Content
- 1 Description of an ornamental shrub, use in landscape design
- 2 Outdoor planting and care
- 3 Breeding methods for Japanese quince for transplant
- 4 Chaenomeles pruning rules
- 5 Pests and diseases
- 6 Varieties for growing in the Moscow region
- 7 Harvesting in autumn, storing fruits
- 8 Jam making
- 9 Japanese quince: photo, description, characteristics
- 10 Features of growing Japanese quince
- 11 Reproduction of Japanese quince
- 12 Disease and pest control of Japanese quince
- 13 Japanese quince: photo and description of the bush
- 14 Chemical overview
- 15 Growing and care
- 16 Landing
- 17 Reproduction
- 18 Diseases and pests
- 19 Quince harvesting
- 20 Chaenomeles Japanese - description of the species
- 21 The main varieties of Japanese quince
- 22 Features of growing Japanese quince
- 23 Japanese quince care
- 24 Reproduction of Japanese quince
If you want to decorate your site, create an original hedge and at the same time harvest healthy fruits, pay attention to the Japanese quince.
Description of an ornamental shrub, use in landscape design
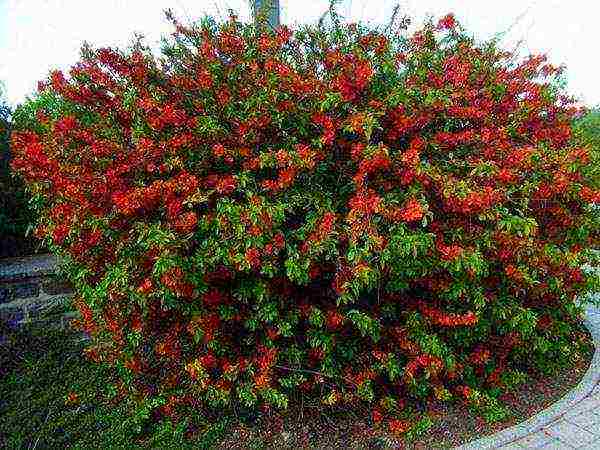
Japanese quince is a low-growing ornamental shrub. She will decorate any garden in spring, when many huge (for its small stature) orange-red flowers with a diameter of up to 4 cm, which are strewn with all the branches, are blooming on it.
In summer, the plant attracts the eye with its glossy foliage with pouring fruits. In autumn, it is strewn with medium-sized yellow fruitsresembling small apples.
Gardeners mainly plant low shrubs for decorative purposes. A group of 3-5 plants looks very good on lawns. A small bush of quince will decorate a flower bed or an alpine slide, often used in landscape design.
Shrub blooms in May and, due to the uneven opening of the buds, the bright bloom stretches for 2-3 weeks.
Spireas, forsythia and magonia will become worthy partners in garden compositions for her.
Quince has the ability to grow in breadth due to abundant root growth, and this is its quality very often used to strengthen slopes (it holds the soil).
You need to be careful with shrubs, as there are sharp thorns on some varieties.
Henomeles (Japanese quince) due to its frost resistance (withstands frosts down to -25 ° well) suitable for growing in the Moscow region... With frosts below -30 ° C, the buds may freeze, but the bush will not die.
With proper cultivation, the shrub grows up to 40 years old.
Japanese quince, or chaenomeles:
Outdoor planting and care
Quince is not demanding on growing conditions, but there are several conditions that must be taken into account when planting a seedling:
- the planting site should be sunny, since the shrub grows and blooms poorly in shade;
- in order to avoid freezing of the bushes in severe winters, plant them in places protected from northern winds;
- the acidity of the soil should not exceed 6.5pH (slightly acidic);
- having a taproot deeply going into the soil, the plant does not tolerate transplanting from place to place, we plant immediately and forever;
- the distance between the bushes is 1-1.5 m, when forming a hedge 0.8-1 m.
It is preferable to plant quince in the spring; during autumn planting, the plant may not have time to take root and freeze.
Landing rules:
- pour about a bucket of humus with wood ash (0.5 kg) and superphosphate (0.3 kg) added into the dug planting hole (60 * 60 * 50cm), mix with a shovel with a small amount of earth;
- we place the seedling in the hole in such a way that the root collar was at the level of the soil;
- we cover the roots of the plant with earth and water it well;
- it is advisable to mulch the soil around the bushes (sawdust, crushed tree bark, peat).
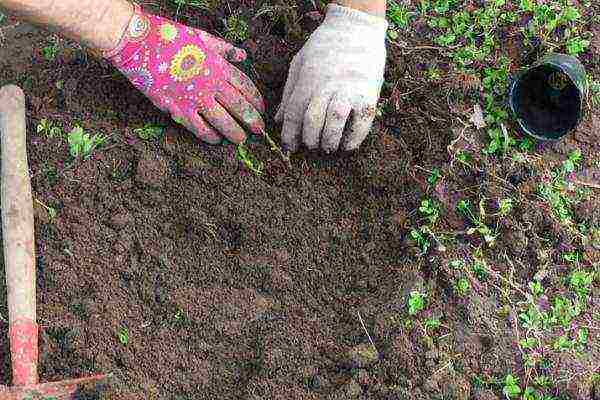 It is preferable to plant quince in spring; during autumn planting, the plant may not have time to take root and freeze
It is preferable to plant quince in spring; during autumn planting, the plant may not have time to take root and freeze
Further care for a young seedling consists of watering, but waterlogging of the soil should not be allowed in order to avoid rotting of the roots, regular loosening of the soil around the bushes.
Since during planting all the necessary batteries were introduced, then no need to feed the plant for two years after planting.
Adult plants in the spring, after the snow melts, are fed with ammonium nitrate about 20 g per bush. In the summer, they give liquid fertilizing with organic matter (diluted mullein or bird droppings). Superphosphate is introduced in the fall.
The plant is winter-hardy, but young seedlings in the conditions of the Moscow region for the winter in the first years after planting are better to insulate.
To do this, you can use spruce branches or cover small plants with covering material (spandbond or lutrasil), put wooden or plastic boxes on top and sprinkle with fallen leaves.
Quince fruiting annually, starting from the third year after planting.
Chaenomeles cross-pollinated plant, therefore, for better pollination and increase yields, 2-3 bushes need to be planted nearby.
Features of planting chaenomeles:
Breeding methods for Japanese quince for transplant
There are several ways to breed Japanese quince.
