Content
- 1 How to grow asparagus in the country - choosing a place and variety
- 2 Sowing seeds and growing asparagus seedlings
- 3 How does asparagus grow from rhizomes?
- 4 Further cultivation and care of asparagus
- 5 Planting asparagus
- 6 Reproduction by dividing the bush
- 7 Propagation by cuttings
- 8 Forcing asparagus in winter
- 9 Asparagus care
- 10 Harvesting
- 11 How to store asparagus properly
- 12 Asparagus varieties
- 13 Diseases and pests of asparagus
- 14 Benefit
- 15 Growing stages
- 16 Perennial and resistant plant
- 17 Growing conditions for asparagus
- 18 About asparagus seeds and proper planting
- 19 Asparagus Shoot Care
- 20 Preparing a permanent bed
- 21 Planting seedlings on a permanent bed
- 22 Harvesting
- 23 How to propagate asparagus
- 24 Outdoor asparagus care
- 25 Features of caring for asparagus in the greenhouse
- 26 Is it possible to grow asparagus at home
- 27 Features of growing asparagus in different regions
- 28 Diseases and pests
- 29 Harvesting and storage

To begin with, it is unlikely that it will be possible to grow a full-fledged asparagus suitable for food on the windowsill. Its long root takes too much space. Therefore, asparagus is often found in apartments as an ornamental plant, while vegetable crops are usually planted in the beds.
How to grow asparagus in the country - choosing a place and variety
No matter how useful asparagus is, growing this delicacy at home does not seem like a very tempting idea to many. The culture is considered quite capricious, requires careful maintenance, the first crop can be harvested only in the third year. Is it worth spending time and energy for the sake of green stems?
The choice of a place for the garden deserves special attention for the reason that this plant is perennial. For 10 or even 20 years, you can count on a stable annual harvest if you plant asparagus in a well-lit place, if possible from the calm south side.
Video about growing asparagus
It is also helpful to know where the asparagus grows in the wild. Usually its strong green stems can be seen along the shores of lakes or rivers: this culture loves light, sandy loam soils rich in humus. Try to prepare just such a soil, or even better - plant asparagus where previously there was a nursery or greenhouse.
The preparation of the garden begins in the fall: the selected area is dug deeply, added to 1 sq. M. 50 g of superphosphate and rotted manure, or peat compost. Immediately after the spring melting of snow, the soil is harrowed, ammonium nitrate, wood ash and potassium chloride are added (the ratio per 1 sq.m. is 20g / 60g / 30g).
Make the beds high so that water does not stagnate on them, as asparagus does not tolerate waterlogged soil at all.

Keep in mind that varieties that require bleaching will need to be more thoroughly spud or covered with boxes for the winter.
To grow asparagus in your summer cottage, you should choose the following varieties:
- Arzhantelskaya. A productive variety, thickened, large shoots with heads of a light lilac shade and delicate pulp. You can harvest the stems in May.
- Snow head. The pulp is more tender than that of the Argentelle variety, with a taste of green peas. Long shoots with a creamy green head are ready to harvest in the first half of May.
- Glory to Braunschweig.Long stems with white heads and light juicy flesh are best for canning.
- Dutch green. The variety is specially bred to obtain green shoots that do not need bleaching.
Keep in mind that varieties that require bleaching will need to be more thoroughly piled up or covered with boxes for the winter.
Sowing seeds and growing asparagus seedlings
Seed propagation is not the most convenient way. Firstly, there is no guarantee that the seed will have good germination. Secondly, caring for delicate seedlings is a lot of hassle and takes extra time.
If you nevertheless decide to experiment with seed reproduction, it remains only to decide: sow asparagus directly on the garden bed immediately after the snow melts, or at the end of March, plant seedlings in an apartment with subsequent transplantation to the site. In Russian climatic conditions, it is better to dwell on the second option, so that fragile plants have more chances to get stronger.

Seed propagation is not the most convenient way
The technology of growing asparagus from seeds is in many ways similar to growing celery seedlings:
- Asparagus seeds germinate for a very long time, therefore, before sowing, they are soaked in warm water for up to four days, changing the water twice a day. Moreover, the container with seedlings should be warm so that the water temperature does not drop.
- After soaking, the swollen seeds are laid out on a damp burlap or other material and left so for about a week until sprouts hatch (periodically, the seed must be moistened).
- Young sprouts are planted in plastic cups or in a box filled with a store-bought loose soil mixture. It is advisable to maintain a distance of 6 cm between the plants on each side. It is enough to bury the seeds into the ground by two centimeters, no more.
- Containers with seedlings should be placed in a well-lit place, and an additional source of light will not interfere, so that the plants gain strength faster.
- The sprouts that appear are lightly sprinkled with peat.
- After 10-15 days, a complex mineral fertilizer is applied to the ground.
- Within a month, water the asparagus, gently loosen the soil and turn the seedlings in different directions to the light for even growth.
- When the stems stretch up to 15 cm in height, planting should be thinned out, leaving the healthiest specimens at a distance of 10 cm from each other.
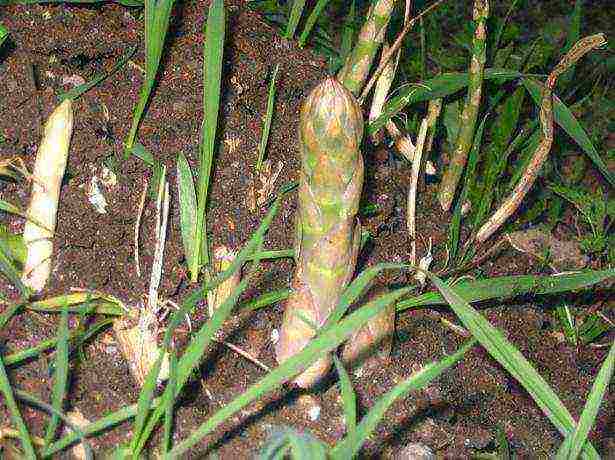

Within a month, water the asparagus, gently loosen the soil and turn the seedlings in different directions to the light for even growth.
In the last days of May, the seedlings must be hardened: every day, subject to good weather, put containers with plants outside. Hardening begins at one hour and gradually increases to 12 hours. By the beginning of June, the seedlings will be fully ready for transplanting to their permanent place in the garden.
For young plants, a bed of 100 cm wide and 30 cm high will be sufficient.A distance of 40 cm should be left between the seedlings, and up to 60 cm between the rows.
How does asparagus grow from rhizomes?
More popular is the propagation of asparagus using segments of rhizomes with live buds. The survival rate of plants in this case is almost 100%. Planting with rhizomes is carried out both in spring and before winter. Let's take a closer look at the technology of planting asparagus in May.
Having chosen the strongest, fleshy rhizomes on the market, divide them into several parts. Carefully place each part in a previously dug hole 50 cm deep, on the bottom of which a mound of earth mixed with humus is poured. Thus, the seedling should be deepened by 25 cm.The optimal distance between the bushes is 15 cm, the intervals between the rows are 50 cm.
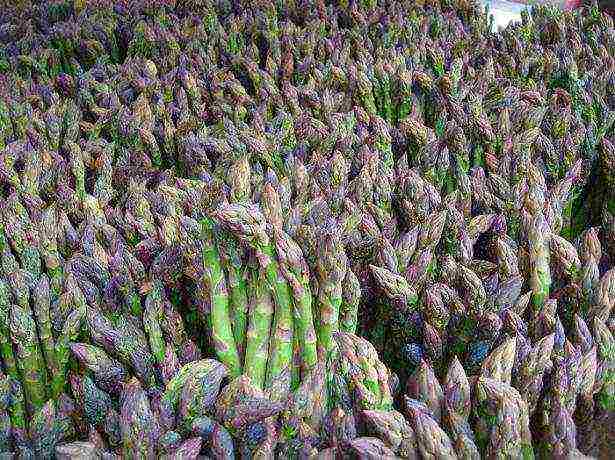

