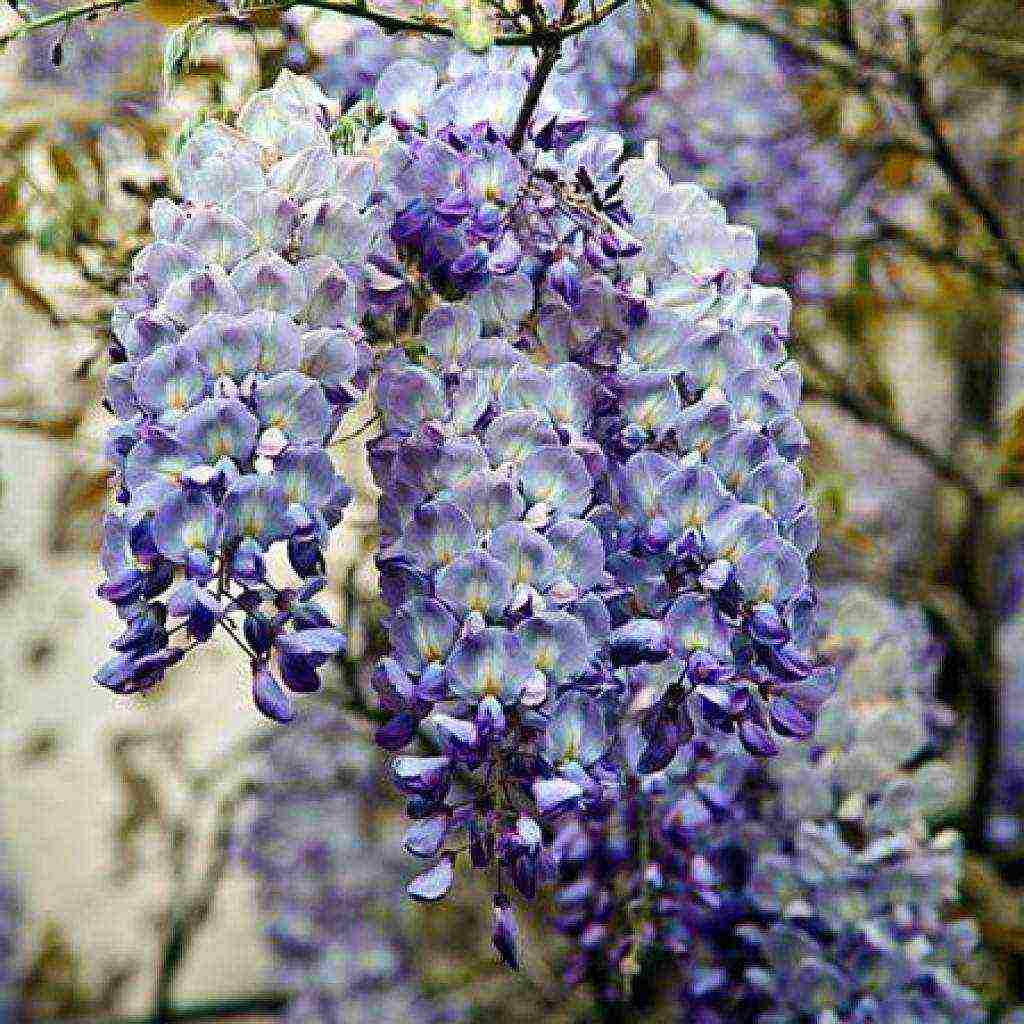
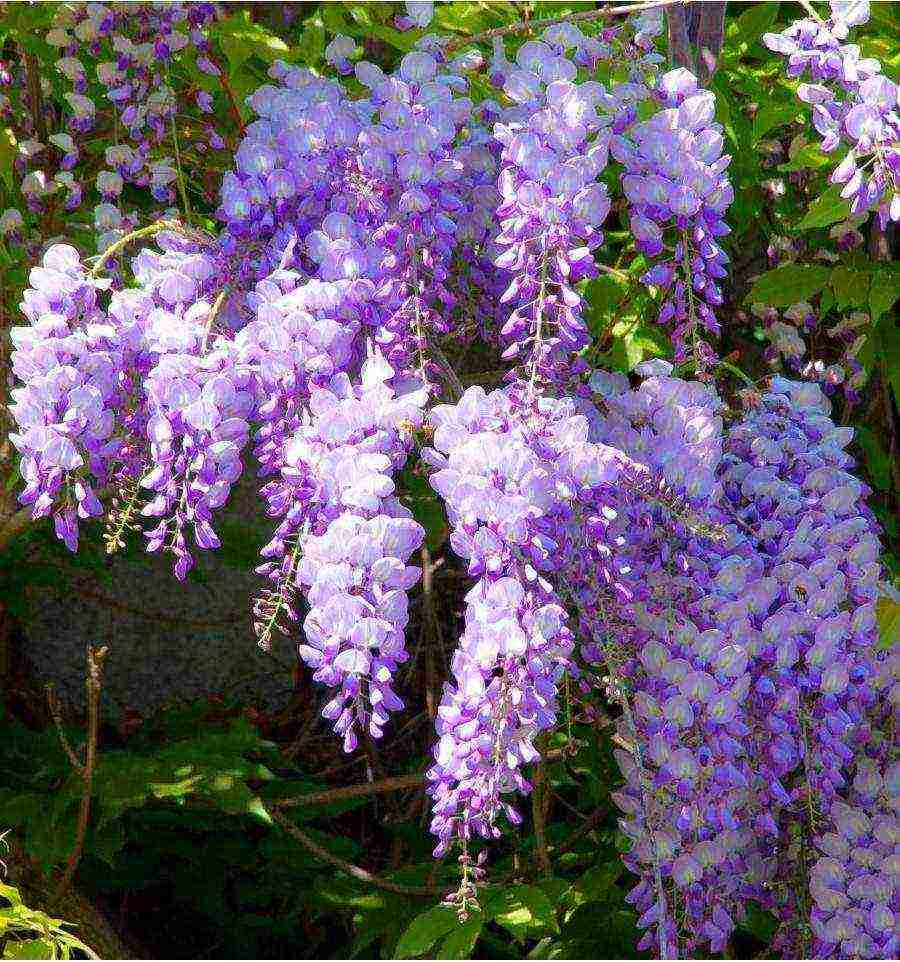
Wisteria blooms from May to July, covered with amazingly beautiful brushes of all shades of purple. White flowers are extremely rare, but this is also possible.If the soil is ideal for the plant, and there is enough sunlight, then the plant will bloom again in September. Its delicate flowers are gathered in clusters, rather long and beautiful. At the same time, they most often bloom at one time, creating an amazingly beautiful picture. But the plant begins to bloom only three years after planting.
The most common varieties
 Chinese wisteria has many varieties, but most of them have purple or lilac flowers. But there are also varieties whose flowers are white.
Chinese wisteria has many varieties, but most of them have purple or lilac flowers. But there are also varieties whose flowers are white.
But these varieties are more common:
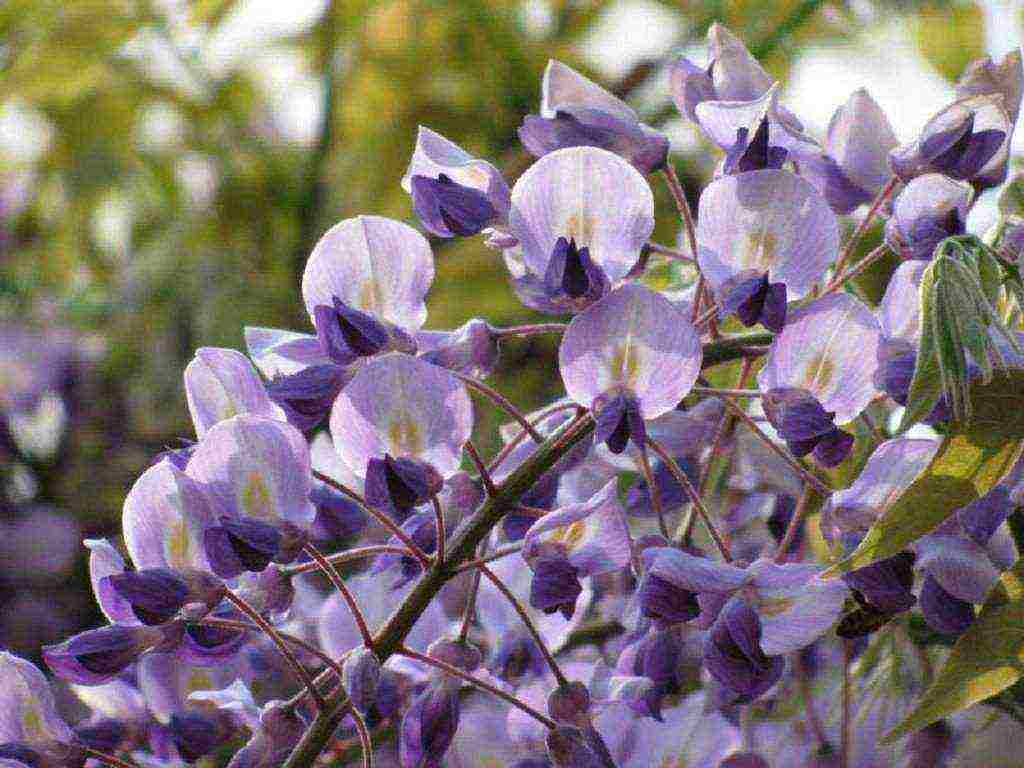
- Blue sapphire - amazingly beautiful liana, which has purple-blue inflorescences. Most often, the plant blooms in May, but belated flowering is possible - in the middle of summer. The clusters of inflorescences have a sweet, even somewhat sugary aroma, and delicate flowers have a delicate purple hue. The brushes grow up to 25 cm. The liana grows to a height of 6 meters and at the same time it twists along the support in a spiral. The annual growth of the plant is up to 2 meters.
- Amethyst... This variety of wisteria begins to bloom very early. The long inflorescences of the purple plant delight the eye of the gardener and neighbors from mid-May until the end of summer. Compared with other varieties, the aroma of this flower is stronger and more intense. This variety does not differ in winter hardiness, and therefore requires careful shelter for the winter.
- Prolific Is a beautiful plant that blooms with delicate blue flowers. This variety of wisteria begins to bloom already in the third year after planting. She gives a very good growth - 2 meters per year. If you plant it at a support, then in a few years you will have a beautiful decoration of a wall or an arch to the courtyard. The plant takes root well and quickly and grows in moist and loose soil.
- Southern belle - this liana has delicate flowers of white-purple color and a moderate intensity of aroma. The peak of flowering intensity occurs in mid-May, and by the end of summer, the flowers completely crumble. The plant prefers a sunny location with moist soil. Perfectly decorates gazebos and gardens.
- Texas white - belongs to dwarf varieties of wisteria and does not grow more than 2.5 meters in height. It begins to bloom in the second year after planting and releases many white flower clusters. The plant prefers high, sunny places with moderately moist soil. Copes with the shelter of trees, arbors.
Wisteria planting rules
 If conditions allow, then grow a wisteria flower every gardener can do it. If you follow the planting rules, then it feels great in urban conditions, and with proper care it tolerates wintering well.
If conditions allow, then grow a wisteria flower every gardener can do it. If you follow the planting rules, then it feels great in urban conditions, and with proper care it tolerates wintering well.
To grow lianas, you need to find a sunny place, but even in partial shade, it feels great. But, when choosing a place for planting, it should be remembered that the plant is very photophilous, and therefore it is worth picking up such a site, the sun over which holds for at least 6 hours.
But it is imperative to protect it from wind and cold, so planting wisteria on the south side of the house would be the best option.
By picking up landing place you need to take into account the fact that wisteria is a perennial plant. Therefore, its further transplantation may cause some difficulties. Its root system goes deep into the soil for at least a couple of meters. Therefore, it should be immediately planted in a permanent place.
Soil for wisteria
 The flower has no special preferences in the soil, but it is still worth planting it in moderately fertile, light and moist soil. The soil must be air permeable and not retain water.
The flower has no special preferences in the soil, but it is still worth planting it in moderately fertile, light and moist soil. The soil must be air permeable and not retain water.
Too much lime in the soil can lead to the rapid death of the flower. He begins to fall ill with chlorosis, which is determined by the strong lightening of the leaves. Too nitrogenous soil is also not needed gLicinia Chinese Blue Sapphire and therefore fertilizer should be applied as rarely as possible, otherwise it will not bloom.
To Chinese Wisteria Blue Sapphire or any other that has taken root faster, you should prepare the soil yourself and fill it in the hole. To do this, you need three parts of turf soil, one part of sand and the same amount of peat. All this is thoroughly mixed and poured into the planting pit. The plant will root quickly and have enough nutrients in such a soil.
Landing rules
Before planting abundantly flowering wisteria or another type of plant in the ground, it is required to soak the sprouts for half an hour in water. After that, you need to prepare a pit with dimensions of 50x50x40 cm.A pre-prepared soil is laid out at the bottom of the pit. You need to cover the plant with soil 10 cm deeper than it grew before transplanting. Bark should be laid on top of the soil.
Planting is carried out at a distance of 30 cm from the support or wall. Do not be afraid that for the first two to three weeks the plant will not show signs of life. It takes a very long time to get used to a new place and begins to grow. At first, Chinese wisteria takes root and all forces go to this process.
Wisteria: planting and care in the open field
 Growing wisteria outdoors can hardly be called a time consuming procedure. She is quite unpretentious and easily tolerates drought. Therefore, you should simply adhere to the rules of agricultural technology and the vine will delight you with active growth and flowering:
Growing wisteria outdoors can hardly be called a time consuming procedure. She is quite unpretentious and easily tolerates drought. Therefore, you should simply adhere to the rules of agricultural technology and the vine will delight you with active growth and flowering:
- water and feed the liana;
- trim;
- shelter for the winter.
Water and feed the plant as needed. Watering should be done so that the soil is slightly moist all the time. During the period of bud formation, it is recommended to additionally intensify watering and spraying of the bushes. Otherwise, the buds will fall off and the vine will not bloom. But you should still prefer spraying the plant, because frequent watering leads to stagnation of water in the roots and their decay. From September, watering should be reduced to a minimum as the plant prepares for winter.
In order for the plant to grow well and bloom profusely, it should be fed with fertilizers. It is optimal if you alternate mineral fertilizers with liquid organic ones. It is recommended to apply fertilizers during the growing season.
In order for the soil not to be washed out and always saturated with useful substances, it is recommended to water it once a season with chalk water.
After the inflorescences wilted, they should be cut off. And it is recommended to tie young twigs, changing the direction of their growth. Pruning wisteria is also needed so that the plant begins to bloom better and for the formation of its crown. Most often, for these purposes, young shoots and twigs are cut off, which prevent flowering bunches from growing and developing. Flowers can develop only on last year's or even older branches, and therefore spring pruning does not affect the splendor of the crown in any way. Pruning is required without fail, otherwise next year of flowering you can not wait.
When growing vines in mid-latitudes and winters are expected to be cold, it is recommended to tie all young shoots, so that later it would be easier to cover them. But in general, Chinese wisteria perfectly tolerates a slight drop in temperature and feels great in conditions up to minus 20 degrees.
Growing wisteria outdoors and in pots is no different. But at the same time it is worth remembering the rule that for the winter it is recommended to transfer the pots with the plant to a place with a humidity of at least 70%.
Indoor watering occurs only as the topsoil dries out. And pruning is carried out in the spring in order to form the crown. After that, the vine can be taken out into the street.
Shelter wisteria for the winter should be carried out in the same way as for bush roses. To do this, first carefully spud the root area. The liana is separated from the support and fixed on a specially prepared shield. After that, the branches should be covered with dry foliage. If winter fell with a small amount of snow, then you should additionally cover the plant with agrotex.
Reproduction of wisteria
 Most often, wisteria is used for reproduction:
Most often, wisteria is used for reproduction:
- seed method;
- vegetative.
But the seed method is suitable only for experienced gardeners, because the plant from them hatches completely unwillingly. Yes, and it takes a lot of care for them. First, the seeds must be sown in pots or boxes, which are recommended to be placed in a warm and humid place. To create a greenhouse effect, cover the boxes with foil. Spraying the soil should be done with a spray bottle. The seeds are kept in this way for at least a month. After that, they should be brought out into the light.
After the first shoots appear, the plants should be planted in separate containers without separating the earthy coma. The container should be pre-treated with a solution of potassium permanganate, but the plants themselves are subjected to the same treatment. To do this, after transplanting, they should be watered with a manganese solution.
But with a similar cultivation method, it is not always possible to get good shoots. According to experts, only 25% of the plants grow. The plant blooms extremely reluctantly, and may never bloom at all.
When breeding wisteria in the middle lane, it is recommended to use layering from an existing adult plant. To do this, in the spring, an incision is made on a strong and formed process. After that, it is recommended to place the cut point in a container with soil and sprinkle it with earth. The plant needs to be watered and fed regularly. By mid-August, roots will appear on it and the layers can be transplanted to a permanent place in the spring.
It is possible to grow wisteria in the Rostov region, only you need to select frost-resistant varieties. And then this beautiful and amazing plant will appear in your garden or small garden. And it can decorate any place where it grows. After all, there are no such amazing flowers on any liana. So plant this amazing flower waterfall and savor its scent.
A charming plant with violet-blue flowers gathered in racemose inflorescences, with an intense sweet aroma. It begins to bloom in May, sometimes also in summer.
HOW LOOKS: The flowers are decorative, violet-blue, clustered in long racemose inflorescences, 20-25 cm long, with an intense sweet aroma. It blooms at the beginning of V, sometimes flowering is repeated in summer. The leaves are pinnately-separated, light green in spring and summer, and yellow in autumn. The stems are twisted clockwise.
How it grows: Vines; shoots twine around the supports. Fast-growing, up to 6 m in height, annual growth of 1–2 m. Strong supports are required.
WHERE TO PLANT: Prefers sunny, warm and sheltered places. Undemanding to soils, loves permeable soil of medium moisture. Not fully frost resistant (zone 6-8). In severe winters, it can freeze slightly.
HOW TO LAND AND CARE: Before planting, soak the plant in water for 10-30 minutes. The plant is planted in a planting pit measuring 40 x 40 x 40 cm with fertile soil, 10 cm of humus and compost are placed at the bottom, we plant 5-10 cm deeper than the plant grew before. We fill the hole with fertile soil. Vines should be planted at least 30 cm away from walls or other plants. Cover the land around the plant with bark, IV fertilize, and intensively add during the growing season. Pour 10 cm before the beginning of winter. Pruning is necessary for flowering. Do the main pruning in VII-VIII, cutting out diseased shoots, shoots creating density and strongly overgrown; the rest of the annual shoots should be cut over 5.˗6. sheet.
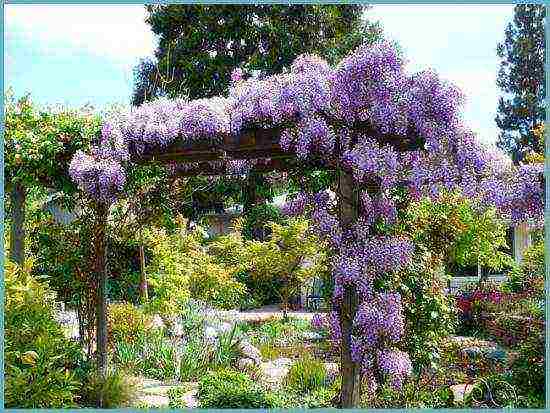
HOW TO USE: The plant is recommended to grow on verandas, pergolas and sturdy structures next to walls.
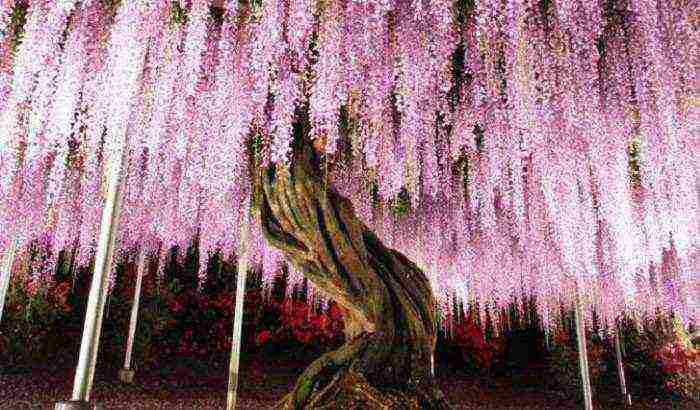
Wisteria (wisteria) is the dream of all gardeners, it ranks first in beauty among perennial weaving plants. The flowering of such a liana resembles a bright colorful waterfall of bunches of flowers, emitting a sweetish pleasant smell. Growing wisteria is actively used by flower growers for decorative purposes.She decorates the walls of houses and gazebos, a terrace, a fence, an arch.
Features of growing wisteria of different varieties

Before buying a vine seedling and planting it in your garden, you should find out which species are suitable for our climatic conditions and what are the features of their cultivation. Wisteria as a genus includes 9 species, but only three are suitable for our area: Chinese, frost-resistant, profusely flowering. When breeding such vines, it is necessary to ensure the following conditions:
- Bright sun. Abundant flowering of wisteria can only be obtained in a sunny area.
- A solid foundation. Liana is a climbing plant, and it needs a good, strong support on which it will grow.
- Stable watering. From spring to summer, the land on which the wisteria grows must be kept moist. The main thing is not to overdo it, the plant does not tolerate excess moisture.
- Top dressing with fertilizers. Like other plants, wisterias need fertilization, especially during the budding period.
- Thorough shelter for the winter. Despite the fact that such a vine is a frost-resistant plant, it is recommended to wrap its twigs with leaves, paper, roofing felt or special covering material for the winter.
- Pruning. For dense flowering, wisteria is cut off 2 times a year (at the end of flowering, after leaf fall).
If the climatic conditions of your region do not allow growing a vine outdoors in the open field, try planting it in a flowerpot, like a standard tree. In autumn and winter, it will decorate the hallway or hall of your home, and in spring and summer it will embellish the terrace or entrance to the house. To form a wisteria crown, you will need to prune the young side shoots several times in the spring.
Chinese (Wisteriachinensis)

