Content
- 1 Choosing seeds
- 2 Preparation of sterile substrate and soil
- 3 Pot selection
- 4 Seed preparation and sowing
- 5 Seedling care
- 6 Growing difficulties
- 7 Video "Growing orchids at home"
- 8 How orchids grow
- 9 What you need to germinate orchids at home
- 10 Preliminary preparation
- 11 Step-by-step instruction
- 12 Possible problems
Orchid is a very beautiful, but at the same time, finicky plant. To grow an orchid from seeds, you will have to make a lot of effort at all stages of its development, follow every millimeter of soil in which it grows, accurately measure the amount of water and fertilizer applied. But the result is worth it: if you take care of it carefully enough, then the output will be a healthy and lush flower. He will delight both the gardener and everyone around him.
Choosing seeds
Let's start with the choice of seed. Several types of these plants are suitable for a home indoor "climate", but phalaenopsis orchid varieties are the most common, which are well adapted to our natural conditions. Gardeners also choose seeds of wanda, cymbidium, zygopatelum, dendrobium.
To choose high-quality material on the Internet, you can focus on the degree of recognition and scale of the manufacturing company. This is certainly not 100%, but large businesses are less likely to run the risk of selling counterfeits. The best option is to consult with other gardeners who will suggest reliable firms. Orchid seeds are often purchased by flower growers in China through special sites. This method is more reliable and less expensive in terms of money.
Although in reality, the seed looks more like dust, but after special treatment, it looks like ordinary garden seeds. Due to this, many dishonest sellers in the market can sell you regular grass for the price of orchids. In order not to fall for fake or low-quality raw materials, you must carefully choose a flower shop and, preferably, with a good reputation. You can also consult with other florists. In terms of reliability and price, this method is not much inferior to the first. In our country, unfortunately, Orchid seeds are very expensive, but the quality often does not match the price.
Preparation of sterile substrate and soil
Before growing orchids from seeds, you need to buy or prepare a special sterile soil. Only such a nutrient medium is suitable for germinating the seeds of a delicate plant.

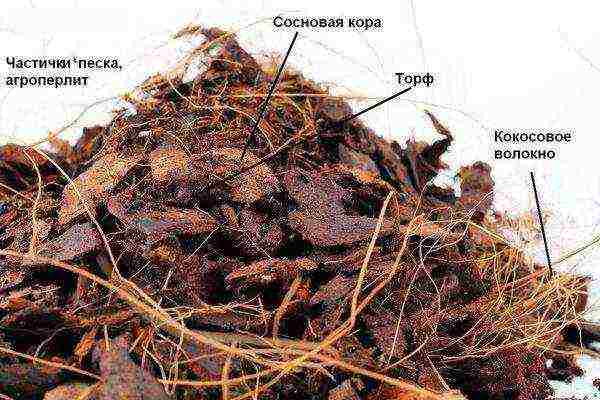
So, to prepare the soil for the germination of Orchids, you need to take simple components: agar-agar (8 g), glucose (10 g), fructose (10 g), activated carbon (1 g), nitrogen-phosphate-potassium fertilizers (1.5 d), root-forming stimulant (5 drops), distilled water (1 l). All components are purchased from gardening stores and drugstores.
The recipe for soil for planting an orchid at home begins with boiling 0.5 liters of distilled water. Then glucose, fructose and agar-agar are added there. The whole is cooked together until the agar-agar is completely dissolved.
Then we take another half liter of water, boil and remove from heat. We add phytostimulant, fertilizer and coal. Mix and combine the two liquids. Now you need to check the pH, since the orchid only grows in an environment with pH 4.8-5.2.
Bringing the pH level to the desired mark, pour the hot solution into sterile flasks, 30 ml in each. After that, you need to sterilize everything again and seal it with a special lid (a piece of cotton wool wrapped in several layers of sterile gauze). Before planting an orchid with seeds in flasks, it is necessary to carry out a 4-5 day check - if mold appears, then this material is unsuitable for growing orchids there.