Having chosen the strongest, fleshy rhizomes on the market, divide them into several parts
When planting, try to spread the root system well, cover the rhizomes on top with a mixture of soil with humus and press down firmly. Then pour a little water over the garden bed.
Further cultivation and care of asparagus
Regardless of whether asparagus is planted with rhizomes or seeds, the subsequent care for it will be the same. Immediately after planting on the plant site, you will need to water abundantly for the first one and a half to two weeks, then sprinkle the holes with peat and reduce watering.
During the summer, it is necessary to regularly remove weeds, loosen the soil in the aisles and water it from time to time so that the earth does not dry out, but it is also impossible to overmoisten it. To speed up the growth of shoots, after the first weeding, you can add fertilizing to the garden bed from water-diluted slurry (6 parts of water per 1 part of slurry). After three weeks, it is recommended to feed the plants with bird droppings diluted 10 times with water. And already before the first frosts, the last feeding with complex mineral fertilizer is carried out.
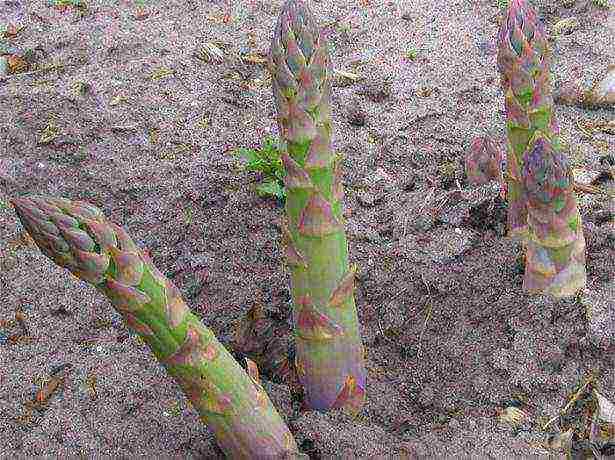

During the summer, it is necessary to regularly remove weeds, loosen the soil in the aisles and water from time to time
For the winter, the upper part of the asparagus is cut off, leaving only "stumps" of 2.5 cm, which are covered with earth, covered with humus and dry leaves on top. The aisles are covered with manure.
Caring for asparagus in the second year looks exactly the same as in the first. And as much as you would like to try juicy shoots, be patient until next year so that they are filled with strength and accumulate more vitamins. Cutting the stems prematurely will nullify all your efforts.
In Europe, it is customary to cut off asparagus shoots only when the height is at least 22 cm, and the diameter is at least 1.6 cm.
In the third year, with the arrival of spring, the planting will need to be hilled so that the asparagus grows long, straight, and its heads do not open ahead of time. From about the end of April, the time for the first harvest begins. Try not to miss the moment when the heads have not yet had time to appear above the surface, otherwise the shoots will lose their presentation, change color and become deeper.
Video about growing asparagus on your site
You can determine readiness by cracking the ground above each plant. As soon as you notice that the soil has risen and cracks have appeared, then it's time to dig up the stems, cutting them to the very root. In warm weather, you can pick asparagus every day or every other day. Just do not remove all the shoots at once, otherwise the plant may die.
After cutting the crop, level the garden bed, sprinkle it with humus on top and compact it slightly. In the future, caring for the asparagus is repeated, as in the first two years.
Rate the article:
(3 votes, average: 2.7 out of 5)
Asparagus is incredibly popular
vegetable culture. What's the secret? Why is it so actively grown, called a miracle plant and a royal vegetable? This is what we will try to figure out.
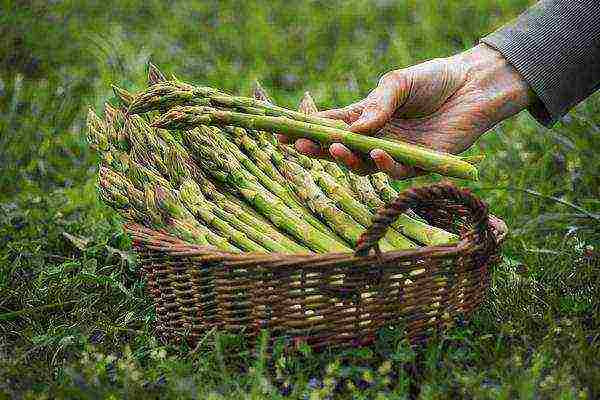

Asparagus is an incredibly popular vegetable crop Asparagus, or asparagus (Asparagus), is a perennial herb up to 1.5 m high. It can grow in one place for about 20 years, forming more than 50 shoots during this time. Feels great in the wild: you can find thickets of asparagus throughout Europe, Asia, Africa and even Siberia. It is unpretentious and cold-resistant, tolerates severe (up to -30 ° C) frosts quite easily, although it can suffer from small (about -5 ° C) spring frosts.

Asparagus, or asparagus is a perennial herb up to 1.5 m high.This representative of the asparagus family is remarkable not so much for the excellent taste of the shoots as for their unique composition: they contain the necessary for the human bodybeta-carotene and choline, thiamine and niacin, folic and ascorbic acids, potassium and iron, magnesium and calcium, sodium, phosphorus, copper, manganese and selenium!
Asparagus -
dioecious plant. Pollen forms on male flowers. On females - small inedible red berries, which contain a maximum of two seeds that remain viable for up to 5 years.

The bright asparagus berries are inedible. The asparagus bush is a tall, highly branching stem that divides into many small stems. Large edible shoots grow from multiple buds located on powerful rhizomes.
Planting asparagus
Asparagus prefers sunny places and fertile soils free from weeds, grows well on sandy loam.
Spring planting
Planting asparagus in early spring before her kidneys begin to grow... The soil during spring planting is fertilized with humus (10 kg per 1 m²). The distance between the rows is at least 60 cm (as the bushes will grow over time), in a row - at least 30 cm, that is, try to place no more than 3-4 plants per 1 m².
The rhizomes are carefully laid in a trench about 30 cm deep and covered in such a way that they appear as if in a depression: this will greatly simplify watering. Water the asparagus with plenty of water immediately after planting.
Autumn planting
The plot for autumn planting should be thoroughly dug up and fertilized, adding 1 m² of soil:
- 60 g superphosphate;
- about 30 g of potassium sulfate;
- 20 g of ammonium sulfate.
When planting asparagus before winter, it is not buried, but a low mound is formed above it to protect the roots from the winter cold. The distance between the plants is the same as for spring planting.
This video shows the asparagus planting process in full detail:
Please note: if you want to get asparagus seeds, it is advisable to plant at least 2 (or more) plants.
Growing asparagus from seeds
Due to poor seed germination, most gardeners do not really like this method, although, if you approach the matter correctly, it will not be difficult to grow asparagus using this method:
- in early April, you need to soak the seeds for two days in warm water with the addition of a growth stimulant;
- sow the prepared seeds in a soil mixture consisting of garden soil, sand, manure and peat (2: 1: 1: 1);
- lightly (by about 1 cm) sprinkle with soil, periodically moisten it from a spray bottle, not allowing it to dry out (if you follow the crops there is no time, cover the container with ordinary glass: this way they will definitely not dry out, but they must be ventilated daily, wiping the glass every time);
- the optimum temperature for seed germination is about + 25 ... + 27 ° C.
Asparagus seeds take a long time to germinate, so be patient. It will take a maximum of a month and a half after sowing, and if you did everything correctly, small charming bushes will appear above the ground - asparagus seedlings.
Asparagus seeds germinate for a long time. They can be transplanted to a permanent place no earlier than mid-June. And when they grow up, it will be possible to replant them both in the spring and in the fall.
Reproduction by dividing the bush
Asparagus reproduces most easily by dividing the bush (this can be done not only in spring, but also in autumn, and even in summer), during transplantation (young plants must be transplanted annually, adults - every 10 years).
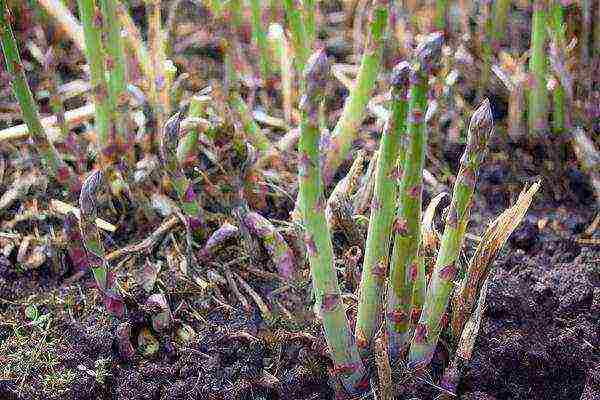