Seeds
Due to the fact that the varietal qualities are not preserved during seed reproduction, it is used when growing rootstocks with further grafting.
Seeds collected from fruits in autumn are stored in moist sand at a temperature of about 0 ° C throughout the winter. (thus they are stratified).
Seeds are sown in planting containers in February - March, after 1.5 months they dive into separate containers and at the end of May and beginning of June the seedlings are ready for planting in open ground.
Regular watering and feeding is carried out until autumn., for the winter, seedlings that are not yet fully strengthened are insulated with fallen leaves.
The easiest way is to plant the seeds collected in the fall in prepared rows, sprinkle with earth, cover with polyethylene and cover with foliage.
The germination of such seeds is excellent., since they have undergone natural stratification, in the spring dense seedlings must be thinned out, leaving the strongest ones. By the fall, the seedlings are ready to be transplanted to a permanent place of growth.
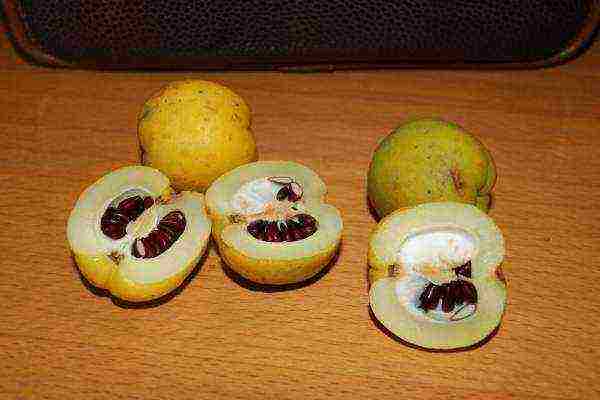 It is best to collect the seeds in the fall and immediately plant them in the beds, covering them with polyethylene
It is best to collect the seeds in the fall and immediately plant them in the beds, covering them with polyethylene
Cuttings
In early June, green cuttings are carried out... Annual cuttings with a "heel" (a piece of last year's wood) are cut. Slices are processed by "Kornevin" for better rooting and planted in the school at an angle.
To maintain humidity, cover the plantings with plastic wrap. By the fall, the seedlings are ready for transplanting to a permanent place, but it is better to do this in the spring.
You can cut ripe cuttings in the fall, dig under a bush at a depth of 20-30 cm, be sure to outline the place.
During the winter, callus forms at the ends of the cuttings, and with the onset of spring, the cuttings are planted immediately in a permanent place.
By dividing the bush
The easiest way to reproduce... Shoots with a well-developed root system are separated from the mother bush (root growth) and transplanted.
Horizontal layering
Quince often grows creeping shoots, having dug in which you can get seedlings for subsequent reproduction.
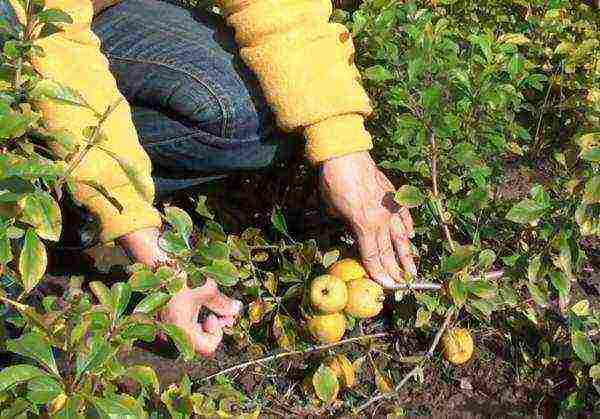 You can bend to the ground and dig in the horizontal layers of Japanese quince
You can bend to the ground and dig in the horizontal layers of Japanese quince
Chaenomeles pruning rules
The shrub tolerates pruning very well, but most gardeners, due to the thorniness of the plant, do not do it in vain. Quince pruning is necessary to improve growth and crown formation for decorative purposes.
There are three types of trimming:
- Sanitary - dry, frozen and broken branches are removed in early spring.
- Formative - they begin to do it from the age of 4, when the branches begin to branch. Shoots growing inside the bush and thickening it are cut out, excess root growth is removed, leaving no more than 2-3 young shoots annually to avoid strong expansion of the bush in breadth. Shoots creeping on the ground are also removed, they take food on themselves and thicken the bush.
- Rejuvenating - it is produced from the age of 8 in the bush, when the annual growth becomes less than 10 cm. Thin and elongated shoots are removed, leaving the strongest 10-12 in the bush. When thinning, you need to remember that the most productive are shoots at the age of 3-4 years, older branches must be removed.
In order to avoid the penetration of diseases into the plant, all sections must be treated with garden varnish.
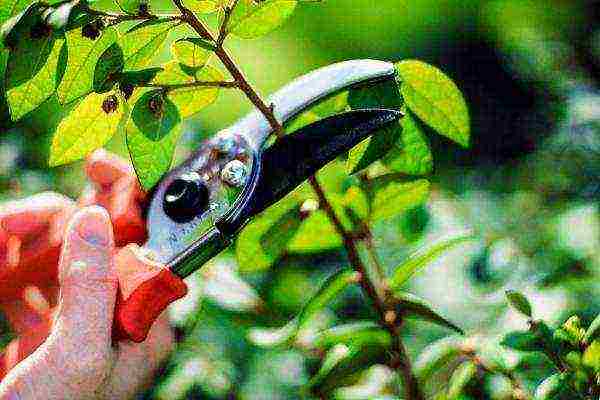 Quince pruning is necessary to improve growth and crown formation for decorative purposes.
Quince pruning is necessary to improve growth and crown formation for decorative purposes.
Pests and diseases
Chaenomeles is not damaged by pests and has great resistance to diseases, but in cool and rainy summers such diseases as:
- leaf necrosis - the appearance of a gray bloom along the edge of the leaf with further spread over the entire surface of the leaf, the leaves dry out;
- cercosporia - manifests itself in the form of dark brown round spots that brighten over time;
- ramulariasis - the formation of brown spots on the leaves.
To combat diseases, spraying shrubs with solutions of copper sulfate (10% concentration) or a solution of foundationol (concentration 0.2%) works effectively.
Varieties for growing in the Moscow region
In central Russia, low-growing varieties up to 1 m in height are grown, with arched branches and a spreading crown.
