Content
- 1 Pros and cons of self-growing seedlings
- 2 How to grow flower seedlings?
- 3 When to sow flowers for seedlings?
- 4 What flowers are best to sow for seedlings?
- 5 Seedling container
- 6 Choosing a soil
- 7 How to prepare the seedling soil yourself?
- 8 We create favorable conditions for growing seedlings
- 9 Presowing seed treatment and sowing
- 10 Basic seedling care
- 11 Seedling picking
- 12 What flowers are grown by seedlings
- 13 General techniques for growing seedlings
- 14 Outcome
- 15 Growing seedlings of annual flowers
- 16 Growing seedlings of perennial flowers
- 17 Flower Seed Stratification
- 18 Soil preparation for planting flowers
- 19 Sowing flower seeds
- 20 Leaving and diving flower seedlings
- 21 Planting flower seedlings in the ground

Winter is still in full swing, but the time for pleasant spring hassles is already approaching for summer residents. February is the first time for sowing seeds. So, it's time to talk about how to grow strong and strong flower seedlings by the beginning of the season.
First of all, let's figure out why this is necessary and whether it is necessary at all, if many flowers can be sown in the spring immediately into open ground.
Pros and cons of self-growing seedlings
Do you need it? Why suffer for several months, create favorable conditions, clutter up all the window sills and shelves in the house, replant, water, take care of - and all this without any guarantees and confidence that everything will turn out as it should? The process of growing flower seedlings has both advantages and disadvantages.
As for the disadvantages, here, first of all, one can name labor costs, a large volume of occupied space and the duration of work. If you grow flower seedlings in an apartment, then after picking the seedlings, you will need a general cleaning. After all, you will have to pour a large amount of soil into various containers.
In addition, it is unlikely that it will be possible to grow a large number of seedlings in the apartment: neither area nor lighting will be enough for this.
Another disadvantage of growing seedlings is that if certain conditions are not met, it can grow weak and unhealthy, subsequently the resulting plants will bloom poorly and often get sick. However, if everything is done correctly, the quality of self-grown seedlings will be higher than that of the purchased one.
The main plus of growing flower seedlings is that such plants bloom earlier than those sown in the ground, and delight us with their lovely flowers for a longer time.
In addition, flowers grown through seedlings suffer less from weeds, since they are ahead of them in growth. Therefore, weeding of flower beds can be minimized: cultivated plants immediately become dominant.
The financial issue is also important. Growing beautiful flowers from seeds is much cheaper than purchasing ready-made seedlings of plants.
How to grow flower seedlings?
First of all, it is worth deciding exactly where you will place the boxes with seedlings. If you live in a private home, this could be a greenhouse, conservatory, or winter garden. But the townspeople have only one option - placing the seedlings on the windowsill.

In this case, you should try to avoid drafts. To increase the placement area when growing seedlings at home, you can install hinged shelves on the window.Just make sure that the upper shelves shade the lower ones as little as possible - they should be located at a sufficiently large distance from each other.
When to sow flowers for seedlings?
The seed bags usually indicate the recommended planting dates for the crop (often with a fairly large delta - for example, from February to April).
Exist two strategies growing seedlings at home:
- Sowing late and creating favorable conditions for rapid growth.
- Early (winter) start and later - artificial containment of the growth of seedlings, mainly by limiting watering: seedlings are rarely watered, only when the soil has significantly dried out.
Do not forget that overgrown seedlings take root worse in the ground. In addition, in case of insufficient lighting, which is inevitable in winter, the seedlings can stretch out strongly and grow weakened (winter sowing means a short daylight hours, an abundance of cloudy days).
Of course, the first strategy looks more expedient. When using it, we save a month and a half of our time (the total growing period is reduced), and the seedlings are healthier and stronger in favorable conditions.
In addition, it is in the first stages of a plant's life that its main characteristics are laid, and flowers grown in better conditions will be stronger and more stable, and their flowering will be abundant and long-lasting.
Unfortunately, this is not always feasible. The intensive (accelerated) method is costly (at least additional lighting). Therefore, those who want to save money can only slowly grow seedlings, limiting watering. With this method, crops are sown in late February - early March.
And with an intensive method of cultivation, the earliest crops (for the most "brooding" flowers) are carried out no earlier than in the second decade of March; most of the flowers are sown in April.
What flowers are best to sow for seedlings?
A beginner should not start with flowers that are difficult to grow, as there is a risk of facing difficult difficulties. For example, the spectacular kobei liana has a very long period of development, the delicate beauty of the eustoma is poorly viable seeds, and the ever-flowering begonia is very small and slowly developing seedlings.
Therefore, for a start, it is better to choose an ornamental sunflower, tunbergia, datura, morning glory, salvia, purslane, mesembriantemum, alissum, Drummond phlox, snapdragon, gazania, celosia, castor oil plant, ornamental cabbage.
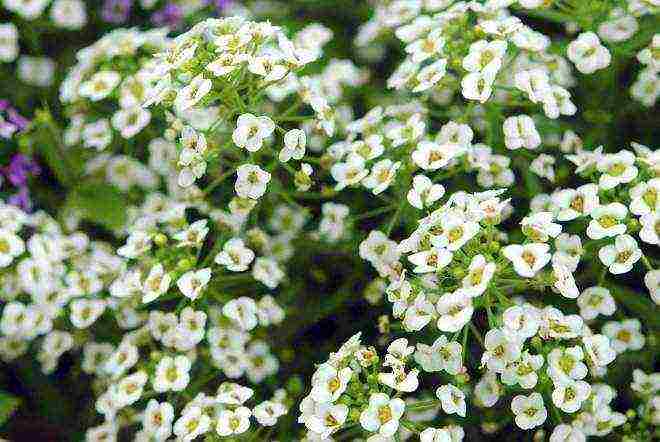

Alissum
As for the popular petunias and mimulus, these are not the easiest flowers to grow. However, if you do decide to sow them, it is better to choose more expensive seeds in granules: it is much easier to work with them.
Seedling container
Dishes for growing seedlings can be very diverse: both specially purchased and improvised. On sale today you can find many options for special sowing boxes and contour cells, micro-greenhouses, peat pots. You can also use disposable plastic dishes, containers, wooden boxes, etc.
In the process of growing seedlings, we need two types of dishes: schools for sowing and germination and individual dishes for growing after picking. As schools, you can use wooden or plastic boxes, balcony boxes, plastic containers in which salads and cakes are sold, etc.
As an individual container for seedlings, contour cells, peat pots, disposable plastic cups, yogurt and sour cream cups, cut plastic bottles, and small plastic pots are suitable. You can also continue to use the boxes after picking, planting plants in them at a greater distance.
As for peat pots, this is a very good option for growing crops that do not tolerate transplanting well, since such seedlings are planted together with a glass, which eliminates damage to the roots. However, be careful: the soil in a peat pot dries out much faster than in ordinary dishes. It is best to place the peat pot not on a pallet, but in a plastic cup with a slightly larger diameter.

The main task of the container is to provide space for growth and development and to protect the roots of the shoots from adverse external influences. Thus, the main requirements for utensils for growing seedlings are as follows:
- rigidity of the form (excludes damage to the root system during transportation or movement);
- opaque walls (light can damage the roots);
- reliable drainage holes or slots (exclude soaking);
- as low as possible thermal conductivity of the walls (reduces stress from temperature fluctuations).
In accordance with these requirements, the utensils at hand need preparation. For example, clear plastic containers should be wrapped in black foil. And be sure to make good drainage holes in the bottom in any container for seedlings.
Individual utensils should not be too small, since during long-term cultivation in cramped containers, the root system is suppressed, the roots twist into a ball, which will subsequently adversely affect the quality and duration of flowering.
All containers must be thoroughly rinsed. Containers in which other plants were previously grown must be decontaminated. It is better to discard dishes in which mold is found.
Choosing a soil
The easiest way is to purchase ready-made soil mixture in the store. However, many gardeners and gardeners do not trust the quality of such soil too much and prefer to cook it on their own.
In addition, one of the significant disadvantages of ready-made soil mixtures is their cost. It is not that high at first glance, but for seedlings after a dive, more soil may be required than you thought. And if you save on the amount of purchased land (that is, pour less into cups or boxes than you should), then this will be at the expense of the quality of seedlings, the roots will not be able to develop normally.
All ready-made soil mixtures can be divided into two types: dry (pressed) and wet. Wet soils include most soils sold in bulk packages. They are completely ready to use.
It is safest to acquire soils that have been disinfected using bio-fermentation at high temperatures (for example, Avtep soils, Earth for seedlings), or with the help of a red Californian worm (Living earth, as well as other soil mixtures containing vermicompost).
As for dry soils in briquettes, they are usually prepared on the basis of high-moor peat (Natural fertile soil, Violet, Torfolin, Torfolin A). These soil mixtures must be soaked before use, after which they increase in volume several times.
It is desirable to add lime to such soils to neutralize acidity, and sand to improve physical characteristics.
For physical qualities, Torfolin is preferable. Violet contains a fairly large amount of mineral fertilizers, so it is more suitable for growing cut seedlings than for germinating seeds.
How to prepare the seedling soil yourself?