Asparagus reproduces most easily by dividing the bush. Each division must have at least one shoot.
Propagation by cuttings
From March to June, cuttings are cut from last year's shoots of an adult plant, which are planted for rooting in moistened sand, covered with a cap (for example, half a plastic bottle) on top.
Cuttings should be regularly sprayed and ventilated by removing the bottle for several hours a day. They will take root in about a month and a half. Then they must be dived into pots of the appropriate size.
Forcing asparagus in winter
This versatile vegetable crop is successfully cultivated not only in summer, but also in winter (in greenhouses) and in spring (in greenhouses). So let's talk about growing asparagus in winter and spring in more detail.
Asparagus can be obtained in winter and early spring by forcing shoots from the rhizomes of adult 5-6-year-old plants:
- in October, the rhizomes of the plants must be dug up and taken to the basement until December, the temperature in which is maintained at a level from 0 to + 2 ° С;
- around the beginning of December, the asparagus rhizomes should be planted in a greenhouse, in small containers, pressing tightly against each other, trying to place at least 18-20 pieces on 1 m².From above they are covered with a bunch (about 20 cm), the containers are additionally covered with a black film;
- the first week in the greenhouse, the temperature is maintained at about + 10 ° С, but as soon as the roots begin to grow, it is raised to + 18 ° С. It is necessary to maintain the temperature regime for about 2 months - all the time while the harvest lasts.
And in the comments to this question, an interesting old way of growing asparagus is described - steam.
Asparagus care
It consists in timely watering, fertilization and loosening of the soil.
Watering is necessary in small portions, systematically. The main thing is to prevent stagnation of water, asparagus cannot stand this. However, the slightest drying out of the soil will also not do it good. Loosening is desirable after each watering, but at least 7-8 times per season.
It is necessary to water the asparagus in small portions, systematically. The yield of asparagus directly depends on nutrition, therefore, feeding begins even before planting and continues throughout the life of the plant:
- during spring planting, humus is introduced into the soil (10 kg per 1 m²);
- in the autumn for 1 m² - 60 g of superphosphate, about 30 g of potassium sulfate and 20 g of ammonium sulfate;
- a month after planting, the soil is spilled with a mullein diluted with water (in a ratio of 1: 5);
- every year after harvesting (around the end of June), the plants must be fed (for 1 m², 30 g of superphosphate, potassium salt and urea) and uncooked (smooth the ridges). Thanks to such measures, we will give the asparagus the opportunity to develop stems and build up mass so that enough nutrients accumulate in the rhizomes by winter;
- at the time of flowering, it is necessary to carry out periodic preventive spraying with a systemic insecticide. This simple procedure will help scare off pests;
- by July, when the asparagus starts growing again, it needs to be fed again with mineral or organic fertilizers. For example, bird droppings diluted in water (1:10);
- the fourth (last) seasonal feeding should be carried out with a special complex fertilizer around the end of October (before the first frost). So, to stop the growth of asparagus, superphosphate and potassium salt (30 g per 1 m²) can be added to the soil.
In autumn, before the frost arrives, all stems must be removed (this applies to both young and old bushes), the lower part of the plants should be spud and covered with peat or compost about 5 cm in height (1.5 buckets per 1 m²) - this way you will save asparagus from freezing.
Harvesting
The first food shoots appear on asparagus only in the fourth year of life. And it is necessary to break them out only when they begin to lift the soil crust. As a rule, harvesting begins in May, and if the spring is early, then from the first ten days of April.
The first food shoots appear on asparagus only in the fourth year of life. Carefully rake the ground where cracks have appeared, and, having found a seedling, cut it off at the base, taking care not to damage the young shoots and rhizomes. It is necessary to cut off all the seedlings: this will only contribute to the growth of new ones. The holes formed after cutting must be covered with earth again.
In the first year of fruiting, harvesting should not be extended for more than a month, so as not to weaken the young rhizomes once again. Collecting seedlings from old plants should be completed by the end of June. The warmer it gets outside, the faster the asparagus begins to grow. But as soon as its shoots appear on the surface of the earth, they lose their taste, turning into a dark pink or purple color. To prevent this, harvest twice a day: early in the morning and in the late afternoon. At a temperature of about + 15 ° C, you need to collect asparagus every 2-3 days.

In the first year of fruiting, harvesting should not be extended for more than a month, so as not to weaken the young rhizomes once again.If you use beautiful openwork greens of asparagus for arranging bouquets, do not cut all branches from one bush: this can adversely affect the plant.Collect the seeds only when the berries acquire a deep red color.
How to store asparagus properly
Store asparagus shoots in a cool, dark place - on the bottom shelf of the refrigerator. So they will not lose their taste for about 3 months. Asparagus is also perfectly preserved in an ordinary wooden box in a cool, well-ventilated cellar. To prevent the shoots from withering, sprinkle them with sand.
Asparagus varieties
There is not just a large, but a huge number of asparagus species (over 300), among which there are vegetable, medicinal and ornamental.
Asparagus varieties In this article we will talk aboutvegetable asparagus and its most common varieties. We have already discussed how green, white and purple asparagus differ.
Variety 'Snow head'
One of the most popular is the mid-early 'Snow Head' variety. Small shoots are distinguished by a pointed greenish-creamy loose head. The pulp is very tender and tastes like green peas.
Mid-early grade 'Snow head'
Variety 'Slava Braunschweig'
A popular late variety, one of the few whose juicy white shoots are good for canning.
Variety 'Slava Braunschweig'
The peculiarity of the variety is not only in the highest gustatory qualities of the shoots resistant to greening, but also in their large quantity.
Variety 'Arzhentelskaya'
Differs in large, low-fiber white shoots with slightly spread head scales.
The 'Arzhentelskaya' variety is prized for its long period of shoot formation, suitable for both canning and fresh use.
Diseases and pests of asparagus
Despite the fact that asparagus is an extremely disease-resistant plant, it can be attacked by the dangerous fungus Helicobasidium purpureum, which can destroy it in a couple of days. The first sign of defeat is shedding of branches. You can get rid of the disease with the help of the drug "Fundazol".
The most dangerous enemies of asparagus are asparagus leaf beetles: their larvae destroy foliage, as a result of which the plants quickly die. For effective control use insecticides "Fitoverm", "Fufanon" and others.
In spring, the plant is attacked by asparagus flies, the larvae of which gnaw small holes in the shoots, because of which their growth stops and, unfortunately, they are no longer suitable for food. In the fight against the asparagus fly, ordinary chlorophos is excellent. Remove all damaged shoots, and treat young plants with the drug.