Of the domestic varieties, the most common are:
- Fragrant - bush up to 1.2 m high, winter-hardy, fruit weight 50-60 g, with a pleasant aroma;
- Nikitskaya - early ripening, medium vigor, winter hardy;
- Vitamin - winter-hardy, compact bush, with bright yellow fruits weighing up to 100 g;
- Muscat - a large-fruited variety (fruits up to 200 g), self-pollinated, winter-hardy;
- Teplovskaya - a variety of late ripening and long-term storage of fruits.
The most famous foreign varieties:
- Gaillardi - variety with large orange flowers;
- Malardi - gorgeous pink flowers with a white border;
- Papel - an interesting variety with yellow flowers and a pink border around the edge of the petal.
 In central Russia, low-growing varieties are grown up to 1 m in height, with arched branches and a spreading crown
In central Russia, low-growing varieties are grown up to 1 m in height, with arched branches and a spreading crown
Harvesting in autumn, storing fruits
Quince fruits are small, hard and sour in taste, but very aromatic and with a high content of vitamin C. They are harvested in September - October, before the onset of frost.
They are stored at an air temperature of 1-2 ° C for 2-3 months. As a result of maturation, they become softer, the sweet aroma is enhanced.
The easiest way is to cut the quince fruits into slices or grate, sprinkle with sugar in a 1: 1 ratio and store in the refrigerator. This blank is used in the preparation of drinks and added to tea.
Jams, jams are also made from the fruits of chaenomelis, and added to compotes. Due to the high iron content, chopped fruits darken quickly.
Japanese quince. Northern lemon:
Jam making
For 1 kg of quince you need: 2 kg of sugar and 1.5 cups of water. Wash the quince, dry it, remove seeds and hard white partitions, cut into small wedges.
Put slices in boiling syrup, boil over low heat for 10 minutes, removing the foam, then remove from heat and leave for 12 hours. Boil the jam again for 10 minutes, etc. until the quince slices become transparent.
We lay out the finished jam in sterilized jars, leave it until winter. In winter, aromatic jam will remind you of the beauty of flowering shrubs and the approaching warm summer.
Japanese quince is unpretentious in cultivation, it is undemanding in attention and it is easy to care for it, but at the same time it is beautiful in flowering and useful in application.
 Almost every owner of a garden plot wants his garden to be not only beautiful, but also unusual. That is why recently gardeners have begun to grow on their plots not only the familiar apple and pear trees, but also exotic plants. These include an incredibly beautiful shrub called Japanese quince or Chaenomeles.
Almost every owner of a garden plot wants his garden to be not only beautiful, but also unusual. That is why recently gardeners have begun to grow on their plots not only the familiar apple and pear trees, but also exotic plants. These include an incredibly beautiful shrub called Japanese quince or Chaenomeles.
This unusual tree, fascinating with its incredible beauty and aroma, will not leave anyone indifferent during flowering. Despite the fact that Japanese quince is an exotic plant, it takes root well and grows in many regions of our country. Even inexperienced gardeners can handle planting and growing Chaenomeles.
Japanese quince: photo, description, characteristics
Chaenomeles belongs to an ornamental and fruit and berry culture, is a thermophilic plant and grows well in regions with a mild climate. A quince tree can grow up to three meters, and a bush - up to a meter.
The plant is different:
-
 smooth, dense, small bright green leaves;
smooth, dense, small bright green leaves; - white, pink or red-orange flowers with a diameter of 3-5 cm;
- spines up to 2 cm long;
- abundant flowering in May-June, which lasts about 20 days;
- apple-shaped or pear-shaped fruits that sit along the entire length of the shoots, the diameter of which can be from 3 to 5 cm, and the weight is about 45 grams.
By the end of September, the beginning of October, the fruits of Chaenomeles ripen. Matured they can be bright orange or green-yellow color... Outside, the fruits are covered with a wax coating, which perfectly protects them from damage. That is why they can tolerate even slight frosts on the tree. About half of the fruit's volume is occupied by brown seeds, which in appearance resemble apple seeds.
Japanese quince begins to bear fruit in the third year of life. From each bush, you can collect from two kilograms of fruit. The fruits, even if they are not yet ripe, are harvested before frost. They can mature when stored at home, but at low temperatures of 3-5 degrees.
Chaenomeles varieties
Japanese quince has a wide variety of varieties (pictured), which allows you to choose a plant that is right for your garden area.
- The variety Crimson and Gold or Magnificent Quince is distinguished by a branched bush that grows up to 1.2 m. The plant blooms with dark red flowers with yellow stamens. The shrub does not require pruning and is most commonly used as a hedge.
- Henomeles Simoni was bred by French breeders. The bush has almost round lodging shoots, crimson-red inflorescences and green fruits.
- The decorative variety Jet Trail is distinguished by frequently creeping shoots, the absence of thorns, curved branches and pale white flowers.
- Japanese quince Vesuvius has a wide crown, but grows no more than one meter. A huge number of its inflorescences are red in color.
- Pink Lady has a wide crown and dark pink or pink flowers. A bush grows up to 1.5 m.
- Henomeles Nivalis both in height and width grows up to two meters. Nivalis blooms with white flowers in May and August.
- Holland quince is distinguished by glossy, dark green leaves, a wide crown and orange-red flowers. In August, there may be a second flowering of this plant.
If you want to grow Japanese bonsai from quince, then it is best for this. Rubra plant... Having planted the cutting at an angle in a suitable container, with further care, to give the bush an aesthetic appearance, it will be necessary to properly prune.
Features of growing Japanese quince
 Cultivation of Chaenomeles is not particularly difficult. When choosing a location for it, it should be borne in mind that the shrub loves well-lit areas. It can grow in partial shade, but it will not bear fruit.
Cultivation of Chaenomeles is not particularly difficult. When choosing a location for it, it should be borne in mind that the shrub loves well-lit areas. It can grow in partial shade, but it will not bear fruit.
Japanese quince is successfully developing practically on any soil... Poor sandy and damp clay soils are suitable for her. However, they should be moderately moist and rich in humus. Chaenomeles absolutely does not tolerate excessively calcareous and saline soils.
Most of the quince varieties are frost-hardy and can hibernate without shelter. However, if the winter is harsh and with little snow, flower buds and annual shoots may freeze slightly. Therefore, it is recommended to plant trees in places where a sufficient layer of snow is formed. In regions with severe winters, the plant should be covered with fallen leaves or spruce branches for the winter.
Landing Chaenomeles
It is best to plant young trees in the spring after the soil has thawed. Autumn planting at the time of massive leaf fall is also possible. However, a heat-loving shrub may not have time to take root and die before frost.