Pot selection
Before planting an orchid, you need to find a good place to germinate. For these purposes, a small glass flask, or a jar with a narrow neck, is well suited. It is important that this vessel can be sterilized and that it can be conveniently closed with a cotton lid.
Further, the seedlings are planted in disposable transparent cups, they are convenient not only for orchids, but also for any seedlings. They clearly show the development of the root system of a houseplant.
After that, it is best to use clay pots of different sizes, according to the parameters of the plant and root system. During growth, the flower is regularly planted in a larger container, as this contributes to its normal development.
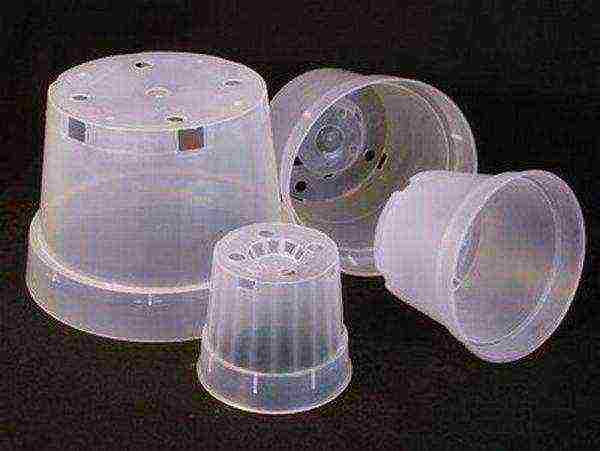

To find out that a grown orchid already has little space in its current pot, you need to look at the hole below. If the roots are already peeping out decently from it, then perhaps it's time to find a larger habitat. The main thing in choosing a pot is to make the orchid comfortable.
Seed preparation and sowing
Planting orchids begins with preparing the seeds. First and foremost is sterilization. Before sowing, all future plants are treated with a solution of bleach. Liquid is poured into the container, seeds are added and gently shaken for 10 minutes.
Also, before planting orchid seeds, you must first prepare the substrate and tools. A pressure-cup is perfect, and a regular gas stove will do.
First you need to boil water and place a flask (jar) with a hot substrate in it and sterilize it at a high temperature. Then the treated seeds are sown into the resulting disinfected solution. This should be done with sterile instruments, for example, a pipette. Then the solution with the seeds is mixed and the jar is corked with cotton wool in gauze.
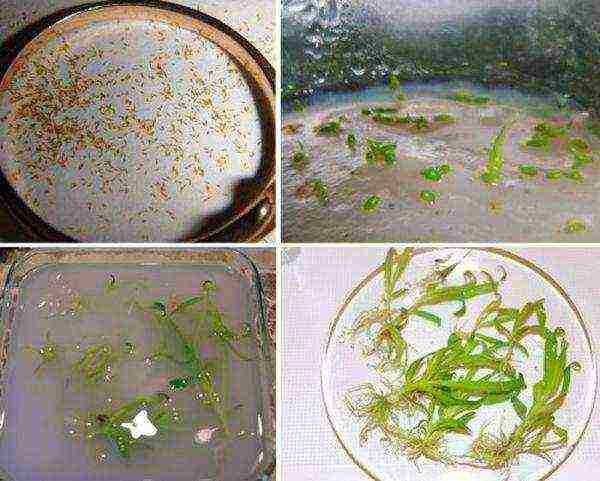

After about a week, orchid inflorescences, leaves and roots will begin to appear.
Seedling care
Growing from seeds is a laborious process, but the result is worth it. Especially when it comes to orchids. After the seedlings have grown sufficiently in the flasks (and this will happen no earlier than a year later), they are moved into the ground. But, before that, the sprouts need to be prepared.
The seedlings are carefully removed from the flask and washed out of the substrate with water. It also helps to separate the plants from one another. Then 2-3 drops of foundationazol are dripped, mixed again and planted with a brush into the prepared soil.