As you can see, it is not so difficult to grow asparagus. How do you feel about asparagus? Share your secrets of growing, caring for and storing this wonderful plant!
For those who do not know how to grow asparagus from seeds, the article will help to understand the intricacies of this matter and the peculiarities of caring for a vegetable crop. To begin with, asparagus is incredibly popular in Europe, America and Southeast Asia. Those who have been there are familiar with the spicy taste of dishes prepared by chefs from long tender stems. Now in our country there are many lovers of appetizing dietary vegetables, and therefore those who would like to grow it on their own in their garden. By the way, asparagus quickly adapted to our climate, and breeders can boast of excellent domestic varieties.

Benefit
Young, slightly underdeveloped stems-pods are used for food, which are tasty not only boiled and baked, but even freshly cut, when they are juicy and crunchy. It seems strange that once in our country, asparagus was used only as an element of the design of flower bouquets. Only sometimes in pre-revolutionary Russia exotic dishes from it were served on the lord's table.
The vegetable is famous not only for its taste and dietary qualities. It contains a whole list of vitamins, including group B, as well as many beneficial trace elements and the amino acid asparagine.Eating asparagus expands peripheral blood vessels, normalizes blood pressure and heart muscle function; has a beneficial effect on liver tissue. In addition, long juicy stems in any form are indicated for diabetes, gout and kidney disease. That is why many are asking the question: how to grow asparagus from seeds at home?

And the demand for a green vegetable is largely determined by the fact that it sprouts in early spring, when the body is deficient in vitamins, and fresh greens have not yet gone.
Growing stages
Certain difficulties in self-cultivation lead to speculation about whether and how to grow asparagus from seeds. The advice of gardeners is, first of all, that it is necessary to collect the vegetable daily, not allowing the young shoots to stand. Further, a large amount of special feeding and organic fertilizers will be required for the entire season.
Third tip: stock up on top-quality seeds in advance. The fact is that asparagus does not divide from the roots, and mature specimens do not take root after transplantation. The only option left is to grow a crop from seeds. Interestingly, this perennial plant is considered a seedling for a very long time - two to three years. To learn how to grow asparagus from seeds in a country house or garden according to all the rules and with good results, you should separate a weed-free and organically fertilized garden for planting a crop.
Planting the prepared seeds is carried out in June, and throughout the summer the garden is loosened and watered. When shoots appear, fertilizing with ammonium nitrate is carried out at the rate of 10 grams of solution per square meter of land. Re-feeding is carried out after 3 weeks. The next year after wintering, the plant blooms.
Perennial and resistant plant
Before answering the question of how to grow asparagus from seeds, you need to know at least a little about the culture itself. Asparagus is a fairly large perennial plant that can grow to a height of about two meters. Although it has no leaves, the long shoots are very branched, and the fibrous roots are huge.

The vegetable blooms with inconspicuous flowers and has beautiful red fruits. Since asparagus is a dioecious plant, male and female flowers are present on different bushes. If you take proper care of it, then the harvest from one specimen can be obtained for 15-20 or even more years, therefore, asparagus can rightfully be considered a green long-liver.
And also, if you are wondering how to grow asparagus from seeds in the garden, it will be useful to know that this is a very resistant and hardy plant. Even with our frosts, you can not cover it for the winter and not do pruning if you did not have time to do it. Subject to the rest of the rules, the harvest will be ensured.
Growing conditions for asparagus
If you decide to breed asparagus for decorative purposes, then you just need to plant it, and it grows on its own. But the cultivation of delicate shoots for consumption is different, so it is necessary to create special conditions for the plant. Namely:
- Loose, fertilized soil is required. It is good if it is sandy loam on your site. When nutrient deficiencies are present, the asparagus stalks will grow thin and coarse.
- In no case should the soil be acidic, otherwise the plant will not take root.
- The key to a good and tasty harvest is abundant watering; with a lack of moisture, the asparagus will taste tough and bitter. But she does not like the proximity of groundwater either.
- The planting beds should be in a sunny location, although a little shade will not hurt the plants too much.
- Annual mulching will ensure the active growth of succulent shoots.

To learn how to grow asparagus from seeds, it must be borne in mind that the roots of this vegetable grow strongly and lie almost at the surface of the soil.Every year they grow from above, and the lower parts die off, so gradually the bush, along with the root system, rises higher to the surface. That is why there is a need for annual mulching, that is, covering the soil at the roots, which prevents drying out, overheating and hypothermia of plants.
About asparagus seeds and proper planting
Asparagus seeds are large, black, in a protective sheath. Before use (usually for planting in the garden this is the beginning of June) they are soaked for three days in a manganese solution, changing it several times, or in ordinary water, also periodically replacing it with fresh water. This procedure will speed up the emergence of seedlings. After that, the seeds are spread on a wet cloth until germination. This takes about one week.
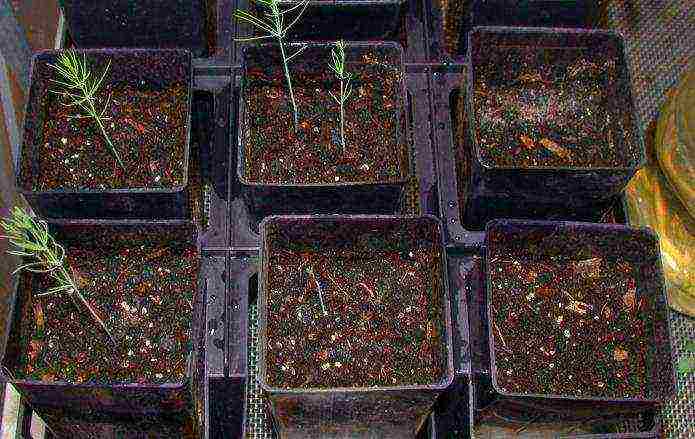

So how to grow asparagus from seeds? The photo shows a variant of early germination of seeds at home, when each seed is planted in a separate pot. It is best to do this in April-May. If you sow directly on the beds, then to get a good harvest, the germinated seeds are laid to a depth of 3 cm in the ground, placing them 5 cm apart in a row.
A distance of at least 20 centimeters is maintained between the rows, otherwise it will be inconvenient to thin out the elongated seedlings. And this must be done immediately after the first shoots appear, since the roots of asparagus grow quickly, and it is impossible to pull them out of the soil without damaging the neighbors.
Asparagus Shoot Care
Care of young asparagus shoots is traditional for most vegetable crops - feeding, weeding, watering and loosening the soil. At the time of emergence, they are fed with ammonium nitrate, and 3 weeks after that, they are fertilized with liquid manure.
Already in September, in the first year of life, the seedlings have 2-3 stems. Peat and compost will be excellent mulch for the plant during the winter. And gardeners have enough time to prepare permanent beds for transplanting asparagus.
Preparing a permanent bed
The preparation of a permanent asparagus bed is carried out in several stages. Autumn digging should be deep enough - 35 centimeters, and spring is accompanied by the introduction of manure (10 kg of fertilizer per 1 square meter). Mineral formulations can be applied in the fall, or just before planting seeds. In this case, 1 square meter of soil will require: 3 g of potassium salt, 2 g of ammonium sulfate, 5 g of superphosphate. You can use ready-made complex fertilizers.
Planting seedlings on a permanent bed
You already know how to grow asparagus from seeds. And how are seedlings planted in permanent beds? To do this, furrows are made in the soil about 40 centimeters in width and depth, observing the distance between them a meter and a half. A layer of rotted manure and a humus roller 5-7 centimeters thick are placed on the bottom, on which the seedlings are placed. It is important to spread the branchy roots so that they do not bulge up.
The distance between individual seedlings should be at least 40 centimeters. As the asparagus grows, the furrow will be leveled by adding soil from the edges. In addition to summer dressings in September, when the growing season ends, the plants will need potassium and phosphorus. Every 5 years, the soil is fertilized with organic matter, for example, rotted manure. Mulching is carried out for the winter, after cutting off the stems.
Harvesting