They take root well biennial seedlings of Japanese quince... When planting the plant, it is necessary to ensure that the root collar remains at the soil level. For plants aged 3-5 years, the planting pits should have a depth of 0.5-0.8 m, and a diameter of up to 0.5 m.
The soil for Chaenomeles is prepared from leafy earth, pitch and peat (2: 1: 2). In addition, it is recommended to add 300 grams of potash nitrate, 200 grams of superphosphate, 500 gamma ash, 1-2 buckets of humus to the planting pit.
It is best to plant quince bushes in small groups of 3-5 plants. To prevent adult plants from crowding each other and not closing, the distance between seedlings should be at least one meter.
Care features
 In the first year after planting the plant regular watering is required... Especially the moisture of the soil must be monitored in dry summers. So that the soil retains moisture, around the young Chaenomeles, the soil is mulched with a layer of 3-5 cm. Wood sawdust or peat are suitable as mulch.
In the first year after planting the plant regular watering is required... Especially the moisture of the soil must be monitored in dry summers. So that the soil retains moisture, around the young Chaenomeles, the soil is mulched with a layer of 3-5 cm. Wood sawdust or peat are suitable as mulch.
In the first two years after planting, young plants are fertilized in the spring with nitrogen fertilizers and slurry, and in the fall - with potash and phosphorus fertilizers.
After 4-5 years, Japanese quince will begin to bloom and bear fruit. For an adult plant special care required:
- Chaenomeles does not need abundant watering. It will be enough once a month.
- Fertilize the plant in the same way as other berry bushes.
- Every spring it is necessary to cut out old branches that are more than five years old lying on the ground.
- It is recommended to form a bush annually to prevent thickening. The number of branches on a tree should not exceed 10-20. Vertical shoots are cut. Pruning is done in the spring, even before the buds appear. Autumn pruning can lead to freezing of the plant.
- For the winter period, it is recommended to protect Quince from the wind. To do this, you can cover it with spruce branches, or even install a snow-retaining shield.
As you can see, caring for Chaenomeles is quite simple and does not require large physical and financial costs. It mainly consists of fertilizing and pruning shrubs.
Reproduction of Japanese quince
You can propagate the plant in several ways:
- seeds;
- cuttings;
- dividing the bush.
Seed propagation
 This is the safest and easiest way to breed quince. Large brown seeds are planted in a prepared soil mixture in late February - early March.
This is the safest and easiest way to breed quince. Large brown seeds are planted in a prepared soil mixture in late February - early March.
About in six weeks seedlings dive into separate seedling cups. The grown seedlings in the ground can be planted in May or June.
Young seedlings require protection from frost for the first winter. If this is not possible, then the quince will need to be planted in the open ground only in the spring of next year.
Propagation by cuttings and grafting
The advantages of such reproduction is that all the varietal qualities of the plant are preserved.
Cuttings should be harvested in early June.It is recommended to cut them in the early morning, in dry weather. When cutting off the stalk, it is necessary to make sure that it is with a small piece of last year's wood, that is, with a "heel". Cut off shoots for a day are soaked in growth stimulants and obliquely planted in a mixture of peat and sand (1: 3). Rooting takes place within 30-40 days, provided that the air temperature is not below + 20C.
In May, a graft is made on a quince seedling with a varietal cuttings:
- During the period of the second sap flow (in July or August), varietal shoots of the plant are harvested.
- A T-shaped incision is made on the bark of the seedling (stock), the edges of which are folded back.
- A varietal shoot with a bud is inserted under the bark.
- Plants are tightly pressed against each other, tied and processed with garden varnish.
The survival rate of the eyes is checked after three to four weeks. In the spring of next year, the bud should sprout again, and the bandage can be removed.
Dividing the bush
Quince bushes give numerous root suckers, and over time they grow in all directions. Due to such offspring, the plant can grow even on a steep slope.
The ideal time to divide the bush is considered to be late spring and late autumn. Root shoots for planting should have a thickness of 0.5 cm and a length of 10-15 cm. From one bush you can separate 5-6 offspring.
Prepared shoots are planted vertically in a permanent place. In the future, caring for them consists in regular watering and mulching the soil under them with shavings, wood chips or humus.
The disadvantage of this method of reproduction is that the root system of young growth is poorly developed, and some seedlings need to be grown at home. The fruits of young plants are smaller than usual at first.
Disease and pest control of Japanese quince
 The main pest of Chaenomeles is aphids. Its appearance can be a real disaster for the plant. Therefore, when it is found, the bush must be immediately treated with special means.
The main pest of Chaenomeles is aphids. Its appearance can be a real disaster for the plant. Therefore, when it is found, the bush must be immediately treated with special means.
With high humidity in damp and cool weather, favorable conditions are created for the appearance of various fungal diseases:
- with necrosis and various spots, the leaves begin to deform and dry out;
- with cercosporosis, various brown spots appear, which fade over time;
- with ramulariasis, brown spots are visible on the leaves.
Effective ways of dealing are using copper-soap liquid and 0.2% foundationol... Spraying the bushes with onion infusion is less dangerous. To do this, 150 grams of husks are infused in 10 liters of water during the day. The resulting infusion of the plant is processed every five days.
Japanese quince, the care of which will not be difficult, can be planted as a single plant, in small groups or along the edge of a garden path, forming a hedge out of it. But this shrub is appreciated not only for its unpretentiousness and beautiful flowering. Quince fruits contain many different biologically active substances and a whole range of vitamins. These remarkable qualities put Chaenomeles among the valuable fruit and berry crops.
Japanese quince
 In gardens, not only ordinary shrubs and trees are often planted, but also exotic ones, which include Japanese quince. Another name is Chaenomeles. The home of the plant is Japan. It is also found in China and Korea, though only a wild variety. Also, the tree is planted in the gardens of Ukraine and Russia. Quince prefers to grow on plains, mountain slopes (up to 1.4 km above sea level), forest edges, clearings and clearings. It can also be found in swampy areas, along water bodies.
In gardens, not only ordinary shrubs and trees are often planted, but also exotic ones, which include Japanese quince. Another name is Chaenomeles. The home of the plant is Japan. It is also found in China and Korea, though only a wild variety. Also, the tree is planted in the gardens of Ukraine and Russia. Quince prefers to grow on plains, mountain slopes (up to 1.4 km above sea level), forest edges, clearings and clearings. It can also be found in swampy areas, along water bodies.