There are several options for suitable seedling mixtures:
- 2 parts sawdust and 1 part sand;
- sawdust, sphagnum and sand in equal proportions;
- 2 parts sphagnum and 1 part sand.
If you have prepared sphagnum or sawdust since autumn (or better, both), then you can prepare one of these mixtures. If not, you can use purchased components: 10 liters of Torfolin A or Violets for 2 liters of sand.
However, in the case of growing seedlings with early sowing dates and without artificial additional lighting, such soils are not suitable: they do not tolerate drying out, and with prolonged cultivation, rare watering is practiced with significant drying out. In this situation, it is better to use soil with natural fertility: containing vermicompost, dung humus, sod land, etc. For example, 2 parts of humus or leafy soil, 1 part of sand, 2 parts of peat, 2 parts of sod land.
Any soil mixtures should be thoroughly mixed, remove large particles, lumps and spill with a solution of potassium permanganate.
We create favorable conditions for growing seedlings
The three main ingredients for success are lighting, temperature and humidity. In this case, the balance of all three elements is important. And the most important thing for seedlings is lighting. Therefore, ideally (for accelerated growing of seedlings), arrange additional lighting using special phytolamps.
Lighting
The optimum illumination level for seedlings is 8000 lux, while on the windowsill even on a sunny March day the illumination is no more than 2500 - 3000 lux, so additional illumination of seedlings may be required in the daytime. During the first 2-3 days after the emergence of seedlings, it is advisable to provide round-the-clock lighting, then 15-16-hour daylight hours.
If your sprouts are still stretched out due to lack of light, you can try using the "cut" seedling method, which is used mainly for tomatoes, but can be successfully used for many flower crops. It consists in cutting off the grown plants above the two lower leaves. The lower part of the sprout continues to grow in the same pot. And the upper part is rooted like a cutting. Thus, the number of seedlings doubles.
But keep in mind: this method is only suitable for those flowers that are easily propagated by cuttings (for example, purslane, begonia, catharanthus).
Humidity
You don't have to worry too much about moisture while the seed boxes are covered with glass or foil, but as soon as you remove them, your delicate seedlings will be in an unfavorable environment! In a heated apartment, the air humidity is close to desert conditions.
Spraying seedlings is, of course, necessary, but it will not save the general situation with air humidity. There is a more efficient method.
Pour water into a long balcony drawer, any other container, or wide bucket. Take a wide piece of thick, absorbent cloth (for example, a terry towel), dip one end of it in water, and spread the other on the battery. A rather large amount of moisture is pumped through such a "wick" per day, so the water will have to be regularly added to the container.
Temperature regime
It should be borne in mind: the higher the air temperature, the more intense lighting and high humidity are needed for seedlings. Therefore, it is undesirable to place seedling boxes in close proximity to the battery.
Most annuals need a slightly higher temperature for seed germination than for further growth. For example, for viola germination, the recommended temperature is 18-20 ° C, but 5-10 ° C is quite enough for the development of seedlings. Accordingly, you can germinate viola in an apartment, and for further growth, transfer it to a balcony or to a cold greenhouse.
Presowing seed treatment and sowing
Large and medium-sized seeds (sweet peas, ornamental beans, castor oil plant, morning glory, kvamoklit, mine lobata, etc.) should be pre-soaked in a solution of Epin, Zircon or any other growth stimulant. Some seeds (for example, peas) also require scarification - breaking the seed coat.
If the seed bag does not indicate that they have been disinfected, you should also pickle the seeds with a pink solution of potassium permanganate. This does not need to be done if the seeds are granular.
The soil is poured into the seed boxes, not filling it up a little to the edge.After that, the surface is leveled, spilled with warm water and the seed furrows are marked. It is convenient to do this with a ruler, slightly pressing it with an edge into the ground.
The depth of the grooves depends on the size of the seeds: it should exceed the seed diameter by 2.5 - 3 times. After that, the seeds are placed at an equal distance from each other and sprinkled with soil.

With very small seeds (purslane, mimulus, mesembriantemum, petunia, begonia), the strategy is somewhat different. They are not buried in the ground, but sown superficially. For more even sowing, it is advisable to pre-mix the seeds with sand.
For this purpose, special seeders are used (instead of them, you can use dishes with holes in the lid for spices). Sow rarely, remember that thickened crops negatively affect the quality of seedlings.
After that, the soil is sprayed and covered with glass or, which is more convenient, with a film.
Basic seedling care
When shoots appear, glass or film is removed from the boxes. It is advisable to use fertilizing watering for seedlings: instead of clean water, a weak solution of complex fertilizer should be used (for example, Kemira Kombi - 1 teaspoon without top for 3 liters of water).
To water the seedlings, you will need a small watering can with a diffuser, which gives not diverging, but parallel streams. Watering is carried out directly on the leaves, so we get a combination of root and foliar feeding.
In a warm room, seedlings should be watered daily, at low temperatures 2-3 times a week is enough.
Seedling picking
Seedling picking is the transplanting of grown seedlings over a greater distance or into personal dishes (cups). It is necessary in order to provide plants with optimal growth space. At the same time, it is possible to cull weak, poorly developing seedlings.

Usually, the picking of seedlings is carried out at the stage of two to four true (that is, not cotyledonous) leaves. The soil for picking should be somewhat richer than for seedlings, because the flowers have already grown up and need more nutrients.
To carry out the pick, you will also need a planting peg. His role can be played, for example, by an old nail file or any stick pointed at the end.
The peg is carefully introduced into the ground, brought under the roots and the shoots are taken out of the school one by one. At the same time, with the other hand, the seedling is held by the cotyledon leaves (not by the stem!).
The soil is poured into the glass, leveled, and a hole is made. After that, the plant is immersed in this hole, deepening it to the cotyledon leaves. With the help of a peg, the soil around is pressed to the roots. After planting, the plant must be watered immediately.
Before planting seedlings from greenhouse or home conditions into open ground, it must be hardened so that the stress from transplanting and changing the environment does not become destructive. For this, the seedlings, some time before disembarkation, begin to be taken out into the open air, each time leaving it on the street for an ever longer time. It is important not to overexpose the seedlings for longer than necessary.
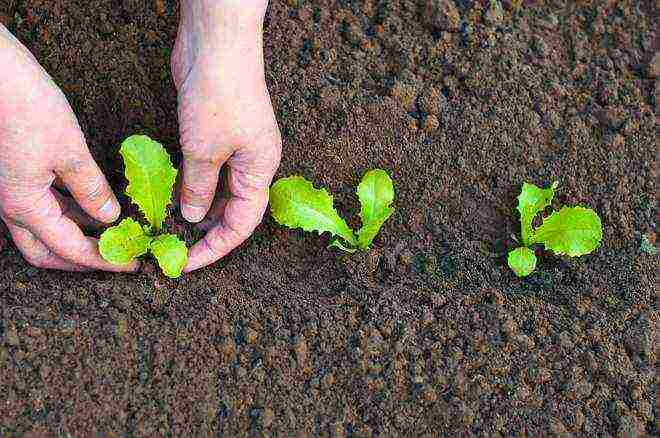

About an hour before planting in open ground, seedlings are spilled abundantly with water. Disembarkation is carried out early in the morning or in the evening.
***
Do not be lazy to grow flower seedlings! This is a very exciting process, and not as complicated as it might seem at first glance.
Annual garden flowers, as well as some perennials, are grown through seedlings. This technique improves seed germination and accelerates flowering. There are many ways of growing flower seedlings and for each flower it is better to choose the most suitable one.