Knowing how to grow asparagus from seed at home in your backyard, you now need to figure out when to harvest it. Cutting shoots begins in the 2nd year; moreover, white shoots that have reached the surface of the covering layer are considered ready, and green shoots that have grown by 15-18 centimeters.
The very first harvest lasts 2-3 weeks, and then the vegetable is harvested for a month and a half every day. You can store fresh asparagus for several weeks in the refrigerator in plastic bags.
In general, knowing the simple rules, you can grow various varieties of juicy asparagus on your own.By the way, it was noticed that female plants give thick and tender shoots, and male plants give a bountiful harvest.
It turns out that asparagus is not at all a new vegetable in our garden plots. Before the revolution, asparagus was eaten with pleasure. Then the vegetable passed into the category of bourgeois, and therefore enemy products and gradually disappeared from our tables and beds. Currently, this food product appears on supermarket shelves, it is a pity that it is more frozen. But growing this royal vegetable in an ordinary garden is not difficult at all. You just need to have a little patience and know the rules of agricultural technology.
How to propagate asparagus
Asparagus is a healthy and tasty vegetable crop. She is incredibly popular in Europe, Asia and America. Several types of asparagus are grown there:
- green;
- purple;
- white;
- legume;
- sea.
 An unusual-looking vegetable - asparagus, extremely popular all over the world
An unusual-looking vegetable - asparagus, extremely popular all over the world
Unfortunately, our gardeners have almost no interest in this crop. And few people know how to grow this delicacy. But asparagus is the earliest vegetable plant that can support the body precisely when the vitamin assortment is very scarce.
 Asparagus is an early vegetable that helps replenish the body's vitamin reserves
Asparagus is an early vegetable that helps replenish the body's vitamin reserves
There are several ways to reproduce this perennial herb, which greatly facilitates the cultivation of asparagus.
Dividing the bush
This is perhaps the easiest and most affordable way of breeding asparagus even for beginners. The survival rate of segments of rhizomes with buds is very high - almost 100%. Moreover, you can engage in this method of breeding in spring, summer and autumn. It is most advisable to divide the bush when transplanting. A 4 or 5 year old plant is suitable for this.
 Asparagus has a very strong root system that extends more than a meter into the soil.
Asparagus has a very strong root system that extends more than a meter into the soil.
- Carefully dig the bush out of the soil, being careful not to damage the roots. To do this, you will have to dig a hole wide and deep, since the roots of the plant are very powerful. It is very convenient to extract the plant with a pitchfork.
- Divide the rhizome into parts with a sharp knife so that each division has at least 1 shoot.
 Each part of the rhizome must have a shoot
Each part of the rhizome must have a shoot - Place a piece of rhizome in the center of the planting hole or trench. Spread out the roots so that they do not twist.
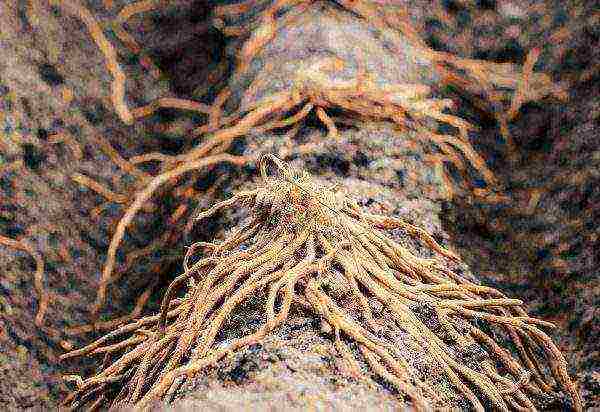 When planting, the roots need to be straightened
When planting, the roots need to be straightened - Cover the roots with a layer of soil of at least 10 cm. In this case, the apical bud should be covered with a 5-cm layer.
 Sprinkle the planted parts of the rhizome with soil after watering
Sprinkle the planted parts of the rhizome with soil after watering - Water the planting. As the soil subsides, the soil needs to be refilled.
If there are a lot of divisions, you can plant them in a trench 30 cm deep and 50 cm wide.The distance between the plants is 50-60 cm.When two-row planting, the distance between the rows should be at least 1 m.
Important information when planting asparagus
- Since asparagus is a perennial plant, nutrients must be added to the soil before planting. For 1 m² you will need
- 15 g of ammonium sulfate;
- 30 g of potassium sulfate;
- 60 g superphosphate;
- mineral fertilizers can be replaced with organic matter. For 1 m², you need to add at least 6 kg of well-rotted humus;
- It is good to grow asparagus after crops and vegetables that require deep digging of the soil, for example, potatoes.
Cuttings
This method of culture propagation is best done from March to June. Green shoots are used as cuttings.
- Cut off the stalk from last year's shoot, dip it in a solution of any root formation stimulant.
 Last year's cuttings can already be rooted
Last year's cuttings can already be rooted - Plant it in a small container with wet sand.
- To create favorable rooting conditions, cover the cutting with a cut plastic bottle.
- In the process of rooting and growth, the cutting should be regularly ventilated and sprayed.
After a month or 1.5, the cutting will take root, after which it is dived into a slightly larger pot.
Seed propagation
In general, growing asparagus from seeds will not be difficult for an experienced gardener.But the unpopularity of this method is primarily due to poor seed germination. Well, caring for seedlings is fraught with some difficulties.
 Asparagus seeds are not often commercially available, but can be harvested by yourself
Asparagus seeds are not often commercially available, but can be harvested by yourself
Planting seedlings
The seeds are soaked before planting to speed up germination. Seed material is sown on seedlings in two ways:
- sowing in seedling pots;
- sowing directly to the garden bed.
The landing dates are different based on the option chosen. Asparagus grown from seeds begins to yield crops only in the 3rd year.
Seedling care
Seedlings can be grown without additional lighting, but it is advisable to put young plants on a window with maximum illumination. The temperature at which seed germination occurs is 25 ° C on average. Watering is carried out moderately, the main thing is not to let the soil dry out too much. To keep conditions comfortable, cover the seed box with a clear bag or glass.