The birthplace of tree-like wisteria is China. The plant is characterized by a dense foliage, the length of the shoots reaches 15-20 m in height. The leaf of Chinese wisteria is large (20-30 cm long), has a complex odd-pinnate shape and consists of 7-13 small leaves. The liana blooms with light purple (in rare cases white) flowers, which are collected in a 40 cm brush and all bloom at the same time. Flowering begins with the appearance of foliage and lasts until the end of summer. This is often repeated in early September.
Wisteria is a thermophilic and light-loving plant, but it develops well in the shade. It is not particularly demanding on the soil, but it is preferable to plant the plant on fertile, moist soil. This vine is well adapted to urban conditions, withstands a short-term drop in temperature to -20C. Wisteria grows quickly, lifting stems up the support from right to left. With systematic pruning, the plant is suitable for growing in pots and tubs.
Frost resistant (Blue Moon)

This plant is native to North America. Wisteria Blue Moon is fast-growing, its maximum length is 8 m. The bush has unpaired leaves (consists of 7-9 leaves) of glossy dark green color. The inflorescence is abundant and dense, reaches a length of 25-30 cm, consists of bluish or blue-purple flowers. Frost-resistant wisteria blooms in early June and blooms for 2-3 weeks.
The main feature of this vine is its good tolerance to extreme cold temperatures down to -40C. It is advisable to plant a plant in a sunny area or on the south side of the building. Wisteria grows on any type of soil, but in order to achieve maximum flowering results, it is recommended to grow it on black soil or loam. It is not recommended to plant a bush in swampy, calcareous places. This type of wisteria is not picky about watering and tolerates drought well. Only young plants need to be systematically watered.
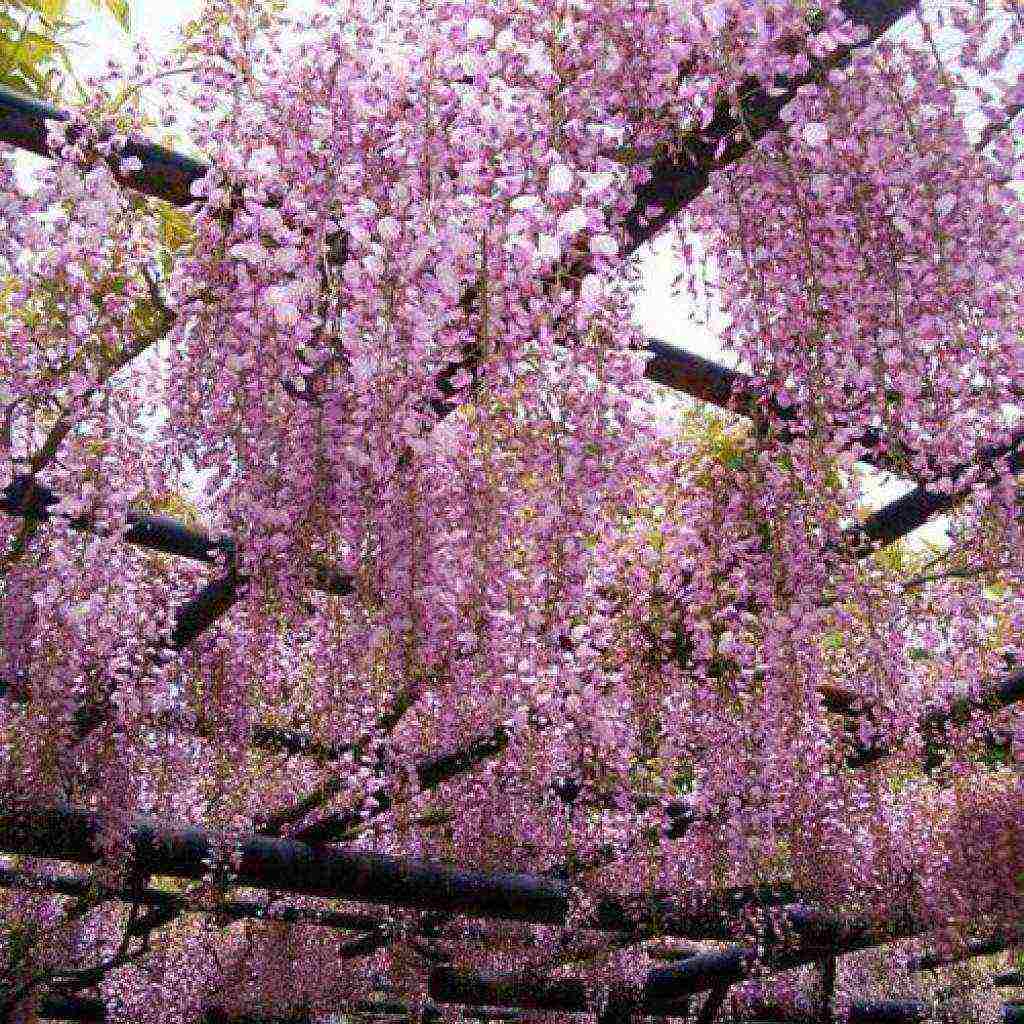
Abundantly flowering or multi-flowered (Wisteria floribunda)

This wisteria was originally developed in Japan. The height of the vine reaches 8-10 meters, has very large leaves (40 cm) with 15-19 small leaves. The size of clusters of inflorescences reaches 50-70 cm.Wisteria blooms after the leaves bloom, in the second half of May, sometimes again at the end of summer. Flowers bloom gradually, starting from the base of the brush, ending with the bottom.
Multi-flowered wisteria withstands frosts well down to -25C. For lianas, sunny areas with light, moderately moist, loose soil, without stagnant water rich in nutrients, are preferred. Multiflorous wisteria twines around the support with stems only clockwise. The color range of flowers is varied: white, pale pink, pale purple, reddish.
Wisteria planting rules
You need to plant 1-2 year old wisteria seedlings. When planting a plant, it is necessary to follow simple rules on which the further growth of the plant and its flowering depend. Wisteria should be provided with a brightly lit place with light fertile soil, strong supports on which it will trudge in the future, a reliable shelter in the winter season.
Location

Sunlight is very important for wisteria, it needs to be in the sun for at least 6 hours a day. But there should be no drafts, the best choice would be the southern, southeast, southwest side of the building. For wisteria shoots, prepare and install a durable, strong wind-resistant support in advance. When choosing a planting site, take into account the toxicity of the plant, therefore it is not recommended to plant wisteria near water sources.
Soil preparation
For abundant flowering of wisteria, light, fertile, well-permeable soil is needed. With an acidic reaction of the earth, it is necessary to lime it a little. Just do not overdo it, from a large amount of lime, the vine loses its attractiveness, its leaves become light. Clay soil before planting wisteria must be drained with organic fertilizers. For a seedling, plants dig a deep hole, fill it with humus, river sand, leaf and clay-sod soil, mixed in equal parts.
The best time to disembark

The planting time of wisteria depends on its breeding method:
- Cuttings. Spring is suitable for good rooting. For this, an annual shoot is chosen, an oblique incision is made in the middle of its length. The stalk is planted in this place in soil fertilized with a nutritious substrate. At the end of summer, cuttings with roots are transplanted as intended.
- Seeds. In December, wisteria beans are sown in a greenhouse in drained soil fertilized with a mixture of leafy, turfy soil and sand (ratio 4: 1: 1). To maintain moisture, the sowing is covered with glass or plastic wrap, and removed to a dark place. After 4 weeks, seedlings appear, they are taken out into the light. When the sprouts grow to a small bush, they are planted in an outdoor greenhouse.
Wisteria care
Taking care of such a gorgeous vine is not so difficult. It will bloom densely only in well-lit areas, protected from gusts of wind. It is important to tie up wisteria shoots constantly so that they can grow and their tips do not dry out. Liana needs to be pruned regularly after flowering so that it blooms more intensively in the next season. If you follow these rules of care, your plant will actively grow and bloom profusely.
From early spring to late summer, the soil of the wisteria should be slightly moist, then the leaves will have a bright saturated green hue. It is also impossible to overflow, the plant does not like too wet soil. In dry periods, the vine is watered more abundantly so that the buds do not crumble due to a lack of moisture. In the second half of December, watering is stopped, the plant needs to prepare for wintering. 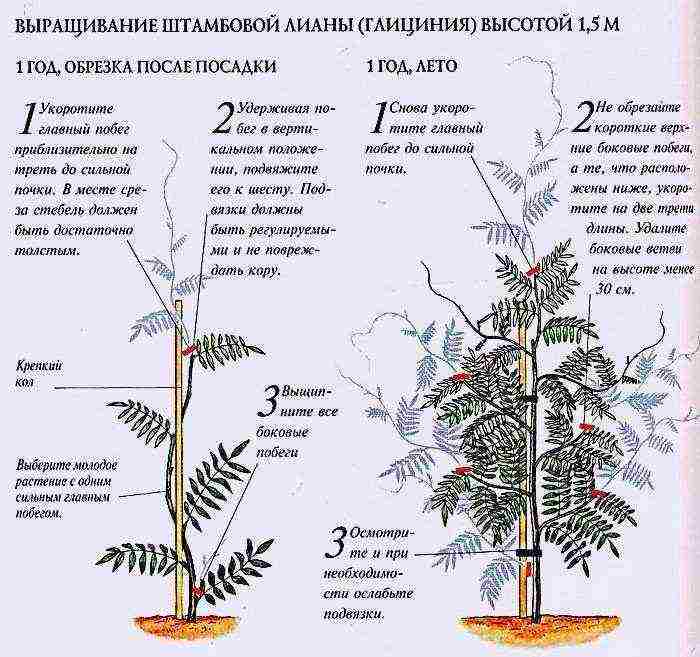
Wisteria lianas grow to large sizes, so that flowers and leaves have a beautiful decorative appearance throughout the season, liquid dressings are required:
- Mineral fertilizer. 1 m2 of territory will need 10 liters of water and 20 g of fertilizers.
- Compost.
- Tinctures of rotted manure (1:20).
- Chalk solution (100 g in 1 bucket of water).
Diseases and pests
Wisteria is resistant to disease, and because of its poisonous properties, it is extremely rarely attacked by pests. It can be:
- Caterpillars that make holes in the leaves. They are rendered harmless by spraying with a biological preparation.
- Green aphid. It affects leaves and flowers, is destroyed by insecticides.
- Clover mite. It is determined by the unnatural bronze color of the leaves, in which case the vine is treated with acaricides.
How and when to prune a plant

The density of wisteria flowering and the longevity of the plant depend on correctly performed and timely pruning. Timing of work plays an important role here. Vines are pruned 2 times a year according to the scheme presented below. Immediately upon landing:
- We cut off the main shoot of the plant with a pruning shears to a strong bud (approximately at a height of 75-90 cm).
- We remove all lateral shoots of the vine to stimulate the growth of the main stem.
- We knit the upper shoot of wisteria vertically, and several others at an angle of 45 degrees.
- At a height of 75-80 cm, we shorten the main stem.
- Form several more horizontal shoots and shorten one third of their length.
2 years and until the end of formation, summer:
- Tie the main stem of the vine to the support.
- Pick up a couple more side shoots and tie them at a 45-degree angle.
- If excess growth will form at the base of the wisteria. Delete it.
- Tie a new main stem of each lateral branch on the liana and shorten all branches of the 2nd order to 20 cm so that they have 3-4 buds.
3 years and beyond:
- We do the same, creating a vertical growth of wisteria and the formation of side shoots.
Video tips for growing wisteria at home
In specialty stores, a wide selection of seedlings of various exotic and domestic plants is presented, there is also wisteria. But it is much more interesting to try to grow such a vine yourself. How to breed this ornamental plant right at home? For details on growing wisteria, from seed setting to sprouting, see the video master class below.
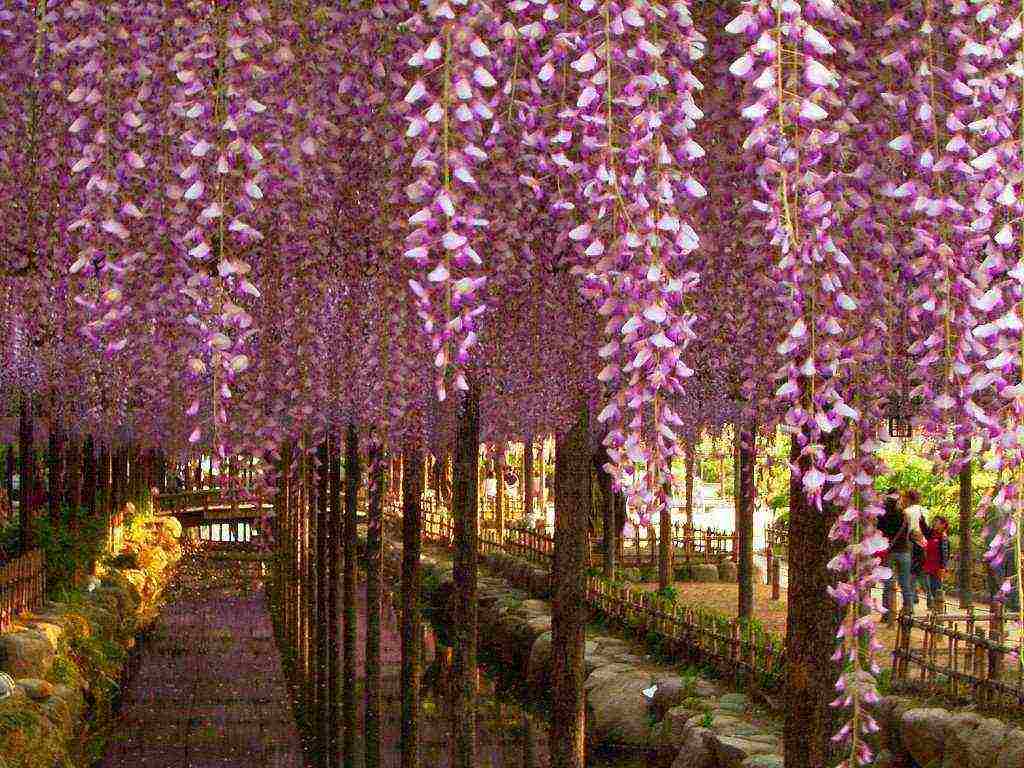
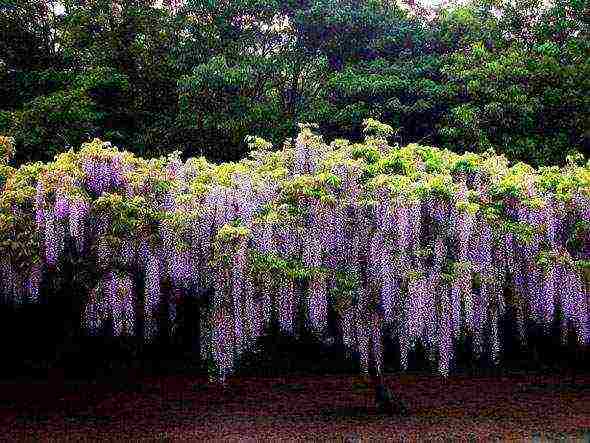
Wisteria or wisteria is a large tree-like vine in the Legume family. It can be called a real blooming miracle, since several times a year the plant is abundantly covered with multi-colored garlands of delicate flowers, similar to streams of colorful rain with a pleasant sweetish aroma. The enchanting wisteria is planted in parks and gardens. She makes an indelible impression on any passer-by. The habitat of wisteria affects the humid subtropical forests of China and Japan, it grows well in the Black Sea region and in the south of Russia. The breeders managed to develop several frost-resistant varieties suitable for temperate climates.