Japanese quince: photo and description of the bush
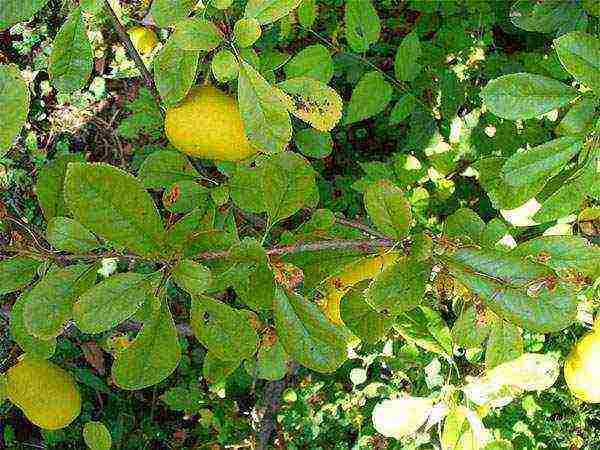
 The plant is a short tree or deciduous shrub, reaching a height of up to three meters and living for about 60-80 years. Distinctive features of quince are:
The plant is a short tree or deciduous shrub, reaching a height of up to three meters and living for about 60-80 years. Distinctive features of quince are:
- Branches. Being felted-fluffy and painted in a green-gray hue, after a while, as they grow, they acquire a black-brown color.At the same time, their pubescence is lost. Black color of the kidneys. The bark is thin, scaly, dark gray or reddish brown. On the branches on the petioles, there are shiny, 5-centimeter egg-shaped leaves with a blunt-toothed edge.
- The flowers have petals of an obovate orange-red color, the diameter of which reaches 4 cm.
- The fruit is a false apple, shaped like a pear or an apple about 4 cm in circumference, covered with a slightly pubescent skin. As for the pulp, it is hard, sweetish-tart, astringent.

Chemical overview
Quince fruits contain a storehouse of components useful for the body. So, vitamin C in them is about 100-150 mg, in addition to it, vitamins E, B1, PP, A, B2, K, B6, various organic acids (citric, malic, tartronic), fatty acids, proteins, sugars, fructose, tanning substances, ethyl esters, antioxidants, glucose, pectins, minerals such as calcium, boron, iron, phosphorus, copper, zinc, pectins, silicon.
Quince seeds contain: amygdalin glycoside, starch, glycerides of myristic and isoleic acids, mucus, tannins, including tannin.
Growing and care
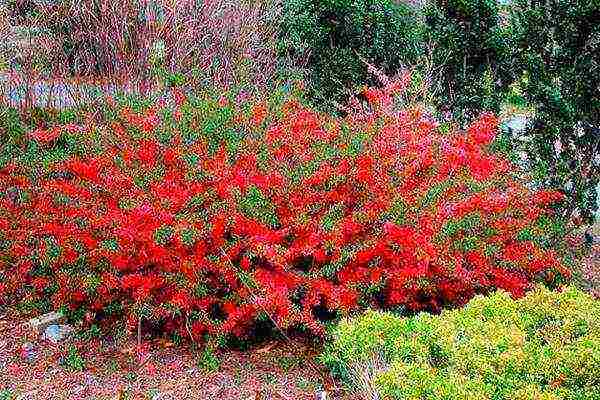 There are no problems in growing quince. For proper development and good growth, all requirements must be met.
There are no problems in growing quince. For proper development and good growth, all requirements must be met.
Where to locate
Quince shrubs love good lighting, so you need to choose a lighted area in your area. In principle, the plant grows well in the shade, but you will not expect fruit from it.
Be especially careful when planting and caring for Japanese quince in the Moscow region. Of all the existing varieties, many winter well without insulation. But in very cold winters, annual plants can freeze slightly. It is recommended to plant trees in areas where there is usually a lot of snow. And if severe winters are a regularity, shrubs cover them for wintering with spruce branches.
The soil
Chaenomeles thrives on any soil. The favorite are moist clayey and poor sandy ones. But they need to be fertilized with humus and moistened. Saline and limestone soils are categorically unacceptable.
Landing
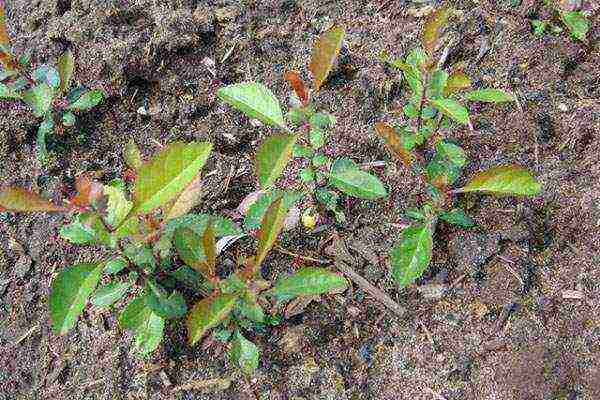 For planting, sand, leafy earth and peat are mixed in a 1: 2: 2 ratio. Additionally, fertilizers are applied to the hole: superphosphate (0.2 kg), 1-2 buckets of humus (1-2 buckets), potassium nitrate (0.3 kg), ash (0.5 kg).
For planting, sand, leafy earth and peat are mixed in a 1: 2: 2 ratio. Additionally, fertilizers are applied to the hole: superphosphate (0.2 kg), 1-2 buckets of humus (1-2 buckets), potassium nitrate (0.3 kg), ash (0.5 kg).
Plant quince shrubs 3-5 in one group. Adult plants are placed at a distance of at least a meter from each other so that the plants develop well.
Young growth is best transferred to the ground to a permanent place with the arrival of spring, when the ground thaws. It is possible to plant Japanese quince in autumn during the period of strong leaf fall. But this is fraught with the fact that the plant will not have enough time to take root until frost and it will die.
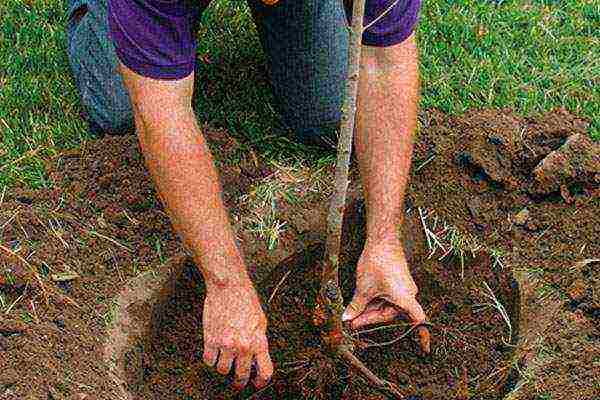 Position the tree so that the root collar is flush with the soil. If the plant is already an adult, 3-5 years old, for them you need to dig a hole 0.5-0.8 m deep and 0.5 m wide.