Seedling flowers requires attention and care
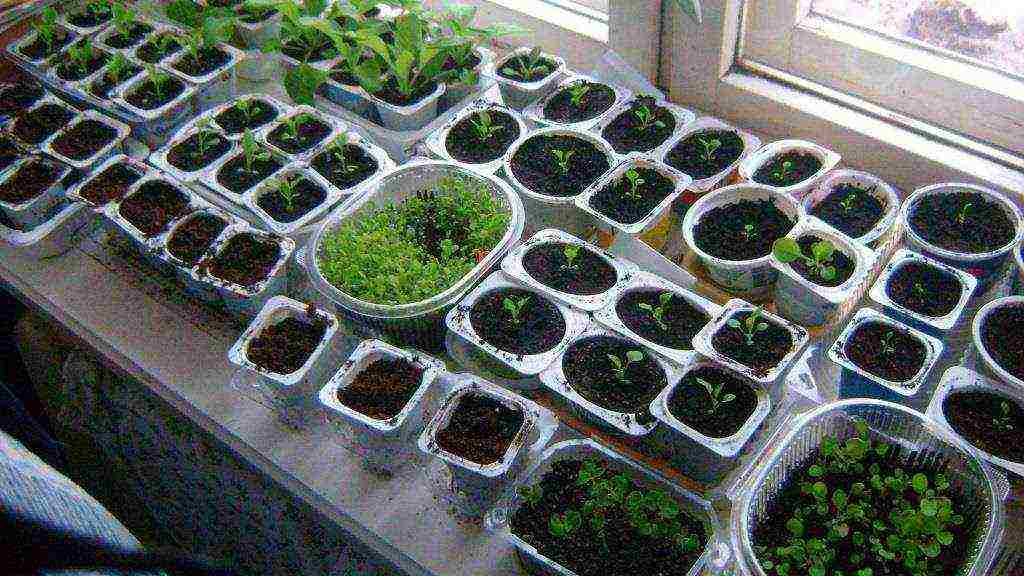

Seedlings of flowers on the windowsill
What flowers are grown by seedlings
The list of garden plants grown through seedlings is quite large - it contains thermophilic crops, as well as flowers that lack a short summer for a full cycle of growth and flowering.

Seedling flowers
The timing of planting flowers for seedlings is very different. Plants with a long germination and growing season should be sown in February. For other crops, two to three weeks are enough before planting in the ground. Tables 1-3 provide descriptions of the most common flowering plants and their preferred planting conditions.
In February, beautifully flowering annuals and some perennials are sown on seedlings - in this case, they will bloom in the year of planting. When sowing flowers in February, it is important to ensure a stable temperature and good illumination, otherwise the seedlings will stretch out and be weak.
Table 1. Flowers that are sown for seedlings in February.
 Azarina |
Perennial vine, when planted in seedlings, blooms in the first year. It hibernates only in warm climates. Seeds of medium size are sown in light peat soil in seedling boxes, followed by picking into pots. The optimum temperature for germination is + 18-22 degrees, the germination period is up to 2 weeks. Can be planted in peat tablets and then transplanted into pots. |
 Pansies |
Seeds are medium in size, sown in late February or early March in shallow furrow boxes. Sprinkle with soil, moisten from a spray bottle and germinate in a warm, dark place. Seeds germinate within 1-2 weeks. Seedlings are dived into separate glasses. Growing in peat tablets is possible. |
 Always blooming begonia |
The seeds are very small, often sold in the form of dragees or granules. It is more convenient to plant granulated seeds in peat tablets, followed by planting in pots. Ordinary seeds are sown on the surface of well-moistened soil in seedling boxes, covered with glass and germinated in diffused light in a warm place. They dive when the seedlings get stronger. The optimum temperature is + 22-23 degrees. Seed germination period is up to 2 weeks. |
 Chinese carnation |
The seed size is average. Before planting, the seeds are soaked in growth stimulants, then dried. Sow in seedling boxes or peat tablets with a 1-1.5 cm embedment. The optimal sowing time is the end of February, the temperature for seedlings is + 20-22 degrees, the germination period is up to 10 days. In the phase of 5-6 true leaves, the bushes are pinched. The plant is light-requiring, backlighting may be required. |
 Lobelia |
The seeds are very small, like dust. Sow on the surface of moistened soil mixed with sand or snow. Germinate in diffused light under a film. Germination temperature - + 20-24 degrees, seedlings appear within a week. The film is not removed until the plants get stronger, watered with a spray bottle. In the phase of 4-5 leaves, several pieces are dived into a pot, pinched 2-3 weeks before planting. Seedlings tolerate moderate shade, cannot stand direct sunlight. Planting date is mid or late February. |
 Nirembergia |
Small seeds are sown in seedling boxes on the surface, for convenience, you can mix them with sand. Germinated under a film with regular ventilation at a temperature of + 22-25 degrees. Seeds sprout in 10-15 days. They dive into separate glasses in the phase of 4-6 leaves. Watering is moderate. The best planting time is late February or early March. |
 Petunia |
The seeds are small, hybrid petunias are usually sold as granules. Granulated seeds are best planted in separate seed cells or peat tablets. Sowing ordinary seeds is carried out in seedling boxes on the soil surface, it can also be planted in the snow. Germinate the seeds in the light under glass, regularly moistening by spraying. Seedlings appear within 10 days. The glass is removed after 2-3 true leaves appear. The pick is performed after the appearance of 5 leaves, after which the plants are pinched to improve the growth of side shoots. |
 Purslane |
Seeds are small, sown in seedling boxes in loose soil with good drainage. Sowing is carried out on the surface, lightly sprinkling with sand. The temperature before germination is + 22-26 degrees, the period is up to 2 weeks. The plant is extremely light-requiring, backlighting is needed in February and March. Watering is regular, but moderate.Pick into separate pots in the phase of 2-3 true leaves. |
 Salvia |
The seeds are small, they are sown in a mixture with sand on the soil surface, and expanded clay drainage must be placed on the bottom of the seedling boxes. Germinate seeds under a film or glass in diffused light at a temperature of + 23-25 degrees for 5-10 days. After the appearance of 2-3 leaves, they dive into separate pots. Salvia needs a long day of light - at least 12 hours; when landing in February, it needs lighting. The plant does not tolerate overflow, the shoots can rot. |
March is the sowing time for most garden flowers for seedlings. In addition to the crops described in table 2, in early March, you can still plant petunia, lobelia and salvia, if you did not have time to do this in February. Marigolds, dahlias, sweet peas and zinnia can be sown in late March, with sufficient light, and they will bloom in June.
Table 2. Flowers that are sown for seedlings in March.
 Ageratum |
The seeds are small, sown on the soil surface in boxes and germinate under glass or foil. Seeds sprout up to 2 weeks at a temperature of + 22-25 degrees. Dive into separate glasses in the phase of 2 true sheets. Watering is moderate, first by spraying, after a dive - from a watering can. The optimal time for planting seeds is the third decade of March. Landing in the ground after the end of frost. |
 Amaranth |
Amaranth seeds are small enough, before sowing they are mixed with coarse sand. Sow in seedling boxes, in grooves, close up to a depth of 0.5-1.0 cm. Germinate at a temperature of at least +20 degrees under a film. They dive in the phase of two true leaves into seedling cells or cups. The plant is light-requiring, backlighting may be required. |
 Aster |
Aster seeds are medium in size. Sow in seedling boxes, in peat soil along the grooves previously shed with potassium permanganate. The seeds themselves can also be pickled with a strong solution of manganese - this will reduce the risk of seedling disease with "black leg". From above, the seeds are covered with calcined river sand in a layer of 1 cm. Seedlings appear at a temperature of + 20-25 degrees within 10 days. Sprouts dive in the phase of two true leaves in separate cups or seedling cells. When growing seedlings of asters, it is important to avoid waterlogging. |
 Scented tobacco |
The seeds are small, they are sown without embedding in the soil. Previously, the soil in the seedling boxes is moistened, after sowing, they are placed in a warm place and covered with foil or glass. Seedlings appear in 2-3 weeks. Plants dive after they get stronger. Watering and temperature when growing seedlings are moderate. |
 Levkoy |
Levkoy seeds are of medium size, they are planted in seedling cassettes with a cell volume of 60-12 ml or in peat tablets. From above, the seeds are covered with river sand, germinated in the light. The temperature before germination is + 12-15 degrees, after the emergence of sprouts, it can be reduced to +10 degrees. Watering is moderate. Levkoy does not tolerate transplanting well, therefore it is necessary to transplant it into larger containers very carefully. |
 Snapdragon |
Seeds are small, when sowing, it is better to mix with sand. They are sown in grooves with a planting depth of 0.5-1 cm in moist soil. Cover with glass or film from above and put away in a warm place. Seedlings appear for a long time, up to three weeks. It is important to monitor their appearance and put them in a well-lit place in time. The temperature when growing seedlings of snapdragons should be at least +18 degrees. Seedlings dive in the phase of 2 leaves, when 4-5 leaves appear, pinch them to form side shoots. |
 Mimulus |
The seeds are small, they are sown superficially on compacted soil in seedling boxes. For seed germination, light is needed, so the box is placed on a cool windowsill and covered with glass. The optimum temperature is + 15-18 degrees, after the emergence of shoots in 3-5 days it is reduced to + 10-12. Dive at the stage of 2-3 leaves. In spacious boxes, instead of picking, you can simply thin out the seedlings. |
 Phlox Drummond |
Seeds are sown in seedling boxes or peat tablets to a depth of no more than 1 cm, sprinkled on top with dry soil without compaction. Germinated in warmth under a film, seedlings appear in a week. Seedlings are rearranged in a sunny place. They dive in the phase of two leaves, without tightening - young shoots take root better. The tablets can be transplanted into pots or cassettes a little later. Watering with warm water, moderate. |