Description of the plant
Wisteria is a perennial deciduous vine. It branches from the very base and after a year the shoots become more durable, woody. They are covered with a brown bark with deep vertical grooves. The length of the vine can reach 18-20 m. The stems of the first year are covered with smooth olive bark.
On young shoots, large, pinnate foliage blooms. The length of one leaf reaches 30 cm. It has 7-13 oval-shaped segments with solid edges and a pointed end. The dark green leaves are covered with a short nap immediately after emergence, but gradually become smooth.
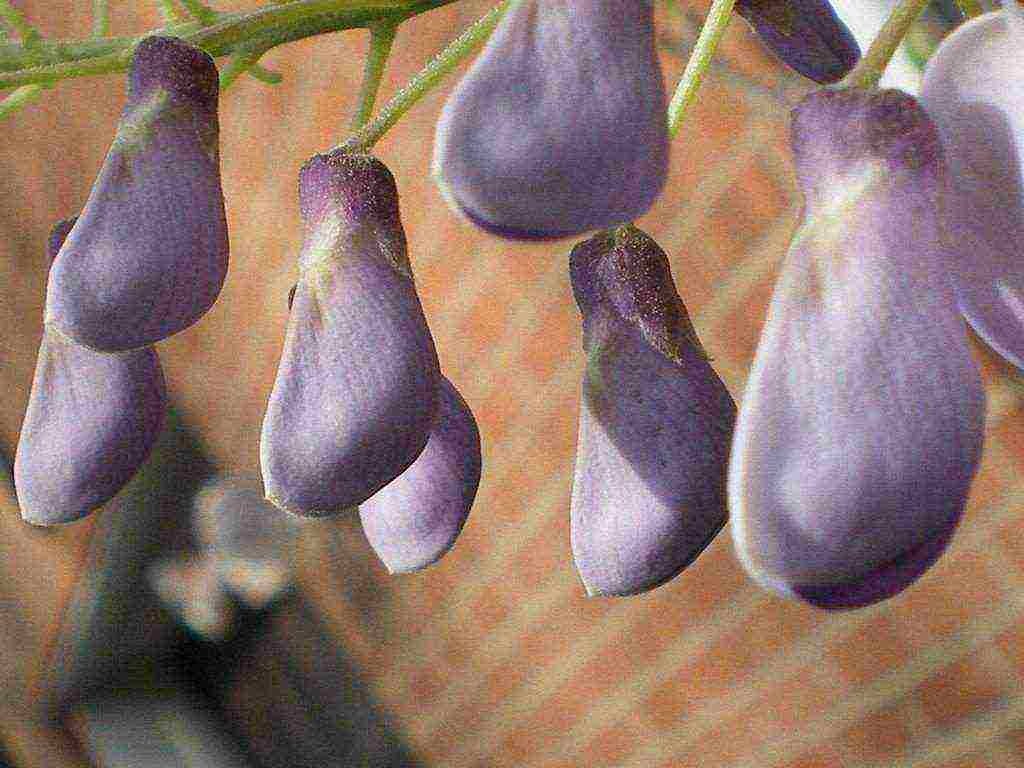
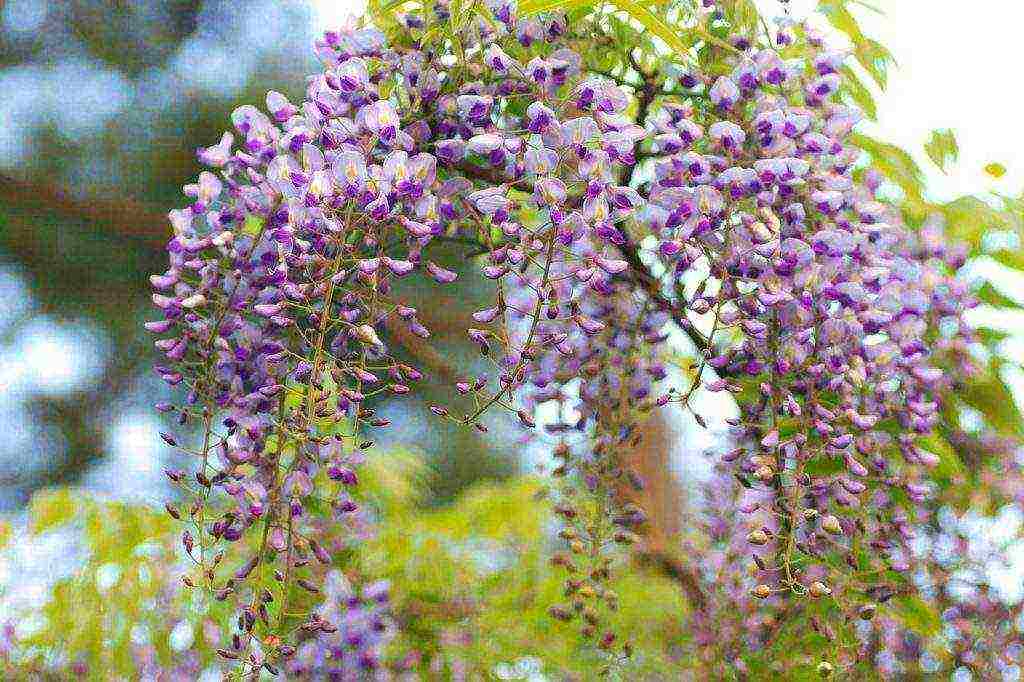
Large inflorescences of some species appear in early spring, before the foliage blooms. Others bloom after the foliage appears. Under favorable conditions, wisteria blooms up to three times a year. Long drooping peduncles are dotted with small moth-shaped flowers. Their structure is typical for all legumes. All racemose inflorescence with closely growing buds looks like a garland. The color of the flowers is dominated by various shades of blue and purple.There are also white, pink and yellow wisterias.
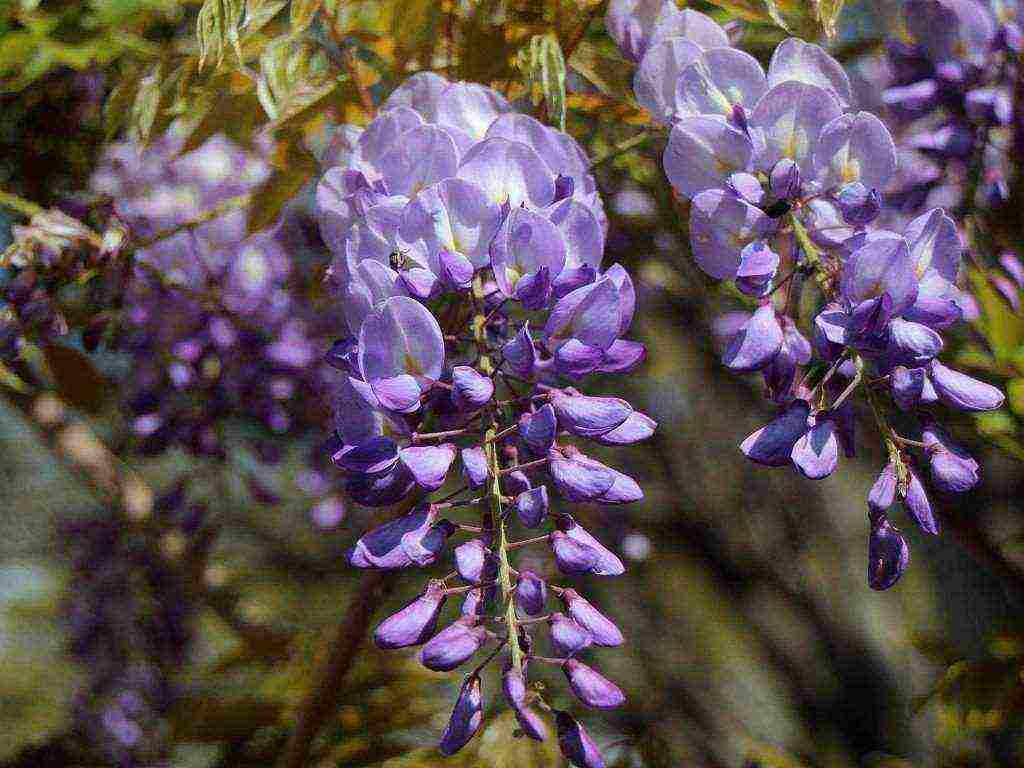
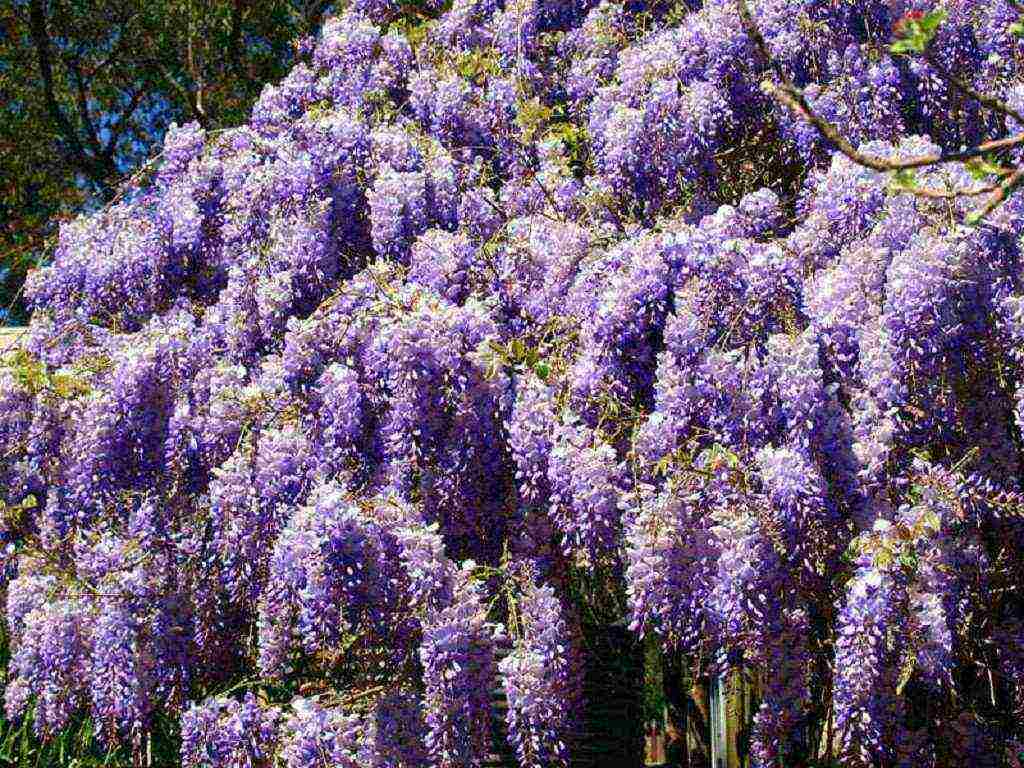
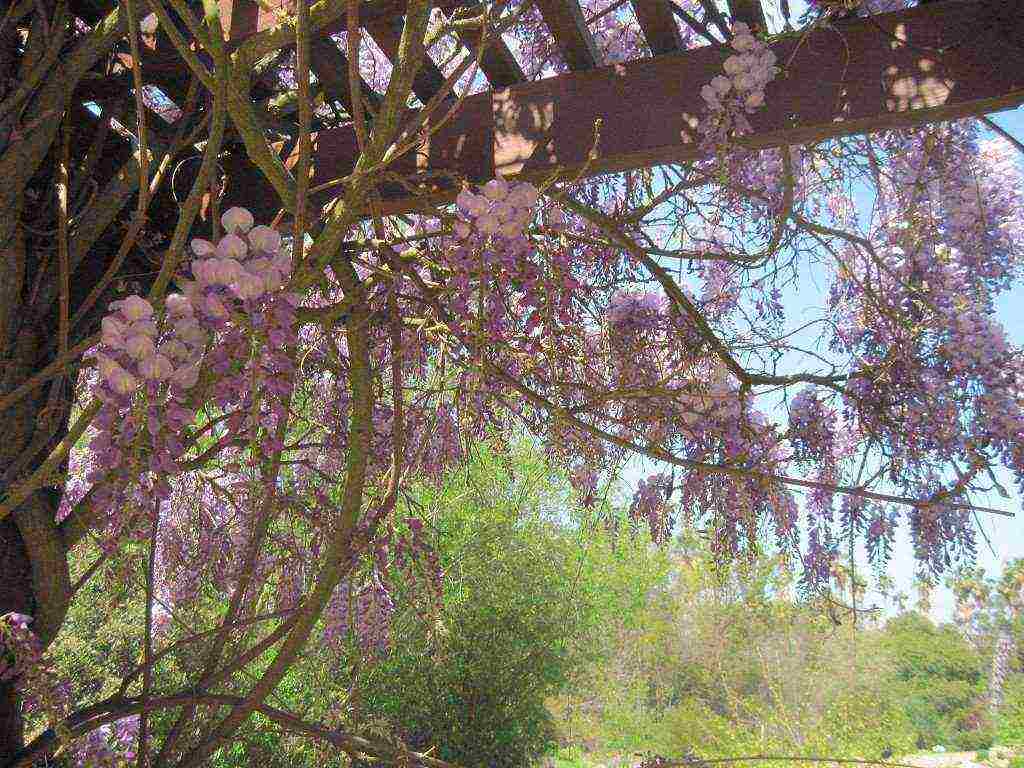
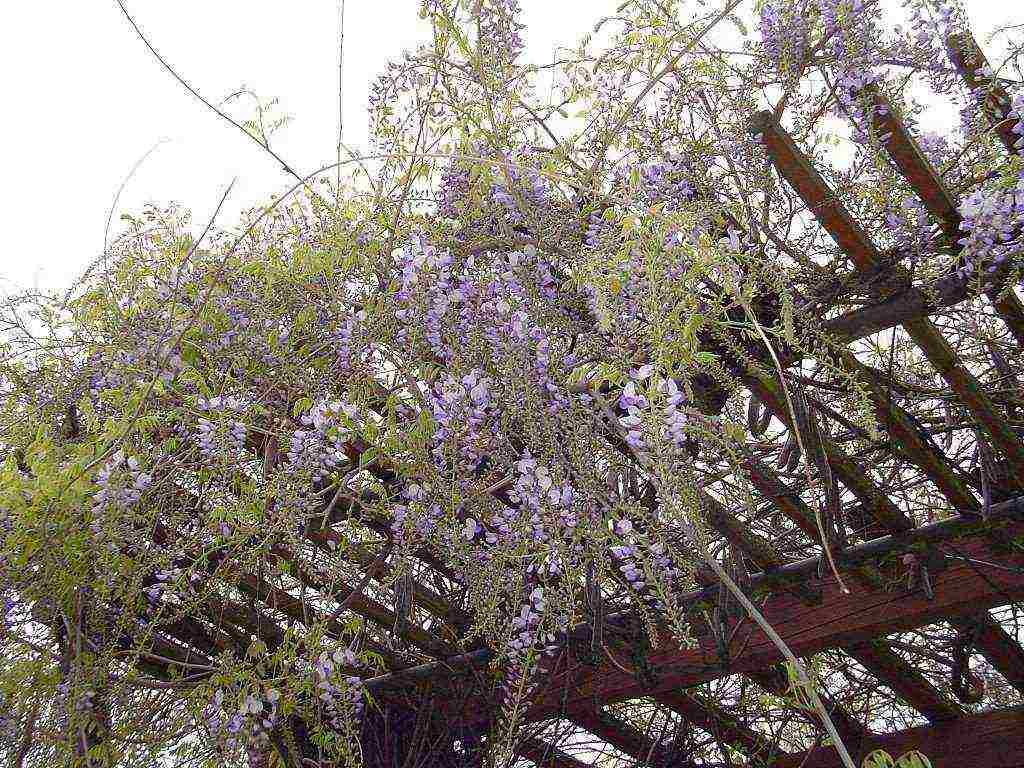
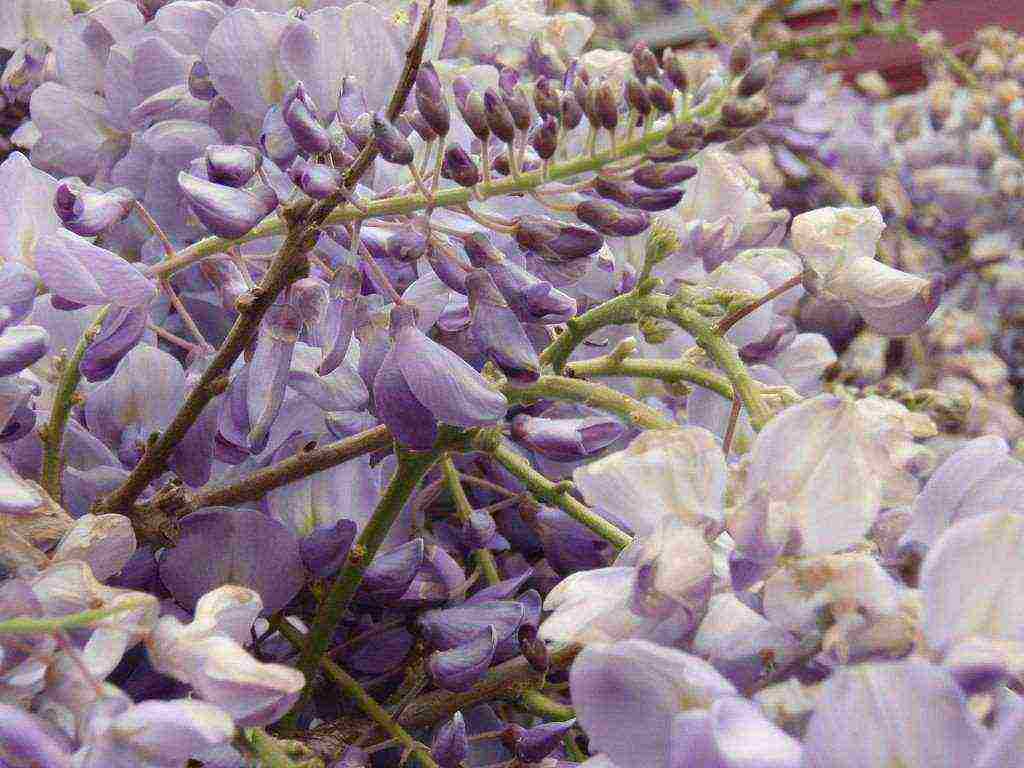
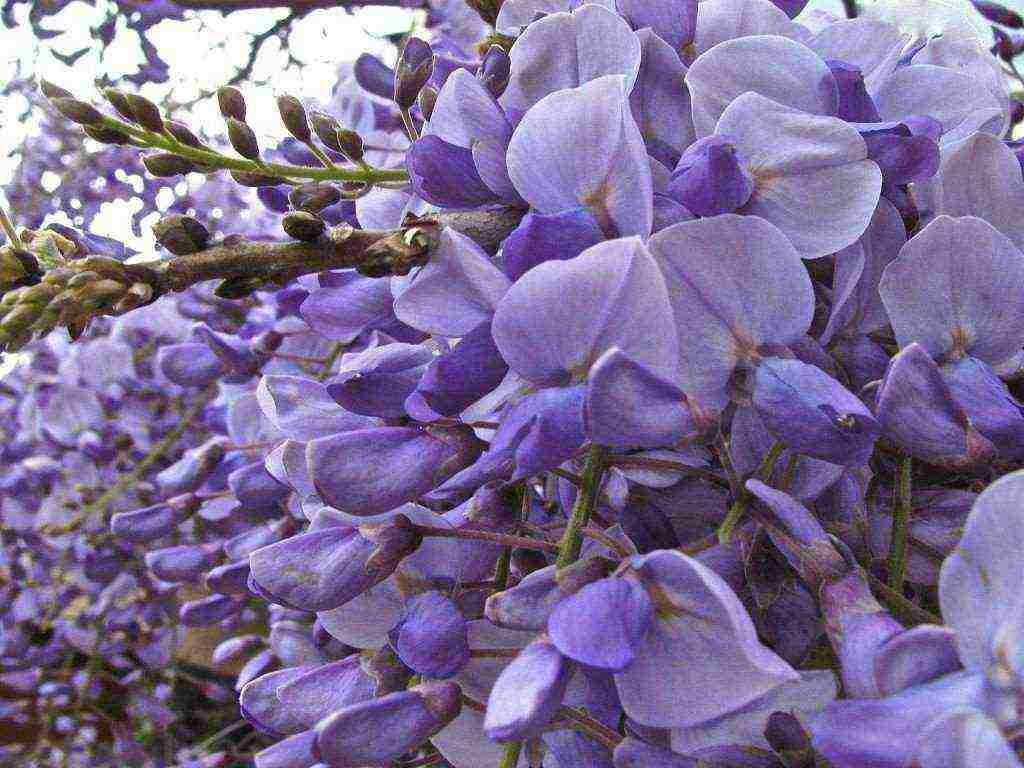
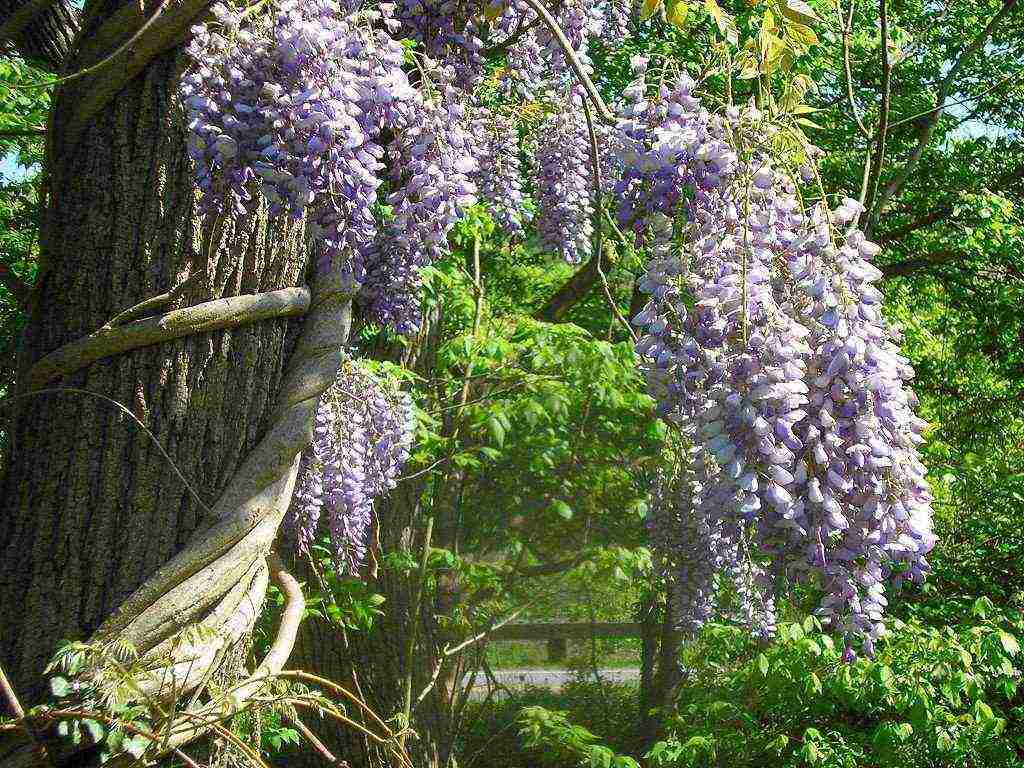
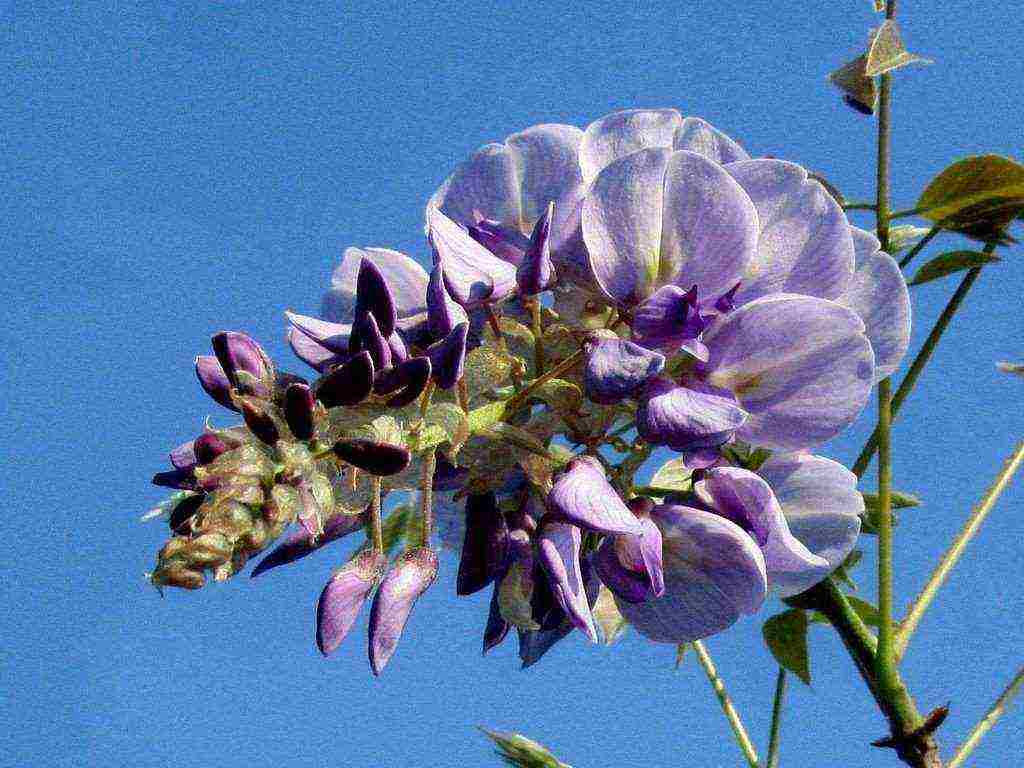
















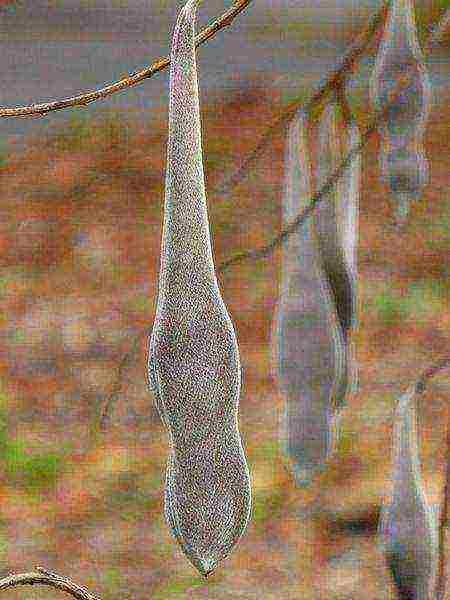
The plant is pollinated by insects, after which long, flat beans of an ash or gray-brown hue ripen. Inside them there are several round flat seeds of dark brown color.
Types and varieties for the garden
In total, 9 species are registered in the wisteria genus, but only 3 of them are especially popular in landscape design. Thanks to the work of breeders, varieties with various colors of petals, as well as frost-resistant, have appeared.
Chinese wisteria. A woody liana, climbing up a support, braids it counterclockwise. The height of the vine reaches 15-20 m. It is covered with alternate pinnate leaves with 7-13 segments. In the spring, before the foliage bloom, drooping racemose inflorescences up to 30 cm long appear. The light purple flowers exude a pleasant intense aroma. The species loves warmth and can only withstand short-term cold snaps down to -20 ° C. Decorative varieties:
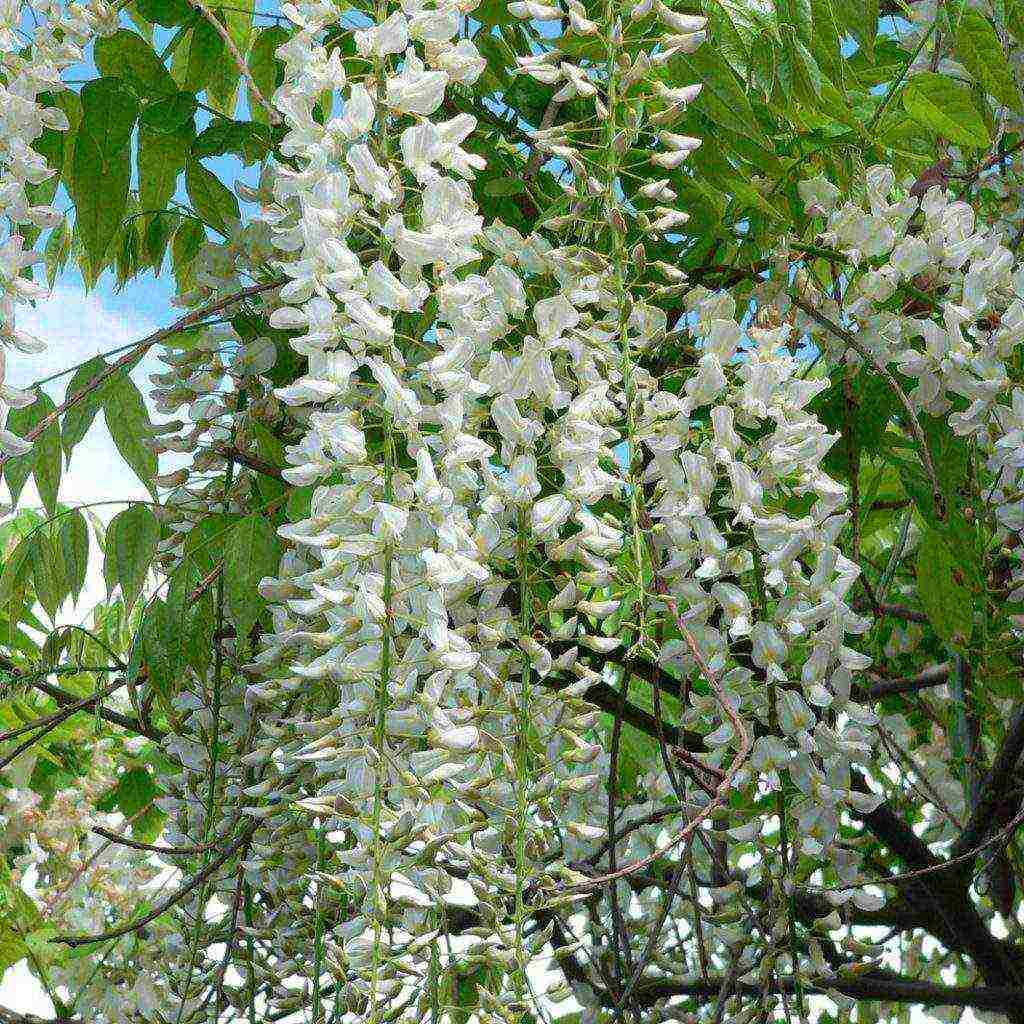
- Alba - with long snow-white inflorescences;
- Captivity - flowers on drooping brushes have a double shape and are painted in a white-lilac shade;
- Sierra Madre - blooms in late March with lavender-purple clusters;
- Blue Sapphire is a vine up to 20 m long covered with large emerald foliage. In May, long racemose inflorescences hang on flexible peduncles, light purple moth flowers bloom on them.