Position the tree so that the root collar is flush with the soil. If the plant is already an adult, 3-5 years old, for them you need to dig a hole 0.5-0.8 m deep and 0.5 m wide.
Reproduction
Japanese quince can be propagated in several ways.
Seed
 The ripe fruit is cored and the seeds are taken out. They must be sown immediately into the ground in the fall. Seed germination is excellent.
The ripe fruit is cored and the seeds are taken out. They must be sown immediately into the ground in the fall. Seed germination is excellent.
If it is impossible to sow before winter, the seeds are sent for stratification: they are kept for 2-3 months in wet sand at + 3 + 5 ° C. When they hatch, the seeds are planted in the ground.
Cuttings
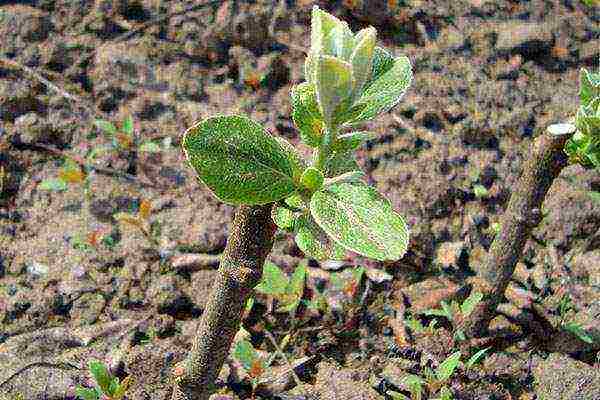 In early June, early in the morning, when it is not very hot and dry, green cuttings are cut so that they have 2 knots. It will be best if you cut the stalk with a "heel" up to 1 cm. Place the cuttings in growth stimulants (for example, a 0.01% indolylbutyric acid solution) for a day. You can use "Kornevin". The prepared material is planted in a substrate (peat and sand, 1: 3) according to the 7 * 5 cm scheme, placing it obliquely.
In early June, early in the morning, when it is not very hot and dry, green cuttings are cut so that they have 2 knots. It will be best if you cut the stalk with a "heel" up to 1 cm. Place the cuttings in growth stimulants (for example, a 0.01% indolylbutyric acid solution) for a day. You can use "Kornevin". The prepared material is planted in a substrate (peat and sand, 1: 3) according to the 7 * 5 cm scheme, placing it obliquely.
Root cuttings
Quince produces a large number of root layers.To get them, you need to dig out the plant and separate the cuttings 0.5 cm thick and 10-15 cm high. At the same time, make sure that the root system is well developed.
From one bush you can "get" no more than 6 divisions.
The resulting shoots are planted vertically and looked after, maintaining the moisture of the substrate and watering. After that, mulching is carried out with chips, humus, shavings.
Diseases and pests
 For the Japanese quince, the most important problem is aphids, at the appearance of which the plant may die. As soon as you notice the first signs of these insects, you should immediately treat with insecticidal preparations.
For the Japanese quince, the most important problem is aphids, at the appearance of which the plant may die. As soon as you notice the first signs of these insects, you should immediately treat with insecticidal preparations.
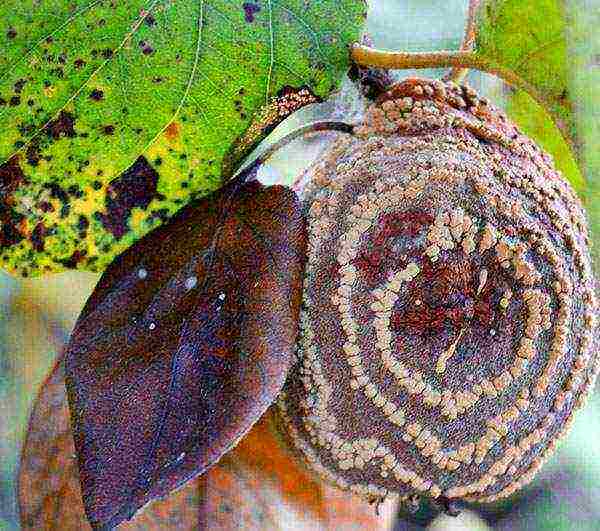
With the onset of cool and damp weather, accompanied by high humidity, trees can undergo a variety of diseases of fungal origin. For example, it could be:
- cercosporosis, which is detected by the appearance of brown spots that fade over time;
- leaf spot and necrosis, leading to drying out and deformation of the foliage;
- ramulariasis, the signal of which is the formation of brown spots on the leaves.
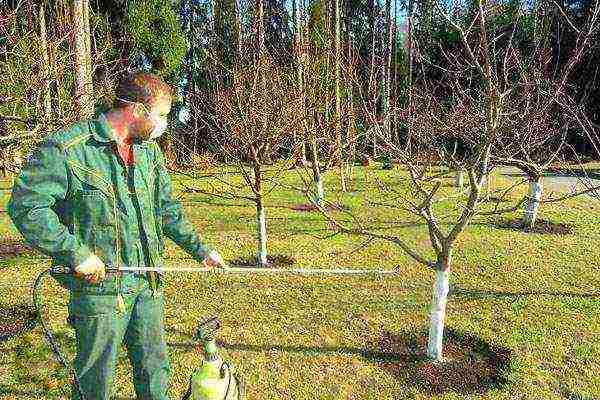 Problems can be dealt with by treating the plant with soap-copper solution and 0.2% foundation. If you are afraid to use chemicals or simply do not recognize them, then you can use onion infusion (0.15 kg of onion husk is poured into 10 liters of water and insisted for a day), which should be sprayed several times with the bushes at intervals of 5 days.
Problems can be dealt with by treating the plant with soap-copper solution and 0.2% foundation. If you are afraid to use chemicals or simply do not recognize them, then you can use onion infusion (0.15 kg of onion husk is poured into 10 liters of water and insisted for a day), which should be sprayed several times with the bushes at intervals of 5 days.
Quince harvesting
 Quince is considered a medicinal plant, and not only fruits, but also leaves and seeds are used.