Seeds Phlox Drummond "Pretty Woman in Raspberry"
In April, seeds of fast-growing flowers are sown, which need no more than 4-6 weeks to set buds. The seeds of these flowers are large enough, the plants sprout well, so you should not rush to planting - the overgrown seedlings take root worse.
Table 3. Flowers that are sown for seedlings in April.
 Marigold |
Seeds are medium in size, sowing can be carried out from mid-March, but most often they are sown in the first or second decade of April. Marigolds are sown in seedling boxes, in grooves to a depth of 1-1.5 cm, carefully watered and placed in a warm place. In the warmth, seedlings appear in 5-7 days. They dive in the phase of two leaves in separate cups, after the appearance of 4-5 leaves, pinch the top. |
 Dahlia annual |
Large enough seeds, germinate quickly. Before planting overnight, soak in aloe juice or for half an hour in Epin. Seeds are planted in moist peat soil in seedling boxes, sprinkled with soil by 1 cm, and compacted. At a temperature of + 22-25 degrees, seedlings will appear in 3-5 days. In the phase of two leaves, the seedlings dive into spacious cups, when the fifth leaf appears, they pinch. |
 Sweet pea |
Sweet pea seeds are large, in a dense shell, it is advisable to scarify them before planting - slightly damage the integrity of the shell. You can do it like this: place the seeds between two sheets of fine sandpaper, gently press and roll. Then they are soaked for 12-24 hours in warm water, then placed in a damp cloth and removed in a warm place. The hatched seeds are planted in separate cups with a volume of 200 ml or more. Seedlings are grown at a temperature of + 12-16 degrees, watered regularly, pinched over the second or third leaf of each shoot. |
 Morning glory |
Ipomoea seeds are large enough. Before planting, their shell is slightly pricked with a needle, and then soaked in water for a day. Germinate seeds in separate cups, three seeds each. The seeding depth is 1.5-2 cm, at a temperature of + 18-20 degrees, shoots appear in a week. As the root system grows, the seedlings are transferred into larger cups. With the active growth of shoots, you need to stick a support in the glass so that the shoots do not get tangled. |
 Cineraria |
Seeds are small, sown on wet soil superficially or under a layer of dry sand. Germinated under a film at a temperature of about +20 degrees. Seedlings appear within a week. You can dive already in the phase of the first true leaf. Watering when growing seedlings is moderate. In poor lighting conditions, additional lighting is required. |
 Zinnia |
Zinnia seeds are large enough, so you can plant them immediately in individual cups, 2-3 seeds are permissible. The soil should be loose and moisture-permeable. Planting depth - 1 cm. At a temperature of + 20-22 degrees, seedlings will appear on the 5-7th day. If the seeds are sown in a seedling box, they are dived into separate glasses in the two-leaf phase. It is not recommended to plant zinnia earlier than mid-April - too mature seedlings do not take root well. To form a lush bush, you can pinch it over 5-6 leaves. |
Growing roses in a greenhouse for sale
Growing roses in a greenhouse for sale is a profitable business, as the demand for the queen of flowers does not decrease even during the winter months. Depending on the region, the profitability can be 200% or more, and the payback period does not exceed two years. How to organize a flower business so that it brings a stable profit, read in this article.
General techniques for growing seedlings
Although different flower crops require different conditions for successful growth and flowering, the methods of planting seeds and caring for plants are the same for many crops. Below we describe the basic techniques for growing flower seedlings.
Seed preparation
Purchased seeds, as a rule, have already been calibrated, disinfected and stratified. Information on this can be found on the seed package. When self-collecting and harvesting flower seeds, all these operations must be done by hand. Before preparation, the seeds are sorted out and debris removed.
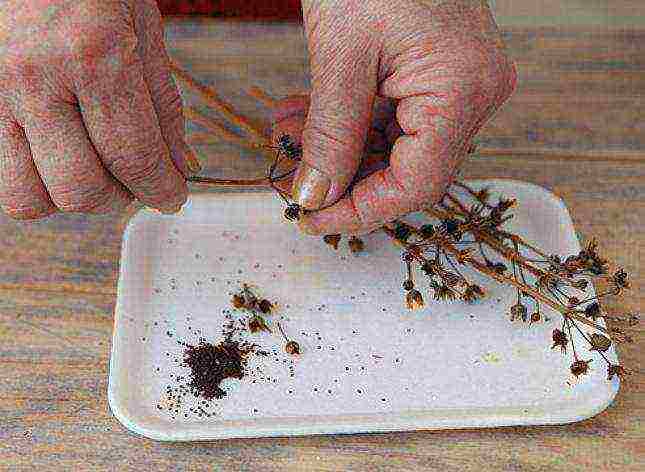

Seed sorting and debris removal
Step 1. Some flower crops need stratification to mimic winter conditions. For this, the seeds are sprinkled with soil in small containers or wrapped in a damp cloth and placed in a plastic container. Seeds are removed in the refrigerator for 4-6 weeks. Inspect from time to time and, if necessary, moisten. Stratification is necessary for asters, lavender, primroses, seeds of conifers.
Stratification methods
Note! Sowing seeds in the snow is also a stratification method. It is suitable for small seeds of lobelia, petunia, carnation.
Step 2. Disinfection is necessary to destroy pathogens of fungal and bacterial infections. For this, the seeds are soaked first in a dark pink solution of potassium permanganate, then washed and soaked in a solution of "Fitosporin-M" or another fungicide. After processing, the seeds are sown within 2-3 days, they cannot be stored longer.

Treatment in a solution of manganese and fungicides
Step 3. Soaking is used for seeds with a hard, dense shell - morning glory, sweet pea, ornamental beans, castor bean. Soaking is carried out in warm water (+ 35-40 ° C) for 6-24 hours. It is convenient to do this in a thermos - a constant temperature is maintained there. When soaking in a glass, the water should be regularly changed to hot.

Soaking seeds in hot water
Step 4. Scarification is another way to speed up the germination of hard seeds. The upper layer of the shell is damaged mechanically - using sandpaper, a file or scratching with a needle. After that, the seeds are soaked.
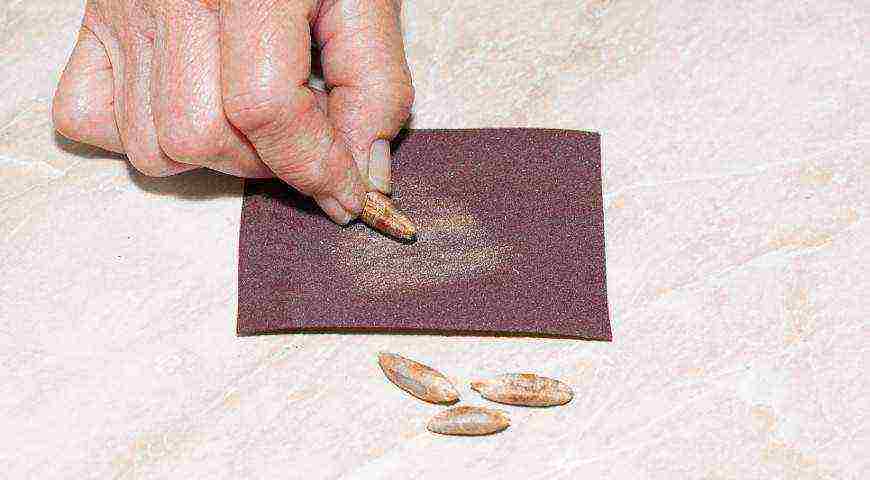