Soil that is suitable for orchids of this age can be prepared from such combinations of elements as: charcoal and pine bark; coal, sphagnum, pine chips; coal, pine bark, peat, humus. If moss is used, then it must first be soaked for a day, so that the insects float away. The bark and peat must be chopped, doused with boiling water and dried.
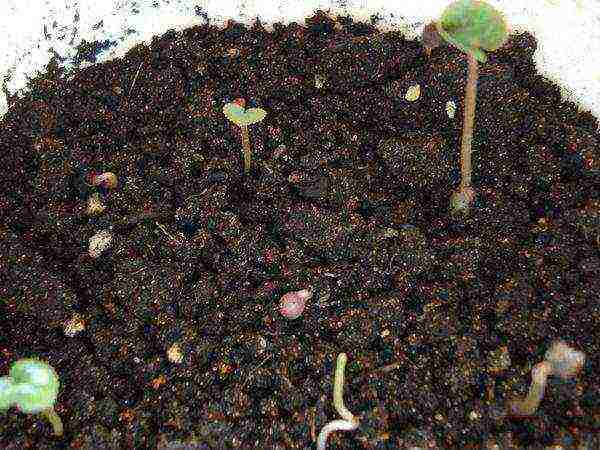

Breeding of orchids cannot take place without observing a certain "climate": humidity 60%, daylight 12-14 hours, temperature 18-23 degrees. At first, it is necessary to strictly observe such measures, since immature orchid sprouts cannot yet adequately cope with any fluctuations in environmental conditions.
Growing difficulties
Growing orchids from seeds at home is always accompanied by some difficulties. And the first is the need to keep everything in sterile (without exaggeration) conditions. Everything is subject to disinfection: flasks, seeds, tools, substrate.Therefore, before growing an orchid from seeds at home, you need to prepare well and qualitatively.
Video "Growing orchids at home"
In this video, you will learn how to properly grow orchids at home.
It is difficult to find an amateur florist who is indifferent to orchids. This is a masterpiece created by nature itself. They are deservedly called "aristocrats of the plant world." Flowers simply fascinate with their tenderness and elegance, as well as a variety of shapes, colors and aromas. They can resemble tropical butterflies, birds, ballerinas, even slippers and lizards. Despite the fact that orchids are demanding to care for and are rather reluctant to breed at home, very few growers are ready to give up their pets. Until recently, it was believed that growing them from seeds was impossible in principle, but now there are chances, although the technology is complex, and the procedure requires its exact adherence. But even in this case, success is not guaranteed.
How orchids grow
Orchids or Orchids (Orchidaceae) are a family of herbaceous perennials. They can be found everywhere, from the tropics to the forest-tundra, but, of course, the brightest varieties, captivating with exotic coloring and the shape of large flowers, live in tropical forests. It is impossible to calculate the exact number of representatives of the family - at the moment, about 35,000 different orchids are known, including natural hybrids (plants have the ability to cross, including interspecific) and varieties bred by breeding. The eight hundred genera that make up the family make up approximately 10% of all plants in the world.
"Cascades" of orchid flowers look very impressive
Humanity has been familiar with orchids for a long time. For the first time they were "domesticated" by the Chinese in about 2000 BC. NS. The name comes from the Greek orchis ("testicle"). The plant owes them the characteristic shape of thickened stems. The Greeks also own beautiful legends about the appearance of orchids on Earth. According to one of them, these are fragments of a rainbow that have fallen from the sky. According to another version, the first orchid grew where Aphrodite dropped her shoe.
Blooming orchids amaze with a variety of shades
Orchids are very different in appearance. In many of them it is difficult to suspect "relatives", even distant ones. But most of them lead an epiphytic or semi-epiphytic lifestyle, living in trees. They use the "master" only as a support, without parasitizing on him.
Most orchids in nature live on trees, but there are also those that grow on stones (the so-called lithophytes)
The orchid obtains the necessary moisture and nutrients from the atmosphere, sucking them in with the help of a developed system of aerial roots covered with a thick layer of a special fabric - velamen.