Quince is considered a medicinal plant, and not only fruits, but also leaves and seeds are used.
Newbie gardeners are worried about when to pick the fruits of the Japanese quince. The fruits are harvested in the fall before the first frost. Then each fruit is well wrapped in paper, placed in a ventilated box and stored in a cool place (6-10 ° C), devoid of light. Even unripe fruits can be stored in this state until February. If there are not enough "apples", they can be placed in a plastic bag and put in the refrigerator. They can be stored there for up to 3 months.
Quince foliage is harvested while the plant is still in bloom. It is laid out on a baking sheet and dried in the shade or in a dryer at a temperature of 40 degrees, transferred to tightly closed containers and used for its intended purpose.
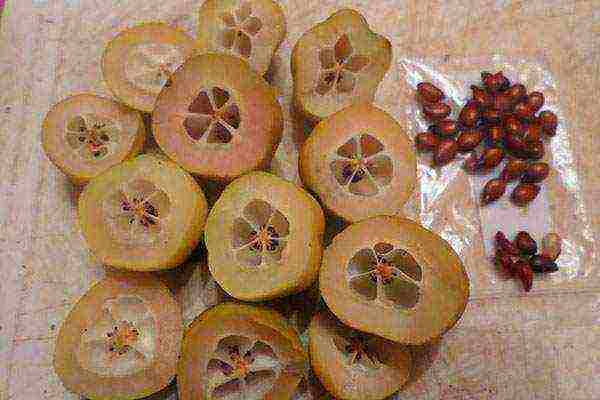 If you need to collect seeds, then they are pulled out of ripe fruits, dried at 40-50 ° C. Then they are transferred to containers with a well-closing lid and stored for no more than a year.
If you need to collect seeds, then they are pulled out of ripe fruits, dried at 40-50 ° C. Then they are transferred to containers with a well-closing lid and stored for no more than a year.
With proper planting and caring for Japanese quince (henomeles), the shrub will not only delight you with a beautiful flowering, and later with a good harvest, but will also support your health.
All about planting and caring for chaenomeles - video
Japanese quince, or chaenomeles, belongs to a species of flowering plants of the Pink family. Its homeland is Japan, but the plant is widely grown both in Europe and in China. The name "chaenomeles" is translated from Greek as "to split an apple". What is so remarkable about the plant? Is it possible to grow it in our country? Today we will talk about Japanese quince, planting and caring for it in the open field.

Japanese chaenomeles - description of the species
Japanese quince is a shrub, no more than 3 meters in height. Young shoots of the plant are scaly-tomentose, green, then they become black-brown and naked. The leaves are obovate, scapular, narrowed to the base, up to 5 cm long. When the plant is young, the leaves are almost bronze, then they become dark green in color. Flowers with a diameter of 5 cm form corymbose inflorescences of 2-6 pieces. They are orange, bright red or pink. Small yellow-green fruits of a rounded shape, edible, ripen by mid-autumn.
The plant has been known since 1874. Despite the fact that the plant is very thermophilic, it can withstand severe frosts. Flower and annual shoots outside the snow level may freeze slightly. In Siberia, the quince cannot boast of such a rapid flowering as the quince grown in the Moscow region.
The main varieties of Japanese quince
Breeders have bred a lot of varieties of Japanese quince. Let's give a brief description of only the most popular of them:
- Papel. The quince is decorative, with beautiful yellow flowers bordered by a pink stripe.
- Malardi. Differs in pink flowers, along the edge they are white.
- Nikolay. A variety of Ukrainian selection, low and thornless, with a spreading crown. It blooms with orange-red flowers, has bumpy yellow fruits.
- Umbilicata. The variety, up to 2 meters high, was bred in Japan. This variety has relatively thorny branches. The plant blooms with pink-red flowers, the fruits are globular up to 90 g.
- Pink Lady. Very bright, beautiful shrub with pink flowers. Spiny shoots. Fruits are bright yellow, firm.
- Simonyi. The variety is originally from France. Reaches a height of 2 meters, has thick thorny branches, white flowers and yellow fruits.
- Likhtar. This variety is winter hardiness. It blooms with bright orange flowers, has large round or ovoid fruits.
- Nivali. French variety with dense, thorny branches. Fruits are yellow, round.
- Crimson End Gold. Small shrub 1 meter high. It blooms with dark red flowers. The fruits of the Japanese quince of this variety are ovoid, green-yellow, distinguished by a thin skin.
- Gaiardi. An ornamental plant that blooms with salmon-orange flowers.
- Merlozi. Variety from Belgium. Differs in irregular pear-shaped green fruits.
- Fascination. Dutch variety with large red flowers and green fruits.
- Clementine. The plant blooms with bright red flowers in May, fragrant fruits appear in late autumn.
You can also often find varieties such as Nika, Fragrant, Vitamin, Rubra, Krasnoplodny, Citrine, Ellie Mossel and others.
Features of growing Japanese quince
Growing Japanese quince, planting and caring for it is determined by the rules for growing garden shrubs.
When and where to plant quince
Better to plant in the spring before the start of sap flow. Autumn planting is less desirable, otherwise the heat-loving plant will not have time to take root before the frost begins. Two-year-old seedlings with a closed root system are used as planting material. Water them well before planting. If seedlings with open roots are used, they need to be inspected, you can soak them in water for several hours, then remove damaged and rotten roots.
It is necessary to plant chaenomeles in light areas, although it tolerates partial shade well, it can develop, but it does not bloom so luxuriantly. The plant prefers a soil rich in humus, it is better if it is light - loamy, soddy-podzolic, sandy loam, and has a slightly acidic reaction. Japanese quince does not tolerate peat soils. For landing, you need to choose a place protected from drafts and winds. Better from the southwest or south side of the house. When choosing a site, it must be remembered that quince will grow in this place for 60 years, she does not like transplanting.
How to land
There are some rules to follow when landing. Prepare the soil for planting in the fall. It is cleared of weeds, then carefully dug up with the addition of sand and leafy earth. When digging, peat-manure compost is added (10 kg are added per square meter). Also, 40 g of fertilizers with phosphorus and potassium are applied.
To plant one seedling, a planting hole is dug, 50-80 cm deep, 50 cm in diameter. Prepare a soil mixture, for this add a couple of buckets of humus, 300 g of superphosphate, 500 g of ash, 30 g of potassium nitrate to the dug soil. If you want to plant a group of plants, they are placed at intervals of 80 cm - 1.5 m from each other. To create a hedge, the distance is reduced to 50 cm. When planting a number of different varieties, you can get a harvest of fruits by autumn. One chaenomeles bush gives about two kilograms of fruit. But sometimes 5 kg can be collected.