Lush wisteria. The plant lives in North America. Its height is 10-15 m. Growth is less aggressive. A distinctive feature is resistance to frost down to -35 ... -40 ° C. 7-9 segments of dark green color grow on the petiole. The length of the brush is 20-30 cm. Varieties:
- Blue moon ("Blue moon") - a frost-hardy variety wakes up a little later and blooms with blue-lilac brushes with a delicate aroma;
- Clara Mac is a less winter-hardy plant with snow-white clusters up to 35 cm in length.
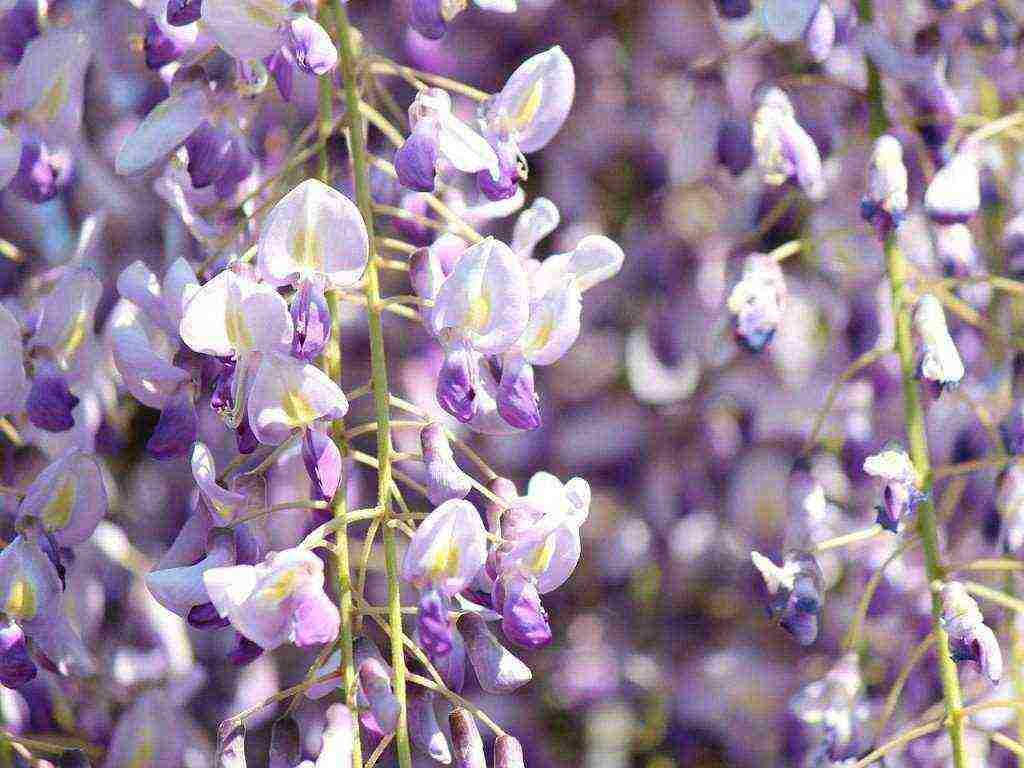

Multiflorous wisteria (profusely flowering). A liana with lignified shoots in length grows to 7-10 m. On a vertical support, it climbs in the direction of clockwise movement. Young stems are covered with large (about 40 cm) dark green, pinnate leaves. There are up to 19 leaf blades on the petiole. The inflorescences on the liana bloom much larger. The length of the brush can reach 50-60 cm. Due to closely spaced flowers and inflorescences, the vine gives the impression of a continuous flowering and fragrant canopy. The buds open from the base of the peduncle, they are colored light purple or blue. The flowering period begins in May.

Breeding features
Wisteria is propagated by cuttings, air layers, grafts and seeds. For seed propagation, it is necessary to prepare pots with sand, leaf and turf soil. Large seeds are evenly distributed on the surface and buried by 1 cm. The soil is watered and covered with foil. The pot is kept at a temperature of + 25 ° C. Seeds germinate in 3-4 weeks. Germination rate is about 25%. The sprouts need to provide bright, diffused light. The film can be removed. With the appearance of two true leaves, the seedlings are transplanted into separate small pots with a lump of earth so as not to damage the rhizome. They are tempered for several hours a day in a cool room. The next spring, the seedlings can be assigned to a permanent place in the garden. Unfortunately, this method is not very efficient. Flowering occurs in 5-10 years, and varietal traits are not transmitted to offspring.
The simplest breeding method for an ordinary gardener is the method of air layering. For him, in early spring, an oblique cut is made on a one-year-old shoot. The stem is tilted and immersed in a container filled with earth. The top must remain free. After 1-3 months, up to half of these shoots take root. To increase rooting, the cut is treated with a preparation for the formation of roots.By August, the layering will be quite strong, but the separation is carried out for the next spring.

In late autumn, after the foliage has fallen off, one-year-old cuttings are harvested. Each should contain 2-3 internodes. The branches are tied in a small bunch and placed in a pot with moist soil. In early spring, cuttings are taken out of storage and planted in a cold greenhouse or directly into open ground. Each branch is covered with a plastic cap. When the cutting takes root and buds open, the cap is removed.
The grafting method is only suitable for experienced gardeners. Grafting of a varietal plant is done on the roots. The procedure is carried out in May-June, so that the plant has time to take root before frost.
Landing rules
For planting wisteria, you should choose a sunny, warm place that is protected from drafts. She will be comfortable from the south side of the house or fence, where direct sunlight falls most of the day. With a lack of sun, flowering and development is reduced.

Planting vines is best done at the end of March, when the snow has completely melted and the ground warms up. Short-term frosts are not terrible for all types of wisteria, but it is better to wait until they pass. The soil for planting should be nutritious and well-drained. Wisteria prefers neutral or slightly alkaline soils. For each seedling, a planting pit is prepared with a depth of 60 cm. Mineral dressing is preliminarily introduced into the ground.
After planting, the plants are well watered. You need to be prepared for the fact that the first year wisteria adapts for a long time and grows slowly. Only after 2-3 years will the long thin shoots turn into dense, tree-like stems.
Care secrets
The charming wisteria is renowned for its undemanding character. Already for 2-3 years, the first inflorescences appear, and after a few more years it will be difficult to count the number of flowering necklaces.

Watering. Wisteria should be watered regularly to keep the soil slightly moist but dry out in the top layer. In dry weather, 1-2 buckets of water are poured under each bush weekly. It is recommended to periodically spray the shoots. During flowering and active growth, irrigation should be more abundant. From the end of summer, watering is gradually reduced and the plant is prepared for wintering.
Fertilizer. In early spring, wisteria is fed with formulations with a high nitrogen content. A little later, add mullein infusion or compost. To prevent the soil from acidifying, it is recommended to periodically fertilize wisteria with chalk water.
Crown formation. The plant needs a garter and direction of all young shoots. Liana quickly gains mass, so the support for it must be reliable and stable. There are 2 main ways to form a crown:
- Stamp - the formation of a kind of tree. The central, most powerful shoot is left by cutting off the lateral processes at the base. Several skeletal branches are formed at the required height. The same form is practiced in miniature, creating bonsai from wisteria.
- Climbing - along the entire length of the vine, the lateral processes are removed to get a single long lash, curled in the right direction.

For more abundant flowering, creepers are pruned twice a year. The first manipulation is planned at the end of flowering. All lateral processes are cut by 2/3. After the foliage has fallen, in November, some of the old and young side branches are removed. Flower buds form on short shoots of the current year. It is also recommended to prune wilted inflorescences.
Wintering. One-year-old plants in the open field are recommended to be removed from the trellis and placed on the ground on top of several boards. From above, the plant is covered with fallen leaves and spruce branches. Most varieties of frost do not tolerate well, often the tips of the branches freeze slightly. Only wisteria "blue moon" can be grown in central Russia. But even its base of the stem is covered with lutrasil and fallen leaves.