Orchid roots sticking out of the pot are normal, they participate in the process of photosynthesis and help absorb moisture from the air.
Based on the characteristics of growth, they are divided into two groups:
- Monopodial orchids. The growth point is the apical shoot bud. It persists throughout the life of the plant, disappearing only with aging or dying off. Such varieties stretch upwards, peduncles and lateral shoots are formed from buds "hiding" in the leaf axils. Most often, adult plants resemble vines or their leaves are gradually collected in a rosette.
- Sympodial orchids. As soon as the youngest shoot is recognized by the plant as sufficiently developed, having reached a certain size, the growth point at its top dies off. At its base, the rhizome forms a new one, from which another shoot or peduncle appears. These orchids only grow in one direction.
Monopodial orchids grow mainly upward, sympodial - to the side
Orchid flowers are very different in size (from a few centimeters to almost a meter in diameter) and color (the expression "all the colors of the rainbow" does not even come close to describing this variety of shades and tones), but their structure is approximately the same. The upper part consists of three sepals, which often grow together to form one "petal". The lower one is two real petals of a smaller size, between which the third is located - the so-called lip, sharply contrasting in color with the general color of the flower. It contains a nectary.In shape, it resembles a bag, slipper or an elongated horn of a gramophone. Flowers are often collected in inflorescences (each with an average of 4-16 buds).
The structure of the flower is approximately the same in most species of orchids, despite the variety of petal colors.
When to collect seeds
If pollination is successful, the fruits ripen - capsules or pods filled with seeds. They are so light that they do not fall to the ground, but glide, caught by the currents of the wind. In order for the seeds to germinate, having reached the soil, the presence of mycelium in this place is necessary, which will provide them with the necessary nutrition.
Orchid seeds are very small, they cannot be examined without a microscope
Orchid leaves are simple, monocotyledonous, most often of a rich dark green color. Petioles are absent. On each stem thickened at the base (tuberidia, often called pseudobulbs), from one to three leaves are formed... In shape, pseudobulbs resemble cylinders, spindles, eggs. In them, orchids store a supply of moisture and nutrients.
Orchid leaves are devoid of veins, most often they are dark green
Video: popular varieties of orchids for growing
In the thickenings at the base of the stem (pseudobulbs), the orchid stores a supply of nutrients
What you need to germinate orchids at home
Mostly at home, orchids reproduce vegetatively. Until recently, it was believed that it was possible to grow them from seeds only in laboratories with special equipment. But now an amateur florist can also try, thereby gaining a unique experience. Success, of course, is difficult to achieve, but if the instructions are followed accurately, it is quite possible.
Collect seeds
To carry out pollination by hand, you will need two orchids blooming at the same time. The pollen from the stamens of one of them is collected with a soft brush or cotton pad and transferred to the pistil of the other. The pollinated flower will wither, this is normal. If he fell out, then the procedure was not crowned with success. Otherwise, after about 1.5–2 weeks, positive changes will be noticeable - the fetus will begin to form.
Each orchid pod or boll contains over a million seeds. Accordingly, they are very small. It is impossible to see them with the naked eye, only through a microscope. The contents of the fruit resemble dust. Collecting seeds at home is problematic, although under the condition of artificial pollination (including interspecific pollination), the pods and pods can be tied quite easily. Therefore, most often the seeds are purchased in online stores. The main supplier is China.
In addition to size, orchid seeds have other physiological characteristics that make it difficult to germinate at home:
- Lack of endosperm (special tissue surrounding the embryo). In it, other plants store starch, amino acids, vegetable oils and other compounds necessary for it. Because of this, the future orchid cannot absorb nutrients directly from the soil. In nature, plants form symbiosis with fungi, attaching to their mycelium. It can be microscopic fungi, such as rhizoctonia or phytophthora, and well-known mushrooms or tinder fungi parasitizing trees.
- High susceptibility to any negative environmental influences. The reason is the same - the absence of endosperm. At home, the slightest violation of sterility leads to the death of seeds. They have no protection against pathogens and pests. Also, the seeds will not survive if you do not create an optimal microclimate for them, or with fluctuations in humidity, temperature, and changes in lighting.