Seed scarification
Step 5. Stimulation is carried out in a solution of "Agat", "Epin" or "Zircon", in aloe juice, as well as in solutions of succinic or boric acid. After stimulation, the seeds give more friendly shoots.
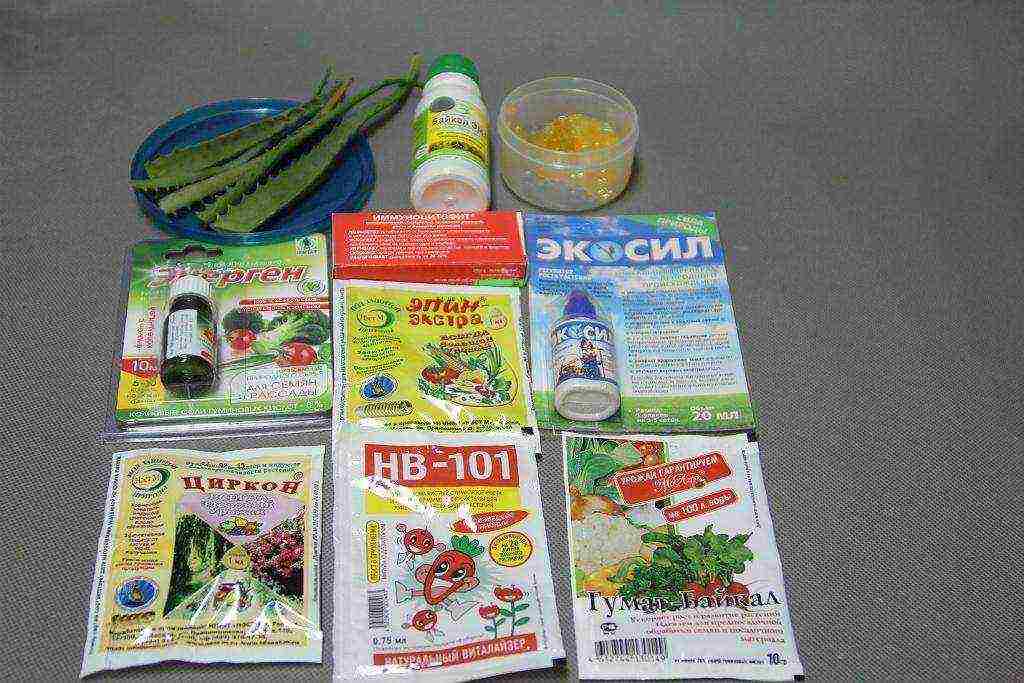

Seed growth stimulants
Note! It is more convenient to process small seeds by placing them in fabric bags.
Preparing soil and seedling containers
To successfully grow flower seedlings, two types of soil are required. At the stage of seed germination and the appearance of the first true leaves, the sprout takes nutrients from the seed. However, during this period, seedlings are very sensitive to fungal and bacterial infections. The main requirement for soil for seed germination is its sterility, moisture and air permeability. These qualities are possessed by mixtures based on peat.

Peat soil
In the second phase of seedling growth, after picking, the root system begins to actively consume nutrients from the soil. For planting seedlings in separate cups, soil rich in humus or vermicompost is more suitable. If the seeds are planted immediately in seedling cups, then it is enough to sprinkle the planting holes and the soil surface with peat or calcined sand.

Nutrient soil
As containers for seedlings, you can use boxes, seedling cassettes, disposable cups and any other container of a suitable size. For germination of heat-loving seeds that require a greenhouse effect, containers with a transparent lid or special mini-greenhouses can be used. Before planting, containers must be washed and disinfected in a solution of potassium permanganate.
Sowing seeds in boxes
Flower seeds are sown in various ways on the soil surface or in buried grooves.Small seeds are sown superficially, which require light for germination (petunia, lobelia, ageratum, fragrant tobacco).
The seeds are pre-mixed with sand so that they are evenly distributed. The finer the seeds, the smaller the sand particles should be. Seeds are sown over the entire surface, watered with a spray bottle and covered with a stack. Germinate in the light.
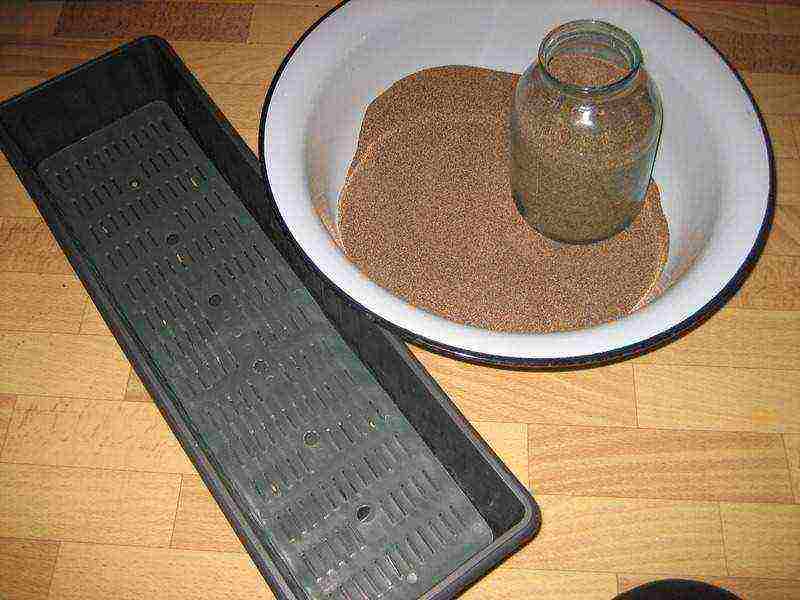

Seedling box and washed calcined river sand
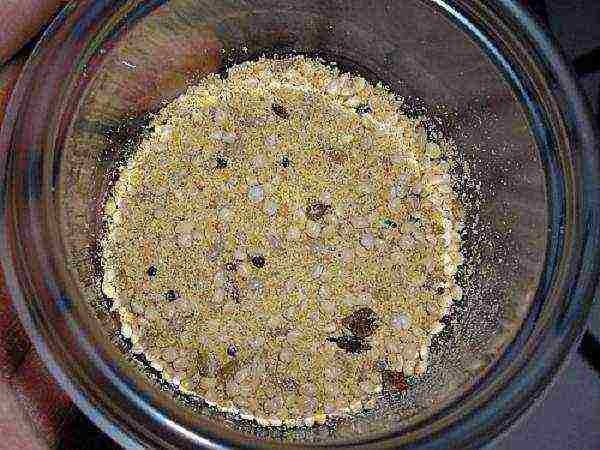

Seeds mixed with sand
Seeds embedded in the soil are sown in this way.
Step 1. Fill the boxes with soil, level it, press the grooves of the required depth with a ruler or other object.
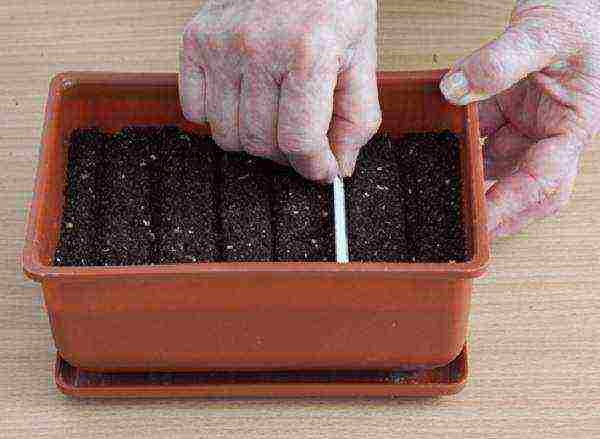

Furrows in the soil for seedlings
Step 2. Seeds are sown in the grooves at the required intervals.
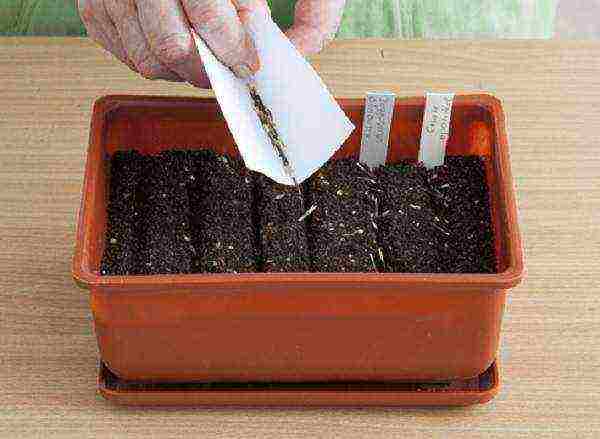