 The first sprouts will not appear soon, after 1.5 months
The first sprouts will not appear soon, after 1.5 months
The first top dressing is applied 4 weeks after germination. Then - a week or two after the pick.
Picking
The picking of asparagus seedlings is carried out when the plants become cramped in the common seedling box. Usually, seedlings that have reached 15 cm in height are subjected to the procedure. Considering that the roots of the seedlings are quite developed, the depth of the new container should correspond to the size of the root system.
- For asparagus seedlings to grow further, they need a free space equal to 5 cm in depth and 5 cm in diameter.
- A few hours before the procedure, the plants are well watered to avoid trauma to the root system. The pick is carried out by the transshipment method - for this, each seedling is pried with a spoon and, together with a lump of earth, is transferred to a new container, while slightly deepening.
 With a spoon, you can easily remove the seedling from the soil
With a spoon, you can easily remove the seedling from the soil - The seedling soil should be light and nutritious. You can independently prepare a soil mixture consisting of the following components:
- 2 parts of fertile soil;
- 1 part peat;
- 1 part of humus;
- 1 part sand.
 The seedling has a rather long root, so the new container must have sufficient depth.
The seedling has a rather long root, so the new container must have sufficient depth.
After a dive, long and thin stems of seedlings can bend to the ground. But do not worry, this is a temporary phenomenon.
Forcing asparagus
This process makes it possible to obtain a delicious and nutritious product in winter or early spring.
- The rhizomes of a 5 or 6 year old plant are dug out of the soil in October and placed in the basement until winter. The storage room temperature should not exceed 2 ° C.
- In early December, asparagus is planted in a greenhouse.
- The planting density in this case is allowed high - at least 20 plants are planted per 1 m².
- The seedlings are covered with rotted humus with a layer of about 20 cm and covered with plastic wrap on top.
- In the first week, the permissible temperature should not exceed 10 ° C.
- As soon as the rhizomes begin to grow, the temperature is increased to 18 ° C.
This temperature should be maintained throughout the entire harvest period.
 The stocking density of asparagus for forcing is high
The stocking density of asparagus for forcing is high
Outdoor asparagus care
Only hardened asparagus seedlings should be planted outdoors. In central Russia, the transplant is carried out in early June. Choose a landing site that is well-lit and windless. If the soil temperature is below 10 ° C, then the asparagus will slow down its growth and development of underground shoots. In this case, you will need a film cover that is easy to install and dismantle.
Considering that the asparagus grows too much, give it space along the fence so that the plant does not interfere with anyone.
Look for a dry site. Groundwater should not approach the soil surface closer than 1.4 m. Before planting, treat the land - dig out perennial crops, fertilize well.In general, take the preparation of the site with full responsibility, because asparagus is able to grow in one place and yield a crop for 20 years, and even a little more.
Watering
Despite the dislike of asparagus for waterlogged soils, planted seedlings should be watered often. This is especially important in the first 2 weeks after planting, until the asparagus has developed a deep root system. In this case, after absorbing moisture, the soil should be loosened in the aisles, but this must be done very carefully so as not to damage the roots. The soil in the asparagus beds should be slightly damp. Insufficient watering will affect the health of the young plant. It will become weak and painful.
So that the soil in the aisles does not dry out very quickly, you can mulch it with a dense plastic film, which will also prevent weeds from growing.
Adult plants are not watered as often as young ones. But, nevertheless, the soil moisture must be monitored. If the soil is dry, the shoots become bitter, fibrous and rough. In order for the asparagus to receive the required amount of moisture, 6 - 8 liters of water per bush is enough when watering.
 Asparagus loves watering in moderation but on time.
Asparagus loves watering in moderation but on time.
Top dressing
The yield of asparagus directly depends on high-quality feeding. But there are some nuances here.
- asparagus practically does not need nitrogen, therefore the share of this element in the plant's nutrition is very small;
- while a lack of copper and potassium will negatively affect the ability of asparagus to form succulent shoots;
- asparagus is very fond of organic matter, so give priority to manure and herbal tinctures.
In order for the asparagus shoots to have greater tenderness and be white (which is especially appreciated by gourmets), you need to pour humus on the garden bed in autumn or May, when the first sprouts begin to appear - 1 bucket of organic matter per plant.
- in spring, in addition to organic matter, the composition of fertilizers includes potassium, calcium and phosphorus. If these substances are applied in dry form, then they do it exclusively for watering;
- in July, a solution of poultry manure can be used to maintain the vigor of the plant after harvest. By the way, note that the indicated concentration of the solution is high - 1/10;
- at the end of October, it is advisable to use complex fertilizers. Most often at this time, planting asparagus is fed with superphosphate and potassium salt - 30 g of each substance per 1 m².
 It is impossible to get a harvest of this wonderful vegetable without feeding.
It is impossible to get a harvest of this wonderful vegetable without feeding.