To plant a tree, you need to pour a mound of soil mixture into the center of the pit, install a seedling in it, spreading the roots.The root collar should be on the surface. The space around the seedling is filled with fertile soil. After planting, the tree is watered abundantly and the surface is compacted. The shoots are shortened by 17 cm.
Japanese quince care
Growing quince, planting and leaving is not difficult. It is necessary to monitor the weeds, prevent the occurrence of pests and diseases, timely prune the bushes, warm them for the winter so that the plant does not freeze, and water.
Watering and feeding
After planting, the first time the quince needs regular watering, especially if there is no rain. After moistening the soil, the soil around the plant is loosened. It is necessary to loosen it to a depth of 10 cm, while simultaneously removing weeds. To keep the trunk circle moist, mulching is carried out. A layer (3-5 cm) of crushed bark, peat or sawdust is laid out on the entire projection of the crown.
For at least a year, the soil will not need additional feeding, because fertilizers were applied during planting. In the second year of life, the quince in the spring needs to be fed with organic and mineral fertilizers. On one trunk circle, add: 100 g of potash fertilizer, 300 g of superphosphate and a bucket of compost. In summer, you can use liquid top dressing with mullein or ammonium nitrate solution.
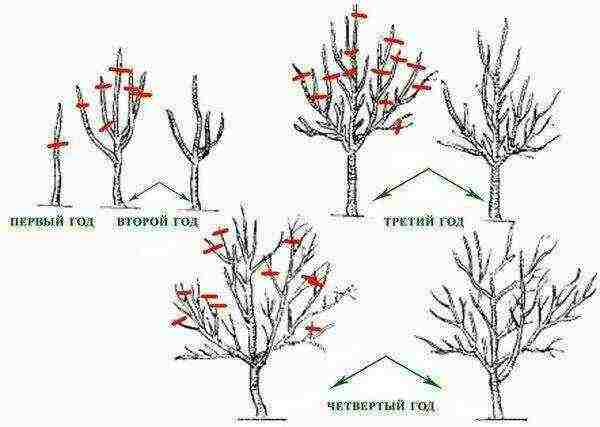
Pruning quince
Japanese quince is the most valuable plant for ornamental gardening. It tolerates fertilization and pruning well. Sanitary pruning is done in the spring. Remove dry, malformed and damaged shoots. Cutting points must be treated with garden pitch. Formative pruning of quince is also carried out in the spring. But it is necessary for plants that are more than 5 years old. It is necessary to ensure that the bush does not thicken and grow in breadth. Each year you need to cut out the root shoots, leaving 3 young offspring. Shoots that are horizontal at a distance of 30 cm are the most valuable. Creeping on the ground, vertically growing shoots must be removed.
Upon reaching the age of 8-10, the growth of the shoots decreases to 10 cm.At this time, rejuvenating pruning is necessary. The bush is first thinned out, leaving no more than 15 strong shoots. Fruits mainly appear on 3-4 year old branches, so gradually you need to change them to young shoots, cutting out old branches.
Quince pest control
Diseases and pests of quince rarely bother, if you do not take care of it at all. Natural disasters can provoke the occurrence of fungal infections. In rainy weather, necrosis or various spotting often occurs. The plant can be affected by ramularia or cytosporosis. Affected shoots are removed and burned. And the rest of the shoots are treated with antifungal chemicals with copper.
The main pests of quince are spider mites and scale insects. It is easier to prevent them from appearing than to try to get rid of them later. Preventive spraying is carried out before bud break, using the drugs Karbofos, Actellik, Aktara. Sometimes reprocessing is not required.
Preparing for winter
Quince is prepared for winter in late autumn. The trunk circle should be covered with spruce branches and a thick layer of dry foliage. Shortened cuttings or seedlings are covered with lutrasil or spunbond. Low-growing shrubs can be covered with cardboard boxes or wooden crates.
Reproduction of Japanese quince
There are several ways of propagation of quince: cuttings, grafting, seeds and root suckers.
Propagation by cuttings
Reproduction by cuttings has an undoubted advantage: the preservation of the varietal properties of the plant. In hot dry weather at the beginning of summer, you need to cut the green cuttings. On each of them, on the lower cut there should be a heel up to 1 cm long (this is a piece of last year's wood). Also, the stalk should have 1-2 buds.
To make sure that the cutting takes root, a growth promoter should be used. It can be Kornevin or indolylbutyric acid. Prepare the substrate, it should contain 1 part of peat and 3 parts of sand.Green cuttings are immersed in it with a lower cut at an angle of 45 degrees. You need to cover the handle with a transparent cap. As soon as the roots grow (after 35-40 days), the plants are transplanted to the right place.
Seed propagation
Reproduction from seeds can be considered the most reliable. Fresh chaenomeles seeds have 80% germination rate. They are sown in the soil before winter, friendly seedlings can be obtained in spring. Long taproots will be formed by biennial seedlings. You need to plant them as quickly as possible in a permanent place.
If time is lost, it was not possible to sow the seeds in the fall, you need to put them in the refrigerator, in a bag with wet sand. There they will remain for 2-3 months. The seeds can be sown in the ground as soon as they hatch.

Reproduction by root suckers
The root shoots of the chaenomeles are quite large. The bush grows very wide. A 20-year-old plant needs an area of about 2 square meters. Root suckers about 5 mm thick and about 15 cm long can be dug up and planted. Young shoots are regularly watered, the soil surface is mulched with chips, shavings or humus. The disadvantage of reproduction of Japanese quince by root suckers can be considered that the suckers' root system is not developed, it has to be grown.
Reproduction by grafting
In May, quince can be grafted with improved copulation. The varietal stalk acts as a scion. The stock will be a seedling of rosaceous crops or the main species. At the end of summer, during the period of active sap flow, you can inoculate with an eye. For this, with a sharp knife, a bud with a piece of bark is cut from the middle part of the varietal shoot. A T-shaped incision is made on the flap (rootstock bark), the edges are folded back, the flap with an eye is inserted. The bent edges are pressed against the flap, the scion is tightly tied at the inoculation site so that the peephole itself is not covered with a bandage. In a month, if everything was done correctly, the peephole should take root. The bandage is removed when a new bud sprout the following year.