It is rather difficult to create not just greenhouse, but "super greenhouse" conditions and absolute sterility at home, without special equipment. In addition, to see the result of your own labor, you have to be patient. Orchids grown from seeds bloom in at least 4-5 years.
Orchid breeding equipment
Regular pots or containers are absolutely not suitable for germinating orchid seeds. You will need specially designed transparent glass flasks or a narrow-necked chemical container with a volume of approximately 200-300 ml. A conical Erlenmeyer flask, for example, is a good choice. If none of this is available, ordinary glass jars with screw caps can be used.
In specialized stores, you can buy flasks for germinating orchid seeds.
The containers must be completely sealed. Stoppers are most often included with the flasks. If not, you can make them yourself by twisting a very tight cotton or gauze swab and wrapping it with several layers of aluminum foil. Be sure to check how tight the homemade cork is against the neck. It is necessary to drill 3-4 holes with a diameter of several mm in the lids of the cans and fill them tightly with the same cotton wool.
In the absence of an alternative, containers for chemical reagents are also suitable.
Nutrient substrate for sowing seeds
Regular soil, even specially designed for growing orchids, is completely unsuitable for seeds. Some growers recommend sowing them in moist finely chopped sphagnum moss, but it is better to use a special nutrient mixture (it is very difficult for moss to maintain complete sterility, the necessary acidity and at the same time provide nutritional value).
It is based on agar-agar - a mixture of polysaccharides obtained from some varieties of brown and red algae. After extraction, it is a white or yellowish powder, but when dissolved in hot water, it turns into a jelly-like mass. The best option for an amateur florist is the so-called Lewis Knudson nutrient medium. The same "substrate" is used by those who grow orchids on an industrial scale. It allows you to grow flowers without creating symbiosis with fungi.
Agar-agar is the basis of any nutrient substrate for germinating orchid seeds
If there is no opportunity to purchase it, the mixture is prepared independently. Each flask should be approximately half full. Required components:
- distilled water (200 ml);
- agar agar (10-15 g);
- glucose and fructose (10 g each);
- potassium carbonate or potash solution;
- orthophosphoric acid.
The last two ingredients are used to bring the medium to the required acidity. The optimum pH for orchid seeds is 4.8–5.2. You can find out the initial value using special indicator strips made of litmus paper. They are easy to obtain at any chemical store. Acid and alkali are added several drops at a time and after each operation the acidity of the mixture is checked again.
She prepares like this:
- Pour agar over a glass of plain water. Leave to swell for a few hours.
- Boil distilled water, add glucose, fructose and agar agar. Stir constantly in one direction (clockwise or counterclockwise).
- Continue heating over low heat or in a water bath until all the powder is dissolved and the mixture becomes jelly-like.
If there are a lot of seeds and there is a desire to experiment, you can try to germinate them in a more exotic "substrate" (ingredients are calculated per liter of distilled water):
- 0.5 kg fresh tomato puree (peeled, chopped in a blender, squeezed out), 0.5 l coconut water (not milk), 1–2 ml liquid fertilizer for orchids, 20 g agar-agar or 200 g potato starch;
- 450 ml of freshly squeezed potato juice, 40 g of icing sugar, 7 ml of fertilizer for orchids, a teaspoon of lemon juice, 15–20 g of agar-agar;
- 10 g of brown sugar and honey, 1 ml of fertilizer for orchids, 5 g of agar-agar;
- 200 g of peeled potatoes crushed in a blender into gruel, 15 g of granulated sugar, 1-2 ml of fertilizer for orchids, 1-2 g of peptone (hydrolyzed protein obtained from milk or animal meat) 10 g of agar-agar;
- 10 g of sugar and honey, 200 g of starch, 3 tablets of activated carbon, ground into powder, 70 g of banana puree, 2-3 ml of fertilizer for orchids.