Weeding and loosening
These are very important steps in caring for a plant that is unusual for our beds. As already noted, shallow loosening should be carried out after each watering - at least 8 times per season. For the asparagus sprouts that are under the mound, it is imperative to get enough oxygen to grow. A homemade device can be used to improve aeration. It consists of a wooden roller, into which nails are driven in, no more than 2 cm long. Rolling with such a roller over the surface of an earthen hill, you destroy the soil crust and restore air circulation.
Always keep asparagus spacing clean. Weeding the weed will save the royal vegetable from many troubles in the form of pests and diseases.
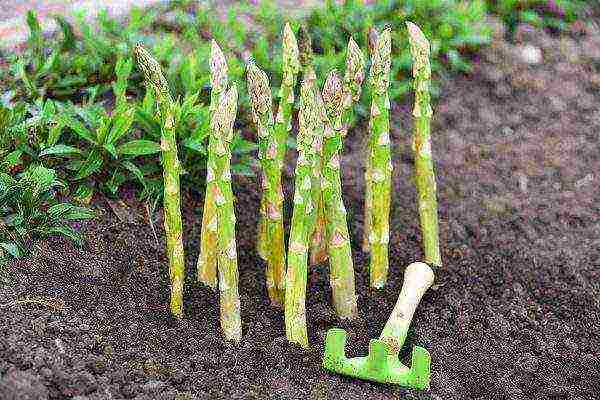 Weeding and loosening asparagus in the beds is the key to a good harvest
Weeding and loosening asparagus in the beds is the key to a good harvest
Hilling
During the growth of the asparagus, it is important to huddle the plant in time. The procedure is carried out when the green branches of the vegetable have reached a height of 20 cm. This process allows the growth buds to transform into succulent shoots. Hilling is especially relevant for young plants that may suffer from frost in winter.
Features of caring for asparagus in the greenhouse
Not all asparagus varieties are suitable for greenhouse cultivation. Early hybrids and varieties have the advantage:
- Arzhentelskaya;
- Franklin;
- Cito;
- Connovers Colossal;
- Marta Washinqton.
 Asparagus Argentelskaya is an excellent variety for greenhouse cultivation
Asparagus Argentelskaya is an excellent variety for greenhouse cultivation
In greenhouse conditions, asparagus is propagated in the usual ways - by dividing the rhizome and seeds. You can grow seedlings right there. This is very convenient, since the plants do not need to be hardened, they are already adapted to the conditions of further growth.
Please note that when greenhouse planting with delenki, the apical bud does not go deeply - it should be in the upper layer of the greenhouse soil.
Necessary conditions for growing
The greenhouse is a special place. Here you can create ideal conditions for growing an early harvest of asparagus. The peculiarity of the plant is that it does not need additional lighting. Sprouts begin to form under the soil layer and, having made their way to the surface, are quite capable of making do with the available light sources.
But the vegetable is more whimsical to the temperature regime. Tender shoots begin to form in the soil at 15 ° C. The maximum indicator should not exceed 25 ° C. It is in this heat interval that asparagus will show excellent yields.
Watering and feeding
Since the conditions of the greenhouse allow maintaining the humidity inside at a higher level, watering is carried out only as needed. Top dressing is carried out with the same fertilizers as in the open field.
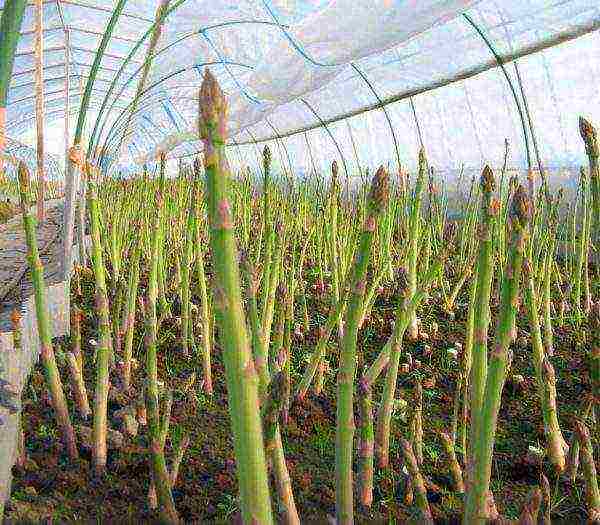 Growing asparagus in a greenhouse produces excellent results
Growing asparagus in a greenhouse produces excellent results
Is it possible to grow asparagus at home
Growing asparagus at home exactly as a vegetable plant is a thankless task. And the question is not even about special care. It's just that the asparagus rhizome needs too much space for normal development, both in depth and in width. It is unlikely that it will be possible to provide the plant with sufficient soil volumes in the conditions of small balconies. But to keep asparagus as an ornamental plant - please. Indoor asparagus (this is how asparagus is called in Latin) will decorate any corner of the apartment with fresh greenery.
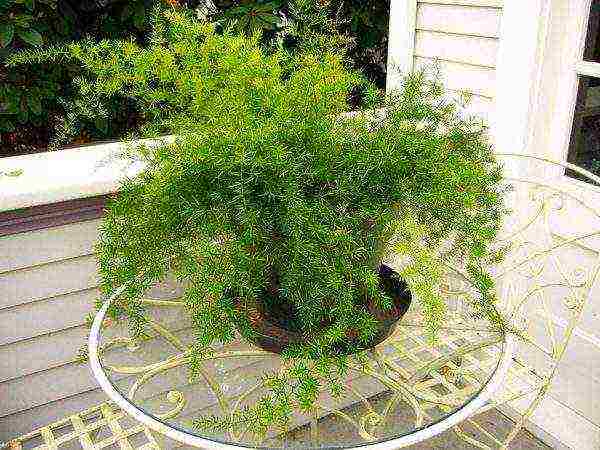 At home, asparagus can only delight you with an abundance of greenery.
At home, asparagus can only delight you with an abundance of greenery.
Features of growing asparagus in different regions
Asparagus can be grown in almost any region, except, perhaps, the Far North. It would seem that a thermophilic plant is able to perfectly withstand low temperatures - up to -30 ° C, even with a slight snow cover. Therefore, this vegetable can be grown in the open field both in the Urals and in Siberia. It's just that in winter, the beds are covered with a thick layer of mulch, for example, with the same manure, which, when re-heated, heats the soil. True, young asparagus is very afraid of frost, even a slight one. Until the moment when the asparagus begins to form a crop, it is better to grow a young plant under a film cover in the cold season.
Gardeners in colder regions have one secret to growing asparagus. They leave only male plants in the beds, which perfectly tolerate low temperatures. But female plants are less cold-resistant.
 In the cold season, Siberian asparagus is cozy under light shelter.
In the cold season, Siberian asparagus is cozy under light shelter.
For central Russia and the Moscow region, as well as for Belarus, there are many varieties of asparagus suitable for open field conditions. The most famous:
- Early yellow;
- Danish white improved;
- Harvest 6.
Subject to agricultural practices, it is possible to get asparagus crops in these climatic conditions without any problems. The most popular growing method is seedling.
In the Kuban, Crimea and Ukraine, asparagus seedlings are planted earlier than in central Russia. This is possible after the second half of May. After all, the abundance of the sun allows the soil to warm up very quickly. A feature of growing asparagus in hot regions is the control over compliance with watering.
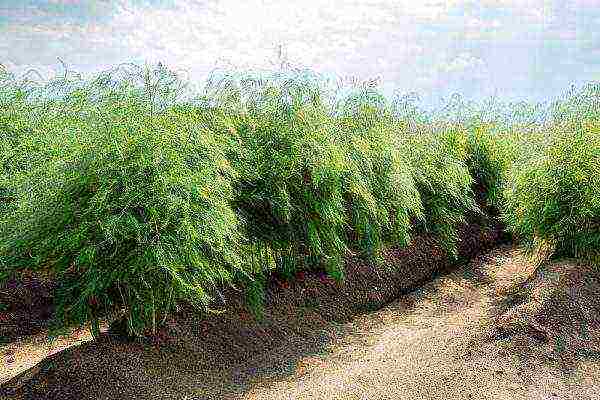 In the south, the abundance of warmth and light benefits asparagus
In the south, the abundance of warmth and light benefits asparagus
Diseases and pests
Asparagus is considered a hardy plant that is rarely affected by diseases and pests. But there are specific diseases that can ruin plantings in the shortest possible time and deprive the long-awaited harvest.
Diseases and control measures