Diseases and pests. With poor soil quality, wisteria can suffer from chlorosis. Fertilization with iron salts serves as a prophylaxis of the disease. Sometimes cicadas, caterpillars, clover mites or aphids settle on the leaves. At the first sign of parasites, the plant is sprayed with an insecticide.
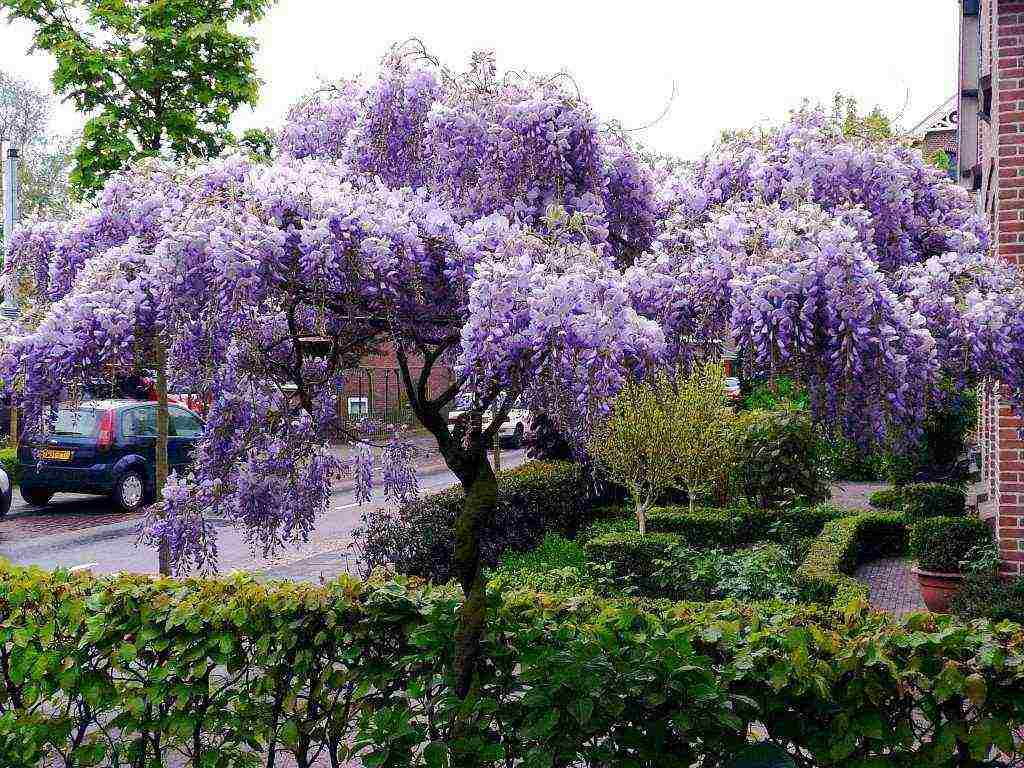
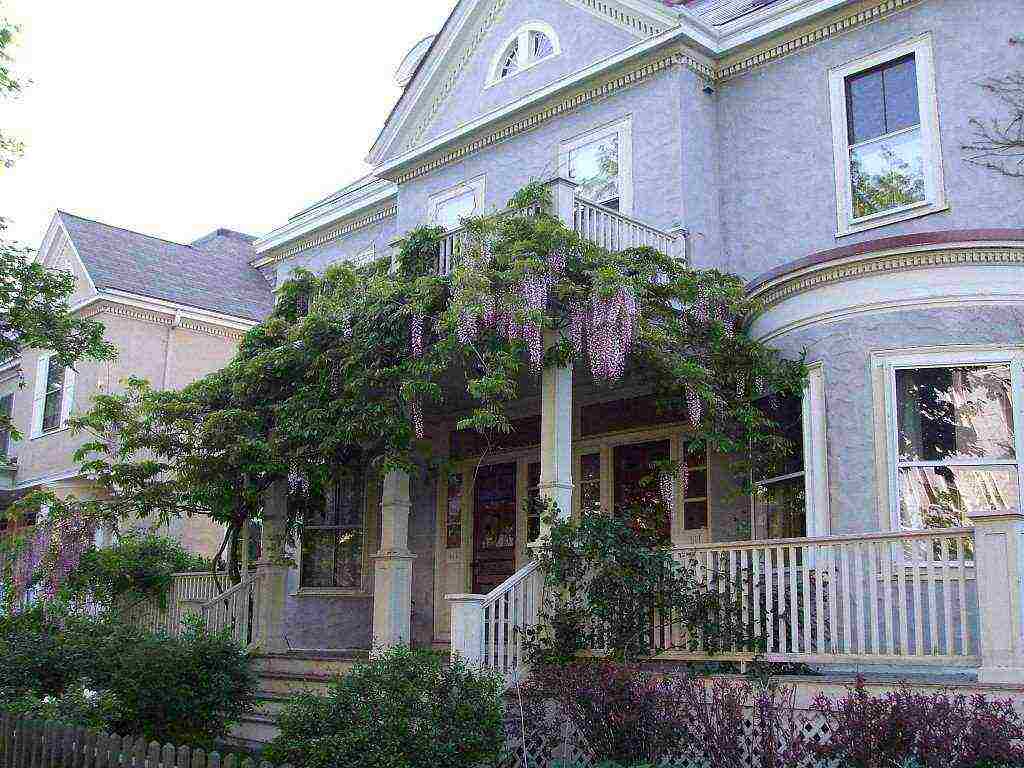
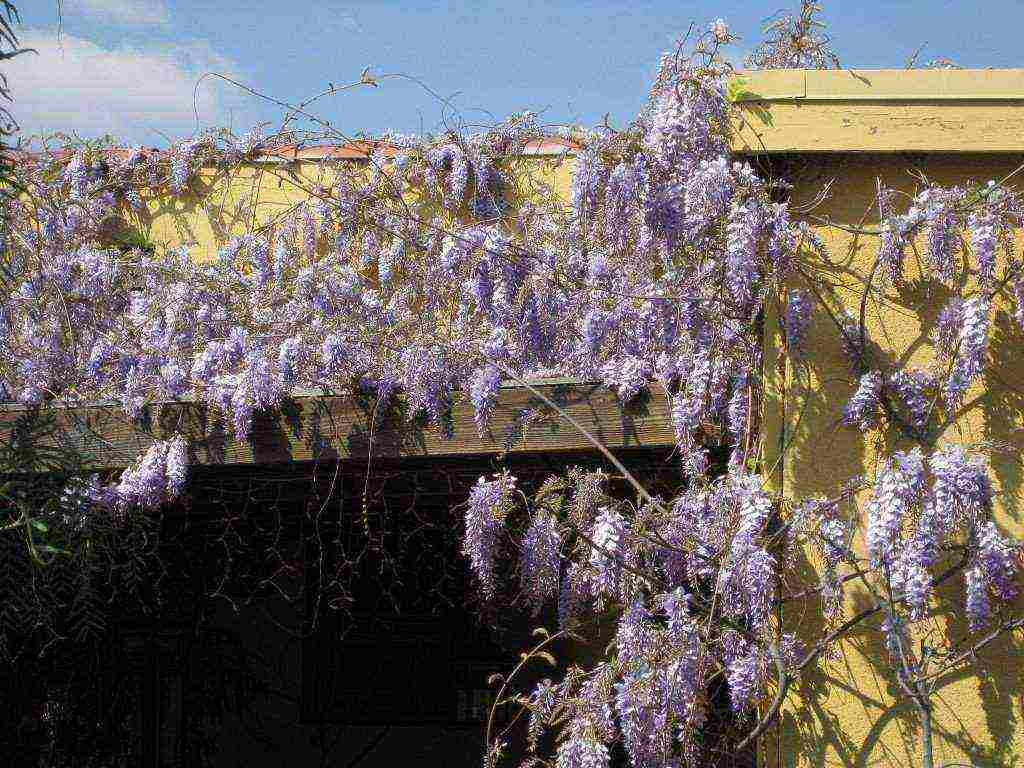
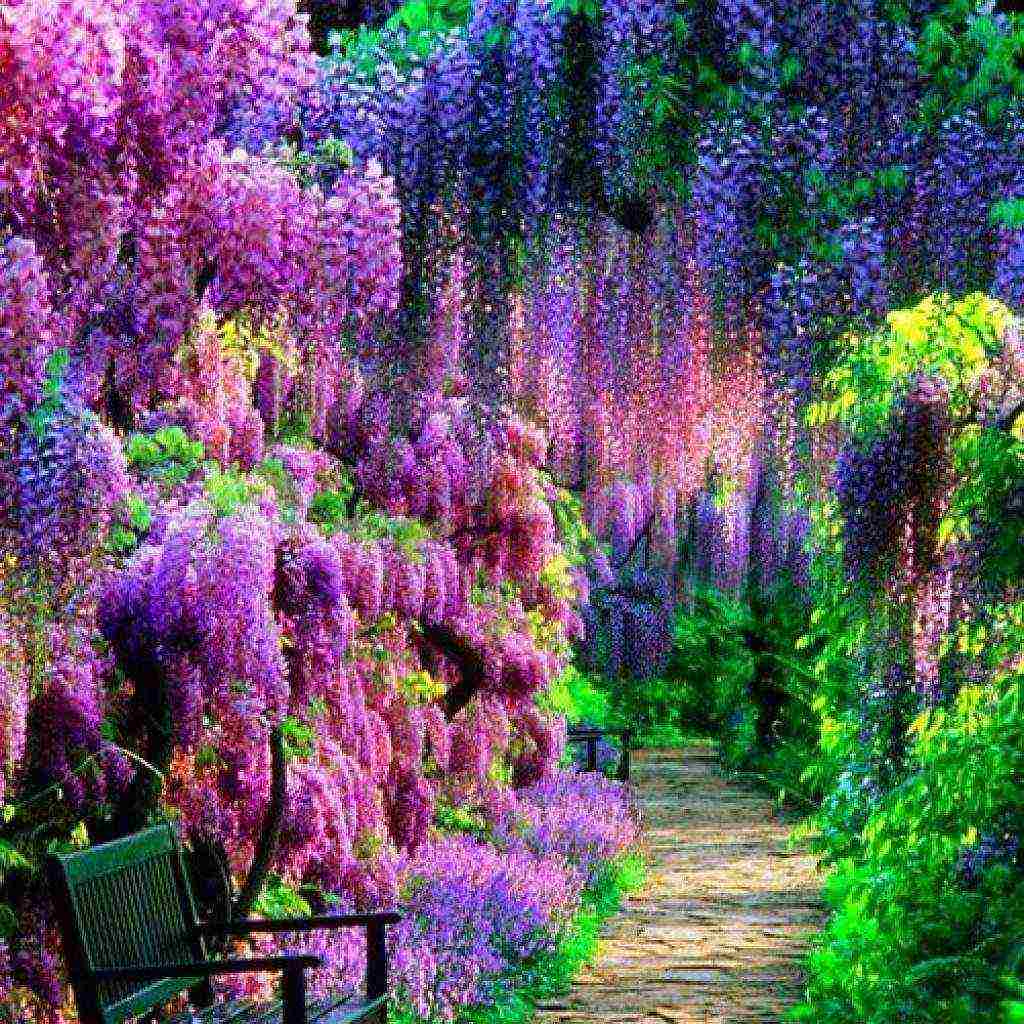
Wisteria in landscape design
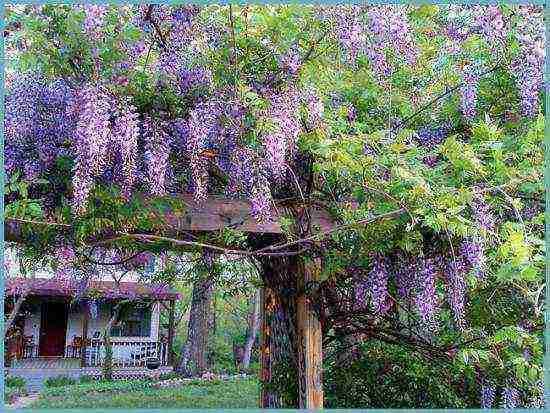
A large, fast-growing vine requires ample space, so a single plant will be enough in a small garden. It is planted near the walls of the house, along the fence, near the gazebo or pergola. With the help of a green cover, you can disguise ugly buildings. Wisteria not only creates an excellent green wall, but also blooms a huge number of bright inflorescences.
On a large territory, arches and corridors made of wisteria look spectacular. Moreover, you can use several plants of the same variety or combine varieties with different colors of inflorescences. Then you get an amazingly beautiful rainbow.
Hyacinths, daffodils, tulips and wolfberry are often planted at the base of the vine. To please yourself with a thermophilic variety, you can plant wisteria in a tub. In the summer, it is taken out into the garden, and in the winter it is removed to a bright, but cool (+ 10 ... + 12 ° C) room.
SUPPORT THE PROJECT - SHARE THE LINK, THANKS!
The greatest joy and affection are delivered to flower growers by flowering and beautiful plants. One of the most beautiful representatives is Chinese wisteria. Planting her on a personal plot means getting a lot of worries. But the beauty of this flower will reward even gardeners who are intimidated by the difficult care and cultivation of this plant.
Photos in the instructions of florists show falling brushes, which are abundantly strewn with lush inflorescences, and their magical aroma will surely adorn any personal plot.
Description and types of wisteria
In various sources, you can see the definition of wisteria as a flower or tree. But in reality it is a liana, with falling branches and a stiff trunk. Under the necessary conditions, namely, in carefully drained soil, under the hot sun, the stem of this plant can grow up to 20 meters .
In their natural environment, wisterias are found in the warm climates of Asian countries - Japan and China. This plant has been planted in America for a long time. A young shoot has a rather thin stem, an adult liana can have a tree-like trunk up to 25 cm in diameter. On the trunk of the plant there are branches with lush leaves collected from small leaves.
In summer, wisteria forms flower brushes. Inflorescences in various varieties of this plant differ in color - pure white, purple, blue. The flower has a rather complex shape that resembles an orchid. The very pleasant smell of the inflorescence is the reason for the name of the vine. Wisteria translates to sweet.
Plant fruits - pods with fur bloom... Due to the structure of the liana fruit, it belongs to the legume family.
Varieties
Today there is 10 varieties of Chinese wisteria... which are in natural conditions. Florists grow only decorative vines. This is wisteria:
- Macrostachia. This hybrid was bred specifically for cold climates - North America, Russia, Scandinavia. The plant is frost-resistant. On a personal plot, it creates an excellent braid for gazebos, terraces, and house facades. Brushes 35 cm in diameter and consist of lilac inflorescences with a pronounced odor.
- Alba. This type of wisteria blooms with white tassels. The aroma is slightly worse than that of other hybrids, but pure white inflorescences are more expressive, they are planted in city squares, in different flower arrangements;
- Chinese. This variety creates rather beautiful clusters with aromatic bluish inflorescences. In the backyard, this plant winds around the pillars of the terrace, gazebos, various frames;
- Floribunda. It is a Japanese plant that looks like a vine with 45cm clusters of various colors.There are also dwarf species of this vine. They take much longer to grow, creating a bush-like shape that is great for bonsai;
- Beautiful. The hybrid, which turned out after the selection of the first two varieties, he absorbed their best qualities. Flower brushes are longer, up to 30 cm, flowers are larger, pure white.
How to grow wisteria?
Wisterias - fast growing plants... which immediately cling to any possible support. This quality has made them popular with both landscape designers and novice florists who appreciate the romantic style.
A developing liana requires a frame made of thick reinforcement, steel or wood. The more mature the plant, the thicker the stem and the heavier the green foliage. Small wisterias look great in pots as indoor flowers. The pot must be wide and equipped with a sturdy steel rod. Moreover, the vine looks great in a pot on the loggia.
Planting creepers in a personal plot will require reliable support... A lot of effort must be made and pruning creepers. A heavily overgrown, massive plant will break under its own weight without proper pruning.
An ideal place for wisteria on a personal plot is a house facade, well-lit by the sun, a gazebo wall, or a special shed. Chinese wisteria needs constant warmth. Only under the sun will it bloom beautifully with a lot of inflorescences.
Experienced flower growers know that all varieties of this vine are quite capricious. Planting and grooming require great care. There are a number of rules to keep in mind:
- liana, which is planted from seeds, will begin to bloom only after 8 years;
- seedlings purchased in stores take root up to 4 years old, before sprouting flower buds;
- before flowering weekly, it is necessary to fertilize the soil near the roots;
- it is not necessary to water the vine strongly, but constantly;
- sometimes the plant does not bloom at all for several years. This vine needs to be "pushed" by adding potash groundbaits to the ground in the fall;
- it is advisable to avoid nitrogen additions. In legumes, nitrogen creates a strong deciduous mass, but not the formation of inflorescences.
For a more beautiful flowering, the plant requires prune 2 times a year... Large branches form in the summer, after a couple of weeks, when the brushes dry and fade. In this case, you can correct the wireframe. Small vines are pruned in the fall.
In winter, these manipulations with wisteria cannot be performed. In winter, the vine forms buds of inflorescences, and the most beautiful and large ones can be accidentally cut off.
In the fall, it is necessary to remove all dead parts of the shrub that interfere with the germination of young branches. Experienced gardeners recommend looking at the vine from a distance of 7 steps. This way you can better see the difference in color on old branches and new shoots that grow from them.
Side branches need shorten to 20 cm... The old branches are also made smaller so that there are only 5 buds. This will help the vine to concentrate its vitality on creating inflorescences on short branches.
In the summertime, you can perform the same procedure with side branches, leaving a few leaves on each shoot. It is necessary to cut off large "clinging" branches in the form in which they decided to line the vine. Pruning won't do any harm. Elastic shoots They will grow rather quickly, and will fix where they were directed.
How do I prepare the seeds?
Large pods make the plant look less attractive in spring. It is advisable to cut them without removing a significant part of the stem, as there may be buds of inflorescences.
You can plant this plant from seeds that are collected from the pods. Remember - the new plant will not be identical to the mother vine.
Ripened pods placed in a large cardboard bag and left to dry in a warm place. For example, you can leave a package on the torpedo of a car for several weeks.When the pods are opened, the seeds are easily removed from the shell.
For cultivation, planting in a deep pot is required. The seeds are deepened into the ground by 3 cm and watered. It is advisable to use a mixture of soil with the addition of sand for growing. The seed pot must be placed in the shade. Many growers cover the pot with glass to protect against heat loss. During germination, it is necessary to add water so that the soil is constantly moistened.
When the shoots appear, the pot must be rearranged to a lighted area (not to direct sunlight). When the shoots form several leaves, they transplanted into different containers... Do not transplant small seedlings directly into the ground. Liana must grow at least 25 cm.
How to grow wisteria in the suburbs?
The natural habitat of this plant is the tropics. In the northern regions, the liana suffers from frost. Many varieties of lianas cannot even endure autumn in our climate. The minimum temperature for a plant should be at least 10C. Even when the roots survive in the soil and then create shoots, the frozen specimen will not discard the inflorescences for a long time.
This plant in the Moscow region develops well only with special protection in the winter. Florists do not place seedlings in the ground in the first spring, but they are planted in special barrels. For escapes a container with a volume of 45-55 liters is required... Liana needs strong support, as well as a garter.
In the fall, you need to keep an eye on the weather forecast. If the temperature drops below 15C at night, the plant must be moved into the house. It is desirable that it be a basement or cellar.
In winter, the vine is inactive. The plant does not need bright lighting, watering can be done every 7 days. In a highly heated and bright room in winter, the vine will die. Already from the beginning of spring, the barrel with the plant is moved to the bright part of the room, and watering is carried out every two days. When the temperature at night will be more than 10C, the vine can be placed on open ground.
An adult liana needs to be spud before winter. In this case, the plant is removed from the supports, fixed to the ground and covered with straw, leaves, unnecessary clothing. By this time, the main part of the shoots must be cut off. With secure cover, wisteria can tolerate temperature about -22C .
Caring flower growers achieve the survival of the plant for many years, as well as double flowering of wisteria. Growing vines from mothers makes wisteria more resistant to frost.
The main disadvantages of wisteria
Certain natural specificity This plant can greatly perplex the grower who first grew wisteria:
- you should not choose a living tree as a support for this plant. Liana will eventually "strangle" the tree with powerful lashes. The plant can only be fixed near dead and dried trees;
- the vine develops late foliage in the spring. Its bare branches will begin to contrast with the greenery of the rest of the plants that has appeared;
- flowering is not constant, and not intense all the time;
- in hot weather, the leaves of this plant acquire a dark brown hue;
- the increased allergy and toxicity of liana pollen makes it impossible to grow it in the backyard, where small children often walk;
- the foliage and fruits of the creeper are very poisonous. After contact with the plant, the whole body should be thoroughly washed with soap.
Chinese wisteria creates a magnificent romantic atmosphere on the backyard. This vine will fit perfectly in any landscape design... masks the facades of old houses, as well as dead trees. The aroma of blossoming inflorescences is very pleasant to the sense of smell, and also clears the air space from pathogens. Caring for a vine is quite difficult, but the result obtained will reward you for all your efforts.
Anyone who first saw a blooming wisteria cannot believe for a long time that there is a living plant in front of him.Long flower brushes look so impressive that first of all a designer with wild imagination comes to mind, not mother nature. Wisteria, often called wisteria, is one of the most beautiful flowering vines. From a distance, her brushes resemble a foamy waterfall, she blooms so profusely that branches and leaves are often not visible behind purple, blue or white clusters. Wisteria is gorgeous, growing and caring for it will be the topic of our article.
general description
Wisteria (Wisteria) is a small genus of woody lianas, consisting of only 9 species, belonging to the Legume family. It originates from China and Japan.
A tree-like deciduous liana, depending on the species, reaching from 8 to 20 meters with feathery, unpaired beautiful leaves with 7-19 segments - this is what wisteria looks like. This plant blooms in spring with purple or white flowers, collected in fragrant cluster inflorescences ranging in size from 30 to 50 cm.The fruit is a bean up to 15 cm long.
Wisteria loves warmth, growing it in an area with a temperate and cold climate is difficult, the further north you move, the better shelter this vine requires for the winter. It should be noted that its plantings tolerate the polluted air of cities well.
Types and varieties
Although the plant is represented by 9 species, on the territory of the countries of the former Soviet Union, Chinese wisteria and abundant flowering or multi-flowered wisteria are most often grown.
Chinese wisteria
Chinese wisteria grows up to 15-20 meters, its unpaired leaf, about 30 cm in size, has from 7 to 11 (sometimes 13) leaves, pubescent at the beginning of the growing season, later - smooth. The stems circle the support counterclockwise.
Loose brushes up to 30 cm long consist of an abundance of fragrant flowers, usually light purple, less often white. Chinese wisteria blooms at the same time as the leaves appear, and all of its flowers open almost simultaneously.
With good care in August-September, repeated flowering may occur, not as abundant as the first, but also very attractive. This species can withstand a short-term temperature drop to 20 degrees below zero.
Description of the most popular varieties:
- "Alba" - white with short tassels;
- "Prolific" - abundantly flowering and with longer brushes than the original species;
- "Sierra Madre" - wisteria of this variety blooms earlier than others with purple-violet flowers;
- "Captivity" - wisteria, which has a double flower;
- "Blue Sapphire" - begins to bloom in May or early summer with violet-blue flowers with a strong sweetish aroma.
 Chinese wisteria "Alba"
Chinese wisteria "Alba"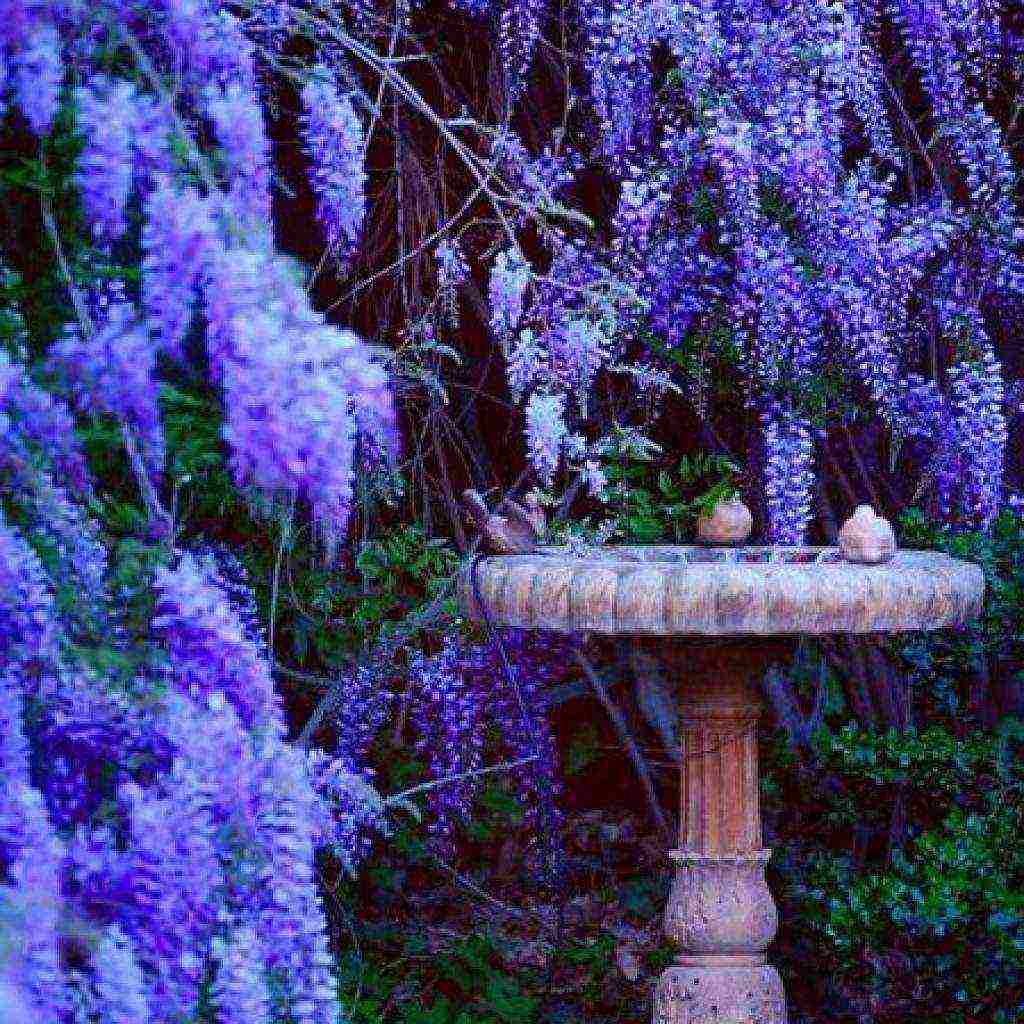  Chinese wisteria "Blue sapphire"
Chinese wisteria "Blue sapphire"
Wisteria abundantly flowering or multi-flowered
More frost-resistant wisteria, abundantly flowering or multi-flowered, very similar to Chinese, but blooms 2-3 weeks later and only after the appearance of leaves. Its leaf blade reaches 40 cm and has 11-19 segments. Wisteria grows profusely up to 8 meters, its shoots twist clockwise.
Flower brushes reach half a meter, but in varietal plants they can exceed a meter in length. First, the flowers bloom at the base of the brush, then at the top. The most popular varieties:
- "Alba" - white inflorescences up to 60 cm long;
- "Celestina" - with lilac-blue flowers;
- "Multiyuga" - a variety with tassels 0.9-1.2 meters long and lilac-blue flowers with a yellow base;
- "Rosea" is a white-pink wisteria, its flower about 45 cm in size has purple wings and a boat;
- "Royal Pearl" - with purple-violet flowers and brushes measuring 30-50 cm.
There is a form "Variegata" - with multi-colored leaves.
 Wisteria profusely flowering or multi-flowered "Rosea"
Wisteria profusely flowering or multi-flowered "Rosea"  Wisteria profusely flowering or multi-flowered "Variegata"
Wisteria profusely flowering or multi-flowered "Variegata"
Wisteria of other species
Large wisteria is represented by a single variety.Wisteria with the name "Blue Moon" is the most frost-resistant of the existing ones and can withstand frosts up to 40 degrees, it grows quickly and blooms up to 3 times a season with purple-blue flowers.
An unusually beautiful variety with double purple flowers "Double Black Dragon". Interestingly, its origin is unknown, as well as its species - this blooming purple wisteria has signs of different species, experts attribute it either to Chinese or to multi-flowered.
 Large-scale wisteria "Blue moon"
Large-scale wisteria "Blue moon"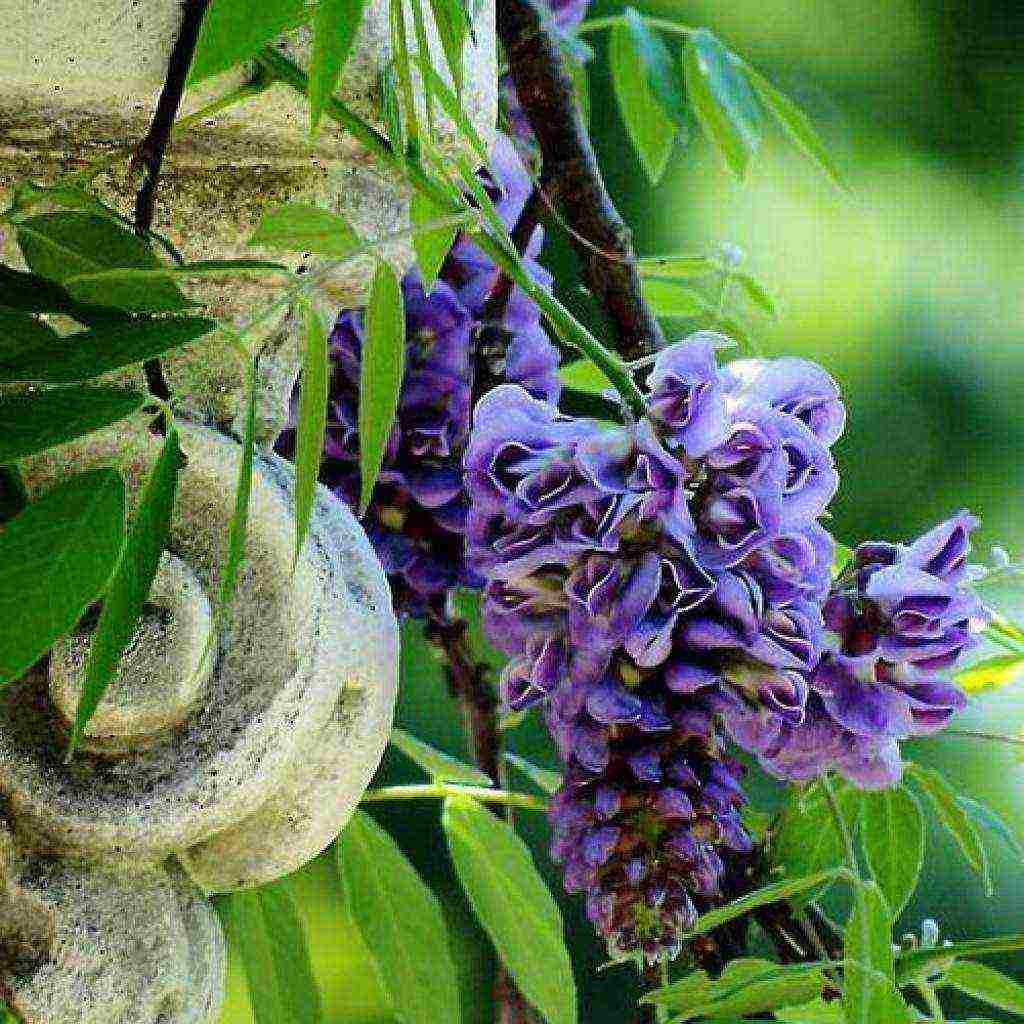  Wisteria "Double Black Dragon"
Wisteria "Double Black Dragon"
Japanese wisteria usually blooms with white flowers less abundantly than the types listed above, moreover, its frost resistance is much lower.
Wisteria propagation methods
Wisteria is propagated by cuttings, seeds and layering.
Growing from seeds
It is easy to grow wisteria from seeds, but it must be borne in mind that wisteria from seeds does not inherit varietal traits, moreover, it may not bloom at all. Sometimes, though quite rarely, the liana grown from seeds is superior to the mother in decorative qualities.
Wisteria seeds do not lose their germination for 2-3 years. Sowing time: end of November - beginning of December; directly into the soil - in early spring, as soon as the snow melts. For germination of seeds, a substrate of the following composition is made up:
- sheet soil - 4 parts;
- turf soil - 1 part;
- sand - 1 part.

The seeds are placed on the ground and lightly crushed with sand or peat, then covered with glass or film and kept in a dark place at a temperature of 20-25 degrees. It is very important that the soil does not dry out, but it is not waterlogged either - wisteria seeds can easily rot.
Seedlings usually appear in a month, and after another 10-15 days they need to be exposed in a bright place, slightly shading in order to accustom them to the sun. Wisteria seedlings dive in separate pots in the phase of two true leaves, taking them out of the ground with a tablespoon so as not to damage the root. Seedlings are planted in a permanent place only the next year after germination.
Wisteria grown from seed will be much easier to care for than grafted or cuttings. But it will bloom not earlier than in 4-6 years.
Propagation by cuttings
Shrubs and woody vines with soft wood cuttings are difficult to reproduce, including wisteria. But propagation by cuttings is still possible.
Apical cuttings about 15 cm long are taken at the very end of flowering or immediately after flowering. The lower leaves are cut off, and the upper ones are shortened by 2/3, the lower cut is treated with heteroauxin and planted in a mixture of sand, peat and fertile soil. Planting is done with a slope of about 30 degrees, burying one bud completely into the ground, the second should be at the level of the soil. This shows that strongly elongated shoots with rare internodes are not suitable for propagation by cuttings.
The box with cuttings should be in a shady place, protected from strong winds, but with good ventilation. It is best to cover the plantings with transparent film, ventilate and spray them daily. A few days after the new leaves hatch, the shelter must be removed.