Sowing seeds
Step 3. A layer of soil 1-1.5 cm thick is poured on top.
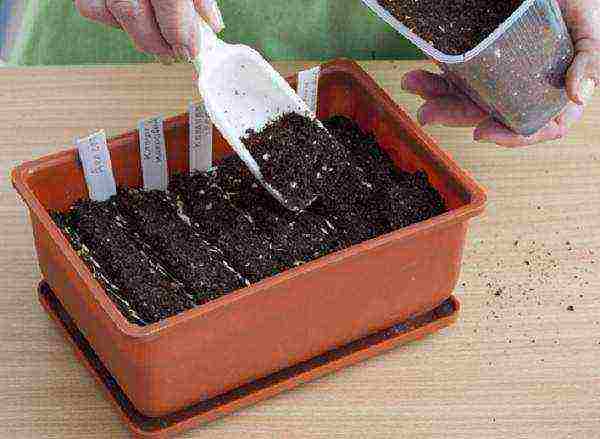

Backfilling the seeds with a layer of soil
Step 4. Water gently from a watering can until the topsoil is moistened.
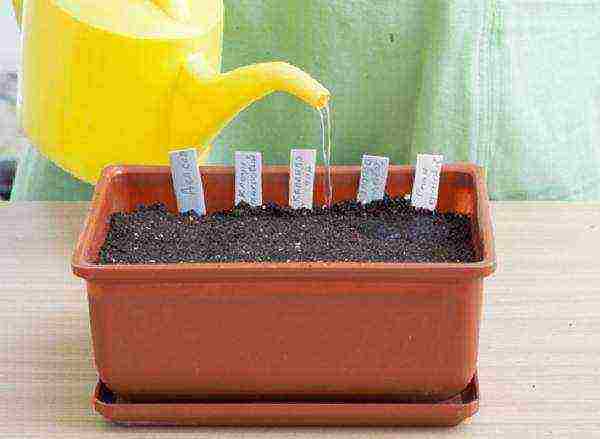

Watering planted seeds
Step 5. Cover the box with a lid or foil and put it in a warm place until shoots appear.
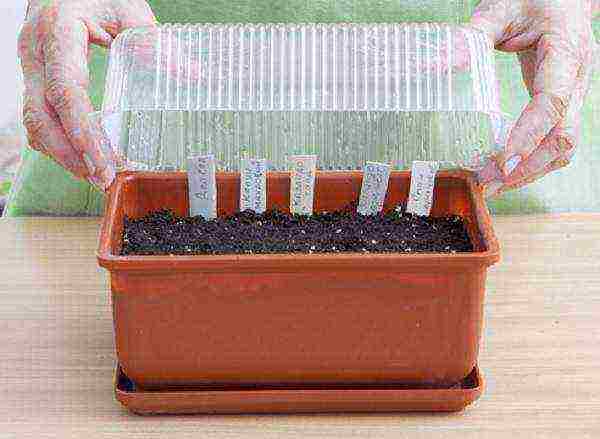

Seedling box cover
Step 6. Once or twice a day, before emergence, the film is lifted to ventilate and remove condensation - the latter can be used to moisten the soil, allowing it to drain along the walls of the box.
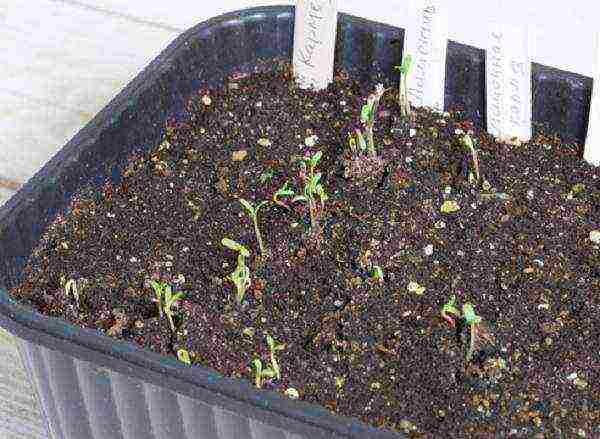

Airing seedlings
Step 7. Water the seedlings when the top layer of the soil dries up from a small watering can with settled warm water.

Watering seedlings
Note! Planting seeds in seedling cassettes or glasses is carried out in the same way, it is allowed to plant 2-3 seeds. The excess sprout can then be removed.
Plant picking
Plants usually dive in the phase of 2 true leaves - by this time the sprouts are switching to root nutrition, but the root system itself has not yet grown, therefore it is almost not damaged during transplantation. Exceptions are plants with very delicate stems such as lobelia. It is better to replant it after the appearance of 4-5 true leaves.
Step 1. Prepare seedling cups and fill them with a nutritious soil mixture, water and allow the water to evenly saturate the soil. In the center, make a 2-3 cm depression with a pencil or other object.

Seedling cassettes with soil
Step 2. Pry the sprout in the seedling box with a small spatula or a teaspoon handle. Carefully take it out together with an earthen lump.

Removing seedlings from the box
Step 3. Place the roots with an earthen lump in the depression and press the soil from one or more sides, taking care not to damage the root. Add soil if necessary.
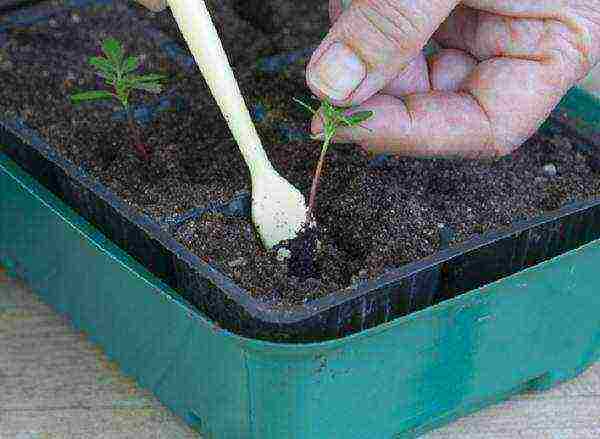

Planting a sprout in a separate cup
Cups with transplanted seedlings are placed in a warm place with diffused light for several days. Water only when the topsoil dries out and very carefully so as not to overflow. After the seedlings take root, you can water them as usual, feed them and pinch them.

Seedlings after picking
Growing in peat tablets
Peat tablets are convenient for planting flower crops that do not tolerate picking and handling. They are pressed peat soil, which, when wet, swells and increases in height by about 5-7 times, its diameter remains the same.
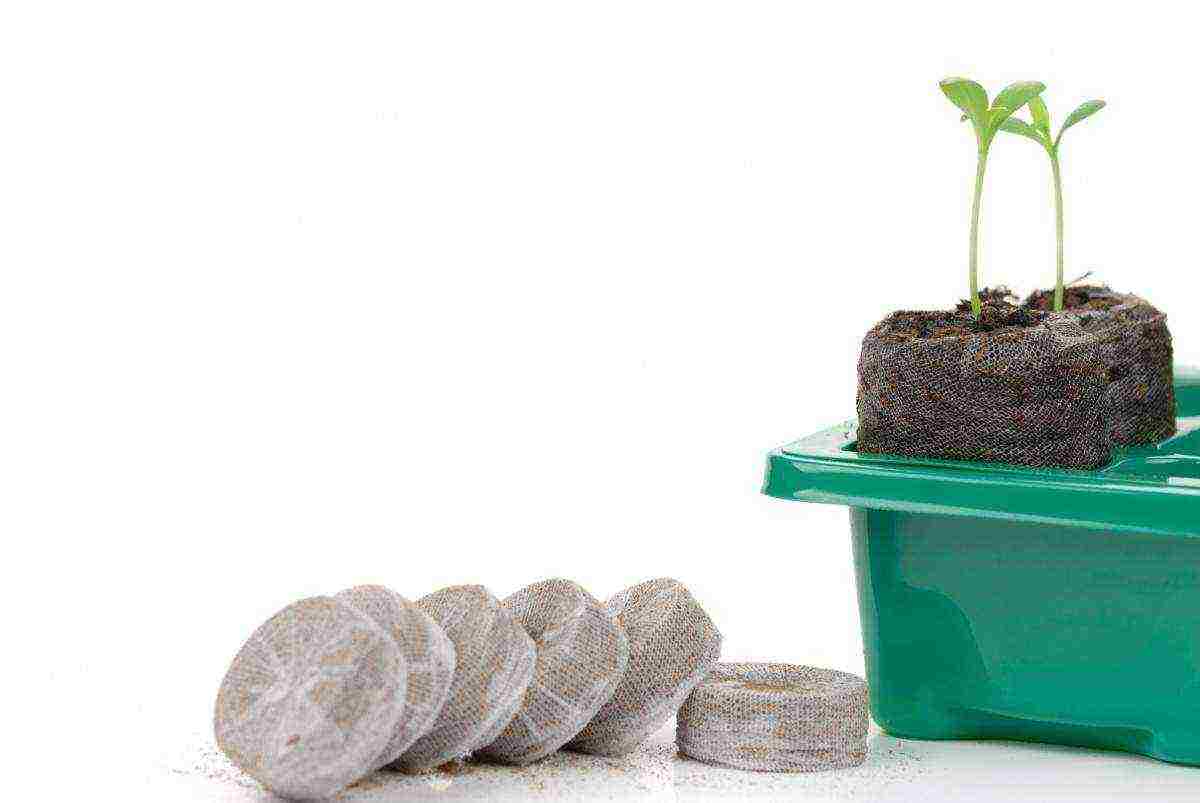