When making these mixtures, half of the water is used to make agar jelly. The rest of the ingredients are placed in hot, but not boiling water (temperature about 95 ° C). Stir well for 2-3 minutes and pour in the resulting jelly. The components of the Knudson environment are added to it in the order in which they are located in the package.
Video: preparing a nutrient substrate
Preliminary preparation
The main preliminary preparation is to create complete and absolute sterility. Disinfection is applied to the dishes, the nutrient mixture, and the seeds themselves.
In laboratory conditions, special autoclaves are used to sterilize dishes; at home, you can do with an ordinary oven or pressure cooker. Flasks and jars are calcined for at least half an hour at a temperature of 130–150 ° C. Homemade plugs must first be heated by dipping them into boiling water.
Orchid seed containers can be sterilized in a conventional oven
Then the containers are sterilized again, along with the contents. Each of them is poured into 30-40 g of hot nutrient mixture per 100 ml of the total volume and tightly closed. The second procedure will take about the same amount of time. When pouring it into a container, make sure that it does not fall on the walls - this way you will create a breeding ground not for orchid seeds, but for bacteria.
You can also place the vessels in a pot of boiling water and hold them in a water bath for about 20 minutes. Let the vessels cool down, repeat the procedure twice with an interval of 24 hours.
The containers filled with the nutrient mixture are sterilized again
Finished cans are left closed for 4-5 days to check the quality of sterilization. If during this time the formula has not become moldy, disinfection was successful. The plugs must be additionally wrapped with a layer of foil. Do not tilt the containers until the jelly hardens. In the absence of seeds, the vessels can be stored in the refrigerator for 2-3 months. To make the jelly liquid again, it is melted in a water bath.
The seeds are sterilized in a solution of calcium hypochlorite, also known as bleach (10 g of substance per 100 ml of distilled water). They are left in the liquid for 10-15 minutes, shaking the vessel continuously. Then they are sown immediately.
Step-by-step instruction
Compared to everything else, the seeding itself is a relatively simple procedure. But here, too, complete sterility is required. The germination time, depending on the type of orchid, varies from a week or one and a half to 6-9 months.
The germination process of orchid seeds looks like this
At all stages of cultivation, the required conditions do not change. Orchids are provided with bright diffused light, placing its source about 30 cm above the plantings at a slight angle, daylight hours for at least 14 hours, temperature 25-28 ° C without sudden changes and humidity not less than 70%.
Seeds are sown over steam to maintain a sterile environment
- Place a wire rack or wire mesh over a wide pot of boiling water. Securely fix the container with the nutrient mixture on it. The lid from it should be located here, above the steam.
- With a sterile syringe or a special chemical pipette, remove the seeds in small portions from the solution in which they were sterilized, and spread them over the surface of the substrate without touching it. Everything needs to be done as quickly as possible.
- Gently shake the flasks to distribute the seeds evenly. Close the vessels tightly and place in the chosen location.A home mini-greenhouse, florarium or homemade "greenhouse" is suitable for them.
- The smallest green "balls" should appear first. They then form hair-like rhizoids (to absorb nutrients). Then leaves appear and, last of all, roots (when the plant will have 2-3 true leaves).
- After about a year, remove the seedlings from the jar using tongs in a circular motion, as if twisting, and gently rinse off the nutrient mixture from them. An alternative is to pour some warm water into the vessel, shake slightly in a circular motion. Pour the mixture with seedlings into a shallow wide container, add 2-3 ml of 0.5% Fundazole solution. Let stand for 10-15 minutes and remove the seedlings with a soft thin brush.
- Fill plastic cups with drainage material. The height of the container should be approximately the same as the diameter of the roots. It is better if they are transparent - this will make it possible to control the state of the root system.
- Transplant the orchids into a substrate of shredded sphagnum moss, fern rhizomes, and pine roots (1: 1: 1). The more uniform it is, the better. To prevent the development of mold, activated charcoal, crushed into powder, is added (10 tablets per liter of the finished mixture). Previously, all the components of the substrate must be poured with boiling water and left for half an hour.