Such plantings should overwinter either in cold greenhouses, if in winter the temperature there is about 10 degrees, or in a room with the same temperature and dim lighting. Cuttings can be planted directly into open ground only in the south, otherwise the wisteria will die. Growing cuttings can be considered successful even if 30% of the plantings survive by next spring. When the buds are swollen, it will be possible to plant the wisteria in a permanent place. The planted stalk must be covered from the sun for the first time.
Reproduction by layering
What's the easiest way to grow wisteria? An easy, reliable, but unproductive method of propagation is layering. In the spring, at the very beginning of the growing season, you need to choose a good low-lying annual shoot, bend it, cut it, powder the wound surface with heteroauxin.Then plant it with a cut down either in a pot placed next to it, or in the ground, for reliability, fixing the branch with bent electrodes.
Do not forget to water the layers and insulate the pot for the winter. A young plant can be planted next spring.
Reproduction by grafting
A varietal cutting is grafted in winter on the root of a plant grown from seeds. Only a specialist can vaccinate on the roots, the care and cultivation of a grafted plant at first cannot be called easy either. Let's leave this breeding method to nurseries.
Planting wisteria in the ground
Often novice gardeners are interested in the question of when to plant wisteria: in the spring or in the fall? It is planted and transplanted in the spring. Before planting wisteria, choose a well-lit, wind-sheltered location with nutritious, well-drained soil.

Dig a 60x60 cm depression about 50 cm deep. If necessary, lay drainage, then fill the hole with fertile soil. Plant at the same depth as wisteria used to grow. Her planting ends with a garter to the support and abundant watering.
Caring for wisteria after disembarkation
Planting and caring for the wisteria is not particularly difficult.
During active growth, the vine is watered systematically, but not overmoistening. In the fall, watering is gradually reduced, but do not forget that if the fall is dry, it is necessary to do a pre-winter moisture charge. Wisteria is prone to freezing, and this procedure cannot be neglected.
The first three years of wisteria need regular feeding. From the beginning of the growing season until the end of flowering, it is fed twice a month with complex mineral fertilizers. At the end of August and September, feed the plant with potassium monophosphate or any other phosphorus-potassium fertilizer that does not contain nitrogen at all.
Starting from the fourth year after disembarkation, you can feed the wisteria 4 times per season:
- The first feeding (immediately after the beginning of the growing season) with a nitrogen content;
- The second and third (during the period of bud formation and in the midst of flowering) - little nitrogen, a lot of phosphorus and potassium;
- Fourth (end of August - September) - phosphorus-potassium dressing.
Do not feed the wisteria with organic fertilizers - they contain high doses of nitrogen, and the plant belongs to the legumes that produce it themselves.
Post-flowering care


Remove wilted buds regularly during flowering. The wisteria has faded. Further care consists in watering, loosening, feeding, removing weeds and pruning.
Trimming and shaping
This vine can easily form a small tree or bonsai. Wisteria at the age of several decades has a rather thick trunk - up to 20-30 cm. But even at a younger age, old shoots cannot be called thin. If you want to get something exotic and not like a vine, you need to start shaping from the first years of life.
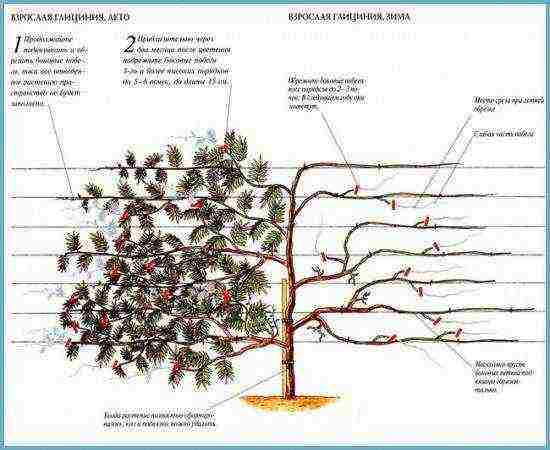
Correct and timely pruning is the key to abundant long flowering. To obtain a large number of flower buds immediately after flowering, cut off last year's shoots, leaving no more than 30 cm (the remaining cuttings can be rooted). In mid-August, shorten the growth of the current year, leaving 4-5 buds, and in the spring, after removing the shelter, trim another 2-3 internodes.
Perhaps this is the most difficult stage in caring for a wisteria. In the southernmost regions, it grows without shelter, a little further north it is spud like roses. The further north the wisteria grows, the more serious shelter it needs. In the fall, it is removed from the support, laid on the ground, covered with spruce branches, covered with agrofibre, if necessary, additionally covered with leaves.

But there will come a time when you simply cannot remove the wisteria from the support. Then you will have to install a special covering structure around the support. The older the plant, the more frost it can tolerate.
Pests, diseases and possible problems
Wisteria rarely gets sick and is affected by pests.Use insecticides to control insects.
If the soil is excessively alkaline, iron may no longer be absorbed - treat the wisteria with a complex of chelates on the leaf or pour it with iron chelate.
Why doesn't wisteria bloom? There may be several reasons:
- Too short cut;
- There were no shaping scraps;
- Excess nitrogen fertilizers and lack of phosphorus;
- Flower buds are frozen in winter;
- The plant is too young;
- Wisteria is grown from seed and will not bloom at all.
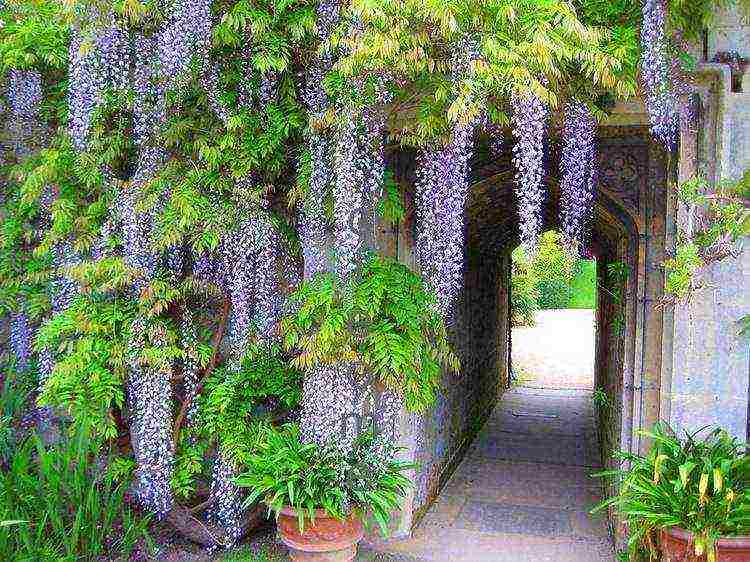
Wisteria in landscape design




Wisteria is beautiful in itself and does not need to be emphasized. But it will look great against the background of green plantings or in the company of tulips growing at the foot.
Wisteria will look especially beautiful against the background of a building wall or as a frame for a gazebo, balcony or terrace.
Formed as a standard tree or bonsai, the plant will effectively look like a tub plant anywhere in the garden or at home, during flowering it must be displayed in the most prominent place.

>
 Light purple and white brushes of blooming wisteria leave no one indifferent. Since spring, this tree-like liana delights the eye with its flowering, which lasts all summer. Outdoors, wisteria is widely used as an ornamental plant. This article will discuss the features of planting and caring for this beautiful vine.
Light purple and white brushes of blooming wisteria leave no one indifferent. Since spring, this tree-like liana delights the eye with its flowering, which lasts all summer. Outdoors, wisteria is widely used as an ornamental plant. This article will discuss the features of planting and caring for this beautiful vine.
Varieties and varieties
The wisteria tree liana also has a second name, "wisteria". The subtropics are considered a natural habitat, however, cultivated species are able to grow in almost any climate, and some varieties bred by American biologists can withstand severe winter frosts without shelter and retain the ability to bloom.

Wisteria is an incredibly beautiful liana that can be easily grown even in the north of Russia.
There are 9 types of wisteria in total, but most often you can find several of them:
- Chinese wisteria represents a liana up to 20 m high with brushes of a light lilac shade up to 30 cm long. Some varieties can have flowers of double appearance and white color.

Chinese wisteria
- Japanese wisteria it is half the length of the Chinese one, and rarely reaches more than 8-9 m, but at the same time it has larger leaves and clusters of inflorescences. However, the flowers themselves are smaller. Very often, Japanese wisteria is called multi-flowered or profusely flowering. This is due to the fact that the number of leaves and flower brushes in her is much greater than in the Chinese one. Depending on the shape of the garden, the shades of flowers can be white, pink or light purple.

Japanese wisteria
- Recently, wisteria is gaining great popularity. Blue moon... This is a frost-resistant wisteria, its perennial vines are able to withstand frosts down to -37 C without damage. This species was bred not so long ago. Blooms in large inflorescences of a blue hue in early summer. Flowering lasts up to two weeks.

Wisteria Blue Moon
Planting wisteria
When planting wisteria, it must be borne in mind that the plant is perennial, and a place for it must be chosen for many years. If you want to achieve maximum flowering, then it is worth choosing an area where the vine will be in the sun for at least half a day. In addition to the sun, care must be taken to ensure that the place is sufficiently protected from the wind, and the soil is nutritious and well-drained. Wisteria gives preference to slightly alkaline soils.
Planting wisteria is best done in the spring, after the last frost has passed. Despite the fact that most varieties of wisteria are frost-resistant, it is not worth putting young plants at risk once again.

For wisteria, it is imperative to determine a sunny place on the site
Most often, wisteria is grown from seedlings. Before planting, the soil is dug up with mineral fertilizer, after which holes 50 cm deep are dug into which young plants are placed.
If you plant wisteria from seeds, then the vine will not bloom soon. In the best case, after 5 years, but very often only by 10 years.
Wisteria care
Wisteria care begins with a garter of young shoots. Since the vine grows for a long time and has a high windage, the support must be durable and capable of withstanding wind loads.
Advice. It is best to tie the wisteria to the support, because independent weaving around the support can lead to the fact that it will be very difficult to remove the vine to prepare for winter in the fall.
The soil should not be calcareous, otherwise the wisteria leaves will brighten and lose their decorative effect.
Watering. Too wet soil can cause the plant to shed leaves and buds. Therefore, you should observe moderation in watering from the beginning of flowering until the end of summer. In summer, additional spraying can be carried out so as not to overwhelm the roots with water. In September, watering should be minimized and the plant should be prepared for winter.

The soil around the wisteria should not be too waterlogged.
Pruning. A very important condition for the flowering of wisteria is timely and correctly carried out pruning. Wisteria flowers develop on vines of last year and even earlier. Sometimes on young shoots of this year. Therefore, for the correct formation of flower buds at the beginning of summer or at the end of May (depending on the wisteria flowering season), the shoots of the last year are shortened, leaving no more than 30 cm.
In the fall, the shoots of the new season are cut off by cutting off 4 buds. After that, in early spring, during the garter of the vines to the support, last year's shoots are reduced by another 2 buds. By following these simple pruning rules, you will achieve the most decorative and lush flowering, which is so prized in wisteria.

Pruning wisteria
Preparing for winter. Many varieties of wisteria are preferable to cover for the winter, especially in the northern regions. Young shoots are considered the most vulnerable. In autumn, it is recommended to untie them from the support and lay them on the ground. The root part is buried in a thick layer of earth, and the shoots are covered with spruce branches, a layer of leaves or a special covering material. The older the plant becomes, the higher its frost resistance, respectively, the less it needs winter shelter.
Scheme: pruning and shaping vines
Advice. In severe frosts, some of the young shoots still die, but you should not be upset because of this, because this is exactly the material that needs to be pruned.
Fertilizing and feeding wisteria
It is impossible to take your eyes off the photo with blooming wisteria. To achieve the same flowering on your vine, you should pay a little attention to feeding. During active life, it is recommended to fertilize wisteria at least once a week, while it is best to alternate liquid mineral fertilizers with organic ones (for example, with mullein infusion diluted with water in a ratio of 1:20). A one-time top dressing in the summer, you can add a chalk solution. To do this, you need to dilute 100 g of chalk in a bucket of warm water and water the plant at the root.

No need to feed wisteria too often
Advice. Experienced gardeners remind that wisteria refers to legumes, therefore, you need to be careful with nitrogen-containing fertilizers.
Reproduction of wisteria
There are many ways to reproduce this beautiful vine.
The easiest way to propagate wisteria is grafting... In late autumn, the vine is cut off from the bush, cut into cuttings, tied and removed to a cool place, after burying it in a damp base. In early spring, the vine is taken out of the basement and planted under plastic bottles. It can be planted both in a cold greenhouse and immediately at a permanent location. About half of the cuttings planted will take root.
In December, you can try to multiply wisteria inoculation... It must be done exclusively on the roots, because the wood of the vine is too soft, and it will not be possible to vaccinate.

Wisteria propagates well by cuttings
A fairly effective breeding method is rooting of cuttings... In autumn, when all the leaves fall off, the lowest shoots scar slightly, tilt to the ground and sprinkle with soil so that only the tops remain on the surface. Shoots ring from the side of the mother bush in the spring, when buds begin to appear. And in the fall, it is necessary to check whether the root system of the layers has developed enough. If the roots have not yet grown enough, then the layers are left in this form for another year. If the root system has developed enough, then the layers are dug up and planted in a new place.
The breeding method is also widespread. winter cuttings... The best time for this is February. The shoot prepared in advance must be split lengthwise into two parts and cut the resulting halves into cuttings. The length of the cutting is about 5 cm, and there must be a kidney in the center of each. Cuttings are planted in boxes, maintaining a small distance between them, and the soil is sprinkled with sand on top. The boxes are stored in the greenhouse until rooting.

Young liana
Another way that brings almost 100% of the result is reproduction shoots of this year... In order for the root system to form faster, the lower edges of the cuttings must be treated with synthetic phytohormones in accordance with the instructions. After the cuttings have stood in the solution for 12 hours, they are washed with running water and planted in a greenhouse with a friable substrate prepared from equal parts of sand, earth and peat. You can plant the stalks in boxes, which must be covered with glass and removed in a light shade and watered once a day, maintaining sufficient soil moisture. When the first shoots appear, they switch to moderate watering (once every three days). In the fall, they are transferred to a sunny place or shading is removed.

Wisteria seeds
Reproduction of wisteria seeds many gardeners consider it ineffective, because the flowering of such vines may not start, or begin only after a few years. And the decorative properties are very rarely preserved. However, some seedlings from seeds give unexpected results and young vines overshadow the maternal ones in their decorative qualities. Such findings are subsequently used for selection.
The seeds are sown in a greenhouse in the middle of winter. When sowing directly into open ground, it is best to do this in early spring. Seeds germinate late. However, this method of reproduction also has its advantages - plants grown from seeds from the first days are adapted to natural surprises and are much more resistant and hardy.
Pests and diseases of wisteria
Wisteria is quite resistant to diseases, but from time to time it is occupied by aphids, which can be easily corrected with an insecticide. Some gardeners also noticed the raids of the clover mite, which is successfully destroyed by acaricidal preparations. Of the diseases, wisteria can be overcome by chlorosis, if you place your vine on alkaline soil. You can identify this disease by yellowing and falling leaves. As a treatment, it is necessary to make top dressing with iron salts.
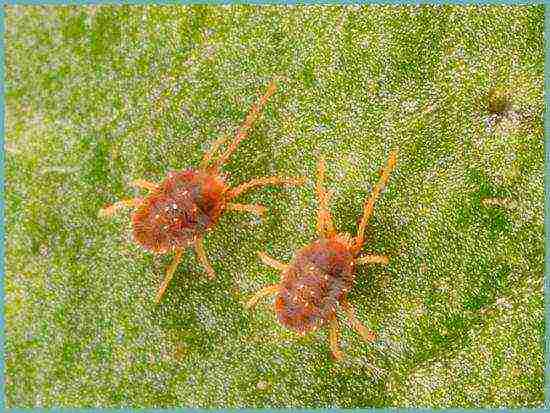

Clover mite
Wisteria in the garden
The bloom of wisteria is an unforgettable maelstrom of colors, in which long brushes of many shades - blue, red, white - rush downward like an unrestrained waterfall, exuding a sweet aroma. In Japan, a walk in a garden with blooming wisteria is equated with a walk in paradise.

Perennial flowers can be planted under wisteria
Very often in landscape design, wisteria is used as vertical gardening of the site. Despite the fact that the liana occupies a minimum of area, its decorative effect is exceptional.It is used to decorate unsightly walls, fences and any other buildings and technical structures that can spoil the overall appearance. This vine will help zone areas, acting as a screen and creating natural shelters from the sun and wind. To create an original ensemble, try planting hyacinths and daffodils at the base of the wisteria. The hazel grouse, white tulips or wolfberry will look good against the background of wisteria. Numerous photos will tell you how best to decorate your garden with this beautiful vine.
Unpretentious in care, wisteria can please the eye of any picky gardener.
How to properly crop wisteria: video
Wisteria: photo