Peat tablets
Step 1. The tablets are placed in a container and filled with warm water. It is better to pour water in a little, 1-2 cm, and add as the tablets swell. As soon as they stop absorbing water, the excess is drained.
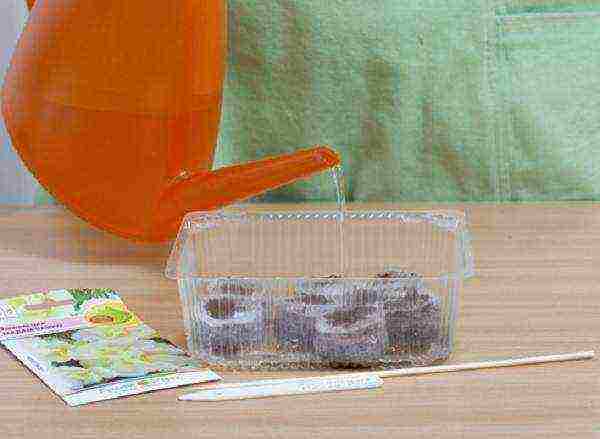

Soaking peat tablets
Step 2. The wetted tablets are placed in a mini-greenhouse. There is a small depression in the center of the tablet; if its dimensions are insufficient, the hole is widened or deepened. Pre-prepared or germinated seeds are placed in tablets. This can be done by hand, using tweezers or a toothpick (depending on the size of the seeds). The pelleted and granulated seeds are then watered with water until they are completely moistened. If necessary, fill the hole with peat soil mixture.
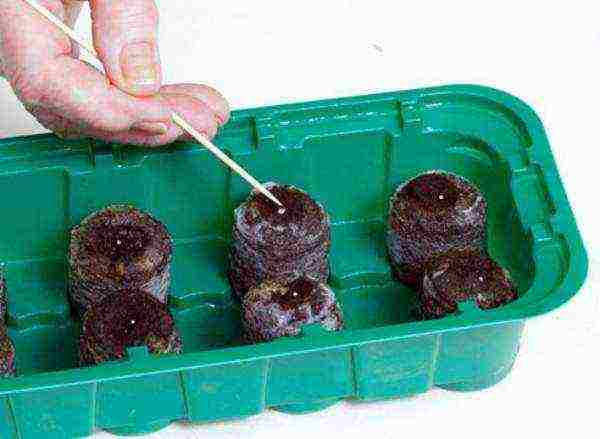

Planting seeds in tablets
Step 3. Cover the greenhouse with a lid or film and put it in a warm place, maintaining a temperature suitable for this type of seed. The cover is periodically removed for ventilation.
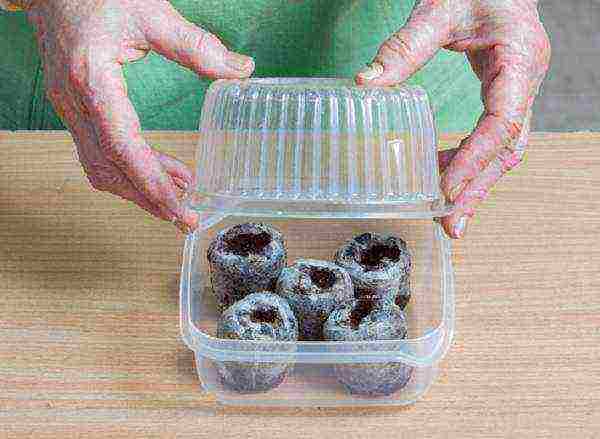

Germinating seeds in peat tablets
Step 4. After germination of seeds and the appearance of several true leaves, as well as a developed root system, the plants, along with the tablets, are transplanted into a larger pot or on a flower bed.

Transplanting seedlings grown in peat tablets
Note! The peat soil from which the tablets are made is not very rich in nutrients. Therefore, when growing seedlings in tablets for a long time, watering is best done with a weak solution of complex flower fertilizer.
Sowing small seeds in the snow
Flowers with very small seeds that do not require planting in the soil are convenient to plant in the snow. When the snow melts, the soil is moderately moistened by soft melt water, and small seeds along with it are planted to a shallow depth, as happens in natural conditions. In addition, there is a short-term stratification of seeds, which contributes to friendly seedlings.
Step 1. Seedling boxes are filled with peat soil by 2/3, compacted, but not watered. 2-3 cm of snow is laid on top, and it is also compacted and leveled.
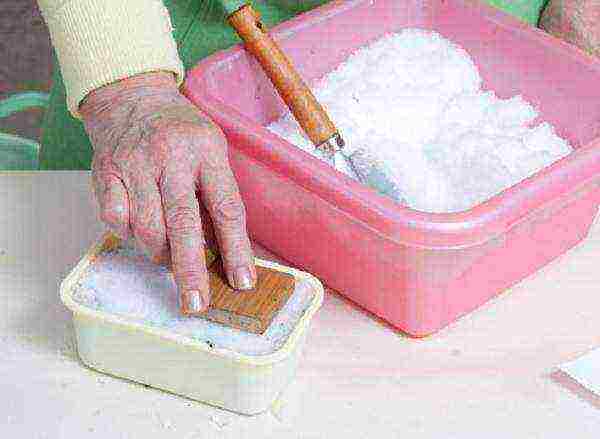

Filling the seedling boxes with soil and snow
Step 2. Seeds are scattered over the surface of the snow - they are clearly visible on a white background, therefore they are easy to evenly distribute.
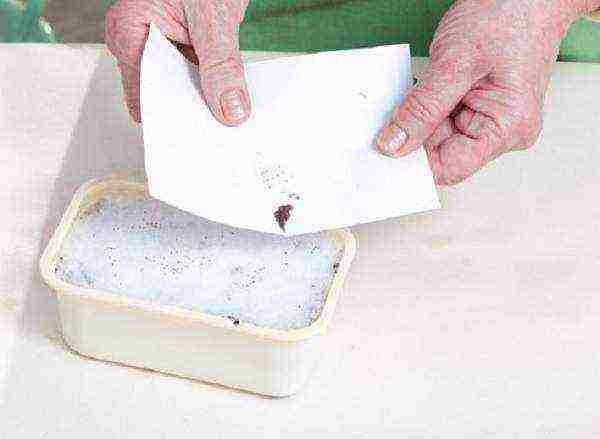

Sowing seeds in the snow
Step 3. Cover the box with a transparent lid, glass or foil and leave in a warm place with diffused light. The cover or film is regularly removed and the soil is ventilated for 10-20 minutes. The condensate is removed. Water the soil from a spray bottle only when the top layer dries out.