- Do not water the seedlings, but spray regularly with soft water warmed to room temperature. Do not allow the substrate to dry out completely.
- After about 4–6 months, repot the matured orchids into adult plant soil again and take care of them as usual.
Photo gallery: germination of orchid seeds
Some orchidists recommend diving seedlings after the appearance of the first and each subsequent leaf, and when the plant forms four, plant them in individual containers. But with such frequent transplants, it is difficult to maintain the necessary sterility.
Orchid substrate bears little resemblance to soil in the usual sense of the word; the more homogeneous it is, the better
If you have not the seeds themselves, but the fruits of orchids, and they have not yet burst, wash them thoroughly in hot water with soap and a sharp disinfected scalpel, cut them over steam. There should also be a ready-made flask where you can sow the contents of the "box".
When the fruit is already cracked, pour its contents into a sterile container, fill it with distilled water. Add a few drops of hydrogen peroxide and shake vigorously for 10-15 minutes. Then remove them with a syringe or pipette and sow immediately.
Seeds are sown without touching the substrate
Video: sowing orchid seeds
Possible problems
An attempt to grow orchids from seed at home ends in failure much more often than in success. The first problems may arise already at the stage of acquiring planting material. Since it is most often ordered directly from China, no instructions in Russian are included. Sometimes it is incomprehensible neither the time for collecting seeds (germination lasts no more than a year), nor the type of plant, nor even whether it is an orchid in general or a lawn grass.
Further, the main difficulty is compliance with complete sterility. If mold begins to develop in containers with germinating seeds, you can try to change the substrate:
- Prepare new agar jelly.
- Add some warm water to the flask, shake the liquid.
- Pour the contents of the vessel into a shallow bowl, add 2-3 drops of a 1% solution of any fungicide (Fundazol, Skor, Abiga-Peak), hydrogen peroxide and biostimulant.
- After 10-15 minutes, remove the seedlings and place them in fresh substrate as described above.
When young orchids have already been transplanted into the ground, they are often exposed to a pathogenic fungus that provokes the development of rot. Often the florist himself is to blame for this, being overly zealous with watering.If, at the same time, it is also quite cool in the room, it is almost impossible to avoid the appearance of pathogenic microflora.
Orchid rot is the most common disease affecting young plants.
Rot is treatable, but at a very early stage in the development of the disease. You need to start acting as soon as you notice the first black-brown spots on the roots and leaves. If they have already blurred, the soil has become moldy and spreads an unpleasant putrefactive smell, the orchid can only be thrown away.
- Remove the plant from the pot, remove the substrate from the roots.
- Examine them carefully, cut off all areas affected by rot to healthy tissue with a sharp disinfected knife. Do the same with the leaves.
- Soak the roots for half an hour in a bright pink solution of potassium permanganate or any fungicide (5–7 ml per liter of water). Sprinkle the "wounds" on the leaves with crushed activated carbon, chalk, colloidal sulfur or cinnamon.
- Sterilize the pot, prepare a new substrate. Disinfect him too.
- Transplant the orchid by adding granules of Glyocladin, Trichodermin to the soil during transplantation.
- Water it for 2-3 months, alternating between ordinary water and a solution of Baikal-EM, Alirin-B, Maxim. The dosage of the drug is halved compared to that recommended by the manufacturer.
To prevent the plant from dying, it must be properly taken care of, otherwise there is a real risk of losing orchids grown with such difficulty from seeds.
Video: how orchids are grown from seeds on an industrial scale
Before you plan to purchase orchid seeds for growing them at home, you need to soberly assess your own strengths and capabilities. This is a painstaking and time-consuming procedure that requires care, accuracy and strict adherence to all conditions. The result, and even more so for the flowering of new plants, will take a long time. On the other hand, all the inconveniences and difficulties are more than compensated for by the satisfaction of success, because it is so nice to realize that you succeeded in something that many did not succeed, and to be the owner of a truly unique flower.