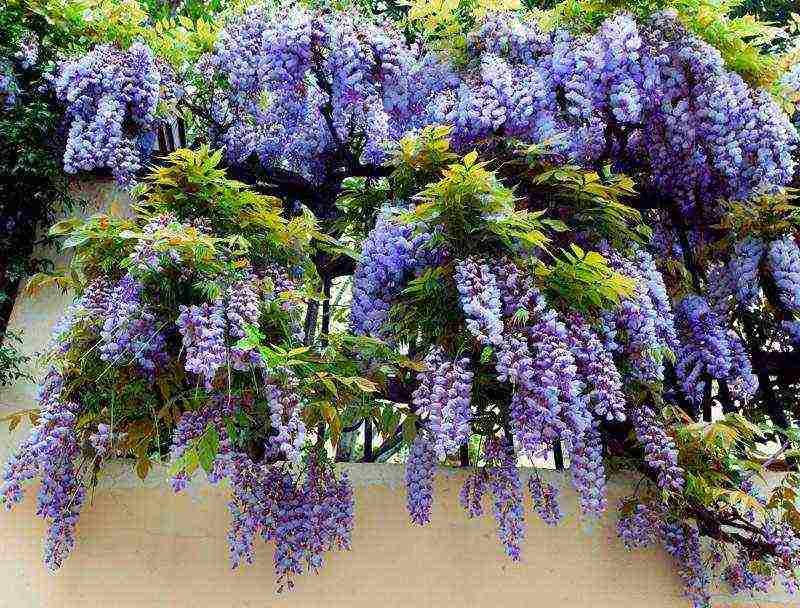
The wisteria flower attracts gardeners with its unsurpassed beauty and fragrant aroma. During flowering, wisteria (the second name of the plant) is covered with many flowering brushes, which, like a waterfall, fall from the bush. If you want to create a recreation area on your garden plot and are looking for a suitable flower for its decoration, then wisteria will come in handy more than ever. It is often used for vertical gardening, and the Japanese compare a walk in the park with a flowering plant to a walk in the Gardens of Eden. Naturally, in order to grow a healthy shrub and achieve abundant flowering, you should create favorable microclimatic conditions for it. We invite you to consider the characteristic features of the plant, its main types, as well as the recommendations of specialists for the care of wisteria.
What does wisteria look like
 Wisteria is also called wisteria. It is a tall, tree-like climbing subtropical plant from the legume family.
Wisteria is also called wisteria. It is a tall, tree-like climbing subtropical plant from the legume family.
Wisteria is a tree-like, flowering deciduous liana with hanging branches. An adult plant can grow up to 15-20 meters in height. It has odd-pinnate leaves up to 40 centimeters in length, which in the first few years of the plant's life are covered with small villi. The flowers are collected in drooping clusters up to 50 centimeters in length, and can be colored purple, snow-white or purple. Wisteria is characterized by a fairly long flowering, which lasts from late March to early September. It is often used in landscape design to create unusual flower arrangements, disguise unsightly buildings and decorate parks. It can be grown as a liana, exquisitely wrapped around a fence, or a gazebo, or a standard tree that decorates the garden.
Wisteria is widely used in plots and gardens
Types and varieties of wisteria
Wisteria is a representative of the genus of dendroid climbing plants of the legume family, numbering 9 varieties. Almost all of them prefer a tropical climate, so for a long time they could not be grown on the territory of Russia. Fortunately, thanks to the efforts of breeders, many varieties have appeared that do not require special care and are able to withstand temperatures as low as -23 ° C. It is interesting that even a guest house in the resort area of Lazarevskoye and Feodosia was named after this beautiful flower. We propose to consider a description of the most common types, as well as study their characteristic features.
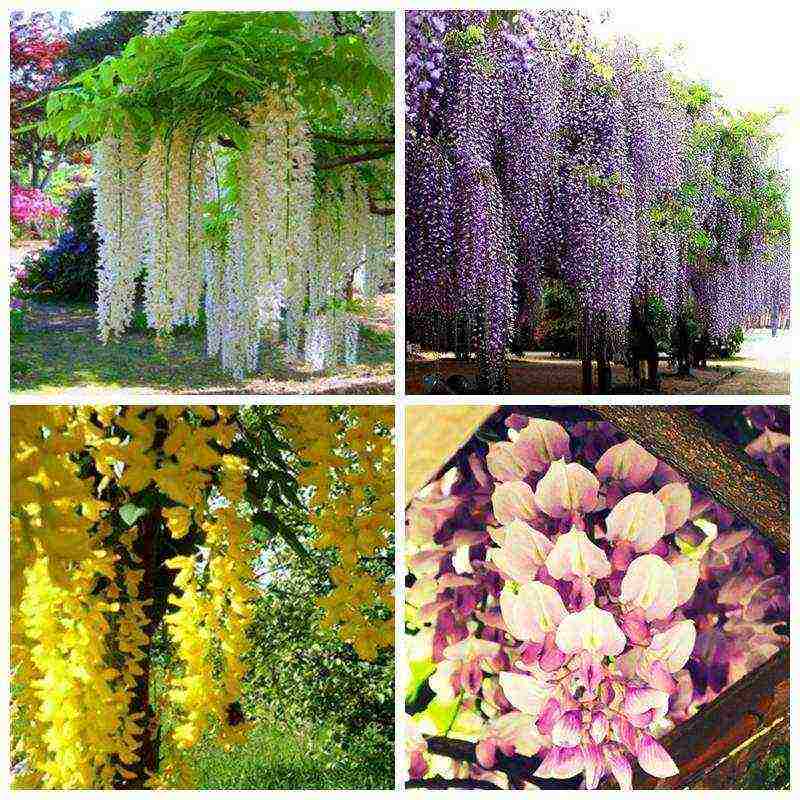 There are various types of wisteria, the flowers of which can vary in shades.
There are various types of wisteria, the flowers of which can vary in shades.
Chinese wisteria blue sapphire
Blue sapphire is a leafy liana, which in natural conditions can grow up to 15-20 meters in height. It has odd-pinnate, large leaves. Young shoots are densely pubescent, but after some time they become smooth. The flowers are pale purple in color, gather in loose clusters, reaching 20-30 centimeters in length. Get ready for the fact that the wisteria grows rather quickly, braiding all the supports encountered in its path. We recommend that you prepare a separate place for the flower in advance, so as not to injure it later.Often, gardeners give the liana a standard shape by pruning. In this case, it grows up to only 6 meters and grows like a free-standing tree. During flowering, which lasts from September to August, the wisteria exudes a pleasant aroma that spreads throughout the site. Also, a variety of Chinese wisteria called prolific has gained popularity among gardeners.
 Chinese Wisteria Blue Sapphire has a delicate purple color of flowers
Chinese Wisteria Blue Sapphire has a delicate purple color of flowers
Wisteria alba
It is a decorative perennial deciduous liana. The plant has many cascading shoots that can grow up to 25 meters in length. Massive stems (up to 30-35 centimeters in diameter) lignify over time. In the early stages of growth, young shoots should be directed in the right direction, because after they have hardened, it will be almost impossible to give them the desired shape. During the flowering period, wisteria is densely covered with clusters of snow-white flowers. There are also hybrids with pink and lavender buds. The main advantage of the alba is the long flowering time. It blooms twice in one season: at the beginning of spring and towards the end of summer. Note that this variety is less frost-resistant than the previous one. Alba can be grown in the Rostov region, Crimea or Transcarpathia.
 Wisteria Alba has beautiful snow-white earrings - inflorescences
Wisteria Alba has beautiful snow-white earrings - inflorescences
Wisteria wisteria floribunda (profusely flowering, multi-flowered)
The profusely flowering wisteria is a relatively small, woody vine. With proper care and timely pruning, it reaches 8-10 meters in height. Abundantly covered with large leaves, consisting of 11-19 dense ovoid leaves and reaching up to 40 centimeters in length. It is interesting that the stems of the plant twist strictly clockwise, their diameter at the base, as a rule, is 20-30 centimeters. Over the years, they lignify, and light green shoots are covered with dark gray bark. Flowering lasts from March to May, but with proper care it can repeat from July to August. During this period, a lot of purple-blue hanging racemose inflorescences, capable of reaching up to 60 centimeters in length, are formed on the tops of wisteria branches. The fruits are stored on the liana throughout the winter.
 Wisteria floribunda - a small tree with a profusely blooming crown
Wisteria floribunda - a small tree with a profusely blooming crown
Wisteria macrostachia (large-walled)
The homeland of wisteria macrostachia is North America. It is distinguished from previous varieties by dense, large inflorescences. The value of this species lies in the fact that it served as the basis for the creation of two frost-resistant varieties: Blue Moon and Clara Mac. The most widespread is the first grade, so below we will consider it in more detail.
 Wisteria macrostachia has large, in comparison with other species, flowers
Wisteria macrostachia has large, in comparison with other species, flowers
Wisteria frost-resistant blue moon
Wisteria blue moon is better than other hybrids suitable for growing in the middle lane, as it has increased frost resistance, which allows it to winter well even with temperature drops up to -40 ° C. This variety is a tree-like, deciduous, rapidly growing liana, the stems of which grow up to 8 meters in length. It has complex, pinnate leaves, consisting of 7-9 small pointed leaves. Cone-shaped inflorescences, painted in blue-lilac color, abundantly cover the plant. Typically, this variety is used for vertical landscaping of gardens, arbors, terraces, unsightly walls and buildings. If you create favorable conditions for wisteria, it will delight you with long and repeated flowering. As we have already noted, this species is characterized by increased frost resistance, therefore it can be grown even in cool latitudes, for example, in the Urals.
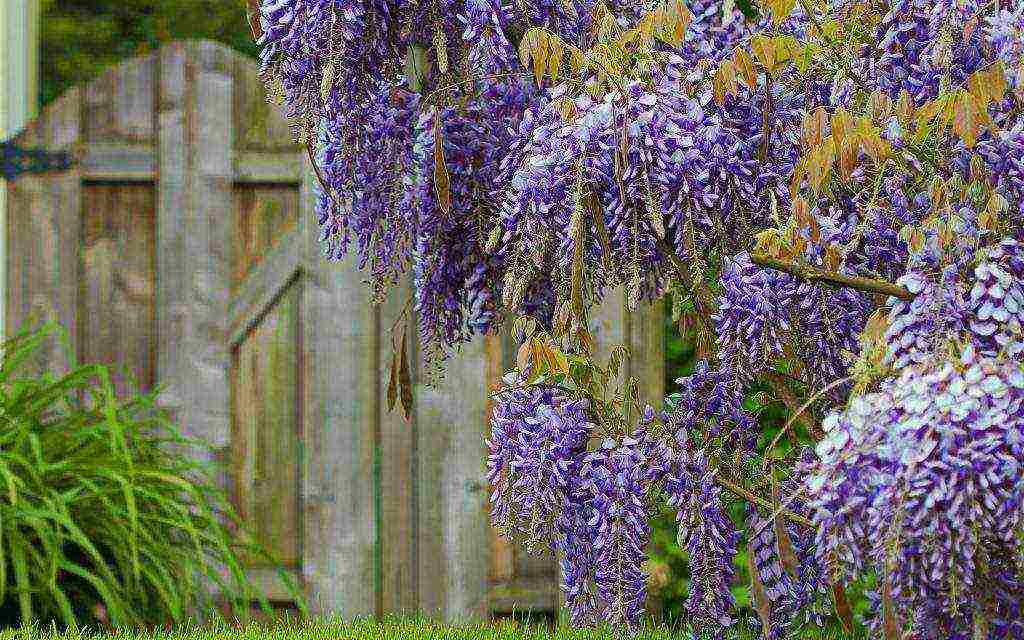 Wisteria blue moon is one of the large-flowered wisteria species that can be grown even in the Ural latitudes
Wisteria blue moon is one of the large-flowered wisteria species that can be grown even in the Ural latitudes
Indoor wisteria
Wisteria is a flower that can be grown not only outdoors, but also indoors. Naturally, indoor wisteria requires constant pruning, because the plant grows quite quickly, reaching up to 2 - 3 meters in height. A standard tree can be an excellent decoration for a winter garden or hall. In the fall, the tree is planted in a compact container, and then transferred to a dry, well-lit room with an air temperature of 15 - 20 ° C. In early spring, young shoots are pruned, forming a beautiful crown, and in summer they are taken out to the balcony or placed in the garden. If caring for a flower seems too difficult for you, artificial wisteria can also become a decoration of your apartment.
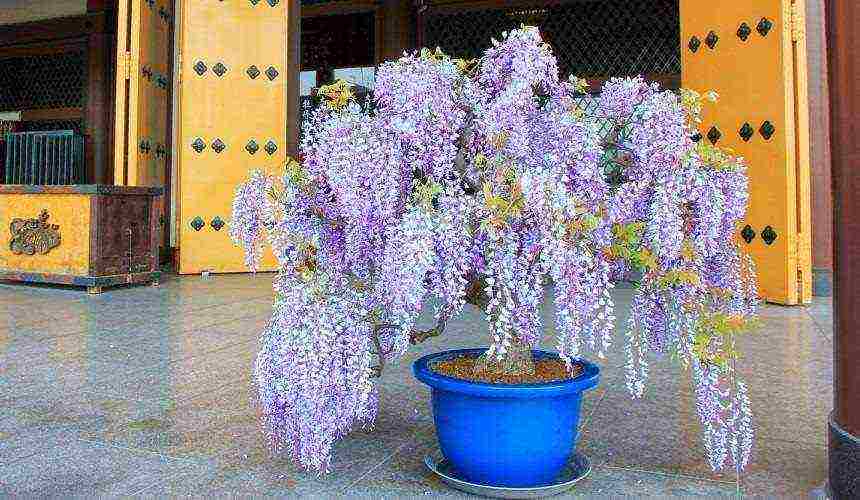 Small wisteria tree can be grown at home
Small wisteria tree can be grown at home
Wisteria bonsai
Recently, wisteria bonsai has gained immense popularity, so more and more flower growers are trying to master the art of its cultivation. Wisteria is great for creating bonsai, as it is distinguished by its plasticity, rapid growth, unpretentious care and excellent decorative properties. Of course, you will have to spend a lot of time and effort to grow a dwarf tree, but we assure you that the result will pleasantly surprise you. Wisteria bonsai looks very exotic, so it can become a real highlight of your interior.
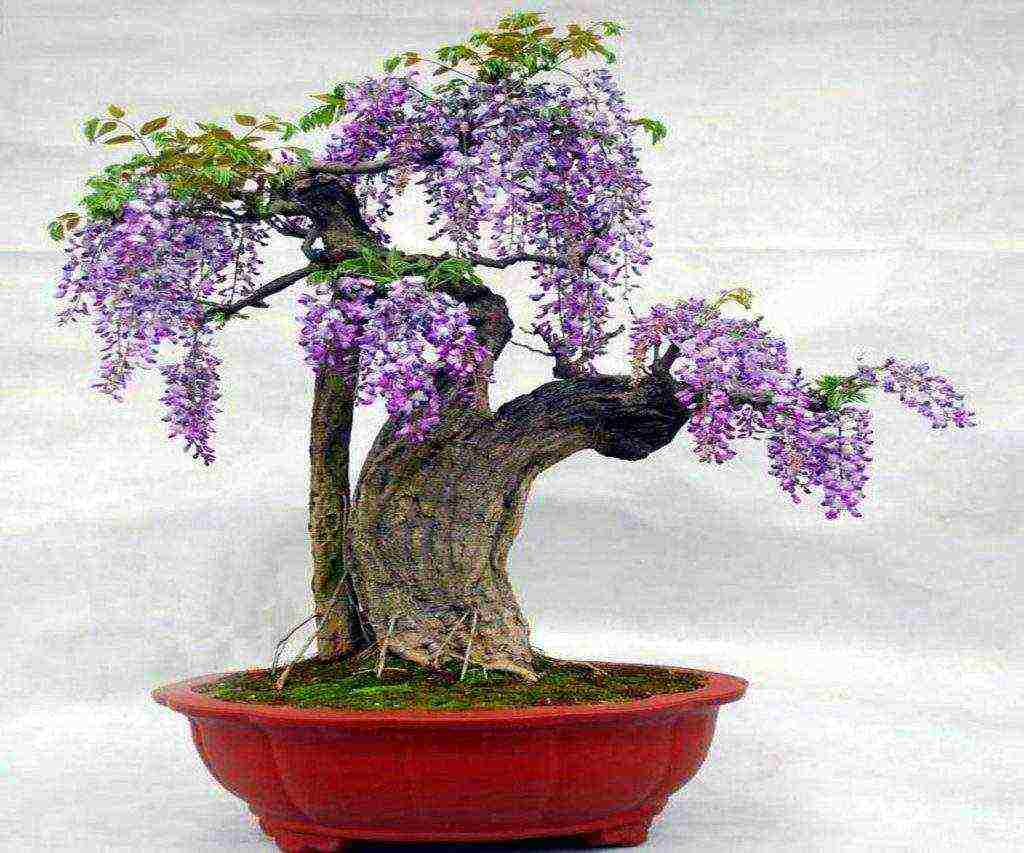 Wisteria can be grown at home as bonsai
Wisteria can be grown at home as bonsai
Beautiful wisteria
It is a liana with densely pubescent shoots that can reach up to 10 meters in length. It has compound leaves, which are also covered with tiny whitish-gray hairs. Small flowers gather in beautiful hanging inflorescences. White racemes, densely covering the plant, can grow up to 50 centimeters in length. Flowering lasts from early May to June, and in July, bean-shaped fruits form on the wisteria. When planting, one should take into account the fact that with age, the stems of the liana become very lignified and its weight increases significantly. We recommend that you immediately select a full-fledged support for it, so that in the future you will not have problems with weaving it. When buying seedlings, keep in mind that full flowering will occur only in the second or third year after planting. The fact is that this species adapts to a new place for a rather long time, therefore, in the first years after planting, you should not expect the appearance of many inflorescences.
 Wisteria beautiful has dense whitish inflorescences
Wisteria beautiful has dense whitish inflorescences
Shrub wisteria
It is also known as American wisteria, since the United States is considered its homeland. For many years, the shrub wisteria has been successfully grown in Russia, Belarus and Ukraine. The plant feels good both indoors and in the garden. Powerful vine shoots can reach 15 meters in height, twine clockwise. The stems of mature plants become lignified, which leads to an increase in tree weight. Consider this feature when choosing a support. The flowering period falls in May-June. A distinctive feature of this species is the relatively small inflorescences and the lack of a pleasant aroma in the buds. The bright leaves consist of 9-15 segments and open along with the flowers. At the end of flowering, fruits in the form of pods with beans are formed on the branches. The described variety is excellent for bonsai formation.
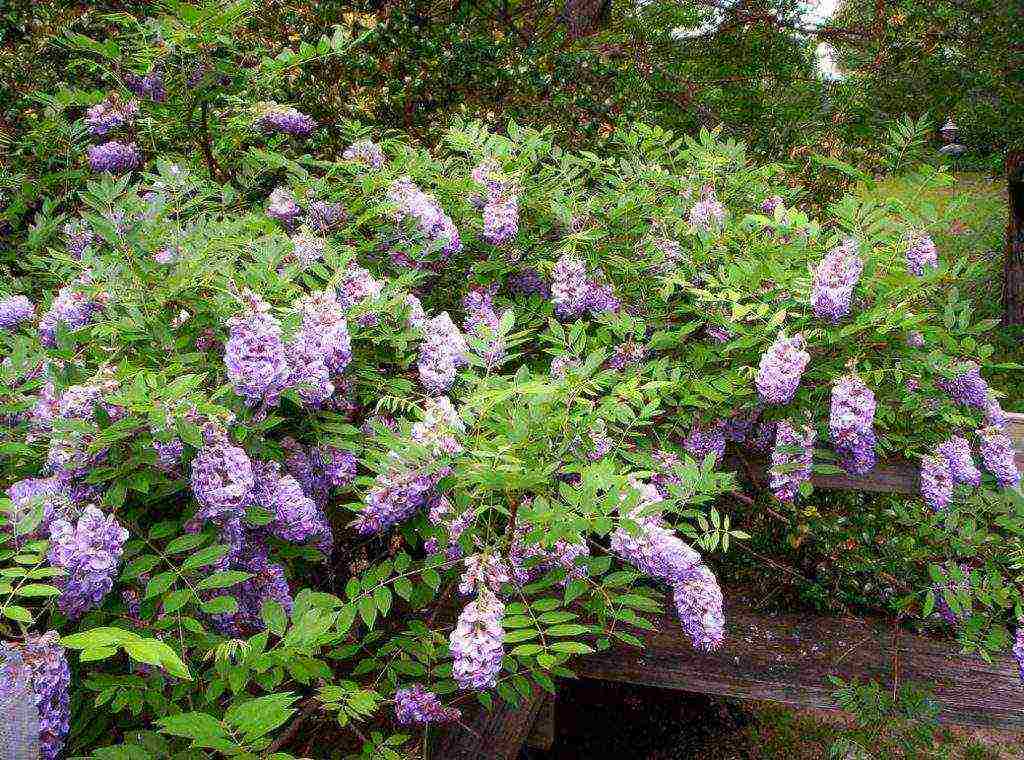 Shrub wisteria differs in small inflorescences and shrub height
Shrub wisteria differs in small inflorescences and shrub height
Japanese wisteria
It is somewhat more compact than Chinese wisteria and rarely grows above 8-9 meters. Despite this, the Japanese variety has rather large leaves (up to 40 centimeters) and bright brushes that abundantly cover the liana. The color of the flowers depends on the variety you purchased and can be white, pink or pale purple. In flower shops, you can find varieties with double flowers or hybrids with variegated leaves.This species is distributed exclusively in the southern regions, so it is not able to withstand the effects of low temperatures. With regard to decorative properties, in this matter, Japanese wisteria is also slightly inferior to Chinese.
 Japanese wisteria is a small thermophilic tree with large lush inflorescences
Japanese wisteria is a small thermophilic tree with large lush inflorescences
How to care for wisteria at home
If you decide to decorate your apartment or garden with this outlandish plant, you definitely need to familiarize yourself with the recommendations for caring for it.
Remember that the growth rate and splendor of the wisteria bloom depends on your efforts. In addition, the correct placement of the plant, timely watering, feeding and pruning are the key to its health and resistance to all kinds of diseases.
Lighting
Wisteria is a long-liver; in nature there are trees that are 100-150 years old. It is appreciated for its exuberant flowering, which largely depends on the place of planting. Wisteria is a light-loving plant, therefore it is recommended to place it in well-lit places. For at least 5-6 hours a day, the vine should be exposed to direct sunlight. Otherwise, the leaves will fade, and the inflorescences on the tree will be much smaller. The best choice would be the location of the wisteria near the southern wall of the house, where it will be protected from drafts, strong winds and will be able to get enough of the sun's rays.
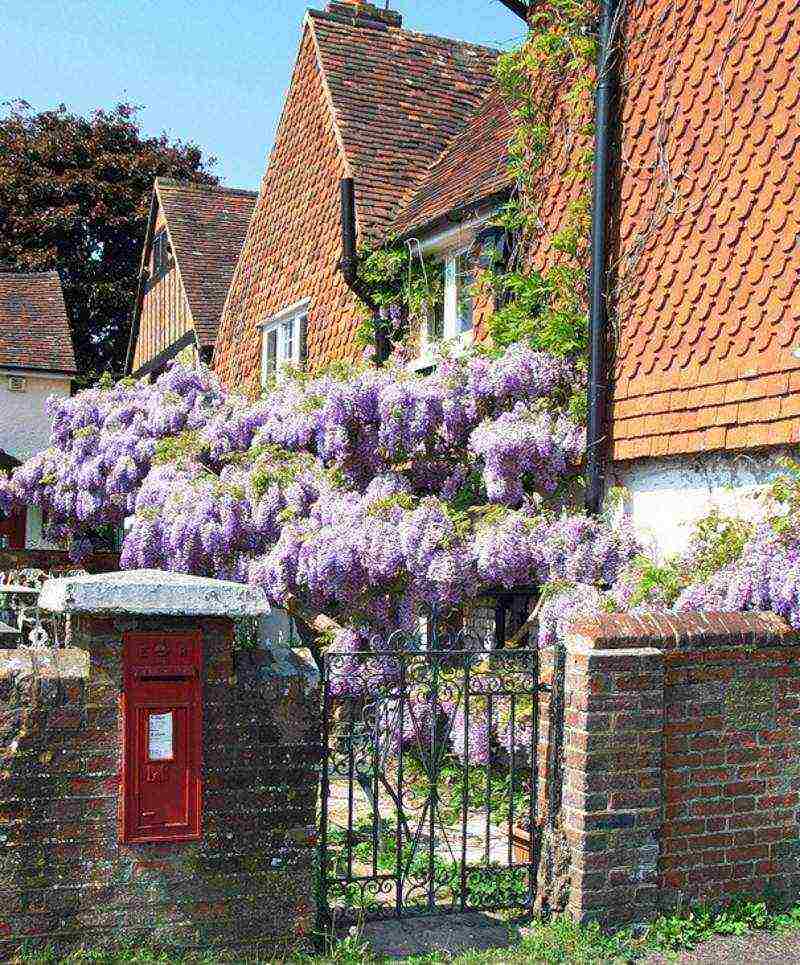 Wisteria is very fond of sunlight, so it should be placed on the south side of the house.
Wisteria is very fond of sunlight, so it should be placed on the south side of the house.
Temperature
The main factor that for a long time prevented the spread of wisteria in our country is its thermophilicity. The delicate plant simply could not withstand the harsh Russian winters, because its homeland is the subtropical regions. Fortunately, the many years of work of breeders have borne fruit and now on the market you can find many varieties that can withstand temperatures from - 20 ° C to - 40 ° C. The optimum temperature for wisteria in the summer is 20-30 ° C. In winter, homemade wisteria requires special care, so we recommend moving it to a room with a temperature of 10-15 ° C. In spring, the tree should be placed on a balcony or terrace.
 Some types of wisteria can withstand the high freezing temperatures of Russian conditions
Some types of wisteria can withstand the high freezing temperatures of Russian conditions
Humidity