Watering from a spray bottle
Note! The layer of snow should not be too thick, otherwise the soil will get very wet and the seeds will rot. To prevent waterlogging, it is better to make drainage or holes in the box.
Seedling care
Before planting in the ground, caring for the seedlings consists in regular watering, feeding with complex fertilizers, pinching and additional lighting. In this case, the technology of growing each flower crop should be taken into account.
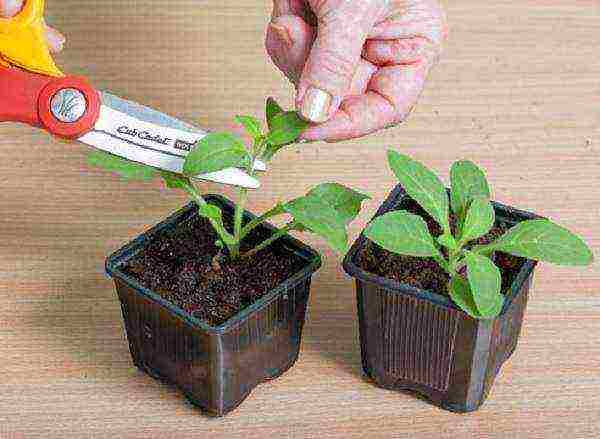

Nipping seedlings
You can learn about the technology of growing seedlings of popular garden flowers from the videos below.
Video - Growing garden aster seedlings
Video - Growing marigold seedlings
When you follow the step-by-step instructions for growing seedlings, you will get strong, healthy, abundant flowering plants. They will decorate your garden area, give it charm and uniqueness.
A beautiful flower garden can become a "highlight" of any country house or cozy summer cottage, so you should also take care of flower seedlings in advance, choosing the desired varieties for seedlings, distributing them according to the sowing dates, preparing the soil and containers. The seeds can be bought in a specialized store or you can take care of their preparation yourself. To do this, at the end of the growing season, you need to collect the seeds in the buds and store them in a dry and warm place. For exfoliation, fabric bags or gauze are used: dried buds are put inside and rubbed, and then sifted through a sieve.
Depending on the flowering period of the species, the collection of planting material can be carried out at any time, but most often from August to October. Before sowing, from procedures, it is necessary to carry out stratification, disinfection and hardening of seeds. For even seedlings, heat treatment is possible, re-hardening of seedlings and seedlings (except for lavender) is not recommended, since the flowers are heat-loving plants and may die.
Growing flowers from seeds at home
Almost all ornamental plants love high humidity and long daylight hours, so before growing flower seeds for seedlings, prepare a place on the veranda or windowsill. Drip irrigation is ideal until 2-3 leaves appear, then regular spraying in the morning and evening. Until the first shoots, during the "black earth" period, the seedlings should be kept under a film or cover.
How to grow petunia from seeds
Sow petunia in small containers on a closed balcony, or on a windowsill in a room, at the end of winter. They are very small and require shallow sowing, which often causes some difficulties for growers.
Seedling petunia
The main secret of success lies in maintaining the optimal air temperature (20-22 degrees) and moderate soil moisture for germination and successful rooting of seedlings. In such conditions, the first shoots appear on the 5-7th day. We dive young seedlings into a separate container when they get stronger.
How to grow lavender from seeds
For lavender, south-facing windowsills are ideal. You will need a short, wide pot, good drainage, and an alkaline potting soil.
The first sprouts from lavender seeds
For good germination, lavender needs a little stress: immediately after planting, the container is placed in the refrigerator for re-hardening, previously covered with a film. With the appearance of the first shoots, lavender needs good lighting, in order to avoid stretching the seedlings, it is advisable to provide it with additional lighting. The grown plants need regular watering - in the morning and in the evening, as well as gradual accustoming to the humidity and air temperature in the room where it will grow.
How to grow a rose from seeds
Most often, roses are propagated by cuttings, but with the help of seeds taken from donated bouquets, you can decorate your garden with really rare specimens. Before sowing, a well-dried material should be soaked in Kornevin's solution and kept for a day at a low temperature.
Sowing rose seeds for seedlings
Seeds should be germinated on a damp cloth. The first seedlings can be seen after 1.5-2 months, after which they are transplanted into peat pots or another container. Young rose sprouts need drip irrigation and long daylight hours: use artificial light sources and automatic irrigation systems.
How to grow an orchid from seeds
Orchid family members are capricious and unable to germinate in a normal environment. Their seeds are microscopic and do not have their own food reserves, which is why it is so difficult to provide them with suitable conditions.
For germination, you will need a special hydrogel, which will be the basis of the substrate. Seeds sterilized with a solution of calcium hydrochloride (10 mg per 100 ml of water) are placed in it.
Orchid seedlings in hydrogel
At a temperature of 18-22 degrees in the room, and sufficient lighting (13-15 hours), the emergence of seedlings can take from a week to several months. In the future, traditional soil is used for orchid seedlings: well-soaked moss or finely chopped pine bark.
Outcome
Knowing how to prepare and grow flower seeds for seedlings for germination, you can prepare in advance by purchasing everything you need. And having prepared the seed material from the donated bouquets, decorate your site with beautiful and unusual plants.
Growing seedlings of annual flowers
Annual flowers brighten and liven up any garden. As a rule, when forming flower beds, they are used simultaneously with perennial flowers. The main difference between annuals and perennials is the life cycle.
Growing seedlings of annuals flowers perform in the following cases:
- If the plants are characterized by a long growing season.
- If you want to achieve early flowering.
Before you start sowing seeds for seedlings of annual flowers, carefully study the biological characteristics of the variety on which you have chosen. So, seedlings of flowers such as asters, dahlias and zinnias can be grown at different times, depending on when you plan to receive the flowers.
If you want annual flower crops to bloom in early September, sowing seeds should be done between April 15 and 20, because the flower blooms about 80 days after the first shoots appear. In addition, after planting, the plant needs time to adapt.
Growing seedlings of perennial flowers
In the open field, most of the seeds of perennial crops do not germinate successfully. Having sowed the varieties you like, having completed a number of complex preparatory work, having made a lot of effort to care, you can wait in vain for the first shoots. Such an unfortunate failure in the work you have done can be avoided by growing seedlings perennial flowers indoors. Only in this way will you artificially create a suitable environment for it and get the desired result.
Grow seedlings perennial flowers at home at any time of the year. Keep in mind, however, that if the seeds are sown in late winter or early spring, the sprouts will become too elongated to move into the garden in early summer.
Flower Seed Stratification
Whether we plant annuals or perennials, for a successful growing seedlings of flowers seed stratification is required. Without using this process, florist attempts often end in failure. So, the seeds of a large number of perennial varieties have a very dense shell, which significantly prevents the germination of the seedling. For annual flowers, stratification is also needed.
The essence of the seed stratification procedure is the effect of low temperature on the seeds. The duration of the stratification process is different. For flowers such as phlox, aconine, peonies, this period should last several months. For delphiniums, snapdragons, asters are enough for three to four weeks.
Soil preparation for planting flowers
Thinking about how grow flower seedlings at home, remember that half of your success in this business depends on the correct substrate. You can purchase ready-made potting mix at a specialty store, or you can make your own. All that needs to be taken into account in this case is that the substrate must contain nutrients in the right amount, have the ability to pass water and be fresh (in no case should seeds be sown in previously used soil).
Before starting sowing, the substrate should be steamed. To do this, pour the earth into a metal container, moisten it and put it in the oven for two hours. The maximum oven temperature should be no more than 85 ° C. Otherwise, useful organic substances will begin to evaporate from the soil.
The most popular substrate consists of the following components: sand, peat and turf in a ratio of 1: 3: 1, respectively.
Sowing flower seeds
At growing seedlings of flowers at home it is very important to maintain the correct seeding density and depth:
- When sowing small seeds, carefully mix them with sand and scatter evenly over the surface of the soil. It is advisable not to cover very small seeds with earth at all, but simply cover them with film or glass.
- Cover larger seeds with a layer of sand or earth, double the thickness of the seeds.
If the seeds are overly covered with earth, then the seedlings of flowers simply will not germinate. Sowing too shallow will cause the roots of the plants to come to the surface. In both cases, the seedlings will be very weak.
Leaving and diving flower seedlings
Caring for seedlings of flowers consists in loosening the soil and timely abundant watering (always with water at room temperature). After emergence, place the containers in the brightest place. If there is little lighting, use artificial sources:
- Reflective screens - it can be food foil, an old mirror or just a sheet of white Whatman paper, which are installed on the sides of the window, as well as on the windowsill between the windows and the room.
- Fluorescent lamps - they are installed above the seedlings at a height of 15-20 cm and as the seedlings grow, they are raised up.
When seedling flowers get strong enough you can do it dive, that is, seating in boxes or in separate cups at some distance from each other. Place the containers with dived plants in partial shade, and then three to four days after rooting, put the seedlings back in bright places.
Planting flower seedlings in the ground
Before planting in the ground, flowers must be hardened. To do this, first take the plants outside for the day and if frosts are not expected, you can leave them overnight. After a positive temperature is established during the day, feel free to plant flowers in open ground. In order not to injure fragile seedlings during transplantation, we recommend growing them in peat pots. When the time comes to plant seedlings, they are not removed from such a container when planting.
So, these are the basic tips on the topic, how to grow flower seedlings, following which you can get luxurious seedlings of annuals and perennials at home.
Video: Growing flower seedlings at home
Flowers. Growing flower seedlings
All our articles from the heading "Floriculture" "" "
Source