Root rot, or fusarium.The disease affects the roots and root collar. As a result, the whole bush suffers - the branches begin to crumble and soon the plant dies. In the initial stage of the disease, Fundazol helps. If the disease is neglected, you will have to dig up and destroy the entire bush.
 The defeat of the root system leads to the death of the entire plant.
The defeat of the root system leads to the death of the entire plant.
Rust. In June, the affected asparagus shoots become dark in color. The areas affected by the disease increase in size - this spores mature, which then move to healthy leaves. Rust takes over the asparagus ridge gradually. Therefore, carefully inspect the plantings in order to use fungicides to fight the fungus if the first signs are detected.
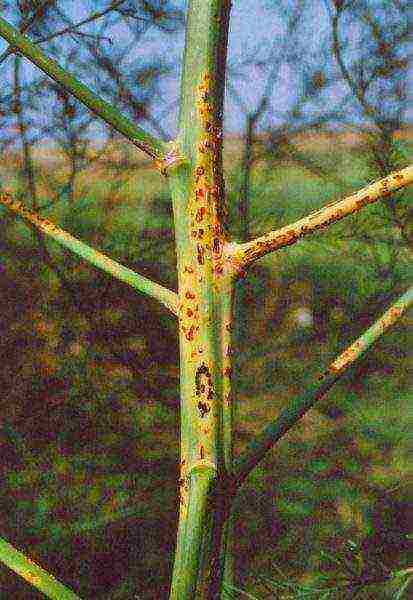 Staining asparagus stems is a sure sign of rust
Staining asparagus stems is a sure sign of rust
Pests
Asparagus fly. From mid-May to late June, the fly lays eggs inside the asparagus shoots. A week later, larvae appear, which begin to eat away at the core of the shoot. As a result, the stem bends and then breaks and dries up. To control the fly, insecticides are used, for example, Actellik.
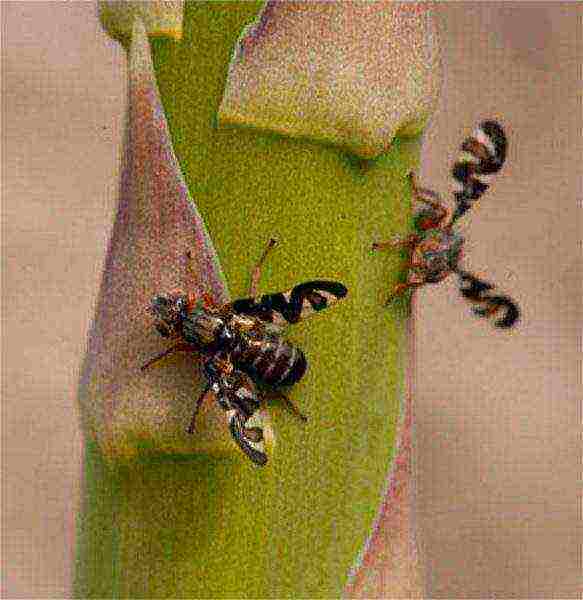 Asparagus fly larvae eat away the asparagus stems from the inside
Asparagus fly larvae eat away the asparagus stems from the inside
Asparagus rattle. The beetle and its larva eat the stems, foliage, and berries. The plant first stops growing and then dries out completely. To combat the pest, the soil in asparagus plantings is treated with Actellik's solution. Beetles are collected by hand.
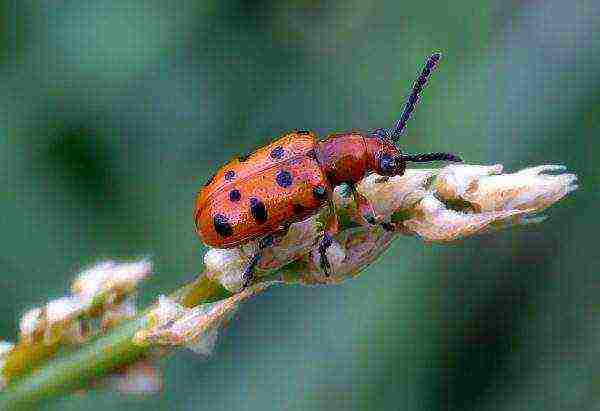 This beautiful beetle is a dangerous enemy for asparagus.
This beautiful beetle is a dangerous enemy for asparagus.
Prevention and treatment
Most often, asparagus suffers from diseases and pests as a result of improper care.
- do not plant asparagus on heavy soils;
- before planting, bring the acidity level to normal values - pH 6 - 7;
- inspect the plantings every week in order to identify the first signs of diseases and pests;
- do not leave the remnants of roots and stems in the aisles;
- do not pour asparagus, this leads to root diseases;
- if marigolds, calendula, basil or cherry tomato bushes are planted around the perimeter of the asparagus garden, the number of pests will significantly decrease;
- in the fall, you need to cut off all drying asparagus shoots and burn them.
In autumn and early spring, asparagus beds should be treated with fungicides - Topaz, Fitosporin. Bordeaux liquid is especially loved by gardeners.
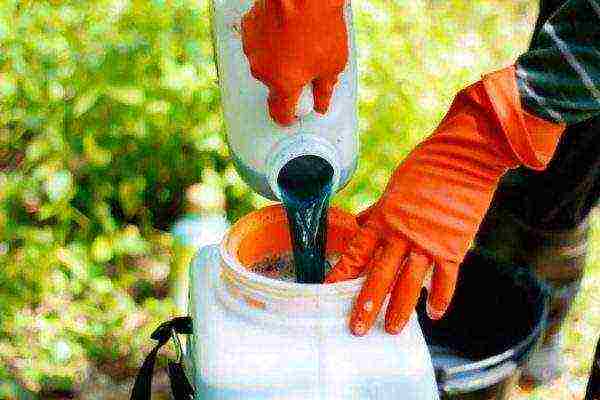 Prevention is the best means of protecting plants from diseases and pests
Prevention is the best means of protecting plants from diseases and pests
Harvesting and storage
Harvesting of this amazing vegetable will begin only in the 3rd year after planting the seedlings. Strong and fairly dense bushes above the surface of the garden will tell you about the readiness of the plant to form edible shoots. If in due time the plant looks frail, then it is better to postpone harvesting for another year.
Shoots reach technical ripeness by about mid-April. Of course, you need to focus on the early maturity of the variety. Ready-to-eat shoots have a diameter of at least 1 - 2 cm. In length, they can grow from 15 to 20 cm. The main thing is to have time to cut off the shoots before their heads begin to open.
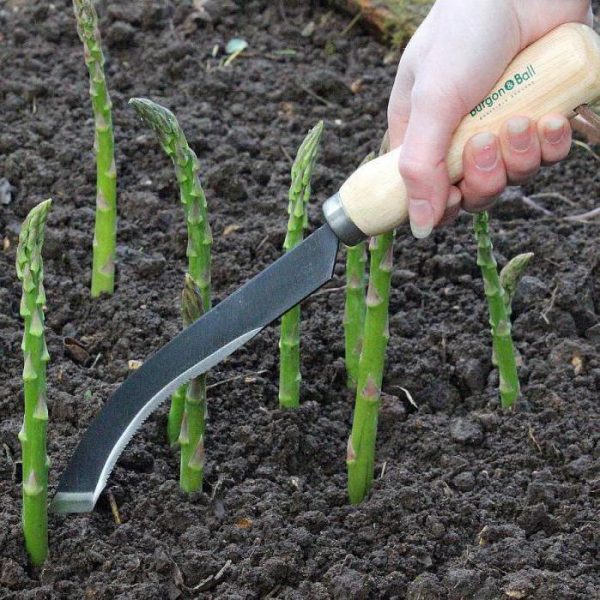 It is best to cut off asparagus shoots with a special knife.
It is best to cut off asparagus shoots with a special knife.
- it is recommended to cut 2 - 3 shoots from a young bush. But no more than 5 pieces. The yield of asparagus is growing every year. Three-year plantings from 1 m² will yield 2 kg of shoots. Next year this figure will increase to 5 kg;
- before cutting off the shoot, carefully scoop the soil away from it. To avoid damaging the rhizome, cut 2 to 3 cm above it. After that, carefully cover the stump with humus or peat compost;
- shoots are harvested every 2 days. But in the south, especially in hot weather, this happens every day, sometimes up to 2 times a day.
Shoots of this vegetable, which is not quite familiar to us, are not stored for a long time. Asparagus is best preserved in the refrigerator if it is wrapped in a damp cloth and placed vertically in the vegetable and herb drawer. Do not wash shoots before laying!
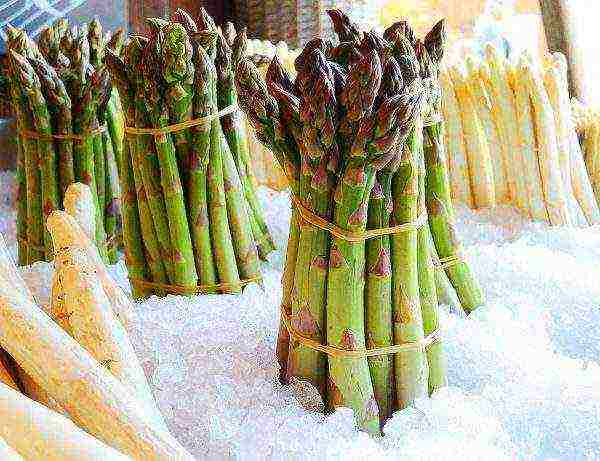 Asparagus shoots in the refrigerator are stored in a strictly upright position
Asparagus shoots in the refrigerator are stored in a strictly upright position
On the 3rd day of storage, asparagus begins to lose its taste - juicy and soft shoots become tough and dry.
Asparagus shoots can be frozen by wrapping them in a cloth, plastic wrap or bag. Under the influence of low temperatures, asparagus is able to retain its juiciness.
The most optimal storage conditions are high humidity - 90%, and temperatures from 0 to 1 ° C. It is this environment that allows you to preserve the taste of asparagus for 3 to 4 weeks.
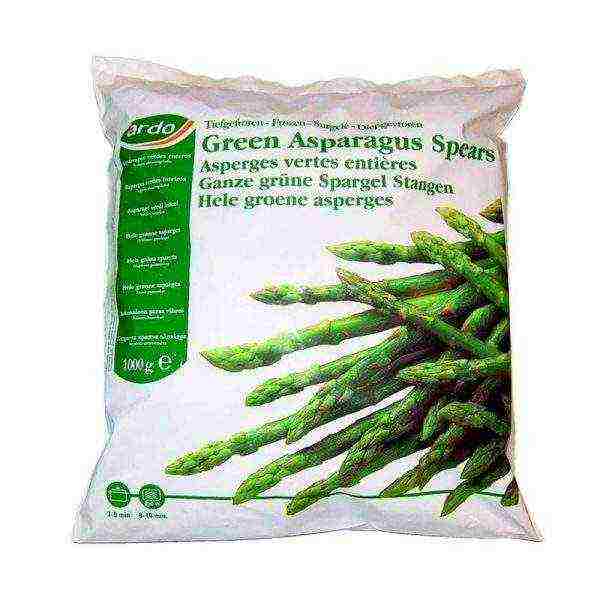 Shock freezing keeps the asparagus shoots juicy
Shock freezing keeps the asparagus shoots juicy
There is nothing difficult in growing asparagus. And the time before the start of the harvest will fly by unnoticed, because in addition to asparagus, other plants grow in the garden. But when the time comes to harvest and taste the harvest, the family will definitely appreciate your efforts. After all, asparagus is not only a tasty product, but also very healthy. In addition, the plant is able to revive any boring corner of the site with its lush greenery.
Good day! My name is Irina. I live in a wonderful place - Crimea. Educator by education. I love nature and animals very much. I have been fond of floriculture for a long time, but I have just begun to master garden wisdom. My motto is live, learn. Rate the article:
(0 votes, average: 0 out of 5)