From the beginning of flowering, it is necessary to regularly sprinkle the wisteria with warm, settled water. Their frequency should be determined based on the air temperature. From the beginning of autumn, the number of spraying must be reduced, and in winter it must be stopped altogether.
Watering
The plant requires regular watering, but does not tolerate excess moisture. Excessive moisture can cause the leaves to fall off and the buds shed by the wisteria. In early spring, when the herbaceous vine is preparing to bloom, it needs to be watered frequently and abundantly. Once the buds are formed, it should be reduced slightly so as not to harm the wisteria. The soil should be slightly damp, so water only as needed. In early October, the amount of watering should be minimized, since during this period the plant begins to prepare for wintering.
 Wisteria does not tolerate overflow, it needs moderate watering
Wisteria does not tolerate overflow, it needs moderate watering
Top dressing
Liana is characterized by a fairly rapid growth: in one season, shoots can grow by 1-3 meters. Naturally, this requires a significant amount of energy from the plant. Experts recommend regular feeding with complex mineral fertilizers to stimulate abundant flowering and rapid growth of wisteria.
 For faster growth, wisteria is fed with mineral fertilizers
For faster growth, wisteria is fed with mineral fertilizers
Bloom
Depending on the variety, wisteria blooms can last from 2 weeks to a month. Some hybrids bloom up to 2-3 times per season. During this period, the flower requires frequent spraying, moderate watering and frequent feeding.It is advisable to prune creepers from time to time, removing dried or faded inflorescences. Also, in advance, take care of the support from which the racemose buds will beautifully descend.
Wisteria blooms for a very long time and in the warm season, wisteria releases brushes - inflorescences
How to prune wisteria for flowering
Pruning is carried out in two cases: to stimulate the formation of a larger number of inflorescences and to give the plant the desired shape. If you decide to design wisteria as a standard tree, then select one powerful stem and remove all the rest. In the event that you are using a vine for vertical gardening, strongly growing side shoots should also be cut off. This is done so that the wisteria directs all its forces to the formation of buds. Take a good look at the vine, and then remove the young stems that stick out unaesthetically from the bush or cover the flower clusters. In addition, the formation of inflorescences on young shoots is possible only if their length does not exceed 30 centimeters. At the end of flowering, you should give the plant the desired shape, so cut off the side shoots by 20-40 centimeters, and in August, shorten them by another 15 centimeters.
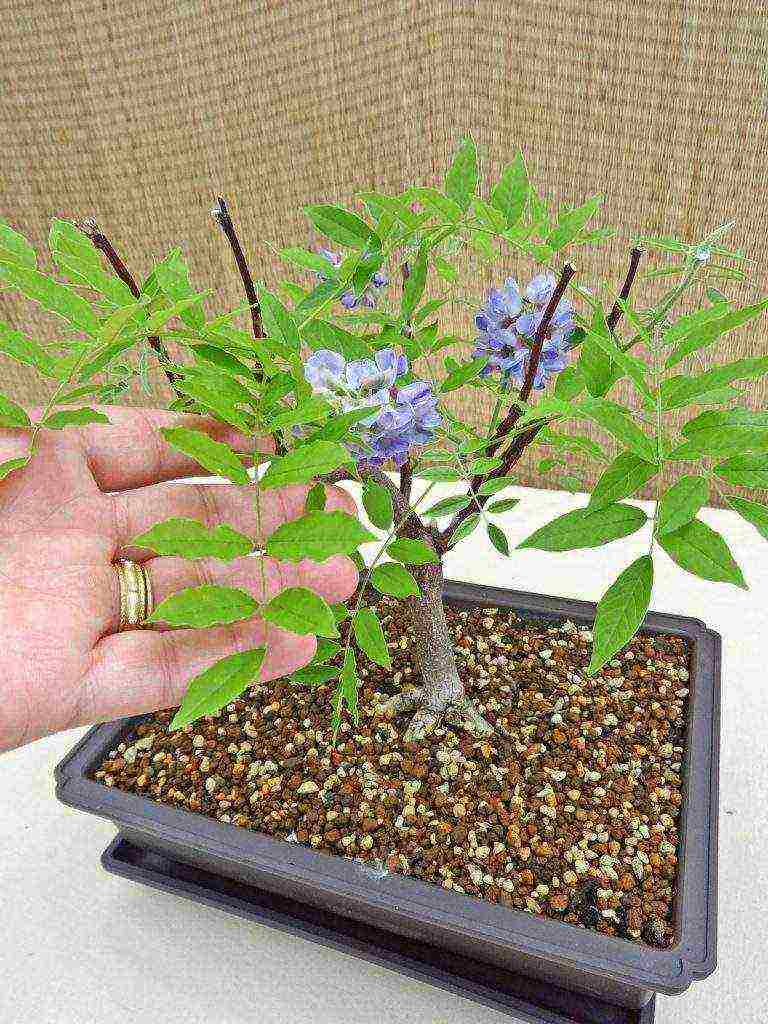 To form the direction of growth of wisteria in the spring, it must be cut off.
To form the direction of growth of wisteria in the spring, it must be cut off.
How wisteria reproduces
If you become the proud owner of a delicate wisteria, you will no doubt want to propagate this beautiful plant. Standard trees will give your garden an exotic look, and vines will allow you to hide imperfections in buildings, decorate gazebos or create an incredible "living" fence. There are several breeding methods, we will consider each of them in more detail so that you can choose the right one for yourself.
Stem and root cuttings
This is the simplest method that even novice gardeners can easily perform. In October or November, carefully cut the vines from the creeper and divide into small cuttings using a pruner. Then put them in a container with a damp substrate and place in a cool place, such as a basement. In March, cuttings can be planted in a school or placed in a permanent place in the garden, covered with plastic bottles. This method practically does not differ from grape propagation, but the success rate is only 50%. Winter cuttings are carried out from February to March. The prepared stems are carefully cut in half along the axis, and then the resulting halves are divided into small cuttings 5 centimeters in length.
It is important that there is one bud in the center of each cutting.
Next, the seedlings are rooted in boxes with a substrate at a distance of 5 centimeters from each other and sprinkled with a small amount of sand. When placing the cuttings, make sure that the bud is at the top. Propagation by root cuttings is also possible, but this method requires a lot of time and effort. In March, the plant is dug up, the young roots are significantly cut off, and part of the large roots at the root collar is also cut off. After all the manipulations, the tree is planted in its usual place. The procedure stimulates the emergence of many new roots that can quickly form adventitious buds, from which stems soon appear. It is these roots that you will need for grafting.
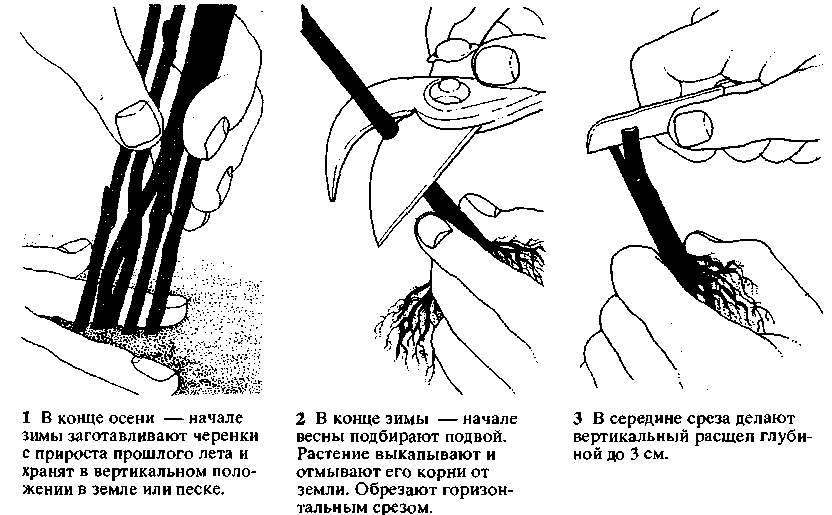 Reproduction scheme of wisteria by cuttings
Reproduction scheme of wisteria by cuttings
In the fall, the wisteria is dug up again, inspected for the presence of young roots and a transverse incision is made with the help of a pruner near the root collar, removing them. The thickness of the root cuttings should be in the range of 5 to 15 centimeters, so you can immediately get rid of the thin tips of the roots and lateral roots. To avoid the occurrence of diseases, treat the seedlings with a fungicide. Next, they should be planted in a prepared, moistened substrate and placed in a warm, bright room. Within a month you will be able to notice the appearance of the first stems, and in the fall the plant will be ready for planting in open ground.
Layers
This is perhaps the most effective method. It is carried out in late autumn, after the foliage has completely fallen off. Examine the vine, select a few powerful lower shoots, cut them slightly, bend them down, and then attach them to the ground using a special hairpin. The resulting layers must be sprinkled with earth so that only their tops remain on the surface. In April, the stems must be looped from the side of the mother plant. By the fall, the plant will take root, and you can transplant it to the desired area. If the stalk develops very slowly, then it is better to postpone the transplant until the next season.
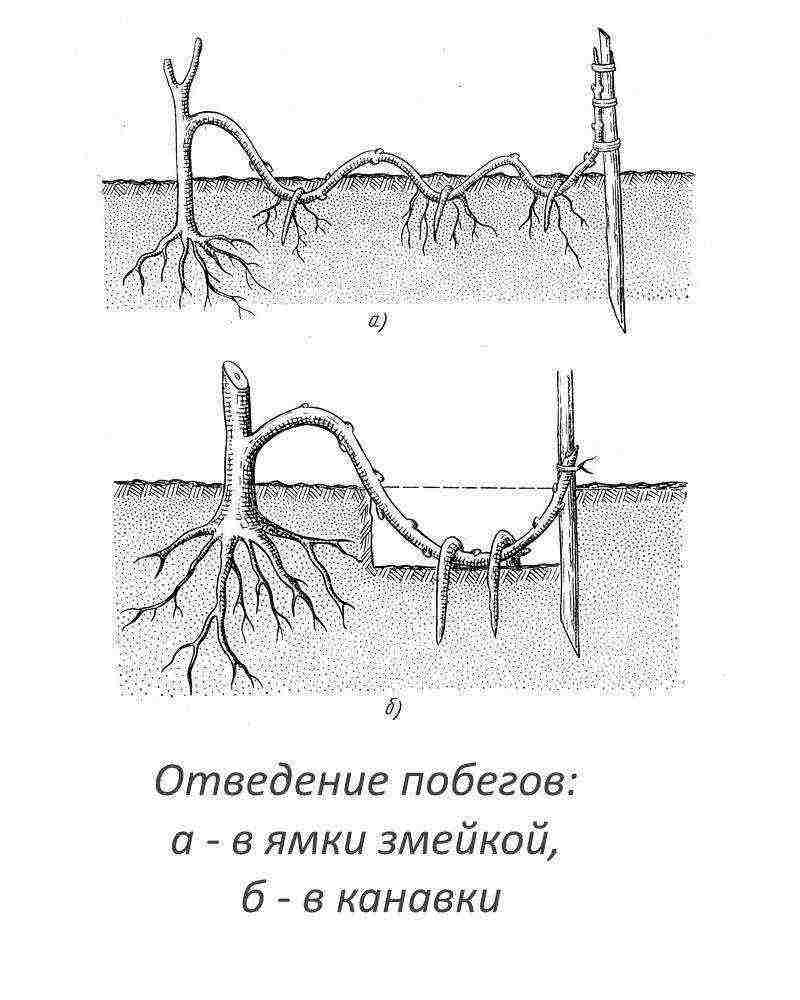 Wisteria propagation scheme by layering
Wisteria propagation scheme by layering
Seeds
Experts do not recommend propagating wisteria by seeds, since some seedlings grown in this way do not bloom. Planting material is sown in special containers with a substrate in December or January. If you want to sow seeds directly into open ground, then do it in March or April. Wisteria is characterized by late germination, and seed germination lasts up to 3 years. Seeds planted in a container must be germinated at a temperature of 22-25 ° C, regularly moistening the soil. The first shoots will appear 3-4 weeks after planting, and starting from 5 weeks they can be taken out in the sun. As soon as the seedlings form the first pair of true leaves, dive them into individual pots. From this moment on, the seedlings must be prepared for planting in open ground. Take them out to the balcony or to an unheated room every day. By April, young wisterias will be ready to move to their summer cottage.
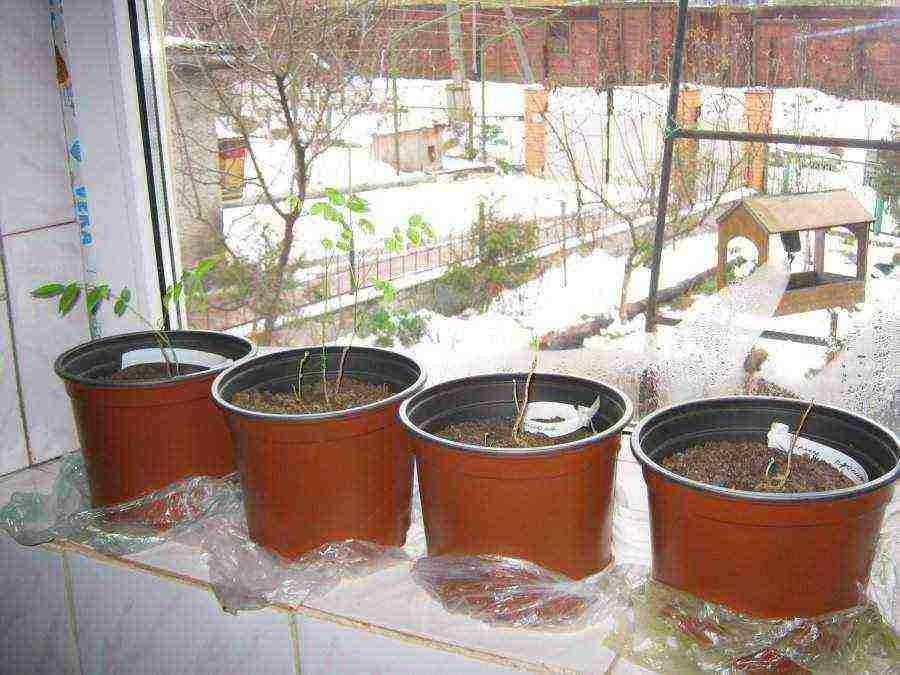 Wisteria seedlings can be grown from seeds
Wisteria seedlings can be grown from seeds
How to plant wisteria
Now that you have learned about all possible breeding methods, you should talk about planting a plant in open ground. Whether the wisteria will take root in a new place depends on the quality of the soil, the correct placement and planting.
The soil
Wisteria is not very demanding on the soil, but prefers to grow on loose, fertile, well-drained soils. If you decide to grow it in a flowerpot, we recommend purchasing a suitable substrate in a specialized flower shop. You can cook it yourself by mixing 4 parts of leafy soil with 1 part of turf and 1 part of sand. To protect the plant from pest infestation and the occurrence of fungal infections, pre-calcine the soil in the oven or treat it with fungicides.
Growing wisteria in a pot
Container growing involves the formation of a standard tree. It will serve as an unusual decor for a hall or winter garden. Such a plant can be taken out into the fresh air no earlier than June. Note that indoor species have a rather small root system, so it is better to give preference to small containers. In spacious flowerpots, the flower will rapidly increase the green mass, which will negatively affect flowering. In the summer, it is better to keep the wisteria outdoors, but in the winter time it should be transferred to a room where the air temperature ranges from 8 to 10 ° C. Please note that keeping in a well-heated room in winter will lead to the death of the tree. You can even send the plant to the basement, but from mid-January it needs to be gradually adapted to higher temperatures. By the beginning of March, wisteria is transferred to a room or to a glazed balcony.
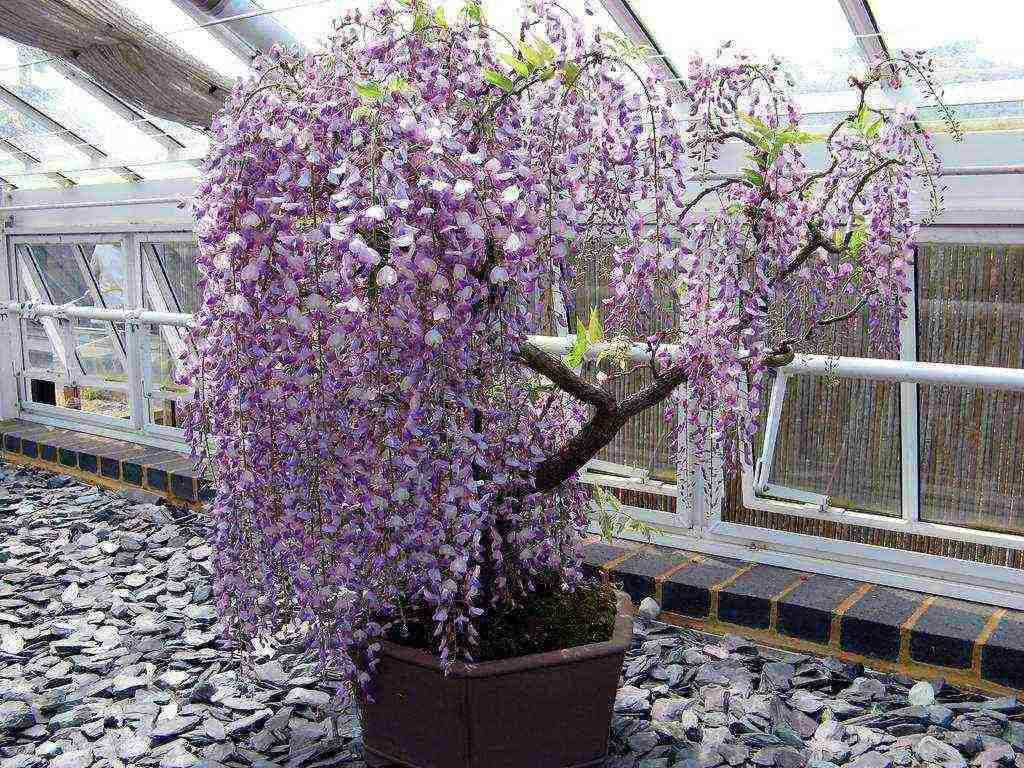 Wisteria can be grown in a pot indoors almost all year round, but in winter it is taken to a cooler place.
Wisteria can be grown in a pot indoors almost all year round, but in winter it is taken to a cooler place.
Planting wisteria in open ground
In early spring, as soon as the last frosts have passed, seedlings can be planted. Even if you prefer frost-resistant wisteria, you should not expose the immature plant to the risk of frostbite. Wisteria is a perennial, so immediately decide on its location.The selected area should be protected from drafts and at least 5-6 hours a day in the sun. Next, consider a step-by-step algorithm for planting a plant.
- Dig holes 60x60x50 centimeters in size.
- Apply complex mineral fertilizers to the soil. As a rule, it is enough to take 20-30 grams per 1 square meter, but it is better to use the mixture according to the dosages indicated on the package.
- Place the seedlings vertically in the holes, and then fill them with soil so that the growth points or leaves are on the surface.
- Moisten the soil well, sprinkle it with sand on top.
 Wisteria is mainly planted in open ground, where it can reach its full growth.
Wisteria is mainly planted in open ground, where it can reach its full growth.
Don't worry if the wisteria won't grow at first. The fact is that it takes a long time to adapt to new conditions, so you should be patient and, of course, take care of the tree.
Care after landing
After planting, the first step is to mulch the young wisteria 10 centimeters above the neck. For these purposes, peat or dry composted grass can be used. Spread the mulch in an even layer and leave it on throughout the year. In summer, it will protect the root system from overheating, and in winter, on the contrary, it will help to avoid frostbite. By the way, in winter, you need to take care of the shelter. This is especially true for species that do not tolerate low temperatures. Your main task after planting a plant is to carry out timely watering, feeding and loosening the soil. If you follow the recommendations carefully, next year the seedling will delight you with bright shoots.
 In order for the wisteria to be comfortable in summer and warm in winter, you can mulch the soil around the trunk
In order for the wisteria to be comfortable in summer and warm in winter, you can mulch the soil around the trunk
Diseases and pests of wisteria
Unfortunately, wisteria does not have an increased resistance to diseases, so you will have to constantly monitor the plant and carry out preventive treatments. The most common disease is powdery mildew. Infection can be identified by the disgusting whitish layer covering the leaves. It can be easily erased with a damp cloth, but reappears after a few hours. If you do not take action in time, the leaves will dry up and fall off, the branches will bend, and the vine will stop developing. Modern fungicides, for example, Vitaros, Fundazol or Previkur, will help to solve the problem. Treat the ground stems with a solution prepared according to the instructions, and after a couple of weeks, repeat the procedure to consolidate the result. Chlorosis is also common, which occurs when there is a lack of iron in the soil. The leaves lose their ability to produce chlorophyll and begin to turn yellow. In such a situation, experts recommend replanting the plant to another place or replacing the soil in the flowerpot, having previously enriched it with iron. For these purposes, you can use drugs such as Ferovit or Antichlorosis. To bring the plant back to life faster, spray the stems and foliage rather than pouring it under the root.
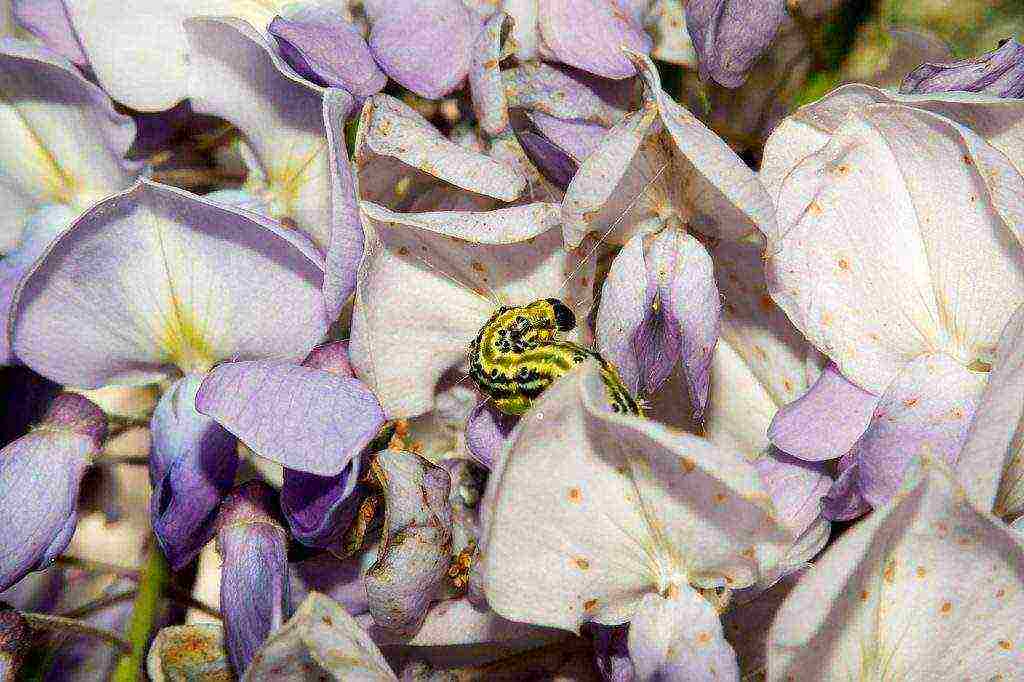 Wisteria can be attacked by pests such as caterpillars
Wisteria can be attacked by pests such as caterpillars
How poisonous is wisteria
When planting a plant, one should take into account the fact that all its parts are poisonous. But poisoning can only be caused if the fruits, flowers or leaves of wisteria are eaten. Such a meal can cause diarrhea, colic, dizziness and even vomiting. If you have decorated a summer cottage with a vine, immediately explain to the children that you should not eat beautiful flowers. Also, make sure that your pets do not feast on wisteria. Do not place wisteria near ponds with fish to eliminate the risk of their death. Otherwise, the plant is completely harmless. Of course, it will not be superfluous to play it safe and protect yourself, so wear rubber gloves when doing garden work.
Wisteria is a riot of colors and colors that will surely win you over.With its help, it will not be difficult to clean up old buildings, arrange a fence or decorate a gazebo, and wisteria grown in the form of a standard tree will help bring a touch of exoticism into the interior. If you only dream of purchasing this wonderful plant, we suggest you watch a video master class on creating wisteria from beads, where assembly and decoration of a delicate tree are described in detail.
Join the discussion!
We would be interested to know your point of view, leave your opinion
in comments
😼


